- 1Department of Pharmacy, Third Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China
- 2Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China
Background: Osteoarthritis is characterized by articular cartilage degradation, involving inflammation-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix destruction. Eucommia ulmoides and Achyranthes bidentata constitute a classic herbal pair for OA treatment, yet their combinatorial effects and molecular mechanisms remain unelucidated.
Methods: The EU-AB extract was prepared via aqueous decoction. An LPS-induced ATDC5 chondrocyte inflammatory model and an MIA-induced rat OA model were established. Therapeutic efficacy was evaluated using Lequesne scores, ELISA, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. Bioactive components were identified by HPLC-TOF/MS, while RNA-seq and molecular interaction analyses validated underlying mechanisms.
Results: The EU-AB extract significantly suppressed the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-3/13) and inflammatory cytokines (NO, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β) in both ATDC5 cells and rat serum (P < 0.05). Concurrently, it reduced Lequesne scores and joint swelling in MIA-induced OA rats (P < 0.05) while ameliorating histopathological cartilage damage. Among 35 compounds identified by HPLC-TOF/MS, pinoresinol diglucoside (PIN) from EU and chikusetsusaponin Ⅳa (CHI) from AB demonstrated synergistic effects, downregulating pro-apoptotic proteins (Caspase-3/9, Bax) through activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway and promotion of Akt phosphorylation.
Conclusion: The herbal pair aqueous extract suppresses osteoarthritis via the bioactive component group CHI-PIN, demonstrating synergistic anti-inflammatory effects in MIA rats, likely mediated by PI3K-Akt-regulated apoptosis.
Introduction
OA affects over 500 million people globally, characterized by progressive cartilage degradation, subchondral bone remodeling, and synovial inflammation (Abramoff and Caldera, 2020). This leads to debilitating pain, joint dysfunction, and significant socioeconomic burden (Colletti and Cicero, 2021). Conventional pharmacotherapies (NSAIDs, corticosteroids) offer symptomatic relief but carry substantial side effects with limited disease-modifying efficacy (Liang et al., 2022).
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has gained attention for its holistic approach, particularly herb pairs like EU and AB (Zhou et al., 2023). The EU-AB originates from “The Couplet Medicines of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Encyclopedia”. Combining the above can multiply the power of tonifying the liver and kidneys and strengthening the muscles and bones. EU demonstrates chondroprotective effects through PI3K-Akt-mediated suppression of IL-1β, IL-6, and RANKL/OPG imbalance (Huang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2016; Chong et al., 2022). AB exerts its effects by inhibiting the action of MMP-3 and MMP-13 (Zhao et al., 2021). EU and AB can likely exert anti-OA effects by inhibiting cell apoptosis and exerting anti-inflammatory actions (Zhang et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2020). Moreover, their active components have been proven to effectively promote bone formation (Yang et al., 2020), angiogenesis (He et al., 2023), and stimulate tissue development and regeneration from various perspectives.
Clinical formulations containing EU-AB (e.g., Duhuo Jisheng decoction) show efficacy, yet mechanistic validation of their synergistic interaction remains absent despite network pharmacology predictions of multi-target effects (Jian et al., 2020). However, whether the pair can treat OA as expected and the key molecular mechanisms have yet to be experimentally verified.
In previous studies, we confirmed the EU-AB have synergistic anti-inflammatory effect on RAW264.7 cells (Gao et al., 2022), analyzed the crucial components in pairs and explored the reasons for the changes in the content after their combination (Chen et al., 2024). This article further clarifies the anti-OA effects of the pair, uncovers the key components that contribute to the synergistic effect, and anchors the related pathways for regulation, providing insights into the potential molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic therapeutic effects of the pair on OA.
Methods
Material
EU (Batch No.: 191231) and AB (Batch No.: 210326) were procured from the Shanghai Hongqiao Traditional Chinese Medicine Slices Company, and voucher specimens were stored in the Pharmacy Department of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University. EU is the dried bark of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv., and AB, belonging to the family Amaranthaceae, is the dried root of Achyranthes bidentata Bli. Celecoxib capsules (CL) were bought from Sichuan Guowei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Tenghuang Jiangu capsules (TH) were acquired from Gansu Xifeng Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. ELISA kits for MMP-3, MMP-13, NO, iNOS, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were received from Jiangsu Meimian Industrial Co., Ltd. Sodium iodate was sourced from Sigma and the Total RNA Kit for total RNA extraction was procured from Yeasen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Gefitinib (GEF) and dexamethasone (DEX) were obtained from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. The standard substances CHI and PIN were supplied by Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and the proteins Akt, p-Akt, Bax, Caspase-3, and Caspase-9 were obtained from CST.
Drug preparation
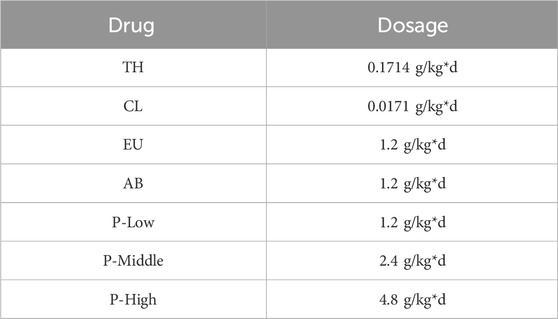
Take 100 g EU and 100 g AB. Add water at 1:10 ratio to soak overnight in a beaker. The next day, heat the solution to 100°C and maintain for 1 h. Repeat this process 3 times. Filter, prepare extract paste, store at −20°C. Dilute with water to required concentration before use. For single herbs: take 200 g EU or 200 g AB, prepare using same method as herb-pair water extract. CL and TH were dissolved in purified water to achieve their respective target concentrations. All treatments were administered via intragastric administration for 4 weeks, with drug-specific doses detailed in Table 1. The concentration for monomer groups was experimentally determined to be 10−6 M.
Animal modeling and grouping
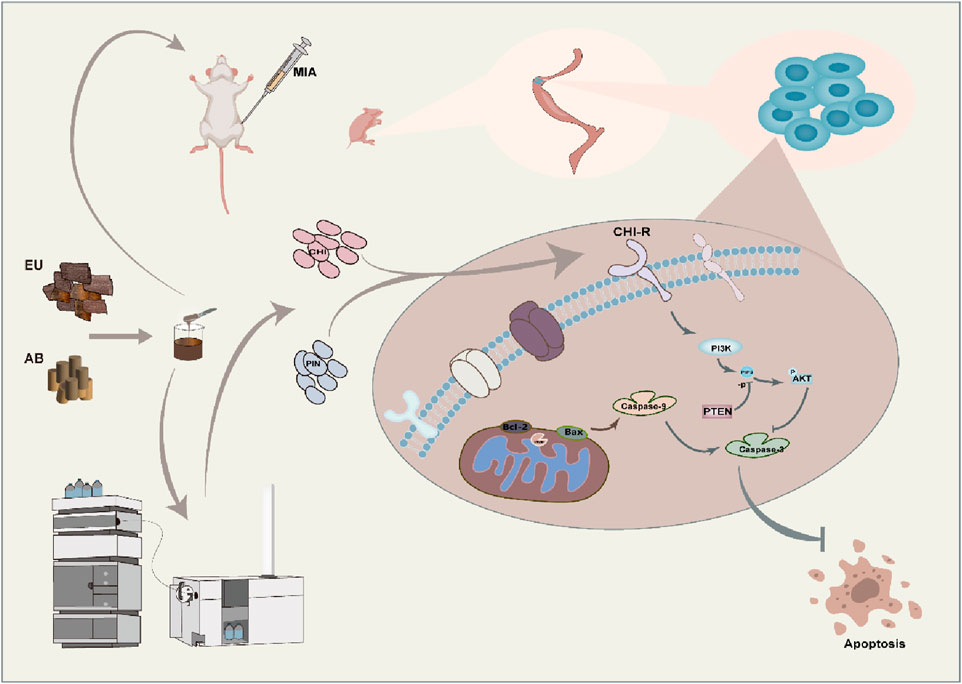
Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (200 ± 20 g) of specific pathogenfree grade were supplied by Shanghai Regen Biological Co., Ltd. (experimental animal production license number: SCXK 2019-0002). All SD rats were kept in the animal room of the School of Pharmacy of Naval Medical University, under a fixed room temperature of 20°C and a 12-h light/dark cycle. The experiment initially randomly assigned 72 rats into the following 9 groups: control, model, CL, TH, EU, AB, low-dose pair (P-L), medium-dose pair (P-M), and high-dose pair (P-H). Each group contained 8 rats with sex-balanced distribution. However, due to attrition unrelated to the research protocol, the final sample size per group was reduced to 6 rats. Except for the control group, the remaining eight groups underwent model construction: after anesthesia with 2% pentobarbital and waiting for about 5 min until the rats had no limb reflexes. The right hind limbs were bent to 90°. Using an insulin syringe, 50 µL of MIA was slowly injected into the joint cavities of rats. The needle was slowly withdrawn, and fluid seepage was checked (Chun et al., 2021).
Assessment indicators
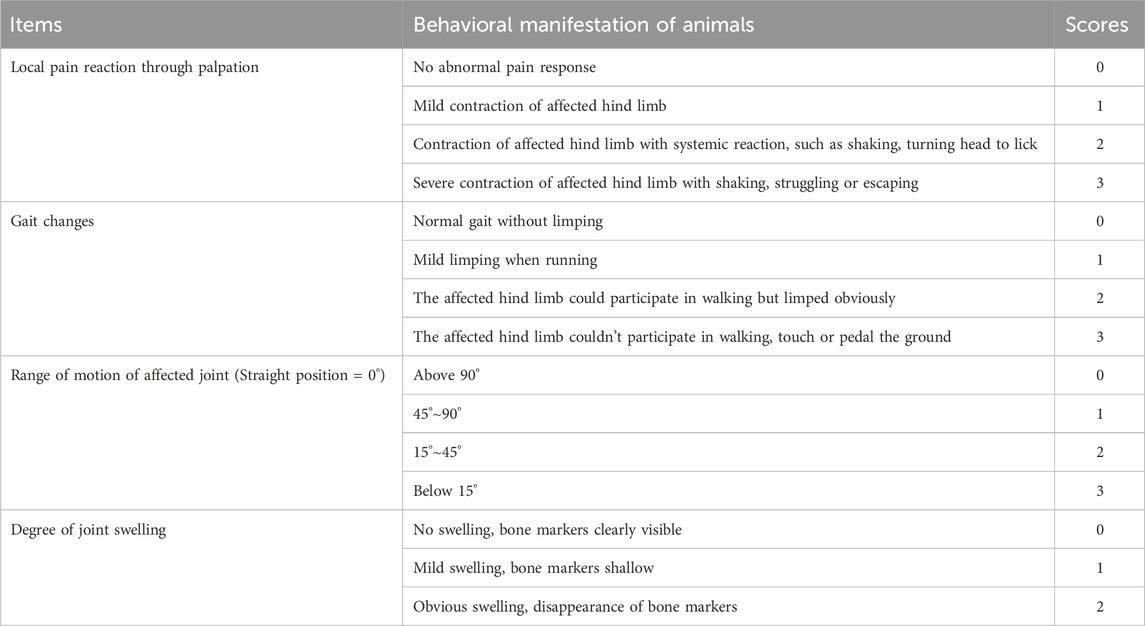
Measurements of the following indicators were performed on days 0, 7, 14, and 21. The joint diameter of the affected limb was measured by wrapping a cotton thread around the swollen area of the rat joint (Abdel-Rahman et al., 2020). Electric von Frey was used to determine the mechanical pain threshold (Liao et al., 2020), and behavioral scoring was used to assess the rats’ responses to pain, gait changes, range of motion of the joints, and joint swelling in four aspects (Shi et al., 2020). The scoring table can be found in Table 2.
Histological evaluation
After the fourth week of drug administration, all rats were decapitated and killed, the right knee joints were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and sections were stained with H&E and Safranin O-Fast Green staining to assess histological differences (Chun et al., 2021). The most severe areas of each section were selected and scored using the OASRI and the Modified Mankin’s score (Cai et al., 2020).
Immunohistochemistry
The sections were then processed for immunohistochemistry. After incubation with 10% goat serum at room temperature for 30 min, 50–100 µL of MMP-3/13 antibody was added and incubated overnight at 4°C. Following TBST washing, the secondary antibody was added. After color development, counterstaining, drying, and mounting, the state of the joint sections was observed under a microscope (Xie et al., 2023).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
During the second week of the experiment, blood was collected from rats via the orbital sinus. Blood samples were left at room temperature for 2 h and then centrifuged at 3,500 rpm for 10 min to obtain the supernatant. The serum levels of NO, IL-1β, MMP-3, MMP-13, TNF-α, and IL-6 were measured following the instructions provided with the ELISA kits.
HPLC-MS method
The mobile phase comprises 0.1% formic acid in water (A) and acetonitrile (B). The system was equilibrated for 3 min at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min with a column temperature of 25°C and an injection volume of 2 μL. The gradient elution program was as follows: 0–10 min, 15%–30% B; 10–20 min, 30%–70% B; 20–30 min, 70% B. The TOF mass spectrometer was equipped with an AJS-ESI source, operating in positive and negative ion modes, with a sheath gas temperature of 350 °C, a drying gas flow rate of 10 L/min, a nebulizer pressure of 40 psi, a fragmentor voltage of 160 V, and a capillary voltage of 3500 V. Aligent 6,470 Series QQQ Triple quad mass spectrometry (Aligent, United States) was applied in mass spectrometry, Mass spectrometric detection was using dynamic multiple response monitoring (dMRM) mode equipped with AJS-ESI source in the negative ion mode. The parameters were set as follows: nebulizer gas temperature 325°C, drying gas flow rate 10 L/min, nebulizer pressure 40 psi, sheath gas temperature 350°C, sheath gas flow rate 11 L/min, capillary voltage 3500 V, nozzle voltage 1500 V, and nitrogen as the collision gas.
Cell isolation and differentiation
Newborn fetuses were euthanized for subsequent experiments. The fetuses were disinfected with 75% ethanol, and the hind limb skin was cut open using surgical scissors. Muscle tissue was removed as much as possible. The hind limbs were collected, placed in a culture dish, and washed several times with pre-cooled PBS. They were digested for 60 min with 2 mg/mL trypsin-EDTA solution, washed several times with PBS, and digested for 90 min with 3 mg/mL collagenase D solution. The digestion was continued overnight with a 0.5 mg/mL collagenase D solution. The next day, once complete digestion was achieved, the fragments were repeatedly blown with a pipette gun, filtered through a 40 µm sterile filter, and centrifuged at 300 × g for 5 min. After washing with PBS and centrifugation, cells were resuspended in DMEM and transferred to a new culture dish. The cell culture was observed daily, and the culture fluid was replaced on the third day (Lu et al., 2023). ATDC5 murine embryonic carcinoma cells were bought from iCell Bioscience Inc.
Cell membrane chromatography construction
Approximately 107 ATDC5 cells were harvested and cultured on ice. Then PBS was added to wash thrice. The cells were scraped off, sonicated at 400 W every 10 s, and centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 10 min to remove the supernatant. Centrifugation was performed again at 12,000 rpm for 20 min to obtain the cell membrane pellet resuspended in 5 mL physiological saline. Silica gel was added to react and form the stationary phase of the cell membrane and rotated overnight at 4 °C; then, the column was packed the next day. The flow conditions for the packed cell membrane column were as follows: from 0 to 5 min, a flow rate from 0.2 to 1.0 mL/min; from 5 to 5.5 min, 1.0 mL/min. When the pressure stabilized, the cell membrane chromatography column was packed. The mobile phase was 10 mM ammonium acetate, with a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min, a column temperature of 37°C, and an injection volume of 5 µL (Chai et al., 2022).
Genome sequencing
Differential gene expression was determined after drug treatment in a primary chondrocyte model. RNA sequencing and data analysis were performed using Genewiz (China). Total RNA was extracted from primary mouse chondrocytes using a Total RNA Kit. RNA quality was assessed with the Agilent 2,100 Bioanalyzer, and further procedures were implemented only once the RNA met the required standards. The collected RNA samples were subjected to library construction and sequencing. The general steps were as follows: mRNA was captured using magnetic beads with poly T probes and fragmented at high temperatures using a magnesium ion solution. Random primers were used to synthesize double-stranded cDNA, and the ends were repaired using the dA tail reagent. Polymerase chain reaction amplification was performed using P5 and P7 primers, followed by validation. The samples were then loaded onto an Illumina HiSeq/Illumina Novaseq/MGI2000 instrument for sequencing. Data analysis was conducted using R language scripts.
Immunoblotting assay
Proteins obtained after treatment with radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane. After blocking at room temperature for 60 min, the membrane was incubated with the primary antibody overnight. After washing with TBST, the secondary antibody was added and incubated for 1 h. The membrane was developed and photographed using an imaging system.
Evaluation of synergistic effect
The effect of combining two single drugs/compounds was evaluated using King’s formula:
Statistical analysis
The experimental data were processed using GraphPad Prism software (version 8.0). Except for OARSI and Mankin scores, which were analyzed using non-parametric tests, all other data were evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD post hoc test for multiple comparisons, and Welch’s ANOVA was applied to part of the data. Details can be found in the Supplementary Material. A difference was considered significant when P < 0.05 and highly significant when P < 0.01. The results compared with the blank control group are indicated by #, while those compared with the model group are indicated by *.
Results
Inflammatory response inhibition in ATDC5 cells
To determine the effect of the aqueous extract of the pair on inflammation inhibition, ATDC5 cells were examined. The ATDC5 cells used in the experiment were differentiated into chondrocytes after 21 days of stimulation with ITS. LPS can induce an inflammatory response in ATDC5 cells and increase the expression of the MMP family. After intervention with 10 μg/mL LPS for 24 h, the levels of the inflammatory factors NO, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the cell supernatant increased (Figure 1A, P < 0.01), confirming the successful establishment of the model. Intervention with EU and AB alone inhibited the trend of increased inflammatory factors (P < 0.01), and the same inhibitory effect on inflammatory factors was found in the medium and high-dose groups of the pair (P < 0.01). Subsequently, protein expression in ATDC5 inflammatory model cells was measured after intervention with single herbs and the pair (Figure 1B). The expression of iNOS, COX-2, MMP-3, and MMP-13 proteins was significantly increased in the model group (P < 0.01). The single herbs of EU and AB did not exhibit a significant inhibitory trend, while the high-dose group, after combined use, downregulated the expression of iNOS, COX-2, MMP-3, and MMP-13 proteins (P < 0.05).
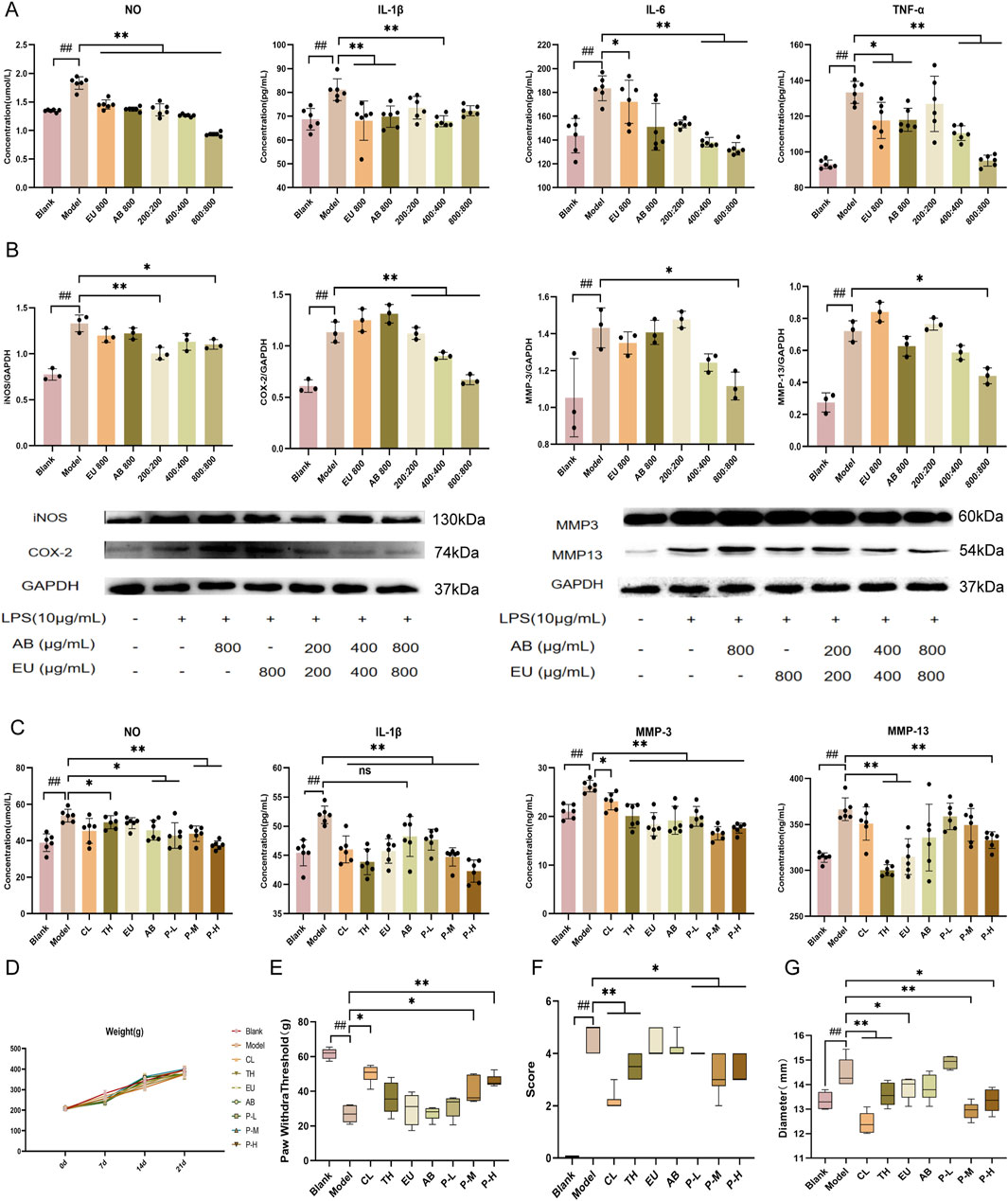
Figure 1. Inhibition of inflammatory response by the aqueous extract of the pair and improvement of behavior in OA rats. (A) Expression of NO, IL-1β, MMP-3, and MMP-13 in the supernatant of ATDC5 cells. (B) Expression of proteins iNOS, COX-2, MMP-3, and MMP-13 in ATDC5 cells. (C) Expression of iNOS, COX-2, MMP-3, and MMP-13 in the serum of rats. (D) Changes in body weight of rats within 21 days of administration. Changes in mechanical pain threshold (E), behavioral score (F), and joint diameter (G) after intervention with the herbal pair in model rats. Data are expressed as mean ± SD.
Inhibition of inflammatory responses in OA rats
The blank group was not intervened and was intragastrically administered an equal dose of physiological saline during the experimental period. In the in vivo experiment, the CL and TH groups were used as positive controls. All rats simulated the pathological characteristics of OA after intra-articular injection of MIA, which was manifested by increased levels of NO, IL-1β, MMP-3, and MMP-13 in the serum, reduced mechanical pain threshold, knee swelling, and a significant decrease in the animal behavior score according to the Lequesne scoring (Figures 1C–G) after modeling. It was found that the pair group could also reverse this trend in the rat model, and through the observation of joint diameter, mechanical pain threshold, and behavior in rats, the swelling was reduced, the pain was relieved, and the behavior was improved after modeling. Moreover, the body weight of all experimental groups of rats after 3 weeks of intragastric administration was non-significantly different from that of the normal group, and drug intervention did not cause severe adverse reactions in the rats.
Protection of joints in OA rats by the pair
HE and Safranin O staining of the pair group depicted a certain degree of repair effect on the articular cartilage (Figure 2A). The cartilage structure was relatively intact, with cracks only on the surface, which did not affect the entire structure, and the staining degree of the cartilage matrix was relatively light. According to the staining results, the joints of each group were graded and scored, and the OARSI grade and Mankin’s score of the pair group decreased. In the immunohistochemical results of MMP-3 and MMP-13 (Figure 2A), the pair group significantly inhibited the production of proteases and reduced cartilage degradation.
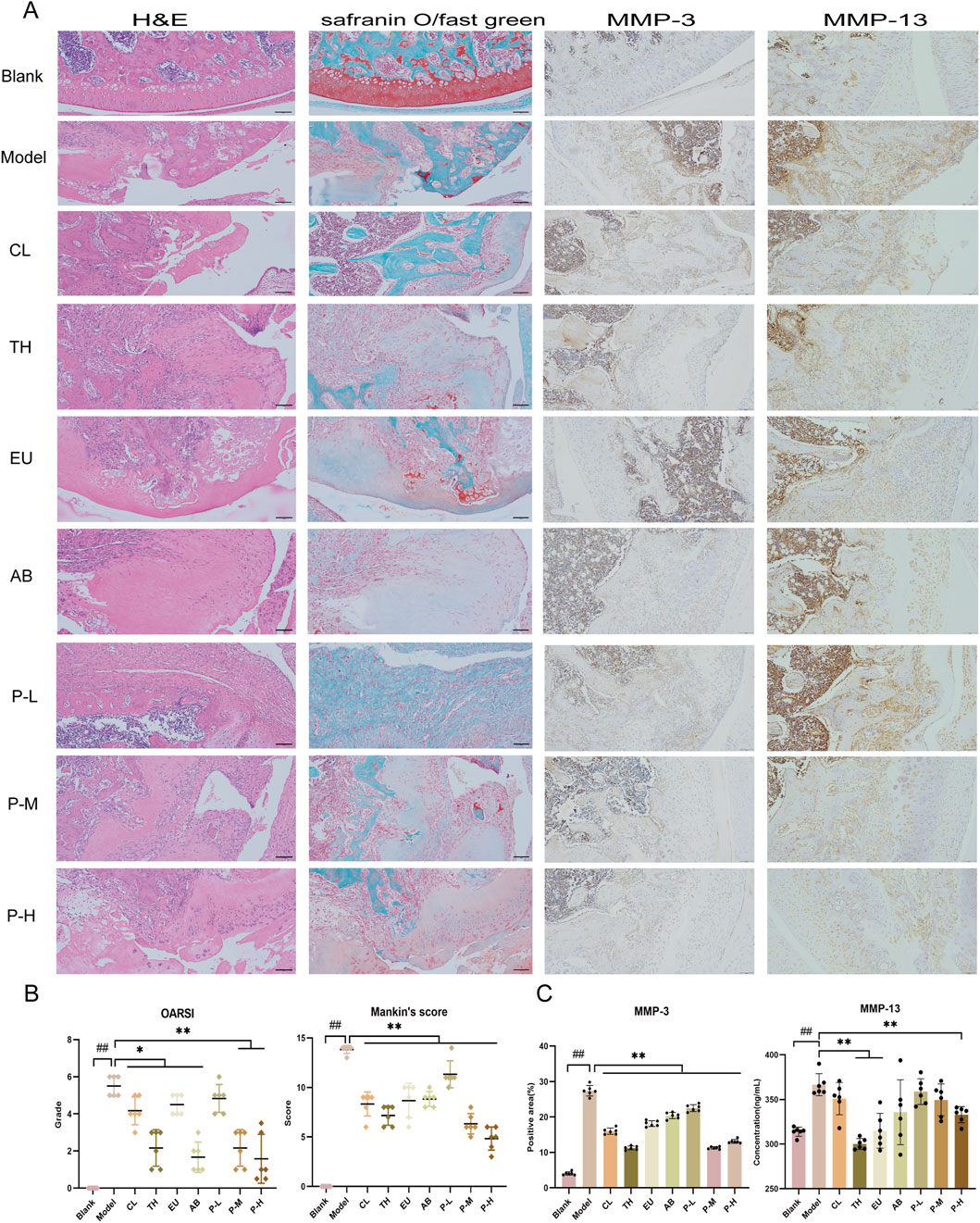
Figure 2. The pair inhibits cartilage matrix degradation and delays the pathological process in joints. (A) From left to right are the HE, Safranin O, and immunohistochemical staining for MMP-3 and MMP-13 in the knee joints of rats after the intervention. (B) OARSI grading and Mankin’s scoring of articular cartilage. (C) Expression of immunohistochemical MMP-3 and MMP-13 in each group. Data are expressed as mean ± SD.
Synergistic effect of the aqueous extract against OA
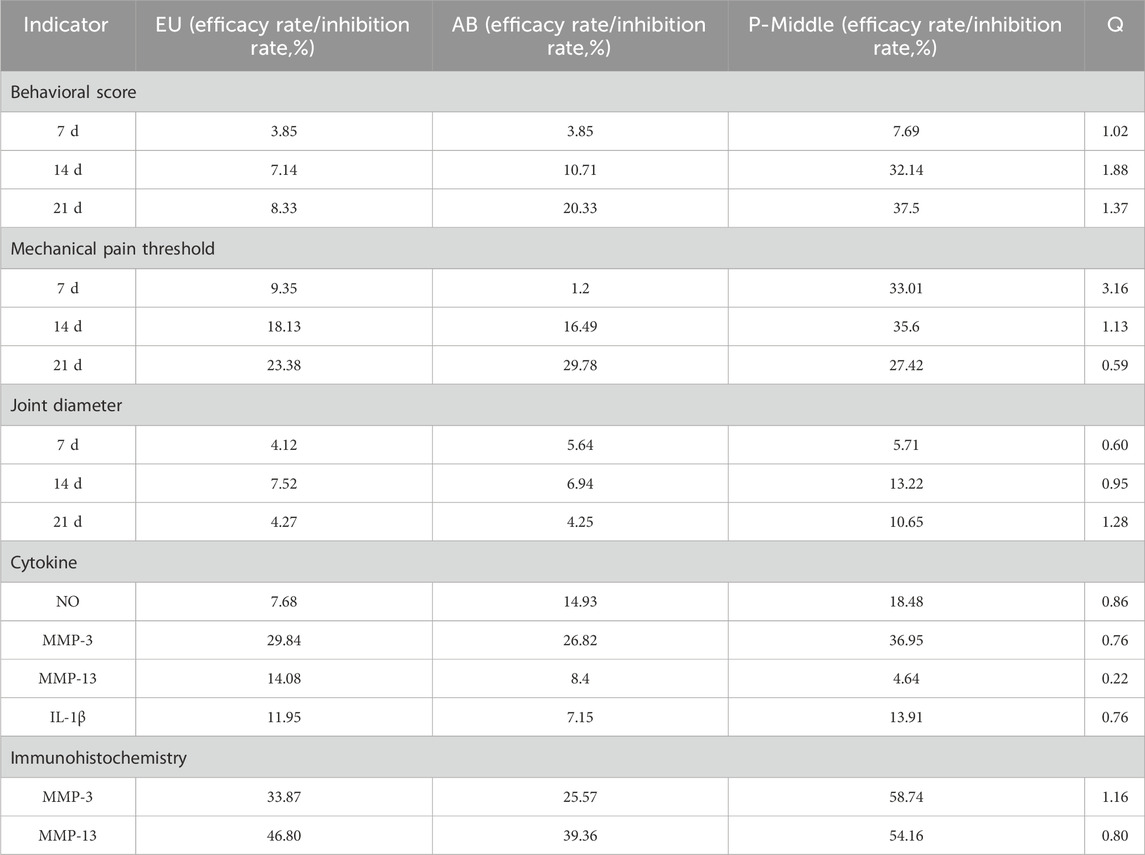
The synergistic effects of the aqueous extract on behavior, mechanical pain, joint diameter, cytokine levels, and immunohistochemistry were calculated using King’s formula by comparing the effects obtained from the medium-dose group of the pair with those of the single herb (Figure 2B). The results are presented in Table 3. On the 7th day, the herbal pair illustrated a synergistic effect in relieving pain. On the 14th day, the effect on improving behavior was significant, and on the 21st day, it synergistically alleviated the affected limb swelling. Additionally, immunohistochemical results indicated that the herbal pair synergistically inhibited the expression of MMP-3 on the articular cartilage surface (Figure 2C).
CHI has an affinity for ATDC5 cell membranes
EU and AB were mixed in a 1:1 ratio, ground to a suitable particle size, and then extracted by soaking, boiling, and filtering to obtain the filtrate. After freeze-drying, the aqueous extract was obtained in syrup form. Before injection into the liquid phase system, the extract was dissolved in water to a 0.02 g/mL concentration. A total of 35 compounds were detected in the crude aqueous extract of the pair in positive and negative ion modes (Figure 3A). The details of each compound are listed in Table 4. These included 8 lignans, 7 phenylpropanoids, 4 steroidal compounds, 7 saponins, 2 alkaloids, 4 cycloartane ether compounds, and 3 others. Among the nine monomers that entered the bloodstream, the CHI from AB depicted retention behavior on the chondrocyte membrane chromatography column (Figure 3D). From EU, the compound PIN was selected to pair with CHI, and the structures of these two monomers are displayed in Figure 3C.
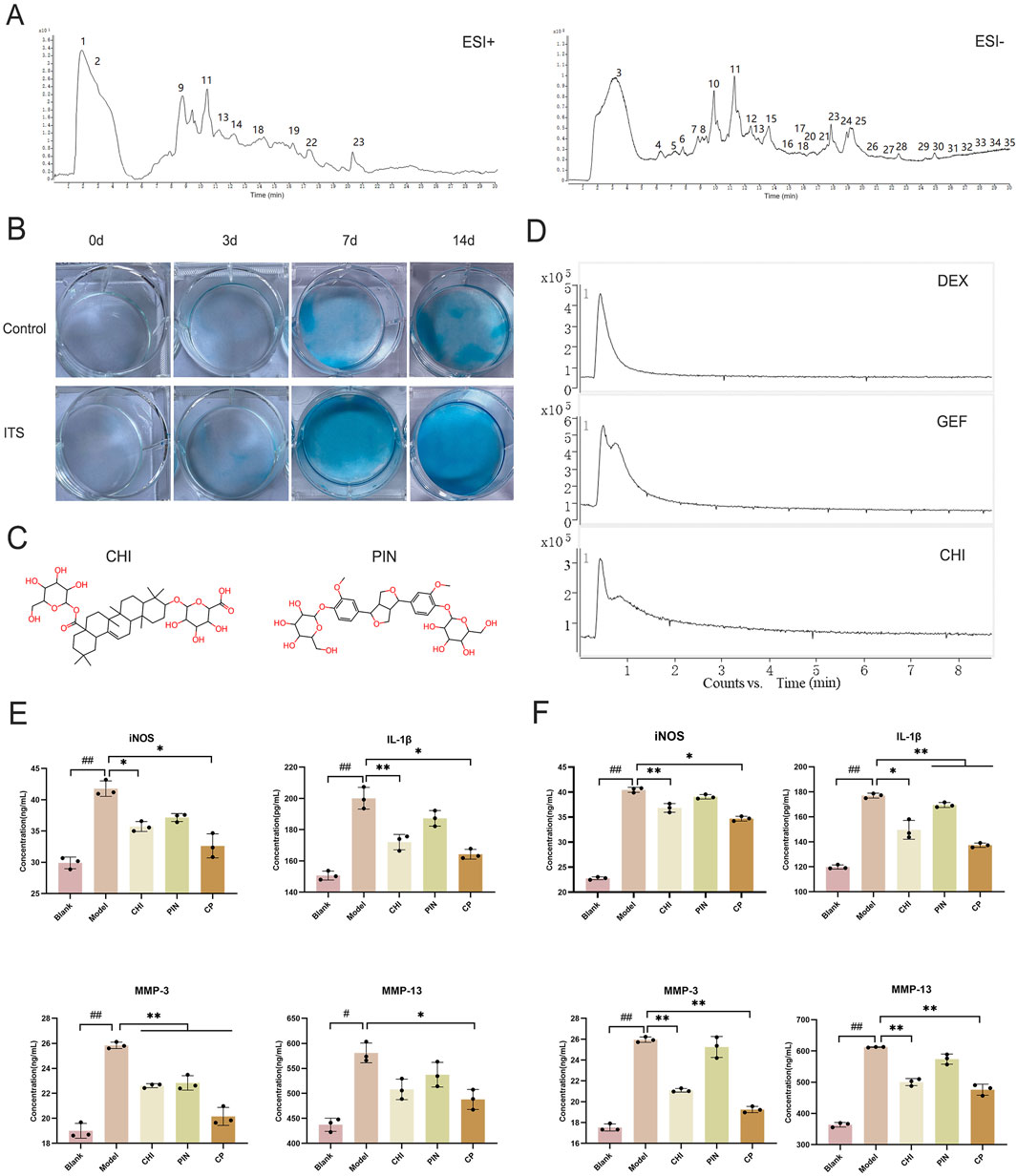
Figure 3. The effective component group inhibited the inflammatory response in ATDC5 cells and primary chondrocytes. (A) Total ion chromatogram of the herbal pair aqueous extract in positive and negative ionization modes. (B) Degree of differentiation of primary chondrocytes at 0, 3, 7, and 14 days with and without ITS. (C) Chemical structures of CHI and PIN. (D) Retention of DEX, GEF, and CHI on the chondrocyte membrane chromatography column. Expression levels of iNOS, IL-1β, MMP-3, and MMP-13 in the supernatant of ATDC5 cells (E) and primary chondrocytes (F) after intervention with single compound and compound groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SD.
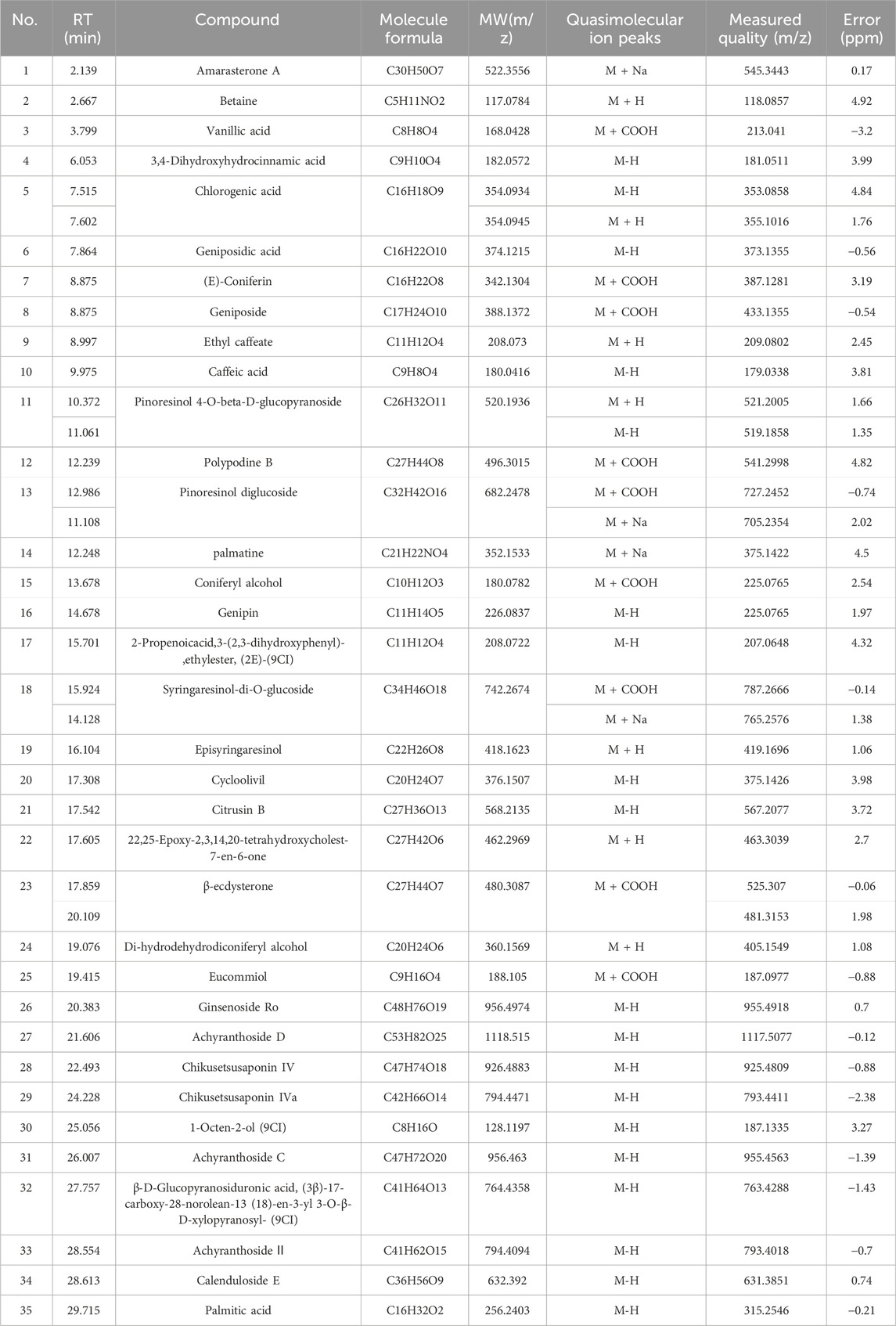
Table 4. TOF/MS results for the identification of the chemical components in the aqueous extracts of the drug pair.
CHI-PIN inhibited inflammatory responses through the PI3K-Akt pathway
Primary chondrocytes were successfully isolated from suckling mice, and their degree of differentiation was identified using Alcian Blue. Chondrocytes in the third passage contained the most proteoglycans, exhibiting the most obvious degree of differentiation (Figure 3B), consistent with reported results. The monomers suppressed the expression of iNOS, IL-1β, MMP-3, and MMP-13 in ATDC5 cells and primary chondrocytes (Figures 3E,F). This trend was more pronounced after pairing, and by comparing the model group with the treatment group, 384 differential genes were identified, with 160 downregulated genes and 224 upregulated genes in the treatment group compared to the model group (Figures 4A–D). These genes were mainly concentrated in the JAK-STAT, TGF-β, and PI3K-Akt pathways. We selected Akt and p-Akt, key signaling molecules in the classical signaling pathway of OA, the PI3K-Akt pathway, for verification (Figure 4E). Akt expression did not differ significantly among the groups. However, p-Akt depicted a downward trend in the model group, while it was highly expressed in the treatment group. Since the PI3K-Akt pathway is closely related to chondrocyte apoptosis, it was hypothesized that monomers can exert an inhibitory effect on apoptosis through this pathway. To verify this hypothesis, the protein levels of Bax, Caspase-3, and Caspase-9 in the apoptosis pathway were measured, and the treatment group could counteract the increase in these protein levels caused by the model intervention.
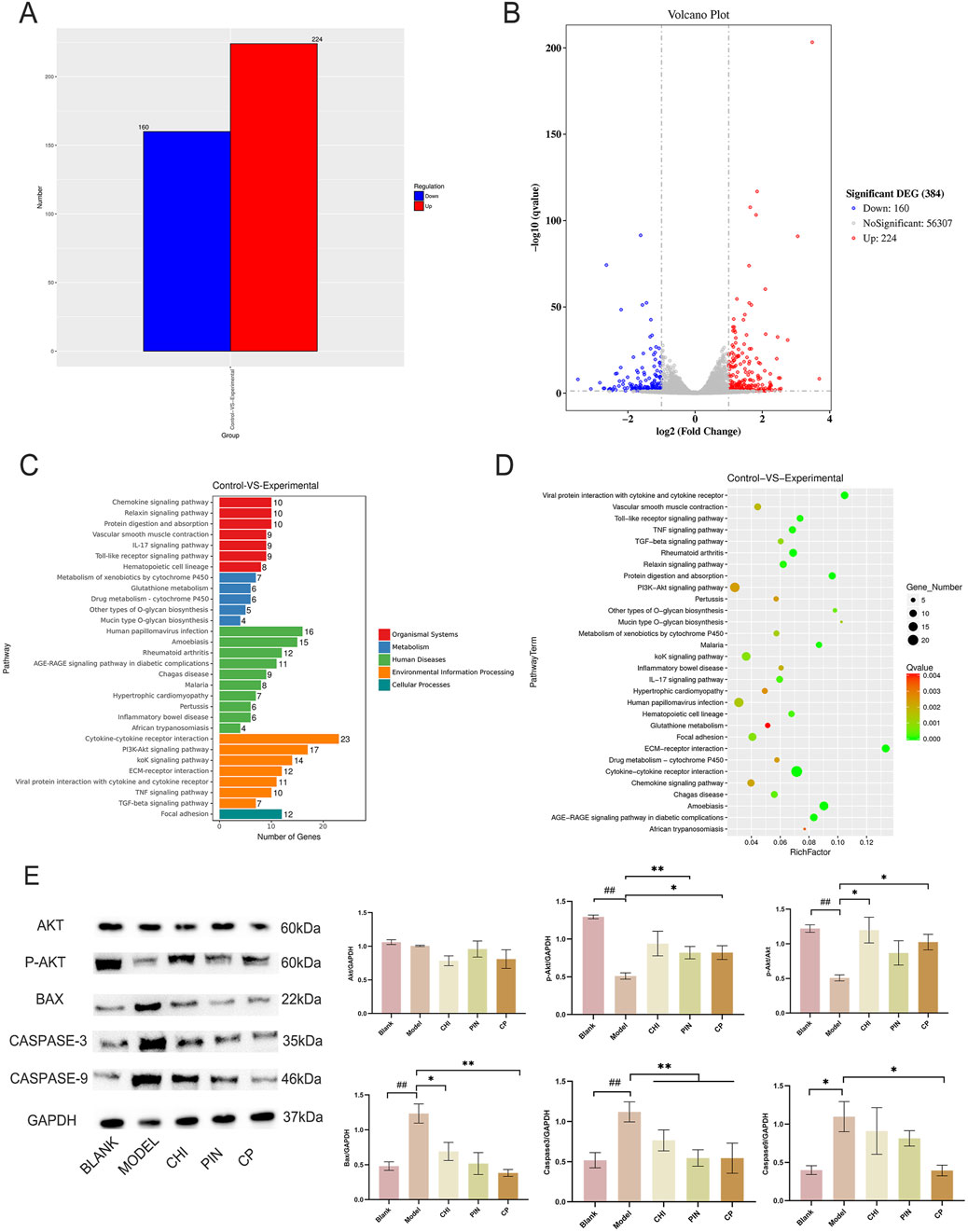
Figure 4. The pair’s key components inhibit apoptosis through the PI3K-Akt pathway. Histogram of differential gene expression between the experimental group after administration and the model group (A), volcano plot (B), KEGG pathway annotation diagram (C), and KEGG enrichment analysis bubble chart (D). Immunoblotting bands and analysis results of Akt, p-Akt, BAX, Caspase-3, and Caspase-9 proteins after intervention with monomers and the monomer group (E). Data are expressed as mean ± SD.
Discussion
The King’s formula method serves as a classical pharmacological framework for evaluating drug synergy. Its validity stems from a pragmatic simplification of the Bliss Independence principle, rendering it particularly suitable for rapid preliminary screening of combinatorial drug potential (Tallarida, 2011). Although the conventional Q-value criterion provides an empirical threshold, it cannot establish probabilistic distribution models. This study preliminarily identifies synergistic tendencies in aqueous herb-pair extracts through this method, aiming to guide further mechanistic investigations. Notably, while the herb-pair aqueous extract combination demonstrated suboptimal synergy in suppressing IL-1β and MMP-13 levels, it exhibited therapeutic potential across distinct OA phases: During the acute phase (7d), the combination may alleviate mechanical allodynia via rapid modulation of ion channels or neuroplasticity. In the chronic phase (21d), joint structural improvements (reduced diameter) likely originate from chondroprotection. This dual-phase efficacy fully satisfies the OARSI guideline efficacy criterion of *'≥50% pain relief + joint structural stabilization'* (Bannuru et al., 2019) – the primary therapeutic target. Critically, drug interactions may evolve temporally; the observed IL-1β/MMP-13 antagonism could reflect compensatory inflammatory activation, warranting long-term safety evaluation.
MIA-induced osteoarthritis models reach pain threshold within 3–7 days (Xu et al., 2020). The herb pair demonstrated optimal synergistic analgesia on day 7, with more pronounced synergistic effects on limb swelling and behavioral improvements during mid-late stages. This indicates that effective pain control in early OA creates conditions for deeper intervention by the herb pair in later phases, while fundamental regulatory effects during mid-late stages consolidate initial efficacy and prevent recurrence (Yunus et al., 2020; Ahmad et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023). The aqueous extract modulated inflammatory cytokines comparably to positive control groups, with superior inhibition of NO and MMP-3. Studies suggest balanced modulation of NO concentrations can bidirectionally regulate MMP secretion (Prado et al., 2021). When MMPs are inhibited, extracellular matrix is protected from degradation, preventing cellular damage and reducing inflammatory mediator release–establishing a self-reinforcing therapeutic cycle. Our findings reveal the herb pair’s mechanism not only targets upstream inflammatory signaling but also effectively addresses downstream effector molecules (NO) and tissue-destructive matrix metalloproteinases. Therefore, we focus on elucidating how this dual-phase intervention occurs, with primary emphasis on identifying the key active constituents responsible for these effects.
We employed CMC to screen monomers binding to ATDC5 chondrocyte membranes. LPS-induced ATDC5 cells represent a classical osteoarthritis model–when cultured with ITS, they differentiate into mature chondrocytes, offering high reproducibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of culture. Among nine blood-exposed monomers, CHI bound to ATDC5 membranes. Although no EU components directly bound, certain EU constituents may enhance CHI-membrane affinity synergistically. CHI, a representative triterpenoid saponin from Achyranthes bidentata, effectively suppresses inflammation and bone destruction in rheumatoid mice (Guo et al., 2021) and inhibits IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 in RAW264.7 cells (Xu et al., 2021). Elevated CHI levels in vivo and in vitro post-pairing further suggest EU components facilitate this process. Through in vitro validation, the optimal monomer combination was CHI- PIN. PIN, a characteristic EU compound, demonstrates chondroprotective effects in rabbit models (Lou et al., 2022). Individually, both CHI and PIN exhibit anti-OA potential. To validate synergistic anti-inflammatory effects, primary chondrocytes (authenticated by Alcian blue staining) were selected as physiologically relevant models. Monomer proportions mirrored their natural ratios in aqueous extracts to ensure translational relevance. Synergistic efficacy was replicated exclusively with the CHI-PIN combination–other pairings showed inferior effects–indicating their pivotal role in herb-pair synergy. Transcriptomic analysis revealed 39 significantly enriched pathways between OA and CHI-PIN treated groups. Focusing on OA-relevant pathways (Wang et al., 2022), subsequent protein verification confirmed pronounced PI3K-Akt pathway activation following CHI-PIN intervention.
In OA, the degree of degeneration of articular cartilage is closely related to the homeostatic environment of the cartilage and the state of chondrocytes (Sun et al., 2020; Liu Z. et al., 2022). When p67phox is activated, the PI3K-Akt pathway is activated, leading to a significant increase in AKT phosphorylation. On the one hand, this leads to an increase in the expression of Col2a1 and ACAN, promoting the synthesis of the extracellular matrix of chondrocytes to ensure the toughness and compressive strength of cartilage (Liu Z. M. et al., 2022). Contrarily, chondrocytes effectively alleviate the blocking effect of OA in the G0/G1 phase because PTEN is silenced, promoting cell proliferation (Huang et al., 2017; Zhan et al., 2023). Moreover, in IL-1β-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes, activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway can block this process (Zhu et al., 2023; Saeed et al., 2023), as the Bax gene is located downstream of this pathway. When the pathway is activated, it can inhibit the expression of the Bax gene. In our model group, the protein expression of the pro-apoptotic genes Bax, Caspase-3, and Caspase-9 was significantly increased. However, when the intervention was applied to the monomer group, secretion of these proteins was inhibited. CHI-PIN, a regulator of the PI3K-Akt pathway, can be used to treat OA by activating the PI3K-Akt pathway to promote Akt phosphorylation, thereby inducing chondrocyte proliferation and reducing apoptosis to a certain extent to prevent cartilage degeneration and maintain the extracellular matrix in the cartilage to sustain the homeostatic environment of the cartilage. While our mechanistic investigation focused on the PI3K-Akt pathway and confirmed its central role, osteoarthritis pathogenesis involves complex signaling networks. Although there are web-based pharmacological studies pointing to a relationship between the Cortex EU-AB pair and the PI3K-Akt pathway, we have not directly verified whether the whole extract acts through this pathway. In addition, this includes classical inflammatory/catabolic pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK, which exhibit extensive crosstalk with PI3K-Akt. We did not systematically evaluate CHI-PIN’s effects on NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation or MAPK phosphorylation status. Although PI3K-Akt activation sufficiently explains observed protective effects–including anti-apoptotic and pro-anabolic actions–we cannot exclude concurrent modulation of other pathways by CHI-PIN or their potential contribution to the synergistic efficacy.
We declare that during the animal experimentation process, random exclusion was implemented to standardize experimental group sizes following unexpected attrition. We acknowledge that eliminating healthy animals without predetermined criteria risks distorting data distribution. However, retrospective validation confirms the reliability of post-exclusion datasets for core endpoints. We recognize this methodological limitation and commit to implementing rigorous prospective protocols for handling missing data in future studies.
Conclusion
The aqueous extract of the herbal pair effectively inhibits osteoarthritis progression and demonstrates a synergistic trend in the MIA rat model. Furthermore, our findings strongly suggest that CHI-PIN represents a key bioactive component group within the extract, likely exerting its anti-inflammatory effects by mediating apoptosis through the PI3K-Akt pathway.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of Naval Medical University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. LL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. YH: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – review and editing. FX: Writing – review and editing. MG: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review and editing. SZ: Resources, Software, Writing – review and editing. ZW: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. XJ: Resources, Software, Writing – review and editing. YZ: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. LB: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Project for the Military (grant number 2023ZY024).
Acknowledgments
We thank Home for Researchers editorial team (www.home-for-researchers.com) for language editing service.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1571884/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
OA, Osteoarthritis; EU-AB, Eucommia ulmoides and Achyranthes bidentata; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; H&E, Hematoxylin and eosin; MMPs, expression of matrix metalloproteinases; NO, nitric oxide; IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; iNOS, Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase; COX, Cyclooxygenase; CHI, chikusetsusaponin Ⅳa; PIN, pinoresinol diglucoside; PI3K-Akt, Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-Protein Kinase B signaling; Bax, Bcl-2 Associated X; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; RANKL, Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand; OPG, Osteoprotegerin; PEG2, Polyethylene Glycol 2; CL, Celecoxib capsules; TH, Tenghuang Jiangu capsules; GEF, Gefitinib; DEX, dexamethasone; P-L, low-dose pair; P-M, medium-dose pair; P-H, high-dose pair.
References
Abdel-Rahman, R. F., Abd-Elsalam, R. M., Amer, M. S., El-Desoky, A. M., and Mohamed, S. O. (2020). Manjarix attenuated pain and joint swelling in a rat model of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Food Funct. 11 (9), 7960–7972. doi:10.1039/d0fo01297a
Abramoff, B., and Caldera, F. E. (2020). Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med. Clin. North Am. 104 (2), 293–311. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2019.10.007
Ahmad, N., Ansari, M. Y., and Haqqi, T. M. (2020). Role of iNOS in osteoarthritis: pathological and therapeutic aspects. J. Cell Physiol. 235 (10), 6366–6376. doi:10.1002/jcp.29607
Bannuru, R. R., Osani, M. C., Vaysbrot, E. E., Arden, N., Bennell, K., Bierma-Zeinstra, S., et al. (2019). OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 27 (11), 1578–1589. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2019.06.011
Cai, Z., Hong, M., Xu, L., Yang, K., Li, C., Sun, T., et al. (2020). Prevent action of magnoflorine with hyaluronic acid gel from cartilage degeneration in anterior cruciate ligament transection induced osteoarthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 126, 109733. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109733
Chai, X., Gu, Y., Lv, L., Chen, C., Feng, F., Cao, Y., et al. (2022). Screening of immune cell activators from astragali radix using a comprehensive two-dimensional NK-92MI cell membrane chromatography/C(18) column/time-of-flight mass spectrometry system. J. Pharm. Anal. 12 (5), 725–732. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2022.05.006
Chen, C., Huang, Y., Bao, L., and Jun, B. (2023). Inhibition of nitric oxide and its synthase by Chinese medicine in treatment of osteoarthritis: research advances. Pharm. J. Chin. People's Liberation Army 36 (2), 165–171. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-926.2023.02.017
Chen, C., Lv, L., Huang, Y., Gao, M., Jiang, X., Ge, X., et al. (2024). Optimized ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for detecting compositional changes in Eucommia ulmoides and Achyranthes bidentata paired decoctions in vitro and in vivo. Acta Chromatogr. 36 (1), 31–44. doi:10.1556/1326.2022.01090
Chong, X., Chen, J., Zheng, N., Zhou, Z., Hai, Y., Chen, S., et al. (2022). PIK3CA mutations-mediated downregulation of circLHFPL2 inhibits colorectal cancer progression via upregulating PTEN. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 118. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01531-x
Chun, J. M., Lee, A. Y., Nam, J. Y., Lee, M. Y., Choe, M. S., Lim, K. S., et al. (2021). Protective effects of Phlomis umbrosa extract on a monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis model and prediction of molecular mechanisms using transcriptomics. Phytomedicine 81, 153429. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153429
Colletti, A., and Cicero, A. F. G. (2021). Nutraceutical approach to chronic osteoarthritis: from molecular research to clinical evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (23), 12920. doi:10.3390/ijms222312920
Gao, M., Chen, C., Zhang, Q., Bian, J., and Bao, L. (2022). Anti-inflammatory effect of couplet medicinals of achyranthes bidentata-Eucommia ulmoides on mouse macrophage RAW264.7. China Pharm. 33 (03), 308–312. doi:10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2022.03.09
Guo, X., Ji, J., Zhang, J., Hou, X., Fu, X., Luo, Y., et al. (2021). Anti-inflammatory and osteoprotective effects of chikusetsusaponin ⅣA on rheumatoid arthritis via the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 93, 153801. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153801
He, Y., Kam, H., Wu, X., Chen, Q., and Lee, S. M. Y. (2023). Dual effect of aucubin on promoting VEGFR2 mediated angiogenesis and reducing RANKL-Induced bone resorption. Chin. Med. 18 (1), 108. doi:10.1186/s13020-023-00786-w
Huang, L., Lyu, Q., Zheng, W., Yang, Q., and Cao, G. (2021). Traditional application and modern pharmacological research of Eucommia ulmoides oliv. Chin. Med. 16 (1), 73. doi:10.1186/s13020-021-00482-7
Huang, Z., Zhang, N., Ma, W., Dai, X., and Liu, J. (2017). MiR-337-3p promotes chondrocytes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by regulating PTEN/AKT axis in osteoarthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 95, 1194–1200. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.016
Jian, G. H., Su, B. Z., Zhou, W. J., and Xiong, H. (2020). Application of network pharmacology and molecular docking to elucidate the potential mechanism of eucommia ulmoides-Radix achyranthis bidentatae against osteoarthritis. BioData Min. 13, 12. doi:10.1186/s13040-020-00221-y
Liang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhu, Y., and Wang, Q. (2022). Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine for knee osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytomedicine 100, 154029. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154029
Liao, T., Ding, L., Wu, P., Zhang, L., Li, X., Xu, B., et al. (2020). Chrysin attenuates the NLRP3 inflammasome Cascade to reduce synovitis and pain in KOA rats. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 3015–3027. doi:10.2147/dddt.S261216
Liu, Z., Zheng, N., Li, J., Zheng, D., Jiang, X., Ge, X., et al. (2022). N6-methyladenosine-modified circular RNA QSOX1 promotes colorectal cancer resistance to anti-CTLA-4 therapy through induction of intratumoral regulatory T cells. Drug Resist Updat 65, 100886. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2022.100886
Liu, Z. M., Shen, P. C., Lu, C. C., Chou, S. H., and Tien, Y. C. (2022). Suramin enhances chondrogenic properties by regulating the p67(phox)/PI3K/AKT/SOX9 signalling pathway. Bone Jt. Res. 11 (10), 723–738. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.1110.Bjr-2022-0013.R2
Lou, H., Zhang, Y., Fang, J., and Jin, Y. (2022). Network pharmacology-based prediction and verification of the potential targets of pinoresinol diglucoside for OA treatment. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 1–10. doi:10.1155/2022/9733742
Lu, J., Miao, Z., Jiang, Y., Xia, W., Wang, X., Shi, Y., et al. (2023). Chrysophanol prevents IL-1β-Induced inflammation and ECM degradation in osteoarthritis via the Sirt6/NF-κB and Nrf2/NF-κB axis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 208, 115402. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115402
Prado, A. F., Batista, R. I. M., Tanus-Santos, J. E., and Gerlach, R. F. (2021). Matrix metalloproteinases and arterial hypertension: role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide in vascular functional and structural alterations. Biomolecules 11 (4), 585. doi:10.3390/biom11040585
Saeed, H., Leibowitz, B. J., Zhang, L., and Yu, J. (2023). Targeting Myc-driven stress addiction in colorectal cancer. Drug Resist Updat 69, 100963. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2023.100963
Shi, X., Yu, W., Wang, T., Battulga, O., Wang, C., Shu, Q., et al. (2020). Electroacupuncture alleviates cartilage degradation: improvement in cartilage biomechanics via pain relief and potentiation of muscle function in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 123, 109724. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109724
Sun, K., Luo, J., Guo, J., Yao, X., Jing, X., and Guo, F. (2020). The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 28 (4), 400–409. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2020.02.027
Tallarida, R. J. (2011). Quantitative methods for assessing drug synergism. Genes Cancer 2 (11), 1003–1008. doi:10.1177/1947601912440575
Wang, J., Li, Y., Sun, W., Liu, J., and Chen, W. (2018). Synergistic effects of rmhTRAIL and 17-AAG on the proliferation and apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells. Hematology 23 (9), 620–625. doi:10.1080/10245332.2018.1449338
Wang, J. Y., Yuan, Y., Chen, X. J., Fu, S. G., Zhang, L., Hong, Y. L., et al. (2016). Extract from Eucommia ulmoides oliv. Ameliorates arthritis via regulation of inflammation, synoviocyte proliferation and osteoclastogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 194, 609–616. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.038
Wang, Z., Efferth, T., Hua, X., and Zhang, X. A. (2022). Medicinal plants and their secondary metabolites in alleviating knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Phytomedicine 105, 154347. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154347
Xie, W., Qi, S., Dou, L., Wang, L., Wang, X., Bi, R., et al. (2023). Achyranthoside D attenuates chondrocyte loss and inflammation in osteoarthritis via targeted regulation of Wnt3a. Phytomedicine 111, 154663. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154663
Xu, G., Lei, H., Yuan, Q., Chen, H., and Su, J. (2021). Inhibition of chikusetsusaponin IVa on inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cell line via MAPK pathway. Z Naturforsch C J. Biosci. 76 (3-4), 103–110. doi:10.1515/znc-2019-0107
Xu, J., Yan, L., Yan, B., Zhou, L., Tong, P., and Shan, L. (2020). Osteoarthritis pain model induced by intra-articular injection of mono-iodoacetate in rats. J. Vis. Exp. 159. doi:10.3791/60649
Yang, N., Liu, D., Zhang, X., Li, J., Wang, M., Xu, T., et al. (2020). Effects of ginsenosides on bone remodelling for novel drug applications: a review. Chin. Med. 15, 42. doi:10.1186/s13020-020-00323-z
Yunus, M. H. M., Nordin, A., and Kamal, H. (2020). Pathophysiological perspective of osteoarthritis. Med. Kaunas. 56 (11), 614. doi:10.3390/medicina56110614
Zhan, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, R., Chen, Q., Teng, F., Huang, Y., et al. (2023). CircPTEN suppresses human clear cell renal carcinoma progression and resistance to mTOR inhibitors by targeting epigenetic modification. Drug Resist Updat 71, 101003. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2023.101003
Zhang, L., Shi, X., Huang, Z., Mao, J., Mei, W., Ding, L., et al. (2020). Network pharmacology approach to uncover the mechanism governing the effect of Radix achyranthis bidentatae on osteoarthritis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 20 (1), 121. doi:10.1186/s12906-020-02909-4
Zhang, Y., Wang, J. Y., Wang, H., Chen, X. Y., Zhang, L., and Yuan, Y. (2021). An alcohol extract prepared from the Male flower of Eucommia ulmoides oliv. Promotes synoviocyte apoptosis and ameliorates bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. Med. 16 (1), 113. doi:10.1186/s13020-021-00522-2
Zhao, X., Kim, D., Suminda, G. G. D., Min, Y., Yang, J., Kim, M., et al. (2021). Inhibitory effects of IL-6-Mediated matrix Metalloproteinase-3 and -13 by Achyranthes japonica nakai root in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis mice models. Pharm. (Basel) 14 (8), 776. doi:10.3390/ph14080776
Zhou, G., Zhang, X., Gu, Z., Zhao, J., Luo, M., and Liu, J. (2023). Research progress on the treatment of knee osteoarthritis combined with osteoporosis by single-herb Chinese medicine and compound. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 10, 1254086. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1254086
Keywords: drug pair, osteoarthritis, synergies, Pi3k-akt, apoptosis
Citation: Chen C, Lv L, Huang Y, Xie F, Gao M, Zeng S, Wang Z, Jiang X, Zhan Y and Bao L (2025) The Eucommia ulmoides - Achyranthes bidentata pair and their active monomers exert synergistic therapeutic potential for osteoarthritis through the PI3K-AKT pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1571884. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1571884
Received: 06 February 2025; Accepted: 25 July 2025;
Published: 11 August 2025.
Edited by:
Antonella Smeriglio, University of Messina, ItalyReviewed by:
Andrea Mastinu, University of Brescia, ItalyMarco Biagi, University of Parma, Italy
Hee Geun Jo, Gachon University, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Lv, Huang, Xie, Gao, Zeng, Wang, Jiang, Zhan and Bao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Leilei Bao, YW5uYWJhbzIxMkBzbW11LmVkdS5jbg==; Yangyang Zhan, emhhbnlfYmlvbG9neUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Chun Chen1†
Chun Chen1† Leilei Bao
Leilei Bao