- 1Zhejiang Academy of Science & Technology for Inspection & Quarantine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Pharmacology & Immunology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, United States
- 3Hollings Cancer Center, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, United States
Layilin (encoded by LAYN), a C-type lectin transmembrane receptor, serves as a critical molecular bridge between extracellular matrix (ECM) sensing and intracellular signaling through its interaction with cytoskeletal adaptors. Initially identified for its cytoskeletal functions, layilin has since emerged as a pleiotropic modulator of both physiological homeostasis and pathological conditions. Elevated expression of layilin is associated with poor prognosis in multiple cancers, thereby highlighting its oncogenic potential. Beyond cancer, it plays a pivotal role in rheumatoid arthritis, fibrotic progression, and chronic inflammatory diseases. This review comprehensively synthesizes the structural features, expression dynamics, and disease mechanisms of layilin, emphasizing its biological functions. Key knowledge gaps persist, particularly in understanding its spatiotemporal regulation and crosstalk with immune checkpoints. Future research should prioritize cell-type-specific mechanistic studies using advanced experimental models and the development of layilin-targeted immunotherapies. These efforts will pave the way for precise interventions in diseases driven by the dysregulation of layilin-dependent ECM signaling.
1 Introduction
Layilin, encoded by the LAYN gene, is a transmembrane receptor that was first identified in 1998 (1) for its interactions with cytoskeletal regulators, including talin (2), merlin, and radixin (3). Its unique ability to bridge extracellular matrix (ECM) signals with intracellular responses has positioned it as a critical player in cell adhesion and migration (1). Although early studies have focused on these functions, emerging evidence has revealed its pleiotropic functions in pathological processes, including tumor progression, inflammatory disorders, and immune dysregulation. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying its cell type-specific and context-dependent roles remain poorly understood.
The functional significance of layilin is closely linked to its interaction with hyaluronan (HA) (4), a glycosaminoglycan whose biological effects highly depend on its molecular weight (5, 6). High-molecular-weight HA (HMW-HA, > 500 kDa) maintains tissue homeostasis and promotes anti-inflammatory responses, whereas low-molecular-weight HA (LMW-HA, < 120 kDa) is associated with pro-inflammatory responses (7). Notably, layilin exhibits a distinct preference for binding LMW-HA (< 70 kDa) (8), suggesting that it is a specialized sensor of tissue inflammation and a key mediator of immune responses in the tumor microenvironment (TME) (9). This unique binding specificity underscores the role of layilin in distinguishing between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals, making it a critical regulator of tissue homeostasis and disease progression.
This review aims to provide a comprehensive synthesis of the current knowledge on layilin, encompassing its structural features, expression patterns, and dual roles in physiological homeostasis and disease pathogenesis. We particularly focus on its involvement in tumor progression, inflammatory disorders, and signaling networks, highlighting its potential as a cancer immunotherapy and a therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases. By addressing critical gaps in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms and context-dependent functions of layilin, this review seeks to guide future research and therapeutic developments.
2 Characteristics of layilin
Layilin is a 55 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a critical molecular link between ECM components and intracellular cytoskeletal networks. Initially identified through its interaction with talin in membrane ruffles (1), its expression has been documented in humans, hamsters, mice, and pigs (1, 10). Layilin is encoded by the LAYN gene on human chromosome 11q23.1 (UniProt ID: Q6UX15). The full-length 382-amino acid (aa) protein is composed of four distinct domains (Figure 1): a signal peptide (aa 1–21); extracellular domain (aa 22–235), featuring a C-type lectin-like domain (aa 45–185) that explicitly recognizes HA; transmembrane domain (aa 236–256) characterized by LAYILI sequence that gives the protein its name; and cytoplasmic tail (aa 257–382), which contains two functional YXXΦ motifs (YNVI and YDNM) (1) and binding interfaces for both talin’s F3 domain (2) and ERM family proteins (radixin/merlin) (3). These structural features indicate that layilin orchestrates and enables dynamic membrane-cytoskeleton coupling during cell migration and may regulate receptor internalization via clathrin-mediated endocytosis (1). Its expression is particularly prominent in actively migrating cells, where it localizes to leading-edge ruffles, underscoring its role in cell motility and adhesion dynamics (1). An intriguing, unexplored question is whether the considerable energy demands of layilin-mediated migration necessitate an interface with metabolic pathways, akin to the role of MFSD8 in endothelial metabolism (11). Addressing this, along with the precise mechanisms regulating its interactions, remains a crucial goal for future investigation.
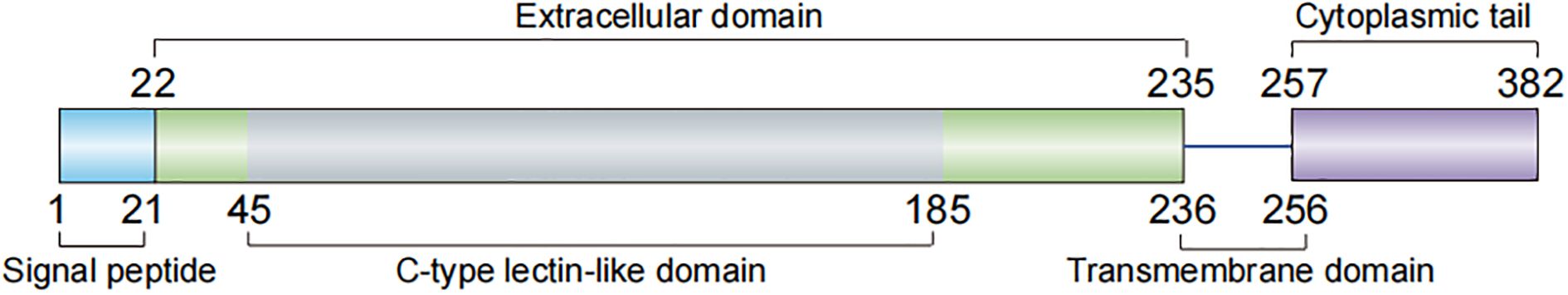
Figure 1. Molecular structure of human layilin. The full-length layilin protein is composed of four distinct domains: a signal peptide (aa 1–21), extracellular domain (aa 22–235), transmembrane domain (aa 236–256), and cytoplasmic tail (aa 257–382). aa, amino acid.
3 Regulation of layilin expression
Layilin expression is widely and tightly regulated across diverse cell types (1). Its expression is dynamically controlled through cytokine-dependent mechanisms that display remarkable cell-type specificity. In immune cells, T-cell receptor (TCR) activation combined with either interleukin-2 (IL-2) or transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) stimulation potently induces the expression of layilin in regulatory T cells (Tregs) (12). In contrast, vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) upregulates layilin in activated CD8+ T cells through the transcription factor NR4A1 (13). Inflammatory mediators exert divergent effects on the expression of layilin. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) upregulates layilin expression in both chondrocytes (14) and human renal carcinoma cells, whereas TGF-β lacks this effect in renal carcinoma cells (15). Similarly, Murata et al. (16) reported that layilin expression in human chondrocytes and synoviocytes was downregulated by interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), potentially modulating HA-mediated signaling pathways. The pathological context further expands the regulatory spectrum of layilin expression. For example, the community-acquired respiratory distress syndrome (CARDS) toxin induces layilin upregulation in A549 cells (17), suggesting a potential role in host-pathogen interactions. Collectively, these findings establish layilin as a versatile microenvironmental sensor whose expression is precisely controlled by multiple regulatory networks, including immune cytokines and pathogenic factors. This intricate regulation underscores the functional adaptability of layilin in physiological and pathological contexts.
4 Ligand recognition and membrane signaling
Layilin functions as a multifunctional receptor that mediates diverse extracellular signals via its ligand-binding capacity. Bono et al. (4) identified HA as a principal ligand, establishing the role of layilin in ECM-cytoskeleton communication, cell motility, adhesion, spreading, and signal transduction. Forteza et al. (8) reported that cigarette smoke-derived LMW-HA binds to layilin in the airway epithelium, activating the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. This pathway suppresses E-cadherin expression and increases the epithelial permeability. Conversely, Kim et al. (18) observed that 35-kDa HA (HA35) binding to layilin upregulates zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) expression, enhancing tight junction integrity and reducing intestinal permeability both in vitro and in vivo. Bellos et al. (19) further corroborated this protective effect during short-term ethanol exposure. These opposing outcomes highlight the diverse and context-dependent functional roles of layilin signaling networks. The clinical success of HA therapy in inflammatory disorders illustrates the potential of modulating the HA pathway (20). Layilin, given its specificity for pro-inflammatory LMW-HA, thus emerges as a rational target for developing next-generation, receptor-specific anti-inflammatory strategies. Beyond HA, Glasgow et al. (21) identified glycosylated collagens as additional ligands for layilin, underscoring its capacity for immune modulation and its multifunctionality across different biological contexts. Furthermore, the functional spectrum of layilin extends to organelle regulation. Tsutiya et al. (22) revealed its mitochondrial targeting and control over fission dynamics through cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) and dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) activation, adding mechanistic depth to its pleiotropic functions. Collectively, these findings suggest that layilin is a versatile receptor that integrates extracellular ligands with membrane signaling and organelle homeostasis, highlighting its critical role in diverse physiological and pathological processes.
5 Role of layilin in cancer
Emerging evidence highlights the multifaceted roles of layilin in oncology (Figure 2), influencing both tumor-intrinsic mechanisms and the TME. In tumor cells, layilin promotes malignant glioma invasion through snail family transcriptional repressor 1 (SNAI1), which suppresses nuclear metastasis associated 1 family member 3 (MTA3) (23), while also inhibiting low-density lipoprotein (LDL) uptake (24). Genetic suppression of layilin reduces metastatic progression and extends survival in murine models of lung adenocarcinoma (25). MALAT-1, a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), mediates LAYN upregulation, enhancing tumor cell motility and implicating layilin as a driver of lung cancer aggressiveness (26). This places layilin among the growing list of genes under lncRNA control. This paradigm is further exemplified in other biological contexts, such as by lncRNA Gm2044 during germ cell development (27). Mälarstig et al. (28) identified layilin as a relevant factor in tumor development in breast cancer, while Vogeley et al. (29) demonstrated that layilin facilitates the adhesion of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in breast cancer cells, but not glioma cells, thereby promoting metastatic progression.
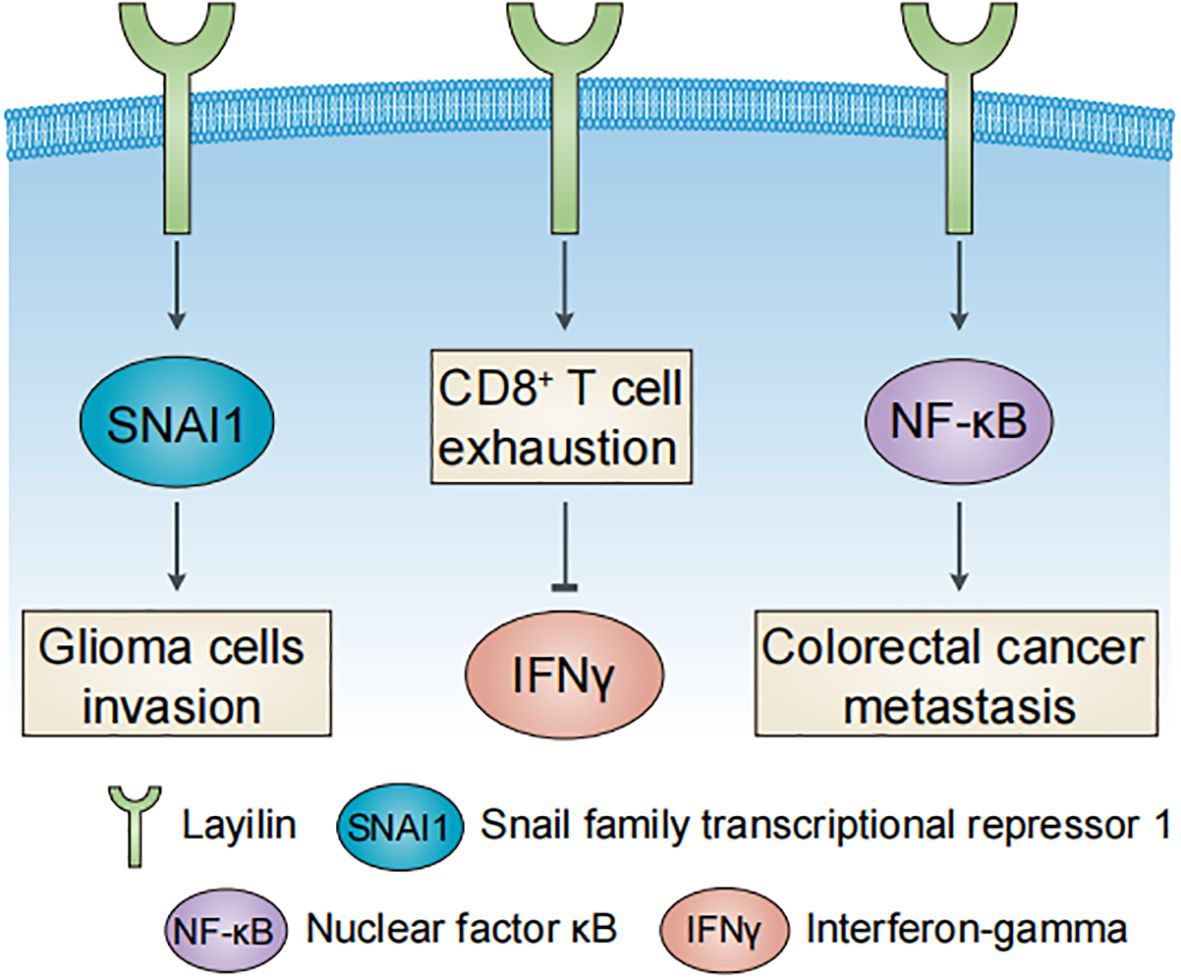
Figure 2. Major roles of layilin in human cancers. Layilin promotes glioma cell invasion, colorectal cancer metastasis, and CD8+ T cell exhaustion in liver cancer.
Within the TME, layilin drives colorectal cancer metastasis and CCL20 secretion via the NF-κB signaling pathway to recruit tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) (30). In liver cancer, layilin marks exhausted CD8+ T cells that suppress interferon-gamma (IFNγ) production (9). Elevated expression of layilin predicts a better response to anti-VEGFR2 and anti-PD-1 combination therapy in lung adenocarcinoma, which is mechanistically linked to the downregulation of layilin in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells (13). However, in melanoma, layilin enhances the cellular adhesiveness and cytotoxic potential of CD8+ T cells through integrin αLβ2 (LFA-1) interaction (31). These contrasting findings underscore the context-dependent role of layilin in CD8+ T cells and highlight the need for further investigation of its function within the TME.
Bioinformatics studies have consistently associated elevated LAYN expression with poor prognosis in multiple malignancies, including hepatocellular carcinoma (9, 32), skeletal undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (33), gastrointestinal cancers (34, 35), breast cancer (28, 36), lung cancer (37, 38), and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (39). Pan-cancer analyses further link LAYN to immunosuppressive features and metastatic potential (40, 41), although the underlying mechanisms remain to be fully elucidated. Collectively, these findings suggest that layilin is a multifunctional regulator of tumor immunity and progression, and its effects are likely dependent on cellular context, tumor type, and TME. The apparent contradictions in the functions of layilin highlight the complexity of its roles and underscore the need for systematic investigations to fully explain its therapeutic potential in cancer settings.
6 Layilin and other diseases
Layilin plays diverse roles in inflammatory and fibrotic diseases across multiple organ systems, and pleiotropic roles in tissue homeostasis and disease pathogenesis. In renal diseases, layilin contributes to fibrotic progression by mediating TNFα-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during glomerulonephritis (15) and serves as a risk biomarker for kidney failure progression (42). Elevated layilin levels in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) predict the development of plastic bronchitis (17). Additionally, layilin participates in airway epithelial homeostasis by facilitating apical actin cap formation and multiciliated cell (MCC) differentiation (10). Shimazaki et al. (43) demonstrated that layilin regulates EMT-related proteins in synovial fibroblasts in rheumatic diseases, while Asano et al. (14) identified its involvement in cartilage degradation in joint diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Future work should investigate whether layilin contributes to EMT by interfacing with the transcriptional circuits that regulate this process in diverse pathologies (44). Emerging evidence also links layilin to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Altered layilin expression in monocytes has been proposed as a potential contributor to SLE pathogenesis (45). As evidenced by impaired tissue repair in mice with Treg cell-specific LAYN deletion, layilin is essential for cutaneous wound healing (12, 46) and skin inflammation (47). Moreover, layilin has been associated with allergic diseases (48) and cellular senescence (49), suggesting its broad involvement in immune dysregulation and aging-related processes. These findings demonstrate that layilin functions as a pleiotropic modulator of tissue inflammation and homeostasis, and its diverse functions are likely dependent on cellular context and disease state. Looking forward, key questions remain regarding the molecular basis of layilin’s pleiotropy. It is crucial to determine if it operates through a core immunometabolic interface, similar to the SIRT6-mediated link between metabolism and inflammatory control (50). Furthermore, the paradigm of single-cell transcriptome-based biomarker prediction (51) offers a powerful strategy to unravel layilin's tissue-specific signaling heterogeneity and accelerate the development of layilin-targeted clinical markers.
7 Conclusions
Layilin has emerged as a functionally versatile transmembrane receptor that plays a pivotal role in mediating dynamic crosstalk between ECM signaling and immune regulation. An open question remains whether layilin, much like the interferon-regulated transcriptional control observed in other immune modulators (52), employs a similar mechanism to direct immune cell function. Its unique molecular architecture enables context-dependent modulation of cellular responses, contributing to its dual roles in diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and organ fibrosis. Therapeutically, layilin represents a promising target, not only in combination with immune checkpoint blockade to overcome resistance (13), but also within the broader context of its potential intersections with metabolic and transcriptional networks. However, critical knowledge gaps remain, including its cell type-specific actions, spatiotemporal regulation of ligand-receptor interactions, and crosstalk with canonical immune pathways. Future research should prioritize the development of cell-selective therapeutic strategies to target disease-driving functions while preserving its physiological roles. These advances will accelerate the translation of layilin biology into precision medicine for tumors and inflammatory diseases, potentially establishing new paradigms for treating therapy-resistant conditions (53).
Author contributions
CJ: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Resources. YZ: Validation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Borowsky ML and Hynes RO. Layilin, a novel talin-binding transmembrane protein homologous with C-type lectins, is localized in membrane ruffles. J Cell Biol. (1998) 143:429–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.2.429
2. Wegener KL, Basran J, Bagshaw CR, Campbell ID, Roberts GC, Critchley DR, et al. Structural basis for the interaction between the cytoplasmic domain of the hyaluronate receptor layilin and the talin F3 subdomain. J Mol Biol. (2008) 382:112–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.087
3. Bono P, Cordero E, Johnson K, Borowsky M, Ramesh V, Jacks T, et al. Layilin, a cell surface hyaluronan receptor, interacts with merlin and radixin. Exp Cell Res. (2005) 308:177–87. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.04.017
4. Bono P, Rubin K, Higgins JM, and Hynes RO. Layilin, a novel integral membrane protein, is a hyaluronan receptor. Mol Biol Cell. (2001) 12:891–900. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.891
5. Tavianatou AG, Caon I, Franchi M, Piperigkou Z, Galesso D, and Karamanos NK. Hyaluronan: molecular size-dependent signaling and biological functions in inflammation and cancer. FEBS J. (2019) 286:2883–908. doi: 10.1111/febs.14777
6. Garantziotis S and Savani RC. Hyaluronan biology: A complex balancing act of structure, function, location and context. Matrix Biol. (2019) 78-79:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.02.002
7. Jin C and Zong Y. The role of hyaluronan in renal cell carcinoma. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1127828. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127828
8. Forteza RM, Casalino-Matsuda SM, Falcon NS, Valencia Gattas M, and Monzon ME. Hyaluronan and layilin mediate loss of airway epithelial barrier function induced by cigarette smoke by decreasing E-cadherin. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:42288–98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.387795
9. Zheng C, Zheng L, Yoo JK, Guo H, Zhang Y, Guo X, et al. Landscape of infiltrating T cells in liver cancer revealed by single-cell sequencing. Cell. (2017) 169:1342–56.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.035
10. Cavard A, Redman E, Mercey O, Abelanet S, Plaisant M, Arguel MJ, et al. The MIR34B/C genomic region contains multiple potential regulators of multiciliogenesis. FEBS Lett. (2023) 597:1623–37. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14630
11. Xiang Q, Chen Y, Cheng X, Fang X, Liu Y, Huang Y, et al. Non-targeted metabolomics reveals the potential role of MFSD8 in metabolism in human endothelial cells. Mol Biotechnol. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01396-7
12. Mehta P, Gouirand V, Boda DP, Zhang J, Gearty SV, Zirak B, et al. Layilin anchors regulatory T cells in skin. J Immunol. (2021) 207:1763–75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000970
13. Yang B, Deng B, Jiao XD, Qin BD, Lu Y, Zhang W, et al. Low-dose anti-VEGFR2 therapy promotes anti-tumor immunity in lung adenocarcinoma by down-regulating the expression of layilin on tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. Cell Oncol. (2022) 45:1297–309. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00718-0
14. Asano K, Arito M, Kurokawa MS, Omoteyama K, Okamoto K, Suematsu N, et al. Secretion of inflammatory factors from chondrocytes by layilin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2014) 452:85–90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.053
15. Adachi T, Arito M, Suematsu N, Kamijo-Ikemori A, Omoteyama K, Sato T, et al. Roles of layilin in TNF-α-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of renal tubular epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2015) 467:63–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.09.121
16. Murata M, Yudoh K, Shimizu H, Beppu M, Nakamura H, Kato T, et al. Layilin, a talin-binding hyaluronan receptor, is expressed in human articular chondrocytes and synoviocytes and is down-regulated by interleukin-1β. Mod Rheumatol. (2013) 23:478–88. doi: 10.1007/s10165-012-0686-x
17. Ma Y, Gu Y, Zhang X, Gu W, Wang T, Sun H, et al. High expression of MUC5AC, MUC5B, and layilin plays an essential role in prediction in the development of plastic bronchitis caused by MPP. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:911228. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.911228
18. Kim Y, West GA, Ray G, Kessler SP, Petrey AC, Fiocchi C, et al. Layilin is critical for mediating hyaluronan 35kDa-induced intestinal epithelial tight junction protein ZO-1 in vitro and in vivo. Matrix Biol. (2018) 66:93–109. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.09.003
19. Bellos DA, Sharma D, McMullen MR, Wat J, Saikia P, de la Motte CA, et al. Specifically sized hyaluronan (35 kDa) prevents ethanol-induced disruption of epithelial tight junctions through a layilin-dependent mechanism in Caco-2 cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. (2019) 43:1848–58. doi: 10.1111/acer.14140
20. Gomati A, Teggaz M, and Allam M and Mahmalji W. Hyaluronic acid as a treatment for refractory bacillus calmette-guérin-induced cystitis: A narrative review. Bladder. (2025) 12:e21200038. doi: 10.14440/bladder.2024.0066
21. Glasgow JE, Byrnes JR, Barbee SD, Moreau JM, Rosenblum MD, and Wells JA. Identifying and antagonizing the interactions between layilin and glycosylated collagens. Cell Chem Biol. (2022) 29:597–604.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2022.01.003
22. Tsutiya A, Arito M, Tagashira T, Sato M, Omoteyama K, Sato T, et al. Layilin promotes mitochondrial fission by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 and dynamin-related protein 1 activation in HEK293T cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 549:143–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.02.091
23. Kaji T, Arito M, Tsutiya A, Sase T, Onodera H, Sato T, et al. Layilin enhances the invasive ability of malignant glioma cells via SNAI1 signaling. Brain Res. (2019) 1719:140–7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.05.034
24. Ushimaru S, Arito M, Tsutiya A, Sato T, Omoteyama K, Sato M, et al. Roles of layilin in regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor in malignant glioma cells. J St Marianna Univ. (2020) 11:53–9. doi: 10.17264/stmarieng.11.53
25. Chen Z, Zhuo W, Wang Y, Ao X, and An J. Down-regulation of layilin, a novel hyaluronan receptor, via RNA interference, inhibits invasion and lymphatic metastasis of human lung A549 cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. (2008) 50:89–96. doi: 10.1042/BA20070138
26. Tano K, Mizuno R, Okada T, Rakwal R, Shibato J, Masuo Y, et al. MALAT-1 enhances cell motility of lung adenocarcinoma cells by influencing the expression of motility-related genes. FEBS Lett. (2010) 584:4575–80. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.10.008
27. Zhu Q, Sun J, An C, Li X, Xu S, He Y, et al. Mechanism of LncRNA Gm2044 in germ cell development. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1410914. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1410914
28. Mälarstig A, Grassmann F, Dahl L, Dimitriou M, McLeod D, Gabrielson M, et al. Evaluation of circulating plasma proteins in breast cancer using Mendelian randomisation. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:7680. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43485-8
29. Vogeley C, Degistirici Ö, Twarock S, Wladarz J, Reiners O, Gorges T, et al. The regulatory effect of hyaluronan on human mesenchymal stem cells’ fate modulates their interaction with cancer cells in vitro. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:21229. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00754-0
30. Yang Y, Chen Z, Chu X, Yan Q, He J, Guo Y, et al. Targeting LAYN inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis and tumor-associated macrophage infiltration induced by hyaluronan oligosaccharides. Matrix Biol. (2023) 117:15–30. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2023.02.005
31. Mahuron KM, Moreau JM, Glasgow JE, Boda DP, Pauli ML, Gouirand V, et al. Layilin augments integrin activation to promote antitumor immunity. J Exp Med. (2020) 217:e20192080. doi: 10.1084/jem.20192080
32. Xiao S, Lu L, Lin Z, Ye X, Su S, Zhang C, et al. LAYN serves as a prognostic biomarker and downregulates tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cell function in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2024) 11:1031–48. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S464806
33. Yuan LL, Chen Z, Qin J, Qin CJ, Bian J, Dong RF, et al. Single-cell sequencing reveals the landscape of the tumor microenvironment in a skeletal undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma patient. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1019870. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1019870
34. Pan JH, Zhou H, Cooper L, Huang JL, Zhu SB, Zhao XX, et al. LAYN is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in gastric and colon cancers. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:6. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00006
35. Liao K, Yang Q, Xu Y, He Y, Wang J, Li Z, et al. Identification of signature of tumor-infiltrating CD8 T lymphocytes in prognosis and immunotherapy of colon cancer by machine learning. Clin Immunol. (2023) 257:109811. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109811
36. Zhao D, Li W, Wang Y, Zhang G, Bai X, and Yu H. HTRA1 expression is associated with immune-cell infiltration and survival in breast cancer. Transl Cancer Res. (2023) 12:3503–21. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-773
37. Wang H, Meng D, Guo H, Sun C, Chen P, Jiang M, et al. Single-cell sequencing, an advanced technology in lung cancer research. Onco Targets Ther. (2021) 14:1895–909. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S295102
38. De Simone M, Arrigoni A, Rossetti G, Gruarin P, Ranzani V, Politano C, et al. Transcriptional landscape of human tissue lymphocytes unveils uniqueness of tumor-infiltrating T regulatory cells. Immunity. (2016) 45:1135–47. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.10.021
39. Chen Q, Chen J, Lu Z, Nian R, Li W, Yao Z, et al. The prognostic value of LAYN in HPV-related head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its influence on immune cell infiltration. Discov Oncol. (2024) 15:57. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-00913-5
40. Jiawen W, Jinfu W, Jianyong L, Yaoguang Z, and Jianye W. Comprehensive landscape of the miRNA-regulated prognostic marker LAYN with immune infiltration and stemness in pan-cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:10989–1011. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04986-7
41. Rigopoulos C, Georgakopoulos-Soares I, and Zaravinos A. A multi-omics analysis of an exhausted T cells’ molecular signature in pan-cancer. J Pers Med. (2024) 14:765. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070765
42. Kobayashi H, Looker HC, Satake E, Saulnier PJ, Md Dom ZI, O’Neil K, et al. Results of untargeted analysis using the SOMAscan proteomics platform indicates novel associations of circulating proteins with risk of progression to kidney failure in diabetes. Kidney Int. (2022) 102:370–81. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.04.022
43. Shimazaki K, Arito M, Sato T, Omoteyama K, Sato M, S. Kurokawa M, et al. Roles of layilin in human synovial fibroblasts revealed by proteomic analysis. Integr Mol Med. (2017) 4:1–7. doi: 10.15761/imm.1000316
44. Li XP, Qu J, Teng XQ, Zhuang HH, Dai YH, Yang Z, et al. The emerging role of super-enhancers as therapeutic targets in the digestive system tumors. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:1036–48. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.78535
45. Liu C, Wang Y, Zhang YH, Yuan Z, Zhang Z, Zeng X, et al. Elevated layilin-positive monocyte levels in the peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus reflect their autoimmune status. Immunol Invest. (2023) 52:879–96. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2249531
46. Loffredo LF, Savage TM, Ringham OR, and Arpaia N. Treg-tissue cell interactions in repair and regeneration. J Exp Med. (2024) 221:e20231244. doi: 10.1084/jem.20231244
47. Gouirand V, Clancy S, Macon C, Valle J, Pauli M, Truong HA, et al. Layilin regulates Treg motility and suppressive capacity in skin. eLife. (2025) 14:RP105277. doi: 10.7554/eLife.105277
48. Wang H, Pang J, Zhou Y, Qi Q, Tang Y, Gul S, et al. Identification of potential drug targets for allergic diseases from a genetic perspective: A mendelian randomization study. Clin Transl Allergy. (2024) 14:e12350. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12350
49. Rovillain E, Mansfield L, Lord CJ, Ashworth A, and Jat PS. An RNA interference screen for identifying downstream effectors of the p53 and pRB tumour suppressor pathways involved in senescence. BMC Genomics. (2011) 12:355. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-355
50. Wang J, Luo J, Rotili D, Mai A, Steegborn C, Xu S, et al. SIRT6 protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in human pulmonary lung microvascular endothelial cells. Inflammation. (2024) 47:323–32. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01911-5
51. He Y, Guo Y, Liang X, Hu H, Xiong X, and Zhou X. Single-cell transcriptome and microbiome profiling uncover ileal immune impairment in intrauterine growth-retarded piglets. Curr Pharm Des. (2025). doi: 10.2174/0113816128411269250707073647
52. Kang S, Wu Q, Yang B, and Wu C. Estrogen enhanced the expression of IL-17 by tissue-resident memory γδT cells from uterus via interferon regulatory factor 4. FASEB J. (2022) 36:e22166. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101443RR
Keywords: layilin, LAYN, extracellular matrix, hyaluronan receptor, therapeutic target
Citation: Jin C and Zong Y (2025) Layilin: a multifunctional hyaluronan receptor in physiology and pathology. Front. Oncol. 15:1721065. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1721065
Received: 09 October 2025; Accepted: 11 November 2025; Revised: 10 November 2025;
Published: 01 December 2025.
Edited by:
Prakash Lingasamy, Celvia CC AS, EstoniaReviewed by:
Prasanna Srinivasan Ramalingam, Vellore Institute of Technology, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Jin and Zong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yunfeng Zong, em9uZ0BtdXNjLmVkdQ==
 Chenchen Jin
Chenchen Jin Yunfeng Zong
Yunfeng Zong