- 1School of Comprehensive Health Management, Xihua University, Chengdu, China
- 2School of Food and Bioengineering, Xihua University, Chengdu, China
- 3School of Pharmaceutical and Environmental Engineering, Sichuan Vocational College of Chemical Technology, Luzhou, China
Metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), previously known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a common liver condition marked by excessive fat accumulation exceeding 5% in the liver without significant alcohol consumption. It is closely linked to metabolic disorders such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia, with a rising global prevalence projected to escalate from 25% to 56% over the next decade. The pathogenesis of MAFLD is multifaceted, involving insulin resistance, inflammation, and oxidative stress, with progressive symptoms that can lead to severe liver conditions including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Current treatment options are limited, as established medications show variable efficacy and safety. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (S. baicalensis) a traditional Chinese herb rich in flavonoids, has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic effects on MAFLD. Its pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating properties, position S. baicalensis as a promising candidate for MAFLD management. This article reviews the latest research progress of S. baicalensis in the treatment of MAFLD, explores its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and the development of related products, aiming to clarify the pathogenesis of MAFLD and promote the development of new treatment and prevention strategies based on traditional Chinese medicine.
1 Introduction
NAFLD is a common liver disease characterized by fat accumulation of more than 5% in the liver without excessive alcohol consumption. This disease is closely associated with metabolic syndromes and is commonly observed in individuals with obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension (Palma et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2018). The pathogenesis of NAFLD is complex and involves multiple factors such as insulin resistance, inflammatory responses, and oxidative stress. Clinically, NAFLD presents a wide range of symptoms, with many patients experiencing no noticeable signs in the early stages. As the disease progresses, symptoms like fatigue and discomfort in the right upper abdomen may occur. NAFLD can further advance to NASH, a more severe inflammatory condition of the liver that can lead to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma (Figure 1) (Ohtani et al., 2023). The global prevalence of NAFLD is rising annually, with projections indicating that prevalence will increase significantly from the current 25%–56% in China, the United States, and most European countries over the next decade (Huang et al., 2020). Lifestyle factors such as sedentary behavior and poor dietary habits are significant contributors to the development of NAFLD. Therefore, lifestyle interventions—including low-calorie diets, regular exercise, and weight management—are considered effective strategies for treatment and prevention (Elvira-Torales et al., 2019).
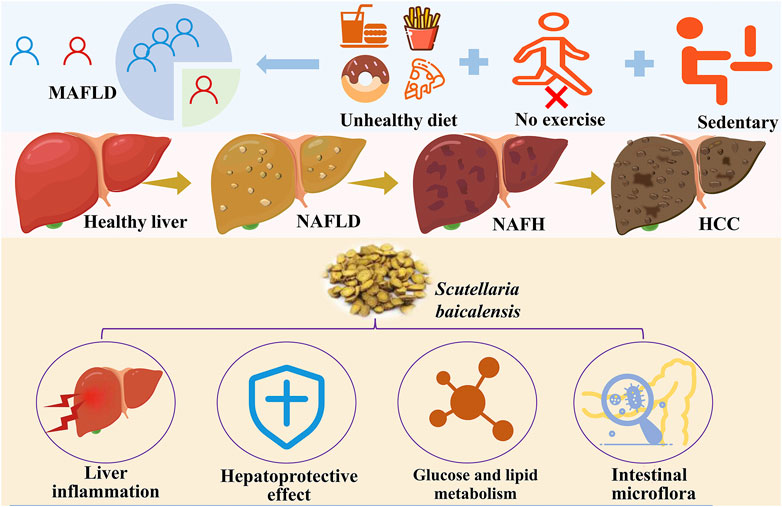
Figure 1. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and potential protective methods of MAFLD (Created by iconfont. cn).
As NAFLD gains increasing attention globally, there is a growing recognition of the inherent limitations of the term “nonalcoholic.” This characterization places excessive emphasis on the absence of alcohol consumption while neglecting the significance of metabolic risk factors that drive the progression of NAFLD. The term NASH is even more complex, as “steatohepatitis” adds an additional layer of difficulty. In this context, diagnosing NASH not only requires the exclusion of alcohol intake but also histological confirmation of steatohepatitis. Studies have demonstrated significant inter- and intra-observer variability in the histological features, particularly ballooned hepatocytes, which are the main pathological hallmark. Given the lack of clarity regarding the relationship between NAFLD and metabolic risk factors, coupled with the overemphasis on alcohol, an international expert panel suggested in 2020 that the condition be renamed MAFLD. Consequently, this article will consistently use the term MAFLD.
Although several medications, such as metformin, vitamin E, and pioglitazone, are currently used to treat MAFLD (Guo et al., 2022), their efficacy and safety remain debated, and no specific drug for this condition has been established. Metformin has limited efficacy in reducing liver fat in the treatment of MAFLD (Goldberg et al., 2021), and long-term treatment may induce hepatotoxicity (Cone et al., 2010; Hashmi, 2011; Miralles-Linares et al., 2012). Vitamin E supplementation notably raised the risk of prostate cancer in healthy men (Klein et al., 2011). Pioglitazone is known to increase the risk of heart failure and fractures and might be associated with bladder cancer (Portillo-Sanchez et al., 2019; Azoulay et al., 2012; Violi and Cangemi, 2010). In summary, MAFLD is not only a significant concern for liver health but also poses a challenge to global public health. As its prevalence continues to rise, early detection and intervention will be key to improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of associated complications. Thus, it is crucial to develop new treatment and prevention strategies, particularly those targeting metabolic abnormalities.
S. baicalensis, commonly known as Huangqin, is a perennial herbaceous plant belonging to the Lamiaceae family, primarily distributed in China and other East Asian regions (Jiang et al., 2017; Zhao Q. et al., 2016). The earliest documentation of S. baicalensis can be found in Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica (Shennong Bencao Jing in Chinese), a classic Chinese herbal text written between 200 and 250 AD, which highlights its use for treating conditions related to bitterness, as well as lung and liver issues. The authoritative traditional Chinese medicine text “Bencao Gangmu” first published in 1,593, further reports S. baicalensis’s applications in treating diarrhea, dysentery, hypertension, hemorrhage, insomnia, inflammation, and respiratory infections (Chen et al., 2018; Orzechowska et al., 2020; Ji et al., 2015; Zhi et al., 2019; Yoon et al., 2020).
S. baicalensis is rich in flavonoids, including baicalin and baicalein, which contribute to its pharmacological activities (Hai-Juan et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2021). In recent years, there has been growing interest in S. baicalensis’s potential role in the treatment of MAFLD, a metabolic disorder characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver (Chen et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2010; Sun et al., 2019). The pathogenesis of MAFLD is complex, involving factors such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism dysregulation. Given S. baicalensis’s anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating properties, it is emerging as a promising candidate for MAFLD treatment research (Younossi et al., 2016; Semanticscholar, 2019; Yan et al., 2023; Na and sciences, 2019).
This review conducted a comprehensive literature search and screening of studies on S. baicalensis and its bioactive metabolites, such as baicalin and wogonin, in the treatment of MAFLD. Databases including PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science were systematically searched using combinations of the keywords “S. baicalensis” or its bioactive metabolites with “MAFLD” or “NAFLD.”The exclusion criteria were as follows: (I) Studies that did not investigate S. baicalensis or its bioactive metabolites for the treatment of MAFLD; (II) Studies in which S. baicalensis or its derivatives were not the primary intervention; (III) Studies focusing solely on the general pharmacological properties of S. baicalensis without specific relevance to MAFLD.
This review summarizes the current studies of S. baicalensis used for the treatment of MAFLD of pharmacological activity, mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics and development of S. baicalensis-related products, to provide an important foundation for clarifying the pathogenesis of MAFLD and developing novel approaches for treatment and prevention based on Chinese herbal medicines.
2 The pathogenesis of MAFLD
MAFLD is widely recognized as a complex condition with multifactorial etiology, involving various contributors such as lipid metabolism disorders, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, inflammatory activation, insulin resistance (IR), leptin resistance, oxidative stress, and dysbiosis of the gut microbiota (Rives et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021; Wei et al., 2016). Among these, lipid metabolism disorders are central to the pathogenesis of MAFLD. Under normal circumstances, the liver regulates lipid synthesis and degradation through multiple mechanisms. However, in MAFLD patients, abnormal lipogenesis leads to significantly elevated levels of free fatty acids while fatty acid oxidation is markedly reduced (Metabolizm, 2012; Veracruz et al., 2021). This metabolic imbalance not only results in the accumulation of triglycerides (TG) in hepatocytes but also promotes the development of insulin resistance, subsequently triggering severe inflammatory responses (Hanley et al., 2004; Leung et al., 2008; Samuel et al., 2004; Singal et al., 2014; Szabo et al., 2015; Vozarova et al., 2002). Additionally, ER stress plays a critical role in the progression of MAFLD. When hepatocytes encounter excess lipids or other stressors, ER dysfunction can lead to the accumulation of unfolded proteins, initiating an ER stress response (Cullinan and Chemistry, 2004; Ajoolabady et al., 2023; Malhotra et al., 2008). This stress state activates multiple signaling pathways, resulting in inflammation and apoptosis of liver cells (Yu et al., 2019). Inflammatory responses are pivotal in the progression from MAFLD to NASH. Activated inflammatory cells in the liver, such as Kupffer cells and macrophages, release various pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which exacerbate hepatocyte damage and promote liver fibrosis (Kazankov et al., 2018).
Furthermore, insulin resistance and leptin resistance are significant metabolic features of MAFLD. Insulin resistance diminishes the liver’s response to insulin, disrupting glucose and lipid metabolism, while leptin resistance leads to energy imbalance, further exacerbating hepatic lipid accumulation. These metabolic abnormalities are closely linked to the onset of MAFLD and may contribute to disease progression. Oxidative stress represents another critical pathological mechanism; in MAFLD patients, levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are significantly elevated. Excess ROS can induce lipid peroxidation, protein damage, and DNA injury, exacerbating hepatocyte apoptosis and inflammatory responses. According to research by James P. Hardwick (Osborne et al., 2022), CYP4V2 may play a crucial role in regulating the progression of fat liver-related metabolic diseases. As simple steatosis progresses to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), ROS levels continue to rise, further underscoring the significance of oxidative stress in the advancement of MAFLD.
In the pathophysiology of MAFLD, the “two-hit” hypothesis is widely accepted. This theory posits that the progression of MAFLD occurs in two phases. The “first hit” refers to the accumulation of triglycerides within hepatocytes (i.e., steatosis) and the development of hepatic insulin resistance, which renders the liver more susceptible to subsequent damage. The “second hit” encompasses the secondary injuries resulting from the first hit, including alterations in the synthesis of lipotoxic factors, increased inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and liver fibrosis (Borrelli et al., 2018; Byrne and Hepatology, 2015; Haas et al., 2015; Rada et al., 2020). Moreover, ethnic and genetic differences significantly influence the occurrence of MAFLD. Research indicates that certain genetic variations may increase an individual’s susceptibility to MAFLD, while environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle, can interact with genetic predispositions, further impacting the disease’s development (Caliceti et al., 2016).
As such, the “two-hit” hypothesis is often viewed by scientists as insufficient to explain all the molecular and metabolic abnormalities associated with MAFLD. In contrast, the “multiple-hit” theory suggests that the onset of MAFLD results from the combined effects of various damaging factors, including insulin resistance, adipokine secretion from adipose tissue, and the interplay between environmental (dietary) and genetic factors, such as epigenetics (Pierantonelli and Transplantation, 2019; Fang et al., 2018). The “multi-organ multiple impact” theory was proposed to explain the progression of MAFLD/NASH, arguing that free fatty acids, derived from lipolysis or de novo lipogenesis from dietary fats, exacerbate the burden on the liver. While fatty acids can be metabolized through β-oxidation and triglyceride degradation, saturation of these pathways leads to the formation of lipotoxic lipids, which may cause oxidative damage, ER stress, inflammation, and even cell death. Additionally, non-hepatic organs may directly or indirectly facilitate the development of NASH (Stefan et al., 2019; Kanwal et al., 2021; Long et al., 2022).
Recent studies have highlighted the potential protective effects of S. baicalensis, a traditional Chinese medicine, against MAFLD. Active metabolites in S. baicalensis, such as baicalin, have been shown to possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid metabolism-improving properties (Liu et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Shi et al., 2020; Na and sciences, 2019). Research indicates that Scutellaria can reduce fat accumulation in hepatocytes and suppress inflammatory responses by regulating the expression of lipid metabolism-related genes (Shi et al., 2020; Geethangili et al., 2021). Furthermore, Scutellaria may promote gut health by improving the composition of the gut microbiota, thereby indirectly alleviating the symptoms of MAFLD (Ansari et al., 2020). Therefore, S. baicalensis can treat numerous pathophysiological mechanisms associated with NAFLD to ameliorate it.
3 The therapeutic mechanism of S. baicalensis for MAFLD
According to a comprehensive analysis of the literature, bioactive substances from S. baicalensis, including baicalin and baicalein, have been demonstrated antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities (Zhong and Liu, 2018; Xin et al., 2014), thereby alleviating liver damage and improving the pathological state of MAFLD. The therapeutic effects of S. baicalensis on MAFLD also involved other pathophysiological processes, including the improvement of insulin resistance, regulation of dyslipidemia, and modulation of the gut microbiota.
It has been suggested that S. baicalensis improves insulin sensitivity by modulating signaling pathways such as insulin signaling, thereby ameliorating disorders of glucose and lipid metabolism (Noh et al., 2021). In terms of regulating dyslipidemia, S. baicalensis has been found to reduce serum levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides, and other lipids through various mechanisms (Yan et al., 2022). Furthermore, during the combined treatment of MAFLD with other drugs, S. baicalensis has been shown to enhance therapeutic efficacy through its multitarget actions. These findings have demonstrate that S. baicalensis could treat or improve MAFLD through multiple pathways, and the specific mechanisms will be discussed in the following sections.
3.1 S. baicalensis regulates liver inflammation in the treatment of MAFLD
The development of MAFLD is closely associated with chronic inflammation caused by an imbalance between anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory markers. Extensive experimental studies have shown that S. baicalensis could alleviate hepatic inflammation by blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway, thus treating or delaying the onset of MAFLD. Furthermore, S. baicalensis treats MAFLD by controlling hepatic inflammation, altering macrophage polarization (Junior et al., 2021), and exhibiting antioxidant effects through the regulation of Nrf2 transcription factors and other mechanisms (Xin et al., 2014).
In multiple in vitro and in vivo studies, it has been well established that S. baicalensis exhibits potent anti-inflammatory effects and is demonstrated as a potential anti-inflammatory agent that plays an important role in reducing the inflammatory response in MAFLD. Therefore, we will next review the therapeutic effects of S. baicalensis on MAFLD inflammation, focusing on three key aspects: the NF-κB signaling pathway, macrophages, and oxidative stress.
3.1.1 The NF-κB signaling pathway
The activation of NLRP3 has plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of MAFLD (Zou et al., 2022). Numerous studies have demonstrated that the NF-κB-mediated signaling pathway increases NLRP3 expression, which subsequently elevates the expression levels of inflammatory factors such as Pro-IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6. The NLRP3 inflammasome is composed of three proteins: NLRP3, ASC, and pro-caspase-1 (Shao et al., 2015). Upon activation of NLRP3, pro-caspase-1 undergones autolytic cleavage and cleaves the precursors of inflammatory cytokines, activating their inflammatory activity. It also cleaves GSDMD, releasing its N-terminal fragment, GSDMD-N, which forms pores on the cell membrane, resulting in membrane rupture and pyroptotic cell death (Fu et al., 2024). This process causes fibrosis in normal hepatocytes and accelerates the progression of MAFLD.
While treating MAFLD rats with S. baicalensis, researchers have discovered through molecular docking techniques that baicalin exhibited high affinity for TLR4 and NF-κB. This finding suggests that baicalin might alleviate inflammation and treat MAFLD by forming a robust hydrogen bond network with various amino acid residues of TLR4 and NF-κB, thereby blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway (Yan et al., 2023). Another study demonstrated the antifibrotic effects of baicalin in SD rats with thioacetamide-induced cirrhosis, revealing that its mechanism involved inhibition of NLPR3 and NF-κB signaling pathways, thereby reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines (Zaghloul et al., 2022). Gao et al. established a mouse model of MAFLD using a high-fat diet (HFD) and treated the mice with baicalin. They have found that intervention with baicalin inhibited the activity of NF-κB, reduced its nuclear translocation, and downregulated the expression of inflammation-related genes, thereby alleviating hepatic inflammatory responses. Additionally, activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway and inhibition of SREBP1 together improved overall liver function (Gao et al., 2023). In summary, baicalin has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects by blocking NF-κB activation and inhibiting NLRP3, thereby reducing the production of inflammatory factors and improving hepatic metabolic function, providing new insights for the treatment of MAFLD.
3.1.2 Macrophages
Based on their functional status, macrophages are classified into pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages and anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. M1 macrophages induce robust inflammatory responses by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, and TNF-α, but excessive activation resultes in tissue damage. In contrast, M2 macrophages exhibite anti-inflammatory and reparative functions, primarily through the secretion of Arg-1, IL-10, TGF-β, and matrix metalloproteinases, contributing to tissue repair, wound healing and cellular debris clearance (Arabpour et al., 2021; Gordon and Martinez, 2010). In the treatment of MAFLD, M1 macrophages have been identified as primary effector cells responsible for excessive hepatic inflammatory responses (Junior et al., 2021). A study demonstrated that baicalin could repolarize lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced M1 macrophages into an M2 phenotype characterized by the downregulation of IRF5, TNF-α, and IL-23 (Zhu et al., 2016). Furthermore, subsequent research revealed that baicalin could induce the differentiation of macrophages into the anti-inflammatory M2c subtype and significantly enhance the expression and secretion of anti-inflammatory factors such as IL-10, IL-13 and IL-4 by activating the MERTK signaling pathway and suppressing it at the same time pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-12 and IFN-γ. This mechanism not only promoted immune tolerance and tissue repair but also improved the pathological symptoms of diet-induced MAFLD in murine models by enhancing hepatic HDL production and circulation, improving triglyceride transport, and inhibiting fatty acid synthesis (Junior et al., 2021).
Researchers have discovered that baicalin inhibits pan-apoptosis in Kupffer cells in a mouse model of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, thereby alleviating hepatic inflammation and organ damage (You et al., 2024). Similarly, Liu et al. demonstrated that baicalin treatment in a choline-deficient diet-induced mouse model of MAFLD significantly reduced macrophage infiltration and reversed hepatic lipid accumulation by suppressing the TLR4 signaling cascade. This effect protected the mice from MAFLD progression and inhibited further disease-related fibrosis (Liu et al., 2020). In another study, it was found that baicalin significantly decreased Ly6Chi monocytes, M1 adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs), and M1 Kupffer cells in HFD-induced obese mice. Conversely, it increased anti-inflammatory M2 ATMs, hepatic CD4+ T cells, and the CD4/CD8 ratio (Noh et al., 2021). The study demonstrated that CD4+ T cells suppressed inflammatory responses by regulating the function of ATM, whereas CD8+ T cells promoted the polarization of M1 macrophages. Consequently, increasing the CD4/CD8 ratio enhances immune surveillance, inhibited inflammation, and significantly improved obesity by modulating glucose and lipid metabolism, thereby preventing further hepatic fat accumulation (Conroy et al., 2016; Nishimura et al., 2009). In summary, baicalin has exhibited substantial potential in the treatment of MAFLD by regulating macrophage polarization and inflammatory responses.
3.1.3 Regulating inflammation through oxidative stress
Oxidative stress plays a critical role in the pathological states of the liver (Tauil et al., 2024). Park et al. used a LPS-induced liver injury mouse model and found that heat-treated S. baicalensis significantly inhibited reactive ROS level in both serum and liver. The mechanism underlying this effect was likely associated with the suppression of oxidative stress-mediated activation of MAPK (p38, ERK and JNK), NF-κB and AP-1, which effectively ameliorated liver damage in LPS-treated mice (Park et al., 2017). Zhong et al. found that in diet-induced NASH mice, baicalin treatment alleviated oxidative stress damage in liver tissue by reducing MDA levels and significantly enhancing the activity of SOD (Zhong and Liu, 2018). Further studies showed that baicalin or baicalein significantly reduced oxidative stress in MAFLD mice and NASH rats by upregulating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in the liver and increasing the activities of SOD and catalase, thereby protecting the liver from ROS -induced damage was protected and preventing further damage (Xin et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2023). In addition, Gao et al. by applying baicalin in a tissue-engineered MAFLD liver model, observed that it significantly alleviated oxidative stress in the model through various mechanisms, including reducing ROS levels, enhancing the expression and activity of antioxidant enzymes, and mitigating cell apoptosis (Gao et al., 2022). Taken together, the therapeutic effects of baicalin and its active metabolites in the treatment of MAFLD may be achieved primarily through antioxidant stress mechanisms (Figure 2).
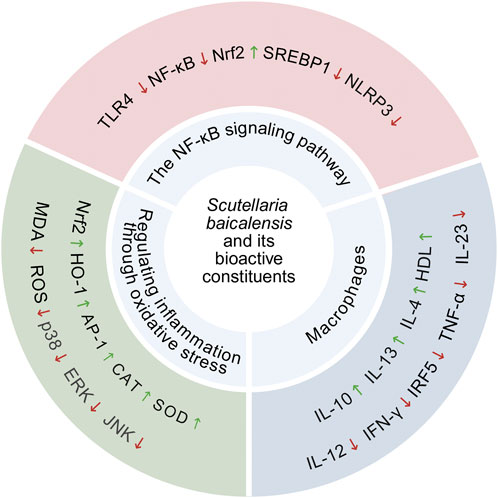
Figure 2. S. baicalensis and its bioactive metabolites regulates molecular targets related to oxidative stress and inflammation, including enzymes, proteins, chemical molecules, and inflammatory factors and Anti-inflammatory factor.
3.2 S. baicalensis delays MAFLD through its hepatoprotective effect
Multiple studies have shown that S. baicalensis exerts significant hepatoprotective effects, with its mechanisms varying depending on the type of liver injury. LPS stimulation induces the release of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, triggering liver damage and potentially progressing to MAFLD (Laveti et al., 2013). Studies have shown that baicalin significantly reduces the release of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α by downregulating TLR4 expression and inhibiting NF-κB activation, thereby exerting protective effects against LPS-induced liver damage (Cheng et al., 2017).
Researchers have used carbon tetrachloride to induce liver damage to establish a liver fibrosis model. The studies have shown that baicalin can could reduce the serum activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferasev (AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and improve liver damage caused by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) (Qiao et al., 2011). Baicalin magnesium, a water-soluble compound isolated from S. baicalensis aqueous solution, significantly improves liver injury, lipid deposition, inflammatory response, and oxidative stress in a high-fat diet-induced NASH model, thereby providing protective effects on the liver (Guan et al., 2023).
In drug-induced liver injury, S. baicalensis has also shown significant preventive and curative effects. In a mouse model of acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury, baicalin treatment was effective in reducing the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, and MPO, thereby achieving a protective effect on the liver (Liao et al., 2016). Another study demonstrated that baicalein and baicalin alleviated APAP-induced liver injury by activating the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Molecular docking results indicated that baicalein and baicalin might block the interaction between Nrf2 and Keap1, inducing Nrf2 phosphorylation to activate Nrf2, thereby exerting antioxidant effects through its downstream proteins to reduce APAP-induced hepatotoxicity (Shi et al., 2018). Zhao et al. discovered that exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with baicalin successfully alleviated hepatocyte ferroptosis following acute liver injury. The main mechanism was that baicalin upregulated the expression of P62, which regulated hepatocyte iron homeostasis through activation of the Keap1-NRF2 pathway (Zhao et al., 2022).
Taken together, S. baicalensis exhibites protective effect against various types of liver injury. In LPS-induced inflammation-related liver injury, baicalin inhibited the TLR4-NF-κB pathway to exert its effect. In liver injury models induced by CCl4 and HFD, metabolites of S. baicalensis improved several biomarkers. In case of drug-induced liver injury, S. baicalensis alleviated the damage through multiple mechanisms, such as the reduction of inflammatory factors, the activation of antioxidant pathways and the regulation of relevant signaling pathways (Figure 3).
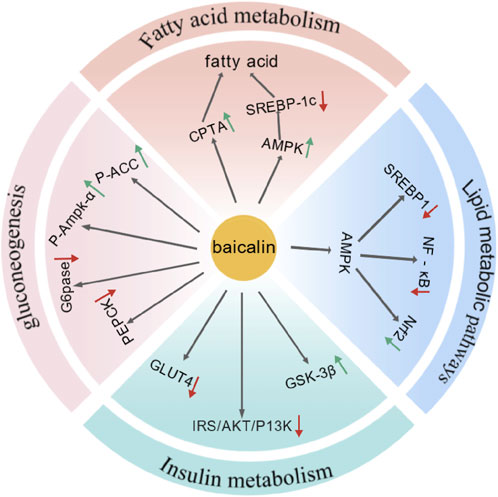
Figure 3. S. baicalensis and its active metabolites had exhibited protective effects against various liver injuries by reducing inflammatory factors, activating antioxidant pathways, and regulating related pathways (Created by BioGDP.com).
3.3 S. baicalensis is treates MAFLD by improving glucose and lipid metabolism
The key bioactive compounds in S. baicalensis significantly improve the symptoms of MAFLD by regulating lipid and glucose metabolism. Multiple mechanisms are involved in improving glucose and lipid metabolism. In terms of lipid metabolism, they regulate fatty acid metabolism, promote fatty acid oxidation, and reduce fatty acid synthesis (Li et al., 2022b). In terms of glucose metabolism, the primary mechanism involved modulation of insulin signaling pathways and inhibition of gluconeogenesis-related pathways, thereby enhancing insulin sensitivity and decreasing glucose production in the liver (Wang et al., 2017).
3.3.1 The lipid metabolism
Baicalin and baicalein have been shown to regulate lipid metabolism by modulating the pathways involved in fatty acid metabolism, lipid synthesis, and fat breakdown, thereby reducing hepatic fat accumulation. The study found that baicalein inhibited SREBP1c/ChREBP, activated AMPK and PPARα signaling pathways, and modulate the processes of fatty acid synthesis, elongation, and oxidation, thereby exerting a preventive effect against liver steatosis caused by fructose consumption in rats (Li et al., 2022b). Dai et al., through chemoproteomics analysis, have identified CPT1A as one of the critical targets within carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), which serves as a rate-limiting enzyme in mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation. Treatment with baicalin resulted in significant reductions in body weight, liver weight and blood lipid levels in mice fed a high-fat diet. Overall, baicalin was found to bind CPT1A, activate its activity, and accelerate fatty acid degradation, thereby significantly alleviating nutritional hepatic steatosis-related symptoms. (Dai et al., 2018).
In addressing alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis, baicalin was able to ameliorate alcohol-induced pathological changes both in vivo and in vitro. This effect was achieved by activating lipolysis through the regulation of competitive binding between PNPLA3 and ATGL, mediated by SREBP1c (Li et al., 2022a). In non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis, baicalin improves high-fat diet-induced MAFLD by inhibiting SREBP1 and NF-κB signaling pathways via AMPK-mediated mechanisms and activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway (Gao et al., 2023). The activation of AMPK had attenuates the proteolytic processing of SREBP-1c, suppressed lipogenesis, and stimulated fatty acid oxidation, ultimately leading to reduced fat accumulation in the liver (Fang et al., 2018). Moreover, Guo et al. conducted an experiment in which male rats were divided into three groups: normal diet, high-fat diet, and high-fat diet with long-term baicalin administration. Their results demonstrated that prolonged baicalin treatment significantly reduced body weight, liver weight, and blood lipid levels in high-fat diet-induced obese rats (Guo et al., 2009).
3.3.2 The glucose metabolism
Insulin resistance is a key feature of MAFLD, and studies have demonstrated that S. baicalensis and its active metabolites improve MAFLD treatment by regulating glucose metabolism. Multiple studies have shown that baicalin activates the insulin signaling pathway and enhances insulin sensitivity. As key regulators of glycogen synthesis, AKT/GSK-3β have been implicated in these processes. In HepG-2 cells with insulin resistance, Wang et al. found that baicalin suppressed gluconeogenesis by activating AMPK or AKT (Wang et al., 2017). Using a similar model, Miao et al. observed in insulin-resistant HepG-2 cells and prediabetic mice that baicalin prevented downregulation of the IRS/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, reducing GLUT4 expression, and mitigating enhanced GSK-3β activity, thereby improving dyslipidemia and hyperglycemia in obese mice (Miao et al., 2024). Furthermore, Xi et al. revealed that baicalin activated the AKT signaling pathway and inhibited GSK3β activity, elucidating the mechanism by which baicalin enhanced insulin sensitivity and reduced ectopic fat storage (Xi et al., 2016). Taken together, baicalin alleviates insulin resistance and regulates hepatic glucose metabolism by activating the insulin signaling pathway.
Additionally, baicalin can reduce glucose production by inhibiting the expression of genes related to gluconeogenesis. A HFD induced insulin resistance and ectopic fat storage in skeletal muscle, which is a key feature of metabolic syndrome (Xi et al., 2016). Using high-fat diet-induced obese mice as a model, Fang et al. found that baicalin inhibited the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, which in turn suppressed the expression and activity of PGC-1α.Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is was a key enzyme in fatty acid synthesis, and baicalin alleviated the inhibitory effects of high-fat diet-induced phosphorylation of skeletal muscle ACC and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPKα) (Xi et al., 2016). Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) are key enzymes in hepatic gluconeogenesis, and their activity directly impactes blood glucose levels. Baicalin reduced the expression of these key enzymes, thereby decreasing fatty acid synthesis and storage (Fang et al., 2019). Using a high-fat diet-induced obese mouse model, Fang et al. found that baicalin inhibited the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, which in turn suppressed the expression and activity of PGC-1α. This led to a reduction in the expression and activity of gluconeogenesis-related enzymes, significantly improving hepatic insulin resistance and gluconeogenic activity in high-fat diet-induced obese mice (Fang et al., 2019).
In summary, S. baicalensis has significantly improved glucose and lipid metabolism through the regulation of multiple signaling pathways and mechanisms, thereby effectively treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (Figure 4).
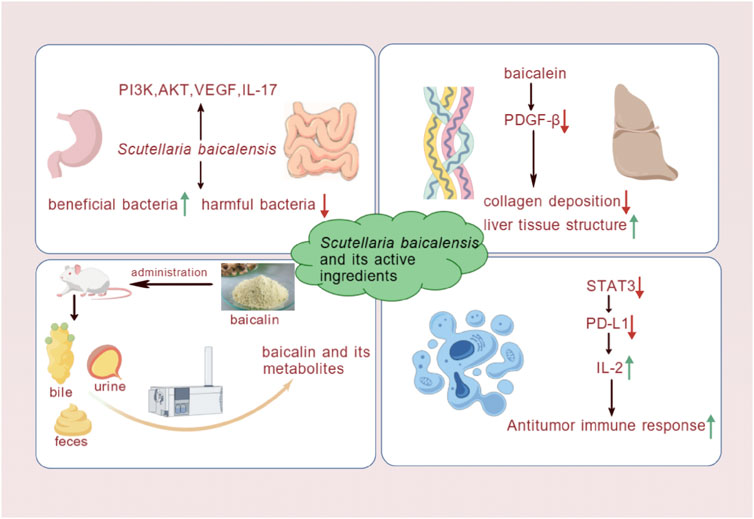
Figure 4. Baicalin had treated MAFLD by regulating signaling pathways and mechanisms involved in fatty acid metabolism, lipid synthesis and decomposition, insulin resistance, and gluconeogenesis (Created by BioGDP.com).
3.4 S. baicalensis treatment for MAFLD by other routes
S. baicalensis and its active metabolites have demonstrated multifaceted effects in the treatment of MAFLD. They not only modulated hepatic inflammation, hepatoprotection, and glucose-lipid metabolism but also exhibited potential mechanisms, including gut microbiota regulation, anti-hepatic fibrosis, and metabolic modulation. These studies have enriched the application of S. baicalensis in liver disease treatment and revealed its potential value. A comprehensive analysis of these studies provides a deeper understanding of the multifaceted roles of S. baicalensis and its active metabolites in the treatment of liver diseases.
The gut microbiota palys an important role in the pathogenesis of MAFLD. Hu et al. demonstrated that baicalin exerted its effects on the treatment of liver disease by regulating the gut-liver axis, improving gut barrier function, reducing intestinal permeability, and inhibiting inflammatory responses (Hu et al., 2021). Moreover, gut microbiota dysbiosis had been one of the key contributors to MAFLD. Studies have demonstrated that baicalin exerts inhibitory effects on a range of harmful bacteria. At a concentration of 500 μg/mL, baicalin significantly inhibits the biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans by downregulating the expression of genes associated with biofilm formation and reducing the activity of related enzymes (Elango et al., 2021). Both in vitro and in vivo, baicalin exhibits notable antibacterial effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, inhibiting its biofilm formation and motility (Yan et al., 2024). Baicalin had regulates gut microbiota homeostasis by increasing the production of SCFAs, enhancing the abundance of beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. This improves gut microbiota balance and alleviated hepatic fat accumulation and inflammation (Ju et al., 2019). Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota may have facilitated the progression of MAFLD to liver fibrosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and NASH. The mechanisms and pharmacological effects of gut microbiota modulation in MAFLD treatment are still in the early stages of research and further validation through cell and animal studies is required.
In MAFLD, liver fibrosis gradually develops due to the combined effects of metabolic disturbances, oxidative stress, and inflammatory responses. Liver fibrosis, a severe condition characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix, leads to impaired liver function. Under the stimulation of Wnt signaling caused by PyGO1 mutations, the replication of senescent hepatocytes is halted, activating ductal responses that exacerbate liver fibrosis in MAFLD patients. Consequently, liver fibrosis represents a critical factor in the progression of MAFLD (Fabris et al., 2024). Experimental studies have shown that S. baicalensis has shown significant effectiveness in the treatment of heart failure. Sun et al. used a CCl4-induced rat model of liver fibrosis and administered baicalein for a long period of time. The study found that baicalein inhibited the synthesis of PDGF-β receptor proteins, significantly reducing the degree of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, as evidenced by decreased collagen deposition and improved liver tissue architecture (Sun et al., 2010). Taken together, S. baicalensis has likely ameliorates liver fibrosis, thereby potentially preventing the progression of MAFLD to more severe liver diseases, providing both theoretical and experimental evidence for the treatment of MAFLD.
HCC is one of the leading cancers worldwide, with over 600,000 deaths occurring annually due to HCC (Song et al., 2012). In the United States, the incidence of HCC has increased significantly due to MAFLD. Analysis of this study indicates that MAFLD was an important cause of HCC (Younossi et al., 2015). S. baicalensis and its metabolites have shown antitumor effects, although their mechanisms of interaction with molecular targets are still under investigation. Theoretically, their therapeutic potential in HCC may involve inhibiting cell proliferation, promoting apoptosis and autophagy, suppressing VEGF expression, and exerting anti-inflammatory effects (Ma et al., 2023). Ke et al. further validated through experiments that baicalin and baicalein inhibited STAT3 activity, downregulated IFN-γ-induced PD-L1 expression, restored T cell activity, and increased IL-2 secretion. These effects enhanced T cell-mediated antitumor immune responses, blocked the PD-L1/PD-1 signaling pathway, and strengthened antitumor immunity, thereby synergistically inhibiting tumor growth and improving the immune microenvironment (Ke et al., 2019).
Although flavonoids are generally not well-absorbed after being metabolized in the gut and liver, certain metabolites have shown significant pharmacological activity. As a metabolic disease, MAFLD may be modulated by baicalin and its aglycone through the regulation of metabolic processes related to the pathogenesis of MAFLD, providing new approaches for the treatment of metabolic disorders (Fang et al., 2020). Zhang et al. established a rat liver microsomal-hydrogel system and used the Phase II metabolism (MHCCS-II) cell culture system to predict the metabolic effects of drugs. They found that baicalein (BA) enhanced the antitumor effects on HepG2 and MCF-7 cells through metabolic processes. This study provided a potential framework for in vitro investigations into the pharmacological effects of baicalin metabolites, acting as substrates for UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT) during Phase II metabolism (Zhang et al., 2019). Using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS), the metabolism and excretion of S. baicalensis extract and its metabolites in rats were investigated. The results revealed that five metabolites—baicalin, baicalein, oroxylin A, oroxylin A-7-O-β-D-glucuronide, and scutellarin—were predominantly excreted in the urine, with lower amounts found in feces and bile. Baicalin, baicalein, and their metabolites were primarily eliminated via renal excretion (Zhou et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2012). However, variations in experimental animals, dosage, and detection methods may have produced different results in different studies.
By reviewing the above literature, we have found that the use of S. baicalensis in the treatment of MAFLD provides strong scientific evidence. However, further studies are needed to deepen the understanding of its mechanisms of action and promote its clinical application (Figure 5).
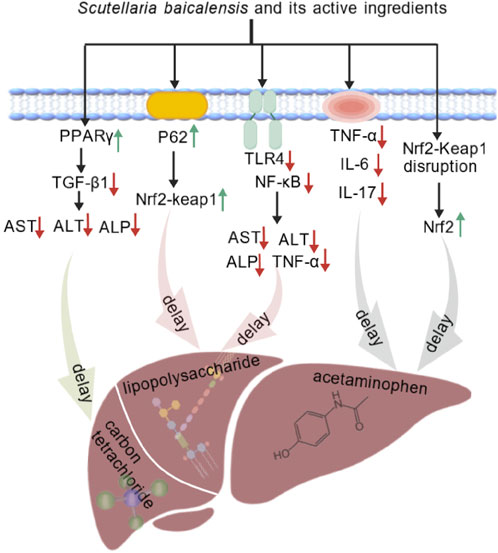
Figure 5. S. baicalensis and its active metabolites had provided theoretical and experimental evidence for the treatment of MAFLD by regulating intestinal microbiota, mitigating liver fibrosis, modulating metabolism, and elucidating potential mechanisms of action in liver cancer treatment (Created by BioGDP.com).
4 S. baicalensis combined with other drugs for the treatment of MAFLD
The pathogenesis of MAFLD is complex, involving disturbances in lipid metabolism, inflammatory responses, and other factors. In recent years, progress has been made in studies exploring the combined use of S. baicalensis and other drugs in the treatment of MAFLD, providing new insights and methods for the comprehensive treatment of this disease.
Zhao et al. established an MAFLD model using HFDs and conducted experiments with different combinations of puerarin, baicalin, and berberine. The results indicated that the combined treatment of puerarin, baicalin, and berberine upregulated the expression levels of liver proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ and insulin receptor (IR). This contributed to improving insulin resistance as a therapeutic mechanism. Moreover, the combination therapy enhanced overall therapeutic efficacy through multiple targets (Zhao W. et al., 2016). Cui et al. investigated the therapeutic effects of S. baicalensis and Coptis chinensis rhizome on type 2 diabetes (T2DM) induced by a HFD combined with low-dose streptozotocin (STZ). The combination therapy primarily improved the pathological features of rats by regulating the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, key target proteins in the MAPK signaling pathway, insulin signaling, and the activity of enzymes related to glucose metabolism. The study also indicated that the combination treatment was more effective than monotherapy (Cui et al., 2018).
Liver fibrosis is a key intermediate step in the progression of MAFLD to more severe liver diseases, and its severity has influenced the prognosis and outcome of the disease. S. baicalensis has been found to play a therapeutic role in liver fibrosis, blocking the progression of MAFLD to more severe liver conditions. The combination of S. baicalensis and Rhei Rhizoma reduced liver fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine (DMN), mainly by regulating redox status, inhibiting oxidative stress, and reducing the expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), thereby protecting the liver from fibrotic damage (Pan et al., 2015).
With the increasing integration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Western medicine, not only has the compatibility of S. baicalensis with other Chinese herbal medicines attracted attention, but its combined use with modern pharmacological agents has also become a growing area of research interest. A study conducted on Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats demonstrated that co-administration of metformin with S. baicalensis resulted in more significant reductions in blood glucose and serum cholesterol levels compared to metformin alone, without adversely affecting the pharmacological actions of metformin (Han et al., 2017). In a 20-week clinical study conducted in 2016, the combination of S. baicalensis and metformin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D) was shown to improve glucose metabolism and significantly enhance glucose tolerance by modulating the composition and function of the gut microbiota, while also effectively reducing inflammatory markers (Shin et al., 2020).
Given the substantial overlap in pathophysiological mechanisms between MAFLD and T2D—particularly the tight association between gut microbiota dysbiosis and metabolic inflammation—this combined therapeutic strategy, which targets the gut microbiota to improve metabolic and inflammatory status, may offer a novel approach and theoretical basis for clinical interventions in MAFLD.
Figure 6 summarizes the potential mechanisms of S. baicalensis combined with other drugs in the treatment of MAFLD. The combination of S. baicalensis, puerarin, and berberine has been confirmed to upregulate the expression of PPAR-γ and IR in the liver, thereby enhancing insulin receptor sensitivity and reducing the generation of inflammatory cytokines. The combined application of S. baicalensis and Coptis chinensis can inhibit the expression of P38, ERK, and JNK proteins in the MAPK signaling pathway, while upregulating the levels of key glycolytic enzymes such as GK, PFK, PK, and GS, thus accelerating glycolytic reactions and fatty acid synthesis, and reducing glucose and lipid levels in the liver. Moreover, the combination of S. baicalensis and metformin can modulate the gut microbiota, thereby improving glucose metabolism and reducing inflammation. These effects subsequently impact the development of MAFLD, effectively treating the condition and impeding its progression. Additionally, the combination of S. baicalensis and rhubarb can alleviate liver fibrosis by reducing the expression of the important marker α-SMA in activated HSCs. In summary, the combination of S. baicalensis with other drugs has shown broad application prospects.
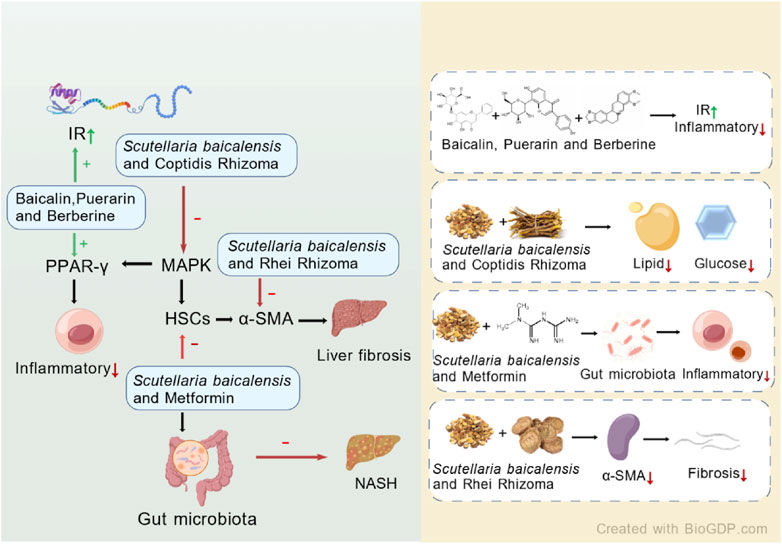
Figure 6. Potential mechanisms of S. baicalensis combined with other drugs in the treatment of MAFLD (Created by BioGDP.com).
5 S. baicalensis-pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and toxicity
Given the significant pharmacological effects of baicalein in the treatment of MAFLD, its pharmacokinetics had become a key focus of our attention. Numerous studies in the literature have also explored this topic. However, the low oral bioavailability of baicalin (<2.2%) and its poor solubility may limit its clinical efficacy (Lu et al., 2022). The reasons may be as follows: S. baicalensis and its major metabolites, such as flavonoid glycosides, are highly polar compounds that cannot pass through the lipid bilayer via passive diffusion, resulting in poor absorption in the intestine (Fang et al., 2017). Baicalin is the predominant metabolite found in blood following oral administration of baicalin and baicalein. Studies indicate that baicalin undergoes a complex metabolic process in vivo, which includes gastrointestinal hydrolysis, enterohepatic circulation, and carrier-mediated transport. Baicalin is primarily metabolized via glucuronidation, and it is hydrolyzed in the gastrointestinal tract by microbial enzymes into its active metabolite, baicalein (Xiang et al., 2021). In the liver and intestine, baicalein is predominantly glucuronidated by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs), resulting in the formation of baicalin and baicalein-6-O-glucuronide as two major metabolites (Son et al., 2021). Studies investigating the pharmacokinetics of orally administered baicalin, influenced by gut microbiota, and the concurrent role of hepatic enzymes and transport proteins in baicalein metabolism, suggest that baicalin and its metabolites are primarily excreted via bile, with a portion being eliminated in urine (Kang et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2011).
Although the oral bioavailability of baicalin is relatively low, studies have demonstrated that its tissue distribution is predominantly concentrated in the liver, kidneys, and lungs. After 30 minutes of oral administration of baicalin liposomes, the drug concentrations in the liver, kidneys, and lungs were 5.59, 2.33, and 1.25 times higher, respectively, compared to the baicalin suspension (Wei et al., 2014). Moreover, studies have shown that the drug concentration in the lungs after intravenous injection was significantly higher than in the liver, kidney, spleen, and other tissues as well as in plasma (Zhao Q. et al., 2016). Moreover, in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), the baicalin concentration in lung tissue was higher than that in the kidneys or liver after oral administration (Zhu et al., 2013). Other studies have found that the highest concentration of baicalin was reached in the kidneys after oral administration, whereas the compound accumulated predominantly in the lungs after intravenous injection of liposomal baicalin (Zhao Q. et al., 2016).
To improve the efficacy and address the limited bioavailability of single-agent drugs, drug complexes, nanoparticles, nanoliposomes, and other synergistic compound delivery methods have been employed. Numerous studies have shown that liposomal carriers could enhance the oral bioavailability of drugs (Liu et al., 2020; Wei et al., 2014). Targeted nanoparticles promote the in vivo and in vitro bioavailability of baicalin. In cells treated with baicalin liposomes (BAA1), ApoA1-modified nanoparticles effectively enhanced baicalin uptake in HEPG-2 cells (Xu et al., 2022). An innovative oral baicalein-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle (SLNB) significantly enhanced the bioavailability of baicalein. Compared to free baicalein, the oral relative bioavailability of SLNB increased by approximately 300% (Joshi et al., 2021). Xxx et al. administered baicalin liposomes nasally for the treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. The results demonstrated that baicalin liposomes exhibited favorable pharmacokinetic properties in vivo, effectively enhancing the concentration of the drug in brain tissue, while showing good pharmacological efficacy and safety (Xiang et al., 2020). Zhao et al. prepared baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions (BAN-1 and BAN-2) through internal or external drug addition methods and evaluated them both in vitro and in vivo. Their findings indicated that the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions, especially BAN-1, were highly effective in improving the oral bioavailability of baicalin (Zhao et al., 2013). Furthermore, the use of novel formulations, such as MSCs-derived exosomes, has the potential to improve bioavailability (Zhao et al., 2022).
The metabolism of S. baicalensis and its active metabolites has been shown to influence their activity and toxicity. An oxidative stress study on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (MAFLD) demonstrated, through CCK-8 assays, that baicalin concentrations ranging from 0.01 nM to 100 µM had no cytotoxic effects on HepG2 cells at 24 and 48 h (Cheng et al., 2017). A dose of 400 mg·kg−1·d−1 of baicalin was administered for 14 weeks to high-fat diet mice without toxicity, significantly improving insulin resistance and lipid abnormalities in skeletal muscle. Clinical evaluations of a single oral dose of 100–2,800 mg baicalein in healthy subjects have shown good tolerance with no evidence of liver or kidney toxicity (Li et al., 2014). However, currently, there are no clinical research literatures reporting on the potential risks of long-term use of S. baicalensis and its contraindications. While current research has demonstrated the short - term safety and efficacy of S. baicalensis, future studies should prioritize long - term clinical trials and translational research to define its potential risks, contraindications, and optimal use in treating MAFLD.
6 Production development
S. baicalensis, a traditional Chinese medicine with a rich history, has garnered significant attention due to its remarkable pharmacological effects. It is extensively utilized in traditional Chinese medicine for its abilities to clear heat and detoxify, reduce inflammation, and protect the liver. Recent modern research has further validated its considerable potential in antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-tumor applications. Currently, the total number of AR patents worldwide has reached 12,403, with China holding the majority, accounting for over three-fifths of the total. Detailed information regarding AR patents is presented in Figure 7. In the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) formulas based on S. baicalensis include Qinian Pian, Jingtaihong Zhike Granules, Xinqin Pian, Zhaoqin Qingre Heji, Compound Qinlan Oral Liquid, and Gegen Qinlian Wan. Additionally, the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia includes a total of 248 formulas containing S. baicalensis, involving 185 prescriptions. The main dosage forms are as follows: pills (31.05%), tablets (18.95%), capsules (15.32%), granules (14.11%), and oral liquids (10.89%).
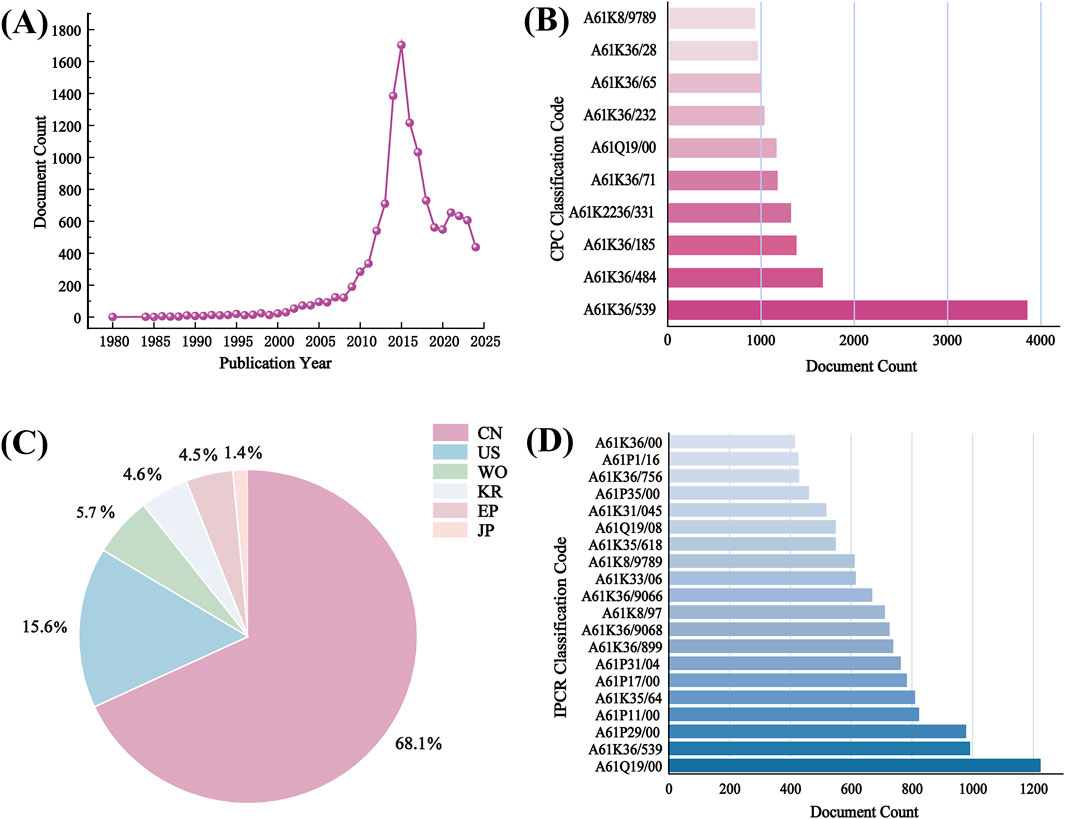
Figure 7. Analysis of 12403 patents browsed on LENS.ORG (https://www.lens.org/) using search terms “S. baicalensis”. (A) Patent applications per year; (B) CPC classification code; (C) Jurisdictions (CN, China; US, United States; WO, World Intellectual property organization; KR, South Korea; EP, European Patent Office; JP, Japan); (D) IPCR classification code.
The market demand for S. baicalensis has been increasing year by year, with widespread applications in the fields of pharmaceuticals, health supplements, and cosmetics. The China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) (nmpa. gov. cn) has announced 82 S. baicalensis related drugs, including Huangqin tablets, Huangqin capsules, Baicalin capsules, Xiongdan Huangqin eye drops, Sanhuang tablets, Yinzhihuang oral solution, etc.
In modern society, the fast-paced lifestyle and increasing work pressures have led many people to gradually overlook the importance of healthy eating and regular exercise. This unhealthy lifestyle has evident impacts on the body, with gastrointestinal issues becoming common among many individuals. To address this, S. baicalensis sesame oil soft capsules have emerged as a specialized health product aimed at improving gastrointestinal health.
With the rapid development of the economy, people’s awareness of skincare has also been continuously rising. Simultaneously, there is a growing preference for natural and harmless cosmetics, leading to the widespread incorporation of natural plant extracts in products. Plant extracts are commonly used in cosmetics, and S. baicalensis, as a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, has found extensive applications in this field. In 2020, the number of recorded extracts from S. baicalensis roots exceeded 20,000. Among the recorded metabolites primarily focused on soothing and anti-aging properties, S. baicalensis root extract ranked among the top ten in both quantity and growth rate. Currently, S. baicalensis is mainly applied in cosmetics for purposes such as whitening, soothing, and sun protection. To better utilize S. baicalensis resources, it is essential to conduct in-depth, multifaceted research on its mechanisms of action, exploring biochemical, cellular, animal, and human perspectives. Additionally, as consumer demand for anti-aging products increases, it is anticipated that S. baicalensis will have broad application prospects in this area.
Moreover, with the advancement of modern pharmacological research, the therapeutic potential of S. baicalensis in liver injury and liver diseases has garnered increasing attention. S. baicalensis and its primary active metabolites are widely incorporated in various TCMs for the treatment of liver damage and liver diseases. For instance, TCM formulations listed in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, such as Longdan Xiegan Wan and Qinggan Lidan Oral Liquid, contain S. baicalensis and are used for clearing heat, detoxification, liver protection, and bile regulation. Additionally, Shugan Ning Injection, composed of S. baicalensis extract among other metabolites, is used as an adjunctive therapy for viral hepatitis and liver dysfunction. Furthermore, commercially available Baicalin capsules are commonly employed as supplementary treatments for viral hepatitis and liver dysfunction, exerting hepatoprotective effects through multiple mechanisms, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral actions. Some compound preparations, such as Chaiqin Qingning Capsules, combine various herbal metabolites and are used to alleviate symptoms of colds and fever while improving liver function. To further expand the therapeutic applications of S. baicalensis in liver diseases, it is essential to delve deeper into its pharmacological mechanisms and safety profiles at the cellular, animal model, and clinical levels, facilitating its transition from a traditional herbal remedy to a modern pharmaceutical agent.
Furthermore, S. baicalensis has a long history of application in dietary practices, particularly in nourishing diets aimed at enhancing health. This botanical drug can be easily integrated into various culinary creations, seamlessly incorporating health benefits into daily meals. It pairs well with a variety of metabolites, including meats, rice, and vegetables, allowing for the preparation of delicious and nutritious dishes, such as red date and Huangqin chicken stew and Huangqin stewed black beans. The recipe for Huangqin chicken stew, found in the “Medicinal Cuisine Handbook,” is a nourishing dish suitable for those suffering from Qi and blood deficiency due to serious illness, prolonged sickness, or excessive postpartum blood loss. S. baicalensis is known for its ability to tonify Qi, elevate Yang, strengthen the surface, stop sweating, promote diuresis, nourish blood, expel toxins, and aid in wound healing. The hen used in the dish is beneficial for invigorating Qi and nourishing blood, enhancing overall vitality. Together, they provide a synergistic effect that nourishes Qi, replenishes blood, and strengthens the essence. These traditional recipes not only highlight the versatility of this botanical drug but also emphasize its role in promoting overall health.
Despite the optimistic outlook, challenges remain between foundational research and the industrialization of products centered around S. baicalensis. Ongoing research aimed at revealing active metabolites and understanding their mechanisms of action is crucial for overcoming these obstacles. As research progresses, it is expected that effective and safe clinical drugs and health products will soon be developed, further expanding the application prospects of S. baicalensis, not only in the realms of food and dietary supplements but also in everyday essentials. Ultimately, this will contribute to the establishment of a healthier society. Through continuous innovation and exploration, the full potential of S. baicalensis will be realized, benefiting individuals and communities worldwide.
7 Discussion and outlook
There are currently no internationally approved treatments for MAFLD. The causes are diverse, the cost of screening is high, and the results remain uncertain. No satisfactory preventive or therapeutic medications have been identified (Liu et al., 2023; Younossi et al., 2018; Qu et al., 2021). Interventions based solely on lifestyle modifications have led to limited improvement in MAFLD, and in cases of severe disease, they have failed to prevent further progression. Therefore, research into effective treatments for MAFLD is of great importance.
As shown in Table 1, this review summarizes a total of 57 experimental studies involving various hepatic and metabolic diseases, including fatty liver disease, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, and diabetes. Among these, seven studies involved in vitro experiments, primarily utilizing human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines such as HepG2 and SMMC-7721, as well as engineered liver models. These studies mainly focused on lipid metabolism and inflammatory pathways, such as AMPK/NF-κB signaling. However, these models lack a complete hepatic microenvironment, including immune interactions and dynamic fibrogenesis, which limits their ability to fully recapitulate the complex pathophysiological features of MAFLD.
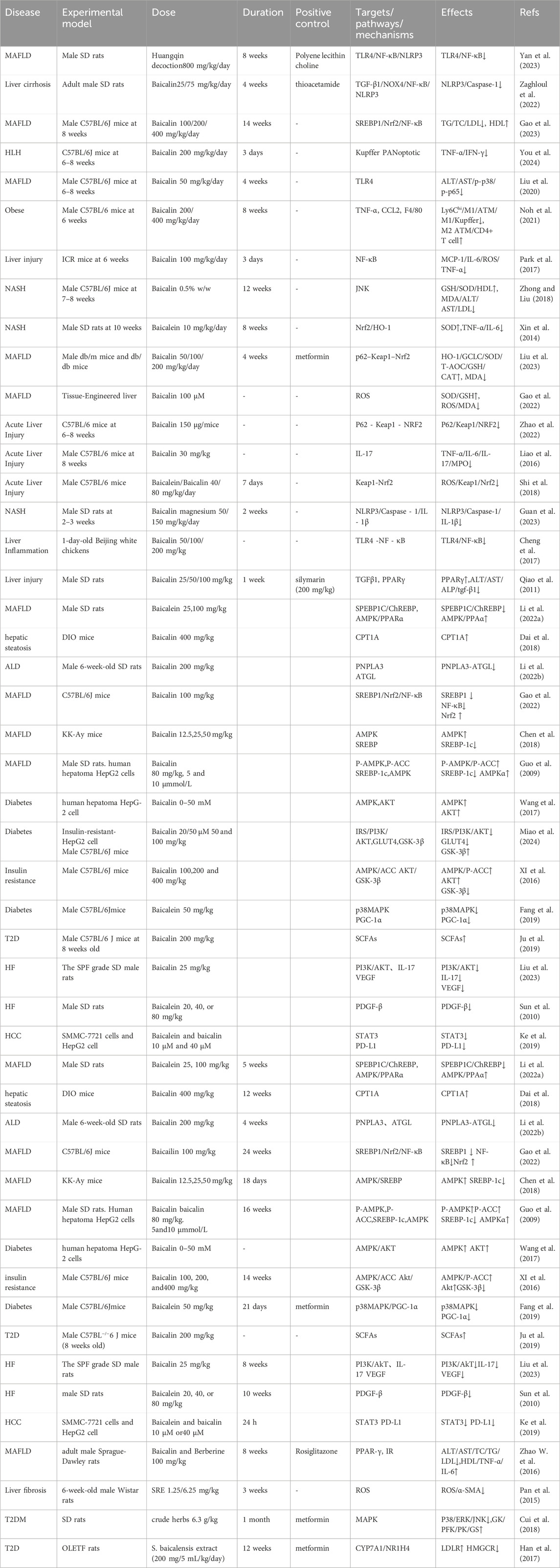
Table 1. Mechanisms and targets of S. baicalensis in treating MAFLD and related diseases: A summary of experimental studies.
In contrast, 50 studies employed in vivo models, predominantly using SD rats (29 studies) and C57BL/6 mice (18 studies). The disease models included alcoholic liver disease (ALD); short-term ethanol administration for 4 weeks in SD rats, without the use of classical chronic alcohol consumption models), NAFLD/MAFLD or NASH; induced by high-fat diet or in genetic db/db mice, and liver fibrosis (induced by thioacetamide, TAA). Notably, the ALD models used in these studies feature short intervention durations and simplified pathogenic mechanisms, which differ significantly from the chronic disease course observed in human alcoholism.
It is worth noting that the vast majority of these studies are preclinical, with only one clinical trial reported to date. There remains a lack of robust and consistent clinical data to support the findings. Future research should focus on conducting multicenter, long-term clinical trials (lasting 6 months to 2 years) with large sample sizes encompassing various stages of disease progression. These studies should integrate biochemical markers (e.g., liver enzymes), imaging techniques, and histopathological evaluation to comprehensively assess drug efficacy and safety. Bridging this translational gap between basic research and clinical application remains a critical priority.
S. baicalensis, as a promising therapeutic agent, has been extensively studied for its efficacy in treating MAFLD. A substantial body of research has demonstrated its diverse therapeutic activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, metabolic regulation, and hepatoprotective properties, which provide hope for the treatment of MAFLD patients. However, significant challenges remained in translating S. baicalensis into clinical therapy for MAFLD.
At present, most clinical studies and animal experiments related to S. baicalensis focused primarily on adult animals and adult populations. However, the incidence of MAFLD in children and adolescents is steadily increasing and has become one of the most important pathogenic factors of chronic liver disease in children (Hatton et al., 2018). It is still unclear whether there are differences in the pathophysiological mechanisms of MAFLD between these two age groups (Nobili et al., 2016). Additionally, there are significant differences in drug sensitivity between children and adults (Assunção et al., 2017). Therefore, developing effective treatment strategies for children suffering from this disease holds great value.
(a) During the drug development process, the active metabolites of S. baicalensis, due to their complexity and diversity, along with the challenges in standardizing quality, led to instability in therapeutic effects. Therefore, ensuring the quality and stability of S. baicalensis materials has become one of the key directions for future research.
In addition, the bioavailability of the active metabolites of S. baicalensis was relatively low and the absorption in the gastrointestinal tract was limited after oral administration, which significantly affected the therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacokinetic studies of S. baicalensis and its active metabolites revealed that the drug was primarily concentrated in the lungs and kidneys after intravenous injection of baicalin. However, in the context of treating MAFLD with S. baicalensis, the goal was to target the liver. Therefore, the development of new formulations of S. baicalensis and its active metabolites was necessary to enable targeted delivery to the liver while improving the bioavailability of baicalin. This represented one of the major challenges for future research on S. baicalensis and its active metabolites in the treatment of MAFLD.
(b) Although S. baicalensis had demonstrated multi-target potential in the treatment of MAFLD, the underlying mechanisms were not yet fully understood. The multi-target mechanisms of S. baicalensis were intertwined with the complex pathophysiology of MAFLD, making research more difficult. When designing and evaluating studies on S. baicalensis for the treatment of MAFLD, these influencing factors had to be carefully taken into account, and targeted research strategies had to be developed. To date, research on S. baicalensis in MAFLD has primarily focused on animal models and small-scale preclinical studies, with a lack of large-scale, multi-center, randomized controlled clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety in diverse populations.
(c) Existing studies have provided limited insight into the long-term efficacy and potential adverse effects of S. baicalensis in the treatment of MAFLD. It remained to be determined whether prolonged use of S. baicalensis could affect liver and kidney function or whether significant drug interactions or other side effects had occurred. Further systematic studies were required to ensure safety and feasibility for clinical application.
In conclusion, S. baicalensis and its active compounds have demonstrated complex and diverse pharmacological effects that may have had significant implications for the treatment of MAFLD. Mechanisms of action included inhibiting liver inflammation, providing liver protection, and regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Additionally, S. baicalensis alleviated hepatic fat accumulation by modulating gut microbiota homeostasis. Furthermore, S. baicalensis alleviated fat accumulation in the liver by modulating the homeostasis of the gut microbiota. In addition, it has shown a synergistic effect in combination with other drugs, offering new possibilities for personalized treatment. These results suggest that S. baicalensis has significant potential as a drug candidate for the treatment of MAFLD. However, in order for S. baicalensis to be used in the clinical treatment of MAFLD, further research was required to ensure the stability of its quality, investigate the liver-targeting effects of the experimental drug, improve its bioavailability, and explore the underlying mechanism.
Despite existing evidence suggesting that S. baicalensis and its major active metabolites, such as baicalin and baicalein, hold therapeutic potential in the management of MAFLD, several limitations remain. Most studies to date have been conducted primarily in animal models, including high-fat diet and alcohol-induced models, with heterogeneous methodologies that undermine the comparability of findings and their clinical translational value. Furthermore, systematic studies on the pharmacokinetic properties, bioavailability, and liver-targeting distribution characteristics of S. baicalensis metabolites are still lacking, particularly with regard to their metabolic transformation mechanisms in relation to gut microbiota. More importantly, clinical investigations focusing on the use of S. baicalensis for the treatment of MAFLD are limited, and robust, high-quality clinical evidence supporting its safety and efficacy is still absent.
Future research should focus on a more in-depth understanding of the in vivo metabolism of key metabolites of S. baicalensis, elucidating their mechanisms of action. Concurrently, the development of novel drug delivery systems, including nanoparticles, liposomes, and prodrugs, is essential to enhance their bioavailability and liver targeting. Further optimization of animal models to better reflect human metabolic characteristics, along with strengthened preclinical toxicology studies, will facilitate the translation of these findings into clinical applications. Additionally, exploring the interactions between S. baicalensis, dietary factors, gut microbiota, and host metabolic networks could provide valuable insights for personalized intervention strategies. Overall, continued efforts in both fundamental mechanistic research and formulation optimization, alongside the gradual implementation of systematic clinical trials, are necessary to lay a solid foundation for the application of S. baicalensis in the prevention and treatment of MAFLD.
Author contributions
LC: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. EL: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XZ: Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XL: Writing – review and editing. QD: Writing – review and editing. YL: Writing – review and editing. GH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LL: Writing – review and editing. YH: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. State Key Laboratory of Southwestern Chinese Medicine Resources (SKLTCM202413); Supported by Sichuan Provincial Natural Science Foundation’s Youth Fund (no: 2025ZNSFSC1659); Talent Introduction Project of Xihua University (no: Z241026).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Sichuan Provincial Natural Science Foundation’s Youth Fund (no: 2025ZNSFSC1659), Talent Introduction Project of Xihua University(no: Z241026), and Sichuan Traditional Chinese Medicine Health Industry Development and Rural Revitalization Research Center Project (no: DJKYB202321). Furthermore, we extend our heartfelt thanks to the authors of the key studies reviewed here for their contributions to the field.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ajoolabady, A., Kaplowitz, N., Lebeaupin, C., Kroemer, G., Kaufman, R. J., Malhi, H., et al. (2023). Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases. Hepatology 77: 619–639. doi:10.1002/hep.32562
Ansari, A., Bose, S., Lim, S.-K., Wang, J. H., Choi, Y. H., and Kim, H. (2020). Combination of Scutellaria baicalensis and metformin ameliorates diet-induced metabolic dysregulation in mice via the gut-liver-brain Axis. Brain Axis 48, 1409–1433. doi:10.1142/S0192415X2050069X
Arabpour, M., Saghazadeh, A., and Rezaei, N. (2021). Anti-inflammatory and M2 macrophage polarization-promoting effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 97, 107823. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107823
AssunçãO, S. N. F., Sorte, N. C. B., Alves, C. D., Mendes, P. S. A., and Silva, L. R. (2017). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) pathophysiology in obese children and adolescents: update. Nutr. Hosp. 34, 727–730. doi:10.20960/nh.723
Azoulay, L., Yin, H., Filion, K. B., Assayag, J., Majdan, A., Pollak, M. N., et al. (2012). The use of pioglitazone and the risk of bladder cancer in people with type 2 diabetes: nested case-control study. Bmj 344, e3645. doi:10.1136/bmj.e3645
Borrelli, A., Bonelli, P., Tuccillo, F. M., Goldfine, I. D., Evans, J. L., Buonaguro, F. M., et al. (2018). Role of gut microbiota and oxidative stress in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to hepatocarcinoma: current and innovative therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol. 15, 467–479. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2018.01.009
Byrne, C. D., and Hepatology, G. T. J. J. O. (2015). NAFLD: a multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 62, S47–S64. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.012
Caliceti, C., Franco, P., Spinozzi, S., Roda, A., and Cicero, A. F. G. (2016). Berberine: new insights from pharmacological aspects to clinical evidences in the management of metabolic disorders. Curr. Med. Chem. 23, 1460–1476. doi:10.2174/0929867323666160411143314
Cheng, P., Wang, T., Li, W., Muhammad, I., Wang, H., Sun, X., et al. (2017). Baicalin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver inflammation in chicken by suppressing TLR4-mediated NF-κB pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 547. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00547
Chen, M., Xiao, H., Chen, B., Bian, Z., and Kwan, H. Y. (2021). The advantages of using Scutellaria baicalensis and its flavonoids for the management of non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Funct. Foods 78, 104389. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2021.104389
Chen, Q., Liu, M., Yu, H., Li, J., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). Scutellaria baicalensis regulates FFA metabolism to ameliorate NAFLD through the AMPK-mediated SREBP signaling pathway. J. Nat. Med. 72, 655–666. doi:10.1007/s11418-018-1199-5
Cone, C. J., Bachyrycz, A. M., and Murata, G. H. (2010). Hepatotoxicity associated with metformin therapy in treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Pharmacother. 44, 1655–1659. doi:10.1345/aph.1P099
Conroy, M. J., Dunne, M. R., Donohoe, C. L., and Reynolds, J. V. (2016). Obesity-associated cancer: an immunological perspective. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 75, 125–138. doi:10.1017/S0029665115004176
Cui, X., Qian, D. W., Jiang, S., Shang, E. X., Zhu, Z. H., and Duan, J. A. (2018). Scutellariae radix and Coptidis rhizoma improve glucose and lipid metabolism in T2DM rats via regulation of the metabolic profiling and MAPK/PI3K/akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3634. doi:10.3390/ijms19113634
Cullinan, S., and Chemistry, J. D. J. J. O. B. (2004). PERK-Dependent activation of Nrf2 contributes to redox homeostasis and cell survival following endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 20108–20117. doi:10.1074/jbc.M314219200
Dai, J., Liang, K., Zhao, S., Jia, W., Liu, Y., Wu, H., et al. (2018). Chemoproteomics reveals baicalin activates hepatic CPT1 to ameliorate diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, E5896–e5905. doi:10.1073/pnas.1801745115
Elango, A. V., Vasudevan, S., Shanmugam, K., Solomon, A. P., and Neelakantan, P. (2021). Exploring the anti-caries properties of baicalin against Streptococcus mutans: an in vitro study. Biofouling 37, 267–275. doi:10.1080/08927014.2021.1897789
Elvira-Torales, L. I., Martin-Pozuelo, G., Gonzalez-Barrio, R., Navarro-González, I., Pallarés, F. J., Santaella, M., et al. (2019). Ameliorative effect of spinach on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced in rats by a high-fat diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 1662. doi:10.3390/ijms20071662
Fabris, L., Campello, E., Cadamuro, M., and Simioni, P. (2024). The evil relationship between liver fibrosis and cardiovascular disease in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): looking for the culprit. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1870, 166763. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166763
Fang, Y.-L., Chen, H., Wang, C.-L., and Liang, L. (2018). Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescence: from “two hit theory” to “multiple hit model”. “multiple hit model 24, 2974–2983. doi:10.3748/wjg.v24.i27.2974
Fang, P., Sun, Y., Gu, X., Shi, M., Bo, P., Zhang, Z., et al. (2019). Baicalin ameliorates hepatic insulin resistance and gluconeogenic activity through inhibition of p38 MAPK/PGC-1α pathway. Phytomedicine 64, 153074. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153074
Fang, P., Yu, M., Shi, M., Bo, P., Gu, X., and Zhang, Z. (2020). Baicalin and its aglycone: a novel approach for treatment of metabolic disorders. Pharmacol. Rep. 72, 13–23. doi:10.1007/s43440-019-00024-x
Fang, Y., Cao, W., Xia, M., Pan, S., and Xu, X. (2017). Study of structure and permeability relationship of flavonoids in caco-2 cells. Nutrients 9, 1301. doi:10.3390/nu9121301
Fu, J., Schroder, K., and Wu, H. (2024). Mechanistic insights from inflammasome structures. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 24, 518–535. doi:10.1038/s41577-024-00995-w
Gao, W., Xu, B., Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Duan, Z., Chen, Y., et al. (2022). Baicalin attenuates oxidative stress in a tissue-engineered liver model of NAFLD by scavenging reactive oxygen species. Nutrients 14, 541. doi:10.3390/nu14030541
Gao, Y., Liu, J., Hao, Z., Sun, N., Guo, J., Zheng, X., et al. (2023). Baicalin ameliorates high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-mediated regulation of SREBP1/Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytother. Res. 37, 2405–2418. doi:10.1002/ptr.7762
Geethangili, M., Lin, C.-W., Mersmann, H. J., and Ding, S. T. (2021). Methyl brevifolincarboxylate attenuates free fatty acid-induced lipid metabolism and inflammation in hepatocytes through AMPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 10062. doi:10.3390/ijms221810062
Goldberg, R. B., Tripputi, M. T., Boyko, E. J., Budoff, M., Chen, Z. Z., Clark, J. M., et al. (2021). Hepatic fat in participants with and without incident diabetes in the diabetes prevention program outcome study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 106, e4746–e4765. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab160
Gordon, S., and Martinez, F. O. (2010). Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity 32, 593–604. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2010.05.007
Guan, X., Shen, S., Liu, J., Song, H., Chang, J., Mao, X., et al. (2023). Protective effecs of baicalin magnesium on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis rats are based on inhibiting NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23, 72. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-03903-2
Guo, H. X., Liu, D. H., Ma, Y., Liu, J. F., Wang, Y., Du, Du , et al. (2009). Long-term baicalin administration ameliorates metabolic disorders and hepatic steatosis in rats given a high-fat diet. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 30: 1505–1512.
Guo, X., Yin, X., Liu, Z., and Wang, J. (2022). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) pathogenesis and natural products for prevention and treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 15489. doi:10.3390/ijms232415489
Haas, J. T., Francque, S., and Physiology, B. S. J. A. R. O. (2015). Pathophysiology and mechanisms of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 78: 181–205. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105331
Hai-Juan, Z., Hai-Yan, Z., Yun-Yi, Z., Yan, L., Hong, L., and Dao-Feng, C. (2019). In vivo effect of quantified flavonoids-enriched extract of Scutellaria baicalensis root on acute lung injury induced by influenza A virus. Phytomedicine 57 105–116. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.12.009
Han, K., Bose, S., Wang, J. H., Lim, S. K., Chin, Y. W., Kim, Y. M., et al. (2017). In vivo therapeutic effect of combination treatment with metformin and Scutellaria baicalensis on maintaining bile acid homeostasis. PLoS One 12, e0182467. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0182467
Hanley, A., Williams, K., Festa, A., Wagenknecht, L., D'Agostino, R. B., Kempf, J., et al. (2004). Elevations in markers of liver injury and risk of type 2 diabetes: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes 53, 2623–2632. doi:10.2337/diabetes.53.10.2623
Hashmi, T. (2011). Probable hepatotoxicity associated with the use of metformin in type 2 diabetes. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, bcr0420114092. doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2011.4092
Hatton, G., Alterio, T., Nobili, V., and Mann, J. P. (2018). Unmet needs in pediatric NAFLD research: what do we need to prioritize for the future? Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 12, 961–967. doi:10.1080/17474124.2018.1512853
Huang, D. Q., EL-Serag, H. B., and Gastroenterology, R. L. J. N. R. (2020). Global Epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18: 223–238. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-00381-6
Hu, Q., Zhang, W., Wu, Z., Tian, X., Xiang, J., Li, L., et al. (2021). Baicalin and the liver-gut system: pharmacological bases explaining its therapeutic effects. Pharmacol. Res. 165, 105444. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105444
Jiang, D., Zhao, Z., Zhang, T., Zhong, W., Liu, C., Yuan, Q., et al. (2017). The chloroplast genome sequence of Scutellaria baicalensis provides insight into intraspecific and interspecific chloroplast genome diversity in Scutellaria. Genes (Basel). 8, 227. doi:10.3390/genes8090227
Ji, S., Li, R., Wang, Q., Miao, W. j., Li, Z. w., Si, L. l., et al. (2015). Anti-H1N1 virus, cytotoxic and Nrf2 activation activities of chemical constituents from Scutellaria baicalensis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 176, 475–484. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.018
Joshi, H. A., Patwardhan, R. S., Sharma, D., Sandur, S. K., and Devarajan, P. V. (2021). Pre-clinical evaluation of an innovative oral nano-formulation of baicalein for modulation of radiation responses. Int. J. Pharm. 595, 120181. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120181
Ju, M., Liu, Y., Li, M., Cheng, M., Zhang, Y., Deng, G., et al. (2019). Baicalin improves intestinal microecology and abnormal metabolism induced by high-fat diet. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 857, 172457. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172457
Junior, L. A. I. Y. S., Nguyen, H. T., Salmanida, F. P., and Chang, K. T. (2021). MERTK(+/hi) M2c macrophages induced by baicalin alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 10604. doi:10.3390/ijms221910604
Kang, M. J., Ko, G. S., Oh, D. G., Kim, J. S., Noh, K., Kang, W., et al. (2014). Role of metabolism by intestinal microbiota in pharmacokinetics of oral baicalin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 371–378. doi:10.1007/s12272-013-0179-2
Kanwal, F., Shubrook, J. H., Adams, L. A., Pfotenhauer, K., Wai-Sun Wong, V., Wright, E., et al. (2021). Clinical care pathway for the risk stratification and management of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 161, 1657–1669. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.049
Kazankov, K., JøRGENSEN, S. M. D., Thomsen, K. L., Møller, H. J., Vilstrup, H., George, H., et al. (2018). The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16: 145.140–159. doi:10.1038/s41575-018-0082-x
Ke, M., Zhang, Z., Xu, B., Zhao, S., Ding, Y., Wu, X., et al. (2019). Baicalein and baicalin promote antitumor immunity by suppressing PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 75, 105824. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105824
Klein, E. A., Thompson, I. M., Tangen, C. M., Crowley, J. J., Lucia, M. S., Goodman, P. J., et al. (2011). Vitamin E and the risk of prostate cancer: the selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial (SELECT). Jama 306, 1549–1556. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.1437
Laveti, D., Kumar, M., Hemalatha, R., Sistla, R., Naidu, V. G. M., Talla, V., et al. (2013). Anti-inflammatory treatments for chronic diseases: a review. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 12, 349–361. doi:10.2174/18715281113129990053
Leung, D. H., Williams, K., Fraley, J. K., and Klish, W. J. (2008). Age- and ethnic-specific elevation of ALT among obese children at risk for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): implications for screening. Clin. Pediatr. 48, 50–57. doi:10.1177/0009922808321678
Liao, C. C., Day, Y. J., Lee, H. C., Liou, J. T., Chou, A. H., and Liu, F. C. (2016). Baicalin attenuates IL-17-mediated acetaminophen-induced liver injury in a mouse model. PLoS One 11, e0166856. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0166856
Li, M., Shi, A., Pang, H., Xue, W., Li, Y., Cao, G., et al. (2014). Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of a single ascending dose of baicalein chewable tablets in healthy subjects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 156, 210–215. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.08.031
Li, P., Chen, Y., Ke, X., Zhang, R., Zuo, L., Wang, M., et al. (2022a). Baicalin ameliorates alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis by suppressing SREBP1c elicited PNPLA3 competitive binding to ATGL. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 722, 109236. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2022.109236
Li, P., Zhang, R., Wang, M., Chen, Y., Chen, Z., Ke, X., et al. (2022b). Baicalein prevents fructose-induced hepatic steatosis in rats: in the regulation of fatty acid de novo synthesis, fatty acid elongation and fatty acid oxidation. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 917329. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.917329
Liu, D.-H., Luo, Y.-H., Liang, J.-C., and Huang, Y. k. (2010). Baicalin regulates lipid metabolism in high-fat feeding SD rat liver and the mechanism involves modulation of AMPK-alpha pathway. J. hepatology 18: 711–712. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2010.09.017
Liu, W. J., Chen, W. W., Chen, J. Y., Sun, Y. B., Chang, D., Wang, C. X., et al. (2023). Baicalin attenuated metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 signalling pathway in db/db mice. Phytother. Res. 39, 1663–1678. doi:10.1002/ptr.8010
Liu, J., Yuan, Y., Gong, X., Zhang, L., Zhou, Q., Wu, S., et al. (2020). Baicalin and its nanoliposomes ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via suppression of TLR4 signaling cascade in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 80, 106208. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106208
Long, M. T., Noureddin, M., and Gastroenterology, J. K. L. J. (2022). AGA clinical practice update: diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals. Expert Rev. 163, 764–774.e761. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.06.023
Lu, Q., Zhou, L., Wang, Z., Li, X., Ding, L., Qiu, Y., et al. (2022). Baicalin alleviate apoptosis via PKC-MAPK pathway in porcine peritoneal mesothelial cells induced by glaesserella parasuis. Molecules 27, 5083. doi:10.3390/molecules27165083
Ma, M. Y., Niu, X. J., Wang, Q., Wang, S. M., Li, X., and Zhang, S. H. (2023). Evidence and possible mechanism of Scutellaria baicalensis and its bioactive compounds for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Ann. Med. 55, 2247004. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2247004
Malhotra, J. D., Miao, H., Zhang, K., Wolfson, A., Pennathur, S., Pipe, S. W., et al. (2008). Antioxidants reduce endoplasmic reticulum stress and improve protein secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 18525–18530. doi:10.1073/pnas.0809677105
Metabolizm, W. R. J. Ż. C. I. (2012). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease - pathogenesis and management. 39: 309–319.
Miao, L., Zhang, X., Zhang, H., Cheong, M. S., Chen, X., Farag, M. A., et al. (2024). Baicalin ameliorates insulin resistance and regulates hepatic glucose metabolism via activating insulin signaling pathway in obese pre-diabetic mice. Phytomedicine 124, 155296. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155296
Miralles-Linares, F., Puerta-Fernandez, S., Bernal-Lopez, M. R., Tinahones, F. J., Andrade, R. J., and Gomez-Huelgas, R. (2012). Metformin-induced hepatotoxicity. Diabetes Care 35, e21. doi:10.2337/dc11-2306
Na, H.-Y., and Sciences, B.-C. L. J. I. J. O. M. (2019). Scutellaria baicalensis alleviates insulin resistance in diet-induced obese mice by modulating inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 727. doi:10.3390/ijms20030727
Nishimura, S., Manabe, I., Nagasaki, M., Eto, K., Yamashita, H., Ohsugi, M., et al. (2009). CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat. Med. 15, 914–920. doi:10.1038/nm.1964
Nobili, V., Alisi, A., Newton, K. P., and Schwimmer, J. B. (2016). Comparison of the phenotype and approach to pediatric vs adult patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 150, 1798–1810. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.009
Noh, J. W., Kwon, O. J., and Lee, B. C. (2021). The immunomodulating effect of baicalin on inflammation and insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 5531367. doi:10.1155/2021/5531367
Ohtani, N., Kamiya, T., and Kawada, N. (2023). Recent updates on the role of the gut-liver axis in the pathogenesis of NAFLD/NASH, HCC, and beyond. Hepatol. Commun. 7, e0241. doi:10.1097/HC9.0000000000000241
Orzechowska, B. U., Wrobel, G., Turlej, E., Jatczak, B., Sochocka, M., and Chaber, R. (2020). Antitumor effect of baicalin from the Scutellaria baicalensis radix extract in B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia with different chromosomal rearrangements. Int. Immunopharmacol. 79, 106114. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106114
Osborne, N., Leahy, C., Lee, Y.-K., Rote, P., Song, B. J., and Hardwick, J. P. (2022). CYP4V2 fatty acid omega hydroxylase, a druggable target for the treatment of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). MAFLD 195, 114841. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114841
Palma, R., Pronio, A., Romeo, M., Scognamiglio, F., Ventriglia, L., Ormando, V. M., et al. (2022). The role of insulin resistance in fueling NAFLD pathogenesis: from molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. J. Clin. Med. 11, 3649. doi:10.3390/jcm11133649
Pan, T. L., Wang, P. W., Huang, C. H., Leu, Y. L., Wu, T. H., Wu, Y. R., et al. (2015). Herbal formula, Scutellariae radix and Rhei rhizoma attenuate dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in a rat model. Sci. Rep. 5, 11734. doi:10.1038/srep11734
Park, C. H., Shin, M. R., An, B. K., Joh, H. W., Lee, J. C., Roh, S. S., et al. (2017). Heat-processed scutellariae radix protects hepatic inflammation through the amelioration of oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 45, 1233–1252. doi:10.1142/S0192415X17500689
Pierantonelli, I., and Transplantation, G. S.-B. J. (2019). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: basic pathogenetic mechanisms in the progression from NAFLD to NASH. Transplantation 103: e1-e13. doi:10.1097/TP.0000000000002480
Portillo-Sanchez, P., Bril, F., Lomonaco, R., Barb, D., Orsak, B., Bruder, J. M., et al. (2019). Effect of pioglitazone on bone mineral density in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a 36-month clinical trial. J. Diabetes 11, 223–231. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.12833
Qiao, H., Han, H., Hong, D., Ren, Z., Chen, Y., and Zhou, C. (2011). Protective effects of baicalin on carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury by activating PPARγ and inhibiting TGFβ1. Pharm. Biol. 49, 38–45. doi:10.3109/13880209.2010.493179
Qu, W., Ma, T., Cai, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, P., She, Z., et al. (2021). Liver fibrosis and MAFLD: from molecular aspects to novel pharmacological strategies. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 8, 761538. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.761538
Rada, P., GonzáLEZ-RodríGUEZ, Á., GarcíA-MonzóN, C., and M Valverde, Á. (2020). Understanding lipotoxicity in NAFLD pathogenesis: is CD36 a key driver? Cell Death Dis. 11 (9), 802. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03003-w
Rives, C., Fougerat, A., Ellero-Simatos, S., Loiseau, N., Guillou, H., Gamet-Payrastre, L., et al. (2020). Oxidative stress in NAFLD: role of nutrients and food contaminants. Biomolecules 10, 1702. doi:10.3390/biom10121702
Samuel, V. T., Liu, Z.-X., Qu, X., Elder, B. D., Bilz, S., Befroy, D., et al. (2004). Mechanism of hepatic insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 32345–32353. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313478200
Semanticscholar, I. E. C. J. (2019). Scutellaria baicalensis is useful in the treatment of cancer and liver disease.
Shao, B. Z., Xu, Z. Q., Han, B. Z., Su, D. F., and Liu, C. (2015). NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 6, 262. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00262
Shi, L., Hao, Z., Zhang, S., Wei, M., Lu, B., Wang, Z., et al. (2018). Baicalein and baicalin alleviate acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating Nrf2 antioxidative pathway: the involvement of ERK1/2 and PKC. Biochem. Pharmacol. 150, 9–23. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.026
Shi, L., Zhang, S., Huang, Z., Hu, F., Zhang, T., Wei, M., et al. (2020). Baicalin promotes liver regeneration after acetaminophen-induced liver injury by inducing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 160, 163–177. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.05.012
Shin, N. R., Gu, N., Choi, H. S., and Kim, H. (2020). Combined effects of Scutellaria baicalensis with metformin on glucose tolerance of patients with type 2 diabetes via gut microbiota modulation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 318, E52–e61. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00221.2019
Singal, A. G., Manjunath, H., Yopp, A. C., Beg, M. S., Marrero, J. A., Gopal, P., et al. (2014). The effect of PNPLA3 on fibrosis progression and development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. a meta-analysis 109, 325–334. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.476
Son, S. H., Kang, J., Ahn, M., Nam, S., Jung, Y. W., Lee, K. Y., et al. (2021). Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of baicalein prodrugs. Pharmaceutics 13, 1516. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13091516
Song, P., Tobe, R. G., Inagaki, Y., Kokudo, N., Hasegawa, K., Sugawara, Y., et al. (2012). The management of hepatocellular carcinoma around the world: a comparison of guidelines from 2001 to 2011. Liver Int. 32, 1053–1063. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2012.02792.x
Stefan, N., HäRING, H.-U., and Cusi, K. (2019). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: causes. Diagnosis, Cardiometabolic Consequences, Treat. Strategies 7, 313–324. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30154-2
Sun, H., Che, Q. M., Zhao, X., and Pu, X. P. (2010). Antifibrotic effects of chronic baicalein administration in a CCl4 liver fibrosis model in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 631, 53–60. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.01.002
Sun, W., Liu, P., Wang, T., Wang, X., Zheng, W., and Li, J. (2019). Baicalein reduces hepatic fat accumulation by activating AMPK in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells and high-fat diet-induced non-insulin-resistant mice. Food Funct. 11, 711–721. doi:10.1039/c9fo02237f
Szabo, G., Gastroenterology, J. P. J. N. R., and Hepatology, H. (2015). Inflammasome activation and function in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 12: 387–400. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2015.94
Tauil, R. B., Golono, P. T., DE Lima, E. P., de Alvares Goulart, R., Guiguer, E. L., Bechara, M. D., et al. (2024). Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: the influence of oxidative stress, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunctions, and the role of polyphenols. Pharm. (Basel) 17, 1354. doi:10.3390/ph17101354
Veracruz, N., Hameed, B., Saab, S., and Wong, R. J. (2021). The association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and extrahepatic cancers. Stroke, Extrahepatic Cancers 11, 45–81. doi:10.1016/j.jceh.2020.04.018
Violi, F., and Cangemi, R. (2010). Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 1185–1186. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1006581
Vozarova, B., Stefan, N., Lindsay, R., Saremi, A., Pratley, R. E., Bogardus, C., et al. (2002). High alanine aminotransferase is associated with decreased hepatic insulin sensitivity and predicts the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 51, 1889–1895. doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.6.1889
Wang, T., Jiang, H., Cao, S., Chen, Q., Cui, M., Wang, Z., et al. (2017). Baicalin and its metabolites suppresses gluconeogenesis through activation of AMPK or AKT in insulin resistant HepG-2 cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 141, 92–100. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.049
Wang, Y., Tai, Y.-L., Zhao, D., Zhang, Y., Yan, J., Kakiyama, G., et al. (2021). Berberine prevents disease progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through modulating multiple pathways. Cells 10, 210. doi:10.3390/cells10020210
Wang, Y., Yang, J., Li, X., and Wang, J. (2012). The metabolism of baicalin in rat and the biological activities of the metabolites. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 404529. doi:10.1155/2012/404529
Wei, S., Zhang, M., Yu, Y., Lan, X., Yao, F., Yan, X., et al. (2016). Berberine attenuates development of the hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetic mice and in palmitate-incubated HepG2 cells through suppression of the HNF-4α Mir122 pathway. PLoS One 11, e0152097. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0152097
Wei, Y., Guo, J., Zheng, X., Wu, J., Zhou, Y., Yu, Y., et al. (2014). Preparation, pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of baicalin-loaded liposomes. Int. J. Nanomedicine 9, 3623–3630. doi:10.2147/IJN.S66312
XI, Y. L., Li, H. X., Chen, C., Liu, Y. Q., Lv, H. M., Dong, S. Q., et al. (2016). Baicalin attenuates high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and ectopic fat storage in skeletal muscle, through modulating the protein kinase B/Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 14, 48–55. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1009.2016.00048
Xiang, H., Lei, H., Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Qiu, Y., et al. (2021). Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on molecular targets: mechanisms of baicalin and baicalein against hyperuricemic nephropathy. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 424, 115594. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2021.115594
Xiang, Y., Long, Y., Yang, Q., Zheng, C., Cui, M., Ci, Z., et al. (2020). Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and toxicity of Baicalin liposome on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury rats via intranasal administration. Brain Res. 1726, 146503. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146503
Xin, H. G., Zhang, B. B., Wu, Z. Q., Hang, X. F., Xu, W. S., Ni, W., et al. (2014). Treatment with baicalein attenuates methionine-choline deficient diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 738, 310–318. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.06.006
Xu, W., Niu, Y., Ai, X., Xia, C., Geng, P., Zhu, H., et al. (2022). Liver-targeted nanoparticles facilitate the bioavailability and anti-HBV efficacy of baicalin in vitro and in vivo. Biomedicines 10, 900. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10040900
Yan, B. F., Wang, Y., Wang, W. B., Ding, X. J., Wei, B., Liu, S. J., et al. (2023). Huangqin decoction mitigates hepatic inflammation in high-fat diet-challenged rats by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 303, 115999. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115999
Yang, J., Xiang, D., Xiang, D., He, W., Liu, Y., Lan, L., et al. (2020). Baicalin protects against 17α-ethinylestradiol-induced cholestasis via the sirtuin 1/hepatic nuclear receptor-1α/farnesoid X receptor pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 1685. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01685
Yan, P., Liu, J., Huang, Y., Yi, T., Zhang, H., Dai, G., et al. (2024). Baicalin enhances antioxidant, inflammatory defense, and microbial diversity of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1465346. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2024.1465346
Yan, X., Zhang, Y., Peng, Y., and Li, X. (2022). The water extract of Radix scutellariae, its total flavonoids and baicalin inhibited CYP7A1 expression, improved bile acid, and glycolipid metabolism in T2DM mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 293, 115238. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115238
Yoon, E.-J., Lee, M. Y., Choi, B. I., Lim, K. J., Hong, S. Y., and Park, D. (2020). Pharmaceutical advantages of GenoTX-407, A combination of extracts from Scutellaria baicalensis root and magnolia officinalis bark. Antioxidants (Basel). 9, 1111. doi:10.3390/antiox9111111
You, Y. P., Yan, L., Ke, H. Y., Li, Y. P., Shi, Z. J., Zhou, Z. Y., et al. (2024). Baicalin inhibits PANoptosis by blocking mitochondrial Z-DNA formation and ZBP1-PANoptosome assembly in macrophages. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 46, 430–447. doi:10.1038/s41401-024-01376-8
Younossi, Z. M., Koenig, A. B., Abdelatif, D., Fazel, Y., Henry, L., and Wymer, M. (2016). Global Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 64: 73–84. doi:10.1002/hep.28431
Younossi, Z. M., Otgonsuren, M., Henry, L., Venkatesan, C., Mishra, A., Erario, M., et al. (2015). Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the United States from 2004 to 2009. Hepatology 62, 1723–1730. doi:10.1002/hep.28123
Younossi, Z., Anstee, Q. M., Marietti, M., Hardy, T., Henry, L., Eslam, M., et al. (2018). Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 11–20. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109
Yu, C. L., Yang, S. F., Hung, T. W., Lin, C. L., Hsieh, Y. H., and Chiou, H. L. (2019). Inhibition of eIF2α dephosphorylation accelerates pterostilbene-induced cell death in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in an ER stress and autophagy-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 10, 418. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1639-5
Zaghloul, R. A., Zaghloul, A. M., and EL-Kashef, D. H. (2022). Hepatoprotective effect of Baicalin against thioacetamide-induced cirrhosis in rats: targeting NOX4/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways. Life Sci. 295, 120410. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120410
Zhang, L., Li, C., Lin, G., Krajcsi, P., and Zuo, Z. (2011). Hepatic metabolism and disposition of baicalein via the coupling of conjugation enzymes and transporters-in vitro and in vivo evidences. Aaps J. 13, 378–389. doi:10.1208/s12248-011-9277-6
Zhang, Z., Ma, G., Xue, C., Sun, H., Wang, Z., Xiang, X., et al. (2019). Establishment of rat liver microsome-hydrogel system for in vitro phase II metabolism and its application to study pharmacological effects of UGT substrates. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 34, 141–147. doi:10.1016/j.dmpk.2019.01.005
Zhao, X. Y., Xiong, X., Liu, T., Mi, L., Peng, X., Rui, C., et al. (2018). Long noncoding RNA licensing of obesity-linked hepatic lipogenesis and NAFLD pathogenesis. Nat. Commun. 9, 2986. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-05383-2
Zhao, L., Wei, Y., Huang, Y., He, B., Zhou, Y., and Fu, J. (2013). Nanoemulsion improves the oral bioavailability of baicalin in rats: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Nanomedicine 8, 3769–3779. doi:10.2147/IJN.S51578
Zhao, Q., Zhang, Y., Wang, G., Hill, L., Weng, J-K., Chen, X-Y., et al. (2016). A specialized flavone biosynthetic pathway has evolved in the medicinal plant. Scutellaria Baicalensis. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1501780
Zhao, S., Huang, M., Yan, L., Zhang, H., Shi, C., and Liu, J. (2022). Exosomes derived from baicalin-pretreated mesenchymal stem cells alleviate hepatocyte ferroptosis after acute liver injury via the keap1-NRF2 pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 8287227. doi:10.1155/2022/8287227
Zhao, W., Liu, L., Wang, Y., Mao, T., and Li, J. (2016). Effects of a combination of puerarin, baicalin and berberine on the expression of proliferator-activated receptor-γ and insulin receptor in a rat model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 11, 183–190. doi:10.3892/etm.2015.2846
Zhi, H., Jin, X., Zhu, H., Li, H., Zhang, Y., Lu, Y., et al. (2019). Exploring the effective materials of flavonoids-enriched extract from Scutellaria baicalensis roots based on the metabolic activation in influenza A virus induced acute lung injury. Injury 177, 112876. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112876
Zhong, X., and Liu, H. (2018). Baicalin attenuates diet induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via suppressing JNK signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 98, 111–117. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.026
Zhou, Y., Wang, L., Gong, Z. P., Li, Y. T., Jin, Y., Zheng, L., et al. (2024). Comparative study on excretion of Shuganning Injection and Scutellariae Radix extract in bile, urine, and feces of rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 49, 809–818. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20231106.201
Zhu, H., Qian, Z., He, F., Liu, M., Pan, L., Zhang, Q., et al. (2013). Novel pharmacokinetic studies of the Chinese formula Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang in MCAO rats. Phytomedicine 20, 767–774. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2012.11.012
Zhu, W., Jin, Z., Yu, J., Liang, J., Yang, Q., Li, F., et al. (2016). Baicalin ameliorates experimental inflammatory bowel disease through polarization of macrophages to an M2 phenotype. Int. Immunopharmacol. 35, 119–126. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2016.03.030
Keywords: metabolic associated fatty liver disease, Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, pharmacological activities, pharmacokinetics, production development
Citation: Chen L, Liu E, Zhao X, Liu X, Dong Q, Lou Y, Huang G, Li L and He Y (2025) Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease treatment: research progress. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1565461. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1565461
Received: 23 January 2025; Accepted: 20 May 2025;
Published: 05 June 2025.
Edited by:
Wei Peng, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Cong-En Zhang, Capital Medical University, ChinaYiteng Xia, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Liu, Zhao, Liu, Dong, Lou, Huang, Li and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guoying Huang, Y29ndW95aW5nc2ZAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Ling Li, bGlsaW5nMjAyMzNAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Yuxin He, aGV5dXhpbjY2QDEyNi5jb20=
 Liping Chen
Liping Chen Enhe Liu2
Enhe Liu2