- 1Department of Ultrasound, Dalian Municipal Friendship Hospital, Dalian, China
- 2Department of Oncology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 3Department of Ultrasound, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of a treatment strategy that actively integrates imaging features and serum biomarkers into contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS)-guided microwave ablation (MWA) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted, and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) meeting the inclusion criteria were selected. The methodological quality of the included studies was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool, and RevMan 5.3 software was employed for meta-analysis. The primary endpoints included complete tumor ablation rate, local recurrence rate (LRR), local progression rate (LPR), recurrence-free survival (RFS), and complication rate.
Results: A total of seven RCTs involving 1,039 HCC patients (407 in the treatment group, 632 in the control group) were included. Meta-analysis demonstrated the following: The complete ablation rate was significantly higher in the treatment group than in the control group (risk ratio [RR] = 1.06; 95% confidence interval [CI] = [1.01, 1.10]; p = 0.010). The local recurrence rate was significantly lower in the treatment group (risk difference [RD] = − 0.09; 95% CI = [− 0.17, −0.01]; p = 0.02). No significant differences were observed in RFS (RR = 1.11; 95% CI = [1.00, 1.24]; p = 0.06), LPR (RR = 1.55; 95% CI = [0.78, 3.07]; p = 0.21), or complication rates (RR = 1.13; 95% CI = [0.66, 1.91]; p = 0.66) between the two groups. Heterogeneity among studies was low (I2 ≤ 34%), and funnel plot analysis indicated minimal publication bias.
Conclusion: CEUS-guided MWA combined with imaging features and serum biomarkers is associated with significant improvements in complete tumor ablation rates and a reduction in local recurrence. This strategy provides evidence-based support for optimizing precision local control in HCC, but its impact on long-term survival requires validation through future studies with extended follow-up.
Introduction
In the field of malignant tumor treatment, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), ranking as the sixth most common malignancy globally and the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality, exhibits high invasiveness and insidious onset characteristics. Consequently, most patients are diagnosed at advanced stages, missing the optimal window for surgical resection, with a long-term 5-year survival rate stagnating at 10%–15%, imposing a substantial burden on both patient quality of life and healthcare systems (1, 2). Although surgical resection remains the gold standard for radical HCC treatment, it is applicable to only approximately 20% of early-stage patients. For those with intermediate-to-advanced stages, multifocal lesions, or concomitant cirrhosis, minimally invasive therapies have emerged as critical alternatives (3, 4).
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS)-guided microwave ablation (MWA), characterized by precise targeting, minimal invasiveness, and repeatability, has gained widespread application in HCC management. This technique induces irreversible tumor necrosis through thermal coagulation effects, achieving local radical control (5). Imaging features, serving as direct manifestations of tumor morphology and hemodynamics, can delineate lesion size, margins, internal architecture, and vascular patterns, providing essential guidance for ablation zone planning and electrode placement. Meanwhile, serum biomarkers (e.g., alpha-fetoprotein [AFP], des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin [DCP]) reflect tumor biological behavior and therapeutic response, functioning as key quantitative indicators for dynamic efficacy evaluation (6).
However, studies relying solely on imaging or serological markers have limitations: imaging features may fail to accurately identify microscopic residual lesions, whereas serum biomarkers are susceptible to interference from hepatic/renal function and other factors (7, 8). Although prior research has explored the combined application of these modalities, discrepancies in sample sizes and evaluation criteria have led to contentious conclusions. Therefore, this meta-analysis aims to evaluate the efficacy of a specific clinical strategy: the active integration of multiparametric data—specifically, quantifiable CEUS characteristics (e.g., hemodynamic perfusion patterns like “fast-in-fast-out”) and key serum biomarkers (e.g., AFP and DCP)—into the procedural planning and execution of CEUS-guided MWA for HCC. Unlike prognostic studies that merely assess correlations, our objective is to determine whether clinically acting upon this combined information leads to superior outcomes compared with a control strategy that does not formally integrate such data. This systematic review of RCTs is designed to provide the most robust evidence regarding the causal benefit of this integrated guidance strategy, and its findings hold significant clinical implications for advancing precision ablation therapy.
Materials and methods
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria
Study design
This meta-analysis included randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Participants
Eligible participants were patients with HCC confirmed either pathologically or clinically, with complete baseline data and no severe organ dysfunction.
Interventions
The experimental group received CEUS-guided MWA combined with imaging features and serum biomarkers. The control group received standard MWA guidance (e.g., conventional US or CEUS) without formally integrating imaging features and serum biomarkers for treatment planning and evaluation.
Outcomes
The primary outcomes included complete ablation rate, local recurrence rate, recurrence-free survival, local progression rate, and complication incidence. All outcomes were assessed using clearly defined evaluation methods.
Exclusion criteria
Study design
Studies that were non-RCTs, such as retrospective studies or case reports, were excluded.
Participants
Patients with concurrent malignancies, severe comorbidities, or incomplete data were not eligible for inclusion.
Data integrity
Studies with unavailable key parameters, such as procedural duration or efficacy metrics, or with ambiguous evaluation protocols, were excluded to ensure data reliability.
Confounding factors
Studies with uncontrolled significant confounders, such as inconsistent treatment regimens, were excluded to minimize bias.
Search strategy
PubMed, MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and Web of Science were searched for all relevant studies of interest up until July 2025 to ensure data timeliness and scientific rigor. The search strategy was designed to encompass four key concepts: (1) the disease (hepatocellular carcinoma), (2) the intervention (microwave ablation), (3) the guidance modality (contrast-enhanced ultrasound), and (4) the predictive factors (imaging features and serum biomarkers). Core concepts were linked using the Boolean operator “AND” to ensure that retrieved records pertained to the combined strategy, while synonyms and related terms within each conceptual group were combined using “OR”.
The PubMed search strategy was structured as follows: (“hepatocellular carcinoma” OR “HCC” OR “liver cancer”) AND (“microwave ablation” OR “microwave thermoablation” OR “MWA”) AND (“contrast-enhanced ultrasound” OR “contrast media” OR “CEUS” OR “ultrasonography”) AND ([“imaging features” OR “radiomic features” OR “radiomics” OR “fast-in-fast-out” OR “wash-in” OR “wash-out”] OR [“serum markers” OR “biomarkers” OR “alpha-fetoprotein” OR “AFP” OR “des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin” OR “DCP” OR “PIVKA-II”]). Similar strategies, adapted to the specific syntax of each database, were applied to the other databases. In addition, the reference lists of retrieved articles and relevant reviews were manually screened to identify any additional eligible studies.
Study selection and data extraction
Two independent reviewers screened the titles/abstracts of all retrieved studies, excluding those that were irrelevant. Articles deemed potentially eligible underwent full-text assessment. The data extracted from each study included: (1) study characteristics (authors, publication year, country); (2) sample size and baseline data (age, gender, tumor size/number); (3) intervention details (CEUS parameters, MWA power/duration); (4) imaging features and serum biomarker evaluation (methods, cutoffs, values); and (5) outcomes (complete ablation rate, recurrence/progression rates, survival, complications). Any disagreements between reviewers were resolved through discussion or third-party adjudication.
Quality assessment
The methodological quality of included studies was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool. This assessment considered the following domains: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding (participants/personnel/outcome assessors), incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other potential sources of bias. Assessments were independently conducted by two reviewers, and any discrepancies were resolved by consensus.
Imaging features and serum biomarkers
Among the included studies, the most frequently utilized imaging features for planning and assessing CEUS-guided MWA were as follows. First, vascular pattern characteristics, particularly the “wash-in and wash-out” pattern, were a critical feature used across studies to define viable tumor tissue and margins. Second, tumor margin definition was considered important; poorly defined or irregular margins were often cited as an indicator for extending the ablation zone. Third, internal enhancement patterns were assessed, with heterogeneous enhancement regarded as a sign of viable tumor tissue, guiding the placement of ablation antennae.
The serum biomarkers integrated into the treatment algorithm primarily included AFP and prothrombin induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II (PIVKA-II; also known as DCP). AFP was the most commonly used marker. Preoperative elevation of AFP—typically > 20 or > 400 ng/mL depending on the study—was used for risk stratification. A postoperative decline, such as a reduction > 50% or normalization to < 20 ng/mL, served as a key metric for evaluating treatment response and predicting recurrence. PIVKA-II was used in several studies, with cutoff values ranging from 40 to 100 mAU/mL. Elevated preablation levels of PIVKA-II were associated with higher tumor aggressiveness and were used to justify more extensive ablation margins.
The combination of imaging features and serum biomarkers was applied dynamically during CEUS-guided MWA. Imaging defined the anatomical target, while serum biomarkers provided complementary biological information. For instance, a patient with an ill-defined margin on CEUS and a high preoperative AFP level would undergo an extended ablation protocol.
Statistical analysis
Analyses were performed using RevMan 5.3. Dichotomous outcomes (e.g., ablation success, recurrence) were expressed as odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), while continuous variables were analyzed using mean differences (MDs) with 95% CI. Heterogeneity was assessed via Cochran’s Q and I2 tests. Fixed-effects models were applied if p > 0.10 and I2 < 50%; otherwise, random-effects models were used. Subgroup/sensitivity analyses were conducted to address heterogeneity. Forest and funnel plots were employed to visualize results and assess publication bias, respectively. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Literature search results
The initial database searches yielded 423 articles. After applying the eligibility criteria, seven studies were included in the analysis (Figure 1).
Characteristics of included studies
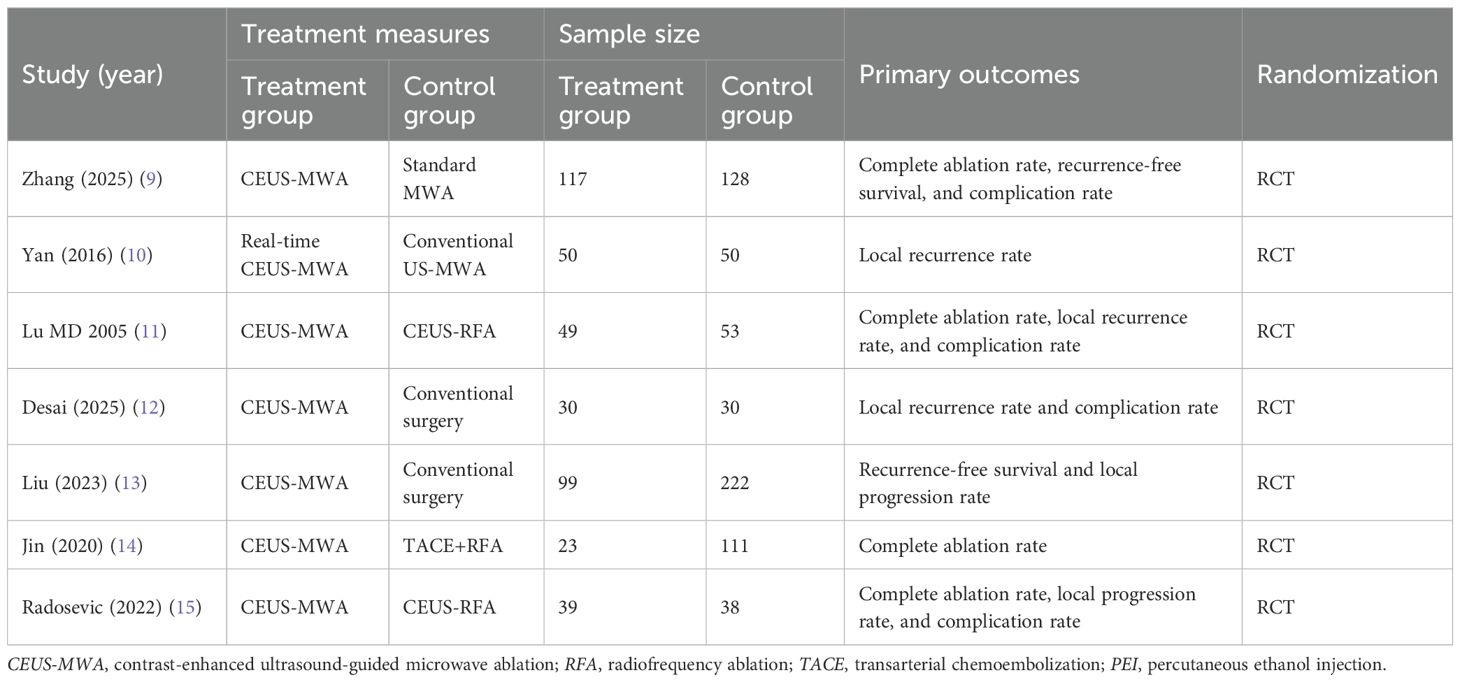
A total of seven studies involving 1,039 participants were included, comprising 407 cases in the treatment group and 632 cases in the control group. All studies were RCTs (Table 1).
Quality assessment of included studies
All included RCTs were evaluated for quality using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool. Among the seven included studies, no significant sources of bias were identified, and all were rated as “low risk” (Figure 2).
Meta-analysis results
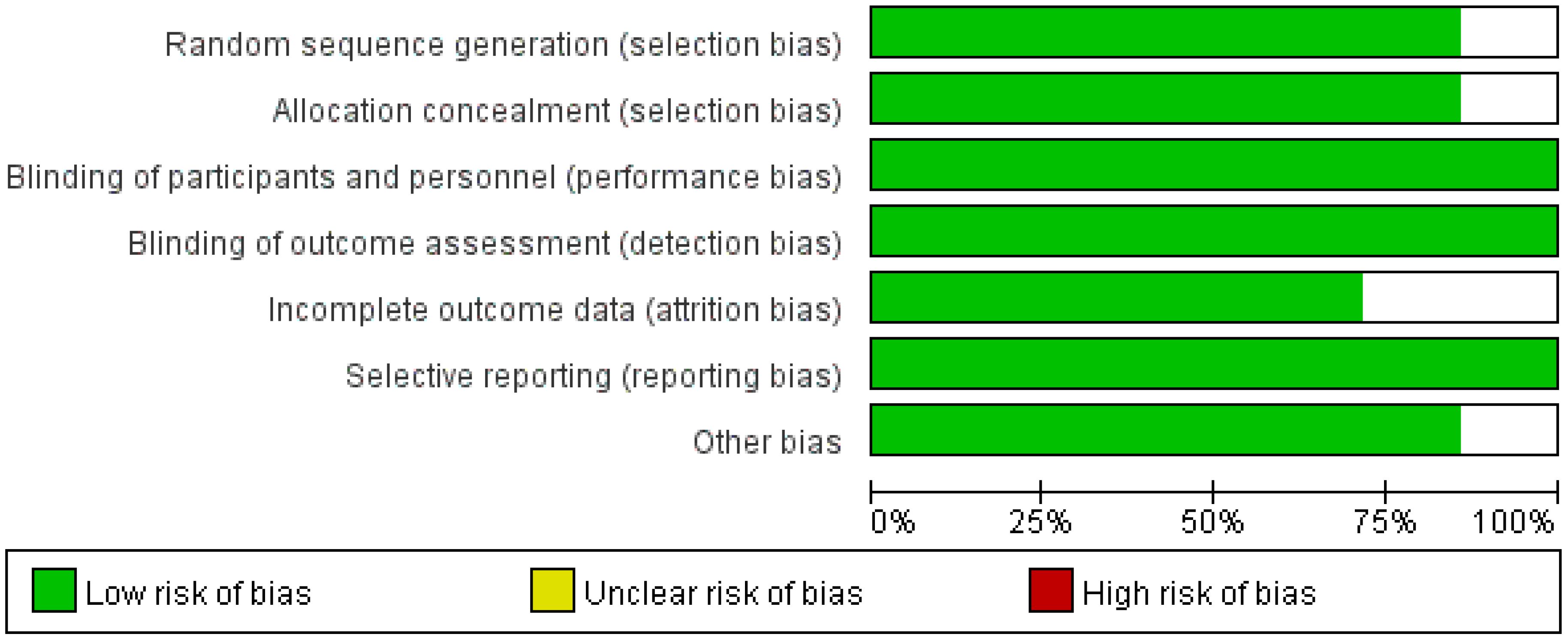
Complete tumor ablation rate
A total of four studies were included for the analysis of the complete tumor ablation rate. The Q-test and I2 test indicated low heterogeneity among the studies (p = 0.21; χ2 = 4.55; df = 3; I2 = 34%). The results demonstrated a statistically significant difference between the treatment and control groups (Z = 2.58; p = 0.010), with a pooled risk ratio (RR) of 1.06 (95% CI = [1.01, 1.10]), suggesting that the treatment group achieved superior complete tumor ablation rates compared with the control group. The funnel plot was approximately symmetric, indicating minimal publication bias (Figures 3, 4).
Local recurrence rate
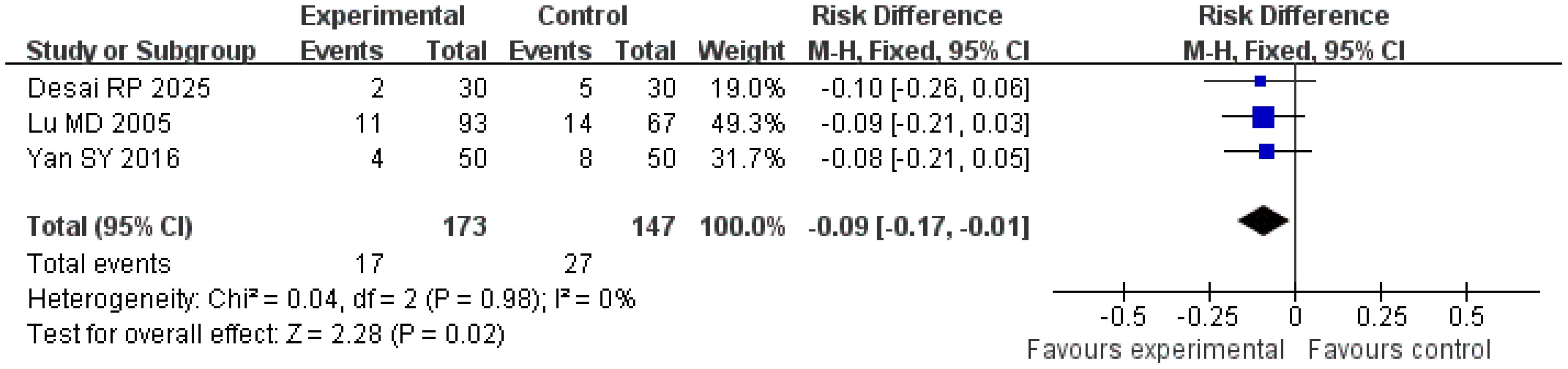
A total of three studies were included in the analysis of local recurrence rates. The Q and I2 test results (p = 0.98; χ2 = 0.04; df = 2; I2 = 0%) indicated no significant heterogeneity among the studies. Pooled effect size analysis revealed a risk difference (RD) of − 0.09 (95% CI = [− 0.17, − 0.01]), demonstrating a statistically significant difference between the two groups (Z = 2.28; p = 0.02), suggesting that the treatment group had a lower local recurrence rate compared with the control group. The funnel plot was approximately symmetric, indicating low publication bias (Figures 5, 6).
Recurrence-free survival
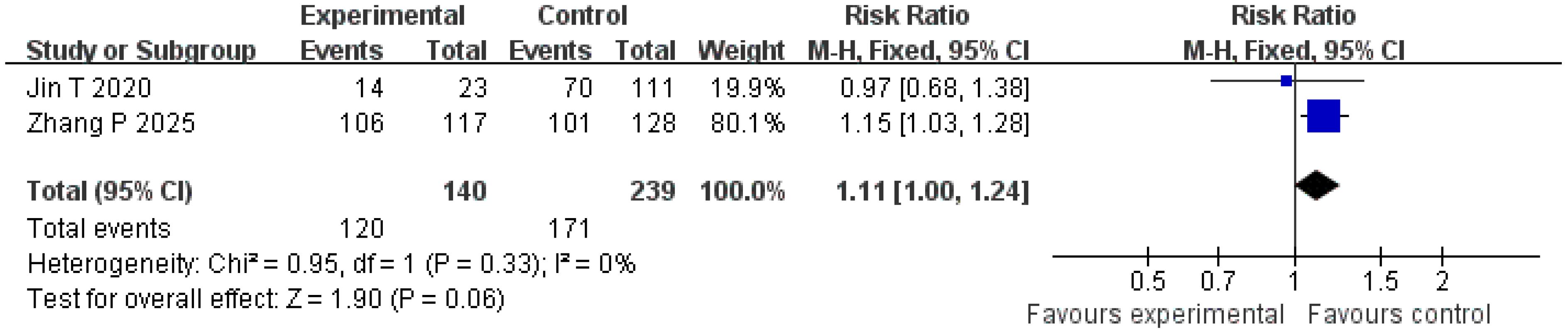
Two studies were included in the analysis of recurrence-free survival. The Q and I2 test statistics revealed no significant heterogeneity among studies (p = 0.33; χ2 = 0.95; df = 1; I2 = 0%). Pooled effect size analysis demonstrated a RR of 1.11 (95% CI = [1.00, 1.24]), indicating a positive trend favoring the treatment group, but this did not reach conventional statistical significance (p = 0.06). It is important to note that this analysis, based on only two studies, is likely underpowered to detect a clinically important difference, and the nonsignificant result may reflect a type II error. The funnel plot was approximately symmetric, indicating low publication bias (Figures 7, 8).
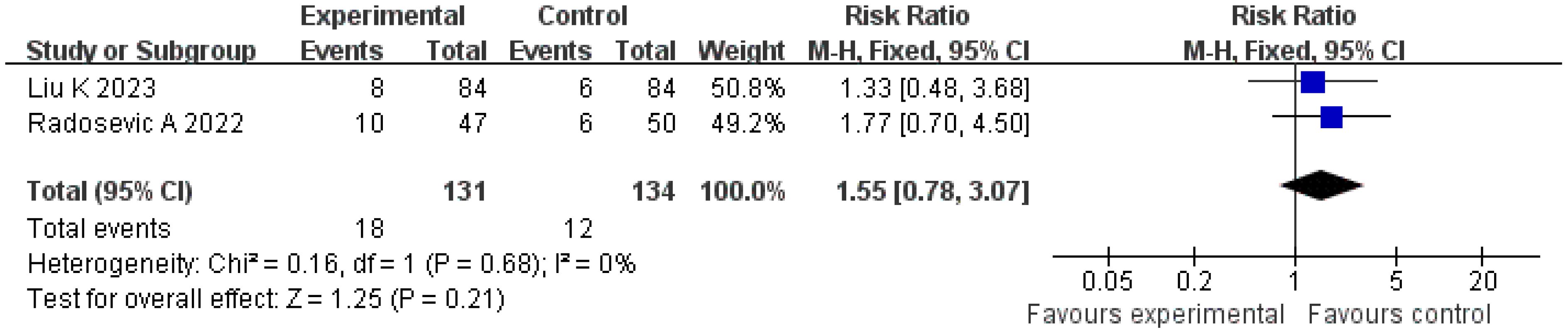
Local tumor progression rate
A total of two studies were included in the analysis of local tumor progression rates. The Q and I2 test results (p = 0.68, χ2 = 0.16, df = 1; I2 = 0%) indicated no significant heterogeneity among the studies. Pooled effect size analysis revealed no statistically significant difference between the two groups (RR = 1.55; 95% CI = [0.78, 3.07]; p = 0.21). As this analysis included only two studies, the wide confidence interval, overlapping both potential harm and benefit, indicates substantial uncertainty. These results should be interpreted with caution due to the very limited power. The funnel plot was approximately symmetric, suggesting low publication bias (Figures 9, 10).
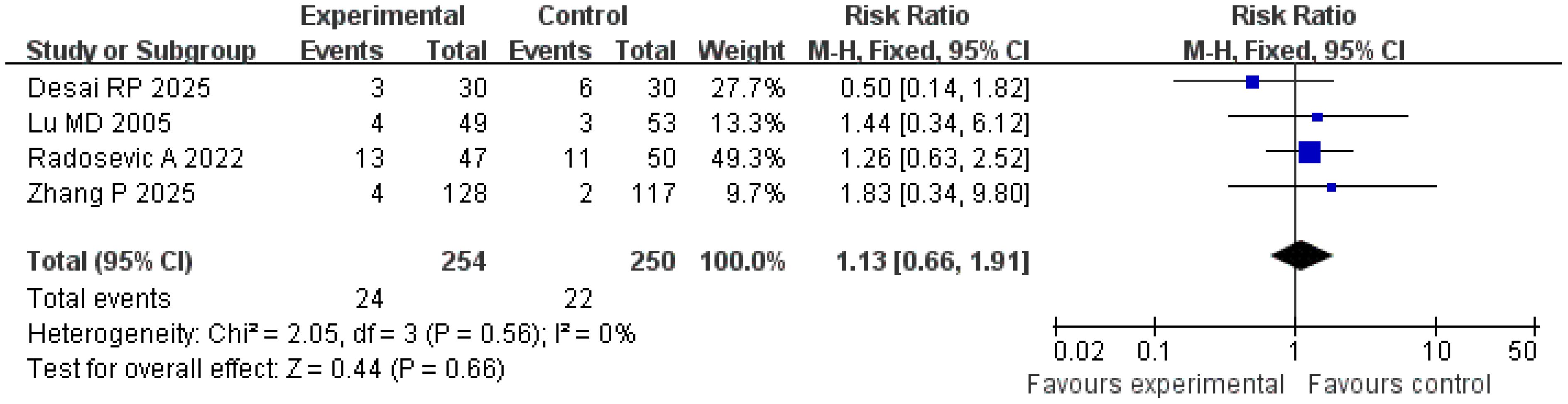
Complication incidence
A total of four studies were included in the analysis of complication incidence. The results of the Q and I2 tests were as follows: p = 0.56 (χ2 = 2.05; df = 3), I2 = 0%, indicating no significant heterogeneity among the studies. In the pooled effect size analysis, the RR was 1.13, with a 95% CI of [0.66, 1.91]. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups (Z = 0.44; p = 0.66). The funnel plot was approximately symmetric, suggesting a low risk of publication bias (Figures 11, 12). It is important to note that the reported complications were predominantly major adverse events. Data on minor complications (e.g., postablation syndrome, transient pain, or biochemical abnormalities) were inconsistently reported across studies, precluding their meaningful analysis.
Discussion
HCC, a malignant tumor with high global incidence and mortality, remains a key and challenging focus in clinical research. Due to its insidious symptoms in the early stages, most patients miss the optimal timing for surgical resection at diagnosis. Therefore, minimally invasive treatments have become important options for patients with intermediate- to advanced-stage disease or those who are not eligible for surgery. CEUS-guided MWA, as a precise and minimally invasive treatment modality, induces irreversible tumor necrosis through thermal coagulation and has demonstrated significant advantages in the management of HCC. However, the traditional evaluation mode that relies solely on imaging or serological indicators has limitations. Imaging features may fail to identify small residual lesions, and serum markers can be affected by factors such as liver or kidney function. In this study, a meta-analysis was conducted to systematically evaluate the efficacy of CEUS-guided MWA combined with imaging features and serum markers in the treatment of HCC. The results showed that this strategy significantly improved the complete tumor ablation rate and reduced the local recurrence rate without increasing the risk of complications, providing important evidence-based support for the precise treatment of HCC.
The complete tumor ablation rate is the primary indicator for evaluating the efficacy of local ablation treatment, directly affecting both short-term outcomes and long-term survival of patients. This meta-analysis included four studies comprising a total of 692 patients. The results showed that the complete tumor ablation rate in the treatment group was significantly higher than in the control group (RR = 1.06; 95% CI = [1.01, 1.10]; p = 0.010), and heterogeneity among the studies was low (I2 = 34%), indicating that this conclusion is highly reliable. This result may be closely related to the synergistic effect of complementary data types: real-time hemodynamic information from CEUS and quantitative biological activity from tumor markers: the real-time blood perfusion information provided by CEUS can accurately locate tumor boundaries and tiny satellite lesions, ensuring that the ablation range covers all lesions, while dynamic monitoring of serum markers (such as alpha-fetoprotein, abnormal prothrombin) can identify potential residual lesions at an early stage and guide supplementary ablation (16, 17). For example, Zhang et al. found that in patients exhibiting the “fast-in and fast-out” imaging features on contrast-enhanced ultrasound combined with a high preoperative alpha-fetoprotein level (> 400 ng/mL), the complete ablation rate was 9% higher than that in the group guided by conventional ultrasound after adjusting the ablation power and range (9). In addition, a study by Lu et al. reported that, when comparing CEUS-guided MWA and radiofrequency ablation, dynamic evaluation combined with serum markers significantly improved the complete tumor ablation rate in the CEUS-guided MWA group, further confirming the value of multimodal evaluation in optimizing the ablation strategy (11).
Local recurrence is a key factor affecting the prognosis of HCC patients, and its occurrence is closely associated with tumor residue, microvascular invasion, and incomplete treatment (18, 19). An analysis of three studies involving 320 patients in this research showed that the local recurrence rate in the treatment group was significantly lower than in the control group (RD = − 0.09; 95% CI = [− 0.17, − 0.01]; p = 0.02), with no obvious heterogeneity (I2 = 0%), suggesting that combining imaging and serological indicators can effectively reduce the recurrence risk. The potential mechanism underlying this result is as follows: imaging features (such as tumor size, boundary clarity, and presence of capsule) can predict tumor invasiveness, while serum marker levels (such as alpha-fetoprotein-L3 subtype, abnormal prothrombin) can reflect tumor biological activity (20–22). For example, Yan et al. reported that in patients with a “fuzzy boundary and rich blood supply” on imaging and an abnormal prothrombin level > 40 mAU/mL, the 1-year local recurrence rate in the treatment group was 12% lower than that in the control group when ablation time was prolonged and the ablation range expanded (10). A randomized controlled trial by Desai et al. confirmed that dynamic evaluation combining contrast-enhanced ultrasound features and the postoperative decline in alpha-fetoprotein could reduce the local recurrence risk by 23%, further supporting the importance of multi-index combined monitoring in recurrence prevention and control (12).
Recurrence-free survival is an important indicator reflecting the long-term prognosis of patients. An analysis of two studies involving 379 patients in the present research showed that the recurrence-free survival in the treatment group was slightly higher than in the control group (RR = 1.11; 95% CI = [1.00, 1.24]; p = 0.06). Although this observed trend toward improved recurrence-free survival (RFS; RR = 1.11; p = 0.06) was not statistically significant, it is clinically encouraging. However, this conclusion is tentative, as the analysis was underpowered; the failure to reach statistical significance likely reflects a type II error rather than conclusive evidence of no effect. Future studies with larger sample sizes and longer follow-up are needed to definitively determine the impact on long-term survival. The observed trend may be influenced by the small sample size and differences in follow-up time: the follow-up period in the study by Liu et al. was 18 months, whereas that in the study by Zhang et al. was 24 months. Variations in follow-up periods may affect the stability of the results (9, 13). In addition, the recurrence-free survival is influenced by multiple factors, including tumor stage and liver function reserve. Differences in baseline characteristics (such as Child–Pugh grade and tumor number) in the included studies may reduce the observed significance of differences between groups (23, 24). Future studies with larger sample sizes and long-term follow-up are needed to further evaluate the impact of this strategy on recurrence-free survival.
The local progression rate reflects the invasive ability of the tumor at the primary site or in adjacent tissues. An analysis of two studies involving 265 patients in the present research showed no statistically significant difference in the local progression rate between the treatment and control groups (RR = 1.55; 95% CI = [0.78, 3.07]; p = 0.21). This result may be related to the multifactor-driven mechanism of local progression: pathological features, such as microvascular invasion and the distribution of satellite lesions, may exceed the predictive capacity of imaging and serum indicators, making it difficult to completely control progression risk through imaging and serological evaluations alone (25, 26). For example, a study by Radosevic et al. found that in patients with portal vein tumor thrombus, the local progression rate remained as high as 28% even when the treatment-group protocol was applied, suggesting that additional molecular markers (such as vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix metalloproteinase) may need to be incorporated to further optimize the evaluation system (15).
Safety is a key consideration in minimally invasive treatment. An analysis of four studies involving 504 patients in the present research showed no statistically significant difference in complication rates between the treatment and control groups (RR = 1.13; 95% CI = [0.66, 1.91]; p = 0.66), with no significant heterogeneity among the studies (I2 = 0%), indicating that the strategy of combining imaging features and serum markers does not increase treatment risk (27). Common complications included bleeding, infection, and subcapsular liver hematoma. The occurrence of complications is closely related to the operative technique and tumor location (such as adjacent to large blood vessels or gallbladder) and is independent of the evaluation method (28). For example, Radosevic et al. confirmed that precise positioning and individualized adjustment of ablation parameters in the treatment group resulted in a severe complication rate (such as massive bleeding, bile leakage) comparable to that in the control group (< 5%), further verifying the safety of this strategy (15).
Moving forward, the logical evolution of combining imaging features and serum biomarkers lies in the development of integrated predictive algorithms. Our findings suggest that the synergistic use of anatomical and biological data provides a rich dataset suitable for machine learning or artificial intelligence models. Such tools, as explored in recent literature (29), aim to synthesize multimodal data (e.g., CEUS perfusion patterns, AFP, and DCP levels) to generate individualized prognostic scores or risk stratifications. These algorithms hold the potential to transform current standardized surveillance and follow-up protocols into a dynamic, predictive, and truly patient-specific process, ultimately enabling earlier intervention for recurrence and optimizing long-term management strategies.
This meta-analysis has several limitations. First, the relatively small number of included studies (n = 7), comprising a total of 1,039 patients, while demonstrating low heterogeneity, may limit the statistical power and generalizability of our findings, particularly for subgroup analyses. Second, although restricting the analysis to RCTs enhances internal validity, it excludes real-world evidence from observational studies and precludes adjustment for patient-level prognostic factors using aggregate data, potentially affecting generalizability and leaving room for residual confounding. Third, clinical heterogeneity exists across the included studies, particularly regarding control interventions (encompassing conventional ablation, surgical resection, RFA, and TACE) as well as the definitions, thresholds, and assessment timing for both imaging features and serum biomarkers. Consequently, our findings support the principle of a multimodal assessment rather than endorsing a specific, universal protocol. Although the consistent benefit observed across comparator types supports the broad utility of this strategy, this variability precludes definitive protocol recommendations. The consistent direction of benefit across studies with different control interventions strengthens the proposition that integrating imaging and biomarker data provides a universal enhancement to the CEUS-MWA procedure, regardless of the alternative treatment being used for comparison. Fourth, the relatively short follow-up durations (≤ 24 months) prevent assessment of long-term outcomes, such as overall survival and 3–5-year recurrence rates, confining our conclusions to intermediate endpoints. Fifth, safety assessment was limited by inconsistent reporting, which focused primarily on major complications and likely underestimated the burden of minor adverse events due to the absence of standardized grading systems. Finally, the conceptual amalgamation of diverse imaging and biomarker elements into a single “combined strategy” obscures the individual contribution of specific parameters, highlighting the need for future research to delineate their relative importance. Furthermore, although our search encompassed major electronic databases and clinical trial registries, we did not systematically search non-English and regional grey literature, which may have resulted in the omission of relevant studies and introduced potential selection bias.
Based on the findings and limitations of this analysis, future research should prioritize several key directions. First, large-scale, multicenter randomized controlled trials with standardized imaging protocols, harmonized biomarker thresholds, and extended follow-up durations (≥ 5 years) are needed to validate long-term survival benefits and establish durable local control. Second, studies should move beyond the current composite strategy to identify the most impactful elements through detailed analysis of specific imaging features and biomarker combinations. Third, the integration of advanced technologies—including radiomics, artificial intelligence, and emerging liquid biopsy tools such as circulating tumor DNA—should be explored to develop predictive models for treatment response and enable ultrasensitive detection of minimal residual disease. Fourth, standardized prospective collection and reporting of adverse events using validated classification systems are essential to establish a comprehensive safety profile. Finally, a future comprehensive meta-analysis incorporating well-conducted prospective cohorts could provide broader perspectives into the real-world effectiveness of this multimodal approach.
In conclusion, CEUS-guided MWA that integrates specific CEUS findings—particularly hemodynamic patterns—with serological tumor biomarkers such as AFP and DCP can significantly improve complete tumor ablation rates and reduce the local recurrence risk, offering an optimized strategy for minimally invasive treatment of HCC.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XZ: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Conceptualization, Validation, Resources, Software, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Methodology. DZ: Data curation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources. Visualization, Software, Writing – review & editing. YSh: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Software, Investigation, Visualization, Validation. YSo: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Software, Investigation, Resources. YD: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Software, Visualization, Methodology, Formal Analysis. LL: Investigation, Project administration, Validation, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Software, Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Xia Y, Zhou Q, Jiang X, Tu W, Liu Q, Li L, et al. Investigation into the efficiency and prognostic elements of CT-guided 125I particle implantation for liver cancer. Cancer Imaging. (2025) 25:89. doi: 10.1186/s40644-025-00909-6
2. Lim RY, Koh B, Ng CH, Kulkarni AV, Liu K, Wijarnpreecha K, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance and survival in a contemporary asia-pacific cohort. JAMA Netw Open. (2025) 8:e2520294. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.20294
3. Li X, Xu Y, Ou Y, Li H, and Xu W. Optimizing treatment selection for early hepatocellular carcinoma based on tumor biology, liver function, and patient status. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2025) 12:777–90. doi: 10.2147/jhc.S514248
4. Giuliante F, Famularo S, Grasselli S, Sangiovanni A, Vitale A, Cabibbo G, et al. Minimally invasive hepatectomy vs. thermoablation for single small (≤3 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: A weighted real-life national comparison. JHEP Rep. (2025) 7:101420. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2025.101420
5. Fu Y, Zhu Q, Zhao X, Lu J, and Wang W. Efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma at specific anatomic sites of the liver: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. (2025) 25:505. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04081-w
6. Dong F, Wu Y, Li W, Li X, Zhou J, Wang B, et al. Advancements in microwave ablation for tumor treatment and future directions. iScience. (2025) 28:112175. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112175
7. Li R and Yu Y. Clinical study on ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. (2025) 17:3640–8. doi: 10.62347/eshv1093
8. Wang Q, Zhang XY, Yang JF, and Tao YL. Comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging parameters and serum markers in preoperative rectal cancer evaluation: Combined diagnostic value. World J Gastrointest Oncol. (2025) 17:103809. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.103809
9. Zhang P, Zhou Q, and Zeng Z. The impact of ultrasound contrast-enhanced fusion virtual navigation technology-guided microwave ablation (MWA) and standard MWA on the local tumor progression of hepatocellular carcinoma with unclear ultrasound images. Eur J Med Res. (2025) 30:451. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02608-1
10. Yan SY, Zhang Y, Sun C, Cao HX, Li GM, Wang YQ, et al. Comparison of real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and standard ultrasonography in liver cancer microwave ablation. Exp Ther Med. (2016) 12:1345–8. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3448
11. Lu MD, Xu HX, Xie XY, Yin XY, Chen JW, Kuang M, et al. Percutaneous microwave and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective comparative study. J Gastroenterol. (2005) 40:1054–60. doi: 10.1007/s00535-005-1671-3
12. Desai RP, Koladiya BC, and Ray RU. Role of intraoperative ultrasound in enhancing accuracy and outcomes in liver tumor resection procedures. Eur J Cardiovasc Med. (2025) 15.
13. Liu K, Zheng H, Sui X, Liu B, Meng M, Feng Y, et al. Microwave ablation versus surgical resection for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score-matched study of long-term therapeutic outcomes. Eur Radiol. (2023) 33:1938–48. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09135-1
14. Jin T, Liu X, Zhang H, Cao Y, Dai C, Tang S, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to large vessels: a propensity score matching analysis. Int J Hyperthermia. (2020) 37:955–64. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2020.1804076
15. Radosevic A, Quesada R, Serlavos C, Sánchez J, Zugazaga A, Sierra A, et al. Microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver Malignancies: a randomized controlled phase 2 trial. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03802-x
16. Zhao L, Jiang L, Liu Y, Wang X, Song J, Sun Y, et al. Integrated analysis of circulating tumour cells and circulating tumour DNA to detect minimal residual disease in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Med. (2022) 12:e793. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.793
17. Xu Y, Cai J, Zhong K, Wen Y, Cai L, He G, et al. Plasma-only circulating tumor DNA analysis detects minimal residual disease and predicts early relapse in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing curative resection. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1119744. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1119744
18. Ngo HTT, Nguyen DD, Dang MX, Doan TTP, and Thai TT. Early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients without microscopic vascular invasion: clinicopathological characteristics and risk factors. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2025) 12:1167–75. doi: 10.2147/jhc.S524683
19. Zheng J, Wang S, Xia L, Sun Z, Chan KM, Bernards R, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: signaling pathways and therapeutic advances. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2025) 10:35. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02075-w
20. Luo L, Wang X, Peng X, Zhong R, Xuan X, Lin H, et al. Analysis of the optimal patterns of serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP), AFP-L3% and protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II (PIVKA-II) detection in the diagnosis of liver cancers. PeerJ. (2025) 13:e19712. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19712
21. Takada H, Tsuchiya K, Yasui Y, Nakakuki N, Tamaki N, Suzuki S, et al. Irregular vascular pattern by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and high serum Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein level predict poor outcome after successful radiofrequency ablation in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2016) 5:3111–20. doi: 10.1002/cam4.932
22. Matsuura K, Oura S, Matsuki H, Kitano Y, and Shintani H. Absence of low internal echoes as an indicator of non-aggressive components in hepatocellular carcinomas: A case report. Cureus. (2025) 17:e86616. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86616
23. Chen M, Ren C, Wang M, Yu M, Wu B, Zhuang B, et al. Validation of an albumin-indocyanine green-based China liver cancer staging system to evaluating resectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients and comparison with the Child-Pugh-based China liver cancer staging system. Front Oncol. (2025) 15:1450333. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1450333
24. Yoshitomi K, Hayashi T, Oe S, Shibata M, Honma Y, Harada M, et al. Child-Pugh grade deterioration stratified by the etiology after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization as initial treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:3707. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53709-6
25. Hwang YJ, Bae JS, Lee Y, Hur BY, Lee DH, and Kim H. Classification of microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with prognosis and magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2023) 29:733–46. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0034
26. Yang G, Chen Y, Wang M, Wang H, and Chen Y. Impact of microvascular invasion risk on tumor progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after conventional transarterial chemoembolization. Oncologist. (2025) 30:oyae286. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae286
27. Bates KR, Jones W, Liggett MR, Zaza NN, Vitello DJ, and Bentrem DJ. Complications following open versus minimally invasive resection of gastric adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. (2025) 131:1302–12. doi: 10.1002/jso.28073
28. Pivetta LGA, Da Costa Ferreira CP, De Carvalho JPV, Konichi RYL, Kawamoto VKF, Assef JC, et al. Hepatic subcapsular hematoma post-ERCP: Case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2020) 72:219–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.05.074
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), microwave ablation (MWA), imaging features, serum biomarkers, meta-analysis
Citation: Zou X, Zhao D, Shang Y, Song Y, Deng Y and Lu L (2025) Combined imaging and serum biomarkers in CEUS-guided microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1687044. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1687044
Received: 16 August 2025; Accepted: 20 October 2025;
Published: 05 November 2025.
Edited by:
Francisco Tustumi, University of São Paulo, BrazilReviewed by:
Antonio Giovanni Solimando, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyWenzhen Ding, People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Zou, Zhao, Shang, Song, Deng and Lu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lin Lu, bHVsdGh1YTIwMDBAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Xiaoli Zou1
Xiaoli Zou1 Yu Song
Yu Song Yimei Deng
Yimei Deng Lin Lu
Lin Lu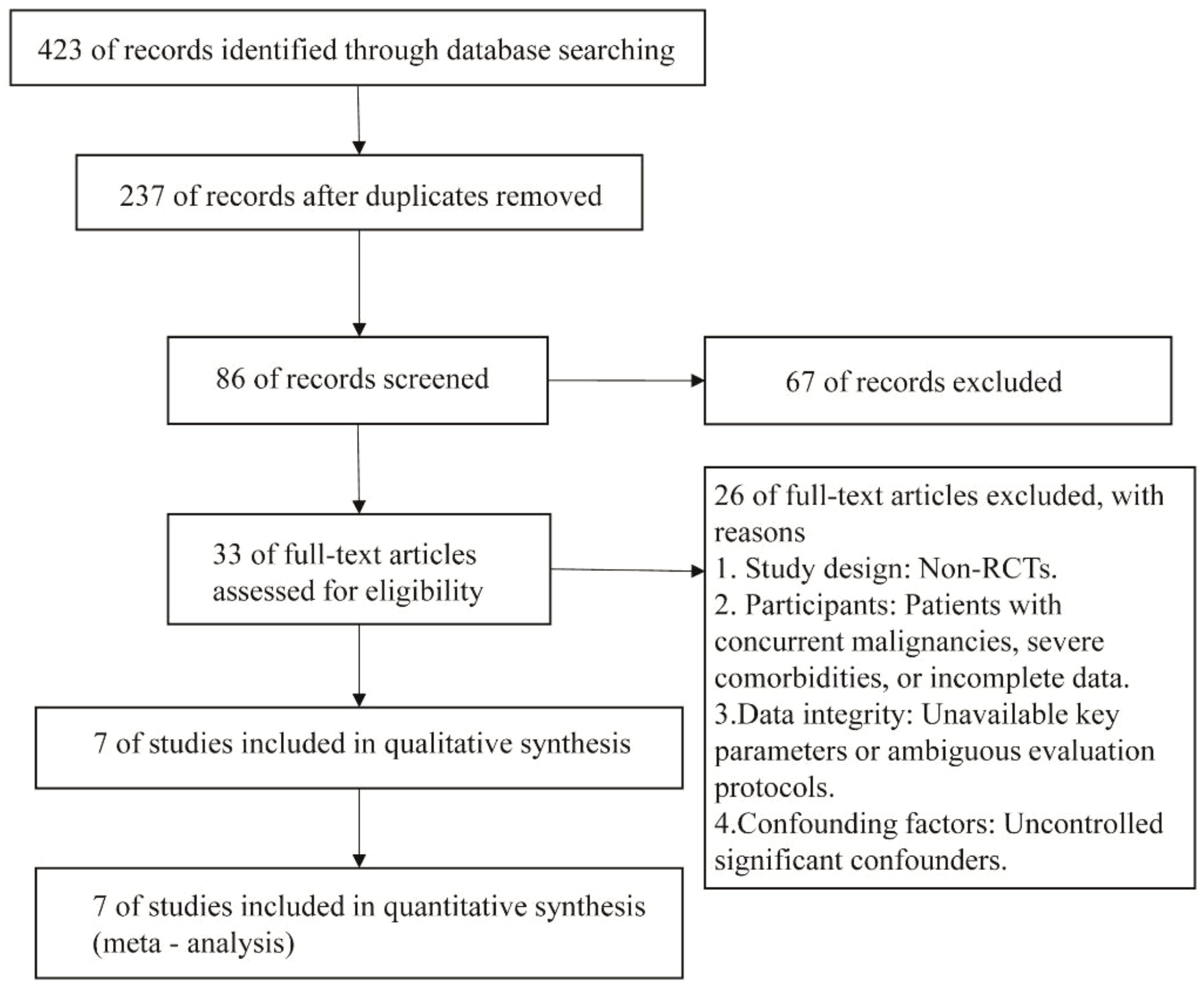
![Funnel plot with effect sizes on the x-axis labeled “RR” and standard errors on the y-axis labeled “SE(log[RR]).” The plot includes several data points represented by squares and a symmetrical inverted triangle formed by dashed lines, indicating standard error boundaries.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1687044/fonc-15-1687044-HTML/image_m/fonc-15-1687044-g004.jpg)
![Funnel plot displaying the standard error of the logarithm of the relative risk (SE(log[RR])) along the vertical axis and the relative risk (RR) on the horizontal axis. Data points are represented by squares scattered within the triangular funnel, bordered by blue dashed lines, centered around a RR of 1.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1687044/fonc-15-1687044-HTML/image_m/fonc-15-1687044-g012.jpg)