- 1The First Clinical College, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
- 2Department of Urology, The First Affiliated hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Urology and Andrology of Ganzhou, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
- 4Department of Graduate, The First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
The ubiquitin (Ub) system has been demonstrated to play a crucial role in various cellular processes, including immune responses, cell development, and programmed cell death. Ubiquitination, a form of post-translational modification, occurs in eukaryotic cells and involves several key components, such as Ub-activating enzymes, Ub-binding enzymes, and Ub-protein ligases. Recently, deubiquitinating enzymes—proteases that reverse the modification of proteins by removing Ub or Ub-like molecules, or by remodeling Ub chains on target proteins—have been identified as significant regulators of ubiquitination-mediated degradation. These enzymes profoundly influence cellular pathways and numerous biological processes, including the DNA damage response and DNA repair mechanisms. Recent studies increasingly demonstrate a relationship between ubiquitination, deubiquitination, and urinary diseases. The roles of these processes in urinary diseases are complex, encompassing various aspects of signaling, protein stability, and cellular metabolism. As research advances, the specific mechanisms by which these processes influence urologic diseases will be further clarified. This review examines recent discoveries in this field, aiming to provide new strategies and targets for the diagnosis and treatment of urologic diseases.
Introduction
Proteins are synthesized from the genetic code encoded in DNA and are subsequently translated into polypeptide chains. These proteins can undergo modifications through chemical alterations known as post-translational modifications (PTMs) (Chen and Tsai, 2022; Singh and Ostwal, 2019). PTMs have been shown to regulate protein function by influencing various aspects of protein behavior, including activity, localization, stability, and interactions with other proteins (Mowen and David, 2014). Common PTMs include methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, glycosylation, and phosphorylation, each involving the attachment of specific chemical groups or protein modifiers. These modifications impact localization, stability, interactions, folding, and gene expression (Bhat et al., 2021; Narita et al., 2019; Rape, 2018; Yang and Qian, 2017). PTMs play a critical role in regulating essential biological processes, such as cellular signal transduction, cell signaling pathways, cellular metabolism, differentiation, metastasis, the cell cycle, and proliferation (Chen T. et al., 2024). Ubiquitination, a specific type of PTM, involves the covalent attachment of ubiquitin to a target substrate, thereby affecting the substrate protein’s function by regulating its localization and stability (Popovic et al., 2014). Ubiquitination is an ATP-dependent cascade reaction that covalently attaches ubiquitin, a protein composed of 76 amino acids and expressed throughout various tissues, to a substrate protein (Hershko and Ciechanover, 1998). Initially, ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s) bind to ubiquitin for activation and subsequently transfer the activated ubiquitin to ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s). Finally, ubiquitin ligases (E3s) facilitate the transfer of ubiquitin from E2 to the substrate (Hershko and Ciechanover, 1998). Ubiquitination modifications of substrate proteins are recognised and degraded by the proteasome machinery (Chen X. et al., 2024; Berndsen and Wolberger, 2014), with E3 ligases playing a crucial role in the ubiquitination process due to their substrate specificity. The human genome contains approximately 1,000 E3 ligases, which can be categorized into three main groups: those homologous to E3s containing the E6AP C-terminal (HECT) structural domain, the RBR family of E3s, and the really interesting E3s that possess the RING finger structural domain (Tang et al., 2019). Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUB) remove ubiquitin molecules and reverse the process of ubiquitination to precisely regulate protein stability or function (Antao et al., 2020) (Figure 1). Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) encompass six primary classes: ubiquitin-specific proteases (USPs), which modify ubiquitin chains through cysteine activity; ovarian tumour proteases (OTUs), which selectively cleave specific chain types (e.g., K48); ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCHs), which remove ubiquitin precursors; the Machado-Josephine Disease Structural Domains (MJD) family, which targets long-chain modifications; JAMM/MPN + metalloproteinases (zinc-dependent, e.g., PSMD14) that specifically process K63 chains; and the MINDY family, which preferentially degrades K48 long chains. These families work synergistically to regulate the reversibility of ubiquitin signaling, influencing critical processes such as protein degradation and DNA repair (Harrigan et al., 2018; Mevissen and Komander, 2017). Among these deubiquitinating enzymes, USPs represent the largest family, responsible for cleaving ubiquitin from its substrates. Dysregulation of USPs is linked to a range of diseases, including neurodegeneration, inflammation, and cancer (Parihar and Bhatt, 2021; Do and Baek, 2021; Liu J. et al., 2021). It is evident that maintaining a balance between ubiquitination and deubiquitination is crucial for sustaining appropriate protein levels and their functions (Snyder and Silva, 2021).
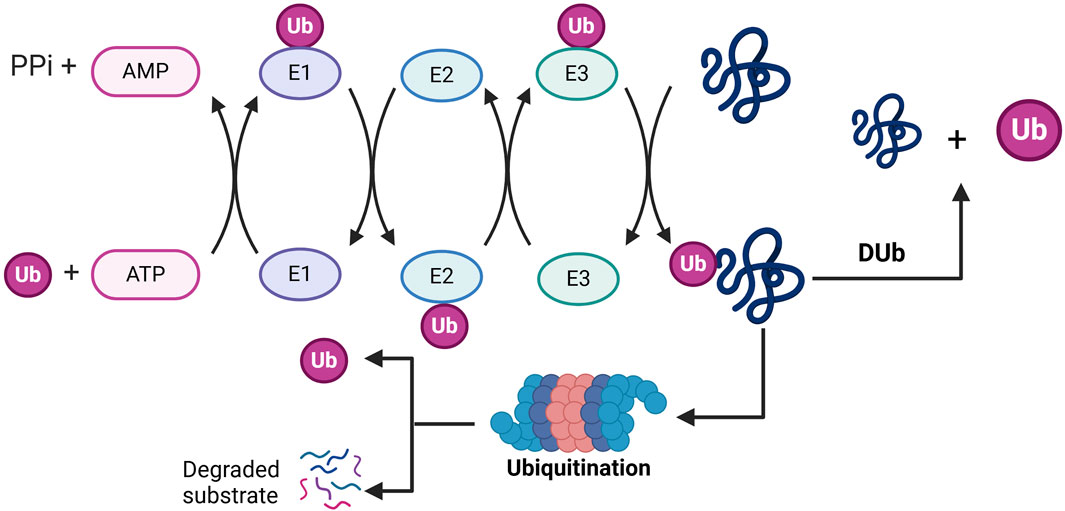
Figure 1. Molecular mechanisms by which ubiquitination and deubiquitination regulate substrate degradation: in the ubiquitination phase (left), ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1) consumes ATP, attaches ubiquitin (Ub) to itself via a thioester bond, and subsequently transfers it to ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2), where ubiquitin conjugating enzyme (E3) covalently binds the ubiquitin to substrate proteins to form a multimeric ubiquitin chain (Ub+) that labels the substrate and is degraded by the proteasome (Degraded substrate). In the deubiquitination phase (right), deubiquitinating enzymes (Dub) shear the ubiquitin chain, reversing the ubiquitination process and maintaining substrate protein stability. PPi, pyrophosphoric acid; Ub, ubiquitin; Dub, deubiquitination.
Prostate, kidney, and bladder cancers (BCa) represent the most prevalent tumors within the urinary system (Hashemi et al., 2022). Urologic tumors account for approximately 10% of the total incidence of tumors, with prostate cancer constituting 29% of cancer cases among men (Siegel et al., 2023). According to the American Cancer Society, it is projected that there will be up to 169,360 new cases of urologic tumors in the United States in 2024, resulting in an estimated 32,350 deaths (Siegel et al., 2024). These tumors are a significant cause of mortality among men globally (Safiri et al., 2021). Currently, the primary treatments for urologic tumors include surgery, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy; however, these cancers are often inadequately monitored and treated (Teo et al., 2019). A growing body of evidence suggests that a deeper understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms of urologic malignancies may provide a promising approach to enhance therapeutic strategies and improve prognostic outcomes (Chen and Lu, 2015; Rosellini et al., 2023). In this context, the emerging roles of ubiquitination and deubiquitination in the regulation of oncogenes or tumour suppressors provides a novel and promising avenue for research. Ubiquitination regulates the activation and inhibition of tumor-associated signaling pathways (e.g., Hippo, HIF-1α) by tagging substrate proteins with E3 ubiquitin ligases, leading to their degradation or alteration of activity via the proteasome (Wang et al., 2022). Conversely, deubiquitination is mediated by deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), which stabilize pro-carcinogenic proteins (e.g., AURKA, PKM2) through the removal of their ubiquitin chains, thereby enhancing the proliferation, migration, and invasion capabilities of tumor cells (Wang et al., 2023). Additionally, both processes influence tumor immune escape by regulating the stability of immune checkpoint proteins (e.g., PD-L1) and provide energy to support tumor growth through metabolic reprogramming (e.g., activation of glycolysis) (Hu et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2020). Recent studies have indicated that ubiquitination and deubiquitination are implicated in various pathologies, including prostate (Liang et al., 2018), bladder (Shen et al., 2024), and kidney cancers (Dushukyan et al., 2017). Furthermore, our findings indicate that these processes also play a crucial role in the development and progression of other diseases affecting the urinary system, such as chronic kidney disease (Zeng et al., 2024), kidney injury (Shen et al., 2021), and renal fibrosis (Saritas et al., 2019). In this review, we examine the role of ubiquitination in the development and progression of urological diseases. Additionally, we discuss the role of deubiquitination in the regulation of these conditions. We also describe compounds that target ubiquitination and deubiquitination to influence the progression of urinary diseases. Finally, we outline the challenges and future prospects for targeting these processes in the treatment of patients with urological diseases.
The role of ubiquitination in prostate cancer
SPOP E3 ubiquitin ligase in prostate cancer
Cullin-Ring ligases (CRLs) represent the largest family of ubiquitin E3 ligases and play a crucial role in regulating numerous essential cellular processes, including cell cycle progression (Petroski and Deshaies, 2005). Based on the Cullin scaffolding proteins—Cullin1, 2, 3, 4A, 4B, 5, and 7—CRLs are categorized into seven subfamilies, designated as CRL1 through CRL7 (Petroski and Deshaies, 2005; Wang et al., 2014). Recently, the CRL3 subfamily complex has emerged as a significant regulator of various cellular processes, with disruptions in this degradation pathway linked to a range of human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer (Genschik et al., 2013). Structurally, CRL3 comprises the scaffolding protein Cullin 3, the RING protein RBX1, and one of the numerous BTB structural domain interface proteins that facilitate the recruitment of protein substrates for polyubiquitination (Genschik et al., 2013). SPOP (spotted POZ protein), a substrate-interacting junction protein within the Cullin 3-based E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, exhibits a mutation rate of 10%–15% and is a critical molecular feature of prostate cancer (PCa) (Wang Z. et al., 2020; Liu D. et al., 2021). Notably, these SPOP mutations are predominantly located in the substrate-binding MATH structural domain (Cheng et al., 2018). PCa-associated missense mutations in the MATH domain of SPOP impair substrate binding and ubiquitination, resulting in the upregulation of oncogenic substrate levels and enhanced PCa cell proliferation and invasion. This suggests a potential tumor-suppressor role for SPOP in PCa. Prostate leucine zipper (PrLZ), a member of the tumor protein D52 (TPD52) family, serves as a significant prostate-specific and androgen-responsive oncogene implicated in the malignant progression of PCa (Wang et al., 2004). In their study, Fan et al. demonstrated a direct interaction between SPOP and PrLZ using a pull-down assay. SPOP interacts with the unique N-terminus of PrLZ, while ERK1/2, a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, plays a vital role in signal transduction and cancer progression (Sun et al., 2015). The research by Fan et al. indicates that ERK1/2-mediated phosphorylation of PrLZ at the Ser40 site stabilizes PrLZ by disrupting its binding to SPOP, thereby facilitating the proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells (Table 1) (Fan et al., 2022). Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (HnRNPK) is a nucleic acid-binding protein that regulates a wide range of biological events. HnRNPK is a specific member of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (HnRNP) family and is involved in various cellular processes occurring in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. In addition to sharing functions with other HnRNPs, HnRNPK plays a critical role in regulating DNA transcription, pre-mRNA processing, and translation, particularly during oncogene expression (Lu and Gao, 2016; Gallardo et al., 2020). These characteristics contribute to HnRNPK’s multiple roles in the cell cycle, apoptosis, and tumor metastasis (Li et al., 2018). In the study conducted by Wu et al., SPOP was found to promote HnRNPK degradation in PCa cells in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, SPOP influences PrCa cell proliferation by regulating HnRNPK abundance through the post-translational ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (Wu et al., 2021).
Activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2) is a member of the ATF/CREB bZIP family of transcription factors that heterodimerizes with members of the JUN and FOS transcription factor families (Lopez-Bergami et al., 2010). SPOP interacts with ATF2 in vivo via the N-terminal substrate-bound MATH domain, and ATF2 has been identified as a bona fide substrate of the SPOP-CUL3-RBX1 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Impaired binding of SPOP mutants to the ATF2 protein leads to reduced proteasomal degradation and subsequent accumulation of ATF2 in prostate cancer cell lines and specimens. This accumulation contributes, in part, to SPOP inactivation-induced prostate cancer cell migration and invasion (Ma et al., 2018). Additionally, there is evidence that SPOP specifically interacts with proteins through its N-terminal MATH structural domain in the context of prostate cancer. Recent studies have begun to unveil the potential oncogenic activity of Cdc20 (Kidokoro et al., 2008), with genetic ablation of Cdc20 primarily resulting in elevated apoptosis (Manchado et al., 2010). High expression of Cdc20 is strongly correlated with advanced clinical stages and poor prognosis in various human cancers, including prostate cancer (Mao et al., 2016). The E3 ligase function of SPOP serves as a novel Cdc20 ligand by facilitating the polyubiquitylation of Cdc20, leading to its subsequent degradation via the 26S proteasome. Thus, the SPOP E3 ligase acts as a novel negative regulator of Cdc20, which in turn influences cell viability and apoptosis in prostate cancer (Wu F. et al., 2017). c-MYC proteins have been identified as novel substrates of SPOP, while Cul3/Rbx1 serves as a new E3 ligase system for c-MYC, playing a crucial role in the regulation of proliferation and c-Myc expression in prostate luminal epithelial cells. In this context, SPOP directly binds to the c-Myc protein, facilitating its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation (Geng et al., 2017). Additionally, fusions of proto-oncogenes to strong promoters or enhancers can lead to the upregulation of mRNA levels. A notable example is the E26 translationally specific (ETS) family of transcription factor fusions in prostate cancer (Kumar-Sinha et al., 2008), with the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion being the most prevalent, occurring in approximately 50% of prostate cancer cases (Tomlins et al., 2005). SPOP has been reported to specifically interact with ERG, promoting its ubiquitination and degradation through WT-SPOP, which negatively regulates ERG-mediated prostate cancer cell migration and invasion (Gan et al., 2015).
TRAF proteins in prostate cancer: TRAF6/TRAF4
TRAF is a class of cytoplasmic junction proteins, comprising six classical members (TRAF1-TRAF6) and one non-classical member (TRAF7) in mammals. The TRAF family of proteins plays a significant role in signaling mediated by the TNFSF and TLR/ILR receptor superfamilies, regulating the activation of various signaling pathways, including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) (Kashiwada et al., 1998). Additionally, the TRAF family is implicated in critical cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, survival, and apoptosis, as well as in immune and inflammatory responses (Bradley and Pober, 2001). The N-terminal region of TRAF6 contains a RING finger domain and five zinc fingers; the RING domain is responsible for its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, while the zinc fingers primarily provide structural support for the RING domain’s function (Lamothe et al., 2008). At the C-terminal end, there exists a TRAF structural domain composed of a convoluted helix and a conserved TRAF-C domain (Rothe et al., 1994). This C-terminal TRAF domain facilitates important biological functions by mediating self-binding interactions with receptors and other signaling proteins that act upstream of TRAF6 (Wajant et al., 2001). Recently, TRAF6 has been found to play a role in ubiquitination processes in prostate cancer. Specifically, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) activation is dependent on phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase (PI3K), with TRAF6 polyubiquitinating p85α, the regulatory subunit of PI3K. This action promotes the formation of a complex between the TGF-β type I receptor (TβRI) and p85α, leading to the activation of PI3K and AKT, which subsequently influences the migration of prostate cancer cells (Hamidi et al., 2017). Abnormal elevations of JARID1B and histone H3 lysine four trimethylation (H3K4me3) are frequently observed in various diseases, including PCa. Their expression has been associated with TRAF6, as demonstrated in a study by Lu et al. SKP2 (S-phase kinase-associated protein-2) serves as the E3 ligase and F-box protein component of the SKP2 SCF complex (Skp1-Cul1-F-Box), which triggers the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of p27 and other proteins (Carrano et al., 1999). In the study, SKP2 modulated H3K4me3 levels by regulating TRAF6-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination of JARID1B, a key demethylase of H3K4me3, thereby influencing prostate cancer migration and recurrence (Lu et al., 2015). Additionally, Lu et al. reported that SKP2 and TRAF6 are involved in another mechanism of ubiquitination in prostate cancer (Ngollo et al., 2014). The levels of SKP2 and zeste homologue enhancer 2 (EZH2) are highly correlated with the aggressive features of human PCa. Their findings indicate a positive correlation between SKP2 and EZH2, with SKP2 stabilizing EZH2 by reducing TRAF6-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination of EZH2 (Lu et al., 2017). Importantly, EZH2 plays a critical role in PCa progression, distant metastasis, and castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) (Min et al., 2010).
TRAF4 is a RING finger domain E3 ubiquitin ligase that is part of the TNF receptor (TNFR)-related junction protein family. Unlike other members of the TRAF family, TRAF4 does not interact directly with TNFR. It is amplified and overexpressed in various cancer types, playing a significant role in promoting cancer progression and metastasis (Ruan et al., 2022). Singh et al. demonstrated that TRAF4 expression is significantly higher in metastatic prostate cancer compared to primary tumors, highlighting its critical role in prostate cancer cell invasion. TrkA, a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), binds to nerve growth factor (NGF) at the cell membrane and activates the Ras/MAPK, PI3K, and PLCγ signaling pathways, promoting cell survival, proliferation, and invasion (Molloy et al., 2011). The authors showed that TRAF4 facilitates TrkA ubiquitination through atypical K27 and K29 ubiquitin linkages within its kinase structural domain. This post-translational modification enhances TrkA kinase activity, increases its tyrosine phosphorylation levels, and activates subsequent downstream signaling pathways, thereby promoting prostate cancer metastasis (Singh et al., 2018). Additionally, another study indicated that TRAF4 plays a significant role in desmoplasia-resistant prostate cancer, a condition that presents a major clinical challenge, where the androgen receptor (AR) remains a key oncogenic factor. AR ubiquitination has been shown to modulate AR activity and contribute to the progression of CRPC (Xu et al., 2009). Singh et al. demonstrated that TRAF4 mediates atypical K27-linked AR ubiquitination at its C-terminus. This atypical ubiquitination enhances the interaction between AR and the pioneer transcription factor FOXA1, subsequently altering the AR genome binding profile and promoting the development of CRPC (Singh et al., 2023).
MDM2, TRIM and F-box proteins in prostate cancer
Mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) has been shown to act as an oncogene in a variety of tumours including prostate, breast, ovarian and liver cancers (Qin et al., 2017; Zheng et al., 2023; Wang W. et al., 2020). It not only serves as a negative regulator of p53 but is also linked to poor prognosis, a high likelihood of recurrence, and resistance to therapy in cancer. Targeted MDM2 therapy is believed to enhance the sensitivity of prostate cancer to androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), either in a p53-dependent or independent manner. Consequently, targeted MDM2 therapy is increasingly recognized as a promising therapeutic strategy in clinical oncology (Feng et al., 2016). Yan et al. discovered that MDM2 directly targets the p53 protein to facilitate its ubiquitylation and degradation, thereby influencing the invasion and migration of PCa cells (Yan et al., 2023). Iron death is an iron-dependent mode of programmed cell death characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxides, primarily regulated by antioxidant systems such as GPX4 and glutathione. Key regulators include genes such as System Xc- (SLC7A11), the FSP1-CoQ10 pathway, and NRF2—molecules that influence the process of iron death by regulating cystine uptake, lipid metabolism, and oxidative stress. This process holds potential in cancer therapy; for instance, inducing iron death could enhance the anti-cancer effects of photodynamic therapy (Liu et al., 2022; Chang et al., 2024). Alkylglycerol phosphate synthase (AGPS) is a crucial enzyme in ether lipid synthesis that promotes peroxisome formation and increases the susceptibility of tumor cells to iron death (Benjamin et al., 2013). Zhang et al. revealed that MDM2 promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of AGPS in a p53-independent manner. Additionally, TrkA enhances the degradation of AGPS and can regulate the progression of PCa by modifying the phosphorylation of AGPS, which amplifies the function of MDM2 in the ubiquitination and degradation of AGPS. TrkA inhibitors have the potential to protect AGPS and promote iron death in prostate cancer, exhibiting improved anticancer efficacy when combined with iron death inducers (Zhang et al., 2024).
The tripartite motif (TRIM) family constitutes the largest subfamily of proteins that contain RING structural domains. In addition to an N-terminal RING structural domain, these proteins possess one or two additional zinc-binding B-box structural domains (B-box 1 and B-box 2) and a complex helical region, thus giving rise to the acronym TRIM, or RBCC, which denotes both the module and the entire family (Reymond et al., 2001). The RING structural domain confers E3 ubiquitin ligase activity to TRIM family members within the ubiquitination cascade (Meroni and Diez-Roux, 2005; Komander and Rape, 2012). TRIM36, a novel androgen-responsive gene, has been shown to regulate tumor plasticity in neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) by repressing glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4) expression in a manner dependent on HK2 ubiquitination. The proposed mechanism involves the upregulation of TRIM36 during androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), which enhances the ubiquitination of HK2 linked to lysine 48, thereby inhibiting glycolysis. Furthermore, depletion of HK2 leads to a reduction in GPx4 expression, ultimately promoting ferroptosis. The inhibition of glycolysis and activation of ferroptosis are integral to neuroendocrine differentiation (NED) in PCa, and these effects can be reversed by sh-TRIM36. The reduction of GPx4 expression by TRIM36 via HK2 ubiquitination represents a crucial mechanism for regulating NEPC (Zhao et al., 2023). Transmembrane tetraspanins (TSPAN) are small transmembrane glycoproteins characterized by four highly conserved transmembrane structural domains, and they are expressed across a broad range of organisms. Research has demonstrated that TSPAN18 can directly interact with STIM1, protecting it from E3 ligase TRIM32-mediated ubiquitination. Additionally, TSPAN18 has been shown to promote PCa cell metastasis by modulating the STIM1-dependent Ca2+ signaling pathway, thereby further elucidating the positive role of TSPAN18 in regulation-mediated carcinogenesis (Zhou et al., 2023). SERPINH1 was initially identified as an endoplasmic reticulum retention protein, and recent studies have established a connection between aberrant SERPINH1 expression and tumorigenesis in malignant tumors (Xiong et al., 2020). It has been reported that SERPINH1 is upregulated in PCa bone metastasis, where it induces PCa cell bone metastasis in vivo, promotes cellular proliferation, and attenuates apoptosis. This study demonstrates that SERPINH1 binds to P62, reduces TRIM21-mediated degradation of K63-linked P62 ubiquitination, and enhances PCa proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. Furthermore, SERPINH1 regulates the ubiquitination and degradation of P62, thereby promoting PCa bone metastasis, which may be considered a potential target for the treatment of metastatic PCa (Tang et al., 2024).
The Cullin-RING ligase complex family includes Skp1-Cullin1-F-box protein (SCF)-type ligases, which are composed of Skp1, Cullin1 (Cul1), Rbx1, and F-box proteins, and represents one of the large E3 enzyme families (Lin et al., 2019). F-box proteins, known as subunits of the SCF E3 ligase complex, are commonly categorized into three subfamilies: FBXW (F-box with WD 40 amino acid repeats), FBXL (F-box with leucine-rich amino acid repeats), and FBXO (F-box with uncharacterized structural domains). F-box proteins have been implicated in the development of various diseases, including cancer (Yan et al., 2020). Zhou et al. discovered that F-box and WD repeat structural domain 2 (FBXW2) is downregulated in highly metastatic PCa cells and tissues. They found that FBXW2 binds to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) at its shared degron motif (TSNNST), promoting EGFR ubiquitination and degradation. Furthermore, overexpression of FBXW2 in both in vitro and in vivo PCa models resulted in reduced growth and metastasis, whereas depletion of FBXW2 produced the opposite effect. Thus, FBXW2 inhibits PCa cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting EGFR for ubiquitination and degradation, thereby suppressing downstream EGFR signaling (Zhou et al., 2022). NDR1 is a crucial kinase in the HIPPO pathway, involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and the maintenance of tissue morphology (Century et al., 1997). It has been demonstrated that NDR1 phosphorylates β-catenin at the Ser33/37 locus, which enhances its interaction with FBXO11. This interaction facilitates the FBXO11-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent cytoplasmic degradation of β-catenin, while the NDR1-FBXO11 complex inhibits β-catenin’s nuclear translocation by promoting JNK2 ubiquitination. Consequently, NDR1 and FBXO11 collaboratively regulate β-catenin activity in prostate cancer cells through a mechanism of dual phosphorylation-driven ubiquitination, potentially suppressing EMT (Xuan et al., 2024). The miR-30 family functions as tumor suppressors in various cancers, including PCa (Kao et al., 2014). Studies have indicated that miR-30e is downregulated in PCa cells and is implicated in the regulation of the cell cycle, apoptosis, and drug sensitivity. Furthermore, miR-30e has been shown to interact with the mRNAs of AR, FBXO45, SRSF7, and MYBL2, thereby altering their expression in PCa cells. Notably, in the case of miR-30e’s interaction with FBXO45, FBXO45 mRNA is not expressed in PCa cells. In this context, FBXO45 mRNA is the target of miR-30e; FBXO45 directly targets and degrades p73, while the knockdown of FBXO45 results in the stabilization of p73 and induces apoptosis in a p53-independent manner (Ganapathy et al., 2022).
Other ubiquitin enzymes in prostate cancer
The androgen receptor plays a crucial role in all stages of prostate carcinogenesis, including the progression of PCa (Chan and Dehm, 2014). It comprises an N-terminal structural domain (NTD), a DNA-binding structural domain (DBD), a hinge region, and a ligand-binding structural domain (LBD) (Gel and mann, 2002). Downregulation of the AR remains an effective treatment strategy for PCa, even during the phase of depot resistance (Fletcher et al., 2019). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is highly expressed in various organs and tissues, and there is increasing evidence that AHR plays a significant role in cellular homeostasis and disease (Hahn et al., 2009). Studies have demonstrated that AHR functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase, mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of AR in prostate cancer (Chen et al., 2020). Siah2, a RING-finger-type ubiquitin ligase characterized by its N-terminal catalytic RING domain, two zinc fingers, and a C-terminal substrate-binding domain (SBD), has recently been identified as an E3 ubiquitin ligase for AR. This ligase specifically targets NCOR1-binding, inhibitory, and cytokine-conjugating enzymes for degradation. Furthermore, Siah2 is involved in lipid metabolism, cell motility, and the proliferation of prostate cancer cells (Jing et al., 2018). Forkhead box protein A1 (FOXA1) acts as a transcriptional activator of steroid hormone receptors, including AR. In CRPC, the nuclear localization and overexpression of FOXA1 enhance tumor growth and metastasis by facilitating cell cycle progression (Jain et al., 2011). SKP2 is a substrate-recognizing component of the SCF E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Celada et al. demonstrated a direct interaction between SKP2 and FOXA1 proteins in PCa. FOXA1 serves as a substrate for SKP2-mediated ubiquitination via the K6 and K29 linkages. Through this pathway, SKP2 catalyzes the nonclassical ubiquitination of FOXA1, leading to its lysosome-dependent degradation, which promotes the ontogeny and progression of PCa (Celada et al., 2023).
Approximately 75% of the human genome is transcribed into RNA, with only 3% being translated into protein-coding mRNAs. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are classified into various categories based on their length, shape, and location. Numerous studies have underscored the significant role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in various cancers, where many miRNAs are found to be highly expressed in cancer cells, thereby promoting cancer development. Similar to miRNAs, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) also function as oncogenes or tumor suppressors, influencing tumorigenesis and progression (Yan and Bu, 2021). In their research, Dallavalle et al. established a connection between miRNA dysregulation and altered protein ubiquitination, revealing that miR-424 is upregulated in prostate tumors and correlates with invasive features. They demonstrated that the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 interacts with STAT3, mediating its ubiquitination and degradation, while miR-424 promotes STAT3 stabilization and activity, thereby facilitating tumor progression by targeting COP1 (Dallavalle et al., 2016). Additionally, lncRNAs play a role in the ubiquitination process, as highlighted in another study on prostate cancer, which found that the lncRNA MIAT is highly expressed in prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) tissues and is associated with poor prognosis. Inhibition of MIAT was shown to suppress the malignant biological behaviors of PRAD cells, while depletion of MIAT enhanced the immune response of CD8+ T cells and hindered the immune escape of PRAD cells. Further investigations revealed that MIAT downregulates TP53 protein expression through ubiquitin modification by recruiting the transducin β-like protein 1X (TBL1X). Silencing TP53 or overexpressing TBL1X was sufficient to diminish the tumor suppressor effects of MIAT knockdown in both in vitro and in vivo models (Gong et al., 2023). The ASB family of proteins comprises a group of E3 ubiquitin ligases characterized by an N-terminal anchor protein repeat domain that facilitates substrate recognition, as well as a C-terminal suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) box that plays a role in protein ubiquitination (Liu et al., 2019). ASB1 is a key member of the ASB family and one study analysed expression levels in tumour tissue and adjacent paracancerous tissue using data from TCGA and GTEx. Their analysis showed that ASB1 expression was significantly downregulated in prostate cancer tissues compared to paraneoplastic tissues, which was further confirmed by qRT-PCR experiments, and that silencing of ASB1 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation in vitro. This investigation further elucidated that ASB1 interacts with CHCHD3 and enhances its K48-linked ubiquitination, thereby influencing the behavior of prostate cancer cells (Zhao et al., 2024). UBE2N (also known as Ubc13) is an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme responsible for the synthesis of lysine 63-linked polyubiquitin chains (Cheng et al., 2014). Recent findings indicate that the upregulation of UBE2N correlates with poor prognosis in prostate cancer, and that the knockdown of UBE2N inhibits cell viability and glycolysis in prostate cancer cells. Additionally, UBE2N promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of Axin1, and the overexpression of Axin1 negates the effects of UBE2N on the viability and glycolysis of prostate cancer cells (Yang et al., 2024).
The role of ubiquitination in bladder cancer
Long-stranded noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 1 (lncRNA SNHG1) is well-known for its association with tumor stage, size, and overall survival (Thin et al., 2019). The overexpression of MDM2 has been reported to counteract the inhibitory effects of miR-379–5p on the proliferation, migration, and invasive capabilities of bladder cancer cells (Wu D. et al., 2017). In the presence of EGFR, MDM2 binds to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and modulates the ubiquitination of the PPARγ protein in colon cancer cells (Xu et al., 2016). Cai et al. observed that bladder cancer patients with high SNHG1 expression exhibited poorer prognoses. They further demonstrated that SNHG1 promotes the proliferation of bladder cancer cells by inhibiting apoptosis, thereby corroborating their hypothesis that SNHG1 can inhibit apoptosis. Additionally, they found that SNHG1 enhances the proliferation of bladder cancer cells through the suppression of apoptosis and promotes MDM2 expression by binding to miR-9-3p, which in turn facilitates the ubiquitination and downregulation of PPARγ. This cascade of events leads to increased proliferation of bladder cancer cells in vitro and contributes to tumorigenesis in vivo (Table 2) (Cai et al., 2022). Another study reported that lncRNA and MDM2 influence cancer progression through ubiquitination in bladder cancer, particularly investigating the mechanism by which lncRNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) regulates adriamycin (ADM) resistance in bladder cancer cells. This study demonstrates that PVT1 interacts with and enhances MDM2 expression, leading to the upregulation of MDM2-mediated aurora kinase B (AURKB) activity, which mechanistically increases the ubiquitination of p53 by MDM2. Collectively, these findings indicate that PVT1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and drug resistance through the upregulation of MDM2 and AURKB-mediated p53 ubiquitination (Jiang et al., 2022). Conversely, circPKN2, another non-coding RNA, has been shown to inhibit BC cell proliferation and migration in vitro. The proposed mechanism suggests that circPKN2 recruits STUB1, thereby facilitating the ubiquitination of SCD1, which inhibits the WNT pathway and promotes ferroptosis in BC. Additionally, the study reveals a regulatory role for the splicing factor QKI in the biogenesis of circPKN2. Animal studies further demonstrate that circPKN2 enhances ferroptosis in BC cells in vivo, while inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis (Liu et al., 2024).
ER-embedded RING finger protein 26 (RNF26) is a critical E3 ubiquitin ligase that mediates the ubiquitination of spirochete ubiquitination 1 (SQSTM1) through its interaction with the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2J1. This interaction facilitates the anchoring of homologous vesicles to the perinuclear region of the cell and promotes the termination of EGF-induced AKT signaling (Cremer et al., 2021). Furthermore, RNF26 has been shown to interact with another E3 ligase, TRIM21, enhancing its K48-linked ubiquitination in bladder cancer cells. In this context, TRIM21 functions as an E3 ligase that mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of ZHX3. The RNF26/TRIM21 complex is implicated in the proliferation and migration of bladder cancer cells via ZHX3 (Yao et al., 2024). Additionally, TRIM65 was identified as a significant oncogenic factor in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (UCB) through screening of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and was validated in numerous clinical UCB tissue samples by Wei et al. Their study revealed that TRIM65 regulates cytoskeletal rearrangement and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in UCB cells through the ubiquitination of ANXA2, which ultimately enhances the invasiveness of these cells (Wei et al., 2018). ZMYND8 is an epigenetic regulator that has been identified as a common oncogene in various tumors. Qiu et al. first reported that the level of ZMYND8 protein was significantly elevated in BCa samples compared to normal tissues. Their predictive bioinformatics analysis indicated that the E3 ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 directly interacts with ZMYND8 and facilitates its degradation through a polyubiquitylation mechanism. Low levels of FBXW7 are identified as a risk factor that promotes and relies on the accumulation of ZMYND8 protein, thereby facilitating the growth and migration of BCa (Qiu et al., 2021). Additionally, UBE2S, as part of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), has been shown to promote tumor development by either degrading or stabilizing various proteins. Notably, UBE2S expression is strongly correlated with lymphatic metastasis and serves as an independent prognostic factor in BCa patients. In this study, UBE2S knockdown inhibited BCa migration and invasion in vitro, as well as lymphatic metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, UBE2S interacts with TRIM21 to induce the ubiquitination of lipoma preferred partner (LPP) via K11 linkage, with LPP acting to inhibit the pro-metastatic effects of UBE2S on BCa (Xiao et al., 2023).
The role of ubiquitination in kidney disease
Ubiquitination in kidney cancer
Large tumor suppressor 1 (LATS1) is a serine/threonine kinase belonging to the AGC kinase family and has been identified as a tumor suppressor that is downregulated in various types of human cancers (Visser and Yang, 2010). In clear cell renal cell carcinomas, SPOP is consistently overexpressed and accumulates in the cytoplasm of ccRCC cells, in contrast to its predominant nuclear localization in other cell types (Liu et al., 2009). SPOP has been identified as a novel E3 ligase for LATS1 in ccRCC cells, with the E3 ubiquitin ligase Cullin3/SPOP mediating the stability of LATS1 through polyubiquitination, leading to its degradation in a degron-dependent manner in renal carcinoma. This study collectively demonstrates that SPOP promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of LATS1, thereby enhancing renal cancer cell invasion (Table 3) (Wang L. et al., 2020). Additionally, serine/threonine protein phosphatase-5 (PP5), which belongs to the phosphoprotein phosphatase (PPP) family, is unique in that it is encoded by a single gene, with its regulatory and catalytic domains contained within the same polypeptide. PP5 plays a crucial role in regulating hormone- and stress-induced signaling networks that enable cells to respond appropriately to genomic stresses (Golden et al., 2008). Through mass spectrometry (MS) analysis, Dushukyan et al. identified VHL as a binding partner for PP5, revealing that the VHL E3 ligase ubiquitinates and degrades PP5 in the proteasome. They further discovered that the VHL E3 ligase targets the K185 and K199 residues in PP5 for ubiquitination, and that the downregulation of PP5 leads to apoptosis in VHL-deficient ccRCC cells (Dushukyan et al., 2017).
Ubiquitination in kidney injury
The pathogenesis of acute kidney injury (AKI) is linked to the activation of several signaling pathways, notably Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway is crucial in the context of severe AKI (Lim and Nusse, 2013). S100 calcium-binding protein A16 (S100A16), a novel member of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins, serves as a multifunctional signaling factor implicated in various pathogenic mechanisms, including tumors, disturbances in glucose and lipid metabolism, and chronic kidney disease (CKD) (Heizmann et al., 2002). Research has demonstrated that S100A16 knockdown mitigates renal injury in mouse models of AKI, and it has been shown to reduce the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in these models. Further mechanistic studies indicate that S100A16 regulates HRD1 in the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by physically binding to and promoting the ubiquitination of GSK3β and CK1α (Sun et al., 2022). Additionally, another study reported that HRD1 is involved in kidney injury through ubiquitination, highlighting that X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) and its downstream target HRD1 are engaged in AKI by modulating the NRF2/HO-1-mediated response to oxidative stress, which is recognized as a critical factor in kidney injury. This research elucidates the involvement of XBP1 and HRD1 in the interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and mitochondrial dysfunction via the regulation of the NRF2/HO-1-mediated response to reactive oxygen species (ROS) signaling. Downregulation of XBP1 in renal epithelial cells results in decreased HRD1 expression and enhanced NRF2/HO-1 function. HRD1, an E3 ligase, facilitates NRF2 downregulation via the ubiquitination degradation pathway. The downregulation of XBP1 protects the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting HRD1-mediated ubiquitination of NRF2 (Zhang J. et al., 2021). Another investigation into ischemia-reperfusion revealed an association between the E3 ubiquitin ligase gene WWP2 and acute AKI. This study demonstrated that WWP2 was downregulated while p53 was upregulated in ischemia-reperfusion (IR)-induced HK-2 cells. Furthermore, WWP2 overexpression promoted proliferation and inhibited apoptosis in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2), indicating a protective role against AKI through the mediation of p53 ubiquitination and degradation (Che et al., 2020)。Calcium oxalate (CaOx) crystals, which form in the kidney, can cause renal epithelial damage and contribute to the progression of crystalline nephropathy. Bioinformatics analysis has predicted the ubiquitination binding site of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) to U-box protein 1 (STUB1), thereby confirming STUB1’s role as a ubiquitin ligase in CFTR degradation. Knockdown of STUB1 resulted in upregulation of CFTR expression, while STUB1 overexpression produced the opposite effect. Additionally, knockdown of CFTR negated the impact of STUB1 deficiency on autophagy. In vivo experiments indicated that CFTR overexpression mitigated renal tissue injury and CaOx deposition in mice, with STUB1-mediated ubiquitination of CFTR playing a crucial role in alleviating calcium oxalate-associated renal injury by regulating autophagy (Hou et al., 2024).
Ubiquitination in renal fibrosis and chronic kidney disease
TGF-β plays a crucial role in regulating various biological processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, and extracellular matrix production. Upon the binding of TGF-β to its type II serine/threonine kinase receptor (TβRII), TβRI is activated, which leads to the phosphorylation and activation of downstream receptor-regulated Smads (R-Smads) (Böttinger and Bitzer, 2002; Feng and Derynck, 2005). Recent findings indicate that Smurf2 is induced in the renal tubules of human fibrotic kidneys. In vitro studies have shown that TGF-β1 induces Smurf2 expression in renal tubular cells; moreover, the overexpression of the Smad co-repressor protein SnoN completely abolishes TGF-β1-mediated Smurf2 mRNA induction in HKC-8 cells. The E3 ligase Smurf2 specifically downregulates Smad2, as well as SnoN, Ski, and TGIF in renal tubular epithelial cells, thereby influencing the progression of renal fibrosis (Tan et al., 2008). Thrombosis and hemorrhage represent two opposing pathologies that are prevalent in the CKD population. Platelet homeostasis is central to the pathogenesis of these conditions, which varies among individuals with CKD, although the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Lan et al. demonstrated that platelet counts are reduced in both patients with advanced CKD (Adv-CKD) and in a corresponding mouse model, with a positive correlation observed between platelet counts and circulating Klotho levels. They identified that the ubiquitin ligase UBE2O regulates the ubiquitination and degradation of Bcl-xL in platelets. Furthermore, oxidative stress induced by Adv-CKD in platelets activates p38MAPK, which promotes the phosphorylation of Bcl-xL. This phosphorylation enhances the binding of UBE2O to Bcl-xL, leading to its subsequent degradation. Consequently, the lifespan of platelets is diminished in CKD patients, resulting in decreased platelet counts (Lan et al., 2022).
The role of deubiquitination in urologic diseases
Deubiquitination in prostate cancer
Persistent aberrant activation of the AR signaling pathway is a significant factor in the progression of CRPC. Currently, one of the primary therapeutic strategies for CRPC involves tumor suppression by targeting the AR, with enzalutamide being a prominent example. However, CRPC tumor cells often develop resistance to drugs such as enzalutamide through mechanisms including AR point mutations, AR amplification, alterations in androgen biosynthesis, and other factors (Fujita and Nonomura, 2019). As research advances, it has become evident that the regulation of the AR signaling pathway in CRPC is influenced by various elements, including LncRNAs that have recently been implicated in malignant tumors. Zhang et al. reported that the LncRNA PCBP1-AS1 was significantly upregulated in CRPC. Targeting PCBP1-AS1 in vitro markedly inhibited the proliferation and migration of CRPC cell lines. Furthermore, in vivo inhibition of PCBP1-AS1 significantly suppressed tumor growth. Investigating the underlying mechanism, they discovered that PCBP1-AS1 stabilized the USP22-AR/AR-V7 complex, enhanced the deubiquitination of AR/AR-V7, and prevented the protein from being degraded via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway by binding to the NTD of AR/AR-V7 (Table 4) (Zhang B. et al., 2021). Additionally, another study demonstrated that USP22 modulates both the androgen receptor and Myc to drive AR-driven cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth in CRPC cells (Nag and Dutta, 2020). The PD-L1/PD-1 signaling pathway is a crucial component of tumor immunosuppression; however, the expression of PD-L1 is regulated by complex mechanisms, including gene transcription as well as post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications. Evidence indicates that the expression of PD-L1 protein is often regulated through the proteasomal degradation pathway (Lim et al., 2016). Fu et al. demonstrated that NDR1 enhances the level of PD-L1 expression in PCa and facilitates immune evasion by tumors. They employed mass spectrometry to identify and analyze USP10, a deubiquitinating enzyme associated with NDR1 that stabilizes PD-L1 (Fu et al., 2024). Additionally, insulin-like growth factor (IGF) mediates various biological activities, such as growth, anti-apoptosis, and differentiation in numerous cell types. The biological effects of IGF are primarily mediated by insulin receptor substrates (IRS)-1 and IRS-2 (Jones and Clemmons, 1995). The deubiquitinase, ubiquitin-specific peptidase 9X (USP9X), has been identified as a novel binding partner for IRS-2. In a human prostate cancer cell line, small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown of USP9X resulted in decreased levels of IGF-IR and IRS-2 proteins, along with increased ubiquitination of these proteins. The knockdown of USP9X inhibited the basal activation of the Erk1/2 pathway, while ectopic expression of IRS-2 significantly restored this pathway; however, IGF-IR did not have the same effect. This suggests that the stabilization of IRS-2 by USP9X is essential for the basal activation of Erk1/2 (Furuta et al., 2018). The NADPH oxidase (Nox) family of enzymes specializes in the production of ROS. ROS generated by Nox are implicated in various signaling cascades and pathophysiological conditions, including cancer. A genome-wide screen for deubiquitinating enzymes that regulate Nox organizer 1 (NoxO1) protein expression was conducted using a CRISPR/Cas9-mediated DUB knockdown library. This screen identified cylindromatosis (CYLD) as a binding chaperone that regulates NoxO1 protein expression. It was demonstrated that the overexpression of CYLD promotes the ubiquitination of NoxO1 and shortens its half-life. Furthermore, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockdown of CYLD in PC-3 cells enhanced cell proliferation, migration, colony formation, and invasion in vitro (Haq et al., 2022).
Deubiquitination in bladder cancer
Ubiquitin-specific protease 21 (USP21) is a member of the USP family of DUB characterized by a C-terminal catalytic DUB structural domain. USP21 is believed to catalyze the hydrolysis of ubiquitinated histone H2A (ubH2A) and facilitate transcriptional initiation (Nakagawa et al., 2008). A study conducted by Chen et al. demonstrated that USP21 is highly expressed in BC, with its expression correlating to tumor size, metastasis, and poor survival outcomes. They further established that USP21 promotes BC cell metastasis by deubiquitinating and stabilizing EZH2 (Chen et al., 2017). Additional insights into the role of USP21 in bladder cancer were provided by Ma et al., who identified USP21 as a deubiquitinase for p65 that prevents the degradation of the K48-linked ubiquitin chain on p65, thereby promoting the growth, EMT, and metastasis of bladder cancer cells through its deubiquitinating activity. Notably, 20-hydroxyecdysone (20-HE) can directly inhibit NF-κB/p65 signaling at the transcriptional level while also serving as an inhibitor of USP21, leading to p65 protein degradation and the blockade of its activation, ultimately preventing the progression of bladder cancer (Ma et al., 2024). Recent studies have shown that TMPO antisense RNA 1 (TMPO-AS1) functions as a competing endogenous RNA by forming a sponge for microRNA (miRNA) in various cancers. A new study further demonstrates that TMPO-AS1 is upregulated in BC tissues, where it promotes BC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and survival in vitro. OTUB1 is a founding member of the OTU structural domain deubiquitinase family, classified as cysteine proteases. It is highly expressed in several organs, including the kidney, spleen, and prostate (Balakirev et al., 2003). The enzyme specifically recognizes Lys48-linked polyubiquitin chains, and its catalytic activity is reliant on the classical catalytic triad composed of Cys91, His265, and Asp267 (Zhu et al., 2021). Structural analysis has revealed that the unique N-terminal alpha helix of OTUB1 plays a critical role in substrate binding and catalytic regulation by making direct contact with proximal ubiquitin molecules (Mevissen et al., 2013). E2F1, a member of the E2F transcription factor family, which consists of eight proteins, acts as a transcriptional activator. This study reveals that TMPO-AS1 regulates the protein level of E2F1 through protein stabilization, specifically by enhancing E2F1 stability via OTUB1-mediated deubiquitylation. Additionally, E2F1 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of BC cells while inhibiting apoptosis in vitro. Overall, TMPO-AS1 regulates the malignant phenotype of BC cells through its interaction with E2F1 (Zhang Y. et al., 2021).
Deubiquitination in kidney cancer
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) is the most significant oncogene in kidney cancer, being lost or mutated in over 70% of cases. Research conducted across various laboratories has demonstrated that the pVHL-associated complex possesses E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. The loss of VHL results in the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor α (HIF-α), which includes HIF1α and HIF2α, along with other potential substrates such as ZHX2 and SFMBT1 (Kaelin, 2002). HIF2α, a crucial subunit of HIF, has been shown to facilitate renal carcinogenesis and the progression of renal cancers both in vitro and in vivo (Raval et al., 2005). Hong et al. performed a deubiquitinase complementary DNA (cDNA) library binding screen, revealing that ubiquitin-specific peptidase 37 (USP37) is a DUB that binds to and enhances the deubiquitination of HIF2α. Consequently, USP37 promotes the stability of HIF2α in an enzyme-dependent manner, and the depletion of USP37 results in the downregulation of HIF2α in ccRCC, leading to reduced primary renal tumorigenesis and spontaneous lung metastasis (Hong et al., 2020). Conversely, recently developed HIF2α inhibitors have been shown to inhibit tumor growth in certain preclinical renal cancer models, but not in others (Chen et al., 2016). Therefore, targeting factors within the HIF2α-independent signaling pathway in ccRCC, such as ZHX2, may prove to be crucial. Xie et al. demonstrated that ZHX2 promotes ccRCC tumorigenesis independently of HIF. They conducted a cDNA library binding screen and identified USP13 as a DUB that interacts with ZHX2 and facilitates its deubiquitination. USP13 enhances ZHX2 protein stability in an enzyme-dependent manner, and its depletion results in ZHX2 downregulation in ccRCC. Furthermore, USP13 is essential for ccRCC tumor growth in vivo, and its effects are partially mediated through its regulation of ZHX2 (Xie et al., 2022).
Targeted ubiquitination regulates urologic diseases
A number of compounds have been identified that target ubiquitination and modulate urological disorders (Figure 2).Carbidopa, a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor commonly used in conjunction with L-DOPA for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (Seeberger and Hauser, 2009), has garnered significant interest in recent years due to its potential anticancer effects. These effects may be associated with the activation of the AHR, which plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. AHR is overexpressed in various tumors, including pancreatic cancer, suggesting that it could serve as an important drug target for certain tumor types (Koliopanos et al., 2002). Research has demonstrated that Carbidopa inhibits PCa growth in vivo and reduces AR protein levels through AHR-induced proteasomal degradation. Additionally, Carbidopa treatment has been shown to increase AHR protein levels while decreasing AR protein levels in tumor tissue (Chen et al., 2020). Yuanhuacine, an active ingredient isolated from Daphne genkwa, has demonstrated efficacy in inhibiting tumorigenesis across various cancers. Studies indicate that yuanhuacine inhibits PCa cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner while also inducing apoptosis. Furthermore, yuanhuacine has been shown to impede PCa cell invasion and migration. Mechanistically, yuanhuacine reduces the ubiquitination and degradation of the p53 protein, leading to an increase in p53 levels. This effect is regulated by the inhibition of both the phosphorylation and total protein levels of MDM2 in murine models. Additionally, yuanhuacine has been found to inhibit the expression of LINC00665, and the upregulation of LINC00665 counteracts the yuanhuacine-mediated inhibition of MDM2 protein expression, thereby suppressing p53 levels through enhanced ubiquitination in yuanhuacine-treated cells (Yan et al., 2023). Protein hydrolysis-targeted chimeric molecules, known as Protacs, exploit the ubiquitin-dependent protein hydrolysis system of eukaryotic cells to target proteins for degradation. Notably, studies have devised Protac-A, which incorporates a peptide ‘degron’ from hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha to bind to the VHL E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Treatment with Protac-A in androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells results in G1 phase blockade, mediated by the degradation of the AR-specific inhibitor of hormones. The degradation of AR specifically inhibits the proliferation of hormone-dependent prostate cancer cells (Rodriguez-Gonzalez et al., 2008). Cephalomannan, a small molecule compound, inhibits the activity of the UBE2S promoter (Zhang R. Y. et al., 2021). Xiao et al. demonstrated that UBE2S expression progressively decreases in a dose-dependent manner in cephalomannan-treated BCa cells. Mechanistically, cephalomannan inhibits BCa metastasis in vitro and in vivo in a dose-dependent manner by targeting UBE2S. Furthermore, cephalomannan reduces the expression of the mesenchymal marker N-calmodulin, suggesting that it effectively blocks EMT in BCa-like tissues (Xiao et al., 2023).
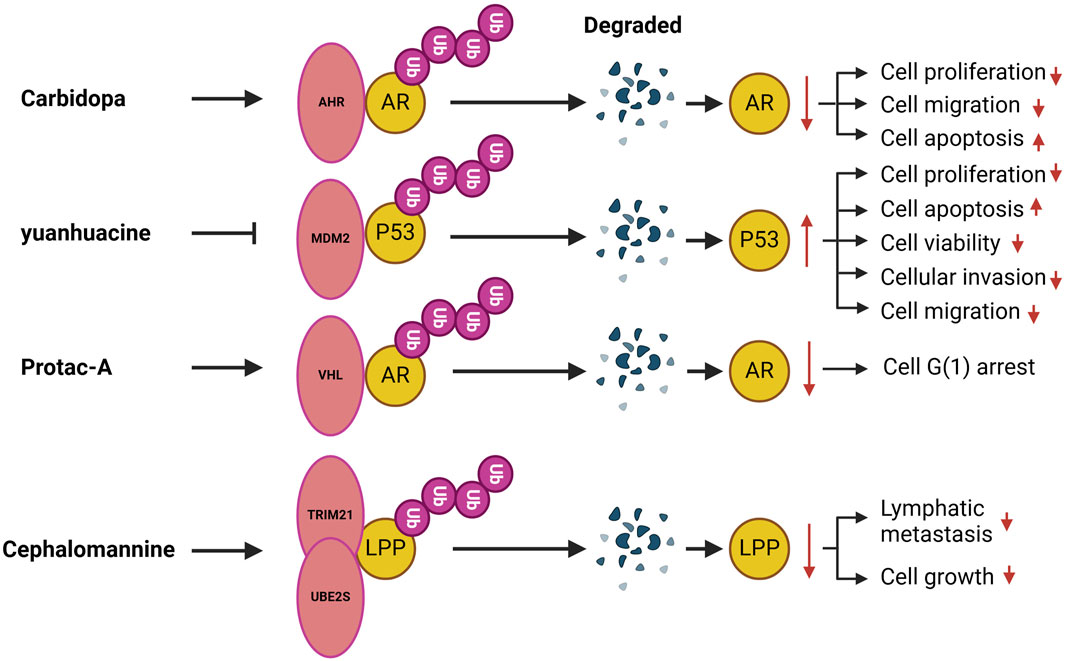
Figure 2. Compounds target ubiquitination in urological disorders. AHR, Aromatic hydrocarbon receptor; MDM2, Mouse double minute 2; VHL, Von Hippel Lindau; TRIM, The tripartite motif; LPP, Lipoma preferred partner.
Conclusion
Over the past few decades, significant efforts have been dedicated to elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying urologic diseases. In this review, we present a comprehensive summary of the current research advancements regarding the roles of ubiquitination and deubiquitination in urinary diseases and their therapeutic strategies. While E3 ubiquitin ligases and DUBs have been shown to regulate processes associated with urinary diseases, several important issues warrant discussion. In several studies, researchers have identified a role for ubiquitination in the pathogenesis of urinary tract diseases. However, these studies do not specify a clear E3 ubiquitin ligase or deubiquitinase. For instance, silencing FAM46B enhances β-catenin protein expression by inhibiting its ubiquitination, which in turn promotes cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in PC (Liang et al., 2018). Additionally, n6-methyladenosine enhances the translation of ENO1 by inhibiting PCNA ubiquitination, thereby facilitating the progression of bladder cancer (Shen et al., 2024). Furthermore, SIRT3 mediates the ubiquitination and degradation of mitofusin 2, which inhibits ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury (Shen et al., 2021). Although these studies suggest a significant role for ubiquitination in disease progression, they do not identify specific ubiquitinating enzymes. Similar to ubiquitination, other PTMs, including acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and SUMOylation, play significant roles in the progression of urologic diseases. Complex interactions and crosstalk among these various PTMs have been observed. For instance, research indicates that the ubiquitination and SUMOylation modifications of a target protein can be differentially regulated based on the specific stimulus or environmental context. This regulation can occur in a synchronized manner, where SUMOylation facilitates or dictates ubiquitin-mediated degradation; in a competitive manner, where SUMOylation inhibits ubiquitination; or in an independent manner, where SUMOylation has minimal impact on ubiquitination (Chen and Lu, 2015). Additionally, studies have demonstrated that NDR1/FBXO11 enhances phosphorylation-mediated ubiquitination of β-catenin, thereby inhibiting metastasis in prostate cancer (Xuan et al., 2024). Therefore, it is imperative to further investigate the mechanisms through which ubiquitination and deubiquitination contribute to the development of urological diseases. The role of UPS in urologic diseases has led to the identification of potential therapeutic targets, which have prompted further investigation into corresponding inhibitors. Notable examples include Carbidopa, yuanhuacine, Protac-A, and cefaglumine. Research is also focusing on targeted inhibitors of E1 enzymes, E2 enzymes, E3 ligases, deubiquitinases, and additional targets such as MDM2 inhibitors, IAP inhibitors, and SKP2 inhibitors (Ye et al., 2021). Consequently, multi-target combination therapy appears to be a promising direction for future research. To the best of our knowledge, this represents the first comprehensive report on the subject, aiming to provide an objective and thorough summary while exploring potential connections and offering insights for the future clinical development of relevant targeted drugs.
Author contributions
LG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology. PL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization. JZ: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review and editing. WL: Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review and editing. QC: Methodology, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. LC: Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. FZ: Resources, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. HZ: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. LZ: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. BQ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Scientific Research Project of Jiangxi Provincial Health and Wellness Commission (No. SKJP20203656) and the Special Fund for Postgraduate Innovation of Jiangxi Province 2023 (No. YC2024-S839).
Acknowledgments
All figures are created with BioRender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Antao, A. M., Tyagi, A., Kim, K. S., and Ramakrishna, S. (2020). Advances in deubiquitinating enzyme inhibition and applications in cancer therapeutics. Cancers (Basel) 12, 1579. doi:10.3390/cancers12061579
Balakirev, M. Y., Tcherniuk, S. O., Jaquinod, M., and Chroboczek, J. (2003). Otubains: a new family of cysteine proteases in the ubiquitin pathway. EMBO Rep. 4, 517–522. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor824
Benjamin, D. I., Cozzo, A., Ji, X., Roberts, L. S., Louie, S. M., Mulvihill, M. M., et al. (2013). Ether lipid generating enzyme AGPS alters the balance of structural and signaling lipids to fuel cancer pathogenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 14912–14917. doi:10.1073/pnas.1310894110
Berndsen, C. E., and Wolberger, C. (2014). New insights into ubiquitin E3 ligase mechanism. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 21, 301–307. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2780
Bhat, K. P., Ümit Kaniskan, H., Jin, J., and Gozani, O. (2021). Epigenetics and beyond: targeting writers of protein lysine methylation to treat disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20, 265–286. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-00108-x
Böttinger, E. P., and Bitzer, M. (2002). TGF-beta signaling in renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13, 2600–2610. doi:10.1097/01.asn.0000033611.79556.ae
Bradley, J. R., and Pober, J. S. (2001). Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). Oncogene 20, 6482–6491. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204788
Cai, H., Xu, H., Lu, H., Xu, W., Liu, H., Wang, X., et al. (2022). LncRNA SNHG1 facilitates tumor proliferation and represses apoptosis by regulating PPARγ ubiquitination in bladder cancer. Cancers (Basel) 14, 4740. doi:10.3390/cancers14194740
Carrano, A. C., Eytan, E., Hershko, A., and Pagano, M. (1999). SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat. cell Biol. 1, 193–199. doi:10.1038/12013
Celada, S. I., Li, G., Celada, L. J., Lu, W., Kanagasabai, T., Feng, W., et al. (2023). Lysosome-dependent FOXA1 ubiquitination contributes to luminal lineage of advanced prostate cancer. Mol. Oncol. 17, 2126–2146. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.13497
Century, K. S., Shapiro, A. D., Repetti, P. P., Dahlbeck, D., Holub, E., and Staskawicz, B. J. (1997). NDR1, a pathogen-induced component required for Arabidopsis disease resistance. Sci. (New York, N.Y.) 278, 1963–1965. doi:10.1126/science.278.5345.1963
Chan, S. C., and Dehm, S. M. (2014). Constitutive activity of the androgen receptor. Adv. Pharmacol. (San Diego, Calif.) 70, 327–366. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-417197-8.00011-0
Chang, Q., Wang, P., Zeng, Q., and Wang, X. (2024). A review on ferroptosis and photodynamic therapy synergism: enhancing anticancer treatment. Heliyon 10, e28942. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28942
Che, H., He, W., Feng, J., Dong, W., Liu, S., Chen, T., et al. (2020). WWP2 ameliorates acute kidney injury by mediating p53 ubiquitylation and degradation. Cell Biochem. Funct. 38, 695–701. doi:10.1002/cbf.3533
Chen, J., and Tsai, Y. H. (2022). Applications of genetic code expansion in studying protein post-translational modification. J. Mol. Biol. 434, 167424. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167424
Chen, T., Liu, J., Li, S., Wang, P., and Shang, G. (2024a). The role of protein arginine N-methyltransferases in inflammation. Seminars Cell Dev. Biol. 154, 208–214. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.08.005
Chen, W., Hill, H., Christie, A., Kim, M. S., Holloman, E., Pavia-Jimenez, A., et al. (2016). Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist. Nature 539, 112–117. doi:10.1038/nature19796
Chen, X., Ma, J., Wang, Z. W., and Wang, Z. (2024b). The E3 ubiquitin ligases regulate inflammation in cardiovascular diseases. Seminars Cell Dev. Biol. 154, 167–174. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2023.02.008
Chen, Y., Zhou, B., and Chen, D. (2017). USP21 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis through suppressing EZH2 ubiquitination in bladder carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 10, 681–689. doi:10.2147/ott.S124795
Chen, Z., Cai, A., Zheng, H., Huang, H., Sun, R., Cui, X., et al. (2020). Carbidopa suppresses prostate cancer via aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of androgen receptor. Oncogenesis 9, 49. doi:10.1038/s41389-020-0236-x
Chen, Z., and Lu, W. (2015). Roles of ubiquitination and SUMOylation on prostate cancer: mechanisms and clinical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 4560–4580. doi:10.3390/ijms16034560
Cheng, J., Fan, Y. H., Xu, X., Zhang, H., Dou, J., Tang, Y., et al. (2014). A small-molecule inhibitor of UBE2N induces neuroblastoma cell death via activation of p53 and JNK pathways. Cell Death Dis. 5, e1079. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.54
Cheng, J., Guo, J., Wang, Z., North, B. J., Tao, K., Dai, X., et al. (2018). Functional analysis of Cullin 3 E3 ligases in tumorigenesis. Biochimica Biophysica Acta. Rev. Cancer 1869, 11–28. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.11.001
Cremer, T., Jongsma, M. L. M., Trulsson, F., Vertegaal, A. C. O., Neefjes, J., and Berlin, I. (2021). The ER-embedded UBE2J1/RNF26 ubiquitylation complex exerts spatiotemporal control over the endolysosomal pathway. Cell Rep. 34, 108659. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108659
Dallavalle, C., Albino, D., Civenni, G., Merulla, J., Ostano, P., Mello-Grand, M., et al. (2016). MicroRNA-424 impairs ubiquitination to activate STAT3 and promote prostate tumor progression. J. Clin. Investigation 126, 4585–4602. doi:10.1172/jci86505
Do, H. A., and Baek, K. H. (2021). Cellular functions regulated by deubiquitinating enzymes in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 69, 101367. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2021.101367
Dushukyan, N., Dunn, D. M., Sager, R. A., Woodford, M. R., Loiselle, D. R., Daneshvar, M., et al. (2017). Phosphorylation and ubiquitination regulate protein phosphatase 5 activity and its prosurvival role in kidney cancer. Cell Rep. 21, 1883–1895. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.074
Fan, Y., Hou, T., Dan, W., Zhu, Y., Liu, B., Wei, Y., et al. (2022). ERK1/2 inhibits Cullin 3/SPOP-mediated PrLZ ubiquitination and degradation to modulate prostate cancer progression. Cell Death Differ. 29, 1611–1624. doi:10.1038/s41418-022-00951-y
Feng, F. Y., Zhang, Y., Kothari, V., Evans, J. R., Jackson, W. C., Chen, W., et al. (2016). MDM2 inhibition sensitizes prostate cancer cells to androgen ablation and radiotherapy in a p53-dependent manner. Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.) 18, 213–222. doi:10.1016/j.neo.2016.01.006
Feng, X. H., and Derynck, R. (2005). Specificity and versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 659–693. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.022404.142018
Fletcher, C. E., Sulpice, E., Combe, S., Shibakawa, A., Leach, D. A., Hamilton, M. P., et al. (2019). Androgen receptor-modulatory microRNAs provide insight into therapy resistance and therapeutic targets in advanced prostate cancer. Oncogene 38, 5700–5724. doi:10.1038/s41388-019-0823-5
Fu, M., Li, J., Xuan, Z., Zheng, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2024). NDR1 mediates PD-L1 deubiquitination to promote prostate cancer immune escape via USP10. Cell Commun. Signal. 22, 429. doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01805-5
Fujita, K., and Nonomura, N. (2019). Role of androgen receptor in prostate cancer: a review. World J. Men's Health 37, 288–295. doi:10.5534/wjmh.180040
Furuta, H., Yoshihara, H., Fukushima, T., Yoneyama, Y., Ito, A., Worrall, C., et al. (2018). IRS-2 deubiquitination by USP9X maintains anchorage-independent cell growth via Erk1/2 activation in prostate carcinoma cell line. Oncotarget 9, 33871–33883. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.26049
Gallardo, M., Malaney, P., Aitken, M. J. L., Zhang, X., Link, T. M., Shah, V., et al. (2020). Uncovering the role of RNA-Binding protein hnRNP K in B-cell lymphomas. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 112, 95–106. doi:10.1093/jnci/djz078
Gan, W., Dai, X., Lunardi, A., Li, Z., Inuzuka, H., Liu, P., et al. (2015). SPOP promotes ubiquitination and degradation of the ERG oncoprotein to suppress prostate cancer progression. Mol. Cell 59, 917–930. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.026
Ganapathy, K., Ngo, C., Andl, T., Coppola, D., Park, J., and Chakrabarti, R. (2022). Anticancer function of microRNA-30e is mediated by negative regulation of HELLPAR, a noncoding macroRNA, and genes involved in ubiquitination and cell cycle progression in prostate cancer. Mol. Oncol. 16, 2936–2958. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.13255
Gelmann, E. P. (2002). Molecular biology of the androgen receptor. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 3001–3015. doi:10.1200/jco.2002.10.018
Geng, C., Kaochar, S., Li, M., Rajapakshe, K., Fiskus, W., Dong, J., et al. (2017). SPOP regulates prostate epithelial cell proliferation and promotes ubiquitination and turnover of c-MYC oncoprotein. Oncogene 36, 4767–4777. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.80
Genschik, P., Sumara, I., and Lechner, E. (2013). The emerging family of CULLIN3-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRL3s): cellular functions and disease implications. EMBO J. 32, 2307–2320. doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.173
Golden, T., Swingle, M., and Honkanen, R. E. (2008). The role of serine/threonine protein phosphatase type 5 (PP5) in the regulation of stress-induced signaling networks and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27, 169–178. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9125-z
Gong, Z., Zhang, H., Ge, Y., and Wang, P. (2023). Long noncoding RNA MIAT regulates TP53 ubiquitination and expedites prostate adenocarcinoma progression by recruiting TBL1X. Biochimica Biophysica Acta. Mol. Cell Res. 1870, 119527. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2023.119527
Hahn, M. E., Allan, L. L., and Sherr, D. H. (2009). Regulation of constitutive and inducible AHR signaling: complex interactions involving the AHR repressor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 77, 485–497. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2008.09.016
Hamidi, A., Song, J., Thakur, N., Itoh, S., Marcusson, A., Bergh, A., et al. (2017). TGF-β promotes PI3K-AKT signaling and prostate cancer cell migration through the TRAF6-mediated ubiquitylation of p85α. Sci. Signal. 10, eaal4186. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aal4186
Haq, S., Sarodaya, N., Karapurkar, J. K., Suresh, B., Jo, J. K., Singh, V., et al. (2022). CYLD destabilizes NoxO1 protein by promoting ubiquitination and regulates prostate cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 525, 146–157. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.032
Harrigan, J. A., Jacq, X., Martin, N. M., and Jackson, S. P. (2018). Deubiquitylating enzymes and drug discovery: emerging opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17, 57–78. doi:10.1038/nrd.2017.152
Hashemi, M., Mirzaei, S., Barati, M., Hejazi, E. S., Kakavand, A., Entezari, M., et al. (2022). Curcumin in the treatment of urological cancers: therapeutic targets, challenges and prospects. Life Sci. 309, 120984. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120984
Heizmann, C. W., Fritz, G., and Schäfer, B. W. (2002). S100 proteins: structure, functions and pathology. Front. Biosci. 7, d1356–d1368. doi:10.2741/a846
Hershko, A., and Ciechanover, A. (1998). The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 425–479. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.425
Hong, K., Hu, L., Liu, X., Simon, J. M., Ptacek, T. S., Zheng, X., et al. (2020). USP37 promotes deubiquitination of HIF2α in kidney cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117, 13023–13032. doi:10.1073/pnas.2002567117
Hou, Y., Huang, C., Huang, Z., Huang, J., and Zhu, B. (2024). STUB1 exacerbates calcium oxalate-induced kidney injury by modulating reactive oxygen species-mediated cellular autophagy via regulating CFTR ubiquitination. Urolithiasis 52, 55. doi:10.1007/s00240-024-01547-6
Hu, X., Wang, J., Chu, M., Liu, Y., Wang, Z. W., and Zhu, X. (2021). Emerging role of ubiquitination in the regulation of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 29, 908–919. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.12.032
Jain, R. K., Mehta, R. J., Nakshatri, H., Idrees, M. T., and Badve, S. S. (2011). High-level expression of forkhead-box protein A1 in metastatic prostate cancer. Histopathology 58, 766–772. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.03796.x
Jiang, X., Li, H., Fang, Y., and Xu, C. (2022). LncRNA PVT1 contributes to invasion and doxorubicin resistance of bladder cancer cells through promoting MDM2 expression and AURKB-mediated p53 ubiquitination. Environ. Toxicol. 37, 1495–1508. doi:10.1002/tox.23501
Jing, Y., Nguyen, M. M., Wang, D., Pascal, L. E., Guo, W., Xu, Y., et al. (2018). DHX15 promotes prostate cancer progression by stimulating Siah2-mediated ubiquitination of androgen receptor. Oncogene 37, 638–650. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.371
Jones, J. I., and Clemmons, D. R. (1995). Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr. Rev. 16, 3–34. doi:10.1210/edrv-16-1-3
Kaelin, W. G. (2002). Molecular basis of the VHL hereditary cancer syndrome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 673–682. doi:10.1038/nrc885
Kao, C. J., Martiniez, A., Shi, X. B., Yang, J., Evans, C. P., Dobi, A., et al. (2014). miR-30 as a tumor suppressor connects EGF/Src signal to ERG and EMT. Oncogene 33, 2495–2503. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.200
Kashiwada, M., Shirakata, Y., Inoue, J. I., Nakano, H., Okazaki, K., Okumura, K., et al. (1998). Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activity in CD40 signaling along a ras-independent pathway. J. Exp. Med. 187, 237–244. doi:10.1084/jem.187.2.237
Kidokoro, T., Tanikawa, C., Furukawa, Y., Katagiri, T., Nakamura, Y., and Matsuda, K. (2008). CDC20, a potential cancer therapeutic target, is negatively regulated by p53. Oncogene 27, 1562–1571. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210799
Koliopanos, A., Kleeff, J., Xiao, Y., Safe, S., Zimmermann, A., Büchler, M. W., et al. (2002). Increased arylhydrocarbon receptor expression offers a potential therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 21, 6059–6070. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205633
Komander, D., and Rape, M. (2012). The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 81, 203–229. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-060310-170328
Kumar-Sinha, C., Tomlins, S. A., and Chinnaiyan, A. M. (2008). Recurrent gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 497–511. doi:10.1038/nrc2402
Lamothe, B., Campos, A. D., Webster, W. K., Gopinathan, A., Hur, L., and Darnay, B. G. (2008). The RING domain and first zinc finger of TRAF6 coordinate signaling by interleukin-1, lipopolysaccharide, and RANKL. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 24871–24880. doi:10.1074/jbc.M802749200
Lan, Q., Du, C., Xiong, J., Wu, Y., Liao, W., Liu, C., et al. (2022). Renal Klotho safeguards platelet lifespan in advanced chronic kidney disease through restraining Bcl-xL ubiquitination and degradation. J. Thrombosis Haemostasis 20, 2972–2987. doi:10.1111/jth.15876
Li, D., Wang, X., Mei, H., Fang, E., Ye, L., Song, H., et al. (2018). Long noncoding RNA pancEts-1 promotes neuroblastoma progression through hnRNPK-mediated β-Catenin stabilization. Cancer Res. 78, 1169–1183. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-2295
Liang, T., Ye, X., Liu, Y., Qiu, X., Li, Z., Tian, B., et al. (2018). FAM46B inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in prostate cancer through ubiquitination of β-catenin. Exp. Mol. Med. 50, 1–12. doi:10.1038/s12276-018-0184-0
Lim, S. O., Li, C. W., Xia, W., Cha, J. H., Chan, L. C., Wu, Y., et al. (2016). Deubiquitination and stabilization of PD-L1 by CSN5. Cancer cell 30, 925–939. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.010
Lim, X., and Nusse, R. (2013). Wnt signaling in skin development, homeostasis, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 5, a008029. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a008029
Lin, M., Xu, Y., Gao, Y., Pan, C., Zhu, X., and Wang, Z. W. (2019). Regulation of F-box proteins by noncoding RNAs in human cancers. Cancer Lett. 466, 61–70. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.09.008
Liu, C., Zou, Z., Lu, S., Jin, K., Shen, Y., Huang, T., et al. (2024). CircPKN2 promotes ferroptosis in bladder cancer by promoting the ubiquitination of Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1. Cancer gene Ther. 31, 1251–1265. doi:10.1038/s41417-024-00784-6
Liu, D., Augello, M. A., Grbesa, I., Prandi, D., Liu, Y., Shoag, J. E., et al. (2021b). Tumor subtype defines distinct pathways of molecular and clinical progression in primary prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investigation 131, e147878. doi:10.1172/jci147878
Liu, J., Cheng, Y., Zheng, M., Yuan, B., Wang, Z., Li, X., et al. (2021a). Targeting the ubiquitination/deubiquitination process to regulate immune checkpoint pathways. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6, 28. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00418-x
Liu, J., Ghanim, M., Xue, L., Brown, C. D., Iossifov, I., Angeletti, C., et al. (2009). Analysis of Drosophila segmentation network identifies a JNK pathway factor overexpressed in kidney cancer. Sci. (New York, N.Y.) 323, 1218–1222. doi:10.1126/science.1157669
Liu, M., Kong, X. Y., Yao, Y., Wang, X. A., Yang, W., Wu, H., et al. (2022). The critical role and molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis in antioxidant systems: a narrative review. Ann. Transl. Med. 10, 368. doi:10.21037/atm-21-6942
Liu, P., Verhaar, A. P., and Peppelenbosch, M. P. (2019). Signaling size: ankyrin and SOCS Box-Containing ASB E3 ligases in action. Trends Biochem. Sci. 44, 64–74. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2018.10.003
Lopez-Bergami, P., Lau, E., and Ronai, Z. (2010). Emerging roles of ATF2 and the dynamic AP1 network in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10, 65–76. doi:10.1038/nrc2681
Lu, J., and Gao, F. H. (2016). Role and molecular mechanism of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K in tumor development and progression. Biomed. Rep. 4, 657–663. doi:10.3892/br.2016.642
Lu, W., Liu, S., Li, B., Xie, Y., Adhiambo, C., Yang, Q., et al. (2015). SKP2 inactivation suppresses prostate tumorigenesis by mediating JARID1B ubiquitination. Oncotarget 6, 771–788. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.2718
Lu, W., Liu, S., Li, B., Xie, Y., Izban, M. G., Ballard, B. R., et al. (2017). SKP2 loss destabilizes EZH2 by promoting TRAF6-mediated ubiquitination to suppress prostate cancer. Oncogene 36, 1364–1373. doi:10.1038/onc.2016.300
Ma, J., Chang, K., Peng, J., Shi, Q., Gan, H., Gao, K., et al. (2018). SPOP promotes ATF2 ubiquitination and degradation to suppress prostate cancer progression. J. Exp. Clin. cancer Res. 37, 145. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0809-0
Ma, Q., Wu, F., Liu, X., Zhao, C., Sun, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2024). 20-hydroxyecdysone suppresses bladder cancer progression via inhibiting USP21: a mechanism associated with deubiquitination and degradation of p65. Transl. Oncol. 45, 101958. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2024.101958
Manchado, E., Guillamot, M., de Cárcer, G., Eguren, M., Trickey, M., García-Higuera, I., et al. (2010). Targeting mitotic exit leads to tumor regression in vivo: modulation by Cdk1, Mastl, and the PP2A/B55α,δ phosphatase. Cancer Cell 18, 641–654. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2010.10.028
Mao, Y., Li, K., Lu, L., Si-Tu, J., Lu, M., and Gao, X. (2016). Overexpression of Cdc20 in clinically localized prostate cancer: relation to high Gleason score and biochemical recurrence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Cancer Biomarkers 16, 351–358. doi:10.3233/cbm-160573
Meroni, G., and Diez-Roux, G. (2005). TRIM/RBCC, a novel class of ‘single protein RING finger’ E3 ubiquitin ligases. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 27, 1147–1157. doi:10.1002/bies.20304
Mevissen, T. E., Hospenthal, M. K., Geurink, P. P., Elliott, P. R., Akutsu, M., Arnaudo, N., et al. (2013). OTU deubiquitinases reveal mechanisms of linkage specificity and enable ubiquitin chain restriction analysis. Cell 154, 169–184. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.046
Mevissen, T. E. T., and Komander, D. (2017). Mechanisms of deubiquitinase specificity and regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 86, 159–192. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-044916
Min, J., Zaslavsky, A., Fedele, G., McLaughlin, S. K., Reczek, E. E., De Raedt, T., et al. (2010). An oncogene-tumor suppressor cascade drives metastatic prostate cancer by coordinately activating Ras and nuclear factor-kappaB. Nat. Med. 16, 286–294. doi:10.1038/nm.2100
Molloy, N. H., Read, D. E., and Gorman, A. M. (2011). Nerve growth factor in cancer cell death and survival. Cancers (Basel) 3, 510–530. doi:10.3390/cancers3010510
Mowen, K. A., and David, M. (2014). Unconventional post-translational modifications in immunological signaling. Nat. Immunol. 15, 512–520. doi:10.1038/ni.2873
Nag, N., and Dutta, S. (2020). Deubiquitination in prostate cancer progression: role of USP22. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 6, 16. doi:10.20517/2394-4722.2020.23
Nakagawa, T., Kajitani, T., Togo, S., Masuko, N., Ohdan, H., Hishikawa, Y., et al. (2008). Deubiquitylation of histone H2A activates transcriptional initiation via trans-histone cross-talk with H3K4 di- and trimethylation. Genes Dev. 22, 37–49. doi:10.1101/gad.1609708
Narita, T., Weinert, B. T., and Choudhary, C. (2019). Functions and mechanisms of non-histone protein acetylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol. 20, 156–174. doi:10.1038/s41580-018-0081-3
Ngollo, M., Lebert, A., Dagdemir, A., Judes, G., Karsli-Ceppioglu, S., Daures, M., et al. (2014). The association between histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) and prostate cancer: relationship with clinicopathological parameters. BMC Cancer 14, 994. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-994
Parihar, N., and Bhatt, L. K. (2021). Deubiquitylating enzymes: potential target in autoimmune diseases. Inflammopharmacology 29, 1683–1699. doi:10.1007/s10787-021-00890-z
Petroski, M. D., and Deshaies, R. J. (2005). Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 9–20. doi:10.1038/nrm1547
Popovic, D., Vucic, D., and Dikic, I. (2014). Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Med. 20, 1242–1253. doi:10.1038/nm.3739
Qin, J. J., Li, X., Wang, W., Zi, X., and Zhang, R. (2017). Targeting the NFAT1-MDM2-MDMX network inhibits the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells, independent of p53 and androgen. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 917. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00917
Qiu, F., Jin, Y., Pu, J., Huang, Y., Hou, J., Zhao, X., et al. (2021). Aberrant FBXW7-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of ZMYND8 enhances tumor progression and stemness in bladder cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 407, 112807. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112807
Rape, M. (2018). Ubiquitylation at the crossroads of development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 59–70. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.83
Raval, R. R., Lau, K. W., Tran, M. G. B., Sowter, H. M., Mandriota, S. J., Li, J. L., et al. (2005). Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 5675–5686. doi:10.1128/mcb.25.13.5675-5686.2005
Reymond, A., Meroni, G., Fantozzi, A., Merla, G., Cairo, S., Luzi, L., et al. (2001). The tripartite motif family identifies cell compartments. EMBO J. 20, 2140–2151. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.9.2140
Rodriguez-Gonzalez, A., Cyrus, K., Salcius, M., Kim, K., Crews, C. M., Deshaies, R. J., et al. (2008). Targeting steroid hormone receptors for ubiquitination and degradation in breast and prostate cancer. Oncogene 27, 7201–7211. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.320
Rosellini, M., Marchetti, A., Mollica, V., Rizzo, A., Santoni, M., and Massari, F. (2023). Prognostic and predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 20, 133–157. doi:10.1038/s41585-022-00676-0
Rothe, M., Wong, S. C., Henzel, W. J., and Goeddel, D. V. (1994). A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 78, 681–692. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90532-0
Ruan, X., Zhang, R., Li, R., Zhu, H., Wang, Z., Wang, C., et al. (2022). The research progress in physiological and pathological functions of TRAF4. Front. Oncol. 12, 842072. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.842072
Safiri, S., Kolahi, A. A., and Naghavi, M.Global Burden of Disease Bladder Cancer Collaborators (2021). Global, regional and national burden of bladder cancer and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global Burden of Disease study 2019. BMJ Glob. Health 6, e004128. doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2020-004128
Saritas, T., Cuevas, C. A., Ferdaus, M. Z., Kuppe, C., Kramann, R., Moeller, M. J., et al. (2019). Disruption of CUL3-mediated ubiquitination causes proximal tubule injury and kidney fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 9, 4596. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-40795-0
Seeberger, L. C., and Hauser, R. A. (2009). Levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone in Parkinson's disease. Expert Rev. Neurother. 9, 929–940. doi:10.1586/ern.09.64
Shen, C., Liu, J., Xie, F., Yu, Y., Ma, X., Hu, D., et al. (2024). N6-Methyladenosine enhances the translation of ENO1 to promote the progression of bladder cancer by inhibiting PCNA ubiquitination. Cancer Lett. 595, 217002. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217002
Shen, L., Zhang, Q., Tu, S., and Qin, W. (2021). SIRT3 mediates mitofusin 2 ubiquitination and degradation to suppress ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Exp. Cell Res. 408, 112861. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112861
Siegel, R. L., Giaquinto, A. N., and Jemal, A. (2024). Cancer statistics. CA a cancer J. Clin. 74, 12–49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Wagle, N. S., and Jemal, A. (2023). Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 73, 17–48. doi:10.3322/caac.21763
Singh, H. R., and Ostwal, Y. B. (2019). Post-Translational modification, phase separation, and robust gene transcription. Trends Genet. 35, 89–92. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2018.11.002
Singh, R., Karri, D., Shen, H., Shao, J., Dasgupta, S., Huang, S., et al. (2018). TRAF4-mediated ubiquitination of NGF receptor TrkA regulates prostate cancer metastasis. J. Clin. Investigation 128, 3129–3143. doi:10.1172/jci96060
Singh, R., Meng, H., Shen, T., Lumahan, L. E. V., Nguyen, S., Shen, H., et al. (2023). TRAF4-mediated nonproteolytic ubiquitination of androgen receptor promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120, e2218229120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2218229120
Snyder, N. A., and Silva, G. M. (2021). Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs): regulation, homeostasis, and oxidative stress response. J. Biol. Chem. 297, 101077. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101077
Sun, T., Liu, Z., and Yang, Q. (2020). The role of ubiquitination and deubiquitination in cancer metabolism. Mol. Cancer 19, 146. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01262-x
Sun, Y., Fan, Y., Wang, Z., Li, M., Su, D., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). S100A16 promotes acute kidney injury by activating HRD1-induced ubiquitination and degradation of GSK3β and CK1α. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79, 184. doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04213-5
Sun, Y., Liu, W. Z., Liu, T., Feng, X., Yang, N., and Zhou, H. F. (2015). Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 35, 600–604. doi:10.3109/10799893.2015.1030412
Tan, R., He, W., Lin, X., Kiss, L. P., and Liu, Y. (2008). Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor-2 in the fibrotic kidney: regulation, target specificity, and functional implication. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 294, F1076–F1083. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00323.2007
Tang, C., Lai, Y., Li, L., Situ, M. Y., Li, S., Cheng, B., et al. (2024). SERPINH1 modulates apoptosis by inhibiting P62 ubiquitination degradation to promote bone metastasis of prostate cancer. iScience 27, 110427. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2024.110427
Tang, R., Langdon, W. Y., and Zhang, J. (2019). Regulation of immune responses by E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b. Cell. Immunol. 340, 103878. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.11.002
Teo, M. Y., Rathkopf, D. E., and Kantoff, P. (2019). Treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 70, 479–499. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-051517-011947
Thin, K. Z., Tu, J. C., and Raveendran, S. (2019). Long non-coding SNHG1 in cancer. Clin. Chimica Acta; Int. J. Clin. Chem. 494, 38–47. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2019.03.002
Tomlins, S. A., Rhodes, D. R., Perner, S., Dhanasekaran, S. M., Mehra, R., Sun, X. W., et al. (2005). Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Sci. (New York, N.Y.) 310, 644–648. doi:10.1126/science.1117679
Visser, S., and Yang, X. (2010). LATS tumor suppressor: a new governor of cellular homeostasis. Cell cycleGeorget. (Tex.) 9, 3892–3903. doi:10.4161/cc.9.19.13386
Wajant, H., Henkler, F., and Scheurich, P. (2001). The TNF-receptor-associated factor family: scaffold molecules for cytokine receptors, kinases and their regulators. Cell. Signal. 13, 389–400. doi:10.1016/s0898-6568(01)00160-7
Wang, L., Lin, M., Chu, M., Liu, Y., Ma, J., He, Y., et al. (2020c). SPOP promotes ubiquitination and degradation of LATS1 to enhance kidney cancer progression. EBioMedicine 56, 102795. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102795
Wang, Q. D., Shi, T., Xu, Y., Liu, Y., and Zhang, M. J. (2023). USP21 contributes to the aggressiveness of laryngeal cancer cells by deubiquitinating and stabilizing AURKA. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 39, 354–363. doi:10.1002/kjm2.12649
Wang, R., Xu, J., Saramäki, O., Visakorpi, T., Sutherland, W. M., Zhou, J., et al. (2004). PrLZ, a novel prostate-specific and androgen-responsive gene of the TPD52 family, amplified in chromosome 8q21.1 and overexpressed in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 64, 1589–1594. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3331
Wang, W., Zafar, A., Rajaei, M., and Zhang, R. (2020b). Two birds with one stone: NFAT1-MDM2 dual inhibitors for cancer therapy. Cells 9, 1176. doi:10.3390/cells9051176
Wang, Y., Liu, X., Huang, W., Liang, J., and Chen, Y. (2022). The intricate interplay between HIFs, ROS, and the ubiquitin system in the tumor hypoxic microenvironment. Pharmacol. Ther. 240, 108303. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108303
Wang, Z., Liu, P., Inuzuka, H., and Wei, W. (2014). Roles of F-box proteins in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 14, 233–247. doi:10.1038/nrc3700
Wang, Z., Song, Y., Ye, M., Dai, X., Zhu, X., and Wei, W. (2020a). The diverse roles of SPOP in prostate cancer and kidney cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 17, 339–350. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0314-z
Wei, W. S., Chen, X., Guo, L. Y., Li, X. D., Deng, M. H., Yuan, G. J., et al. (2018). TRIM65 supports bladder urothelial carcinoma cell aggressiveness by promoting ANXA2 ubiquitination and degradation. Cancer Lett. 435, 10–22. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.036
Wu, D., Niu, X., Tao, J., Li, P., Lu, Q., Xu, A., et al. (2017b). MicroRNA-379-5p plays a tumor-suppressive role in human bladder cancer growth and metastasis by directly targeting MDM2. Oncol. Rep. 37, 3502–3508. doi:10.3892/or.2017.5607
Wu, F., Dai, X., Gan, W., Wan, L., Li, M., Mitsiades, N., et al. (2017a). Prostate cancer-associated mutation in SPOP impairs its ability to target Cdc20 for poly-ubiquitination and degradation. Cancer Lett. 385, 207–214. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.10.021
Wu, H. L., Li, S. M., Huang, Y. C., Xia, Q. D., Zhou, P., Li, X. M., et al. (2021). Transcriptional regulation and ubiquitination-dependent regulation of HnRNPK oncogenic function in prostate tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 21, 641. doi:10.1186/s12935-021-02331-x
Xiao, K., Peng, S., Lu, J., Zhou, T., Hong, X., Chen, S., et al. (2023). UBE2S interacting with TRIM21 mediates the K11-linked ubiquitination of LPP to promote the lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer. Cell Death Dis. 14, 408. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-05938-2
Xie, H., Zhou, J., Liu, X., Xu, Y., Hepperla, A. J., Simon, J. M., et al. (2022). USP13 promotes deubiquitination of ZHX2 and tumorigenesis in kidney cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119, e2119854119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2119854119
Xiong, G., Chen, J., Zhang, G., Wang, S., Kawasaki, K., Zhu, J., et al. (2020). Hsp47 promotes cancer metastasis by enhancing collagen-dependent cancer cell-platelet interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117, 3748–3758. doi:10.1073/pnas.1911951117
Xu, K., Shimelis, H., Linn, D. E., Jiang, R., Yang, X., Sun, F., et al. (2009). Regulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity and specificity by RNF6-induced ubiquitination. Cancer Cell 15, 270–282. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.02.021
Xu, Y., Jin, J., Zhang, W., Zhang, Z., Gao, J., Liu, Q., et al. (2016). EGFR/MDM2 signaling promotes NF-κB activation via PPARγ degradation. Carcinogenesis 37, 215–222. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgv252
Xuan, Z., Chen, C., Sun, H., Yang, K., Li, J., Fu, M., et al. (2024). NDR1/FBXO11 promotes phosphorylation-mediated ubiquitination of β-catenin to suppress metastasis in prostate cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 20, 4957–4977. doi:10.7150/ijbs.98907
Yan, H., and Bu, P. (2021). Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays Biochem. 65, 625–639. doi:10.1042/ebc20200032
Yan, L., Lin, M., Pan, S., Assaraf, Y. G., Wang, Z. W., and Zhu, X. (2020). Emerging roles of F-box proteins in cancer drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 49, 100673. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2019.100673
Yan, M., Li, X., Gu, J., Gao, G., Wu, Z., and Xue, P. (2023). Blockage of MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination by yuanhuacine restrains the carcinogenesis of prostate carcinoma cells by suppressing LncRNA LINC00665. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 37, e23265. doi:10.1002/jbt.23265
Yang, B., Chen, W., Tao, T., Zhang, J., Kong, D., Hao, J., et al. (2024). UBE2N promotes cell viability and glycolysis by promoting Axin1 ubiquitination in prostate cancer cells. Biol. Direct 19, 35. doi:10.1186/s13062-024-00469-y
Yang, X., and Qian, K. (2017). Protein O-GlcNAcylation: emerging mechanisms and functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 452–465. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.22
Yao, D., Xin, F., and He, X. (2024). RNF26-mediated ubiquitination of TRIM21 promotes bladder cancer progression. Am. J. Cancer Res. 14, 4082–4095. doi:10.62347/tecq5002
Ye, P., Chi, X., Cha, J. H., Luo, S., Yang, G., Yan, X., et al. (2021). Potential of E3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer immunity: opportunities and challenges. Cells 10, 3309. doi:10.3390/cells10123309
Zeng, Y., Guo, M., Wu, Q., Tan, X., Jiang, C., Teng, F., et al. (2024). Gut microbiota-derived indole-3-propionic acid alleviates diabetic kidney disease through its mitochondrial protective effect via reducing ubiquitination mediated-degradation of SIRT1. J. Adv. Res. 73, 607–630. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2024.08.018
Zhang, B., Zhang, M., Shen, C., Liu, G., Zhang, F., Hou, J., et al. (2021b). LncRNA PCBP1-AS1-mediated AR/AR-V7 deubiquitination enhances prostate cancer enzalutamide resistance. Cell Death Dis. 12, 856. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04144-2
Zhang, B., Zhang, M., Shen, C., Liu, G., Zhang, F., Hou, J., et al. (2021a). Downregulation of XBP1 protects kidney against ischemia-reperfusion injury via suppressing HRD1-mediated NRF2 ubiquitylation. Cell Death Discov. 7, 44. doi:10.1038/s41420-021-00425-z
Zhang, R. Y., Liu, Z. K., Wei, D., Yong, Y. L., Lin, P., Li, H., et al. (2021d). UBE2S interacting with TRIM28 in the nucleus accelerates cell cycle by ubiquitination of p27 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6, 64. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00432-z
Zhang, Y., Huang, Z., Li, K., Xie, G., Feng, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2024). TrkA promotes MDM2-mediated AGPS ubiquitination and degradation to trigger prostate cancer progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 43, 16. doi:10.1186/s13046-023-02920-w
Zhang, Y., Zhu, Y., Xiao, M., Cheng, Y., He, D., Liu, J., et al. (2021c). The long non-coding RNA TMPO-AS1 promotes bladder cancer growth and progression via OTUB1-Induced E2F1 deubiquitination. Front. Oncol. 11, 643163. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.643163
Zhao, C., Xu, Z., Que, H., Zhang, K., Wang, F., Tan, R., et al. (2024). ASB1 inhibits prostate cancer progression by destabilizing CHCHD3 via K48-linked ubiquitination. Am. J. Cancer Res. 14, 3404–3418. doi:10.62347/feiz7492
Zhao, X., Zhou, T., Wang, Y., Bao, M., Ni, C., Ding, L., et al. (2023). Trigred motif 36 regulates neuroendocrine differentiation of prostate cancer via HK2 ubiquitination and GPx4 deficiency. Cancer Sci. 114, 2445–2459. doi:10.1111/cas.15763
Zheng, J., Miao, F., Wang, Z., Ma, Y., Lin, Z., Chen, Y., et al. (2023). Identification of MDM2 as a prognostic and immunotherapeutic biomarker in a comprehensive pan-cancer analysis: a promising target for breast cancer, bladder cancer and ovarian cancer immunotherapy. Life Sci. 327, 121832. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121832
Zhou, Q., Chen, X., Yao, K., Zhang, Y., He, H., Huang, H., et al. (2023). TSPAN18 facilitates bone metastasis of prostate cancer by protecting STIM1 from TRIM32-mediated ubiquitination. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 42, 195. doi:10.1186/s13046-023-02764-4
Zhou, T., Chen, T., Lai, B., Zhang, W., Luo, X., Xia, D., et al. (2022). FBXW2 inhibits prostate cancer proliferation and metastasis via promoting EGFR ubiquitylation and degradation. Cell. Mol. life Sci. 79, 268. doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04320-3
Keywords: ubiquitination, deubiquitination, urinary system, molecular mechanisms, targeted therapy
Citation: Gan L, Luo P, Zou J, Li W, Chen Q, Cheng L, Zhang F, Zhong H, Zheng L and Qian B (2025) The role of ubiquitination and deubiquitination in urological tumours. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1532878. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532878
Received: 28 November 2024; Accepted: 08 July 2025;
Published: 23 July 2025.
Edited by:
Xiao-Dong Zhang, Wuhan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Andreas Damianou, University of Oxford, United KingdomPeng Huang, Sichuan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Gan, Luo, Zou, Li, Chen, Cheng, Zhang, Zhong, Zheng and Qian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liying Zheng, NTEyMTg2NTBAcXEuY29t; Biao Qian, cWIyMDAzXzIwMDBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Lifeng Gan
Lifeng Gan Peiyue Luo1,2,3
Peiyue Luo1,2,3 Junrong Zou
Junrong Zou Wei Li
Wei Li Qi Chen
Qi Chen Le Cheng
Le Cheng Biao Qian
Biao Qian