- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 2College of Nursing, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 3Innovative institute of Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 4College of Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 5Shandong Co-Innovation Center of Classic TCM Formula, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
Shenling Baizhu San (SLBZS) is a formulation of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) recorded in the Song Dynasty medical book Taiping Huimin Heji Jufang (AD 1078–1085). It comprises eleven herbs: Ginseng Radix Et Rhizoma, Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma, Poria, Dioscoreae Rhizoma, Nelumbinis Semen, Coicis Semen, Lablab Semen Album, Amomi Fructus, Platycodonis Radix, Glycyrrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma, and Jujubae Fructus. SLBZS has been employed for over 900 years in the treatment of pulmonary and gastrointestinal disorders because of its qualities that enhance spleen function, tonify the lungs, supplement qi, and mitigate diarrhoea. This study meticulously examined and synthesised the clinical relevance and pharmacological mechanisms of SLBZS, concentrating on respiratory diseases, in response to the increasing volume of clinical data about SLBZS. Meanwhile, according to the five principles of Q-marker determination, including quality transmission and traceability, metabolites specificity, formula compatibility environment, association between metabolites and effectiveness, metabolites measurability, the potential quality markers (Q-markers) that SLBZS in the treatment of respiratory diseases were predicted. This study will provide additional clinical research, clarify pharmacological mechanisms, and set quality control criteria for SLBZS in the treatment of respiratory diseases.
1 Introduction
Shenling Baizhu San (SLBZS) originated from the medicinal book Taiping Huimin Heji Jufang in the Northern Song Dynasty. As a formula of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), it is composed of Renshen (Ginseng Radix Et Rhizoma), Baizhu (Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma), Fuling (Poria), Shanyao (Dioscoreae Rhizoma), Lianzi (Nelumbinis Semen), Yiyiren (Coicis Semen), Baibiandou (Lablab Semen Album), Sharen (Amomi Fructus), Jiegeng (Platycodonis Radix), Gancao (Glycyrrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma) and Dazao (Jujubae Fructus) (The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 2020) (Table 1). SLBZS promotes useful qi and supports the spleen, alleviates dampness, and possesses anti-diarrhoeal properties. It is typically employed for diarrhoea resulting from spleen deficiency and dampness, as well as for lung qi deficit, phlegm dampness, cough, and asthma. The recipe incorporates Renshen, Baizhu, and Fuling to enhance qi and spleen function, eliminate moisture, and facilitate transportation. Shanyao and Lianzi enhance spleen and qi, possess astringent properties for the intestines, and serve as antidiarrheal agents; Baibiandou and Yiyiren effectively eliminate dampness and mitigate diarrhoea; Sharen works to eliminate dampness, promote qi circulation, and harmonise the stomach. SLBZS may serve as adjunctive medications for addressing gastrointestinal disorders, including ulcerative enteritis and persistent diarrhoea in clinical settings (Chen et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). Jiegeng facilitates lung qi circulation, alleviates obstructions, and regulates qi flow, rendering SLBZS effective in treating respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and bronchial asthma (Mao et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2023). The metabolites of SLBZS are intricate, particularly regarding the pharmacological mechanisms and quality marker metabolites in the treatment of respiratory disorders, which remain ambiguous and require more clarification.
The metabolites of TCM formulae are essential for clarifying their pharmacological effects. Previous research has comprehensively documented the aqueous extract of a specific TCM botanical medication in SLBZS, along with the metabolites found in the serum (Wang et al., 2025; Wu et al., 2024; Han et al., 2025). Specific metabolites have exhibited beneficial effects on respiratory diseases (Li B. S. et al., 2021; Zhongyin et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2025). Nonetheless, there is inadequate evidence regarding the metabolites of SLBZS and the specific active metabolites that facilitate its therapeutic effects on respiratory illnesses. Quality markers (Q-markers) are active metabolites that signify the pharmacological properties, effectiveness, and quantifiability of TCM botanical drugs. This will act as a reference for the quality control of TCM botanical drugs and formulae, specifically focusing on metabolites with potential pharmacological effects, thereby becoming crucial for the development and application of TCM botanical drugs and formulae (Wu et al., 2024).
Recent years have seen the therapeutic efficacy of SLBZS validated by substantial foundational research and clinical trials, with the development of a broad array of qualitative and quantitative procedures for its chemical analysis and quality control. Nevertheless, these research findings have not been thoroughly synthesized. This research analyses the clinical application and pharmacological effects of SLBZS, utilizing the five principles of Q-marker to predict potential Q-markers of SLBZS in the treatment of respiratory illnesses. This study aims to improve the quality control standards of TCM botanical drugs and formulae, while providing insights and a basis for the ongoing development and implementation of SLBZS.
2 Methods of data acquisition
This study utilises primary literature obtained from the PubMed, Web of Science, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases. The search keywords are “Shenling Baizhu San”, “Respiratory System”, “Clinical Application”, “Pharmacological mechanism”, “metabolites”, “Ginseng Radix Et Rhizoma”, “Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma”, “Poria”, “Dioscoreae Rhizoma”, “Nelumbinis Semen”, “Coicis Semen”, “Lablab Semen Album”, “Amomi Fructus”, “Platycodonis Radix”, “Glycyrrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma”, “Jujubae Fructus” and their combinations. The search ended on 31 January 2025, without any preceding time limitations established. The criteria for admission and disqualification were delineated as follows: 1) Clinical application of SLBZS or its modified variants in the treatment of respiratory disorders; 2) Pharmacological mechanisms associated with SLBZS or its modified variants in managing respiratory disorders; 3) Pharmacological mechanisms of the herbal metabolites found in SLBZS for respiratory disorder treatment; 4) Identification and quantitative assessment of metabolites in SLBZS. Reviews, meta-analyses, and case reports were excluded from the research. In the screening process, we initially reviewed titles and abstracts to find relevant studies that fit the inclusion criteria, followed by a thorough analysis of full-text publications, resulting in the inclusion of 64 papers.
3 Clinical application of SLBZS in respiratory diseases
3.1 Clinical application of SLBZS in COPD
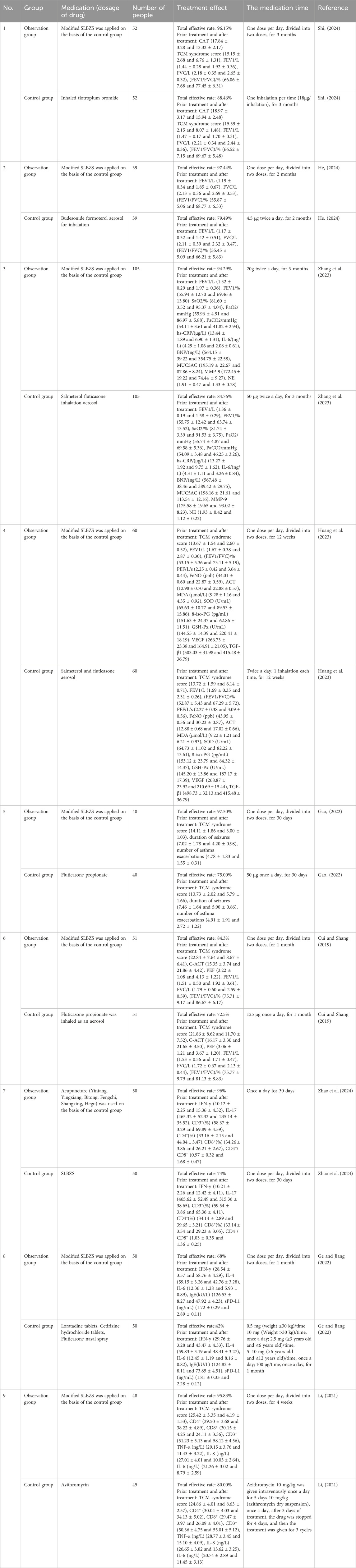
COPD is a common respiratory disorder caused by alveolar or airway irregularities arising from continuous exposure to significant levels of toxic gases or particles. It is chiefly characterised by persistent airway obstruction, associated with elevated rates of disability and mortality (Wang et al., 2024a). A randomised controlled trial (Shi, 2024) assigned 104 patients with stable COPD to a control group and an observation group in a 1:1 ratio. The control group was administered tiotropium bromide powder inhalation, while the observation group received modified SLBZS alongside the control group’s treatment. The findings indicated that modified SLBZS might markedly decrease the COPD assessment test (CAT) score and enhance pulmonary function metrics, including forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and the FEV1/FVC ratio. A randomised controlled trial involving 78 COPD patients with lung-qi deficit (He, 2024) revealed that the combination of modified SLBZS significantly improved the overall effective treatment rate, FVC, FEV1, and FEV1/FVC in comparison to the administration of budesonide and formoterol inhalation powder alone. The effect was significantly superior to that of inhaling powder aerosol alone. A study by Zhang et al. (2023) demonstrated that the combination of SLBZS and salmeterol improved the overall efficacy of COPD treatment and improves FVC, FEV1, and FEV1/FVC ratios compared to salmeterol alone. Concurrently, it can improve arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2), arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2), mucin 5AC (MUC5AC) in induced sputum, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), neutrophil elastase (NE), serum hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and plasma Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) levels, exhibiting superiority compared to salmeterol alone.
3.2 Clinical application of SLBZS in asthma
Asthma is a common chronic respiratory disorder defined by dyspnoea, chest tightness, wheezing, and other symptoms. There are approximately 300 million sufferers worldwide, with the incidence increasing each year (Li et al., 2020). Huang et al. (2023) found that SLBZS, when combined with salmeterol fluticasone aerosol, substantially mitigated clinical symptoms such as cough and expectoration, while also reducing diurnal peak expiratory flow (PEF), FEV1, FEV1/FVC, and other pulmonary function parameters in patients with chronic persistent bronchial asthma. It also elevated fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels, Asthma Control Test (ACT) scores, and other metrics, while significantly reducing the recurrence rate of bronchial asthma. A distinct randomised controlled trial (Gao, 2022) demonstrated that the combination of SLBZS and fluticasone propionate aerosol markedly reduces the duration and frequency of asthma attacks in children, while also improving clinical symptoms such as wheezing and cough, in comparison to fluticasone propionate aerosol alone. A separate study (Cui and Shang, 2019) demonstrated that modified SLBZS in conjunction with flixxdone might diminish the asthma Control Test (C-ACT) score and enhance FVC, FEV1, peak expiratory flow (PEF), FEV1/FVC, and other pulmonary ventilation function metrics in paediatric asthma patients.
3.3 Clinical application of SLBZS in allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is an allergic disorder of the nasal mucosa, predominantly induced by exposure to allergens in susceptible individuals. It manifests as nasal itching, sneezing, excessive nasal discharge, and nasal congestion, which can easily trigger asthma and sinusitis (Schaefer et al., 2023). Zhao et al. (2024) discovered that the combination of SLBZS and acupuncture alleviates clinical symptoms such as nasal itching, nasal congestion, dizziness, shortness of breath, rhinorrhea, and sneezing in patients with allergic rhinitis. Additionally, it enhances serum levels of interferon-γ (IFN-γ), Cluster of Differentiation 3+ (CD3+), Cluster of Differentiation 4+ (CD4+), and the CD4+/Cluster of Differentiation 8+ (CD8+) ratio, while diminishing interleukin-17 (IL-17) and CD8+ levels. A distinct randomised controlled trial (Ge and Jiang, 2022) demonstrated that the SLBZS combination, in contrast to standard treatment (loratadine tablets, cetirizine hydrochloride tablets and fluticasone nasal spray), significantly reduced serum concentrations of interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and immunoglobulin E (EIgE), while augmenting levels of INF-γ and Soluble Programmed Death Ligand-1 (sPD-L1) in patients with rhinitis. Clinical symptoms that require alleviation encompass nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, nasal pruritus, sneezing, fatigue, dyspnoea, lethargy, and reduced vocal quality.
3.4 Others
SLBZS exhibits a favourable therapeutic impact on pneumonia and recurrent respiratory tract infections. A randomised controlled trial (Li, 2021) indicated that modified SLBZS combined with azithromycin significantly reduced serum concentrations of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-8 (IL-8), IL-6, and CD8+, while enhancing levels of CD3+ and CD4+, thereby promoting lesion absorption and the alleviation of lung rales in paediatric patients with Mycoplasma pneumonia. Furthermore, SLBZS combined with massage (Wang, 2024) can significantly improve expectoration, relieve cough, and decrease sputum volume in paediatric patients, while simultaneously lowering inflammatory markers such as IL-4 and TNF-α in sputum. A distinct study (Chen, 2018) revealed that SLBZS combined with pidotimod can reduce serum concentrations of IL-6, TNF-α, procalcitonin (PCT), and cysteinyl leukotriene (Cysl-Ts) in patients with recurrent respiratory tract infections, while also mitigating clinical symptoms such as cough, tonsil hypertrophy, and lung rales.
In summary, SLBZS or modified SLBZS are commonly employed alongside drugs such as tiotropium bromide powder and salmeterol for the treatment of respiratory disorders, exhibiting considerable efficacy (Table 2). Nevertheless, the clinical examination of SLBZS has certain constraints. 1) Methodological constraints are present. Incorporating studies with limited sample sizes (e.g., 78 or 104 cases) may compromise the statistical validity of the findings and elevate the likelihood of a Type II error. 2) The description of the randomisation mechanism is absent. The randomisation grouping lacks a detailed description of the precise mechanism for random sequence generation and allocation concealment, potentially leading to selection bias. 3) Blinding was either defective or omitted. The study did not specify if a double-blind design was implemented, and both patients and assessors were cognisant that subgroups could introduce measurement bias. 4) The dosing specification lacks precision. This study indicates that several physicians may recommend differing dosages for the identical disease. Adequate scientific research on the correlation between dosage and effect are lacking, thereby compromising the efficacy and safety of treatment. 5) Functional testing were conducted individually. Lung function metrics, including FEV1 and FVC, were largely singular and, albeit being statistically significant, did not demonstrate a minimal clinically relevant difference (MCID). 6) Insufficient follow-up. All trials had a follow-up duration of 6 months or less and did not provide evidence on the long-term efficacy and adverse effects, such as herbal liver and kidney damage, of SLBZS. Future investigations in clinical research on TCM will focus on enhancing experimental design, expanding sample inclusion, investigating dose-effect relationships, augmenting the assessment of functional indicators, and prolonging the follow-up period.
4 Pharmacological mechanisms of SLBZS in respiratory diseases
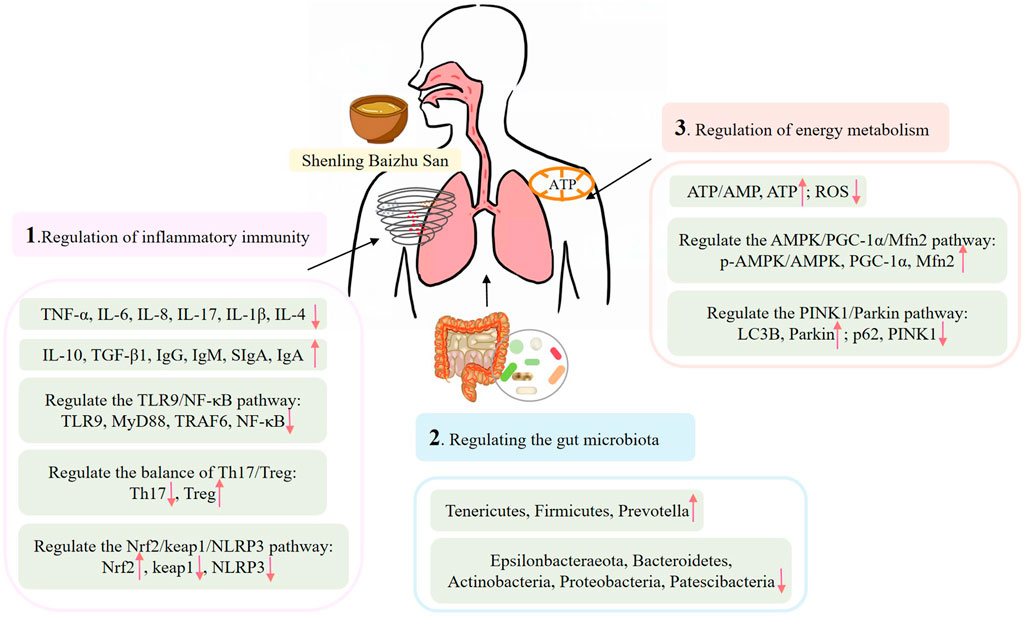
Pharmacological mechanisms suggest that SLBZS may therapeutically influence COPD, asthma, recurrent respiratory tract infections, pulmonary fibrosis, pneumonia, and other respiratory ailments by inhibiting inflammatory responses in lung tissue and airways, modulating immune function, enhancing gastrointestinal microbiota, and restoring mitochondrial energy metabolism (Figure 1).
4.1 Regulation of inflammatory immunity
Gao et al. (2024) found that SLBZS significantly reduced the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and other inflammatory mediators in a COPD cell model induced by cigarette smoke extract (CSE), while also preventing cellular apoptosis. The process may pertain to the modulation of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) 9/nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway. A study by Ouyang and Xu (2019) investigated the impact of SLBZS on airway inflammation in young asthmatic rats, revealing that SLBZS diminished the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the lung tissue. The underlying mechanism may involve a reduction in IL-17 levels and an elevation in interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) levels. Li C. H. et al. (2024) established that SLBZS can reduce inflammatory infiltration in lung tissue, restore epithelial tissue shape, lower serum and alveolar lavage fluid concentrations of IL-17, and increase IL-10 levels. This may transpire via the regulation of the Th17/Treg equilibrium and the reestablishment of immunological function. Wang et al. (2020) found that SLBZS improves peak inspiratory flow (PIF), peak expiratory flow (PEF), and minute ventilation (MV) in rats with recurrent respiratory tract infection (RRTI), possibly associated with the modulation of serum immunoglobulin A (IgA), immunoglobulin G (IgG), immunoglobulin M (IgM), and other immune factors, along with a decrease in NF-κB p65 expression in the trachea. Furthermore, it inhibited the levels of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-4 in serum. Deng et al. (2024) developed a rat model of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through intratracheal administration of bleomycin, discovering that modified SLBZS markedly diminished inflammatory infiltration and collagen proliferation in the lung tissue of rats, as well as reduced the expression of IL-1β and TNF-ɑ in lung tissue. The proposed mechanism of action may involve the modulation of the Nrf2/Keap1/NLRP3 signalling pathway, thereby delaying the pathological progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in rats through the regulation of pyroptosis.
4.2 Regulating the gut microbiota
Feng et al. (2020) found that SLBZS may reduce bacterial load in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of mice with pneumonia. It can reduce the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-8, interleukin-12 (IL-12), and IFN-γ in lung tissue homogenate, increase the concentrations of IL-10 and other inflammatory mediators, and improve lung injury in mice. The process may relate to the augmentation of species diversity and abundance of gut bacteria. Wu et al. (2022) established a juvenile Balb/c mouse model demonstrating intestinal flora dysbiosis and pulmonary inflammation via the injection of antibiotics alongside lipopolysaccharide. SLBZS was found to increase IL-10 levels in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of this juvenile mouse model, while simultaneously reducing levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and serum IgM. The procedure may entail improving the Shannon index of intestinal microbiota, adjusting the levels of Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria, and mitigating the immune and inflammatory reactions in the lungs of juvenile rats. Ouyang et al. (2020) conducted a study that established a mouse model of asthma typified by intestinal flora dysbiosis induced by antibiotics, sensitisation, and aerosol challenge. The study indicated that SLBZS could reduce inflammatory infiltration in the lung tissue of model mice, possibly by increasing the relative abundance of key bacteria such Pseudoprevotella.
4.3 Regulation of energy metabolism
Inadequate skeletal muscle energy metabolism directly leads to respiratory failure in persons with COPD. Hu et al. (2020) established a mouse model of COPD with the application of cigarette smoke. SLBZS was discovered to protect mitochondrial energy metabolism in COPD mice by augmenting the expression of phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), and mitochondrial fusion protein 2 (Mfn2), thereby maintaining normal skeletal muscle function in these mice. A separate study (Zhou et al., 2020) demonstrated that SLBZS enhances mitochondrial functions, including reactive oxygen species levels, mitochondrial ATP production, and membrane potential, mitigates oxidative damage, and decreases early apoptosis of cells via the PTEN induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1)/Parkin pathway-mediated mitophagy in a COPD myoblast model.
While the aforementioned research indicate that the mechanism of action of SLBZS in treating respiratory disorders may involve the reduction of inflammatory responses, the modulation of gut flora, and the regulation of energy metabolism, other limitations persist. 1) Experimental models exhibit variations. Contemporary research predominantly relies on animal models (e.g., bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis, COPD resulting from cigarette smoke exposure); nonetheless, notable discrepancies exist in the immune microenvironment and disease progression between these models and human conditions. The regulation mechanism of Th17/Treg equilibrium in murine asthma models may not completely replicate the heterogeneity of human asthma. 2) Disintegration of route analyses. Numerous studies indicate that pathways including NF-κB and NLRP3 are implicated in SLBZS; however, there is an absence of comprehensive study on the upstream and downstream elements of these pathways across the research. Is there cross-regulation between the TLR9/NF-κB pathway (Gao et al., 2024) and the NLRP3 pathway (Deng et al., 2024)? This division may obscure the fundamental objectives of SLBZS. The absence of validation for protein phosphorylation and the lack of TLR9 knockdown rescue trials complicate the exclusion of off-target effects. 3) Lack of flora specificity. Alterations in gut flora abundance have been noted to correlate with enhancements in lung inflammation in studies (Feng et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2022); however, these studies predominantly rely on correlation analyses, necessitating further validation of causality through faecal transplantation experiments or controlled antibiotic clearance studies of flora. Conversely, current research has solely documented alterations at the phylum level (e.g., Mycobacterium anisopliae, Mycobacterium thickum); however, distinct strains within the same phylum may exhibit divergent immunomodulatory effects, necessitating future functional validation at the strain level. 4) Clinical significance. Energy metabolism research often utilises acute damage models to assess mitochondrial function; however, skeletal muscle depletion in COPD patients is a protracted process. The sustainability of SLBZS in regulating AMPK/PGC-1α throughout the chronic progression of the disease requires more examination. Currently, research on energy metabolism has predominantly concentrated on skeletal muscle; however, the metabolic reprogramming of lung tissues, such as alveolar epithelial cells and fibroblasts, is equally vital in pulmonary fibrosis and asthma. Future studies should prioritise investigating whether SLBZS exerts a selective impact on mitochondria across various tissues.
5 Q-marker prediction analysis of SLBZS treatment for respiratory diseases
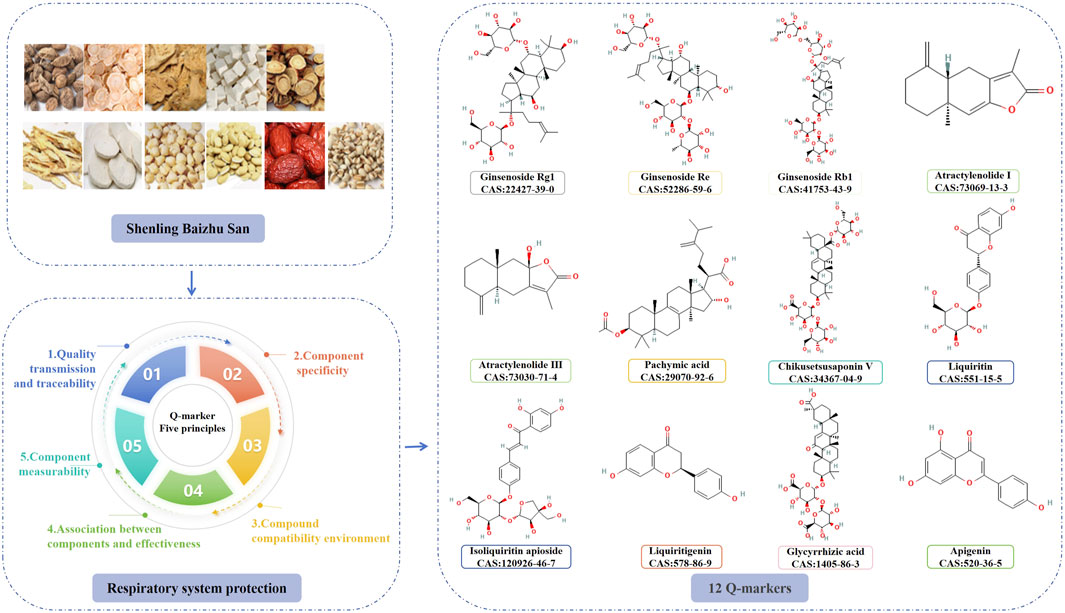
Substantial progress has been achieved in the clinical documentation and pharmacological investigation of SLBZS for respiratory illnesses; however, the active components necessitate further elucidation. Liu Changxiao, a member of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, presented the Q-marker for TCM botanical medications, a novel concept designed to enhance quality control and improve the quality of TCM formulae. It includes five principles: quality transmission and traceability, metabolites specificity, formula compatibility environment, association between metabolites and effectiveness, metabolites measurability (Liu, 2021). The five concepts of Q-markers were utilised to forecast prospective Q-markers for SLBZS in the management of respiratory disorders (Figure 2).
5.1 Q-marker prediction based on quality transmission and traceability
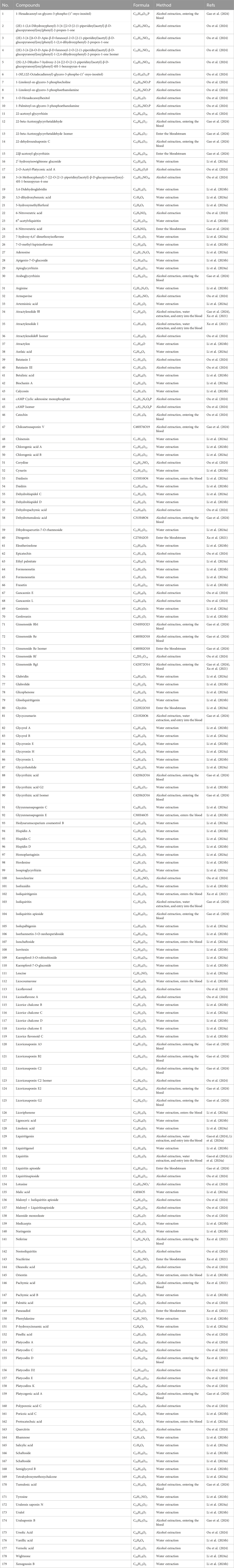
The metabolites are the essential foundation for the efficacy of TCM formulae Liquid chromatography, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, and more technologies can rapidly and accurately identify metabolites. In a study conducted by Ou et al. (2024), 83 metabolites were identified in the ethanol extract of SLBZS utilising UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS technology. These included 26 triterpenoid saponins, 15 flavonoid glycosides, eight flavonoids, seven triterpenoids, six alkaloids, five phospholipids, four fatty acids, four sesquiterpenoids, two fatty acid esters, two nucleotides, one nucleoside, one stilbene, one coumarin, and one phenanthrene. The metabolites of the aqueous extract of SLBZS were analysed using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS technology, resulting in the identification of 104 metabolites, comprising 63 flavonoids, 14 organic acids, 13 terpenes, five coumarins, and nine other compounds (Li C. H. et al., 2024).
The blood constituents and metabolites of TCM botanical medications represent the primary active metabolites. Consequently, the examination of serum pharmacochemistry is essential for finding quality markers in TCM botanical drugs. Gao et al. (2024) used UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS technology to analyze SLBZS serum and identified a total of 108 metabolites, including 30 prototype components and 78 metabolites. Among them, 30 prototype components mainly included one alkaloid compound from Yiyiren. Four flavonoid glycosides from Gancao; There were 18 triterpene saponins, including 13 from Gancao, four from Renshen, and one from Baibiandou. There were three triterpene acids, two from Fuling and one from Jiegeng. Two flavonoids from Gancao; one sesquiterpenoid from Baizhu; one phospholipid compound from Baibiandou. The metabolic pathways of 78 metabolites mainly included glucuronidation, sulfation, methylation, hydroxylation, and acetylation. Li L. et al. (2024) using UPLC-Q-TOF to analyse serum containing SLBZS, identifying 11 prototype components and 17 metabolites. The eleven prototype components comprised eight flavonoids, one phenolic acid, one terpenoid, and one coumarin. The metabolic pathways of 17 metabolites primarily encompassed phase I metabolism, including methylation, reduction, and double reduction, as well as phase II metabolism, comprising glucuronidation and sulfation. Moreover, Xu et al. (2021) employed UHPLC-MS/MS technology, identifying the presence of panaxadiol, ginsenoside Rg1, atractylenolide I, atractylenolide III, pachymic acid, neferine, nuciferine, diosgenin, platycodin D, and isoliquiritigenin in the serum of rats administered SLBZS via gavage. The specifics of SLBZS in the bloodstream are presented in Table 3. Triterpene saponins, flavonoid glycosides, alkaloids, flavonoids, triterpenoids, and other metabolites are hypothesised to be the principal compounds by which SLBZS exerts its pharmacological effects.
5.2 Q-marker prediction based on metabolites specificity
Renshen is the desiccated root and rhizome of Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. It mostly consists of flavonoids, polysaccharides, saponins, and various other compounds. Ginsenosides are considered the principal active component among them (Ratan et al., 2020). The principal metabolites of Renshen include ginsenoside Rb1, ginsenoside Re, and ginsenoside Rg1 (Han et al., 2018).
Baizhu is the desiccated rhizome of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. It mostly comprises sesquiterpenes, triterpenes, polysaccharides, and other constituents (Zhu L. X. et al., 2018). Atractylenolide I and atractylenolide III serve as the distinctive metabolites of Baizhu (Xie et al., 2023).
Fuling is the desiccated sclerotia of Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf, mostly consisting of triterpenoids, polysaccharides, sterols, diterpenoids, and other chemicals. Triterpenoids are widely regarded as the distinctive metabolites of Fuling (Zhu L. et al., 2018; Zhu et al., 2020).
Shanyao is the desiccated rhizome of Dioscorea opposita Thunb. The primary active constituents of Shanyao include phenolic acids, flavonoids, and polysaccharides. Batatasins and dioscin serve as the distinctive metabolites of Shanyao (Liu et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2020).
Lianzi is the desiccated and mature seed of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. Lianzi primarily comprises alkaloids, polyphenols, triterpene saponins, and other constituents. Neferine and nuciferine serve as the distinctive metabolites of lotus seed (Pei, 2021).
Yiyiren is the desiccated and mature seed of Coix lacryma-jobi L. var. Mayuen (Roman.) Stapf, primarily composed of esters, fatty acids, polysaccharides, and phenols (Pan et al., 2023). Fatty acids and their lipids constitute the active components of Yiyiren, while Coixenolide serves as a distinctive metabolite of Yiyiren (Lu et al., 2022).
Baibiandou is the desiccated and fully developed seed of the leguminous species Dolichos lablab L. It mostly comprises polysaccharides, saponins, alkaloids, amino acids, and various other chemical constituents. Total saponins of white lentil and pekolic acid serve as distinctive metabolites of Baibiandou (Li, 2018; Han, 2021).
Jiegeng is the desiccated root of Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC., mostly comprising saponins, flavonoids, phenolic acids, and various other chemical constituents. Platycodin serves as a distinctive metabolite of Jiegeng (Zhang et al., 2022).
Gancao refers to the desiccated roots and rhizome of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. Gancao primarily comprises triterpene saponins, flavonoids, coumarin, polysaccharides, and various other chemical constituents. Glycyrrhizic acid and celiose-glycyrrhizin serve as distinctive metabolites of Gancao (Cheng et al., 2021; Shang et al., 2022).
Sharen is the desiccated and mature fruit of Amomum villosum Lour., Amomum villosum Lour. var. xanthioides T. L. Wu et Senjen, or Amomum longiligulare T. L. Wu, primarily comprising various chemical constituents, including volatile oil, which is typically regarded as the active component of amomum kernel, with bornyl acetate serving as a distinctive metabolite of Sharen (Feng et al., 2024).
Dazao is the desiccated and mature fruit of Ziziphus jujuba Mall. The composition mostly includes sugars, triterpenoids, phenolic acids, and other constituents, with ursolic acid and oleanolic acid serving as the distinctive metabolites of Dazao (Lu et al., 2021).
5.3 Q-marker prediction based on the formula compatibility environment
This TCM formula consists of Renshen, Baizhu, Fuling, Shanyao, Lianzi, Baibiandou, Sharen, Jiegeng, Gancao, and Dazao in the proportions of 15:15:15:15:9:9:12:6:6:10:7.5. Renshen has the ability to enhance qi levels in the body, particularly in the spleen and lungs. Baizhu exhibits properties of moisture desiccation, spleen energising, deficiency replenishment, and qi enhancement, whereas Fuling is distinguished by its capacity to alleviate water retention, promote moisture, and stimulate the spleen. The aforementioned three herbs are crucial in SLBZS. Shanyao enhances spleen and stomach function, while Lianzi also promotes spleen and stomach vitality, hence augmenting the effects of spleen and qi invigorating. Both Baibiandou and Yiyiren can enhance the efficacy of spleen fortification and dampness reduction. Sharen is capable of both dehumidifying and regulating the air machine. Jiegeng facilitates the enhancement of lung qi. Gancao nourishes qi, while Dazao nourishes the spleen and stomach, serving as adjunctive medications. The amalgamation of these TCM plant medications aims to enhance qi, stimulate the spleen, strengthen the lung, and promote the expulsion of moisture.
In clinical practice, individual TCM herbal remedies are often amalgamated with supplementary botanical medicines to generate a compound. The efficacy and potential pharmacodynamic qualities of TCM botanical drugs depend on the formulation or dosage of the plant. Consequently, it is imperative to forecast Q-markers associated with lung function preservation by integrating TCM within a composite context. A study (Zhang, 2019) demonstrated that the concentrations of ginsenosides Rg1, Re, Rf, Rb1, Rc, Rb2, and Rd elevated, whereas the concentration of atractone diminished after the Renshen-Baizhu compatibility. Another study (Li et al., 2014) indicated a significant increase in the concentrations of ginsenosides Rg1, Re, Rf, Rd, and atractylenolide I in Renshen-Baizhu compatibility. The levels of ginsenosides Rb3 and F1 were significantly elevated in the Renshen-Shanyao compatibility study, whereas the concentrations of 16 ginsenosides, including Rg1, Re, Rf, Rb1, Rg2, Rc, Rb2, Rd, F2, Rg3, protopanaxriol, CK, Rh2, and the total sugar content, were markedly reduced (Zhao, 2015). Yue et al. (2018) analysed the constituents of volatile oil following the compatibility of Baizhu and Fuling, discovering the presence of new components, including 14 substances such as 5-methylfuran aldehyde, glycyrene, terpene olefin, carpinene, and linolenic acid. A subsequent investigation (Wang et al., 2021) demonstrated a considerable rise in the concentrations of platycodin D, glycyrrhizic acid, and liquiritin when Jiegeng-Gancao was combined. The synergistic interaction between active components and certain herbs often accounts for the efficacy and therapeutic effects of TCM formulae. A single plant exhibits various pharmacological metabolites and mechanisms of action in a complex environment, resulting in unique therapeutic advantages.
5.4 Q-marker prediction based on theassociation between metabolites and effectiveness
The metabolites of a drug dictate its pharmacological impact and provide the essential element of Q-marker, which is vital for monitoring prescription quality. Studies suggest that the metabolites of SLBZS in treating respiratory disorders may be associated with the chemical components absorbed in the serum of Renshen, Baizhu, Fuling, Baibiandou, and Gancao. The mechanism of action of the active constituents of SLBZS is depicted in Table 4.
5.4.1 Renshen
Ginsenosides, particularly Rg1, Re, and Rb1, are the unique metabolites of Renshen and serve as the bioactive components of SLBZS, demonstrating considerable therapeutic effectiveness against acute lung injury, pneumonia, asthma, and various respiratory disorders. Ji et al. (2021) established a cellular model of acute lung injury by subjecting lung epithelial cells to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure. They subsequently discovered that ginsenoside Rg1 may inhibit cell death by augmenting autophagy and Nrf2 expression. A study by Wang et al. (2019) indicates that ginsenoside Rg1 can alleviate inflammation and lung injury caused by sepsis. This protective effect may be attributed to the decrease of inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in lung tissue, together with the alleviation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Furthermore, ginsenoside Rg1 can suppress lung epithelial-mesenchymal transition via modulating the infiltration of M2 macrophages in lung tissues (Bao et al., 2015; Guan et al., 2017). In a rat model of intestinal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) lung injury, Fang et al. (2014) demonstrated that ginsenoside Re increased serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and malonaldehyde (MDA), showcasing its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. Shaukat et al. (2019) assessed the anti-inflammatory properties of ginsenoside Rb1 in mice with acute lung injury, discovering its regulation of NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathways via TLR2, therefore preserving lung function in the subjects. Furthermore, ginsenoside Rb1 may exert an anti-asthmatic effect by modulating the Th1/Th2 balance (Chen et al., 2015).
5.4.2 Baizhu
Atractylolide I and atractylolide III are the principal metabolites of Baizhu. Research has shown that atractylolide I and atractylolide III provide advantageous effects on lung damage, asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, and other ailments. In an in vitro investigation, Fu et al. (2021) demonstrated that atractonolide III could ameliorate lung injury caused by sepsis, potentially through the inhibition of Forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) and Vanin 1 (VNN1) protein expression, thereby decreasing lung tissue inflammation and suppressing cellular apoptosis. Atractylenolide III was demonstrated in a separate investigation to enhance autophagy failure, subsequently reducing apoptosis and alleviating lung fibrosis in silicotic mice (Tan et al., 2023). Atractylodes III can suppress the activation of the nucleotide-binding oligomerisation domain, NLRP3 inflammasome, restore Th1/Th2 balance in an asthma animal model, prevent death of bronchial epithelial cells, and demonstrate significant anti-asthma efficacy (Zhu et al., 2020). Moreover, research indicates that atractylenolide III can reduce oxidative stress in lung tissue and mitigate the symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis, asthma, and other conditions (Zhang et al., 2021; Huai and Ding, 2020). Atractylenolide I mitigates lung function impairment and reduces the inflammatory response in mice with acute lung injury via inhibiting TLR4 expression and NF-κB activation (Zhang et al., 2015). Atractylenolide I can also modulate the Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway to enhance lung function in a rat model of recurrent respiratory infections (Wang et al., 2024b).
5.4.3 Fuling
Pachymaric acid shown an optimum protective effect on lung function in the study of anti-pulmonary fibrosis and anti-pneumonia. A study (Li et al., 2023) demonstrated that pachymic acid can mitigate the symptoms of pulmonary oedema and pulmonary fibrosis in rats, potentially via decreasing endoplasmic reticulum stress and enhancing mitochondrial activity. Pachymic acid may also mitigate lung fibrosis by diminishing inflammatory responses and oxidative stress (Wang et al., 2023). Pachymic acid may alleviate pneumonia symptoms in rats by reducing lung inflammation and avoiding cell death, potentially through the modulation of the NF-κB and MAPK signalling pathways (Gui et al., 2021).
5.4.4 Baibiandou
Chikusetsusaponin V, derived from Baibiandou, has shown effectiveness in alleviating acute lung injury. Su et al. (2019) developed a mouse model of acute lung injury utilising lipopolysaccharide and found that chikusetsusaponin V ameliorated lung pathological damage by reducing the concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and other inflammatory mediators in alveolar lavage fluid, while also inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signalling pathway.
5.4.5 Gancao
Glycyrrhizin, isorhamnetin, glycyrrhizin, and apigenin are the primary components of liquorice, demonstrating therapeutic effects against lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis. Liquiritin exhibits effective effectiveness in mitigating acute lung injury. Zhou et al. (2023) developed lung damage models utilising LPS in zebrafish and mice, revealing that Liquiritin markedly diminishes inflammation. This action may be ascribed to its suppression of the C-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK)/Nur77/c-Jun signalling pathway. A separate study (Liu et al., 2020) indicated that the anti-acute lung injury activity of liquiritin may be associated with transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1), transient receptor potential A1 (TRPA1) targets, and the NF-κB signalling system. Research indicated that isoliquiritin apioside may safeguard the lungs by mitigating lung epithelial ferroptosis induced by hypoxia-inducible factor (Hif)-1α-mediated ferroptosis in the context of acute lung injury resulting from ischemia/reperfusion (II/R) (Zhongyin et al., 2022). Liquiritigenin is an active component of Gancao. Research indicates that liquiritigenin safeguards lung cells by dose-dependently suppressing the manufacture of α-hemolysin by Staphylococcus aureus (Dai et al., 2013). Liquiritigenin may provide an anti-pulmonary fibrosis effect, potentially through the modulation of the Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)/Nrf2 signalling pathway to influence myofibroblast development (Hua and Ren, 2024). The preventive influence of glycyrrhizic acid on pulmonary function merits our consideration. Research indicates that glycyrrhizic acid can mitigate oxidative stress, diminish inflammation, and avert pulmonary fibrosis to improve lung damage caused by sodium nitrite (Elsherbini et al., 2021). The enhancement of lung function by glycyrrhizic acid is associated with the suppression of autophagy (Qu et al., 2019), apoptosis (Zhao et al., 2016), and immunological modulation (Ma et al., 2013). Apigenin is a flavonoid constituent of Gancao. Research indicates that apigenin safeguards lung function by modulating inflammatory responses, oxidative stress levels (Liu et al., 2018), correcting immunological imbalances, and reducing cellular apoptosis (Yu et al., 2023). Moreover, apigenin can mitigate the senescence of lung fibroblasts via the SIRT1-NAD-CD38 axis (Li J. et al., 2021).
5.5 Q-marker prediction based on metabolites measurability
TCM formulations comprise many TCM botanical drugs in specific ratios, making it essential to identify the principal metabolites that mediate their pharmacological effects. Therefore, Q-markers must be measurable.
Liu et al. (2018) employed the HPLC method to quantitatively assess the constituents of SLBZS, revealing concentrations of 3.12–3.29 mg/g for ginsenoside Rg1, 1.78–1.99 mg/g for Rb1, 1.65–1.82 mg/g for ginsenoside Re, 1.07–1.22 mg/g for liquiritin, and 4.55–4.89 mg/g for glycyrrhizic acid, respectively. This technique is exceptionally sensitive and specific, suitable for the quality control of SLBZS. Furthermore, Wang et al. (2024c) developed a quick determination method for ginsenosides Rb1, Rg1, and Re utilising near-infrared hyperspectral imaging (NIR-HSI) technology, thereby enhancing and supplementing the quality control method of SLBZS. A study by Xu et al. (2021) assessed the pharmacokinetics of the active constituents of SLBZS in rat serum, revealing that the serum concentrations of shendiol, ginsenoside Rg1, atractylenolide I, atractylenolide III, pachymic acid, neferine, nuciferine, diosgenin, platycodin D, and isoglycyrrhizin exhibited significant correlations (0.44–397.50, 0.63–388.50, 0.44–400.50, 0.54–490, 0.31–279.00, 0.41–367.50, 0.38–355.50, 0.50–447.00, 0.42–382.50, 0.39–356.10 ng/mL), which may serve as a benchmark for the quality control of SLBZS. A separate study (Ren et al., 2020) employed high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray detection to quantify the concentrations of four components: liquiritinapioside, liquiritin, isoliquiritin apioside, and glycyrrhizic acid, yielding percentages of 0.26%–2.27%, 0.33%–5.07%, 0.14%–0.81%, and 0.77%–9.76%, respectively. Furthermore, quantitative analysis methods utilising HPLC for liquiritigenin, chikusetsusaponin V, and apigenin have been developed (Pei et al., 2019; Long et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2023).
In conclusion, according to the five principles established by Q-marker, the principal metabolites of SLBZS in the management of respiratory diseases include ginsenoside Rg1, ginsenoside Re, ginsenoside Rb1, atractylenolide I, atractonolide III, pachymic acid, Chikusetsusaponin V, liquiritin, isoliquiritin apioside, liquiritigenin, glycyrrhizic acid, and apigenin. Nonetheless, numerous issues persist in the study process concerning quality markers. 1) Constraints of metabolite detection methodologies. While UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS can swiftly identify numerous metabolites, its ability to differentiate isomers (e.g., ginsenoside Rg1 and Re) requires the integration of retention time or derivatisation techniques, and metabolites present in low concentrations may be overlooked due to inadequate ionisation efficiency. Moreover, certain blood-borne components may fail to achieve therapeutic quantities owing to limited protein binding or swift metabolism, whilst some undiscovered components may exert indirect effects via metabolism by gut flora. 2) Strengthen the hierarchical evaluation of data about component efficacy. The lung-protective action of ginsenoside Rg1 has only been confirmed in a murine model (Ji et al., 2021), and there is an absence of clinical randomised controlled trials to substantiate it. 3) Challenges in the practical implementation of quantifiable standards: HPLC-ELSD is appropriate for saponins lacking UV absorption (e.g., Chikusetsusaponin V) but exhibits lower sensitivity compared to LC-MS/MS; NIR-HSI is rapid yet necessitates a substantial sample size for calibration, potentially rendering it unsuitable for small batch production. The Q-marker prediction of SLBZS is hindered by the absence of in vivo target validation for most components through knockout experiments, inadequate data on pharmacokinetic interactions in compounding, and a deficiency of evidence-based medical research linking existing quality control criteria (e.g., glycyrrhizic acid) to clinical efficacy. This can be enhanced in the future by integrating web-based pharmacological prediction-experimental validation closed-loop studies with real-world data.
6 Conclusion
This study consolidated clinical records and established that SLBZS is useful in treating COPD, asthma, allergic rhinitis, mycoplasma pneumonia, recurrent respiratory tract infections, and other respiratory disorders. Pharmacological investigations concurrently demonstrate that SLBZS has advantages including the reduction of inflammation in lung tissue and airways, modulation of immunological responses, enhancement of gastrointestinal flora, and restoration of mitochondrial energy metabolism. This study aimed to elucidate the metabolites of SLBZS in the treatment of respiratory disorders by employing the five principles of Q-marker measurement to identify Q-markers relevant to SLBZS through five distinct criteria. In conclusion, twelve constituents, including ginsenoside Rg1, ginsenoside Re, ginsenoside Rb1, atractylenolide I, atractonolide III, pachymic acid, Chikusetsusaponin V, liquiritin, isoliquiritin apioside, liquiritigenin, glycyrrhizic acid, and apigenin, may function as Q-markers for SLBZS in the treatment of respiratory disorders. The clinical implementation of this formula encounters several challenges, such as non-standard randomisation, a restricted sample size, dosage imprecision, and insufficient monitoring of adverse effects. The pharmacological mechanism exhibits challenges such as unclear chemical ingredients, insufficient animal and cellular models, and an absence of thorough exploration of the mechanism of action. Moreover, there are challenges such as the lack of standardised research methodology for predicting quality markers and insufficient exploration of the relationship between quality markers. All of these difficulties have hindered the execution and progression of this method. Future endeavours should concentrate on broadening therapeutic uses, clarifying pharmacological mechanisms, and finding quality indicators.
Author contributions
ZG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. TW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LF: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. QW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. YW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft. ZW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft. GL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. CO: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. HZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft. HY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019ZD23), the Jinan City-University Integration Project (JNSX2024019), and TCM Science and Technology Project of Shandong Province (Q-2022058).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bao, S., Zou, Y., Wang, B., Li, Y., Zhu, J., Luo, Y., et al. (2015). Ginsenoside Rg1 improves lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammatory responses and modulating infiltration of M2 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 28 (1), 429–434. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2015.06.022
Chen, D. (2018). To investigate the effect of Shenling baizhu powder combined with pidotimod on children with recurrent respiratory tract infection and its influence on the improvement of inflammatory factors and immune indicators. Anti-Infection Pharm. 15 (09), 1519–1521. doi:10.13493/j.issn.1672-7878.2018.09-017
Chen, J., Shen, B., and Jiang, Z. (2022). Traditional Chinese medicine prescription Shenling BaiZhu powder to treat ulcerative colitis: clinical evidence and potential mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 978558. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.978558
Chen, M. Y., Liu, W., Chou, G. X., and Wang, Y. L. (2020). Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities ofDioscorea opposita thunb. Acta Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 48 (02), 62–66. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19664/j.cnki.1002-2392.200035.
Chen, T., Xiao, L., Zhu, L., Ma, S., Yan, T., and Ji, H. (2015). Anti-asthmatic effects of ginsenoside Rb1 in a mouse model of allergic asthma through relegating Th1/Th2. Inflammation 38 (5), 1814–1822. doi:10.1007/s10753-015-0159-4
Cheng, M., Zhang, J., Yang, L., Shen, S., Li, P., Yao, S., et al. (2021). Recent advances in chemical analysis of licorice (Gan-Cao). Fitoterapia 149, 104803. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104803
Cui, H. Q., and Shang, L. L. (2019). Clinical observation on treatment of bronchial asthma inChildren with flixotide combined with shenling baizhu powder. Clin. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 31 (02), 309–312. doi:10.16448/j.cjtcm.2019.0092
Dai, X. H., Li, H. E., Lu, C. J., Wang, J. F., Dong, J., Wei, J. Y., et al. (2013). Liquiritigenin prevents Staphylococcus aureus-mediated lung cell injury via inhibiting the production of α-hemolysin. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 15 (4), 390–399. doi:10.1080/10286020.2013.771344
Deng, X. M., Huang, F., Shang, C., Liu, Y., Duan, X. Q., Wu, X. Z., et al. (2024). Experimental study of modified Shenlingbaizhu powder regulating Nrf2/keap1/NLRP3 signaling pathway to improve idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lishizhen Med. Materia Medica Res. 35 (09), 2081–2085.
Elsherbini, A. M., Maysarah, N. M., El-Sherbiny, M., Al-Gayyar, M. M., and Elsherbiny, N. M. (2021). Glycyrrhizic acid ameliorates sodium nitrite-induced lung and salivary gland toxicity: impact on oxidative stress, inflammation and fibrosis. Hum. and Exp. Toxicol. 40 (4), 707–721. doi:10.1177/0960327120964555
Fang, F., Qiu, L., Liao, J. H., Kuang, X. C., Zou, L. H., Jiao, Y., et al. (2014). Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect of ginsenoside re on the lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia reperfusion in rats. Cent. South Pharm. 12 (06), 521–524. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tuBS4Ucce5tA2i8_DOUYCjPXH7Afw10ONFqjtmF17wp8fXVi_yxPNctmifctSR9TQJglVPlABxTo66rginOU95LJfKb_TDK-XBtlKCn-A_BbEXWdpRdZOQU&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Feng, J., Dai, W., Zhang, C., Chen, H., Chen, Z., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). Shen-ling-Bai-zhu-san ameliorates inflammation and lung injury by increasing the gut microbiota in the murine model of Streptococcus pneumonia-induced pneumonia. BMC complementary Med. Ther. 20 (1), 159. doi:10.1186/s12906-020-02958-9
Feng, L., Wang, Z., Lei, Z., Zhang, X., Zhai, B., Sun, J., et al. (2024). Amomum villosum Lour.: an insight into ethnopharmacological, phytochemical, and pharmacological overview. J. Ethnopharmacol. 335, 118615. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118615
Fu, J. D., Gao, C. H., Li, S. W., Tian, Y., Li, S. C., Wei, Y. E., et al. (2021). Atractylenolide III alleviates sepsis-mediated lung injury via inhibition of FoxO1 and VNN1 protein. Acta cir. bras. 36 (8), e360802. doi:10.1590/ACB360802
Gao, G. L. (2022). Effect of Shenling baizhu powder combined with fluticasone propionate aerosol on children with asthma of lung-spleen qi deficiency in remission stage. Clin. Med. 42 (08), 115–117. doi:10.19528/j.issn.1003-3548.2022.08.045
Gao, Z., Wang, J., Lu, G., Wu, Q., Wang, S., Wu, X., et al. (2024). Exploration the mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS, network pharmacology and in vitro experimental verification. J. Ethnopharmacol. 324, 117728. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117728
Ge, L. L., and Jiang, B. X. (2022). Effect of modified shenling baizhu powder in the AdjuvantTreatment of allergic rhinitis in children with lung spleen qi deficiency syndrome. Chin. Foreign Med. Res. 20 (10), 36–40. doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2022.10.010
Guan, S., Xu, W., Han, F., Gu, W., Song, L., Ye, W., et al. (2017). Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary epithelial-mesenchymal transition via inhibition of the TGF-β1/smad pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 7171404. doi:10.1155/2017/7171404
Gui, Y., Sun, L., Liu, R., and Luo, J. (2021). Pachymic acid inhibits inflammation and cell apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced rat model with pneumonia by regulating NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Allergologia Immunopathol. 49 (5), 87–93. doi:10.15586/aei.v49i5.468
Han, J. (2021). Content determination and component analysis of total saponins in LablabSemen albums. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 49 (08), 195–198. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tsSb0T6-efnwq8ZgGZi7xauvykPGI-lk-O1yQh4JzRVaPRtkU5WphuWgQmTP0bt_rUgLCMhgdq3mburHrClWCiU7FMwT_J-jcsMIn9IaY0wndL88e1gzV_5f1T1eiak2FMawZK3vqJS6A==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Han, S. Y., Bae, M. G., and Choi, Y. H. (2018). Stereoselective and simultaneous analysis of ginsenosides from ginseng berry extract in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS: application to a pharmacokinetic study of ginseng berry extract. Mol. Basel, Switz. 23 (7), 1835. doi:10.3390/molecules23071835
Han, X., Sun, C., Ding, H., Deng, S., Li, M., Lou, J., et al. (2025). Integration of transcriptomics and metabolomics reveals the mechanism of Glycyrrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma extract inhibiting CCL5 in the treatment of acute pharyngitis. Phytomedicine Int. J. phytotherapy Phytopharm. 137, 156360. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156360
He, L. P. (2024). Shenling baizhu powder combined with western medicine inthe treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease withLung and spleen qi deficiency Type. Chin. Med. Mod. Distance Educ. China 22 (24), 159–161.
Hu, T., Zhou, X. Y., Xue, D., and Zhou, L. H. (2020). Study on the protective effect and mechanism of the method ofstrengthening the spleen to benefit the lung on themitochondrial energy metabolism of skeletal muscle of micewith chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tianjin J. Traditional Chin. Med. 37 (11), 1294–1298.
Hua, Q., and Ren, L. (2024). The SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway mediates the anti-pulmonary fibrosis effect of liquiritigenin. Chin. Med. 19 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/s13020-024-00886-1
Huai, B., and Ding, J. (2020). Atractylenolide III attenuates bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis and oxidative stress in rat model via Nrf2/NQO1/HO-1 pathway activation. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 42 (5), 436–444. doi:10.1080/08923973.2020.1806871
Huang, S. R., Yang, H. F., Ding, H. B., and Li, X. Y. (2023). Effect of Shenling Baizhu powder combined with salmeterol and fluticasone inthe treatment of chronic bronchial asthma on the balance of body oxidationand antioxidation. Shaanxi J. Traditional Chin. Med. 44 (06), 730–733+737. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tsNipvM8N6U2RQHHGhJ3F8JY-j-YlE9efNvrXVrwHEOHPsuJPU1amkjNvA4FT1_vLptbXUKrvKGVUmGLLG9timgM_DGl6EqBgF2MeqERkXwmjYhUHVV2JZsqXYT5r-tW50=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Ji, Q., Sun, Z., Yang, Z., Zhang, W., Ren, Y., Chen, W., et al. (2021). Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on LPS-induced apoptosis of lung epithelial cells. Mol. Immunol. 136, 168–174. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2018.11.003
Li, B. S., Zhu, R. Z., Lim, S. H., Seo, J. H., and Choi, B. M. (2021a). Apigenin alleviates oxidative stress-induced cellular senescence via modulation of the SIRT1-NAD[formula: see text]-CD38 Axis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 49 (5), 1235–1250. doi:10.1142/S0192415X21500592
Li, C. H., Fu, Q. Q., and Zhao, K. Z. (2024a). Study on the therapeutic effect of shenling baizhu san onAlleviating bronchial asthma in mice by regulating Th17/treg balance. Hubei J. Traditional Chin. Med. 46 (11), 3–6.
Li, H. Y. (2018). Study on the antidiarrheal ingredients and quality standard standardization of white lentil. Hunan University of Chinese Medicine. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tulOBPSMUpGesBgkJRaXIxVy1CjcmTwKNHlV6mI2k8UP7-OxKykGedvGhkVlU5Eo9_zRFPL7kC0hA8RZOycpk8EAaFs28rQOKpWRqV8WT6uQ9G1Y_XSHyvE1xw_vQej0RezFYw-qE6jgQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Li, J., Lu, K., Sun, F., Tan, S., Zhang, X., Sheng, W., et al. (2021b). Panaxydol attenuates ferroptosis against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J. Transl. Med. 19 (1), 96. doi:10.1186/s12967-021-02745-1
Li, L., Jin, R. J., and Ji, L. (2023). Pachymic acid ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 39, 5382, 5390. doi:10.1002/tox.23824
Li, L., Zhang, Y. L., Chen, M. Q., Bai, S. S., Wang, Z. J., Fang, H. H., et al. (2024b). Analysis on chemical composition and constituents absorbedin the blood of shenling baizhu san by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Traditional Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 35 (04), 553–562. doi:10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2024.04.013
Li, M. X., Sun, L., Meng, Z. Q., Ding, G., Wang, Z. Z., and Xiao, W. (2014). Content changes of chemical constituents in ginseng radix and AtractylodisMacrocephalae rhizoma before and after compatibility. Chin. Traditional Herb. Drugs 45 (24), 3549–3552. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tu11L0qJy7vW-YRk7GpSNFFS_MCB59cG2okY5V-ZYNNNpcn9hk0u7hbzl3eP4YaoEz-2chBq4pgWOx96Tug1zSEj9VJCLBk6g_OB6EjNbEZH7s_zFRQvBHeuEHFa75gBOu1fLYGY855BQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Li, W., Gao, R., Xin, T., and Gao, P. (2020). Different expression levels of interleukin-35 in asthma phenotypes. Respir. Res. 21 (1), 89. doi:10.1186/s12931-020-01356-6
Li, Y. H. (2021). Effect of Shenling baizhu powder combined with azithromycin in the treatment of children with mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Henan Med. Res. 30 (16), 3004–3006.
Liu, C. J., and Zhu, Q. (2018). Study on HPLC characteristic fingerprint of shenlingbaizhu powder and simultaneous determination of lts five indicative components. China Pharm. 27 (15), 12–16. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tuV5dnSJdetzDWbpVqmbhpVvUkRopGYDXzndZgiR9YmT_U5RKb-3ffZ0v2wE685wRUSKOUqp7JIVrlZQDP_KH0mDoiGskpVkwCEB90GzFO8ZbzbTNAPn9QwP05zfDhykzQmb8JZ_T_lHg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Liu, C. X. (2021). Five-year review on development of quality markers of traditional Chinese medicine. Chin. Traditional Herb. Drugs 52 (09), 2511–2518. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tvF0BDaUGIio3A1x1P272I0VWl-HjMhBLMZAj_ksr_JfLy3KMbtsoXKaBM83wYUA06B8rwjqjZpxlTtjdFwts0Ejgy2EsXyhpkqP-ldeC17zhQDuID8RKR1EaMkCKH1rLe3rvLhjCshtA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Liu, H., Li, X., Xu, H., Wang, X., Gong, Z., Xu, Y., et al. (2024). Rapid identification and determination of chemical components of huai yam based on UPLC-Q-Exactive-MS and fragmentation patterns. Nat. Prod. Res., 1–7. 1, 7. doi:10.1080/14786419.2024.2337117
Liu, Y., Li, Z., Xue, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., and Wang, J. (2018). Apigenin reverses lung injury and immunotoxicity in paraquat-treated mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 65, 531–538. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2018.10.046
Liu, Z., Wang, P., Lu, S., Guo, R., Gao, W., Tong, H., et al. (2020). Liquiritin, a novel inhibitor of TRPV1 and TRPA1, protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury. Cell calcium 88, 102198. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102198
Long, J., Zhou, C. Y., Tian, L., Tu, X., Hu, X. L., and Shi, J. Q. (2022). Determination of 13 components in panacis japonici rhizoma and lts tota saponins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS. J. Hubei Minzu Univ. Ed. 39 (03), 56–61. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13501/j.cnki.42-1590/r.2022.03.014.
Lu, G. Y., Xing, X. Y., Wang, J. Y., Wang, Y., Ma, K., and Wang, S. J. (2022). Research progress of Shenling Baizhu San and predictive analysis on its quality markers. China J. Chin. Materia Medica 47 (19), 5171–5181. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220421.201
Lu, Y., Bao, T., Mo, J., Ni, J., and Chen, W. (2021). Research advances in bioactive components and health benefits of jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 22 (6), 431–449. doi:10.1631/jzus.B2000594
Ma, C., Ma, Z., Liao, X. L., Liu, J., Fu, Q., and Ma, S. (2013). Immunoregulatory effects of glycyrrhizic acid exerts anti-asthmatic effects via modulation of Th1/Th2 cytokines and enhancement of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in ovalbumin-sensitized mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 148 (3), 755–762. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.04.021
Mao, Y., Hu, G., Meng, Q., Li, X., Sun, X., Zhou, J., et al. (2021). Efficacy of Shenling Baizhu San on stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 272, 113927. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.113927
Ou, C. X., Liu, Y. Y., Gao, Z., Wang, J. Y., Wu, Q. L., Zhao, H. J., et al. (2024). Effects of Platycodonis radix on the chemical constituents in shenling baizhu san by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Res. Pract. Chin. Med. 38 (05), 46–54. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13728/j.1673-6427.2024.05.008.
Ouyang, X. R., Liang, Y. N., Lin, X. L., and Xu, H. (2020). Effect of shen ling baizhu powder on airway inflammation and regulation of GutMicrobiota in asthmatic mice. Traditional Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 31 (11), 1282–1288. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tvEdzf7HRsVcxsgW63xXoblnYAxeojG3BcsrQDwCl8cLX_SWMWwlx_jqxsFqVq1VlmUJCgTgWcY--76xwVThkhj4szY4h6tYTgZbjGZwMOJHPbIqTw85xxKvBSAZvqCjEM=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Ouyang, X. R., and Xu, H. (2019). Inhibitory effect of ShenLing baizhu powder on AirwayInflammation in young asthmatic rats. Traditional Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 30 (07), 812–815. doi:10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2019.07.010
Pan, X., Shen, Q., Zhang, C., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Chang, Z., et al. (2023). Coicis Semen for the treatment of malignant tumors of the female reproductive system: a review of traditional Chinese medicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1129874. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1129874
Pei, H. T. (2021). Chemical constituents of differents parts from Nelumbo nucifera, and sedative effect of Nelumbinis Semen. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2021.004693.
Pei, Y. Q., Shi, H. P., Yan, H., Huang, S. L., Dong, W., and Wang, G. Q. (2019). Quality evaluation of Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma Praeparata Cum Melle basedon HPLC fingerprint and multi-component quantitative analysis by QAMS. Chin. Traditional Herb. Drugs 50 (18), 4293–4304. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tu7H8sEkMqFK7Nmq0d5Eh30qLCCqmwI8H281hnRbMAJPW-I33v_eVAQIdsAgRg8vobqAO7N8fQd-4A0TJ3AEEq0kdfeguATwQQC2iCg92ru2eEnXVsrVHqtPJmOf3vDWgM=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Qu, L., Chen, C., He, W., Chen, Y., Li, Y., Wen, Y., et al. (2019). Glycyrrhizic acid ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating autophagy through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (4), 2042–2055. PMID: 31105816; PMCID: PMC6511780.
Ratan, Z. A., Haidere, M. F., Hong, Y. H., Park, S. H., Lee, J. O., Lee, J., et al. (2020). Pharmacological potential of ginseng and its major component ginsenosides. J. ginseng Res. 45 (2), 199–210. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2020.02.004
Ren, X., Hu, C., and Zhang, L. Z. (2020). Determination of four active components in radix glycyrrhizae by HPLC-CAD. Anhui Med. Pharm. J. 24 (07), 1304–1308. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tuFU7G7xTw9T6Lkmmp6uDg059FbnrCS3qCldjnLHOzz4wU66PD7bQAcgsdxe2I6C-vBGhVG72DZH1j9BGWotbbbAypRhUs0BkSPWYNsBzv7i5syDJqIlUUG7gXD4p7Dxbo=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Schaefer, M., Zimmermann, K., and Enck, P. (2023). A randomized controlled trial of effects of open-label placebo compared to double-blind placebo and treatment-as-usual on symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 8372. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-34790-9
Shang, Z., Liu, C., Qiao, X., and Ye, M. (2022). Chemical analysis of the Chinese herbal medicine licorice (Gan-Cao): an update review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 299, 115686. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115686
Shaukat, A., Guo, Y. F., Jiang, K., Zhao, G., Wu, H., Zhang, T., et al. (2019). Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates Staphylococcus aureus-induced Acute Lung Injury through attenuating NF-κB and MAPK activation. Microb. Pathog. 132, 302–312. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2019.05.003
Shi, C. S. (2024). To observe the effect of Shenlingbaizhu powder combined with tiotropium bromide in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in remission stage and its influence on pulmonary function. Med. Forum 28 (07), 145–148. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19435/j.1672-1721.2024.07.046.
Su, K., Zhang, G., Zhang, X., and Jiang, W. (2019). Chikusetsusaponin V attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by modulation of the NF-κB and LXRα. Int. Immunopharmacol. 70, 174–179. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.02.023
Tan, S., Yang, S., Kang, H., Zhou, K., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Atractylenolide III ameliorated autophagy dysfunction via epidermal growth factor receptor-mammalian target of rapamycin signals and alleviated silicosis fibrosis in mice. Laboratory investigation; a J. Tech. methods pathology 103 (2), 100024. doi:10.1016/j.labinv.2022.100024
Wang, C., Yu, J., Guo, Y., Jiang, M., Zhong, K., and Wang, X. (2025). Separation and purification of ginsenosides and flavonoids in from the leaves and stems of Panax quinquefolium by high-speed countercurrent chromatography and online-storage inner-recycling countercurrent chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 48 (2), e70073. doi:10.1002/jssc.70073
Wang, C. C., Zhang, Y. L., Geng, W. J., Gui, S. Y., Peng, D. Y., and Wang, J. T. (2021). Study on Herbal Drug Pair of Platycodonis Radix and Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizomain Classical Prescription Jiegeng Tang. Mod. Chin. Med. 23 (05), 826–831. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20200227001.
Wang, H., Hou, Y. N., Yang, M., Feng, Y., Zhang, Y. L., Smith, C. M., et al. (2022). Herbal formula shenling baizhu san for chronic diarrhea in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Integr. cancer Ther. 21, 15347354221081214. doi:10.1177/15347354221081214
Wang, Q. L., Yang, L., Peng, Y., Gao, M., Yang, M. S., Xing, W., et al. (2019). Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates SIRT1 to ameliorate sepsis-induced lung inflammation and injury via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 6453296. doi:10.1155/2019/6453296
Wang, S., Tan, W., Zhang, L., and Jiang, H. (2023). Pachymic acid protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing fibrotic, inflammatory, and oxidative stress pathways in mice. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 196, 3344, 3355. doi:10.1007/s12010-023-04686-5
Wang, X. L., Li, W., Zhu, S., Shi, X. C., and Chen, W. (2024c). Effect of atractylenolide l on lung injury in rats with RecurrentRespiratory tract infection of lung and spleen qi deficiency byRegulating the Pl3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Traditional Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 35 (02), 216–223. doi:10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2024.02.008
Wang, Y., Wang, S., Bai, R., Li, X., Yuan, Y., Nan, T., et al. (2024a). Prediction performance and reliability evaluation of three ginsenosides in Panax ginseng using hyperspectral imaging combined with a novel ensemble chemometric model. Food Chem. 430, 136917. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136917
Wang, Y., Zhang, N., Liu, F., Zhou, J., Teng, G., and Huang, H. (2024b). A new perspective for improving COPD: ginsenoside Rg3 links SIRT1 to inhibit mitochondrial autophagy. Discov. Med. 36 (191), 2386–2398. doi:10.24976/Discov.Med.202436191.220
Wang, Y. J., Wei, D. D., Wang, H. J., Cao, J. X., and Li, J. Y. (2020). Effects of shenling baizhu powder on lmmune function in ratswith recurrent respiratory tract infections of qi-deficiency ofLung and spleen. Inf. Traditional Chin. Med. 37 (05), 33–37. doi:10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.200126
Wang, Y. L. (2024). Effect of Shenlingbaizhu powder combined with massage on cough in children. Guangming J. Chin. Med. 39 (01), 95–97. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tso74SrWIaBsJmQLDbiThy-QkNZ2aPco2OUPm-qyRvRce_HlQtqEaLKfYdFAYtLlnmBfABHIcfK7UPCauTQtdzMnTlJEDgnLzKselv1dHiVzm15wrxqoSKW8lAEV91AOJo=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Wu, Q., Ou, C., Wang, J., Wu, X., Gao, Z., Zhao, Y., et al. (2024). Jiawei Kongsheng Zhenzhong Pill: marker compounds, absorption into the serum (rat), and Q-markers identified by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1328632. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1328632
Wu, T., Hou, W., Li, S., Liu, C., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Integrated analysis and separation of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors from triterpenes of Poria cocos using bioaffinity ultrafiltration UPLC-Q-Exactive, molecular docking and target-based multiple complex networks. Fitoterapia 175, 105856. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2024.105856
Wu, Y. L., Liu, X. P., Jia, Y. X., Wang, X. R., Wu, Y., Li, Y. Y., et al. (2022). Effect of shenling baizhu powder on pulmonary lmmuneInflammatory response in juvenile mice with intestina dysbiosis. Chin. J. Inf. Traditional Chin. Med. 29 (11), 79–85. doi:10.19879/j.cnki.1005-5304.202111648
Xie, Z., Lin, M., He, X., Dong, Y., Chen, Y., Li, B., et al. (2023). Chemical constitution, pharmacological effects and the underlying mechanism of atractylenolides: a review. Mol. Basel, Switz. 28 (10), 3987. doi:10.3390/molecules28103987
Xu, C., Xu, H., Dai, X., Gui, S., and Chen, J. (2025). Effects and mechanism of combination of Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharides and Platycodon saponins in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats through the gut-lung axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 341, 119305. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.119305
Xu, X., Wang, W., Chen, Y., Zhang, Q., Li, B., Zhong, Y., et al. (2021). Simultaneous determination of ten bioactive components from shenling baizhu san in rat plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS: application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study in normal and two models of ulcerative colitis rats. Evidence-based complementary Altern. Med. 2021, 3518241. doi:10.1155/2021/3518241
Yang, Y., Jiang, Z. M., Ni, L., Wang, J. H., Yang, Z. R., Liu, S. Q., et al. (2023). Content determination of vanillic Acid,Ferulic acid and apigenin in kalimeris indica by HPLC. China Pharm. 32 (21), 83–86. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tvqG4IVSQdD8hUtYYcGIniPP_HzG0kl8jIsQCIYFRiIvLGk3zrNsWqgJWtsx9ExMeXRY69qTmp9fNAlTcdX6QL3mu5m8SdtxDFQ8S4DPGao9XMRfPmz627AToe_RyIj5ZQ=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Yu, H., Huang, X., Zhu, H. H., Wang, N., Xie, C., Zhou, Y. L., et al. (2023). Apigenin ameliorates non-eosinophilic inflammation, dysregulated immune homeostasis and mitochondria-mediated airway epithelial cell apoptosis in chronic obese asthma via the ROS-ASK1-MAPK pathway. Phytomedicine Int. J. phytotherapy Phytopharm. 111, 154646. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154646
Yue, M. Y., Yu, H. Y., Zhou, Q. M., and Pan, Y. (2018). GC-MS in analysis of chemical composition of volatile oil in different ratio ofAtractylodis Macrocephalae rhizoma and Poria. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 24 (11), 61–66. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20181108.
Zhang, J. L., Huang, W. M., and Zeng, Q. Y. (2015). Atractylenolide I protects mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 765, 94–99. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.08.022
Zhang, L., Yi, H., Jiang, D., and Li, Z. (2021). Protective effects of Atractylenolide III on inflammation and oxidative stress in ovalbumin-induced asthma mice and its possible mechanisms. General physiology biophysics 40 (2), 137–146. doi:10.4149/gpb_2020046
Zhang, L. F., Duan, B., Liu, F., Tian, X. Z., and Zhang, Y. F. (2023). Effect and mechanism of shenling baizhu powder in treatment of stable phase of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Liaoning J. Traditional Chin. Med. 50 (12), 109–112. doi:10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2023.12.031
Zhang, S., Chai, X., Hou, G., Zhao, F., and Meng, Q. (2022). Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC.: a review of phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and traditional use. Phytomedicine Int. J. phytotherapy Phytopharm. 106, 154422. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154422
Zhang, S. Y. (2019). Study on the compatibility mechanism of Ginseng Radixcombined with Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma in thetreatment ofchronic atrophic gastritis. Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.26988/d.cnki.gcdzu.2019.000298.
Zhao, H., Zhao, M., Wang, Y., Li, F., and Zhang, Z. (2016). Glycyrrhizic acid prevents sepsis-induced acute lung injury and mortality in rats. J. Histochem. Cytochem. official J. Histochem. Soc. 64 (2), 125–137. doi:10.1369/0022155415610168
Zhao, L. (2015). Research on quality evaluation and effectiveness of the compatibility ofginseng and other 4 Chinese medicines. Jilin Agricultural University. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=9CXCstbk-tvUBB2rg1qw81olbVpyb13C8rrNPSaKyHDR583Ok_B7lJZg3Ql8m1B3pelDEt9GkcEBwQxKG94Y44cPgJHKBw4JLwvTI0RIOEO7WnATKsEeFxQ2OFGzqJHWIVQDKoBBvJn0qkY6wsdE8Q==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
Zhao, L. P., Yan, C. D., Li, Y. L., Zhang, Y., and Yue, Y. G. (2024). Clinical efficacy of shenling baizhu powder combined withAcupuncture and moxibustion on allergic rhinitis with QiDeficiency in lungs and spleen syndrome and effect on SerumIFN-y and lL-17 levels. World J. Integr. Traditional West. Med. 19 (11), 2203–2207. doi:10.13935/j.cnki.sjzx.241116
Zhongyin, Z., Wei, W., Juan, X., and Guohua, F. (2022). Isoliquiritin apioside relieves intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by blocking Hif-1α-mediated ferroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 108, 108852. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108852
Zhou, H., Yang, T., Lu, Z., He, X., Quan, J., Liu, S., et al. (2023). Liquiritin exhibits anti-acute lung injury activities through suppressing the JNK/Nur77/c-Jun pathway. Chin. Med. 18 (1), 35. doi:10.1186/s13020-023-00739-3
Zhou, X. Y., Song, Y. H., Xue, D., Zhang, L. H., and Hu, T. (2020). Protective mechanism of Shenling Baizhu powder on the injured cells of COPDskeletal muscle based on mitochondrial autophagy. J. Guangdong Pharm. Univ. 36 (03), 369–374. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16809/j.cnki.2096-3653.2020021803.
Zhu, B., Zhang, Q. L., Hua, J. W., Cheng, W. L., and Qin, L. P. (2018). The traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.: a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 226, 143–167. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2018.08.023
Zhu, C., Zhang, L., Liu, Z., Li, C., Bai, Y., and Wang, L. (2020). Atractylenolide III reduces NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Th1/Th2 imbalances in both in vitro and in vivo models of asthma. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. and physiology 47 (8), 1360–1367. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13306
Zhu, L., Xu, J., Zhang, S., Wang, R., Huang, Q., Chen, H., et al. (2018b). Qualitatively and quantitatively comparing secondary metabolites in three medicinal parts derived from Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf using UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS-based chemical profiling. J. Pharm. Biomed. analysis 150, 278–286. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2017.11.066
Zhu, L. X., Xu, J., Wang, R. J., Li, H. X., Tan, Y. Z., Chen, H. B., et al. (2018a). Correlation between quality and geographical origins of Poria cocos revealed by qualitative fingerprint profiling and quantitative determination of triterpenoid acids. Mol. Basel, Switz. 23 (9), 2200. doi:10.3390/molecules23092200
Keywords: Shenling Baizhu San, respiratory diseases, clinical application, pharmacological mechanisms, quality markers
Citation: Gao Z, Wang T, Fu L, Wu Q, Wang Y, Wu Z, Lu G, Ou C, Zhao H and Yu H (2025) Clinical application, potential pharmacological targets and quality marker prediction of a TCM formulation used (Shenling Baizhu San) in the treatment of respiratory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1575903. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1575903
Received: 13 February 2025; Accepted: 16 May 2025;
Published: 29 May 2025.
Edited by:
Irina Ielciu, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hatieganu, RomaniaReviewed by:
Wang Lingchong, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaJinpeng Chen, Independent Researcher, Tianjin, China
Tingting Bai, Inner Mongolia Medical University, China
Siat Yee Fong, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Wang, Fu, Wu, Wang, Wu, Lu, Ou, Zhao and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haijun Zhao, aGFpanVuemhhb0BzZHV0Y20uZWR1LmNu; Huayun Yu, MDEwMDAwMjlAc2R1dGNtLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zu Gao
Zu Gao Tong Wang2†
Tong Wang2† Zhichun Wu
Zhichun Wu Chunxue Ou
Chunxue Ou Haijun Zhao
Haijun Zhao Huayun Yu
Huayun Yu