- 1Lugouqiao Second Community Health Service Center, China Aerospace Science & Industry Corporation 731 Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Cardiological Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences Guang’anmen Hospital, Beijing, China
Epigenetic modifications play a critical role in the pathogenesis and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Among these, DNA hydroxymethylation has garnered increasing attention in the fields of oncology, hematology, and neurological disorders, serving as a key mechanism for untangling molecular pathways underlying disease etiology. Although emerging evidence has begun to illuminate the role of DNA hydroxymethylation in cardiovascular conditions such as coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis, its implications in atrial fibrillation remain underexplored. This review aims to summarize current understanding and discuss potential mechanisms through which DNA hydroxymethylation may contribute to the development and progression of atrial fibrillation.
1 Overview of atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most common clinical arrhythmias, characterized by the loss of regular, organized electrical activity and mechanical contraction in the atria, which are replaced by rapid and disorganized fibrillatory activity. The development of AF is closely associated with multiple factors, including advanced age, sex, obesity, genetic predisposition, and unhealthy lifestyle habits. It is also significantly linked to various comorbidities such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease, heart failure, diabetes, hyperthyroidism, chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and metabolic syndrome (Schnabel et al., 2009; Tomaszuk-Kazberuk et al., 2020; Wasmer et al., 2017).
AF poses serious health risks and often leads to severe complications such as heart failure, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, dementia, and even death. It contributes to high rates of disability and mortality, making it a condition of major clinical concern (Benjamin et al., 2019; Alonso et al., 2021).
With the accelerating aging of the global population, the prevalence of AF is increasing annually. Among individuals aged 80 years and older, the prevalence exceeds 10% (Sagris et al., 2021). It is estimated that AF affects approximately 2%–3.4% of the global population (Chugh et al., 2014; Kjerpeseth et al., 2021; Williams et al., 2020; Zoni-Berisso et al., 2014), significantly impairing patients’ quality of life and imposing a substantial economic burden on families and society (Lehto et al., 2022; Colilla et al., 2013; Piccini et al., 2012). For instance, in the United States, the estimated annual medical cost per AF patient ranges between $2,000 and $14,200, with the total national cost for treating AF and its complications exceeding $28 billion per year (Dieleman et al., 2020). According to the Framingham Heart Study, all-cause mortality is 50%–90% higher in patients with AF compared to those without the condition (Alonso et al., 2021).
The pathophysiology of AF is complex and closely related to structural remodeling of the atria, primarily involving loss of cardiac cells and interstitial fibrosis (Iwasaki et al., 2011). Atrial fibrosis serves as a key substrate for the initiation and maintenance of abnormal electrical activity in AF, promoting reentrant arrhythmias (Heijman et al., 2016; Li et al., 1999). The size of the atria and the extent of myocardial fibrosis directly influence treatment outcomes and the risk of complications (Gal and Marrouche, 2017; Zahid et al., 2016). Additionally, oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, abnormalities in mitochondrial energy metabolism, and dysregulation of calcium signaling are recognized as important pathophysiological mechanisms contributing to the onset and progression of AF.
Current clinical management strategies for AF primarily include: restoration and maintenance of sinus rhythm, control of ventricular rate, and prevention of thromboembolic events. The main approaches for restoring sinus rhythm are catheter radiofrequency ablation and antiarrhythmic drug therapy. However, both methods have limitations. Radiofrequency ablation carries a risk of recurrence, while antiarrhythmic drugs may have potential side effects such as pro-arrhythmia. Therefore, further investigation into the pathological mechanisms of AF, along with optimization of diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive strategies, is essential to provide safer, more effective, and durable solutions for patients.
2 Overview of DNA hydroxymethylation
Epigenetics refers to modifications in gene expression that lead to phenotypic changes without alterations in the underlying DNA sequence. Major epigenetic mechanisms include: (1) genomic DNA methylation; (2) modifications of DNA-associated proteins; and (3) regulation by non-coding RNAs (Ameer et al., 2020). Among these, DNA methylation at the 5-position of cytosine has been extensively studied. This process is catalyzed by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), which transfer a methyl group (-CH3) to the 5′cytosine within CpG islands-regions rich in CpG dinucleotides often located in promoter areas. Methylation at these sites typically inhibits the binding of transcription factors, thereby suppressing gene transcription and influencing phenotypic outcomes.
Closely related to DNA methylation is DNA hydroxymethylation (DNAhm), another key epigenetic modification occurring at the DNA level. DNA hydroxymethylation involves the oxidation of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), a reaction catalyzed by ten-eleven translocation (TET) enzymes in an Fe2+- and α-ketoglutarate (α-KG)-dependent manner (Guallar et al., 2018; Tahiliani et al., 2009). 5hmC plays important roles in gene regulation, particularly in cardiac cells during development and under pathological conditions such as hypertrophy (Greco et al., 2016). It is associated with transcriptional activation and can modulate the activity of transcription start sites (TSS) and active enhancers (Ficz et al., 2011; Pastor et al., 2011; Tsagaratou et al., 2014). In the absence of genetic mutations, 5hmC levels are primarily regulated by TET enzyme activity.
Studies by Olsen et al. indicate that ischemic and inflammatory processes-common in conditions such as coronary artery disease-promote oxidative stress, which may lead to oxidative DNA damage and the accumulation of oxidized DNA bases (Olsen et al., 2017; Barzilai and Yamamoto, 2004). 5hmC is implicated in DNA repair mechanisms, particularly the base excision repair (BER) pathway (He et al., 2011; Krokan and Bjørås, 2013). BER involves the removal of damaged bases by DNA glycosylases, creating an apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) site. This is followed by cleavage by AP endonucleases or phosphodiesterases, with subsequent gap filling by DNA polymerases and ligation by DNA ligases. 5hmC can be further oxidized by TET enzymes to form 5-formylcytosine (5 fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC), which may be excised by thymine DNA glycosylase (TDG) to regenerate unmodified cytosine. Alternatively, 5hmC can be deaminated by enzymes such as AID/APOBEC, yielding 5-hydroxymethyluracil (5hmU), which is then repaired through glycosylase-mediated pathways involving uracil-DNA glycosylase (UNG) or TDG, ultimately restoring standard bases (Krokan and Bjørås, 2013).
Using selective chemical labeling followed by low-input whole-genome sequencing (hmC-Seal), Dong et al. compared 56 individuals with normal coronary arteries (NCA), 53 with stable coronary artery disease (sCAD), and 58 with acute myocardial infarction (AMI). They found that 5hmC-modified SOX9 regulates fibrosis-related genes activated under ischemic injury, promoting disease progression. Similarly, 5hmC-marked RUNX2 was associated with vascular smooth muscle cell calcification, suggesting both may serve as potential prognostic biomarkers in AMI (Dong et al., 2020).
Notably, 5hmC levels increase absolutely during postnatal maturation of murine cardiomyocytes, consistent with observations in neurons (Münzel et al., 2010; Song et al., 2011; Szulwach et al., 2011; Lister et al., 2013). However, 5hmC content is inversely correlated with proliferative status across tissues (Bachman et al., 2014). Thus, high 5hmC levels in adult cardiomyocytes may reflect their low proliferative capacity and terminally differentiated state.
DNA hydroxymethylation is highly dynamic during cardiac development and disease (Greco et al., 2016). Although 5hmC may attract or repel chromatin remodelers, its functional impact often depends on coexistence with active histone marks-such as H3K79me2, H3K9ac, H3K27ac, or H3K4me3-thereby amplifying their effects. For instance, the fetal gene Myh7, encoding α-myosin heavy chain, undergoes substantial 5hmC loss during cardiac maturation. In hypertrophic cardiomyocytes, enhancers near Myh7 become specifically hydroxymethylated, affecting genes involved in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, fatty acid oxidation, and energy production. This promotes myocardial hypertrophy, increasing heart weight, enhancing contractility, and elevating cardiac output-key adaptations supporting heart maturation.
3 Potential mechanisms by which DNA hydroxymethylation influences atrial fibrillation
Currently, research on DNA hydroxymethylation in the cardiovascular system remains limited, with very few studies focusing specifically on AF. Existing evidence indicates that TET2 expression is significantly upregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and aortic atherosclerotic plaques of elderly patients with CAD, accompanied by elevated levels of both DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation, which correlate positively with the severity of coronary atherosclerosis (Jiang et al., 2019). A study involving 10 young and 10 elderly healthy women revealed that age-related changes in DNAhm and genes with high DNAhm levels are involved in regulating the immune system during aging (Johnson et al., 2020).
Atrial fibrillation exhibits a strong age-dependent prevalence. Moreover, CAD, which involves varying degrees of myocardial ischemia, contributes to both structural and electrical remodeling of the heart. Consequently, patients with CAD have a higher likelihood of developing AF compared to the general population. During the pathogenesis of AF, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs)-particularly the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2-play crucial roles in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and development. Activation of ERK1/2 occurs through phosphorylation mediated by MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK). Studies have shown that ERK1/2 is activated in cardiac cells exposed to neurohormones such as angiotensin II (Pan et al., 2005; Takahashi et al., 2005; de Jonge et al., 2007). ERK signaling integrates inputs from multiple receptor systems and distal signaling pathways, ultimately promoting cardiac hypertrophy-a finding consistent with clinical observations that hypertension is a strong and independent predictor of AF. According to the Framingham Heart Study, individuals with hypertension have a 1.8-fold higher risk of developing new-onset AF compared to those with normal blood pressure (Benjamin et al., 1994).
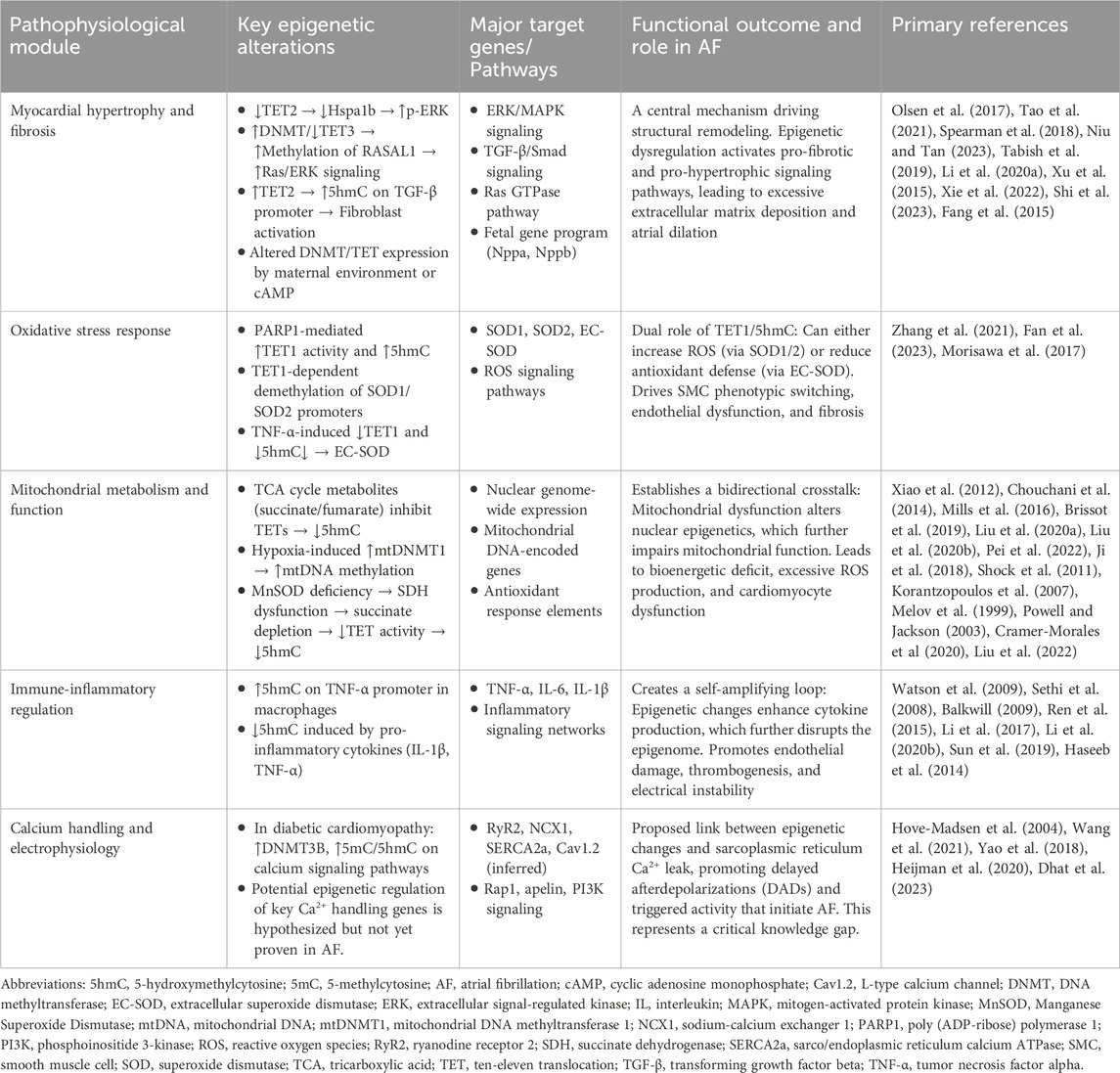
Given these connections, it is plausible that DNA hydroxymethylation may participate in the pathogenesis of AF. This review explores potential mechanisms through the following aspects (Table 1; Figure 1).
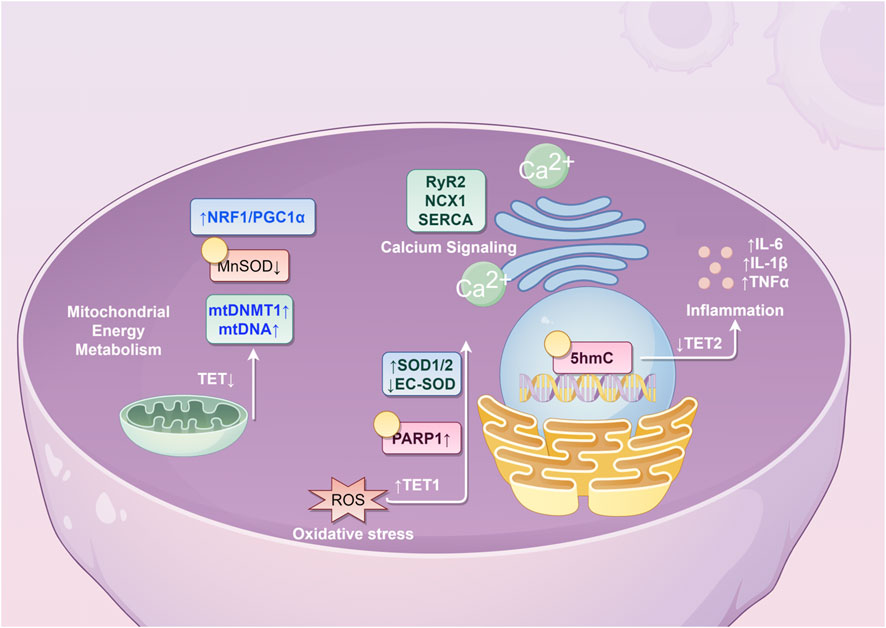
Figure 1. Potential molecular mechanisms underlying the role of 5hmC in atrial fibrillation. (NRF1, nuclear respiratory factor 1; PCG1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α; MnSOD, Manganese Superoxide Dismutase; mtDNMT1, mitochondrial DNA methyltransferase 1; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; TET, ten-eleven translocation; RyR2, ryanodine receptor 2; NCX1, sodium-calcium exchanger 1; SERCA, sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; EC-SOD, extracellular superoxide dismutase; PARP1, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; 5hmC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine).
3.1 5hmC in cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis
Cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis represent key pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the development and progression of atrial fibrillation. Cardiac hypertrophy refers to the enlargement of cardiomyocytes in response to sustained physiological or pathological stimuli, serving to maintain cardiac reserve and output. Myocardial fibrosis, a central feature of chronic ischemic heart disease, often results from atherosclerotic coronary artery stenosis leading to moderate-to-severe ischemia. This condition promotes both cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and collagen fiber proliferation, perpetuating a cycle of ischemic injury and hypoxia that may ultimately progress to heart failure, increased mortality, and reduced quality of life.
Studies indicate that TET enzymes and 5hmC play dynamic roles in postnatal cardiac development, with TET2 being the predominant dioxygenase in the heart (Tao et al., 2021). Knock out of TET2 leads to reduced hydroxymethylation in the cardiac genome, altered transcriptomic profiles, and manifestations of cardiac dysfunction, progressive hypertrophy, and fibrosis. This may be attributed to diminished expression of Hspa1b-a regulator of the ERK pathway-resulting in enhanced ERK phosphorylation, pathway hyperactivation, and subsequent induction of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Spearman et al. reported that abnormal maternal conditions lead to decreased expression of TET1-3 and DNMT3a, promoting myocardial fibrosis in adult offspring (Spearman et al., 2018). Furthermore, Niu et al. demonstrated that TET2 upregulates 5hmC modification in the TGF-β promoter region, enhancing fibroblast proliferation (Niu and Tan, 2023).
A genome-wide profiling study of DNA hydroxymethylation in a murine model of dilated cardiomyopathy identified over 2000 genes with differential 5hmC modifications, which were enriched in pathways related to inflammation, tissue fibrosis, cell death, cardiac remodeling, cardiomyocyte growth and differentiation, and sarcomere organization (Tabish et al., 2019). Given the clinical coexistence of dilated cardiomyopathy and AF, these pathways may contribute to the pathophysiology of AF, suggesting a potential mechanistic link mediated by 5hmC.
Li et al. reported that hypermethylation of Ras protein activator-like 1 (RASAL1) and Ras association domain family 1 (RASSF1) leads to their downregulation, subsequent activation of the Ras/ERK pathway, and promotion of cardiac fibrosis (Li et al., 2020a). Similarly, Xu et al. found that TGFβ1 upregulates RASAL1 promoter methylation, suppresses its expression, increases Ras-GTP activity and endothelial–mesenchymal transition (EndMT), thereby exacerbating fibrosis (Xu et al., 2015). Notably, TET3, an enzyme promoting hydroxymethylation, was significantly reduced in fibrotic cardiomyocytes. These findings suggest that a balance between promoter methylation and hydroxymethylation of RASAL1 plays a critical role in regulating cardiac fibrosis and remodeling.
Moreover, NEIL3 expression is elevated in cardiomyocytes of heart failure patients and post-myocardial infarction mice, particularly in fibroblast-rich regions involved in proliferation, differentiation, extracellular matrix regulation, and scar formation (Olsen et al., 2017). NEIL3-dependent DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation collectively modulate cardiac fibroblast proliferation and contribute to structural remodeling. Chronic catecholamine-induced activation of the cAMP pathway also promotes cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Xie et al. showed that reduced hydroxymethylation in the miR-3571 promoter downregulates its expression, upregulates claudin 1 (CLDN1) and ERK1/2, and facilitates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, thereby contributing to cardiovascular pathogenesis (Xie et al., 2022).
Under hypoxic conditions, reduced TET2 expression in vascular endothelial cells impairs its DNA demethylase activity at specific STAT3 target gene promoters, inhibiting the STAT3 pathway and angiogenesis, which consequently impedes blood flow recovery, reduces capillary density, and promotes cardiac fibrosis and remodeling (Shi et al., 2023). Fang et al. demonstrated that the stable cAMP analog DBcAMP alters the expression of DNMTs and TETs, increases DNA methylation in cardiomyocytes, and upregulates markers of hypertrophy such as Myh6, Myh7, Myh7b, Tnni3, ANP, BNP, Gata4, Mef2c, Mef2d, Nfatc1, miR208a, and miR208b (Fang et al., 2015). However, changes in 5hmC levels were not assessed in this study.
Given the interplay between DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation in regulating myocardial fibrosis, further investigation using atrial fibrillation animal models may help elucidate the role of 5hmC in the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. Such studies could enhance our understanding of the disease and inform novel therapeutic and preventive strategies.
3.2 5hmC in oxidative stress
During the development of atherosclerosis, vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) undergo a phenotypic transition from a contractile to a synthetic state. Studies have shown that oxidative stress activates poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1), which in turn promotes the expression of TET1 and increases PARylation-dependent 5hmC levels, contributing to vascular remodeling (Zhang et al., 2021). Furthermore, Fan et al. demonstrated that TET1 downregulates 5mC levels in the promoters of superoxide dismutase (SOD) 1 and SOD2, thereby enhancing their expression. This leads to the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest, and promotion of inflammation and fibrosis (Fan et al., 2023).
Extracellular superoxide dismutase (EC-SOD) is a secreted antioxidant enzyme predominantly localized in the vascular wall, where it plays a protective role against oxidative stress by safeguarding vascular endothelial function. Evidence suggests that tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) markedly suppresses TET1 expression in fibroblasts, thereby altering DNA hydroxymethylation and significantly reducing EC-SOD levels. This process exacerbates vascular endothelial injury and accelerates the progression of cardiovascular diseases (Morisawa et al., 2017).
3.3 5hmC in mitochondrial energy metabolism
TCA cycle is central to mitochondrial redox reactions that generate energy and support cardiac cell function. Key intermediates of this cycle, fumarate and succinate, act as competitive inhibitors of α-KG-dependent enzymes that regulate DNA hydroxymethylation levels (Xiao et al., 2012). Fe(II), α-KG, fumarate, and succinate play crucial roles in maintaining mitochondrial function (Chouchani et al., 2014; Mills et al., 2016; Brissot et al., 2019). Elevated levels of fumarate and succinate in the TCA cycle inhibit TET enzyme activity, leading to dysregulation of DNA hydroxymethylation (Liu et al., 2020a; Liu et al., 2020b). On one hand, the mitochondrial TCA cycle modulates 5hmC levels by influencing the activity of TET enzymes, thereby affecting cardiac function (Pei et al., 2022). On the other hand, fumarate, succinate, and α-KG are vital intermediates for mitochondrial integrity; hence, mitochondrial dysfunction suppresses TET activity and disrupts DNA hydroxymethylation (Ji et al., 2018).
Similar to the nuclear genome, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) also undergoes DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation. Mitochondrial DNA methyltransferase 1 (mtDNMT1), present in the mitochondrial matrix, binds to mtDNA and facilitates its methylation. Studies indicate that under hypoxic conditions, transcription factors nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator (PGC) 1α upregulate mtDNMT1, enhancing mtDNA methylation and modulating mitochondrial function (Shock et al., 2011). Manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide (O2•−) into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), protecting mitochondria from oxidative damage. Its expression correlates positively with oxidative stress levels (Korantzopoulos et al., 2007). As atrial fibrosis progresses, MnSOD secretion by atrial cardiac cells decreases. Cells deficient in MnSOD exhibit elevated O2•− levels, loss of redox homeostasis, inactivation of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters, and reduced succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) activity (Melov et al., 1999; Powell and Jackson, 2003).
Succinate serves as a direct regulator of TET enzyme activity. Cramer-Morales et al. demonstrated that deficiency in MnSOD leads to downregulation of SDH activity, resulting in reduced succinate levels and impaired TET function. This decrease in genomic DNA hydroxymethylation is accompanied by a corresponding increase in DNA methylation, ultimately contributing to abnormalities in cardiac electrical conduction and contractility (Cramer-Morales et al., 2020). A case-control study by Liu et al. further reported that MnSOD levels are significantly elevated in patients with paroxysmal AF compared to both non-AF controls and those with persistent AF, suggesting that MnSOD may serve as an independent risk factor for paroxysmal AF (Liu et al., 2022).
However, research on mtDNA hydroxymethylation in the context of AF progression remains limited. In cardiovascular diseases such as AF and heart failure, mitochondrial function in cardiac cells is a focal point of investigation. Alterations in myocardial energy supply directly affect contractility, cardiac output, and consequently, both systemic and coronary perfusion. Therefore, exploring dynamic changes in mtDNA hydroxymethylation may offer novel insights into myocardial mitochondrial energy metabolism, quality control mechanisms, and reveal new pathophysiological pathways involved in AF, potentially informing future therapeutic and preventive strategies.
3.4 5hmC in the regulation of immune-inflammatory responses
Multiple inflammatory markers and mediators-including C-reactive protein (CRP), TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, IL-8, and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1-are implicated in the pathogenesis of AF. These molecules may contribute to AF progression by promoting endothelial injury, activating prothrombin, and enhancing platelet activation (Watson et al., 2009).
TNF-α, a glycoprotein hormone consisting of 185 amino acids, is primarily synthesized by monocytes and macrophages. As a key mediator under pathophysiological conditions, TNF-α can either induce or suppress the production of various inflammatory molecules-such as cyclooxygenases, matrix metalloproteinases, and cytokines-thereby driving inflammatory progression (Sethi et al., 2008; Balkwill, 2009). Previous studies have demonstrated that TNF-α is involved in the pathophysiology of AF (Ren et al., 2015; Li et al., 2017; Li et al., 2020b). Elevated levels of TNF-α are observed in AF patients and correlate positively with left atrial diameter and AF duration. Moreover, TNF-α serves as a significant predictor of adverse outcomes, including ischemic stroke.
Notably, during the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages and following lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, the 5hmC level at the TNF-α promoter region increases specifically, leading to the upregulation of TNF-α expression (Sun et al., 2019). Furthermore, studies by Haseeb et al. indicate that proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α can downregulate DNA hydroxymethylation levels, thereby modulating gene expression and contributing to immune-inflammatory regulation, which in turn promotes the development of AF (Haseeb et al., 2014).
3.5 5hmC in calcium signaling
Spontaneous calcium leakage from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in cardiac cells may underlie triggered electrical activity and contribute to the pathogenesis of AF (Hove-Madsen et al., 2004). Abnormal calcium release, often manifested as increased frequency of calcium sparks and calcium waves (SCaWs), promotes spontaneous efflux of calcium through ryanodine receptor 2 (RyR2) channels, subsequently activating the sodium–calcium exchanger (NCX1). The electrogenic exchange of one calcium ion for three sodium ions via NCX1 generates a transient inward depolarizing current, which may serve as a trigger for AF (Wang et al., 2021). Yao et al. demonstrated that AF is associated with enhanced activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in atrial cardiomyocytes, which can lead to ectopic electrical activity, aberrant sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release, shortened atrial effective refractory period, and atrial hypertrophy (Yao et al., 2018; Heijman et al., 2020).
In diabetic cardiomyocytes, upregulation of DNMT3B, MBD2, and MeCP2 has been observed, accompanied by accumulation of both 5mC and 5hmC (Dhat et al., 2023). Calcium signaling was identified as one of the pathways most significantly affected by these DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation modifications. Genomic regions with hypermethylation were enriched in genes related to Rap1, apelin, and phosphatidylinositol signaling, whereas metabolic pathways were most strongly influenced by hyperhydroxymethylation. Nevertheless, the roles of DNA hydroxymethylation and methylation in calcium signaling specifically in the context of AF remain underexplored and warrant further investigation.
4 Conclusion
Current research on 5hmC in the context of AF remains limited. However, significant progress has been made in understanding its role in related cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, including heart failure, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and hypertension. These advances may provide valuable insights into the epigenetic mechanisms underlying AF.
The recent development of innovative sequencing technologies for 5hmC-such as the selective chemical labeling method (hmC-Seal)-offers powerful tools for elucidating the epigenetic features of AF. For instance, the application of hmC-Seal to circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) enables precise mapping of hydroxymethylated sites, facilitating disease diagnosis and prediction. This approach holds promise for identifying diagnostic biomarkers, thereby reducing the need for invasive procedures and improving patient convenience.
Furthermore, a deeper understanding of 5hmC dynamics may contribute to the development of targeted epigenetic therapies aimed specifically at modulating DNA hydroxymethylation. Such strategies could potentially inhibit the initiation and progression of AF, ultimately reducing its incidence, disability, and mortality rates.
Author contributions
SF: Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JS: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Figure 1 is drawn using Figdraw (https://www.figdraw.com).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alonso, A., Almuwaqqat, Z., and Chamberlain, A. (2021). Mortality in atrial fibrillation. Is it changing? Trends Cardiovasc Med. 31 (8), 469–473. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2020.10.010
Ameer, S. S., Hossain, M. B., and Knöll, R. (2020). Epigenetics and heart failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (23), 9010. doi:10.3390/ijms21239010
Bachman, M., Uribe-Lewis, S., Yang, X., Williams, M., Murrell, A., and Balasubramanian, S. (2014). 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine is a predominantly stable DNA modification. Nat. Chem. 6 (12), 1049–1055. doi:10.1038/nchem.2064
Balkwill, F. (2009). Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9 (5), 361–371. doi:10.1038/nrc2628
Barzilai, A., and Yamamoto, K. (2004). DNA damage responses to oxidative stress. DNA Repair (Amst) 3 (8-9), 1109–1115. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.03.002
Benjamin, E. J., Levy, D., Vaziri, S. M., D'Agostino, R. B., Belanger, A. J., and Wolf, P. A. (1994). Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. The framingham heart study. JAMA 271 (11), 840–844. doi:10.1001/jama.1994.03510350050036
Benjamin, E. J., Muntner, P., Alonso, A., Bittencourt, M. S., Callaway, C. W., Carson, A. P., et al. (2019). Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2019 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation 139 (10), e56–e528. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659
Brissot, P., Troadec, M. B., Loréal, O., and Brissot, E. (2019). Pathophysiology and classification of iron overload diseases; update 2018. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 26 (1), 80–88. doi:10.1016/j.tracli.2018.08.006
Chouchani, E. T., Pell, V. R., Gaude, E., Aksentijević, D., Sundier, S. Y., Robb, E. L., et al. (2014). Ischaemic accumulation of succinate controls reperfusion injury through mitochondrial ROS. Nature 515 (7527), 431–435. doi:10.1038/nature13909
Chugh, S. S., Havmoeller, R., Narayanan, K., Singh, D., Rienstra, M., Benjamin, E. J., et al. (2014). Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a global burden of disease 2010 study. Circulation 129 (8), 837–847. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005119
Colilla, S., Crow, A., Petkun, W., Singer, D. E., Simon, T., and Liu, X. (2013). Estimates of current and future incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the U.S. adult population. Am. J. Cardiol. 112 (8), 1142–1147. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.05.063
Cramer-Morales, K. L., Heer, C. D., Mapuskar, K. A., and Domann, F. E. (2020). Succinate accumulation links mitochondrial MnSOD depletion to aberrant nuclear DNA methylation and altered cell fate. J. Exp. Pathol. 1 (2), 60–70.
de Jonge, H. W., Dekkers, D. H. W., Houtsmuller, A. B., Sharma, H. S., and Lamers, J. M. J. (2007). Differential signaling and hypertrophic responses in cyclically stretched vs Endothelin-1 stimulated neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cell. Biochem. Biophys. 47 (1), 21–32. doi:10.1385/cbb:47:1:21
Dhat, R., Mongad, D., Raji, S., Arkat, S., Mahapatra, N. R., Singhal, N., et al. (2023). Epigenetic modifier alpha-ketoglutarate modulates aberrant gene body methylation and hydroxymethylation marks in diabetic heart. Epigenetics Chromatin 16 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/s13072-023-00489-4
Dieleman, J. L., Cao, J., Chapin, A., Chen, C., Li, Z., Liu, A., et al. (2020). US health care spending by payer and health condition, 1996-2016. JAMA 323 (9), 863–884. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.0734
Dong, C. R., Chen, J., Zheng, J., Liang, Y., Yu, T., Liu, Y., et al. (2020). 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signatures in circulating cell-free DNA as diagnostic and predictive biomarkers for coronary artery disease. Clin. Epigenetics 12 (1), 17. doi:10.1186/s13148-020-0810-2
Fan, Y., Yuan, Y., Xiong, M., Jin, M., Zhang, D., Yang, D., et al. (2023). Tet1 deficiency exacerbates oxidative stress in acute kidney injury by regulating superoxide dismutase. Theranostics 13 (15), 5348–5364. doi:10.7150/thno.87416
Fang, X., Robinson, J., Wang-Hu, J., Jiang, L., Freeman, D. A., Rivkees, S. A., et al. (2015). cAMP induces hypertrophy and alters DNA methylation in HL-1 cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 309 (6), C425–C436. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00058.2015
Ficz, G., Branco, M. R., Seisenberger, S., Santos, F., Krueger, F., Hore, T. A., et al. (2011). Dynamic regulation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mouse ES cells and during differentiation. Nature 473 (7347), 398–402. doi:10.1038/nature10008
Gal, P., and Marrouche, N. F. (2017). Magnetic resonance imaging of atrial fibrosis: redefining atrial fibrillation to a syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 38 (1), 14–19. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv514
Greco, C. M., Kunderfranco, P., Rubino, M., Larcher, V., Carullo, P., Anselmo, A., et al. (2016). DNA hydroxymethylation controls cardiomyocyte gene expression in development and hypertrophy. Nat. Commun. 7, 12418. doi:10.1038/ncomms12418
Guallar, D., Bi, X., Pardavila, J. A., Huang, X., Saenz, C., Shi, X., et al. (2018). RNA-Dependent chromatin targeting of TET2 for endogenous retrovirus control in pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Genet. 50 (3), 443–451. doi:10.1038/s41588-018-0060-9
Haseeb, A., Makki, M. S., and Haqqi, T. M. (2014). Modulation of ten-eleven translocation 1 (TET1), isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) expression, α-Ketoglutarate (α-KG), and DNA hydroxymethylation levels by interleukin-1β in primary human chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 289 (10), 6877–6885. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.512269
He, Y. F., Li, B. Z., Li, Z., Liu, P., Wang, Y., Tang, Q., et al. (2011). Tet-mediated formation of 5-carboxylcytosine and its excision by TDG in Mammalian DNA. Science 333 (6047), 1303–1307. doi:10.1126/science.1210944
Heijman, J., Algalarrondo, V., Voigt, N., Melka, J., Wehrens, X. H. T., Dobrev, D., et al. (2016). The value of basic research insights into atrial fibrillation mechanisms as a guide to therapeutic innovation: a critical analysis. Cardiovasc Res. 109 (4), 467–479. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvv275
Heijman, J., Muna, A. P., Veleva, T., Molina, C. E., Sutanto, H., Tekook, M., et al. (2020). Atrial myocyte NLRP3/CaMKII nexus forms a substrate for postoperative atrial fibrillation. Circ. Res. 127 (8), 1036–1055. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316710
Hove-Madsen, L., Llach, A., Bayes-Genís, A., Roura, S., Rodriguez Font, E., Arís, A., et al. (2004). Atrial fibrillation is associated with increased spontaneous calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in human atrial myocytes. Circulation 110 (11), 1358–1363. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000141296.59876.87
Iwasaki, Y. K., Nishida, K., Kato, T., and Nattel, S. (2011). Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: implications for management. Circulation 124 (20), 2264–2274. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.019893
Ji, F., Zhao, C., Wang, B., Tang, Y., Miao, Z., and Wang, Y. (2018). The role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mitochondria after ischemic stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 96 (10), 1717–1726. doi:10.1002/jnr.24274
Jiang, D., Sun, M., You, L., Lu, K., Gao, L., Hu, C., et al. (2019). DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation are associated with the degree of coronary atherosclerosis in elderly patients with coronary heart disease. Life Sci. 224, 241–248. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.021
Johnson, N. D., Huang, L., Li, R., Li, Y., Yang, Y., Kim, H. R., et al. (2020). Age-related DNA hydroxymethylation is enriched for gene expression and immune system processes in human peripheral blood. Epigenetics 15 (3), 294–306. doi:10.1080/15592294.2019.1666651
Kjerpeseth, L. J., Igland, J., Selmer, R., Ellekjær, H., Tveit, A., Berge, T., et al. (2021). Prevalence and incidence rates of atrial fibrillation in Norway 2004-2014. Heart 107 (3), 201–207. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2020-316624
Korantzopoulos, P., Kolettis, T. M., Galaris, D., and Goudevenos, J. A. (2007). The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 115 (2), 135–143. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.04.026
Krokan, H. E., and Bjørås, M. (2013). Base excision repair. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 5 (4), a012583. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a012583
Lehto, M., Halminen, O., Mustonen, P., Putaala, J., Linna, M., Kinnunen, J., et al. (2022). The nationwide Finnish anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation (FinACAF): study rationale, design, and patient characteristics. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 37 (1), 95–102. doi:10.1007/s10654-021-00812-x
Li, D., Fareh, S., Leung, T. K., and Nattel, S. (1999). Promotion of atrial fibrillation by heart failure in dogs: atrial remodeling of a different sort. Circulation 100 (1), 87–95. doi:10.1161/01.cir.100.1.87
Li, J. Y., He, Y., Ke, H. H., Jin, Y., Jiang, Z. Y., and Zhong, G. Q. (2017). Plasma oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers are associated with the sizes of the left atrium and pulmonary vein in atrial fibrillation patients. Clin. Cardiol. 40 (2), 89–94. doi:10.1002/clc.22633
Li, S., Li, P., Liu, W., Shang, J., Qiu, S., Li, X., et al. (2020a). Danhong injection alleviates cardiac fibrosis via preventing the hypermethylation of Rasal1 and Rassf1 in TAC mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 3158108. doi:10.1155/2020/3158108
Li, B., Po, S. S., Zhang, B., Bai, F., Li, J., Qin, F., et al. (2020b). Metformin regulates adiponectin signalling in epicardial adipose tissue and reduces atrial fibrillation vulnerability. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24 (14), 7751–7766. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15407
Lister, R., Mukamel, E. A., Nery, J. R., Urich, M., Puddifoot, C. A., Johnson, N. D., et al. (2013). Global epigenomic reconfiguration during Mammalian brain development. Science 341 (6146), 1237905. doi:10.1126/science.1237905
Liu, R., Chen, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, G., Cheng, Y., Feng, Z., et al. (2020a). High ratio of ω-3/ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids targets mTORC1 to prevent high-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome and mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 79, 108330. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108330
Liu, R., Chen, L., Wang, Z., Zheng, X., Wang, Y., Li, H., et al. (2020b). Downregulation of the DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is involved in mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal impairment in high fat diet-induced diabetic mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 148, 42–51. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.12.042
Liu, H., Wang, Q., Liu, D., Li, Z., Fu, Y., Tse, G., et al. (2022). Manganese superoxide dismutase as a novel oxidative stress biomarker for predicting paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 11 (17), 5131. doi:10.3390/jcm11175131
Melov, S., Coskun, P., Patel, M., Tuinstra, R., Cottrell, B., Jun, A. S., et al. (1999). Mitochondrial disease in superoxide dismutase 2 mutant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96 (3), 846–851. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.3.846
Mills, E. L., Kelly, B., Logan, A., Costa, A. S. H., Varma, M., Bryant, C. E., et al. (2016). Succinate dehydrogenase supports metabolic repurposing of mitochondria to drive inflammatory macrophages. Cell. 167 (2), 457–470.e13. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.064
Morisawa, S., Yasuda, H., Kamiya, T., Hara, H., and Adachi, T. (2017). Tumor necrosis factor-α decreases EC-SOD expression through DNA methylation. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 60 (3), 169–175. doi:10.3164/jcbn.16-111
Münzel, M., Globisch, D., Brückl, T., Wagner, M., Welzmiller, V., Michalakis, S., et al. (2010). Quantification of the sixth DNA base hydroxymethylcytosine in the brain. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49 (31), 5375–5377. doi:10.1002/anie.201002033
Niu, C., and Tan, S. (2023). TET2 promotes keloid hyperplasia by regulating 5hmC modification in the TGFβ promoter region. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol 16, 1063–1070. doi:10.2147/CCID.S409621
Olsen, M. B., Hildrestrand, G. A., Scheffler, K., Vinge, L. E., Alfsnes, K., Palibrk, V., et al. (2017). NEIL3-Dependent regulation of cardiac fibroblast proliferation prevents myocardial rupture. Cell. Rep. 18 (1), 82–92. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.009
Pan, J., Singh, U. S., Takahashi, T., Oka, Y., Palm-Leis, A., Herbelin, B. S., et al. (2005). PKC mediates cyclic stretch-induced cardiac hypertrophy through rho family GTPases and mitogen-activated protein kinases in cardiomyocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 202 (2), 536–553. doi:10.1002/jcp.20151
Pastor, W. A., Pape, U. J., Huang, Y., Henderson, H. R., Lister, R., Ko, M., et al. (2011). Genome-wide mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in embryonic stem cells. Nature 473 (7347), 394–397. doi:10.1038/nature10102
Pei, S., Zhao, H., Chen, L., He, X., Hua, Q., Meng, X., et al. (2022). Preventive effect of ellagic acid on cardiac dysfunction in diabetic mice through regulating DNA hydroxymethylation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70 (6), 1902–1910. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07574
Piccini, J. P., Hammill, B. G., Sinner, M. F., Jensen, P. N., Hernandez, A. F., Heckbert, S. R., et al. (2012). Incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation and associated mortality among medicare beneficiaries, 1993-2007. Circ. Cardiovasc Qual. Outcomes 5 (1), 85–93. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.111.962688
Powell, C. S., and Jackson, R. M. (2003). Mitochondrial complex I, aconitase, and succinate dehydrogenase during hypoxia-reoxygenation: modulation of enzyme activities by MnSOD. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 285 (1), L189–L198. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00253.2002
Ren, M., Li, X., Hao, L., and Zhong, J. (2015). Role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation: a novel potential therapeutic target? Ann. Med. 47 (4), 316–324. doi:10.3109/07853890.2015.1042030
Sagris, M., Vardas, E. P., Theofilis, P., Antonopoulos, A. S., Oikonomou, E., and Tousoulis, D. (2021). Atrial fibrillation: pathogenesis, predisposing factors, and genetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (1), 6. doi:10.3390/ijms23010006
Schnabel, R. B., Sullivan, L. M., Levy, D., Pencina, M. J., Massaro, J. M., D'Agostino, R. B., et al. (2009). Development of a risk score for atrial fibrillation (framingham heart study): a community-based cohort study. Lancet 373 (9665), 739–745. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60443-8
Sethi, G., Sung, B., and Aggarwal, B. B. (2008). TNF: a master switch for inflammation to cancer. Front. Biosci. 13, 5094–5107. doi:10.2741/3066
Shi, Y., Li, B., Huang, X., Kou, W., Zhai, M., Zeng, Y., et al. (2023). Loss of TET2 impairs endothelial angiogenesis via downregulating STAT3 target genes. Cell. Biosci. 13 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/s13578-023-00960-5
Shock, L. S., Thakkar, P. V., Peterson, E. J., Moran, R. G., and Taylor, S. M. (2011). DNA methyltransferase 1, cytosine methylation, and cytosine hydroxymethylation in Mammalian mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (9), 3630–3635. doi:10.1073/pnas.1012311108
Song, C. X., Szulwach, K. E., Fu, Y., Dai, Q., Yi, C., Li, X., et al. (2011). Selective chemical labeling reveals the genome-wide distribution of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Biotechnol. 29 (1), 68–72. doi:10.1038/nbt.1732
Spearman, A. D., Ke, X., Fu, Q., Lane, R. H., and Majnik, A. (2018). Adverse maternal environment leads to cardiac fibrosis in adult Male mice. Birth Defects Res. 110 (20), 1551–1555. doi:10.1002/bdr2.1428
Sun, F., Abreu-Rodriguez, I., Ye, S., Gay, S., Distler, O., Neidhart, M., et al. (2019). TET1 is an important transcriptional activator of TNFα expression in macrophages. PLoS One 14 (6), e0218551. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0218551
Szulwach, K. E., Li, X., Li, Y., Song, C. X., Wu, H., Dai, Q., et al. (2011). 5-hmC-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging. Nat. Neurosci. 14 (12), 1607–1616. doi:10.1038/nn.2959
Tabish, A. M., Arif, M., Song, T., Elbeck, Z., Becker, R. C., Knöll, R., et al. (2019). Association of intronic DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation alterations in the epigenetic etiology of dilated cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 317 (1), H168–h180. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00758.2018
Tahiliani, M., Koh, K. P., Shen, Y., Pastor, W. A., Bandukwala, H., Brudno, Y., et al. (2009). Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science 324 (5929), 930–935. doi:10.1126/science.1170116
Takahashi, H., Takeishi, Y., Seidler, T., Arimoto, T., Akiyama, H., Hozumi, Y., et al. (2005). Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of diacylglycerol kinase-zeta inhibits endothelin-1-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circulation 111 (12), 1510–1516. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000159339.00703.22
Tao, H., Xu, W., Qu, W., Gao, H., Zhang, J., Cheng, X., et al. (2021). Loss of ten-eleven translocation 2 induces cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through modulating ERK signaling pathway. Hum. Mol. Genet. 30 (10), 865–879. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddab046
Tomaszuk-Kazberuk, A., Koziński, M., Kuźma, Ł., Bujno, E., Łopatowska, P., Rogalska, E., et al. (2020). Atrial fibrillation is more frequently associated with nonobstructive coronary lesions: the bialystok coronary project. Pol. Arch. Intern Med. 130 (12), 1029–1036. doi:10.20452/pamw.15635
Tsagaratou, A., Äijö, T., Lio, C. W. J., Yue, X., Huang, Y., Jacobsen, S. E., et al. (2014). Dissecting the dynamic changes of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in T-cell development and differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111 (32), E3306–E3315. doi:10.1073/pnas.1412327111
Wang, X., Chen, X., and Dobrev, D. (2021). The crosstalk between cardiomyocyte calcium and inflammasome signaling pathways in atrial fibrillation. Pflugers Arch. 473 (3), 389–405. doi:10.1007/s00424-021-02515-4
Wasmer, K., Eckardt, L., and Breithardt, G. (2017). Predisposing factors for atrial fibrillation in the elderly. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 14 (3), 179–184. doi:10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2017.03.010
Watson, T., Shantsila, E., and Lip, G. Y. (2009). Mechanisms of thrombogenesis in atrial fibrillation: virchow's triad revisited. Lancet 373 (9658), 155–166. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60040-4
Williams, B. A., Chamberlain, A. M., Blankenship, J. C., Hylek, E. M., and Voyce, S. (2020). Trends in atrial fibrillation incidence rates within an integrated health care delivery system, 2006 to 2018. JAMA Netw. Open 3 (8), e2014874. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.14874
Xiao, M., Yang, H., Xu, W., Ma, S., Lin, H., Zhu, H., et al. (2012). Inhibition of α-KG-dependent histone and DNA demethylases by fumarate and succinate that are accumulated in mutations of FH and SDH tumor suppressors. Genes. Dev. 26 (12), 1326–1338. doi:10.1101/gad.191056.112
Xie, Y., Tan, J., Qin, Y., Cao, Y., Wang, Y., Li, A., et al. (2022). MiR-3571 modulates the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting claudin 1. Int. J. Med. Sci. 19 (3), 511–524. doi:10.7150/ijms.64639
Xu, X., Tan, X., Tampe, B., Nyamsuren, G., Liu, X., Maier, L. S., et al. (2015). Epigenetic balance of aberrant Rasal1 promoter methylation and hydroxymethylation regulates cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res. 105 (3), 279–291. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvv015
Yao, C., Veleva, T., Scott, L., Cao, S., Li, L., Chen, G., et al. (2018). Enhanced cardiomyocyte NLRP3 inflammasome signaling promotes atrial fibrillation. Circulation 138 (20), 2227–2242. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035202
Zahid, S., Cochet, H., Boyle, P. M., Schwarz, E. L., Whyte, K. N., Vigmond, E. J., et al. (2016). Patient-derived models link re-entrant driver localization in atrial fibrillation to fibrosis spatial pattern. Cardiovasc Res. 110 (3), 443–454. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvw073
Zhang, C., Chen, X., Wang, J. K., Li, Y., Cui, S. J., Wang, Z., et al. (2021). Phenotypic switching of atherosclerotic smooth muscle cells is regulated by activated PARP1-Dependent TET1 expression. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 28 (7), 716–729. doi:10.5551/jat.55343
Keywords: DNA hydroxymethylation, atrial fibrillation, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, oxidative stress, calcium signaling
Citation: Fan S and Shi J (2025) Research progress on DNA hydroxymethylation in atrial fibrillation: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1591675. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1591675
Received: 11 March 2025; Accepted: 18 September 2025;
Published: 08 October 2025.
Edited by:
Thiago Almeida Pereira, Stanford University, United StatesReviewed by:
Ullas Valiya Chembazhi, University of Pennsylvania, United StatesMuhammad Imran, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Fan and Shi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shaowei Fan, NDc4NTI1OTcwQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Shaowei Fan
Shaowei Fan Jingjing Shi
Jingjing Shi