- 1Department of Urology, Pingxiang Affiliated Hospital, Pingxiang, China
- 2Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 3Department of Urology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
- 4Department of Urology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China
- 5Department of Urology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Background: Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) offer novel therapeutic options for advanced urological cancers, but their efficacy and safety vary across cancer types. Many non-urothelial cancer ADC trials are small, nonrandomized studies with limited validated evaluation indicators. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ADCs across various urological cancers.
Methods: Relevant studies were identified through searches in Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CNKI, VIP database and WanFang dataset, including randomized controlled trials, single-arm studies, and retrospective analyses on ADCs for advanced urological cancers. RoB 2.0, MINORS, and NOS were used for quality assessment, with R 4.4.0 for data analysis.
Results: This meta-analysis included 46 studies with 3,250 patients, covering urothelial cancer (29 studies), renal cell carcinoma (5 studies), testicular cancer (2 studies), and metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (10 studies). Three ADCs for urothelial cancer have received approval, including enfortumab vedotin (EV), sacituzumab govitecan (SG), and the HER2-ADC vedicilizumab (RC-48)/disitamab vedotin (DV). For urothelial cancer, the pooled overall response rate (ORR) was 43% (95% CI: 39%–47%) and disease control rate (DCR) was 76% (95% CI: 71%–80%). Median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were 11.55 months (95% CI: 10.63–12.47) and 5.52 months (95% CI: 5.32–5.72) for enfortumab vedotin (EV), and 15.30 months (95% CI: 11.21–19.40) and 5.80 months (95% CI: 4.88–6.72) for DV. DV combined with immunotherapy achieved a pooled median PFS of 9.78 months (95% CI: 7.73–11.83). For renal cell carcinoma, the ORR was 6% (95% CI: 2%–10%) with median OS of 12.71 months (95% CI: 9.67–15.75). For metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, ADC efficacy was higher in chemotherapy-experienced patients (ORR: 17% vs. 5%).
Conclusion: ADCs demonstrate efficacy and safety in treating urological cancers, but further clinical trials are needed, particularly for renal, testicular, and prostate cancers, to support personalized treatment strategies.
1 Introduction
Globally, urological cancer accounting for 13% in all cancers has led to substantial public health burden worldwide, especially in aging societies (Bray et al., 2024; Dy et al., 2017). Urological cancers primarily comprise bladder, prostate, kidney, and testicular cancers (Bray et al., 2024). Bladder cancer was the fourth most frequent disease in 2023, with a significant rate of mortality and recurrence, according to cancer statistics. The most common disease and the second leading cause of death for men is prostate cancer (Siegel et al., 2023). As reported in World Cancer Research Fund International, kidney and testicular cancer were ranked as the 14th and 20th among all cancers, with approximately 430,000 and 74,500 new cases in 2020 worldwide (World Cancer Research Fund International, 2023). Nowadays, urological cancers have been a long-standing problem that requires more new treatments to be offered in the future.
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are designed to maximize cancer cell death while reducing cytotoxicity towards non-cancer cells and are emerging as a more promising option for targeted cancer therapies (Gabison et al., 2024). ADCs have been recognized as “biological missiles,” “Trojan horses,” and “smart chemotherapies” to a certain degree, consisting of major three components, the payload drug, the monoclonal antibody, and the chemical linker (Colombo et al., 2024). Payload drugs, known as the ‘magic bullet’ with their high cytotoxicity, are responsible for causing cancer cell death. The main compounds are monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), nomethoxycyaline F (MMAF), and maytansinoids (DM1 and DM4). The monoclonal antibody (mAb) as the navigation system could specifically recognize and bind to specific antigens on the outer layer of cancer cells to minimize the cytotoxicity towards noncancerous cells. The chemical linker handles the combination of payloads and monoclonal antibodies (Marks and Naidoo, 2022; McCombs and Owen, 2015).
Eleven of the more than 370 new ADCs that have made it into clinical trials so far have received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (Tarantino et al., 2022; Drago et al., 2021; Maecker et al., 2023). Numerous ADCs have been used in phase I, II, and III clinical trials for urological cancers (de Vries et al., 2023; Kollmannsberger et al., 2021; Koshkin et al., 2022; Milowsky et al., 2016; Powles et al., 2024a). In particular, three ADCs for urothelial cancer have received approval. They are enfortumab vedotin (EV), sacituzumab govitecan (SG), and the HER2-ADC vedicilizumab (RC-48). The first 2 pharmacological agents were granted approval by the FDA (U.S.Food and administration, 2021; Chang et al., 2021), whereas RC-48 is the drug that China has authorized and cleared for the treatment of urothelial cancer (Sheng et al., 2021). In the EV-302 Phase III clinical trial, the EV plus pembrolizumab group achieved an overall response rate (ORR) of 67.7% (95% CI: 63.1%–72.1%) and a disease control rate (DCR) of 86.5% in patients, more than double that of the chemotherapy group (Powles et al., 2024a). In the EV-103 study, the ORR in EV group was 45.2% (33.5%–57.3%) (O'Donnell et al., 2023). Other single-arm studies have reported variations in survival duration and tumor response rates for enfortumab vedotin (EV) in the treatment of urothelial cancer. The ORR ranges from 25% to 56% in the 1.25 mg/kg EV group (Takahashi et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2021). According to data from many studies, enfortumab vedotin (EV) may present safety risks because of the 55% (Yu et al., 2021) rate of grade 3 or worse treatment-related side events and the 44.8% prevalence of peripheral sensory neuropathy (Powles et al., 2021) in the general population. Meanwhile, in the SG clinical trials, the ORR ranged from 28.9% to 32% (Pet et al., 2024; Bardia et al., 2021). Similarly, in the RC-48 clinical trials, the ORR varied from 26.3% to 50% (Xu et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2023) demonstrating that it is necessary to pool all relevant studies to verify the efficacy and safety of ADCs in urothelial cancer. Many clinical trials in phases I and II have been conducted in recent years, despite the fact that the Food and Drug Administration has not approved any pharmaceutical drugs for the treatment of prostate, renal, or testicular cancers. Despite these advancements, the efficacy and safety of ADCs vary across different types of urological cancers. Many clinical trials for non-urothelial cancers are small, non-randomized studies with limited validated evaluation indicators. Therefore, a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis is needed to evaluate the overall efficacy and safety of ADCs across various urological cancers. This study aims to compile and analyze all relevant studies, including randomized controlled trials, single-arm studies, and retrospective analyses, to provide a comprehensive assessment of ADCs in treating urological cancers.
It seeks to offer additional therapeutic insights into the use of ADCs for treating diverse urological cancers and expand clinical treatment options. This article is presented in compliance with the PRISMA reporting checklist.
2 Methods
2.1 Search strategy
Literature on antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for treating advanced urological cancers was retrieved from seven databases: Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CNKI, VIP database and WanFang data, with the final search conducted on 18 October 2024. The European Society of Medical Oncology’s (ESMO) meeting abstracts were also examined. The subject terms and free words looked up were “Urologic Neoplasms” OR “Carcinoma, Transitional Cell” OR “Kidney Neoplasms” OR “Carcinoma, Renal Cell” OR “Urinary Bladder Neoplasms” OR “Prostatic Neoplasms” OR “Testicular Neoplasms” AND “Immunoconjugates” OR “enfortumab vedotin” OR “sacituzumab govitecan” OR “disitamab vedotin” OR “Brentuximab Vedotin”. In addition, the original literature’s references were personally reviewed to make sure all pertinent papers were included. The Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) website (registration number CRD42024617523) makes the study protocol publicly accessible. We also searched for unpublished studies by contacting experts in the field and checking clinical trial registries (ClinicalTrials.gov, WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, EU Clinical Trials Register) for ongoing or completed but unpublished trials. Authors of identified studies were contacted to obtain any additional unpublished data.
2.2 Selection criteria
Studies that satisfied the following inclusion requirements were added to the meta-analysis: 1) participants received urological cancer diagnoses that were either locally advanced or metastatic (urothelial, kidney, testicular or prostate) based on the ESMO guideline criteria for urological cancers (Powles et al., 2022; Powles et al., 2024b; Oldenburg et al., 2022; Parker et al., 2020); 2) treatments employing antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or combine immunotherapy with ADCs; 3) study types encompassed randomized controlled trials, non-randomized controlled trials, and retrospective studies; 4) outcomes reported patient-related metrics such as overall response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), duration of response (DOR), and adverse events (AEs). The Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1 (Eisenhauer et al., 2009) was used to measure tumor remission. We excluded meta-analyses, reviews, guidelines, letters, consensus documents, editorials, conference abstracts, case reports, and animal studies. Two researchers (TL and XX) independently screened the articles using the predetermined criteria for inclusion and exclusion. The two reviewers discussed and resolved any discrepancies that arose during the screening process; two more investigators (YR and ZL) decided on any issues that remained.
2.3 Data extraction and quality assessment
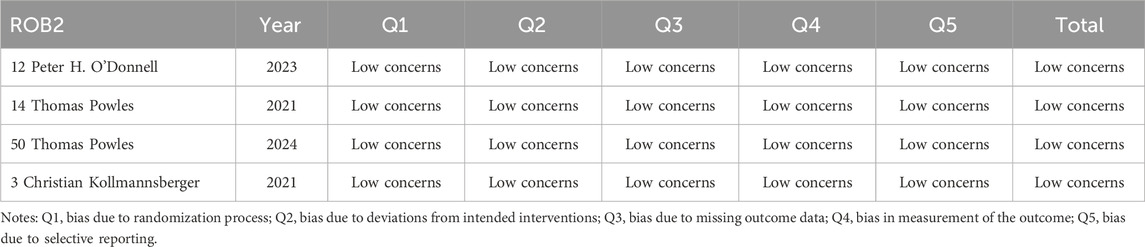
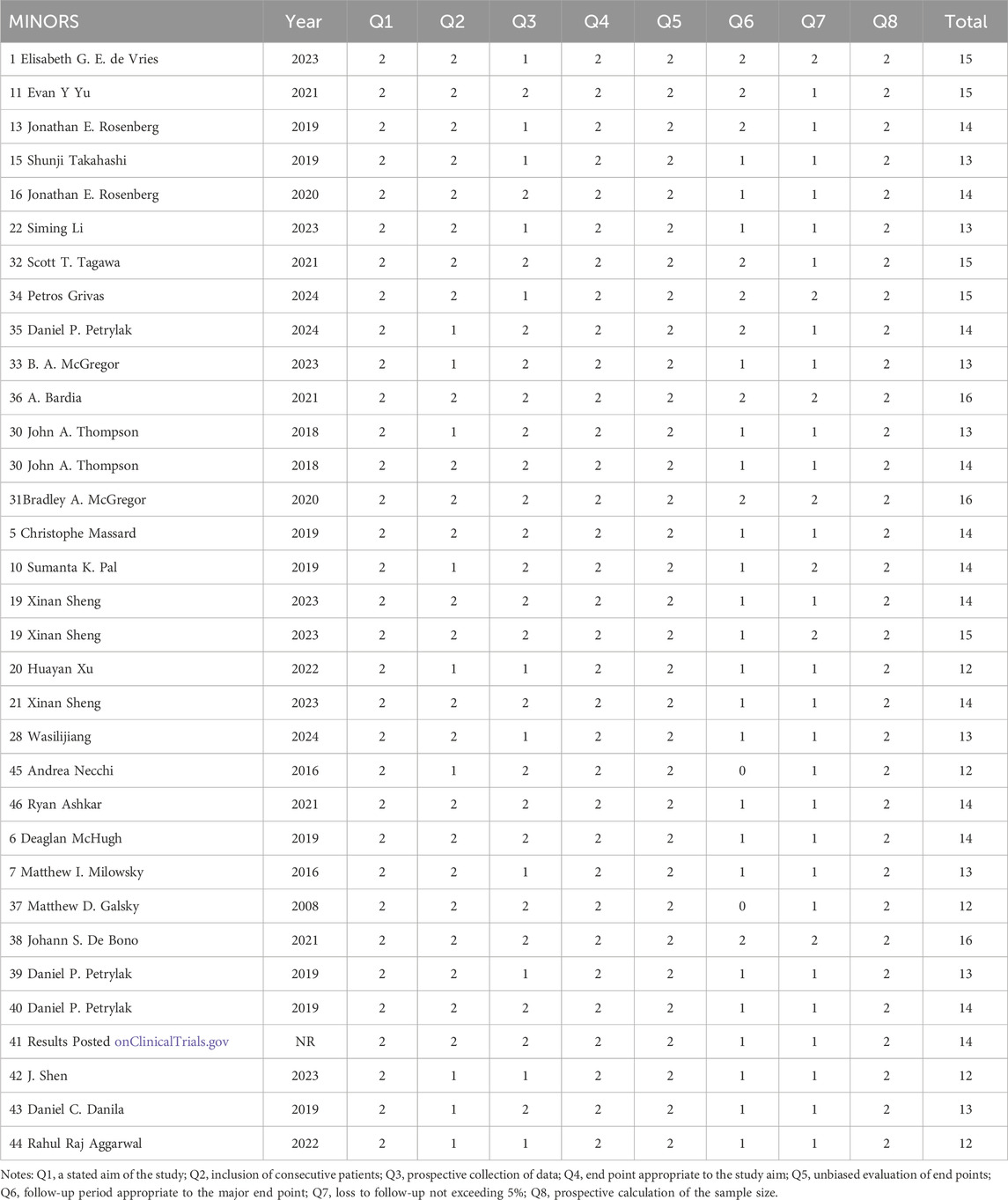
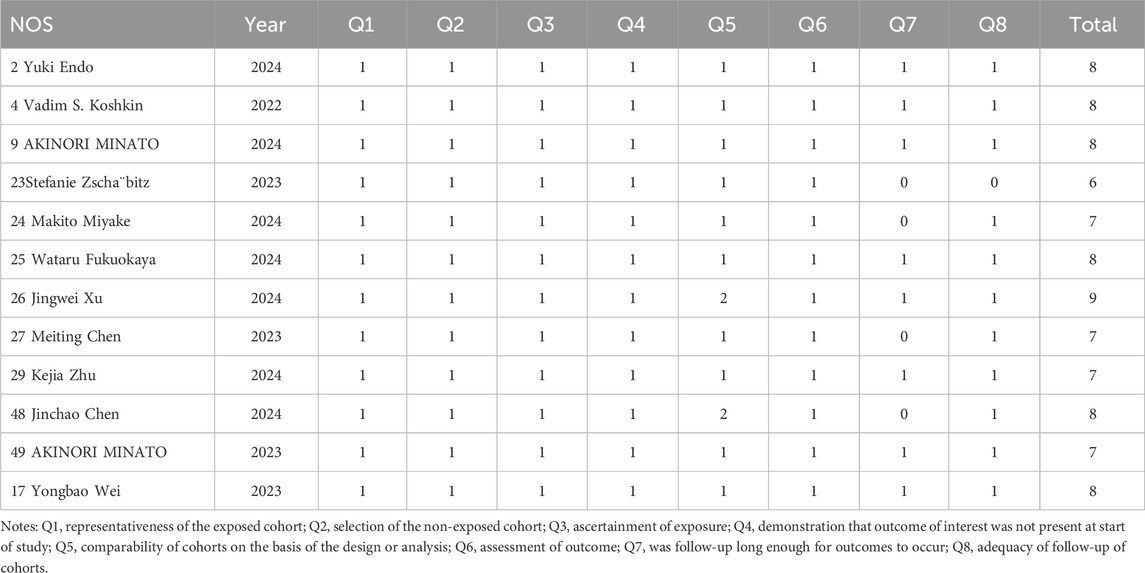
Data were independently retrieved from all included studies by two researchers (TL and XX), who then assessed the methodological quality of each study. The extracted data encompassed the author’s name, year of publication, National Clinical Trials identifier, country, sample size, study type, cancer type, HER2 expression, median age, intervention, molecular target, payload, median follow-up time, prior therapy, metastasis or not, lines of previous therapy, and endpoints reported. ORR, DCR, DOR, PFS, OS, the frequency of any adverse events (AEs), and the occurrence of grade 3 or higher AEs were used to evaluate clinical efficacy and safety results. Depending on the format of the included studies, the quality assessment can be divided into three categories: The updated Cochrane Collaboration’s Risk of Bias tool (RoB 2.0) (Sterne et al., 2019) was used to assess the methodological quality and risk of bias of randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS) (Slim et al., 2003) was used to evaluate single-arm experiments, and the Newcastle Ottawa Scale (NOS) (Stang, 2010) methodological index was used to evaluate cohort studies.
2.4 Statistical analysis
R version 4.4.0 was used to analyze the data for the meta-analysis. Heterogeneity was evaluated through the chi-squared test and the I2 statistic, with a p-value of <0.05 considered indicative of statistical significance. When there was significant heterogeneity (p < 0.05 and I2 > 50%), we used a random-effects model; otherwise, we employed a fixed-effects model. Sensitivity analyses were performed to evaluate the overall results’ stability and dependability. A funnel plot and Egger’s test were also used to investigate possible publication bias; a p-value of less than 0.05 indicates significance in statistics.
3 Results
3.1 Study selection
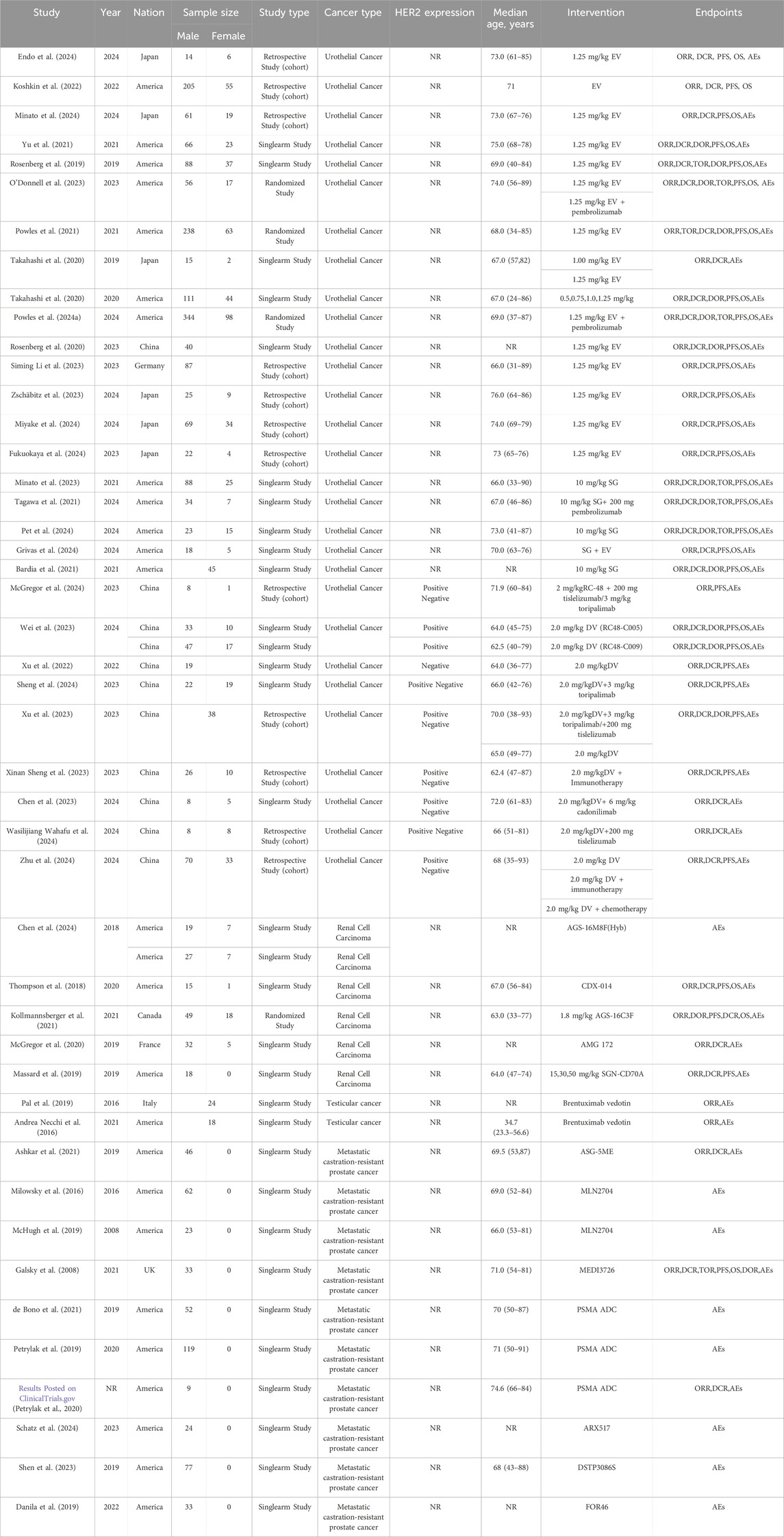
The preliminary search across seven databases (PubMed = 1,291, Embase = 2,725, Cochrane Library = 260, Web of Science = 1,995, CNKI = 9, VIP database = 5 and WanFang data = 9) yielded a total of 6,292 published studies. 140 studies were kept for additional review after duplicates were eliminated and titles and abstracts were screened. Following full-text assessment, 94 studies were excluded for reasons such as the absence of original data or accessible information, data duplication, failure to report relevant outcomes, or inclusion of only a single clinical trial on the TDM-1 drug. In the end, the meta-analysis had 46 studies with 3,250 patients that satisfied the inclusion criteria (Kollmannsberger et al., 2021; Koshkin et al., 2022; Milowsky et al., 2016; Powles et al., 2024a; O'Donnell et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2021; Powles et al., 2021; Pet et al., 2024; Bardia et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2023; Endo et al., 2024; Minato et al., 2024; Rosenberg et al., 2019; Takahashi et al., 2020; Rosenberg et al., 2020; Siming Li et al., 2023; Zschäbitz et al., 2023; Miyake et al., 2024; Fukuokaya et al., 2024; Minato et al., 2023; Tagawa et al., 2021; Grivas et al., 2024; McGregor et al., 2024; Wei et al., 2023; Sheng et al., 2024; Xinan Sheng et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2023; Wasilijiang Wahafu et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2024; Thompson et al., 2018; McGregor et al., 2020; Massard et al., 2019; Pal et al., 2019; Andrea Necchi et al., 2016; Ashkar et al., 2021; McHugh et al., 2019; Galsky et al., 2008; de Bono et al., 2021; Petrylak et al., 2019; Petrylak et al., 2020; Schatz et al., 2024; Shen et al., 2023; Danila et al., 2019; Aggarwal et al., 2022). Among these studies, 29 studies involved urothelial cancer, 5 studies related to renal cell carcinoma, 2 studies involved testicular cancer, 10 studies were on metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The National Clinical Trials Registry made the complete study results available, so even if NCT0202013567 was not original, it was nonetheless included in the analysis. Figure 1 shows the flowchart that depicts the literature selection procedure. Of the patients included, 198 had renal cell carcinoma, 42 had testicular cancer, 478 had metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, and 2,532 had confirmed urothelial carcinoma. Table 1 and Supplementary Table S1 provide detailed information about each included study.
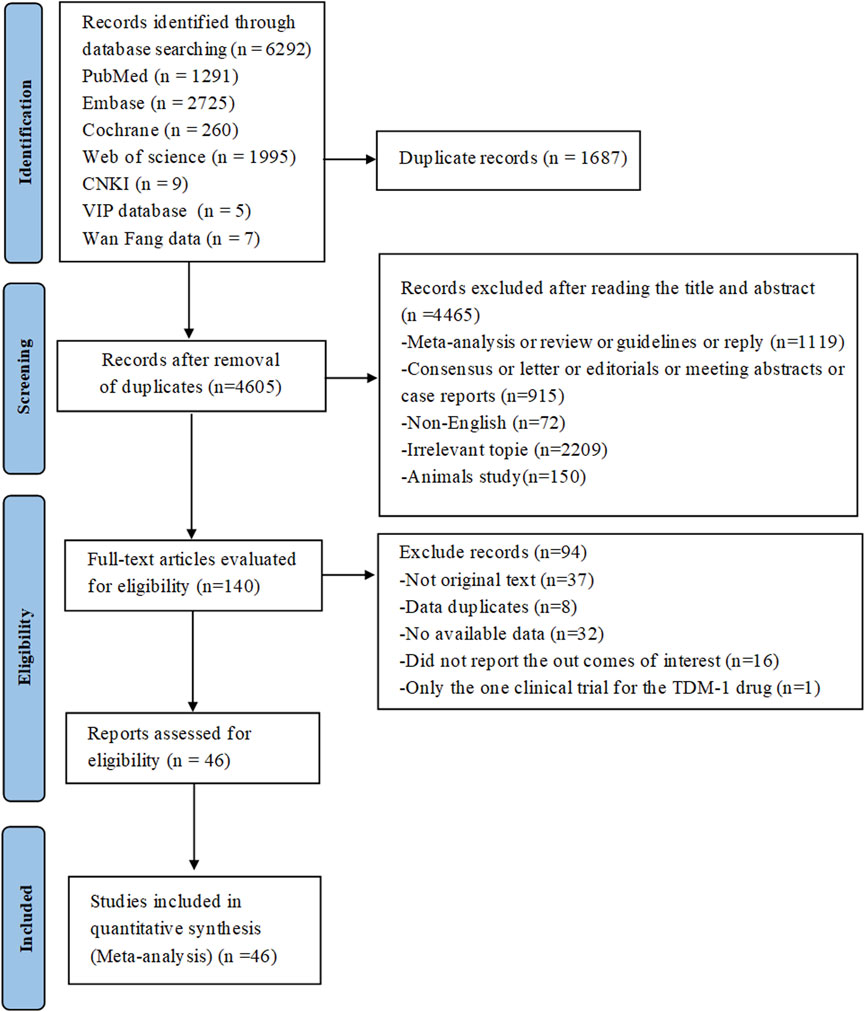
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram of the study process. PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis.
3.2 Quality assessment
The updated Cochrane Collaboration’s Risk of Bias tool (RoB 2.0) (Sterne et al., 2019) was used to examine four randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Random sequence creation, allocation concealment, participant and staff blinding, outcome assessor blinding, insufficient outcome data, selective reporting, and other possible sources of bias are among the seven domains that are assessed by the tool. Each domain is rated as low risk, high risk, or some concerns. For random sequence generation, all RCTs used appropriate methods to generate random sequences, such as computer-generated random numbers, ensuring low risk of bias in this domain. Allocation concealment was adequately addressed in all studies, with methods like sealed envelopes or centralized randomization systems, maintaining low risk. Blinding of participants and personnel was not always possible due to the nature of the interventions, leading to some concerns in this domain for two studies. However, blinding of outcome assessment was successfully implemented in all RCTs, resulting in low risk. Incomplete outcome data was minimal, with no significant dropouts or missing data, thus maintaining low risk. Selective reporting was assessed by comparing the study protocol and the published results, and all studies were found to have low risk in this domain. Other potential biases, such as funding sources and conflicts of interest, were also evaluated and found to be low risk. All randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were judged to have low risk of bias. Twelve cohort studies were assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (Stang, 2010), with the evaluation concentrating on three main areas: selection of the study population (scored 0–4), comparability between groups (scored 0–2), and outcome measurement (scored 0–3). And the maximum total score is 9. All cohort studies scored well on selection and outcome measurement, with scores ranging from 7 to 9. The comparability between groups was adequately addressed in all studies, ensuring high quality. Detailed scores for each study are provided in Tables 2–4. Studies that achieved a total score of 6 or higher were considered to be of high quality, and all of the cohort studies met this criterion. The Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies (MINORS), which consists of 12 criteria for evaluation, was used to evaluate thirty single-arm studies. Eight of these criteria are specifically applicable to non-randomized controlled studies, including clearly defined study objectives, uniformity in patient inclusion, and anticipated data collection, among other aspects34. Each criterion is scored from 0 to 2, with a maximum score of 16. All single-arm studies scored well on clearly stated aims and appropriate endpoints. However, only 15 studies calculated the sample size, and 10 studies had a loss to follow-up rate of less than 10%. The overall quality scores ranged from 12 to 16, indicating high methodological quality.
All of the studies included were categorized as low-risk, and the quality evaluation details are included in Tables 2–4.
3.3 Tumor response
3.3.1 Urothelial cancer
23 studies that were part of the analysis assessed the efficacy of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for urothelial cancer; the overall response rate (ORR) varied from 19% to 70%. Given the significant heterogeneity (I2 = 61.2%; p < 0.0001), a random-effects model was employed. The pooled ORR for all ADCs was 43% (95% CI: 39%–47%). Subgroup analyses were performed based on different interventions. The results revealed a pooled ORR of 46% (95% CI: 39%–53%) for patients treated with DV intervention, 43% (95% CI: 38%–48%) for those receiving EV intervention, 30% (95% CI: 20%–40%) for those treated with SG intervention, and 70% (95% CI: 47%–87%) for patients receiving a combination of SG and EV interventions (Figure 2a). Due to variations in HER2 status among urothelial cancer patients receiving DV treatment, a reanalysis of the studies was conducted. For the six studies reporting HER2 status, a subgroup analysis was performed based on IHC 0/1+ or IHC 2+/3+ classification. A pooled ORR of 49% (95% CI: 42%–57%) for patients with IHC 0/1+ and 60% (95% CI: 48%–71%) for patients with IHC 2+/3+ was found by the subgroup analysis (Figure 2b). Subgroup analysis was performed for the 29 studies that included various ADC monotherapies and combination therapies with immunotherapy. Patients treated with DV monotherapy had a pooled ORR of 45% (95% CI: 38%–53%), while those treated with DV in combination with immunotherapy had a pooled ORR of 64% (95% CI: 55%–72%) (Figure 2c). Patients receiving SG monotherapy had a pooled ORR of 30% (95% CI: 20%–40%), while those receiving SG combination therapy with pembrolizumab had a pooled ORR of 41% (95% CI: 26%–58%) (Figure 2d). Additionally, patients receiving EV monotherapy had a pooled ORR of 43% (95% CI: 38%–48%), while patients receiving EV combination therapy with pembrolizumab had a pooled ORR of 67% (95% CI: 63%–71%) (Figure 2e). For differences in drug dose on EV monotherapy, we also performed subgroup analysis. A pooled ORR of 43% (95% CI: 40%–45%) for individuals receiving 1.25 mg/kg and 23% (95% CI: 12%–34%) for patients taking a different dosage was found by subgroup analysis by doses of medication (Figure 2f). A pooled DCR of 76% (95% CI: 71%–80%) with considerable heterogeneity (I2 = 77.0%; p < 0.0001) was found after analyzing DCR data from 21 trials on ADCs. The subgroup analysis showed that patients receiving DV intervention had a pooled DCR of 88% (95% CI: 79%–96%), patients receiving EV intervention had a pooled DCR of 74% (95% CI: 69%–79%), patients receiving SG intervention had a pooled DCR of 65% (95% CI: 55%–75%), and patients receiving SG combination therapy with EV intervention had a pooled DCR of 83% (95% CI: 61%–95%) (Figure 3a). For the 25 studies of including different ADC drugs monotherapy and combination therapy with immunotherapy, subgroup analysis was performed. The subgroup analysis by ADCs drugs monotherapy or combination therapy indicated a pooled DCR of 88% (95% CI: 79%–96%) for DV monotherapy patients and 91% (95% CI: 85%–97%) for DV combination therapy with immunotherapy patients (Figure 3b). A pooled DCR of 65% (95% CI: 55%–75%) was observed for patients receiving SG monotherapy, and 63% (95% CI: 47%–78%) for those treated with SG combination therapy with pembrolizumab (Figure 3c). Similarly, the pooled DCR was 74% (95% CI: 69%–79%) for patients on EV monotherapy, and 87% (95% CI: 84%–90%) for patients receiving EV in combination with pembrolizumab (Figure 3d). Eight of the 46 studies that were part of the study revealed a median DOR (I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.5210). All ADCs had a pooled median DOR of 7.64 months (95% CI: 6.86–8.43). According to subgroup analysis, the DV group’s pooled median DOR was 8.09 months (95% CI: 5.26–10.91), the EV group’s was 7.61 months (95% CI: 6.78–8.45), and the SG group’s was 7.35 months (95% CI: 2.77–11.93) (Figure 3e).
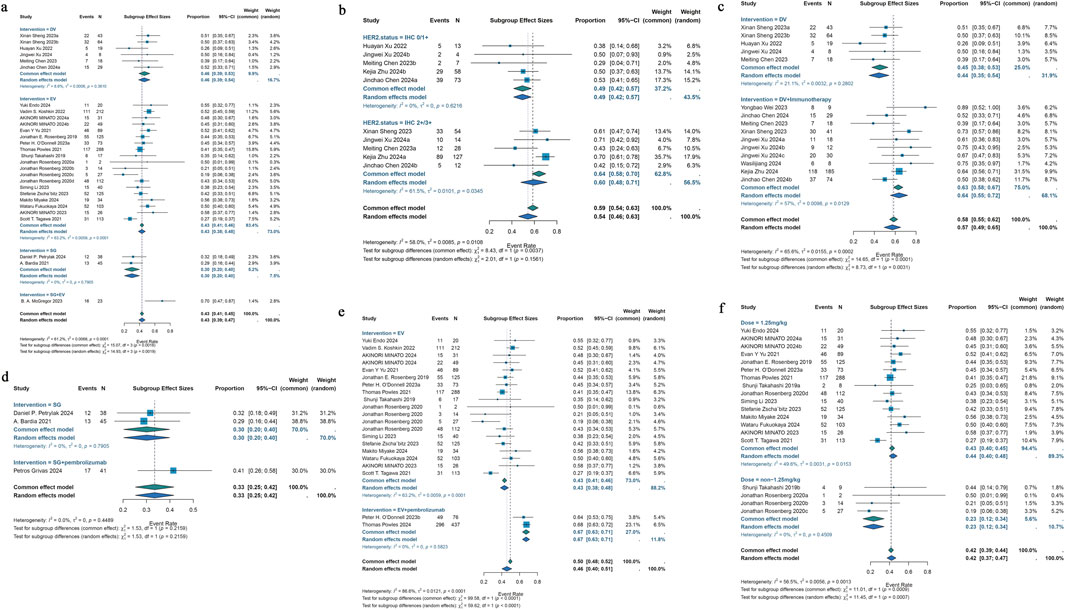
Figure 2. Forest plot for the pooled results of the different subgroup analysis in urothelial cancer studies. (a) ORR for intervention subgroup analysis (comparing EV, DV, SG, and combination therapies), (b) ORR for HER2 receptor status subgroup analysis (comparing IHC 0/1+ vs. IHC 2+/3+), (c) ORR for DV therapy whether combination with pembrolizumab therapy (comparing DV monotherapy vs. DV + pembrolizumab), (d) ORR for SG therapy whether combination with pembrolizumab therapy (comparing SG monotherapy vs. SG + pembrolizumab), (e) ORR for EV therapy whether combination with pembrolizumab therapy (comparing EV monotherapy vs. EV + pembrolizumab), (f) ORR for drug dose subgroup analysis (comparing 1.25 mg/kg vs. non-1.25 mg/kg EV dose). ORR, overall response rate; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; DV, disitamab vedotin; SG, sacituzumab govitecan; EV, enfortumab vedotin.
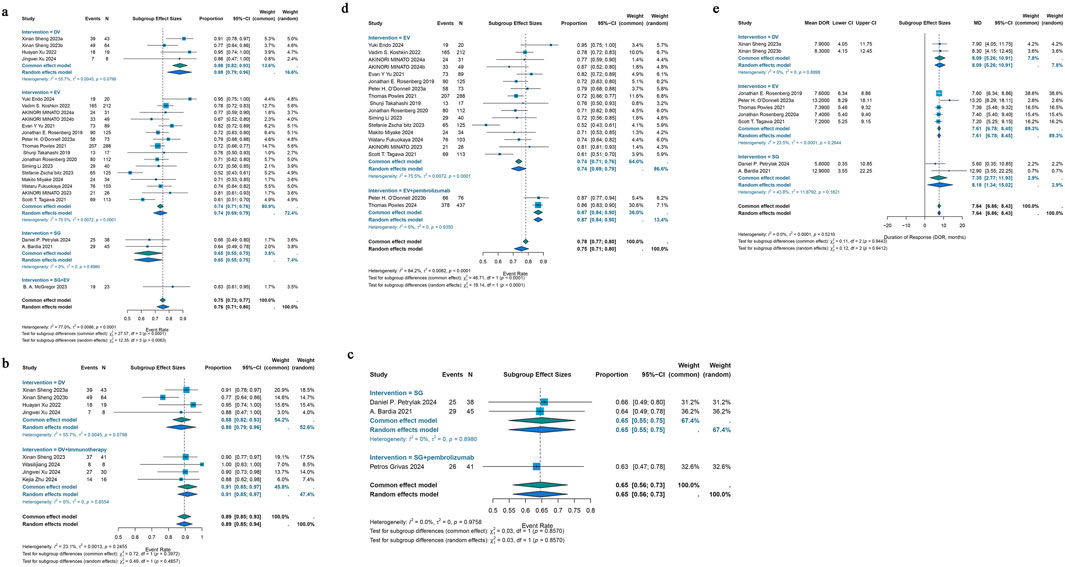
Figure 3. Forest plot for the pooled results of the different subgroup analysis in urothelial cancer studies. (a) DCR for intervention subgroup analysis, (b) DCR for DV therapy whether combination with pembrolizumab therapy, (c) DCR for SG therapy whether combination with pembrolizumab therapy, (d) DCR for EV therapy whether combination with pembrolizumab therapy, (e) DOR for intervention subgroup analysis in urothelial cancer studies. DCR, disease control rate; DOR, duration of response. DV, disitamab vedotin; SG, sacituzumab govitecan; EV, enfortumab vedotin.
3.3.2 Renal cell carcinoma
Five included studies demonstrated that ADCs were effective in treating renal cell cancer, with ORRs ranging from 5% to 7%. The pooled ORR was 6% (95% CI: 2%–10%) after a common-effects model was utilized (I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.9766) (Figure 4a). A pooled DCR of 39% (95% CI: 15%–63%) was found by analyzing the DCR data from these 5 trials; there was also notable heterogeneity (I2 = 92.4%; p < 0.0001) (Figure 4b).
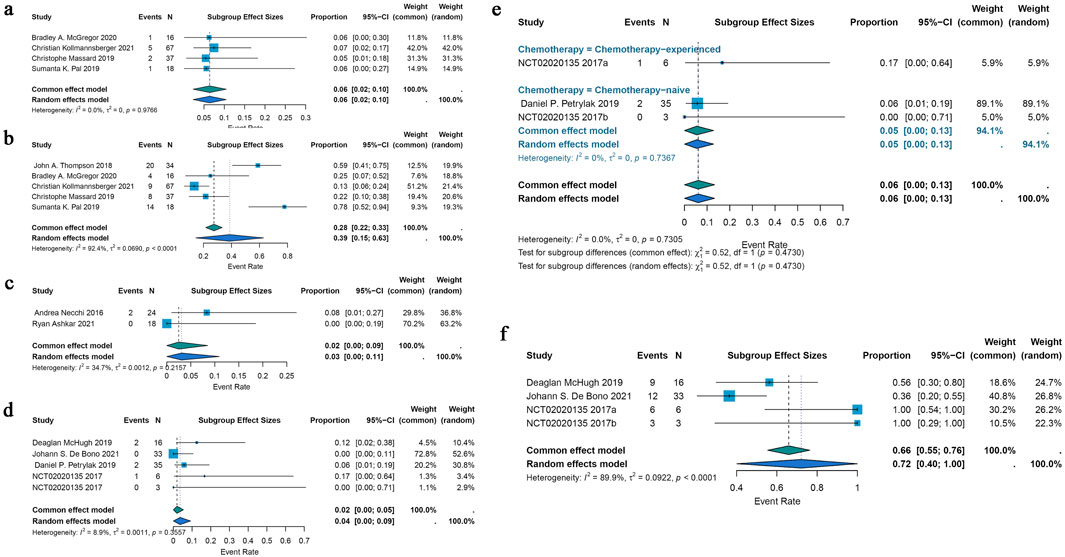
Figure 4. Forest plot for the pooled results of ORR, DCR in other urological cancers. (a) The pooled ORR for renal cell carcinoma studies, (b) the pooled DCR for renal cell carcinoma studies, (c) the pooled ORR in testicular cancer studies, (d) the pooled ORR in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, (e) ORR in chemotherapy-experienced group and chemotherapy-naive group for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, (f) the pooled DCR in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. ORR, overall response rate; DCR, disease control rate.
3.3.3 Testicular cancer
Only two included studies evaluated the efficacy of ADCs for testicular cancer, and their ORRs varied from 0% to 8%. A common effects model was employed in the research (I2 = 34.7%; p = 0.2157). Using the identical brentuximab vedotin of ADCs, the study revealed a pooled ORR of 2% (95% CI: 0%–9%) (Figure 4c).
3.3.4 Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
The efficacy of ADCs for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer was assessed in four studies that were part of the analysis; the ORR spanned 0%–17%. The pooled ORR for all ADCs was 2% (95% CI: 0%–5%) using a common-effects model (I2 = 8.9%; p = 0.3557) (Figure 4d). A subgroup analysis based on the various forms of chemotherapy was conducted. According to this study, individuals with chemotherapy-experience had a pooled ORR of 17% (95% CI: 0%–64%) while patients without chemotherapy had a pooled ORR of 5% (95% CI: 0%–13%) (Figure 4e). A pooled DCR of 72% (95% CI: 40%–100%) with considerable heterogeneity (I2 = 89.9%; p < 0.0001) was seen when DCR data from three trials on ADCs were analyzed (Figure 4f).
3.4 Survival
3.4.1 Urothelial cancer
For urothelial cancer, complete median OS data could only be extracted from 13 studies. Using a common-effects model, the pooled median OS was 11.90 months (95% CI: 11.04–12.77) (I2 = 45.0%; p = 0.0396). Analysis of subgroups was done based on interventions. Subgroup analysis showed a pooled median OS of 15.30 months (95% CI: 11.21–19.40) in patients with DV intervention, 11.55 months (95% CI: 10.63–12.47) in patients with EV intervention, and 14.42 months (95% CI: 11.02–17.82) in patients with SG intervention (Figure 5a). Of the 46 included trials, 20 studies had entire median PFS data that could be retrieved. In a random-effects model, the pooled median PFS was 6.07 months (95% CI: 5.48–6.65) (I2 = 66.2%; p < 0.0001). Subgroup analysis was conducted according to interventions. Subgroup analysis showed a pooled median PFS of 5.80 months (95% CI: 4.88–6.72) for DV monotherapy patients, 9.78 months (95% CI: 7.73–11.83) for DV combination therapy with immunotherapy patients, 5.52 months (95% CI: 5.32–5.72) for patients with EV monotherapy, 12.50 months (95% CI: 9.40–15.60) for patients with EV combination therapy with pembrolizumab, 5.99 months (95% CI: 4.26–7.72) for patients with SG monotherapy, 5.30 months (95% CI: 1.90–8.70) for patients with SG combination therapy with pembrolizumab (Figure 5b).
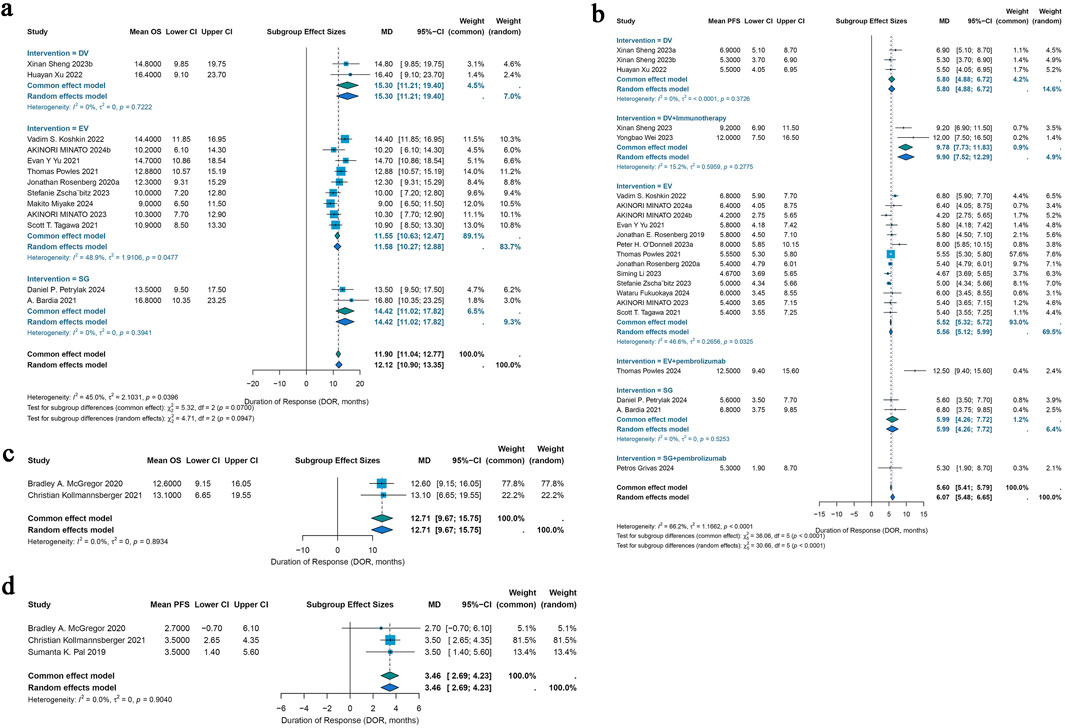
Figure 5. Forest plots for the pooled results of OS and PDS in urological cancer studies. (a) OS for different interventions subgroup analysis in urothelial cancer, (b) PFS for subgroup analysis of different monotherapy interventions and combination therapy with pembrolizumab interventions in urothelial cancer. (c) The pooled OS in renal cell carcinoma, (d) the pooled PFS in renal cell carcinoma. OS, overall survival; PFS, progress free survival.
3.4.2 Renal cell carcinoma
For renal cell carcinoma, median OS data were fully obtainable from only two studies, yielding a pooled median OS of 12.71 months under a common-effects model (95% CI: 9.67–15.75) with no observed heterogeneity (I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.8934) (Figure 5c). Among the 46 studies included, median PFS data were completely available in just three studies, resulting in a pooled median PFS of 3.46 months, also calculated using a common-effects model (95% CI: 2.69–4.23), with heterogeneity similarly absent (I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.9040) (Figure 5d).
3.5 Toxicity
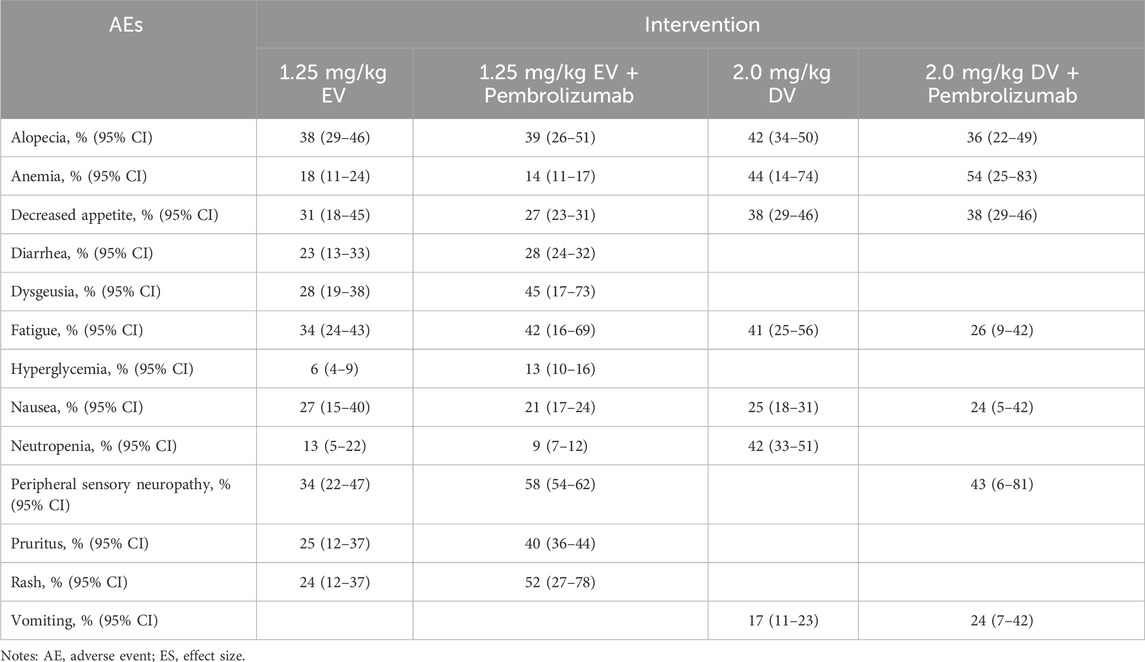
The analysis focused on the most frequent and clinically significant adverse events (AEs), including both all-grade and grade ≥ III, associated with urothelial cancer treatments. These interventions comprised EV monotherapy, EV combined with pembrolizumab, DV monotherapy, and DV in combination with pembrolizumab (Table 5), most patients had grade 1 or 2 adverse effects while undergoing treatment. With rates of 58% (95% CI: 54%–62%), 34% (95% CI: 22%–47%), and 34% (95% CI: 24%–43%), respectively, alopecia, peripheral sensory neuropathy, and dysgeusia were the three most frequently reported adverse effects in the EV monotherapy group. For EV combination therapy with pembrolizumab, peripheral sensory neuropathy, rash, and fatigue, with incidences of 38% (95% CI: 29%–46%), 52% (95% CI: 27%–78%), and 45% (95% CI: 17%–73%) were the most common adverse events. In the DV monotherapy group, anemia, alopecia, and neutropenia were more frequently reported, with corresponding rates of 44% (95% CI: 14%–74%), 42% (95% CI: 34%–50%), and 42% (95% CI: 33%–51%). Peripheral sensory neuropathy, anemia, and decreased appetite were the most common adverse events (AEs) for DV combined therapy with pembrolizumab, occurring in 54% (95% CI: 25%–83%), 43% (95% CI: 6%–81%), and 38% (95% CI: 29%–46%).
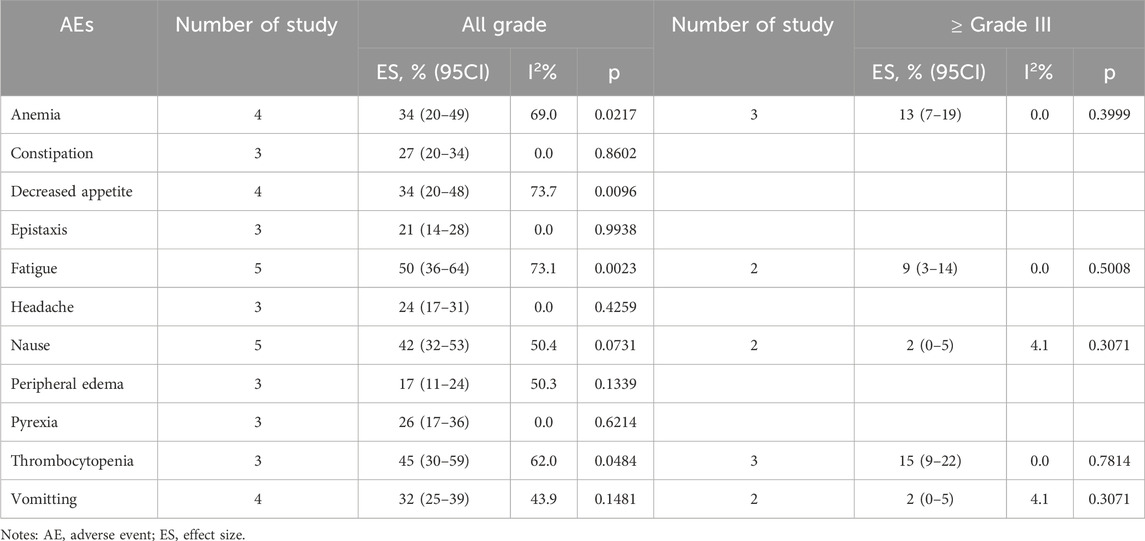
All ADCs were examined collectively to evaluate metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer and renal cell carcinoma overall safety (Tables 6, 7). Fatigue 50% (95% CI: 36%–64%), thrombocytopenia 45% (95% CI: 30%–59%), and nausea 42% (95% CI: 32%–53%) were the most frequent adverse events (AEs) among patients with renal cell carcinoma who received ADCs. Furthermore, peripheral neuropathy was the most frequent adverse event (AE) among patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer undergoing ADCs (58%; 95% CI: 40%–76%), fatigue (44%; 95% CI: 29%–59%), and nausea (40%; 95% CI: 28%–53%).
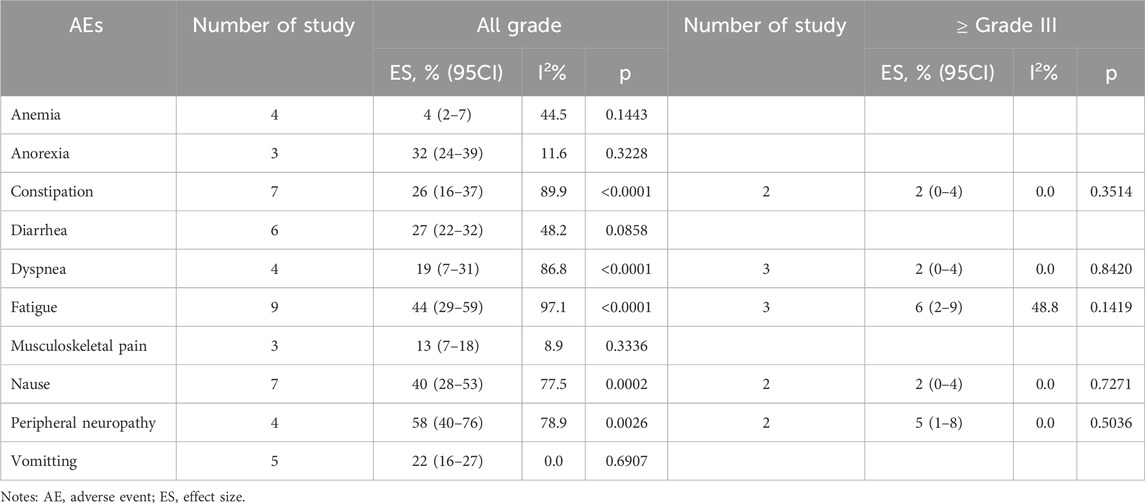
Table 7. Pooled results of adverse events of ADCs in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
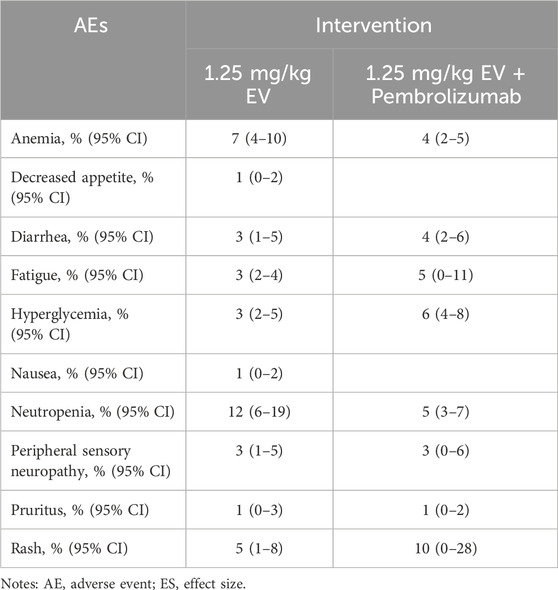
The incidence of high-grade AEs (above grade III) was small (Tables 6–8). Among patients with urothelial cancer, the incidence of neutropenia was 12% (95% CI: 6%–19%) in 1.25 mg/kg EV group, which is the most frequent high-grade AEs. And the incidences of thrombocytopenia and anemia were 15% (95% CI: 9%–22%) and 13% (95% CI: 7%–19%) respectively for renal cell carcinoma patients, which are the highest incidence of high-grade AEs.
3.6 Sensitivity analysis
In order to evaluate the reliability of the pooled effect sizes for ORR, DCR, DOR, OS, and PFS in patients with urothelial cancer, ORR, DCR, and PFS in patients with renal cell carcinoma, ORR in patients with testicular cancer, and ORR and DCR in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, we performed sensitivity analyses for outcomes with I2 >50% by sequentially excluding individual studies.
The sensitivity analysis of all included studies showed that the pooled results with 95% CI for both the DV and EV intervention groups in urothelial cancer, as well as the metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer group, were not notably influenced by any single study. This implies that the meta-analysis’s overall conclusions are solid and trustworthy. Supplementary Figure S1 displays the sensitivity analysis’s comprehensive findings.
3.7 Publication bias
In this study, publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots and Egger’s test. For the included urothelial cancer studies, the combined ORR (Egger’s test: p = 0.9173), DCR (Egger’s test: p = 0.828), median DOR (Egger’s test: p = 0.167) and median OS (Egger’s test: p = 0.0782) demonstrated no publication bias, but its median PFS (Egger’s test: p = 0.0469) had detected publication bias, but this did not affect the overall conclusions. For studies of renal cell carcinoma, the combined ORR (Egger’s test: p = 0.514), DCR (Egger’s test: p = 0.1399), and median PFS (Egger’s test: p = 0.4339) demonstrated no publication bias. About metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer studies, the combined ORR (Egger’s test: p = 0.1455) and DCR (Egger’s test: p = 0.4876) demonstrated no publication bias.
Due to the limited number of included studies, it was not possible to assess the combined ORR of patients with testicular cancer and the median OS of patients with renal cell carcinoma for publication bias. Supplementary Figure S2 provides a full account of the publishing bias results. Most AEs were free of publication bias, but publication bias was present for decreased appetite, dysgeusia, hyperglycemia, nausea and neutropenia in EV monotherapy group of urothelial cancer studies, constipation in renal cell carcinoma studies and constipation, dyspnea, fatigue in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer studies, among all grades AEs. Among the grade ≥ III AEs, publication bias was observed for decreased appetite, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, peripheral sensory neuropathy in EV monotherapy group of urothelial cancer studies.
4 Discussion
With over 100 ADCs currently in clinical research and 11 FDA-approved drugs currently in clinical utilization, ADCs are effective therapies for many kinds of cancers (Bordeau et al., 2023). They have the ability to minimize off-target effects while delivering strong cytotoxic chemicals straight to tumor cells. ADCs, first proposed by Ehrlich, enable selective binding tumor cells by fusing the effectiveness of cytotoxic medications with the accuracy of targeted antibodies. Because of the antibodies’ remarkable specificity and affinity for specific epitopes on the target antigen, this method enables the highly effective delivery of medicines, improving the index of therapy (Marei et al., 2022; Strebhardt and Ullrich, 2008; Hoffmann et al., 2018). Currently, three FDA-approved ADCs have been approved for the treatment of urological cancer. They are EV, SG, and RC-48. Compared with chemotherapy, pembrolizumab plus enfortumab vedotin showed a 55% lower risk of progressive disease or mortality. Furthermore, compared to the chemotherapy group, the percentage of urothelial carcinoma patients who showed an overall response was substantially higher in the enfortumab vedotin-pembrolizumab group (Powles et al., 2024a). In patients with urothelial cancer, single-agent EV produced a remarkable and encouraging outcome of 43% (Rosenberg et al., 2020). Reduced PSA and/or CTCs in individuals with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer were linked to prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) (Petrylak et al., 2019). All of the aforementioned findings underscore the robust efficacy of ADC therapy in treating urothelial cancers. Nevertheless, some research findings contradict this conclusion. When comparing AGS-16C3F to axitinib, the PFS of patients with renal cell carcinoma of any histology was not improved. The findings demonstrated that, in comparison to axitinib, AGS-16C3F did not increase PFS (Kollmannsberger et al., 2021). Based on existing research, we have found that almost all patients experienced adverse reactions at any level. Compared to the usual therapy group, the ADC groups experienced fewer treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or higher (Powles et al., 2024a). But some studies showed the incidence of some ≥ grade III adverse reactions, such as diarrhea, have the opposite effect (Kollmannsberger et al., 2021). Therefore, in light of the advancements in clinical trials, a meta-analysis, which is a high-quality evidence evaluation, reviewing the safety and efficacy of various ADC types in the treatment of advanced urological cancers is desperately needed. A total of 3,250 patients were included in this meta-analysis, which comprised 30 single-arm studies, 12 retrospective cohort studies, and 4 randomized controlled trials. We comprehensively assessed the differences in efficacy across various subgroups and examined the safety profile of ADCs in treating advanced urological cancers. Among the included studies, twenty-eight focused on advanced urothelial cancer, six on renal cell carcinoma, two on testicular cancer, and ten on metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. ADCs produced encouraging ORR and DCR in urothelial cancer, according to the pooled analysis, with PFS, OS, and DOR offering insightful information. All things considered, the results show that ADCs have a solid safety record and good therapeutic efficacy when used to treat these types of cancer.
For urothelial cancer, regardless of the interventions (including HER2 status, monotherapy, combination therapy with immunotherapy, and drug dosage), the pooled results from all studies showed an overall response rate (ORR) of 43% (95% CI: 39%–47%) and a disease control rate (DCR) of 76% (95% CI: 71%–80%). All treatment groups achieved median survival times, with a pooled median progression-free survival (PFS) of 6.07 months (95% CI: 5.48–6.65) and a median overall survival (OS) of 11.90 months (95% CI: 11.04–12.77). Additionally, the median duration of response (DOR) for urothelial cancer patients was 7.64 months. Subgroup analysis suggested higher ORR with SG-EV combination (70%) versus single-agent SG (30%) or EV (43%) and higher DCR (83% vs. 74%, 65%) than patients with DV intervention and EV intervention, indicating that SG combination with EV treatment was likely to have a better effect on advanced urothelial cancer. These results highlight the potential of ADCs as a first-line treatment option for patients with advanced urothelial cancer. Mutations in the HER2 gene are common in many types of cancer and play a major role in the development of new tumors and the spread of existing ones. Mechanistically, HER2 overexpression increases receptor clustering and subsequent endocytosis, promoting more efficient cellular uptake of DV (Majumdar and Siahaan, 2012). Furthermore, as demonstrated in HER2-overexpressing ovarian cancer models, accelerated internalization leads to faster lysosomal trafficking where proteolytic enzymes more efficiently cleave the linker, resulting in significantly higher intra-tumoral MMAE concentrations compared to serum levels (Zhu et al., 2021).Since overexpression of HER2 is connected to more aggressive disease, a higher risk of metastasis, and lower overall survival rates, it is strongly associated with a bad prognosis in urothelial cancer (Jimenez et al., 2001; Gan et al., 2021). Studies have indicated that patients receiving DV treatment with HER2 IHC 3+ expression tend to derive greater clinical benefits compared to those with HER2 IHC 2+ expression (Lei et al., 2023). This suggests that higher levels of HER2 overexpression may enhance the therapeutic efficacy of DV treatment in urothelial cancer patients. The powerful and remarkable efficiency of DV was also revealed by the ORR of 60% in IHC 2+/3+ expression compared to 49% in IHC 0/1+ expression of urothelial cancer. For the 29 studies of including different ADCs monotherapy and combination therapy with immunotherapy, subgroup analysis was performed. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved EV monotherapy for the treatment of patients with locally advanced (LA) or metastatic urothelial cancer (mUC) who have had at least one course of therapy and are not eligible for cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The favorable results seen in cohort 2 of the phase II EV-201 research served as the foundation for its authorization (Yu et al., 2021; Pet et al., 2024). The combination of EV and pembrolizumab was approved as the initial treatment for individuals with mUC who are ineligible for cisplatin and whose condition worsens after taking a checkpoint inhibitor (CPI) (Food and Administration, 2023). In 2015, it was suggested that ADC and immunotherapy might work better in combination (Gerber et al., 2016). Subsequent clinical data have confirmed this view, with the combination of ADC and immunotherapy providing significant clinical benefit to patients in several clinical trials for different types of cancer, including breast, lung and urothelial cancers. Through processes like immunogenic cell death, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and dendritic cell activation, ADCs interact with immune cells and cancer. These interactions can work in concert with immunotherapy. ADCs specifically promote T cell infiltration into the tumor microenvironment by stimulating tumor-specific adaptive immunity. Immunocheckpoint inhibitors, meanwhile, aid in reviving worn-out T cells, boosting anticancer immune responses even more (Nicolò et al., 2022). We found that the DCR of almost all patients receiving combination therapy with immunotherapy were higher than those receiving monotherapy. Compared to ADCs monotherapy, the combination therapy even more nearly doubled the figures of median PFS and ORR in urothelial cancer patients. From the data we analyzed, the ORR, DCR, DOR and OS of the DV group were better than those of the EV and SG groups. A humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets Nectin-4 is combined with a microtubule-disrupting agent, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), and a cleavable mc-val-cit-PABC linker to form EV, an ADC. Another ADC is SG, which is made up of a topoisomerase I inhibitor (SN-38) coupled to an anti-Trop-2 antibody (sacituzumab) via the hydrolyzable CL2A linker. Disitamab vedotin (DV/RC48) is an ADC that uses a monoclonal antibody (hertuzumab) to target the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) and is connected to MMAE by a mc-val-cit-PABC linker (Yu et al., 2023). By preferentially delivering MMAE to HER2-positive cells or tumor tissues, RC48-ADC has strong targeted delivery and release capabilities. This leads to less off-target toxicity and increased anti-tumor activity, which in turn reduces systemic toxicity and improves therapeutic efficacy (Li et al., 2020). The efficacy of an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is significantly influenced by the specificity and affinity of the antibody for the tumor antigen, as well as the dynamics of protein turnover between the cell membrane and cytoplasm (Hamilton et al., 2022). These factors contribute to the efficient targeting and internalization of the ADC, which are essential for delivering the therapeutic payload to the cancer cells and ensuring effective treatment outcomes. For safety and efficacy considerations, IgG1 antibodies are commonly employed in the construction of the immunoglobulin component of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). This choice helps minimize hypersensitivity reactions and enhances immune-mediated cytotoxicity. Additionally, the stability of the payload is largely determined by the linker used, which plays a critical role in controlling the timing of drug release. An optimal linker ensures that the therapeutic payload is released at the target site, avoiding premature or delayed drug activation that could compromise treatment effectiveness (Emens et al., 2019; Hamilton et al., 2021; Emens et al., 2020). Otherwise, the quantity of cytotoxic molecules attached to each antibody, or the drug-to-antibody ratio that occurs affects the drug’s stability and therapeutic efficacy (Emens et al., 2019). Finally, the payload plays a crucial role in inducing the direct cytotoxic effect (Fu et al., 2022; Peters et al., 2024). For differences in drug dose on EV monotherapy, we also performed subgroup analysis. EV should be administered intravenously on days 1, 8, and 15 of a cycle (28 days) at a dose of 1.25 mg/kg (up to a dose 125 mg) until the disease progresses or the toxicity becomes intolerable for both monotherapy and combination therapy. We also investigated whether varying doses of EV would lead to differences in efficacy. The results of our subgroup analysis revealed a higher overall response rate (ORR) in the 1.25 mg/kg dose group (43%, 95% CI: 40%–45%) compared to the non-1.25 mg/kg dose group (23%, 95% CI: 12%–34%). These findings suggest that a dose of 1.25 mg/kg of EV is more effective and may be preferable for urothelial cancer patients. ADCs had a hopeful DCR for renal cell carcinoma, according to the pooled analysis, while PFS and OS also had a reference value that demonstrated good efficacy and consistent safety. An ORR and DCR of 6% (95% CI: 2%–10%) and 39% (95% CI: 15%–63%), respectively, were included in the combined findings of all five investigations. Only three studies showed a median OS of 12.71 (95% CI: 9.67–15.75) months and two studies showed a median PFS of 3.46 (95% CI: 2.69–4.23) months. This suggests that further research is needed to identify more effective ADCs or combination therapies for this cancer type. Similarly, the limited number of studies on testicular cancer and metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer highlights the need for additional clinical trials to fully assess the potential of ADCs in these settings. For testicular cancer, only two studies treated with brentuximab vedotin were included showing an ORR of 2% (95% CI: 0%–9%). Therefore, we conclude that ADCs may have an important role in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma and testicular cancer, but more data are needed to support it. With regard to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, though there are no ADCs approved for prostate cancer, there are some ADCs targeting different antigens in clinical studies, such as PSMA, TROP-2, STEAP1, TF and DLL-3 (Sardinha et al., 2023). In our meta-analysis, the pooled results from all four studies revealed an ORR of 2% (95% CI: 0%–5%) and a DCR of 72% (95% CI: 40%–100%). We performed subgroup analyses to look more closely at how previous chemotherapy affected study results. The pooled ORR for chemotherapy-experienced patients was 17% (95% CI: 0%–64%), whereas the ORR for chemotherapy-naïve patients was 5% (95% CI: 0%–13%). Thus, chemotherapy-experienced patients demonstrated a higher overall response rate (ORR) compared to chemotherapy-naïve patients. Taken together, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) offer patients with advanced urological cancers new therapeutic alternatives with regard to clinical efficacy. According to our research of adverse events (AEs), almost all patients had at least one occurrence; in cases with urothelial cancer, peripheral sensory neuropathy, alopecia, and anemia were the most frequent. Most of the adverse reactions that occurred ≥ grade III had an incidence of less than 10%, which was greatly reduced. This indicates that ADCs are generally well-tolerated, although careful monitoring and management of side effects are essential. The most common AEs for renal cell carcinoma patients receiving ADCs were fatigue 50% (95% CI: 36%–64%), thrombocytopenia 45% (95% CI: 30%–59%) and nausea 42% (95% CI: 32%–53%). Additionally, peripheral neuropathy was the most frequent adverse event (AE) among patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer undergoing ADCs (58%; 95% CI: 40%–76%), fatigue (44%; 95% CI: 29%–59%), and nausea 40% (95 CI: 28%–53%). Above all, only three AEs ≥ grade III occurred at more than 10%. They were rash 10% (95% CI: 0%–28%) in urothelial cancer patients, thrombocytopenia 15% (95% CI: 9%–22%) and anemia 13% (95% CI: 7%–19%) respectively for renal cell carcinoma patients. Our results complement the recent study by Ren et al. on ADC monotherapies for urothelial carcinoma (Ren et al., 2024). While both studies share seven overlapping clinical trials, our analysis incorporated additional patient stratification and expanded the scope to include combination strategies with immunotherapy, ultimately encompassing 29 studies compared to their 12 monotherapy-focused investigations. Otherwise, we supplemented the analysis of efficacy with DOR to support the conclusion, which increased the reliability. These findings not only confirm the value of ADCs in urothelial carcinoma management but also highlight combination approaches as a promising therapeutic advancement with significant clinical potential.
While our analysis demonstrates promising clinical efficacy of ADCs in urological cancers, these benefits must be carefully balanced against their economic implications for real-world implementation. Currently, ADC therapies remain costly due to complex development and manufacturing processes, and their cost-effectiveness varies across healthcare systems (Zhu et al., 2022; Yeh et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). While improved response rates and survival outcomes may offset some of these expenses, broader accessibility will require pricing reforms, biosimilar competition, and value-based reimbursement models (Conti et al., 2021; Engelberg et al., 2022). Additionally, future studies should incorporate quality-of-life and cost-effectiveness analyses to better define their real-world utility. Despite these challenges, ADCs represent a significant therapeutic advance, and optimizing their affordability will be crucial for equitable patient access.
Our current meta-analysis has a number of limitations. First, a thorough investigation of the true effectiveness of ADCs in these advanced cancers was impeded by the small number of trials on patients with renal cell carcinoma, testicular cancer, and metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Additionally, some subgroup analyses were not possible for these groups. More high-quality studies are needed to fully understand ADC potential in these cancers. It is important to note that our analysis included both early-phase studies (Phase I) and late-phase studies (Phase II and III), as well as patients at different stages, due to incomplete reporting of trial characteristics. Moreover, some included studies were terminated after Phase I, which may limit the clinical applicability of the pooled results. Therefore, future research should focus on conducting more robust, later-phase clinical trials in well-defined patient populations to confirm the efficacy and safety of ADCs in different urological cancer types. Also, our meta-analysis is limited by the significant heterogeneity observed across the studies for most of the investigated clinical indications. This heterogeneity is likely due to differences in study populations, treatment protocols, and outcome measures. The low sample sizes of many included studies further complicate the interpretation of the results. For instance, several studies included in our analysis had sample sizes of less than 50 patients, which limits the statistical power and precision of the effect estimates (Figure 2). These limitations make it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about the comparative clinical efficacy of different ADCs. Despite these challenges, our meta-analysis remains valuable for several reasons. First, it provides a comprehensive synthesis of the available evidence, highlighting the potential benefits of ADCs in treating urological cancers. Second, it identifies areas where further research is needed, particularly in renal cell carcinoma, testicular cancer, and metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Future studies should aim to address these limitations by including larger sample sizes and using standardized outcome measures. Additionally, the use of random-effects models in our analysis helps account for the observed heterogeneity, providing a more conservative estimate of the treatment effects. Notably, with further clinical exploration of the use of ADCs in combination with immunotherapy, as well as the use of more types of ADCs in advanced urological cancers, it is believed that more promising therapeutic options will be available for patients in the near future.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, the effectiveness and safety of administering ADCs to patients with advanced urological cancer, especially urothelial cancer, was fully validated by our meta-analysis. Meanwhile, renal cell carcinoma, testicular cancer, and metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer all need further research to address these limitations by including larger sample sizes and using standardized outcome measures. It also warned us to be aware of several major adverse events related to various ADCs during the treatment of these cancers. The clinical data does have certain limitations, though, and further extensive multicenter randomized controlled studies are required to confirm our results.
Author contributions
TL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. Y-ZR: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. ZL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. MC: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. YY: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. LZ: Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financed by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82303876), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2023M741584), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2023A1515010325), President’s Foundation of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University (No. YQ202202).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer SCZ declared a shared affiliation with the author YY to the handling editor at the time of review.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1583654/full#supplementary-material
References
Aggarwal, R. R., Vuky, J., VanderWeele, D. J., Rettig, M., Heath, E. I., Beer, T. M., et al. (2022). Phase 1a/1b study of FOR46, an antibody drug conjugate (ADC), targeting CD46 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 40, 3001. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.3001
Andrea Necchi, D. M., Anichini, A., Raggi, D., Giannatempo, P., Nicolai, N., Colecchia, M., et al. (2016). An open-label, single-group, phase 2 study of brentuximab vedotin as salvage therapy for males with relapsed germ-cell tumors (GCT): results at the end of first stage (FM12GCT01). 34 480. Available online at: https://ascopubs.org/doi/10.1200/jco.2016.34.2_suppl.480.
Ashkar, R., Feldman, D. R., Adra, N., Zaid, M. A., Funt, S. A., Althouse, S. K., et al. (2021). Phase II trial of brentuximab vedotin in relapsed/refractory germ cell tumors. Invest New Drugs 39, 1656–1663. doi:10.1007/s10637-021-01134-1
Bardia, A., Messersmith, W. A., Kio, E. A., Berlin, J. D., Vahdat, L., Masters, G. A., et al. (2021). Sacituzumab govitecan, a Trop-2-directed antibody-drug conjugate, for patients with epithelial cancer: final safety and efficacy results from the phase I/II IMMU-132-01 basket trial. Ann. Oncol. official J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 32, 746–756. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2021.03.005
Bordeau, B. M., Nguyen, T. D., Polli, J. R., Chen, P., and Balthasar, J. P. (2023). Payload-binding fab fragments increase the therapeutic index of MMAE antibody-drug conjugates. Mol. Cancer Ther. 22, 459–470. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-22-0440
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74, 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Chang, E., Weinstock, C., Zhang, L., Charlab, R., Dorff, S. E., Gong, Y., et al. (2021). FDA approval summary: enfortumab vedotin for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Clin. cancer Res. official J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 27, 922–927. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-2275
Chen, M., Yao, K., Cao, M., Liu, H., Xue, C., Qin, T., et al. (2023). HER2-targeting antibody-drug conjugate RC48 alone or in combination with immunotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a multicenter, real-world study. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 72, 2309–2318. doi:10.1007/s00262-023-03419-1
Chen, J., Wang, M., Qi, X., Long, H., Qi, N., Wu, L., et al. (2024). RC48-Antibody-Drug conjugate in metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a multicenter real-world study in China. Clin. Genitourin. cancer 22, 102093. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2024.102093
Colombo, R., Tarantino, P., Rich, J. R., LoRusso, P. M., and de Vries, E. G. E. (2024). The journey of antibody-drug conjugates: lessons learned from 40 Years of development. Cancer Discov. 14, 2089–2108. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-24-0708
Conti, R. M., Frank, R. G., and Gruber, J. (2021). Regulating drug prices while increasing innovation. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, 1921–1923. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2113764
Danila, D. C., Szmulewitz, R. Z., Vaishampayan, U., Higano, C. S., Baron, A. D., Gilbert, H. N., et al. (2019). Phase I study of DSTP3086S, an antibody-drug conjugate targeting six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 1, in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 37, 3518–3527. doi:10.1200/jco.19.00646
de Bono, J. S., Fleming, M. T., Wang, J. S., Cathomas, R., Miralles, M. S., Bothos, J., et al. (2021). Phase I study of MEDI3726: a prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with mCRPC after failure of abiraterone or enzalutamide. Clin. Cancer Res. 27, 3602–3609. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-4528
de Vries, E. G. E., Rüschoff, J., Lolkema, M., Tabernero, J., Gianni, L., Voest, E., et al. (2023). Phase II study (KAMELEON) of single-agent T-DM1 in patients with HER2-positive advanced urothelial bladder cancer or pancreatic cancer/cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 12, 12071–12083. doi:10.1002/cam4.5893
Drago, J. Z., Modi, S., and Chandarlapaty, S. (2021). Unlocking the potential of antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 18, 327–344. doi:10.1038/s41571-021-00470-8
Dy, G. W., Gore, J. L., Forouzanfar, M. H., Naghavi, M., and Fitzmaurice, C. (2017). Global burden of urologic cancers, 1990-2013. Eur. Urol. 71, 437–446. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.10.008
Eisenhauer, E. A., Therasse, P., Bogaerts, J., Schwartz, L. H., Sargent, D., Ford, R., et al. (2009). New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 45, 228–247. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Emens, L. A., Esteva, F., Beresford, M., Saura, C., De Laurentiis, M., Kim, S. B., et al. (2019). Overall survival (OS) in KATE2, a phase II study of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor atezolizumab (atezo)+trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) vs placebo (pbo)+T-DM1 in previously treated HER2+ advanced breast cancer (BC). Ann. Oncol. 30, v104. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdz242
Emens, L. A., Esteva, F. J., Beresford, M., Saura, C., De Laurentiis, M., Kim, S. B., et al. (2020). Trastuzumab emtansine plus atezolizumab versus trastuzumab emtansine plus placebo in previously treated, HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (KATE2): a phase 2, multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet Oncol. 21, 1283–1295. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30465-4
Endo, Y., Akatsuka, J., Takeda, H., Hasegawa, H., Yanagi, M., Toyama, Y., et al. (2024). Real-world insights into efficacy and safety of enfortumab vedotin in Japanese patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma: findings, considerations, and future directions. Curr. Oncol. Tor. Ont. 31, 759–768. doi:10.3390/curroncol31020056
Engelberg, A. B., Avorn, J., and Kesselheim, A. S. (2022). A new way to contain unaffordable medication costs - exercising the government's existing Rights. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 1104–1106. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2117102
Food, U., and Administration, D. (2023). FDA grants accelerated approval to enfortumab vedotin-ejfv with pembrolizumab for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. FDA. Available online at: www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-enfortumab-vedotin-ejfv-pembrolizumab-locally-advanced-or-metastatic.
Fu, Z., Zhou, Y., Yan, T., and Lu, Y. (2022). Numerical modelling of drying induced cracks in wood discs using the extended finite element method. J. Renew. Mater. 11, 93–102. doi:10.32604/jrm.2022.021808
Fukuokaya, W., Koike, Y., Yata, Y., Komura, K., Uchimoto, T., Tsujino, T., et al. (2024). Real world evidence of enfortumab vedotin in patients with advanced urothelial cancer: a multicenter observational study. Int. J. urology official J. Jpn. Urological Assoc. 31, 342–347. doi:10.1111/iju.15368
Gabison, E. E., Rousseau, A., Labetoulle, M., Gazzah, A., and Besse, B. (2024). Ocular adverse events associated with antibody-drug conjugates used in cancer: focus on pathophysiology and management strategies. Prog. Retin Eye Res. 103, 101302. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2024.101302
Galsky, M. D., Eisenberger, M., Moore-Cooper, S., Kelly, W. K., Slovin, S. F., DeLaCruz, A., et al. (2008). Phase I trial of the prostate-specific membrane antigen-directed immunoconjugate MLN2704 in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 2147–2154. doi:10.1200/jco.2007.15.0532
Gan, K., Gao, Y., Liu, K., Xu, B., and Qin, W. (2021). The clinical significance and prognostic value of HER2 expression in bladder cancer: a meta-analysis and a bioinformatic analysis. Front. Oncol. 11, 653491. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.653491
Gerber, H. P., Sapra, P., Loganzo, F., and May, C. (2016). Combining antibody-drug conjugates and immune-mediated cancer therapy: what to expect? Biochem. Pharmacol. 102, 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2015.12.008
Grivas, P., Pouessel, D., Park, C. H., Barthelemy, P., Bupathi, M., Petrylak, D. P., et al. (2024). Sacituzumab govitecan in combination with pembrolizumab for patients with metastatic urothelial cancer that progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy: TROPHY-U-01 cohort 3. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 42, 1415–1425. doi:10.1200/jco.22.02835
Hamilton, E. P., Kaklamani, V., Falkson, C., Vidal, G. A., Ward, P. J., Patre, M., et al. (2021). Impact of anti-HER2 treatments combined with atezolizumab on the tumor immune microenvironment in early or metastatic breast cancer: results from a phase ib study. Clin. Breast Cancer 21, 539–551. doi:10.1016/j.clbc.2021.04.011
Hamilton, E. P., Shapiro, C., Boni, V., Martin Jimenez, M., Del Conte, G., Cortés, J., et al. (2022). 162O Primary analysis from DS8201-A-U105: a 2-part, open label, phase Ib trial assessing trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) with nivolumab (nivo) in patients (pts) with HER2-expressing advanced breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 33, S196. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.03.181
Hoffmann, R. M., Coumbe, B. G. T., Josephs, D. H., Mele, S., Ilieva, K. M., Cheung, A., et al. (2018). Antibody structure and engineering considerations for the design and function of Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs). Oncoimmunology 7, e1395127. doi:10.1080/2162402x.2017.1395127
Jimenez, R. E., Hussain, M., Bianco, F. J., Vaishampayan, U., Tabazcka, P., Sakr, W. A., et al. (2001). Her-2/neu overexpression in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: prognostic significance and comparative analysis in primary and metastatic tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 7, 2440–2447.
Kollmannsberger, C., Choueiri, T. K., Heng, D. Y. C., George, S., Jie, F., Croitoru, R., et al. (2021). A randomized phase II study of AGS-16C3F versus axitinib in previously treated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. 26, 182-e361. doi:10.1002/onco.13628
Koshkin, V. S., Henderson, N., James, M., Natesan, D., Freeman, D., Nizam, A., et al. (2022). Efficacy of enfortumab vedotin in advanced urothelial cancer: analysis from the urothelial cancer network to investigate therapeutic experiences (UNITE) study. Cancer 128, 1194–1205. doi:10.1002/cncr.34057
Lei, H., Ling, Y., Yuan, P., Yan, X., Wang, L., Shi, Y., et al. (2023). Assessment of the expression pattern of HER2 and its correlation with HER2-targeting antibody-drug conjugate therapy in urothelial cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 3, 121–128. doi:10.1016/j.jncc.2023.02.003
Li, L., Xu, M. Z., Wang, L., Jiang, J., Dong, L. H., Chen, F., et al. (2020). Conjugating MMAE to a novel anti-HER2 antibody for selective targeted delivery. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 12929–12937. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202012_24196
Maecker, H., Jonnalagadda, V., Bhakta, S., Jammalamadaka, V., and Junutula, J. R. (2023). Exploration of the antibody-drug conjugate clinical landscape. MAbs 15, 2229101. doi:10.1080/19420862.2023.2229101
Majumdar, S., and Siahaan, T. J. (2012). Peptide-mediated targeted drug delivery. Med. Res. Rev. 32, 637–658. doi:10.1002/med.20225
Marei, H. E., Cenciarelli, C., and Hasan, A. (2022). Potential of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 22, 255. doi:10.1186/s12935-022-02679-8
Marks, S., and Naidoo, J. (2022). Antibody drug conjugates in non-small cell lung cancer: an emerging therapeutic approach. Lung Cancer 163, 59–68. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.11.016
Massard, C., Soria, J. C., Krauss, J., Gordon, M., Lockhart, A. C., Rasmussen, E., et al. (2019). First-in-human study to assess safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the anti-CD27L antibody-drug conjugate AMG 172 in patients with relapsed/refractory renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 83, 1057–1063. doi:10.1007/s00280-019-03796-4
McCombs, J. R., and Owen, S. C. (2015). Antibody drug conjugates: design and selection of linker, payload and conjugation chemistry. Aaps J. 17, 339–351. doi:10.1208/s12248-014-9710-8
McGregor, B. A., Gordon, M., Flippot, R., Agarwal, N., George, S., Quinn, D. I., et al. (2020). Safety and efficacy of CDX-014, an antibody-drug conjugate directed against T cell immunoglobulin mucin-1 in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Investig. new drugs 38, 1807–1814. doi:10.1007/s10637-020-00945-y
McGregor, B. A., Sonpavde, G. P., Kwak, L., Regan, M. M., Gao, X., Hvidsten, H., et al. (2024). The Double Antibody Drug Conjugate (DAD) phase I trial: sacituzumab govitecan plus enfortumab vedotin for metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. official J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 35, 91–97. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2023.09.3114
McHugh, D., Eisenberger, M., Heath, E. I., Bruce, J., Danila, D. C., Rathkopf, D. E., et al. (2019). A phase I study of the antibody drug conjugate ASG-5ME, an SLC44A4-targeting antibody carrying auristatin E, in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Investig. new drugs 37, 1052–1060. doi:10.1007/s10637-019-00731-5
Milowsky, M. I., Galsky, M. D., Morris, M. J., Crona, D. J., George, D. J., Dreicer, R., et al. (2016). Phase 1/2 multiple ascending dose trial of the prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted antibody drug conjugate MLN2704 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 34, 530.e515–530. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.07.005
Minato, A., Kimuro, R., Ohno, D., Tanigawa, K., Kuretake, K., Matsukawa, T., et al. (2023). Efficacy and tolerability of enfortumab vedotin for metastatic urothelial carcinoma: early experience in the real world. Anticancer Res. 43, 4055–4060. doi:10.21873/anticanres.16594
Minato, A., Furubayashi, N., Tomoda, T., Masaoka, H., Song, Y., Hori, Y., et al. (2024). Clinical outcomes of enfortumab vedotin in advanced urothelial carcinoma with prior avelumab versus pembrolizumab therapy. Anticancer Res. 44, 3419–3426. doi:10.21873/anticanres.17162
Miyake, M., Nishimura, N., Oda, Y., Miyamoto, T., Ohmori, C., Takamatsu, N., et al. (2024). Enfortumab vedotin following platinum-based chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced urothelial carcinoma: response, survival and safety analysis from a multicentre real-world Japanese cohort. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 54, 329–338. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyad170
Nicolò, E., Giugliano, F., Ascione, L., Tarantino, P., Corti, C., Tolaney, S. M., et al. (2022). Combining antibody-drug conjugates with immunotherapy in solid tumors: current landscape and future perspectives. Cancer Treat. Rev. 106, 102395. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2022.102395
O'Donnell, P. H., Milowsky, M. I., Petrylak, D. P., Hoimes, C. J., Flaig, T. W., Mar, N., et al. (2023). Enfortumab vedotin with or without pembrolizumab in cisplatin-ineligible patients with previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 41, 4107–4117. doi:10.1200/jco.22.02887
Oldenburg, J., Berney, D. M., Bokemeyer, C., Climent, M. A., Daugaard, G., Gietema, J. A., et al. (2022). Testicular seminoma and non-seminoma: ESMO-EURACAN Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 33, 362–375. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.01.002
Pal, S. K., Forero-Torres, A., Thompson, J. A., Morris, J. C., Chhabra, S., Hoimes, C. J., et al. (2019). A phase 1 trial of SGN-CD70A in patients with CD70-positive, metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 125, 1124–1132. doi:10.1002/cncr.31912
Parker, C., Castro, E., Fizazi, K., Heidenreich, A., and Procopio, G. (2020). Prostate cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 31, 1119–1134. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.011
Petrylak, D. P., Tagawa, S. T., Jain, R. K., Bupathi, M., Balar, A., Kalebasty, A. R., et al. (2024). TROPHY-U-01 cohort 2: a phase II study of sacituzumab govitecan in cisplatin-ineligible patients with metastatic urothelial cancer progressing after previous checkpoint inhibitor therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 42, 3410–3420. doi:10.1200/jco.23.01720
Peters, S., Loi, S., André, F., Chandarlapaty, S., Felip, E., Finn, S. P., et al. (2024). Antibody–drug conjugates in lung and breast cancer: current evidence and future directions—a position statement from the ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation. Ann. Oncol. 35, 607–629. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2024.04.002
Petrylak, D. P., Kantoff, P., Vogelzang, N. J., Mega, A., Fleming, M. T., Stephenson, J. J., et al. (2019). Phase 1 study of PSMA ADC, an antibody-drug conjugate targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen, in chemotherapy-refractory prostate cancer. Prostate 79, 604–613. doi:10.1002/pros.23765
Petrylak, D. P., Vogelzang, N. J., Chatta, K., Fleming, M. T., Smith, D. C., Appleman, L. J., et al. (2020). PSMA ADC monotherapy in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer following abiraterone and/or enzalutamide: efficacy and safety in open-label single-arm phase 2 study. Prostate 80, 99–108. doi:10.1002/pros.23922
Powles, T., Rosenberg, J. E., Sonpavde, G. P., Loriot, Y., Durán, I., Lee, J. L., et al. (2021). Enfortumab vedotin in previously treated advanced urothelial carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 1125–1135. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035807
Powles, T., Bellmunt, J., Comperat, E., De Santis, M., Huddart, R., Loriot, Y., et al. (2022). Bladder cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. official J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 33, 244–258. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2021.11.012
Powles, T., Valderrama, B. P., Gupta, S., Bedke, J., Kikuchi, E., Hoffman-Censits, J., et al. (2024a). Enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab in untreated advanced urothelial cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 390, 875–888. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2312117
Powles, T., Albiges, L., Bex, A., Comperat, E., Grünwald, V., Kanesvaran, R., et al. (2024b). Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 35, 692–706. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2024.05.537
Ren, J. W., Chen, Z. Y., Bai, Y. J., and Han, P. (2024). Efficacy and safety of antibody-drug conjugates in the treatment of urothelial cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective clinical trials. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1377924. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1377924
Rosenberg, J. E., O'Donnell, P. H., Balar, A. V., McGregor, B. A., Heath, E. I., Yu, E. Y., et al. (2019). Pivotal trial of enfortumab vedotin in urothelial carcinoma after platinum and anti-programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 37, 2592–2600. doi:10.1200/jco.19.01140
Rosenberg, J., Sridhar, S. S., Zhang, J., Smith, D., Ruether, D., Flaig, T. W., et al. (2020). EV-101: a phase I study of single-agent enfortumab vedotin in patients with nectin-4-positive solid tumors, including metastatic urothelial carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 38, 1041–1049. doi:10.1200/jco.19.02044
Sardinha, M., Palma Dos Reis, A. F., Barreira, J. V., Fontes Sousa, M., Pacey, S., and Luz, R. (2023). Antibody-drug conjugates in prostate cancer: a systematic review. Cureus 15, e34490. doi:10.7759/cureus.34490
Schatz, C. A., Zitzmann-Kolbe, S., Moen, I., Klotz, M., Nair, S., Stargard, S., et al. (2024). Preclinical efficacy of a PSMA-targeted actinium-225 conjugate (225Ac-Macropa-Pelgifatamab): a targeted alpha therapy for prostate cancer. Clin. cancer Res. official J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 30, 2531–2544. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-23-3746
Shen, J., Pachynski, R., Nordquist, L., Adra, N., Bilen, M., Aggarwal, R., et al. (2023). 1804P APEX-01: first-in-human phase I/II study of ARX517 an anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) in patients (pts) with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Ann. Oncol. 34, S974–S975. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2023.09.2752
Sheng, X., Yan, X., Wang, L., Shi, Y., Yao, X., Luo, H., et al. (2021). Open-label, multicenter, phase II study of RC48-ADC, a HER2-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Clin. cancer Res. official J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 27, 43–51. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-2488
Sheng, X., Wang, L., He, Z., Shi, Y., Luo, H., Han, W., et al. (2024). Efficacy and safety of disitamab vedotin in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a combined analysis of two phase II clinical trials. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 42, 1391–1402. doi:10.1200/jco.22.02912
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Wagle, N. S., and Jemal, A. (2023). Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 73, 17–48. doi:10.3322/caac.21763
Siming Li, Y. S., Dong, H., Guo, H., Li, Y., Kadeerbai, H., Xu, C., et al. (2023). EV-203: phase 2 trial of enfortumab vedotin in patients with previously treated advanced urothelial carcinoma in China. 41 e16574. Available online at: https://ascopubs.org/.doi:10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_suppl.e16574
Slim, K., Nini, E., Forestier, D., Kwiatkowski, F., Panis, Y., and Chipponi, J. (2003). Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J. Surg. 73, 712–716. doi:10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
Stang, A. (2010). Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 25, 603–605. doi:10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
Sterne, J. A. C., Savović, J., Page, M. J., Elbers, R. G., Blencowe, N. S., Boutron, I., et al. (2019). RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 366, l4898. doi:10.1136/bmj.l4898
Strebhardt, K., and Ullrich, A. (2008). Paul Ehrlich's magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 473–480. doi:10.1038/nrc2394
Tagawa, S. T., Balar, A. V., Petrylak, D. P., Kalebasty, A. R., Loriot, Y., Fléchon, A., et al. (2021). TROPHY-U-01: a phase II open-label study of sacituzumab govitecan in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma progressing after platinum-based chemotherapy and checkpoint inhibitors. J. Clin. Oncol. official J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 39, 2474–2485. doi:10.1200/jco.20.03489
Takahashi, S., Uemura, M., Kimura, T., Kawasaki, Y., Takamoto, A., Yamaguchi, A., et al. (2020). A phase I study of enfortumab vedotin in Japanese patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Invesst New Drugs 38, 1056–1066. doi:10.1007/s10637-019-00844-x
Tarantino, P., Carmagnani Pestana, R., Corti, C., Modi, S., Bardia, A., Tolaney, S. M., et al. (2022). Antibody-drug conjugates: smart chemotherapy delivery across tumor histologies. CA Cancer J. Clin. 72, 165–182. doi:10.3322/caac.21705
Thompson, J. A., Motzer, R. J., Molina, A. M., Choueiri, T. K., Heath, E. I., Redman, B. G., et al. (2018). Phase I trials of anti-ENPP3 antibody-drug conjugates in advanced refractory renal cell carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 24, 4399–4406. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-18-0481
U.S.Food and administration (2021). FDA grants accelerated approval to sacituzumab govitecan for advanced urothelial cancer. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-sacituzumab-govitecan-advanced-urothelial-cancer.
Wang, J., Yi, Y., Wan, X., Zeng, X., Peng, Y., and Tan, C. (2022). Cost-effectiveness analysis of trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer in the USA. Adv. Ther. 39, 4583–4593. doi:10.1007/s12325-022-02273-4
Wasilijiang Wahafu, S. W., Qiao, X., Zhang, Xi, Wang, M., Han, S., Cui, Yu, et al. (2024). Disitamab vedotin (DV, RC48-ADC) combined with cadonilimab (anti-PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (la/mUC): An open-label, single-arm, phase II study. 42 e16572. Available online at: https://ascopubs.org/doi/10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.e16572.
Wei, Y., Zhang, R., Yu, C., Hong, Z., and Lin, L. (2023). Disitamab vedotin in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors for locally and locally advanced bladder urothelial carcinoma: a two-center's real-world study. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1230395. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1230395
World Cancer Research Fund International (2023). Cancer trends. Available online at: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends.
Xinan Sheng, L. Z., Yang, K., Zhang, S., Xu, H., Yan, X., Li, S., et al. (2023). Disitamab vedotin, a novel humanized anti-HER2 antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), combined with toripalimab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: an open-label phase 1b/2 study. 41 4566. Available online at: https://ascopubs.org/doi/10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_suppl.4566.
Xu, H., Zhou, L., Yan, X., Li, S., Chi, Z., Cui, C., et al. (2022). A phase II study of RC48-ADC in HER2-negative patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. 40 4519. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.4519
Xu, J., Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Chu, X., Li, Y., Li, G., et al. (2023). Real-world effectiveness and safety of RC48-ADC alone or in combination with PD-1 inhibitors for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a multicenter, retrospective clinical study. Cancer Med. 12, 21159–21171. doi:10.1002/cam4.6680
Yeh, Y., Chen, C., and Ko, Y. (2022). Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of trastuzumab emtansine in women with HER2-positive locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 18, 1061–1072. doi:10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_1095_21
Yu, E. Y., Petrylak, D. P., O'Donnell, P. H., Lee, J. L., van der Heijden, M. S., Loriot, Y., et al. (2021). Enfortumab vedotin after PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors in cisplatin-ineligible patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma (EV-201): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 22, 872–882. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(21)00094-2
Yu, J., Wu, S., Li, R., Jiang, Y., Zheng, J., Li, Z., et al. (2023). Novel ADCs and combination therapy in urothelial carcinoma: latest updates from the 2023 ASCO-GU Cancers Symposium. J. Hematol. and Oncol. 16, 85. doi:10.1186/s13045-023-01475-9
Zhu, Y., Zhu, X., Wei, X., Tang, C., and Zhang, W. (2021). HER2-targeted therapies in gastric cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1876, 188549. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188549
Zhu, Y., Liu, K., Wang, M., Wang, K., and Zhu, H. (2022). Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine for patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Breast 66, 191–198. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2022.10.010
Zhu, K., Chang, Y., Zhao, D., Guo, A., Cao, J., Wu, C., et al. (2024). Expression of HER2 in high-grade urothelial carcinoma based on Chinese expert consensus and the clinical effects of disitamab vedotin-tislelizumab combination therapy in the treatment of advanced patients. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1355081. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1355081
Keywords: antibody-drug conjugates, urological cancers, efficacy, safety, meta-analysis
Citation: Liu T, Xie X, Ren Y-Z, Li Z, Cai M, Yu Y and Zhuo L (2025) Efficacy and safety of antibody-drug conjugates in the treatment of advanced urological cancers: a systematic review and a meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1583654. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1583654
Received: 26 February 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Fenglei Huang, Boehringer Ingelheim, GermanyReviewed by:
Kata Mazalin, Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH and Co KG, AustriaShan-Chao Zhao, Southern Medical University, China
Wenbin Chen, Shanghai JiaoTong University School of Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Xie, Ren, Li, Cai, Yu and Zhuo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maoping Cai, bXBjYWkyNEBtLmZ1ZGFuLmR1LmNu; Yuzhong Yu , MTM1MzQ2MjA0OUBxcS5jb20=; Lin Zhuo, emh1b2xpbnB4QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Tian Liu1†
Tian Liu1† Xiao Xie
Xiao Xie Yuzhong Yu
Yuzhong Yu Lin Zhuo
Lin Zhuo