- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Nantong Third People’s Hospital, Nantong, Jiangsu, China
- 3Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, The Affiliated Taizhou People’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Taizhou School of Clinical Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Taizhou, Jiangsu, China
Background: Sintilimab plus a Bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) is an approved first-line regimen for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC) in China. However, data on its safety and efficacy in patients with impaired liver function remain limited. We assessed the clinical outcomes of this combination therapy in HCC patients with Child-Pugh class A (CP-A) and class B (CP-B) liver function.
Methods: In this multicenter retrospective cohort study, 99 patients with advanced uHCC (73 CP-A; 26 CP-B) who received first-line Sin/Bev were included. Tumor response was assessed using modified RECIST criteria, and adverse events (AEs) were graded per CTCAE v5.0. Survival outcomes, including overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and time to hepatic decompensation (TTD), were analyzed via Kaplan-Meier estimates and Cox proportional hazards models.
Results: The objective response rates (ORR) of patients with CP-A and CP-B treated with Sin/Bev were 50.7% and 57.7%, respectively, and both could achieve good anti-tumor efficacy. CP-B had inferior survival: median OS (15 vs 22 months, p=0.044), PFS (8 vs 14 months, p=0.014), and TTD (7 vs 15 months, p<0.001). The CP-B cohort demonstrated comparable incidence rates of grade 3–4 AEs to the CP-A group (34.6% vs 34.2%). Hemorrhagic events and thrombocytopenia emerged as predominant grade 3–4 AEs in CP-B patients (15.4% for both).
Conclusions: Sin/Bev demonstrated encouraging short-term anti-tumor activity in HCC of CP-A and CP-B, while survival outcomes were affected by differences in hepatic function. Although the regimen was generally well tolerated, patients with impaired liver reserve require vigilant monitoring and comprehensive supportive strategies to maximize therapeutic outcomes.
1 Introduction
Liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality globally, following lung and colorectal cancers, and ranks as the sixth most common malignancy worldwide (1). Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the predominant form of primary liver cancer, is primarily associated with chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV), as well as exposure to aflatoxins, heavy alcohol intake, obesity, diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (2–4). In early-stage HCC, curative interventions such as hepatic resection, liver transplantation, and local ablative therapies including percutaneous ethanol injection, radiofrequency ablation, and cryotherapy-are typically considered, contingent upon preserved hepatic function (5). However, the majority of patients present with advanced disease or impaired hepatic reserve, rendering them ineligible for surgical resection. These individuals are typically managed with systemic therapies, often in combination with locoregional approaches such as transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) or hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) (6).
Recent therapeutic advances, particularly in molecular-targeted agents and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have significantly improved clinical outcomes in patients with intermediate and advanced HCC (7). Despite this progress, the pivotal clinical trials evaluating first-line systemic therapies-including the REFLECT trial (lenvatinib), the IMbrave150 trial (atezolizumab plus bevacizumab), the HIMALAYA trial (durvalumab plus tremelimumab), the CheckMate 9DW (nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus lenvatinib or sorafenib), and the CARES-310 study (camrelizumab plus apatinib)-have almost exclusively enrolled patients with preserved hepatic function, classified as Child-Pugh class A (CP-A) (8–13). In the phase II-III ORIENT-32 trial conducted in China, the combination of sintilimab (an anti-programmed death-1 [PD-1] antibody) and bevacizumab (a monoclonal antibody targeting vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF]) significantly reduced the risk of disease progression and death in patients with unresectable HCC (14). However, only 4% of trial participants had moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh B7), leaving substantial uncertainty regarding the applicability of these findings to patients with more advanced liver dysfunction.
To address this gap, there is a pressing need for studies specifically evaluating the safety and efficacy of combination immunotherapy in patients with Child-Pugh class B (CP-B) HCC, a population that is frequently underrepresented in clinical trials yet commonly encountered in routine practice.
Parallel efforts have highlighted the albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade as an objective and reproducible tool for assessing liver function and prognostic stratification in patients with HCC (15). The ALBI grade correlates robustly with established hepatic scoring systems, including the Child-Pugh (CP) classification and the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score, and may offer enhanced discriminatory power in heterogeneous patient populations (16). Critically, recent research positions ALBI not merely as a complementary metric, but as a pivotal prognostic factor that outperforms CP classification in predicting survival outcomes (17–19). Furthermore, elevated ALBI grade independently associates with increased gastrointestinal bleeding risk following atezolizumab-bevacizumab (A+B) therapy, underscoring its clinical utility for risk stratification during systemic treatment regimens (17).
In this multicenter retrospective cohort study, we evaluated the clinical outcomes of patients with advanced HCC and CP-A or CP-B hepatic function who received sintilimab in combination with bevacizumab as first-line systemic therapy in real-world settings across four institutions in China. Beyond the Child-Pugh classification, we further sought to characterize liver function using the albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade, with a particular focus on exploring whether on-treatment ALBI dynamics could serve as an early indicator for long-term survival.
2 Methods
2.1 Patients
We conducted a multicenter, retrospective analysis of patients seen at The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Taizhou People’s Hospital, Nantong Third People’s Hospital, and The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University.
Patients who had a prior diagnosis of HCC classified as Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage B or C, and CP-A or B, and received sintilimab plus bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) as first-line systemic therapy were included between August 2020 and December 2024. The diagnosis of HCC was confirmed by either histopathological examination or non-invasive assessment, in accordance with criteria established by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) for patients with cirrhosis. Specifically, for non-invasive diagnosis, typical imaging findings on dynamic contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were required, in combination with elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels, in line with AASLD guidelines.
Eligibility required patients ≥18 years with radiologically measurable disease, not amenable to curative surgical resection or locoregional therapies, such as radiofrequency ablation, TACE, or HAIC, or to have experienced disease progression following such treatments. To avoid potential confounding effects, a minimum interval of 6 weeks was required between the last locoregional therapies and the initiation of sintilimab plus bevacizumab. Patients were excluded if they had Child-Pugh class C cirrhosis, radiologically unmeasurable intrahepatic lesions, confirmed non-HCC malignancies, incomplete baseline or follow-up data, or loss of follow-up.
2.2 Treatment and assessment
The treatment regimen followed the standard institutional protocol. Dose modifications, including temporary interruption or dose reduction, were implemented at the discretion of the attending physicians, based on each patient’s clinical status, tolerance, and adverse event (AE) profile. Treatment with sintilimab and bevacizumab was continued until the onset of intolerable toxicity or radiological confirmation of disease progression.
Tumor assessment was conducted using dynamic contrast-enhanced CT or MRI. Baseline imaging was obtained prior to treatment initiation, and follow-up scans were performed every 6–8 weeks in accordance with institutional guidelines. Tumor response was evaluated using the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours (mRECIST), which involves measuring the diameters of target lesions to determine whether the response status corresponds to complete response, partial response, stable disease, or progressive disease. Treatment-emergent adverse events were graded using the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 5.0.
2.3 Statistical analyses
Patient demographics and clinical characteristics were stratified by Child-Pugh class for comparative analysis. Categorical variables were expressed as frequencies and percentages and analyzed using either the Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Continuous variables were reported as mean and standard deviation (SD).
The Kaplan-Meier method was used to calculate median overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and time to hepatic decompensation (TTD). OS was defined as the interval from initiation of sintilimab plus bevacizumab to death from any cause. Patients who were alive at the time of data cutoff (December 30, 2024) were censored on that date. PFS was defined as the time from treatment initiation to radiologically confirmed progression based on mRECIST or death from any cause, with censoring at the last follow-up for those without an event. TTD was defined as the interval from the first dose of therapy to the occurrence of either: (a) laboratory-confirmed decline in hepatic synthetic function (e.g. serum bilirubin elevation), or (b) clinical signs of portal hypertension, such as hepatic encephalopathy, ascites requiring intervention, or acute variceal bleeding. Safety outcomes in the CP-B group were compared with those in the CP-A group. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted using Cox proportional hazards regression to evaluate prognostic factors for OS and PFS. Missing data were handled using a complete-case analysis approach, excluding cases with unavailable key variables from the relevant statistical tests. A two-sided p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 27.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA).
3 Results
3.1 Patients characteristics
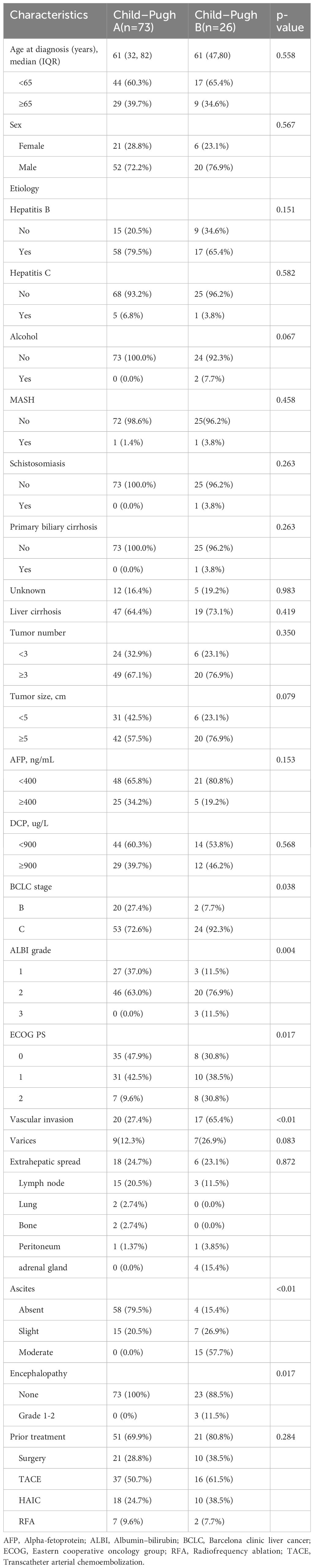
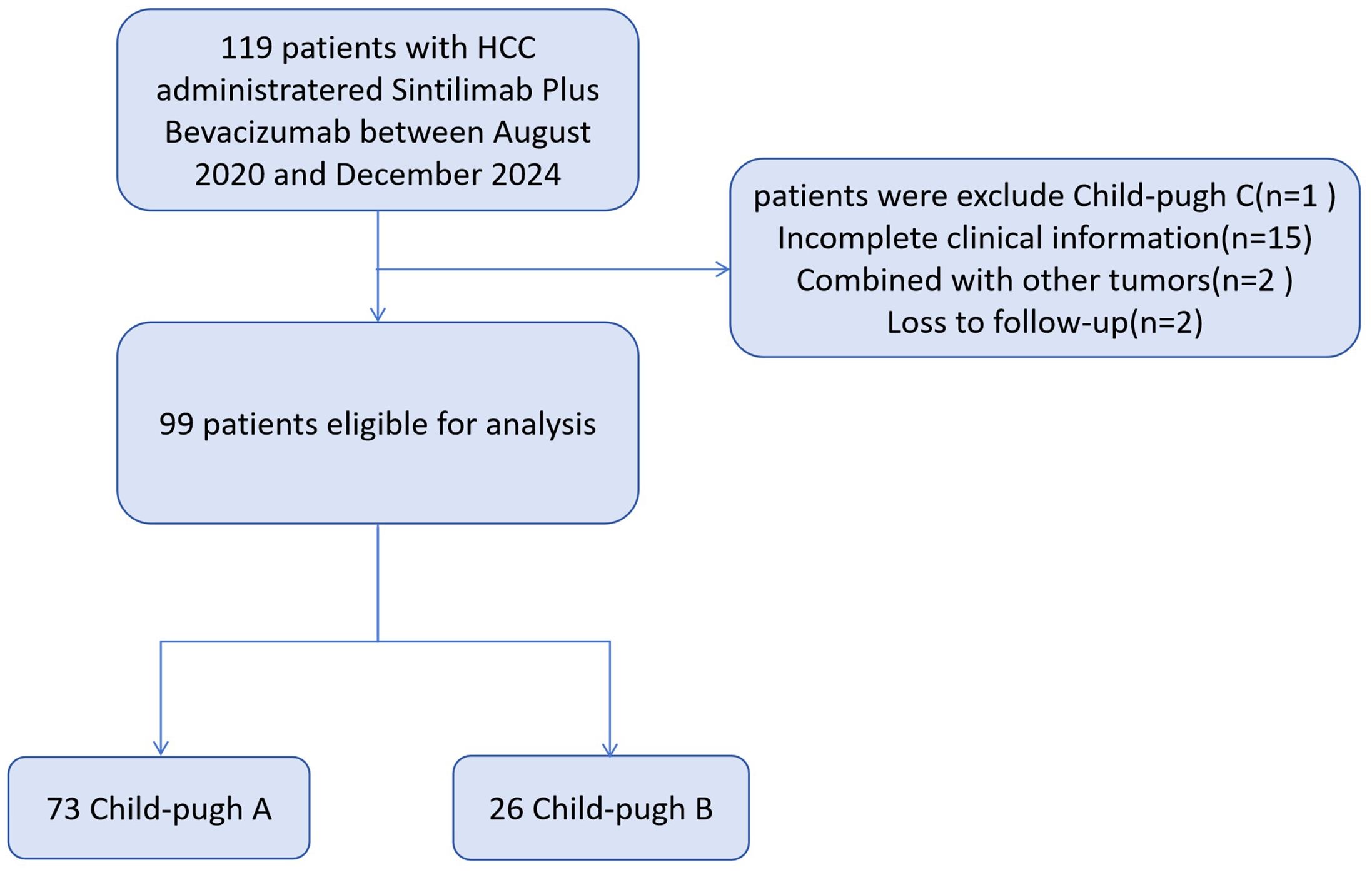
Baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. From August 2020 to December 2024, a total of 99 patients with unresectable HCC were included (73 Child-Pugh A; 26 Child-Pugh B; Figure 1). The median age was 61 years in both groups, and most patients were male, the proportion of males was 72.2% in Child-Pugh Group A and 76.9% in Group B. Hepatitis B virus was the predominant etiology, present in 79.5% of Child-Pugh A and 65.4% of Child-Pugh B patients. Multifocal tumors (≥3 lesions) were more frequent in CP-B (76.9% vs 67.1%). The CP-A cohort had a higher rate of prior local treatment than the CP-B cohort (61.6% vs 53.8%), with TACE being the most common. Extrahepatic metastasis occurred in 23.1% of CP-B patients, mainly adrenal involvement. In CP-A, lymph node metastasis was most common, followed by lung and bone.
The CP-B cohort showed more severe disease features than CP-A. They had higher proportions of BCLC stage C (92.3% vs 72.6%; p=0.038), ALBI grade 3 (11.5% vs 0.0%; p=0.004), ECOG PS 2 (30.8% vs 9.6%; p=0.017), and vascular invasion (65.4% vs 27.4%; p<0.01). Moderate ascites (57.7% vs 0.0%; p<0.01) and hepatic encephalopathy (11.5% vs 0.0%; p=0.017) were also significantly more frequent in CP-B.
3.2 Treatment outcomes
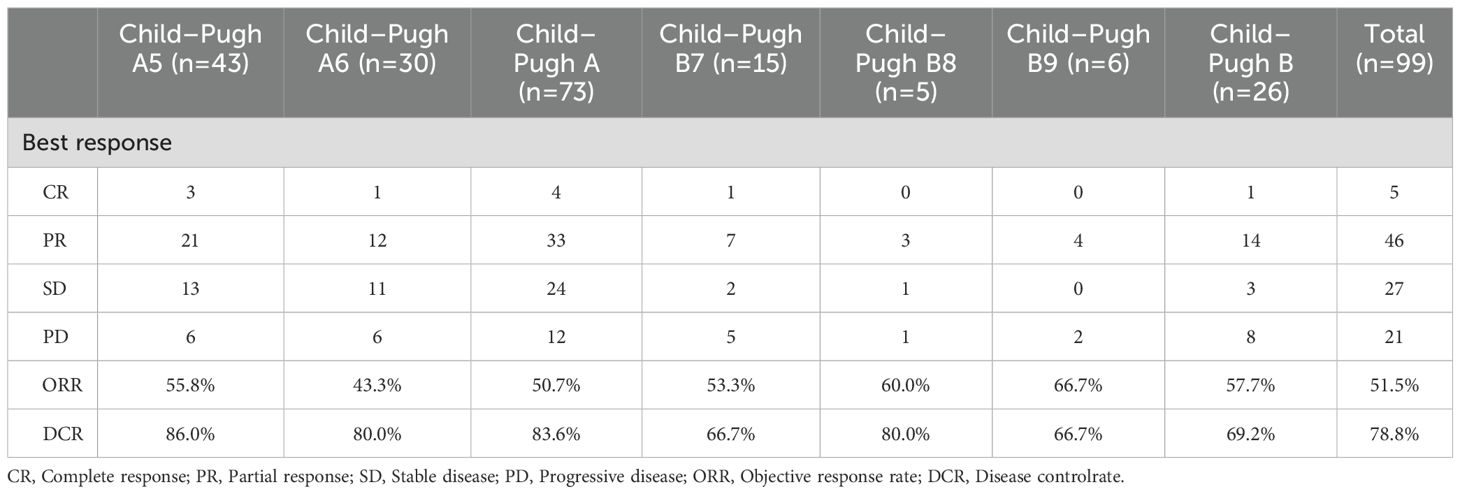
Treatment responses are summarized in Table 2. Both Child-Pugh cohorts demonstrated robust antitumor activity based on mRECIST assessments, with comparable objective response rates (ORR) observed between CP-A and CP-B subgroups (50.7% vs 57.7%). In the Child-Pugh A group (n=73), a complete response (CR) was achieved in 4 patients (5.5%), and a partial response (PR) was observed in 33 patients (45.2%). In the CP-B subgroup, 1 (3.8%) and 14 (53.8%) patients had CR and PR, respectively. Among CP-B8–9 patients (n=11), an objective response rate (ORR) of 63.6% (7/11) was achieved. This robust efficacy underscores the therapeutic potential of this regimen in advanced liver dysfunction and addresses a pivotal unmet clinical need in this marginalized subgroup. The CP-A cohort demonstrated a higher disease control rate (DCR, CR+PR+SD) compared with the CP-B group (83.6% vs 69.2%).
Patients with CP-A liver function demonstrated a significantly longer median OS of 22 months (95% CI 19.3-24.7) compared to 15 months (95% CI 11.7-18.3) in those with CP-B liver function (Figure 2a). Further stratification of CP-B patients revealed distinct survival patterns: those with CP-B7 achieved an mOS of 18 months (95% CI 4.9-31.1), whereas patients with more advanced CP-B8–9 liver dysfunction showed a reduced mOS of 15 months (95% CI 12.4–17.6; Figure 2b). Consistent with liver function analysis, the Barcelona clinical hepatocellular carcinoma (BCLC) stage also affected the survival indicators OS (P = 0.041; Figure 2c). When evaluating survival based on ALBI score, patients with ALBI grade 1 had an mOS of 22 months (95% CI 19.3-24.7), while those with grade 2 had an mOS of 18 months (95% CI 13.4-22.6; Figure 2d). Analysis of PFS according to baseline liver function revealed significant disparities between CP classes. Patients with CP-A exhibited a median PFS of 14 months (95% CI 9.2-18.8), substantially longer than the 8-month mPFS in CP-B patients (95% CI 4.7-11.3; Figure 3a; p=0.014). Subgroup analysis of CP-B patients demonstrated a gradational decline: CP-B7 patients maintained an mPFS of 11 months (95% CI 6.6-15.4), whereas those with CP-B8–9 showed faster progression with an mPFS of 7 months (95% CI 5.3-8.7; Figure 3b). Consistent with liver function stratification, analysis by BCLC stage revealed significant differences (p=0.018): BCLC-B patients achieved an mPFS of 18 months (95% CI 8.3-27.7), compared with 11 months (95% CI 9.7-12.3) for BCLC-C patients (Figure 3c). Patients with ALBI grade 2 had an mPFS of 11 months (95% CI 9.5-12.5; Figure 3d).
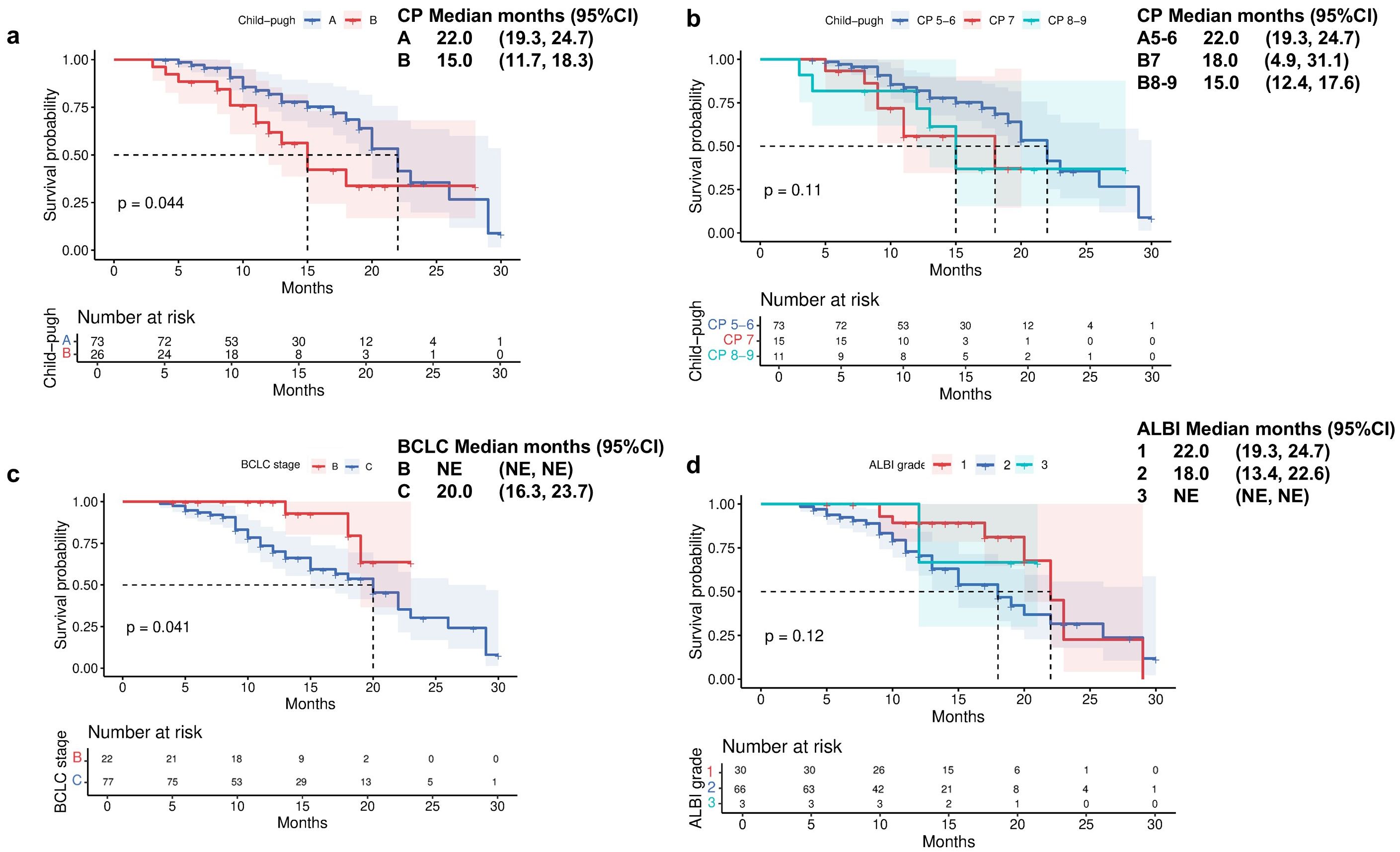
Figure 2. Overall survival by (a) Child-Pugh liver status (A vs B), (b) Child-Pugh liver status (A5/6 vs B7 vs B8/9), (c) Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage (B vs C), and (d) ALBI grade liver function.
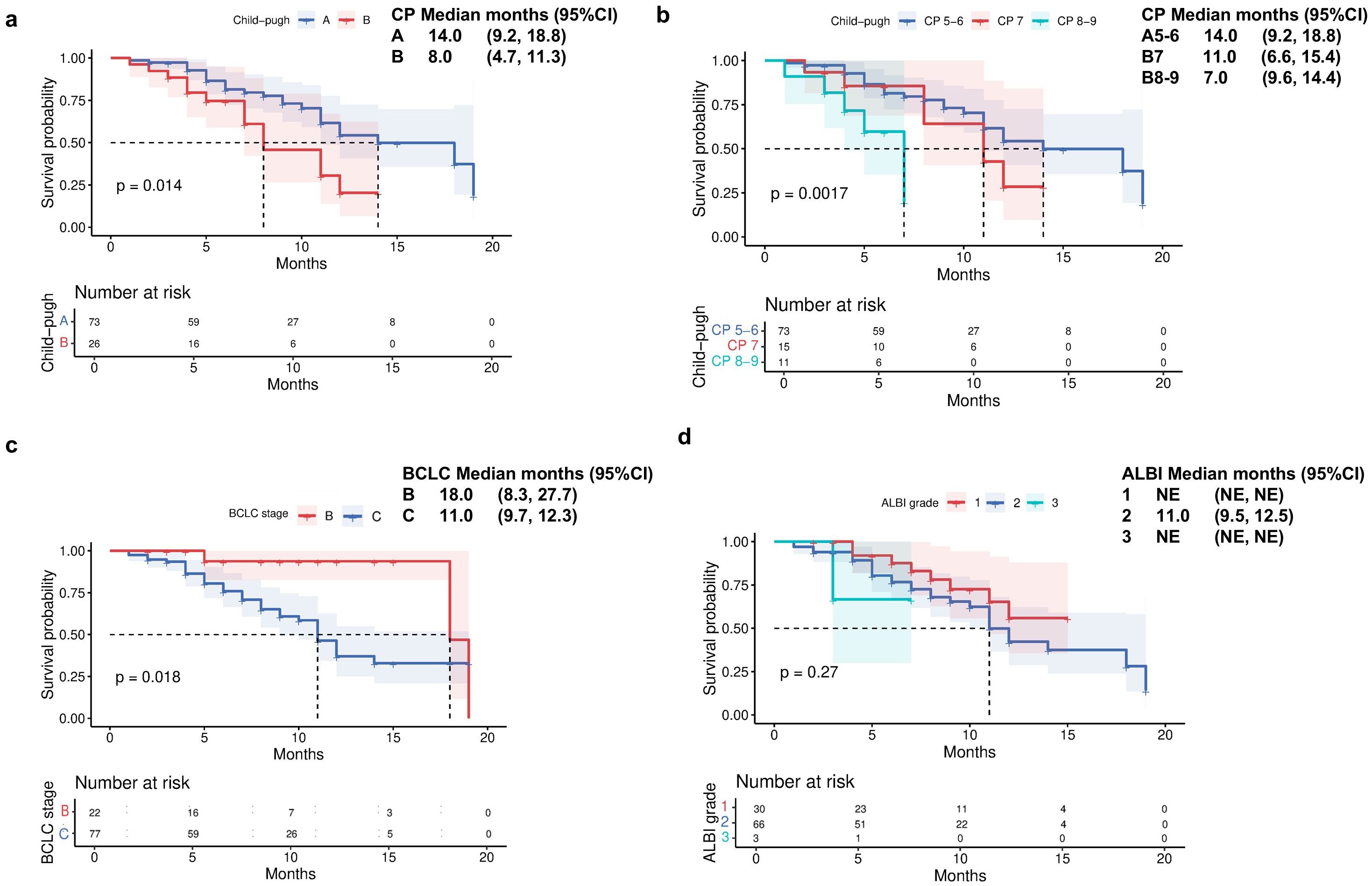
Figure 3. Progression-free survival by (a) Child-Pugh liver status (A vs B), (b) Child-Pugh liver status (A5/6 vs B7 vs B8/9), (c) Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage (B vs C), and (d) ALBI grade liver function.
The median TTD was 15 months for CP-A patients, compared with 7 months (95% CI 4.5-9.5) for CP-B patients (p<0.001; Figure 4a). Subgroup analysis within CP-B showed that CP-B7 patients had a median TTD of 8 months (95% CI 2.4-13.6), while CP-B 8–9 patients had a reduced median of 6 months (95% CI 3.9-8.1; Figure 4b).
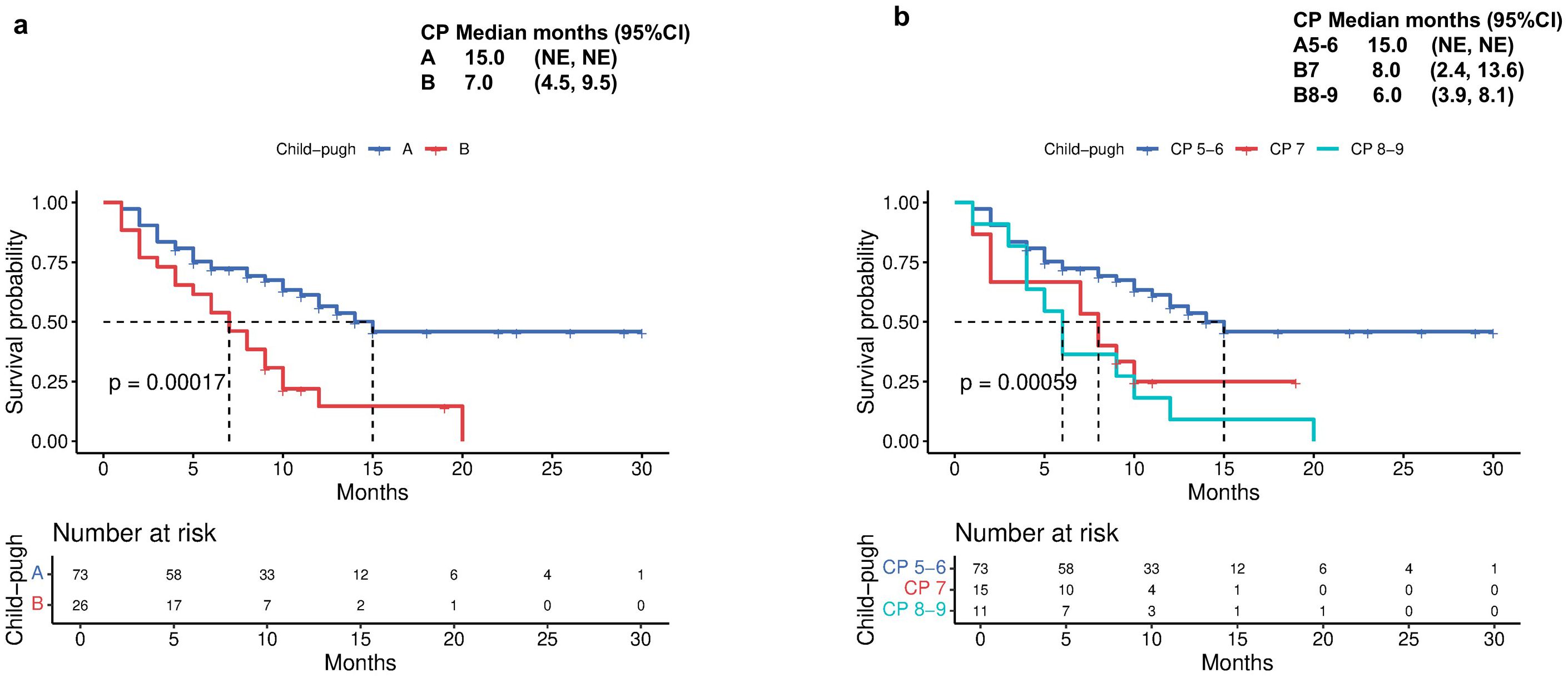
Figure 4. Time to decompensation (TTD) by (a) Child-Pugh liver status (A vs B) and (b) Child-Pugh liver status (A5/6 vs B7 vs B8/9).
Patients with improved ALBI grade at 6 months (n=84) demonstrated significantly longer OS compared to those with deteriorated ALBI (22 months vs 17 months, p=0.027, Figure 5a). Similarly, progression-free survival was markedly prolonged in the ALBI-improvement cohort (14 months vs 8 months, p=0.014, Figure 5b).
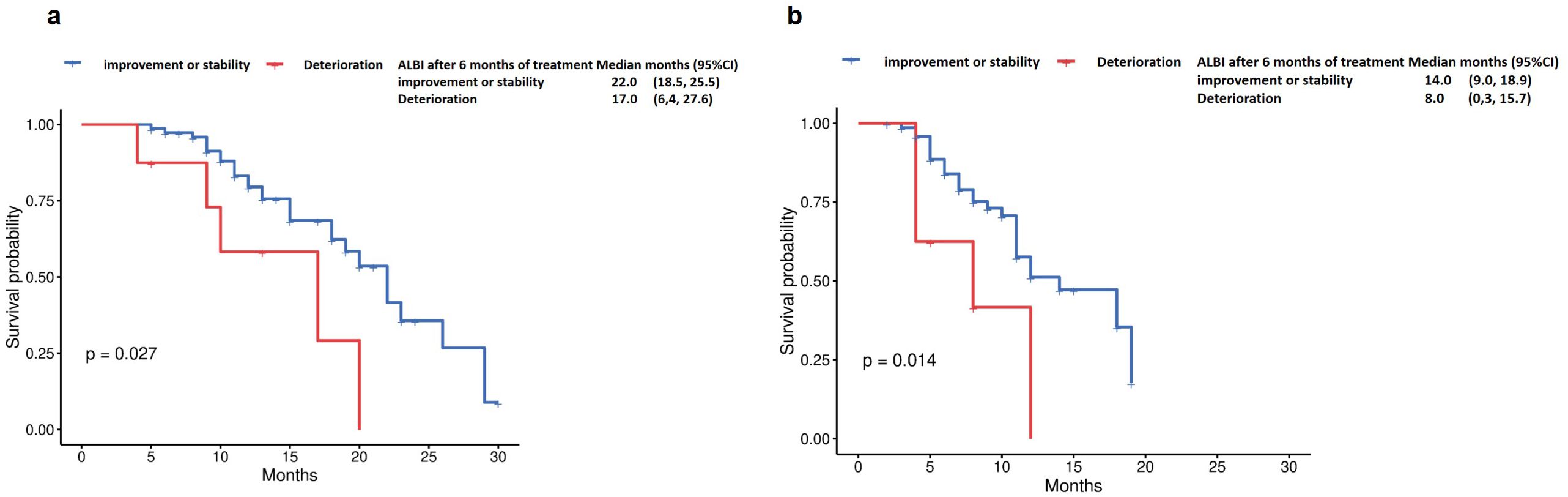
Figure 5. Overall survival by (a) ALBI after 6 months of treatment (Deterioration vs improvement or stability), and Progression-free survival by (b) ALBI after 6 months of treatment (Deterioration vs improvement or stability).
To account for the baseline imbalance in tumor stage between CP-A and CP-B groups, we performed subgroup analyses restricted to patients with BCLC-C stage (n=77). This analysis revealed that median PFS was 11 months for CP-A versus 6 months for CP-B (p=0.012, Figure 6a). Median OS was 22 months for CP-A patients versus 15 months for CP-B patients (p=0.05, Figure 6b).
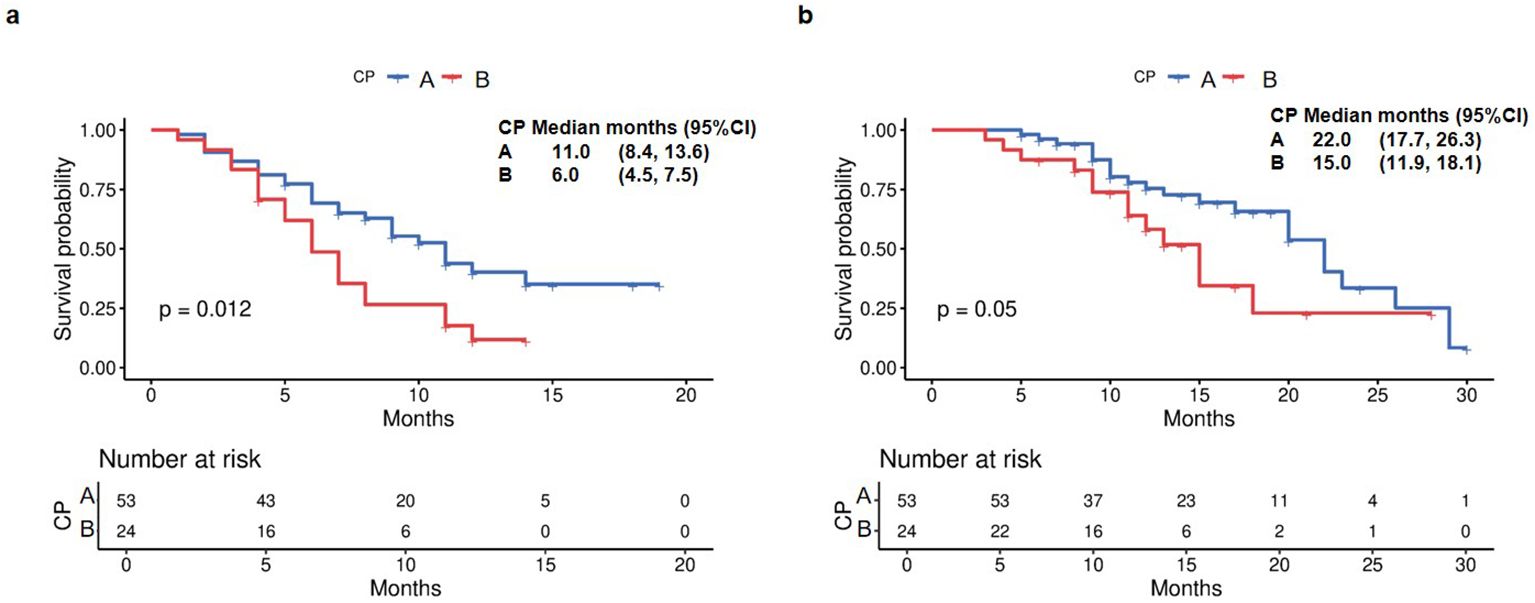
Figure 6. Kaplan Meier survival curves of PFS and OS in the BCLC-C subgroup. (a) PFS in the BCLC-C subgroup. (b) OS in the BCLC-C subgroup.
3.3 Univariate and multivariate analysis for factors predictive of survival
In univariate analysis (Table 3; Figure 7a), several variables demonstrated prognostic significance for overall survival (OS). A higher CP score was associated with worse OS. Specifically, patients with CP-B had a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.974 (95% CI 0.995-3.917; p=0.052) compared with CP-A, indicating a potential negative impact. BCLC stage C showed a trend toward unfavorable prognosis versus stage B (HR 3.160, 95% CI 0.965-10.353; p=0.057). Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) was a critical factor, with PS 2 associated with poorer OS compared to PS 0 (HR 2.302, 95% CI 0.941-5.633; p=0.068). Vascular invasion was significantly associated with reduced OS (HR 2.431, 95% CI 1.257-4.705; p=0.008), as was the presence of encephalopathy (HR 4.917, 95% CI 1.474-16.408; p=0.010).
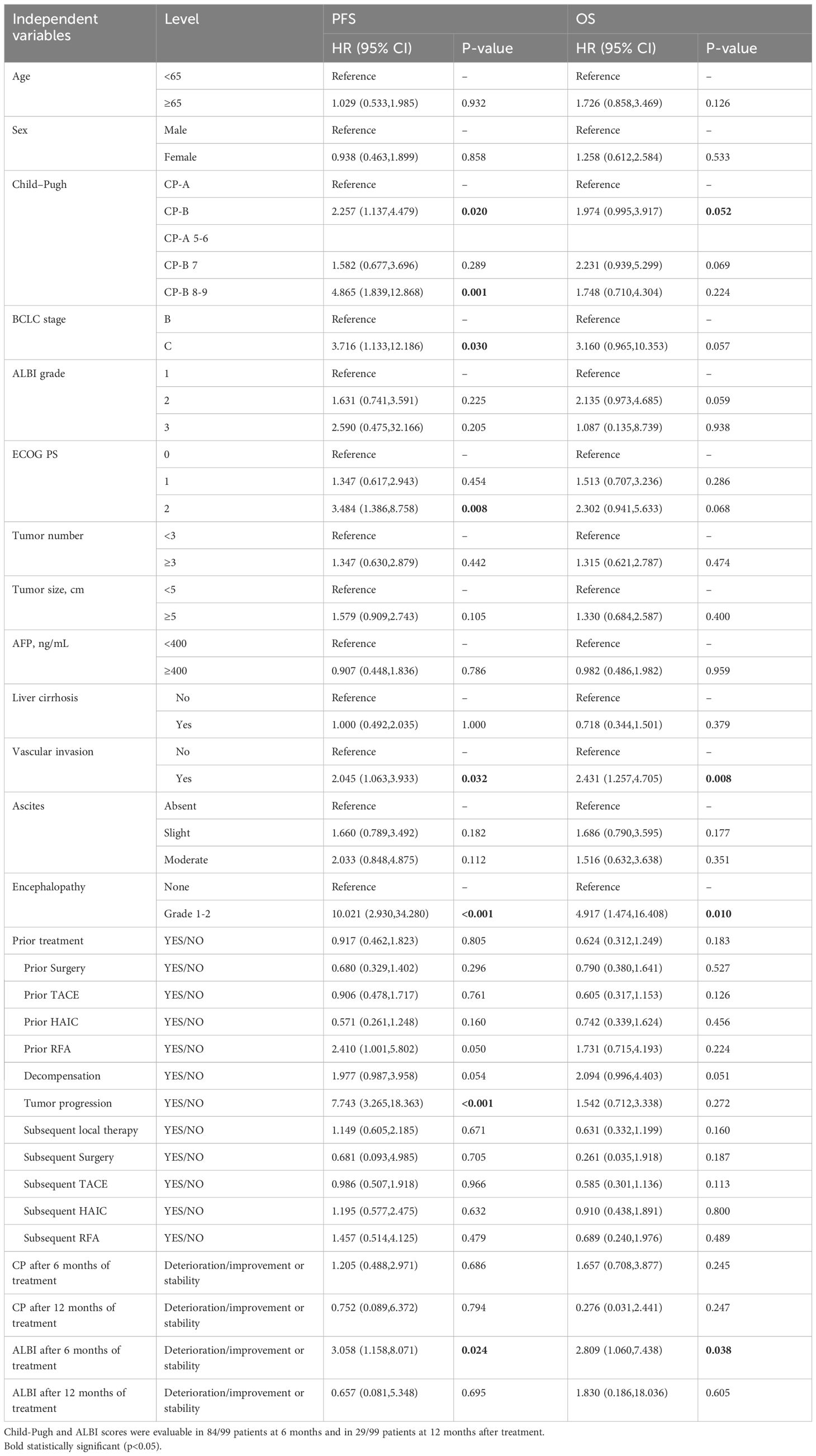
Table 3. Univariate analysis for factors predictive of progression free survival and overall survival.
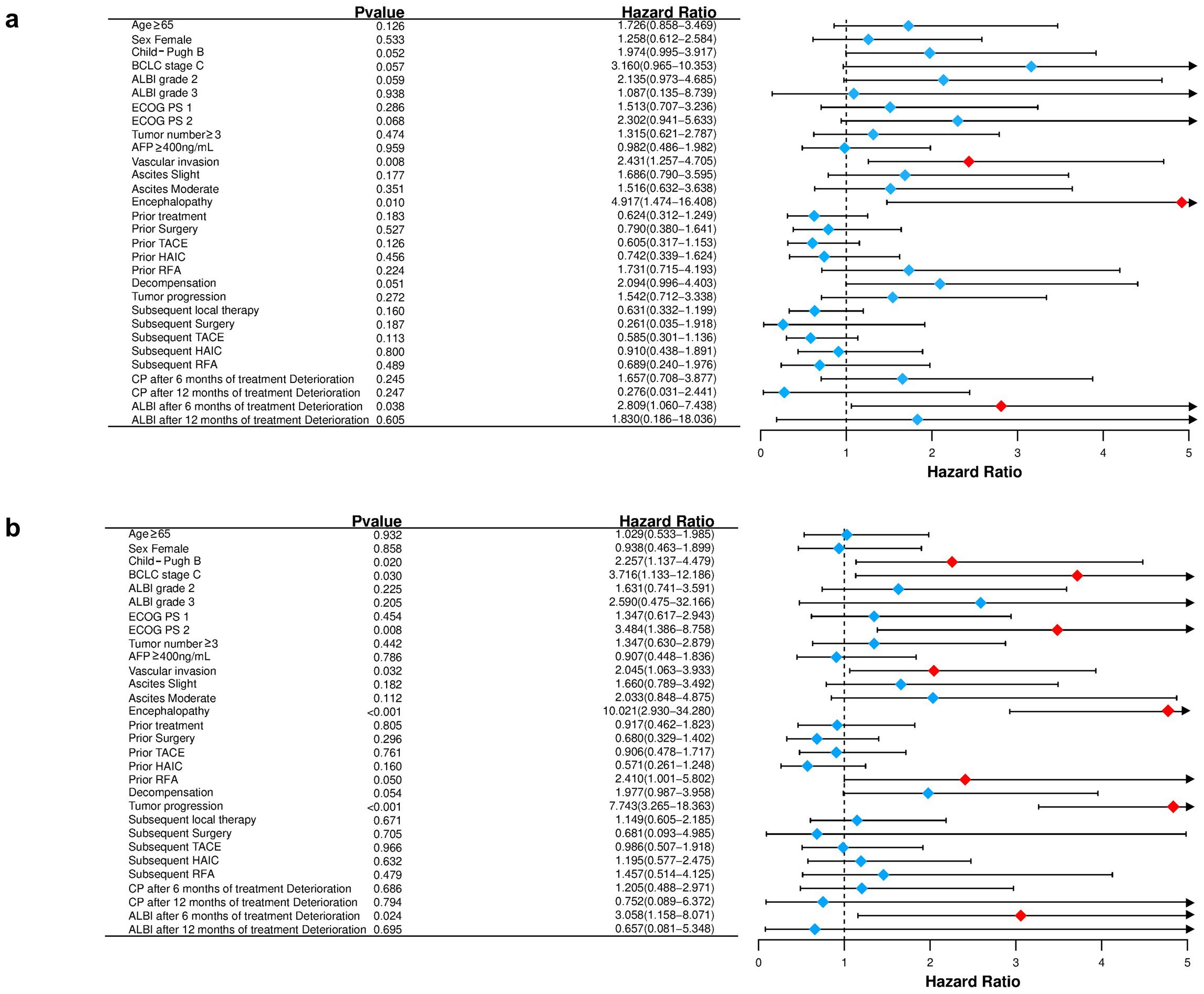
Figure 7. Forest plot for overall survival (a) and progression-free survival (b) of the matched cohorts of patients.
For PFS (Figure 7b), univariate analysis revealed that CP-B patients had a higher risk of progression (HR 2.257, 95% CI 1.137-4.479; p=0.020). Higher ALBI grades showed a trend toward negative prognosis, with ALBI grade 3 associated with HR 2.590 (95% CI 0.475-32.166; p=0.205). ECOG PS 2 was significantly associated with poorer PFS (HR 3.484, 95% CI 1.386-8.758; p=0.008). Tumor progression was a strong negative predictor (HR 7.743, 95% CI 3.265-18.363; p<0.001). Prior RFA was associated with a favorable trend (HR 2.410, 95% CI 1.001-5.802; p=0.050).
In multivariate analysis for OS (Table 4), CP-B status remained an independent predictor of reduced survival (HR 2.540, 95% CI 1.016-6.345; p=0.046). Deterioration in ALBI grade after 6 months of treatment was also an independent predictor of worse OS (HR 3.204, 95% CI 1.056-9.723; p=0.040). For PFS, CP-B showed a non-significant trend (HR 1.857, 95% CI 0.783-4.402; p=0.160), while ALBI grade deterioration after 6 months remained a significant negative prognostic factor (HR 3.353, 95% CI 1.083–10.384; p=0.036).
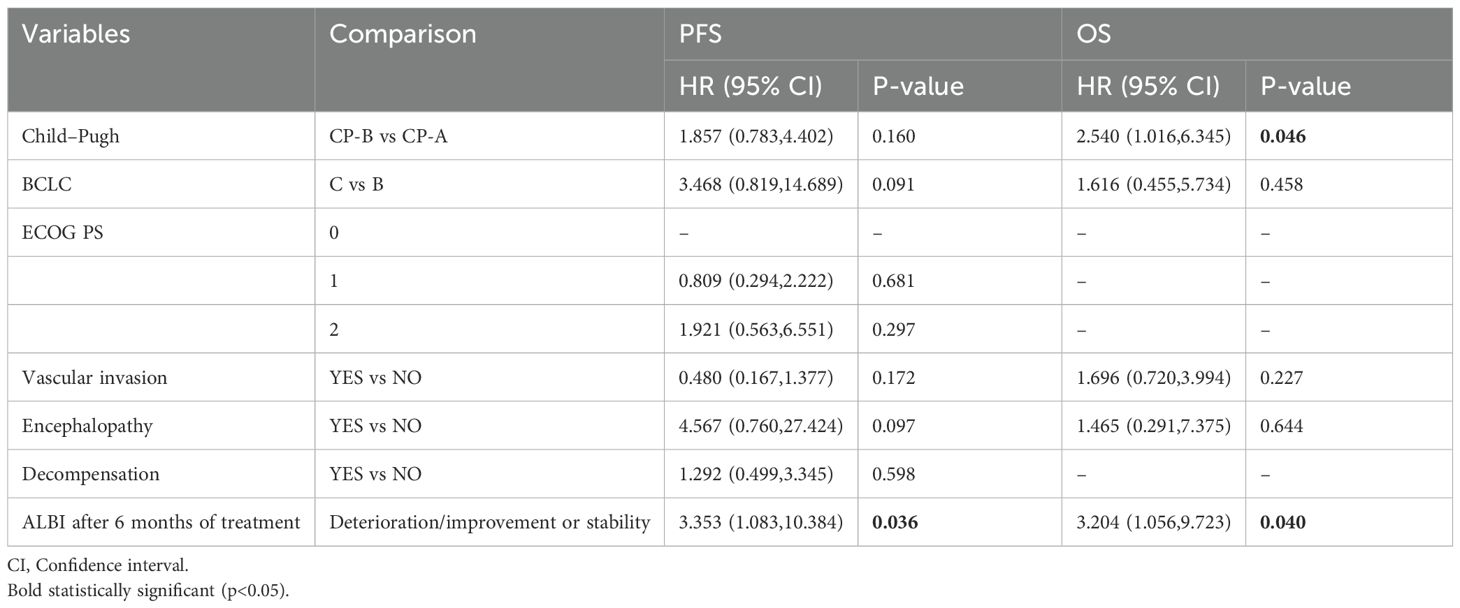
Table 4. Multivariate analysis for factors predictive of progression free survival and overall survival.
3.4 Safety
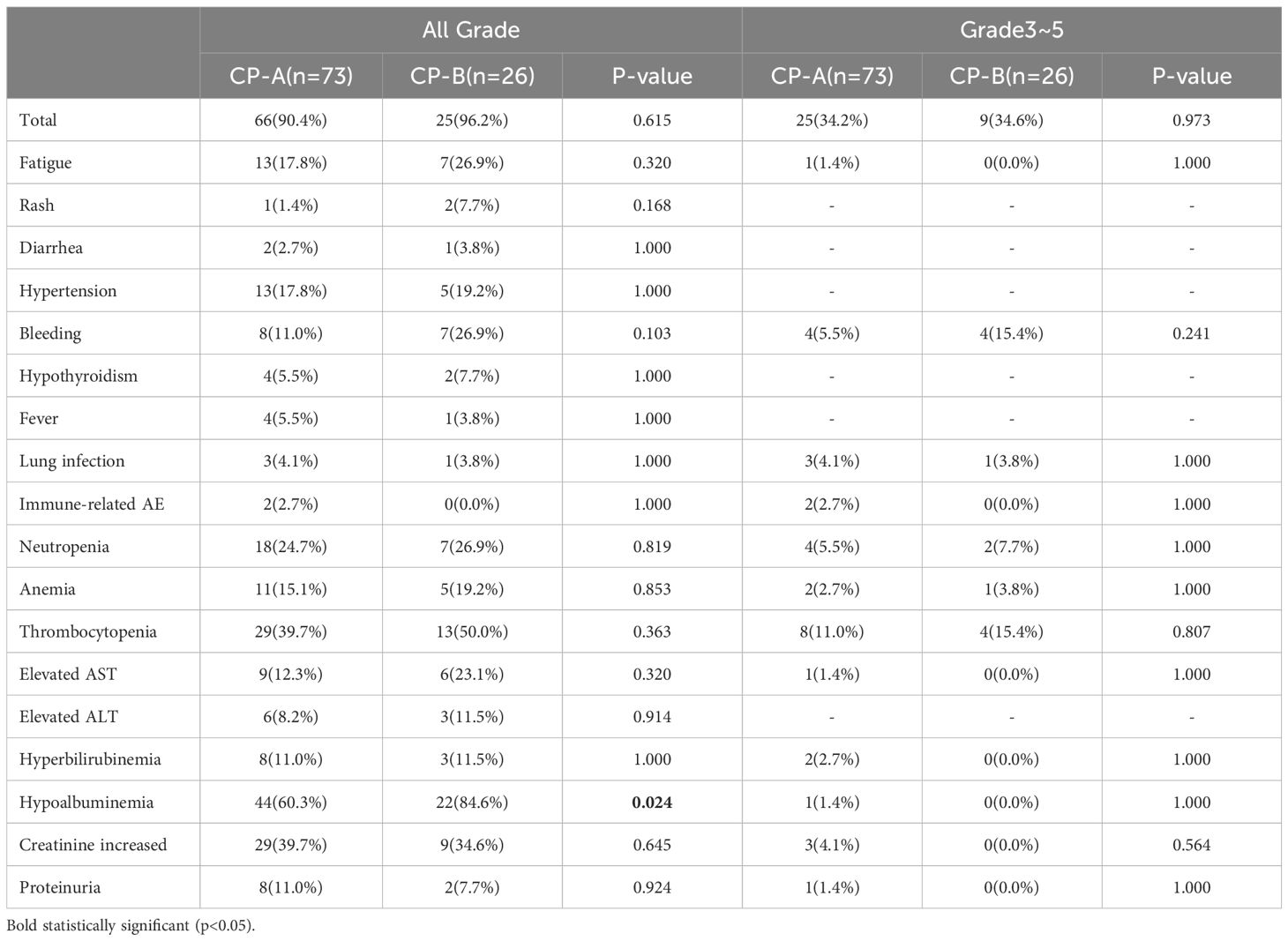
The majority of patients experienced adverse events (AEs), with a comparable incidence between CP-A (90.4%, 66/73) and CP-B (96.2%, 25/26) groups (p=0.615; Table 5).
In the CP-A group (n=73), the most frequent adverse events (AEs) of any grade were hypoalbuminaemia (n=44, 60.3%), thrombocytopenia (n=29, 39.7%), and increased creatinine (n=29, 39.7%). In the CP-B group (n=26), hypoalbuminemia (22 cases, 84.6%) and thrombocytopenia (n=13, 50.0%) were most frequently observed. Hypoalbuminemia showed a significant difference between the two groups (60.3% vs 84.6%, p=0.024). Notably, any-grade bleeding was more frequent in CP-B patients (26.9% vs 11.0%; p=0.103), though this did not reach statistical significance.
The incidence of grade 3–5 AEs was similar across groups, with 34.2% (25/73) in CP-A and 34.6% (9/26) in CP-B (p=0.973). The most common included thrombocytopenia (n=12, 13.2%) and bleeding (n=8, 8.8%). One patient died due to gastrointestinal bleeding.
Ten patients (10.1%) discontinued treatment due to AEs, primarily from bleeding (n=6, 6.06%), immune-related pneumonitis (n=1, 1.01%), diarrhea (n=1, 1.01%), fatigue (n=1, 1.01%), and proteinuria (n=1, 1.01%).
4 Discussion
In this retrospective study, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of sintilimab plus bevacizumab in patients with unresectable HCC and impaired liver function (Child-Pugh B) across four tertiary centers. Compared with the ORIENT-32 trial, this study demonstrated superior outcomes with sintilimab-bevacizumab in HCC patients, showing a median overall survival of 20 months and objective response rate of 51.5% (14). This enhanced efficacy may be attributed to rigorous liver function management during treatment and combined local therapies administered to most patients (53/99; including TACE [n=45], HAIC [n=27], radiofrequency ablation [n=10], and surgery [n=6]). Post-progression treatment may have also affected survival outcomes. After disease progression, 47.6% of patients continued sintilimab plus bevacizumab, including four who received additional locoregional therapy, while others switched to tislelizumab plus donafenib (14.2%), lenvatinib (14.2%), or apatinib (19.0%). Notably, ORIENT-32 was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, where treatment delays and deferred tumor assessments may have compromised response evaluation and attenuated the observed response rate.
Unlike randomized controlled trials (e.g., ORIENT-32) and a Chinese retrospective study that primarily enrolled CP-A patients, our real-world analysis encompassed both CP-A and CP-B populations across four tertiary centers (14, 20). This study demonstrates that sintilimab-bevacizumab achieved clinically meaningful outcomes in the CP-B HCC, with an objective response rate (ORR) of 57.7% and median overall survival (OS) of 15 months. In the CP-A group, the ORR (50.7%) was comparable to that of CP-B, and the OS was longer (22 months).
The shorter survival observed in CP-B patients despite a similar response rate may be explained by impaired hepatic reserve. This conclusion is further reinforced by our subgroup analysis, which confirmed the survival disadvantage even among patients with identical BCLC-C stage, and the results of multivariate analysis also suggested that impaired liver function was an independent predictor of poorer survival. Deteriorated liver function likely leads to early treatment discontinuation or limits tolerance to subsequent therapies (21). Moreover, hepatic decompensation may contribute more to mortality than tumor progression itself (22). These findings suggest that sintilimab-bevacizumab achieves meaningful antitumor activity in both CP-A and CP-B patients, while long-term prognosis remains heavily influenced by hepatic functional reserve.
Treatment of HCC in patients with impaired hepatic function continues to present a significant clinical challenge (23). Previous studies have reported median overall survival (mOS) of only 2–5 months in untreated patients with Child-Pugh B liver function (24, 25). Even with monotherapy, efficacy remains limited: sorafenib has shown survival of 2.5-5.2 months, lenvatinib demonstrates an mOS of around 3.7 months, while nivolumab yields a median PFS of 2.7 months and an ORR of 12% (26–29).
Most clinical trials have excluded or included only a limited number of CP-B patients, leaving a gap in evidence for this subgroup. In a previous multicenter retrospective study, it was reported that the mOS of HCC patients treated with atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab was 16.8 months and 6.7 months, respectively, for Child-Pugh A and Child-Pugh B patients, while in another multicenter retrospective study in Korea, the mOS of Child-Pugh B HCC patients was 7.7 months (30, 31). In an American study, 226 patients (70.1%) with Child-Pugh A and 86 patients (26.7%) with Child-Pugh B HCC were treated with atezolizumab and bevacizumab as first-line therapy, with a reported mOS of 21.6 months and 6.4 months in Child-Pugh A and Child-Pugh B patients (32). By contrast, our study observed a longer mOS of 15 months in CP-B patients, which may be partially explained by a lower proportion of patients with extrahepatic disease and by the optimized supportive and hepatic management in our cohort.
Importantly, the relatively favorable outcomes observed with sintilimab-bevacizumab in CP-B patients compared with other immune-based regimens may reflect both pharmacologic and clinical advantages. Pharmacologically, sintilimab and bevacizumab undergo proteolytic degradation rather than hepatic or renal metabolism, minimizing additional hepatic metabolic burden (33–36). This pharmacokinetic property may allow better drug exposure and tolerance in cirrhotic patients, particularly those with reduced hepatic reserve (37). Bevacizumab has been reported to modulate hepatic hemodynamics and alleviate vascular abnormalities, which may improve hepatic microcirculation and portal pressure, thereby facilitating hepatic perfusion and immune delivery (38, 39). Moreover, sintilimab’s distinct PD-1 binding characteristics may promote stable immune activation, potentially contributing to its sustained efficacy even in CP-B patients (40).
Our findings were consistent with the preliminary results presented at the 2024 ESMO Congress, where the mOS and mPFS in Child-Pugh B patients receiving FOLFOX-HAIC plus sintilimab and IBI305 were reported as 13.55 and 7.35 months, respectively (41). Among Child-Pugh A patients specifically, our observed mOS of 22 months is comparable to the results from CHANCE001 (19.2 months) and CHANCE2201 (22.5 months) (41, 42), supporting the robustness of this combination regimen even in broader real-world populations.
Given the inherent subjectivity of the Child-Pugh classification, we additionally incorporated the ALBI grade as a complementary tool for liver function assessment. Crucially, we identified on-treatment ALBI dynamics as a pivotal prognostic determinant. Patients who maintained or improved their ALBI grade at 6 months achieved superior OS (22 vs 17 months, p=0.027) and PFS (14 vs 8 months, p=0.014), indicating that early hepatic function stabilization, rather than baseline status alone, dictates long-term outcomes with immunotherapy combinations. Both univariate and multivariate analyses confirmed ALBI deterioration at 6 months as an independent predictor of poorer survival. These findings highlight its potential utility in refining patient stratification and treatment planning.
In this study, irAEs were defined as clinically confirmed immune-mediated events requiring immunosuppressive therapy or specialist management. Laboratory abnormalities such as elevated AST, ALT, or bilirubin were recorded separately and not classified as irAEs unless accompanied by clinical signs of immune-mediated hepatitis. This stricter definition likely contributed to the lower observed incidence (2.7%).
Safety remains a crucial concern in combined immunotherapy for HCC, particularly in cirrhotic patients. In our study, CP-B patients experienced a slightly higher overall AE rate (96.2% vs 90.4%) and a similar incidence of grade 3–5 events (34.6% vs 34.2%). Hypoalbuminemia was the most frequent AE in both groups, while thrombocytopenia predominated among severe AEs. CP-B patients had notably higher rates of gastrointestinal bleeding and hypoalbuminemia. Nonetheless, most AEs were grade 1–2 and manageable with supportive care. Serious AEs necessitating treatment discontinuation were uncommon and most frequently related to bleeding from portal hypertension.
We employed a comprehensive approach to AE risk mitigation: all cirrhotic patients underwent pre-treatment oesophagogastroduodenoscopy to screen for varices and received appropriate pharmacological or endoscopic intervention where indicated. Proton pump inhibitors were administered for ulcer prophylaxis, and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) was considered in select cases. Regular monitoring of coagulation parameters and occult bleeding, as well as prompt symptomatic management, ensured treatment safety. Permanent discontinuation was reserved for grade ≥3 hemorrhagic events.
Notably, sintilimab and bevacizumab are degraded by proteolytic enzymes rather than metabolized through hepatic or renal pathways, which likely contributes to their favorable hepatic and renal safety profiles (43). In our study, treatment-related liver and kidney function impairment was uncommon, particularly compared with reports of TKI-based regimens such as lenvatinib or sorafenib (29). This metabolic characteristic provides an additional safety advantage in patients with impaired hepatic reserve.
These findings emphasize the importance of integrated oncologic and hepatologic management in HCC patients, where both tumor burden and hepatic functional reserve dictate prognosis (44). CP-B status and ALBI deterioration independently predicted shorter OS, PFS, and time-to-discontinuation (TTD), reinforcing the need for individualized treatment planning and vigilant monitoring.
This study has several limitations. Its retrospective design introduces inherent selection bias, as reflected by baseline imbalances between groups, specifically the exclusion of 15 patients for “incomplete information” increases the possibility of such bias. Despite involving four institutions, the sample size remains relatively small, and the follow-up period was not long enough to evaluate long-term outcomes, as many patients were still being followed at the time of data cutoff. Moreover, all participants were enrolled from tertiary centers in China, and most had HBV-related HCC, which may limit the generalizability of our findings to populations with different etiologies or from other geographic regions.
In conclusion, the combination of sintilimab and bevacizumab demonstrates clinically meaningful antitumor activity in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma across Child-Pugh A and B cohorts. However, survival outcomes were strongly affected by differences in hepatic function reserve and on-treatment liver functional dynamics. Although the regimen was generally well tolerated, patients with impaired liver reserve require vigilant monitoring and comprehensive supportive strategies to maximize therapeutic outcomes.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Informed consent was waived due to the retrospective design of the study and the use of anonymized clinical data, as approved by the institutional ethics committee.
Author contributions
YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. JW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. SX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. SL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. YL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Project administration. XP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. WZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by a grant from the Horizontal Project Fund of Soochow University (H231223).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. de Martel C, Georges D, Bray F, Ferlay J, and Clifford GM. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob Health. (2020) 8:e180–e90. doi: 10.1016/s2214-109x(19)30488-7
3. Rumgay H, Ferlay J, de Martel C, Georges D, Ibrahim AS, Zheng R, et al. Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by subtype. Eur J Cancer. (2022) 161:108–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.11.023
4. Donato F, Gelatti U, Tagger A, Favret M, Ribero ML, Callea F, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatitis C and B virus infection, alcohol intake, and hepatolithiasis: A case-control study in Italy. Cancer Causes Control. (2001) 12:959–64. doi: 10.1023/a:1013747228572
5. Liu CY, Chen KF, and Chen PJ. Treatment of liver cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. (2015) 5:a021535. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021535
6. Galle PR, Tovoli F, Foerster F, Wörns MA, Cucchetti A, and Bolondi L. The treatment of intermediate stage tumours beyond tace: from surgery to systemic therapy. J Hepatol. (2017) 67:173–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.007
7. Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: the 2022 update. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:681–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018
8. Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet. (2018) 391:1163–73. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30207-1
9. Galle PR, Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Zhu AX, Kim TY, et al. Patient-reported outcomes with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (Imbrave150): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:991–1001. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(21)00151-0
10. Sangro B, Chan SL, Kelley RK, Lau G, Kudo M, Sukeepaisarnjaroen W, et al. Four-year overall survival update from the phase iii himalaya study of tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Oncol. (2024) 35:448–57. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.02.005
11. Yau T, Galle PR, Decaens T, Sangro B, Qin S, da Fonseca LG, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus lenvatinib or sorafenib as first-line treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (Checkmate 9dw): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2025) 405:1851–64. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(25)00403-9
12. Qin S, Chan SL, Gu S, Bai Y, Ren Z, Lin X, et al. Camrelizumab plus rivoceranib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (CARES-310): A randomised, open-label, international phase 3 study. Lancet. (2023) 402:1133–46. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)00961-3
13. Cheng AL, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim TY, et al. Updated efficacy and safety data from imbrave150: atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. Sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:862–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.030
14. Ren Z, Xu J, Bai Y, Xu A, Cang S, Du C, et al. Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) versus sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (ORIENT-32): A randomised, open-label, phase 2–3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:977–90. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(21)00252-7
15. Demirtas CO, D'Alessio A, Rimassa L, Sharma R, and Pinato DJ. ALBI grade: evidence for an improved model for liver functional estimation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. JHEP Rep. (2021) 3:100347. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100347
16. Chen B and Lin S. Albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score at admission predicts possible outcomes in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Med (Baltimore). (2017) 96:e7142. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000007142
17. Stefanini B, Fulgenzi CAM, Scheiner B, Korolewicz J, Cheon J, Nishida N, et al. ALBI grade enables risk stratification for bleeding events and refines prognostic prediction in advanced hcc following atezolizumab and bevacizumab. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2025) 12:671–83. doi: 10.2147/jhc.S462701
18. Celsa C, Cabibbo G, Fulgenzi CAM, Battaglia S, Enea M, Scheiner B, et al. Hepatic decompensation is the major driver of mortality in patients with HCC treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab: the impact of successful antiviral treatment. Hepatology. (2025) 81:837–52. doi: 10.1097/hep.0000000000001026
19. Kudo M, Finn RS, Cheng AL, Zhu AX, Ducreux M, Galle PR, et al. Albumin-bilirubin grade analyses of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A post hoc analysis of the phase iii imbrave150 study. Liver Cancer. (2023) 12:479–93. doi: 10.1159/000529996
20. Zeng X, Jia Y, Chen H, Luo Q, Zhao H, Liang G, et al. A real-world analysis of survival and cost-effectiveness of sintilimab plus bevacizumab biosimilar regimen in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:9213–9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04775-2
21. Fessas P, Kaseb A, Wang Y, Saeed A, Szafron D, Jun T, et al. Post-registration experience of nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: an international study. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e001033. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001033
22. Pasta A, Calabrese F, Jaffe A, Labanca S, Marenco S, Pieri G, et al. Safety and efficacy of atezolizumab/bevacizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and impaired liver function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Cancer. (2024) 13:227–37. doi: 10.1159/000533991
23. Tandon P and Garcia-Tsao G. Prognostic indicators in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of 72 studies. Liver Int. (2009) 29:502–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01957.x
24. Giannini EG, Farinati F, Ciccarese F, Pecorelli A, Rapaccini GL, Di Marco M, et al. Prognosis of untreated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. (2015) 61:184–90. doi: 10.1002/hep.27443
25. Jeon D, Song GW, Lee HC, and Shim JH. Treatment patterns for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with child-pugh class B and their impact on survival: A Korean nationwide registry study. Liver Int. (2022) 42:2830–42. doi: 10.1111/liv.15464
26. Kudo M, Matilla A, Santoro A, Melero I, Gracián AC, Acosta-Rivera M, et al. Checkmate 040 cohort 5: A phase I/II study of nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and child-pugh B cirrhosis. J Hepatol. (2021) 75:600–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.047
27. Marrero JA, Kudo M, Venook AP, Ye SL, Bronowicki JP, Chen XP, et al. Observational registry of sorafenib use in clinical practice across child-pugh subgroups: the gideon study. J Hepatol. (2016) 65:1140–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.020
28. McNamara MG, Slagter AE, Nuttall C, Frizziero M, Pihlak R, Lamarca A, et al. Sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with advanced child-pugh B hepatocellular carcinoma-a meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. (2018) 105:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.09.031
29. Huynh J, Cho MT, Kim EJ, Ren M, Ramji Z, and Vogel A. Lenvatinib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed to child-pugh B liver function. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2022) 14:17588359221116608. doi: 10.1177/17588359221116608
30. D'Alessio A, Fulgenzi CAM, Nishida N, Schönlein M, von Felden J, Schulze K, et al. Preliminary evidence of safety and tolerability of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and child-pugh a and B cirrhosis: A real-world study. Hepatology. (2022) 76:1000–12. doi: 10.1002/hep.32468
31. Cheon J, Kim H, Kim HS, Kim CG, Kim I, Kang B, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with child-pugh B advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2023) 15:17588359221148541. doi: 10.1177/17588359221148541
32. Storandt MH, Zemla TJ, Patell K, Naleid N, Gile JJ, Tran NH, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab as first-line systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-institutional cohort study. Oncologist. (2024) 29:986–96. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae142
33. Easl clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2025) 82:315–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.08.028
34. Shih T and Lindley C. Bevacizumab: an angiogenesis inhibitor for the treatment of solid Malignancies. Clin Ther. (2006) 28:1779–802. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.11.015
35. Silvestris N, Argentiero A, Cosmai L, Porta C, Gesualdo L, Brunori G, et al. Management of targeted therapies in cancer patients with chronic kidney disease, or on haemodialysis: an associazione italiana di oncologia medica (Aiom)/societa' Italiana di nefrologia (Sin) multidisciplinary consensus position paper. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2019) 140:39–51. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.05.016
36. Zhang L, Lin W, Tan F, Li N, Xue Q, Gao S, et al. Sintilimab for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. biomark Res. (2022) 10:23. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00363-7
37. Lau G, Obi S, Zhou J, Tateishi R, Qin S, Zhao H, et al. Apasl clinical practice guidelines on systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma-2024. Hepatol Int. (2024) 18:1661–83. doi: 10.1007/s12072-024-10732-z
38. Huang Y, Feng H, Kan T, Huang B, Zhang M, Li Y, et al. Bevacizumab attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats by inhibiting activation of hepatic stellate cells. PloS One. (2013) 8:e73492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073492
39. Zhu AX, Holalkere NS, Muzikansky A, Horgan K, and Sahani DV. Early antiangiogenic activity of bevacizumab evaluated by computed tomography perfusion scan in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist. (2008) 13:120–5. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2007-0174
40. Wang J, Fei K, Jing H, Wu Z, Wu W, Zhou S, et al. Durable blockade of pd-1 signaling links preclinical efficacy of sintilimab to its clinical benefit. MAbs. (2019) 11:1443–51. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2019.1654303
41. Fukumura D, Kloepper J, Amoozgar Z, Duda DG, and Jain RK. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using antiangiogenics: opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2018) 15:325–40. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.29
42. Jin ZC, Chen JJ, Zhu XL, Duan XH, Xin YJ, Zhong BY, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody/tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without transarterial chemoembolization as first-line treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (Chance2201): A target trial emulation study. EClinicalMedicine. (2024) 72:102622. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102622
43. Sheng J, Srivastava S, Sanghavi K, Lu Z, Schmidt BJ, Bello A, et al. Clinical pharmacology considerations for the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Clin Pharmacol. (2017) 57 Suppl 10:S26–s42. doi: 10.1002/jcph.990
Keywords: sintilimab, bevacizumab, Child-Pugh B, hepatocellular carcinoma, systemic treatment
Citation: Zhang Y, Miao Y, Sun W, Yu Y, Wang J, Xiao S, Lu S, Wang X, Li Y, Pan X and Zhao W (2025) Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) in advanced HCC with Child-Pugh A/B liver function: a real-world multicenter retrospective study. Front. Oncol. 15:1681663. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1681663
Received: 07 August 2025; Accepted: 23 October 2025;
Published: 05 November 2025.
Edited by:
Lekshmi R. Nath, Dr. Lekshmi R. Nath, IndiaReviewed by:
Hongwei Wang, Beijing Cancer Hospital, ChinaLi-Jun Wang, Beijing Cancer Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Miao, Sun, Yu, Wang, Xiao, Lu, Wang, Li, Pan and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weifeng Zhao, emhhb3dlaWZlbmdAc3VkYS5lZHUuY24=; Yang Li, bGl5YW5nMjAxNjA1QDEyNi5jb20=; Xiucheng Pan, eHpweGM2OEAxMjYuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Yuanxu Zhang
Yuanxu Zhang Youhan Miao2†
Youhan Miao2† Wei Sun
Wei Sun Yixing Yu
Yixing Yu Shuang Xiao
Shuang Xiao Weifeng Zhao
Weifeng Zhao