Abstract
Background:
Despite therapeutic interventions, tuberculosis (TB) remains a persistent challenge. Combination therapy integrating Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) with conventional anti-TB medications demonstrates therapeutic benefits, necessitating a meta-analysis evaluating the adjunctive use of oral commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation (CCPP).
Objectives:
This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of different oral TCMs combined with biomedicine for tuberculosis treatment, utilizing network meta-analysis techniques.
Methods:
A computer-based search was conducted across various databases including the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Database, VIP Database, SinoMed, PubMed, EMbase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library, covering records from database inception to 22 January 2025. Data analysis utilized Stata 18.0, R software (version 4.4.1), and Review Manager 5.4.
Results:
A total of 100 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included, with a total sample size of 12,747 participants (6,639 in the experimental group and 6,108 in the control group), evaluating 12 distinct interventions. Network meta-analysis revealed the following optimal combinations: FeiJieHe Pill combined with standard biomedicine demonstrated superior efficacy for clinical response rate improvement (OR = 8.43, 95% CI [1.79, 39.69]). KangLao Pill combined with standard biomedicine was the most effective for negative conversion rate (OR = 11.55, 95% CI [3.04, 43.93]). Bu Jin Tablet combined with standard biomedicine demonstrated superior efficacy for lesion absorption rate (OR = 7.46, 95% CI [3.32, 16.75]). FeiJieHe Pill combined with standard biomedicine was the most effective for cavity absorption (OR = 5.11, 95% CI [2.04, 12.85]). JieHe Pill combined with conventional biomedicine yielded the greatest improvement in both CD3+ T lymphocyte response (OR = 5.6, 95% CI [3.4, 7.8]) and CD4+ T lymphocyte response (OR = 5.1, 95% CI [2.9, 7.3]).
Conclusion:
Combination therapy utilizing oral CCPP alongside conventional biomedicine has a significant enhanced efficacy relative to conventional biomedicine monotherapy across multiple tuberculosis treatment metrics, including clinical efficacy rate, negative conversion rate, lesion absorption rate, cavity absorption rate, and improvement rates of CD3+ and CD4+ T lymphocyte levels.
Systematic Review Registration:
https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42024589122, identifier CRD42024589122.
1 Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB), an airborne infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, persists as a major global health threat in 21st century and remains one of the key infectious diseases controlled in China. According to the World Health Organization’s 2023 report (Wei and LiuYuhon, 2024), global TB incidence reached 10.6 million new cases in 2022, including 748,000 cases in China, ranking the third among high-burden nations. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination programs and standardized modern pharmaceutical interventions render the TB epidemic both preventable and controllable. However, the emergence of drug-resistant strains, particularly multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, poses new challenge to TB control (Hui et al., 2020). Currently, biomedicine primarily treats TB with oral anti-TB medications, emphasizing early, combined, appropriate, regular, and full-course use. The conventional 2HRZE/4HR regimen comprises 2-month of therapy with Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, and Ethambutol followed by 4 months of Isoniazid and Rifampicin. While demonstrating clinical efficacy, long-term use of this regimen carries potential multi-organ toxicity risks (Shah et al., 2020; Prasad et al., 2019). Furthermore, treatment discontinuation secondary to adverse drug effects in newly diagnosed patients may predispose to develop drug-resistant TB development. A study by Zou Xia-li et al. (Xiali et al., 2017) identified a 2.38-fold increased risk of drug resistance development among TB patients experiencing anti-TB drug-related adverse reactions during initial treatment, with this the risk increased to 4.20-fold in individuals with prior treatment-associated adverse reactions. Correspondingly, Wei et al. (Wei et al., 2015) determined that anti-TB drug adverse reactions constitute the primary cause of treatment discontinuation in this patient population. Improving the efficacy of anti-TB drugs and reducing their side effects has become an urgent issue in modern TB management.
TB corresponds to the “pulmonary tuberculosis” classification within Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Specialized texts such as Shí Yào Shén Shū (Ten Medicines Divine Book) of the Yuan Dynasty (Ge, 2019) documented early therapeutic approaches. The treatment principles of “tonifying the deficiency” and “killing parasites” established in Yīxué Zhèng Zhuàn (The Correct Transmission of Medicine) of the Ming Dynasty remain clinically relevant. TCM posits pulmonary tuberculosis as a chronic infectious disease caused by vital energy deficiency and infection of “consumption worms” that invade the lungs. Previous studies demonstrate that synergistic integration of TCM and biomedicine enhances the efficacy of anti-TB drugs, shortens treatment time, and mitigates side effects. Zhang Zhi-jie et al. (Zhijie, 2018) found that compared with simply using biomedicine, Qinghao Biejia Tang significantly improved the cure rate for drug-resistant TB. Similarly, Kang Guannan et al. (Guannan et al., 2023) observed higher cure rate, negative conversion rate, and cavity improvement rate following Kangfuxin Liquid combination therapy relative to anti-TB drugs alone, while also alleviating hemoptysis symptoms and reducing side effects.
Although multiple studies support enhanced treatment outcomes and reduced toxicity from adjunctive administration of oral traditional commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation (CCPP) alongside anti-TB biomedicine, the optimal therapeutic profile and comparative advantages of specific formulations remain undetermined. This study conducts a network meta-analysis comparing the efficacy of different oral CCPP as adjunctive therapy to anti-TB drugs, aiming to provide better treatment options for clinical practice.
2 Materials and methods
This study protocol received registration on the PROSPERO platform with the registration number CRD42024589122.
2.1 Literature search
To perform literature search, we have used multiple databases like China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) (https://oversea.cnki.net/index/), Wanfang (http://www.wanfangdata.com/), VIP Full Text Journals Database (https://www.fjlib.net/English/digitalresources/201804/t20180414_349923.htm), SinoMed (https://www.sinomed.com/), PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), Embase (https://www.embase.com), Web of Science (https://www.webofscience.com), and Cochrane Library (https://www.cochranelibrary.com/). The databases were screen up to 22 January 2025, based on a robust literature screening and data extraction strategy. The languages considered were Chinese and English.
2.2 Literature screening and data extraction
Three researchers participated in the literature screening and data extraction, with one designated as the group leader. In the event of any disagreement during the screening process, the group leader was responsible for making the final decision. According to the diagnostic criteria for pulmonary tuberculosis (
Chuanjun et al., 2023;
Guofang and Xiwei, 2020;
Radiology, 2018), a confirmed diagnosis required meeting at least one of the following conditions, along with mandatory fulfillment of condition C:
A. Persistent cough and sputum production lasting for 2 weeks or more, with or without hemoptysis, blood-streaked sputum, or systemic symptoms.
B. Radiographic findings suggestive of pulmonary tuberculosis.
C. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum or other specimens, confirmed by smear microscopy, culture, or molecular biological methods.
There were no restrictions regarding gender, age, prior treatment history (initial treatment or retreatment), or drug resistance status.
The control group received a standard anti-tuberculosis monotherapy regimen or monotherapy combined with adjunctive treatments such as hepatoprotective or hemostatic agents to alleviate complications. The experimental group was administered a single oral Chinese patent medicine in addition to the control regimen. The total treatment duration was the same for both groups.
Studies were excluded if they met any of the following criteria: non-randomized controlled trials (non-RCTs), narrative reviews, systematic reviews, conference abstracts, clinical guidelines, studies with undefined treatment durations, animal or in vitro experiments, academic theses, or topics for which fewer than three relevant studies were available.
The outcome indicators collected included the following: A. Clinical efficacy rate; B. Sputum conversion rate; C. Lesion absorption rate; D. Cavity closure rate; E. Improvement rate of CD3+ T lymphocytes; F. Improvement rate of CD4+ T lymphocytes; G. Incidence of adverse reactions.
2.3 Literature quality assessment
Methodological quality evaluation of included RCTs utilized Cochrane Handbook standards (Higgins et al., 2023) assessing dimensions of randomization method, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and staff, blinding of outcome assessors, completeness of data, selective reporting of outcomes, and other biases. If there were any disagreements during the evaluation, consensus was reached through in-depth discussion with the group leader. Each evaluation item was classified as “low risk”, “unclear”, or “high risk”. All results were systematically documented within RevMan 5.4 software (Cochrane Collaboration, 2020), facilitating generation of corresponding risk of bias visualizations.
2.4 Statistical analysis
A network meta-analysis was conducted using the “netmeta” package (Rücker et al., 2024) in R (version 4.4.1) (R Core Team, 2024), and forest plots were generated.Binary outcomes employed odds ratio (OR) as the effect size measure, while continuous outcomes utilized standardized mean difference (MD), with reported 95% confidence intervals (CI). If the 95% CI for a binary variable does not include 1, or the 95% CI for a continuous variable does not include 0, statistical significance between groups was considered to be present. Evidence network were constructed using Stata 18.0 (StataCorp, 2023), featuring nodes proportional to intervention-specific sizes and interconnecting. To rank the effectiveness of different interventions, the Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) was used, with higher SUCRA values indicating a greater probability of being among the most effective treatments. No fixed SUCRA threshold was applied. This interpretation follows established methodological guidance in network meta-analysis (Salanti et al., 2011; Rücker and Schwarzer, 2015). Additionally, comparison-corrected funnel plots were drawn to examine publication bias in the included studies. Additional details are provided in the Supplementary Material (Supplementary Files 1–3).
3 Results
3.1 Literature search
A total of 15,036 articles were identified, with 100 articles meeting final inclusion criteria as exclusively two-arm RCTs. For multiple reports of the same study (such as clinical trial registration records and journal articles), the version with the most comprehensive or recent iteration was retained, and related studies were merged before data extraction. The literature screening flowchart is shown in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1
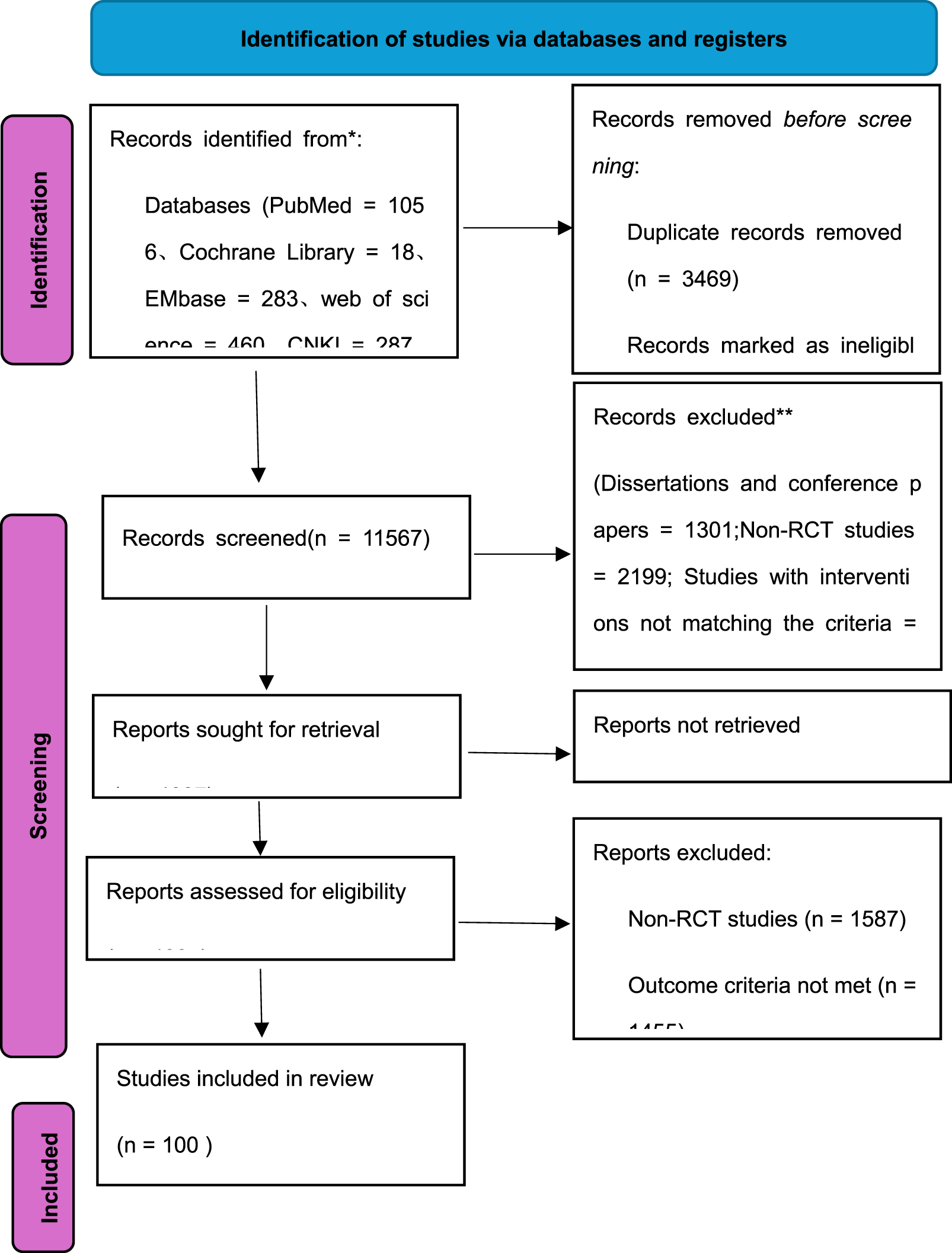
PRISMA flow diagram of the studies selection process.
3.2 Characteristics of included literature
The 100 included articles (
Jian, 2002;
Yanpei and Shuyu, 2002;
Ming, 2004;
Wei et al., 2004;
Donghua and Ganhong, 2005;
Liuxing, 2005;
Mengqiu et al., 2006;
Lidong and Shuqing, 2007;
Wulu et al., 2007;
Xuewen, 2007;
Yujuan, 2007;
Ge et al., 2009;
Kai, 2009;
Shouyue, 2009;
Xian, 2009;
Xiuxia, 2009;
Fuyuan and MeiMingxing, 2010;
Guiqiu, 2010,
Jun, 2010;
Bing and Yuanai, 2011;
Shiqi, 2011;
Fengyan, 2012;
Xinhua, 2012;
Dan et al., 2013;
Hualiang, 2013;
Hunxi and Zhanqi, 2013;
Lidong et al., 2013;
Wen-ge et al., 2013;
Xuhua et al., 2013;
Zhongming, 2013;
Long et al., 2014;
Qianxin et al., 2014;
Qing and Wengfang, 2014;
Xiue et al., 2014;
Jinghua et al., 2015;
Min-shuang et al., 2015;
Tianfeng, 2015;
Yunxiao and Guosheng, 2015;
Yuxia, 2015;
Juan et al., 2016;
Junguo et al., 2016;
Shiming et al., 2016;
Shuang, 2016;
Shuhua and Fujian, 2016;
Wei, 2016;
Zhenru, 2016;
Ji et al., 2017;
Jun et al., 2017;
Xing et al., 2017;
Yongyi et al., 2017;
Junjie, 2018;
Lingwei, 2018;
Liping, 2018;
Xiaoni, 2018;
Xiaoru et al., 2018;
Di et al., 2019;
Guizhen, 2019;
Hai-xian et al., 2019;
Junmei et al., 2019;
Meng, 2019;
Qingfeng, 2019;
Zhibo et al., 2019;
Bin, 2020;
Guannan et al., 2020;
Hui et al., 2020;
Shuangli et al., 2020;
Weiyong et al., 2020;
Xian-hui and Shu-lin, 2020;
Qiang, 2021;
Qiong et al., 2021;
Wei-wei, 2021;
Chenyong et al., 2022;
Jiafu and Lanhua, 2022;
Juan, 2022;
Qihuang, 2022;
Jun et al., 2022;
Xiaohua, 2022;
Xuehu et al., 2022;
Xueyun, 2022;
Chang et al., 2022;
Guannan et al., 2023;
Chuanjun et al., 2023;
Junguo, 2023;
Qiaoe et al., 2023;
Yawei et al., 2023;
Yuxia, 2023;
Peiqian et al., 2024;
Xinlei and Rong, 2024;
Yuelian, 2024) were all two-arm experiments, with a total sample size of 12,747 participants: 6,639 in the experimental group and 6,108 in the control group. These studies involved 12 different interventions:
• Bai Ling Capsule: seven studies (Yanpei and Shuyu, 2002; Donghua and Ganhong, 2005; Ge et al., 2009; Juan et al., 2016; Shuhua and Fujian, 2016; Hui et al., 2020; Shuangli et al., 2020)
• Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule: five studies (Tianfeng, 2015; Xiaoru et al., 2018; Junmei et al., 2019; Chuanjun et al., 2023; Yawei et al., 2023)
• Bu Jin Tablet: four studies (Jian, 2002; Xian, 2009; Jun, 2010; Yunxiao and Guosheng, 2015)
• FeiJieHe Pill: five studies (Ming, 2004; Fengyan, 2012; Xinhua, 2012; Qing and Wengfang, 2014; Di et al., 2019)
• Fei Tai Capsule: seven studies (Donghua and Ganhong, 2005; Mengqiu et al., 2006; Hualiang, 2013; Junguo et al., 2016; Ji et al., 2017; Hai-xian et al., 2019; Xian-hui and Shu-lin, 2020)
• Jian Pi Run Fei Pill: seven studies (Wulu et al., 2007; Shouyue, 2009; Fuyuan and MeiMingxing, 2010; Bing and Yuanai, 2011; Hunxi and Zhanqi, 2013; Wei, 2016; Chenyong et al., 2022)
• Jie He Ling Tablet: four studies (Lidong and Shuqing, 2007; Zhongming, 2013; Shuang, 2016)
• Jie He Pill: 34 studies (Guiqiu, 2010; Shiqi, 2011; Dan et al., 2013; Lidong et al., 2013; Xuhua et al., 2013; Hunxi and Zhanqi, 2013; Qianxin et al., 2014; Min-shuang et al., 2015; Yuxia, 2015; Junguo et al., 2016; Juan et al., 2016; Zhenru, 2016; Xing et al., 2017; Yongyi et al., 2017; Lingwei, 2018; Liping, 2018; Guizhen, 2019; Meng, 2019; Bin, 2020; Chenyong et al., 2022; Jiafu and Lanhua, 2022; Juan, 2022; Jun et al., 2022; Chang et al., 2022; Junguo, 2023; Qiaoe et al., 2023; Yuxia, 2023; Peiqian et al., 2024; Xinlei and Rong, 2024; Yuelian, 2024)
• Kangfuxin Liquid: 10 studies (Wen-ge et al., 2013; Min-shuang et al., 2015; Xiaoru et al., 2018; Hai-xian et al., 2019; Zhibo et al., 2019; Guannan et al., 2020; Xiaohua, 2022; Xuehu et al., 2022; Xueyun, 2022; Guannan et al., 2023)
• KangLao Pill: five studies (Jinghua et al., 2015; Xiaoni, 2018; Qingfeng, 2019; Weiyong et al., 2020; Chenyong et al., 2022)
• Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule: six studies (Long et al., 2014; Xiue et al., 2014; Juan et al., 2016; Shiming et al., 2016; Jun et al., 2017; Junjie, 2018)
• Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule: six studies (Wei et al., 2004; Liuxing, 2005; Xuewen, 2007; Yujuan, 2007; Kai, 2009; Xiuxia, 2009)
The baseline characteristics of the two groups were comparable. The basic information of the included literature is shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Included in study | Sample size | Age (years) | Interventions | Treatment course | Outcome measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | T | C | T | C | |||
| Jian (2002) | 31 | 28 | — | — | BJ+Bio | Bio | 9 | ①② |
| Yanpei and Shuyu (2002) | 48 | 30 | 60–86 | 60–84 | BL+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①②⑤ |
| Ming (2004) | 50 | 50 | 14–60 | 16–59 | FJH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ① |
| Wei et al. (2004) | 64 | 64 | 18–76 | 18–74 | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①② |
| Donghua and Ganhong (2005) | 62 | 60 | 26–67 | 25–66 | BL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②④ |
| Liuxing (2005) | 128 | 64 | — | — | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①④ |
| Pu et al. (2005) | 38 | 15 | — | — | FT+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③ |
| Mengqiu et al. (2006) | 168 | 85 | — | — | FT+Bio | Bio | 8 | ①②③⑤⑥⑦ |
| Xuewen (2007) | 64 | 64 | 18–76 | 18–74 | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①③④⑤ |
| Lidong and Shuqing (2007) | 75 | 75 | — | — | JHL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①③⑤ |
| Wulu et al. (2007) | 241 | 100 | — | — | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 2 | ①②④⑤ |
| Yujuan (2007) | 67 | 65 | — | — | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 9 | ①②③⑤ |
| Shuqin et al. (2008) | 70 | 70 | 18–65 | 18–65 | JHL+Bio | Bio | 8 | ①③④⑤ |
| Shouyue (2009) | 168 | 85 | 18–72 | 18–72 | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 8 | ①③④⑤ |
| Kai (2009) | 53 | 52 | — | — | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①② |
| Xian (2009) | 30 | 30 | 19–65 | 25–68 | BJ+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①④ |
| Xiuxia (2009) | 132 | 130 | 21–68 | 20–70 | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 21 | ①②⑤ |
| Ge et al. (2009) | 123 | 121 | 16–67 | 18–66 | BL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②④⑤ |
| Fuyuan and Meimingxing (2010) | 90 | 90 | X70 | X70 | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②⑤ |
| Guiqiu (2010) | 36 | 38 | — | — | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①②③⑤ |
| Jun (2010) | 26 | 22 | — | — | BJ+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③ |
| Shiqi (2011) | 30 | 26 | 60–87 | 61–88 | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 | ① |
| Bing and Yuanai (2011) | 100 | 100 | 25–71 | 23–70 | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 8 | ①②③⑤ |
| Xinhua (2012) | 50 | 50 | — | — | FJH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③④ |
| Fengyan (2012) | 32 | 32 | — | — | FJH+Bio | Bio | 12 | ①②⑤ |
| Lidong et al. (2013) | 50 | 50 | — | — | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①②④ |
| Wen-ge et al. (2013) | 63 | 57 | 24–57 | 27–56 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①③⑤ |
| Dan et al. (2013) | 39 | 38 | — | — | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①③④⑤ |
| Hunxi and Zhanqi (2013) | 100 | 90 | 11–75 | 19–68 | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑤ |
| Zhongming (2013) | 75 | 75 | — | — | JHL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑤ |
| Hualiang (2013) | 60 | 57 | — | — | FT+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②④ |
| Xuhua et al. (2013) | 22 | 22 | — | — | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①④⑤ |
| Qing and Wengfang (2014) | 40 | 40 | — | — | FJH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②⑤ |
| Long et al. (2014) | 50 | 50 | — | — | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 9 | ①④ |
| Qianxin et al. (2014) | 92 | 90 | — | — | JH+Bio | Bio | 2 | ①②⑤ |
| Xiue et al. (2014) | 97 | 98 | 31.6 ± 2.4 | 32.1 ± 2.1 | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 8 | ①②③⑥⑦ |
| Jian and Li (2014) | 24 | 24 | 68.5 ± 6.2 | 67.2 ± 5.7 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑥⑦ |
| Jinghua et al. (2015) | 53 | 53 | 21–73 | 20–73 | KL+Bio | Bio | 3 | ① |
| Xiang (2015) | 50 | 58 | 22–87 | 23–88 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①④ |
| Min-shuang et al. (2015) | 56 | 58 | 42.18 ± 6.34 | 43.08 ± 6.63 | JH+Bio | Bio | 18 | ①⑤⑥⑦ |
| Tianfeng (2015) | 43 | 42 | 30–58 | 31–58 | BFHX+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①④ |
| Yunxiao and Guosheng (2015) | 40 | 40 | — | — | BJ+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③⑤ |
| Yuxia (2015) | 45 | 45 | 18–66 | 18–65 | JH+Bio | Bio | 2 | ①②⑤ |
| Shuhua and Fujian (2016) | 60 | 60 | 18–80 | 16–78 | BL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①② |
| Shiming et al. (2016) | 51 | 50 | 18–64 | 29–65 | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 18 | ①②③⑤ |
| Qi et al. (2016) | 150 | 150 | — | — | BL+Bio | Bio | 8 | ①②④⑤ |
| Juan et al. (2016) | 56 | 53 | — | — | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 8 | ①②③⑤ |
| Wei (2016) | 48 | 48 | 13–74 | 16–72 | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑤ |
| Zhenru (2016) | 34 | 34 | 20–62 | 21–61 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ②⑥⑦ |
| Liping and Chun (2016) | 42 | 28 | — | — | FT+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①② |
| Junguo et al. (2016) | 40 | 38 | 18–65 | 17–64 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②⑤ |
| Qi (2016) | 56 | 56 | 45.2 ± 3.4 | JH+Bio | Bio | 12 | ①② | |
| Shuang (2016) | 40 | 38 | — | — | JHL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②④ |
| Yongyi et al. (2017) | 55 | 55 | 19–66 | 17–67 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②④⑤ |
| Ji et al. (2017) | 58 | 55 | — | — | FT+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③⑤ |
| Xing et al. (2017) | 185 | 175 | — | — | JH+Bio | Bio | 12 | ①②③⑤ |
| Jun et al. (2017) | 56 | 53 | — | — | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 8 | ①②③⑤ |
| Xu et al. (2018) | 90 | 90 | 45.6 ± 9.9 | 42.8 ± 10.5 | BFHX+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③ |
| Liping (2018) | 43 | 43 | 18.3–76.5 | 18.1–76.9 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②⑤⑥⑦ |
| Lingwei (2018) | 60 | 60 | — | — | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ②④ |
| Junjie (2018) | 57 | 57 | 19–63 | 20–62 | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 9 | ①⑤ |
| Xiaoru et al. (2018) | 54 | 54 | 33.8 ± 5.7 | 33.7 ± 5.3 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ① |
| Xiaoni (2018) | 50 | 50 | 24–63 | 25–65 | KL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①④ |
| Di et al. (2019) | 35 | 35 | 19–58 | 18–60 | FJH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ② |
| Zhibo et al. (2019) | 68 | 67 | 35.9 ± 10.5 | 36.3 ± 10.1 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③⑤ |
| Meng (2019) | 40 | 40 | 13–74 | 12–75 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑤ |
| Junmei et al. (2019) | 41 | 41 | 22–68 | 21–69 | BFHX+Bio | Bio | 4 | ①⑤⑦ |
| Hai-xian et al. (2019) | 30 | 30 | 33–59 | 31–61 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①③⑤ |
| Guizhen (2019) | 55 | 50 | 25–66 | 29–63 | JH+Bio | Bio | 9 | ①③④⑤ |
| Qin (2019) | 53 | 53 | 24–77 | 23–78 | FT+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③⑤ |
| Qingfeng (2019) | 30 | 30 | 32–69 | 33–68 | KL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ① |
| Guannan et al. (2020) | 158 | 158 | 72.87 ± 7.12 | 73.91 ± 7.37 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①③④⑤ |
| Hui et al. (2020) | 220 | 180 | 48.82 ± 6.94 | 49.46 ± 6.95 | BL+Bio | Bio | 12 | ①②③⑤⑦ |
| Weiyong et al. (2020) | 50 | 50 | — | — | KL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①④ |
| Xian-hui and Shu-lin (2020) | 75 | 75 | 32–60 | 36–65 | FT+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③④⑤ |
| Bin (2020) | 50 | 50 | 25–76 | 22–75 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②④⑤ |
| Shuangli et al. (2020) | 90 | 90 | 18–60 | 18–58 | BL+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦ |
| Qiong et al. (2021) | 101 | 101 | 17–75 | 16–72 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ① |
| Wei-wei (2021) | 62 | 62 | 60–81 | 60–76 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑥⑦ |
| Qiang (2021) | 60 | 60 | 49.14 ± 10.66 | 48.85 ± 10.27 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③④⑤ |
| Qihuang (2022) | 37 | 37 | 35–71 | 32–72 | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①④⑤ |
| Xuehu et al. (2022) | 60 | 60 | 19–65 | 20–64 | KF+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①②③⑤ |
| Yan et al. (2022) | 56 | 56 | 32–67 | 30–68 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③④ |
| Jia (2022) | 50 | 50 | 25–67 | 24–69 | JH+Bio | Bio | 2 | ① |
| Jiafu and Lanhua (2022) | 38 | 38 | 25–73 | 24–72 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ②⑤ |
| Xueyun (2022) | 60 | 60 | 37.62 ± 6.91 | 38.15 ± 7.11 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③④⑤ |
| Xiaohua (2022) | 34 | 34 | 23–64 | 24–66 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑤⑥⑦ |
| Juan (2022) | 100 | 100 | 57.83 ± 5.09 | 52.17 ± 6.07 | JH+Bio | Bio | 9 | ①②③ |
| Chenyong et al. (2022) | 41 | 39 | 6–15 | 7–16 | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 3 | ①②③④⑤ |
| Tao and Fei (2022) | 40 | 40 | 26–75 | 24–75 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③④⑤ |
| Yawei et al. (2023) | 76 | 76 | 39–75 | 35–75 | BFHX+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑤ |
| Guannan et al. (2023) | 94 | 94 | 24–68 | 19–70 | KF+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①②③⑤ |
| Qiaoe et al. (2023) | 100 | 100 | 23–74 | 22–74 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①④ |
| Junguo (2023) | 30 | 30 | 70.48 ± 2.61 | 70.44 ± 2.23 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ②⑤⑦ |
| Yan et al. (2023) | 35 | 35 | 55.61 ± 11.12 | 52.47 ± 10.49 | KL+Bio | Bio | 6 | ③⑥⑦ |
| Yuxia (2023) | 38 | 38 | 19–80 | 19–80 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ①⑤ |
| Hu et al. (2023) | 68 | 68 | 41.87 ± 11.35 | 42.82 ± 11.02 | BFHX+Bio | Bio | 5 | = 1 \* GB3 ①②③④⑤⑥⑦ |
| Peiqian et al. (2024) | 49 | 49 | 15–17 | 15–18 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ⑤⑥⑦ |
| Xinlei and Rong (2024) | 104 | 103 | 49.44 ± 12.79 | 50 ± 15.01 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | = 2 \* GB3 ②④⑤ |
| Yuelian (2024) | 49 | 49 | 52.97 ± 7.05 | 54.11 ± 6.83 | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 | ②③④⑥⑦ |
Characteristics of the included randomized controlled trials.
3.3 Literature quality assessment
All 100 included articles documented randomization procedures, with 28 employing random number tables (Mengqiu et al., 2006; Hualiang, 2013; Hunxi and Zhanqi, 2013; Xiue et al., 2014; Min-shuang et al., 2015; Juan et al., 2016; Zhenru, 2016; Ji et al., 2017; Jun et al., 2017; Xiaoru et al., 2018; Junmei et al., 2019; Hai-xian et al., 2019; Bin, 2020; Guannan et al., 2020; Weiyong et al., 2020; Qiang, 2021; Qihuang, 2022; Xiaohua, 2022; Xueyun, 2022; Guannan et al., 2023; Chuanjun et al., 2023; Qiaoe et al., 2023; Chenyong et al., 2022; Yawei et al., 2023; Yuxia, 2023; Peiqian et al., 2024; Xinlei and Rong, 2024; Yuelian, 2024), one utilizing random pairing (Jun, 2010), one applying random ordering (Wen-ge et al., 2013), two implementing random sampling (Juan et al., 2016; Jun et al., 2022), one adopting randomized controlled design (Chang et al., 2022), one using stratified block randomization (Guannan et al., 2020), two applying computer randomization (Xian-hui and Shu-lin, 2020; Juan, 2022); one implementing random parallel design (Chenyong et al., 2022), one using pathogen number draw (Yongyi et al., 2017), all rated as low risk. Studies mentioning randomization without methodological specification received unclear risk ratings. The investigation by Liu Xing et al. (Xing et al., 2017) implemented double-blind method and was rated as low risk, whereas Gao Mengqiu et al. (Mengqiu et al., 2006) applied single-blind method without specifying personnel responsible for implementation. All the included studies had complete data, with no evidence of selective reporting or other biases documented. Detailed risk of bias assessments are presented in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2
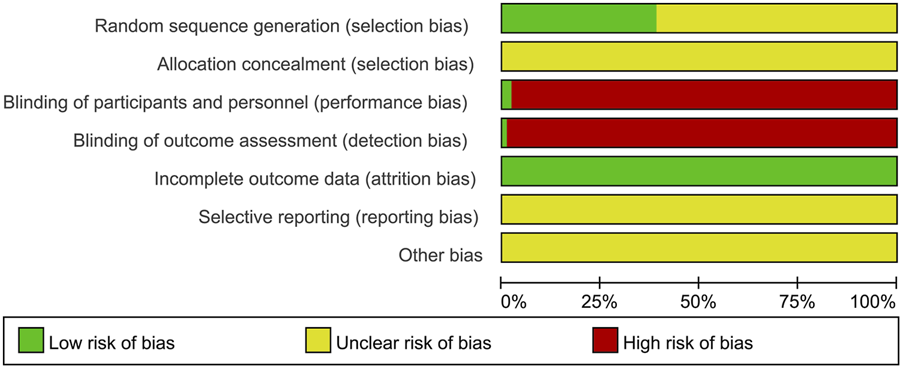
Percentages of items with risks of bias of included articles. In the domain of random sequence generation, 38 studies reported specific methods of randomization, while 62 studies merely mentioned randomization without providing details of the method used. For allocation concealment, none of the included studies reported any information. Regarding blinding of participants and personnel, one study reported a double-blind design, and another study adopted a single-blind design. In terms of blinding of outcome assessment, only one study reported using a double-blind approach. All included studies had complete outcome data. None of the studies mentioned selective reporting or other sources of bias. The term “other biases” refers to potential sources of bias such as funding-related bias, selective reporting bias, data collection bias, and study design bias.
3.4 Evidence network
Fifty-three studies reported clinical efficacy rates, resulting in 12 direct comparisons, while 78 studies reported negative conversion rates yielding 12 direct comparisons. Evaluation of lesion absorption rates occurred across 56 studies generating 11 direct comparisons., with cavity absorption rates assessed in 42 studies forming 11 direct comparisons. 13 studies quantified CD3+ T lymphocyte improvement rates forming seven direct comparisons, complemented by 16 studies examining CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rates forming seven direct comparisons. No closed loops were formed between the outcome indicators, so inconsistency tests were not conducted, with the complete evidence network structure depicted in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3
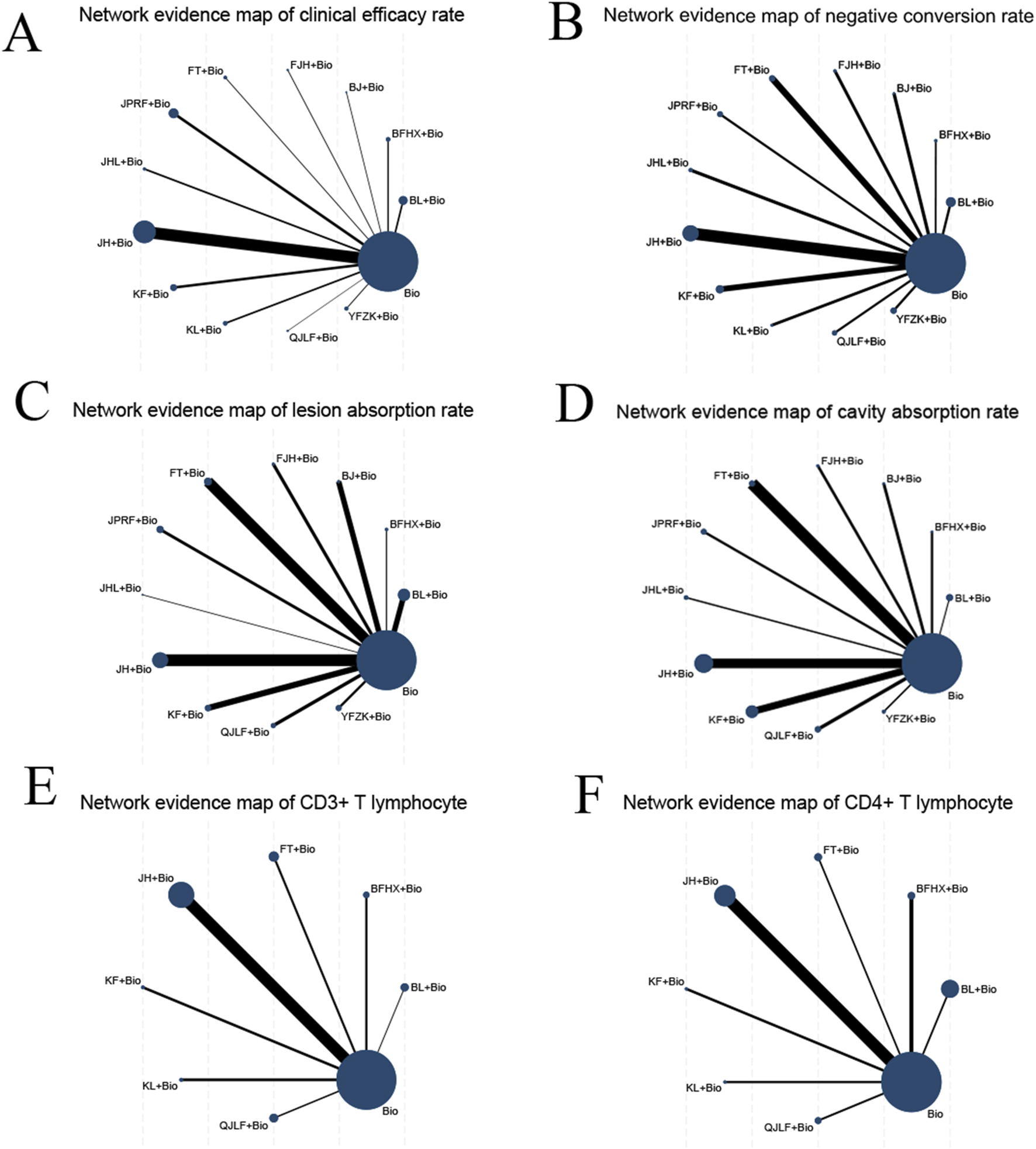
Network evidence maps comparing different outcomes: (A) network evidence map for clinical efficacy rate; (B) network evidence map for negative conversion rate; (C) network evidence map for lesion absorption rate; (D) network evidence map for cavity absorption rate; (E) network evidence map for improvement rate of CD3+ T lymphocytes; (F) network evidence map for improvement rate of CD4+ T lymphocytes.
3.5 Network meta-analysis
3.5.1 Clinical efficacy rate
Assessment of clinical efficacy across 53 studies reported clinical efficacy rate, incorporating 13 interventions, including 12 types of oral TCMs, enrolled 6,625 participants. The network meta-analysis demonstrated significantly enhanced clinical efficacy for combinations of standard biomedicine with: FeiJieHe Pill (OR = 8.43,95% CI [1.79, 39.7]), Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule (OR = 4.88, 95% CI [2.72, 8.74]), Kangfuxin Liquid (OR = 2.60, 95% CI [1.79, 3.78]), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (OR = 2.56, 95% CI [1.02, 6.46]), Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (OR = 2.54, 95% CI [1.58, 4.10]), Jian Pi Run Fei Pill (OR = 2.49, 95% CI [1.67, 3.71]), Fei Tai Capsule (OR = 2.48, 95% CI [1.46, 4.23]), KangLao Pill (OR = 2.16, 95% CI [1.42, 3.28]), Bai Ling Capsule (OR = 2.11, 95% CI [1.47, 3.03]), and Jie He Pill (OR = 2.14, 95% CI [1.77, 2.58]), all relative to biomedicine monotherapy. SUCRA ranking for clinical efficacy revealed the following hierarchy of therapeutic combinations: FeiJieHe Pill with standard biomedicine (SUCRA = 90.9%) exhibited the highest probability of superiority, followed sequentially by Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule (SUCRA = 87.2%), Bu Jin Tablet (SUCRA = 61.5%), Kangfuxin Liquid (SUCRA = 54.3%), Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (SUCRA = 51.3%), Jie He Ling Tablet (SUCRA = 50.7%), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (SUCRA = 50.3%), Jian Pi Run Fei Pill (SUCRA = 49.7%), Fei Tai Capsule (SUCRA = 49.2%), KangLao Pill (SUCRA = 36.2%), Bai Ling Capsule (SUCRA = 34%), and Jie He Pill (SUCRA = 33.7%), with all relative to standard biomedicine monotherapy (SUCRA = 1.1%). In summary, the combination of FeiJieHe Pill with standard biomedicine potentially represents the optimal approach for improving clinical efficacy, as visually summarized in Figures 4A,B.
FIGURE 4
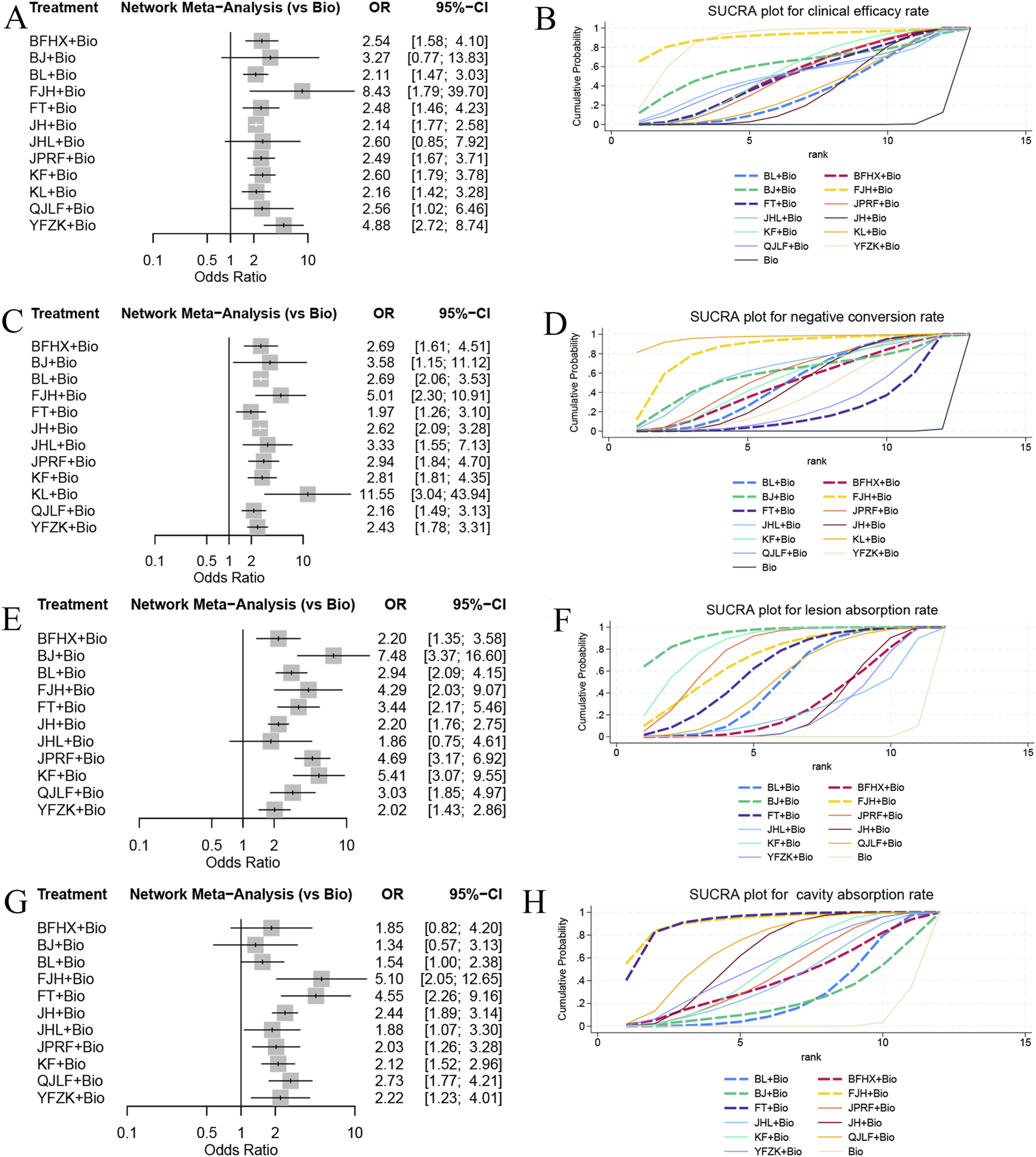
Forest plots and SUCRA ranking charts showing comparative effects on clinical efficacy rate, negative conversion rate, lesion absorption rate, and cavity absorption rate: (A) Forest plot of clinical efficacy rate; (B) SUCRA ranking chart for clinical efficacy rate; (C) Forest plot of negative conversion rate; (D) SUCRA ranking chart for negative conversion rate; (E) Forest plot of lesion absorption rate; (F) SUCRA ranking chart for lesion absorption rate; (G) Forest plot of cavity absorption rate; (H) SUCRA ranking chart for cavity absorption rate.
3.5.2 Negative conversion rate
A total of 78 studies reported the negative conversion rate, involving 13 interventions, including 12 types of oral TCMs, with 9,955 participants. The network meta-analysis results demonstrated significantly greater negative conversion rate for combination of standard biomedicine with: KangLao Pill (OR = 11.55, 95% CI [3.04, 43.93]), FeiJieHe Pill (OR = 5.01, 95% CI [2.30,10.91]), Jie He Ling Tablet (OR = 3.33, 95% CI [1.55, 7.13]), Bu Jin Tablet (OR = 3.58, 95% CI [1.15,11.12]), Jian Pi Run Fei Pill (OR = 2.94, 95% CI [1.84, 4.70]), Kangfuxin Liquid (OR = 2.81, 95% CI [1.81, 4.35]), Bai Ling Capsule (OR = 2.69, 95% CI [2.06, 3.53]), Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (OR = 2.69, 95% CI [1.61, 4.51]), Jie He Pill (OR = 2.62, 95% CI [2.09, 3.28]), Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule (OR = 2.43, 95% CI [1.78, 3.31]), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (OR = 2.16, 95% CI [1.49, 3.13]), and Fei Tai Capsule (OR = 1.97, 95%CI [1.26, 3.10]), all relative to standard biomedicine monotherapy. SUCRA ranking for negative conversion rate established a probabilistic hierarchy wherein KangLao Pill combined with standard biomedicine (SUCRA = 96.5%) showed the highest superiority probability, followed sequentially by FeiJieHe Pill (SUCRA = 84.2%), Jie He Ling Tablet (SUCRA = 63.3%), Bu Jin Tablet (SUCRA = 59.7%), Jian Pi Run Fei Pill (SUCRA = 57.4%), Kangfuxin Liquid (SUCRA = 53.8%), Bai Ling Capsule (SUCRA = 50.2%), Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (SUCRA = 49.2%), Jie He Pill (SUCRA = 47.3%), Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule (SUCRA = 38.7%), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (SUCRA = 28%), and Fei Tai Capsule (SUCRA = 21.6%), all benchmarked against standard biomedicine monotherapy (SUCRA = 0.2%). In summary, KangLao Pill combined with standard biomedicine potentially represents the optimal approach for improving negative conversion rates, as visualized in Figures 4C,D.
3.5.3 Lesion absorption rate
A total of 56 studies reported lesion absorption rate, involving 12 interventions, including 11 types of oral TCMs, with a total of 7,676 patients. The network meta-analysis showed a higher lesion absorption rate for the combinations of standard biomedicine with: Bu Jin Tablet (OR = 7.48, 95% CI [3.37,16.60]), Kangfuxin Liquid (OR = 5.41, 95% CI [3.07, 9.55]), Jian Pi Run Fei Pill (OR = 4.69, 95% CI [3.17, 6.62]), FeiJieHe Pill (OR = 4.29, 95% CI [2.03, 9.07]), Fei Tai Capsule (OR = 3.44, 95% CI [2.17, 5.46]), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (OR = 3.03, 95% CI [1.85, 4.97]), Bai Ling Capsule (OR = 2.94, 95% CI [2.09, 4.15]), Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (OR = 2.20, 95% CI [1.35,3.58]), Jie He Pill (OR = 2.20, 95% CI [1.76, 2.75]), and Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule (OR = 2.02, 95% CI [1.43, 2.86]), than using biomedicine monotherapy. SUCRA ranking for clinical efficacy revealed the following hierarchy of therapeutic combinations of Bu Jin Tablet with standard biomedicine (SUCRA = 93.4%) exhibited the highest lesion absorption rate, followed sequentially by Kangfuxin Liquid (SUCRA = 84.5%), Jian Pi Run Fei Pill (SUCRA = 77.3%), FeiJieHe Pill (SUCRA = 71.5%), Fei Tai Capsule (SUCRA = 63.5%), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (SUCRA = 52.3%), Bai Ling Capsule (SUCRA = 50%), Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (SUCRA = 30%), Jie He Pill (SUCRA = 23.7%), Jie He Ling Tablet (SUCRA = 25.3%), Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule (SUCRA = 24.1%) all relative to standard biomedicine monotherapy (SUCRA = 0.9%). In summary, the combination of Bu Jin Tablet with standard biomedicine may be the best approach for improving lesion absorption rate, as visually summarized in Figures 4E,F.
3.5.4 Cavity absorption rate
A total of 42 studies reported cavity absorption rate, involving 12 interventions, including 11 types of TCMs, enrolled 5,148 patients. The network meta-analysis results showed significantly greater cavity absorption rate for combination of standard biomedicine with: FeiJieHe Pill (OR = 5.10, 95% CI [2.05, 12.65]), Fei Tai Capsule (OR = 4.55, 95% CI [2.26, 9.16]), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (OR = 2.73, 95% CI [1.77, 4.21]), Jie He Pill (OR = 2.44, 95% CI [1.89, 3.14]), Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule (OR = 2.22, 95% CI [1.23, 4.01]), Kangfuxin Liquid (OR = 2.12, 95% CI [1.52, 2.96]), Jian Pi Run Fei Pill (OR = 2.03, 95% CI [1.26, 3.28]), and Jie He Ling Tablet (OR = 1.88, 95% CI [1.07, 3.30]), all relative to biomedicine monotherapy. SUCRA ranking for cavity absorption rate established a probabilistic hierarchy wherein FeiJieHe Pill combined with standard biomedicine (SUCRA = 91.9%) showed the highest superiority probability, followed by Fei Tai Capsule (SUCRA = 91.1%), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (SUCRA = 69.9%), Jie He Pill (SUCRA = 62.7%), Yi Fei Zhi Ke Capsule (SUCRA = 53.5%), Kangfuxin Liquid (SUCRA = 51.1%), Jian Pi Run Fei Pill (SUCRA = 46.1%), Jie He Ling Tablet (SUCRA = 41.2%), Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (SUCRA = 40.5%), Bai Ling Capsule (SUCRA = 26.1%), Bu Jin Tablet (SUCRA = 22.4%), all benchmarked against standard biomedicine monotherapy (SUCRA = 3.4%). In summary, the combination of FeiJieHe Pill with standard biomedicine may be the best approach for improving cavity absorption rate, as visualized in Figures 4G,H.
3.5.5 CD3+ T lymphocyte and CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate
A total of 13 studies involving 1,519 participants across eight interventions, comprising seven types of oral TCMs, reported CD3+ T lymphocyte improvement rates. The network meta-analysis revealed superior improvement rate of CD3+ T lymphocytes for JieHe pill combined with conventional biomedicine (OR = 5.6, 95% CI [3.4, 7.8]) than monotherapy. Separately, 16 studies encompassing 2,057 participants under eight interventions (including seven oral TCM types) documented CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate. The network meta-analysis results show that the improvement rate of CD4+ T lymphocytes was significantly enhanced outcomes for the combination of conventional biomedicine with JieHe pill (OR = 5.1, 95% CI [2.9, 7.3]), Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (OR = 4.7, 95% CI [0.1, 9.2]), and Bai Ling Capsule (OR = 4.5, 95% CI [0.2, 8.8]) compared to biomedicine monotherapy. SUCRA ranking for CD3+ T lymphocyte improvement rate indicated the following hierarchy: the combination of standard biomedicine with Jie He Pill demonstrated superiority over Kangfuxin Liquid combination therapy (SUCRA = 67.6%), followed by Kangfuxin Liquid (SUCRA = 63.5%), Fei Tai Capsule (SUCRA = 60.7%), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (SUCRA = 59.2%), KangLao Pill (SUCRA = 53%), Bai Ling Capsule (SUCRA = 52.8%), standard biomedicine monotherapy (SUCRA = 22%), and Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (SUCRA = 21.3%), as shown in Figures 5A,B. For CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate, the probability ranking positioned Jie He Pill combined with standard biomedicine (SUCRA = 66.5%) first, followed by Bu Fei Huo Xue Capsule (SUCRA = 60.4%), Bai Ling Capsule (SUCRA = 58.7%), Kangfuxin Liquid (SUCRA = 56.3%), KangLao Pill (SUCRA = 48.9%), Qi Jia Li Fei Capsule (SUCRA = 47.1%), and Fei Tai Capsule (SUCRA = 44.9%), each outperforming standard biomedicine monotherapy (SUCRA = 17.2%), as shown in Figures 5C,D.
FIGURE 5
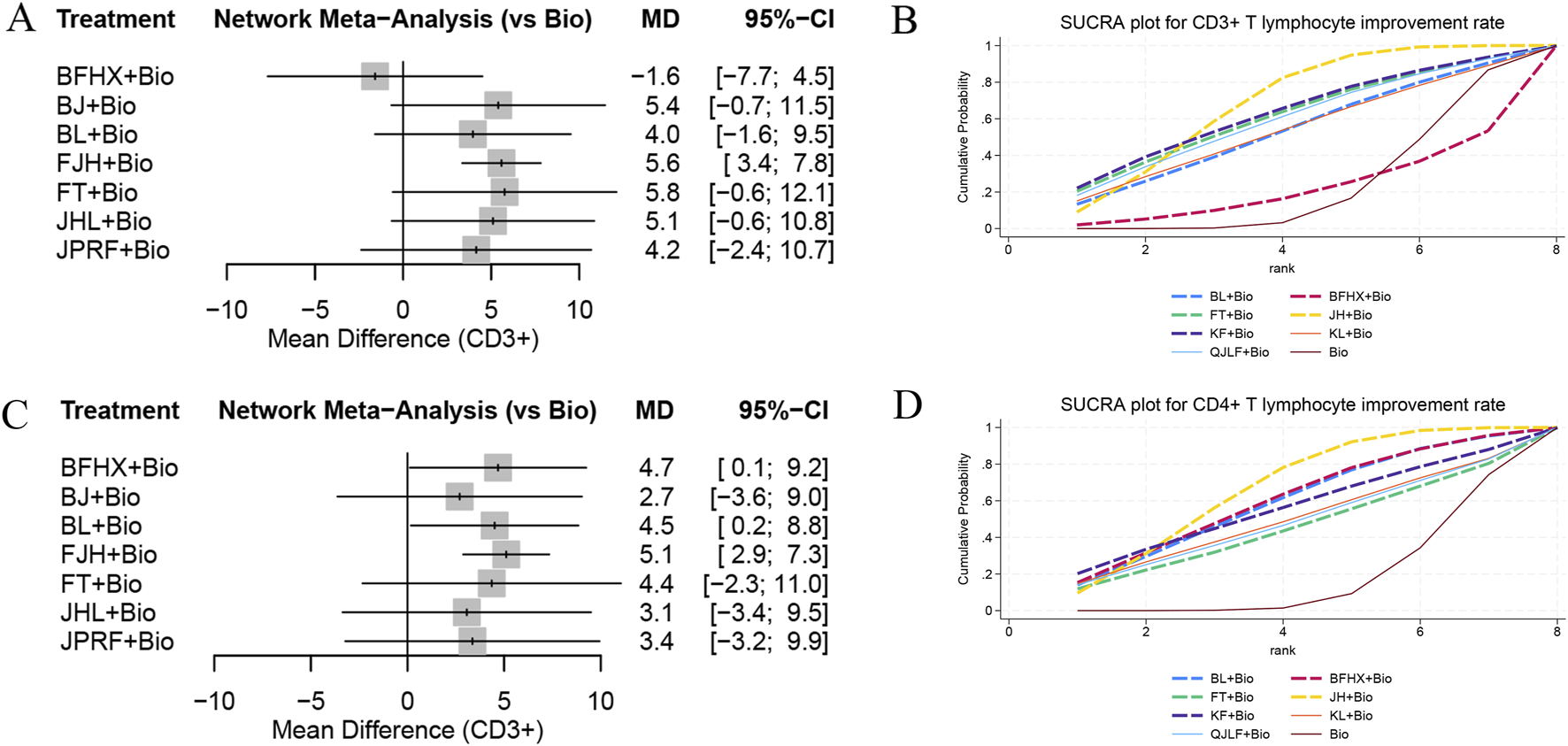
Forest plots and SUCRA ranking charts for CD3+ T lymphocyte improvement rate and CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate: (A) forest plot of CD3+ T lymphocyte improvement rate; (B) SUCRA ranking chart for CD3+ T lymphocyte improvement rate; (C) forest plot of CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate; (D) SUCRA ranking chart for CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate.
3.6 Adverse reactions
Safety assessment across 61 encompassing 8,573 participants (4,496 in the experimental group and 4,077 in the control group) The majority of adverse reactions in both groups were related to the digestive system, characterized by mild, self-limiting manifestations. The experimental group reported 586 adverse reactions (approximate incidence 13%), compared with 1,022 adverse reactions (approximate incidence 25%) in controls. Since the types of adverse reactions reported in the included studies varied, only a descriptive analysis is provided here, as detailed in Table 2.
TABLE 2
| Included in study | Interventions | Adverse reactions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | T | C | |
| Junmei et al. (2019) | BFHX+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of skin allergy, 1 case of gout, and 2 cases of liver function impairment. | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 2 cases of skin allergies, 1 case of gout, and 3 cases of liver function impairment. |
| Yawei et al. (2023) | BFHX+Bio | Bio | 3 cases of dizziness, 2 cases of liver function impairment, 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of peripheral neuritis, 2 cases of rash. | 2 cases of dizziness, 1 case of liver function impairment, 6 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 2 cases of rash. |
| Hu (2023) | BFHX+Bio | Bio | 5 cases of abnormal liver function, and 2 cases of dry mouth. | 10 cases of abnormal liver function, and 6 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. |
| Yunxiao and Guosheng (2015) | BJ+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of abnormal liver function. | 5 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Yanpei and Shuyu (2002) | BL+Bio | Bio | 9 cases of adverse reactions. | 17 cases of adverse reactions. |
| Ge et al. (2009) | BL+Bio | Bio | 12 cases of abnormal liver function. | 31 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Qi et al. (2016) | BL+Bio | Bio | 15 cases of abnormal liver function, 1 case of kidney function injury, 13 cases of dizziness and tinnitus, and 7 cases of blood system reactions. | 17 cases of abnormal liver function, 7 cases of kidney function injury, 16 cases of dizziness and tinnitus, and 19 cases of blood system reactions. |
| Hui et al. (2020) | BL+Bio | Bio | 29 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 3 cases of abnormal kidney function, 5 cases of abnormal liver function, 9 cases of hypothyroidism, 10 cases of blood system abnormalities, and 7 cases of neurological dysfunction. | 35 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 12 cases of abnormal kidney function, 16 cases of abnormal liver function, 13 cases of hypothyroidism, 22 cases of blood system abnormalities, and 12 cases of neurological dysfunction. |
| Shuangli et al. (2020) | BL+Bio | Bio | 11 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of abnormal kidney function, 2 cases of abnormal liver function, 4 cases of blood system injuries, and 3 cases of neurological injuries. | 17 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 6 cases of abnormal kidney function, 8 cases of abnormal liver function, 11 cases of blood system injuries, and 6 cases of neurological injuries. |
| Fengyan (2012) | FJH+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of abnormal liver function, and 1 case of gastrointestinal reaction. | 3 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Qing and Wenfang (2014) | FJH+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of abnormal liver function. | 3 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Mengqiu et al. (2006) | FT+Bio | Bio | 1 case of elevated transaminase levels, and 1 case of Achilles tendon pain caused by levofloxacin. | Not reported. |
| Ji et al. (2017) | FT+Bio | Bio | 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of allergic reaction, 4 cases of liver injury, 3 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 2 cases of gout, and 1 case of other conditions. | 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 2 cases of allergic reactions, 5 cases of liver injury, 4 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 1 case of gout, and 1 case of other conditions. |
| Qingfeng (2019) | FT+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 3 cases of functional impairment, 2 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 1 case of gout, and 1 case of other conditions. | 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 6 cases of functional impairment, 5 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 2 cases of gout, and 1 case of other conditions. |
| Xian-hui and Shu-lin (2020) | FT+Bio | Bio | 4 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of allergic reaction, 5 cases of abnormal liver function, 4 cases of leukopenia, 2 cases of gout. | 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 3 cases of allergic reactions, 4 cases of abnormal liver function, 3 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), and 1 case of gout. |
| Lidong and Shuqing (2007) | JHL+Bio | Bio | 1 case of mildly abnormal liver function, and 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. | Not reported. |
| Shuqin et al. (2008) | JHL+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of mild liver function impairment. | Not reported. |
| Zhongming (2013) | JHL+Bio | Bio | 1 case of gastrointestinal reaction, and 1 case of liver function impairment. | Not reported. |
| Guiqiu (2010) | JH+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of liver function impairment. | Not reported. |
| Dan et al. (2013) | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 cases of adverse reactions. | 7 cases of adverse reactions. |
| Xuhua et al. (2013) | JH+Bio | Bio | 4 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of abnormal liver function, and 1 case of abnormal kidney function. | 8 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 5 cases of abnormal liver function, 1 case of abnormal kidney function, and 2 cases of rash. |
| Qianxin et al. (2014) | JH+Bio | Bio | 6 cases of abnormal liver function. | 19 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Min-shuang et al. (2015) | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. | 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. |
| Yuxia (2015) | JH+Bio | Bio | 1 case of abnormal liver function. | 5 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Junguo et al. (2016) | JH+Bio | Bio | 1 case of abnormal liver function. | 4 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Yongyi et al. (2017) | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 cases of abnormal liver function. | 6 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Xing et al. (2017) | JH+Bio | Bio | 5 cases of adverse reactions. | 8 cases of adverse reactions. |
| Liping (2018) | JH+Bio | Bio | 1 case of abnormal liver function, 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of abnormal kidney function. | 2 cases of abnormal liver function, 4 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 3 cases of abnormal kidney function. |
| Meng (2019) | JH+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of abnormal liver function. | 4 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 3 cases of abnormal liver function, and 3 cases of abnormal kidney function. |
| Guizhen (2019) | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 7 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 6 cases of liver function impairment. | 10 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 18 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 16 cases of liver function impairment, and 6 cases of joint pain. |
| Bin (2020) | JH+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of joint pain. | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of joint pain, and 1 case of abnormal liver and kidney function. |
| Qiang (2021) | JH+Bio | Bio | 5 cases of abnormal liver function, 11 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 5 cases of allergic reactions, 2 cases of vision impairment, and 3 cases of other reactions. | 4 cases of abnormal liver function, 13 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 4 cases of allergic reactions, 3 cases of vision impairment, and 2 cases of other reactions. |
| Qihuang (2022) | JH+Bio | Bio | 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of neuritis. | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of neuritis. |
| Jiafu and Lanhua (2022) | JH+Bio | Bio | 1 case of gastrointestinal reaction, and 1 case of headache. | 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 2 cases of headaches. |
| Tao and Fei (2022) | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 cases of abnormal liver function, 7 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 3 cases of allergic reactions, and 1 case of vision impairment. | 2 cases of abnormal liver function, 8 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 3 cases of allergic reactions, and 2 cases of vision impairment. |
| Junguo (2023) | JH+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal issues, and 1 case of abnormal liver and kidney function. | 3 cases of gastrointestinal issues, and 1 case of dizziness. |
| Yuxia (2023) | JH+Bio | Bio | 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of abnormal liver function, and 2 cases of peripheral neuritis. | 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 2 cases of abnormal liver function, 1 case of reduced vision, and 3 cases of peripheral neuritis. |
| Peiqian et al. (2024) | JH+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of liver and kidney injury, 1 case of dizziness, and 1 case of rash. | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of rash. |
| Xinlei and Rong (2024) | JH+Bio | Bio | 3 cases of gastrointestinal dysfunction, 1 case of liver function impairment, 1 case of neurological damage, and 2 cases of rash. | 15 cases of gastrointestinal discomfort, 2 cases of liver function impairment, 3 cases of neurological damage, and 7 cases of rash. |
| Wulu et al. (2007) | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 4 cases of mild liver function impairment, and 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. | A total of 5 cases including liver function impairment, gastrointestinal reactions, neurological symptoms, and leukopenia (reduced white blood cells). |
| Shouyue (2009) | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 12 cases of adverse reactions. | 69 cases of adverse reactions. |
| Fuyuan and Meimingxing (2010) | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 4 cases of mild liver function impairment, and 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. | 4 cases of severe side effects, and 14 cases of mild side effects. |
| Bing and Yuanai (2011) | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 1 case of allergic reaction, 7 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 10 cases of abnormal liver function, and 1 case of abnormal urinalysis. | 3 cases of allergic reactions, 23 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 29 cases of abnormal liver function, and 4 cases of abnormal urinalysis. |
| Hunxi and Zhanqi (2013) | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 9 cases of adverse reactions. | 26 cases of adverse reactions. |
| Wei (2016) | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 4 cases of adverse reactions. | 11 cases of adverse reactions. |
| Chenyong et al. (2022) | JPRF+Bio | Bio | 1 case of gastrointestinal reaction, 1 case of peripheral neuritis, and 1 case of rash. | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 1 case of peripheral neuritis, 3 cases of rash, and 2 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Wen-ge et al. (2013) | KF+Bio | Bio | 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 4 cases of abnormal liver function, and 2 cases of rash. | 6 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 4 cases of abnormal liver function, and 2 cases of rash. |
| Zhibo et al. (2019) | KF+Bio | Bio | 10 cases of adverse reactions. | 12 cases of adverse reactions. |
| Hai-xian et al. (2019) | KF+Bio | Bio | 5 cases of elevated uric acid, 3 cases of liver function impairment, 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of knee joint pain. | 3 cases of elevated uric acid, 4 cases of liver function impairment, 10 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of knee joint pain. |
| Guannan et al. (2020) | KF+Bio | Bio | 9 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 6 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 6 cases of abnormal liver function, and 5 cases of elevated bilirubin levels. | 8 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 11 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 6 cases of abnormal liver function, and 5 cases of elevated bilirubin levels. |
| Xuehu et al. (2022) | KF+Bio | Bio | 4 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. | Not reported. |
| Xueyun (2022) | KF+Bio | Bio | 1 case of allergic reaction, 1 case of liver injury, 1 case of gastrointestinal reaction, and 3 cases of gout. | 2 cases of allergic reactions, 2 cases of liver injuries, 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 3 cases of gout. |
| Xiaohua (2022) | KF+Bio | Bio | 1 case of gastrointestinal reaction, and 1 case of thrombocytopenia (reduced platelets). | 4 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 2 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), 2 cases of thrombocytopenia (reduced platelets), and 1 case of abnormal liver function. |
| Guannan et al. (2023) | KF+Bio | Bio | 1 case of gastrointestinal reaction, 1 case of allergic reaction, 2 cases of liver injuries, 2 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), and 1 case of gout. | 8 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 3 cases of allergic reactions, 2 cases of liver injuries, 3 cases of leukopenia (reduced white blood cells), and 2 cases of gout. |
| Shiming et al. (2016) | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 5 cases of abnormal liver function, 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, and 1 case of hypokalemia (low blood potassium). | 4 cases of abnormal liver function, 4 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 2 cases of dizziness, and 2 cases of tinnitus. |
| Juan et al. (2016) | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 10 cases of elevated uric acid, 2 cases of abnormal liver function, and 1 case of joint pain. | 8 cases of elevated uric acid, and 3 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Jun et al. (2017) | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 2 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 10 cases of elevated uric acid, 2 cases of abnormal liver function, and 1 case of joint pain. | 8 cases of elevated uric acid, and 3 cases of abnormal liver function. |
| Junjie (2018) | QJLF+Bio | Bio | 4 cases of elevated uric acid, 2 cases of abnormal liver function, and 3 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. | 2 cases of elevated uric acid, 2 cases of abnormal liver function, and 2 cases of joint pain. |
| Xuewen (2007) | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 8 cases of mild liver function impairment, and 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. | 7 cases of mild liver function impairment, and 5 cases of gastrointestinal reactions. |
| Yujuan (2007) | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 10 cases of adverse reactions. | 12 cases of adverse reactions. |
| Xiuxia (2009) | YFZK+Bio | Bio | 10 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 8 cases of liver function impairment, and 5 cases of rash. | 38 cases of gastrointestinal reactions, 16 cases of liver function impairment, and 4 cases of rash. |
Adverse reactions reported in the included randomized controlled trials.
3.7 Publication bias assessment
This study conducted a publication bias assessment for the included literature and created a comparison-adjusted funnel plot. Due to the poor symmetry of the generated comparison-adjusted funnel plot using Egger’s test, which demonstrated statistically significant publication bias for the following outcomes: clinical efficacy (P = 0.001), negative conversion rate (P < 0.001), lesion absorption (P = 0.004), cavity absorption (P = 0.001), CD3+ T lymphocyte improvement rate (P = 0.049), and CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate (P = 0.027), as visualized in Figure 6.
FIGURE 6
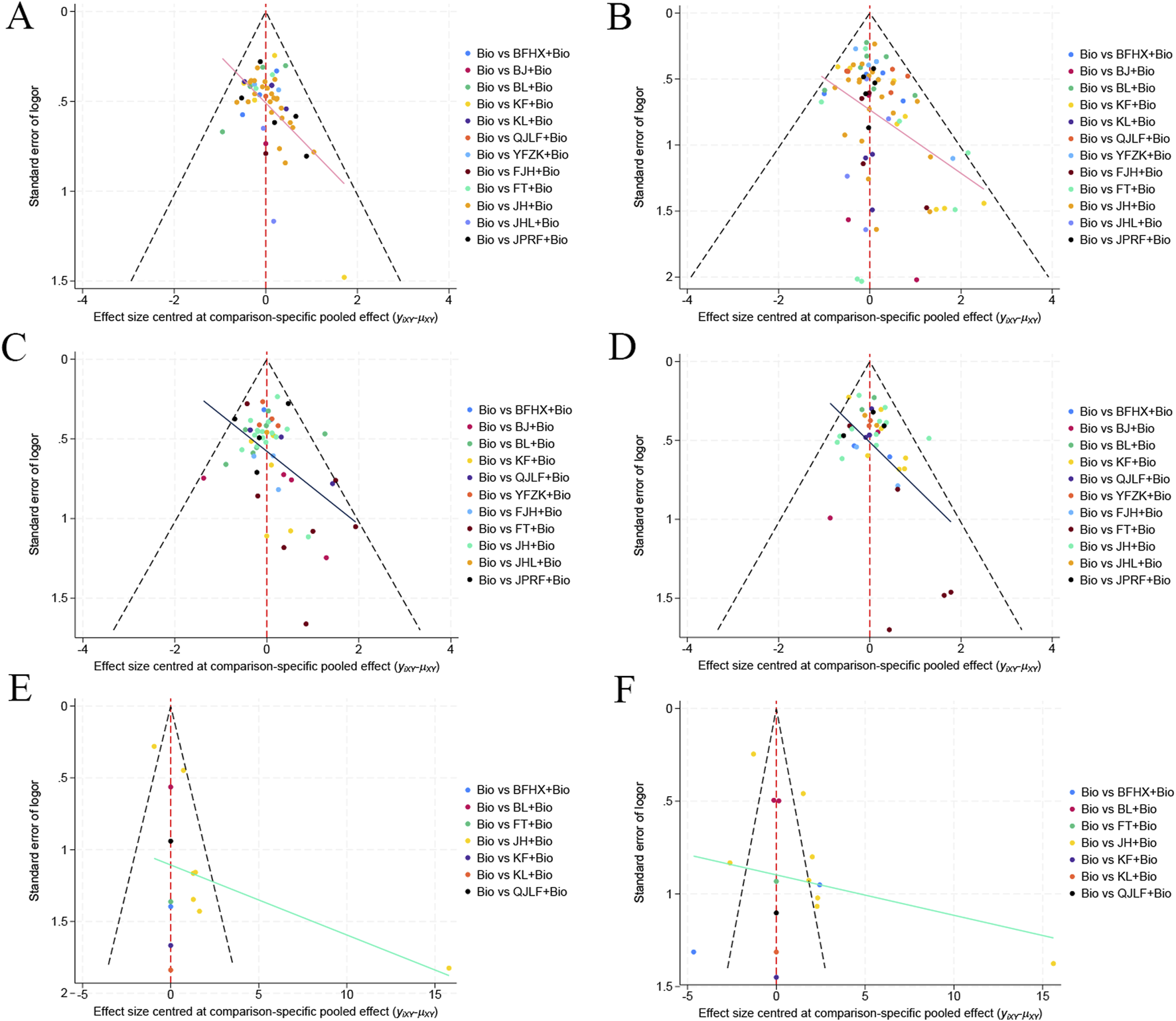
Comparison of various outcome indicators shown through adjusted funnel Plots: (A) Network evidence map of clinical efficacy rate; (B) Network evidence map of negative conversion rate; (C) Network evidence map of lesion absorption rate; (D) Network evidence map of cavity absorption rate; (E) Network evidence map of CD3+ T lymphocyte improvement rate; (F) Network evidence map of CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate.
4 Discussion
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a Gram-positive bacillus characterized by a unique lipid-rich, utilizes this structural feature for host survival and antimicrobial resistance (Gagneux, 2012). Following phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages during the initial infection, the bacterium replicates intracellularly due to their lipid membrane composition, thereby evading immune clearance (Pieters, 2008). In the pathological process of pulmonary tuberculosis, both the immune response and the direct toxic effects of the bacteria cause damage to lung tissue. Common tissue damage includes necrosis, fibrosis, and cavity formation. Although partial parenchymal repair may occur, persistent inflammation and fibrosis may lead to irreversible lung function impairment, ultimately affecting the quality of life among patients.
TCM classifies pulmonary tuberculosis as “lung tuberculosis”, attributing its pathogenesis to dual mechanisms: deficiency of vital energy and invasion by the tuberculosis pathogen. The former refers to insufficient vital energy, while the latter refers to the invasion of the “tuberculosis insect”, which damages the lung yin, leading to lung yin deficiency, and may progressively develop into both qi and yin deficiency. Progressive disease evolution may induce depletion of yin with yang transformation, potentially culminating in severe dual yin-yang deficiency without timely intervention (Cheng-Li et al., 2021). Therefore, TCM treatment for TB emphasizes both tonifying resistance and eliminating the pathogen: tonifying the body by strengthening the immune system, including methods like replenishing qi and blood, strengthening the spleen, and boosting energy; eliminating the pathogen involves targeting the removal of TB pathogens and their associated pathological changes, often using methods like nourishing the yin, moistening the lungs, generating body fluids, and detoxifying.
This study synthesizes 100 RCTs, including 12 types of oral TCMs, and analyzes six outcome indicators. Indirect comparisons among included oral TCMs suggest optimal therapeutic outcomes with combined oral TCM and standard biomedicine. The network meta-analysis indicates that the combination of FeiJieHe Pill with standard biomedicine shows strong effects in improving clinical efficacy and cavity absorption rates. FeiJieHe Pill contain threekey medicinal metabolites: Earthworm, Bletilla striata, and prepared Polygonum multiflorum. Modern pharmacological studies indicat the capacity of Earthworm to downregulate Bcl-2-associated X protein expression while upregulating B-cell lymphoma-2 protein expression, conferring a good immune-enhancing effect (Cheng-Li et al., 2021). Bletilla striata polysaccharides exhibit strong adhesion properties, forming a protective membrane on wound surfaces and adjusting the t-PA/PAI-1 ratio, restoring the balance of the coagulation system (Yuxuan et al., 2018; Jia, 2022). Prepared Polygonum multiflorum, a traditional tonic, demonstrates validated immunoenhancing activity in modern pharmacology (Ya et al., 2019; Donglin et al., 2021). In terms of improving negative conversion rates, KangLao Pill combined with standard biomedicine exhibited strong effects. KangLao Pill is primarily composed of two botanical drugs: Siegesbeckia orientalis and Morus root bark. Modern pharmacological studies reveal that the metabolites of Siegesbeckia orientalis (Chrysophanol I and II) exhibit strong inhibitory effects onMycobacterium tuberculosis (Buhan et al., 1980), while Mulberry Root Bark Polysaccharides (PMA) are a unique plant polysaccharide that can regulate spleen lymphocytes in mice and enhance immune modulation (Kim et al., 2000). In parallel, Bu Jin Tablet combined with standard biomedicine exhibited optimal efficacy for lesion absorption rate improvement. This formulation integrates traditional restorative agents: antler gelatin, silkworm, tortoise shell gelatin, red ginseng, polygonatum, Poria, and gecko, all traditional tonics. Modern pharmacological studies validate immune-enhancing or anti-aging effects of these botanical metabolites (Fang and Dao-Pei:, 2006; Xiue et al., 2014; Lili et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2020; Hongying et al., 2021; Ping et al., 2022). In terms of improving the improvement rate of CD3+ T lymphocytes and CD4+ T lymphocytes, the combination of Tuberculosis Pills with conventional biomedicine shows significant advantages. JieHe Pill incorporates three principalmetabolites: turtle shell, stem of hundred-leaf, and soft-shelled turtle shell. Modern pharmacological research has shown that turtle shell contains various active metabolites such as animal gelatin, collagen, protein, calcium, and phosphorus, which can enhance immunity through Th1 and Th2 cells modulation while exerting antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects (Donglin et al., 2021). The stem of hundred-leaf contains multiple metabolites like stem alkaloids, proto-stem alkaloids, and deoxy-stem alkaloids, which can regulate anchor protein subtype 1 to relax smooth muscles, and have expectorant and antitussive effects (Chang et al., 2022). Soft-shelled turtle shell similarly contains animal gelatin, bone collagen, calcium, and phosphorus that can improve immunity, enhance hematopoietic function, and effectively reduce inflammation factor levels (Wenjia et al., 2023). Concerning adverse reactions, the addition of oral TCM to standard anti-TB drugs demonstrated no increased adverse reactions. On the contrary, among 60 studies reporting adverse reactions, the experimental group had fewer adverse reactions than the control group. However, the definitions and descriptions of adverse reactions varied among different studies, making quantitative evaluation difficult. Therefore, standardized reporting of adverse reactions to oral TCM is crucial for guiding clinical practice, assessing safety, and providing reliable decision-making support. Regarding publication bias, clinical efficacy, negative conversion rate, lesion absorption rate, cavity absorption rate, and CD4+ T lymphocyte improvement rate all showed varying degrees of publication bias, potentially compromising the reliability of these findings.
This study has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, the overall methodological quality of the included studies was moderate. None of the studies reported allocation concealment, and only one study employed a double-blind design while another used a single-blind design. The lack of blinding and allocation concealment may introduce selection bias and detection bias, thereby reducing the credibility of the results. Second, although all included CCPPs were labeled in the original studies as having adjuvant anti-tuberculosis effects, there is a lack of direct comparisons between different CCPPs. Consequently, the comparative results in this study are derived entirely from indirect evidence and should be interpreted with caution. Moreover, for immunological outcomes such as the improvement rates of CD3+ and CD4+ T lymphocytes, some intervention combinations demonstrated statistically significant effects; however, the wide confidence intervals suggest potential small-sample effects, which may undermine the stability of the findings. Third, most included studies did not report medication adherence or loss to follow-up, which may confound the assessment of treatment efficacy. Due to certain limitations inherent in studies on commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation, not all of the original publications provided detailed information on extraction processes or chemical fingerprinting. The available information was mainly obtained from drug package inserts or the Pharmacopoeia of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (Commission, 2020). Finally, there was inconsistency in the definition of “clinical efficacy rate” across studies, which may have introduced substantial heterogeneity in the pooled analysis and affected the robustness of the conclusions.
5 Conclusion
The integration of oral TCMs combined with standard biomedicine in the included studies demonstrated enhanced efficacy across at least one outcome measure. Among these regimens, FeiJieHe Pill combined with conventional biomedicine exhibits optimal efficacy for improving clinical efficacy and cavity absorption rate. JieHe Pill combined with conventional biomedicine similarly shows superior efficacy regarding the enhancement of the recovery rate of CD3+ T lymphocytes and CD4+ T lymphocytes. KangLao Pill combined with standard biomedicine achieves maximal improvement in negative conversion rates, while Bu Jin Tablet combined with standard biomedicine demonstrates the greatest effectiveness for lesion absorption rate improvement. The conclusions of this study also require verification through multi-center, large-sample, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
Statements
Author contributions
JJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft. HW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Software, Writing – review and editing. ZL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. JT: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. FW: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program, Grant No. 82374399); the Key Project of the Anhui Provincial Department of Education (Grant No. 2024AH050994); and the Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center, Institute of Health – Institute of Xin’an Medicine and Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine (“Jiebang Guashuai” Major Breakthrough Project, Grant No. 2023CXMMTCM005). No commercial funding was received. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1588586/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
T, Experimental group; C, Control group; Bio, biomedicine; —, Not reported; BL, Bailing Capsule; BFHX, Bu Fei HuoXue Capsule; BJ, Bu Jin Tablet; FJH, FeiJieHe Pill; FT, Fei Tai Capsule; JPRF, Jian Pi Run Fei Pill; JHL, Jie He Ling Tablet; JHW, Jie He Pill; KF, KangFu Xin Liquid; KL, KangLao Pill; QJLFJN, QiJia LiFei Capsule; YFZKJN, YiFei ZhiKe Capsule.
References
1
Bin Z. (2020). Effect of jiehe pills on sputum negative conversion and levels of IFN-γ and IL-17 in initial treatment for patients with smear positive pulmonary tuberculosis. New Chin. Med.52. 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2020.11.016
2
Bing Z. Yuanai Z. (2011). Integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine therapy for the treatment of 200 cases with recurrent sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis: a clinical study. Guangming J. Chin. Med.26.
3
Buhan H. Wenshen C. Yan H. (1980). Study on the effective components of Ardisia japonica for antituberculosis activity. Chin. Pharm. J.39.
4
Chang L. Yanli M. Shuang L. Xiaoxi W. Bo W. Xin W. et al (2022). Effect of baibu (Radix Stemonae) on expression of cough factor TRPA1 in mice infected with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae. Chin. Archives Traditional Chin. Med.40, 107-110+283–284.
5
Chen Z. Liu J. Kong X. Li H. (2020). Characterization and immunological activities of polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum. Biol. Pharm. Bull.43, 959–967. 10.1248/bpb.b19-00978
6
Cheng-Li B. Man-Jiao F. Yan-Ke L. Ke Y. Li Y. Li Z. et al (2021). Effect of Chinese medicine treatment on improving cellular immune status of patients with refractory extensive-drug-resistant tuberculosis. J. Guangzhou Univ. Traditional Chin. Med.38, 1107–1112. 10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2021.06.006
7
Chenyong W. Xiaojiao P. Zhiwei Y. Lihong Z. Yanbing H. Yanling C. (2022). Efficacy of Jianpi Runfei pills combined with conventional antituberculosis drugs in the treatment of pediatric pulmonary tuberculosis and its impact on lung function. Mod. J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med.31.
8
Chuanjun X. Puxuan L. Yuling H. Li C. Fang W. (2023). Expert consensus on imaging diagnosis of drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. Electron. J. Emerg. Infect. Dis.8, 63–74. 10.19871/j.cnki.xfcrbzz.2023.05.013
9
Cochrane Collaboration, (2020). Review Manager (RevMan), Version 5.4. London, United Kingdom: Cochrane Collaboration.
10
Commission C. P. (2020). Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (Volume IV). Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press.
11
Dan L. De-Bing D. Chun-Qiao X. Yuzhu C. Zhijie C. Zhu J. (2013). Clinical efficacy of Jie-he-wan as adjunctive therapy for with the MDR-TB and their effects on immunological functions. China J. Mod. Med.23, 70–74.
12
Di B. Yu W. Jing A. (2019). Clinical effect analysis of Feijihe pills in adjuvant treatment of cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis. China Pract. Med.14, 94–95. 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2019.26.053
13
Donghua L. Ganhong H. (2005). Curative effects of bailing capsule combined with antituberculotic on pulmonary tuberculosis: a report of 62 cases. Chin. J. General Pract.3 (520), 474. 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4152.2005.06.027
14
Donglin G. Ying W. Jianbo Y. Qi W. Yue L. Hongyu J. et al (2021). On the progress of the extraction, separation and structural analysis of polysaccharides from Polygonum multiflorum. Chin. Pharm. Aff.35, 1166–1172. 10.16153/j.1002-7777.2021.10.012
15
Fang L. Dao-Pei L. (2006). Preparation of placental-eluted gamma globulin and its immunosuppressive effect in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Hematol., 529–534.
16
Fengyan S. (2012). Clinical study of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine therapy for the treatment of multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. World Health Dig.9, 185–186. 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5085.2012.04.145
17
Fuyuan C. Meimingxing (2010). The effect observation of Jianpi Runfei pill adjuvant therapy of old patients with pulmonary tuberculosis in 90 cases. Guide China Med.8. 10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2010.21.022
18
Gagneux S. (2012). Host-pathogen coevolution in human tuberculosis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci.367, 850–859. 10.1098/rstb.2011.0316
19
Ge K. (2019). Shi Yao Shen Shu. Fuzhou, China: Fujian Science and Technology Publishing House Co., Ltd.
20
Ge Y. Ye Y. Ying X. Qi N. (2009). Curative efficacy on pulmonary tuberculosis with combined bailing capsule and anti-tuberculosis drug treatment: a 123 cases analysis. China Mod. Dr. 35–39.
21
Guannan K. Lili H. Qingyan M. Shujun G. Xiaofei L. Ping D. (2020). Clinical study on the effect of Kangfuxin Liquid combined with second-line drugs on elder multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients. J. Xinjiang Med. Univ., 43.
22
Guannan K. Lili H. Xiaofei L. Ping D. Tao S. Yanqing M. (2023). Effect of Kangfuxin liquid combined with standard chemotherapy scheme in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis and its effect on serum α1-acid glycoprotein and haptoglobin levels. China Med.18.
23
Guiqiu S. (2010). Efficacy observation of tuberculosis pills in the treatment of 36 cases with recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis. China Health Care Nutrition19 (6), 2.
24
Guizhen W. (2019). Efficacy observation of tuberculosis pills combined with antituberculosis chemotherapy in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Conval. Med.28.
25
Guofang D. Xiwei L. (2020). Expert consensus on a standard of activity judgment of pulmonary tuberculosis and its clinical implementation. Chin. J. Antituberc.42, 301–307.
26
Hai-Xian Q. Qi-Wen H. Mei-Jin H. Qinglan P. Fenlian D. (2019). The curative effect of Kangfuxin liquid on cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis. Trait Pharm. J.31.
27
Higgins J. P. T. Thomas J. Chandler J. Cumpston M. Li T. Page M. J. Welch V. A. (2023). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. London, United Kingdom: Cochrane.
28
Hongying J. Su W. Xiaochen S. Yanyan Z. (2021). Research Progress Regarding Aging Mechanism and Anti-aging of Di huang Yin zi. Liaoning J. Traditional Chin. Med.48, 248–252.
29
Hu X. Wang K. Liang R. X. Cao Y. Zhou X. L. Zhao Y. et al (2023). Clinical observation of Bufei Huoxue Capsule combined with chemotherapy in treatment of rifampicin-susceptible retreated pulmonary tuberculosis (yin and yang deficiency type) and analysis of prognostic factors. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs54, 4245–4252.
30
Hualiang L. (2013). Clinical observation of feitai capsules as an adjunctive therapy for recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Emerg. Traditional Chin. Med.22, 954–964.
31
Hui S. Jie C. Yangbing O. Yongrui Y. Chichuan L. Xin L. et al (2020). Efficacy of Bailing capsule combined with levofloxacin in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Med. J. West China32.
32
Hunxi L. Zhanqi X. (2013). Clinical observation of Jianpi Runfei pills combined with Western medicine in the treatment of 100 cases of pulmonary tuberculosis. Inn. Mong. J. Traditional Chin. Med.32.
33
Ji W. Yan Z. Jianfang Z. Malong F. (2017). Efficacy observation of feitai capsules combined with 2HRZE/4HR chemotherapy in the treatment of initial sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients. China Prev. Med. J.29.
34
Jia L. (2022). Clinical efficacy observation of Chinese herbal tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive treatment for severe tuberculosis cases. Chin. Sci. Technol. J. Database (8), 3.
35
Jiafu Q. Lanhua Z. (2022). Clinical analysis of tuberculosis pill combined with linezolid in the treatment of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis. Clin. Med. Eng.29, 477–478.
36
Jian W. (2002). Observation of the efficacy of a treatment regimen including bujin tablets for multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. Youjiang Med. J.30, 423. 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1383.2002.05.035
37
Jian Z. Li L. (2014). Efficacy observation of Chinese herbal tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive therapy for elderly patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Clin. Pulm. Med.19, 366–368.
38
Jinghua D. Jianchun L. Xiaoju W. Aiming W. (2015). Effect of Kanglao pill combined with Anti- tuberculosis Western medicine on Th17 cells and regulatory T cells balanced state of tuberculosis patients. Chin. J. Traditional Med. Sci. Technol. 22 (4), 371–372.
39
Juan W. (2022). Clinical efficacy observation of tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive treatment for secondary pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. Sci. Technol. J. Database.
40
Juan W. Ru G. Jing W. Qingfeng W. (2016). Observation on the clinical efficacy of the Qijialifeiljiaonang for the retreatment pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Antituberc.
41
Jun Z. (2010). Efficacy observation of chemotherapy combined with bujin tablets in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Natl. Med. Front. China.
42
Jun W. Ru G. Jing W. Qingfeng W. (2017). Observation on the clinical efficacy of the QIJIALIFELJIAONANG for the re treatment pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Antituberc.
43
Jun X. Yu-Tao H. Xin Y. Wei X. Bingqi Z. Mengjiao H. (2022). Pharmacological activity of traditional Chinese medicine Baiji and its application in new wound dressing. Hainan Med. J.33, 371–373.
44
Junguo Y. (2023). Clinical efficacy analysis of tuberculosis pills combined with antituberculosis drugs in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. Sci. Technol. J. Database.
45
Junguo Z. Liping W. Yan S. (2016). Jiehewan adjuvant treatment of tuberculosis. Jilin J. Chin. Med. 36 (8), 790–792.
46
Junjie W. (2018). Observation of the use of Qijia Lipei capsules as an adjunctive treatment for recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Mod. Clin. Med.44.
47
Junmei N. Zhengkui L. Bianfang Z. (2019). Clinical efficacy of Bufei Huoxue capsules combined with 2HRZE/4HR regimen in treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Med. J. Chin. People’s Health31, 116–118.
48
Kai L. (2009). Clinical observation of Yifei Zhike capsules as an adjunctive therapy for recurrent sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Guide China Med.7, 70–71.
49
Kim H. M. Han S. B. Lee K. H. Lee C. W. Kim C. Y. Lee E. J. et al (2000). Immunomodulating activity of a polysaccharide isolated from Mori Cortex Radicis. Arch. Pharm. Res.23, 240–242. 10.1007/BF02976452
50
Lidong F. Shuqing F. (2007). Efficacy observation of tuberculosis spirit tablets as an adjunctive therapy for sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis in initial treatment cases. Chin. J. Prim. Med. Pharm.14.
51
Lidong F. Lilei F. Ling G. (2013). Observation on clinical efficacy of tuberculosis pills adjuvant therapy on retreatment smear positive pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Med. Pest Control29, 570–571.
52
Lili W. Bei Z. Hao C. Liting F. Jingui H. (2018). Effects of different extract of Gekko gecko Linnaeus on immune function of aging model mice. Chin. J. Geriatric Care16, 17–20.
53
Lingwei L. (2018). Clinical efficacy observation of tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive treatment for multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. Electron. J. Clin. Med. Literature5, 167–168. 10.16281/j.cnki.jocml.2018.03.093
54
Liping J. (2018). Efficacy observation of tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive treatment for newly diagnosed sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients. J. Pract. Traditional Chin. Med.34.
55
Liping W. Chun J. (2016). Clinical study on the Feitai capsule in the adjunctive treatment of new smear positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Chinese Community Doctors32, 98–99.
56
Liuxing S. (2005). Clinical efficacy observation of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine therapy for recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis: a study of 128 cases. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med., 63–64. 10.16367/j.issn.1003-5028.2005.10.049
57
Long J. Weihua H. Mingxia G. Xiuying Z. Lihua W. (2014). Clinical observation of Qijia Lipei capsules as an adjunctive therapy for refractory pulmonary tuberculosis in traditional Chinese medicine. J. Clin. Med. Pract.18.
58
Meng L. (2019). Efficacy of Chinese herbal tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive treatment for newly diagnosed sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Chin. J. Mod. Drug Appl.13.
59
Mengqiu G. Lizhen Z. Songlin Y. Qingfeng Z. Qing Z. Ji Y. et al (2006). Observation of recent efficacy and safety of lung-tai capsules as an adjunctive therapy for recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis in a Chinese herbal medicine context. Chin. J. Tuberc. Respir. Dis.29.
60
Min-Shuang S. Chun-Xia W. Hui X. Guomei W. (2015). Clinical observation of Moxifloxacin combined with Jiehe pill in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. China Pharm.26, 5092–5094.
61
Ming L. (2004). Clinical observation of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis in 50 cases. Chin. J. Coal Industry Med.1231.
62
Peiqian C. Zhigang W. Miaomiao T. (2024). Clinical study on Jiehe pills combined with routine Western medicine for drug-resistant tuberculosis of yin deficiency resulting in vigorous fire type. New Chin. Med.56, 61–65. 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2024.09.013
63
Pieters J. (2008). Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the macrophage: maintaining a balance. Cell Host Microbe3, 399–407. 10.1016/j.chom.2008.05.006
64
Ping W. Yukun W. Shangming W. Tianming Y. Daikui Y. Liangliang L. et al (2022). Ffects of Poria polysaccharides on immune function in rats. Shandong J. Animal Sci. Veterinary Med.43, 11–14+17.
65
Pu W. Yongai L. Xicheng H. Yun Q. (2005). Combined use of Feitai capsule and antituberculosis agents in initial treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Chongqing Med. Univ., 881–883.
66
Prasad R. Singh A. Gupta N. (2019). Adverse drug reactions in tuberculosis and management. Indian J. Tuberc.66, 520–532. 10.1016/j.ijtb.2019.11.005
67
Qi N. Lixuan T. Ye Y. Jin Z. Yuhuan D. Zhidan X. (2016). Clinical study of bailing capsules as an adjunctive treatment for first-time relapsed sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Chin. J. Antituberc.38, 61–63.
68
Qi Z. (2016). Efficacy observation of tuberculosis pills combined with western medicine in the treatment of multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med.37, 434–435.
69
Qiang L. (2021). Clinical study of tuberculosis pills combined with antituberculosis chemotherapy drugs in the treatment of initial sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Harbin Med. J.41, 42–43.
70
Qianxin W. Yuxian Y. Jianhong S. Chengxing J. Yangxing J. (2014). Short-term efficacy observation of tuberculosis pills combined with chemotherapy in the initial treatment of sputum-positive cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis. New Chin. Med.46, 52–53. 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2014.12.024
71
Qiaoe X. Yongqiang L. Man Y. Wenjun Y. (2023). Clinical efficacy observation of tuberculosis pills combined with antituberculosis drugs in the treatment of recurrent refractory tuberculosis cases. J. North Pharm.20, 43–45.
72
Qihuang C. (2022). Exploration of the efficacy and value of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine treatment methods applied to pulmonary tuberculosis patients. J. North Pharm.19.
73
Qin X. (2019). Feitai capsule combined with linezolid in the treatment of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med.40, 469–471.
74
Qing L. Wengfang G. (2014). Efficacy observation of feijie pills as an adjunctive therapy for initial treatment of sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. Med. J. Metallurgical Industry31, 620.
75
Qingfeng Z. (2019). Clinical observation of antituberculosis pills as an adjunctive treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Pract. Traditional Chin. Med.35, 1494–1495.
76
Qiong H. Xiaodong G. Xiaoqin L. Haitao H. Jianghong L. Shijun M. et al (2021). Observation on clinical effects of tuberculosis pills combined with antituberculosis drugs in the treatment of recurrent refractory tuberculosis. West. J. Traditional Chin. Med.34, 110–114.
77
Radiology C. S. O. I. D. O. C. S. O. (2018). The expert consensus on imaging and grading diagnosis of tuberculosis. Electron. J. Emerg. Infect. Dis.3, 118–127. 10.19871/j.cnki.xfcrbzz.2018.02.015
78
Rücker G. Schwarzer G. (2015). Ranking treatments in frequentist network meta-analysis works without resampling methods. BMC Med. Res. Methodol.15, 58. 10.1186/s12874-015-0060-8
79
Rücker G. K. U. König J. Schwarzer G. (2024). Netmeta: network meta-analysis using Frequentist methods. R. package version 2.0-1.
80
Salanti G. Ades A. E. Ioannidis J. P. (2011). Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol.64, 163–171. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.03.016
81
Shah I. Poojari V. Meshram H. (2020). Multi-drug resistant and extensively-drug resistant tuberculosis. Indian J. Pediatr.87, 833–839. 10.1007/s12098-020-03230-1
82
Shiming L. Peng Z. Shuxiang G. (2016). Clinical observation of Qijia-lifei capsule on the treatment of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis. Hebei J. Traditional Chin. Med.38, 1240–1243.
83
Shiqi W. (2011). Clinical efficacy of tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive therapy to antituberculosis drugs in treating 30 cases of pulmonary tuberculosis in the elderly. Chin. J. Gerontology31, 698–699.
84
Shouyue J. (2009). Clinical analysis of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine therapy for recurrent sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Clin. Res.22, 483–484.
85
Shuang Z. (2016). Evaluation on the effectiveness and safety of jiehelining tablets combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of primary smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. Med. Mod. Distance Educ. China14 (21), 75–76.
86
Shuangli Z. Meng L. Hui S. Jie C. Xin L. Chichuan L. et al (2020). Clinical efficacy of bailing capsule combined with Levofloxacin on multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Materia Medica36, 223–226. 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2020.03.034
87
Shuhua G. Fujian Y. (2016). Efficacy observation of bailing capsules as an adjunctive treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis in 60 cases. Hejiang J. Traditional Chin. Med.
88
Shuqin F. Lidong F. Lilei F. (2008). Effect of combination of Jieheling and phthisical on retreated positive bacteria pulmonary tuberculosis. Hebei J. Tradit. Chin. Med.30, 1085–1086.
89
StataCorp (2023). Stata statistical software: release 18. College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC.
90
R Core Team (2024). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
91
Tao Y. Fei W. (2022). Clinical effect of tuberculosis pill combined with four anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy drugs in the treatment of pathogenic positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Hemorheol.32, 83–85.
92
Tianfeng S. (2015). Clinical report on the efficacy of bufeihuoxue capsules combined with conventional Western medicine in the treatment of drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. For all Health9, 91–92.
93
Wei W. (2016). Clinical study on the efficacy of Jianpi Runfei pills combined with Western medicine in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. World Latest Med. Inf.16, 185+191.
94
Wei S. Liuyuhon (2024). Interpretation of WHO global tuberculosis report2023. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis.5, 15–19. 10.19983/j.issn.2096-8493.2024006
95
Wei Y. Hong-Wen L. Zhen-Jing S. (2004). Yifeizhike capsules in treating secondarybacteria-discharging pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Shandong Med. Coll.26.
96
Wei X. L. Yin J. Zou G. Y. Zhang Z. T. Walley J. Harwell J. et al (2015). Treatment interruption and directly observed treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in China. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis.19, 413–419. 10.5588/ijtld.14.0485
97
Wei-Wei L. (2021). Effects of adjuvant therapy with tuberculous pill on immune function and cytokines in elderly patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Shenzhen J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med.31.
98
Weiyong W. Hua C. Jianhong H. Pingru C. (2020). Clinical observation of antituberculosis pills combined with moxifloxacin in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. China Pract. Med.15, 131–133. 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.03.063
99
Wen-Ge H. Xiang-Yu Y. Jing W. Lingling Y. (2013). Clinical research on the efect of Kangfuxin liquid in the retreatment of bacteria positive pulmonary tuberculosis. West China Med. J.
100
Wenjia L. Zongkai L. Xiaosu C. Zhaidong L. (2023). Network pharmacology-based discussion on molecular mechanism of “Different Treatment of the Same Disease” in the treatment of cancerous fever by Qinghao Bijia Tang and Buzhong Yiqi Tang. West. J. Traditional Chin. Med.36, 20–26.
101
Wulu L. Anqi T. Genquan Q. Li L. Changsheng Z. (2007). Clinical study of Jianpi Runfei pills as an adjunctive therapy in short-course chemotherapy for tuberculosis. Chin. J. Antituberc., 86–87.
102
Xiali Z. Zhihong D. Shixiong H. (2017). Risk factors of patients with drug resistant tuberculosis in Shaoyang, Hunan, 2014-2015. China Trop. Med.17, 236–240. 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2017.03.06
103
Xian W. (2009). Clinical observation of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine therapy for pulmonary tuberculosis: a study of 30 cases. Inf. Traditional Chin. Med.26, 51–52.
104
Xian-Hui W. Shu-Lin Y. (2020). Clinical effect of Feitai Capsules combined with Western antituberculosis drug in the treatment of preliminary smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. China Mod. Med.27, 137–140.
105
Xiang L. (2015). Brief analysis of the clinical effectiveness of integrated traditional chinese and western medicine therapy in the treatment of 50 cases of tuberculosis. Guide Chin. Med.13, 191.
106
Xiaohua W. (2022). Efficacy observation of Kangfuxin liquid combined with the 2HRZE/4HR chemotherapy regimen in the treatment of initially treated sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Jiangxi Med. J.57.
107
Xiaoni Z. (2018). Clinical efficacy analysis of antituberculosis pills combined with moxifloxacin in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. World Latest Med. Inf.18, 99+102. 10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2018.59.065
108
Xiaoru W. Zhongping W. Yunfei H. Yi X. Wanfeng T. (2018). Efficacy observation of Kangfuxin liquid as an adjunctive treatment for sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Rural Med. Pharm.25.
109
Xing L. Bing O. Yan-Duo L. Yalian S. Changying H. Lu W. et al (2017). Clinical efficacy of Jiehe pills combined with Levofloxacin such as anti-tuberculosis drugs in tuberculosis patients with multi-drug resistance. Anti-Infection Pharm.14.
110
Xinhua Z. (2012). Study on the efficacy of Feijie pill in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis and its effects on symptom improvement. Contemp. Med. Symp.10, 704–705.
111
Xinlei J. Rong S. (2024). The efficacy of tuberculosis pill adjuvant to conventional quadruple anti-tuberculosis therapy in the treatment of secondary pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Med. Guide26, 804–807.
112
Xiue X. Mingying L. Xia W. Zhenxuan W. Haozen S. (2014). Efficacy and safety of Qijialifei capsule in adjuvant chemotherapy for retreatment pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Antituberc. 36 (11), 948–952.
113
Xiuxia W. (2009). Clinical evaluation on the therapeutic effect of Yifeizhike capsules on drug resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. China Mod. Med.16, 25–27.
114
Xuehu D. Fei D. Xincan C. (2022). Clinical study of Kangfuxin solution on treating initial smear positive tuberculosis patients. J. Binzhou Med. Univ.45.
115
Xuewen C. (2007). Clinical research on the curative effects of yifeizhike capsule on secondary bacteria-discharge pulmonary tuberculosis. Hebei Med., 1268–1270.
116
Xueyun T. (2022). Efficacy of Kangfuxin liquid combined with the 2HRZE/4HR regimen in the treatment of initially treated sputum-positive cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis patients with hemoptysis. Med. Equip.35.
117
Xu H. Yaomin S. Baochun X. (2018). Clinical observation on 82 cases of initial pulmonary tuberculosis by adjuvant treatment of bufei huoxue capsule. J. Tradit. Chin. Med.59, 1671–1673+1684.
118
Xuhua W. Xiaobing Z. Qiang X. (2013). Clinical observation of the treatment of relapsed sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients with Chinese herbal tuberculosis pills. For All Health7, 27–28.
119
Ya W. Li-Na Y. Tian-Tian S. Jiejie H. Jia L. Minghua H. et al (2019). Structural characterization of polysaccharide from Polygonum multiflorum and its immunomodulatory activity. Chin. Traditional Herb. Drugs50, 2290–2295.
120
Yan H. Xiangrong Z. Yi L. (2022). Clinical efficacy of tuberculosis pill combined with standard chemotherapy for tuberculosis and its effect on IgG, IgA and IgM. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med.40, 255–258.
121
Yan Z. Qianhong W. Fan W. Fengying J. Zhen Q. Yingxi M. et al (2023). Evaluation of the curative effect of the combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine on retreated pulmonary tuberculosis. Anhui Med. Pharm. J.27, 615–619.
122
Yanpei Z. Shuyu G. (2002). Efficacy observation of bailing capsules as an adjuvant treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis in the elderly. Zhejiang Clin. Med. J.4, 603–604. 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7664.2002.08.035
123
Yawei C. Baocang Z. Cunli W. Fenglu C. (2023). Observation on efficacy of Bufei Huoxue capsules combined with anti-tuberculosis drugs in treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Liaoning J. Traditional Chin. Med.50.
124
Yongyi C. Yunhe R. Fen D. (2017). Randomized parallel controlled study on the treatment of initial smear positive pulmonary tuberculosis with 2HRZE/4HR combined with tuberculosis. J. Pract. Traditional Chin. Intern. Med.31, 52–54. 10.13729/j.issn.1671-7813.2017.07.20
125
Yuelian T. (2024). Clinical efficacy of tuberculosis pills combined with conventional Western medicine in the treatment of recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis with Qi-Yin deficiency syndrome. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use17, 50–53. 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2024.31.014
126
Yujuan T. (2007). Clinical efficacy observation of Yifei Zhike capsules as an adjunctive therapy for multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. World Health Dig.4.
127
Yunxiao W. Guosheng Y. (2015). Clinical efficacy observation of bujin tablets as an adjunctive treatment for initial sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use8, 39–41. 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2015.32.023
128
Yuxia Z. (2015). Analysis of the efficacy of using Chinese herbal tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive treatment for newly diagnosed sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Contemp. Med. Symp.
129
Yuxia Z. (2023). Clinical efficacy of tuberculosis pills combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of recurrent and refractory tuberculosis cases. Renowned Dr., 171–173.
130
Yuxuan L. He XIAOMEI Fucheng Z. Fangli G. Xingbang H. Yuhan L. (2018). Research progress on the main bioactive compounds and pharmacological effects of Bletilla striata. Hunan Agric. Sci., 107–109. 10.16498/j.cnki.hnnykx.2018.003.028
131
Zhenru W. (2016). Efficacy of tuberculosis pills as an adjunctive therapy for multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis and its impact on immune function. China Pract. Med.
132
Zhibo C. Pianpian T. Bohua W. (2019). Clinical efficacy of Kangfuxin Liquid combined with standard chemotherapy regimen in the treatment of cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis complicated with hemoptysis. Mod. Diagnosis Treat.
133
Zhijie Z. (2018). Clinical efficacy analysis of Qinghao Biejia decoction in the treatment of fever in patients with drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. Heilongjiang J. Traditional Chin. Med.47, 38–39.
134
Zhongming L. (2013). Discussion on the efficacy of the Chinese patent medicine tuberculosis spirit tablets as an adjunctive therapy for initial treatment of sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Pract. Clin. Med.14.
Summary
Keywords
pulmonary tuberculosis, oral commercial Chinese polyherbal, biomedicine, combination therapy, network meta-analysis, randomized controlled trials
Citation
Jiang J, Zhang S, Wang H, Zhang L, Li Z, Tong J and Wu F (2025) Oral commercial Chinese polyherbal preparations combined with conventional biomedicine for pulmonary tuberculosis: network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1588586. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1588586
Received
06 March 2025
Accepted
24 September 2025
Published
28 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Quansheng Feng, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Reviewed by
Swayam Prakash, University of California, Irvine, United States
Yong Xu, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Jiang, Zhang, Wang, Zhang, Li, Tong and Wu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fan Wu, wufan200610@126.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.