- 1College of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Chengdu Wenjiang District People’s Hospital, Chengdu, Sichuan
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Personalized Drug Therapy Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Lung cancer is the most prevalent malignant tumor worldwide and remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Despite advances in treatment development, lung cancer patients often face poor quality of life and low survival rates. Increasing evidence highlights the significant roles of autophagy and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in the initiation, progression, and therapeutic response of lung cancer. Autophagy and ncRNAs can function as both tumor-promoting and tumor-suppressing factors in lung cancer. Therefore, investigating the roles of autophagy and ncRNAs in lung cancer provides valuable insights into its pathophysiology. At the same time, non-coding RNA also plays an important role in regulating autophagy. This study reveals that autophagy affects the occurrence and development of lung cancer through multiple pathways. Then, we also studied that in lung cancer, ncRNAs (e.g., lncRNAs, miRNAs, circRNAs and piRNAs) can regulate autophagy to promote or inhibit tumorigenesis, metastasis and drug resistance in lung cancer. Finally, the problems and solutions of autophagy and ncRNAs in the treatment of lung cancer were explored. These findings suggest that autophagy and ncRNAs can be potential targets for the treatment of lung cancer.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor that originates in the bronchial mucosa or lung glands. It is one of the most prevalent cancers worldwide (Li Y. et al., 2023). Based on histopathological characteristics, lung cancer is primarily categorized into non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer. NSCLC, which includes adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma [with adenocarcinoma being the most common, followed by squamous cell carcinoma (Abdelaziz et al., 2018)], is the most common subtype, accounting for 85%–90% of all lung cancer cases. In 2020, there are an estimated 2.2 million new cases of lung cancer and 1.8 million deaths from lung cancer (Leiter et al., 2023). Currently, lung cancer ranks as the second most common cancer globally in terms of incidence, but it is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality (Siegel et al., 2023). Globally, lung cancer is the primary cause of cancer death among men and the second among women, following breast cancer (Leiter et al., 2023). The main clinical symptoms are cough, expectoration, hemoptysis, asthma, chest pain, dyspnea and so on. Current treatment options for lung cancer commonly include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The prognosis varies depending on factors such as tumor type, stage, patient age, and gender; however, overall, the five-year survival rate for lung cancer remains low. In terms of prevention, key measures include reducing smoking, avoiding occupational and environmental exposure, and undergoing regular health screenings. Recently, there is growing evidence that autophagy may specifically regulate lung cancer through regulating autophagy-related genes expression and some signaling pathways (Liu et al., 2017).
Autophagy is a highly conserved catabolic process in eukaryotic cells, mediated by autophagy-related genes (Atgs) (Levine and Kroemer, 2019). Alongside the proteasome system, it is one of the cell’s two primary degradation pathways. Fundamentally, autophagy functions to clear damaged or unnecessary organelles, invading pathogens, and misfolded proteins, helping to maintain cellular homeostasis and supply energy (Nemchenko et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2013). Recently, it has also been linked to health maintenance and longevity (Levine and Kroemer, 2008). There are at least three major types of autophagy including macro-autophagy (hereafter referred to as autophagy), micro-autophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). Autophagy consists of four basic steps: 1) the initial stage induced by nutrient restriction or removal of damaged or redundant organelles; 2) the formation of bilayer membrane-bound autophagosomes encapsulating organelles, proteins and cytoplasm; 3) the formation stage of autolysosome; 4) the autolysosome cargo digestion and renewal. The above autophagy process is regulated by multiple autophagy-related proteins, including the unc-51-like kinase 1 complex (ULK1C), phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P), double FYVE domain protein 1 (DFCP1), and phosphatidylinositol-interacting WD repeat protein (WIPI), which are crucial for autophagosome formation. Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (MAP1LC3) is involved in autophagosome maturation, while autophagic lysosome formation is associated with the homotypic fusion and protein sorting (HOPS) complex, syntaxin 17 (STX 17), vesicle-associated membrane proteins 7 and 8 (VAMP 7/8), and synaptosome-associated protein 29 (SNAP 29). Studies have shown that many non-coding RNAs can regulate autophagy (Figure 1).
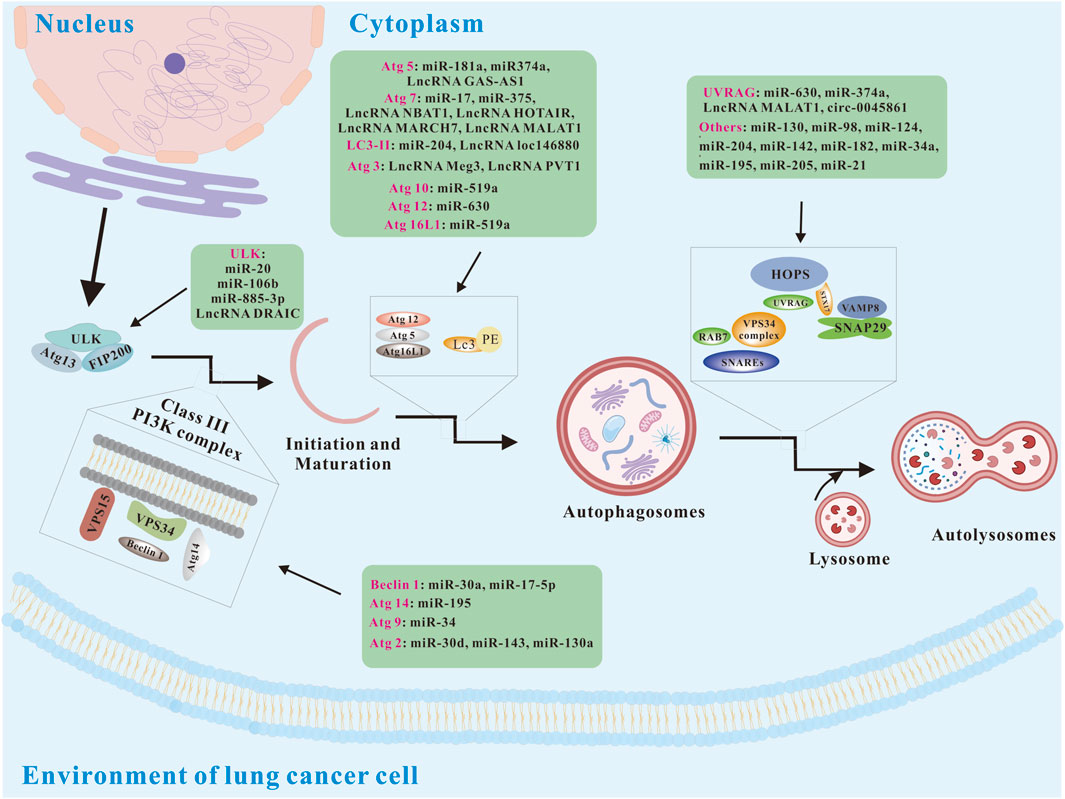
Figure 1. Basic autophagy pathways and modulation via ncRNAs (modified from (Rezaei et al., 2020)). Atg 2, autophagy-related 5; Atg 5, autophagy-related 5; Atg 9, autophagy-related 9; Atg 10, autophagy-related 10; Atg 12, autophagy-related 12; Atg 13, autophagy-related 13; Atg14, autophagy-related 14; Atg 16L1, autophagy-related 16 like 1; FIP200, focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200; HOPS, homotypic fusion and protein sorting; LC3, Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; STX17, syntaxin 17; SNAP29, synaptosome-associated protein 29; SNAREs, soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors; ULK, unc-51-like kinase; UVRAG, UV radiation resistance associated; VAMP8, vesicle-associated membrane proteins 8; VPS 15, vesicular protein sorting 15; VPS34, vesicular protein sorting 34.
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) refers to RNA molecules transcribed from the genome that do not encode proteins (Slack and Chinnaiyan, 2019). ncRNAs can be broadly divided into two main types: basic structural ncRNAs and regulatory ncRNAs. Within regulatory ncRNAs, these molecules are further categorized based on their length, structure, and location. The four primary types of regulatory ncRNAs involved in cancer include microRNA (miRNA), long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), circular RNA (circRNA), and PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) (Hon et al., 2021). LncRNAs and circRNAs are both over 200 nucleotides in length; however, lncRNAs are linear, whereas circRNAs are circular (Hon et al., 2021). LncRNAs play key roles in various biological processes, such as epigenetic regulation, cell cycle control, and cell differentiation. CircRNAs serve multiple functions as well, acting as miRNA sponges, transcriptional regulators, and binding partners for RNA-binding proteins (Zhao et al., 2014). miRNAs are single-stranded molecules approximately 20–24 nucleotides long and regulate post-transcriptional gene expression by pairing with complementary sequences in the 3′UTR of target mRNA transcript (Vos et al., 2019). PiRNAs, ranging from about 24 to 31 nucleotides, are primarily found in mammalian germ cells and stem cells. By binding to Piwi proteins to form piRNA complexes, they regulate gene silencing pathways (Zeng et al., 2020).
A substantial body of evidence shows that ncRNAs and autophagy play critical roles in human malignancies. ncRNAs can function as either oncogenes or tumor suppressors, influencing cancer initiation and progression, while autophagy can similarly act as a tumor suppressor or pro-cancer factor in regulating cancer development. Moreover, many ncRNAs can be released from cancer cells into the blood or urine, where they serve as diagnostic markers or prognostic indicators. Notably, these ncRNAs, acting as tumor markers, may have a close relationship with autophagy. This article reviews recent advances in understanding the roles of these key ncRNAs and autophagy in lung cancer (Figure 2).
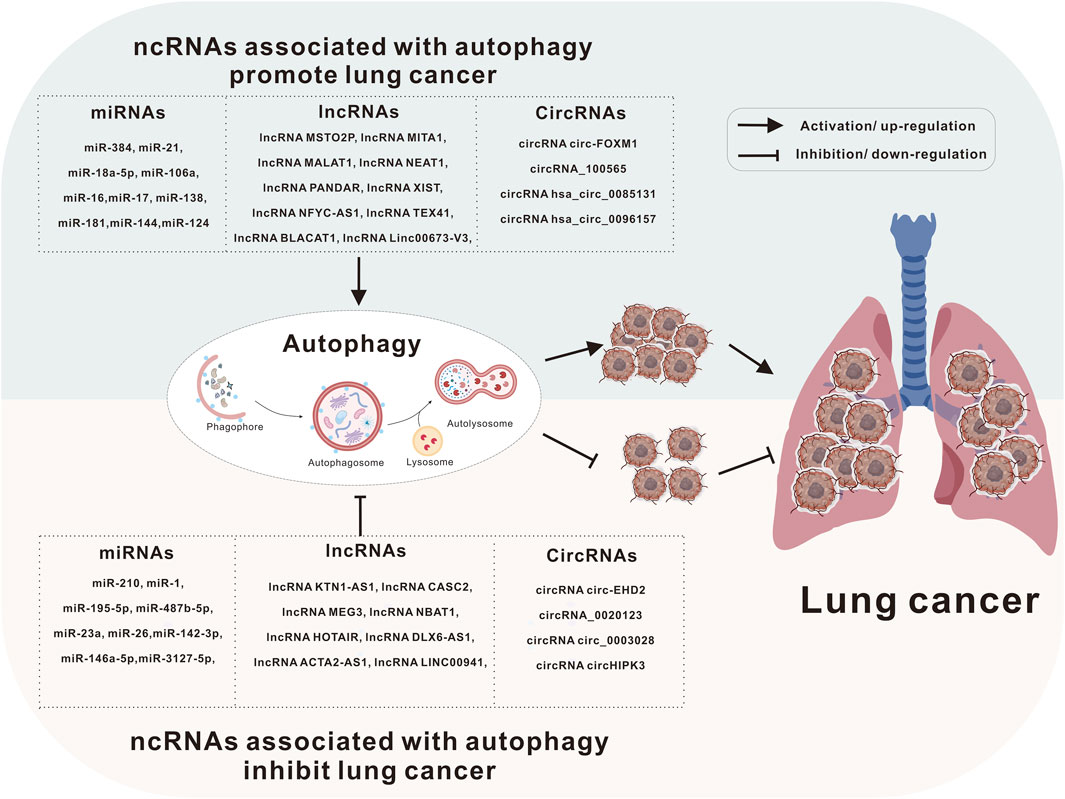
Figure 2. Autophagy and ncRNAs are involved in the development of lung cancer. Lung cancer can be caused by a variety of causes, including heredity, long-term inhalation of toxic substances (e.g., smoking), and even some treatment methods may also be factors leading to lung cancer. Autophagy and ncRNAs are involved in the pathological process of lung cancer through different mechanisms.
2 Autophagy in lung cancer
A number of studies have shown that autophagy is closely related to the occurrence, development and prognosis of lung cancer. Although the role of autophagy in lung cancer cells needs to be further evaluated, it seems to be involved in the occurrence of lung cancer and plays a dual role of promotion or inhibition at different stages of lung cancer development (Chen L. et al., 2019; Chen P. et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2019; Ju et al., 2019).
2.1 Autophagy-related genes in lung cancer
Autophagy-related genes play a crucial role in the formation of autophagosomes (Shi and Jiang, 2022). Additionally, abnormal expression of Atgs may be an important factor affecting lung cancer. Recently, Kim et al. found that USP15 interacted with BECN1 and induced deubiquitination of BECN1, thereby attenuating autophagy induction and negatively regulating lung cancer progression (Kim et al., 2022). Cai et al. reported that casein kinase 1 alpha 1 (CK1α) acted as an autophagy inducer to activate autophagy regulation and inhibited tumor growth through the PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a/Atg7 axis. It is worth noting that blocking CK1α-induced Atg7-dependent autophagy and carcinogenic HRasV12 synergistically initiate tumorigenesis of lung epithelial cells (Cai et al., 2018). Guo et al. showed that Overexpression of the TSTA3 gene promoted the malignant characteristics of lung squamous cell carcinoma by regulating LAMP2-mediated autophagy and tumor microenvironment (Guo et al., 2023). Zhang et al. reported that miRNA-153-3p inhibited autophagy and promoted gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting the expression of autophagy-related gene ATG5 (Zhang W. et al., 2019). These studies provided direct evidence that abnormal expression of autophagy-related genes was closely related to the occurrence and progression of lung cancer.
2.2 Autophagy-related signaling pathway in lung cancer
2.2.1 mTOR-related signaling pathway
Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a major regulator of cell growth and metabolism, promoting anabolic processes such as ribosome biogenesis and the synthesis of proteins, nucleotides and lipids, and inhibiting catabolic processes such as autophagy. Dysregulation of mTOR signaling is associated with many human diseases, including diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases and cancer (lung cancer) (Shimobayashi and Hall, 2014). PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway, as a classic insulin signaling pathway, participates in the occurrence and development of various diseases by mediating autophagy. For instance, Di et al. found that ailanthone enhanced cisplatin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in NSCLS through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (Di et al., 2024). Prucalopride, a dihydrobenzofuran formamide compound and highly selective 5-HT4 receptor agonist, was reported by Chen et al. to inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and migration of lung cancer cells by blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway (Chen M. et al., 2019). Xu et al. identified C-C motif ligand 2 (CCL2), a well-known CC chemokine involved in tumor progression, as a promoter of metastasis and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and autophagy pathways (Xu et al., 2023). Additionally, Luo et al. reported that SLL-1A-16, a novel organoselenium compound, demonstrated anti-proliferative effects on NSCLC by inducing autophagy and inhibiting cell proliferation via the Akt/mTOR pathway (Luo X. et al., 2024). Wang et al. found that CAMK2 inhibitor 1 (CAMK2N1) promoted autophagy and apoptosis through the Akt/mTOR pathway, effectively inhibiting invasion, migration, and angiogenesis in NSCLC. The adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/mTOR signaling pathway is another critical pathway that plays a pivotal role in maintaining energy and redox balance at both cellular and organismal levels (Inoki et al., 2012). Dysregulation of this pathway can disrupt these balances and contribute to tumor development. Ma et al. reported that COTE-1 (also known as FAM189B), which encoded a membrane protein, was widely expressed in various tissues and activated autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway to promote proliferation and invasion in small cell lung cancer (Ma et al., 2023). Zhu et al. found that cycloastragenol induced protective autophagy through the AMPK/ULK1/mTOR pathway and promoted apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by upregulating NOXA expression (Zhu et al., 2024). Additionally, Luo et al. demonstrated that pseudolaric acid B (PAB) inhibited NSCLC progression through the ROS/AMPK/mTOR/autophagy signaling pathway (Luo D. et al., 2024). Li et al. reported that resveratrol induced autophagy and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by activating the NGFR-AMPK-mTOR pathway (Li et al., 2022a). The above studies have shown that mTOR-related signaling pathways are closely related to the occurrence and progression of lung cancer.
2.2.2 EGFR signaling pathway
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor for epithelial growth factor cell proliferation and signal transduction. In the process of organogenesis and tissue repair, the EGFR pathway usually provides a strong signal for epithelial cell proliferation/survival (Goldkorn and Filosto, 2010). EGFR can initiate lung tumorigenesis by activating pro-survival and anti-apoptotic cellular responses, including increased proliferation, motility, angiogenesis, vasculogenic mimicry, and invasiveness (Prenzel N et al., 2001; Levantini et al., 2022). For instance, Wang et al. reported that combination of betulinic acid (BA) and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) exerted a synergistic anti-tumor effect by inducing autophagy-related cell death through the EGFR signaling pathway (Wang et al., 2024). Yu et al. found that blocking EGFR-SQSTM1 interaction with short peptide SAH-EJ2 interference inhibited lung cancer by activating autophagy and inhibiting EGFR signal transduction (Yu et al., 2020). Thyroid hormone receptor interactor 13 (TRIP13) is an ATP enzyme that is overexpressed in a variety of tumors and is involved in tumor drug resistance. Xiao et al. found that TRIP13 overexpression promoted gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating autophagy and phosphorylation of EGFR signaling pathway (Xiao et al., 2023).
2.2.3 Others signaling pathway
Recent research found by Guo et al. showed that quercetin induced pro-apoptotic autophagy in human lung cancer cells through the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway in vitro (Guo et al., 2021). Li et al. reported that programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) promotes primary resistance of EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma cells to EGFR-TKIs, potentially by inducing autophagy via the MAPK signaling pathway (Li N. et al., 2024). Additionally, Chen et al. demonstrated that baicalin participates in ferritinophagy and modulates macrophage immunity through the KEAP1-NRF2/HO-1 axis, thereby enhancing NSCLC sensitivity to cisplatin (Chen et al., 2024). Ding et al. reported that regulator of G protein signaling 20 (RGS20) activated autophagy and promoted the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting PKA-Hippo signaling pathway (Ding et al., 2024). Fan et al. found that bruceine D induced lung cancer cell apoptosis and autophagy via the ROS/MAPK signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo (Fan et al., 2020). Bai et al. reported that protein disulfide isomerase family 6 (PDIA6), an oncogene, inhibited JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway by interacting with MAP4K1, thereby inhibiting cisplatin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in NSCLC cells (Bai et al., 2019). Zhang et al. found that phanginin R (PR) induced cytoprotective autophagy in NSCLC cells via the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway, and inhibition of autophagy could further improve the anti-cancer potential of PR (Zhang L. L. et al., 2020). Liu et al. reported that YZT, a novel PDK1/MEK dual inhibitor, induces protective autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer cells through the PDK1/Akt signaling pathway (Liu R. et al., 2023).
2.3 Autophagy and NSCLC drug resistance
Autophagy is a crucial survival mechanism under stress, playing a key role in maintaining cell homeostasis and regulating proliferation (Mizushima et al., 2020). In early cancer development, autophagy helps safeguard normal cells from tumorigenesis by preventing DNA damage and mutations. In established solid tumors, autophagy facilitates tumor progression by promoting growth, survival, chemotherapy resistance, and metastasis in response to stressors such as hypoxia, drug exposure, and nutrient deprivation (Mulcahy Levy and Thorburn, 2019; Leonardi et al., 2022). Thus, autophagy plays a dual role in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), influencing both tumor progression and drug resistance.
2.3.1 Autophagy and traditional chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC
Chemotherapy remains a primary treatment for NSCLC; however, drug resistance poses a significant challenge. Studies have linked NSCLC chemoresistance to protective autophagy. For instance, Chen et al. found that cisplatin treatment upregulated autophagy-related genes in NSCLC, suggesting that autophagy contributes to cisplatin resistance in A549 cells (Chen et al., 2018). Using autophagy inhibitors, or knocking down the expression of autophagy-related genes or proteins, could enhance the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to cisplatin (Chen J. et al., 2022). Moreover, autophagy strengthens tumor resistance by modulating the tumor microenvironment and immune response (Xia et al., 2021). However, chemotherapy can trigger both protective autophagy and autophagic cell death. Bai et al. reported that esomeprazole inhibited V-ATPase expression, inducing autophagy and leading to paclitaxel (PTX) accumulation in A549/Taxol-resistant cells. This significantly reduced cell proliferation and resistance (Bai et al., 2020). These findings suggest that autophagy’s role in NSCLC chemoresistance varies depending on the drug and tumor cell type. Therefore, targeting autophagy in NSCLC treatment requires careful consideration.
2.3.2 Autophagy and molecular targeted drug resistance in NSCLC
It has been reported that approximately 73.9% of NSCLC patients have driver gene mutations, with EGFR, ALK, and ROS1 being the most common (Sholl et al., 2015; Wen et al., 2019). Recent advancements have led to the development of molecular targeted therapies, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (Liu and Mao, 2024), and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (Dzul Keflee et al., 2022), for NSCLC. These therapies have notably improved the prognosis and extended survival in patients with driver gene-positive NSCLC. However, the benefits are often short-lived, as most patients develop resistance within a year of treatment (Miller et al., 2022). Drug resistance arises from multiple factors, with autophagy playing a significant role. For instance, Li et al. found that osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR-TKI, induces autophagy in NSCLC cells. Increased autophagy correlated with osimertinib resistance in both in vitro and in vivo studies. Suppressing autophagy enhanced the drug’s cytotoxicity in both resistant and sensitive cells (Li L. et al., 2019). Lu et al. demonstrated that lorlatinib triggered both apoptosis and protective autophagy in ALK-positive NSCLC cells. However, this protective autophagy reduced lorlatinib’s cytotoxic effects on ALK-positive NSCLC cells. Combining lorlatinib with the autophagy inhibitor CQ activated the Foxo3a/Bim axis, suppressing autophagy and enhancing apoptosis in both in vitro and in vivo models (Lu et al., 2022).
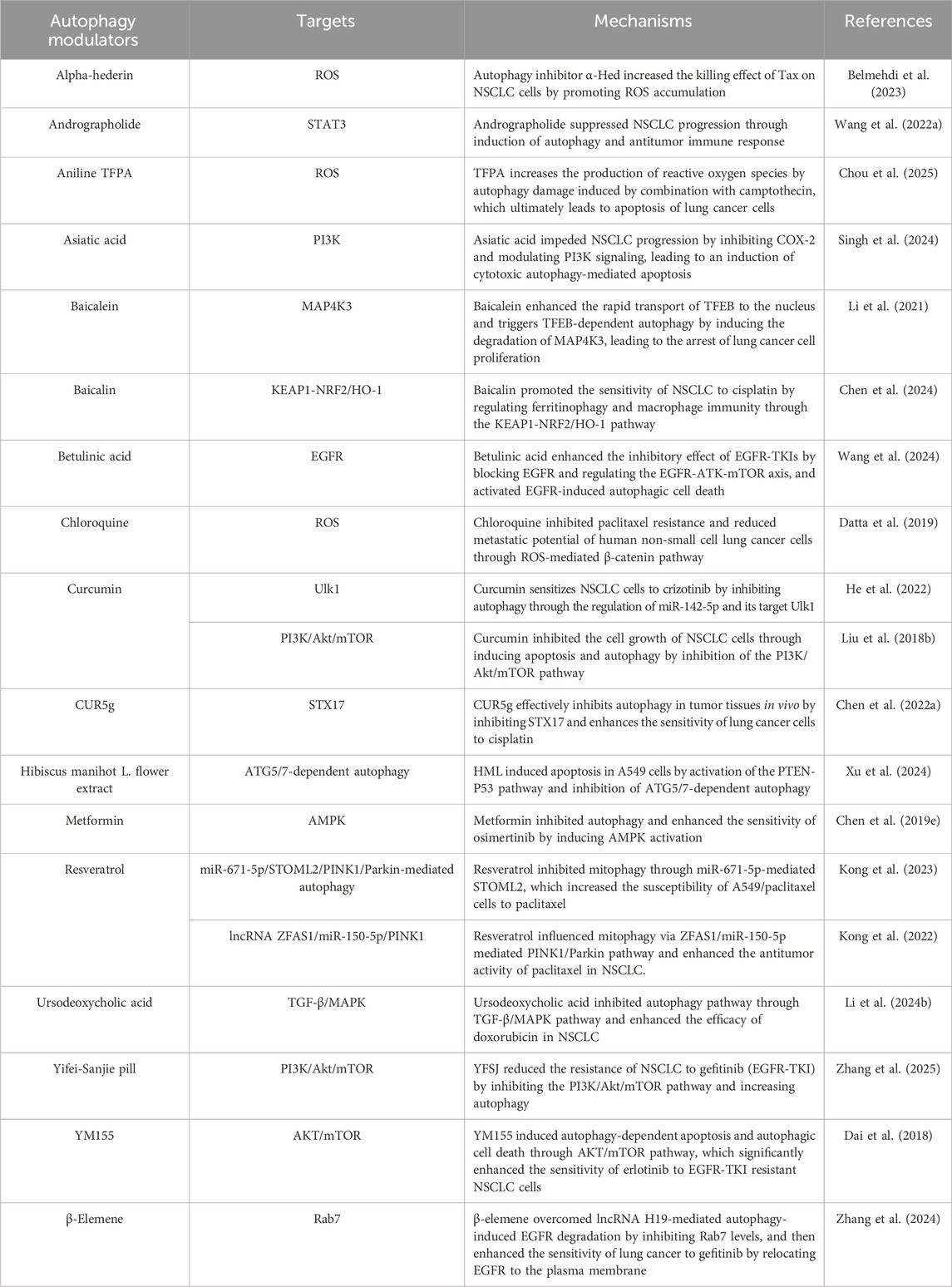
These findings suggest that autophagy significantly contributes to lung cancer development. As such, targeting autophagy with specific modulators could represent a promising therapeutic strategy (Table 1). In summary, tumor cells manipulate autophagy through various signaling pathways to counteract drug toxicity, thus enhancing their survival. Therefore, combining autophagy modulators with targeted therapies may help overcome drug resistance in NSCLC. Nevertheless, further research is needed to precisely control autophagy for therapeutic benefit.
3 ncRNAs in lung cancer
3.1 MiRNA in LC
3.1.1 miRNAs in the modulation of cell proliferation and metastasis in LC
A growing body of research highlights the critical role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in regulating cell proliferation, tumor metastasis, and angiogenesis. For instance, Gao et al. found that elevated levels of miR-485-5p suppressed tumor cell invasion by targeting the FLOT2 protein, thereby reducing the ability of cancer cells to infiltrate surrounding tissue (Gao et al., 2019). Similarly, Mao et al. reported that exosomal miR-375-3p disrupted the vascular barrier, increasing its permeability and subsequently facilitating cancer cell migration and metastasis (Mao et al., 2021). In addition, Ma et al. observed that lower expression of miR-320b was associated with improved overall survival in lung cancer patients. MiR-320b exerts its effects by targeting hepatocyte nuclear factor 4γ, thereby inhibiting tumor growth, invasion, and angiogenesis in xenograft models (Ma et al., 2021).
3.1.2 MiRNAs related with chemotherapy in LC
Moreover, miRNAs are key regulators of multidrug resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Shi et al. observed that elevated levels of miR-20a in exosomes from tumor-associated fibroblasts in NSCLC patients, which contributed to cisplatin resistance in NSCLC cells. Inhibition of PTEN, a direct target of miR-20a, was shown to suppress both cell proliferation and chemoresistance in NSCLC (Shi et al., 2022). Hao et al. reported that miR-369-3p, which was overexpressed in NSCLC, directly targeted the SLC35F5 gene. By regulating nucleotide sugar transport, it influenced drug assimilation and ultimately contributed to cisplatin resistance (Hao et al., 2017). Haque et al. identified Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) as a novel target of miR-506-3p, noting its abnormal activation in epidermal growth factor receptor-resistant (ER) cells. Reduced miR-506-3p expression in ER cells enhanced resistance to EGFR-TKIs by modulating SHH signaling, upregulating E-cadherin, and suppressing vimentin (Haque et al., 2020). Wu et al. discovered that low miR-630 expression in EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma conferred TKI resistance via the miR-630/YAP1/ERK feedback loop. As a result, miR-630 may serve as a potential biomarker for predicting treatment response and clinical outcomes in patients receiving TKI therapy. Additional insights into the role of miRNAs in lung cancer are provided in studies by Lobera et al. (2023) and Gilyazova et al. (2023).
3.2 LncRNAs in LC
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are RNA molecules exceeding 200 nucleotides in length that do not encode proteins (Mercer et al., 2009; Volders et al., 2013). They serve as key regulators in a wide range of biological processes and signaling pathways, and are strongly associated with disease onset and progression. While the roles of certain lncRNAs are well-characterized, the functions of most remain largely unknown. Recent research indicates that aberrant lncRNA expression contributes to tumor development, invasion, and drug resistance through various mechanisms across different cancer types (Huarte, 2015; Lin and Yang, 2018). Uncovering new molecular pathways involving lncRNAs may offer promising therapeutic targets and enhance our understanding of lung cancer pathogenesis and its intricate regulatory networks (Ding et al., 2018; Bader et al., 2011; Hayes et al., 2014; Tang et al., 2017; Tian et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2014).
3.2.1 LncRNAs related with chemotherapy in LC
Among lncRNA-related research, the majority focuses on their involvement in chemotherapy response. One mechanism involves direct regulation of downstream genes by lncRNAs, which alters lung cancer chemosensitivity. For instance, Xu et al. showed that lncRNA XIST bound to SMAD2, inhibiting its nuclear translocation. This suppressed SMAD2-induced transcription of p53 and NLRP3, thereby reducing cisplatin (DDP)-induced pyroptosis and decreasing chemosensitivity (Xu et al., 2020). Similarly, elevated levels of lncRNA UCA1 have been linked to cisplatin resistance in NSCLC patients (Li C. et al., 2019). In addition, lncRNAs contributed to drug resistance by acting within the competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network. Ge et al. reported that lncRNA SNHG1 targeted miR-330-5p, leading to increased DCLK1 expression. This activated PI3K/AKT signaling and promoted cisplatin resistance (Ge et al., 2021). Additionally, Zhu et al. found that lncRNA FGD5-AS1 interacted with miR-142 to upregulate PD-L1 expression, which reduces cisplatin sensitivity (Zhu et al., 2021). Chen et al. found that lncRNA MALAT1 was highly expressed in the tissues of gemcitabine-resistant patients. MALAT1 upregulated PBOV1 level through sponge miR-27a-5p, thereby promoting gemcitabine resistance in NSCLC (Chen W. et al., 2022).
3.2.2 LncRNAs related with radiotherapy in LC
Radiotherapy remains a key treatment modality for lung cancer. Over the past two decades, significant advancements in radiotherapy, such as stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), have improved treatment efficacy while minimizing radiation-induced damage to healthy tissues, ultimately enhancing patient survival and prognosis. Emerging evidence suggested that certain lncRNAs affected the radiosensitivity of lung cancer by directly regulating downstream gene expression, thereby contributing to tumor progression. For instance, Gao et al. demonstrated that lncRNA PCAT1 exerted an immunosuppressive effect and was associated with NSCLC invasion. The increase of PCAT1 expression was inversely correlated with immune cell infiltration in NSCLC tissues. Further investigation revealed that PCAT1 reduced radiosensitivity by activating SOX2 through modulation of the cGAS/STING signaling pathway (Gao et al., 2022).
Additionally, lncRNAs also act as competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) to modulate radiosensitivity in lung cancer. Ma et al. found that lncRNA protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor G-type antisense RNA 1 (lncRNA PTPRG-AS1) reduced NSCLC radiosensitivity by sponging miR-200c-3p, leading to upregulation of TCF4 expression (Ma et al., 2020). Jiang et al. showed that lncRNA cytoskeleton regulator (lncRNA CYTOR) was upregulated in NSCLC and reduced radiosensitivity by downregulating miR-206 and activating prothymosin α (Jiang et al., 2021). Moreover, in a research by Wang et al. it was found that overexpression of lncRNA hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α antisense RNA 1 (HNF1A-AS1) sponged miR-92a-3p, leading to upregulation of MAP2K4. This, in turn, activated JNK phosphorylation and promoted radioresistance in NSCLC (Wang et al., 2021).
Overall, lncRNAs modulate NSCLC radiosensitivity through diverse mechanisms, including gene expression regulation and signaling pathway modulation. However, Given the complexity and functional diversity of lncRNAs, further research is needed to elucidate their regulatory networks and explore their potential as biomarkers or therapeutic targets for clinical application.
3.2.3 LncRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in LC
Advances in detection technologies have led to the identification of numerous lncRNAs as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in lung cancer. For example, Weber et al. found that MALAT1 was readily detectable in the peripheral blood of NSCLC patients compared to healthy controls, suggesting its potential as a diagnostic biomarker (Weber et al., 2013). Beyond diagnosis, MALAT1 is also linked to patient prognosis. Schmidt et al. reported that high MALAT1 expression correlated with poor prognosis in NSCLC, and when combined with thymosin β4, it served as an independent prognostic indicator for early-stage disease (Schmidt et al., 2011). In addition, lncRNA NEAT1 (Jen et al., 2017) and TUG1 (Da et al., 2021) were highly expressed in NSCLC tissues, which were associated with the poor prognosis of NSCLC patients, highlighting their potential as prognostic markers. Additional insights into the role of lncRNAs in lung cancer progression are provided in the work of Ge et al. (2024).
3.3 CircRNAs in LC
Studies have shown that circRNA is involved in multiple cellular biochemical processes of NSCLC, including proliferation, differentiation, metastasis, apoptosis and ferroptosis, indicating that circRNAs plays a vital role in NSCLC (Shanshan et al., 2021; Lu et al., 2019; Shang et al., 2019). In addition, circRNAs could induce tumor drug resistance through a variety of methods, including inhibiting cancer cell apoptosis, enhancing autophagy, accelerating drug excretion from cells, promoting DNA damage repair, and maintaining the characteristics of tumor stem cells (Fan et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2019; Xie H. et al., 2022; Zhong et al., 2021).
3.3.1 CircRNAs mediating specific drug resistance of NSCLC
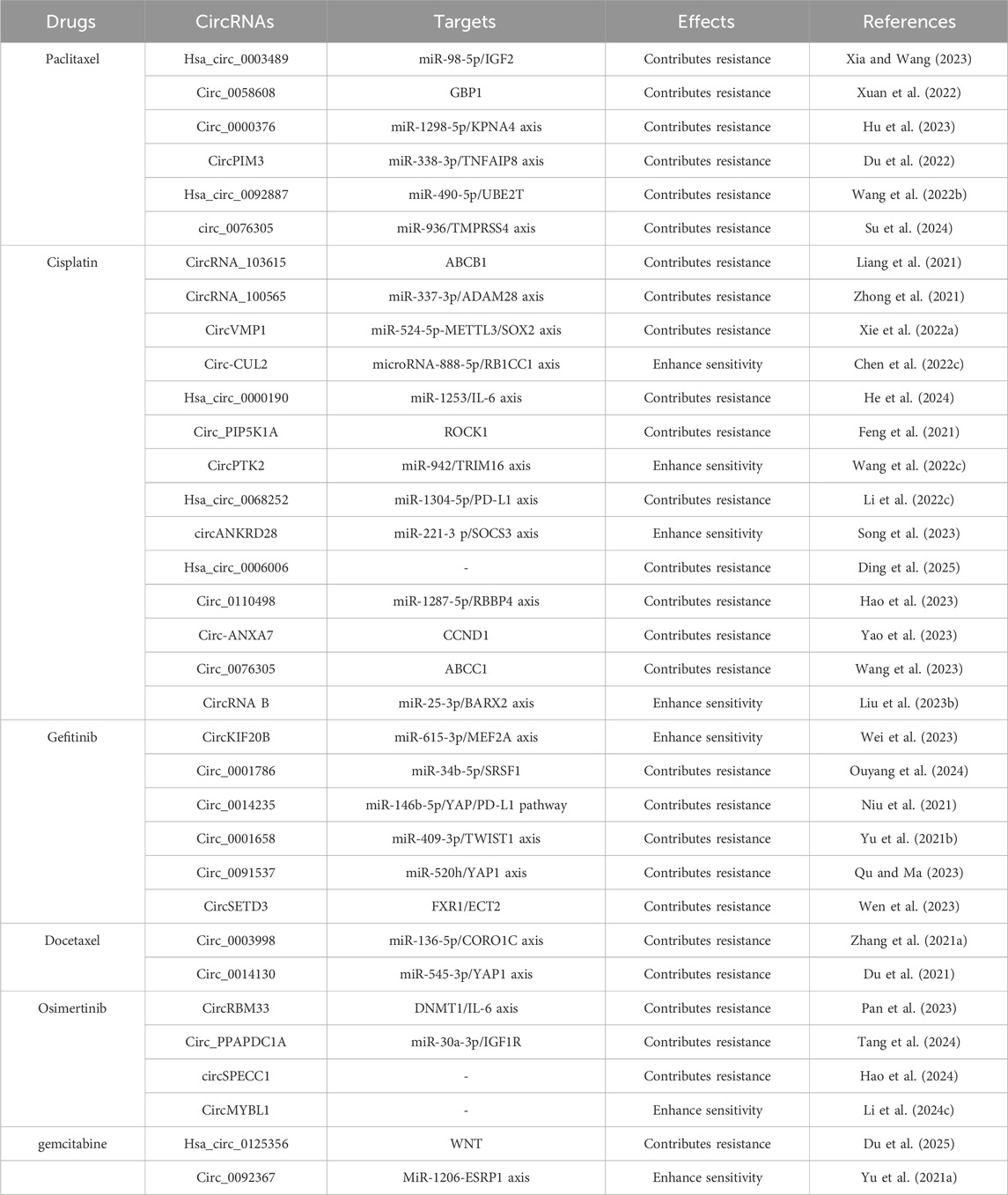
Emerging studies have shown that circRNAs could contribute to drug resistance in NSCLC, affecting agents such as paclitaxel (PTX), docetaxel (DTX), cisplatin, pemetrexed, gemcitabine, and osimertinib. (1) Regarding PTX resistance, Guo et al. demonstrated that circ_0011292 promoted PTX resistance in NSCLC by modulating the miR-379-5p/TRIM65 axis (Guo et al., 2022). Similarly, Xia et al. proved that overexpression of hsa_circ_0003489 drove PTX resistance by modulating miR-98-5p/IGF2 (Xia and Wang, 2023). These findings suggested that targeting circ_0011292 and circ_0002874 could be a potential therapeutic strategy to reverse PTX resistance. (2) Regarding DTX resistance, Zhang et al. reported that circ_0003998 reduced drug sensitivity of lung cancer cells to DTX by modulating the miR-136-5p/CORO1C axis (Zhang W. et al., 2021). In addition, Du et al. showed that high levels of circ_0014130 led to DTX resistance by regulating the miR-545-3p/YAP1 axis (Du et al., 2021). (3) For cisplatin resistance, He et al. identified that hsa_circ_0000190 promoted NSCLC cell resistance to cisplatin via the modulation of the miR-1253/IL-6 axis (He et al., 2024). Conversely, Song et al. found that circANKRD28 suppressed cisplatin resistance in NSCLC through the miR-221-3p/SOCS3 axis (Song et al., 2023). (4) For pemetrexed resistance, Zheng et al. manifested that circ_PVT1 enhanced resistance to both cisplatin and pemetrexed via the miR-145-5p/ABCC1 axis (Zheng and Xu, 2020). Mao et al. pointed out that circ CDR1-AS was highly expressed in lung cancer and promoted pemetrexed and CDDP chemotherapy resistance by regulating the EGFR/PI3K signaling pathway (Mao and Xu, 2020). (5) In gemcitabine resistance, Du et al. indicated that hsa_circ_0125356 acted as a driver of gemcitabine resistance via the miR-582-5p/FGF9 axis and WNT pathway (Du et al., 2025). In addition, Yu et al. pointed out that loss of circ_0092367 induced invasive EMT characteristics and gemcitabine resistance in NSCLC through regulating the miR-1206/ESRP1 axis (Yu S. et al., 2021). (6) In crizotinib resistance, Pan et al. showed that circRBM33 promotes resistance by regulating the DNMT1/IL-6 axis (Pan et al., 2023). Tang et al. manifested that circ_PPAPDC1A enhanced osimertinib resistance by sponging miR-30a-3p and activating the IGF1R pathway (Tang et al., 2024). Additional details on circRNA-mediated drug resistance in NSCLC are summarized in Table 2.
3.3.2 CircRNAs as therapeutic targets to overcome drug resistance in NSCLC
As discussed, CircRNAs play a critical role in drug resistance in lung cancer and thus represent promising therapeutic targets. Current research primarily focuses on suppressing circRNA expression to restore the sensitivity of NSCLC cells to chemotherapy. For example, Zhang et al. demonstrated that shRNA-mediated knockdown of circ_0072088 significantly reduced cisplatin resistance in NSCLC cells (Zhang L. et al., 2022). Similarly, silencing circ_0004015 via siRNA and shRNA suppressed cisplatin resistance in NSCLC (Li Y. et al., 2022). Zheng et al. further demonstrated that inhibiting hsa_circ_0074027 reduced chemotherapy resistance by modulating the miR-379-5p/IGF1 signaling axis (Zheng et al., 2021). Additional insights into circRNAs as therapeutic targets in overcoming NSCLC drug resistance are detailed in the study by Yan et al. (2022).
4 Biologic functions and molecular mechanism of non-coding RNAs-medicated autophagy in lung cancer
During the progression of lung cancer, abnormally regulated ncRNAs and autophagy are important factors that regulate related signaling pathways at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional and post-translational levels, thereby changing various malignant behaviors and therapeutic responses of lung cancer.
4.1 MiRNAs-medicated autophagy promoted the progression of lung cancer
4.1.1 MiRNAs promoted autophagy to promoted lung cancer
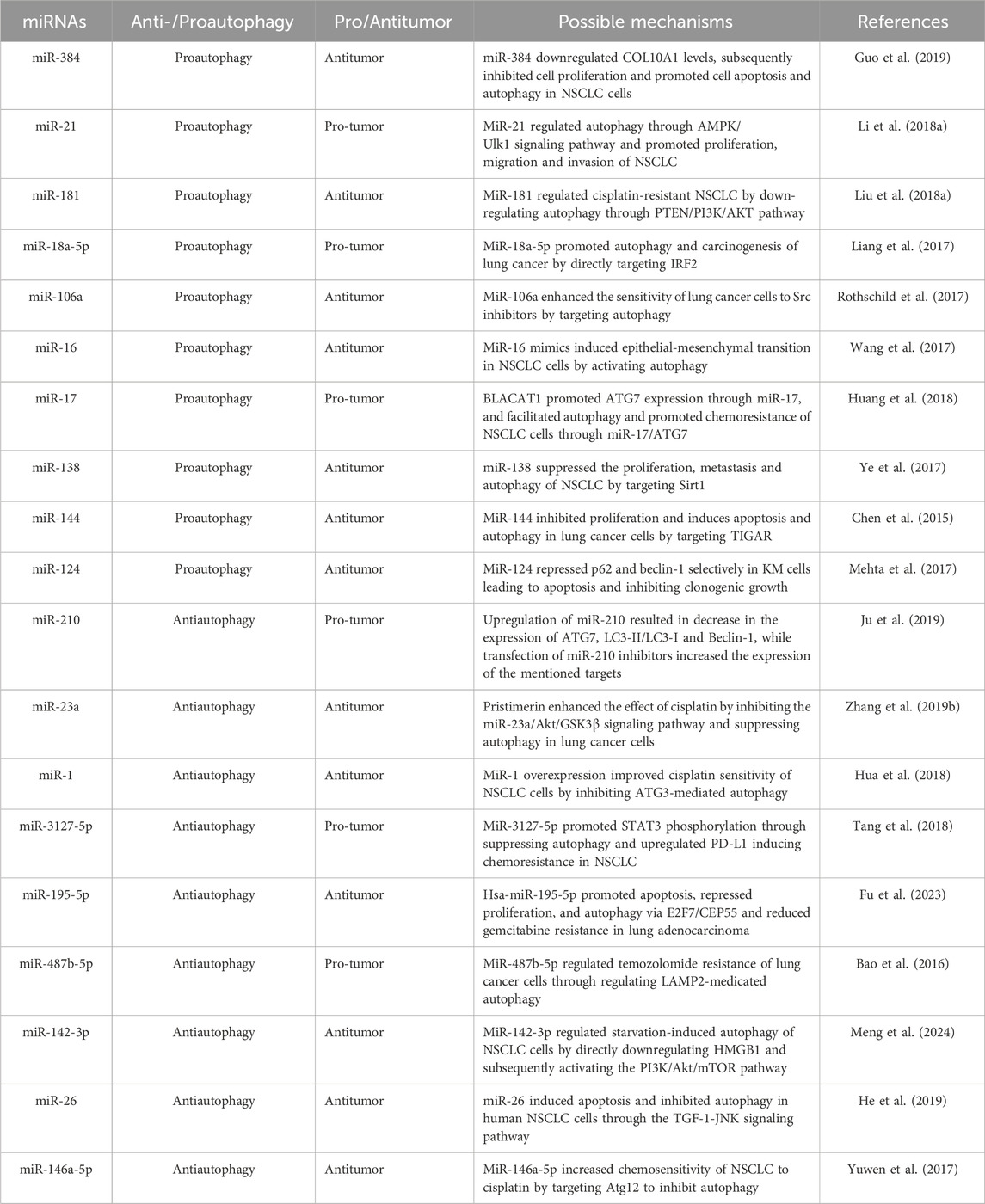
Many studies have explored the molecular mechanism of lung cancer, many of which have confirmed the key role of miRNAs and autophagy in lung cancer progression and drug resistance (Li S. et al., 2018; Liu J. et al., 2018) (Figure 3). On the one hand, miRNAs can act as pro-survival factors for lung cancer by regulating autophagy. For instance, miRNAs promoted lung cancer tumorigenesis by promoting autophagy. Li et al. reported that miRNA-21 promoted the proliferation, migration and invasion of NSCLC cells through reducing autophagy via AMPK/ULK1 signaling pathway (Li S. et al., 2018). Liang et al. reported that miR-18a-5p promoted autophagy and carcinogenesis of lung cancer by directly targeting IRF2 (Liang et al., 2017).
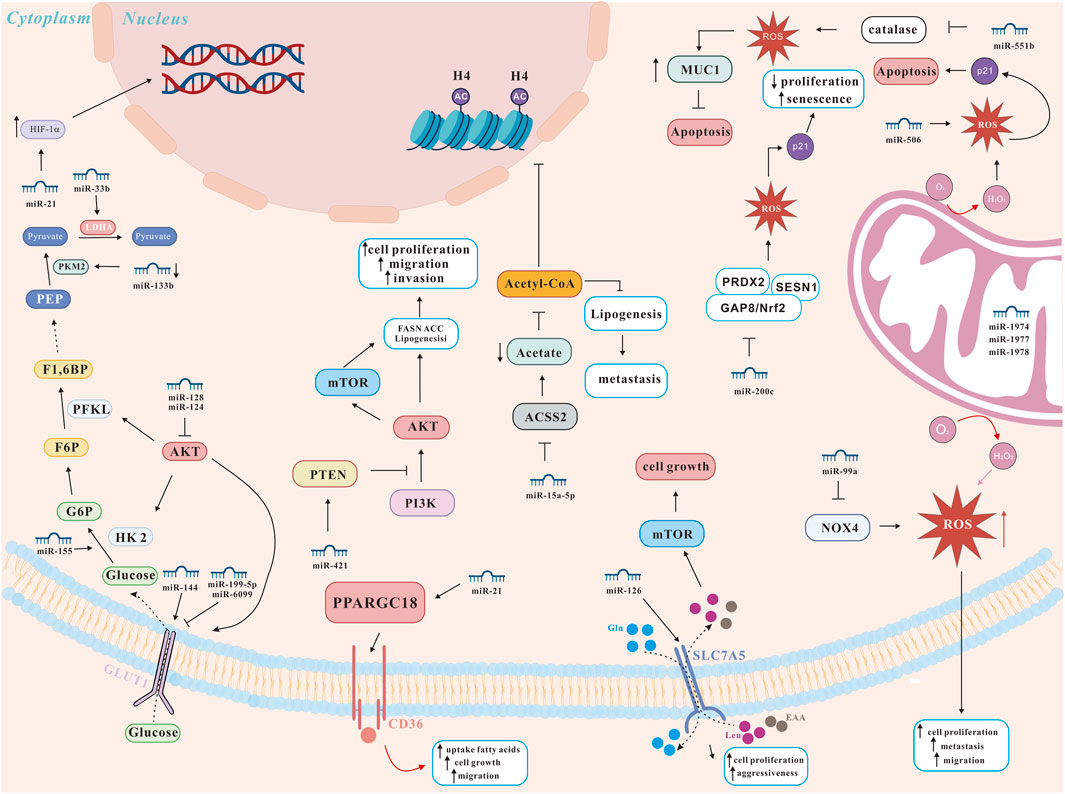
Figure 3. miRNA network regulating lung cancer metabolism (modified from (Carrà et al., 2024)). ACSS2, AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated acetyl-CoA synthetase 2; AKT, protein kinase B; GLUT, glucose transporters; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; HK2, hexokinase 2; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; MUC1, transmembrane glycoprotein mucin 1; NOX4, NADPH oxidase 4; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PFKL, phosphofructokinase, liver type; PKM2, pyruvate kinase isoenzyme M2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PPARGC1B, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta; PRDX2, peroxiredoxin 2; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SESN1, sestrin 1.
4.1.2 MiRNAs inhibited autophagy to promoted lung cancer
In addition, miRNAs could also promote lung cancer by inhibiting autophagy. For instance, Ju et al. reported that miR-210 directly targeted ATG7 to reduce the level of autophagy and promoted the proliferation of lung cancer cells (Ju et al., 2019). Tang et al. reported that miR-3127-5p promoted STAT3 phosphorylation through suppressing autophagy and upregulated PD-L1 resulting in chemoresistance in NSCLC (Tang et al., 2018). Furthermore, Bao et al. found that miR-487b-5p promoted proliferation and migration of temozolomide-resistance lung cancer cells through Lamp2-medicated autophagy (Bao et al., 2016). The above results indicated that miRNA promoted the progression of lung cancer by regulating autophagy.
4.2 MiRNAs-medicated autophagy inhibited the progression of lung cancer
4.2.1 MiRNAs promoted autophagy to inhibited lung cancer
On the other hand, miRNAs can also act as pro-death factors in lung cancer by regulating autophagy such as miRNA-106a, a member of the miR-17 family, has been found to be abnormally expressed in a variety of cancers (Pan et al., 2016), and is closely related to the occurrence, development and prognosis of cancer (Zhao et al., 2019). Han et al. reported that upregulation of miR-106a promoted metastasis by targeting tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 (TP53INP1)-mediated metastasis progression, including cell migration, autophagy-dependent death, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Han et al., 2021). Guo et al. reported that miR-384 inhibited cell proliferation and promoted cell apoptosis and autophagy in NSCLC cells through down-regulating collagen α-1(X) chain (COL10A1) levels (Guo et al., 2019). Chen et al. showed that miR-144 targeted p53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) and increased autophagy, thereby promoting apoptosis and inhibiting lung cancer cell proliferation (Chen et al., 2015). In addition, Ye et al. suggested that miR-138 suppressed the proliferation, metastasis and autophagy of NSCLC cells by targeting Sirt1 (Ye et al., 2017).
4.2.2 MiRNAs inhibited autophagy to inhibited lung cancer
In a research by Hua et al., it was demonstrated that miR-1 overexpression improved cisplatin chemosensitivity of NSCLC cells by inhibiting ATG3-mediated autophagy (Hua et al., 2018). In an academic study conducted by He et al. it was reported that miR-26 promoted apoptosis and suppressed autophagy in NSCLC cells by inhibiting TGF-β1-JNK signaling pathway (He et al., 2019). Furthermore, both miR-142-3p and miRNA-153-3p promoted the proliferation of lung cancer through inhibiting the autophagy pathway (Zhang W. et al., 2019; Meng et al., 2024). More about the relationship between miRNAs-medicated autophagy in lung cancer is shown in Table 3.
4.3 LncRNAs-medicated autophagy promoted the progression of lung cancer
4.3.1 LncRNAs promoted autophagy to promoted lung cancer
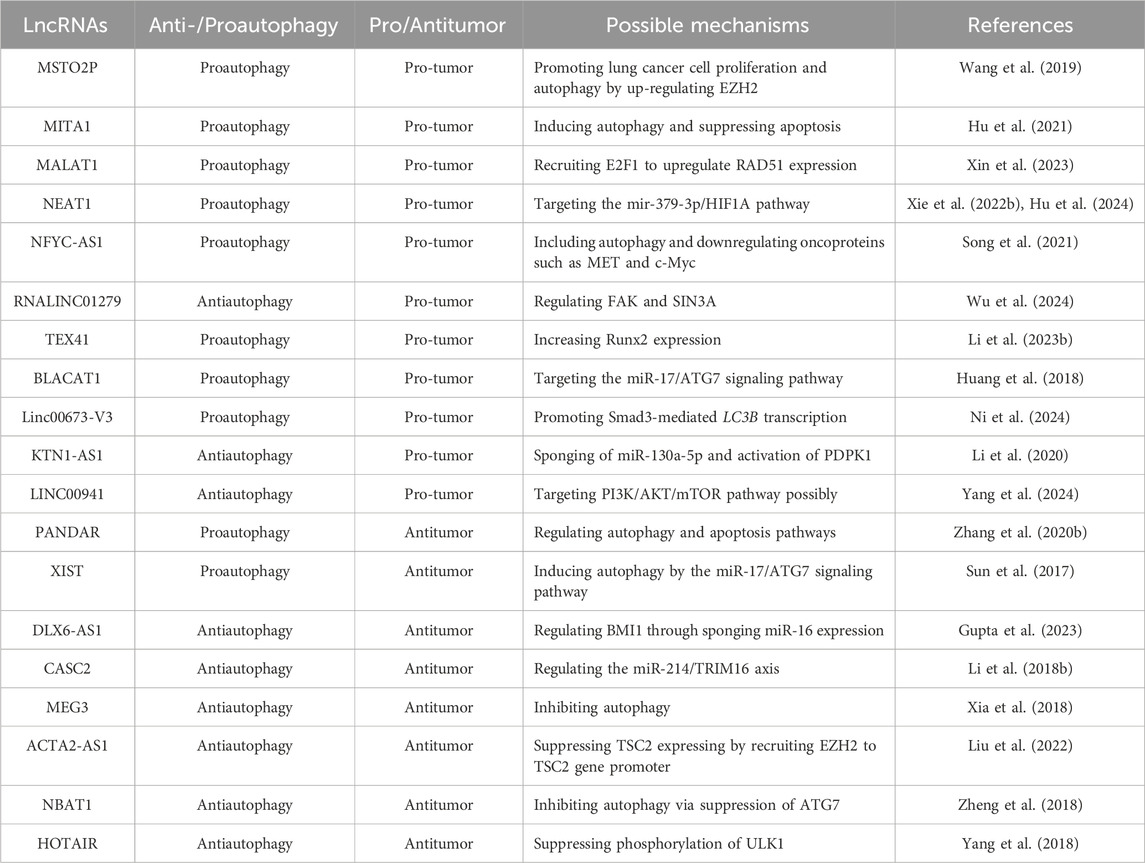
Numerous studies have also highlighted the critical roles of both autophagy and lncRNAs in lung cancer progression. Like autophagy-related miRNAs, autophagy-related lncRNAs can function as both promoters and suppressors of lung cancer. For instance, Wang et al. demonstrated that lncRNA MSTO2P enhanced lung cancer cell proliferation and autophagy by upregulating EZH2 expression (Wang et al., 2019). Hu et al. found that lncRNA MITA1 increased gefitinib resistance in lung cancer cells through autophagy induction (Hu et al., 2021). Similarly, Xin et al. demonstrated that lncRNA MALAT-1 facilitated autophagy and NSCLC growth by recruiting E2F1 to upregulate RAD51 expression (Xin et al., 2023). Furthermore, Furthermore, Xie and Hu et al. reported that lncRNA NEAT1 enhanced NSCLC drug resistance and suppressed apoptosis by inducing autophagy (Xie Y. et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2024). Song et al. revealed that lncRNA NFYC-AS1 promoted the proliferation of lung cancer by regulating autophagy and apoptosis (Song et al., 2021). In addition, lncRNAs such as, TEX41 (Li R. et al., 2023), BLACAT1 (Huang et al., 2018), Linc00673-V3 (Ni et al., 2024) promoted lung cancer cell growth or mediated resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs via activating autophagy.
4.3.2 LncRNAs inhibited autophagy to promoted lung cancer
Wu et al. reported that LINC01279 was highly expressed in lung cancer cells, and inhibiting the function of LINC01279 reduced the growth of xenograft tumors of NSCLC cells. Further studies have found that knockdown of LINC01279 or SIN3A activated autophagy and apoptosis of NSCLC cells. Therefore, LINC01279 promoted the occurrence and development of lung cancer by regulating FAK and SIN3A to inhibit autophagy in lung cancer cells (Wu et al., 2024). In a research by Li et al., it was found that lncRNA KTN1-AS1 was upregulated in NSCLC tissues and positively correlated with poor prognosis. In addition, knockdown of KTN1-AS1 inhibited the growth and proliferation of NSCLC cells and increased apoptosis. Further studies have found that KTN1-AS1 regulated the expression of miR-130a-5p target gene PDPK1 in NSCLC cells to inhibit autophagy in lung cancer cells. Therefore, KTN1-AS1 inhibited autophagy in lung cancer cells through miR-130a-5p/PDPK1 signaling pathway (Li et al., 2020). Furthermore, Yang et al. reported that LINC00941 was a diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma and promoted tumorigenesis through inhibiting cell autophagy (Yang et al., 2024). The above three lncRNAs promoted lung cancer cells growth of by inhibiting autophagy pathway.
4.4 LncRNAs-medicated autophagy inhibited the progression of lung cancer
4.4.1 LncRNAs promoted autophagy to inhibited lung cancer
Additionally, lncRNAs-medicated autophagy can act as pro-death factors in lung cancer. For instance, Zhang et al. demonstrated that the expression of lncRNA PANDAR and autophagy-related gene BECN1 was downregulated in lung cancer. Further studies showed that the high expression of PANDAR increased the expression level of BECN1, promoted autophagy and apoptosis, and inhibited the proliferation of NSCLC. Therefore, lncRNA PANDAR was a tumor suppressor that inhibited the proliferation of NSCLC cells by up-regulating the activation of autophagy and apoptosis pathways (Zhang L. et al., 2020). Another related study showed that the expression of lncRNA-XIST in non-small cell lung cancer tissues was significantly higher than that in adjacent normal tissues. In addition, knockdown of lncRNA-XIST reduced basal autophagy and autophagic flux in NSCLC cells. Further studies found that knockdown of XIST weakened autophagy-dependent NSCLC chemotherapy resistance. Therefore, overexpression of lncRNA XIST has been linked to increased cisplatin resistance in chemotherapy, mediated through autophagy activation via the miR-17/ATG7 signaling pathway (Sun et al., 2017).
4.4.2 LncRNAs inhibited autophagy to inhibited lung cancer
LncRNAs could also inhibited lung cancer by inhibiting autophagy such as Gupta et al. reported that targeting lncRNA DLX6-AS1 enhanced miR-16 activity, inducing autophagy and apoptosis, while regulating BMI1 through miR-16 sponging, thereby inhibiting lung cancer growth (Gupta et al., 2023). Li et al. found that lncRNA CASC2 inhibited autophagy and promoted apoptosis in NSCLC cells via regulating the miR-214/TRIM16 axis (Li Q. et al., 2018). Furthermore, lncRNAs such as MEG3 (Xia et al., 2018), ACTA2-AS1 (Liu et al., 2022), NBAT1 (Zheng et al., 2018), HOTAIR (Yang et al., 2018), have been implicated to suppressing lung cancer cell growth or mediating resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs via inhibiting autophagy mechanisms. More about the relationship between lncRNAs-medicated autophagy in lung cancer is shown in Table 4.
4.5 CircRNAs-medicated autophagy promoted the progression of lung cancer
4.5.1 CircRNAs promoted autophagy to promoted lung cancer
Unlike traditional linear RNAs, circular RNAs (circRNAs) have a closed-loop structure, making them resistant to RNA exonucleases. This unique structure ensures their stability and resistance to degradation. Functionally, circRNAs are abundant in miRNAs-binding sites and act as miRNAs sponges within cells. This interaction alleviates the suppressive effects of miRNAs on their target genes, thereby enhancing target gene expression. Studies have shown that autophagy and circRNAs were crucial in lung cancer progression. Notably, some circRNAs regulate lung cancer cell growth by enhancing autophagy. For instance, Wei et al. demonstrated that circular RNA circ-FOXM1 promoted autophagy and drived NSCLC progression by suppressing miR-149-5p expression and upregulating ATG5 levels (Wei et al., 2021). Zhong et al. identified that circRNA_100565 as a contributor to cisplatin resistance in NSCLC by promoting autophagy and suppressing apoptosis via the miR-337-3p/ADAM28 axis (Zhong et al., 2021). Likewise, Kong et al. reported that circular RNA hsa_circ_0085131 enhanced cisplatin resistance in NSCLC cells by stimulating autophagy (Kong, 2020). Additionally, circular RNA Hsa_circ_0010235 (Zhang F. et al., 2021) and circular RNA Hsa_circ_0096157 (Lu et al., 2024) have been reported to facilitate NSCLC growth through autophagy activation.
4.5.2 CircRNAs inhibited autophagy to promoted lung cancer
Yang and Zhang identified that circular RNA hsa_circ_0020123 suppressed autophagy by sponging specific miRNAs, thereby promoting lung cancer cell growth (Zhang H. et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2022). Similarly, Guan et al. demonstrated that circular RNA circ_0003028 inhibited autophagy and drived tumorigenesis in NSCLC by modulating GOT2 expression via miR-1298-5p (Guan et al., 2021). Additionally, circular RNA circHIPK3 and circular RNA EHD2 have been shown to facilitate NSCLC growth by inhibiting autophagy (Chen X. et al., 2019; Zhang F. et al., 2022). For further details on circRNAs-medicated autophagy in lung cancer, refer to Table 5.
5 Limitations of the study
Notably, autophagy and ncRNAs (miRNAs, lncRNAs, circRNAs) are pivotal in lung cancer development and progression. These molecules can function as cancer promoters, driving lung cancer growth and chemoresistance, or as tumor suppressors, inhibiting tumor progression. However, several limitations persist in understanding and analyzing the roles of autophagy and ncRNAs in lung cancer: 1) Individual Variability: the heterogeneity among lung cancer patients and the complexity of the tumor microenvironment result in substantial individual differences in ncRNAs expression levels and autophagy activity. These variations complicate the accurate assessment of their roles in lung cancer progression. 2) Unclear mechanisms: while ncRNAs significantly influence lung cancer by modulating autophagy pathways, the precise mechanisms of many ncRNAs remain poorly understood. Moreover, it is often unclear whether ncRNA-based therapies act solely through autophagy, requiring further research. 3) Lack of specificity: current ncRNA-based drugs and autophagy modulators often lack disease specificity, potentially causing collateral damage to normal tissues and limiting their clinical application in lung cancer treatment. 4) Drug delivery challenges: delivering ncRNAs and autophagy modulators faces significant barriers, including instability, low specificity, and limited tumor-targeting efficiency. These issues reduce therapeutic efficacy and increase the risk of systemic side effects. 5) Insufficient Monitoring Tools: the dual role of autophagy and ncRNAs in lung cancer (both tumor-suppressing and tumor-promoting) underscores the need for reliable real-time monitoring tools. Without these, dynamic changes in autophagy and ncRNAs during treatment may lead to suboptimal outcomes or adverse effects.
6 Future directions
To address the limitations mentioned above, the following strategies may offer valuable insights:
(1) Identifying highly specific biomarkers: Ideally, highly specific markers can include ncRNAs expression profiles and detectable autophagy-related genes or proteins (such as in blood or sputum). These markers could provide accurate insights into dynamic changes during lung cancer progression. Monitoring these markers can reduce invasive diagnostic procedures, lower economic burdens, track tumor progression and treatment response, and guide personalized therapeutic strategies. It is believed that in the future, with the continuous development of high-throughput screening technology, bioinformatics prediction, luciferase reporter gene assay, mass spectrometry analysis technology, more and more high-specificity will be reported.
(2) Designing Targeted ncRNA Therapeutics: The specificity of ncRNA modulators is critical for minimizing off-target effects and improving therapeutic efficacy. By focusing on autophagy-related pathways (e.g., Beclin1 or mTORC1), ncRNA mimics or inhibitors could be tailored for specific tumor stages (characterized by excessive autophagy activation or inhibition). Combining ncRNA-based therapies with traditional treatments, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy, may further amplify therapeutic benefits and reduce adverse drug reactions.
(3) Implementing real-time monitoring: Real-time systems to monitor ncRNA expression, autophagy activity, and drug concentrations during treatment are critical, given the dual role of autophagy in lung cancer. Advanced imaging techniques, like nanoparticle-based probes, could track autophagic flux and ncRNAs dynamics in vivo, preventing excessive or insufficient drug modulation that could worsen the disease or lead to drug resistance.
(4) Using targeted drug delivery systems: Efficient delivery of ncRNA-based therapies remains a key challenge. Utilizing targeted delivery methods, such as lipid nanoparticles or exosomes, could enhance the stability and tumor specificity of these drugs, significantly reducing side effects and improving therapeutic outcomes.
(5) Focus on the subcellular distribution of ncRNAs: The factors driving the subcellular distribution of circRNAs and the biogenesis and transport of ncRNAs (including extracellular transport and degradation) were investigated by using live cell imaging techniques.
7 Conclusion
In general, existing studies have shown that ncRNA and autophagy play an important role in the occurrence and progression of lung cancer, which makes them potential therapeutic targets. However, the specific mechanism between ncRNA and autophagy still needs further study. The development of ncRNA-based therapeutic strategies, especially ncRNAs that regulate autophagy pathways, may provide new ideas and methods for the treatment of lung cancer. In addition, since current autophagy modulators and ncRNA drugs often lack sufficient targeting and specificity, improving the targeting and efficacy of these drugs will be an important topic in future research.
Author contributions
JL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SS: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by the Key Research and Development Project of the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Provincial, China (No. 2022YFS0059).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support from Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Wenjiang District People’s Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Southwest Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdelaziz, H. M., Gaber, M., Abd-Elwakil, M. M., Mabrouk, M. T., Elgohary, M. M., Kamel, N. M., et al. (2018). Inhalable particulate drug delivery systems for lung cancer therapy: nanoparticles, microparticles, nanocomposites and nanoaggregates. J. Control. Release. 269, 374–392. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.11.036
Bader, A. G., Brown, D., Stoudemire, J., and Lammers, P. (2011). Developing therapeutic microRNAs for cancer. Gene. Ther. 18, 1121–1126. doi:10.1038/gt.2011.79
Bai, Y., Liu, X., Qi, X., Liu, X., Peng, F., Li, H., et al. (2019). PDIA6 modulates apoptosis and autophagy of non-small cell lung cancer cells via the MAP4K1/JNK signaling pathway. EBioMedicine 42, 311–325. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.045
Bai, Z., Ding, N., Ge, J., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Wu, N., et al. (2020). Esomeprazole overcomes paclitaxel-resistance and enhances anticancer effects of paclitaxel by inducing autophagy in A549/Taxol cells. Cell. Biol. Int. 45, 177–187. doi:10.1002/cbin.11481
Bao, L., Lv, L., Feng, J., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Han, S., et al. (2016). MiR-487b-5p regulates temozolomide resistance of lung cancer cells through LAMP2-medicated autophagy. DNA. Cell. Biol. 35, 385–392. doi:10.1089/dna.2016.3259
Belmehdi, O., Taha, D., Abrini, J., Ming, L. C., Khalid, A., Abdalla, A. N., et al. (2023). Anticancer properties and mechanism insights of α-hederin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165, 115205. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115205
Cai, J., Li, R., Xu, X., Zhang, L., Lian, R., Fang, L., et al. (2018). CK1α suppresses lung tumour growth by stabilizing PTEN and inducing autophagy. Nat. Cell. Biol. 20, 465–478. doi:10.1038/s41556-018-0065-8
Carrà, G., Petiti, J., Tolino, F., Vacca, R., and Orso, F. (2024). MicroRNAs in metabolism for precision treatment of lung cancer. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 29, 121. doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00632-3
Chen, H., Li, F., and Xue, Q. (2022c). Circ-CUL2/microRNA-888-5p/RB1CC1 axis participates in cisplatin resistance in NSCLC via repressing cell advancement. Bioengineered 13, 2828–2840. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.2024395
Chen, H., Lin, C., Lu, C., Wang, Y., Han, R., Li, L., et al. (2019e). Metformin-sensitized NSCLC cells to osimertinib via AMPK-dependent autophagy inhibition. Clin. Respir. J. 13, 781–790. doi:10.1111/crj.13091
Chen, J., Shen, Y., Wu, B., Yang, P., Sun, G., Liu, X., et al. (2022a). CUR5g, a novel autophagy inhibitor, exhibits potent synergistic anticancer effects with cisplatin against non-small-cell lung cancer. Cell. death. Discov. 8, 435. doi:10.1038/s41420-022-01217-9
Chen, J., Zhang, L., Zhou, H., Wang, W., Luo, Y., Yang, H., et al. (2018). Inhibition of autophagy promotes cisplatin-induced apoptotic cell death through Atg5 and Beclin 1 in A549 human lung cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 17, 6859–6865. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.8686
Chen, L., Han, X., Hu, Z., and Chen, L. (2019a). The PVT1/miR-216b/Beclin-1 regulates cisplatin sensitivity of NSCLC cells via modulating autophagy and apoptosis. Cancer. Chemother. Pharmacol. 83, 921–931. doi:10.1007/s00280-019-03808-3
Chen, M., Zhu, L. L., Su, J. L., Li, G. L., Wang, J., and Zhang, Y. N. (2019c). Prucalopride inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through blocking of the PI3K/AKT/mTor signaling pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 39, 173–181. doi:10.1177/0960327119883409
Chen, P., Huang, H. P., Wang, Y., Jin, J., Long, W. G., Chen, K., et al. (2019b). Curcumin overcome primary gefitinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cells through inducing autophagy-related cell death. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer. Res. 38, 254. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1234-8
Chen, S., Li, P., Li, J., Wang, Y., Du, Y., Chen, X., et al. (2015). MiR-144 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis and autophagy in lung cancer cells by targeting TIGAR. Cell. Physiol. biochem. 35, 997–1007. doi:10.1159/000369755
Chen, W., Tan, X., Yang, Q., Fang, Z., and Xu, Y. (2022b). MALAT1 enhances gemcitabine resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by directly affecting miR-27a-5p/PBOV1 axis. Cell. Signal. 94, 110326. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110326
Chen, X., Mao, R., Su, W., Yang, X., Geng, Q., Guo, C., et al. (2019d). Circular RNA circHIPK3 modulates autophagy via MIR124-3p-STAT3-PRKAA/AMPKα signaling in STK11 mutant lung cancer. Autophagy 16, 659–671. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1634945
Chen, Y., Bao, S., Wang, Z., Fang, Z., and Tang, H. (2024). Baicalin promotes the sensitivity of NSCLC to cisplatin by regulating ferritinophagy and macrophage immunity through the KEAP1-NRF2/HO-1 pathway. Eur. J. Med. Res. 29, 387. doi:10.1186/s40001-024-01930-4
Chou, H. L., Lin, I. L., Chen, Y. T., Chang, W. T., Yu, A., Chen, W. C., et al. (2025). Aniline TFPA enhances camptothecin-induced anti-NSCLC by modulating oxidative stress and impairing autophagy. Cancer. Cell. Int. 25, 81. doi:10.1186/s12935-025-03657-6
Da, M., Zhuang, J., Zhou, Y., Qi, Q., and Han, S. (2021). Role of long noncoding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 in cancers. Mol. Med. 27, 51. doi:10.1186/s10020-021-00312-4
Dai, C. H., Shu, Y., Chen, P., Wu, J. N., Zhu, L. H., Yuan, R. X., et al. (2018). YM155 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors through the mechanism of autophagy induction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Basis. Dis. 1864, 3786–3798. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.10.015
Datta, S., Choudhury, D., Das, A., Mukherjee, D. D., Dasgupta, M., Bandopadhyay, S., et al. (2019). Autophagy inhibition with chloroquine reverts paclitaxel resistance and attenuates metastatic potential in human nonsmall lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells via ROS mediated modulation of β-catenin pathway. Apoptosis 24, 414–433. doi:10.1007/s10495-019-01534-y
Di, J., Bo, W., Wang, C., and Liu, C. (2024). Ailanthone increases cisplatin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in cisplatin resistance non-small cell lung cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway. Curr. Med. Chem. 31. doi:10.2174/0109298673315460240816091032
Ding, M., Zhao, J., and Li, X. (2025). Hsa_circ_0006006 is a potential biomarker for prognosis and cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Hereditas 162, 32. doi:10.1186/s41065-025-00392-w
Ding, X., Li, X., Jiang, Y., Li, Y., Li, H., Shang, L., et al. (2024). RGS20 promotes non-small cell lung carcinoma proliferation via autophagy activation and inhibition of the PKA-Hippo signaling pathway. Cancer. Cell. Int. 24, 93. doi:10.1186/s12935-024-03282-9
Ding, X., Zhang, S., Li, X., Feng, C., Huang, Q., Wang, S., et al. (2018). Profiling expression of coding genes, long noncoding RNA, and circular RNA in lung adenocarcinoma by ribosomal RNA-depleted RNA sequencing. FEBS. Open. Bio. 8, 544–555. doi:10.1002/2211-5463.12397
Du, D., Cao, X., Duan, X., and Zhang, X. (2021). Blocking circ_0014130 suppressed drug resistance and malignant behaviors of docetaxel resistance-acquired NSCLC cells via regulating miR-545-3p-YAP1 axis. Cytotechnology 73, 571–584. doi:10.1007/s10616-021-00478-z
Du, L., Guo, D., Sun, C., Yan, X., Lin, S., and Xu, S. (2022). CircPIM3 regulates taxol resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via miR-338-3p/TNFAIP8 axis. Anticancer. Drugs. 34, 115–125. doi:10.1097/cad.0000000000001347
Du, X., Luo, W., Li, H., Gu, Q., Huang, P., Wang, C., et al. (2025). Hsa_circ_0125356 promotes gemcitabine resistance by modulating WNT canonical and non-canonical pathways via miR-582-5p/FGF9 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer. 24, 59. doi:10.1186/s12943-025-02259-0
Dzul Keflee, R., Leong, K. H., Ogawa, S., Bignon, J., Chan, M. C., and Kong, K. W. (2022). Overview of the multifaceted resistances toward EGFR-TKIs and new chemotherapeutic strategies in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 205, 115262. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115262
Fan, D., Yang, Y., and Zhang, W. (2022). A novel circ_MACF1/miR-942-5p/TGFBR2 axis regulates the functional behaviors and drug sensitivity in gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. BMC. Pulm. Med. 22, 27. doi:10.1186/s12890-021-01731-z
Fan, J., Ren, D., Wang, J., Liu, X., Zhang, H., Wu, M., et al. (2020). Bruceine D induces lung cancer cell apoptosis and autophagy via the ROS/MAPK signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cell. death. Dis. 11, 126. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2317-3
Feng, N., Guo, Z., Wu, X., Tian, Y., Li, Y., Geng, Y., et al. (2021). Circ_PIP5K1A regulates cisplatin resistance and malignant progression in non-small cell lung cancer cells and xenograft murine model via depending on miR-493-5p/ROCK1 axis. Respir. Res. 22, 248. doi:10.1186/s12931-021-01840-7
Fu, L., Li, Z., Wu, Y., Zhu, T., Ma, Z., Dong, L., et al. (2023). Hsa-miR-195-5p inhibits autophagy and gemcitabine resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells via E2F7/CEP55. Biochem. Genet. 61, 1528–1547. doi:10.1007/s10528-023-10330-y
Gao, F., Wu, H., Wang, R., Guo, Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, T., et al. (2019). MicroRNA-485-5p suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of small cell lung cancer cells by targeting flotillin-2. Bioengineered 10, 1–12. doi:10.1080/21655979.2019.1586056
Gao, Y., Zhang, N., Zeng, Z., Wu, Q., Jiang, X., Li, S., et al. (2022). LncRNA PCAT1 activates SOX2 and suppresses radioimmune responses via regulating cGAS/STING signalling in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 12, e792. doi:10.1002/ctm2.792
Ge, P., Cao, L., Zheng, M., Yao, Y., Wang, W., and Chen, X. (2021). LncRNA SNHG1 contributes to the cisplatin resistance and progression of NSCLC via miR-330-5p/DCLK1 axis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 120, 104633. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2021.104633
Ge, X., Shen, Z., and Yin, Y. (2024). Comprehensive review of LncRNA-mediated therapeutic resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. Cell. Int. 24, 369. doi:10.1186/s12935-024-03549-1
Gilyazova, I., Gimalova, G., Nizamova, A., Galimova, E., Ishbulatova, E., Pavlov, V., et al. (2023). Non-coding RNAs as key regulators in lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 560. doi:10.3390/ijms25010560
Goldkorn, T., and Filosto, S. (2010). Lung injury and cancer: mechanistic insights into ceramide and EGFR signaling under cigarette smoke. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 43, 259–268. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2010-0220RT
Guan, H., Sun, C., Gu, Y., Li, J., Ji, J., and Zhu, Y. (2021). Circular RNA circ_0003028 contributes to tumorigenesis by regulating GOT2 via miR-1298-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Bioengineered 12, 2326–2340. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1935064
Guo, C., Wang, H., Jiang, H., Qiao, L., and Wang, X. (2022). Circ_0011292 enhances paclitaxel resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-379-5p/TRIM65 axis. Cancer. biother. Radiopharm. 37, 84–95. doi:10.1089/cbr.2019.3546
Guo, H., Ding, H., Tang, X., Liang, M., Li, S., Zhang, J., et al. (2021). Quercetin induces pro-apoptotic autophagy via SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway in human lung cancer cell lines A549 and H1299 in vitro. Thorac. Cancer. 12, 1415–1422. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.13925
Guo, Q., Zheng, M., Xu, Y., Wang, N., and Zhao, W. (2019). MiR-384 induces apoptosis and autophagy of non-small cell lung cancer cells through the negative regulation of Collagen α-1(X) chain gene. Biosci. Rep. 39, BSR20181523. doi:10.1042/bsr20181523
Guo, Y., Hao, Y., Shen, L., Du, Y., Wang, X., Gao, L., et al. (2023). TSTA3 overexpression promotes malignant characteristics in LUSC by regulating LAMP2-mediated autophagy and tumor microenvironment. Cancer. Cell. Int. 23, 285. doi:10.1186/s12935-023-03109-z
Gupta, S., Silveira, D. A., Mombach, J. C. M., and Hashimoto, R. F. (2023). The lncRNA DLX6-AS1/miR-16-5p axis regulates autophagy and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer: a Boolean model of cell death. RNA. Res. 8, 605–614. doi:10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.08.003
Han, L., Huang, Z., Liu, Y., Ye, L., Li, D., Yao, Z., et al. (2021). MicroRNA-106a regulates autophagy-related cell death and EMT by targeting TP53INP1 in lung cancer with bone metastasis. Cell. death. Dis. 12, 1037. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04324-0
Hao, D., Li, Y., Shi, J., and Jiang, J. (2023). Circ_0110498 facilitates the cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by mediating the miR-1287-5p/RBBP4 axis. Thorac. Cancer. 14, 662–672. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.14787
Hao, G. J., Ding, Y. H., Wen, H., Li, X. F., Zhang, W., Su, H. Y., et al. (2017). Attenuation of deregulated miR-369-3p expression sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin via modulation of the nucleotide sugar transporter SLC35F5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 488, 501–508. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.05.075
Hao, Z., Feng, F., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Li, J., and Huang, J. (2024). Circular RNA SPECC1 promoted tumorigenesis and osimertinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma via a circular RNA-microRNA network. J. Thorac. Dis. 16, 8754–8770. doi:10.21037/jtd-2024-2144
Haque, I., Kawsar, H. I., Motes, H., Sharma, M., Banerjee, S., Banerjee, S. K., et al. (2020). Downregulation of miR-506-3p facilitates EGFR-TKI resistance through induction of sonic hedgehog signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 9307. doi:10.3390/ijms21239307
Hayes, J., Peruzzi, P. P., and Lawler, S. (2014). MicroRNAs in cancer: biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends. Mol. Med. 20, 460–469. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2014.06.005
He, H., Li, T., and Morelli, M. B. (2024). Hsa_circ_0000190 promotes NSCLC cell resistance to cisplatin via the modulation of the miR-1253/IL-6 axis. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2024, 6647810. doi:10.1155/2024/6647810
He, Y., Liu, H., Jiang, L., Rui, B., Mei, J., and Xiao, H. (2019). MiR-26 induces apoptosis and inhibits autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing TGF-β1-JNK signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1509. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01509
He, Y. Z., Yu, S. L., Li, X. N., Bai, X. H., Li, H. T., Liu, Y. C., et al. (2022). Curcumin increases crizotinib sensitivity through the inactivation of autophagy via epigenetic modulation of the miR-142-5p/Ulk1 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. Biomark. 34, 297–307. doi:10.3233/cbm-210282
Hon, C. C., Yan, H., and Bu, P. (2021). Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays. Biochem. 65, 625–639. doi:10.1042/ebc20200032
Hu, J., Dong, S. W., Pei, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, J., and Wei, X. P. (2021). LncRNA MITA1 promotes gefitinib resistance by inducing autophagy in lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 551, 21–26. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.02.130
Hu, S., Zhang, Q., Sun, J., Xue, J., and Wang, C. (2023). Circular RNA circ_0000376 promotes paclitaxel resistance and tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer via positively modulating KPNA4 by sponging miR-1298-5p. Cancer. 14, 2116–2126. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.14994
Hu, W., Cao, W., and Liu, J. (2024). LncRNA-NEAT1 facilitates autophagy to boost pemetrexed resistance in lung adenocarcinoma via the mir-379-3p/HIF1A pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 43, 9603271241292169. doi:10.1177/09603271241292169
Hua, L., Zhu, G., and Wei, J. (2018). MicroRNA-1 overexpression increases chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting autophagy related 3-mediated autophagy. Cell. Biol. Int. 42, 1240–1249. doi:10.1002/cbin.10995
Huang, F. X., Chen, H. J., Zheng, F. X., Gao, Z. Y., Sun, P. F., Peng, Q., et al. (2018). LncRNA BLACAT1 is involved in chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating autophagy. Int. J. Oncol. 54, 339–347. doi:10.3892/ijo.2018.4614
Huang, X., Li, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, W., Li, B., Wang, L., et al. (2019). Circular RNA AKT3 upregulates PIK3R1 to enhance cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer via miR-198 suppression. Mol. Cancer. 18, 71. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0969-3
Huarte, M. (2015). The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat. Med. 21, 1253–1261. doi:10.1038/nm.3981
Inoki, K., Kim, J., and Guan, K.-L. (2012). AMPK and mTOR in cellular energy homeostasis and drug targets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 52, 381–400. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134537
Jen, J., Tang, Y. A., Lu, Y. H., Lin, C. C., Lai, W. W., and Wang, Y.-C. (2017). Oct4 transcriptionally regulates the expression of long non-coding RNAs NEAT1 and MALAT1 to promote lung cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 16, 104. doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0674-z
Jiang, G., Yu, H., Li, Z., and Zhang, F. (2021). LncRNA cytoskeleton regulator reduces non-small cell lung cancer radiosensitivity by downregulating miRNA-206 and activating prothymosin α. Int. J. Oncol. 59, 88. doi:10.3892/ijo.2021.5268
Ju, S., Liang, Z., Li, C., Ding, C., Xu, C., Song, X., et al. (2019). The effect and mechanism of miR-210 in down-regulating the autophagy of lung cancer cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 215, 453–458. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2018.12.018
Kim, M. J., Min, Y., Jeong, S. K., Son, J., Kim, J. Y., Lee, J. S., et al. (2022). USP15 negatively regulates lung cancer progression through the TRAF6-BECN1 signaling axis for autophagy induction. Cell. death. Dis. 13, 348. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04808-7
Kong, F., Xie, C., Zhao, X., Zong, X., Bu, L., Zhang, B., et al. (2022). Resveratrol regulates PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy via the lncRNA ZFAS1-miR-150-5p-PINK1 axis, and enhances the antitumor activity of paclitaxel against non-small cell lung cancer. Toxicol. Res. 11, 962–974. doi:10.1093/toxres/tfac072
Kong, F., Zhang, L., Zhao, X., Zhao, L., Wang, P., Zhang, R., et al. (2023). Resveratrol augments paclitaxel sensitivity by modulating miR-671-5p/STOML2/PINK1/Parkin-mediated autophagy signaling in A549 cell. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 38, e23557. doi:10.1002/jbt.23557
Kong, R. (2020). Circular RNA hsa_circ_0085131 is involved in cisplatin-resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by regulating autophagy. Cell. Biol. Int. 44, 1945–1956. doi:10.1002/cbin.11401
Leiter, A., Veluswamy, R. R., and Wisnivesky, J. P. (2023). The global burden of lung cancer: current status and future trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 20, 624–639. doi:10.1038/s41571-023-00798-3
Leonardi, L., Siberil, S., Alifano, M., Cremer, I., and Joubert, P.-E. (2022). Autophagy-related gene signature highlights metabolic and immunogenic status of malignant cells in non-small cell lung cancer adenocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 14, 3462. doi:10.3390/cancers14143462
Levantini, E., Maroni, G., Del Re, M., and Tenen, D. G. (2022). EGFR signaling pathway as therapeutic target in human cancers. Semin. Cancer. Biol. 85, 253–275. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.04.002
Levine, B., and Kroemer, G. (2008). Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 132, 27–42. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018
Levine, B., and Kroemer, G. (2019). Biological functions of autophagy genes: a disease perspective. Cell 176, 11–42. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.048
Li, C., Fan, K., Qu, Y., Zhai, W., Huang, A., Sun, X., et al. (2019b). Deregulation of UCA1 expression may be involved in the development of chemoresistance to cisplatin in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer via regulating the signaling pathway of microRNA-495/NRF2. J. Cell. Physiol. 235, 3721–3730. doi:10.1002/jcp.29266
Li, C., Zhao, W., Pan, X., Li, X., Yan, F., Liu, S., et al. (2020). LncRNA KTN1-AS1 promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer via sponging of miR-130a-5p and activation of PDPK1. Oncogene 39, 6157–6171. doi:10.1038/s41388-020-01427-4
Li, J., Fan, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Yu, Y., and Ma, M. (2022a). Resveratrol induces autophagy and apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer cells by activating the NGFR-AMPK-mTOR pathway. Nutrients 14, 2413. doi:10.3390/nu14122413
Li, J., Xu, J., Wu, G., Ren, Y., Wang, X., and Zhang, Q. (2022c). Circular RNA hsa_circ_0068252 functions in cisplatin resistance and immune response via miR-1304-5p/PD-L1 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Chemotherapy 67, 223–233. doi:10.1159/000525231
Li, J., Yan, L., Luo, J., Tong, L., Gao, Y., Feng, W., et al. (2021). Baicalein suppresses growth of non-small cell lung carcinoma by targeting MAP4K3. Biomed. Pharmacother. 133, 110965. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110965
Li, L., Wang, Y., Jiao, L., Lin, C., Lu, C., Zhang, K., et al. (2019a). Protective autophagy decreases osimertinib cytotoxicity through regulation of stem cell-like properties in lung cancer. Cancer. Lett. 452, 191–202. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.03.027
Li, N., Zuo, R., He, Y., Gong, W., Wang, Y., Chen, L., et al. (2024a). PD-L1 induces autophagy and primary resistance to EGFR–TKIs in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma via the MAPK signaling pathway. Cell. death. Dis. 15, 555. doi:10.1038/s41419-024-06945-7
Li, Q., Chen, K., Dong, R., and Lu, H. (2018b). LncRNA CASC2 inhibits autophagy and promotes apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cellsviaregulating the miR-214/TRIM16 axis. RSC. Adv. 8, 40846–40855. doi:10.1039/c8ra09573f
Li, R., L, Y., Hu, F., Liao, Y., Tang, J., Shen, Y., et al. (2023b). LncRNA TEX41 regulates autophagy by increasing Runx2 expression in lung adenocarcinoma bone metastasis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 15, 949–966.
Li, S., Zeng, X., Ma, R., and Wang, L. (2018a). MicroRNA-21 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by regulating autophagy activity via AMPK/ULK1 signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 16, 2038–2045. doi:10.3892/etm.2018.6370
Li, Y., Wang, N., Huang, Y., He, S., Bao, M., Wen, C., et al. (2024c). CircMYBL1 suppressed acquired resistance to osimertinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer. Genet. 284-285, 34–42. doi:10.1016/j.cancergen.2024.04.001
Li, Y., Yan, B., and He, S. (2023a). Advances and challenges in the treatment of lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 169, 115891. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115891
Li, Y., Yang, X., and Xiong, X. (2022b). Circ_0004015 silencing represses cisplatin chemoresistance and tumor progression by reducing KLF8 in a miR-198-dependent manner in non-small cell lung cancer. Genomics 114, 110294. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110294
Li, Y., Zhao, H., Shen, Z., Zheng, Y., Jiang, Y., Song, Y., et al. (2024b). Enhancing DOX efficacy against NSCLC through UDCA-mediated modulation of the TGF-β/MAPK autophagy pathways. Sci. Rep. 14, 27169. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-73736-7
Liang, C., Zhang, X., Wang, H. M., Liu, X. M., Zhang, X. J., Zheng, B., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-18a-5p functions as an oncogene by directly targeting IRF2 in lung cancer. Cell. death. Dis. 8, e2764. doi:10.1038/cddis.2017.145
Liang, H., Lin, Z., Lin, H., Zhao, L., and Huang, W. (2021). CircRNA_103615 contributes to tumor progression and cisplatin resistance in NSCLC by regulating ABCB1. Exp. Ther. Med. 22, 934. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10366
Lin, C., and Yang, L. (2018). Long noncoding RNA in cancer: wiring signaling circuitry. Trends. Cell. Biol. 28, 287–301. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2017.11.008
Liu, F., Gao, S., Yang, Y., Zhao, X., Fan, Y., Ma, W., et al. (2018b). Antitumor activity of curcumin by modulation of apoptosis and autophagy in human lung cancer A549 cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Rep. 39, 1523–1531. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6188
Liu, G., Pei, F., Yang, F., Li, L., Amin, A., Liu, S., et al. (2017). Role of autophagy and apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 367. doi:10.3390/ijms18020367
Liu, J., Xing, Y., and Rong, L. (2018a). MiR-181 regulates cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer via downregulation of autophagy through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol. Rep. 39, 1631–1639. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6268
Liu, R., Chen, Z., Hu, G., Yu, Z., Li, Q., Liu, D., et al. (2023a). A novel PDK1/MEK dual inhibitor induces cytoprotective autophagy via the PDK1/Akt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharm. (Basel) 16, 244. doi:10.3390/ph16020244
Liu, X., Zhang, X., and Du, S. (2022). Long non-coding RNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits the cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells through inhibiting autophagy by suppressing TSC2. Cell. Cycle. 21, 368–378. doi:10.1080/15384101.2021.2020433
Liu, Y., Hu, Y., Zhao, C., and Lu, Q. (2023b). CircRNA B cell linker regulates cisplatin sensitivity in nonsmall cell lung cancer via microRNA-25-3p/BarH-like homeobox 2 axis. Anticancer. Drugs. 34, 640–651. doi:10.1097/cad.0000000000001349
Liu, Y., and Mao, J. (2024). Progress of immunotherapy in EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo. Fei. Ai. Za. Zhi. 26, 934–942. doi:10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.106.26
Lobera, E. S., Varela, M. A., Jimenez, R. L., and Moreno, R. B. (2023). MiRNA as biomarker in lung cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 50, 9521–9527. doi:10.1007/s11033-023-08695-9
Lu, C., Yu, R., Zhang, C., Lin, C., Dou, Y., Wu, D., et al. (2022). Protective autophagy decreases lorlatinib cytotoxicity through Foxo3a-dependent inhibition of apoptosis in NSCLC. Cell. death. Discov. 8, 221. doi:10.1038/s41420-022-01027-z
Lu, H., Han, X., Ren, J., Ren, K., Li, Z., and Sun, Z. (2019). Circular RNA HIPK3 induces cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer through sponging miR-149. Cancer. Biol. Ther. 21, 113–121. doi:10.1080/15384047.2019.1669995
Lu, H., Kong, J., Cai, S., Huang, H., Luo, J., and Liu, L. (2024). Hsa_circ_0096157 silencing suppresses autophagy and reduces cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by weakening the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Mol. Biol. Rep. 51, 703. doi:10.1007/s11033-024-09552-z
Luo, D., He, F., Liu, J., Dong, X., Fang, M., Liang, Y., et al. (2024b). Pseudolaric acid B suppresses NSCLC progression through the ROS/AMPK/mTOR/autophagy signalling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 175, 116614. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116614
Luo, X., Wang, J., Wang, R., Lian, J., Guo, M., Zhou, H., et al. (2024a). SLL-1A-16 suppresses proliferation and induces autophagy in non-small-cell lung cancer cells via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. RSC. Med. Chem. 15, 3460–3468. doi:10.1039/d4md00405a
Ma, Q., Niu, R., Huang, W., Da, L., Tang, Y., Jiang, D., et al. (2020). Long Noncoding RNA PTPRG Antisense RNA 1 reduces radiosensitivity of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells via regulating miR-200c-3p/TCF4. Technol. Cancer. Res. Treat. 19, 1533033820942615. doi:10.1177/1533033820942615
Ma, Y., Feng, H., Wang, Y., Hu, L., Su, X., Li, N., et al. (2023). COTE-1 promotes the proliferation and invasion of small cell lung cancer by regulating autophagy activity via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Probes. 71, 101918. doi:10.1016/j.mcp.2023.101918
Ma, Y. S., Shi, B. W., Guo, J. H., Liu, J. B., Yang, X. L., Xin, R., et al. (2021). MicroRNA-320b suppresses HNF4G and IGF2BP2 expression to inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth of lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 42, 762–771. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgab023
Mao, S., Zheng, S., Lu, Z., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, G., et al. (2021). Exosomal miR-375-3p breaks vascular barrier and promotes small cell lung cancer metastasis by targeting claudin-1. Cancer. Res. 10, 3155–3172. doi:10.21037/tlcr-21-356
Mao, Y., and Xu, R. (2020). Circular RNA CDR1-AS contributes to pemetrexed and cisplatin chemoresistance through EGFR/PI3K signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 123, 109771. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109771
Mehta, A. K., Hua, K., Whipple, W., Nguyen, M. T., Liu, C. T., Haybaeck, J., et al. (2017). Regulation of autophagy, NF-κB signaling, and cell viability by miR-124 in KRAS mutant mesenchymal-like NSCLC cells. Sci. Signal. 10, eaam6291. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aam6291
Meng, J., Song, Z., Cong, S., Sun, Q., Ma, Q., Shi, W., et al. (2024). Regulatory role of the miR-142-3p/CDC25C axis in modulating autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. Res. 13, 552–572. doi:10.21037/tlcr-24-82
Mercer, T. R., Dinger, M. E., and Js, M. (2009). Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 155–159. doi:10.1038/nrg2521
Miller, K. D., Nogueira, L., Devasia, T., Mariotto, A. B., Yabroff, K. R., Jemal, A., et al. (2022). Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA. Cancer. J. Clin. 72, 409–436. doi:10.3322/caac.21731
Mizushima, N., Longo, D. L., and Levine, B. (2020). Autophagy in human diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1564–1576. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2022774
Mulcahy Levy, J. M., and Thorburn, A. (2019). Autophagy in cancer: moving from understanding mechanism to improving therapy responses in patients. Cell. death. Differ. 27, 843–857. doi:10.1038/s41418-019-0474-7
Nemchenko, A., Chiong, M., Turer, A., Lavandero, S., and Hill, J. A. (2011). Autophagy as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 51, 584–593. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.06.010
Ni, H., Tang, S., Lu, G., Niu, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2024). Linc00673-V3 positively regulates autophagy by promoting Smad3-mediatedLC3Btranscription in NSCLC. Life. Sci. Alliance. 7, e202302408. doi:10.26508/lsa.202302408
Niu, R., Li, D., Chen, J., and Zhao, W. (2021). Circ_0014235 confers Gefitinib resistance and malignant behaviors in non-small cell lung cancer resistant to Gefitinib by governing the miR-146b-5p/YAP/PD-L1 pathway. Cell. Cycle. 21, 86–100. doi:10.1080/15384101.2021.2009986
Ouyang, K., Xie, D., Liao, H., He, Y., and Xiong, H. (2024). Circ_0001786 facilitates gefitinib resistance and malignant progression in non-small cell lung cancer via miR-34b-5p/SRSF1. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 19, 178. doi:10.1186/s13019-024-02651-9
Pan, J., Xing, J., Yu, H., Wang, Z., Wang, W., and Pan, Y. (2023). CircRBM33 promotes migration, invasion and mediates osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell line. Ann. Transl. Med. 11, 252. doi:10.21037/atm-22-6346
Pan, Y. J., Zhuang, Y., Zheng, J. N., and Pei, D. S. (2016). MiR-106a: promising biomarker for cancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 5373–5377. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.10.042
Prenzel N, F. O., Streit, S., Hart, S., and Ullrich, A. (2001). The epidermal growth factor receptor family as a central element for cellular signal transduction and diversification. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 8, 11–31. doi:10.1677/erc.0.0080011
Qu, R., and Ma, J. (2023). Circ_0091537 promotes gefitinib chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer by mediating the miR-520h/YAP1 network. Anticancer. Drugs. 34, 1151–1161. doi:10.1097/cad.0000000000001505
Rezaei, S., Mahjoubin-Tehran, M., Aghaee-Bakhtiari, S. H., Jalili, A., Movahedpour, A., Khan, H., et al. (2020). Autophagy-related microRNAs in chronic lung diseases and lung cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 153, 103063. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.103063
Rothschild, S. I., Gautschi, O., Batliner, J., Gugger, M., Fey, M. F., and Tschan, M. P. (2017). MicroRNA-106a targets autophagy and enhances sensitivity of lung cancer cells to Src inhibitors. Lung. Cancer. 107, 73–83. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.06.004
Schmidt, L. H., Spieker, T., Koschmieder, S., Schäffers, S., Humberg, J., Jungen, D., et al. (2011). The long noncoding MALAT-1 RNA indicates a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer and induces migration and tumor growth. J. Thorac. Oncol. 6, 1984–1992. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182307eac
Shang, Q., Yang, Z., Jia, R., and Ge, S. (2019). The novel roles of circRNAs in human cancer. Mol. Cancer. 18 (9), 6. doi:10.1186/s12943-018-0934-6
Shanshan, W., Hongying, M., Jingjing, F., Yiming, Y., Yu, R., and Rui, Y. (2021). CircDTL functions as an oncogene and regulates both apoptosis and ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Front. Genet. 12, 743505. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.743505
Shi, L., Zhu, W., Huang, Y., Zhuo, L., Wang, S., Chen, S., et al. (2022). Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-20a suppresses the PTEN/PI3K-AKT pathway to promote the progression and chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 12, e989. doi:10.1002/ctm2.989
Shi, S., and Jiang, P. (2022). Therapeutic potentials of modulating autophagy in pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 156, 113967. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113967
Shimobayashi, M., and Hall, M. N. (2014). Making new contacts: the mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 155–162. doi:10.1038/nrm3757
Sholl, L. M., Aisner, D. L., Varella-Garcia, M., Berry, L. D., Dias-Santagata, D., Wistuba, I. I., et al. (2015). Multi-institutional oncogenic driver mutation analysis in lung adenocarcinoma: the lung cancer mutation consortium experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 10, 768–777. doi:10.1097/jto.0000000000000516
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Wagle, N. S., and Jemal, A. (2023). Cancer statistics, 2023. CA. Cancer. J. Clin. 73, 17–48. doi:10.3322/caac.21763
Singh, J., Hussain, Y., Meena, A., Sinha, R. A., and Luqman, S. (2024). Asiatic acid impedes NSCLC progression by inhibiting COX-2 and modulating PI3K signaling. FEBS. Lett. 598, 3036–3052. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.15027
Slack, F. J., and Chinnaiyan, A. M. (2019). The role of non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell 179, 1033–1055. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.017
Song, S., Shi, Y., Zeng, D., Xu, J., Yang, Y., Guo, W., et al. (2023). CircANKRD28 inhibits cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer through the miR-221-3p/SOCS3 axis. J. Gene. Med. 25, e3478. doi:10.1002/jgm.3478
Song, Y., Du, J., Lu, P., Zou, Q., Zeng, S., Liu, M., et al. (2021). LncRNA NFYC-AS1 promotes the development of lung adenocarcinomas through autophagy, apoptosis, and MET/c-Myc oncogenic proteins. Ann. Transl. Med. 9, 1621. doi:10.21037/atm-21-4995
Su, L., Gou, J., Zhou, C., Li, J., Wu, J., Shen, L., et al. (2024). Knockdown of circ_0076305 decreases the paclitaxel resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating TMPRSS4 via miR-936. Toxicol. Res. 13, tfae102. doi:10.1093/toxres/tfae102
Sun, W., Zu, Y., Fu, X., and Deng, Y. (2017). Knockdown of lncRNA-XIST enhances the chemosensitivity of NSCLC cells via suppression of autophagy. Oncol. Rep. 38, 3347–3354. doi:10.3892/or.2017.6056
Tang, D., Zhao, D., Wu, Y., Yao, R., Zhou, L., Lu, L., et al. (2018). The miR-3127-5p/p-STAT3 axis up-regulates PD-L1 inducing chemoresistance in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 22, 3847–3856. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13657
Tang, R. X., Chen, W. J., He, R. Q., Zeng, J. H., Liang, L., Li, S. K., et al. (2017). Identification of a RNA-Seq based prognostic signature with five lncRNAs for lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 8, 50761–50773. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.17098
Tang, Y. F., Liu, Z. H., Zhang, L. Y., Shi, S. H., Xu, S., Ma, J. A., et al. (2024). Circ_PPAPDC1A promotes osimertinib resistance by sponging the miR-30a-3p/IGF1R pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer. 23, 91. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-01998-w
Tian, X., Zhang, H., Zhang, B., Zhao, J., Li, T., and Zhao, Y. (2017). Microarray expression profile of long non-coding RNAs in paclitaxel-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 38, 293–300. doi:10.3892/or.2017.5691
Volders, P. J., Helsens, K., Wang, X., Menten, B., Martens, L., Gevaert, K., et al. (2013). LNCipedia: a database for annotated human lncRNA transcript sequences and structures. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 41, D246–D251. doi:10.1093/nar/gks915
Vos, P. D., Leedman, P. J., Filipovska, A., and Rackham, O. (2019). Modulation of miRNA function by natural and synthetic RNA-binding proteins in cancer. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 76, 3745–3752. doi:10.1007/s00018-019-03163-9
Wang, H., Du, X., Liu, W., Zhang, C., Li, Y., Hou, J., et al. (2024). Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR-TKIs exerts synergistic anti-tumor effects against wild-type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy-related cell death via EGFR signaling pathway. Respir. Res. 25, 215. doi:10.1186/s12931-024-02844-9
Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Wu, Q., Wang, Y. B., and Wang, W. (2017). MiR-16 mimics inhibit TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via activation of autophagy in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 39, 247–254. doi:10.3892/or.2017.6088
Wang, L., Zhang, Z., and Tian, H. (2022b). Hsa_circ_0092887 targeting miR-490-5p/UBE2T promotes paclitaxel resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 37, e24781. doi:10.1002/jcla.24781
Wang, L. J., Sun, G., and Chen, Y. F. (2019). LncRNA MSTO2P promotes proliferation and autophagy of lung cancer cells by up-regulating EZH2 expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 3375–3382. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201904_17701
Wang, X., Wang, H., Jiang, H., Qiao, L., and Guo, C. (2023). Circular RNAcirc_0076305 promotes cisplatin (DDP) resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating ABCC1 through miR-186-5p. Cancer. biother. Radiopharm. 38, 293–304. doi:10.1089/cbr.2020.4153
Wang, X., Zhang, H., Yang, H., Bai, M., Ning, T., Deng, T., et al. (2020). Exosome-delivered circRNA promotes glycolysis to induce chemoresistance through the miR-122-PKM2 axis in colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 14, 539–555. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.12629
Wang, X. R., Jiang, Z. B., Xu, C., Meng, W. Y., Liu, P., Zhang, Y. Z., et al. (2022a). Andrographolide suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer progression through induction of autophagy and antitumor immune response. Pharmacol. Res. 179, 106198. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106198
Wang, Y., Wu, Y., and Xie, S. (2022c). CircPTK2 inhibits cell cisplatin (CDDP) resistance by targeting miR-942/TRIM16 axis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Bioengineered 13, 3651–3664. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.2024321
Wang, Z., Liu, L., Du, Y., Mi, Y., and Wang, L. (2021). The HNF1A-AS1/miR-92a-3p axis affects the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer by competitively regulating the JNK pathway. Cell. Biol. Toxicol. 37, 715–729. doi:10.1007/s10565-021-09595-z
Wang, Z. V., Ferdous, A., and Hill, J. A. (2013). Cardiomyocyte autophagy: metabolic profit and loss. Heart. Fail. Rev. 18, 585–594. doi:10.1007/s10741-012-9350-y
Weber, D. G., Johnen, G., Casjens, S., Bryk, O., Pesch, B., Jöckel, K. H., et al. (2013). Evaluation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 as a candidate blood-based biomarker for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC. Res. Notes. 6, 518. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-6-518
Wei, H., Li, L., Zhang, H., Xu, F., Chen, L., Che, G., et al. (2021). Circ-FOXM1 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer development by regulating the miR-149-5p/ATG5 axis. Cell. Cycle. 20, 166–178. doi:10.1080/15384101.2020.1867780
Wei, S. L., Ye, J. J., Sun, L., Hu, L., Wei, Y. Y., Zhang, D. W., et al. (2023). Exosome-derived circKIF20B suppresses gefitinib resistance and cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. Cell. Int. 23, 129. doi:10.1186/s12935-023-02974-y
Wen, C., Li, Y., Huang, Y., Wang, N., He, S., Bao, M., et al. (2023). CircSETD3 mediates acquired resistance to gefitinib in non-small lung cancer cells by FXR1/ECT2 pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 154, 106344. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2022.106344
Wen, S., Dai, L., Wang, L., Wang, W., Wu, D., Wang, K., et al. (2019). Genomic signature of driver genes identified by target next-generation sequencing in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 24, e1070–e1081. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0572
Wu, J., H, X., Li, X., Zhou, H., Chen, X., Chen, Y., et al. (2024). Suppression of the long non-coding RNA LINC01279 triggers autophagy and apoptosis in lung cancer by regulating FAK and SIN3A. Discov. Oncol. 15, 3. doi:10.1007/s12672-023-00855-4
Xia, H., Green, D. R., and Zou, W. (2021). Autophagy in tumour immunity and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 21, 281–297. doi:10.1038/s41568-021-00344-2
Xia, H., Qu, X., Liu, L. Y., Qian, D. H., and Jing, H. Y. (2018). LncRNA MEG3 promotes the sensitivity of vincristine by inhibiting autophagy in lung cancer chemotherapy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 22, 1020–1027. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201802_14384
Xia, S., and Wang, C. (2023). Hsa_circ_0003489 drives PTX resistance of human NSCLC cells through modulating miR-98-5p/IGF2. Pharmacogenomics. Pers. Med. 16, 805–815. doi:10.2147/pgpm.S416360
Xiao, Z., Li, M., Zhang, X., Rong, X., and Xu, H. (2023). TRIP13 overexpression promotes gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via regulating autophagy and phosphorylation of the EGFR signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 49, 84. doi:10.3892/or.2023.8521
Xie, H., Yao, J., Wang, Y., and Ni, B. (2022a). Exosome-transmitted circVMP1 facilitates the progression and cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-524-5p-METTL3/SOX2 axis. Drug. Deliv. 29, 1257–1271. doi:10.1080/10717544.2022.2057617
Xie, Y., Zheng, Z. W., He, H. T., and Chang, Z. B. (2022b). LncRNA NEAT1 induces autophagy through the miR-128-3p/ADAM28 axis to suppress apoptosis of nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Kaohsiung. J. Med. Sci. 38, 933–949. doi:10.1002/kjm2.12582
Xin, R., Hu, B., Qu, D., and Chen, D. (2023). WITHDRAWN: oncogenic lncRNA MALAT-1 recruits E2F1 to upregulate RAD51 expression and thus promotes cell autophagy and tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther., 102199. doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2023.102199
Xu, H., Wang, J., Al-Nusaif, M., Ma, H., and Le, W. (2023). CCL2 promotes metastasis and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer via PI3K/Akt/mTOR and autophagy pathways. Cell. Prolif. 57, e13560. doi:10.1111/cpr.13560
Xu, M., Zhao, M., Zhu, M., Yuan, H., Li, Z., Yan, P., et al. (2024). Hibiscus manihot L. flower extract induces anticancer activity through modulation of apoptosis and autophagy in A549 cells. Sci. Rep. 14, 8102. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-58439-3
Xu, X., Zhou, X., Chen, Z., Gao, C., Zhao, L., and Cui, Y. (2020). Silencing of lncRNA XIST inhibits non-small cell lung cancer growth and promotes chemosensitivity to cisplatin. Aging (Albany NY) 12, 4711–4726. doi:10.18632/aging.102673
Xuan, X., Wang, Z., and Wang, Y. (2022). Circ_0058608 contributes to the progression and taxol resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by sponging miR-1299 to upregulate GBP1. Anticancer. Drugs 34, 103–114. doi:10.1097/cad.0000000000001346
Yan, T., Tian, X., Liu, F., Liu, Q., Sheng, Q., Wu, J., et al. (2022). The emerging role of circular RNAs in drug resistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 12, 1003230. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1003230
Yang, J., Lin, J., Liu, T., Chen, T., Pan, S., Huang, W., et al. (2014). Analysis of lncRNA expression profiles in non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) and their clinical subtypes. Cancer 85, 110–115. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.05.011
Yang, Q., Yong, X., Chen, X., Huang, R., Wang, X., Xu, Z., et al. (2024). LINC00941 is a diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis through cell autophagy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 28, e70076. doi:10.1111/jcmm.70076
Yang, X. P., Zheng, Y. Z., Tan, J., Tian, R. J., Shen, P., Cai, W. J., et al. (2022). Circ_0020123 regulates autophagy, glycolysis, and malignancy by upregulating IRF4 through eliminating miR-193a-3p-mediated suppression of IRF4 in non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasma 69, 392–403. doi:10.4149/neo_2022_211013N1449
Yang, Y., Jiang, C., Yang, Y., Guo, L., Huang, J., Liu, X., et al. (2018). Silencing of LncRNA-HOTAIR decreases drug resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer cells by inactivating autophagy via suppressing the phosphorylation of ULK1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 497, 1003–1010. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.141
Yao, J., Zhang, H. Y., Gu, S., Zou, J. L., Zhang, Q., and Qu, R. C. (2023). Circular RNA-AnnexinA7 accelerates cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via modulating microRNA-545-3p to mediate Cyclin D1. Acta. Biochim. Pol. 70, 295–304. doi:10.18388/abp.2020_6539
Ye, Z., Fang, B., Pan, J., Zhang, N., Huang, J., Xie, C., et al. (2017). MiR-138 suppresses the proliferation, metastasis and autophagy of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting Sirt1. Oncol. Rep. 37, 3244–3252. doi:10.3892/or.2017.5619
Yu, J. J., Zhou, D. D., Cui, B., Zhang, C., Tan, F. W., Chang, S., et al. (2020). Disruption of the EGFR-SQSTM1 interaction by a stapled peptide suppresses lung cancer via activating autophagy and inhibiting EGFR signaling. Cancer. Lett. 474, 23–35. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.01.004
Yu, S., Wang, M., Zhang, H., Guo, X., and Qin, R. (2021a). Circ_0092367 inhibits EMT and gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via regulating the miR-1206/ESRP1 axis. Genes 12, 1701. doi:10.3390/genes12111701
Yu, X., Fu, X., Zhang, X., Bai, C., and Wang, Y. (2021b). Circ_0001658 regulates gefitinib resistance of non-small cell lung cancer through miR-409-3p/TWIST1 axis. Anticancer. Drugs . 33, 158–166. doi:10.1097/cad.0000000000001257
Yuwen, D. L., Sheng, B. B., Liu, J., Wenyu, W., and Shu, Y. Q. (2017). MiR-146a-5p level in serum exosomes predicts therapeutic effect of cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 21, 2650–2658.
Zeng, Q., Wan, H., Zhao, S., Xu, H., Tang, T., Oware, K. A., et al. (2020). Role of PIWI-interacting RNAs on cell survival: proliferation, apoptosis, and cycle. IUBMB. Life. 72, 1870–1878. doi:10.1002/iub.2332
Zhang, F., Cheng, R., Li, P., Lu, C., and Zhang, G. (2021b). Hsa_circ_0010235 functions as an oncogenic drive in non-small cell lung cancer by modulating miR-433-3p/TIPRL axis. Cancer. Cell. Int. 21, 73. doi:10.1186/s12935-021-01764-8
Zhang, F., Zhang, T., Zhao, Z., Ji, Y., Peng, Y., and Zhao, L. (2022c). Circular RNA Eps15-homology domain containing protein 2 motivates proliferation, glycolysis but refrains autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer via crosstalk with microRNA-3186-3p and forkhead box K1. Bioengineered 13, 6464–6475. doi:10.1080/21655979.2022.2031385
Zhang, H., Huang, T., Yuan, S., Long, Y., Tan, S., Niu, G., et al. (2022b). Circ_0020123 plays an oncogenic role in non-small cell lung cancer depending on the regulation of miR-512-3p/CORO1C. Thorac. Cancer. 13, 1406–1418. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.14408
Zhang, J., Qu, Z., Xiao, X., Adelson, D. L., Wang, F., Wei, A., et al. (2025). A novel sensitizer reduces EGFR-TKI resistance by regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and autophagy. Heliyon 11, e41104. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41104
Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Xia, S., Yang, L., Wu, D., Zhou, Y., et al. (2020b). Long noncoding RNA PANDAR inhibits the development of lung cancer by regulating autophagy and apoptosis pathways. J. Cancer 11, 4783–4790. doi:10.7150/jca.45291
Zhang, L., Wu, Y., Hou, C., and Li, F. (2022a). Circ_0072088 knockdown contributes to cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits tumor progression by miR-944/LASP1 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Gene. Med. 24, e3414. doi:10.1002/jgm.3414
Zhang, L. L., Bao, H., Xu, Y. L., Jiang, X. M., Li, W., Zou, L., et al. (2020a). Phanginin R induces cytoprotective autophagy via JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Med. Chem. 20, 982–988. doi:10.2174/1871520620666200414095828
Zhang, R., Zheng, Y., Zhu, Q., Gu, X., Xiang, B., Gu, X., et al. (2024). β-Elemene reverses gefitinib resistance in NSCLC cells by inhibiting lncRNA H19-mediated autophagy. Pharmaceuticals 17, 626. doi:10.3390/ph17050626
Zhang, W., Dong, Y. Z., Du, X., Peng, X. N., and Shen, Q. M. (2019a). MiRNA-153-3p promotes gefitinib-sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting ATG5 expression and autophagy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 2444–2452. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201903_17391
Zhang, W., Song, C., and Ren, X. (2021a). Circ_0003998 regulates the progression and docetaxel sensitivity of DTX-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells by the miR-136-5p/CORO1C axis. Technol. Cancer. Res. Treat. 20, 1533033821990040. doi:10.1177/1533033821990040
Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Hui, B., Sun, W., Li, B., Shi, F., et al. (2019b). Pristimerin enhances the effect of cisplatin by inhibiting the miR-23a/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway and suppressing autophagy in lung cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 43, 1382–1394. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4057
Zhao, H., Yan, P., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, M., Wang, Z., et al. (2019). Clinical significance of tumor miR-21, miR-221, miR-143, and miR-106a as biomarkers in patients with osteosarcoma. Inter. J. Biol. Markers. 34, 184–193. doi:10.1177/1724600819843537
Zhao, W., An, Y., and Liang, Y.XW., X (2014). Role of HOTAIR long noncoding RNA in metastatic progression of lung cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 18, 1930–1936.
Zheng, F., and Xu, R. (2020). CircPVT1 contributes to chemotherapy resistance of lung adenocarcinoma through miR-145-5p/ABCC1 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 124, 109828. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109828
Zheng, S., Wang, C., Yan, H., and Du, Y. (2021). Blocking hsa_circ_0074027 suppressed non-small cell lung cancer chemoresistance via the miR-379-5p/IGF1 axis. Bioengineered 12, 8347–8357. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1987053
Zheng, T., Li, D., He, Z., Feng, S., and Zhao, S. (2018). Long noncoding RNA NBAT1 inhibits autophagy via suppression of ATG7 in non-small cell lung cancer. Am. J. Cancer. Res. 8, 1801–1811.
Zhong, Y., Lin, H., Li, Q., Liu, C., and Shen, J. (2021). CircRNA_100565 contributes to cisplatin resistance of NSCLC cells by regulating proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy via miR-337-3p/ADAM28 axis. Cancer. Biomark. 30, 261–273. doi:10.3233/cbm-201705
Zhu, F., Niu, R., Shao, X., and Shao, X. (2021). FGD5-AS1 promotes cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cell via the miR-142-5p/PD-L1 axis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 47, 523–532. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4816
Keywords: lung cancer, autophagy, non-coding RNA, therapeutic target, chemoresistance
Citation: Li J, Gan J, Shi S, Huang J and Yang Y (2025) The potential of targeting autophagy-related non-coding RNAs in the treatment of lung cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1551258. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1551258
Received: 25 December 2024; Accepted: 30 April 2025;
Published: 14 May 2025.
Edited by:
Valerie R. Wiersma, University Medical Center Groningen, NetherlandsReviewed by:
Alejandro A. Canales-Aguirre, CONACYT Centro de Investigación y Asistencia en Tecnología y Diseño del Estado de Jalisco (CIATEJ), MexicoTupa Basuroy, Cleveland Clinic Foundation Lerner Research Institute, United States
Copyright © 2025 Li, Gan, Shi, Huang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Yang, eXl4cG93ZXJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Juan Li
Juan Li Jimei Gan1,2†
Jimei Gan1,2† Yong Yang
Yong Yang