- Center for Healthcare Policy Research, School of International Pharmaceutical Business, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, China
Background: The escalating economic burden of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) in China necessitates cost-effective first-line treatments. Cetuximab-β, a newer version of Cetuximab, is approved for first-line RAS/BRAF wild-type mCRC. This study evaluates the cost-effectiveness of Cetuximab-β with FOLFIRI for mCRC patients, comparing it to Cetuximab plus chemotherapy to guide clinical decision-making and policy development.
Methods: We conducted a network meta-analysis (NMA) of six randomized controlled trials to compare overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and adverse events (AEs). Subsequently, a cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) was performed using a 10-year partitioned survival model from the Chinese healthcare payer perspective. Costs were standardized to 2024 US dollars ($1 = ¥7.25). Both costs and outcomes were discounted annually at 5%. The model estimated life-years (LYs), quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), total costs, and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICER). Model uncertainty was evaluated via one-way sensitivity analysis, probabilistic sensitivity analysis, and scenario analyses.
Results: The NMA showed comparable efficacy between Cetuximab-β and Cetuximab, with Cetuximab demonstrating an OS HR of 1.10 (95% CI 0.67–1.90) and a PFS HR of 0.94 (95% CI 0.49–1.80) compared with Cetuximab-β, along with a trend towards a more favorable safety profile for Cetuximab-β. CEA showed Cetuximab-β reduced costs by $12,005.54 ($34,996.43 vs. $47,001.97) and gained 0.10 QALYs (1.90 vs. 1.80 QALYs) versus Cetuximab, yielding a dominant ICER (-$120,743/QALY). Sensitivity and scenario analyses confirmed robustness.
Conclusion: Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI represents a dominant, cost-saving strategy compared to Cetuximab plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment of RAS/BRAF wild-type mCRC in China.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a pressing global health issue due to its high incidence and mortality rates. Globally, CRC ranks as the third most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths, with an estimated 1.93 million new cases and 903,900 deaths annually (Bray et al., 2024). In China, CRC poses a substantial burden, ranking second in incidence and fourth in mortality, accounting for approximately 517,100 new cases and 240,000 deaths each year (Han et al., 2024). These statistics highlight the urgent need for optimized treatment strategies and targeted resource allocation to mitigate the CRC burden worldwide and in China.
The nonspecific symptoms of CRC, such as diarrhea, constipation, rectal bleeding, and abdominal pain, often lead to delayed diagnoses (Holtedahl et al., 2021). As a result, many patients are diagnosed at advanced stages, frequently accompanied by distant metastases. Approximately 20% of CRC cases are metastatic at diagnosis, and an additional 25% of initially localized cases eventually progress to metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) (Biller and Schrag, 2021; Kelly et al., 2014). At this stage, curative surgical options are typically unavailable, and prognosis remains poor.
The RAS gene is a key determinant in selecting first-line treatment for mCRC, with about 50% of mCRC patients exhibiting RAS gene mutations (NCCN, 2024). Despite advancements in treatment, including the development of targeted therapies and immunotherapies like PD-1 inhibitors, the overall survival for patients remains low, particularly for those with BRAF mutations or mismatch repair-deficient cancers (Yang et al., 2023). For patients with RAS wild-type (WT) mCRC, early clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Cetuximab, a recombinant anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) monoclonal antibody, when combined with FOLFIRI (a chemotherapy regimen combining calcium folinate, fluorouracil, and irinotecan) or FOLFOX (a chemotherapy regimen including calcium folinate, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin). Cetuximab-β, a newer version of Cetuximab, is produced in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells rather than the mouse SP2/0 cell line used for Cetuximab. Unlike the SP2/0 cell line, CHO cells lack the gene for α-1,3-galactosyltransferase, resulting in a glycosylation profile for Cetuximab-β that contains lower levels of galactose-α-1,3-galactose (Gal (α 1-3) Gal) (Chung et al., 2008). Since pre-existing IgE antibodies targeting Gal (α 1-3) Gal have been associated with adverse reactions (AEs) to Cetuximab, Cetuximab-β may exhibit a reduced incidence of AEs (Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology Colorectal Cancer Expert Committee, 2024; Wang and Guo, 2017; Lammerts van Bueren et al., 2011).
Recently, Cetuximab-β was approved for use in combination with FOLFIRI as a first-line treatment for patients with mCRC based on the results of a phase III clinical trial (009mCRCIIIP) (FOLFIRI, 2024). However, its cost-effectiveness compared to existing treatments has not yet been fully assessed. This study aims to conduct a pharmacoeconomic evaluation of Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI for patients with RAS/BRAF wild-type mCRC in China, comparing it with Cetuximab plus chemotherapy. The findings are intended to inform clinical decision-making and guide policy development regarding adopting Cetuximab-β in routine practice.
Methods
Network meta-analysis
Study selection and assessment of risk of bias
We conducted a systematic literature search in PubMed, the Cochrane Library, and the Web of Science for eligible publications up to 30 June 2024. The search terms were: (Cetuximab-β OR Cetuximab OR FOLFIRI OR FOLFOX) AND (“metastatic colorectal cancer”) AND (“RAS/BRAF wild type”) AND random*. Additionally, we planned to contact the marketing department of the relevant pharmaceutical company to request supplementary data, such as unpublished clinical trial outcomes. The risk of bias for included clinical trials was assessed using RevMan software (version 5.4) following the methodology outlined in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions.
Statistical analysis
The primary outcomes of the network meta-analysis (NMA) include efficacy (Hazard ratios (HR) for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) and safety (relative risk (RR) for grade 3/4 AEs) comparisons between cetuximab β plus FOLFIRI, and Cetuximab plus chemotherapy. HR and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for OS and PFS were calculated using R software (version 4.1.1) and the ‘netmeta’ package for each treatment regimen. Due to observed heterogeneity across clinical trials, we applied a random effects model to estimate treatment effects. An indirect comparison of the safety profiles was conducted by calculating the RR and its 95% CI for grade 3/4 AEs, considered severe according to standard clinical trial grading criteria.
Cost-effectiveness analysis
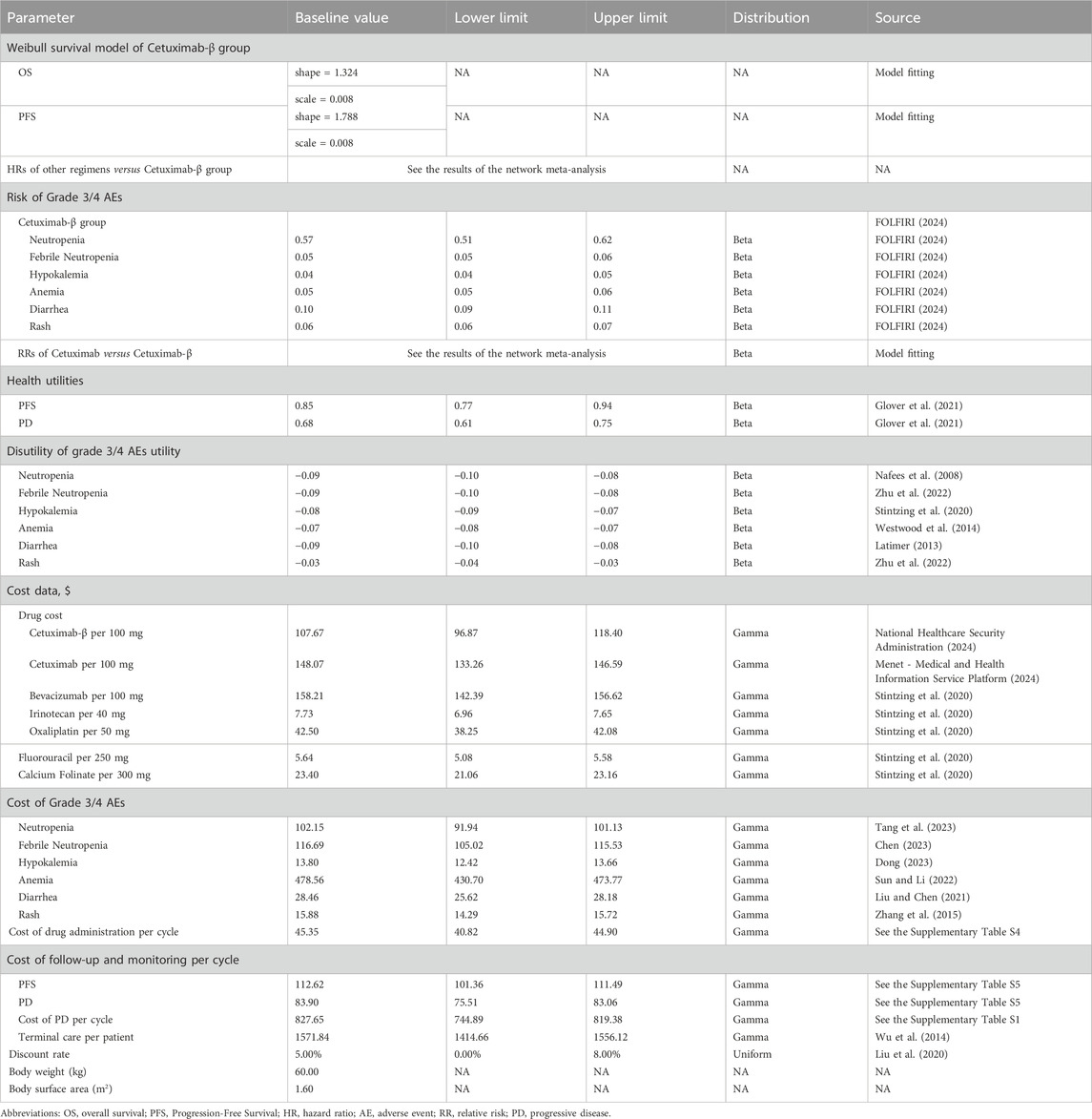
In this cost-effectiveness analysis, we compared Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI with Cetuximab plus chemotherapy, all of which are approved for the treatment of patients with RAS/BRAF WT mCRC in China. A 5% annual discount rate was applied to both costs and effectiveness to account for the time value of money, in line with standard pharmacoeconomic evaluation practices. The primary outcomes measured were life-years (LYs), quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), overall costs, and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) between the treatment regimens. The willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold was determined following the China Guidelines for Pharmacoeconomic Evaluations (2020) (Liu et al., 2020), set at three times the per capita 2023 Chinese GDP, or approximately $37,023 per QALY. This threshold is used to assess whether a treatment provides sufficient value relative to its cost. The study was conducted in adherence to the Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS) guidelines (Husereau et al., 2022). As no individual patient-level data were used in the analysis, this study does not qualify as human subjects research and thus did not require review or approval by an institutional review board or ethics committee.
Patients and treatments
The study population consisted of patients with RAS/BRAF WT mCRC receiving first-line treatment. Cetuximab-β was administered at an initial dose of 400 mg/m2 during the first week, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly thereafter, with Cetuximab given at the same dosage regimen. According to the package insert, Cetuximab-β is approved for use in combination with FOLFIRI, while Cetuximab is approved for use with either FOLFIRI or FOLFOX. The proportion of patients receiving FOLFIRI or FOLFOX was based on data from the study (Xu et al., 2020). In the event of disease progression, patients were switched to subsequent treatments, as detailed in Supplementary Table S1, and received the best supportive care until death. Grade 3/4 AEs, defined as severe or life-threatening, included neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, anemia, hypokalemia, diarrhea, and rash. For this analysis, we assumed a patient weight of 60 kg and a body surface area of 1.6 m2 (Huang et al., 2017).
Model structure
Partitioned survival modeling (PSM) is particularly suited for oncology applications as it directly utilizes the two most frequently reported trial endpoints - PFS and OS (Llovet et al., 2008; Woods et al., 2020). This approach was preferred to state-transition modeling given its ability to incorporate published Kaplan-Meier data from comparator trials when individual patient-level data are unavailable (Glover et al., 2021). Therefore, A PSM with a 1-month cycle was developed using Excel 2020 in this stady. The PSM included three mutually exclusive health states: PFS, progressive disease (PD), and death (Supplementary Figure 1). The time horizon for the model was set to 10 years, as more than 99% of the cohort was expected to have died within this period.
Effectiveness
The survival curves for OS and PFS in patients treated with Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI were derived by fitting individual patient data from the 009mCRCIII-P clinical trial (Holtedahl et al., 2021) to a parametric survival model in R software (version 4.1.1) (Zhu et al., 2022), incorporating natural mortality data from the Chinese population to extrapolate long-term outcomes. The Weibull distribution was identified as the best-fitting model based on Akaike’s information criterion (AIC) and Bayesian information criterion (BIC), outperforming alternative models such as log-logistic, Gompertz, exponential, and log-normal distributions (Supplementary Tables S2, S3; Supplementary Figures 2–5) (Latimer, 2013). The shape (γ) and scale (λ) parameters of the Weibull distribution were estimated using R. Survival curves for patients receiving Cetuximab plus chemotherapy were derived by adjusting the survival data of Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI using results from the network meta-analysis.
Health utility values for the PFS state and the PD state were assumed to be 0.85 and 0.68, respectively, based on previously published data (Wu et al., 2017). Additionally, the disutility values associated with grade 3/4 AEs were incorporated into the analysis.
Cost inputs
In this analysis, direct medical costs were considered from the perspective of Chinese payers. These costs included drug costs, administration costs, management of grade 3/4 AEs with an incidence rate greater than 5%, terminal care, follow-up, and monitoring. The prices for drugs, administration, and part of the follow-up (details of the follow-up program are presented in Supplementary Table S5) and monitoring costs were obtained from the medical and health information service platform of Menet and the official website of the provincial healthcare pricing bureaus of China. The remaining costs were sourced from previously published literature (Table 1). All costs in the study were converted to USD 2,024 based on the exchange rate ($1 = ¥7.25) and consumer price index.
Sensitivity analyses
We conducted both one-way sensitivity analysis and probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) to assess the uncertainty of the model results. In the one-way sensitivity analysis, we varied each parameter within its 95% CI reported in the literature. If no CIs were available, we applied a default variance of ±10% from the baseline values. Additionally, PSA was performed using 1,000 Monte Carlo simulations to evaluate the probability of the treatment regimens being cost-effective.
Scenario analyses
To evaluate the robustness of the model results, scenario analyses were conducted to test key assumptions and explore the impact of alternative settings. One key assumption was that Cetuximab-β, developed as an improved formulation of Cetuximab, is equivalent to Cetuximab in terms of efficacy and safety. A scenario analysis was performed to assess the cost-effectiveness outcomes under this assumption of equivalence. Additionally, the impact of varying the model’s time horizon was examined by testing time horizons of 5, 15, 25, and 35 years to assess the long-term cost-effectiveness of the treatment regimens.
Results
Network meta-analysis
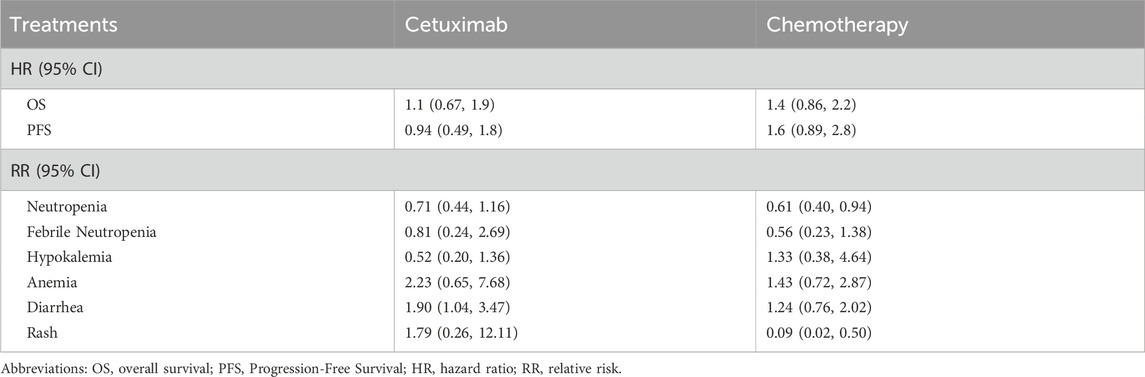
The NMA included data from six RCTs, (FOLFIRI, 2024; Qin et al., 2018; Bokemeyer et al., 2009; Tveit et al., 2012; Bokemeyer et al., 2011; Van Cutsem et al., 2015) comprising three phase II and three phase III studies, with a total of 1,750 patients (Supplementary Table S6). A comparison of baseline characteristics across the studies is provided in Supplementary Table S7, the literature screening procedure is shown in Supplementary Figure S6, and the NMA model diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S7. Of the study population, 257 patients received Cetuximab-β, 579 received Cetuximab, and 869 received chemotherapy alone. The risk of bias assessment is shown in Supplementary Figure S8.
The NMA indicated that mCRC patients receiving Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI had reduced PFS (HR 0.94; 95% CI 0.49–1.80 for Cetuximab vs. Cetuximab-β) compared to those treated with Cetuximab plus chemotherapy, but nevertheless demonstrated longer OS (HR 1.10; 95% CI 0.67–1.90 for Cetuximab vs. Cetuximab-β), though neither outcome reached statistical significance. The incidence of diarrhea was significantly lower in the Cetuximab-β group than in the Cetuximab group (RR = 1.90, 95% CI, 1.04–3.47). No significant differences were observed between the two groups for the other five AEs (Table 2).
Cost-effectiveness analysis
Base-case analysis
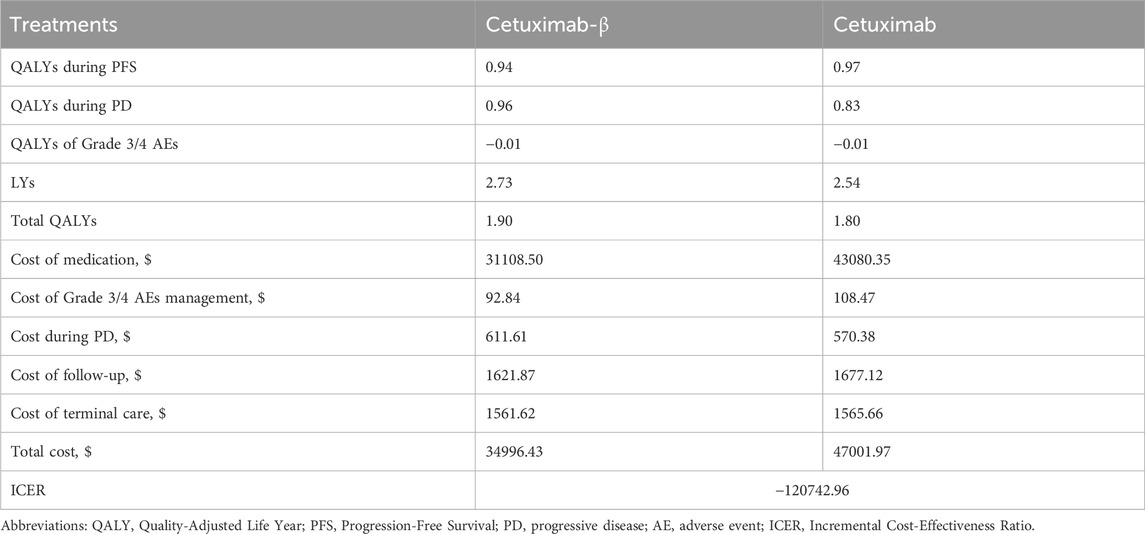
Over a 10-year time horizon, treatment with Cetuximab-β resulted in a cost of $34996.43, providing 1.90 QALYs and 2.73 LYs. In contrast, Cetuximab incurred a cost of $47001.97, providing 1.80 QALYs and 2.54 LYs (Table 3). The ICER for Cetuximab-β compared to Cetuximab was negative (-$120742.96 per QALY), reflecting cost savings with Cetuximab-β.
Sensitivity analysis
In comparing Cetuximab-β with Cetuximab, the results of the one-way sensitivity analysis revealed that parameters such as the cost of Cetuximab and Cetuximab-β, and the utility value for the PD and PFS had the greatest impact on the base case results (Figure 1). Nevertheless, the ICER values obtained after varying all parameters remained below the WTP threshold, indicating that these changes did not alter the conclusions of the analysis, thus confirming the robustness of the base case results.
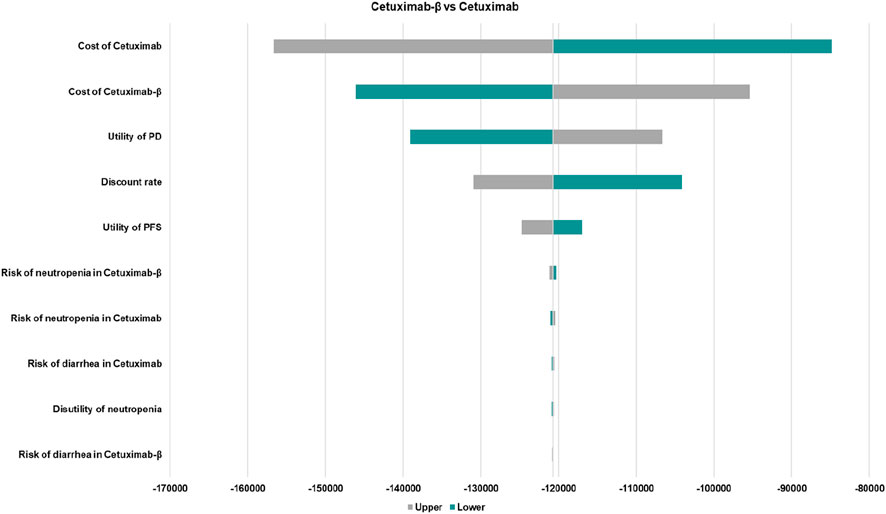
Figure 1. The one-way sensitivity analyses of Cetuximab-β vs. Cetuximab. PFS, Progression-Free Survival; PD, Disease Progressed. Only the top ten parameters with the greatest impact on the results are shown.
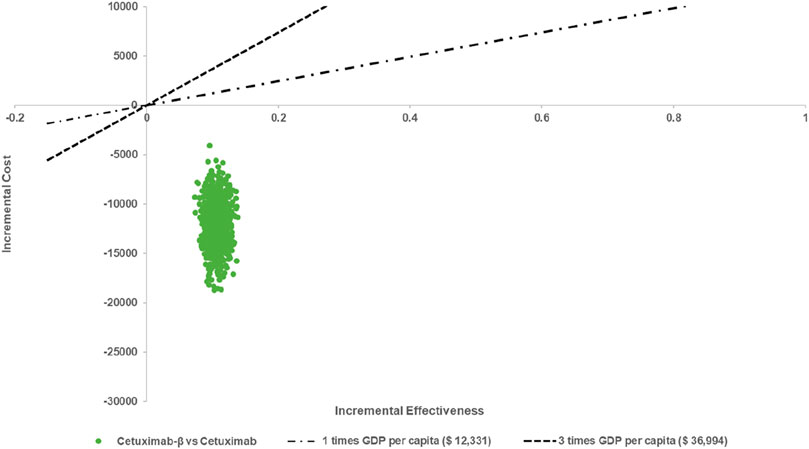
The results of the PSA indicated that, when comparing Cetuximab-β to Cetuximab, Cetuximab-β had an 100% probability of being cost-effective under WTP threshold (Figures 2, 3).
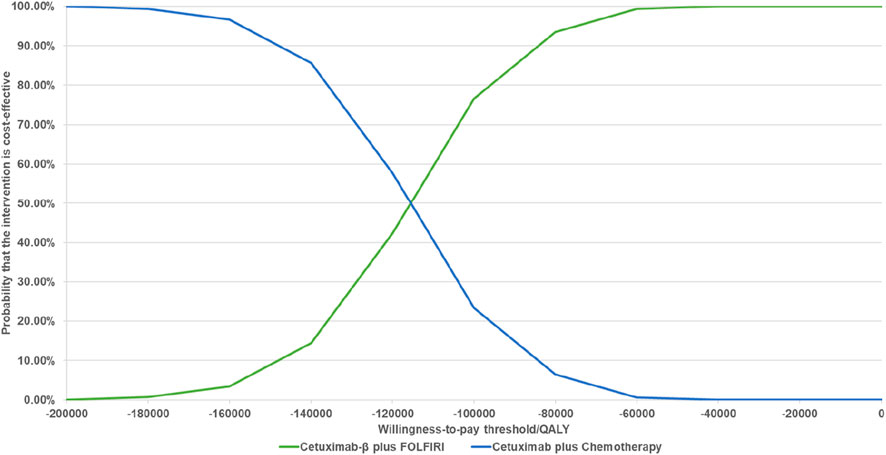
Figure 3. Cost-effectiveness Acceptability Curves (When the WTP is less than 3 times per capita, Cetuximab β is 100% cost-effective compared with Cetuximab).
Scenario analyses
The scenario analysis results indicated that, under the assumption of equivalence between Cetuximab-β and Cetuximab, the incremental cost of Cetuximab-β compared with Cetuximab was -$10,567.38, suggesting a cost saving (Table 4). This cost difference was primarily attributed to the lower price of Cetuximab-β, as well as its specific administration with FOLFIRI, which is less expensive compared to FOLFOX. In contrast, Cetuximab can be administered with either FOLFIRI or FOLFOX, contributing to the higher overall cost for Cetuximab.
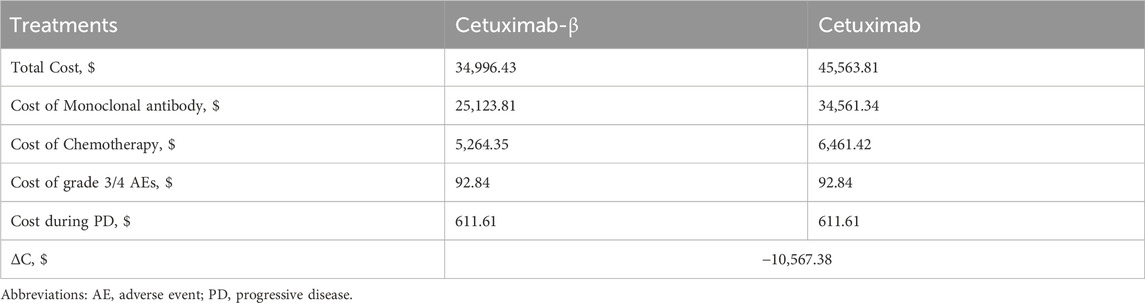
Table 4. The scenario analysis results under the assumption of equivalence between Cetuximab-β and Cetuximab.
The scenario analysis evaluating different study time horizons demonstrated that extending the time horizon from 10 to 35 years did not significantly alter the outcomes compared to the base case analysis (Supplementary Figure S9). These findings support the appropriateness of using a 10-year time horizon for the primary analysis.
Discussion
In recent years, the economic burden of CRC has increased, with healthcare spending per patient rising significantly (Wang et al., 2023). Studies indicate that direct healthcare expenditure for CRC patients in China now exceeds the country’s GDP per capita in the same year (Huang et al., 2017). This growing economic burden is driven in part by the high mortality associated with mCRC, which remains one of the leading causes of death among CRC patients. As a result, there is a pressing need for the development of new therapies to address metastatic disease.
Cetuximab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the EGFR, is a mainstream treatment in immunotherapy for mCRC. Despite its established efficacy in improving survival outcomes, its high cost, along with potential severe adverse effects such as skin toxicity and gastrointestinal disorders, has led to concerns among patients and healthcare providers (Rimassa et al., 2019; Kasper et al., 2020). To address some of these challenges, Cetuximab-β—a modified version of the original drug—was developed, aiming to offer a more cost-effective and tolerable alternative (FOLFIRI, 2024) (Shi et al., 2019). However, there remains a significant gap in the study, with no direct comparisons of the cost-effectiveness between Cetuximab-β and Cetuximab. This study aims to fill this gap by evaluating the economic impact of Cetuximab-β in combination with FOLFIRI, comparing it with the combination of Cetuximab. The findings of this analysis will provide valuable insights for healthcare policy and resource allocation decisions for RAS/BRAF WT mCRC patients in China, supporting evidence-based decision-making for policymakers.In the NMA, no significant differences in PFS or OS were found between Cetuximab-β and Cetuximab, suggesting equivalent efficacy. In terms of safety, Cetuximab-β was associated with a lower incidence of hypokalemia and rash compared to Cetuximab, although these differences were not statistically significant. However, diarrhea occurred significantly less frequently with Cetuximab-β. Hematologic toxicities, including neutropenia and febrile neutropenia, were higher common with Cetuximab-β, but this difference was not statistically significant. Since hematologic toxicities were primarily chemotherapy-related, we conclude that Cetuximab-β offers comparable efficacy and a superior safety profile compared to Cetuximab.
In the cost-effectiveness analysis, Cetuximab-β improved effectiveness by 0.10 QALYs and reduced overall costs by $12,005.54 compared to Cetuximab, resulting in an ICER of -$120,742.96 per QALY. Although the NMA found no statistically significant difference in OS (HR for Cetuximab vs. Cetuximab-β = 1.10, 95% CI 0.67–1.90), the PSM extrapolation projected a numerically longer mean OS duration for Cetuximab-β (2.73 LYs vs. 2.54 LYs). Over the 10-year time horizon, this small difference cumulatively resulted in a gain in LYs, which translated to the incremental 0.10 QALY gain. The cost reduction associated with Cetuximab-β primarily arises from lower drug costs. Additionally, Cetuximab-β not only extends LYs for patients with mCRC but also reduces the cost of managing AEs compared to Cetuximab. These findings suggest that Cetuximab-β is more effective and cost-effective than Cetuximab, with an ICER that falls within the cost-effective range. Sensitivity analyses revealed that the cost difference between Cetuximab-β and Cetuximab was a key determinant of cost-effectiveness, with price sensitivity being the most influential factor. This was further confirmed in a separate study assuming identical efficacy and safety, which demonstrated that mCRC patients treated with Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI saved $10,567.38 compared to those receiving Cetuximab plus chemotherapy.
Our findings challenge the presumption that novel biologics inevitably increase healthcare expenditures by demonstrating Cetuximab-β′s unique cost-saving profile, while reconciling divergent conclusions from prior Chinese cost-effectiveness analyses. Notabely, Cetuximab-β fundamentally differs from originator Cetuximab in its economic performance: (Wang et al., 2020) reported unfavorable economics for originator Cetuximab + FOLFOX (ICER $164,044/QALY), a divergence attributable not only to chemotherapy backbone differences (FOLFOX’s higher cost vs. FOLFIRI), but more critically to Cetuximab-β′s intrinsic price advantage. Crucially, while Wu et al. (2017) showed originator Cetuximab’s cost-effectiveness required patient assistance programs (PAP; ICER $14,049/QALY), Cetuximab-β achieves dominance without subsidies through its biosimilar pricing—resolving the accessibility barrier that plagued originator biologics in resource-limited settings. As the first Asian CEA of this specific biosimilar, our work positions cetuximab-β as a self-sustaining solution to China’s “efficacy-cost paradox.”
Our findings indicate that at China’s WTP threshold ($37,023/QALY), Cetuximab-β is highly likely to be cost-effective, with direct per-patient savings of $12,005 (equivalent to 32.4% of China’s GDP per capita). This robust economic advantage presents a significant opportunity for inclusion in national reimbursement lists. Unlike PAP-dependent originator biologics, cetuximab-β′s inherent affordability establishes a sustainable biosimilar pricing paradigm that aligns with DRG payment reforms—enabling hospitals to maintain therapeutic efficacy while reducing episode-based costs. Resources liberated by Cetuximab-β adoption could be strategically reallocated to address systemic gaps in CRC screening, directly combating the late-stage diagnoses that drive metastatic burden.
Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, due to the lack of direct head-to-head comparison studies between Cetuximab-β and Cetuximab, we conducted a NMA to indirectly assess their efficacy and safety. However, clinical and methodological differences across the included studies, such as variations in patient populations and study designs, may introduce bias (Seitidis et al., 2022; Yun et al., 2023). We compared baseline characteristics across studies and found few clinically significant differences, which suggests that our results are relatively stable. Additionally, the use of a random-effects model helps mitigate potential bias. Second, while Cetuximab can be combined with either FOLFIRI or FOLFOX, Cetuximab-β is typically combined only with FOLFIRI. Consequently, our analysis compares Cetuximab-β with FOLFIRI and Cetuximab with either FOLFIRI or FOLFOX, which may introduce bias. However, previous studies have reported similar efficacy and safety profiles for FOLFIRI and FOLFOX (Yoshino et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023), suggesting that this bias is unlikely to significantly affect the results. Third, we inferred the long-term survival benefit based on short-term survival data from the included studies. However, these estimates may change with longer follow-up, representing an inherent limitation of our model. Thus, it is necessary to validate these health outcomes using real-world data to assess the model’s accuracy.
Conclusion
In brief, Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI demonstrated equivalent efficacy in prolonging OS and PFS compared to Cetuximab plus chemotherapy, but it exhibited a better safety profile. Additionally, Cetuximab-β plus FOLFIRI was found to be a more cost-effective first-line treatment strategy for mCRC in China, with a WTP threshold of $36,994 per QALY, compared to Cetuximab plus chemotherapy. These findings can guide clinicians in selecting optimal treatment strategies and inform reimbursement policies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of China Pharmaceutical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
RT: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MY: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. WZ: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. MZ: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. LW: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. YL: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. FC: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The present study was supported by the 2025 Jiangsu Province Graduate Student Research Innovation Program (KYCX25_1088). The generation of this article was supported by the Simcere Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Jiangsu, China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that this study received funding from Simcere Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Jiangsu, China. The funder had the following involvement in the study: data collection.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1568385/full#supplementary-material
References
Biller, L. H., and Schrag, D. (2021). Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a review. JAMA 325 (7), 669–685. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0106
Bokemeyer, C., Bondarenko, I., Makhson, A., Hartmann, J. T., Aparicio, J., de Braud, F., et al. (2009). Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin with and without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 27 (5), 663–671. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.8397
Bokemeyer, C., Bondarenko, I., Hartmann, J. T., de Braud, F., Schuch, G., Zubel, A., et al. (2011). Efficacy according to biomarker status of cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: the OPUS study. Ann. Oncol. official J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 22 (7), 1535–1546. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq632
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA a cancer J. Clin. 74 (3), 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Chen, P. (2023). Cost-effectiveness analysis of atezolizumab as adjuvant therapy for completely resected stage IB–IIIA NSCLC. Master's thesis, Chengdu, China: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China.
Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology Colorectal Cancer Expert Committee (2024). Chinese expert consensus on maintenance therapy with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies for RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer (2024 edition). Chin. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 27 (4), 316–325. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20240301-00081
Chung, C. H., Mirakhur, B., Chan, E., Le, Q. T., Berlin, J., Morse, M., et al. (2008). Cetuximab-induced anaphylaxis and IgE specific for galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. N. Engl. J. Med. 358 (11), 1109–1117. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa074943
Dong, E. L. (2023). Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of DNF-N versus DPF-P in the treatment of locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma using a markov model. Master's thesis, Guangzhou, China: Guangzhou Medical University.
FOLFIRI (2024). CMAB009 combined with FOLFIRI first-line treatment in patients with RAS/BRAF wild-type, metastatic colorectal cancer. ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03206151 (Accessed June 26, 2024).
Glover, M., Caplin, M., Leeuwenkamp, O. R., and Longworth, L. (2021). Use of [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE in the treatment of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: results of a UK cost-effectiveness modelling study. EJC Suppl. EJC official J. EORTC, Eur. Organ. Res. Treat. Cancer 16, 14–23. doi:10.1016/j.ejcsup.2021.06.003
Han, B., Zheng, R., Zeng, H., Wang, S., Sun, K., Chen, R., et al. (2024). Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 4 (1), 47–53. doi:10.1016/j.jncc.2024.01.006
Holtedahl, K., Borgquist, L., Donker, G. A., Buntinx, F., Weller, D., Campbell, C., et al. (2021). Symptoms and signs of colorectal cancer, with differences between proximal and distal colon cancer: a prospective cohort study of diagnostic accuracy in primary care. BMC Fam. Pract. 22 (1), 148. doi:10.1186/s12875-021-01452-6
Huang, H. Y., Shi, J. F., Guo, L. W., Bai, Y. N., Liao, X. Z., Liu, G. X., et al. (2017). Expenditure and financial burden for the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in China: a hospital-based, multicenter, cross-sectional survey. Chin. J. cancer 36 (1), 41. doi:10.1186/s40880-017-0209-4
Husereau, D., Drummond, M., Augustovski, F., de Bekker-Grob, E., Briggs, A. H., Carswell, C., et al. (2022). Consolidated health economic evaluation reporting standards 2022 (CHEERS 2022) statement: updated reporting guidance for health economic evaluations. Value Health 25, 3–9. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2021.11.1351
Kasper, S., Meiler, J., Knipp, H., Höhler, T., Reimer, P., Steinmetz, T., et al. (2020). Biweekly cetuximab plus FOLFOX6 as first-line therapy in patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: the CEBIFOX trial. Clin. colorectal cancer 19 (4), 236–247. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2020.03.003
Kelly, M. E., Spolverato, G., Le, G., Mavros, M., Doyle, F., Pawlik, T., et al. (2014). Synchronous Co lorectal liver metastasis: a network meta-analysis review comparing classical, combined, and liver-first surgical strategies. J. Surg. Oncol. 111, 341–351. doi:10.1002/jso.23819
Lammerts van Bueren, J. J., Rispens, T., Verploegen, S., van der Palen-Merkus, T., Stapel, S., Workman, L. J., et al. (2011). Anti-galactose-α-1,3-galactose IgE from allergic patients does not bind α-galactosylated glycans on intact therapeutic antibody Fc domains. Nat. Biotechnol. 29 (7), 574–576. doi:10.1038/nbt.1912
Latimer, N. R. (2013). Survival analysis for economic evaluations alongside clinical trials--extrapolation with patient-level data: inconsistencies, limitations, and a practical guide. Med. Decis. Mak. Int. J. Soc. Med. Decis. Mak. 33 (6), 743–754. doi:10.1177/0272989X12472398
Liu, X. Y., and Chen, W. (2021). Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of osimertinib as first-line treatment for EGFR-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. World Clin. Drugs 42 (02), 135–142. doi:10.13683/j.wph.2021.02.010
Liu, G., Hu, S., Wu, J., Wu, J. H., Dong, H., Li, H. C., et al. (2020). China guidelines for pharmacoeconomic evaluations (Chinese-English version). Beijing: China Market Press.
Llovet, J. M., Di Bisceglie, A. M., Bruix, J., Kramer, B. S., Lencioni, R., Zhu, A. X., et al. (2008). Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 100 (10), 698–711. doi:10.1093/jnci/djn134
Menet - Medical and Health Information Service Platform (2024). Drug Bidding database. Available online at: https://db.menet.com.cn/#/bid?nav=3 (Accessed June 30, 2024).
Nafees, B., Stafford, M., Gavriel, S., Bhalla, S., and Watkins, J. (2008). Health state utilities for non small cell lung cancer. Health Qual. life outcomes 6, 84. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-6-84
National Healthcare Security Administration (2024). List of medicines under national basic medical insurance, work-related injury insurance and maternity insurance. Available online at: https://www.nhsa.gov.cn/module/download/downfile.jsp?classid=0&filename=de66e92b7edd4056ac41c0c4d3c011f3.pdf (Accessed November 28, 2024).
NCCN (2024). NCCN clinical practice guidelines in colon/rectal cancer guideline. Available online at: http://www.nccn.org (Accessed June, 2024).
Qin, S., Li, J., Wang, L., Xu, J., Cheng, Y., Bai, Y., et al. (2018). Efficacy and tolerability of first-line cetuximab plus leucovorin, fluorouracil, and Oxaliplatin (FOLFOX-4) versus FOLFOX-4 in patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: the Open-Label, randomized, phase III TAILOR trial. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 36 (30), 3031–3039. doi:10.1200/JCO.2018.78.3183
Rimassa, L., Bozzarelli, S., Pietrantonio, F., Cordio, S., Lonardi, S., Toppo, L., et al. (2019). Phase II Study of tivantinib and cetuximab in patients with KRAS Wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and emergence of MET overexpression: Lesson learned for future trials with EGFR/MET dual inhibition. Clin. colorectal cancer 18 (2), 125–132. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2019.02.004
Seitidis, G., Nikolakopoulos, S., Hennessy, E. A., Tanner-Smith, E. E., and Mavridis, D. (2022). Network meta-analysis techniques for synthesizing prevention science evidence. Prev. Sci. official J. Soc. Prev. Res. 23 (3), 415–424. doi:10.1007/s11121-021-01289-6
Shi, Y., Li, J., Xu, J., Sun, Y., Wang, L., Cheng, Y., et al. (2019). CMAB009 plus irinotecan versus irinotecan-only as second-line treatment after fluoropyrimidine and oxaliplatin failure in KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer patients: promising findings from a prospective, open-label, randomized, phase III trial. Cancer Commun. Lond. Engl. 39 (1), 28. doi:10.1186/s40880-019-0374-8
Stintzing, S., van Oostrum, I., Pescott, C. P., Ronga, P., Heeg, B., and Heinemann, V. (2020). Cost-effectiveness of FOLFIRI + cetuximab vs FOLFIRI + bevacizumab in the first-line treatment of RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer in Germany: data from the FIRE-3 (AIO KRK-0306) study. J. Med. Econ. 23 (5), 448–455. doi:10.1080/13696998.2019.1709848
Sun, Z., and Li, Y. (2022). Cost-effectiveness analysis of camrelizumab combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of advanced squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 42 (20), 2148–2152. doi:10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.20.13
Tang, Y. Q., Zhao, M. Y., and Tang, W. X. (2023). Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of sintilimab versus camrelizumab as first-line treatment for advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Health Econ. Res. 40 (02), 34–40.
Tveit, K. M., Guren, T., Glimelius, B., Pfeiffer, P., Sorbye, H., Pyrhonen, S., et al. (2012). Phase III trial of cetuximab with continuous or intermittent fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (nordic FLOX) versus FLOX alone in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: the NORDIC-VII study. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 30 (15), 1755–1762. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0915
Van Cutsem, E., Lenz, H. J., Köhne, C. H., Heinemann, V., Tejpar, S., Melezínek, I., et al. (2015). Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan plus cetuximab treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 33 (7), 692–700. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.59.4812
Wang, C., and Guo, H. (2017). Characterization of N-glycosylation in an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody produced by different expression systems. Sheng wu gong cheng xue bao = Chin. J. Biotechnol. 33 (6), 1018–1027. doi:10.13345/j.cjb.170074
Wang, H., Huang, L., Gao, P., Zhu, Z., Ye, W., Ding, H., et al. (2020). Cost-effectiveness analysis of cetuximab combined with chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer based on the TAILOR trial. BMJ open 10 (2), e030738. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-030738
Wang, R., Lian, J., Wang, X., Pang, X., Xu, B., Tang, S., et al. (2023). Survival rate of colorectal cancer in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 13, 1033154. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1033154
Westwood, M., Joore, M., Whiting, P., van Asselt, T., Ramaekers, B., Armstrong, N., et al. (2014). Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) mutation testing in adults with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol. Assess. Winch. Engl. 18 (32), 1–166. doi:10.3310/hta18320
Woods, B. S., Sideris, E., Palmer, S., Latimer, N., and Soares, M. (2020). Partitioned survival and State transition models for healthcare decision making in oncology: where are we now? Value health J. Int. Soc. Pharmacoeconomics Outcomes Res. 23 (12), 1613–1621. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2020.08.2094
Wu, B., Li, T., Cai, J., Xu, Y., and Zhao, G. (2014). Cost-effectiveness analysis of adjuvant chemotherapies in patients presenting with gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy. BMC cancer 14, 984. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-984
Wu, B., Yao, Y., Zhang, K., and Ma, X. (2017). RAS testing and cetuximab treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis in a setting with limited health resources. Oncotarget 8 (41), 71164–71172. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.17029
Xu, R., Wang, W., Zhu, B., Lin, X., Ma, D., Zhu, L., et al. (2020). Disease characteristics and treatment patterns of Chinese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective study using medical records from China. BMC cancer 20 (1), 131. doi:10.1186/s12885-020-6557-5
Yang, M., Xu, Z., Mi, M., Ding, Y., Pan, Y., Yuan, Y., et al. (2023). CSCO guidelines for metastatic colorectal cancer: personalized medicine in clinical practice. Cancer Biol. and Med. 20 (9), 640–645. doi:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0211
Yoshino, T., Hooda, N., Younan, D., Muro, K., Shitara, K., Heinemann, V., et al. (2024). A meta-analysis of efficacy and safety data from head-to-head first-line trials of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors versus bevacizumab in adult patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer by sidedness. Eur. J. cancer (Oxford, Engl. 1990) 202, 113975. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2024.113975
Yun, L., YuMei, Z., Bn, V., Tang, Q., and Feng, C. (2023). The efficacy, safety, and economic outcomes of using ferric derisomaltose for the management of iron deficiency in China: a rapid health technology assessment. Cureus 15 (11), e48717. doi:10.7759/cureus.48717
Zhang, C. X., Zhang, H. M., Shi, J. N., Wang, D., and Ma, A. X. (2015). Pharmacoeconomic analysis of erlotinib versus pemetrexed in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. J. New Drugs 24 (14), 1616–1623.
Zhou, F., Wang, W., Xia, L., Dai, J., Wu, H., Yang, L., et al. (2023). 612P updated results from the multicenter phase II study of fruquintinib plus mFOLFOX6/FOLFIRI as first-line therapy in advanced metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Ann. Oncol. 34, S439. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2023.09.1803
Zhu, Y., Liu, K., Wang, K., and Peng, L. (2022). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitors in Chinese patients with advanced radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: a network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 909333. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.909333
Keywords: Cetuximab-β, Cetuximab, metastatic colorectal cancer, network meta-analysis, cost-effectiveness analysis
Citation: Tong R, Yang M, Zhang W, Zhou M, Wang L, Lu Y and Chang F (2025) Network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis comparing Cetuximab-β and Cetuximab for Chinese patients with RAS/BRAF wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1568385. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1568385
Received: 29 January 2025; Accepted: 20 August 2025;
Published: 15 September 2025.
Edited by:
Yonggang Zhang, Sichuan University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Tong, Yang, Zhang, Zhou, Wang, Lu and Chang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Chang, Y3B1Y2ZAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Yun Lu, bHV5dW5jcHVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Rongjun Tong
Rongjun Tong Mengyu Yang†
Mengyu Yang† Linning Wang
Linning Wang Yun Lu
Yun Lu Feng Chang
Feng Chang