- 1The Second Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
- 2The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
Ferroptosis is a new type of controlled cell death. It is distinguished by its reliance on iron and the production of lipid peroxidation. The role of ferroptosis in stroke has attracted a lot of attention recently. The purpose of this review is to clarify the connection between ferroptosis and stroke and to investigate the potential contribution of natural products to the clinical management of stroke and the discovery of novel medications. In this review, we summarize in detail the mechanism of ferroptosis after stroke, especially the relevant targets of ferroptosis after stroke. Furthermore, we summarize the natural products and herbal medicine currently employed in ferroptosis along with their mechanisms of action, highlighting the potential and challenges of clinical translation. We included 55 articles and classified them. After systematic screening, We think that ginkgolide B, kellerin, loureirin C, quercetin, icariside II, salvianolic acid A, berberine, Dl-3-n-butylphthalide is an effective candidate drug for the treatment of stroke.
1 Introduction
Stroke, which contributes to a growing portion of the global medical burden, can be broadly classified into ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke, with the latter incorporating intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) (GBD, 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators, 2024). Ischemic stroke is characterized by brain, spinal cord, or retinal infarction, representing approximately 85% of all strokes globally (Tsao et al., 2023). In accordance with the secondary stroke prevention guidelines established by the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology, antiplatelet medications, including aspirin, clopidogrel, and dipyridamole, have become the primary therapeutic alternative (Medina-Inojosa et al., 2023). Nevertheless, a substantial problem has emerged: certain patients exhibit resistance to aspirin, which could potentially undermine the efficacy of these medications (Venketasubramanian et al., 2022). Given this predicament, it is imperative to create novel therapeutic agents that are effective for individuals who are resistant to conventional remedies.
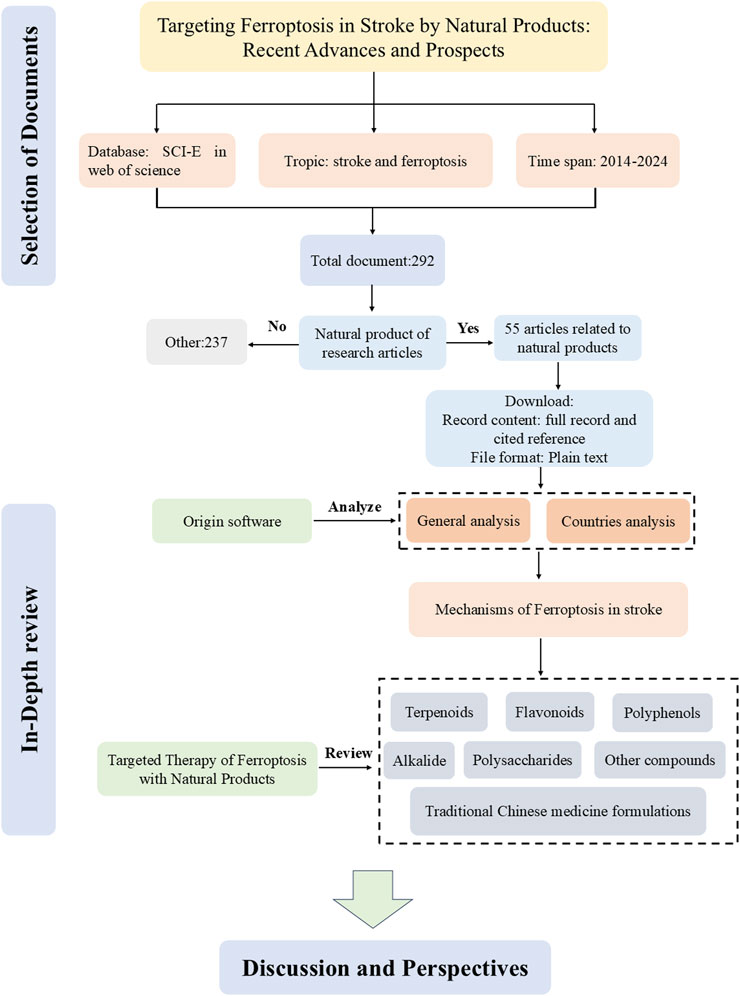
Ferroptosis, a type of programmed cell death associated with stroke, was initially identified in 2012 and displays distinctive features, such as changes in the structure and density of mitochondria (Dixon et al., 2012; Xu et al., 2023a). Thus, a complete understanding of the function of ferroptosis in stroke could serve to offer new intervention targets. Natural products are the metabolites or plant metabolites of insects, microbes, marine, plant, and animal extracts, as well as many more endogenous chemical plant metabolites and metabolites found in human and animal bodies (Xing et al., 2023). They are proven to be a valuable source of new drugs (Liang et al., 2021). Many natural products have shown good therapeutic effects on stroke (Liu et al., 2023a). In this review, we summarize the mechanisms of ferroptosis in stroke and in detail the natural products of anti-ferroptosis therapy. Figure 1 shows a flowchart summarizing natural products that target ferroptosis after strokes.
2 Research trends on ferroptosis in stroke
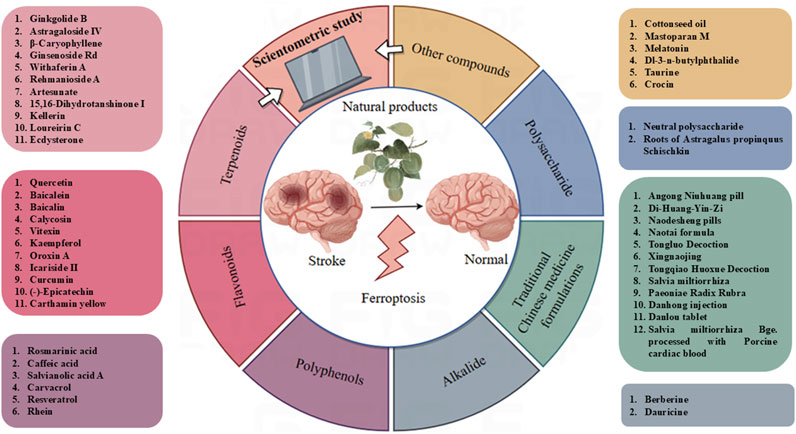
Ferroptosis is a novel form of regulatory cell death associated with the formation of iron-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxides (Dixon et al., 2012). Disordered iron metabolism in cells leads to the generation of excessive iron ions, which produce a significant quantity of ROS via the Fenton reaction (Dixon et al., 2012). ROS target polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) within the lipid membrane, generating lipid peroxides, compromising the integrity of the cell membrane, disrupting mitochondrial activity, and ultimately resulting in ferroptosis (Dixon et al., 2012). Figure 2 illustrates the distinction between ferroptosis cells and normal cells.
The terms, “ferroptosis” and “stroke” as topic, were searched in Web of Science (SCI-E) core collection database. The article was refined and used for scientometric analysis. The time span is from 1 January 2014, to 31 December 2024. Original articles related to natural products were included in our study after being read in full by the researchers. The first paper, published in 2014, was titled “(−)-Epicatechin protects hemorrhagic brain via synergistic Nrf2 pathways” (Figure 3A). Most papers were published in the year 2023, while the most cited year was 2021. So far, research in the field of the therapeutic on the ferroptosis of stroke on natural products is increasingly ongoing. A total of 24 countries contributed to the publications included in this study. Among them, China published the most papers, followed by American, Canada, Japan, Germany, Spain, Australia, South Korea, England, and Singapore (Figure 3B). Next, we conducted a thorough review of these 293 articles, and 55 of them were included in our study (Figure 1).
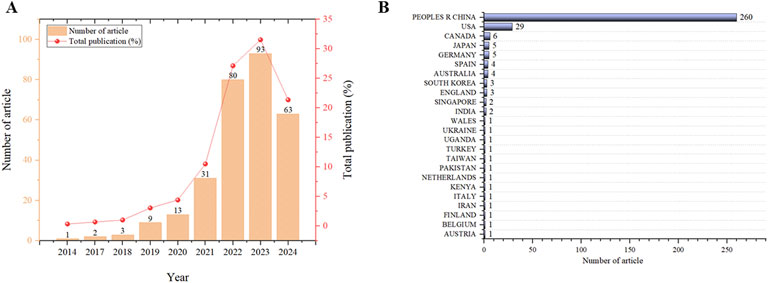
Figure 3. Scientometric study of ferroptosis on stroke. (A) Number of publications by year. (B) Number of publications by country or region.
3 Mechanisms of ferroptosis in ICH
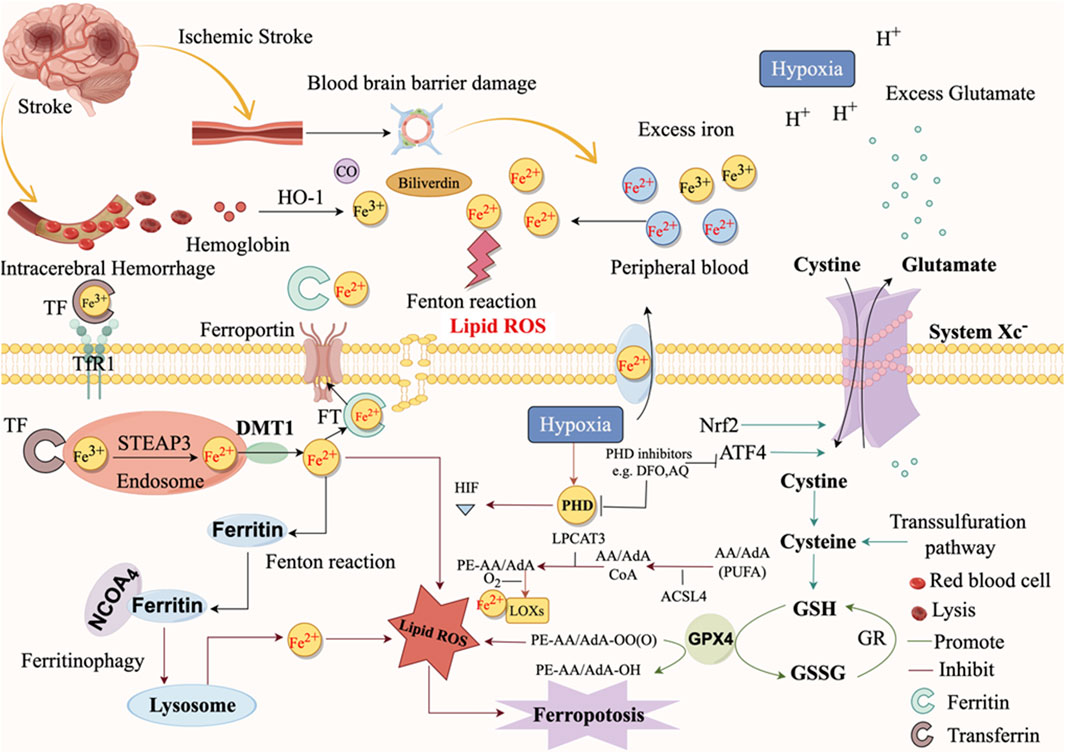
The accumulation of iron ions produced by red blood cells (RBCs) lysis after ICH is the main cause of ferroptosis (Figure 4). The lysis of RBCs in the hematoma is the most contributor of free hemoglobin, followed by the release of heme, which is subsequently degraded into iron, biliverdin, and carbon monoxide (Zhang et al., 2021). Iron ions accumulate after 24 h of ICH, and excessive accumulation is an important characteristic of ferroptosis (Sun et al., 2022). Under physiological conditions, the plasma membrane’s transferrin receptor TFR1 internalizes to facilitate transport (Zhao et al., 2021a). The iron output protein FPN1, which couples with multicopper iron oxidase (like ceruloplasmin) on the plasma membrane, mediates the intracellular iron output (Zhao et al., 2021a). Alternatively, multivesicular and extracellular vesicles containing ferritin can also excrete iron out of the cell (Zhao et al., 2021a). Under ICH conditions, iron is transported to the extracellular space through the iron export protein FPN in microglia, causing a large amount of toxic iron to enter the brain tissue (Hvidberg et al., 2005).
To be specific, two-molecule Fe3+ participates in the transport of iron by binding to one molecule of transferrin, which transports Fe3+ to the intracellular by binding to the membrane protein transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1) on the surface of neurons to form a Tf-Fe3+-TFR1 complex. Fe3+ is then reduced to Fe2+ by the Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of Prostate 3 (STEAP3). Endosomes release Fe2+ into the cytoplasmic labile iron pool (LIP), which requires DMT1/Solute Carrier Family 11 Member 2 (SLC11A2) regulation (Chen et al., 2020; Yao et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2020) (Figure 3). The synthesis of the essential enzyme lipoxygenases (LOXs) in lipid peroxidation (LPO) can be facilitated by Fe2+ in the LIP, which leads to ferroptosis. Furthermore, Fe2+ will engage in the Fenton reaction with hydrogen peroxide to generate hydroxyl radicals, which will in turn damage cellular plant metabolites and induce ferroptosis (Wan et al., 2019). ROS can be generated by iron-catalyzed enzymes, which in turn can induce lipid auto-oxidation, thereby promoting ferroptosis (Chen et al., 2020). Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) also mediates ferritinophagy by binding to ferritin and subsequently transporting iron-bound ferritin to the autophagosome for lysosomal degradation and iron release. NCOA4 knockdown can prevent LPO and ferroptosis by reducing the amount of iron in the intracellular LIP (Fang et al., 2021). Through NCOA4, autophagy-related 5 (ATG5) and autophagy-related 7 (ATG7) promote ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin (Hou et al., 2016). The expression of TFR1 can be stimulated by nitrogen fixation 1 (NFS1), an iron-sulfur cluster biosynthetic enzyme, to improve ferroptosis (Alvarez et al., 2017). Further, heat shock factor-binding Protein 1 (HSPB1) is highly inducible after treatment with Erastin. Once activated, HSBP1 reduces iron levels by inhibiting TFR1 expression (Sun et al., 2015).
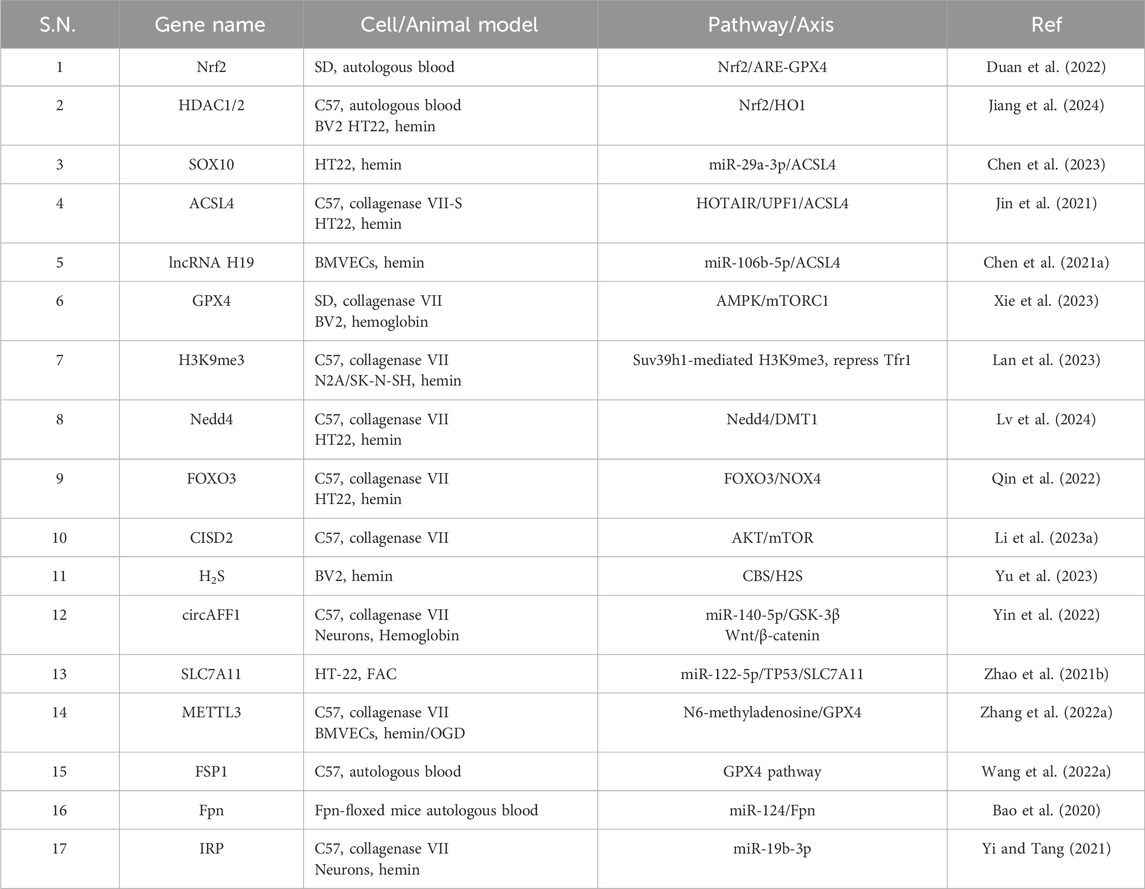
LPO is a critical mechanism that directly initiates ferroptosis. It is the process by which oxygen binds to lipids to generate lipid peroxides by forming peroxyl radicals. The Fenton reaction, which is initiated by iron stimulation, generates lipid ROS, which subsequently induces LPO and ultimately results in ferroptosis (Bai et al., 2019). Furthermore, the oxidation and esterification of PUFAs generate lipid peroxides, which in turn induce LPO (Yang et al., 2016). LPO can attack cells by destroying proteins, DNA, and lipid membranes and activating ferroptosis (Salvador, 2010). Inhibiting LPO has been a critical and effective strategy for safeguarding ICH by reducing ferroptosis. We have summarized the related genes of ferroptosis after ICH, as shown in Table 1.
4 Mechanisms of ferroptosis in ischemic stroke
Following ischemic stroke, the BBB becomes compromised because of the breakdown of tight junction protein (Figure 4). This leads to the release of Fe3+ from the blood into the brain tissue, facilitated by TF and TFR1 (Zhao et al., 2023a). Afterwards, there is an excessive amount of Fe2+ which is then decreased and moved to the cytoplasm. ROS, which are generated quickly via the Fenton reaction, facilitate the degradation of nucleic acids, proteins, and membranes, leading to the occurrence of ferroptosis (Figure 4). When cerebral ischemia reperfusion occurs, the release of excitatory amino acids, represented by Glu, increases and accumulates in the synaptic cristae. The uptake of glutamate within cells reduces while the release of glutamate outside of cells increases, resulting in the inhibition of the system Xc− (Xu et al., 2023a). Some studies have found through metabolomics that gamma-glutamyl dipeptide or tripeptide was found in the cell under Cys deprivation. These metabolites reduced the level of Glu and alleviated the sensitivity to ferroptosis (Kagan et al., 2017). But on the other hand, for cysteine-deprived cells, the catabolism of Gln promoted the synthesis of PUFA, and its decomposition products such as α-ketoglutaric acid could also increase the accumulation of lipid peroxides. These effects of glutamine restored the sensitivity of cells to cysteine-deficient ferroptosis (Gao et al., 2019). It is important to mention that while Gln can be broken down into Glu by the enzymes GLS1 and GLS2, only the catalysis of GLS2 is linked to ferroptosis (Gao et al., 2015).
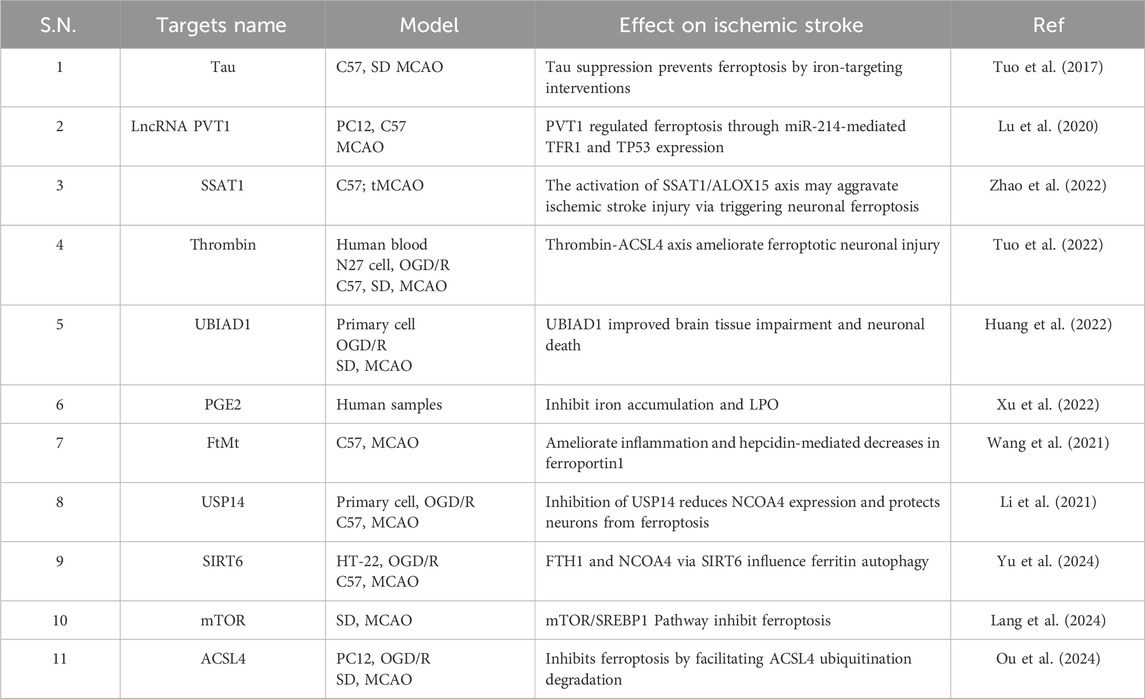
Prior to the proposal of the notion of ferroptosis, there have been multiple instances of abnormal buildup of iron in ischemic brain tissue (Dietrich and Bradley, 1988; Kondo et al., 1995). Research indicates that neurological damage following an ischemic stroke is associated with dysregulation of brain iron metabolism and transport (Selim and Ratan, 2004). The impaired BBB facilitates the entry of circulating iron into brain tissue following an ischemic stroke, while neurons also experience an increase in iron uptake (Bu et al., 2021). The early extravasation of circulating transferrin into ischemic brain parenchyma is induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R), which also activates NF-κB and promotes the expression of the DMT1 1B subtype, thereby enhancing iron uptake (DeGregorio-Rocasolano et al., 2018). In addition to facilitating iron uptake, cerebral ischemia also increases intracellular iron storage. The concentration of ferritin in the plasma and cerebral spinal fluid of individuals with ischemic stroke increases within 24 h. This rise is linked to early neurological impairment and might potentially result in hemorrhagic transformation and severe brain oedema following tPA thrombolysis (Liu, 2021). Interestingly, researchers found that ferritin overexpression attenuated Tau phosphorylation and ROS production, reversed the decreases of glutathione (GSH) and SLC7A11 in rats’ hippocampal neurons after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), and had a protective effect on motor injury and memory deficits (Chen et al., 2021b). We have summarized the related genes of ferroptosis after ischemic stroke, as shown in Table 2.
5 Targeted therapy of ferroptosis with natural products
Whether it is ischemic stroke or ICH, there is still no perfect treatment plan, and there are still many shortcomings. Based on this, many researchers are looking for traditional medicine (Hilkens et al., 2024). Ferroptosis is a distinct mechanism that modulates cellular death and is integral to the pathophysiological processes of neurodegenerative disorders and stroke (Wang et al., 2023a). An increasing amount of evidence indicates that ferroptosis is a significant contributor to neurodegenerative disorders and stroke, making pharmacological inhibition of ferroptosis a viable therapeutic target for these conditions (Wang et al., 2023a). The following table provides a list of studies of natural products that are effective anti-ferroptosis in stroke models (Table 3).
5.1 Terpenoids
The structure of terpene compounds is built from isoprene units (C5 units), which are related to methylglutaric acid. These oxygen-containing derivatives can be alcohol, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, among others. Terpenes are widely found in nature and are the main plant metabolites of essence, resin, pigment, among others, which constitute some plants. Terpenoids also include hormones and vitamins from animals. Recently, many scholars have found that terpenoids have anti-ferroptosis effects.
Ginkgolide B (PubChem CID: 65243) is a terpenoid compound that is generated from plants, namely, from Ginkgo biloba L. It exhibits a range of pharmacological effects, including inhibiting platelet aggregation, reducing inflammation, acting as an antioxidant, and scavenging free radicals (Chen et al., 2022b). Ginkgolide B inhibits the overproduction of ROS, MDA, ACSL4, NCOA4, and Fe2+, while simultaneously increasing the activities of antioxidative enzymes GPX4 and SOD, and FITH1 (Yang et al., 2024a). It achieves its anti-ferroptosis effect by disrupting the NCOA4-FTH1 interaction (Yang et al., 2024a). In addition, molecular docking, and microscale thermophoresis assay were conducted to explore the combination of Ginkgolide B and NCOA4. Therefore, ginkgolide B may be a candidate for the treatment of ferroptosis after stroke.
Astragaloside IV (PubChem CID:13943297) is a lanolin alcohol-derived tetracyclic triterpene saponin extracted from Astragalus membranaceus. It is a white powder with the molecular formula C41H68O14. Studies indicate that astragaloside IV exerts a neuroprotective effect through multiple mechanisms, including its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and anti-apoptotic properties that safeguard nerve cells (Yao et al., 2023). Additionally, it regulates nerve growth factor, inhibits neurodegeneration, and facilitates neuron regeneration (Yao et al., 2023). In MCAO rats, astragaloside IV can inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and NF-κB, increasing the levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4 (Zhang et al., 2023a). Mechanism studies indicate that astragaloside IV triggered the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and alleviated ferroptosis due to ischemic stroke induction (Zhang et al., 2023a). Notably, ML385 inhibited these effects, and astragaloside IV increased P62 and Nrf2 levels while decreasing Keap1 levels. P62 silencing decreased astragaloside IV’s effects on the P62/Keap1/Nrf2 pathway and ferroptosis (Wang et al., 2023b). Another study showed that astragaloside IV promoted the transcription of Fto by regulating Atf3, resulting in a decrease of Acsl4 levels, thus improving neuronal injury in ischemic stroke by inhibiting ferroptosis (Jin et al., 2023). Interestingly, in the SAH model, astragaloside IV also exerts its anti-ferroptosis effect through the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway (Liu et al., 2022a). Although many studies have shown that it can treat central nervous system (CNS) diseases, previous pharmacokinetic studies have shown that AS-IV has a poor oral bioavailability and membrane permeability (Li et al., 2023b). There are also studies that suggest that it may affect CNS diseases through intestinal bacteria (Li et al., 2023b). If it is to be developed as a drug, further mechanism studies are needed.
β-Caryophyllene (PubChem CID: 26318) is a class of bicyclic sesquiterpenes found in lemon, grapefruit, nutmeg, pepper, raspberry, blackcurrant, cinnamon leaf oil, and clover leaf oil, whose molecular formula is C15H24 (Sharma et al., 2016). The in vivo study demonstrated that BCP enhanced neurological scores, infarct volume, and pathological features following MCAO/R. They found that BCP significantly increased the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and activated the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, thereby safeguarding against ferroptosis (Hu et al., 2022). β-Caryophyllene decreased OGD/R-induced ROS generation and iron accumulation (Hu et al., 2022). Furthermore, the neuroprotective effects of β-Caryophyllene were reversed by the Nrf2 inhibitor ML385. β-Caryophyllene is a food additive that has been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration and is generally thought to be safe. β-Caryophyllene is also highly available orally and has been studied in RCT in vascular diseases, which I think is a good candidate for the treatment of stroke (Yamada et al., 2023).
Ginsenoside Rd (PubChem CID: 11679800) exhibits diverse pharmacological properties including cardiovascular protection, neuroprotection, anti-aging, anti-tumor, and more (Chen et al., 2022c). The chemical formula of the compound is C48H82O18. Ginsenoside Rd could increase the expression of ZO-1, occluding-1, and claudin-5 in cerebral micro vessels and bEnd.3 cells on the same side of the brain, leading to a decrease in the loss of endothelial cells and leakage of Evans blue dye. As a result, ginsenoside Rd eventually enhances the integrity of the BBB following cerebral I/R injury (Hu et al., 2024). Ginsenoside Rd can mitigate the breakdown of the BBB generated by ischemic stroke by reducing ferroptosis in endothelial cells (Hu et al., 2024). Functionally, ginsenoside Rd protected against tight junction loss and leakage of the BBB by increasing the expression of NRG1, which in turn activated the tyrosine kinase ErbB4 receptor. This activation subsequently triggered the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, ultimately preventing ischemic stroke-induced ferroptosis in endothelial cells (Hu et al., 2024). Despite its potent pharmacological efficacy, ginsenoside Rd is present in plants in relatively low quantities, making its production from ginseng an expensive process.
Withaferin A (PubChem CID: 265237) is a steroid ester plant metabolite with a molecular formula of C28H38O6. Withaferin A treatment was found to suppress ferroptosis and reduce oxidative stress (OS)-related damage in both an in vivo model and an in vitro model of ICH (Zhou et al., 2023a). These effects were attributed, at least in part, to the augmented translocation of Nrf2 and increased expression of HO-1 (Zhou et al., 2023a). More precisely, withaferin A can enhance the production of HO-1, SOD, GSH-Px, and Nrf2 while suppressing the production of MDA (Zhou et al., 2023a). However, the sample size of this study is too small, so more pharmacodynamics studies should be carried out in the future, and then mechanism studies should be carried out.
Rehmanioside A (PubChem CID: 6325881) is an iridoid glycoside that promotes immunity, replenishes blood, and lowers blood sugar (Liu et al., 2017). The chemical formula is C21H32O15. Furthermore, current research has shown that rehmannioside A could decrease OS, enhance cognitive function, and provide a safeguarding impact on neurons (Sun et al., 2019a). Rehmannioside A exhibits neuroprotective properties and enhances cognitive function following cerebral ischemia by suppressing ferroptosis and activating the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 and SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathways (Fu et al., 2022). Specifically, the rehmannioside A group significantly improved the cognitive impairment and neurological deficits compared to the model group and reduced cerebral infarction in MCAO rats (Fu et al., 2022). Furthermore, the rehmannioside A group demonstrated a noticeable increase in cell viability and a reduction in H2O2-induced toxicity (Fu et al., 2022). Further research revealed a significant increase in the expression of p-PI3K, p-Akt, nuclear Nrf2, HO-1, and SLC7A11 in the rehmannioside A group compared to the model group (Fu et al., 2022). In addition, rehmannioside A inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory mediators from microglia and promotes M2 polarization in vitro, thereby protecting co-cultured neurons from apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways (Xiao et al., 2021).
Artesunate (PubChem CID: 6917864) possesses the attributes of cost-effectiveness, rapid onset, little toxicity, and resistance development challenges. Recent research has discovered that artesunate could trigger ferroptosis without relying on xCT (Sun et al., 2019b). Chao Qin’s research found that artesunate caused LPO and the formation of ROS in BV2 cells stimulated by LPS (Xie et al., 2023). However, the use of the ferroptosis inhibitor Fer-1 effectively restored these effects (Xie et al., 2023). Furthermore, artesunate induced ferroptosis in ICH M1-polarised BV2 cells primarily through the AMPK/mTOR/GPX4 axis and partially through Akt phosphorylation inhibition, but not by severing the link between mTORC1 and lysosomes (Xie et al., 2023). However, the in vitro data cannot be considered pharmacological or clinically relevant. More animal experiments should be carried out in the future to verify the anti-ferroptosis effect of artesunate.
15,16-Dihydrotanshinone I (PubChem CID: 11425923, DHT), a lipophilic tanshinone with the chemical formula C18H14O3, is isolated from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge [Lamiaceae; Salviae miltiorrhizae radix et rhizoma]. The in vitro investigation on ferroptosis was reduced by DHT, as evidenced by a decrease in lipid ROS generation, an increase in GPX4 expression and the ratio of GSH/GSSG, and an improvement in mitochondrial function (Wu et al., 2023). The inhibitory effect of DHT on ferroptosis was decreased after Nrf2 silencing. Compared with the pMACO group, DHT significantly increased the expression of GPX4 and reduced the GSH-Px activity. The inhibitory effect of DHT on ferroptosis and its underlying mechanism in pMCAO rats were examined in vivo. However, relying on a few indicators of ferroptosis to prove the anti-ferroptosis effect of DHT is far from sufficient. More in-depth mechanism research is needed in the future.
Kellerin (PubChem CID: 40580807) inhibits microglial activation, thereby exerting a potent anti-inflammatory effect. Its molecular formula is C32H26O12. Kellerin inhibited the production of mitochondrial ROS in vitro, thereby improving the neuronal injury caused by OGD/R and suppressing ferroptosis (Mi et al., 2024). Kellerin directly contacted Akt and raised its phosphorylation, which resulted in an increase in Nrf2 nuclear translocation and the production of its downstream antioxidant genes (Mi et al., 2024). Kellerin provided protection against IS and prevented ferroptosis in vivo, evidenced by its ability to enhance the expression of GSH and GPX4 while decreasing MDA and Fe2+ levels.
Additionally, molecular docking, in conjunction with drug affinity responsive target stability assay (DARTS) and cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA), was conducted to evaluate the possible target proteins for kellerin. The findings indicate that kellerin significantly raised the level of Akt phosphorylation, indicating that it can bind to Akt and encourage phosphorylation. In conclusion, we assert that kellerin may serve as a candidate therapeutic agent for the ongoing management of ferroptosis in stroke.
Loureirin C (PubChem CID: 14157896) is a type of dihydrochalcone obtained from resin extracted from the stem of Chinese Dragon’s Blood (Dracaena cochinchinensis S.C. Chen), with the molecular formula C16H16O4. In mice following MCAO/R, loureirin C not only significantly reduced brain damage and prevented neurons from ferroptosis, but it also reduced ROS accumulation in ferroptosis in a dose-dependent manner following OGD/R (Mi et al., 2024). In addition, loureirin C raises the amount of NQO1, GPX4, and HO-1 following ischemic stroke (Mi et al., 2024). To further prove the anti-ferroptosis effect of Loureirin C, they employed ferroptosis activator (Erastin), aptoptosis inhibitors and pyroptosis inhibitors (Z-VAD-FMK) in OGD/R induced SH-SY5Y cells. The findings suggested Loureirin C could increase the cell survival rate in OGD/R cell model in the presence of Z-VAD-FMK (10 μM) with or without erastin (10 μM). Co-Immunoprecipitation assay suggested that Loureirin C could reduce the level of Nrf2 binding to Keap1. All things considered, we think loureirin C is a candidate medication acting as an antioxidant in ferroptosis stroke treatment.
Ecdysterone (PubChem CID: 5459840), found in Achyranthes bidentata Blume, is a crucial active plant metabolite that has enhanced its medical potential by virtue of its antioxidant and neuroprotective properties. The chemical formula of the compound is C27H44O7. In MCAO rats, ecdysterone improves ischemic stroke by inhibiting ferroptosis and OS, resulting from increased GSH levels and decreased MDA, ROS, LPO, and Fe2+ levels (Sun et al., 2024a). Further research has demonstrated that ecdysterone inhibits ferroptosis in MCAO rats via ACSL4/NCOA4/FTH1pathway (Sun et al., 2024a). To verify the binding between ecdysterone and ACSL4, CETSA was carried out. Ecdysterone enhanced the thermal stability of ACSL4, suggesting that ecdysterone directly interacts with ACSL4 within the cellular environment. This data indicates that ACSL4 is a direct target of ecdysterone. Nevertheless, there is a paucity of research regarding stroke in relation to ecdysterone. Consequently, we assert that this is not a viable candidate drug. Future investigations of the efficacy of mechanisms are essential.
5.2 Flavonoids
Flavonoids were originally referred to as a class of compounds derived from the backbone of 2-phenylchromenone. It now refers to a series of compounds formed by two benzene rings connected to each other through three carbon atoms, i.e., a general term for a class of compounds with a C6-C3-C6 structure. Plants widely distribute flavonoids, most of which exist as glycosides or carbon glycosides produced by sugar synthesis, while others exist in their free form. Flavonoids, particularly quercetin, have demonstrated significant anti-ferroptosis effects in vitro and in vivo (Wendlocha et al., 2024). The favorable effects of this group of chemicals are mainly attributed to their antiatherogenic, antithrombotic, and antioxidant properties (Wendlocha et al., 2024).
Quercetin (PubChem CID: 5280343), a prevalent flavonoid present in medicinal plants, demonstrates therapeutic properties against a range of illnesses, such as alcoholic hepatitis, renal IR injury, and cancer (Chen et al., 2021c). Pharmacokinetic investigations have shown that quercetin can penetrate the BBB, indicating its potential to protect against neurodegenerative diseases (Pavlović et al., 2023; Javadinia et al., 2022). Quercetin enhances neurological function, reduces the size of brain tissue damage caused by MCAO in rats, and mitigates pathological characteristics (Peng et al., 2024). Additionally, quercetin promotes the survival of HT-22 cells when exposed to H2O2 and erastin (Peng et al., 2024). Specifically, quercetin can inhibit MDA, ROS, and Fe2+ expression while increasing SOD and GSH expression (Peng et al., 2024). It was discovered that quercetin inhibited ferroptosis both in vitro and in vivo by up-regulating GPX4 and FTH1 and down-regulating ACSL4 (Peng et al., 2024). Previous detailed publications on quercetin’s research with stroke suggest that it may be a viable candidate for stroke treatment (Zhang et al., 2022b).
Baicalein (PubChem CID: 5281605) is known for its various pharmacological properties, including antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor effects (Srivastava et al., 2021). Pharmacokinetic investigations have demonstrated that baicalein can cross BBB and spread throughout the cerebral nuclei (Zhu et al., 2012). Because of its low toxicity and therapeutic properties, baicalein, a natural bioactive molecule, has been extensively studied for its potential in treating stroke. Baicalein reduces iron levels, LPO generation, and morphological characteristics associated with ferroptosis in the brain tissues of MCAO mice (Li et al., 2022). Furthermore, baicalein suppressed ferroptosis by modulating the expression levels of GPX4, ACSL4, and ACSL3 in OGD/R cells, MCAO mice, and RSL3-stimulated HT22 cells (Li et al., 2022). A preliminary study of baicalin in the preparation of astragali decoction conducted by Zheng et al. reported that after oral administration to rats, baicalin was almost undetectable in serum because Escherichia coli hydrolyzed baicalin to baicalein and oroxylin A (Jung et al., 2012). In contrast, a large amount of metabolic jaundice was detected in the gut contents and a small amount of baicalin was detected in the blood of sterile rats 2 h after oral baicalin administration at the same dose. In normal rats, baicalin but not baicalein was detected in the blood soon after oral administration. This indicates that baicalin was not directly absorbed into the blood and that only its transformation into baicalein by the gut microbiota allowed it to enter the blood circulation.
Baicalin (PubChem CID: 64982) is a flavonoid compound with the molecular formula C21H18O11. It has pharmacological characteristics, including antioxidant, antiapoptotic, and neuroprotective actions, in several illnesses (Zhou et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2018). Baicalin also can inhibit the development of ferroptosis in ICH (Duan et al., 2021). It has been reported to exhibit neuroprotective effects against ICH-induced brain injury as well as reduce iron deposition in multiple tissues (Duan et al., 2021). Baicalin enhanced cell viability and suppressed ferroptosis in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells treated with hemin, erastin and RSL3 (Duan et al., 2021). Specifically, baicalin can promote the expression of GPX4 and SLC7A while inhibiting SLC3A2 and DMT1 (Duan et al., 2021). However, this experiment only detected a few indicators of ferroptosis and did not perform more in-depth research on the mechanisms involved. More and deeper studies are needed in the future.
Calycosin (PubChem CID: 5280448) is a typical phytoestrogen and possesses a variety of pharmacological activities, including anticancer, anti-cardiotoxicity, anti-diabetic nephropathy, and anti-cerebral ischemic activities, its molecular formula is C16H12O5 (Deng et al., 2021). The administration of calycosin resulted in a reduction in ferroptosis, as shown by the measurement of iron accumulation, MDA, SOD, ceramide, and ROS levels, as well as the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins (ACSL4, TfR1, FTH1, and GPX4) (Liu et al., 2023c). However, the sample size is too small, and more basic research should be needed in the future.
Vitexin (PubChem CID: 5280441) is a biologically active flavonoid chemical obtained from many culinary and medicinal plants. The chemical formula of the compound is C21H20O10. Vitexin reduced ferroptosis and protects brain tissue through the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway (Guo and Shi, 2023). In comparison to the Model group, treatment with Vitexin (0.5, 2.5, and 10 nM) significantly reduced the levels of HO-1, SLC7A11, and GPX-4, while increasing the levels of Keap1 and Tfr1. However, the oral bioavailability of vitexin is low and high doses of vitexin may lead to elevated liver enzymes, so we do not consider it a very good candidate drug.
Kaempferol (PubChem CID: 5280863), with a chemical formula of C15H10O6, is a prominent bioflavonoid that can be found in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and medicinal plants. Kaempferol exhibits neuroprotective, antioxidant, and anti-cancer attributes against several disorders linked to lipid oxidation, such as stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer (Nezhad Salari et al., 2024). Kaempferol increased SLC7A11, GPX4, and Nrf2 in OGD/R-treated neurons (Yuan et al., 2021). Kaempferol can also alleviate the accumulation of Fe2+ in OGD/R cells (Yuan et al., 2021). Kaempferol offers defiance against OGD/R-induced ferroptosis by activating the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway, at least to some extent (Yuan et al., 2021). Nonetheless, the entire article relies on data derived from in vitro experiments, which are inadequate for evaluating pharmacological effects if it is a pan-assay interfering drug. Animal experiments should be carried out in the future to fully verify its pharmacological effects.
Oroxin A (PubChem CID: 5320313), also known as baicalein-7-O-glucoside, is a highly effective flavonoid with the molecular formula C21H20O10. Oroxin A against ferroptosis after SAH in vivo (Chen et al., 2024). Following SAH, the levels of FTH1, GPX4, and SLC7A11 exhibited a decline, which was subsequently reversed by oroxin A treatment (Chen et al., 2024). Oroxin A can control ferroptosis through the Nrf2/GPX4 pathway and the CoQ10-FSP1 pathway (Chen et al., 2024). The neuroprotective properties of oroxin A are mediated through the Nrf2/GPX4 pathway, and the inhibitory effects of Oroxin A on ferroptosis and neuroinflammation depend on the transcriptional response of Nrf2. However, oroxin A is poorly utilized when taken orally, and it cannot cross the BBB. We consider it not a promising candidate drug.
Icariside II (PubChem CID: 5488822), a naturally occurring flavonoid companies derived from traditional Chinese medicinal Epimedium sagittatum (Siebold & Zucc.) Maxim. Its molecular formula is C27H30O10, and it possesses several pharmacological activities, such as antioxidant stress, anti-neuroinflammatory, anti-osteoporotic, and anti-cancer properties (Zhang et al., 2023b). Icariside II preconditioning exerts neuroprotective effects by activating the astrocytic Nrf2-mediated OXPHOS/NF-κB/ferroptosis axis (Gao et al., 2023). To be more specific, icariside II preconditioning greatly lowered the production of ROS, MDA, GPX4 levels, SOD2 activity, and SIRT5 activity in MCAO mice (Gao et al., 2023). Compared with the MCAO group, the icariside II precoding group increased the expression of HO-1, NQO-1, SIRT5, and GPX4 (Gao et al., 2023). Surface plasmon resonance assay investigates demonstrate that ICS II interacts with the Nrf2 protein, exhibiting an equilibrium constant (KD) of 1.033 × 10−4 M. Furthermore, Electrophoretic mobility shift assay confirmed that ICS II preconditioning enhanced the binding of Nrf2 to ARE at 2, 4, and 24 h. A competitive assay verified that the cold probe impeded the DNA-binding activity of Nrf2, hence further substantiating the specificity of the binding. All of these results suggest that ICS II probably activates a Nrf2–ARE signaling pathway by targeting Nrf2. LC-MS analysis demonstrated that the quantities of ICS II in the brain homogenates of mice following MCAO injury were elevated compared to those in the sham group, indicating that ICS II can cross the BBB. Therefore, we state that Icariside II is a viable pharmacological candidate for stroke treatment.
Curcumin (PubChem CID: 969516) is a commonly found phenolic molecule derived from the rhizome of Curcuma longa L. with a chemical formula of C21H20O6. It is known to possess strong antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties when used in pharmaceutical applications (Zhang et al., 2018). Curcumin has been observed to have the capacity to modulate ferroptosis processes associated with cancer, tissue injury, and other diseases, as evidenced by the in vitro and in vivo findings described above (Foroutan et al., 2024). Nevertheless, the effectiveness of curcumin is significantly hindered by its undesired water solubility, inadequate oral bioavailability, inefficiency in crossing the BBB, and other physiological barriers (Tran and Tran, 2020). In the experiments of Cong Yang et al., they encapsulated curcumin in Polymer-based nanoparticles (Cur-NPS) and explored the effect of these Cur-NPs to enhance Cur delivery both in vitro and in vivo (Yang et al., 2021). The findings demonstrated that Cur-NPs effectively inhibited erastin-induced ferroptosis in HT22 murine hippocampus cells (Yang et al., 2021). However, all the indicators related to ferroptosis are cell experiments. More animal experiments should be carried out in the future. Moreover, due to the characteristics of curcumin, we believe that curcumin cannot be a candidate drug for the treatment of ICH.
(−)-Epicatechin (PubChem CID: 72276) is a naturally derived flavanol molecule, represented by the molecular formula C15H14O6, which is abundantly present in tea, chocolate, and many botanical drugs. The molecule has a crucial antioxidant role by binding phenolic hydroxyl groups and free radicals, hence achieving free radical scavenging activities. (−)-Epicatechin was found to have the ability to decrease ferroptosis in vivo, as evidenced by its reversal of the rising levels of ROS and Fe2+ (Chang et al., 2014). Furthermore, the levels of lipid ROS and LC3 in H9C2 cells were reduced with (−)-epicatechin treatment (Chang et al., 2014). Additionally, the processes of autophagy and ferroptosis were also mitigated in a manner that depended on the dosage, as shown in vitro (Chang et al., 2014). The co-cultivation of the USP14 inhibitor IU1 and (−)-epicatechin demonstrated that (−)-epicatechin controls ferroptosis via influencing the USP14-autophagy pathway (Chang et al., 2014). However, quantitative experimental methods detected the expressions of several ferroptosis-related genes, including SOD, NQO1, and MDA; these methods are inadequate for evaluating pharmacological effects if the drug is a pan-assay interfering drug.
Carthamin yellow (PubChem CID: 12305280) is derived from the Carthamus tinctorius L., and its chemical formula is C21H22O11. Carthamin yellow mitigated the effects of MCAO-induced ferroptosis by reducing iron and ROS accumulation, decreasing LPO, and restoring the expression levels of proteins linked to ferroptosis (Guo et al., 2021). In addition, carthamin yellow therapy suppressed the accumulation of Fe2+ and ROS and restored the levels of ACSL4, TFR1, GPX4, and FTH1 proteins in the brain (Guo et al., 2021). Compared with the model group, carthamin yellow group also increased SOD and GSH and decreased MDA levels (Guo et al., 2021). Carthamin yellow can cross the BBB; however, its oral bioavailability is limited, and the precise target mechanisms remain ambiguous. Further comprehensive research on the mechanism is necessary for its potential development into medication in the future.
5.3 Polyphenols
Polyphenols are formed by direct connection between hydroxyl (-OH) groups and aromatic nuclei (benzene rings or condensed benzene rings). Polyphenols are widely present in nature and can be classified into volatile phenols and non-volatile phenols based on their volatility. Polyphenols were long believed to be primarily anti-nutrients and not particularly essential to human nutrition (Rana et al., 2022). However, recent research studies have now shown that polyphenolic substances do many biologically important things, including protecting against metabolic disorders and chronic diseases and acting as an antioxidant (Ganesan and Xu, 2017). Consuming polyphenol-rich foods has been associated with a range of health benefits, including optimizing cardiometabolic health and to a lesser extent positively impacting brain functioning in humans.
Rosmarinic acid (PubChem CID: 5281792) is a water-soluble compound with the chemical formula C18H16O8. Rosmarinic acid is a naturally occurring water-soluble phenolic acid compound characterized by its unstable properties, low lipid solubility, and limited cell membrane permeability (Noor et al., 2022). To overcome this drawback, Cui ling Jia et al. used rosmarinic acid encapsulated in liposomes (RosA-LIP) (Jia et al., 2024). The administration of RosA-LIP improved the structural defects of mitochondria and reinstated the integrity of mitochondrial cristae (Jia et al., 2024). The RosA-LIP treatment resulted in an increase in the activity of SOD and CAT, as well as the levels of Nrf2, HO-1, and GSH (Jia et al., 2024). Compared with the model group, the RosA-LIP group significantly reduced the expression of Ptgs2, ACSL4, LPCAT3, 12-Lox, MDA, and 4-HNE (Jia et al., 2024). In addition, RosA-LIP has shown the capability to specifically inhibit the expression of TfR1 in BMECs, resulting in a decrease in the uptake of iron in the brain and minimizing the occurrence of ferroptosis, which is dependent on ACSL4/LPCAT3/Lox, in the ischemic brain (Jia et al., 2024). The specific target of rosmarinic acid remains undetermined, necessitating future investigation for accurate identification.
Caffeic acid (PubChem CID: 689043) is a polyphenolic compound present in a vast array of dietary plant metabolites. Its molecular formula is C9H8O4. In MCAO rat brain and in OGD/R-treated SK-N-SH cells in vitro, caffeic acid decreased the expression of TFR1 and ACSL4, and increased the synthesis of glutathione via the Nrf2 signaling pathway to inhibit ferroptosis (Li et al., 2024a). Application of ML385, an Nrf2 inhibitor, blocked the neuroprotective effects of caffeic acid in both vivo and in vitro models, evidenced by excessive accumulation of iron ions and inactivation of the ferroptosis defense system. This is the initial study on the investigation of caffeic acid in relation to stroke. We suggest that more research should be conducted in the future to validate the efficacy of Caffeic acid on stroke.
Salvianolic acid A (PubChem CID: 5281793) has been identified as a particularly effective agent that possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, as well as the ability to modulate the integrity and functionality of the BBB (Liu et al., 2021). Salvianolic acid A reduced MDA and Fe2+ production and reversed the downregulation of GSH, XCT, and GPX4 (Shi et al., 2024). Further research shows that salvianolic acid A inhibits ferroptosis after ICH through Akt/GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling pathway (Shi et al., 2024). A pharmacokinetic investigation demonstrated that circulatory system exposure to Salvianolic acid A was comparable between sham controls and I/R rats; however, brain exposure to Salvianolic acid A was markedly elevated in I/R rats compared to sham controls (fold change of 9.17), indicating that the increased exposure to Salvianolic acid A facilitated its neuroprotective effect (Feng et al., 2017). In conclusion, we conclude that Salvianolic A is a potential therapeutic agent for stroke treatment.
Carvacrol (PubChem CID: 10364) is a natural compound that occurs in the leaves of several plants and botanical drug including wild bergamot, thyme and pepperwort, but which is most abundant in Origanum vulgare L. The molecular formula of carvacrol is C10H14O. Compare with the model group, carvacrol could increase SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT in MCAO mice and reduce the expression of MDA and Fe2+ (Guan et al., 2019). In vitro experiments indicated that carvacrol significantly decreased the levels of MDA, H2AX protein expression, and hippocampal neuron impairment compared to those in the anoxia/reoxygenation group, but these effects were reversed by silencing GPx4. This study performed in vivo and in vitro experiments to illustrate the protective impact of carvacrol on stroke; nonetheless, there is an insufficient amount of research on carvacrol in the context of stroke, necessitating further pharmacological and mechanistic investigations in the future.
Resveratrol (PubChem CID: 445154), a nonflavonoid polyphenol molecule, possesses potent anti-inflammatory, anti-OS, and anti-apoptotic properties. Pretreatment with resveratrol can effectively prevent iron overload, enhance neuronal survival, increase levels of GSH, reduce levels of ROS, decrease the expression of ACSL4 protein, increase the expression of Ferritin and GPX4 proteins, and mitigate damage to mitochondrial structure following OGD/R injury in vitro (Zhu et al., 2022a). Additionally, resveratrol pretreatment may improve the rate of neuronal survival in vitro and lessen the effects of erastin and RSL3-induced ferroptosis (Zhu et al., 2022a). Resveratrol has been the subject of extensive research on stroke, but the bioavailability is only 1%. Future research should address this drawback. To sum up, we believe that resveratrol is a candidate drug for the treatment of stroke.
Rhein (PubChem CID: 10168) is the primary plant metabolite in several traditional Chinese herbal medicine. It has a variety of pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, antitumor, antifibrosis, and anti-inflammation properties (Wu et al., 2020). The molecular formula of a is C15H8O6. Rhein effectively inhibited OS, intracellular ROS production, and protein expression associated to ferroptosis in both in vivo and in vitro MCAO models. Mechanistically, rhein counteracted OGD/R-induced damage in HT22 cells by modulating the NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway (Liu et al., 2023d). At present, there are relatively few studies on stroke from rhein, and the liver and kidney toxicity of rhein is also very high. More studies should be carried out in the future. We don't think this is a promising candidate drug.
5.4 Alkaloids
Alkaloids are a kind of nitrogen-containing alkaline organic compounds that exist in nature (mainly plants, but some also exist in animals). Most of them have complex ring structures. The ring primarily contains nitrogen, which exhibits significant biological activity. It is one of the important effective plant metabolites in Chinese herbal medicine. Alkaloids are an important plant metabolite of natural products with structural diversity. Currently, researchers have reported over 60 types of alkaloids.
Berberine (PubChem CID: 2353), a bioactive alkaloid extracted from many herbal plant species, has several pharmacological properties such as antibacterial, antidiabetic, and anticancer actions (Song et al., 2020). Berberine mitigates MCAO-induced ferroptosis, as evidenced by the upregulated expression of SLC7A11 but the reduced expression of ACSL4, TFR1, and COX2 (Wang et al., 2023c). Numerous pharmacological investigations on Berberine currently exist, and it is utilized in therapeutic practice. Consequently, we believe that Berberine is an excellent candidate for medication for the treatment of stroke.
Dauricine (PubChem CID: 73400) the molecular formula is C38H44N2O6. It was demonstrated in the ferroptosis model of SH-SY5Y cells that the increase of GPX4 expression by dauricine suppressed ferroptosis in SH-SY5Y cells caused by RSL3 and enhanced cell survival (Peng et al., 2022). In the C57 mouse ICH model, it was demonstrated that dauricine increased the expression of GPX4 (Peng et al., 2022). This experiment validated the therapeutic effect of dauricine on stroke both in vivo and in vitro; nonetheless, there is a deficiency of data about dauricine’s impact on stroke, necessitating further pharmacological and mechanistic investigations in the future.
5.5 Traditional Chinese medicine formulations
Angong Niuhuang pill (AGNHP) originated from Wenbing Tiaobian written by the febrile disease expert Wu Jutong in the Qing Dynasty. In vivo experiments indicated that AGNHP inhibits ROS, LPO, and Fe2+ accumulations in MCAO and ICH rats (Bai et al., 2024). Evidence from in vitro experiments shown that AGNHP mitigated ferroptosis damage caused by erastin in PC12 cells, enhanced cell survival, decreased LPO and Fe2+ concentrations, and boosted mRNA expressions of PPARγ, AKT, and GPX4 (Bai et al., 2024). Subsequent investigation demonstrates that AGNHP reduced the damage caused by MCAO and ICH by inhibiting ferroptosis through the activation of the PPARγ/ATK/GPX4 pathway (Bai et al., 2024).
Di-Huang-Yin-Zi (DHYZ) is a traditional herbal medicine employed for the prevention and treatment of neurological disorders since the Song Dynasty. The treatment with DHYZ reduced levels of ROS and MDA, thereby suppressing the expression of markers associated to ferroptosis, including Fe2+, SLC7A11, and GPX4 (Yang et al., 202b). The mechanism by which DHYZ reduces symptoms and improves the functional capacity of rats with poststroke depression is mostly through the suppression of ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway (Yang et al., 2024b).
Naodesheng pills (NDSP) are commonly prescribed traditional Chinese medicines consisting of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen, C. tinctorius L., Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge and Puerariae Lobatae Radix, and Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments have shown that NDSP can increase the expression of GPX4, SLC7A11, and SOD while inhibiting the expression of MDA, TFR1, DMT1, ROS, and Fe2+ (Yang et al., 2024b). This mechanism is associated with the regulation of ferroptosis via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway (Yang et al., 2024b).
Naotai formula (NTF) is composed of A. membranaceus, Rhizoma Chuanxiong, Lumbricus and Bombyx Batryticatus. NTF could prevent MCAO-induced neuronal ferroptosis in rats by increasing the levels of SCL7A11, GPX4, and GSH (Lan et al., 2020). Hepcidin, BMP6, and SMADs levels were also lowered by NTF treatment, while SLC40A1 and GPX4 levels were raised (Liao et al., 2023).
Tongluo Decoction (TLD), a traditional Chinese medicine prescription, has been extensively employed for the management of ischemic stroke. TLD reduced MDA, ROS and Fe2+ related activity and increased SOD levels (Li et al., 2024b). Compared with the MCAO group, TLD treatment significantly upregulated Nrf2, SLC7A11, FTH1, GPX4 and HO-1 levels (Li et al., 2024b). Mechanistically, TLD rescued endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis but promoted Sonic Hedgehog signaling in rats with MCAO (Hui et al., 2022).
Xingnaojing (XNJ) is a traditional Chinese medicinal agent used clinically for treating stroke. XNJ has been approved by the Chinese National Drug Administration. XNJ reportedly increases BBB permeability, lowers inflammation, and boosts circulation (Qu et al., 2019). Compared with the MCAO group, XNJ can reduce the expression of COX-2, TFR, and DMT1 and increase the expression of GPX4, FPN, and HO-1 (Liu et al., 2023e). Moreover, XNJ increased GPX4 levels and inhibited COX-2 and TFR protein expression after SH-SY5Y cell hypoxia (Liu et al., 2023e).
Tongqiao Huoxue Decoction (TQHX) mainly composed of eight botanical drugs, including Paeoniae Radix Rubra, Rhizoma Chuanxiong, Prunus persica (L.) Batsch, Ziziphus jujuba Mill., Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens. TQHX is employed to improve blood circulation and eradicate blood stasis. In comparison to the MCAO group, the TQHX treatment effectively reduced the levels of MDA, Fe2+, ROS and ACSL4 while simultaneously increasing the expression of SOD, FTH1, and GPX4 (Ou et al., 2024).
Salvia miltiorrhiza (SM) has a long history of application in China. It was first recorded in the Shennong Herbal’s classic of the Eastern Han Dynasty. SM is a commonly employed treatment for vascular diseases, particularly ischemic cardiovascular diseases. The levels of 4-HNE, ACLS4 and MDA in the penumbra of the MCAO mouse brain could be reduced by SM, which was induced by OS upregulation (Ko et al., 2023). In MCAO mice, SM treatment upregulated GPX4 and GSH and reduced FPN1 and ferritin (Ko et al., 2023).
Paeoniae Radix Rubra (PRR), the root of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. or Paeonia veitchii Lynch, is extensively used in Chinese clinical practice to enhanjce blood circulation and alleviate blood stagnation. An in vivo study revealed that PRR enhanced the expression of GPX4, FTH1, Beclin1, LC3 II, and p-Akt in the rat of MCAO (Zhao et al., 2023b). Additionally, the in vitro study showed that PRR can reduce H2O2-induced HT22 cell damage by regulating cytokines like MDA, reduced GSH, and ROS, as well as by elevating the expressions of GPX4 and Beclin1 (Zhao et al., 2023b).
Danhong injection (DHI), a standardized injection that contains S. miltiorrhiza Bunge and C. tinctorius L., is frequently employed to treat cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases. Compared with the model group, DHI increased the expression of SOD, GSH, and SATB1 and decreased the expression of MDA, TfR1, and TF (Zhan et al., 2023). Mechanism research shows that DHI inhibitors ferroptosis in ischemic stroke by regulating the SATB1/SLC7A11/HO-1 pathway (Zhan et al., 2023).
Danlou tablet (DLT) is composed of Pericarpium Trichosanthis, Allium macrostemon Bunge, Puerariae Lobatae Radix, L. chuanxiong Hort., S. miltiorrhiza Bunge [Lamiaceae; Salviae miltiorrhizae radix et rhizoma], Paeoniae Radix Rubra, Alisma plantago-aquatica Linn., A. membranaceus, Drynariae Rhizoma and Curcumae Radix. DLT promotes blood circulation, resolves phlegm and stasis, alleviates stagnation, and dispels congestion. Both vivo and vitro studies showed that DLT markedly decreased the level of COX2 protein, GSSG, and MDA, while simultaneously increasing the levels of SLC7A11, GPX4, and GSH (Liu et al., 2024).
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge processed with Porcine cardiac blood (PCB-DS) aims to enhance the brain-targeted therapy of DS through the BBB. DS shows great potential as a Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of vascular disorders, particularly cerebrovascular disorders. PCB is a characteristic of Chinese herbal medicine, and a pharmacological reference frequently used for the treatment of brain disorders. Prior research demonstrated that PCB-DS mitigated MCAO by downregulating OS, which included reducing intracellular ROS and MDA levels (Zhou et al., 2023b). In both vivo and in vitro studies, PCB-DS modulated Fe2+ levels, GSH, MDA, SOD, ROS, and liperfluo to inhibit ferroptosis (Zhou et al., 202a). Further studies reveal that PCB-DS directly activated GLRX5, therefore reducing the iron-starvation response, and downregulated the SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway to prevent ferroptosis (Zhou et al., 2024a).
5.6 Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are essential plant metabolites of the cell wall of microorganisms, the membrane of animal cells, and higher plants. It is also closely associated with physiological functions. In recent years, there has been a growing focus on polysaccharides as a significant category of bioactive natural products. Various studies have illustrated the bioactivities of natural polysaccharides, which have resulted in their use in the treatment of various diseases.
Neutral polysaccharide (NPGE) is a metabolite extracted from the plant that exhibits immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and antioxidant properties. In contrast to the MCAO group, the NPGE treatment alleviated neuronal ferroptosis by increasing GPX4 levels, decreasing ROS, MDA, and Fe2+ excessive accumulation, and enhancing GSH levels and SOD enzymatic activity (Zhang et al., 2024). Further mechanistic research demonstrates that NPGE reduces cerebral IR injury by inhibiting ferroptosis-mediated neuroinflammation through the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway (Zhang et al., 2024). The pharmacodynamic experiments of NPGE were conducted very comprehensively. In the future, small molecule and protein interaction experiments should be carried out to further confirm the target of NPGE.
Roots of Astragalus propinquus Schischkin (RAP) can raise yang qi and tonifying the spleen and lung qi, thereby facilitating urination and reducing edema. Compared with the MCAO group, RAP could increase the expression of XCT, SLC3A2, IREB2, Nrf2, HO-1, and GPX4 (Chen et al., 2022a). Both granules and injections have the same effect, but granules have the best effect. The Marker for ferroptosis in the article is too simple, with Western blot experiments being the majority. Other experiments (such as immunofluorescence) should be carried out to prove the therapeutic effect of RAP on stroke from multiple perspectives.
5.7 Other compounds
Cottonseed oil (CSO) is a vegetable oil frequently intended for the dissolution of lipid-soluble medications. Prior studies have demonstrated that CSO provides protection against intestinal inflammation, tumor metastasis, OS, and atherosclerosis (Araujo et al., 2019). Notably, current research has demonstrated its effectiveness in treating disorders of the nervous system (Sun et al., 2023). Compared to the MCAO group, CSO reduced the influx of Fe2+, TF, and TF receptors; upregulated anti-ferroptosis proteins (GPX4, xCT, HO1, and FTH1) while down-regulating ferroptosis-related protein ACSL4; raised GSH and SOD activity; and decreased MDA and LPO levels (Sun et al., 2023). Nevertheless, an excessively small sample size may result in erroneous conclusions. Consequently, we suggest that CSO is not an optimal candidate medication for the treatment of stroke. Nevertheless, an excessively small sample size may result in erroneous conclusions. Consequently, we suggest that CSO is not an optimal candidate medication for the treatment of stroke.
Mastoparan M (MM) is a peptide derived from bee venom that has biological activity and mainly affects intracellular signal transduction by acting on the cell membrane. After receiving MM therapy for 24 or 48 h, the ischemic hemisphere of MCAO mice showed a decrease in Fe2+ and MDA levels, but a rise in the expression of the proteins LC3B, x-CT, NRF2, and GPX4 (Sun et al., 2023). In addition, these results were confirmed in three models: OGD/R, peroxidation mediated by H2O2, and ferroptosis triggered by erastin (Sun et al., 2023). However, MM has conducted relatively few studies on stroke, and more fundamental research needs to be carried out in the future.
Melatonin is one of the hormones secreted by the pineal gland, which is an amine hormone produced by the pineal gland. Within the HT-22 cell model, melatonin enhanced cell proliferative capacity, decreased apoptosis, and lowered ROS generation (Sun et al., 2024b). Melatonin’s protective benefits are mediated by its inhibition of ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of controlled cell death, via the regulation of the ACSL4/CYP1B1 pathway, according to further mechanistic investigations (Sun et al., 2024b). Melatonin lower LPO, ROS generation, and ACSL4 protein expression in MCAO mice (Sun et al., 2024b). Another study found that melatonin regulates ACSl4 ubiquitination and impacts ferroptosis by increasing MDM2 expression, which contributes to its therapeutic efficacy in stroke treatment (Ji et al., 2024). Melatonin is an over-the-counter medication in the United States and Canada, and a dietary supplement in mainland China; hence, it is not regarded as a viable pharmaceutical option for stroke treatment.
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide (PubChem CID: 61361, DL-NBP) is a synthetic compound extracted from celery seeds. The effectiveness and safety of the treatment have been assessed in multiple clinical trials conducted in China (Fan et al., 2021). Compared with the MCAO group, DL-NBP could significantly reduce the levels of MDA, ROS, and Fe2+ and increase the expression of GSH, GPx4, and SLC7A11 (Xu et al., 2023b). Further research into the mechanism revealed that DL-NBP presumably acts as a mediator in the SLC7A11/GSH/GPX4 signaling pathway to mitigate ferroptosis (Xu et al., 2023b). There have been many pharmacological studies on DL-NBP, and DL-NBP has also been applied in clinical practice. Therefore, we believe that DL-NBP is an effective candidate drug for the treatment of stroke.
Taurine (PubChem CID: 1123) is an amino acid converted from sulfur-containing amino acids that is widely distributed in various tissues and organs in the body. It mainly exists in the interstitial fluid and intracellular fluid in a free state. Its molecular formula is C2H7NO3S. The current investigation revealed a significant reduction in taurine levels in cerebrospinal fluid among patients with SAH (Liu et al., 2022b). This finding implies that administering taurine treatment after SAH may enhance neurological impairment, reduce OS, regulate iron accumulation, maintain BBB integrity, and prevent neuronal ferroptosis in the SAH model in vivo (Liu et al., 2022b). Thorough investigations suggest that taurine may modulate MDA levels and ROS accumulation, as well as control the expression of SLC7A11 and GPX4, and the AKT/GSK3β pathway in vitro (Liu et al., 2022b). Nonetheless, there exists an absence of research about the treatment of stroke by taurine. Future research should focus on more mechanism and efficacy investigations. Consequently, we do not regard taurine as a viable candidate medication for the treatment of stroke.
Crocin (PubChem CID: 5281233) is a hydrophilic carotenoid that is synthesized in the Crocus sativus L. Compared to the ICH group, the crocin-treated group significantly increased the activities of SOD and GSH-px (Wang et al., 2022b). On the other hand, crocin therapy significantly reduced the concentration of MDA (Wang et al., 2022b). The observed elevation in Fe2+ concentration and the upregulation of GPX4, FTH1, and SLC7A11 genes demonstrated the inhibition of ferroptosis in neuron cells by crocin (Wang et al., 2022b). Mechanistically, crocin alleviates ICH-induced neuronal ferroptosis by facilitating Nrf2 nuclear translocation (Wang et al., 2022b). While there are limited studies on the treatment of ICH by crocin, pertinent research exists regarding the treatment of ischemic stroke by crocin (Shahbaz et al., 2022). Future efficacy studies should be conducted to validate the treatment of ICH by crocin.
6 Clinical translation discussion
Compared with the previous review published by Zhou et al., we have summarized the mechanism of ferroptosis in stroke and summarized its natural products, rather than only focusing on ischemic stroke (Wang et al., 2024b). Another review systematically summarizes the status and progress of TCM in regulating various CNS diseases through the ferroptosis pathway (Zhou et al., 2024b). Its emphasis is on TCM rather than natural products. This article assesses traditional Chinese medical treatment methods, including Chinese herbal medicine, acupuncture, and moxibustion, as well as their mechanisms of action in regulating the ferroptosis pathway (Zhou et al., 2024b). In this review, we systematically summarized the mechanisms and targets of ferroptosis after stroke and summarized the related natural products (Figure 5). We aimed to provide insights into more feasible treatment schemes based on the currently proven effective natural products and Chinese medicine. Although natural products perform well as anti-ferroptosis in stroke animal experiments, there are few clinical applications. Thus, we summarized the clinical trial of the 56 natural products aimed at stroke treatment (Table 4, www.clinicaltrials.gov.). We discovered that clinical trials on stroke only used 7 natural products (Table 4).
From the translation of preclinical evaluation to clinical trial, model animals for stroke are relatively simple and cannot fully represent the more complex pathological features of human beings. This phenomenon may have multiple causes: 1. Regarding natural active plant metabolites, while the pharmacodynamic effects and targets are rather well-defined, research on their remains is inadequate. The study on the in vivo processes (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, toxicokinetic) and safety assessment is insufficient, prolonging the research and development cycle of new pharmaceuticals from laboratory to clinical use; 2. The difficulty of standardizing traditional Chinese medicine. The investigations on herbal extracts and formulations reveal a complex composition, resulting in challenges in target identification, and the mechanisms involved may not be readily or thoroughly clarified. Moreover, the many technologies employed in the manufacturing of herbal extracts and formulations pose a challenge to the quality control of their active plant metabolites. 3. Disease model. Animal models struggle to accurately replicate the pathogenesis of patients, a fundamental issue that hinders the development of laboratory drugs.
Enhanced exploitation of natural products for illness treatment necessitates the development of specific methods and feasible methodologies. 1. Natural products with well-defined targets can improve mechanistic comprehension in fundamental research and promote their use in clinical applications. Biotechnological techniques, such as the cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA) or target-responsive accessibility profiling (TRAP) can be employed to identify the targets of various natural products. 2. The in vivo pharmacokinetic and pharmacological properties should be investigated (Tu et al., 2023). 3. Through pre-clinical research or illness prediction models, the dosage of a particular natural substance must correspond with the optimal type, stage, and timing of the disease. 4. Certain natural products encounter obstacles such as restricted water solubility, diminished bioavailability, or insufficient stability. Structural alteration, nano-delivery, or co-administration may be utilized to enhance efficacy. Utilizing multi-omics and artificial intelligence facilitates a more thorough exploration of the mechanisms behind natural products (Zhu et al., 2022b).
Preclinical models may be utilized to evaluate the efficiency of prospective therapies or procedures, acknowledging that the significance of harm and protective pathways, along with the administration of therapy, may vary between the preclinical model and people. Preclinical models can yield critical insights into the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of prospective treatments, along with potential toxicity. Critical factors must be evaluated when determining whether to forward a medication or technique from preclinical testing in stroke models to clinical trials. Effective translation necessitates diverse expertise, including basic scientists, clinical trialists, neuroimaging specialists, neurosurgeons, and rehabilitation specialists. Clinically significant outcome metrics are essential in preclinical modelling, while recognizing the intrinsic limitations of these models. Conversely, the prospective influence of a target or outcome measure within a model (together with its constraints) must be conveyed to those implementing it in clinical trials. Preliminary collaboration throughout the translational pipeline is expected to produce more resilient preclinical modelling and clinical trial design. At present, neurological impairments serve as the principal outcome measurement to assess preclinical efficacy in clinical trials. Nonetheless, possessing supplementary biomarkers or surrogate measures (e.g., imaging, inflammatory markers, brain oedema, and atrophy), particularly in relation to specific therapeutic target engagement, can be highly beneficial for comparative analysis across species and in clinical trials.
Currently, research on ferroptosis concentrates on four primary aspects: morphological feature assessment, gene expression analysis, protein level evaluation, and biochemical characteristic index measurement. Thus, the absence of definitive and authoritative standards for ferroptosis detection has emerged as a significant concern in preclinical and clinical research. Finally, both the development of natural drugs or traditional Chinese medicine and the exploration of the mechanism of stroke disease need a long way to go.
7 Conclusion
In this review, we summarize the natural products and herbal medicine currently employed in ferroptosis along with their mechanisms of action, highlighting the potential and challenges of clinical translation. This review is to accelerate the development of novel natural and herbal medicine treatments and to offer novel perspectives on how to treat ferroptosis in stroke.
Author contributions
YZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XT: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. RM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. JG: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 8247447), National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2023ZD0505600), State Key Laboratory of Dampness Syndrome of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. SZ2021ZZ06), State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Projects (Grant No. SKLKY2025C0003) and Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (No. 2024B01J1352).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alvarez, S. W., Sviderskiy, V. O., Terzi, E. M., Papagiannakopoulos, T., Moreira, A. L., Adams, S., et al. (2017). NFS1 undergoes positive selection in lung tumours and protects cells from ferroptosis. Nature 551 (7682), 639–643. doi:10.1038/nature24637
Araujo, R. S., Oliveira, A. C., Sousa, F. C. B., Dourado, L. R. B., Guimarães, S. E. F., Silva, W., et al. (2019). Effects of cottonseed oil and ferrous sulfate on the performance and expression of antioxidant enzymes in broilers. Poult. Sci. 98 (9), 3860–3869. doi:10.3382/ps/pez103
Bai, X., Zheng, E., Tong, L., Liu, Y., Li, X., Yang, H., et al. (2024). Angong Niuhuang Wan inhibit ferroptosis on ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke by activating PPARγ/AKT/GPX4 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 321, 117438. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117438
Bai, Y., Meng, L., Han, L., Jia, Y., Zhao, Y., Gao, H., et al. (2019). Lipid storage and lipophagy regulates ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 508 (4), 997–1003. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.039
Bao, W. D., Zhou, X. T., Zhou, L. T., Wang, F., Yin, X., Lu, Y., et al. (2020). Targeting miR-124/Ferroportin signaling ameliorated neuronal cell death through inhibiting apoptosis and ferroptosis in aged intracerebral hemorrhage murine model. Aging Cell 19 (11), e13235. doi:10.1111/acel.13235
Bu, Z. Q., Yu, H. Y., Wang, J., He, X., Cui, Y. R., Feng, J. C., et al. (2021). Emerging role of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke: a new therapeutic target? ASN Neuro 13, 17590914211037505. doi:10.1177/17590914211037505
Chang, C. F., Cho, S., and Wang, J. (2014). (-)-Epicatechin protects hemorrhagic brain via synergistic Nrf2 pathways. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 1 (4), 258–271. doi:10.1002/acn3.54
Chen, B., Wang, H., Lv, C., Mao, C., and Cui, Y. (2021a). Long non-coding RNA H19 protects against intracerebral hemorrhage injuries via regulating microRNA-106b-5p/acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 axis. Bioengineered 12 (1), 4004–4015. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1951070
Chen, G., Chen, X., Niu, C., Huang, X., An, N., Sun, J., et al. (2018). Baicalin alleviates hyperglycemia-induced endothelial impairment 1 via Nrf2. J. Endocrinol. doi:10.1530/JOE-18-0457
Chen, H., Ren, L., and Ma, W. (2023). Mechanism of SOX10 in ferroptosis of hippocampal neurons after intracerebral hemorrhage via the miR-29a-3p/ACSL4 axis. J. Neurophysiol. 129 (4), 862–871. doi:10.1152/jn.00374.2022
Chen, J., Ma, D., Bao, J., Zhang, Y., and Deng, G. (2022a). Roots of Astragalus propinquus Schischkin regulate transmembrane iron transport and ferroptosis to improve cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 7410865. doi:10.1155/2022/7410865
Chen, J., Ou, Z., Gao, T., Yang, Y., Shu, A., Xu, H., et al. (2022b). Ginkgolide B alleviates oxidative stress and ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 ubiquitination to improve diabetic nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 156, 113953. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113953
Chen, J., Shi, Z., Zhang, C., Xiong, K., Zhao, W., and Wang, Y. (2024). Oroxin A alleviates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage by regulating ferroptosis and neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflammation 21 (1), 116. doi:10.1186/s12974-024-03099-3
Chen, J., Wang, Y., Wu, J., Yang, J., Li, M., and Chen, Q. (2020). The potential value of targeting ferroptosis in early brain injury after acute CNS disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 13, 110. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2020.00110
Chen, L., Liu, J., Mei, G., Chen, H., Peng, S., Zhao, Y., et al. (2021c). Quercetin and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a review based on experimental data and bioinformatic analysis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 154, 112314. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112314
Chen, W., Jiang, L., Hu, Y., Tang, N., Liang, N., Li, X. F., et al. (2021b). Ferritin reduction is essential for cerebral ischemia-induced hippocampal neuronal death through p53/SLC7A11-mediated ferroptosis. Brain Res. 1752, 147216. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147216
Chen, Y.-Y., Liu, Q.-P., An, P., Jia, M., Luan, X., and Tang, J.-Y. (2022c). A promising natural neuroprotective agent. Phytomedicine 95, 153883. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153883
DeGregorio-Rocasolano, N., Martí-Sistac, O., Ponce, J., Castelló-Ruiz, M., Millán, M., Guirao, V., et al. (2018). Iron-loaded transferrin (Tf) is detrimental whereas iron-free Tf confers protection against brain ischemia by modifying blood Tf saturation and subsequent neuronal damage. Redox Biol. 15, 143–158. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.026
Deng, M., Chen, H., Long, J., Song, J., Xie, L., and Li, X. (2021). Calycosin: a review of its pharmacological effects and application prospects. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 19 (7), 911–925. doi:10.1080/14787210.2021.1863145
Dietrich, R. B., and Bradley, W. G. (1988). Iron accumulation in the basal ganglia following severe ischemic-anoxic insults in children. Radiology 168 (1), 203–206. doi:10.1148/radiology.168.1.3380958
Dixon, S. J., Lemberg, K. M., Lamprecht, M. R., Skouta, R., Zaitsev, E. M., Gleason, C. E., et al. (2012). Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149 (5), 1060–1072. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Duan, C., Jiao, D., Wang, H., Wu, Q., Men, W., Yan, H., et al. (2022). Activation of the PPARγ prevents ferroptosis-induced neuronal loss in response to intracerebral hemorrhage through synergistic actions with the Nrf2. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 869300. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.869300
Duan, L., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., Su, S., Zhou, L., Lo, P. C., et al. (2021). Baicalin inhibits ferroptosis in intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 629379. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.629379
Fan, X., Shen, W., Wang, L., and Zhang, Y. (2021). Efficacy and safety of DL-3-n-butylphthalide in the treatment of poststroke cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 810297. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.810297
Fang, Y., Chen, X., Tan, Q., Zhou, H., Xu, J., and Gu, Q. (2021). Inhibiting ferroptosis through disrupting the NCOA4-FTH1 interaction: a new mechanism of action. ACS Cent. Sci. 7 (6), 980–989. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.0c01592
Feng, S. Q., Aa, N., Geng, J. L., Huang, J. Q., Sun, R. B., Ge, C., et al. (2017). Pharmacokinetic and metabolomic analyses of the neuroprotective effects of salvianolic acid A in a rat ischemic stroke model. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 38 (11), 1435–1444. doi:10.1038/aps.2017.114
Foroutan, Z., Butler, A. E., Zengin, G., and Sahebkar, A. (2024). Curcumin and ferroptosis: a promising target for disease prevention and treatment. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 82 (2), 343–349. doi:10.1007/s12013-023-01212-6
Fu, C., Wu, Y., Liu, S., Luo, C., Lu, Y., Liu, M., et al. (2022). Rehmannioside A improves cognitive impairment and alleviates ferroptosis via activating PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 and SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway after ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 289, 115021. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115021
Ganesan, K., and Xu, B. (2017). A critical review on polyphenols and health benefits of black soybeans. Nutrients 9 (5), 455. doi:10.3390/nu9050455
Gao, J., Ma, C., Xia, D., Chen, N., Zhang, J., and Xu, F. (2023). Icariside II preconditioning evokes robust neuroprotection against ischaemic stroke, by targeting Nrf2 and the OXPHOS/NF-κB/ferroptosis pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 180 (3), 308–329. doi:10.1111/bph.15961
Gao, M., Monian, P., Quadri, N., Ramasamy, R., and Jiang, X. (2015). Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol. Cell 59 (2), 298–308. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.011
Gao, M., Yi, J., Zhu, J., Minikes, A. M., Monian, P., Thompson, C. B., et al. (2019). Role of mitochondria in ferroptosis. Mol. Cell 73 (2), 354–363. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.042
GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators (2024). Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 403 (10440), 2133–2161. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8
Guan, X., Li, X., Yang, X., Yan, J., Shi, P., Ba, L., et al. (2019). The neuroprotective effects of carvacrol on ischemia/reperfusion-induced hippocampal neuronal impairment by ferroptosis mitigation. Life Sci. 235, 116795. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116795
Guo, H., Zhu, L., Tang, P., Chen, D., Li, Y., Li, J., et al. (2021). Carthamin yellow improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuating inflammation and ferroptosis in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 47 (4), 52. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2021.4885
Guo, L., and Shi, L. (2023). Vitexin improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuating oxidative injury and ferroptosis via keap1/nrf2/HO-1signaling. Neurochem. Res. 48 (3), 980–995. doi:10.1007/s11064-022-03829-0
Hilkens, N. A., Casolla, B., Leung, T. W., and de Leeuw, F. E. (2024). Stroke. Lancet 403 (10446), 2820–2836. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00642-1
Hou, W., Xie, Y., Song, X., Sun, X., Lotze, M. T., Zeh, H. J., et al. (2016). Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 12 (8), 1425–1428. doi:10.1080/15548627.2016.1187366
Hu, Q., Zuo, T., Deng, L., Chen, S., Yu, W., Liu, S., et al. (2022). β-Caryophyllene suppresses ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia reperfusion via activation of the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway in MCAO/R rats. Phytomedicine 102, 154112. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154112
Hu, S., Fei, Y., Jin, C., Yao, J., Ding, H., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Ginsenoside Rd enhances blood-brain barrier integrity after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion by alleviating endothelial cells ferroptosis via activation of NRG1/ErbB4-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 251, 109929. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.109929
Huang, Y., Liu, J., He, J., Hu, Z., Tan, F., Zhu, X., et al. (2022). UBIAD1 alleviates ferroptotic neuronal death by enhancing antioxidative capacity by cooperatively restoring impaired mitochondria and Golgi apparatus upon cerebral ischemic/reperfusion insult. Cell Biosci. 12 (1), 42. doi:10.1186/s13578-022-00776-9
Hui, Z., Wang, S., Li, J., Wang, J., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Compound Tongluo Decoction inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced ferroptosis and promoted angiogenesis by activating the Sonic Hedgehog pathway in cerebral infarction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 283, 114634. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114634
Hvidberg, V., Maniecki, M. B., Jacobsen, C., Højrup, P., Møller, H. J., and Moestrup, S. K. (2005). Identification of the receptor scavenging hemopexin-heme complexes. Blood 106 (7), 2572–2579. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-03-1185
Javadinia, S. S., Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi, K., Mahdian, D., Hosseini, A., Ghalenovi, M., and Javan, R. (2022). A review of the protective effects of quercetin-rich natural compounds for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biotech. Histochem 97 (4), 237–246. doi:10.1080/10520295.2021.1937701
Ji, Q., Zhang, L., and Ye, H. (2024). Melatonin improves stroke through MDM2-mediated ubiquitination of ACSL4. Aging (Albany NY) 16 (2), 1925–1937. doi:10.18632/aging.205469
Jia, C. L., Gou, Y., Gao, Y., Pei, X., Jin, X., Li, B. L., et al. (2024). Rosmarinic acid liposomes suppress ferroptosis in ischemic brain via inhibition of TfR1 in BMECs. Phytomedicine 132, 155835. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155835
Jiang, Z., Yang, H., Ni, W., Gao, X., Pei, X., Jiang, H., et al. (2024). Attenuation of neuronal ferroptosis in intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting HDAC1/2: microglial heterogenization via the Nrf2/HO1 pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (3), e14646. doi:10.1111/cns.14646
Jin, Z., Gao, W., Guo, F., Liao, S., Hu, M., Yu, T., et al. (2023). Astragaloside IV alleviates neuronal ferroptosis in ischemic stroke by regulating fat mass and obesity-associated-N6-methyladenosine-acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 axis. J. Neurochem. 166 (2), 328–345. doi:10.1111/jnc.15871
Jin, Z. L., Gao, W. Y., Liao, S. J., Yu, T., Shi, Q., Yu, S. Z., et al. (2021). Paeonol inhibits the progression of intracerebral haemorrhage by mediating the HOTAIR/UPF1/ACSL4 axis. ASN Neuro 13, 17590914211010647. doi:10.1177/17590914211010647
Jung, M. A., Jang, S. E., Hong, S. W., Hana, M. J., and Kim, D. H. (2012). The role of intestinal microflora in anti-inflammatory effect of baicalin in mice. Biomol. Ther. Seoul. 20 (1), 36–42. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2012.20.1.036
Kagan, V. E., Mao, G., Qu, F., Angeli, J. P. F., Doll, S., Croix, C. S., et al. (2017). Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 13 (1), 81–90. doi:10.1038/nchembio.2238
Ko, G., Kim, J., Jeon, Y. J., Lee, D., Baek, H. M., and Chang, K. A. (2023). Salvia miltiorrhiza alleviates memory deficit induced by ischemic brain injury in a transient MCAO mouse model by inhibiting ferroptosis. Antioxidants (Basel) 12 (4), 785. doi:10.3390/antiox12040785
Kondo, Y., Ogawa, N., Asanuma, M., Ota, Z., and Mori, A. (1995). Regional differences in late-onset iron deposition, ferritin, transferrin, astrocyte proliferation, and microglial activation after transient forebrain ischemia in rat brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 15 (2), 216–226. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1995.27
Lan, B., Ge, J.-W., Cheng, S.-W., Zheng, X.-L., Liao, J., and He, C. (2020). Extract of Naotaifang, a compound Chinese herbal medicine, protects neuron ferroptosis induced by acute cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Integr. Med. 18 (4), 344–350. doi:10.1016/j.joim.2020.01.008
Lan, T., Hu, L., Sun, T., Wang, X., Xiao, Z., Shen, D., et al. (2023). H3K9 trimethylation dictates neuronal ferroptosis through repressing Tfr1. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 43 (8), 1365–1381. doi:10.1177/0271678X231165653
Lang, J., Luo, J., Wang, L., Xu, W., Jia, J., Zhao, Z., et al. (2024). Electroacupuncture suppresses oxidative stress and ferroptosis by activating the mTOR/SREBP1 pathway in ischemic stroke. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 44 (6), 99–110. doi:10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2024051934
Li, C., Sun, G., Chen, B., Xu, L., Ye, Y., He, J., et al. (2021). Nuclear receptor coactivator 4-mediated ferritinophagy contributes to cerebral ischemia-induced ferroptosis in ischemic stroke. Pharmacol. Res. 174, 105933. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105933
Li, M., Meng, Z., Yu, S., Li, J., Wang, Y., Yang, W., et al. (2022). Baicalein ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via regulating GPX4/ACSL4/ACSL3 axis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 366, 110137. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110137
Li, P., Wang, Z., Zhao, T., Cheng, X., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., et al. (2024b). Protective effect of compound tongluo decoction on brain vascular endothelial cells after ischemia-reperfusion by inhibition of ferroptosis through regulating Nrf2/ARE/SLC7A11 signaling pathway. Adv. Biol. (Weinh) 8 (3), e2300416. doi:10.1002/adbi.202300416
Li, R., Zhang, X., Gu, L., Yuan, Y., Luo, X., Shen, W., et al. (2023a). CDGSH iron sulfur domain 2 over-expression alleviates neuronal ferroptosis and brain injury by inhibiting lipid peroxidation via AKT/mTOR pathway following intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J. Neurochem. 165 (3), 426–444. doi:10.1111/jnc.15785
Li, X. N., Shang, N. Y., Kang, Y. Y., Sheng, N., Lan, J. Q., Tang, J. S., et al. (2024a). Caffeic acid alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in rats by resisting ferroptosis via Nrf2 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 45 (2), 248–267. doi:10.1038/s41401-023-01177-5
Li, Z., Hu, E., Zheng, F., Wang, S., Zhang, W., Luo, J., et al. (2023b). The effects of astragaloside IV on gut microbiota and serum metabolism in a mice model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Phytomedicine 121, 155086. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155086
Liang, Z., Currais, A., Soriano-Castell, D., Schubert, D., and Maher, P. (2021). Natural products targeting mitochondria: emerging therapeutics for age-associated neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 221, 107749. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107749
Liao, J., Wei, M., Wang, J., Zeng, J., Liu, D., Du, Q., et al. (2023). Naotaifang formula attenuates OGD/R-induced inflammation and ferroptosis by regulating microglial M1/M2 polarization through BMP6/SMADs signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 167, 115465. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115465
Liu, A., Hu, J., Yeh, T. S., Wang, C., Tang, J., Huang, X., et al. (2023a). Neuroprotective strategies for stroke by natural products: advances and perspectives. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 21 (11), 2283–2309. doi:10.2174/1570159X21666230717144752
Liu, C., He, P., Guo, Y., Tian, Q., Wang, J., Wang, G., et al. (2022b). Taurine attenuates neuronal ferroptosis by regulating GABA(B)/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 193 (Pt 2), 795–807. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.11.003
Liu, C., Liu, E., Li, Z., Li, W., Jin, J., Sui, H., et al. (2024). Danlou tablet attenuates ischemic stroke injury and blood‒brain barrier damage by inhibiting ferroptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 322, 117657. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117657
Liu, C., Ma, R., Wang, L., Zhu, R., Liu, H., and Guo, Y. (2017). Rehmanniae Radix in osteoporosis: a review of traditional Chinese medicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacokinetics and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 198, 351–362. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.021
Liu, C. D., Liu, N. N., Zhang, S., Ma, G. D., Yang, H. G., Kong, L. L., et al. (2021). Salvianolic acid A prevented cerebrovascular endothelial injury caused by acute ischemic stroke through inhibiting the Src signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 42 (3), 370–381. doi:10.1038/s41401-020-00568-2
Liu, H., An, N., Wang, L., Li, Y., Song, K., Sun, Y., et al. (2023e). Protective effect of Xingnaojing injection on ferroptosis after cerebral ischemia injury in MCAO rats and SH-SY5Y cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 301, 115836. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115836
Liu, H., Zhang, T. A., Zhang, W. Y., Huang, S. R., Hu, Y., and Sun, J. (2023d). Rhein attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of ferroptosis through NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. Exp. Neurol. 369, 114541. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114541
Liu, H., Zhao, Z., Yan, M., Zhang, Q., Jiang, T., and Xue, J. (2023c). Calycosin decreases cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 734, 109488. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2022.109488
Liu, X. (2021). Changes and significance of serum CXCL-16, GDF-15, PLA-2 levels in patients with cerebral infarction. Am. J. Transl. Res. 13 (5), 5617–5622.
Liu, Y., Mi, Y., Wang, Y., Meng, Q., Xu, L., and Liu, Y. (2023b). Loureirin C inhibits ferroptosis after cerebral ischemia reperfusion through regulation of the Nrf2 pathway in mice. Phytomedicine 113, 154729. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154729
Liu, Z., Zhou, Z., Ai, P., Zhang, C., Chen, J., and Wang, Y. (2022a). Astragaloside IV attenuates ferroptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 924826. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.924826
Lu, J., Xu, F., and Lu, H. (2020). LncRNA PVT1 regulates ferroptosis through miR-214-mediated TFR1 and p53. Life Sci. 260, 118305. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118305
Lv, B., Fu, P., Wang, M., Cui, L., Bao, L., Wang, X., et al. (2024). DMT1 ubiquitination by Nedd4 protects against ferroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (4), e14685. doi:10.1111/cns.14685
Medina-Inojosa, J. R., Somers, V. K., Garcia, M., Thomas, R. J., Allison, T., Chaudry, R., et al. (2023). Performance of the ACC/AHA pooled cohort cardiovascular risk equations in clinical practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 82 (15), 1499–1508. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2023.07.018
Meng, H., Wu, J., Shen, L., Chen, G., Jin, L., Yan, M., et al. (2022). Microwave assisted extraction, characterization of a polysaccharide from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge and its antioxidant effects via ferroptosis-mediated activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 215, 398–412. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.064
Mi, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Dang, W., Xu, L., Tan, S., et al. (2024). Kellerin alleviates cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via targeting Akt-mediated transcriptional activation of Nrf2. Phytomedicine 128, 155406. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155406
Nezhad Salari, A. M., Rasoulizadeh, Z., Shabgah, A. G., Vakili-Ghartavol, R., Sargazi, G., and Gholizadeh Navashenaq, J. (2024). Exploring the mechanisms of kaempferol in neuroprotection: implications for neurological disorders. Cell Biochem. Funct. 42 (2), e3964. doi:10.1002/cbf.3964
Noor, S., Mohammad, T., Rub, M. A., Raza, A., Azum, N., Yadav, D. K., et al. (2022). Biomedical features and therapeutic potential of rosmarinic acid. Arch. Pharm. Res. 45 (4), 205–228. doi:10.1007/s12272-022-01378-2
Ou, Z., Deng, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, C., et al. (2024). Tongqiao Huoxue Decoction inhibits ferroptosis by facilitating ACSL4 ubiquitination degradation for neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine 130, 155701. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155701
Pavlović, N., Milošević Sopta, N., Mitrović, D., Zaklan, D., Tomas Petrović, A., Stilinović, N., et al. (2023). Principal component analysis (PCA) of molecular descriptors for improving permeation through the blood-brain barrier of quercetin analogues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (1), 192. doi:10.3390/ijms25010192
Peng, C., Ai, Q., Zhao, F., Li, H., Sun, Y., Tang, K., et al. (2024). Quercetin attenuates cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 963, 176264. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176264
Peng, C., Fu, X., Wang, K., Chen, L., Luo, B., Huang, N., et al. (2022). Dauricine alleviated secondary brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by upregulating GPX4 expression and inhibiting ferroptosis of nerve cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 914, 174461. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174461
Qin, Z., Zhu, G., Luo, H., and Deng, Y. (2022). Regulation of FOXO3 on neuronal ferroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage via modulating NOX4 transcription. Eur. Surg. Res. doi:10.1159/000527617
Qu, X. Y., Zhang, Y. M., Tao, L. N., Gao, H., Zhai, J. H., Sun, J. M., et al. (2019). XingNaoJing injections protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury and alleviate blood-brain barrier disruption in rats, through an underlying mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasomes suppression. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 17 (7), 498–505. doi:10.1016/S1875-5364(19)30071-8
Rana, A., Samtiya, M., Dhewa, T., Mishra, V., and Aluko, R. E. (2022). Health benefits of polyphenols: a concise review. J. Food Biochem. 46 (10), e14264. doi:10.1111/jfbc.14264
Salvador, G. A. (2010). Iron in neuronal function and dysfunction. Biofactors 36 (2), 103–110. doi:10.1002/biof.80
Selim, M. H., and Ratan, R. R. (2004). The role of iron neurotoxicity in ischemic stroke. Ageing Res. Rev. 3 (3), 345–353. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2004.04.001
Shahbaz, K., Chang, D., Zhou, X., Low, M., Seto, S. W., and Li, C. G. (2022). Crocins for ischemic stroke: a review of current evidence. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 825842. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.825842
Sharma, C., Al Kaabi, J. M., Nurulain, S. M., Goyal, S. N., Kamal, M. A., and Ojha, S. (2016). Polypharmacological properties and therapeutic potential of β-caryophyllene: a dietary phytocannabinoid of pharmaceutical promise. Curr. Pharm. Des. 22 (21), 3237–3264. doi:10.2174/1381612822666160311115226
Shi, Y., Yan, D., Nan, C., Sun, Z., Zhuo, Y., Huo, H., et al. (2024). Salvianolic acid A inhibits ferroptosis and protects against intracerebral hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 12427. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-63277-4
Song, D., Hao, J., and Fan, D. (2020). Biological properties and clinical applications of berberine. Front. Med. 14 (5), 564–582. doi:10.1007/s11684-019-0724-6
Srivastava, S., Kumar, A., Yadav, P. K., Kumar, M., Mathew, J., Pandey, A. C., et al. (2021). Formulation and performance evaluation of polymeric mixed micelles encapsulated with baicalein for breast cancer treatment. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 47 (9), 1512–1522. doi:10.1080/03639045.2021.2007394
Sun, J., Zhao, K., Zhang, W., Guo, C., and Liu, H. (2024a). Ecdysterone improves oxidative damage induced by acute ischemic stroke via inhibiting ferroptosis in neurons through ACSL4. J. Ethnopharmacol. 331, 118204. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118204
Sun, M., Liu, M., Li, Q., Zhang, X., Liu, S., Yang, H., et al. (2023). Cottonseed oil alleviates ischemic stroke injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Brain Behav. 13 (10), e3179. doi:10.1002/brb3.3179
Sun, M., Shen, X., and Ma, Y. (2019a). Rehmannioside A attenuates cognitive deficits in rats with vascular dementia (VD) through suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 120, 109492. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109492
Sun, X., Ou, Z., Xie, M., Kang, R., Fan, Y., Niu, X., et al. (2015). HSPB1 as a novel regulator of ferroptotic cancer cell death. Oncogene 34 (45), 5617–5625. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.32
Sun, X., Yan, P., Zou, C., Wong, Y. K., Shu, Y., Lee, Y. M., et al. (2019b). Targeting autophagy enhances the anticancer effect of artemisinin and its derivatives. Med. Res. Rev. 39 (6), 2172–2193. doi:10.1002/med.21580
Sun, Y., Jin, H., He, J., Lai, J., Lin, H., and Liu, X. (2024b). Melatonin alleviates ischemic stroke by inhibiting ferroptosis through the CYP1B1/ACSL4 pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 39 (5), 2623–2633. doi:10.1002/tox.24136
Sun, Y., Li, Q., Guo, H., and He, Q. (2022). Ferroptosis and iron metabolism after intracerebral hemorrhage. Cells 12 (1), 90. doi:10.3390/cells12010090
Tran, P. H. L., and Tran, T. T. D. (2020). Developmental strategies of curcumin solid dispersions for enhancing bioavailability. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 20 (16), 1874–1882. doi:10.2174/1871520620666200708103845
Tsao, C. W., Aday, A. W., Almarzooq, Z. I., Anderson, C. A. M., Arora, P., Avery, C. L., et al. (2023). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2023 update: a report from the American Heart association. Circulation 147 (8), e93–e621. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001123
Tu, Y., Tan, L., Tao, H., Li, Y., and Liu, H. (2023). CETSA and thermal proteome profiling strategies for target identification and drug discovery of natural products. Phytomedicine 116, 154862. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154862
Tuo, Q. Z., Lei, P., Jackman, K. A., Li, X. L., Xiong, H., Li, X. L., et al. (2017). Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol. Psychiatry 22 (11), 1520–1530. doi:10.1038/mp.2017.171
Tuo, Q. Z., Liu, Y., Xiang, Z., Yan, H. F., Zou, T., Shu, Y., et al. (2022). Thrombin induces ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7 (1), 59. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00917-z
Venketasubramanian, N., Agustin, S. J., Padilla, J. L., Yumul, M. P., Sum, C., Lee, S. H., et al. (2022). Comparison of different laboratory tests to identify “aspirin resistance” and risk of vascular events among ischaemic stroke patients: a double-blind study. J. Cardiovasc Dev. Dis. 9 (5), 156. doi:10.3390/jcdd9050156
Wan, J., Ren, H., and Wang, J. (2019). Iron toxicity, lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis after intracerebral haemorrhage. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 4 (2), 93–95. doi:10.1136/svn-2018-000205
Wang, B., Zhang, X., Zhong, J., Wang, S., Zhang, C., Li, M., et al. (2022a). Dexpramipexole attenuates white matter injury to facilitate locomotion and motor coordination recovery via reducing ferroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 6160701. doi:10.1155/2022/6160701
Wang, F., Li, W. L., Shen, L. J., Jiang, T. T., Xia, J. J., You, D. L., et al. (2022b). Crocin alleviates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced neuronal ferroptosis by facilitating Nrf2 nuclear translocation. Neurotox. Res. 40 (2), 596–604. doi:10.1007/s12640-022-00500-y
Wang, L., Liu, C., and Tang, B. (2023b). Astragaloside IV mitigates cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of P62/Keap1/Nrf2 pathway-mediated ferroptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 944, 175516. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175516
Wang, P., Cui, Y., Ren, Q., Yan, B., Zhao, Y., Yu, P., et al. (2021). Mitochondrial ferritin attenuates cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 12 (5), 447. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03725-5
Wang, Q., Liu, C., Chen, M., Zhao, J., Wang, D., Gao, P., et al. (2024a). Mastoparan M promotes functional recovery in stroke mice by activating autophagy and inhibiting ferroptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 174, 116560. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116560
Wang, X., Zhang, J., Wang, S., Song, Z., Sun, H., Wu, F., et al. (2023c). Berberine modulates gut microbiota to attenuate cerebral ferroptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 953, 175782. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175782
Wang, Y., Lan, X., Liu, N., Ma, L., DU, J., Wei, W., et al. (2024b). Traditional Chinese medicines derived natural inhibitors of ferroptosis on ischemic stroke. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 22 (8), 746–755. doi:10.1016/S1875-5364(24)60603-5
Wang, Y., Wu, S., Li, Q., Sun, H., and Wang, H. (2023a). Pharmacological inhibition of ferroptosis as a therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases and strokes. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10 (24), e2300325. doi:10.1002/advs.202300325
Wendlocha, D., Kubina, R., Krzykawski, K., and Mielczarek-Palacz, A. (2024). Selected flavonols targeting cell death pathways in cancer therapy: the latest achievements in research on apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis. Nutrients 16 (8), 1201. doi:10.3390/nu16081201
Wu, C., Duan, F., Yang, R., Dai, Y., Chen, X., and Li, S. (2023). 15, 16-Dihydrotanshinone I protects against ischemic stroke by inhibiting ferroptosis via the activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. Phytomedicine 114, 154790. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154790
Wu, J., Wei, Z., Cheng, P., Qian, C., Xu, F., Yang, Y., et al. (2020). Rhein modulates host purine metabolism in intestine through gut microbiota and ameliorates experimental colitis. Theranostics 10 (23), 10665–10679. doi:10.7150/thno.43528
Xiao, S., Wang, C., Yang, Q., Xu, H., Lu, J., and Xu, K. (2021). Rea regulates microglial polarization and attenuates neuronal apoptosis via inhibition of the NF-κB and MAPK signalings for spinal cord injury repair. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25 (3), 1371–1382. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16220
Xie, G., Liang, Y., Gao, W., Wu, L., Zhang, Y., Ye, Z., et al. (2023). Artesunate alleviates intracerebral haemorrhage secondary injury by inducing ferroptosis in M1-polarized microglia and suppressing inflammation through AMPK/mTORC1/GPX4 pathway. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 132 (5), 369–383. doi:10.1111/bcpt.13848
Xing, P., Zhong, Y., Cui, X., Liu, Z., and Wu, X. (2023). Natural products in digestive tract tumors metabolism: functional and application prospects. Pharmacol. Res. 191, 106766. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106766
Xu, S., Li, X., Li, Y., Li, X., Lv, E., Zhang, X., et al. (2023b). Neuroprotective effect of Dl-3-n-butylphthalide against ischemia-reperfusion injury is mediated by ferroptosis regulation via the SLC7A11/GSH/GPX4 pathway and the attenuation of blood-brain barrier disruption. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15, 1028178. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2023.1028178
Xu, Y., Li, K., Zhao, Y., Zhou, L., Liu, Y., and Zhao, J. (2023a). Role of ferroptosis in stroke. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 43 (1), 205–222. doi:10.1007/s10571-022-01196-6
Xu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, K., Yuan, D., Yang, S., Zhou, L., et al. (2022). COX-2/PGE2 pathway inhibits the ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Mol. Neurobiol. 59 (3), 1619–1631. doi:10.1007/s12035-021-02706-1
Yamada, K., Toyota, K., Tsunoda, Y., Matahira, Y., Matsumura, S., Yoshioka, Y., et al. (2023). Effects of inhaled β-caryophyllene on vascular stiffness in smokers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Exp. Ther. Med. 25 (1), 57. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11756
Yang, C., Han, M., Li, R., Zhou, L., Zhang, Y., Duan, L., et al. (2021). Curcumin nanoparticles inhibiting ferroptosis for the enhanced treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage. Int. J. Nanomedicine 16, 8049–8065. doi:10.2147/IJN.S334965
Yang, W. S., Kim, K. J., Gaschler, M. M., Patel, M., Shchepinov, M. S., and Stockwell, B. R. (2016). Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113 (34), E4966–E4975. doi:10.1073/pnas.1603244113
Yang, Y., Wu, Q., Shan, X., Zhou, H., Wang, J., Hu, Y., et al. (2024a). Ginkgolide B attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of ferroptosis through disrupting NCOA4-FTH1 interaction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 318 (Pt B)), 116982. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116982
Yang, Y. Y., Deng, R. R., and Xiang, D. X. (2024c). Naodesheng pills ameliorate cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced ferroptosis via inhibition of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 18, 1499–1514. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S443479
Yang, Z., Jiang, Y., Xiao, Y., Qian, L., Jiang, Y., Hu, Y., et al. (2024b). Di-Huang-Yin-Zi regulates P53/SLC7A11 signaling pathway to improve the mechanism of post-stroke depression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 2), 117226. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117226
Yao, M., Zhang, L., and Wang, L. (2023). Astragaloside IV: a promising natural neuroprotective agent for neurological disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 159, 114229. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114229
Yao, M. Y., Liu, T., Zhang, L., Wang, M. J., Yang, Y., and Gao, J. (2021). Role of ferroptosis in neurological diseases. Neurosci. Lett. 747, 135614. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135614
Yi, X., and Tang, X. (2021). Exosomes from miR-19b-3p-modified ADSCs inhibit ferroptosis in intracerebral hemorrhage mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 661317. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.661317
Yin, M., Chen, W., Li, M., Wang, K., Hu, N., and Li, Z. (2022). circAFF1 enhances intracerebral hemorrhage induced neuronal ferroptosis by targeting miR-140-5p to regulate GSK-3β mediated Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. Brain Res. Bull. 189, 11–21. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.08.005
Yu, X., Wang, S., Wang, X., Li, Y., and Dai, Z. (2024). Melatonin improves stroke by inhibiting autophagy-dependent ferroptosis mediated by NCOA4 binding to FTH1. Exp. Neurol. 379, 114868. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114868
Yu, Y., Li, X., Wu, X., Li, X., Wei, J., Chen, X., et al. (2023). Sodium hydrosulfide inhibits hemin-induced ferroptosis and lipid peroxidation in BV2 cells via the CBS/H(2)S system. Cell Signal 104, 110594. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110594
Yuan, Y., Zhai, Y., Chen, J., Xu, X., and Wang, H. (2021). Kaempferol ameliorates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal ferroptosis by activating nrf2/slc7a11/GPX4 Axis. Biomolecules 11 (7), 923. doi:10.3390/biom11070923
Zhan, S., Liang, J., Lin, H., Cai, J., Yang, X., Wu, H., et al. (2023). SATB1/SLC7A11/HO-1 Axis ameliorates ferroptosis in neuron cells after ischemic stroke by danhong injection. Mol. Neurobiol. 60 (1), 413–427. doi:10.1007/s12035-022-03075-z
Zhang, C., Shi, Z., Xu, Q., He, J., Chen, L., Lu, Z., et al. (2023a). Astragaloside IV alleviates stroke-triggered early brain injury by modulating neuroinflammation and ferroptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Acta Cir. Bras. 38, e380723. doi:10.1590/acb380723
Zhang, J., Tang, L., Li, G. S., and Wang, J. (2018). The anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Ren. Fail 40 (1), 680–686. doi:10.1080/0886022X.2018.1544565
Zhang, L., Ma, J., Yang, F., Li, S., Ma, W., Chang, X., et al. (2022b). Neuroprotective effects of quercetin on ischemic stroke: a literature review. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 854249. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.854249
Zhang, L., Wang, X., Che, W., Yi, Y., Zhou, S., and Feng, Y. (2022a). Methyltransferase-like 3 silenced inhibited the ferroptosis development via regulating the glutathione peroxidase 4 levels in the intracerebral hemorrhage progression. Bioengineered 13 (6), 14215–14226. doi:10.1080/21655979.2022.2084494
Zhang, X., Tang, B., Wen, S., Wang, Y., Pan, C., Qu, L., et al. (2023b). Advancements in the biotransformation and biosynthesis of the primary active flavonoids derived from Epimedium. Molecules 28 (20), 7173. doi:10.3390/molecules28207173
Zhang, Y., Ye, P., Zhu, H., Gu, L., Li, Y., Feng, S., et al. (2024). Neutral polysaccharide from Gastrodia elata alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis-mediated neuroinflammation via the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (3), e14456. doi:10.1111/cns.14456
Zhang, Z., Pang, Y., Wang, W., Zhu, H., Jin, S., Yu, Z., et al. (2021). Neuroprotection of heme oxygenase-2 in mice AfterIntracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 80 (5), 457–466. doi:10.1093/jnen/nlab025
Zhao, F., Peng, C., Li, H., Chen, H., Yang, Y., Ai, Q., et al. (2023b). Paeoniae Radix Rubra extract attenuates cerebral ischemia injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and activating autophagy through the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 315, 116567. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116567
Zhao, H., Li, X., Yang, L., Zhang, L., Jiang, X., Gao, W., et al. (2021b). Isorhynchophylline relieves ferroptosis-induced nerve damage after intracerebral hemorrhage via miR-122-5p/TP53/slc7a11 pathway. Neurochem. Res. 46 (8), 1981–1994. doi:10.1007/s11064-021-03320-2
Zhao, J., Wu, Y., Liang, S., and Piao, X. (2022). Activation of SSAT1/ALOX15 Axis aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via triggering neuronal ferroptosis. Neuroscience 485, 78–90. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.01.017
Zhao, X., Kruzel, M., and Aronowski, J. (2021a). Lactoferrin and hematoma detoxification after intracerebral hemorrhage. Biochem. Cell Biol. 99 (1), 97–101. doi:10.1139/bcb-2020-0116
Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., Xu, Y., Li, K., Zhou, L., Qiao, H., et al. (2023a). The role of ferroptosis in blood-brain barrier injury. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 43 (1), 223–236. doi:10.1007/s10571-022-01197-5
Zhou, R., Wang, J., Han, X., Ma, B., Yuan, H., and Song, Y. (2019). Baicalin regulates the dopamine system to control the core symptoms of ADHD. Mol. Brain 12 (1), 11. doi:10.1186/s13041-019-0428-5
Zhou, S., Gao, X., Chen, C., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2023b). Porcine cardiac blood - Salvia miltiorrhiza root alleviates cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress induced apoptosis through PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 316, 116698. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116698
Zhou, S., Wang, Z., Wang, T., Peng, C., Zhang, J., Liu, C., et al. (2024a). Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. processed with porcine cardiac blood inhibited GLRX5-mediated ferroptosis alleviating cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine 129, 155622. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155622
Zhou, S. Y., Cui, G. Z., Yan, X. L., Wang, X., Qu, Y., Guo, Z. N., et al. (2020). Mechanism of ferroptosis and its relationships with other types of programmed cell death: insights for potential interventions after intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Neurosci. 14, 589042. doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.589042
Zhou, Z., Yu, Y., Miao, J., Wang, G., Wang, Y., Wang, T., et al. (2024b). Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in treating central nervous system diseases by modulating ferroptosis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 52 (7), 1989–2019. doi:10.1142/S0192415X24500770
Zhou, Z. X., Cui, Q., Zhang, Y. M., Yang, J. X., Xiang, W. J., Tian, N., et al. (2023a). Withaferin A inhibits ferroptosis and protects against intracerebral hemorrhage. Neural Regen. Res. 18 (6), 1308–1315. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.355822
Zhu, H., Huang, J., Chen, Y., Li, X., Wen, J., Tian, M., et al. (2022a). Resveratrol pretreatment protects neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation and ischemic injury through inhibiting ferroptosis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 86 (6), 704–716. doi:10.1093/bbb/zbac048
Zhu, H., Wang, Z., Xing, Y., Gao, Y., Ma, T., Lou, L., et al. (2012). Baicalin reduces the permeability of the blood-brain barrier during hypoxia in vitro by increasing the expression of tight junction proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 141 (2), 714–720. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.063
Zhu, Y., Ouyang, Z., Du, H., Wang, M., Wang, J., Sun, H., et al. (2022b). New opportunities and challenges of natural products research: when target identification meets single-cell multiomics. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 12 (11), 4011–4039. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2022.08.022
Glossary
ICH Intracerebral hemorrhage
SAH Subarachnoid hemorrhage
BBB Blood-brain barrier
RBC Red blood cells
HO-1 Heme oxygenase-1
CO Carbon monoxide
TFR1 Transferrin receptor 1
STEAP3 Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of Prostate 3
LIP Labile iron pool
SLC11A2 Solute Carrier Family 11 Member 2
LOXs Lipoxygenases
ROS Reactive oxygen species
NCOA4 Nuclear receptor coactivator 4
ATG5 Autophagy-related 5
ATG7 Autophagy-related 7
NFS1 Nitrogen fixation 1
HSPB1 Heat shock factor-binding Protein 1
PUFAs Polyunsaturated fatty acids
I/R Ischemia-reperfusion
GSH Glutathione
MCAO Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
RosA-LIP Osmarinic acid encapsulated in liposomes
SOD Superoxide Dismutase
MDA Malondialdehyde
GPX4 Glutathione Peroxidase 4
ACSL4 Acyl-Co A synthetase long-chain family member 4
FTH1 Ferritin Heavy Chain 1
LDH Lactate Dehydrogenase
Nrf2 Nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2
Fto Fat mass and obesity-associated protein
Atf3 Activation transcription factor 3
ZO-1 Zonula Occludens 1
xCT Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter
COX2 Cyclooxygenase-2
4-HNE 4-Hydroxynonenal
GSH-Px Glutathione peroxidase
MMP-9 Matrix Metalloprotein 9
OS Oxidative stress
RNS Reactive nitrogen species
CNS Central Nervous System
HDAC1/2 Histone deacetylases 1/2
H3K9me3 Histone H3 Lysine 9 Trimethylation
Nedd4 Neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally downregulated 4
FOXO3 Forkhead box O3
CISD2 CDGSH iron sulfur domain 2
H2S H2S-producing enzymes
circAFF1 circular RNA AFF1
SLC7A11 Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11
METTL3 Methyltransferase like 3
FSP1 Ferroptosis-suppressor-protein 1
Fpn Ferroportin
IRP Iron Regulatory Protein
Tau microtubule-associated protein tau
LncRNA PVT1 plasmacytoma variant translocation 1
SSAT1 Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1
UBIAD1 UbiA prenyltransferase domain containing 1
PGE2 ProstaglandinE2
FtMt Ferritin Mitochondrial
USP14 ubiquitin specific peptidase 14
SIRT6 Sirtuin 6
mTOR Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin
Keywords: natural products, stroke, ferroptosis, Phytomedicine, intracerebral hemorrhage, ischemic stroke
Citation: Zheng Y, Tan X, Wang X, Mao R and Guo J (2025) Targeting ferroptosis with natural products in stroke: therapeutic mechanisms and translational opportunities. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1586345. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1586345
Received: 02 March 2025; Accepted: 15 May 2025;
Published: 29 May 2025.
Edited by:
Huazheng Liang, Monash University - Southeast University Joint Research Institute (Suzhou), ChinaReviewed by:
Ayesha Wadood, Nuclear Institute for Agriculture and Biology, PakistanAlexandra Daniela Rotaru-Zavaleanu, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, Romania
Albeiro Marrugo Padilla, University of Cartagena, Colombia
Copyright © 2025 Zheng, Tan, Wang, Mao and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianwen Guo, amlhbndlbl9ndW9AcXEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yingyi Zheng
Yingyi Zheng Xi Tan1,2†
Xi Tan1,2† Xiaojie Wang
Xiaojie Wang Rui Mao
Rui Mao Jianwen Guo
Jianwen Guo