- Department of Medical Oncology, The Quzhou Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Quzhou People’s Hospital, Quzhou, Zhejiang, China
Background: For advanced biliary tract cancer (BTC) patients with BRCA pathogenic variants who have failed first-line treatment, the optimal treatment strategy remains to be established. Olaparib, the first FDA-approved poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase inhibitors (PARPi), is commonly utilized in clinical practice for breast, ovarian, prostate, and pancreatic cancers that harbor germline or somatic BRCA pathogenic variants through a mechanism known as “synthetic lethality”. However, the proportion of BTC patients with BRCA pathogenic variants is relatively low, estimated at approximately 1%–7% of all BTC cases, leading to inconclusive evidence regarding the efficacy of targeted therapy with PARPi for these patients.
Case presentation: We presented a case of a patient with advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) harboring dual somatic homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene pathogenic variants, specifically BRCA1 and PALB2, who achieved PR lasting approximately 7 months following salvage treatment with olaparib.
Conclusion: We considered that the BTC population with dual HRR pathogenic variants, which include a BRCA pathogenic variant, might represent an advantageous cohort for olaparib treatment. Furthermore, in addition to BRCA pathogenic variant, PALB2 pathogenic variant may potentially serve as the next clinical predictive target for PARP inhibitors in the BTC population. A systematic summary and analysis of existing studies on BTC patients with pathogenic variants indicate that these patients might derive benefits from olaparib; however, further validation in a larger cohort is necessary.
Highlights
• BRCA1 and PALB2 double HRR gene mutations may be associated with an increased risk of resistance to chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors in ICCA patients, while potentially enhancing sensitivity to PARP inhibitor (PARPi) treatment.
• BTC patients with BRCA1/2 mutations may derive clinical benefit from PARPi therapy, and those harboring dual HRR gene mutations (including one BRCA variant) might represent a subgroup worthy of further investigation as potential beneficiaries of PARPi.
• These findings underscore the possible importance of individualized treatment strategies guided by molecular profiling in the second-line setting. Furthermore, PALB2 mutations may emerge as a promising predictive biomarker following BRCA in the context of BTC, pending further validation in larger cohorts.
Introduction
Biliary tract cancer (BTC) is the second most common primary liver tumor (Vogel et al., 2023). Due to its highly invasive, occult, and heterogeneous nature, the prognosis is very poor, with a five-year survival rate of approximately 5% (Zhang et al., 2021). In clinical practice, BTC is categorized into intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA), extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (eCCA), and gallbladder carcinoma (GBC) based on anatomical tumor localization, which accounts for 10%–20%, 20%–30%, and 50%–60% of BTC, respectively (Banales et al., 2020; Javle et al., 2022). In recent years, the mortality rate of iCCA has been rising, reaching approximately 1–2 deaths per 100,000 population, thereby contributing significantly to the overall BTC mortality (Bertuccio et al., 2019). Unfortunately, iCCA typically presents symptoms only in its late stages, rendering surgical intervention impractical for achieving curative outcomes; moreover, the recurrence rate exceeds 75% within 2 years post-surgery (Z et al., 2018). Consequently, palliative systemic chemotherapy remains the standard first-line treatment. However, due to the high heterogeneity of iCCA, patients often develop resistance to standard therapies rapidly, leading to a median survival rate of only 6 months (Kang et al., 2022).
The genetic landscape of BTC has been extensively analyzed, revealing that nearly 40% of patients harbor potentially targetable genetic alterations (Harding et al., 2023). Among these, iCCA harbors more actionable pathogenic variants compared to eCCA and GBC, with common pathogenic variants including IDH1/2 (15%), BAP1 (11%), and FGFR2 alterations (10%) (Goyal et al., 2021; Deiana et al., 2024). For the high-frequency pathological pathogenic variants, several targeted drugs have been approved by the FDA for follow-up treatment, including pemigatinib (Abou-Alfa et al., 2020a), futibatinib (Goyal et al., 2023), and infigratinib (Javle et al., 2021) for FGFR2 fusions, entrectinib for NTRK fusions (Doebele et al., 2020), as well as ivosidenib for IDH1 pathogenic variants (Abou-Alfa et al., 2020b). These targeted therapies offer longer-lasting benefits compared to traditional chemotherapy. Consequently, for patients with advanced iCCA who have failed first-line treatment, the development of individualized treatment plans based on molecular profiling results appears promising. However, the patients carrying BRCA pathogenic variants is relatively small, comprising only 4% of iCCA cases, leading to inconclusive evidence regarding the efficacy of targeted therapy with poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) for these patients (Deiana et al., 2024). Herein, we present the first case of a patient with advanced ICCA harboring dual somatic homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene pathogenic variants (BRCA1 and PALB2) who achieved a partial response following olaparib salvage treatment.
Case presentation
A 62-year-old Chinese woman was admitted to Quzhou People’s Hospital on 24 December 2022, due to paroxysmal pain in the right upper abdomen for nearly 1 month. She had no history of smoking, alcohol use, significant comorbidities, or a family history of cancer. The next day, a contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen revealed a mass-like low-density shadow measuring approximately 6.1 × 4.9 cm in the right hepatic lobe of the liver, accompanied by mild dilation of the distal intrahepatic bile duct. A chest CT and an enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain showed no evidence of metastasis. Subsequently, the patient underwent an extended anatomical middle hepatic lobectomy (including segment IV, segment V, segment VIII, and the paracaval portion of the caudate lobe), combined with resection of the first and second hepatic portal vessels and biliary stricture reconstruction (partial resection and reshaping of the right anterior and posterior bile ducts), as well as lymphadenectomy of the hepatoduodenal ligament on 29 December 2022. The surgery was successfully completed, achieving an R0 resection with negative margins. Postoperative pathological and immunohistochemical analysis confirmed the diagnosis of moderately differentiated cholangiocarcinoma. Immunohistochemistry findings were as follows: CK7 (positive), CK19 (positive), CK20 (positive), CK18 (positive), Hepatocyte (negative), AFP (negative), GPC-3 (negative), CD34 (negative), CD10 (focally positive), CDX-2 (negative); Ki-67 (positive, 60%), and PD-L1 expression of <1%. The results of the next-generation sequencing (NGS) were as follows: BRCA1 (exon 10, p.Q1111fs, VAF: 19.7%), PALB2 (exon 9, p.E956*, VAF: 19.8%), and TP53 (exon 5, p.Q165fs, VAF: 33.6%). Based on these findings, a diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma was made and staged as T4NxM0 according to the 8th edition of the AJCC. The patient received the first postoperative immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy on 28 January 2023, which was tislelizumab (IV 200 mg) + gemcitabine (IV 800 mg on DAY 1/600 mg DAY 8) + oxaliplatin (IV 100 mg day 1). However, due to significant bone marrow suppression, the patient was subsequently treated with four cycles of tislelizumab (IV 200 mg on day 1, every 14 days), S-1 (IV 400 mg DAY2-15, every 14 days), oxaliplatin (IV 100 mg on day 1, every 14 days). Due to right-sided chest pain for 1 week, a repeated chest CT scan was performed on 8 August 2023. The results revealed the right seventh rib exhibited thickening and increased density, accompanied by swelling of the surrounding soft tissue. The patient subsequently underwent stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in this area, with a prescribed dose of 35 Gy in 5 fractions (7 Gy per fraction). The following abdominal CT scan on 11 November 2023, revealed mild dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct, after which the patient received a radiotherapy regimen of 50Gy/2Gy/25f. Due to frequent low back pain, the patient underwent a lumbar spine MRI on 23 January 2024. The MRI revealed multiple patchy shadows in thoracic vertebrae 1, thoracic vertebrae 6–11, and the lumbar vertebrae. Following this, he received a single dose of tislelizumab (200 mg) and a follow-up SBRT treatment regimen of 30 Gy delivered in 3 Gy fractions over 10 sessions. Unfortunately, abdominal CT on 15 March 2024, revealed multiple new metastatic clusters (Figures 1A,B). Given the NGS result and the patient’s ECOG performance status of 2, as well as his strong desire to continue active treatment, we initiated salvage therapy with olaparib, an oral PARP inhibitor targeting BRCA, administered at 150 mg twice daily. Subsequent abdominal CT scans conducted on April 30 (Figures 1C,D)and 4 June 2024 (Figures 1E,F), demonstrated tumor regression, achieving a partial response (PR) according to the RECIST 1.1 criteria. The patient maintained PR without radiographic progression until treatment discontinuation in October 2024 (Figures 1G,H), when therapy was switched to traditional Chinese medicine due to financial limitations. Importantly, the patient tolerated olaparib well, with no treatment-related adverse events reported throughout the course of therapy. Concurrently, notable reductions in tumor markers CA199 and CA153 were observed during olaparib therapy (Figure 2), along with improvement in the patient’s performance status. Unfortunately, he passed away in December 2024 from type II respiratory failure secondary to pneumonia. A summary of the diagnostic approach, treatment regimens, and changes in targeted lesions is presented in Figure 3.
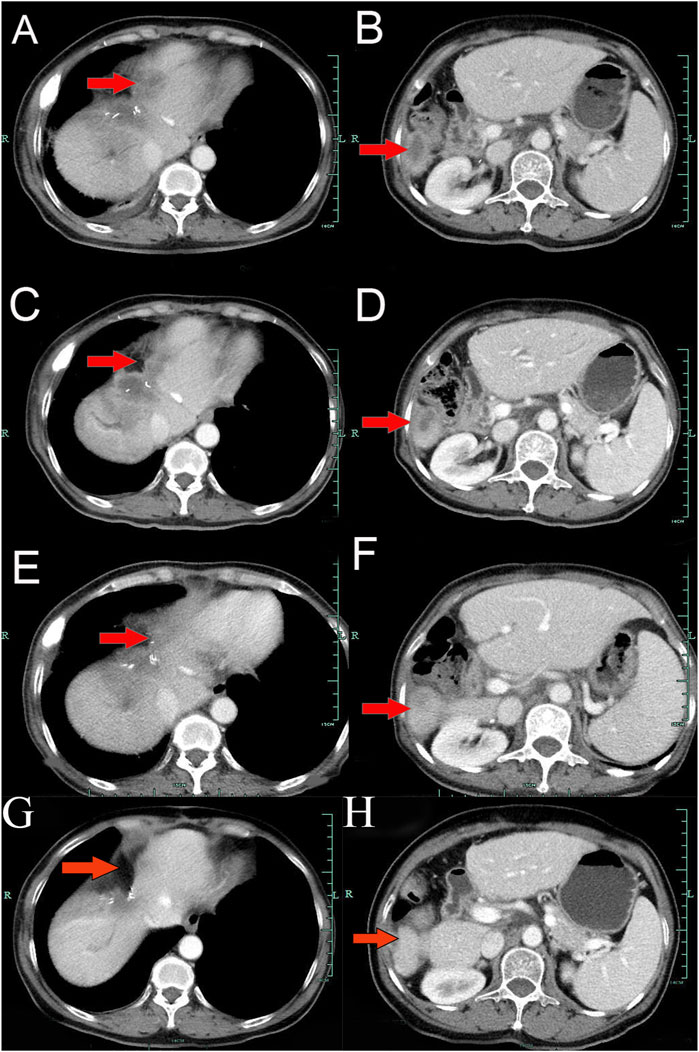
Figure 1. Variations of occupation on Liver areas by CT images during the treatment (red arrowheads). (A,B), March 2024. (C,D), April 2024. (E,F), June 2024. (G,H), October 2024.
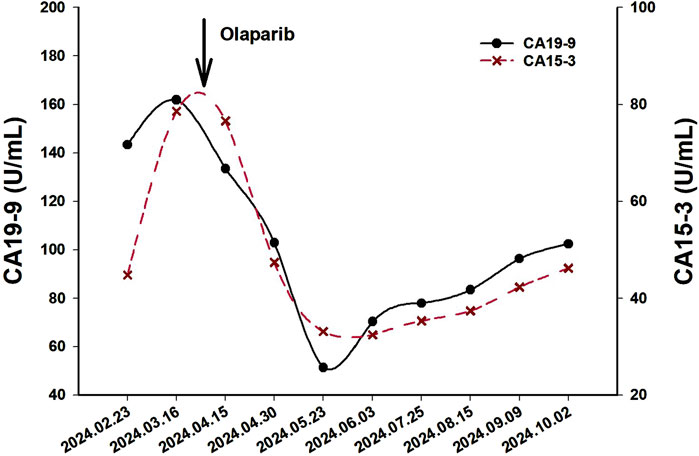
Figure 2. The variations of tumor marker CA19-9 (normal range 0–37 U/mL) and CA15-3 (normal range 0–25 U/mL) from February 23rd to 3 June 2024.
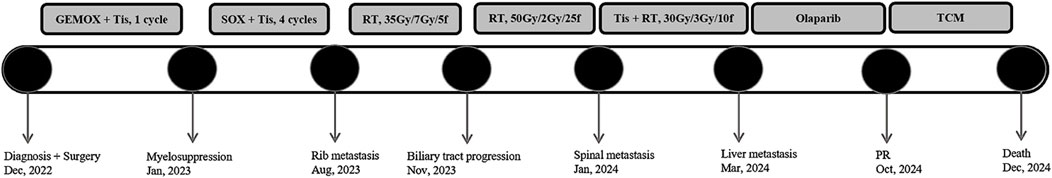
Figure 3. The overview of the approaches to diagnosis, and treatment regimens for each regimen. Abbreviations: GEMOX, Gemcitabine + Oxaliplatin; Tis, Tislelizumab; RT, Radiotherapy; SOX, S-1 +; Oxaliplatin; PR, Partial Response; TCM, Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Discussion
In this report, we presented a case of a patient with advanced ICCA harboring dual somatic HRR gene pathogenic variants, specifically BRCA1 and PALB2, who achieved PR lasting approximately 7 months following salvage treatment with olaparib. Given the notable efficacy observed and thought-provoking nature of this case, we encourage future studies to focus more on BRCA, PALB2, and other HRR pathogenic variants in the BTC population, to broaden the effective targets of PARPi for BTC patients and clarify the characteristics of the beneficial subgroup.
HRR is a critical pathway in the DNA damage response, primarily responsible for repairing DNA double-strand breaks to maintain genomic stability (Qian et al., 2024). BRCA1 and BRCA2 are essential genes involved in HRR, alongside several other important genes, such as PALB2, ATM, and BRIP1 (Ricci et al., 2020). Pathogenic variants in these genes can result in homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) and heightened genetic instability, thereby facilitating the occurrence and progression of various cancers, including breast, ovarian, prostate, and pancreatic cancer. Olaparib, the first FDA-approved PARPi, specifically targets the PARP enzyme, resulting in the accumulation of DNA damage and subsequent apoptosis of cancer cells with HRR gene pathogenic variants, a mechanism known as synthetic lethality. Additionally, current studies have also shown that BRCA gene pathogenic variants are the best clinical biomarkers for response to PARPi among HRR gene pathogenic variants (Wagener-Ryczek et al., 2021).
The current research on olaparib focuses on expanding its therapeutic applications to additional tumor types that may benefit from this treatment and explore other pathological targets. Notably, a deeper understanding of PARPi has revealed that in addition to its efficacy against conventional tumors with BRCA pathogenic variants, cancer patients with PALB2 pathogenic variants also appear to derive benefit from this therapy. For example, olaparib can significantly enhance progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer who carry HRR gene alterations, including PALB2 (de Bono et al., 2020). Additionally, in a Phase II study investigating the efficacy of maintenance rucaparib in patients with platinum-sensitive advanced pancreatic cancer harboring pathogenic germline or somatic variants, two PR and one complete response (CR) were observed in six patients with germline PALB2 pathogenic variants (gPALB2m) following rucaparib treatment (Reiss et al., 2021). In a Phase II study of olaparib for treating metastatic breast cancer associated with HRR gene pathogenic variants, 9 out of the 11 patients with gPALB2m achieved PR, while 2 patients exhibited stable disease (SD) (Tung et al., 2020). Notably, this study also included two patients with somatic PALB2 pathogenic variants (sPALB2m), both of whom achieved SD after olaparib treatment. Simultaneously, the updated ACMG guideline highlights that PALB2 variants confer breast and ovarian cancer risks comparable to BRCA1/2 and recommends reporting these variants as secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing (Miller et al., 2021). Consequently, these findings suggest that PALB2 might become the next key biomarker for PARPi after BRCA.
With the increasing number of studies reporting on BTC associated with BRCA pathogenic variants in recent years, targeted therapy has assumed a pivotal role in treatment. This development is encouraging for BTC patients with limited treatment options in the late stages of the disease and indicates that BTC may also benefit from PARPi. A search in Medline and Embase using the keywords “BRCA,” “BRCA1,” “BRCA2,” “PALB2,” “cholangiocarcinoma,” “Biliary tract cancer,” and “gallbladder carcinoma” identified 22 studies with 56 BTC cases (Table 1), the largest and most recent review to date, covering cases published between 2015 and 2024 (Zhang et al., 2021; Prabhakar et al., 2024; Smith et al., 2023; Almujarkesh et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023; Costa et al., 2023; Kim et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2022; Su et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2016; Thavaneswaran et al., 2023; Joris et al., 2023; He et al., 2022; Yamashita et al., 2023; Dong et al., 2023; Rimini et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021; Xiong et al., 2020; Cheng et al., 2018; Sharma et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2024; Golan et al., 2017). As shown in Table 1, the patient’s age ranged from 39 to 79 years, and a male-to-female ratio of 24:9, of which 32 cases had unclear age and 23 had unclear gender. The pathogenic variant distribution included 12 sBRCA1m, 10 sBRCA2m, 5 gBRCA1m, 7 gBRCA1m, 1 sPALB2m, 3 structural variants BRCA, 1 double BRCA1/2 pathogenic variant, 1 germline and somatic BRCA2 pathogenic variant, and 15 BRCA pathogenic variants for which detailed information was not available. Most patients received PARPi monotherapy or combined immunotherapy, while fewer received platinum-based chemotherapy. Interestingly, PD-1 inhibitors and PARPi appeared in the treatment of 4 of the five CR patients, with 2 of them receiving a combination of Pembrolizumab and olaparib (Smith et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2022; He et al., 2022; Dong et al., 2023; Xiong et al., 2020). Additionally, Nicholas Prabhakar also reported a case of a CCA patient with BRCA1 and BRCA2 co-pathogenic variants who achieved a 15-month PFS after receiving olaparib treatment (Prabhakar et al., 2024). Moreover, Margherita Rimini reported a case of an ICCA patient harboring sPALB2m who achieved a PFS of 3.2 months following PARPi monotherapy (Rimini et al., 2022). To further illustrate the use of PARP inhibitors, Table 2 summarizes key Phase III trials of olaparib in other BRCA/HRD-driven cancers—including HRD-positive breast cancer (OLYMPiAD trial) (Tutt et al., 2021), the POLO trial in pancreatic cancer (Gola et al., 2019; Kindler et al., 2022), and BRCA1/2-mutated prostate cancer (PROfound trial) (de Bono et al., 2020)—which demonstrated significant improvements in both progression-free survival and overall survival.
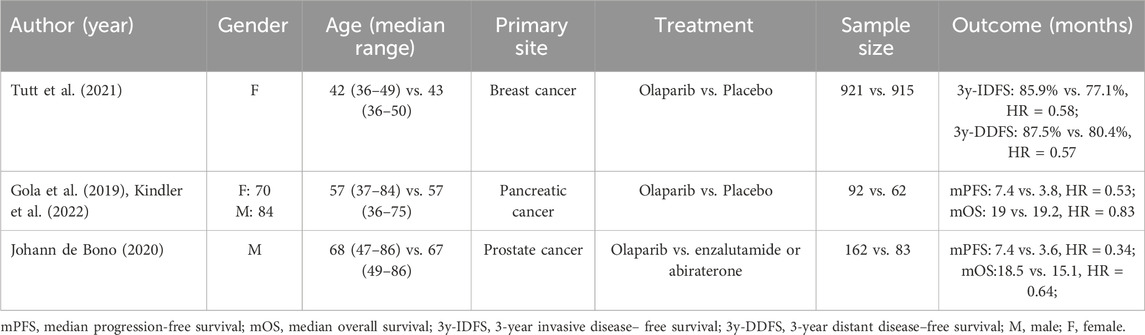
Table 2. Clinical characteristics, treatment regimens, and key outcomes of Phase III trials of olaparib in BRCA/HRD-driven cancers: breast cancer (OLYMPiAD trial), pancreatic cancer (POLO trial), and prostate cancer (PROfound trial).
As illustrated in Figure 3, this advanced patient with dual HRR pathogenic variants exhibited inadequate disease control following systemic chemotherapy and radiotherapy. We hypothesize that the presence of dual HRR pathogenic variants may exacerbate deficiencies in DNA repair function, which could enhance tumor heterogeneity, diminish tumor sensitivity to conventional treatments, and accelerate disease progression (Kiwerska and Szyfter, 2019). Concurrently, the dual pathogenic variants in HRD tumor cells may increase reliance on the PARP-mediated DNA repair mechanism, thereby enhancing the response to PARPi and ultimately resulting in PR. The above literature review indicates that both somatic and germline pathogenic variants of BRCA1/2 can respond positively to PARPi. Furthermore, a patient with a somatic PALB2 pathogenic variant exhibited similar benefits, aligning closely with the findings in this study. Simultaneously, a recent research conducted by Japanese scientists has demonstrated that pathogenic variants of PALB2 are marginally enriched in BTC, suggesting that the PALB2 gene may serve as a potential risk factor. Consequently, we propose two key perspectives: firstly, the BTC population with dual HRR pathogenic variants, one of which includes BRCA, may represent an advantageous cohort for olaparib treatment; secondly, beyond BRCA pathogenic variant, PALB2 pathogenic variant may emerge as the next clinical predictive target for PARPi in the BTC population.
This case report presents several limitations. Firstly, the generalizability of its results may be restricted, and the observed outcomes might be coincidental due to the nature of case reports. Secondly, the HRD evaluation was not conducted on this patient because there is no consensus on HRD scoring criteria. Additionally, the criterion for parameters varies across different detection methods, which further contributes to the variability and uncertainty of the findings. Furthermore, the rapid progression of the patient’s disease, coupled with multiple tumor metastases, has severely limited subsequent treatment options. Given the few reported cases of olaparib’s efficacy in treating BTC with BRCA pathogenic variants and the patient’s strong desire for survival, olaparib salvage treatment was ultimately pursued, resulting in partial remission. Lastly, the optimal treatment strategy for BTC with BRCA pathogenic variants remains to be established.
In summary, this study reported a case of ICCA harboring BRCA1 and PALB2 pathogenic variants, which exhibited rapid progression following a combination of immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy, but achieved partial response after receiving olaparib as salvage treatment. Furthermore, a systematic summary and analysis of reported BTC studies involving BRCA pathogenic variants suggest that such patients may benefit from olaparib. Currently, related clinical trials are underway, which may provide new treatment options for the BTC population, characterized by limited therapeutic alternatives and poor prognosis, and further expand the range of tumors amenable to olaparib treatment. Additionally, the PALB2 pathogenic variant may emerge as a significant clinical predictive target for PARPi in the BTC population.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethical Committee of People′s Hospital of Quzhou. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
JW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. QZ: Software, Writing – original draft. JC: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by Zhejiang Medical Health and Technology Project (2024KY1762), Science and Technology Key Project of Quzhou (2022K48), Instructional Project of Quzhou (2019ASA90177), “New 115” Talent Project of Quzhou, “551” Health High-level Talents of Zhejiang Province, and “258” Talent Project of Quzhou.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient for her participation and agreement to publication of the report. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abou-Alfa, G. K., Macarulla, T., Javle, M. M., Kelley, R. K., Lubner, S. J., Adeva, J., et al. (2020b). Ivosidenib in IDH1-mutant, chemotherapy-refractory cholangiocarcinoma (ClarIDHy): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Oncology 21, 796–807. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30157-1
Abou-Alfa, G. K., Sahai, V., Hollebecque, A., Vaccaro, G., Melisi, D., Al-Rajabi, R., et al. (2020a). Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Oncology 21, 671–684. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30109-1
Almujarkesh, M. K., Damughatla, A. R., Bathla, J., Sugg, K., LaBuda, D., Alkassis, S., et al. (2023). Primary squamous cell biliary carcinoma with liver metastasis is rare but malicious. Gastroenterology Res. 16, 276–279. doi:10.14740/gr1637
Banales, J. M., Marin, J. J. G., Lamarca, A., Rodrigues, P. M., Khan, S. A., Roberts, L. R., et al. (2020). Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: the next horizon in mechanisms and management. Gastroenterology & hepatology 17, 557–588. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-0310-z
Bertuccio, P., Malvezzi, M., Carioli, G., Hashim, D., Boffetta, P., El-Serag, H. B., et al. (2019). Global trends in mortality from intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. hepatology 71, 104–114. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.013
Chen, Y., Fan, X., Lu, R., Zeng, S., and Gan, P. (2024). PARP inhibitor and immune checkpoint inhibitor have synergism efficacy in gallbladder cancer. Genes Immun. 25, 307–316. doi:10.1038/s41435-024-00280-9
Cheng, Y., Zhang, J., Qin, S. K., and Hua, H. Q. (2018). Treatment with olaparib monotherapy for BRCA2-mutated refractory intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a case report. OncoTargets Ther. 11, 5957–5962. doi:10.2147/OTT.S176914
Costa, B. A., Tallón de Lara, P., Park, W., Keane, F., Harding, J. J., and Khalil, D. N. (2023). Durable response after olaparib treatment for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma with germline BRCA2 mutation. Oncol. Res. Treat. 46, 211–215. doi:10.1159/000529919
de Bono, J., Mateo, J., Fizazi, K., Saad, F., Shore, N., Sandhu, S., et al. (2020). Olaparib for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 2091–2102. doi:10.1056/nejmoa1911440
Deiana, C., Ricci, C., Vahabi, M., Ali, M., Brandi, G., and Giovannetti, E. (2024). Advances in target drugs and immunotherapy for biliary tract cancer. Expert Rev. gastroenterology & hepatology 18, 605–630. doi:10.1080/17474124.2024.2416230
Doebele, R. C., Drilon, A., Paz-Ares, L., Siena, S., Shaw, A. T., Farago, A. F., et al. (2020). Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: integrated analysis of three phase 1-2 trials. Oncology 21, 271–282. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30691-6
Dong, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Q., Chen, L., Cao, G., Liu, C., et al. (2023). Triple therapy in biliary tract cancers: Gemox plus immune checkpoint inhibitor in combination with lenvatinib or NGS-guided targeted therapy. J. cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 149, 1917–1927. doi:10.1007/s00432-022-04166-z
Golan, T., Hammel, P., Reni, M., Van Cutsem, E., Macarulla, T., Hall, M. J., et al. (2019). Maintenance olaparib for germline BRCA-mutated metastatic pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 381, 317–327. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903387
Golan, T., Raitses-Gurevich, M., Kelley, R. K., Bocobo, A. G., Borgida, A., Shroff, R. T., et al. (2017). Overall survival and clinical characteristics of BRCA-associated cholangiocarcinoma: a multicenter retrospective study. Oncol. 22, 804–810. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0415
Goyal, L., Kongpetch, S., Crolley, V. E., and Bridgewater, J. (2021). Targeting FGFR inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 95, 102170. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102170
Goyal, L., Meric-Bernstam, F., Hollebecque, A., Valle, J. W., Morizane, C., Karasic, T. B., et al. (2023). Futibatinib for FGFR2-Rearranged intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 228–239. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2206834
Harding, J. J., Khalil, D. N., Fabris, L., and Abou-Alfa, G. K. (2023). Rational development of combination therapies for biliary tract cancers. J. hepatology 78, 217–228. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.09.004
He, M. Y., Yan, F. F., Cen, K. L., and Shen, P. (2022). Long survival after immunotherapy plus paclitaxel in advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a case report and review of literature. World J. Clin. cases 10, 11889–11897. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.11889
Javle, M., Lee, S., Azad, N. S., Borad, M. J., Kate Kelley, R., Sivaraman, S., et al. (2022). Temporal changes in cholangiocarcinoma incidence and mortality in the United States from 2001 to 2017. Oncol. 27, 874–883. doi:10.1093/oncolo/oyac150
Javle, M., Roychowdhury, S., Kelley, R. K., Sadeghi, S., Macarulla, T., Weiss, K. H., et al. (2021). Infigratinib (BGJ398) in previously treated patients with advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements: mature results from a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Gastroenterology & hepatology 6, 803–815. doi:10.1016/s2468-1253(21)00196-5
Joris, S., Denys, H., Collignon, J., Rasschaert, M., T'Kint de Roodenbeke, D., Duhoux, F. P., et al. (2023). Efficacy of olaparib in advanced cancers with germline or somatic mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2 and ATM, a Belgian precision tumor-agnostic phase II study. ESMO open 8, 102041. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.102041
Kang, M. J., Lim, J., Han, S. S., Park, H. M., Kim, S. W., Lee, W. J., et al. (2022). Distinct prognosis of biliary tract cancer according to tumor location, stage, and treatment: a population-based study. Sci. Rep. 12, 10206. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13605-3
Kim, H., Kim, J. Y., and Park, K. U. (2023). Clinical implications of BRCA mutations in advanced biliary tract cancer. Oncology 101, 41–48. doi:10.1159/000527525
Kindler, H. L., Hammel, P., Reni, M., Van Cutsem, E., Macarulla, T., Hall, M. J., et al. (2022). Overall survival results from the POLO trial: a phase III study of active maintenance olaparib versus placebo for germline BRCA-mutated metastatic pancreatic cancer. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 40, 3929–3939. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01604
Kiwerska, K., and Szyfter, K. (2019). DNA repair in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy-a double-edged sword. J. Appl. Genet. 60, 329–334. doi:10.1007/s13353-019-00516-9
Li, W., Ma, Z., Fu, X., Hao, Z., Shang, H., Shi, J., et al. (2021). Olaparib effectively treats local recurrence of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in a patient harboring a BRCA2-inactivating mutation: a case report. Ann. Transl. Med. 9, 1487. doi:10.21037/atm-21-3681
Miller, D. T., Lee, K., Chung, W. K., Gordon, A. S., Herman, G. E., Klein, T. E., et al. (2021). ACMG SF v3.0 list for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing: a policy statement of the American college of medical genetics and genomics (ACMG). official J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 23, 1381–1390. doi:10.1038/s41436-021-01172-3
Prabhakar, N., Chiang, H., Nabrinsky, E., and Eklund, J. (2024). Report of cholangiocarcinoma with transheterozygous BRCA1 and BRCA2 Co-mutation. Cureus 16, e60767. doi:10.7759/cureus.60767
Qian, J., Liao, G., Chen, M., Peng, R. W., Yan, X., Du, J., et al. (2024). Advancing cancer therapy: new frontiers in targeting DNA damage response. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1474337. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1474337
Reiss, K. A., Mick, R., O'Hara, M. H., Teitelbaum, U., Karasic, T. B., Schneider, C., et al. (2021). Phase II study of maintenance rucaparib in patients with platinum-sensitive advanced pancreatic cancer and a pathogenic germline or somatic variant in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2. Journal of clinical oncology. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 39, 2497–2505.
Ricci, A. D., Rizzo, A., Bonucci, C., Tober, N., Palloni, A., Mollica, V., et al. (2020). PARP inhibitors in biliary tract cancer: a new kid on the block? Medicines (Basel, Switzerland) 7
Rimini, M., Macarulla, T., Burgio, V., Lonardi, S., Niger, M., Scartozzi, M., et al. (2022). Gene mutational profile of BRCAness and clinical implication in predicting response to platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. European journal of cancer. Oxf. Engl. 1990, 232–241.
Sharma, M. B., Carus, A., Sunde, L., Hamilton-Dutoit, S., and Ladekarl, M. (2016). BRCA-associated pancreatico-biliary neoplasms: four cases illustrating the emerging clinical impact of genotyping. Acta Oncol. 55, 377–381. doi:10.3109/0284186X.2015.1044023
Smith, J. T., Sama, S., Florou, V., Nevala-Plagemann, C., and Garrido-Laguna, I. (2023). Durable response to first-line PARP inhibition in BRCA-mutated metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: case report. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 14, 2637–2643. doi:10.21037/jgo-23-425
Su, Y. L., Ng, C. T., Jan, Y. H., Hsieh, Y. L., Wu, C. L., and Tan, K. T. (2021). Remarkable response to olaparib in a patient with combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma harboring a biallelic BRCA2 mutation. OncoTargets Ther. 14, 3895–3901. doi:10.2147/OTT.S317514
Thavaneswaran, S., Kansara, M., Lin, F., Espinoza, D., Grady, J. P., Lee, C. K., et al. (2023). A signal-seeking phase 2 study of olaparib and durvalumab in advanced solid cancers with homologous recombination repair gene alterations. Br. J. cancer 129, 475–485. doi:10.1038/s41416-023-02311-0
Tung, N. M., Robson, M. E., Ventz, S., Santa-Maria, C. A., Nanda, R., Marcom, P. K., et al. (2020). TBCRC 048: phase II study of olaparib for metastatic breast cancer and mutations in homologous recombination-related genes. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 38, 4274–4282. doi:10.1200/JCO.20.02151
Tutt, A. N. J., Garber, J. E., Kaufman, B., Viale, G., Fumagalli, D., Rastogi, P., et al. (2021). Adjuvant olaparib for patients with BRCA1-or BRCA2-Mutated breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 2394–2405. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2105215
Vogel, A., Segatto, O., Stenzinger, A., and Saborowski, A. (2023). FGFR2 inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma. Annu. Rev. Med. 74, 293–306. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-042921-024707
Wagener-Ryczek, S., Merkelbach-Bruse, S., and Siemanowski, J. (2021). Biomarkers for homologous recombination deficiency in cancer. J. personalized Med. 11, 612. doi:10.3390/jpm11070612
Xie, Y., Jiang, Y., Yang, X. B., Wang, A. Q., Zheng, Y. C., Wan, X. S., et al. (2016). Response of BRCA1-mutated gallbladder cancer to olaparib: a case report. World J. gastroenterology 22, 10254–10259. doi:10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10254
Xiong, F., Gong, J., and Wang, Q. (2020). Olaparib and pembrolizumab treatment for BRCA1-Mutated and PD-L1-Positive intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma recurrence and metastasis: a case report. OncoTargets Ther. 13, 6385–6391. doi:10.2147/OTT.S250454
Yamashita, Y., Ishii, Y., Serikawa, M., Okamoto, W., Tsuboi, T., Tatsukawa, Y., et al. (2023). A case of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with a germline BRCA1 mutation. Clin. J. gastroenterology 16, 470–475. doi:10.1007/s12328-023-01772-3
Yang, J. X., Jia, Z. Y., Liu, F. T., Wu, W. G., Li, X. C., Zou, L., et al. (2023). Case report: a de novo ERBB3 mutation develops in a gallbladder cancer patient carrying BRCA1 mutation after effective treatment with olaparib. Front. Oncol. 13, 1078388. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1078388
Zhang, W., Shi, J., Wang, Y., Zhou, H., Zhang, Z., Han, Z., et al. (2021). Next-generation sequencing-guided molecular-targeted therapy and immunotherapy for biliary tract cancers. CII 70, 1001–1014. doi:10.1007/s00262-020-02745-y
Zhang, X. F., Beal, E. W., Chakedis, J., Chen, Q., Lv, Y., Ethun, C. G., et al. (2018). Defining early recurrence of hilar cholangiocarcinoma after curative-intent surgery: a multi-institutional study from the US extrahepatic biliary malignancy consortium. World J. Surg. 42, 2919–2929. doi:10.1007/s00268-018-4530-0
Zhou, T., Mahn, R., Möhring, C., Sadeghlar, F., Meyer, C., Toma, M., et al. (2022). Case report: sustained complete remission on combination therapy with olaparib and pembrolizumab in BRCA2-mutated and PD-L1-positive metastatic cholangiocarcinoma after platinum derivate. Front. Oncol. 12, 933943. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.933943
Keywords: BRCA1, PALB2, olaparib, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, efficacy, case report, literature review
Citation: Wang J, Zheng Q and Chen J (2025) The efficacy of olaparib as salvage therapy in an advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patient harboring somatic BRCA1 and PALB2 pathogenic variants: a case report and literature review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1558677. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1558677
Received: 10 January 2025; Accepted: 15 July 2025;
Published: 01 August 2025.
Edited by:
Junmin Zhang, Lanzhou University, ChinaReviewed by:
Siwanon Jirawatnotai, Mahidol University, ThailandIlektra Antonia Mavroeidi, Essen University Hospital, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zheng and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianxin Chen, Y2p4ODEzN0AxNjMuY29t
 Jian Wang
Jian Wang Qinhong Zheng
Qinhong Zheng Jianxin Chen
Jianxin Chen