Abstract
Background:
Abnormalities in trace elements and the incidence of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) have been reported in China. Zinc ions (Zn2+) are known to regulate DNA methylation by stabilizing methylase activity. However, the relationship between DNA methylation and Zn2+ dysregulation in ESCC cells remains unclear. In this study, we examined changes in the biological behavior of ESCC cells treated with or without Zn2+.
Methods:
Biological behaviour changes in ESCC cells treated with or without Zn2+ were analysed. Differences in the methylome and transcriptome of Zn2+-treated cells were determined by reduced representation bisulfite sequencing and RNA sequencing. An MTT cell viability assay was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of cisplatin combined with Zn2+.
Results:
Zn2+ can inhibit the malignant biological behaviour of ESCC cells. CpG methylation levels of promoter regions were decreased after Zn2+ treatment in both ESCC and control cells. The degree of DNA methylation of genes encoding the metal ion-binding factors MT1E, MT1H and MT1X was significantly decreased, but their RNA expression levels were significantly increased after Zn2+ treatment. Zn2+ may enhance the expression of metallothioneins (MTs) via positive feedback through methylation regulation mechanisms. In vitro assays showed that the IC50 of Zn2+ in ESCC cells was significantly lower than that in cells treated with cisplatin alone. In addition, ECa patients with high MT1E expression had a better prognosis.
Conclusion:
Zn2+ can reduce the methylation level and malignant biological behaviour of ESCC cells. The combination of Zn2+ and cisplatin increases ESCC inhibition. Further study of MTs as biomarkers and targets in ESCC is warranted.
Introduction
Oesophageal cancer (ECa) is the eighth most common cancer worldwide, with two primary histological subtypes: oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) (Sung et al., 2021). China exhibits a notably high incidence of ESCC, accounting for nearly half of all ECa-related deaths worldwide (Abnet et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2025). Although significant progress has been made in surgical and multimodal therapies, the 5-year overall survival rate remains at approximately 50% (Yang et al., 2021). One critical factor in ESCC progression is the enhanced invasive behaviour of tumor cells, which plays a major role in lymphatic metastasis. However, the molecular mechanisms driving ESCC development and aggressiveness are not fully understood (Lin et al., 2016; Chang et al., 2017). Moreover, ESCC is found at a high incidence in some areas of China, suggesting a potential interaction between related genes and the environment.
Zinc ions (Zn2+) are important trace elements necessary for the activity of ∼2000 transcription factors and more than 300 enzymes, with an important role in many physiological functions (Vallee and Falchuk, 1993; Levaot and Hershfinkel, 2018). Different organs depend on zinc in various ways, and an excess or deficiency can cause several diseases, such as dermatitis, neuropathy, metabolic bone disease, immune deficiency and cancer (Ho, 2004). Several DNA methylation-related epigenetic factors (DNMT1, DNMT3a and MeCP2) have a CXXC domain, which binds to Zn2+ and is required for catalytic activity (Yusuf et al., 2021), and intracellular Zn2+ deficiency can affect cell proliferation and the degree of DNA methylation (Chen et al., 2021; Yusuf et al., 2021). In addition, ERK-directed phosphatase PP2A activity is reduced when Zn2+ is added to cell lysates; thus, Zn2+ may influence DNMT1 via the MEK/ERK pathway (Huiliang et al., 2021; Zeng et al., 2025). Taken together, these findings suggest that there is a relationship between DNA methylation and intracellular Zn2+ abnormality-induced ESCC; however, no direct experimental data have been reported thus far. Therefore, we aimed to explore the relationship between DNA methylation and Zn2+ abnormalities in ESCC cells and its potential translational application value.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Human normal oesophageal epithelial cells (HEECs) and KYSE-450 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, United States). The ESCC cell (ECA109) was obtained from the cell bank at the Chinese Academy of Science, and the cells were authenticated by short tandem repeat. The cells were cultured in 1640 medium (Gibco, United States) supplemented with 10% FBS (Gibco, United States), 100 U/mL penicillin sodium and 100 μg/mL streptomycin sulfate (Gibco, United States) at 37°C in humidified air containing 5% CO2.
Cell treatment with zinc ions
Cells were cultured in six-well plates at 5 × 10/well. After washing twice with PBS, the cell culture medium was replaced with RPMI 1640 medium (control group) or RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 50 µM ZnSO4 (zinc ion-treated group) (Choi et al., 2018). After 48 h of culture, cells were harvested for flow cytometry or protein or nucleic acid extraction for subsequent experiments.
Flow cytometric analysis and Western blot analysis of apoptosis
Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide staining (PI) were used to evaluate the effects of zinc ions on apoptosis in ESCC and HEEC cells. After the cells were incubated with the different media for 48 h, they were collected, centrifuged, and incubated with Annexin V-FITC/PI for 15 min at room temperature in the dark, followed by BD FACSVia flow cytometry. The cells were lysed with a modified RIPA buffer in the presence of a protease inhibitor cocktail and total protein concentration was measured using the BCA assay. Next, 20 µg of protein was separated via 15% SDS - PAGE using pre-cast gels and electro-transferred to 0.22 µm PVDF membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk in TBST (Tris-buffered solution containing 0.1% Tween - 20) for 2 h at room temperature. Subsequently, the membranes were incubated with primary antibodies, namely, Anti - Cleaved PARP1 antibody ([E51], ab32064, Abcam) and BAX Polyclonal Antibody (50599-2-Ig, Proteintech), overnight at 4°C, with dilutions as per the manufacturers’ instructions. GAPDH served as the internal control. After washed with PBST three times, the membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (Proteintech, 1:5,000) for 1 h at room temperature. Protein bands were visualized and analyzed using an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) detection system.
DNA extraction and reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS)
Total DNA was extracted using a QIAamp Fast DNA Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Dusseldorf, Germany) following the manufacturer’s procedure. A260/280 ratios were assessed by spectrophotometry to determine the quality of the extracted DNA. The fragmented DNA samples were subjected to bisulfite conversion by using MspI (NEB, United States), and Accel-NGS Methyl-Seq DNA Library Kit (Swift, MI, United States) was utilized to attach adapters to single-stranded DNA fragments. The final library DNA was quantified using a Qubit fluorometer and a Quant-iT dsDNA HS Kit (ThermoFisher, Q32854). Bead-based SPRI clean-up was used to remove both oligonucleotides and small fragments and to change the buffer composition. Pair-end 2 × 150 bp (PE150) sequencing was performed using an Illumina NovaSeq™ 6000 (LC-Bio Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China). The methylation calls were filtered based on the minimum coverage >1.
RNA extraction and RNA sequencing
Total RNA was isolated and purified using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, United States) following the manufacturer’s procedure. The amount and purity of each RNA sample were quantified using a NanoDrop ND-1000 (NanoDrop, United States). RNA integrity was determined using a 2100 Bioanalyzer system. Library preparation was performed by enrichment of poly-A tailed transcripts from total RNA, and the library type was strand-specific. The average insert size for the final cDNA library was 300 ± 50 bp. Pair-end sequencing (PE150, 2 × 150 bp) was performed using an Illumina NovaSeq™ 6000 (LC-Bio Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China).
RT-qPCR
Total RNA was extracted using the FastPure Cell/Tissue Total RNA Isolation Kit V2 (Vazyme, Cat. RC112-01) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA was synthesized using the PrimeScript™ RT Master Mix (Takara, RR036A). Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was performed on a QuantStudio 5 real-time PCR system using the BrightCycle Blue Universal SYBR Green qPCR Mix with UDG (ABclonal, RK21220). The amplification reaction procedure was as follows: 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 s and 60°C for 1 min. GAPDH was used as internal control for mRNA, and relative mRNA expression levels were calculated using the 2^−ΔΔCT method. The primer sequences were as follows: MT1E forward: 5′-AAAGGGGCATCGGAGAAGTG-3′, reverse: 5′-CCAGGTTGTGCAGGTTGTTC-3′; MT1H forward: 5′-CATCTGCAAAGGGGCGTCAG-3′, reverse: 5′-CCTGGATTTTACGTGTCATTCTGT-3′; MT1X forward: 5′-CACGCTTTTCATCTGTCCCG-3′, reverse: 5′-GGTCCATTTCGAGGCAAGGA-3′; GAPDH forward: 5′-CTGAGTACGTCGTGGAGTCC-3′, reverse: 5′-GAGGCATTGCTGATGATCTTGA-3′.
Bioinformatic analysis
Cutadapt (Martin, 2011) was used to remove reads that contained adapter contamination, low-quality bases and undetermined bases. Then, sequence quality was verified using FastQC (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/). Reads that passed quality control were mapped to the Homo sapiens reference genome (GRCh38) using Bismark and Samtool (Li et al., 2009; Krueger and Andrews, 2011). For each cytosine site (or guanine corresponding to a cytosine on the opposite strand) in the reference genome sequence, the DNA methylation level was determined by the ratio of the number of reads supporting C (methylated) to that of total reads (methylated and unmethylated) using in-house scripts and MethPipe (Song et al., 2013). Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) were calculated by the R package MethylKit with default parameters (1,000 bp slide windows, 500 bp overlap, p value < 0.05) (Akalin et al., 2012).
The sequence quality of the IP and input samples was verified using fastp software (Chen et al., 2018) and HISAT2 to map reads to the H. sapiens reference genome (GRCh38) (Kim et al., 2015). Mapped reads were assembled by StringTie with default parameters, StringTiewas was used to determine the expression level of all mRNAs from the input libraries by calculating FPKM (total exon fragments/mapped reads (millions) × exon length (kB) (Pertea et al., 2015). Differentially expressed mRNAs were selected with log2 (fold change) > 1 or log2 (fold change) <−1 and p value <0.05 by the R package edgeR (Robinson et al., 2010).
Transwell migration and invasion assay
For the migration assay, cells (1 × 105) were plated in the upper chamber of a Transwell plate and cultured in serum-free medium with or without ZnSO4 for 24 h. Medium containing 10% FBS (500 µl) was added to the lower chamber to create a chemotactic gradient. Then the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with crystal violet (Beyotime). For the invasion assay, diluted Matrigel (Corning) (30 µl) was placed in the upper chamber of the Transwell plate to simulate the extracellular matrix and analyse cell invasion. five fields per membrane were selected for imaging (one central field and four peripheral fields). Cell counting was performed manually to ensure accuracy.
Wound-healing assay
ESCC cells were cultured in six-well plates at 5 × 105/well. When the cell monolayer reached 90% confluence, a uniform scratch was made with a sterile 200 μl pipette tip to create a wound gap. Cells were then washed twice with PBS to remove excess cells. Cells were treated with 50 µM ZnSO4 to be compared to the control condition. Images of the cell monolayer were taken under a microscope at 0, 12, 24, and 48 h. Wound-healing efficiency was assessed by quantifying the scratch area using ImageJ.
MTT cytotoxicity assay
We used an MTT assay to evaluate the cytotoxic effects of cisplatin in combination with Zn2+. Briefly, 2 × 104cells were seeded per well in a 96-well plate and cultured for 24 h. One group of wells received serial concentrations of cisplatin (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, and 100 µM), whereas another group was treated with 50 µM ZnSO4plus various concentrations of cisplatin (0, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, and 2.5 mM). After 48 h of incubation, the medium was replaced with fresh medium containing 2 mg/mL MTT, and plates were incubated for an additional 4 h at 37°C. The absorbance of each well was assessed at 570 nm using an ELISA plate reader (Bio-Tek Instruments) with a reference wavelength of 630 nm.
Statistical analysis
Each condition (control and Zn2+-treated) was performed in six replicates per experiment, and all experiments were repeated three times. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 20.0 statistical software and GraphPad Prism 5.0 software. Concentration differences were analysed by using the Mann–Whitney U, Friedman or Wilcoxon test. The significance of the multiple comparisons was considered statistically significant a P value less than 0.05.
Results
Zn2+ inhibits the malignant biological behaviour of ESCC cells
After 48 h of Zn2+ treatment, we analyzed apoptosis in both ESCC and HEEC cells using flow cytometry. As shown in Figure 1A, Zn2+ treatment significantly increased apoptosis in both cell types when compared to the untreated controls. Notably, the proportion of early apoptotic cells was significantly higher in ESCC than in HEEC cells. Meanwhile, Western blot analysis revealed an increase in the expression levels of BAX and cleaved PARP1 in Zn2+-treated ESCC cells compared to the control group (Figure 1B). Given that BAX is a key pro-apoptotic protein involved in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and that cleaved PARP1 is a hallmark of caspase-mediated apoptosis (Tang et al., 2019), these results suggest that Zn2+ primarily induces apoptosis through the intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway.
FIGURE 1

Zn2+ inhibits the malignant biological behaviour of ESCC cells. (A) Apoptosis of both ECA109 and HEEC cells was determined by flow cytometry-based Annexin VFITC/PI apoptosis assay 48 h after treated with or without Zn2+. Histograms show the percentage of survival and apoptotic cell number. (B) Western blot analysis indicating the expression and activation of BAX and Cleaved PRAP1 in ECA109 cells with Zn2+ treatment. GAPDH was used as a protein loading control. (C) Transwell assay of ECA109 cell lines after Zn2+ treatment. The scale bar is 100 μm. Histograms show the percentage of migrated and invasive ECA109 cell number. (D) (Top) Representative microscopy images of wound closure in Zn2+-treated ESCC cells at 0, 12, 24, and 48 h (Bottom) Quantitative analysis of the scratch wound healing assay. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
We next examined the effect of Zn2+ on the migration and invasion of ESCC cells and found Zn2+ to decrease the cellular motility of ESCC cells. At 24 h, Zn2+ inhibited more cells from crossing the Transwell membrane (Figure 1C). In a Transwell invasion assay, cells treated with Zn2+ also demonstrated inhibited invasion compared with control cells (Figure 1C). Additionally, a wound healing assay performed at 0, 12, 24, and 48 h revealed that Zn2+ significantly impaired ESCC cell migration over time (Figure 1D). These results indicate that Zn2+ directly inhibits ESCC cell migration and invasion, in addition to its pro-apoptotic effects.
Differences in the methylome of Zn2+-treated cells by RRBS analysis
RRBS was performed after cells were treated with or without Zn2+. All four samples showed hypermethylation in the promoter regions, with the methylation level of the distal promoter region close to 90% and that of the intermediate and proximal promoter regions over 70% (Figure 2A). The overall CpG methylation levels of the four samples were uniformly distributed on chromosomes, with a high degree of methylation (circos plot chrobin size = 500 k bp) (Figure 2B). A violin plot was generated to display average CpG methylation in the distal, intermediate and proximal promoter regions of the samples; the overall CpG methylation level of promoter regions was decreased after Zn2+ treatment in both HEEC and ESCC cells (Figure 2C). These results indicate that Zn2+ may affect DNA methylation.
FIGURE 2
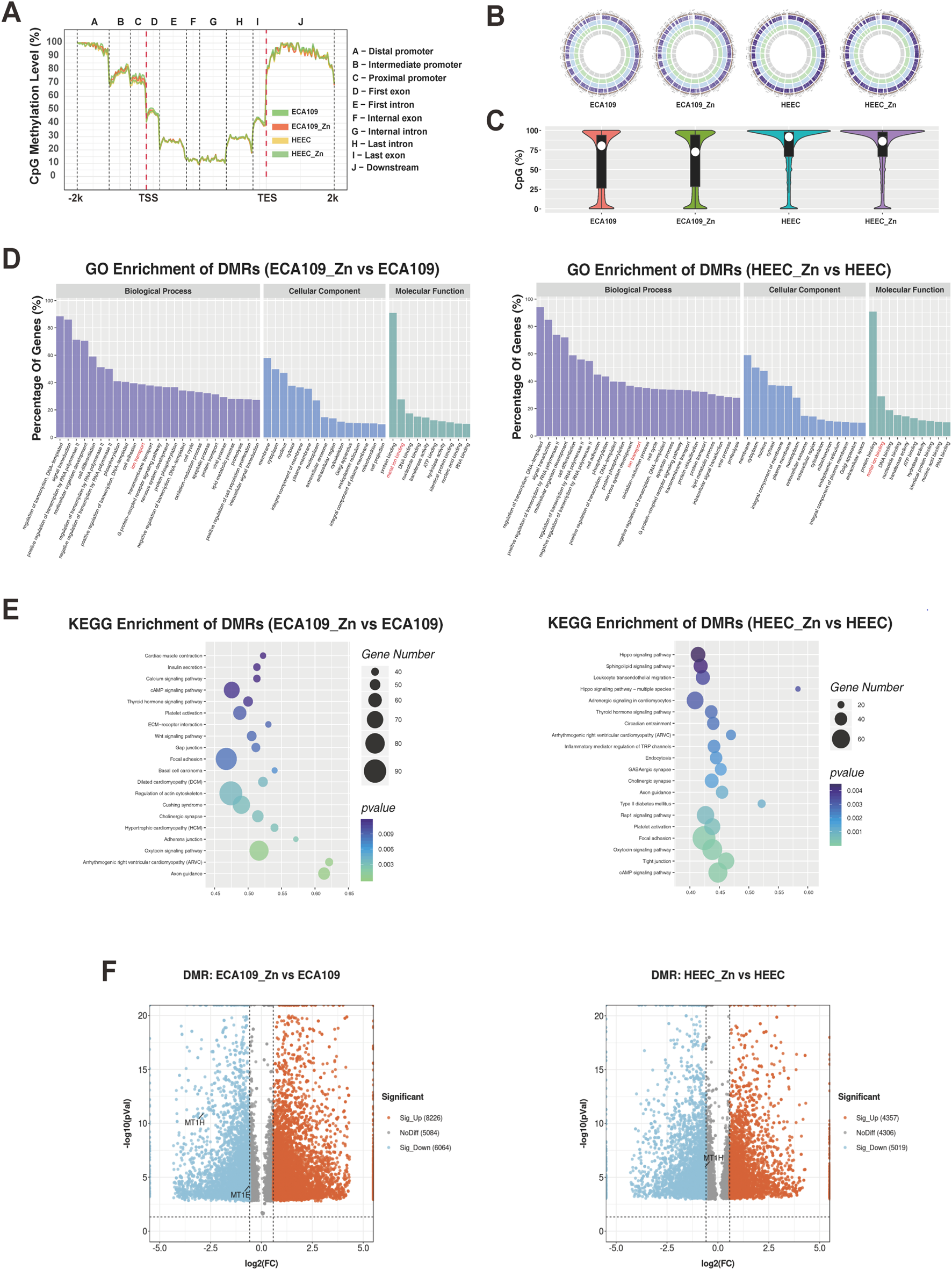
Differences in the methylome of Zn2+-treated cells by RRBS analysis. (A) Line graph of CpG methylation levels of different gene body regions in ECA109 and HEEC cells after treatment with or without Zn2+. (B) Circos plots of the overall CpG methylation levels distributed on chromosomes. (C) Violin plots of the CpG methylation levels of all promoter regions. (D, E) GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially methylated gene regions (DMRs) in ECA109_Zn verse ECA109 and HEEC_Zn verse HEEC. (F) Volcano plots of DMRs included upregulated and downregulated regions in ECA109_Zn verse ECA109 and HEEC_Zn verse HEEC.
Then, GO and KEGG enrichment analyses were performed for DMRs (promoter bin region = 2,000 bp). The biological process category showed enrichment in the regulation of transcription, signal transduction, cell adhesion, ion transport and the cell cycle; associations with protein binding, metal binding and DNA binding were found for the molecular function category (Figure 2D). Interestingly, ion transport and metal ion binding were observed for both HECC and ESCC cells, suggesting that Zn2+ may play a role in the regulation of methylation of related genes. KEGG pathway analysis revealed that DMRs were highly associated with pathways in ESCC and HEEC cells that were different (Figure 2E). All DMRs are plotted as volcano plots in Figure 2F. A total of 4,357 DMRs were upregulated and 5,019 DMRs downregulated in HEEC cells treated with Zn2+; 8,226 DMRs were upregulated and 6,064 DMRs downregulated in ESCC cells treated with Zn2+. Notably, the degree of DNA methylation of the metal ion-binding factor genes MT1E and MT1H was significantly decreased.
Differences in the transcriptome of Zn2+-treated cells by RNA-seq analysis
Zn2+-treated cells were also analysed by RNA-seq. Overall, the expressed genes of four different samples are distributed on all chromosomes (Figure 3A). After Zn2+ treatment, the average level of overall gene expression was slightly increased in both ESCC and HEEC cell lines (Figure 3B), suggesting that these upregulated genes may be associated with decreased methylation.
FIGURE 3

Differences in the transcriptome of Zn2+-treated cells by RNA-seq analysis. (A) Circos plot of the expressed genes distributed on chromosomes in ECA109 and HEEC cells with or without Zn2+ treatment. (B) Box plot of the overall gene expression levels in ECA109 and HEEC cells with or without Zn2+ treatment. (C) GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes in ECA109_Zn verse ECA109 and HEEC_Zn verse HEEC. (D) The heatmap of top 100 DEGs found by GO enrichment analysis in ECA109_Zn verse ECA109 and HEEC_Zn verse HEEC. (E) Volcano plots of DEGs included upregulated and downregulated regions in ECA109_Zn verse ECA109 and HEEC_Zn verse HEEC. (F) Venn plot of shared genes in DEGs between ECA109_Zn verse ECA109 and HEEC_Zn verse HEEC. (G) RT-qPCR validated the expression level of MT1E, MT1H and MT1X in cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. ns, not significant; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Differential expression analysis between the cell lines was next performed using the chi-square test (FDR ≤ 0.05 and fold change ≥ 2). There were 186 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the HECC cell line and 143 in the ESCC cell line (Figure 3F). The results of GO analysis revealed upregulated DEGs to be significantly enriched in the biological processes of ion binding and transport (Figure 3C). The top DEGs in the two groups are presented in heatmap and volcano plots, and expression of Zn2+ transporter-related genes, such as MT1E, MT1H and MT1X, was significantly increased after treatment with Zn2+ (Figures 3D, E). In addition, the intersection of DEGs between the two groups showed 25 common DEGs, including MT1E, MT1H and MT1X (Figure 3F). To further validate the expression of the DEGs, we performed RT-qPCR analysis. The results showed that MT1E (P < 0.0001), MT1H (P = 0.0824), and MT1X (P = 0.0003) expression levels were increased in Zn2+-treated cells compared to the control group (Figure 3G).
Integration of methylome and transcriptome data
We next examined the association between gene expression and DNA methylation. Starburst plots in Figure 4A display DEGs with significant DNA methylation changes (hypermethylation or hypomethylation), and these DEGs were significantly enriched in the mineral absorption pathway in both ESCC and HEEC cells, as shown in Figure 4B. Furthermore, we focused on the metallothionein genes and found that DNA methylation levels of MT1E, MT1H and MT1X were significantly decreased but that their expression levels were increased after Zn2+ treatment (Figure 4C). These findings suggest that Zn2+ can enhance expression of metallothioneins via positive feedback through a methylation regulation mechanism.
FIGURE 4
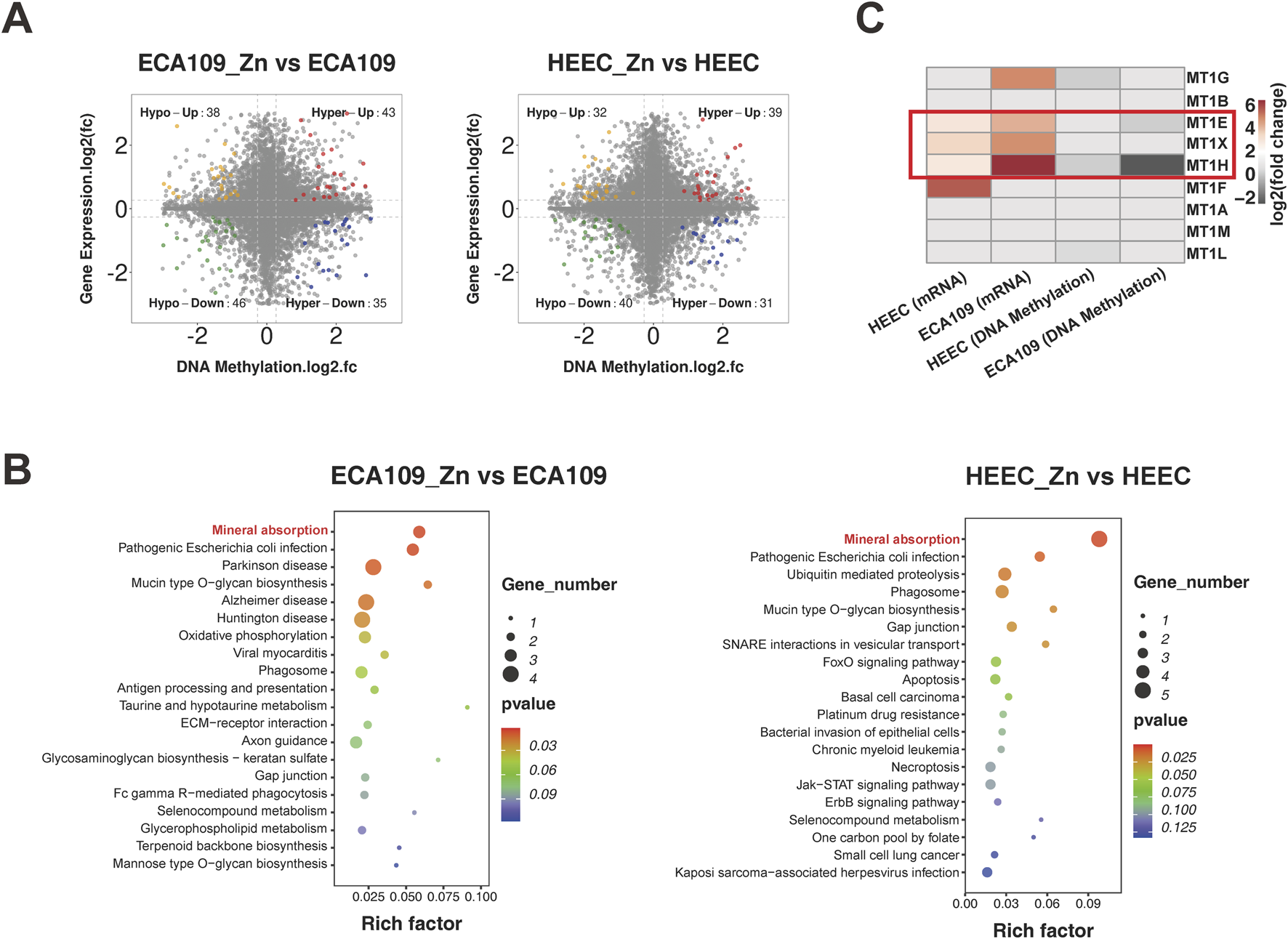
Integration of methylome and transcriptome data. (A) Starburst plots of the relationship between gene expression and DNA methylation in ECA109_Zn verse ECA109 and HEEC_Zn verse HEEC. (B) Dot plot of KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of concurrent DEGs found by conjoint analysis. (C) The heatmap of fold change of metallothionein subsets genes expression and DNA methylation levels in ECA109 and HEEC cells after the treatment of ZnSO4.
Potential application of Zn2+ in the treatment of ESCC
As cisplatin is the main chemotherapy drug for ESCC, we next investigated whether Zn2+ can be used in combination with cisplatin. In vitro assays showed that the IC50 of ESCC cells treated with Zn2+ was significantly lower than that of cells treated without zinc (Figure 5A). In addition, we used TCGA data to analyse MT1E, MT1H and MT1X expression levels in the assessment of ECa prognosis and found that ECa patients with high MT1E expression had a better prognosis (P < 0.01, Figure 5B). Although the detailed pathway changes induced by excess Zn2+ still need to be explored, Zn2+-MT binding status has potential value as a prognostic and therapeutic biomarker for ESCC.
FIGURE 5
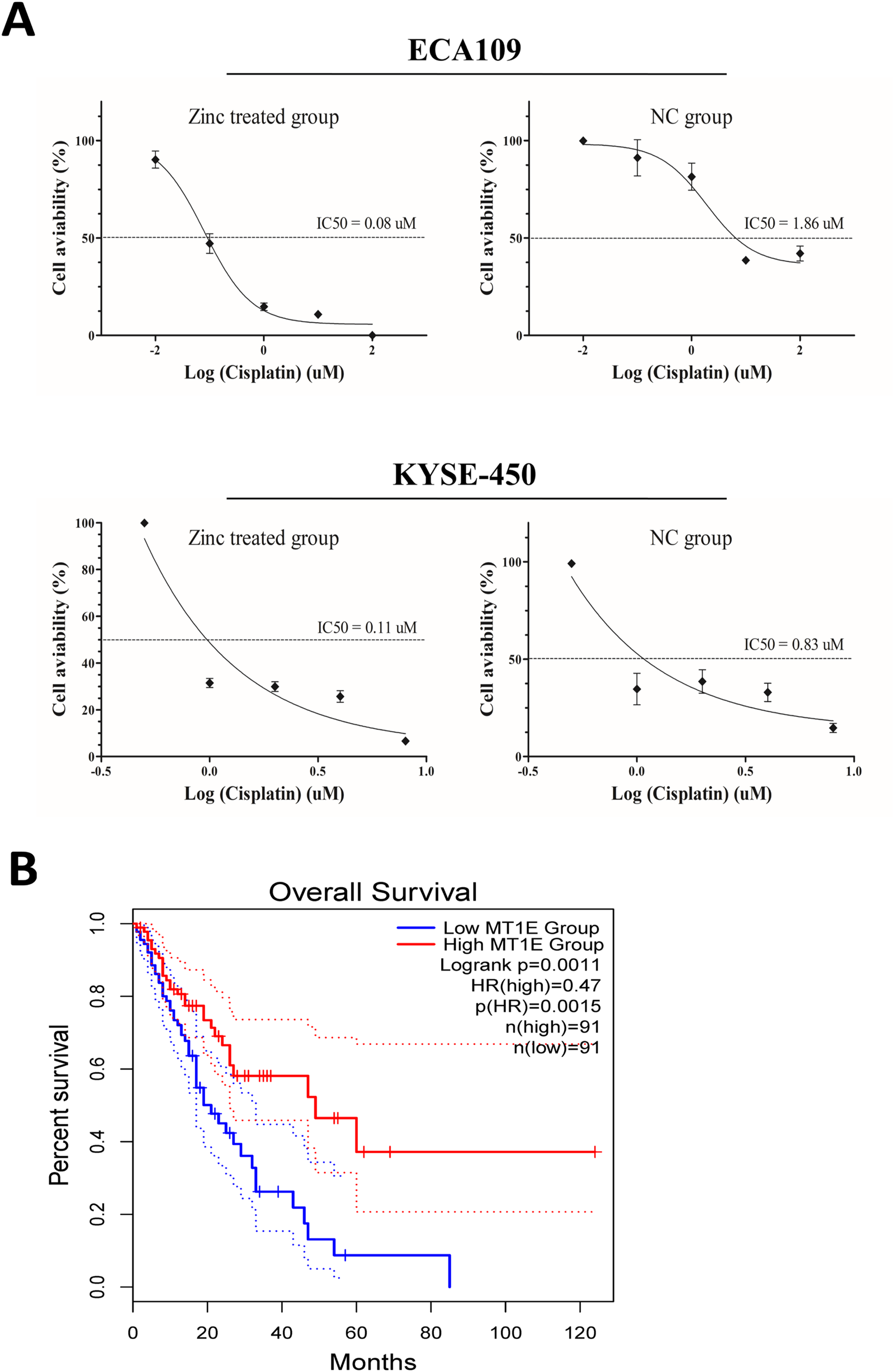
Potential application of Zn2+ in the treatment of ESCC. (A) Dose-response curve and half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of cisplatin with or without ZnSO4 treatment in ECA109 and KYSE-450 cell lines. (B) Kaplan-Meier analysis (overall survival) of ECa patients in the low and high MT1E expression groups via TCGA data analysis.
Discussion
Zn2+ is involved in various metabolic processes, including DNA synthesis and cell division (Levaot and Hershfinkel, 2018). Adequate zinc levels promote cell proliferation and tissue development, although different organs display distinct zinc requirements (Chen et al., 2022). In humans, the majority of Zn2+ intake is absorbed through the small intestine2 (Lee et al., 1989). The oesophagus and intestines are organs of the digestive tract, suggesting that the oesophagus may also have a natural ability to metabolize Zn2+. However, basic research on the role of Zn2+ and ECa development is lacking.
Zn2+ cannot freely enter cells and is transported passively via membrane transporters (Lichten and Cousins, 2009). Several studies have focused on the zinc-related transporter SLC30 or SLC39 (ZIP) family in cancer, reporting that abnormal Zn2+ in cancer cells caused by abnormal zinc transporters can affect AKT/PTEN and ERK/MAPK pathways (Zhu et al., 2021; Prasad et al., 2022). In addition to zinc transporters, four metallothionein isoforms (MT1, MT2, MT3 and MT4) can maximally bind seven zinc ions via tetrahedral coordination to cysteine residues, with a role for Zn2+ storage and releases (Krężel and Maret, 2021). Interestingly, we found that methylation of MT1E, MT1H and MT1X was significantly decreased and that expression of these genes was increased after ESCC cells were treated with Zn2+. When Zn2+ is increased in the environment, cells upregulate MT genes for the storage of Zn2+, and this Zn2+-MT regulatory pathway may be involved in disease and tumorigenesis.
Recent studies have reported an association between the expression of the MT family and tumor (Si and Lang, 2018; Merlos Rodrigo et al., 2020). MT1E is methylated in malignant melanoma and increases sensitivity to cisplatin-induced apoptosis (Faller et al., 2010). MT1H functions as a suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway (Zheng et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2021). MT1X expression is downregulated in HCC tissues, and further research found that MT1X could inhibit the progression and metastasis of HCC, suggesting its use as a prognostic indicator (Liu et al., 2018). MT1 deletion in transgenic mice promotes the expression of IL-6, which leads to a significant reduction in angiogenesis, suggesting that MT1 may be involved in the angiogenesis process by regulating expression of proangiogenic factors (Giralt et al., 2002). Therefore, abnormal expression of MT genes may serve as a biomarker.
To explore the potential application of Zn2+ in ESCC treatment, we conducted in vitro experiments and found that Zn2+-treated ESCC cells exhibited a significantly lower IC50, suggesting that Zn2+ may enhance cisplatin sensitivity by modulating DNA methylation and gene expression involved in drug response. Moreover, numerous studies have demonstrated that cisplatin resistance is a complex process influenced by multiple factors beyond DNA methylation, including altered drug uptake and detoxification (Chen and Chang, 2019), enhanced DNA repair mechanisms (e.g., nucleotide excision repair and mismatch repair) (Kelland, 2007), other epigenetic modifications such as histone alterations and non-coding RNAs(Lumpp et al., 2024), activation of survival signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB and Akt/p53) (Navaei et al., 2022), and metabolic reprogramming involving glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism (Pervushin et al., 2024). These mechanisms collectively drive cisplatin resistance in ESCC.
Furthermore, epidemiological studies have shown a link between dietary Zn2+ deficiency of ESCC (Abnet et al., 2005; Ma et al., 2018). Studies from Linxian, a high ESCC incidence area in China, have shown that serum Zn2+ concentrations are inversely associated with the risk of cancer development (Abnet et al., 2005). We analysed the epigenetic effects of Zn2+ on ESCC and HEEC cells in vitro for the first time and found that Zn2+ has the ability to alter ESCC epigenetic status and related downstream pathways. The regulation of MTs induced by Zn2+ deficiency may be related to the development and progression of ESCC. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the potential combined treatment value of zinc ions and platinum in ESCC cells, suggesting that it is worth further evaluating the specific drug solubility of the two in vivo and in vitro experiments, including the combination index method (Chou, 2010). Future studies are needed to clarify the interaction between Zn2+ and MTs and their regulatory mechanisms, such as to investigate the effects of Zn2+ combined with cisplatin on tumor growth, metastasis, and epigenetic changes in xenograft mouse models or to study the Zn2-dependent drug sensitivity by CRISPR-cas9 knockdown or overexpression of Zn2+ transporter. And, to get more detail about Zn2+ driven effect as drug adjuvant in clinical application.
Conclusion
In summary, Zn2+ reduces global DNA methylation and inhibits the malignant behavior of ESCC cells. Notably, combining Zn2+ with cisplatin further enhances the inhibitory effects on ESCC. We propose that metallothioneins warrant further investigation as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in ESCC.
Statements
Data availability statement
The RNA-seq and RRBS data generated in the present study have been deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive in BIG Data Center, Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences under accession number HRA011558 (publicly accessible at https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa-human).
Author contributions
BZ: Writing – original draft. CW: Writing – original draft. YH: Writing – original draft. XY: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. TY: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. LS: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. QL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review and editing. WM: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. AZ: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82172567), the Key R&D Plan of Jiangxi Province (2021BBG71006), and the Key Project of Science and Technology Innovation of Health Commission of Jiangxi Province (2023ZD005 and 2024ZD008).
Conflict of interest
Author Lize Shen was employed by LC-Bio Technologies.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abnet C. C. Arnold M. Wei W. Q. (2018). Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology154 (2), 360–373. 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.023
2
Abnet C. C. Lai B. Qiao Y. L. Vogt S. Luo X. M. Taylor P. R. et al (2005). Zinc concentration in esophageal biopsy specimens measured by x-ray fluorescence and esophageal cancer risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst.97 (4), 301–306. 10.1093/jnci/dji042
3
Akalin A. Kormaksson M. Li S. Garrett-Bakelman F. E. Figueroa M. E. Melnick A. et al (2012). methylKit: a comprehensive R package for the analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation profiles. Genome Biol.13 (10), R87. 10.1186/gb-2012-13-10-r87
4
Chen B. Yu P. Chan WN. Xie F. Zhang Y. Liang L. et al (2024). Cellular zinc metabolism and zinc signaling: from biological functions to diseases and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.9 (1), 6. 10.1038/s41392-023-01679-y
5
Chang J. Tan W. Ling Z. Xi R. Shao M. Chen M. et al (2017). Genomic analysis of oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma identifies alcohol drinking-related mutation signature and genomic alterations. Nat. Commun.8, 15290. 10.1038/ncomms15290
6
Chen S. Zhou Y. Chen Y. Gu J. (2018). fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics34 (17), i884–i890. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
7
Chen S.-H. Chang J.-Y. (2019). New insights into mechanisms of cisplatin resistance: from tumor cell to microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci.20 (17), 4136. 10.3390/ijms20174136
8
Chen Y. Liu F. X. Liu H. (2021). Effects of dietary zinc deficiency on esophageal squamous cell proliferation and the mechanisms involved. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol.13 (11), 1755–1765. 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i11.1755
9
Choi S. Cui C. Luo Y. Kim S. H. Ko J. K. Huo X. et al (2018). Selective inhibitory effects of zinc on cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through Orai1. Faseb J.32 (1), 404–416. 10.1096/fj.201700227RRR
10
Chou T. C. (2010). Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res.70 (2), 440–446. 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-09-1947
11
Faller W. J. Rafferty M. Hegarty S. Gremel G. Ryan D. Fraga M. F. et al (2010). Metallothionein 1E is methylated in malignant melanoma and increases sensitivity to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Melanoma Res.20 (5), 392–400. 10.1097/cmr.0b013e32833d32a6
12
Giralt M. Penkowa M. Hernández J. Molinero A. Carrasco J. Lago N. et al (2002). Metallothionein-1+2 deficiency increases brain pathology in transgenic mice with astrocyte-targeted expression of interleukin 6. Neurobiol. Dis.9 (3), 319–338. 10.1006/nbdi.2002.0480
13
Ho E. (2004). Zinc deficiency, DNA damage and cancer risk. J. Nutr. Biochem.15 (10), 572–578. 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2004.07.005
14
Huiliang Z. Mengzhe Y. Xiaochuan W. Hui W. Min D. Mengqi W. et al (2021). Zinc induces reactive astrogliosis through ERK-dependent activation of Stat3 and promotes synaptic degeneration. J. Neurochem.159 (6), 1016–1027. 10.1111/jnc.15531
15
Kelland L. (2007). The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer7 (8), 573–584. 10.1038/nrc2167
16
Kim D. Langmead B. Salzberg S. L. (2015). HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods12 (4), 357–360. 10.1038/nmeth.3317
17
Krężel A. Maret W. (2021). The bioinorganic chemistry of mammalian metallothioneins. Chem. Rev.121 (23), 14594–14648. 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00371
18
Krueger F. Andrews S. R. (2011). Bismark: a flexible aligner and methylation caller for Bisulfite-Seq applications. Bioinformatics27 (11), 1571–1572. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr167
19
Lee H. H. Prasad A. S. Brewer G. J. Owyang C. (1989). Zinc absorption in human small intestine. Am. J. Physiol.256 (1 Pt 1), G87–G91. 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.1.G87
20
Levaot N. Hershfinkel M. (2018). How cellular Zn(2+) signaling drives physiological functions. Cell Calcium75, 53–63. 10.1016/j.ceca.2018.08.004
21
Li H. Handsaker B. Wysoker A. Fennell T. Ruan J. Homer N. et al (2009). The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics25 (16), 2078–2079. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
22
Lichten L. A. Cousins R. J. (2009). Mammalian zinc transporters: nutritional and physiologic regulation. Annu. Rev. Nutr.29, 153–176. 10.1146/annurev-nutr-033009-083312
23
Lin E. W. Karakasheva T. A. Hicks P. D. Bass A. J. Rustgi A. K. (2016). The tumor microenvironment in esophageal cancer. Oncogene35 (41), 5337–5349. 10.1038/onc.2016.34
24
Liu Z. Ye Q. Wu L. Gao F. Xie H. Zhou L. et al (2018). Metallothionein 1 family profiling identifies MT1X as a tumor suppressor involved in the progression and metastastatic capacity of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog.57 (11), 1435–1444. 10.1002/mc.22846
25
Lumpp T. Stößer S. Fischer F. Hartwig A. Köberle B. (2024). Role of epigenetics for the efficacy of cisplatin. Int. J. Mol. Sci.25 (2), 1130. 10.3390/ijms25021130
26
Ma J. Li Q. Fang X. Chen L. Qiang Y. Wang J. et al (2018). Increased total iron and zinc intake and lower heme iron intake reduce the risk of esophageal cancer: a dose-response meta-analysis. Nutr. Res.59, 16–28. 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.07.007
27
Martin M. (2011). Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J.17 (1), 10–12. 10.14806/ej.17.1.200
28
Merlos Rodrigo M. A. Jimenez Jimemez A. M. Haddad Y. Bodoor K. Adam P. Krizkova S. et al (2020). Metallothionein isoforms as double agents - their roles in carcinogenesis, cancer progression and chemoresistance. Drug Resist Updat52, 100691. 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100691
29
Navaei Z. N. Khalili-Tanha G. Zangouei A. S. Abbaszadegan M. R. Moghbeli M. (2022). PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a critical regulator of Cisplatin response in tumor cells. Oncol. Res.29 (4), 235–250. 10.32604/or.2022.025323
30
Pertea M. Pertea G. M. Antonescu C. M. Chang T. C. Mendell J. T. Salzberg S. L. (2015). StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol.33 (3), 290–295. 10.1038/nbt.3122
31
Pervushin N. V. Yapryntseva M. A. Panteleev M. A. Zhivotovsky B. Kopeina G. S. (2024). Cisplatin resistance and metabolism: simplification of complexity. Cancers16 (17), 3082. 10.3390/cancers16173082
32
Prasad R. R. Raina K. Mishra N. Tomar M. S. Kumar R. Palmer A. E. et al (2022). Stage-specific differential expression of zinc transporter SLC30A and SLC39A family proteins during prostate tumorigenesis. Mol. Carcinog.61 (5), 454–471. 10.1002/mc.23382
33
Robinson M. D. McCarthy D. J. Smyth G. K. (2010). edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics26 (1), 139–140. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
34
Si M. Lang J. (2018). The roles of metallothioneins in carcinogenesis. J. Hematol. Oncol.11 (1), 107. 10.1186/s13045-018-0645-x
35
Song Q. Decato B. Hong E. E. Zhou M. Fang F. Qu J. et al (2013). A reference methylome database and analysis pipeline to facilitate integrative and comparative epigenomics. PLoS One8 (12), e81148. 10.1371/journal.pone.0081148
36
Sung H. Ferlay J. Siegel R. L. Laversanne M. Soerjomataram I. Jemal A. et al (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA a cancer J. Clin.71 (3), 209–249. 10.3322/caac.21660
37
Tang D. Kang R. Berghe T. V. Vandenabeele P. Kroemer G. (2019). The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res.29 (5), 347–364. 10.1038/s41422-019-0164-5
38
Vallee B. L. Falchuk K. H. (1993). The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol. Rev.73 (1), 79–118. 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.79
39
Wang J. Yang X. Shen W. Huang Y. Mao W. Zhao A. (2025). Insights into the characteristics of cancer incidence in China. Sci. China Life Sci.10.1007/s11427-024-2839-4
40
Yang H. Liu H. Chen Y. Zhu C. Fang W. Yu Z. et al (2021). Long-term efficacy of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery for the treatment of locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the NEOCRTEC5010 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg.156 (8), 721–729. 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.2373
41
Yusuf A. P. Abubakar M. B. Malami I. Ibrahim K. G. Abubakar B. Bello M. B. et al (2021). Zinc metalloproteins in epigenetics and their crosstalk. Life (Basel)11 (3), 186. 10.3390/life11030186
42
Zeng X. Wang Z. Zhao A. Wu Y. Wang Z. Wu A. et al (2025). Zinc nanoparticles from oral supplements accumulate in renal tumours and stimulate antitumour immune responses. Nat. Mater24 (2), 287–296. 10.1038/s41563-024-02093-7
43
Zhang F. Guo S. Zhong W. Huang K. Liu Y. (2021). Integrative analysis of metallothioneins identifies MT1H as candidate prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci.8, 672416. 10.3389/fmolb.2021.672416
44
Zheng Y. Jiang L. Hu Y. Xiao C. Xu N. Zhou J. et al (2017). Metallothionein 1H (MT1H) functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. BMC Cancer17 (1), 161. 10.1186/s12885-017-3139-2
45
Zhu B. Huo R. Zhi Q. Zhan M. Chen X. Hua Z. C. (2021). Increased expression of zinc transporter ZIP4, ZIP11, ZnT1, and ZnT6 predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.65, 126734. 10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126734
Summary
Keywords
oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma, zinc ions, DNA methylation, gene expression, metallothioneins, combination drug therapy, biomarkers
Citation
Zhou B, Wang C, Huang Y, Yang X, Ye T, Shen L, Lv Q, Mao W and Zhao A (2025) Anticancer effects of zinc ion-mediated DNA demethylation in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1559675. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1559675
Received
13 January 2025
Accepted
30 April 2025
Published
27 May 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Wenyi Li, La Trobe University, Australia
Reviewed by
Christian Kweku Adokoh, University of Cape Coast, Ghana
Dattatrya Shetti, Charles University, Czechia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhou, Wang, Huang, Yang, Ye, Shen, Lv, Mao and Zhao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: An Zhao, zhaoan@zjcc.org.cn; Weimin Mao, Maowm@zjcc.org.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.