- 1Department of Urology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 2Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Urological Digital Precision Diagnosis and Treatment, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 3Liaoning Engineering Research Center of Integrated Precision Diagnosis and Treatment Technology for Urological Cancer, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 4Dalian Key Laboratory of Prostate Cancer Research, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 5First Clinical College, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 6Department of Pathology, Dalian Friendship Hospital, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 7College of Pharmacy, Zhongshan College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China
Background: Bronchogenic cysts are benign congenital anomalies originating from embryonic foregut development. Although typically located in the mediastinum or lung parenchyma, retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts are exceedingly rare, with only a limited number of cases reported in the literature. We present a case of a bronchogenic cyst situated in the left retroperitoneal space, along with a concise review of previously documented cases, summarizing their common epidemiological, clinicopathological, and prognostic features.
Case summary: A 48-year-old female was admitted with unexplained left lumbar pain. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a slightly hyperdense cystic mass measuring 43×37×36 mm in the left adrenal region. The lesion was successfully resected using robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery. Histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of a bronchogenic cyst. The patient remained hemodynamically stable and recovered well postoperatively. At the 6-month follow-up, she remained asymptomatic with no evidence of recurrence.
Conclusion: Given the rarity of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts, preoperative imaging is often insufficient to definitively differentiate them from other retroperitoneal neoplasms. Consequently, definitive diagnosis usually depends on postoperative pathological evaluation. This case highlights the diagnostic challenge posed by this rare entity and underscores the importance of pathological examination for definitive diagnosis.
Introduction
Bronchogenic cysts are relatively rare congenital malformations that typically originate from abnormal separation or migration of the trachea and bronchial buds during embryonic foregut development. These cysts are characteristically lined by respiratory epithelium (1). While commonly found in the mediastinum, retroperitoneal locations are exceedingly rare, first reported by Miller et al. in 1953 (2). Due to their generally asymptomatic nature, these cysts are often discovered incidentally on cross-sectional imaging such as CT or MRI. However, a small subset of patients may present with symptoms like pain or fever secondary to infection or mass effect (3, 4). Preoperative differentiating these cysts from other retroperitoneal lesions can be challenging. Surgical resection remains the preferred treatment, and definitive diagnosis is primarily established through histopathological analysis of the resected specimen (5). Herein, we present a case of a retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst in a woman who initially presented with left lumbar pain and successfully underwent robot-assisted laparoscopic resection. Furthermore, we conduct a literature review to comprehensively summarize the clinical features of this rare disease, including its epidemiology, clinical manifestations, imaging characteristics, diagnostic approach, and treatment.
Case presentation
A 48-year-old woman presented to her local hospital with a 3-month history of left lumbar pain and progressive weakness. During this evaluation, an unenhanced abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan incidentally identified a mass in the left adrenal region. To further characterize the retroperitoneal lesion, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the adrenal region was performed. The MRI revealed an irregular mass measuring 43×31×42 mm, which exhibited slightly short T1 and long T2 signal characteristics and showed no contrast enhancement. Subsequently, the patient was referred to our institution for further diagnosis and treatment.
Adrenal mass needs to be differentiated from a variety of diseases, like primary aldosteronism, Cushing ‘s syndrome, pheochromocytoma, nonfunctional adrenal adenoma or adrenal tuberculosis. To exclude these possibilities, we conducted a detailed physical examination and specialized examinations on the patient. The patient denied other typical symptoms or signs such as central obesity, sudden dizziness, palpitations, sweating, nausea, vomiting, or fever. She reported adequate sleep, reduced appetite, normal voiding, and a weight loss of 2 kg over the previous two weeks. She denied any history of trauma, surgery, blood transfusion, or significant medical conditions including hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, or tuberculosis. There was no family history of malignancy or psychiatric illness. On physical examination, the abdomen was flat and soft, without tenderness or rebound. Percussion over the liver and kidney regions was non-tender. Overall, the physical examination findings were unremarkable.
Screening for adrenal hormones, including adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol, and renin-aldosterone-angiotensin II levels measured at 00:00, 08:00, and 16:00, were all within normal limits. Furthermore, other biochemical studies, including complete blood count, coagulation function, liver function, renal function, serum electrolyte concentrations, and blood glucose, revealed no significant abnormalities. Key laboratory test results are shown in Table 1. Contrast-enhanced CT scan revealed a well-circumscribed, slightly hyperdense mass in the left adrenal region, measuring approximately 43×37×36 mm (Figure 1). The lesion was intimately associated with the left adrenal gland, exhibited peripheral calcification, and had a CT value of approximately 74 Hounsfield units. No significant enhancement was observed. Based on imaging characteristics, the mass was considered most consistent with a retroperitoneal cystic lesion. However, an adrenal tumor or a simple adrenal cyst could not be entirely excluded.
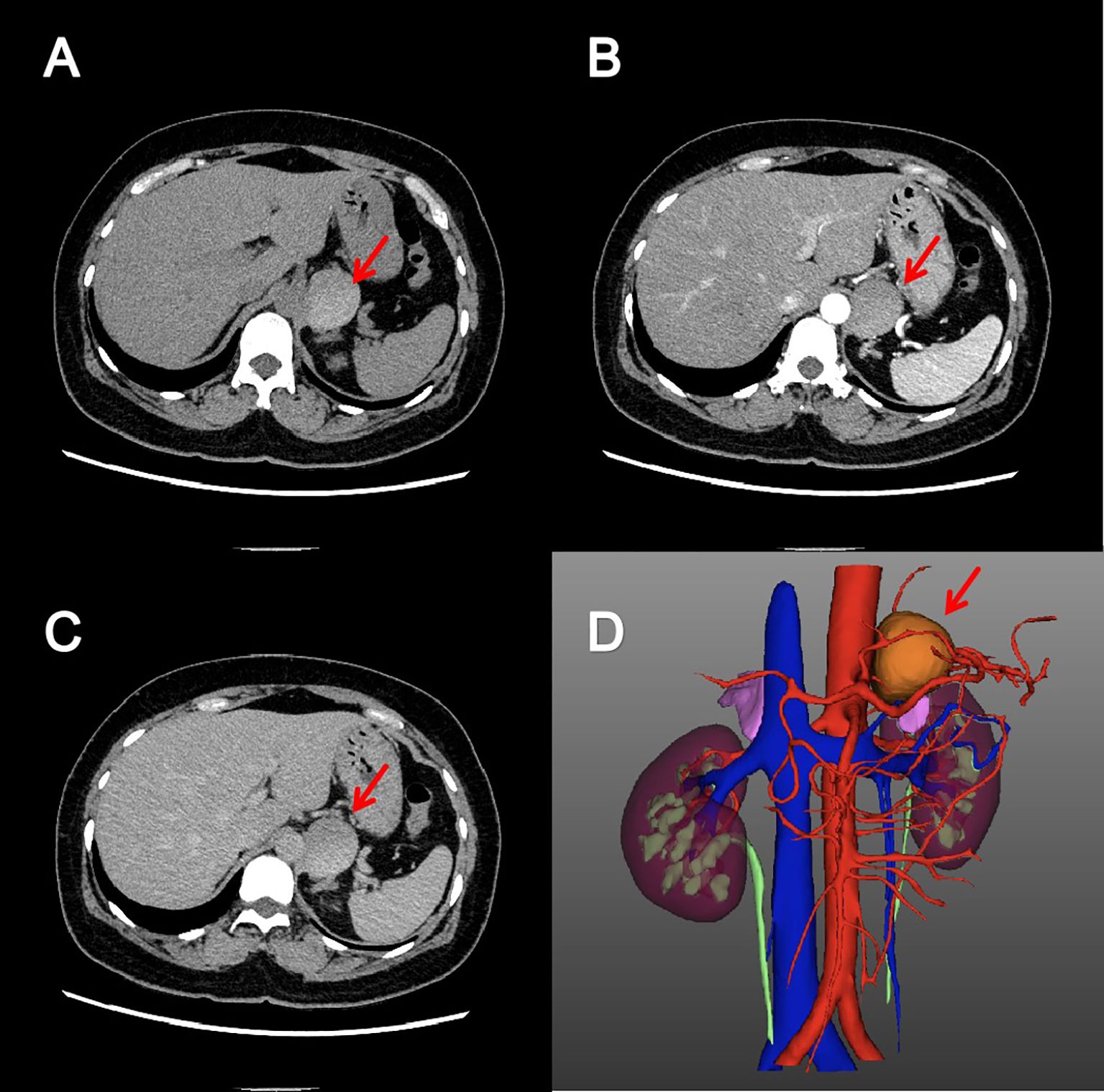
Figure 1. Adrenal enhanced computed tomography image. Axial pre-contrast (A), arterial phase (B) and excretory phase (C) CT images showed a cystic, well-circumscribed mass without enhancement in the left adrenal region. The reconstructed three-dimensional image (D) showed that the mass was closely related to the left adrenal gland.
For definitive diagnosis, the patient underwent robot-assisted laparoscopic resection of the left retroperitoneal lesion via a transabdominal approach. During the surgical exploration, no adhesions were found in the abdominal viscera, and adjacent organs such as the spleen and colon showed no abnormalities. A 3.5×2.5×0.5 cm cyst was found in the left retroperitoneal area adjacent to the upper pole of the left kidney and closely abutting the adrenal gland. The capsule was intact and the surface was smooth, consistent with the cystic manifestations suggested by preoperative imaging. Upon puncture, the cyst yielded a small amount of white, viscous fluid. Macroscopically, the cyst wall was dark gray with a smooth surface (Figure 2A) and a uniform thickness of 0.2 cm. Microscopic examination revealed that the cyst wall was lined by ciliated columnar epithelium and composed of fibrous connective tissue (Figure 2B). Bronchial cartilage (Figure 2C) and subepithelial mucinous glands (Figure 2D) were identified within the cyst wall, along with numerous infiltrating lymphocytes and plasma cells, confirming the diagnosis of a bronchogenic cyst. Postoperative abdominal CT confirmed complete excision. Three days postoperatively, the patient’s condition improved, and she was discharged without complications. At the 6-month follow-up, she remained asymptomatic with no evidence of recurrence.
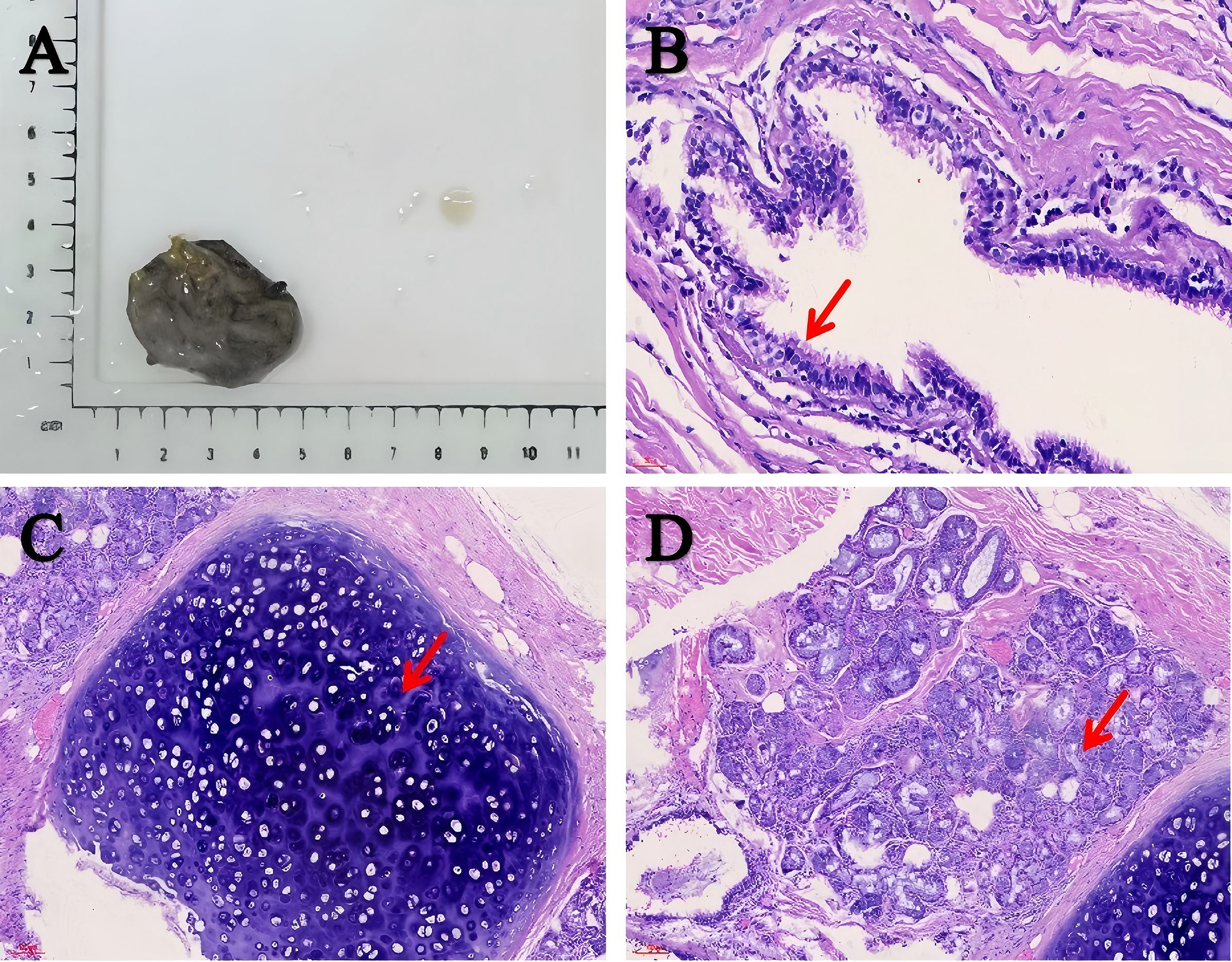
Figure 2. Macroscopic and microscopic manifestations of the cyst. (A) The cyst wall was dark gray and smooth. (B–D) Histopathological analysis was consistent with the diagnosis of bronchogenic cyst. The cyst wall was covered with ciliated columnar epithelial cells (scale bar: 30 μm). The arrow shows the structure of ciliated columnar epithelium (B). The cyst wall was composed of fibrous connective tissue. Bronchial cartilage and mucous glands were found under the epithelium, accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration (scale bar: 100 μm). The arrow shows the cartilage (C) and gland (D) structure.
Discussion
Bronchogenic cysts are congenital developmental abnormalities originating from the primitive foregut and are classified as foregut cysts (6). The cyst wall typically consists of ciliated epithelium, cartilage, smooth muscle, and mucous glands. The cyst contents are usually serous or mucoid but may become purulent if infected (3, 7). During the 3rd to 7th week of embryonic development, abnormalities in the development of the primitive foregut into the trachea and lung buds can occur. This process can lead to detachment of respiratory epithelial cells, which may proliferate aberrantly in ectopic sites, ultimately forming cysts (1, 8). This developmental process may be related to genetic or environmental factors, but the exact pathogenesis remains unclear (9). Based on anatomical location, bronchogenic cysts are classified into mediastinal, intrapulmonary, and ectopic types (8). Mediastinal and intrapulmonary cysts are more common, often occurring in mediastinal regions adjacent to the trachea or esophagus, or within the pulmonary parenchyma (10). Ectopic cysts, which are rarer, may occur in extrathoracic locations, such as the spinal canal and abdominal cavity, potentially leading to misdiagnosis as other cystic lesions (11–13). The exact prevalence is unknown. Although most cases are identified in children and adolescents, diagnosis in adults is not uncommon (14, 15). Generally, there is no significant gender predilection, although some reports indicate a slightly higher incidence in males (16). Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts are even rarer, first reported by Miller et al. in 1953, and account for only 0.03% of all cases (2, 17). They are thought to arise when an embryonic bronchial tree malformation results in a bronchial bud being severed by the developing diaphragm, subsequently migrating into the abdominal cavity and forming a retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst (1, 8). To systematically review this rare entity, we searched PubMed, Embase, and Scopus databases using the keywords “retroperitoneal,” “bronchogenic,” and “cyst.” After screening titles and abstracts, we identified 126 articles published between 2000 and 2024, encompassing the clinical characteristics of 144 patients with retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts. Key clinical characteristics can be found in Table 2. Among the 144 patients, 54% were male and 46% were female, consistent with previous reports of a slight male predominance (Figure 3A). The age at diagnosis ranged from prenatal to 78 years, with a mean age of 42.4 years. The majority (92%) were diagnosed in adulthood (Figure 3B). Most reported patients were from Asia and Europe, accounting for 58% and 25%, respectively (Figure 3C).
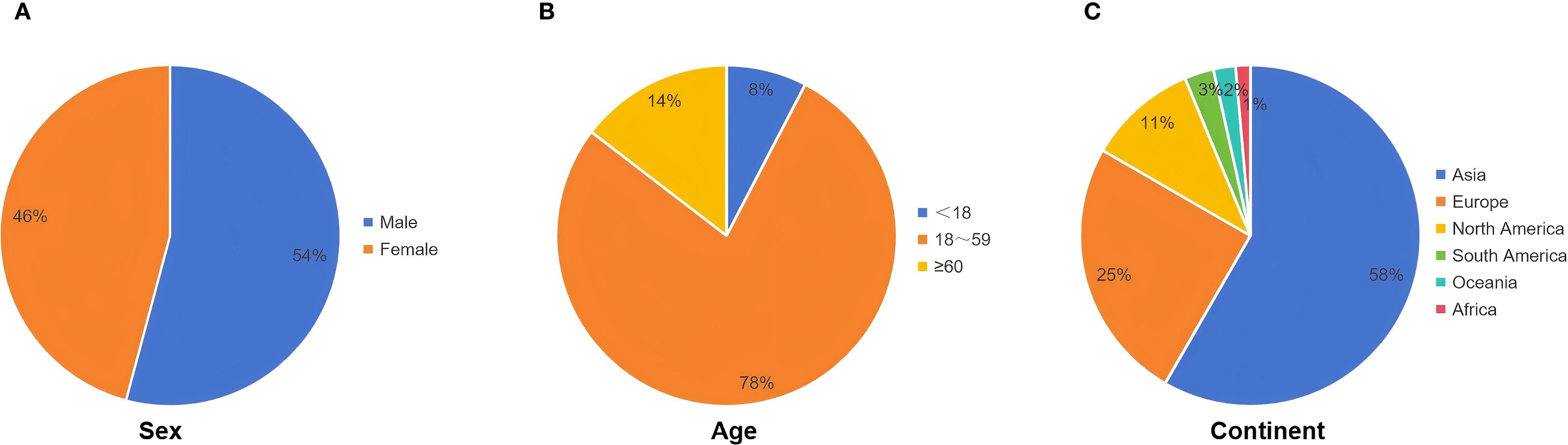
Figure 3. Baseline characteristics of patients in our literature review. (A) Gender composition of patients. (B) Age composition of patients (year). (C) Geographical distribution of patients.
Reports indicate that over 80% of cases occur in the left retroperitoneal region, particularly adjacent to the left adrenal gland, possibly due to the left pericardioperitoneal canal being larger and closing later than the right. The peripancreatic region is the second most common sites (5, 18). Our analysis showed that approximately 79% of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts were located on the left side, with about 55% of these found adjacent to the left adrenal gland. Cysts adjacent to the right adrenal gland accounted for approximately 6%, while those in the pancreatic area represented about 13% of reported cases (Figure 4B). Cao et al. reported an extremely rare case of a multilocular retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst affecting both adrenal glands (19). To date, the mean diameter of reported retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts is approximately 5.5 cm. The largest reported case, described by Mirsadeghi et al. in 2014, measured 20×20×20 cm (20). No significant correlation has been found between cyst size and patient age or gender. The distribution of the longest diameter of the cysts is shown in Figure 4A.
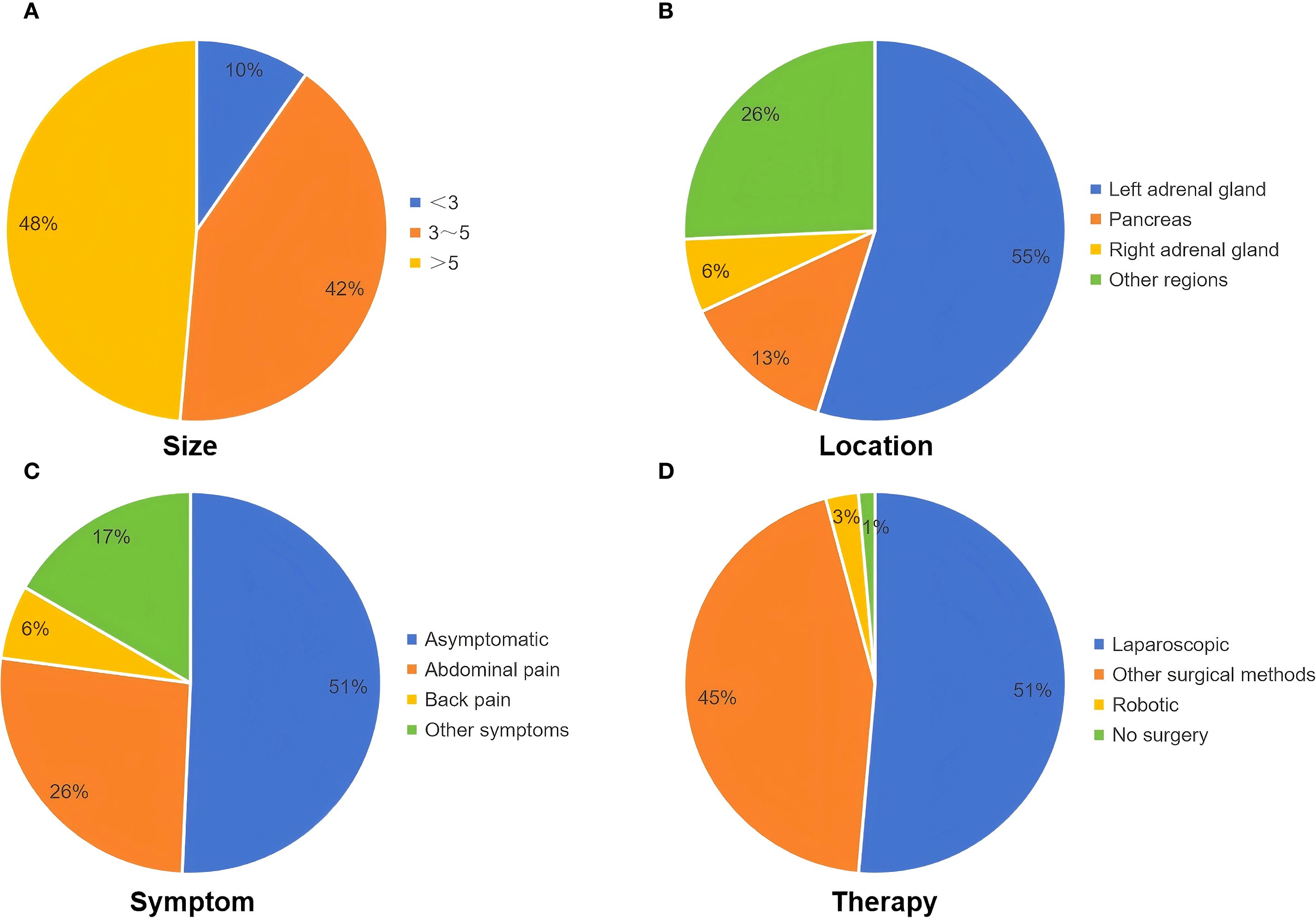
Figure 4. Clinical characteristics of patients in our literature review. (A) The range of the longest diameter of the cyst (cm). (B) The location of the cyst. (C) Symptoms of patients. (D) Treatment of patients.
Most patients are asymptomatic, and the cysts are often discovered incidentally during routine imaging studies. However, when the cyst is sufficiently large to compress surrounding organs or results in complications such as infection, hemorrhage, or rupture, patients may present with symptoms such as abdominal or lumbar pain, fever, and gastrointestinal discomfort (e.g., nausea, vomiting) (4). Owing to nonspecific manifestations, diagnosis based solely on clinical features is difficult. Although these cysts are often adjacent to the adrenal glands or pancreas, they rarely cause abnormalities in adrenal hormones, electrolytes, or pancreatic enzymes (21). Few reported cases of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts have been associated with elevated levels of serum tumor markers, such as carbohydrate antigen (CA) 19–9 and CA 72-4 (22, 23). In a case reported by Bin et al., both serum CA 19–9 and CA 24–2 were elevated preoperatively and normalized following surgical resection (18). Although their clinical significance remains uncertain, tumor markers may assist in distinguishing benign from malignant retroperitoneal masses. In our review, approximately 51% were discovered incidentally and were asymptomatic. Approximately 26% of patients experienced abdominal pain, and approximately 6% presented with back pain, possibly due to mass effect (Figure 4C). A few patients reported nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and gastrointestinal discomfort (e.g., dyspepsia and abdominal fullness). Two patients exhibited persistent fever, which resolved after surgery. Daniel et al. reported a case of a retrorectal bronchogenic cyst where the patient presented with testicular pain, which resolved postoperatively (24). Two patients presented with symptoms of pollakiuria and gross hematuria, although the association with the retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst was unclear.
Given the nonspecific clinical presentation, most retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts are discovered incidentally through imaging studies. However, no established imaging criteria currently exist for diagnosis, limiting the utility of imaging for preoperative confirmation. On ultrasound, retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts typically appear as well-defined, anechoic lesions with no significant internal vascularity. However, the diagnostic value of ultrasound is often limited by interference from bowel gas (4, 17). The results of our literature review indicated that most retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts appeared as hypoechoic or anechoic cystic masses on ultrasound, without specific manifestations. In contrast, CT and MRI are more effective and valuable modalities for preoperative assessment. On CT imaging, retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts generally appear as round or oval homogeneous low-attenuation lesions, with CT values close to that of water. Calcification may be observed in the cyst wall in some cases (3, 25, 26). The cyst contents consist primarily of water and mucoproteins. However, variations in protein content, hemorrhage, or infection within the cyst can influence the CT attenuation values. Following intravenous contrast administration, the lesions typically demonstrate no enhancement (1, 27). On MRI, the cysts show low signal intensity on T1-weighted images (T1WI) and high signal intensity on T2-weighted images (T2WI). High protein content may cause high signal intensity on both T1WI and T2WI. Similar to CT findings, contrast-enhanced MRI typically shows no enhancement (21, 28). Additionally, fat-suppressed T1-weighted sequences help differentiate these cysts from malignant tumors such as teratomas and dermoid cysts. Both CT and MRI are capable of precisely determining lesion location and size. They also play a crucial role in evaluating the relationship between the cysts and adjacent organs, vessels, or nerves (29, 30). This information is essential for accurate cyst localization and surgical planning, facilitating effective treatment strategies. The findings of our literature review were also similar to the above-mentioned common imaging features on CT or MRI. Furthermore, endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) offers unique advantages for diagnosis. It provides clear visualization of the lesion’s location, morphology, internal structure, and relationship with adjacent tissues. This enables effective differentiation between retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts and other retroperitoneal cystic lesions (e.g. pancreatic pseudocysts) or solid masses (e.g. stromal tumors). Importantly, EUS guidance allows for cyst aspiration or biopsy. This enables biochemical and cytological analysis, which is crucial for differentiating benign from malignant lesions (17, 22, 31). Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts must be differentiated from other retroperitoneal lesions, such as adrenal tumors, adrenal cysts, renal cysts, pancreatic pseudocysts, teratomas, neurogenic tumors, stromal tumors, lymphangiomas, and lymphomas (21). Ultimately, histopathological examination remains the gold standard for the definitive diagnosis of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts. The cyst wall is lined by respiratory epithelium, typically ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Additionally, the cyst wall stroma may contain cartilage, bronchial glands, and smooth muscle. Cysts lacking these elements are classified as foregut cysts (3). Notably, the case we reported exhibited characteristic pathological features consistent with a retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Currently, complete surgical resection is the definitive treatment for retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts. Early surgical intervention is recommended for patients with retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts to relieve symptoms, establish a definitive diagnosis, and prevent complications such as hemorrhage, infection, or malignant transformation. Excision is also advised for asymptomatic patients (5, 32). In our review, the vast majority of patients with retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts underwent surgical treatment; only two patients underwent biopsy with subsequent expectant management (31, 33). In recent years, with advancements in surgical techniques, laparoscopic surgery has proven safe and effective, associated with fewer complications and faster patient recovery. Approximately 51% of patients underwent laparoscopic surgery, and four patients underwent robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery (Figure 4D). Whether via traditional open surgery or the increasingly prevalent laparoscopic or robot-assisted laparoscopic approaches, complete excision of the lesion can be achieved. Most patients have favorable outcomes, confirming the safety and efficacy of surgical management (4, 21, 34). Additionally, to our knowledge, most patients have had a favorable prognosis, and there have been no reported cases of recurrence following complete surgical resection.
Conclusion
In summary, retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts are exceedingly rare. Their rarity and often non-specific clinical presentation pose significant challenges to early and accurate diagnosis. Histopathological examination remains the gold standard for definitive diagnosis. Surgical resection is the primary treatment modality, indicated for all patients regardless of clinical symptoms. Minimally invasive approaches (like laparoscopic surgery) are increasingly preferred due to their favorable safety and recovery profiles. Prognosis following surgical resection is generally excellent, with most patients achieving favorable long-term outcomes.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
SX: Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. JGH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. SW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. CC: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JYH: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Validation, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HT: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Validation. LW: Project administration, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. BF: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources. ZL: Resources, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The present study was supported by the Joint Fund Project of Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Program (2023-MSLH-021), the Scientific Research Project of Ministry of Education of Liaoning Province (LJKZZ20220100, LJ212410161046), the Interdisciplinary Research Cooperation Project Team Funding of Dalian Medical University Planning and research category (focusing on planning for recreation) (JCHZ2023001),the Interdisciplinary Research Cooperation Project Team Funding of Dalian Medical University Youth-specific category of free exploration(JCHZ2023020), the United Foundation for Medico-engineering Cooperation from Dalian Neusoft University of Information and the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University (LH-JSRZ-202201), “1+X”Program for Clinical Competency Enhancemen–interdisciplinary Innovation Project, the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University (2022JCXKYB15), the United Foundation for Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics. Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Second Hospital of DaliarMedical University(DMU-2&DICP UN202304), Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Program Project of Dalian Municipal Health Commission (23Z12002) and Industry-University Cooperation Collaborative Education Program of Ministry of Education (231005073090218).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patient for his consent to the publication of this case.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sumiyoshi K, Shimizu S, Enjoji M, Iwashita A, and Kawakami K. Bronchogenic cyst in the abdomen. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. (1985) 408:93–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00739965
2. Miller RF, Graub M, and Pashuck ET. Bronchogenic cysts; anomalies resulting from maldevelopment of the primitive foregut and midgut. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. (1953) 70:771–85.
3. Liang MK, Yee HT, Song JW, and Marks JL. Subdiaphragmatic bronchogenic cysts: a comprehensive review of the literature. Am Surg. (2005) 71:1034–41. doi: 10.1177/000313480507101210
4. Wen Y, Chen W, Chen J, and He X. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst resembling an adrenal tumor: two case reports and literature review. J Int Med Res. (2020) 48:300060520925673. doi: 10.1177/0300060520925673
5. Yuan K, Shu M, Ma Y, Feng W, Ye J, Yuan Y, et al. Ectopic bronchogenic cyst in the retroperitoneal region: a case report and literature review of adult patients. BMC Surg. (2021) 21:347. doi: 10.1186/s12893-021-01341-w
6. Syred K and Weissferdt A. Non-neoplastic mediastinal cysts. Adv Anat Pathol. (2020) 27:294–302. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000261
7. Manz M, Schmeer T, Horcic M, Meier R, and Maurer CA. Bronchogenic cyst: a rare cause of a retroperitoneal mass. Zentralbl Chir. (2009) 134:570–2. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1076885
8. McAdams HP, Kirejczyk WM, Rosado-de-Christenson ML, and Matsumoto S. Bronchogenic cyst: imaging features with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiology. (2000) 217:441–6. doi: 10.1148/radiology.217.2.r00nv19441
9. Hu BY, Yu H, and Shen J. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst clinically mimicking an adrenal mass: three case reports and a literature review. J Int Med Res. (2022) 50:3000605211072664. doi: 10.1177/03000605211072664
10. Liu HS, Li SQ, Cao ZL, Zhang ZY, and Ren H. Clinical features and treatment of bronchogenic cyst in adults. Chin Med Sci J. (2009) 24:60–3. doi: 10.1016/S1001-9294(09)60061-4
11. Jiang C, Wang H, Chen G, Jiang G, and Zhang P. Intradiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst. Ann Thorac Surg. (2013) 96:681–3. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.10.031
12. Xu Q, Feng Y, Ye K, Zhou Y, and Zhan R. Bronchogenic cyst in left anterior cranial fossa. Neurology. (2015) 84:1181–2. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001368
13. Tang J, Zeng Z, Deng S, and Lin F. Ectopic bronchogenic cyst arising from the diaphragm: a rare case report and literature review. BMC Surg. (2021) 21:321. doi: 10.1186/s12893-021-01317-w
14. Sanli A, Onen A, Ceylan E, Yilmaz E, Silistreli E, and Açikel U. A case of a bronchogenic cyst in a rare location. Ann Thorac Surg. (2004) 77:1093–4. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(03)01179-2
15. Fievet L, Gossot D, de Lesquen H, Calabre C, Merrot T, Thomas P, et al. Resection of bronchogenic cysts in symptomatic versus asymptomatic patients: an outcome analysis. Ann Thorac Surg. (2021) 112:1553–8. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2020.05.031
16. Aktogu S, Yuncu G, Halilçolar H, Ermete S, and Buduneli T. Bronchogenic cysts: clinicopathological presentation and treatment. Eur Respir J. (1996) 9:2017–21. doi: 10.1183/09031936.96.09102017
17. Malik A, Naseer QA, Iqbal MA, Han SY, and Dang SC. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin cases. (2024) 12:2586–96. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i15.2586
18. Yang B, Liu L, Tian X, Hou X, Lu M, Ma L, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst resembling an adrenal tumor in adult: Three case reports and literature review. Ann Med Surg (Lond). (2023) 85:473–6. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000182
19. Cao DH, Zheng S, Lv X, Yin R, Liu LR, Yang L, et al. Multilocular bronchogenic cyst of the bilateral adrenal: report of a rare case and review of literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2014) 7:3418–22.
20. Mirsadeghi A FF, Fazli-Shahri A, and Gholipour B. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: a case report. Med J Islam Repub Iran. (2014) 28:56.
21. Gong YY, Qian X, Liang B, Jiang MD, Liu J, Tao X, et al. Retroperitoneal tumor finally diagnosed as a bronchogenic cyst: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin cases. (2022) 10:6679–87. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6679
22. Wang M, He X, Qiu X, Tian C, Li J, and Lv M. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst resembling an adrenal tumor with high levels of serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9: A case report. Med (Baltimore). (2017) 96:e7678. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007678
23. He WT, Deng JY, Liang H, Xiao JY, and Cao FL. Bronchogenic cyst of the stomach: A case report. World J Clin cases. (2020) 8:1525–31. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i8.1525
24. de Barcellos Azambuja D, Oliveira Trindade B, Worm PV, Hamaoui FH, and Iaroseski J. Retrorectal bronchogenic cyst with a sacrococcygeal surgical approach. Cureus. (2022) 14:e31583. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31583
25. Wang SE, Tsai YF, Su CH, Shyr YM, Lee RC, Tsai WC, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking pancreatic cystic lesion. J Chin Med Assoc. (2006) 69:538–42. doi: 10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70325-9
26. Li H, Xu J, Feng Q, Cai Z, and Li J. Case report: The safety of laparoscopic surgery for the retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:1011076. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1011076
27. Xie W, Huang Z, Huang Z, Chen Z, Zhang B, Xie L, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst with fluid−fluid level: A case report and literature review. Exp Ther Med. (2023) 25:5. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11703
28. Kim EY, Lee WJ, and Jang KT. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking a pancreatic cystic tumour. Clin Radiol. (2007) 62:491–4. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2006.10.012
29. Murakami R, Machida M, Kobayashi Y, Ogura J, Ichikawa T, and Kumazaki T. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: CT and MR imaging. Abdom Imaging. (2000) 25:444–7. doi: 10.1007/s002610000019
30. Tong HX, Liu WS, Jiang Y, Liu JU, Zhou JJ, Zhang Y, et al. Giant retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking a cystic teratoma: A case report. Oncol Lett. (2015) 9:2701–5. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3076
31. Byers JT, Gertz HE, French SW, and Wang L. Case report: Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst as a diagnostic dilemma after colon cancer diagnosis. Exp Mol Pathol. (2018) 104:158–60. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.02.002
32. Ishikawa T, Kawabata G, Okada H, Arakawa S, Kamidono S, and Fujisawa M. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst managed with retroperitoneoscopic surgery. J Urol. (2003) 169:1078–9. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000049902.69707.12
33. Brient C, Muller C, Cassagneau P, Taieb D, Sebag F, and Henry JF. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. J Visc Surg. (2012) 149:e361–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2012.05.002
34. Maly T, Mihal V, Michalkova K, Tichy T, Neoral C, and Zonca P. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: prenatal diagnosis of cystoid formation, its progression and surgery. Bratisl Lek Listy. (2014) 115:98–100. doi: 10.4149/BLL_2014_021
35. Reichelt O, Grieser T, Wunderlich H, Möller A, Schubert J, et al. Bronchogenic cyst. A rare differential diagnosis of retroperitoneal tumors. Urol Int. (2000) 64:216–9. doi: 10.1159/000030534
36. Bagolan P, Bilancioni E, Nahom A, Trucchi A, Inserra A, Neri M, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of a bronchogenic cyst in an unusual site. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2000) 15:66–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.2000.00022.x
37. Montesino Semper M, González de Garibay AS, Jiménez Calvo J, Grasa Lanau V, Lozano Uruñuela F, De Pablo Cárdenas A, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking adrenal gland tumor. Arch Esp Urol. (2000) 53:372–4.
38. Haddadin WJ, Reid R, and Jindal RM. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: a rare cause of a mass in the adrenal region. J Clin Pathol. (2001) 54:801–2. doi: 10.1136/jcp.54.10.801
39. Anderson MI, O’Reilly KJ, and Costabile RA. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking a pheochromocytoma. J Urol. (2001) 166:1379–80. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)65774-6
40. Ohashi R. HK and Matsuda E. A case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst with Malignant change. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg. (2001) 31:36–40. doi: 10.5833/jjgs.34.36
41. Ingu A. WA, Ichimiya Y, Saito T, and Abe T. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: A case report. Chest. (2002) p:1357–1359. doi: 10.1378/chest.121.4.1357
42. McCrystal DJ and Borzi PA. Retroperitoneoscopic resection of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts. Pediatr Surg Int. (2002) 18:375–7. doi: 10.1007/s00383-002-0829-9
43. Martin R, Sanz E, de Vicente E, Ortega P, Labrador E, Paumard A, et al. Differential diagnosis of asymptomatic retroperitoneal cystic lesion: a new case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Eur Radiol. (2002) 12:949–50. doi: 10.1007/s003300101119
44. Takahara K, Watsuji T, Kusaka M, Segawa N, Katsuoka Y, and Yamamoto K. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: A case report. Japanese J Clin Urol. (2002) 56:735–7.
45. Takahashi N, Umeda H, Haga N, Kameoka H, Shishido K, and Yamaguchi O. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. A case report. Japanese J Urol. (2002) 93:4 (583–587). M.H. doi: 10.5980/jpnjurol1989.93.583
46. Hamaguchi N, Ohnishi K, Kaihotsu N, Fujishima N, Tamaki M, Ichikawa Y, et al. Subdiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst in the left crus of diaphragm: report of a case. Kyobu Geka. (2002) 55:523–5.
47. Hisatomi E, Miyajima K, Yasumori K, Okamura H, Nonaka M, Watanabe J, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: a rare case showing the characteristic imaging feature of milk of calcium. Abdom Imaging. (2003) 28:716–20. doi: 10.1007/s00261-003-0003-4
48. Kim YC, Goo JM, Han JK, Lee KH, Lee HS, and Im JG. Subphrenic bronchogenic cyst mimicking a juxtahepatic solid lesion. Abdom Imaging. (2003) 28:354–6. doi: 10.1007/s00261-002-0057-8
49. Matsubayashi J, Ishida T, Ozawa T, Aoki T, Koyanagi Y, and Mukai K. Subphrenic bronchopulmonary foregut malformation with pulmonary-sequestration-like features. Pathol Int. (2003) 53:313–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.2003.01475.x
50. Hedayati N, Cai DX, and McHenry CR. Subdiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst masquerading as an “adrenal incidentaloma. J Gastrointest Surg. (2003) 7:802–4. doi: 10.1016/S1091-255X(03)00134-3
51. Andersson R, Lindell G, Cwikiel W, and Dawiskiba S. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst as a differential diagnosis of pancreatic mucinous cystic tumor. Dig Surg. (2003) 20:55–7. doi: 10.1159/000068851
52. Chatti K, Bedioui H, Saïd W, Chelbi M, Saies O, Bouzani A, et al. Diaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst: a rare case report. Ann Chir. (2003) 128:388–90. doi: 10.1016/S0003-3944(03)00117-2
53. Goh BK, Chan HS, and Wong WK. A rare case of “giant” right-sided retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Dig Dis Sci. (2004) 49:1491–2. doi: 10.1023/B:DDAS.0000042253.60289.76
54. Hashine K, Azuma K, Koizumi T, Sumiyoshi Y, Nishimura R, and Kan M. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: A case report. Nishinihon J Urol. (2004) 66:511–3.
55. Eguchi H. OH, Ishikawa O, Kasugai T, Yokoyama S, Sasaki Y, Miyashiro I, et al. A case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts with Malignant regeneration. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg. (2004) p:584–589. doi: 10.5833/jjgs.37.584
56. Ishizuka O, Misawa K, Nakazawa M, and Nishizawa O. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: laparoscopic treatment. Urol Int. (2004) 72:269–70. doi: 10.1159/000077129
57. Kondo H. FK, Aoki K, Cho M, Hirao Y, and Natsume O. A case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Acta Urol. Jpn. (2005) 51:25–9.
58. Paik SS, Jang KS, Han HX, Oh YH, Lee KG, and Choi D. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking pancreatic pseudocyst in a patient with colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2005) 20:802–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.03763.x
59. Song SY, Noh JH, Lee SJ, and Son HJ. Bronchogenic cyst of the stomach masquerading as benign stromal tumor. Pathol Int. (2005) 55:87–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2005.01788.x
60. Frickmann H, Jungblut S, Bargon J, Fellbaum C, and Hanke P. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Urologe A. (2006) 45:1544–6. doi: 10.1007/s00120-006-1161-0
61. Jo WM, Shin JS, and Lee IS. Supradiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst extending into the retroperitoneum. Ann Thorac Surg. (2006) 81:369–70. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.08.033
62. Akos MB, Péter K, Edina N, János H, and Eszter S. Laparoscopic extirpation of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Magy Seb. (2006) 59:37–41.
63. Orellana F, Cárdenas R, Manríquez ME, Ríos H, Suárez L, and Videla D. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: Report of one case. Rev Med Chil. (2007) 135:924–31. doi: 10.4067/s0034-98872007000700014
64. Vucic M. TD, Zovak M, Mijic A, and Kruslin B. Retroperitoneal peripancreatic bronchogenic cyst mimicking pancreatic cystic tumor. Acta Clin Croat. (2007) 46:171–174.
65. Terry NE SC, Check W, and Brower ST. Retroperitoneal foregut duplication cyst presenting as an adrenal mass. Am Surg. (2007) 73:89–92. doi: 10.1177/000313480707300121
66. Chu PY, Hwang TI, Teng TH, and Lee CC. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst successfully treated by laparoscopic surgery. Ann Saudi Med. (2007) 27:199–200. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2007.199
67. Minei S IT and Hirano D. A case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst treated by laparoscopic surgery. Hinyokika Kiyo. (2007) 53:171–4.
68. Zoubeir YZF, Jahid A, Laraqui L, Bernoussi Z, and Mahassini N. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. A case report. Acta Endosc. (2007) 37:559–561. doi: 10.1007/BF02961802
69. Huang MC, Chen LK, Lu TN, Hwang TIS, Lee CC, and Su CT. A rare case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: A case report. Chin J Radiol. (2008) 33:109–13.
70. Roma A, Varsegi M, Magi‑Galluzzi C, Ulbright T, and Zhou M. The distinction of bronchogenic cyst from metastatic testicular teratoma: a light microscopic and immunohistochemical study. Am J Clin Pathol. (2008) 130:265–73. doi: 10.1309/JKJU9VE1P4WXVCPG
71. Onol FF, Baytekin F, Dikbas O, Ergönenç T, and Tanidir Y. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking adrenal tumour in an adult: is differential diagnosis truly possible? J Clin Pathol. (2009) 62:187–9. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2008.061077
72. Chung JM, Jung MJ, Lee W, and Choi S. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst presenting as adrenal tumor in adult successfully treated with retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery. Urology. (2009) 73:442.e13–5. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2008.02.056
73. Obando J, Merkle E, and Bean SM. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2009) 7:A24–e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.11.011
74. Valero Linan AS, González Masía JA, Rueda Martínez JL, Prat Calero A, Bermúdez Rodríguez A, and Vázquez Aragón P. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst in patients with Crohn’s disease. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. (2009) 101:655–6. doi: 10.4321/s1130-01082009000900012
75. El Youssef R, Fleseriu M, and Sheppard BC. Adrenal and pancreatic presentation of subdiaphragmatic retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts. Arch Surg. (2010) 145:302–4. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2010.12
76. Kim HG, Jeong MR, Kang H, Cheong O, Ju JK, Park YK, et al. Intraperitoneal bronchogenic cyst misidentified as gastric submucosal tumor. J Korean Surg Soc. (2010) 79:149–151. doi: 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.2.149
77. Inaba K, Sakurai Y, Umeki Y, Kanaya S, Komori Y, and Uyama I. Laparoscopic excision of subdiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst occurring in the retroperitoneum: report of a case. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. (2010) 20:e199–203. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e3181fcbe92
78. Rud O, May M, Brookman‑Amissah S, Moersler J, Greiner A, and Gilfrich C. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst treated by laparoscopic surgery. Chirurg. (2010) 81:243–6. doi: 10.1007/s00104-009-1799-4
79. Diaz Nieto R, Naranjo Torres A, Gómez Alvarez M, Ruiz Rabelo JF, Pérez Manrique MC, Ciria Bru R, et al. Intraabdominal bronchogenic cyst. J Gastrointest Surg. (2010) 14:756–8. doi: 10.1007/s11605-009-0932-5
80. Sugar I, Vörös A, Diczházi C, Barabás L, Valkó L, Kovács GL, et al. Successfully operated cases of mediastinal and retroperitoneal bronchial cysts. Magy Seb. (2010) 63:168–71. doi: 10.1556/MaSeb.63.2010.4.5
81. Petrina A, Boselli C, Cirocchi R, Covarelli P, Eugeni E, Badolato M, et al. Bronchogenic cyst of the ileal mesentery: a case report and a review of literature. J Med Case Rep. (2010) 4:313. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-313
82. Choe Y.-M. YYH and Chung JC. Multiple duplication cysts with severe anemia in thoracic and abdominal cavity. Am J Gastroenterol. (2010), S385.
83. Zdichavsky M, Beckert S, Kirschniak A, and Königsrainer A. Rare incidence of laparoscopic right adrenalectomy due to a retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: A case report. Surg Endoscopy Other Interventional Techniques. (2011) 25:S160. doi: 10.1007/s00464-011-1604-6
84. Alguraan Z, Agcaoglu O, El‑Hayek K, Hamrahian AH, Siperstein A, Berber E, et al. Retroperitoneal masses mimicking adrenal tumors. Endocr Pract. (2012) 18:335–41. doi: 10.4158/EP11240.OR
85. Parray FQ, Sherwani AY, Dangroo SA, Bisati RA, and Malik NS. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking hydatid liver: a case report. Case Rep Surg. (2012) 2012:312147. doi: 10.1155/2012/312147
86. Govaerts K, Van Eyken P, Verswijvel G, and Van der Speeten K. A bronchogenic cyst, presenting as a retroperitoneal cystic mass. Rare Tumors. (2012) 4:e13. doi: 10.4081/rt.2012.e13
87. Powell G, Burrows C, Houghton A, and Otter M. An incidental peri-adrenal cystic lesion. BMJ Case Rep. (2012) 2012:bcr2012006606. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-006606
88. Piton N, Gobet F, Werquin C, Landreat A, Lefebvre H, Pfister C, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Ann Pathol. (2012) 32:267–70. doi: 10.1016/j.annpat.2012.07.002
89. O’Neal PB, Moore FD, Gawande A, Cho NL, King EE, and Moalem J. Bronchogenic cyst masquerading as an adrenal tumor: a case of mistaken identity. Endocr Pract. (2012) 18:e102–5. doi: 10.4158/EP11186.CR
90. Choi KK, Sung JY, Kim JS, Kim MJ, Park H, Choi DW, et al. Intra-abdominal bronchogenic cyst: report of five cases. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. (2012) 16:75–9. doi: 10.14701/kjhbps.2012.16.2.75
91. Jannasch O, Büschel P, Wodner C, Seidensticker M, Kuhn R, Lippert H, et al. Retroperitoneoscopic and laparoscopic removal of periadrenally located bronchogenic cysts–a systematic review. Pol Przegl Chir. (2013) 85:706–13. doi: 10.2478/pjs-2013-0108
92. Matsuzaki K. OM, Yoshida Y, Yoshioka I, Tsujimura A, and Nonomura N. A case of bronchogenic cyst treated as retroperitoneal tumor. Acta Urol. Jpn. (2013) 59:715–8.
93. Kluger MD, Tayar C, Belli A, Salceda JA, van Nhieu JT, Luciani A, et al. A foregut cystic neoplasm with diagnostic and therapeutic similarities to mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. JOP. (2013) 14:446–9. doi: 10.6092/1590-8577/1402
94. Kohno M, Namura K, Fujikawa A, Sawada T, Oota J, and Moriyama M. A case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst treated by laparoscopic surgery. Hinyokika Kiyo. (2013) 59:359–61.
95. Castro R, Oliveira MI, Fernandes T, and Madureira AJ. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: MRI findings. Case Rep Radiol. (2013) 2013:853795. doi: 10.1155/2013/853795
96. Runge T, Blank A, Schäfer SC, Candinas D, Gloor B, and Angst E. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking a pancreatic or adrenal mass. Case Rep Gastroenterol. (2013) 7:428–32. doi: 10.1159/000355879
97. Cai Y, Guo Z, Cai Q, Dai S, Gao W, Niu Y, et al. Bronchogenic cysts in retroperitoneal region. Abdom Imaging. (2013) 38:211–4. doi: 10.1007/s00261-012-9909-z
98. Dong B, Zhou H, Zhang J, Wang Y, and Fu Y. Diagnosis and treatment of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cysts: A case report. Oncol Lett. (2014) 7:2157–9. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.1974
99. Zdichavsky M. Laparoscopic excision of a deep para-rectal bronchogenic cyst. Surg Endoscopy Other Interventional Techniques. (2014) 28:S196. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3485-y
100. Terasaka T, Otsuka F, Ogura‑Ochi K, Miyoshi T, Inagaki K, Kobayashi Y, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: a rare incidentaloma discovered in a juvenile hypertensive patient. Hypertens Res. (2014) 37:595–7. doi: 10.1038/hr.2014.38
101. Herek D, Erbiş H, Kocyigit A, and Yagci AB. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst originating from diaphragmatic crura. Indian J Surg. (2015) 77:1397–8. doi: 10.1007/s12262-014-1045-2
102. Robertson FP, Tsironis D, and Davidson BR. A diaphragmatic retroperitoneal cyst. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. (2015) 97:e77–8. doi: 10.1308/003588415X14181254790329
103. Zhang D, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhu J, Feng C, Yang C, et al. Challenge in preoperative diagnosis of retroperitoneal mucinous cyst in a pediatric patient. Int J Clin Exp Med. (2015) 8:19540–7.
104. Bulut G, Bulut MD, Bahadır I, and Kotan Ç. Bronchogenic cyst mimicking an adrenal mass in the retroperitoneal region: report of a rare case. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. (2015) 58:96–8. doi: 10.4103/0377-4929.151200
105. Huang H LG, Li H, Yan W, Zhang Y, and Ji Z. Analysis of clinical features of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. (2015) 53:856–9.
106. Trehan M, Singla S, Singh J, Garg N, and Mahajan A. A rare case of intra- abdominal bronchogenic cyst- A case report. J Clin Diagn Res. (2015) 9:PD03–4. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/12949.6761
107. Jiang X, Zeng H, Gong J, and Huang R. Unusual uptake of radioiodine in a retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst in a patient with thyroid carcinoma. Clin Nucl Med. (2015) 40:435–6. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000000664
108. Yoon YR, Choi J, Lee SM, Kim YJ, Cho HD, Lee JW, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst presenting paraadrenal tumor incidentally detected by (18)F-FDG PET/CT. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2015) 49:69–72. doi: 10.1007/s13139-014-0306-0
109. Padnani A, Bawa R, Shah D, and Satterfield J. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: Case report and review of literature. Surg Endoscopy Other Interventional Techniques. (2016) 30:S499. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4771-7
110. Pasquer A, Djeudji F, Hervieu V, Rabeyrin M, and Barth X. A rare retrorectal presentation of a bronchogenic cyst: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2016) 24:112–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.05.028
111. Briseno-Renteria J.I. L.-V.J.F., Estrada-Bujanos JM, Camacho-Trejo VC, Castro-Zazueta S, Quintero-Badillo JE, Tejeda-Andrade CF, et al. Laparoscopic adrenalectomy in a patient with bronchogenic cyst. Rev Mex. Urol. (2018) 78:57–61. doi: 10.24245/revmexurol.v78i1.1650
112. Başoğlu M, Karabulut K, Selçuk Özbalcı G, Aykun N, Çamlıdağ İ, Bülent Güngör B, et al. Laparoscopic resection of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst clinically presenting like adrenal cyst. Turk J Surg. (2022) 38(2):211–3. doi: 10.47717/turkjsurg.2022.4033
113. Mase T, Junichi T, Wada M, Horiba T, Shibata A, and Kobayashi H. A case of bronchogenic cyst with suspected left adrenal tumor. World J Endocrine Surg. (2018) 10:87.
114. Shree Vishnu Siddarth R and Balashanmugham TS. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking an adrenal cyst - A case report. Indian J Urol. (2018) 34:32.
115. Liu Q, Gao Y, Zhao Z, Zhao G, Liu R, and Lau WY. Robotic resection of benign nonadrenal retroperitoneal tumors: A consecutive case series. Int J Surg. (2018) 55:188–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.04.013
116. Pérez Alonso AJ, Á X Argote Camacho , Pérez Durán C, Aneiros Fernández J, and Petrone P. Quiste broncogénico gástrico. Rev Colombiana Cirugía. (2019) 34. doi: 10.30944/20117582.101
117. Cremona F, Sciuto A, Cassano DP, Parente P, and Pirozzi F. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking a pancreatic lesion: A rare mass found in the retroperitoneal region. Chirurgia (Turin). (2019) 32:143–6. doi: 10.23736/S0394-9508.18.04842-8
118. Subramanian JB, K SS, and Selvarangam S. A case report- retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst in relation to the hindgut. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2020) 75:140–2. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.09.038
119. Kim AY, Min SJ, Kim H, and Choi JA. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst located in the presacral space: A case report. Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi. (2021) 82:207–11. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2020.0069
120. Addeo P, Averous G, and Bachellier P. Intraabdominal bronchogenic cyst. Dig Liver Dis. (2020) 52:784–5. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.04.008
121. Tanaka T, Hoshi A, Yamaguchi A, Nonaka H, Nitta S, Kojo K, et al. A case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst successfully resected with retroperitoneoscopic surgery. Hinyokika Kiyo. (2020) 66:307–11. doi: 10.14989/ActaUrolJap_66_9_307
122. Sinha V, Nandi P, Shankar M, and Sardana N. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: A rare case study. Cureus. (2020) 12:e10421. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10421
123. Jayanthi P, Tolia S, and Parikh J. Pancreatic bronchogenic cyst: Easily hidden, difficult to identify. Hpb. (2020) 22:S194. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2020.04.767
124. Qingyu J, Xiaolong L, Ruohan Z, Licong M, Zhichao T, Qingwei C, et al. Computed tomography helps pre-operative evaluation before laparoscopic resection of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst: A case report. J Minim Access Surg. (2021) 17:95–7. doi: 10.4103/jmas.JMAS_72_20
125. Wu LD, Wen K, Cheng ZR, Alwalid O, and Han P. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst in suprarenal region treated by laparoscopic resection: A case report. World J Clin cases. (2021) 9:7245–50. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i24.7245
126. Moghadam E.M. VM, Movahedian AH, and Mosayebi Z. Bronchogenic cyst: A rare cause of a retroperitoneal mass in a neonate. Iran. J Neonatol. (2021), 106–109. doi: 10.22038/ijn.2020.43514.1724
127. Cowan S, Gunawardene A, and Davenport E. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mistaken as an adrenal adenoma. ANZ J Surg. (2021) 91:E526–7. doi: 10.1111/ans.16515
128. Clementino-Filho J, Surjan RCT, Taglieri E, and Ardengh JC. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking a pancreatic cystic lesion with extremely high level of intralesional fluid CA-19.9 antigen: benign in disguise. Indian J Surg. (2022) 84:556–61. doi: 10.1007/s12262-021-03137-x
129. Amano K, Taniguchi H, Ikeda J, Noda Y, Ohe C, Miyasaka C, et al. A case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst diagnosed by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hinyokika Kiyo. (2022) 68:11–6. doi: 10.14989/ActaUrolJap_68_1_11
130. Florez Rial MDP, Ruz Portero S, Valenzuela González M, and Romero Madrid B. Intrapancreatic bronchogenic cyst. A case report. Rev Esp Patol. (2022) 55:292–6. doi: 10.1016/j.patol.2020.11.005
131. Toi N, Kurajoh M, Noda S, and Emoto M. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst adjacent to adrenocortical adenoma. Intern Med. (2022) 61:2821–2. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9188-21
132. Aoyagi T, Kato Y, Tsuyukubo T, Tamura D, Osawa T, Matsuura T, et al. A case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Hinyokika Kiyo. (2022) 68:47–51. doi: 10.14989/ActaUrolJap_68_2_47
133. Tadokoro T, Misumi T, Itamoto T, Nakahara H, Matsugu Y, Ikeda S, et al. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst resected by single-incision laparoscopic surgery in an adolescent female: A case report. Asian J Endosc Surg. (2022) 15:206–10. doi: 10.1111/ases.12973
134. Wang E, Zhang L, Wang Y, and Zhang M. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst adjacent to aortaventralis:A case report. Asian J Surg. (2023) 46:1583–4. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2022.09.085
135. Nunez-Rocha RE, Pérez V, Urango ML, Mejía M, Palau M, and Herrera‑Almario G. Extrapulmonary bronchogenic cyst: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2023) 110:108706. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108706
136. Tao L, Xu F, Fang Q, Hu X, and Zhang L. A rare case of retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst. Chin J Digestive Endoscopy. (2023) 40:836–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321463-20230225-00052
137. Idrees H, Zarrar R, Taslicay CA, and Elsayes KM. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking an adrenal cyst: case report. BJR Case Rep. (2024) 10:uaad001. doi: 10.1093/bjrcr/uaad001
Keywords: bronchogenic cyst, retroperitoneal, adrenal mass, case report, robot-assisted laparoscopy surgery
Citation: Xiang S, Hao J, Zong X, Wen S, Zhang J, Chen C, Hao J, Song Z, Tong H, Wang L, Fan B and Liu Z (2025) Case Report: Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking adrenal mass: Clinical implications and comprehensive literature analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1679794. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1679794
Received: 05 August 2025; Accepted: 15 September 2025;
Published: 01 October 2025.
Edited by:
Benyi Li, University of Kansas Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Jun Pang, Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaWei Xie, LMU Munich University Hospital, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Xiang, Hao, Zong, Wen, Zhang, Chen, Hao, Song, Tong, Wang, Fan and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiyu Liu, bHp5ZG9jdEAxNjMuY29t; Bo Fan, ZmFuYm9AZG11LmVkdS5jbg==; Liang Wang, d2FuZ2xkb2N0QHNpbmEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Shengxiang Xiang1,2,3,4†
Shengxiang Xiang1,2,3,4† Liang Wang
Liang Wang Bo Fan
Bo Fan Zhiyu Liu
Zhiyu Liu