- 1Department of Orthopedics, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital, Taiyuan, China
- 2Department of Cardiology, Shuozhou People’s Hospital, Shuozhou, China
- 3Department of Geriatric Medicine, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Tongji Shanxi Hospital, Taiyuan, China
Purinergic P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) is a widely distributed, non-selective ATP-gated ion channel that plays a crucial role in the regulation of neuropathic pain, inflammatory pain, and cancer pain. Understanding the function and mechanisms of P2X7R in these various pain conditions, as well as utilizing P2X7R-targeted treatments, may offer a promising strategy for alleviating or resolving pathological pain. As a result, P2X7R and its antagonists have been the subject of extensive research, leading to the development of several P2X7R antagonists that have shown promising antinociceptive effects in numerous preclinical studies. However, further investigation and development are still necessary to fully realize their therapeutic potential. This review will provide an overview of the structure and function of P2X7R, its role in different pathological pain conditions, and the latest advances in the development of P2X7R antagonists, with the goal of offering new insights into the treatment of pathological pain.
1 Introduction
Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience, and it is one of the primary reasons patients seek medical care. Not only does pain affect the physical health of the individual, but chronic pain can also have a significant impact on mental health. Additionally, pain can impose a considerable economic burden on both the patient’s family and society at large. Pain varies widely in type and nature, with complex mechanisms underlying its onset. Investigating the generation and pathophysiology of pain provides essential insights for developing effective strategies for its relief or resolution in clinical settings, as well as for the discovery of novel analgesic therapies.
According to the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP), pain is classified into three major types based on its underlying mechanisms: nociceptive pain, neuropathic pain, and nociplastic pain. Nociceptive pain is caused by the activation of nociceptors in response to actual or potential tissue damage (Costigan et al., 2009; Woolf, 2010; Abd-Elsayed and Deer, 2019). Neuropathic pain results from direct injury or dysfunction of the nervous system. Nociplastic pain, on the other hand, arises from central nervous system sensitization without clear evidence of nerve damage or tissue injury (Fitzcharles et al., 2021; Yoo and Kim, 2024). This review primarily focuses on neuropathic pain while also considering the broader category of pathological pain, which includes inflammatory pain and cancer pain.
Current research indicates that P2X7R, a type of extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-gated, non-selective cation channel (Surprenant et al., 1996; Hu et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024), plays a pivotal role in the initiation and maintenance of pathological pain through various peripheral and central mechanisms (Kim, 2016). Due to its significant regulatory role in the onset and progression of pathological pain, P2X7R has emerged as a promising therapeutic target for treating such conditions. As a result, it has become a focal point of research in the field of pain management in recent years.
2 The Biological characteristics of P2X7R
2.1 The structure of P2X7R
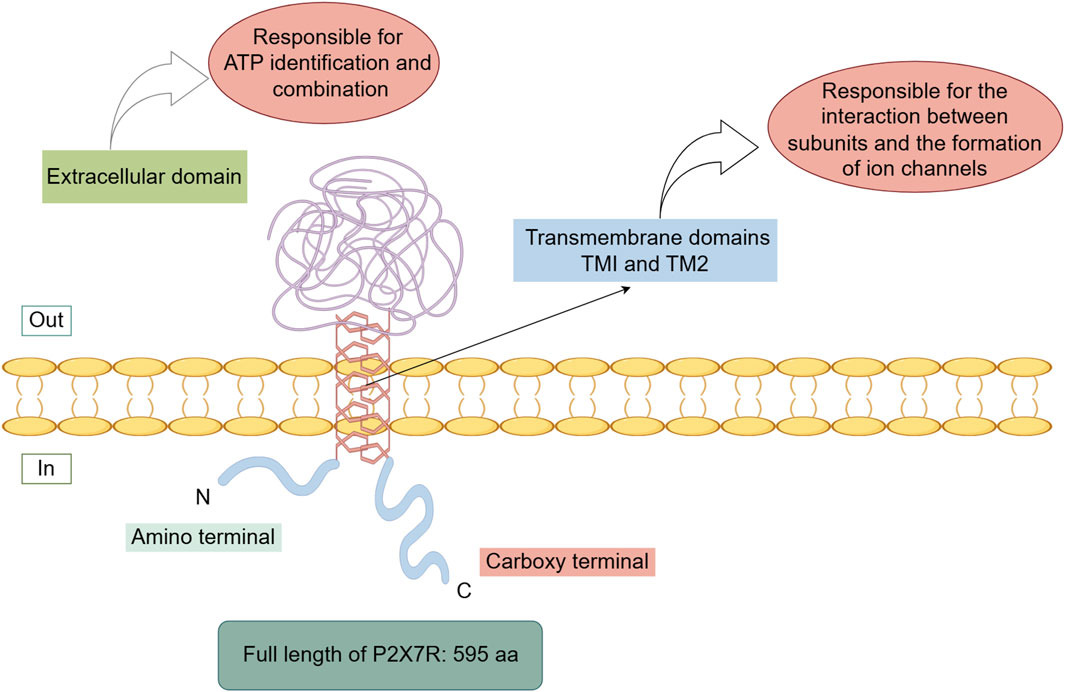
The human P2X7R is a transmembrane protein consisting of 595 amino acids (Roger et al., 2015; Li et al., 2020; Rotondo et al., 2022), located on chromosome 12 (Di Virgilio et al., 2017; Ren and Illes, 2022; Zhang et al., 2023). Both the N-terminus and C-terminus of P2X7R are intracellular. The N-terminus is relatively short, which has the function of regulating calcium influx (Boué-Grabot et al., 2000; Michel et al., 2008; Karasawa and Kawate, 2016) and are associated with interactions involving extracellular-regulated protein kinases. The C-terminus is longer compared to other P2X receptors and serves as the structural basis for its specialized functions. This region participates in many critical functions of P2X7R, such as modulating receptor activity, regulating signaling pathway activation, influencing cellular localization, facilitating protein-protein interactions, and supporting post-translational modifications (Gonnord et al., 2009; Costa-Junior et al., 2011; Lara et al., 2020). It also plays a crucial role in the transition from non-selective ion channel activity to the formation of a large pore upon receptor activation.
P2X7R primarily consists of two transmembrane domains (TM1 and TM2) and a large extracellular domain (Valera et al., 1994; Surprenant et al., 1996; Karasawa and Kawate, 2016; McCarthy et al., 2019). The transmembrane domains are composed of six α-helical structures, with three central α-helices (TM2) residing within the ion permeation pathway, and three peripheral α-helices (TM1) positioned outside this pathway. The extracellular domain is composed of 14 β-strands and four α-helices (Jiang et al., 2021). The transmembrane domains are primarily responsible for subunit interactions and ion channel formation, while the extracellular domain is predominantly involved in ATP recognition and binding (Figure 1).
2.2 The distribution of P2X7R
P2X7R is widely distributed throughout the human body, with expression observed in various cells within the nervous and immune systems. Additionally, it is found in numerous other cell types, including tumor cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, renal cells, and cardiomyocytes (Platania et al., 2019; Dong et al., 2020). Within the central nervous system, P2X7R is predominantly expressed in microglial cells but is also present in some neurons (Kan et al., 2019). In the peripheral nervous system, P2X7R is primarily localized in sensory neurons and certain non-neuronal cells (Wu et al., 2021). In the immune system, P2X7R is mainly found in macrophages, dendritic cells, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, and neutrophils, among other immune cells (von Mücke-Heim and Deussing, 2023). In tumor cells, P2X7R has been identified in various types of cancer, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, bone cancer, and gliomas (Zhang et al., 2020).
2.3 The function of P2X7R
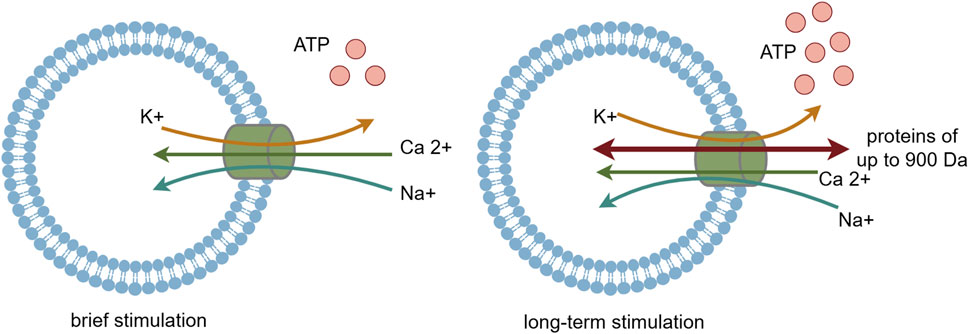
P2X7R is classified as an ATP-activated, ligand-gated ion channel receptor. ATP serves as its natural agonist, and it needs higher concentration of ATP to activate P2X7 receptor compared with other P2XR subtypes. Upon brief ATP stimulation, P2X7R is activated, opening cation channels that lead to an influx of Na+ and Ca2+ and an efflux of K+, with the influx of Ca2+ being predominant (Surprenant et al., 1996; Di Virgilio et al., 2017; Adinolfi et al., 2018). Additionally, activated P2X7R facilitates the release of various inflammatory mediators, including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-18 (IL-18), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) (Perregaux and Gabel, 1998; Solle et al., 2001; Savio et al., 2018; Lara et al., 2020). Among these mediators, IL-1β induces the production of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), nitric oxide synthase (NOS), and other enzymes, contributing to the development of hyperalgesia.
With prolonged ATP stimulation, P2X7R forms non-selective membrane pores that are permeable to large biomolecules up to 900 Da in molecular weight (Steinberg et al., 1987; Falzoni et al., 1995; Surprenant et al., 1996; Virginio et al., 1999; Shih et al., 2011; Hechler and Gachet, 2015). This allows these molecules to enter the cell, disrupting the balance of ion permeability across the cell membrane and ultimately leading to cell death (Figure 2). P2X7R plays a crucial role in various physiological and pathological processes, including inflammation, immune responses, cell death, and neurosignaling. Recent studies have also highlighted P2X7R’s pivotal role in neural conduction, particularly in the transmission of nociceptive signals (Drill et al., 2021), suggesting that P2X7R could be a potential target for the assessment and treatment of pathological pain.
3 P2X7R and pathological pain
3.1 P2X7R and neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain arises from damage to the somatosensory nervous system and is associated with inflammatory stimuli that activate specific neuronal pathways involved in generating nociceptive responses (Finnerup et al., 2021). Research indicates that P2X7R plays a significant role in the development and persistence of neuropathic pain and ATP primarily activates purinergic receptors through damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), subsequently inducing pain (Grace et al., 2018). Commonly used models for studying neuropathic pain include the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model, spared nerve injury (SNI) model, partial sciatic nerve ligation (PNL) model, spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model, and spinal cord transection (SCT) model. SNL, CCI, and SCT have all been shown to increase the expression of P2X7R in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia (DRG) (Yu et al., 2018b; Zhang et al., 2019). Studies by Chessell and Fulgenzi demonstrated that SNI and SNL do not induce hyperalgesia in P2X7R knockout mice (Chessell et al., 2005; Fulgenzi et al., 2008). Li et al. discovered that microvesicles (MVs) secreted by microglia in the cerebrospinal fluid of SNL rats rely on the P2X7R-p38 MAPK pathway to release IL-1β, which contributes to pain by inducing central sensitization. Furthermore, Li et al. found that in an SNL rat model, the expression and production of P2X7R in spinal microglia increase, leading to hyperalgesia (Li et al., 2017). Intrathecal injection of purinergic receptor inhibitors in this model resulted in a dose-dependent reduction in mechanical allodynia. Additionally, studies have shown that in a paclitaxel (a cytostatic/antitumor substance)-induced peripheral neuropathy model, the expression of P2X7R in spinal microglia is upregulated, which correlates with higher levels of mechanical allodynia (Ochi-ishi et al., 2014). Kataoka et al. (2009) demonstrated that in a rat diabetes model, exogenous ATP activated the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) through the P2X7R, which in turn promoted the release of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 (CCL3) in microglia, ultimately leading to hyperalgesia in rats. Lu et al. (Lu et al., 2022) investigated a trigeminal neuralgia (TN) rat model and found that transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells (OEC) to the site of infraorbital nerve ligation reduced P2X7R expression in the trigeminal ganglion. This intervention significantly increased the mechanical pain threshold in the rats’ faces, demonstrating a beneficial therapeutic effect for TN. Liu et al. examined the relationship between the pain-relieving effects of moxibustion (a traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves burning moxa, which is made from dried mugwort, near or on specific points of the body to promote healing) and P2X7R expression levels in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of rats subjected to chronic inflammatory stimulation through colorectal distension. They observed that moxibustion downregulated P2X7R expression, leading to a reduction in pain sensation (Liu et al., 2015b). In addition,In human studies, it has been observed that neuropathic pain patients exhibit significantly higher levels of P2X7R mRNA and protein in lymphocytes and monocytes compared to healthy controls (Luchting et al., 2016).
P2X7 receptors (P2X7Rs) are predominantly expressed in microglia, but they are also found in other glial cells, including astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Activation of P2X7R triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and excitotoxic transmitters such as glutamate and ATP. Additionally, P2X7R may play a role in signal transmission from glial cells to neurons under conditions of elevated ATP concentrations, particularly during neuropathic pain (Zhao et al., 2021).
These findings collectively suggest that P2X7R plays a crucial role in neuropathic pain, and targeting P2X7R may provide a potential therapeutic strategy to alleviate pain in such patients.
3.2 P2X7R and inflammatory pain
Inflammatory pain refers to pain that arises as a result of an inflammatory response triggered by peripheral tissue injury. Recent studies have shown that the P2X7R is closely associated with inflammatory responses and the development of pain, playing a crucial role in the progression of inflammatory pain. P2X7R is a well-characterized pro-inflammatory signaling receptor. During inflammation, elevated extracellular ATP levels activate P2X7R, leading to the release of various pro-inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1β, IL-18, TNF-α, and nitric oxide, which collectively contribute to the induction of inflammatory pain (Staunton et al., 2013; Allsopp et al., 2017). Furthermore, it has been reported that P2X7R activation promotes the assembly and recruitment of components of the NLRP3 inflammasome (Mariathasan et al., 2006; Karmakar et al., 2016). The NLRP3 inflammasome is an intracellular multiprotein complex consisting of the carrier protein caspase-1, the adaptor protein ASC, and the sensor protein NLRP3, which detects danger signals (Huang et al., 2021). Upon activation, NLRP3 triggers the conversion of full-length caspase-1 into its active form (He et al., 2016; Yang et al., 2019). Activated caspase-1 then cleaves pro-IL-1β, leading to the generation and release of mature IL-1β, thus initiating the inflammatory response (Perregaux and Gabel, 1994).
Research has shown that in a rat model of arthritis induced by monosodium iodoacetate (MIA), P2X7R expression is upregulated in spinal microglial cells, leading to the activation of PANX1 channels and the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β. Antagonizing or knocking out spinal microglial P2X7R alleviates MIA-induced mechanical allodynia (Mousseau et al., 2018). In a chronic pancreatitis visceral pain model in rats induced by 2% nitrobenzene sulfonic acid, P2X7R expression in the spinal cord is significantly upregulated. Furthermore, intrathecal injection of siRNA to knock down spinal P2X7R suppresses the expression of nociceptive behaviors in chronic pancreatitis rats (Liu et al., 2015a).
Additionally, Chessell et al. (2005) assessed the relative weight-bearing distribution between the FCA-injected (ipsilateral) and the contralateral hindpaws. Analysis of the ipsilateral/contralateral weight-bearing ration revealed a significant genotype effect. P2X7−/− mice did not exhibit notable hypersensitivity at any time point after FCA injection, while P2X7+/+ mice displayed a significant reduction in the ipsilateral/contralateral ratio at both testing points. Similarly, Fulgenzi and colleagues found that in collagen-induced arthritis model mice and acetic acid-induced visceral pain model mice, the absence of the P2X7R gene prevents the manifestation of hyperalgesia (Fulgenzi et al., 2008). Numerous other studies support these findings. For instance, in carrageenan-induced arthritis, P2X7R mediates hyperalgesia through the release of pro-inflammatory factors and neutrophil migration. Teixeira et al. (2018) found that intra-articular injection of P2X7R agonist—2′(3′)-O-(4-Benzoylbenzoyl) adenosine 5-triphosphate (BzATP) into rat knees activates P2X7R, inducing the release of bradykinin, prostaglandins, sympathetic amines, and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which contribute to the maintenance of knee joint hyperalgesia in rats. In summary, P2X7R plays a crucial role in mediating the development of inflammatory pain.
3.3 P2X7R and cancer pain
Cancer pain refers to pain associated with cancer, caused directly or indirectly by the tumor. The pain is not limited to the tumor site and causes significant suffering for cancer patients. Cancer treatments often involve pain management therapies to alleviate this symptom. P2X7R has been shown to play a crucial role in cancer development, being highly expressed in various malignancies, including lung, colon (Rotondo et al., 2022), bone, prostate (Slater et al., 2004a), breast, and skin cancer (Greig et al., 2003; Slater et al., 2004b), as well as in neuroblastoma (Raffaghello et al., 2006), thyroid carcinoma (Solini et al., 2008), and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. It serves as a target for mediating cancer-related pain (Hansen et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2015; Bernier et al., 2018; Lara et al., 2020).
Research by Zhao et al. (2016) demonstrated that P2X7R plays a significant role in cancer pain. The researchers developed a bone cancer pain model by injecting Lewis lung cancer cells into the bone marrow cavity of the femur in both C57BL/6J wild-type mice and P2X7R knockout mice. Notably, they observed that the P2X7R knockout mice did not exhibit the pain behaviors typically induced by bone cancer in the model. Similarly, Yang et al. (2015) observed that in a rat model of bone cancer, spinal microglial P2X7R expression, phosphorylated p38 MAPK, and IL-18 levels were increased. Inhibition of the spinal P2X7R/p38/IL-18 pathway resulted in a reduction of pain behaviors in late-stage bone cancer. Similarly, Li et al. (2018) observed a mild increase in P2X7R expression in the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) of the midbrain aqueduct in a rat model of bone cancer pain. Intraperitoneal injection of tramadol (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) dose-dependently reduced pain-related behaviors in bone cancer pain rats, and further upregulated P2X7R expression in the vlPAG. The analgesic effect of tramadol was reversed by selective P2X7R antagonists. This suggests that tramadol may reduce norepinephrine (NE) reuptake in the vlPAG, thereby increasing local NE levels, which in turn elevates ATP concentrations and upregulates the expression of P2X7Rs in the vlPAG.
Research suggests that bone cancer pain shares characteristics with both inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Inhibiting P2X7R in spinal microglia can alleviate bone cancer pain by reducing spinal nerve hyperactivity through the p38/IL-18 pathway (Yang et al., 2015). Additionally, it can mitigate bone cancer pain by inhibiting NF-κB/p65, NLRP3-mediated inflammasome formation, and IL-1β expression (Wu et al., 2022). Moreover, P2X7R may not only be involved in mediating pain but also in tumor growth in cancers. Qiu et al., (2014) found that P2X7Rs are highly expressed in prostate cancer cells. Using siRNA technology to downregulate P2X7R expression significantly inhibited ATP or BzATP-induced migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells in vitro, as well as tumor invasion and metastasis in nude mice.
4 The application of P2X7R antagonists in pathological pain
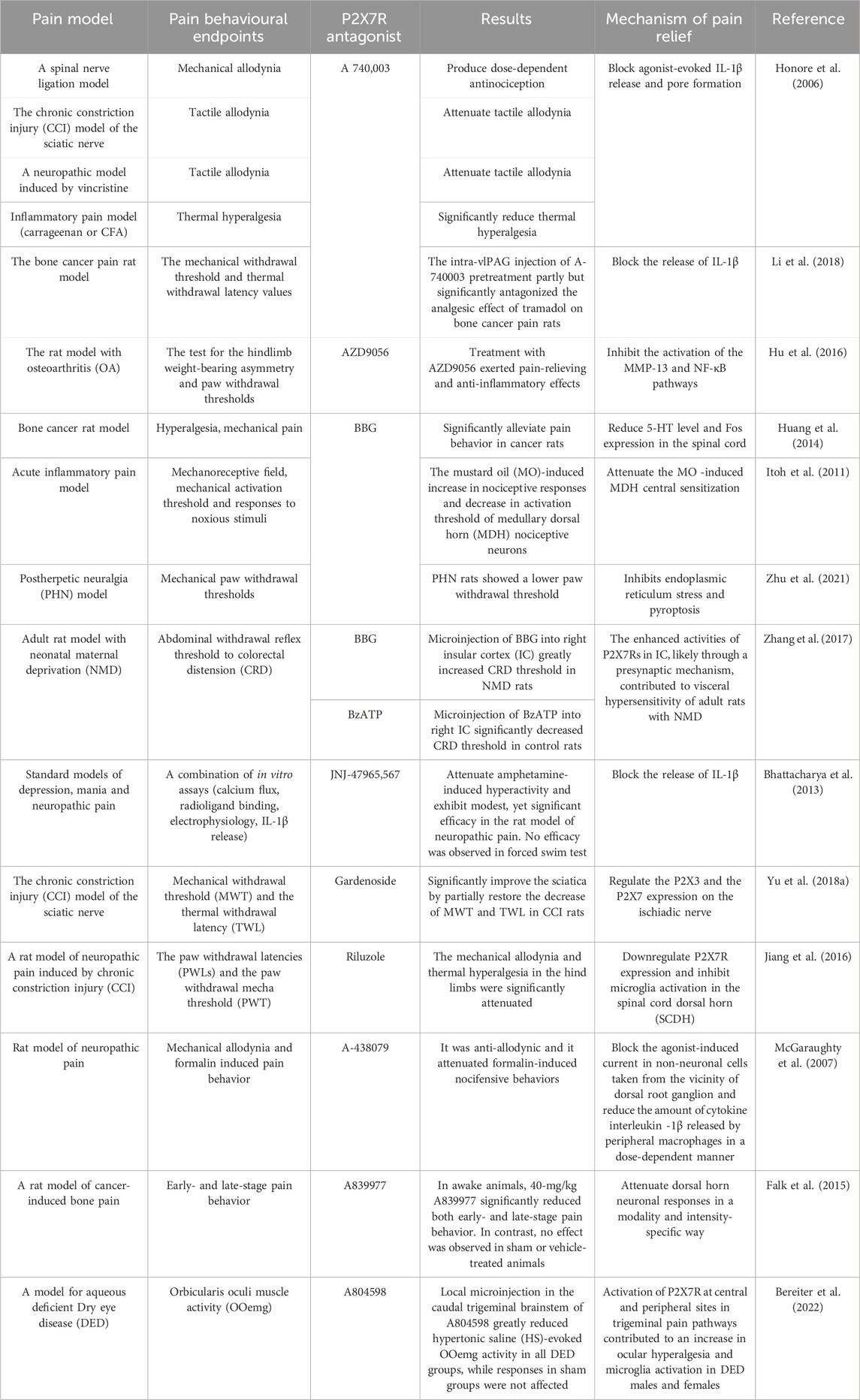
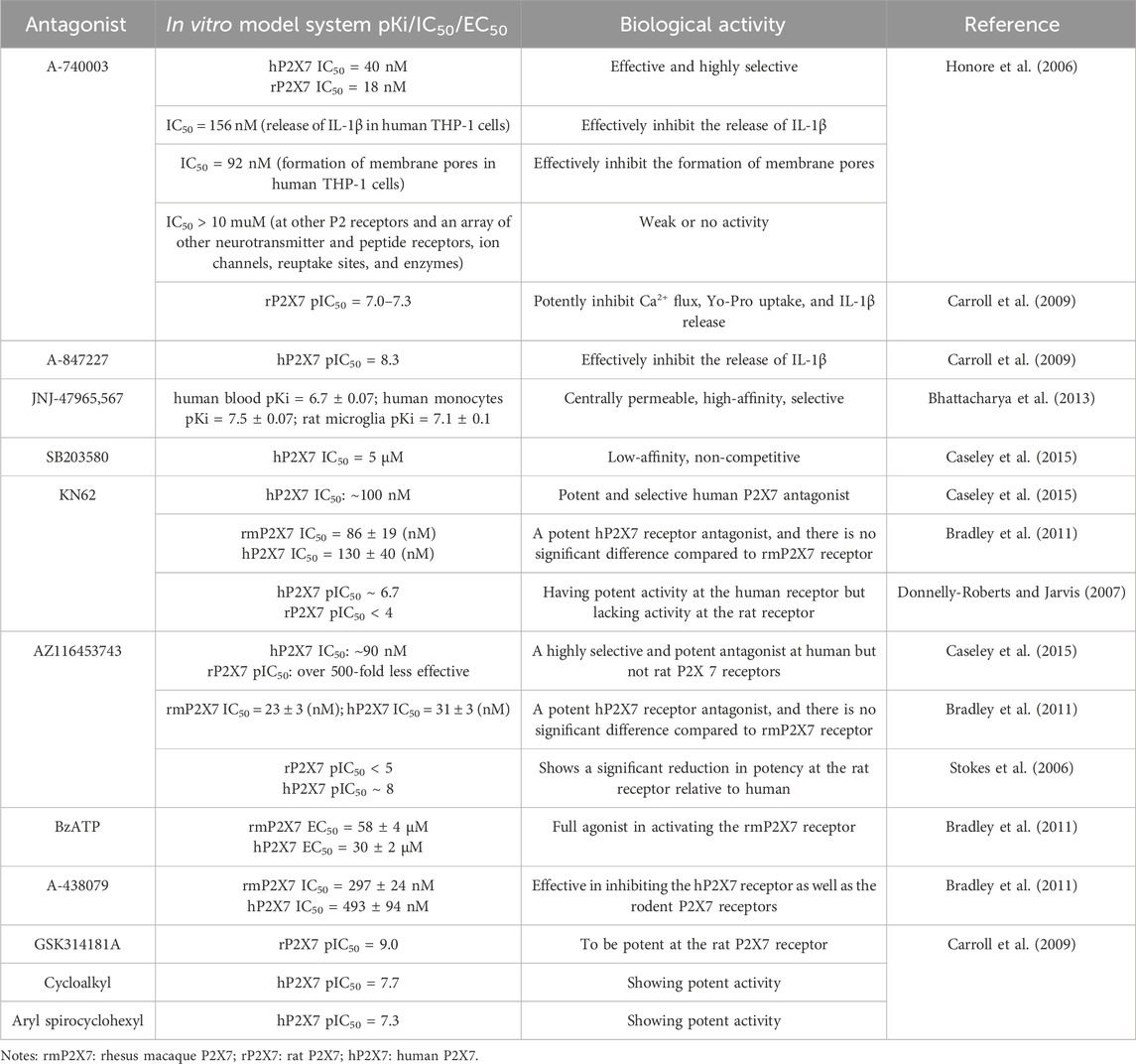
Given the regulatory role of the P2X7R in pathological pain, this receptor has emerged as a promising target for the treatment of such pain and has garnered significant attention within the research community. To date, numerous P2X7R antagonists have been developed, and extensive preclinical studies have been conducted using rodent pain models (Table 1), including in vitro pharmacological investigations (Table 2). These studies have demonstrated that P2X7R antagonists effectively alleviate pain symptoms associated with neurological, inflammatory, and cancer-related conditions by inhibiting P2X7R activity.
4.1 The application of P2X7R antagonists in neuropathic pain
P2X7R antagonists have been shown to alleviate neuropathic pain while also enhancing immune suppression and neuroprotection, a finding confirmed relatively early in various preclinical studies (Honore et al., 2006; Carroll et al., 2009; Andó et al., 2010; Kobayashi et al., 2011). Studies indicate that in a rat spinal cord injury (SCI) model, administration of the P2X7R antagonist Brilliant Blue G (BBG) significantly inhibits neuronal apoptosis. Similarly, intrathecal injection of the P2X7R antagonist A740003 reduces mechanical allodynia induced by SNL and CCI (Chessell et al., 2005). Moreover, intrathecal injection of P2X7R antagonist A438079 alleviates hyperalgesia in mice following trigeminal nerve transection. Bhattacharya et al. (2013) demonstrated that using the P2X7R antagonist JNJ-47965567 with central permeability, high affinity and selectivity in rodent models of central nervous system neuropathic pain reduces Bz-ATP-induced IL-1β release, thereby reducing pain. Yu et al. (Jiang et al., 2016; Yu et al., 2018a) found that non-selective P2X7R inhibitors, such as geniposide and riluzole, inhibit the release of immune factors like NOS, IL-1β, and TNF-α, while also suppressing activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. This ultimately reduces the activation of central microglia and alleviates neuropathic pain in rats. Furthermore, in diabetic neuropathic pain, the P2X7R antagonist BBG can suppress P2X7R-mediated hippocampal glial cell excitation and IL-1β production and release, thereby alleviating diabetes-induced neuropathic pain. In models of sciatic nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain, the application of P2X7R antagonists BBG and A740003 significantly reduces sciatic pain (Li et al., 2018). Additionally, P2X7R antagonist A740003 alleviates CCI and vincristine-induced neuropathic pain, while A438079 attenuates neuropathic pain induced by SNL and CCI (McGaraughty et al., 2007). Thus, the use of P2X7R antagonists has demonstrated efficacy in treating neuropathic pain.
4.2 The application of P2X7R antagonists in inflammatory pain
Given the relationship between P2X7R and inflammatory pain, numerous P2X7R antagonists have been developed to alleviate inflammatory pain, and their efficacy has been confirmed in extensive studies. Research has shown that intra-articular injection of Freund’s Complete Adjuvant (FCA) significantly lowers the nociceptive threshold in rats, increasing P2X7R expression at the mRNA level in nerve fibers and blood vessels of the hind paws. The use of the P2X7R antagonist A740003 markedly reduces inflammatory pain in FCA-induced arthritis model rats and decreases P2X7R expression at the inflammation site. Clark et al. (2010) suggested that P2X7R contributes to pain by targeting microglial cells to release IL-1β, and the administration of P2X7R antagonists, such as A740003, A438079, and oxATP, can inhibit IL-1β release. Zhang et al. (2017) discovered that P2X7R sensitizes rat Insular cortex (IC) neurons through a presynaptic mechanism, and BBG can block P2X7R at presynaptic sites, alleviating inflammatory pain. Teixeira et al. (2018) found that the P2X7R antagonist A740003 could block bradykinin- and dopamine-induced joint hyperalgesia. In animal models of knee osteoarthritis, the use of P2X7R antagonists significantly reduced the concentration of inflammatory factors such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-13), substance P, and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in the joints, thereby alleviating osteoarthritic pain (Hu et al., 2016). Additionally, Itoh et al. (2011) found that the P2X7R antagonist BBG effectively alleviates inflammatory pain induced by mustard oil. A438079 relieves pain behaviors induced by FCA, bee venom, and carrageenan, while A740003 and A438079 reduce spontaneous nociceptive behaviors in the second phase of the formalin pain model, which corresponds to the peripheral inflammatory pain stage. Other studies have shown that the P2X7R antagonist oxATP effectively inhibits inflammatory pain induced by FCA, carrageenan, collagen, lipopolysaccharide, and mustard oil (Fulgenzi et al., 2005; Fulgenzi et al., 2008; Clark et al., 2010). These findings indicate that widely used P2X7R antagonists exhibit significant analgesic effects across various types of inflammatory pain.
4.3 The application of P2X7R antagonists in cancer pain
In addition to their applications in neuropathic and inflammatory pain, P2X7R antagonists are increasingly being utilized for the relief of cancer pain. These include polyene sulfonate acid dyes such as BBG, natural products like emodin and colchicine, and newly synthesized molecules such as A438079, A740003, A804598, AZ 10606120, AZ 11645373, KN-62, and A839977 (Marques-da-Silva et al., 2011; Faria et al., 2012; Jelassi et al., 2013; Custer et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2023). BBG can reduce inflammation and alleviate cancer pain by inhibiting glial cell activation and blocking the release of IL-1β and IL-18 (Halvorson et al., 2005; Yue et al., 2017). Emodin alleviates cancer pain by inhibiting P2X7R activation, reducing ATP-induced intracellular Ca2+ concentrations, decreasing IL-1β release, and lowering ROS production (Jelassi et al., 2013). Colchicine mitigates cancer pain by reducing ROS and NO production, as well as IL-1β secretion. Compounds like A438079, A804598, and AZ 1164537 relieve cancer pain by inhibiting microglial function and inflammatory reactions (Jiang et al., 2017; Rosli et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020), whereas A740003 and AZ 10606120 alleviate cancer pain by reducing calcium influx (Allsopp et al., 2017; Li et al., 2021). KN-62 not only reduces ATP-dependent Ca2+ influx and ethidium bromide uptake but also decreases IL-1β secretion to relieve cancer pain. Falk et al. (2015) demonstrated that intrathecal injection of the P2X7R-specific inhibitor A839977 significantly reduced pain in both the initial and maintenance phases of the breast cancer pain (BCP) model in rats injected with MRMT-1 breast cancer cells. Huang et al. (2014) found that BBG effectively relieved pain in a rat model of bone cancer. Additionally, Falk et al. (2015) discovered that A839977 could effectively alleviate early and late-stage pain behaviors in animal models of bone cancer pain. Honore et al. (2006) found that A740003 had a significant analgesic effect on rats with bone cancer pain.
5 Conclusion
P2X7 is a purinergic receptor involved in pathological pain, exhibiting high expression levels in neuropathic pain, inflammatory pain, and cancer pain. By regulating the opening of cation channels, promoting the release of various inflammatory mediators, and modulating the transmission of nociceptive signals, P2X7R mediates the generation of pain. Therapeutic strategies targeting P2X7R are being extensively researched in the context of pathological pain. In recent years, numerous P2X7R antagonists have been developed, all showing promising pharmacological properties, laying the groundwork for exploring P2X7R’s role in pain management. It has been confirmed that P2X7R plays a crucial role in the initiation and progression of inflammation as well as in the process of pain, with antagonism of P2X7R alleviating pain. However, despite initial insights into the role of P2X7R in pathological pain, many questions remain unresolved, such as the need for further exploration of the mechanisms of action of P2X7R and comprehensive studies on antagonists. Therefore, deeper investigation into the detailed mechanisms of P2X7R in pathological pain, including its effects in different types of diseases and pain conditions, is required. Elucidating its function will provide guidance for the discovery of analgesic drugs and innovations in pain relief methods. Additionally, more clinical trials are needed to confirm the efficacy of P2X7R antagonists—efforts which we must collectively undertake.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
PJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. CW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. FJ: Software, Writing – original draft. HW: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. HH: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. SJ: Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the use of Figdraw for figure creation; all illustrations in this work were designed using Figdraw.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
NOS, Nitric oxide synthase; DAMPs, Damage-associated molecular patterns; CCI, Chronic constriction injury; SNI, Spared nerve injury; PNL, Partial sciatic nerve ligation; SNL, Spinal nerve ligation; SCT, Spinal cord transection; DRG, Dorsal root ganglia; MVs, Microvesicles; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MIA, Monosodium iodoacetate; PANX1, Pannexin1; CFA, Complete Freund’s adjuvant; BzATP, Ammonium salt; vlPAG, Ventrolateral periaqueductal gray; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa-B; NLRP3, Nucleotide-oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor pyrin domain containing protein 3; SCI, Spinal cord injury; BBG, Brilliant blue g; MMP-13, Matrix metallopeptidase 13; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; BCP, Breast cancer pain; MRMT-1, Mammary rat metastasis tumor.
References
Adinolfi, E., Giuliani, A. L., De Marchi, E., Pegoraro, A., Orioli, E., and Di Virgilio, F. (2018). The P2X7 receptor: a main player in inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 151, 234–244. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.021
Allsopp, R. C., Dayl, S., Schmid, R., and Evans, R. J. (2017). Unique residues in the ATP gated human P2X7 receptor define a novel allosteric binding pocket for the selective antagonist AZ10606120. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 725. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-00732-5
Andó, R. D., Méhész, B., Gyires, K., Illes, P., and Sperlágh, B. (2010). A comparative analysis of the activity of ligands acting at P2X and P2Y receptor subtypes in models of neuropathic, acute and inflammatory pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 159 (5), 1106–1117. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00596.x
Bereiter, D. A., Rahman, M., Ahmed, F., Thompson, R., Luong, N., and Olson, J. K. (2022). Title: p2x7 receptor activation and estrogen status drive neuroinflammatory mechanisms in a rat model for dry eye. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 827244. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.827244
Bernier, L. P., Ase, A. R., and Séguéla, P. (2018). P2X receptor channels in chronic pain pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 175 (12), 2219–2230. doi:10.1111/bph.13957
Bhattacharya, A., Wang, Q., Ao, H., Shoblock, J. R., Lord, B., Aluisio, L., et al. (2013). Pharmacological characterization of a novel centrally permeable P2X7 receptor antagonist: JNJ-47965567. Br. J. Pharmacol. 170 (3), 624–640. doi:10.1111/bph.12314
Boué-Grabot, E., Archambault, V., and Séguéla, P. (2000). A protein kinase C site highly conserved in P2X subunits controls the desensitization kinetics of P2X(2) ATP-Gated channels. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (14), 10190–10195. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.14.10190
Bradley, H. J., Browne, L. E., Yang, W., and Jiang, L. H. (2011). Pharmacological properties of the rhesus macaque monkey P2X7 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 164 (2b), 743–754. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01399.x
Carroll, W. A., Donnelly-Roberts, D., and Jarvis, M. F. (2009). Selective P2X(7) receptor antagonists for chronic inflammation and pain. Purinergic Signal 5 (1), 63–73. doi:10.1007/s11302-008-9110-6
Caseley, E. A., Muench, S. P., Baldwin, S. A., Simmons, K., Fishwick, C. W., and Jiang, L. H. (2015). Docking of competitive inhibitors to the P2X7 receptor family reveals key differences responsible for changes in response between rat and human. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 25 (16), 3164–3167. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.06.001
Chessell, I. P., Hatcher, J. P., Bountra, C., Michel, A. D., Hughes, J. P., Green, P., et al. (2005). Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 114 (3), 386–396. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2005.01.002
Clark, A. K., Staniland, A. A., Marchand, F., Kaan, T. K., McMahon, S. B., and Malcangio, M. (2010). P2X7-dependent release of interleukin-1beta and nociception in the spinal cord following lipopolysaccharide. J. Neurosci. 30 (2), 573–582. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3295-09.2010
Costa-Junior, H. M., Sarmento Vieira, F., and Coutinho-Silva, R. (2011). C terminus of the P2X7 receptor: treasure hunting. Purinergic Signal 7 (1), 7–19. doi:10.1007/s11302-011-9215-1
Costigan, M., Scholz, J., and Woolf, C. J. (2009). Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 32, 1–32. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135531
Custer, E. E., Knott, T. K., Ortiz-Miranda, S., and Lemos, J. R. (2018). Effects of calcium and sodium on ATP-Induced vasopressin release from rat isolated neurohypophysial terminals. J. Neuroendocrinol. 30, e12605. doi:10.1111/jne.12605
Di Virgilio, F., Dal Ben, D., Sarti, A. C., Giuliani, A. L., and Falzoni, S. (2017). The P2X7 receptor in infection and inflammation. Immunity 47 (1), 15–31. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.06.020
Dong, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, L., Tian, Z., and Dong, S. (2020). P2X7 receptor acts as an efficient drug target in regulating bone metabolism system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 125, 110010. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110010
Donnelly-Roberts, D. L., and Jarvis, M. F. (2007). Discovery of P2X7 receptor-selective antagonists offers new insights into P2X7 receptor function and indicates a role in chronic pain states. Br. J. Pharmacol. 151 (5), 571–579. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707265
Drill, M., Jones, N. C., Hunn, M., O'Brien, T. J., and Monif, M. (2021). Antagonism of the ATP-gated P2X7 receptor: a potential therapeutic strategy for cancer. Purinergic Signal 17 (2), 215–227. doi:10.1007/s11302-021-09776-9
Falk, S., Schwab, S. D., Frøsig-Jørgensen, M., Clausen, R. P., Dickenson, A. H., and Heegaard, A. M. (2015). P2X7 receptor-mediated analgesia in cancer-induced bone pain. Neuroscience 291, 93–105. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.02.011
Falzoni, S., Munerati, M., Ferrari, D., Spisani, S., Moretti, S., and Di Virgilio, F. (1995). The purinergic P2Z receptor of human macrophage cells. Characterization and possible physiological role. J. Clin. Invest 95 (3), 1207–1216. doi:10.1172/jci117770
Faria, R., Ferreira, L., Bezerra, R., Frutuoso, V., and Alves, L. (2012). Action of natural products on p2 receptors: a reinvented era for drug discovery. Molecules 17 (11), 13009–13025. doi:10.3390/molecules171113009
Finnerup, N. B., Kuner, R., and Jensen, T. S. (2021). Neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to treatment. Physiol. Rev. 101 (1), 259–301. doi:10.1152/physrev.00045.2019
Fitzcharles, M. A., Cohen, S. P., Clauw, D. J., Littlejohn, G., Usui, C., and Häuser, W. (2021). Nociplastic pain: towards an understanding of prevalent pain conditions. Lancet 397 (10289), 2098–2110. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00392-5
Fulgenzi, A., Dell'Antonio, G., Foglieni, C., Dal Cin, E., Ticozzi, P., Franzone, J. S., et al. (2005). Inhibition of chemokine expression in rat inflamed paws by systemic use of the antihyperalgesic oxidized ATP. BMC Immunol. 6, 18. doi:10.1186/1471-2172-6-18
Fulgenzi, A., Ticozzi, P., Gabel, C. A., Dell'Antonio, G., Quattrini, A., Franzone, J. S., et al. (2008). Periodate oxidized ATP (oATP) reduces hyperalgesia in mice: involvement of P2X7 receptors and implications for therapy. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 21 (1), 61–71. doi:10.1177/039463200802100108
Gonnord, P., Delarasse, C., Auger, R., Benihoud, K., Prigent, M., Cuif, M. H., et al. (2009). Palmitoylation of the P2X7 receptor, an ATP-gated channel, controls its expression and association with lipid rafts. Faseb J. 23 (3), 795–805. doi:10.1096/fj.08-114637
Grace, P. M., Strand, K. A., Galer, E. L., Rice, K. C., Maier, S. F., and Watkins, L. R. (2018). Protraction of neuropathic pain by morphine is mediated by spinal damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in male rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 72, 45–50. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.018
Greig, A. V., Linge, C., Healy, V., Lim, P., Clayton, E., Rustin, M. H., et al. (2003). Expression of purinergic receptors in non-melanoma skin cancers and their functional roles in A431 cells. J. Invest Dermatol 121 (2), 315–327. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12379.x
Halvorson, K. G., Kubota, K., Sevcik, M. A., Lindsay, T. H., Sotillo, J. E., Ghilardi, J. R., et al. (2005). A blocking antibody to nerve growth factor attenuates skeletal pain induced by prostate tumor cells growing in bone. Cancer Res. 65 (20), 9426–9435. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-05-0826
Hansen, R. R., Nielsen, C. K., Nasser, A., Thomsen, S. I. M., Eghorn, L. F., Pham, Y., et al. (2011). P2X7 receptor-deficient mice are susceptible to bone cancer pain. Pain 152 (8), 1766–1776. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2011.03.024
He, Y., Hara, H., and Núñez, G. (2016). Mechanism and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 41 (12), 1012–1021. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2016.09.002
Hechler, B., and Gachet, C. (2015). Purinergic receptors in thrombosis and inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 35 (11), 2307–2315. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.115.303395
Honore, P., Donnelly-Roberts, D., Namovic, M. T., Hsieh, G., Zhu, C. Z., Mikusa, J. P., et al. (2006). A-740003 [N-(1-{[(cyanoimino)(5-quinolinylamino) methyl]amino}-2,2-dimethylpropyl)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetamide], a novel and selective P2X7 receptor antagonist, dose-dependently reduces neuropathic pain in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319 (3), 1376–1385. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.111559
Hu, H., Yang, B., Li, Y., Zhang, S., and Li, Z. (2016). Blocking of the P2X7 receptor inhibits the activation of the MMP-13 and NF-κB pathways in the cartilage tissue of rats with osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 38 (6), 1922–1932. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2016.2770
Hu, Q. Q., He, X. F., Ma, Y. Q., Ma, L. Q., Qu, S. Y., Wang, H. Z., et al. (2023). Dorsal root ganglia P2X4 and P2X7 receptors contribute to diabetes-induced hyperalgesia and the downregulation of electroacupuncture on P2X4 and P2X7. Purinergic Signal 19 (1), 29–41. doi:10.1007/s11302-022-09844-8
Huang, Y., Xu, W., and Zhou, R. (2021). NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol. Immunol. 18 (9), 2114–2127. doi:10.1038/s41423-021-00740-6
Huang, Z. X., Lu, Z. J., Ma, W. Q., Wu, F. X., Zhang, Y. Q., Yu, W. F., et al. (2014). Involvement of RVM-expressed P2X7 receptor in bone cancer pain: mechanism of descending facilitation. Pain 155 (4), 783–791. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2014.01.011
Itoh, K., Chiang, C. Y., Li, Z., Lee, J. C., Dostrovsky, J. O., and Sessle, B. J. (2011). Central sensitization of nociceptive neurons in rat medullary dorsal horn involves purinergic P2X7 receptors. Neuroscience 192, 721–731. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.083
Jelassi, B., Anchelin, M., Chamouton, J., Cayuela, M. L., Clarysse, L., Li, J., et al. (2013). Anthraquinone emodin inhibits human cancer cell invasiveness by antagonizing P2X7 receptors. Carcinogenesis 34 (7), 1487–1496. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt099
Jiang, K., Zhuang, Y., Yan, M., Chen, H., Ge, A. Q., Sun, L., et al. (2016). Effects of riluzole on P2X7R expression in the spinal cord in rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 618, 127–133. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.02.065
Jiang, L. H., Caseley, E. A., Muench, S. P., and Roger, S. (2021). Structural basis for the functional properties of the P2X7 receptor for extracellular ATP. Purinergic Signal 17 (3), 331–344. doi:10.1007/s11302-021-09790-x
Jiang, W., Li, M., He, F., Zhou, S., and Zhu, L. (2017). Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome to attenuate spinal cord injury in mice. J. Neuroinflammation 14 (1), 207. doi:10.1186/s12974-017-0980-9
Kan, L. K., Williams, D., Drummond, K., O'Brien, T., and Monif, M. (2019). The role of microglia and P2X7 receptors in gliomas. J. Neuroimmunol. 332, 138–146. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.04.010
Karasawa, A., and Kawate, T. (2016). Structural basis for subtype-specific inhibition of the P2X7 receptor. Elife 5, e22153. doi:10.7554/eLife.22153
Karmakar, M., Katsnelson, M. A., Dubyak, G. R., and Pearlman, E. (2016). Neutrophil P2X7 receptors mediate NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent IL-1β secretion in response to ATP. Nat. Commun. 7, 10555. doi:10.1038/ncomms10555
Kataoka, A., Tozaki-Saitoh, H., Koga, Y., Tsuda, M., and Inoue, K. (2009). Activation of P2X7 receptors induces CCL3 production in microglial cells through transcription factor NFAT. J. Neurochem. 108 (1), 115–125. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05744.x
Kim, S. S. (2016). Manipulation of P2X receptor activities by light stimulation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 7852168. doi:10.1155/2016/7852168
Kobayashi, K., Takahashi, E., Miyagawa, Y., Yamanaka, H., and Noguchi, K. (2011). Induction of the P2X7 receptor in spinal microglia in a neuropathic pain model. Neurosci. Lett. 504 (1), 57–61. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.08.058
Lara, R., Adinolfi, E., Harwood, C. A., Philpott, M., Barden, J. A., Di Virgilio, F., et al. (2020). P2X7 in cancer: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 793. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00793
Li, J., Li, X., Jiang, X., Yang, M., Yang, R., Burnstock, G., et al. (2017). Microvesicles shed from microglia activated by the P2X7-p38 pathway are involved in neuropathic pain induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats. Purinergic Signal 13 (1), 13–26. doi:10.1007/s11302-016-9537-0
Li, M., Luo, S., Zhang, Y., Jia, L., Yang, C., Peng, X., et al. (2020). Production, characterization, and application of a monoclonal antibody specific for the extracellular domain of human P2X7R. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104 (5), 2017–2028. doi:10.1007/s00253-019-10340-0
Li, P., Zhang, Q., Xiao, Z., Yu, S., Yan, Y., and Qin, Y. (2018). Activation of the P2X(7) receptor in midbrain periaqueductal gray participates in the analgesic effect of tramadol in bone cancer pain rats. Mol. Pain 14, 1744806918803039. doi:10.1177/1744806918803039
Li, Z., Huang, Z., Zhang, H., Lu, J., Wei, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). IRE1-mTOR-PERK axis coordinates autophagy and ER stress-apoptosis induced by P2X7-Mediated Ca(2+) influx in osteoarthritis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 695041. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.695041
Liu, P. Y., Lee, I. H., Tan, P. H., Wang, Y. P., Tsai, C. F., Lin, H. C., et al. (2015a). P2X7 receptor mediates spinal microglia activation of visceral hyperalgesia in a rat model of chronic pancreatitis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1 (6), 710–720. doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.07.008
Liu, S., Shi, Q., Zhu, Q., Zou, T., Li, G., Huang, A., et al. (2015b). P2X7 receptor of rat dorsal root ganglia is involved in the effect of moxibustion on visceral hyperalgesia. Purinergic Signal 11 (2), 161–169. doi:10.1007/s11302-014-9439-y
Liu, Y., Wu, Y., Gu, S., Yin, Q., Li, H., Wang, J., et al. (2020). The P2X7 receptor (P2X7R)-specific antagonist A804598 inhibits inflammatory reaction in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Am. J. Transl. Res. 12 (1), 45–53.
Lu, J., Yang, B., Liao, J., Chen, B., Lu, M., Zhang, W., et al. (2022). Olfactory ensheathing cells alleviate facial pain in rats with trigeminal neuralgia by inhibiting the expression of P2X7 receptor. Brain Sci. 12 (6), 706. doi:10.3390/brainsci12060706
Luchting, B., Heyn, J., Woehrle, T., Rachinger-Adam, B., Kreth, S., Hinske, L. C., et al. (2016). Differential expression of P2X7 receptor and IL-1β in nociceptive and neuropathic pain. J. Neuroinflammation 13 (1), 100. doi:10.1186/s12974-016-0565-z
Mariathasan, S., Weiss, D. S., Newton, K., McBride, J., O'Rourke, K., Roose-Girma, M., et al. (2006). Cryopyrin activates the inflammasome in response to toxins and ATP. Nature 440 (7081), 228–232. doi:10.1038/nature04515
Marques-da-Silva, C., Chaves, M. M., Castro, N. G., Coutinho-Silva, R., and Guimaraes, M. Z. (2011). Colchicine inhibits cationic dye uptake induced by ATP in P2X2 and P2X7 receptor-expressing cells: implications for its therapeutic action. Br. J. Pharmacol. 163 (5), 912–926. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01254.x
McCarthy, A. E., Yoshioka, C., and Mansoor, S. E. (2019). Full-length P2X(7) structures reveal how palmitoylation prevents channel desensitization. Cell 179 (3), 659–670. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.09.017
McGaraughty, S., Chu, K. L., Namovic, M. T., Donnelly-Roberts, D. L., Harris, R. R., Zhang, X. F., et al. (2007). P2X7-related modulation of pathological nociception in rats. Neuroscience 146 (4), 1817–1828. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.03.035
Michel, A. D., Chambers, L. J., and Walter, D. S. (2008). Negative and positive allosteric modulators of the P2X(7) receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 153 (4), 737–750. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707625
Mousseau, M., Burma, N. E., Lee, K. Y., Leduc-Pessah, H., Kwok, C. H. T., Reid, A. R., et al. (2018). Microglial pannexin-1 channel activation is a spinal determinant of joint pain. Sci. Adv. 4 (8), eaas9846. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aas9846
Ochi-ishi, R., Nagata, K., Inoue, T., Tozaki-Saitoh, H., Tsuda, M., and Inoue, K. (2014). Involvement of the chemokine CCL3 and the purinoceptor P2X7 in the spinal cord in paclitaxel-induced mechanical allodynia. Mol. Pain 10, 53. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-10-53
Perregaux, D., and Gabel, C. A. (1994). Interleukin-1 beta maturation and release in response to ATP and nigericin. Evidence that potassium depletion mediated by these agents is a necessary and common feature of their activity. J. Biol. Chem. 269 (21), 15195–15203. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(17)36591-2
Perregaux, D. G., and Gabel, C. A. (1998). Post-translational processing of murine IL-1: evidence that ATP-induced release of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta occurs via a similar mechanism. J. Immunol. 160 (5), 2469–2477. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.160.5.2469
Platania, C. B. M., Lazzara, F., Fidilio, A., Fresta, C. G., Conti, F., Giurdanella, G., et al. (2019). Blood-retinal barrier protection against high glucose damage: the role of P2X7 receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 168, 249–258. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.07.010
Qiu, Y., Li, W. H., Zhang, H. Q., Liu, Y., Tian, X. X., and Fang, W. G. (2014). P2X7 mediates ATP-driven invasiveness in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One 9 (12), e114371. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0114371
Raffaghello, L., Chiozzi, P., Falzoni, S., Di Virgilio, F., and Pistoia, V. (2006). The P2X7 receptor sustains the growth of human neuroblastoma cells through a substance P-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res. 66 (2), 907–914. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-05-3185
Ren, W. J., and Illes, P. (2022). Involvement of P2X7 receptors in chronic pain disorders. Purinergic Signal 18 (1), 83–92. doi:10.1007/s11302-021-09796-5
Roger, S., Jelassi, B., Couillin, I., Pelegrin, P., Besson, P., and Jiang, L. H. (2015). Understanding the roles of the P2X7 receptor in solid tumour progression and therapeutic perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1848 (10 Pt B), 2584–2602. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.10.029
Rosli, S., Kirby, F. J., Lawlor, K. E., Rainczuk, K., Drummond, G. R., Mansell, A., et al. (2019). Repurposing drugs targeting the P2X7 receptor to limit hyperinflammation and disease during influenza virus infection. Br. J. Pharmacol. 176 (19), 3834–3844. doi:10.1111/bph.14787
Rotondo, J. C., Mazziotta, C., Lanzillotti, C., Stefani, C., Badiale, G., Campione, G., et al. (2022). The role of purinergic P2X7 receptor in inflammation and cancer: novel molecular insights and clinical applications. Cancers (Basel) 14 (5), 1116. doi:10.3390/cancers14051116
Savio, L. E. B., de Andrade Mello, P., da Silva, C. G., and Coutinho-Silva, R. (2018). The P2X7 receptor in inflammatory diseases: Angel or demon? Front. Pharmacol. 9, 52. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00052
Shih, H., Lee, B., Lee, R. J., and Boyle, A. J. (2011). The aging heart and post-infarction left ventricular remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 57 (1), 9–17. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.08.623
Slater, M., Danieletto, S., Gidley-Baird, A., Teh, L. C., and Barden, J. A. (2004a). Early prostate cancer detected using expression of non-functional cytolytic P2X7 receptors. Histopathology 44 (3), 206–215. doi:10.1111/j.0309-0167.2004.01798.x
Slater, M., Danieletto, S., Pooley, M., Cheng Teh, L., Gidley-Baird, A., and Barden, J. A. (2004b). Differentiation between cancerous and normal hyperplastic lobules in breast lesions. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 83 (1), 1–10. doi:10.1023/B:BREA.0000010670.85915.0f
Solini, A., Cuccato, S., Ferrari, D., Santini, E., Gulinelli, S., Callegari, M. G., et al. (2008). Increased P2X7 receptor expression and function in thyroid papillary cancer: a new potential marker of the disease? Endocrinology 149 (1), 389–396. doi:10.1210/en.2007-1223
Solle, M., Labasi, J., Perregaux, D. G., Stam, E., Petrushova, N., Koller, B. H., et al. (2001). Altered cytokine production in mice lacking P2X(7) receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (1), 125–132. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006781200
Staunton, C. A., Lewis, R., and Barrett-Jolley, R. (2013). Ion channels and osteoarthritic pain: potential for novel analgesics. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 17 (12), 378. doi:10.1007/s11916-013-0378-z
Steinberg, T. H., Newman, A. S., Swanson, J. A., and Silverstein, S. C. (1987). ATP4- permeabilizes the plasma membrane of mouse macrophages to fluorescent dyes. J. Biol. Chem. 262 (18), 8884–8888. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(18)47497-2
Stokes, L., Jiang, L. H., Alcaraz, L., Bent, J., Bowers, K., Fagura, M., et al. (2006). Characterization of a selective and potent antagonist of human P2X(7) receptors, AZ11645373. Br. J. Pharmacol. 149 (7), 880–887. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706933
Surprenant, A., Rassendren, F., Kawashima, E., North, R. A., and Buell, G. (1996). The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science 272 (5262), 735–738. doi:10.1126/science.272.5262.735
Teixeira, J. M., Parada, C. A., and Tambeli, C. H. (2018). A cyclic pathway of P2 × 7, bradykinin, and dopamine receptor activation induces a sustained articular hyperalgesia in the knee joint of rats. Inflamm. Res. 67 (4), 301–314. doi:10.1007/s00011-017-1122-7
Valera, S., Hussy, N., Evans, R. J., Adami, N., North, R. A., Surprenant, A., et al. (1994). A new class of ligand-gated ion channel defined by P2x receptor for extracellular ATP. Nature 371 (6497), 516–519. doi:10.1038/371516a0
Virginio, C., MacKenzie, A., Rassendren, F. A., North, R. A., and Surprenant, A. (1999). Pore dilation of neuronal P2X receptor channels. Nat. Neurosci. 2 (4), 315–321. doi:10.1038/7225
von Mücke-Heim, I. A., and Deussing, J. M. (2023). The P2X7 receptor in mood disorders: emerging target in immunopsychiatry, from bench to bedside. Neuropharmacology 224, 109366. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109366
Woolf, C. J. (2010). What is this thing called pain? J. Clin. Invest 120 (11), 3742–3744. doi:10.1172/jci45178
Wu, P., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhou, G., Wu, X., et al. (2023). Emerging roles of the P2X7 receptor in cancer pain. Purinergic Signal 19 (2), 441–450. doi:10.1007/s11302-022-09902-1
Wu, P., Wu, X., Zhou, G., Wang, Y., Liu, X., Lv, R., et al. (2022). P2X7 receptor-induced bone cancer pain by regulating microglial activity via NLRP3/IL-1beta signaling. Pain Physician 25 (8), e1199–e1210.
Wu, Y., Shen, Z., Xu, H., Zhang, K., Guo, M., Wang, F., et al. (2021). BDNF participates in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain via transcriptionally activating P2X(7) in primary sensory neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 58 (9), 4226–4236. doi:10.1007/s12035-021-02410-0
Yang, Y., Li, H., Li, T. T., Luo, H., Gu, X. Y., Lü, N., et al. (2015). Delayed activation of spinal microglia contributes to the maintenance of bone cancer pain in female wistar rats via P2X7 receptor and IL-18. J. Neurosci. 35 (20), 7950–7963. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.5250-14.2015
Yang, Y., Wang, H., Kouadir, M., Song, H., and Shi, F. (2019). Recent advances in the mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 10 (2), 128. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1413-8
Yoo, Y. M., and Kim, K. H. (2024). Current understanding of nociplastic pain. Korean J. Pain 37 (2), 107–118. doi:10.3344/kjp.23326
Yu, M., Su, B., and Zhang, X. (2018a). Gardenoside suppresses the pain in rats model of chronic constriction injury by regulating the P2X3 and P2X7 receptors. J. Recept Signal Transduct. Res. 38 (3), 198–203. doi:10.1080/10799893.2018.1468782
Yu, M., Zhao, Y., and Zhang, X. (2018b). Gardenoside combined with ozone inhibits the expression of P2X3 and P2X7 purine receptors in rats with sciatic nerve injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 17 (6), 7980–7986. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.8803
Yue, N., Huang, H., Zhu, X., Han, Q., Wang, Y., Li, B., et al. (2017). Activation of P2X7 receptor and NLRP3 inflammasome assembly in hippocampal glial cells mediates chronic stress-induced depressive-like behaviors. J. Neuroinflammation 14 (1), 102. doi:10.1186/s12974-017-0865-y
Zhang, G. P., Liao, J. X., Liu, Y. Y., Zhu, F. Q., Huang, H. J., and Zhang, W. J. (2023). Ion channel P2X7 receptor in the progression of cancer. Front. Oncol. 13, 1297775. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1297775
Zhang, J., Gao, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Sun, S., and Wu, L. A. (2024). Involvement of microglial P2X7 receptor in pain modulation. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (1), e14496. doi:10.1111/cns.14496
Zhang, P. A., Xu, Q. Y., Xue, L., Zheng, H., Yan, J., Xiao, Y., et al. (2017). Neonatal maternal deprivation enhances presynaptic P2X7 receptor transmission in Insular cortex in an adult rat model of visceral hypersensitivity. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 23 (2), 145–154. doi:10.1111/cns.12663
Zhang, W., Liu, Y., Sun, Y., and Liu, Z. (2019). Effects of microencapsulated olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation on neuropathic pain and P2X7 receptor expression in the L4-5 spinal cord segment. Neurosci. Lett. 701, 48–53. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2019.02.013
Zhang, W. J., Hu, C. G., Zhu, Z. M., and Luo, H. L. (2020). Effect of P2X7 receptor on tumorigenesis and its pharmacological properties. Biomed. Pharmacother. 125, 109844. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109844
Zhao, X., Liu, H. Z., and Zhang, Y. Q. (2016). Effect of P2X7 receptor knock-out on bone cancer pain in mice. Sheng Li Xue Bao 68 (3), 224–232.
Zhao, Y. F., Tang, Y., and Illes, P. (2021). Astrocytic and oligodendrocytic P2X7 receptors determine neuronal functions in the CNS. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 14, 641570. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2021.641570
Keywords: P2X7 receptor, pathological pain, neuropathic pain, inflammatory pain, cancer pain
Citation: Jiang P, Wang C, Jia F, Wu H, Hao H and Jing S (2025) P2X7 receptor as a key player in pathological pain: insights into Neuropathic, inflammatory, and cancer pain. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1585545. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1585545
Received: 28 February 2025; Accepted: 25 June 2025;
Published: 11 July 2025.
Edited by:
Natiele Carla da Silva Ferreira, Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (Fiocruz), BrazilReviewed by:
Maree Therese Smith, The University of Queensland, AustraliaAndre Bonavita, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Wang, Jia, Wu, Hao and Jing. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shaoze Jing, MzgwNjMxNzE5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Haihu Hao, aGhoMzMwMUAxMjYuY29t; Hua Wu, d3VodWFAaHVzdC5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Pan Jiang
Pan Jiang Cai Wang1,2†
Cai Wang1,2† Fajing Jia
Fajing Jia Hua Wu
Hua Wu Haihu Hao
Haihu Hao Shaoze Jing
Shaoze Jing