- 1Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Clinical Pharmacology, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 3School of Basic Medical Sciences, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 4Department of Hematology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
High-dose methotrexate (HDMTX) is the cornerstone of the treatment for primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). The prevention of drug-induced toxicities is critical. This study aims to identify key factors associated with HDMTX-induced toxicities (hematotoxicity, hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicit) in 713 Chinese PCNSL patients undergoing 3021 HDMTX treatment courses. Demographic data, administration information, laboratory tests, area under the curve, co-medications, and 30 single nucleotide polymorphisms were collected to analyze the association of HDMTX-related toxicities using PLINK and SPSS. Higher ALB level, female, ABCB1 rs1045642, MTHFR rs1801131, and MTHFD1 rs2236225 were associated with lower risk of anemia, while the combination of furosemide, torasemide, bumetanide, and levetiracetam associating with higher risk. Co-use of torasemide had higher incidence of neutropenia. Higher level of ALB was correlated with less leukopenia; torasemide and rs2236225 were related to more leukopenia. Female, furosemide, rs1801133, ABCG2 rs2231142, ABCC2 rs717620 were related to more thrombocytopenia, while rs1045642 and high ALB were related to less. Rs1801131 and female were correlated with more hepatotoxicity, whereas furosemide was correlated with less. In nephrotoxicity, female and rs1801394 were correlated with less, MTHFR rs1801131 and rs1801133 were correlated with more. In conclusion, higher ALB levels had a lower risk of HDMTX toxicities; loop diuretics and levetiracetam generally accelerated the occurrence of toxicities. Rs1801133 GG, rs1128503 GG + AG, rs2231142 AA+ AC, rs717620 TT + GT were associated with increased risk of toxicity; rs1045642 TT and rs1801394 GG + AG were less likely to develop toxicity.
1 Introduction
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a rare and highly aggressive extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with a poor prognosis (Flosperg et al., 2024). Methotrexate (MTX), a folic acid antagonist, is widely used to treat various malignancies. High-dose methotrexate (HDMTX), defined as a dose exceeding 500 mg/m2, is the cornerstone of PCNSL treatment. Chemotherapy regimens containing HDMTX yield higher survival rates and longer survival times compared to radiotherapy alone or other treatments (Koźmiński et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2012).
Methotrexate inhibits dihydrofolate reductase, disrupting key enzymes involved in DNA and RNA synthesis, thereby preventing the proliferation of rapidly dividing tumor cells (Maksimovic et al., 2020). Methotrexate exhibits non-linear pharmacokinetics, meaning that drug concentration does not proportionally increase with dosage, and its metabolism, transport, and excretion processes are complex. HDMTX is primarily administered intravenously and widely distributed in tissues, with high concentrations in the kidneys, liver, skin, and red blood cells (Mei et al., 2018a; Fischer et al., 2017). MTX has a 50% protein binding rate, so plasma protein levels can affect its pharmacokinetic parameters (Li et al., 2024). Approximately 80%–90% of MTX is excreted unchanged via the kidneys, with the remaining 10% excreted through bile (Methotrexate-methotrexate injection, 2024).
In PCNSL patients, HDMTX pharmacokinetics exhibit significant interindividual variability, mainly in apparent volume of distribution and clearance rate, influenced by factors such as patient pathophysiological status, administration regimen, and polymorphisms in transporters and metabolic enzymes (Mei et al., 2018a). HDMTX treatment can cause various systemic adverse effects, including nephrotoxicity (acute kidney injury in 2%–12% of patients), hepatotoxicity, myelosuppression, and neurotoxicity. Due to these potential toxicities, HDMTX management requires rigorous monitoring and personalized dosing strategies.
This study aims to identify clinical factors associated with HDMTX-induced toxicities and assess the impact of genetic polymorphisms in MTX metabolism pathway and transporters on toxicity occurrence. Early identification of these risk factors can guide clinicians in optimizing dosing strategies, helping to minimize adverse effects while maximizing therapeutic efficacy.
2 Methods
2.1 Patient enrolment and treatment
This study received approval from the Ethics Committee of Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, P.R. China (KY 2019-072-02) and was performed consistent with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. Data were collected through routine clinical monitoring and leftover blood samples. All patients were diagnosed with PCNSL and treated with intravenous HDMTX at Beijing Tiantan Hospital from September 2016 to February 2024. Urine alkalinization with sodium bicarbonate and intravenous hydration (sodium chloride, 1500 mL/m2) were administered. Calcium leucovorin regiment was adjusted according to the plasma MTX level (Methotrexate-methotrexate injection, 2024). To control inflammatory side effects, 5–10 mg dexamethasone was intravenously administered before MTX infusion (Cook et al., 2016).
Inclusion criteria: age ≥18 years; no pregnancy or HIV infection; no missing of required information.
2.2 Data collection
Clinical data of enrolled patients were retrospectively collected. These data included age, gender, body weight, height, MTX dosing time and dosage/m2, CMTX, 0–24 h area under curve (AUC0–24h), and AUC0–48h, albumin (ALB), white blood cell count (WBC), hemoglobin (HGB), platelet (PLT) count, alanine transferase (ALT), aspartate transferase (AST), creatinine (Cr), co-medications, and selected single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
2.3 Toxicity evaluation and plasma MTX concentration
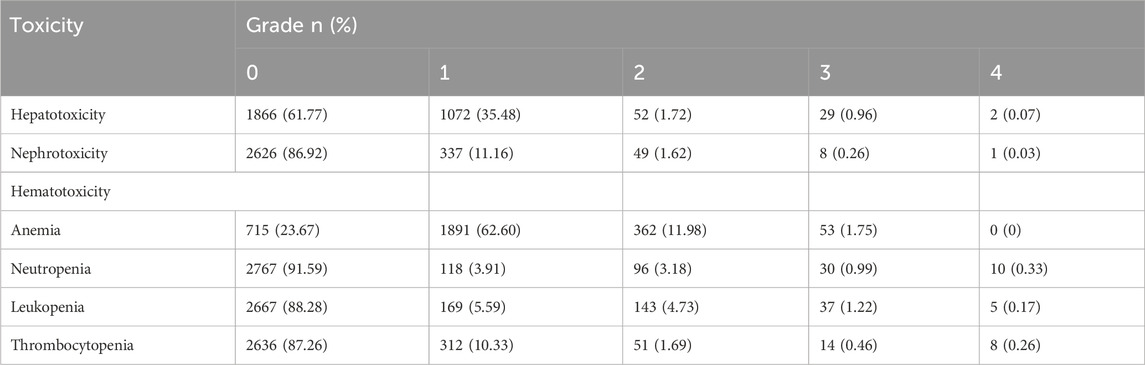
Hematotoxicity (including anemia, neutropenia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia), hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity were assessed according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (version 5.0) (CTCAE, 2024). Hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity were evaluated using the highest values of ALT, AST, and Cr levels during the courses. Grades 1 to 4 of nephrotoxicity are graded 1–1.5 times, 1.5–3 times, 3–6 times, and more than 6 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) respectively. A detailed description of the toxicity assessment criteria was shown in Table 1. Plasma MTX concentrations were determined by a validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method (Mei et al., 2018b).
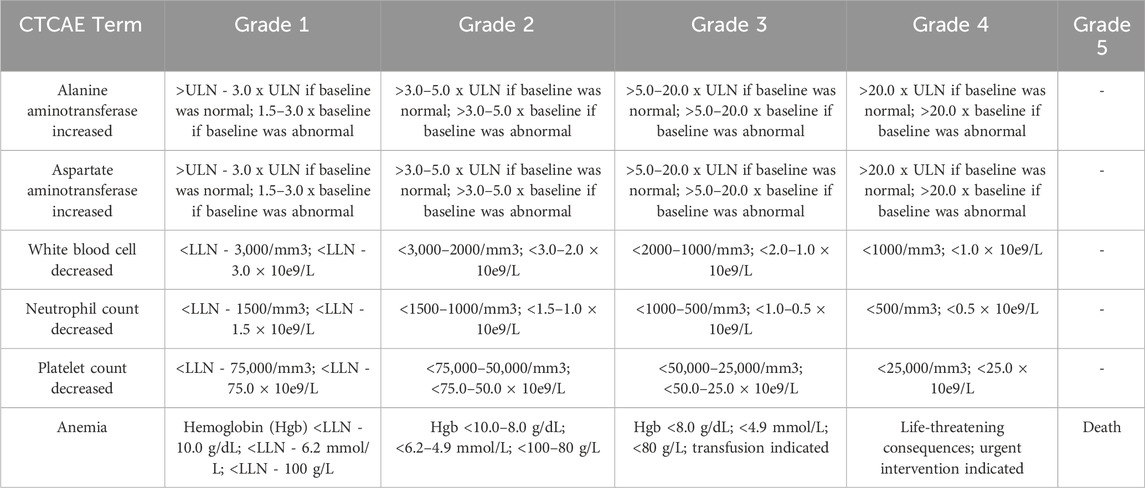
Table 1. Toxicity assessment criteria according to common terminology criteria for adverse events (version 5.0).
2.4 Genotype identification
Thirty SNPs were selected according to the following criteria: with significant influence on MTX pharmacokinetics and/or toxicities; with acceptable mutation frequency (>0.05) in the Chinese population; can be successfully identified by MassArray method (Sequenom, USA). DNA was isolated from the residual monitoring samples, and the genotype of 30 selected SNPs was identified by MassArray method (Ellis and Ong, 2017; Zhang et al., 2023).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed by using SPSS (version 27.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and PLINK (version 1.9, Shaun Purcell, Boston, MA, USA) software. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± SD or interquartile range, and categorical variables were expressed as ratios or proportions. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was evaluated by PLINK (P ≥ 0.05 was acceptable). Independent samples t-test or Mann-Whitney U test was conducted for the continuous variables. Pearson’s Chi-squared test was performed on categorical variables. Using PLINK, univariate logistic regression analysis was performed for different toxicity, and Bonferroni single-step adjustment was performed for P-values. According to the dominant and recessive model results of PLINK, the genotypes with potential influence on HDMTX-induced toxicities were screened. All variables with a p-value <0.05 in the univariate analysis were included in the binary logistic regression analysis. Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to estimate the risk of toxicities for each variable. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Patient characteristics
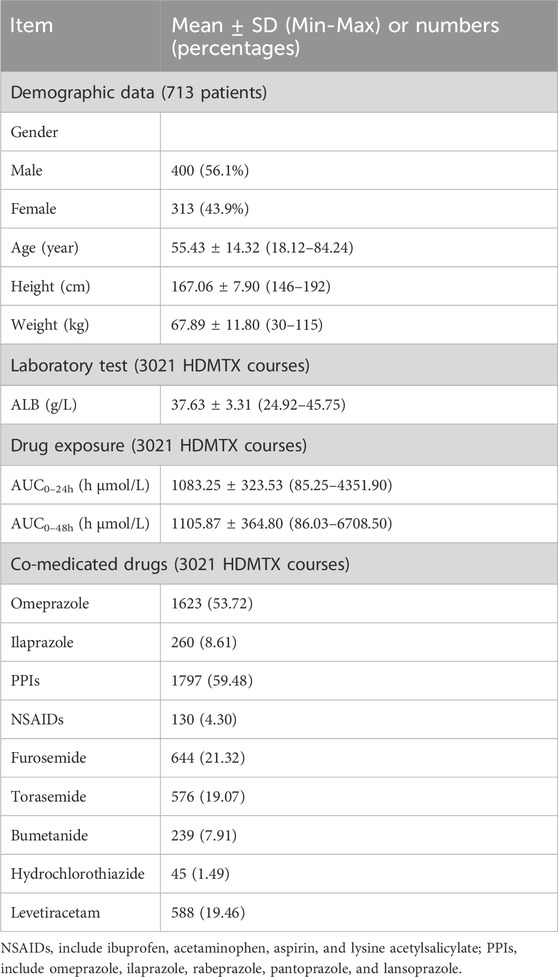
The present study included a total of 713 patients (400 male, 313 female) with 3,021 treatment courses were included. Table 2 presents the clinical characteristics of enrolled patients. The age of 713 patients was 55.43 ± 14.32 years. MTX dose was 3.38 ± 0.75 g/m2. AUC0–24h (h μmol/L) was 1083.25 ± 323.53 h μmol/L, AUC0–48h was 1105.87 ± 364.80 h μmol/L. Table 3 presents the number of courses with grade 1, 2, 3, and 4 of each toxicity.
3.2 Association between polymorphisms and HDMTX-related toxicities
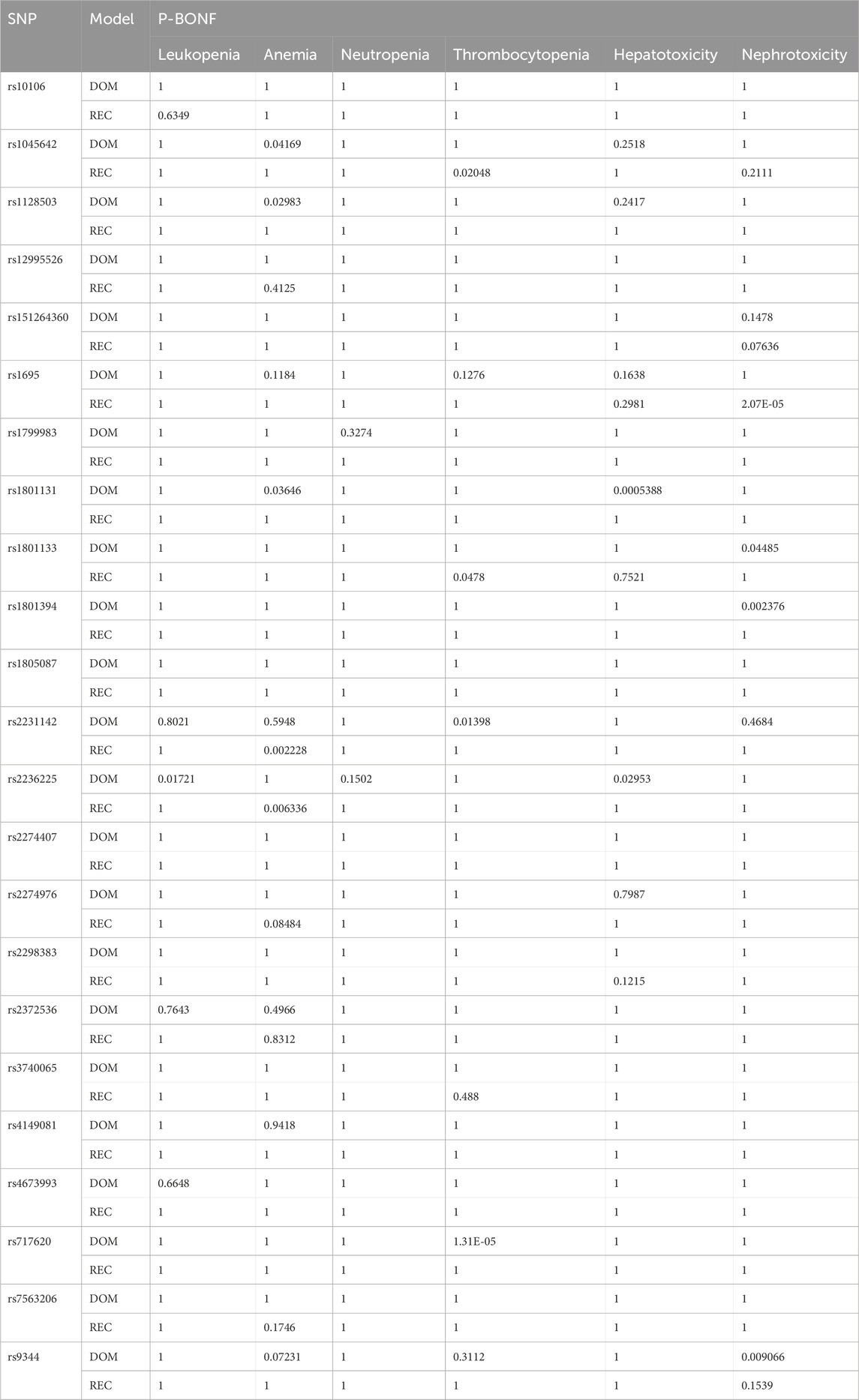
Supplementary Table S1 shows the detailed information of selected SNPs. Rs1051226, rs10760502 and rs2273697 were excluded due to high genotype missing rate (>5%). Rs28364006 appeared to be monomorphic in the sample population and was excluded. Rs3758149, rs2413775, and rs11045879 were not consistent with the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (p < 0.05).
The association between SNPs and toxicities was analyzed by logistic regression using the dominant and recessive models in PLINK. After Bonferroni single-step adjustment, rs1801131 G allele (p-dom = 0.0005388, p-rec = 1) and rs2236225 A allele (p-dom = 0.02953, p-rec = 1) were associated with a higher risk of hepatotoxicity. Rs1801394 G allele (p-dom = 0.002376, p-rec = 1), rs1801133 G allele (p-dom = 0.04485, p-rec = 1), rs9344 G allele (p-dom = 0.009066, p-rec = 0.1539), and rs2231142 T allele (p-dom = 0.04684, p-rec = 1) were associated with a higher risk of AKI, meanwhile rs1695 A allele (p-dom = 1, p-rec = 2.069e-05) were linked to a lower risk of AKI. Rs2236225 G allele (p-dom = 1, p-rec = 0.006336) and rs2231142 G allele (p-dom = 0.5948, p-rec = 0.002228) were associated with low anemia risk, while rs1045642 A allele (p-dom = 0.04169, p-rec = 1), rs1128503 G allele (p-dom = 0.02983, p-rec = 1), and rs1801131 G allele (p-dom = 0.03646, p-rec = 1) were related to high risk of anemia. Rs2231142 T allele (p-dom = 0.01398, p-rec = 1) and rs717620 T allele (p-dom = 1.309e-05, p-rec = 1) were associated with thrombocytopenia, whereas rs1045642 G allele (p-dom = 1, p-rec = 0.02048), rs1801133 A allele (p-dom = 1, p-rec = 0.0478) showed opposite effect on PLT count. Additionally, rs2236225 A allele (p-dom = 0.01721, p-rec = 1) was found relating to high risk of leukopenia (Table 4).
3.3 Population pharmacokinetic model
The referenced population pharmacokinetic model was characterized using a three-compartment model in conjunction with a proportional residual model. Covariate effects on model parameters were evaluated using forward addition and backward elimination approaches. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), ALT, and a combined genotype of ABCC-ABCG-ADORA2A were identified as significant covariates impacting the clearance (CL) of MTX. Additionally, total protein (TP) was found to be a significant covariate influencing inter-compartmental clearance (Q). The results in the model development procedure were in Supplementary Table S2. Detailed parameter estimates and Bootstrap results of model were in Supplementary Table S3. Goodness-of-fit plots for the base and final models (Supplementary Figure S1) show strong correlations between observed and predicted concentrations. CWRES plots indicate that most residuals fall within two standard deviations and are evenly distributed, with no significant biases observed. The VPC analysis (Supplementary Figure S2) demonstrated that most observed concentrations fell within the model’s 80% prediction intervals, with median observed concentrations closely matching the predicted values, indicating acceptable predictive performance (Wei et al., 2025).
3.4 Univariate and multivariate analysis of risk factors for HDMTX-related toxicities
In our patient population, there are relatively few courses in which grades 2–4 occur. Statistically, the results of a separate analysis in each grade are not particularly meaningful. Therefore, we divided the 3,021 courses into two types for univariate and multifactorial analysis: with toxic events and without toxic events. Univariate analyses were used to test the relationship between the patient characteristics and toxicities. The selected patient characteristics were gender, age, body weight, plasma ALB level, AUC0–24h, AUC0–48h, and co-medications (including omeprazole, ilaprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole, ibuprofen, acetaminophen, aspirin, lysine acetylsalicylate, furosemide, torasemide, bumetanide, hydrochlorothiazide, and levetiracetam).
In general, SNPs with potential influence (p < 0.05 with Bonferroni adjustment, detailed in Table 4) and clinical characteristics with p < 0.05 in univariate analyses were stepwise entered into a multivariate binary logistic regression model to identify predictive factors for occurrence of toxicities. The outcome of predictive factors for HDMTX-induced toxicities in patients with PCNSL is shown in Tables 5–10.
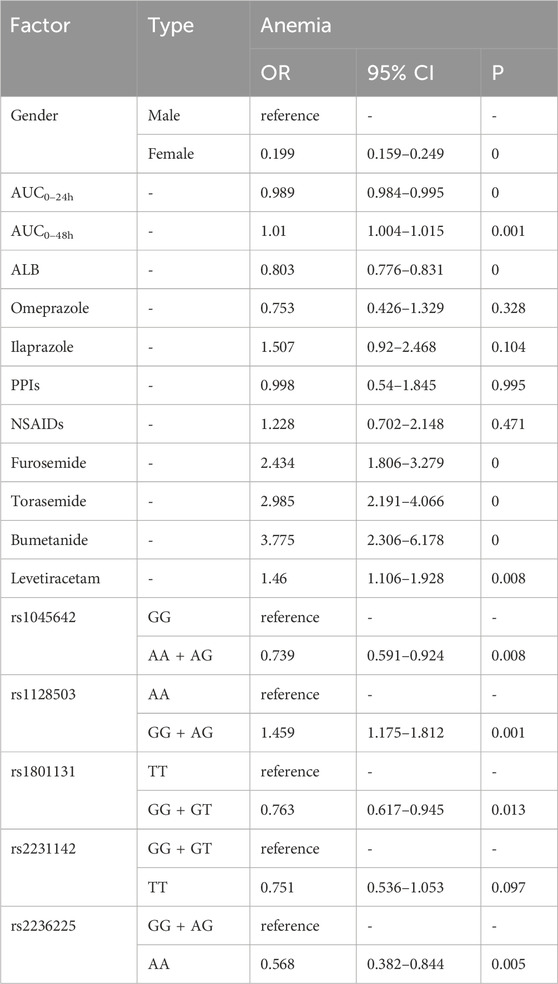
As shown in Table 5, the risk factors for the occurrence of anemia were as follows: higher AUC0–48h [OR = 1.01, p = 0.001], co-medications (furosemide [OR = 2.434, p = 0], torasemide [OR = 2.985, p = 0], bumetanide [OR = 3.775, p = 0], and levetiracetam [OR = 1.46, p = 0.008]), and genotype GG + AG of rs1128503 [OR = 1.459, p = 0.001]. Protective factors for anemia were female [OR = 0.199, p = 0], higher AUC0–24h [OR = 0.989, p = 0], higher level of ALB [OR = 0.803, p = 0], genotype AA + AG of rs1045642 [OR = 0.739, p = 0.008], genotype GG + GT of rs1801131 [OR = 0.763, p = 0.013], and genotype AA of rs2236225 [OR = 0.568, p = 0.005].
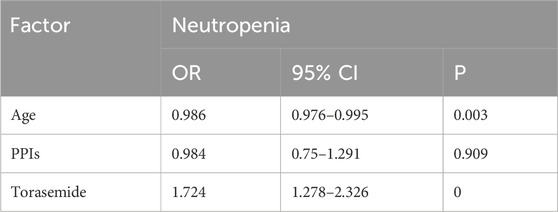
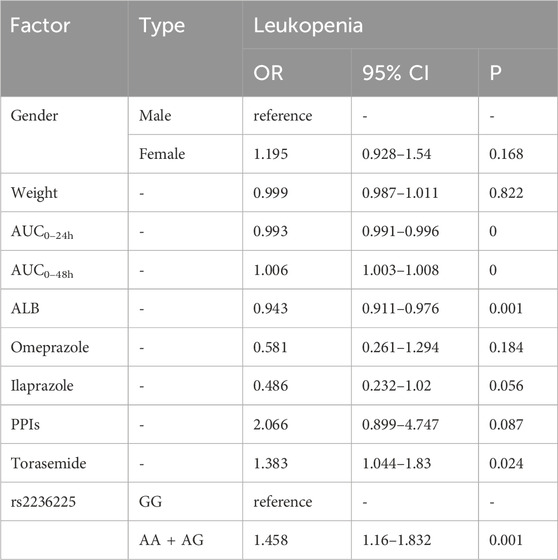
For neutropenia (Table 6), co-use with torasemide [OR = 1.724, p = 0] was presented as a risk factor, while older age [OR = 0.986, p = 0.003] was associated with lower risk. For leucopenia (Table 7), multivariate analysis showed that AUC0–48h [OR = 1.006, p = 0], combination of torasemide [OR = 1.383, p = 0.024, and genotype AA + AG of rs2236225 [OR = 1.458, p = 0.001] were related to higher risk. High ALB level [OR = 0.943, p = 0.001] and AUC0–24h [OR = 0.993, p = 0] were protective factors.
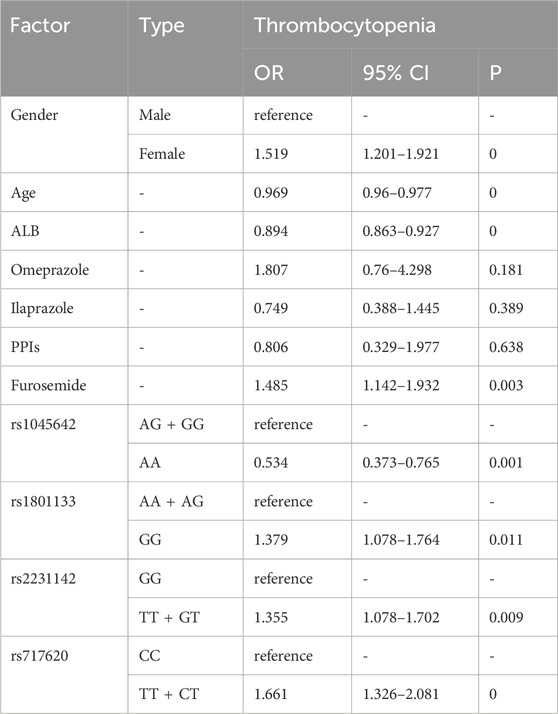
Thrombocytopenia was linked to female [OR = 1.519, p = 0], co-meditating with furosemide [OR = 1.485, p = 0.003], GG type of rs1801133 [OR = 1.379, p = 0.011], TT + GT type of rs2231142 [OR = 1.355, p = 0.009], and TT + CT type of rs717620 [OR = 1.661, p = 0], while older patients [OR = 0.969, p = 0], higher ALB [OR = 0.894, p = 0], and AA genotype of rs1045642 [OR = 0.534, p = 0.001] showed protective effects (Table 8).
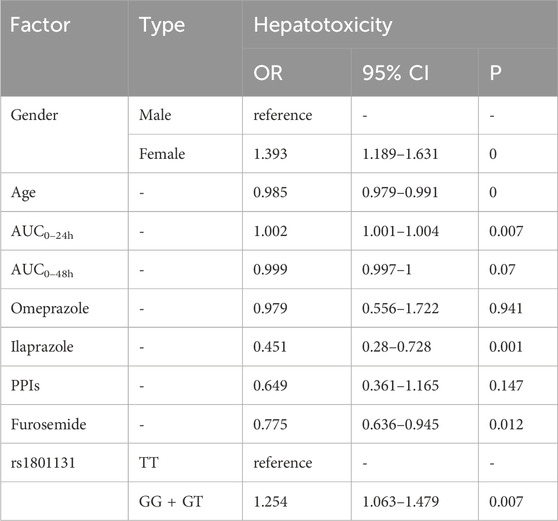
As for hepatotoxicity (Table 9), the older age [OR = 0.985, p = 0], AUC0–48h [OR = 0.999, p = 0.07], use of ilaprazole [OR = 0.451, p = 0.001] and furosemide [OR = 0.775, p = 0.012] have less risk, female patients [OR = 1.393, p = 0], GG and GT types of rs1801131 [OR = 1.254, p = 0.007] compared with its homozygote genotypes TT were associated with hepatotoxicity.
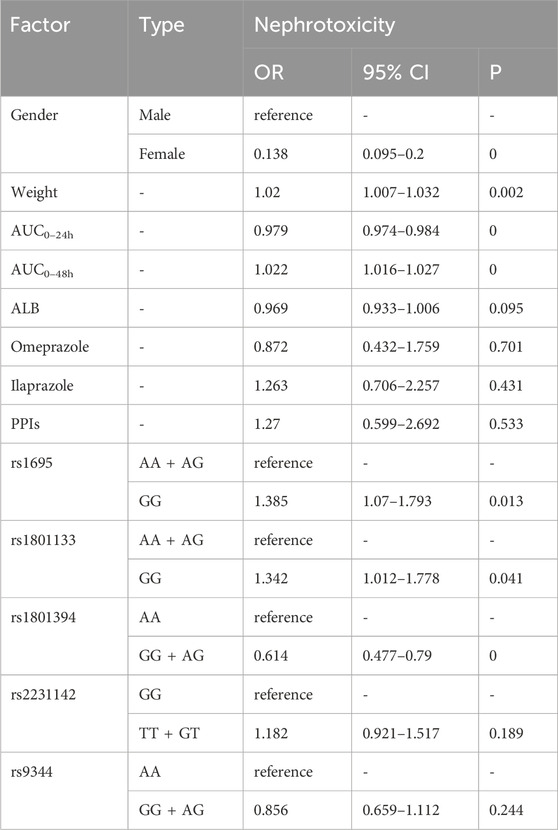
Table 10 illustrates patients with higher body weight [OR = 1.02, p = 0.002], higher AUC0–48h [OR = 1.022, p = 0], GG type of rs1695 [OR = 1.385, p = 0.013], and GG type of rs1801133 [OR = 1.3423, p = 0.041] present higher risk of nephrotoxicity. Female associated with less risk compared with male [OR = 0.138, p = 0]. Factors like AUC0–24h [OR = 0.979, p = 0] and genotype GG and AG of rs1801394 [OR = 0.614, p = 0] also linked to less risk.
4 Discussion
4.1 Drug exposure
During the treatment, delayed MTX excretion in patients leads to increased drug exposure, which subsequently raises the incidence of adverse events. Utilizing drug exposure as a reference index to guide PCNSL treatment can provide early warnings before toxicity occurs, allowing for timely dose adjustments and leucovorin rescue protocols. Studies have found that the AUC of MTX (0–96 h) may be correlate with both toxicity and efficacy (Joerger et al., 2010; Joerger et al., 2012). In a retrospective IELSG study on PCNSL, AUC (>1100 h μmol/L) was identified as an independent predictor of PCNSL treatment efficacy (Ferreri et al., 2004). Another study involving 55 PCNSL patients indicated that for every 100 h μmol/L increase in AUC, disease progression reduced by 18% and overall survival improved by 27%, but no significant relationship was observed between AUC and MTX toxicity (Joerger et al., 2010). To explore the specific impact of AUC on toxicity, we used a population pharmacokinetic model to fit relatively stable drug-time curves for each treatment cycle.
The model used a nonlinear mixed-effects model with a two-compartment model with first-order elimination to describe the pharmacokinetic process of MTX in patients. An exponential error model was used to assess inter-individual variability between parameters, and a proportional model was used to describe residual variability between MTX concentrations. Covariates included in the model were eGFR, ALT, TP, and concomitant use of omeprazole. Scatter plots were used to assess the fit of the base and final models, and typical parameter estimates, standard errors, and 95% CIs obtained from the original data set were consistent with bootstrap results, indicating good stability and reproducibility of the final model. Most of the actual concentrations in the VPC assay fell within the 90% prediction interval of the model, indicating that the predictive ability of the model was adequately predictive.
Our analysis showed that AUC0–24h and AUC0–48h serve as predictive and risk factors respectively for anemia, leukopenia, and nephrotoxicity during the treatment cycles. Patients with larger AUC0–24h had a higher risk of hepatotoxicity, and higher AUC0–48h was associated with lower risk. However, it cannot be ignored that although the results are statistically significant, the ORs related to AUC are very close to 1.
MTX and its metabolite 7-OH MTX can form pH-dependent crystalline precipitates in the renal tubule lumen, leading to crystal nephropathy and renal damage (Howard et al., 2016). MTX is primarily excreted through the kidneys, and impaired renal function results in prolonged exposure to high drug concentrations. Meanwhile, MTX continuously inhibits dihydrofolate reductase, targeting DNA synthesis and suppressing the growth and division of hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow (Bedoui et al., 2019; Hamed et al., 2022). Hence, hematotoxicity and nephrotoxicity were consistent in the results. Apart from affecting folate metabolism, MTX-polyglutamates can accumulate in liver cells and lead to plasma membrane lysis, releasing a large number of reactive oxygen species, causing oxidative damage (Li et al., 2024). However, none of these can explain our results well, and the specific effect of AUC on toxicity is rarely studied.
4.2 Plasma ALB
Retrospective studies of hematologic malignancies patients undergoing HDMTX therapy indicate low ALB levels are significantly associated with delayed MTX clearance (Li et al., 2024). Amitai I et al. found that an ALB level <3.6 g/dL (OR = 4.17, 95% CI: 1.04–6.5, p = 0.04) is strongly associated with AKI (Amitai et al., 2020). This correlation was also observed by Khera S et al., where lower ALB levels (<35 g/L) were an independent risk factor for MTX-induced nephrotoxicity in pediatric ALL patients (OR = 4.71, 95% CI: 1.06–9.86, p = 0.04) (Khera et al., 2022). Higher ALB levels were significantly associated with a lower incidence of hematotoxicity in our study. Methotrexate has a protein binding rate of approximately 50%, and albumin accounts for about 80% of intravascular oncotic pressure. Low serum albumin levels facilitate fluid shift into the interstitial space, leading to extravascular fluid accumulation (such as ascites, pleural effusion, and intracranial effusion). This promotes the diffusion of the polar molecule MTX into third-space fluids, prolonging drug exposure time (Li et al., 2024; Reiss et al., 2016). Additionally, hypoalbuminemia reduces intravascular volume and decreases renal perfusion, which directly contributes to renal injury (Van der Beek et al., 2019). However, the study by Li X et al. in ALL children contradicts our findings, showing higher ALB as a risk factor for MTX-induced leucopenia (OR = 1.084, 95% CI: 1.003–1.171, p = 0.041) and neutropenia (OR = 1.101, 95% CI: 1.019–1.189, p = 0.0015), the odds ratios were very close to 1, suggesting a relatively weak association that may lack clinical significance (Li et al., 2019). Differences in patient characteristics, measurement timing, and adjustment for confounders may have contributed to the observed discrepancy. Further studies are needed to validate these findings across populations.
4.3 Gene polymorphisms
After entering cells, MTX can be converted to the polyglutamate form to inhibit dihydrofolate reductase and prevent the conversion of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate (THF) (Xu et al., 2022). In the purine and pyrimidine synthesis pathway, THF is an essential coenzyme in several transmethylation reactions and is also required for tumor cells to synthesize DNA and RNA. Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1 (MTHFD1) catalyzes the reduction of THF to produce a variety of active folic acid forms (e.g., 5-CH3-THF, 10-CH3-THF and 5,10-CH2-THF) to function as donors of single-carbon units in DNA synthesis (Giletti and Esperon, 2018). In our study, AA mutant homozygote on MTHFD1 rs2236225 was associated with a lower risk of anemia, while the wild-type homozygote GG associated with a lower risk of leukopenia. Studies have shown that A allele can alter the structure of MTHFD domain, reduce the activity of the enzyme, tilt the balance of folic acid, which is conducive to DNA repair and cell proliferation (Erculj et al., 2012). So far, several studies have investigated the effect of MTHFD polymorphism on HDMTX-related toxicity, but conflicting results have been reported and more evidence is needed (Erculj et al., 2012; Windsor et al., 2012; Erculj et al., 2014).
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) can irreversibly convert 5,10-CH2-THF to 5-CH3-THF (Xu et al., 2022). Rs1801133 and rs1801131 mutations reduce the activity of MTHFR, which is not conducive to protein synthesis, but also block the synthesis of THF, affecting DNA and RNA synthesis (Giletti and Esperon, 2018). In our analysis, the GG genotype in rs1801133 was associated with increased nephrotoxicity and thrombocytopenia, G mutation of rs1801131 is a risk factor for hepatotoxicity and a protective factor for anemia. It is worth mentioning that the influence of rs1801131 is much weaker than that of rs1801133 in reports, and some point out that rs1801131 has no obvious correlation with toxicity (Li et al., 2024).
Methionine synthase converts homocysteine into methionine for protein synthesis, and converts 5-CH3-THF into THF (Zhang et al., 2023). Only a few studies have pointed out the relationship between rs1801394 and mucositis with inconsistent results, but we found rs1801394 G allele is reflected as protective factor in occurrence of renal injury (Huang et al., 2008; Gong Y. et al., 2021).
ATP-binding cassette family transporters (involving proteins such as ABCB1, ABCG2 and ABCC1-5) promote the efflux of MTX and its metabolites from cells (Song et al., 2021; Vlaming et al., 2009). Our study found patients with T allele on ABCC2 rs717620 had a higher risk of thrombocytopenia. Liu Y′s study also mentioned T allele at rs717620 showed higher MTX plasma concentration than wild-type CC (Liu et al., 2014). The mutation on rs717620 is located in the 5′-untranslated region and has a negative effect on the activity of ABCC2 promoter. This polymorphism is associated with lower mRNA levels, so the synthesis of ABCC2 is reduced (Grzelj et al., 2021a). This results in diminished MTX elimination and increased in vivo exposure, increasing adverse reactions (Grzelj et al., 2021b; Razali et al., 2020).
In our study, at ABCB1 rs1045642, compared with the CC genotype, patients with the T allele had a lower risk of anemia and thrombocytopenia, which is consistent with the results of Jian Han’s study (Han et al., 2021). Gregers’ study also showed that patients with TT and CT variants had better liver function (Gregers et al., 2015). In the pharmacokinetic model established by Kim et al., patients with T allele had a lower MTX clearance rate, meaning higher drug exposure (Kim et al., 2012). Our study found that the G allele at rs1128503 is a risk factor for anemia. In Zaruma-Torres’s study, the mutation of ABCB1 rs1128503 was not related to the common adverse reactions of MTX, but showed a protective effect on bone marrow suppression (Zaruma-Torres et al., 2015). As the product of ABCB1 gene, P-gp is highly expressed in tumor cells (Li et al., 2023). The synonymous SNP, ABCB1 rs1128503 and rs1045642 polymorphisms did not change the amino acid sequence in the protein it encodes, but may be associated with decreased P-gp expression, and P-gp-mediated MTX transport may be affected (de Rotte et al., 2012).
The protein encoded by the ABCG2 gene not only affects the efflux of MTX, but also linked to anticancer drug resistance (Wang et al., 2011; Gorczyca and Aleksunes, 2020). In our patient population, A allele on rs2231142 have a higher risk of thrombocytopenia. The study by Esmaili MA et al. supported that ABCB1 rs1045642 CT genotype and ABCG2 rs2231142 AC genotype had significantly higher plasma MTX levels within 48 h, with no significant association with MTX-related hematopoietic and hepatic toxicities (Esmaili et al., 2020). The mutant allele A on ABCG2 rs2231142 is related to the decreased function of MTX transporter, leading to higher accumulation of MTX-PG in cells and an increased possibility of toxicity (Li et al., 2023; Baghdadi et al., 2018).
Patients with GG genotype at Glutathione S-transferase Pi 1 (GSTP1) rs1695 may be more prone to nephrotoxicity when treated with HDMTX. The association between GG genotype and central nervous system toxicity was also observed by Kishi S et al. (Kishi et al., 2007) GSTP is a phase II metabolic enzyme, which reduces the toxic of chemotherapy by catalyzing the combination of electrophilic substances and glutathione (Gong J. Y. et al., 2021). In addition to its role in detoxification, GSTP1 is involved in the activation of peroxiredoxin 6 (PRDX6). PRDX6 is a bifunctional antioxidant enzyme that protects cells from oxidative damage by reducing hydrogen peroxide and lipid peroxide (do Nascimento et al., 2021; de Sousa Barros et al., 2022). Reduced enzyme activity was observed in G variants, which not only prevents cellular detoxification, but may also affect the antioxidant response (Baghaei et al., 2022).
4.4 Co-medication
Loop diuretics exert diuretic effects by inhibiting Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporters in the thick ascending limb of the renal loop. On one side, the potent diuretic effect of diuretics may accelerate the excretion of MTX together with its metabolites, and reduce the retention of MTX. However, furosemide, torasemide and bumetanide require renal excretion, which will compete with MTX for OAT transporters secreted by renal tubules, resulting in decreased MTX excretion (Nigam et al., 2015; Nigam, 2018). And from a general dimension, the discharge of a large amount of urine reduces the effective circulating blood volume, leading to renal hypoperfusion, decreased glomerular filtration rate, and decreased MTX excretion (Howard et al., 2016). In our study, the combination of furosemide, torasemide and bumetanide with MTX was significantly associated with the occurrence of hematotoxicity, whereas furosemide appeared to have a decrease in hepatotoxicity. There are other scholars pointed out that furosemide is positively correlated with the occurrence of nephrotoxicity (Liang et al., 2023).
Levetiracetam is observed as a risk factor for methotrexate-induced anemia in our study. There were two reports of cases of delayed MTX elimination while taking levetiracetam concurrently (Bain et al., 2014; Parentelli et al., 2013). However, some studies showed no drug interaction between levetiracetam and HDMTX (DeFino et al., 2021; Lou et al., 2020; Reeves et al., 2016). Both levetiracetam and MTX are primarily excreted through kidney. Co-administration may compete for secretion from the renal tubules, leading to blocked MTX excretion (Reeves et al., 2016).
4.5 Age
Existing studies have explained that in adult patients, delayed excretion of MTX is more pronounced with age, and is a risk factor for acute hepatotoxicity (Zang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2023). In contrast, age was shown to be a protective factor for hepatotoxicity and hematotoxicity in our logistic regression, with OR ranging from 0.98 to 1, indicating that the influence was weak and age is not a strong predictor of toxicity in the our data set. The observed discrepancy in age may be due to the different doses administered to patients with different ages. We first conducted a linear analysis between patient age and drug dosage, which yielded an R2 value of 0.0092, indicating a very weak correlation. Therefore, we further stratified patients into two groups for subgroup analysis:
4.6 Limitations
Our study also has certain limitations: Firstly, the number of treatment cycles with grade 2–4 toxicity is small, especially for grade 3 or 4, so we divided the patients into two groups based on whether they experienced toxicity or not for statistical analysis. Secondly, we only have information on the drug administration during the hospitalization period, and PCNSL patients in our hospital are usually treated with combination chemotherapy, so the interference of other chemotherapy drugs cannot be excluded. Thirdly, as we did not analyze the relationship between 7-OH MTX and toxicity, the effect of 7-OH MTX on hepatotoxicity is unknown (Bremnes et al., 1991; Fuskevag et al., 2000). Given the rarity of PCNSL, the available patient population is inherently limited. This study included all eligible patients from our institution between 2016 and February 2024. And the data cleaning procedures reduced the final sample size, future studies with larger, multicenter cohorts are warranted to validate and extend these findings. We acknowledge that patient comorbidities and concurrent treatments may influence toxicity outcomes. However, due to limitations in the completeness and consistency of retrospective clinical records, we were unable to comprehensively adjust for these confounders. In our study, loop diuretics were associated with increased nephrotoxicity, possibly due to competition for renal tubular secretion with methotrexate. However, due to the lack of MTX clearance data, this mechanism could not be verified directly. After reading some case reports and references, the observed association between levetiracetam and hematologic toxicity also lacks established pharmacologic support. Additionally, diuretics are commonly prescribed for clinical conditions such as heart failure, edema, or impaired renal function—factors which may themselves predispose patients to toxicity. These underlying indications were not fully captured in our dataset, and the possibility of confounding cannot be excluded. These findings should be interpreted with caution, and further studies are needed to explore the underlying mechanisms. One methodological limitation of this study is that formal multicollinearity diagnostics were not conducted for the logistic regression models. Although efforts were made to minimize potential redundancy among covariates by selecting clinically relevant variables and avoiding highly correlated predictors, the lack of quantitative assessment of multicollinearity may affect the interpretability of results.
5 Conclusion
The results show that in PCNSL Chinese patients, higher plasma ALB was associated with a lower risk of HDMTX-related toxicities; the combination of loop diuretics and levetiracetam might increase the occurrence of toxic reactions. MTHFR (rs1801133) GG, ABCB1 (rs1128503) GG and AG, ABCG2 (rs2231142) AA and AC, and ABCC2 (rs717620) TT and GT genotypes were associated with increased MTX toxicities, whereas rs1045642 TT and CT, rs1801394 GG and AG genotypes might have protective effects.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, P.R. China (KY 2019-072-02). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from primarily isolated as part of your previous study for which ethical approval was obtained. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
WL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. RW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. YiL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. SW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. LF: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XS: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. YuL: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. ZZ: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. SM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This manuscript was funded by the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program (PX2024020) and Training Fund for Open Projects at Clinical Institutes and Departments of Capital Medical University (CCMU2023ZKYXY025) and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFC2008305) and Pharmacokinetics and Cerebrospinal Fluid Penetration of Ceftizoxime Tablets in Neurosurgical Postoperative Subjects with Diagnosed or Suspected Central Nervous System Infections (HX-A-2022050).
Acknowledgments
Thanks are given to all patients and authors in our study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1561818/full#supplementary-material
References
Amitai, I., Rozovski, U., El-Saleh, R., Shimony, S., Shepshelovich, D., Rozen-Zvi, B., et al. (2020). Risk factors for high-dose methotrexate associated acute kidney injury in patients with hematological malignancies. Hematol. Oncol. 38, 584–588. doi:10.1002/hon.2759
Baghaei, A., Behjati, M., and Karimian, A. (2022). Association analysis of GSTP1-rs1695 polymorphism with the risk of oral cancer: a literature review, an updated Meta- analysis, and a structural assessment. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev. 23, 3859–3868. doi:10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.11.3859
Baghdadi, L. R., Woodman, R. J., Shanahan, E. M., Wiese, M. D., and Mangoni, A. A. (2018). Genetic polymorphism of the methotrexate transporter ABCG2, blood pressure and markers of arterial function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: repeated cross-sectional study. Pharmgenomics Pers. Med. 11, 205–210. doi:10.2147/PGPM.S170557
Bain, E., Birhiray, R. E., and Reeves, D. J. (2014). Drug-drug interaction between methotrexate and levetiracetam resulting in delayed methotrexate elimination. Ann. Pharmacother. 48, 292–296. doi:10.1177/1060028013511951
Bedoui, Y., Guillot, X., Selambarom, J., Guiraud, P., Giry, C., Jaffar-Bandjee, M. C., et al. (2019). Methotrexate an old drug with new tricks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 5023. doi:10.3390/ijms20205023
Bremnes, R. M., Smeland, E., Huseby, N. E., Eide, T. J., and Aarbakke, J. (1991). Acute hepatotoxicity after high-dose methotrexate administration to rats. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 69, 132–139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1991.tb01286.x
Cook, A. M., McDonnell, A. M., Lake, R. A., and Nowak, A. K. (2016). Dexamethasone co-medication in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy causes substantial immunomodulatory effects with implications for chemo-immunotherapy strategies. Oncoimmunology 5, e1066062. doi:10.1080/2162402X.2015.1066062
DeFino, C. E., Barreto, J. N., Pawlenty, A. G., Ruff, M. W., Carabenciov, I. D., Mara, K. C., et al. (2021). Lack of drug interaction between levetiracetam and high-dose methotrexate in patients with lymphoma. Pharmacotherapy 41, 430–439. doi:10.1002/phar.2516
de Rotte, M. C., Bulatovic, M., Heijstek, M. W., Jansen, G., Heil, S. G., van Schaik, R. H., et al. (2012). ABCB1 and ABCC3 gene polymorphisms are associated with first-year response to methotrexate in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 39, 2032–2040. doi:10.3899/jrheum.111593
de Sousa Barros, J. B., de Faria Santos, K., da Cruz Pereira Bento, D., Prado Assuncao, L. D., da Silva Santos, R., and da Silva Reis, A. A. (2022). Influence of GSTP1 rs1695 polymorphism on survival in Male patients' amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a genetic association study in Brazilian population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 49, 1655–1659. doi:10.1007/s11033-021-06724-z
do Nascimento, M. R., Silva de Souza, R. O., Silva, A. L. J., Lima, E. S., Gonçalves, M. S., and de Moura Neto, J. P. (2021). GSTP1 rs1695 and rs1871042, and SOD2 rs4880 as molecular markers of lipid peroxidation in blood storage. Blood Transfus. 19, 309–316. doi:10.2450/2020.0062-20
Ellis, J. A., and Ong, B. (2017). The MassARRAY® system for targeted SNP genotyping. Methods Mol. Biol. 1492, 77–94. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-6442-0_5
Erculj, N., Kotnik, B. F., Debeljak, M., Jazbec, J., and Dolzan, V. (2012). Influence of folate pathway polymorphisms on high-dose methotrexate-related toxicity and survival in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 53, 1096–1104. doi:10.3109/10428194.2011.639880
Erculj, N., Kotnik, B. F., Debeljak, M., Jazbec, J., and Dolzan, V. (2014). The influence of folate pathway polymorphisms on high-dose methotrexate-related toxicity and survival in children with Non-Hodgkin malignant lymphoma. Radiol. Oncol. 48, 289–292. doi:10.2478/raon-2013-0076
Esmaili, M. A., Kazemi, A., Faranoush, M., Mellstedt, H., Zaker, F., Safa, M., et al. (2020). Polymorphisms within methotrexate pathway genes: relationship between plasma methotrexate levels, toxicity experienced and outcome in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 23, 800–809. doi:10.22038/ijbms.2020.41754.9858
Ferreri, A. J., Guerra, E., Regazzi, M., Pasini, F., Ambrosetti, A., Pivnik, A., et al. (2004). Area under the curve of methotrexate and creatinine clearance are outcome-determining factors in primary CNS lymphomas. Br. J. Cancer 90, 353–358. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601472
Fischer, M., Siva, S., Cook, G. K., Jones, D. R., and Fadda, H. M. (2017). Methotrexate polyglutamate monitoring in patients with crohn's disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 6, 240–245. doi:10.1002/cpdd.279
Flospergher, E., Marino, F., Calimeri, T., Cangi, M. G., Ferreri, A. J. M., Ponzoni, M., et al. (2024). Primary central nervous system marginal zone lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 204, 31–44. doi:10.1111/bjh.19238
Fuskevag, O. M., Kristiansen, C., Lindal, S., and Aarbakke, J. (2000). Maximum tolerated doses of methotrexate and 7-hydroxy-methotrexate in a model of acute toxicity in rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 46, 69–73. doi:10.1007/s002800000111
Giletti, A., and Esperon, P. (2018). Genetic markers in methotrexate treatments. Pharmacogenomics J. 18, 689–703. doi:10.1038/s41397-018-0047-z
Gong, J. Y., Peng, S. Y., Xing, K., Fan, L., Tan, S. L., Luo, Z. Y., et al. (2021b). Evaluating the role of GSTP1 genetic polymorphism (Rs1695, 313A>G) as a predictor in cyclophosphamide-induced toxicities. Med. Baltim. 100, e24423. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000024423
Gong, Y., Luo, L., Wang, L., Chen, J., Chen, F., Ma, Y., et al. (2021a). Association of MTHFR and ABCB1 polymorphisms with MTX-Induced mucositis in Chinese paediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, lymphoma or osteosarcoma-A retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 46, 1557–1563. doi:10.1111/jcpt.13505
Gorczyca, L., and Aleksunes, L. M. (2020). Transcription factor-mediated regulation of the BCRP/ABCG2 efflux transporter: a review across tissues and species. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 16, 239–253. doi:10.1080/17425255.2020.1732348
Gregers, J., Gréen, H., Christensen, I. J., Dalhoff, K., Schroeder, H., Carlsen, N., et al. (2015). Polymorphisms in the ABCB1 gene and effect on outcome and toxicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics J. 15, 372–379. doi:10.1038/tpj.2014.81
Grzelj, J., Marovt, M., Marko, P. B., Mlinaric-Rascan, I., Gmeiner, T., and Smid, A. (2021b). Polymorphism in gene for ABCC2 transporter predicts methotrexate drug survival in patients with psoriasis. Med. Kaunas. 57, 1050. doi:10.3390/medicina57101050
Grzelj, J., Mlinaric-Rascan, I., Marko, P. B., Marovt, M., Gmeiner, T., and Smid, A. (2021a). Polymorphisms in GNMT and DNMT3b are associated with methotrexate treatment outcome in plaque psoriasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 138, 111456. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111456
Hamed, K. M., Dighriri, I. M., Baomar, A. F., Alharthy, B. T., Alenazi, F. E., Alali, G. H., et al. (2022). Overview of methotrexate toxicity: a comprehensive literature review. Cureus 14, e29518. doi:10.7759/cureus.29518
Han, J., Liu, L., Meng, L., Guo, H., Zhang, J., Han, Z. Q., et al. (2021). Effect of polymorphisms of ABCB1 and MTHFR on methotrexate-related toxicities in adults with hematological malignancies. Front. Oncol. 11, 759805. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.759805
Howard, S. C., McCormick, J., Pui, C. H., Buddington, R. K., and Harvey, R. D. (2016). Preventing and managing toxicities of high-dose methotrexate. Oncologist 21, 1471–1482. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0164
Huang, L., Tissing, W. J., de Jonge, R., van Zelst, B. D., and Pieters, R. (2008). Polymorphisms in folate-related genes: association with side effects of high-dose methotrexate in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 22, 1798–1800. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.66
Joerger, M., Ferreri, A. J., Krähenbühl, S., Schellens, J. H., Cerny, T., Zucca, E., et al. (2012). Dosing algorithm to target a predefined AUC in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma receiving high dose methotrexate. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 73, 240–247. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04084.x
Joerger, M., Huitema, A. D., Krähenbühl, S., Schellens, J. H., Cerny, T., Reni, M., et al. (2010). Methotrexate area under the curve is an important outcome predictor in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis from the IELSG no. 20 trial. Br. J. Cancer 102, 673–677. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605559
Khera, S., Sharma, G., Negi, V., and Shaw, S. C. (2022). Hypoalbuminemia and not undernutrition predicts high-dose methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in resource-constrained centers. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 69, e29738. doi:10.1002/pbc.29738
Kim, I. W., Yun, H. Y., Choi, B., Han, N., Park, S. Y., Lee, E. S., et al. (2012). ABCB1 C3435T genetic polymorphism on population pharmacokinetics of methotrexate after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in Korean patients: a prospective analysis. Clin. Ther. 34, 1816–1826. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.06.022
Kishi, S., Cheng, C., French, D., Pei, D., Das, S., Cook, E. H., et al. (2007). Ancestry and pharmacogenetics of antileukemic drug toxicity. Blood 109, 4151–4157. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-10-054528
Koźmiński, P., Halik, P. K., Chesori, R., and Gniazdowska, E. (2020). Overview of dual-acting drug methotrexate in different neurological diseases, autoimmune pathologies and cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 3483. doi:10.3390/ijms21103483
Li, M., Kong, X. Y., and Wang, S. M. (2023). Effects of splicing-regulatory polymorphisms in ABCC2, ABCG2, and ABCB1 on methotrexate exposure in Chinese children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 91, 77–87. doi:10.1007/s00280-022-04498-0
Li, W., Mo, J., Yang, Z., Zhao, Z., and Mei, S. (2024). Risk factors associated with high-dose methotrexate induced toxicities. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 20, 263–274. doi:10.1080/17425255.2024.2332366
Li, X., Sui, Z., Jing, F., Xu, W., Li, X., Guo, Q., et al. (2019). Identifying risk factors for high-dose methotrexate-induced toxicities in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Manag. Res. 11, 6265–6274. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S207959
Liang, C. A., Su, Y. C., Lin, S. J., and Tsai, T. H. (2023). Risk factors for acute kidney injury after high-dose methotrexate therapy: a single-center study and narrative review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 79, 789–800. doi:10.1007/s00228-023-03491-7
Liu, Y., Yin, Y., Sheng, Q., Lu, X., Wang, F., Lin, Z., et al. (2014). Association of ABCC2 -24C>T polymorphism with high-dose methotrexate plasma concentrations and toxicities in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS One 9, e82681. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0082681
Lou, U., Kwok, J., Nguyen, T. A., Zhou, A., and Luk, S. O. (2020). Effect of levetiracetam on time to high-dose methotrexate clearance in patients with hematologic malignancies. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 60, 324–330. doi:10.1002/jcph.1544
Maksimovic, V., Pavlovic-Popovic, Z., Vukmirovic, S., Cvejic, J., Mooranian, A., Al-Salami, H., et al. (2020). Molecular mechanism of action and pharmacokinetic properties of methotrexate. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47, 4699–4708. doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05481-9
Mei, S., Li, X., Jiang, X., Yu, K., Lin, S., and Zhao, Z. (2018a). Population pharmacokinetics of high-dose methotrexate in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. J. Pharm. Sci. 107, 1454–1460. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2018.01.004
Mei, S., Shi, X., Du, Y., Cui, Y., Zeng, C., Ren, X., et al. (2018b). Simultaneous determination of plasma methotrexate and 7-hydroxy methotrexate by UHPLC-MS/MS in patients receiving high-dose methotrexate therapy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 158, 300–306. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2018.06.011
Nigam, S. K. (2018). The SLC22 transporter family: a paradigm for the impact of drug transporters on metabolic pathways, signaling, and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 58, 663–687. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010617-052713
Nigam, S. K., Bush, K. T., Martovetsky, G., Ahn, S. Y., Liu, H. C., Richard, E., et al. (2015). The organic anion transporter (OAT) family: a systems biology perspective. Physiol. Rev. 95, 83–123. doi:10.1152/physrev.00025.2013
Parentelli, A. S., Phulpin-Weibel, A., Mansuy, L., Contet, A., Trechot, P., and Chastagner, P. (2013). Drug-drug interaction between methotrexate and levetiracetam in a child treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 60, 340–341. doi:10.1002/pbc.24371
Razali, R. H., Noorizhab, M. N. F., Jamari, H., James, R. J., Teh, K. H., Ibrahim, H. M., et al. (2020). Association of ABCC2 with levels and toxicity of methotrexate in Malaysian childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 37, 185–197. doi:10.1080/08880018.2019.1705949
Reeves, D., DiDominick, S., Finn, S., Kim, H. J., and Shake, A. (2016). Methotrexate elimination when coadministered with levetiracetam. Ann. Pharmacother. 50, 1016–1022. doi:10.1177/1060028016661572
Reiss, S. N., Buie, L. W., Adel, N., Goldman, D. A., Devlin, S. M., and Douer, D. (2016). Hypoalbuminemia is significantly associated with increased clearance time of high dose methotrexate in patients being treated for lymphoma or leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 95, 2009–2015. doi:10.1007/s00277-016-2795-7
Song, Z., Hu, Y., Liu, S., Jiang, D., Yi, Z., Benjamin, M. M., et al. (2021). The role of genetic polymorphisms in high-dose methotrexate toxicity and response in hematological malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 757464. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.757464
Van der Beek, J. N., Oosterom, N., Pieters, R., de Jonge, R., van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M. M., and Heil, S. G. (2019). The effect of leucovorin rescue therapy on methotrexate-induced oral mucositis in the treatment of paediatric ALL: a systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 142, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.07.003
Vlaming, M. L., Pala, Z., van Esch, A., Wagenaar, E., de Waart, D. R., van de Wetering, K., et al. (2009). Functionally overlapping roles of Abcg2 (Bcrp1) and Abcc2 (Mrp2) in the elimination of methotrexate and its main toxic metabolite 7-hydroxymethotrexate in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 3084–3093. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2940
Wang, F., Liang, Y. J., Wu, X. P., Chen, L. M., To, K. K., Dai, C. L., et al. (2011). Prognostic value of the multidrug resistance transporter ABCG2 gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with de novo acute leukaemia. Eur. J. Cancer 47, 1990–1999. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.03.032
Wang, S. F., Huang, K. W., Chou, Y. C., Lee, H. C., Wu, P. K., Chen, W. M., et al. (2023). Effect of co-medications and potential risk factors of high-dose methotrexate-mediated acute hepatotoxicity in patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer Med. 12, 12354–12364. doi:10.1002/cam4.5936
Wei, S., Zhang, S., Wang, D., Zhang, D., Lu, Q., Mo, J., et al. (2025). Population pharmacokinetics of high-dose methotrexate in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1578033. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1578033
Windsor, R. E., Strauss, S. J., Kallis, C., Wood, N. E., and Whelan, J. S. (2012). Germline genetic polymorphisms May influence chemotherapy response and disease outcome in osteosarcoma: a pilot study. Cancer 118, 1856–1867. doi:10.1002/cncr.26472
Xu, M., Wu, S., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Wang, X., Wei, C., et al. (2022). Association between high-dose methotrexate-induced toxicity and polymorphisms within methotrexate pathway genes in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1003812. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1003812
Zang, Y. N., Wang, S. Z., Qin, Y., Zhang, J. R., Zhao, L. B., and Wang, X. L. (2019). Population pharmacokinetic study of delayed methotrexate excretion in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 57, 402–407. doi:10.5414/CP203423
Zaruma-Torres, F., Lares-Asseff, I., Reyes-Espinoza, A., Loera-Castaneda, V., Chairez-Hernandez, I., Sosa-Macias, M., et al. (2015). Association of ABCB1, ABCC5 and xanthine oxidase genetic polymorphisms with methotrexate adverse reactions in Mexican pediatric patients with ALL. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 30, 195–201. doi:10.1515/dmpt-2015-0011
Keywords: high dose methotrexate, nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, hematotoxicity, risk factors, single nucleotide polymorphism
Citation: Li W, Zhang S, Wu R, Li Y, Wei S, Fu L, Sun X, Liu Y, Zhao Z and Mei S (2025) Risk factors associated with high-dose methotrexate induced toxicities in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1561818. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1561818
Received: 16 January 2025; Accepted: 22 July 2025;
Published: 04 August 2025.
Edited by:
Ahmed Esmat Abdel Moneim, Helwan University, EgyptReviewed by:
Yao Liu, Daping Hospital, ChinaXiaolin Qian, Southern Research Institute, United States
Mona Saber, Cairo University, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Li, Zhang, Wu, Li, Wei, Fu, Sun, Liu, Zhao and Mei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuanbo Liu, eXVhbmJvbEBjY211LmVkdS5jbg==; Zhigang Zhao, MTAyMnp6Z0BzaW5hLmNvbQ==; Shenghui Mei, bWVpc2hlbmdodWkxOTgzQDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Wenshu Li
Wenshu Li Sitian Zhang
Sitian Zhang Ruoyun Wu
Ruoyun Wu Ying Li4
Ying Li4 Shifeng Wei
Shifeng Wei Lin Fu
Lin Fu Yuanbo Liu
Yuanbo Liu Zhigang Zhao
Zhigang Zhao Shenghui Mei
Shenghui Mei