- 1Dr. Marinescu G Gabriel-Cristian CMI, Pitești, Romania
- 2Faculty of Medicine, Transilvania University of Braşov, Braşov, Romania
- 3Department of Psychiatry, University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Iuliu Haţieganu” Cluj-Napoca, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Schizophrenia can lead to significant and long-lasting deficits in patient functionality. The present study proposes a theoretical index that predicts the ability of an antipsychotic to improve the functionality of patients with schizophrenia. An advantage of this theoretical index is that it directly compares 29 first- and second-generation antipsychotics. This theoretical index, named the Antipsychotics Functional Index (AFI), was constructed considering factors such as pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, pharmaceutical form, ease of administration, and safety aspects. A good antipsychotic ranking based on the proposed index results from combining the partial dopaminergic agonist mechanism and a lower frequency of administration. The top-ranked antipsychotic is aripiprazole long-acting injection (LAI) administered every 2 months, 6 weeks, or 1 month, which is the only antipsychotic D2 partial agonist with an LAI formulation. It is followed by paliperidone LAI administered every 6 months. This antipsychotic has the least frequent administration schedule. According to the AFI, the most favorable antipsychotics for functionality are generally second-generation LAI antipsychotics. The D2 partial agonist mechanism has a pharmacodynamic advantage. Based on this functionality index, psychiatrists could select the most suitable antipsychotic for each patient, with the ultimate goal of helping the patient achieve their maximum potential.
1 Introduction
Schizophrenia, a severe psychiatric condition, often manifests during young adulthood and can lead to significant and long-lasting deficits in patient functionality (Patel et al., 2014). These deficits may be accompanied by elevated levels of cardiovascular (Correll et al., 2022) and metabolic (Pillinger et al., 2020) comorbidities, sudden death (Scorza et al., 2021), and reduced life expectancy (Hjorthøj et al., 2017). Globally, schizophrenia ranks among the top 25 causes of disability (Boland et al., 2022; Switaj et al., 2012).
In many traditional communities, the stigma associated with schizophrenia may affect the family as a whole, and it could also restrict, for instance, marital opportunities for younger family members (Boland et al., 2022).
Nonadherence rates are very high in schizophrenia, and it is estimated that 40%–50% of patients become at least partially noncompliant with treatment within 1 or 2 years. Due to the high risk of relapse and other potential consequences (job loss, interference with school, family burden, suicidality, homelessness, and aggressive or violent behavior), treatment adherence has become a critical issue for schizophrenia treatment (Boland et al., 2022). The concept of recovery in schizophrenia involves controlling both positive and negative symptoms and achieving an acceptable level of social and occupational functionality. Inadequate functioning may stem from residual negative and cognitive symptoms, which many antipsychotics do not adequately address, as they are more effective in managing positive symptomatology (Correll, 2020). It is widely acknowledged that sustained antipsychotic treatment is the only approach proven to be effective for achieving remission, maintaining it, and preventing relapses (Ifteni et al., 2021).
The antipsychotics currently in use span a spectrum ranging from silent antagonists of dopamine D2 receptors to nearly full agonists of the same receptors When an antipsychotic binds to D2 receptors, it blocks the action of dopamine on these receptors. If it has no other effect on D2 receptors, it is called silent antagonist or simply antagonist. If it has a stimulating effect on D2 receptors, but less than dopamine, it is called partial agonist. An overly intense agonist effect may fail to treat psychosis, as it cannot adequately control positive symptomatology. This is why partial agonists and silent antagonists of D2 receptors are preferable solutions. Blocking serotoninergic 5HT2A receptors, which is achieved by many atypical antipsychotics, represents an important step in improving their tolerability. Additionally, certain antipsychotics may induce partial agonism in serotoninergic 5HT1A receptors, providing additional benefits (Stahl, 2021).
The functionality and quality of life of patients with schizophrenia have been evaluated for various antipsychotics in clinical studies by comparing them to placebos and/or making direct comparisons (Ishigooka et al., 2022). Additional data have been obtained through meta-analyses and systematic reviews (Leucht et al., 2017; Huhn et al., 2019).
Antipsychotics differ in many parameters, such as pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, posology, and pharmaceutical form, which provide both beneficial effects and inconveniences (Stahl and Djokic, 2023). These differences can influence the functionality of patients with schizophrenia (de Filippis et al., 2021).
The present study proposes a theoretical index that predicts the ability of an antipsychotic to improve the functionality of patients with schizophrenia. An advantage of this index is that it directly compares first- and second-generation antipsychotics.
2 Methodology
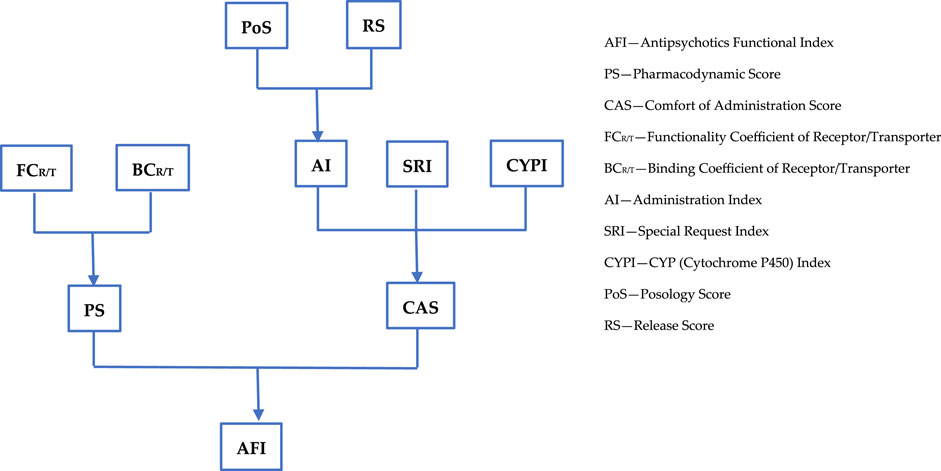
The impact of antipsychotics on patient functioning was analyzed, considering aspects such as pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, pharmaceutical form, ease of administration, and the safety profile. A total of 29 antipsychotics used over time in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia were analyzed: chlorpromazine, flupenthixol, fluphenazine, haloperidol, loxapine, methotrimeprazine, periciazine, perphenazine, pimozide, thioridazine, thiothixene, trifluoperazine, zuclopenthixol, asenapine, clozapine, iloperidone, sertindole, lumateperone, lurasidone, olanzapine, zotepine, paliperidone, quetiapine, amisulpride, risperidone, ziprasidone, aripiprazole, brexpiprazole, and cariprazine. All these antipsychotics were compared to a hypothetical ideal antipsychotic characterized exclusively by beneficial effects known as the theoretical maximum. A parameter called the Antipsychotics Functional Index (AFI) was created according to the algorithm presented in Figure 1.
The general formula for the Antipsychotics Functional Index (AFI) is
and all parameters included in it are defined and described below.
The Antipsychotics Functional Index (AFI) considers two major aspects, namely, pharmacodynamics and comfort of administration. These two aspects are each expressed using a score (percentage): the Pharmacodynamic Score (PS) and the Comfort of Administration Score (CAS).
2.1 Pharmacodynamic score (PS)
To assess effects on patient functionality from a pharmacodynamic perspective, the Pharmacodynamic Score (PS) was defined. This parameter takes into account the pharmacodynamic mechanisms of antipsychotics, which are split based on their pro-functioning and anti-functioning effects. To quantify these effects, a functionality coefficient (FCR/T) is calculated for each receptor/transporter. However, pharmacodynamic mechanisms are not equally addressed by antipsychotics. Thus, the binding coefficient (BCR/T) was created to quantify the degree to which the mechanisms are addressed. Each antipsychotic acts to varying degrees on multiple pharmacodynamic mechanisms. For this reason, the PS calculated for each antipsychotic represents a sum of scores corresponding to mechanisms that are involved to varying degrees. The receptor/transporter-specific score is calculated as the product of the corresponding FCR/T and BCR/T. Consequently, the PS is calculated based on the following formula representing the sum of the products of the mentioned coefficients:
The functionality coefficient (FCR/T) represents the score associated with each receptor or reuptake pump (receptor/transporter) regarding functionality according to the following formula:
where F stands for functionality.
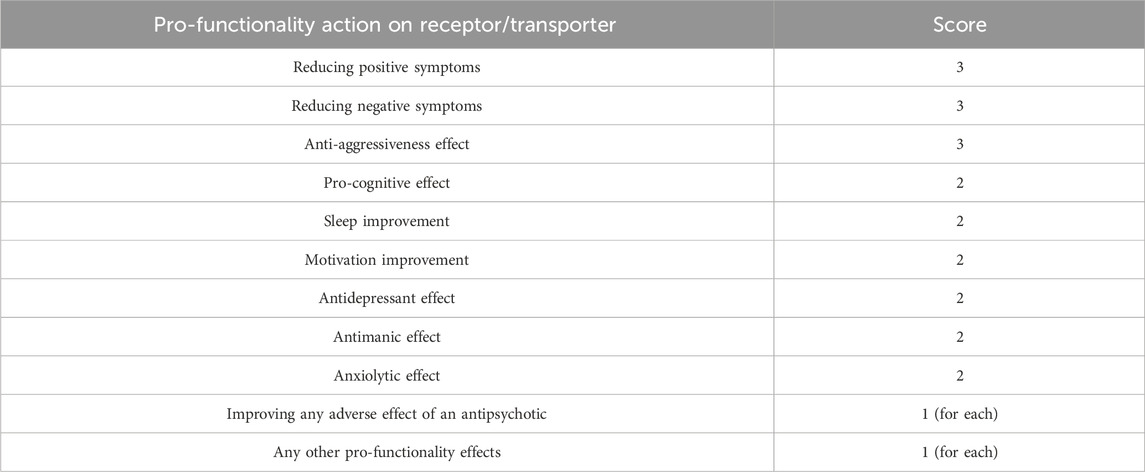
When calculating the FCR/T, both beneficial (rated positively) and unfavorable (rated negatively) actions regarding functionality are considered. Thus, for beneficial actions, scoring is carried out based on the importance of each effect, with values ranging from 3 to 1 according to Table 1. Actions of very high importance for patient functionality (improving positive symptoms, negative symptoms, and aggressiveness) each receive scores of 3. These actions are considered the most important as they alleviate the core symptoms of schizophrenia, and in their absence, functionality remains an unattainable goal. Pro-cognitive actions; improving sleep and motivation; and antidepressant, anxiolytic, and antimanic actions each receive scores of 2, as they are also important in the overall picture of functionality but are not parts of the core symptoms targeted by antipsychotics. Additional actions (improving some side effects and any other additional pro-functional effects) each receive scores of 1.
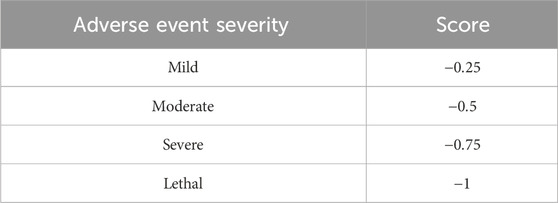
Unfavorable actions affecting functionality are rated negatively, with their values determined based on the intensity of the adverse effects resulting from actions on receptors and reuptake pumps. The severities of adverse effects are rated based on the Merck Reporting Model (Severity-of-adverse-drug-reactions, 2024). This model is presented in Annex 2.
The adverse event scores, classified based on their severities, are presented in Table 2.
For each pharmacological mechanism, the total score of the unfavorable actions results from summing the products of the scores of each type of adverse effect and their numbers, yielding a negative value.
The pro- and anti-functionality actions and their corresponding scores, as well as the functionality coefficient specific to each action on receptors/reuptake pumps, can be found in Table 3.

Table 3. Functionality coefficients for receptors and transporters; NA—not applicable (Stahl, 2021; Procyshyn et al., 2023; Procyshyn et al., 2019).
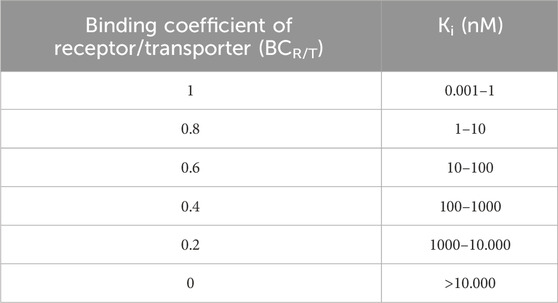
The binding coefficient (BCR/T) is a parameter that expresses the affinity of an antipsychotic for a receptor (R) and/or transporter (T). This parameter is necessary because antipsychotics have different affinities for different substrates, leading to effects with various amplitudes.
The binding coefficient (
The values of ki identified for the main antipsychotics (Procyshyn et al., 2023; PDSP, 2019) form the basis of the BCR/T calculations (Annex 1). The theoretical maximum has a BCR/T equal to 1 for receptors and transporters with positive values of FCR/T (pro-functionality) and a BCR/T equal to 0 for receptors and transporters with negative values of FCR/T (anti-functionality). In the case of D2 receptors, the theoretical maximum is considered to be a partial agonist at this level (pro-functionality) rather than a silent antagonist.
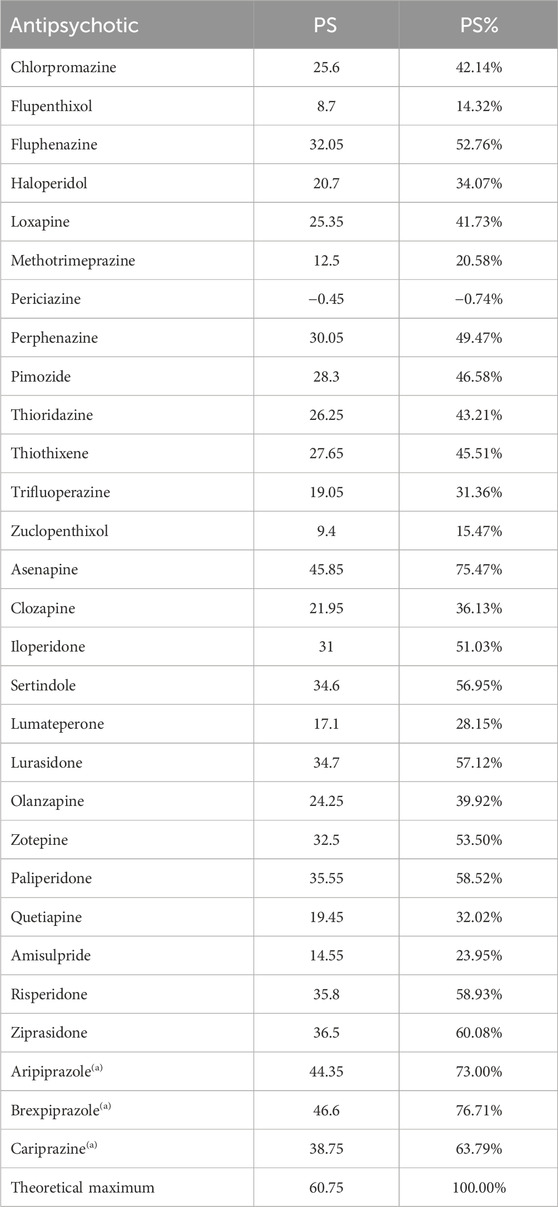
The theoretical maximum PS is calculated for an ideal antipsychotic with a maximum effect for pharmacodynamic pro-functionality actions and an absence of any negative effect regarding functionality. The PS values corresponding to each antipsychotic are expressed as percentages of the theoretical maximum. The numerical PS values for the considered antipsychotics and the theoretical maximum, as well as the percentage values related to the theoretical maximum, are presented in Table 5.
2.2 Comfort of administration score (CAS)
The Comfort of Administration Score (CAS) quantifies how functionality can be influenced by the administration of an antipsychotic. The frequency of administration, the release of the active substance, any special requirements (e.g., post-administration surveillance, special investigations), and the influence of hepatic metabolic activity are taken into account. As for the Pharmacodynamic Score (PS), the Comfort of Administration Score (CAS) is calculated as a percentage of the theoretical maximum. The theoretical maximum is a score corresponding to an ideal antipsychotic that does not create any discomfort related to its administration (minimum administration frequency, constant release of the active substance, no special requirements related to administration, and no influence of liver metabolic activity).
The CAS considers the following criteria:
• The Administration Index (AI), which considers the frequency of administration and the release mode of the active substance.
• The Special Request Index (SRI), which quantifies the special requirements related to the administration of the antipsychotic.
• The CYP Index (CYPI), which expresses the potential for drug interactions generated at the level of cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes.
The CAS represents the sum of these parameters according to the following formula:
The CAS formula equally considers the Administration Index (AI), the Special Request Index (SRI), and the CYP Index (CYPI), which will be discussed below.
The Administration Index (AI) is a parameter that evaluates how the patient’s comfort is influenced by the dosage and pharmaceutical form of the antipsychotic. To obtain this index, two other parameters are defined, namely, the Posology Score (PoS) and Release Score (RS). The formula for the AI is
Meaning the arithmetic mean of the PoS and RS, as they are thought to influence the AI with equal weights.
• The Posology Score (PoS) quantifies how functionality is influenced by the frequency of administration of the antipsychotic. It is thought that infrequent administrations are more protective regarding functionality (e.g., long-acting injectable antipsychotics), while more frequent administrations generate a negative influence. The formula for this parameter is
where NAY represents the Number of Administrations per Year and the value 365.25 results from the average number of days in a year, considering leap years.
The Number of Administrations per Year (NAY) is calculated taking into account administrations that occur once or multiple times a day (oral antipsychotics) or after a specific number of weeks, monthly, or every few months (LAI antipsychotics).
For example, for an antipsychotic administered twice daily (BID), the formula becomes
Long-acting injection (LAI) antipsychotics have the highest values for this parameter (close to 1). The resulting values for each antipsychotic are found in Annex 4. It is important to mention that, in this analysis, it is assumed that a patient’s loss of personal comfort is proportional to the number of administrations. The ideal antipsychotic with which the final comparison is made is one that does not create any discomfort related to administration, which theoretically means zero administrations per year and a theoretical PoS = 1. This is currently impossible but necessary as a reference level for the analysis at hand.
• The Release Score (RS) quantifies the patient’s comfort regarding the medication’s release form. It is based on the premise that orally administered immediate-release substances can generate adverse effects due to greater fluctuations in plasma concentrations, unlike orally administered modified-release forms (extended release) and injectable forms with prolonged release (LAI), for which the smallest plasma fluctuations have been observed. An example would be quetiapine, which is available in both immediate-release and extended-release forms; it is much better tolerated and easier to titrate in the extended-release form. In our computations, the RS has the following values: immediate release = 0, extended release = 0.5, and LAI = 1. An ideal antipsychotic automatically receives a theoretical maximum score of 1 (Annex 4).
The Special Request Index (SRI) quantifies the presence or absence of special administration requirements (e.g., post-administration surveillance for 3 h after olanzapine LAI, ECG monitoring for sertindole, monitoring the number of platelets for clozapine), which in turn influence the patient’s comfort. Thus, the presence of special administration requirements results in a score of 0, while their absence results in a score of 1. An ideal antipsychotic also receives a theoretical maximum score of 1 (Annex 4).
The CYP Index (CYPI) analyzes how the patient’s functionality is influenced by the effect of an antipsychotic on the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP). If an antipsychotic affects the activity of cytochrome enzymes by inhibiting or inducing them, this represents an obstacle or requires a dosage adjustment for other concomitant medications metabolized by the same enzymatic system.
Therefore, influencing cytochrome enzymes, regardless of the direction in which it occurs, results in a score of 0, while the absence of influence receives a score of 1. The ideal antipsychotic does not influence the cytochrome enzymatic system in any way, and it receives the theoretical maximum score of 1 (Annex 4).
The CAS values corresponding to the considered antipsychotics are presented in Annex 4.
Taking all these variables into account, we reach the final formula:
The resulting values for the Antipsychotics Functional Index (AFI) are presented in Annex 3 and Figure 2.
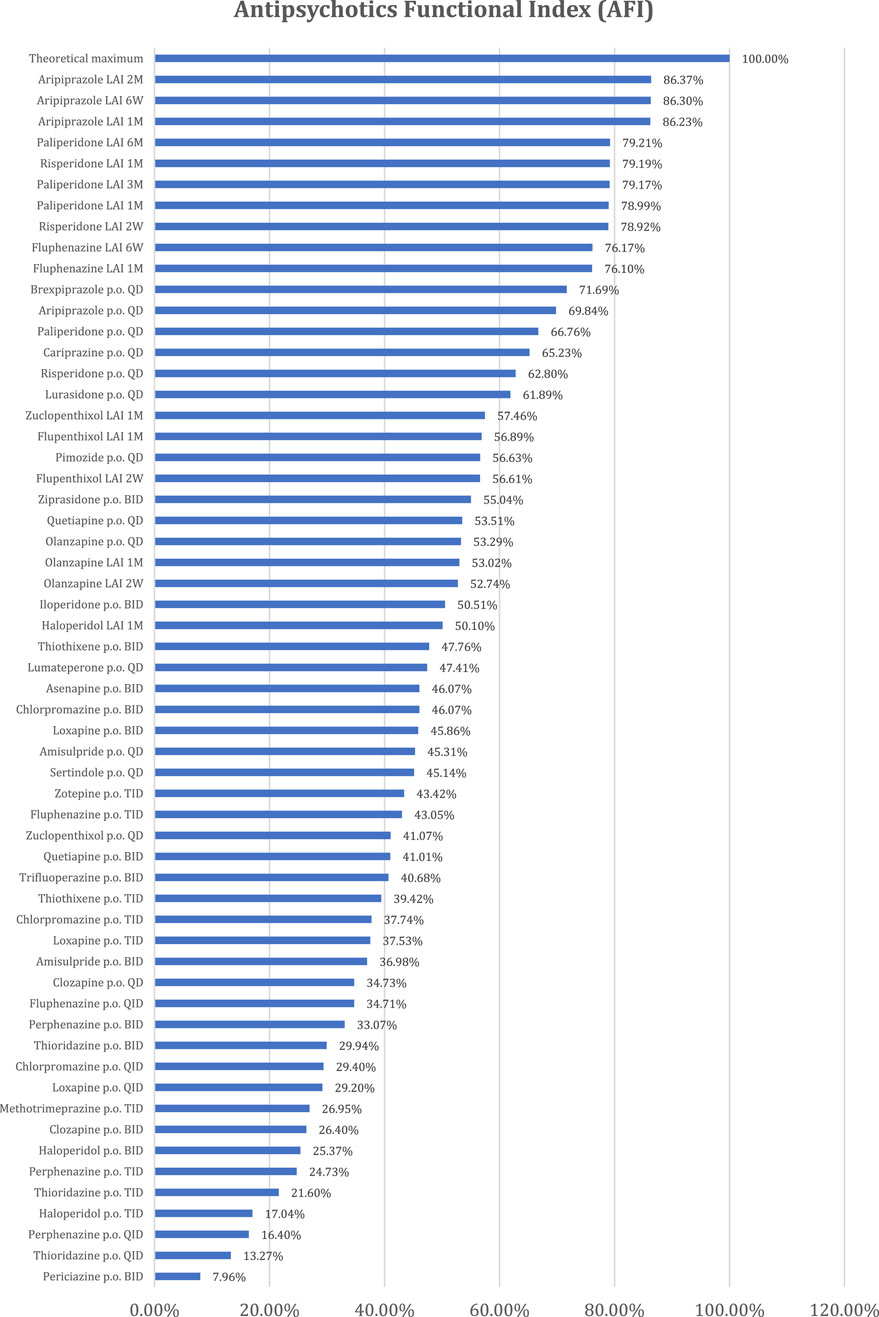
Figure 2. The Antipsychotics Functional Index (AFI) values for each antipsychotic and pharmaceutical form.
3 Discussion
The Pharmacodynamic Score (PS), which evaluates the impact of pharmacodynamic aspects on patient functionality, presents greater values for brexpiprazole, asenapine, aripiprazole, and cariprazine. It was expected that partial agonists of D2 receptors would be the most favorable for functionality due to their particular mode of action, which counterbalances the specific dopaminergic imbalances of the disease, thus offering efficacy and tolerability, essential aspects of functionality. The classification of asenapine among partial D2 agonists is justified by its favorable receptor profile. It has the maximum affinity for 5-HT2A (the highest-rated pro-functionality receptor), 5-HT2C, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, as well as very good affinity, almost at the maximum, for D3, 5-HT1A, and 5-HT1B receptors, which are also favorable for patient functionality. Second-generation antipsychotics are generally better positioned compared to those of the first generation, with some exceptions such as amisulpride, quetiapine, clozapine, and olanzapine. The latter, although proven effective in schizophrenia, are not the most favorable for functionality due to less favorable pro- and anti-functionality ratios.
From the perspective of administration comfort (CAS), the best-ranked antipsychotics are those that achieve optimal administration with minimal frequency, have release modes that do not lead to large fluctuations in plasma concentrations, do not have special administration requirements, and lack interactions with cytochrome enzyme systems. Thus, the best-ranked antipsychotics are long-acting injectables (LAIs) (paliperidone every 6 months, paliperidone every 3 months, aripiprazole every 2 months, and aripiprazole every 6 weeks). Antipsychotics with unfavorable CASs require oral administration multiple times a day, have immediate-release forms, have special administration requirements, and have significant influence on the cytochrome enzyme system. In the cases of thioridazine (p.o. QID) and perphenazine (p.o. QID), negative values are recorded because they meet three of the four conditions mentioned earlier, namely, frequent daily administrations, immediate release, and inhibition of the CYP2D6 enzyme.
The Antipsychotics Functional Index (AFI) is higher for antipsychotics with both high Pharmacodynamic Scores (PSs), which are only correlated with the active substance, and good Comfort of Administration Scores (CASs), which are correlated with both the pharmaceutical forms of antipsychotics and the active substance. Consequently, the best ranking is obtained by the only antipsychotic dopaminergic D2 partial agonist with an LAI formulation (aripiprazole LAI), followed by the atypical LAI antipsychotic with the rarest administrations (paliperidone LAI administered every 6 M). Given this ranking, a better antipsychotic would result from combining a partial dopaminergic agonist with the lowest possible administration frequency.
Although risperidone and paliperidone are pharmacodynamically close, the profile of risperidone is more favorable to functionality. Therefore, risperidone with monthly administration is better positioned than paliperidone with administration every 3 months or 1 month.
Flupenthixol LAI ranks among the atypical antipsychotics in the final AFI ranking, combining a favorable PS (the best among first-generation antipsychotics) with administration every 6 weeks or 1 month, no special administration requirements, and no influence on cytochrome enzyme systems. In its oral-administration variant, flupenthixol no longer maintains the same favorable position for functionality.
Strictly analyzing oral antipsychotics, brexpiprazole is the most favorable for functionality, with the best PS, followed by aripiprazole, paliperidone, cariprazine, risperidone, and lurasidone, which all rank well.
Interestingly, oral olanzapine (QD) is better positioned compared to olanzapine LAI administered monthly or every 2 weeks. This is explained by the special requirements for olanzapine LAI administration (monitoring for 3 h after administration) (Medscape, 2024; Union Register of medicinal products, 2024).
An important influence on functionality is the cognitive and negative symptoms severity. Typical antipsychotics (e.g., haloperidol) decrease dopaminergic activity in the mesocortical tract, that ends in the prefrontal cortex, through D2 receptor antagonism, leading not only to the lack of improvement of these symptoms, but also to a possible worsening. An important step in the beneficial approach to negative and cognitive symptoms was the development of atypical antipsychotics (e.g., risperidone, olanzapine, clozapine) which modulate serotoninergic activity (5-HT2A receptor antagonism with or without 5-HT1A receptor partial agonism) and thus compensating for their tendency to decrease dopaminergic activity in the prefrontal cortex. A more direct way to improve the low prefrontal dopaminergic activity in schizophrenia is through D2 partial agonists (e.g., aripiprazole, cariprazine, brexpiprazole). They bind to free and unstimulated D2 receptors in the prefrontal cortex schizophrenia patients, leading through their action as D2 partial agonists to increase dopamine activity in this area and finally to the improvement of cognitive and negative symptoms. D2 partial agonists also retain the activity of modulating serotonergic receptors, thus improving cognitive and negative symptoms through three mechanisms: D 2 partial agonism, 5-HT2A antagonism and 5-HT1A partial agonism. Based on these actions, they may be theoretically superior to atypical antipsychotics that combine D2 antagonism with serotonergic receptor modulation (Stahl, 2021).
The challenge of this theoretical, predictive concept lies in referencing existing data in the specialized literature, including meta-analyses and systematic reviews, which scrutinize reported clinical studies. It is crucial to confront predictions with observations. Consequently, we note that in a meta-analysis by Leucht et al. (2017), in terms of quality of life, aripiprazole, quetiapine, lurasidone, cariprazine, olanzapine, and paliperidone were identified as the most effective, while in terms of social functioning, thioridazine, lurasidone, olanzapine, risperidone, paliperidone, brexpiprazole, and aripiprazole ranked the best. In a meta-analysis conducted by Huhn et al. (2019), aripiprazole and paliperidone topped the rankings in terms of quality of life, whereas in terms of social functioning, thioridazine, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, lurasidone, and brexpiprazole were the most effective antipsychotics.
The STAR study, which compared oral antipsychotics, found that switching to oral aripiprazole from other oral antipsychotics led to improvements in negative symptoms, somnolence, weight gain, cognitive function, vitality, and mood (Kerwin et al., 2007).
Naber et al. (2015), Naber et al. (2018) provided additional data regarding the functional benefits following treatment with LAI antipsychotics, namely, aripiprazole LAI (1M) and paliperidone LAI (1M). In those studies, aripiprazole LAI demonstrated greater favorability in improving functional outcomes in patients with schizophrenia, particularly in those under 35 years old. Moreover, compared cariprazine vs. risperidone in terms of negative symptoms assessed throughout Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale - Factor Score for Negative Symptoms (PANSS-FSNS) and functionality assessed throughout Personal and Social Performance Scale (PSP), with a clear, statistic significance, superiority for cariprazine (Németh et al., 2017).
Ifteni et al. (2021) proposed the ROLIN scale with the aim of identifying patients who would benefit the most from LAI treatment. This tool considers a range of predictors of good or poor therapeutic outcomes, including age, duration of illness, number of relapses, the therapeutic response to oral antipsychotics, social support for the patient, the pharmaceutical form of the antipsychotic, and therapeutic adherence. Some of these predictors overlap with those considered when calculating the AFI. Thus, the combined use of the ROLIN scale and the AFI by a psychiatrist could provide additional benefits in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia.
Although the theoretical predictive index presented in this paper cannot perfectly align with the data resulting from these studies and meta-analyses, we cannot overlook the fact that in the resulting classification, aripiprazole, paliperidone, risperidone, brexpiprazole, cariprazine, and lurasidone are ranked at the top. An advantage of this predictive index could be that it also considers the pharmaceutical form in which the antipsychotic molecule is presented. Thus, two different methods, including a theoretical method that directly compares antipsychotics and another based on important clinical data, lead to comparable results. Nevertheless, theoretical data which result from our analysis should be correlated with clinical one through clinical functionality scales. Such scales as Heinrichs-Carpenter Quality of Life Scale, Global Assessment of Functionality Scale and others, will provide the real status of patient’s functionality and could be used to compare antipsychotics in terms of functionality.
4 Limitations
The classification of antipsychotics based on AFI represents a personal view of authors. The scores given have sought to take into account all aspects, from efficacy to safety profile, even the pharmaceutical form. However, other visions are possible, with scores conceived in a different way that could change this classification.
In the development of the AFI, only adverse reactions determined by pharmacodynamic action were considered. Adverse reactions based on reports and those mentioned in the summary of product characteristics (SPCs) of each antipsychotic were not taken into consideration. Although a rigorous analysis of the adverse reactions mentioned in the SPCs was conducted, it could not be used because it led to paradoxical results, namely, a superior safety profile for first-generation (typical) antipsychotics compared to second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics. This result was obtained because adverse reactions were reported much more rigorously during the development of atypical antipsychotics and thereafter in their marketing, in accordance with stricter pharmacovigilance legislation. Therefore, in this work, their inclusion in the final formula was abandoned, and the index remained reliant on theoretical and predictive parameters.
5 Conclusion
According to the Antipsychotics Functional Index (AFI), atypical LAI antipsychotics are the most favorable for the functionality of patients with schizophrenia. Among them, the partial agonist mechanism of D2 dopamine is advantageous.
Based on this functionality index, a clinical psychiatrist could, either from the beginning of treatment or during treatment, select the most suitable antipsychotic for their patient, with the ultimate goal of helping the patient achieve their maximum potential.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
MC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. II: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. TA: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. GR: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1662228.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1591763/full#supplementary-material
References
Boland, R., Verduin, M. L., and Ruiz, P. (2022). Kaplan and Sadock's synopsis of psychiatry. 12th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer.
Correll, C. U. (2020). Using patient-centered assessment in schizophrenia care: defining recovery and discussing concerns and preferences. J. Clin. Psychiatry 81 (3), MS19053BR2C. doi:10.4088/JCP.MS19053BR2C
Correll, C. U., Kim, E., Sliwa, J. K., Hamm, W., Gopal, S., Mathews, M., et al. (2021). Pharmacokinetic characteristics of long-acting injectable antipsychotics for schizophrenia: an overview. CNS Drugs 35, 39–59. doi:10.1007/s40263-020-00779-5
Correll, C. U., Solmi, M., Croatto, G., Schneider, L. K., Rohani-Montez, S. C., Fairley, L., et al. (2022). Mortality in people with schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of relative risk and aggravating or attenuating factors. World Psychiatry 21, 248–271. doi:10.1002/wps.20994
de Filippis, R., De Fazio, P., Gaetano, R., Steardo, L., Cedro, C., Bruno, A., et al. (2021). Current and emerging long-acting antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 20 (7), 771–790. doi:10.1080/14740338.2021.1910674
Hjorthøj, C., Stürup, A. E., McGrath, J. J., and Nordentoft, M. (2017). Years of potential life lost and life expectancy in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 4, 295–301. doi:10.1016/s2215-0366(17)30078-0
Huhn, M., Nikolakopoulou, A., Schneider-Thoma, J., Krause, M., Samara, M., Peter, N., et al. (2019). Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 32 oral antipsychotics for the acute treatment of adults with multi-episode schizophrenia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 394: 939–951. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31135-3
Ifteni, P., Petric, P.-S., and Teodorescu, A. (2021). Rating opportunity for long-acting injectable antipsychotic initiation index (ROLIN). Front. Psychiatry 12, 767756. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.767756
Ishigooka, J., Nakagome, K., Ohmori, T., Iwata, N., Inada, K., Iga, J.-I., et al. (2022). Discontinuation and remission rates and social functioning in patients with schizophrenia receiving second-generation antipsychotics: 52-Week evaluation of JUMPs, a randomized, open-label study. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 76, 22–31. doi:10.1111/pcn.13304
Kerwin, R., Millet, B., Herman, E., Banki, C. M., Lublin, H., Pans, M., et al. (2007). A multicentre, randomized, naturalistic, open-label study between aripiprazole and standard of care in the management of community-treated schizophrenic patients schizophrenia trial of aripiprazole: (STAR) study. Eur. Psychiatry 22, 433–443. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.03.002
Leucht, S., Leucht, C., Huhn, M., Chaimani, A., Mavridis, D., Helfer, B., et al. (2017). Sixty years of placebo-controlled antipsychotic drug trials in acute schizophrenia: systematic review, bayesian meta-analysis, and meta-regression of efficacy predictors. AJP Adv. 174, 927–942. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.16121358
Medscape (2024). Available online at: https://reference.medscape.com/drug/zyprexa-relprevv-olanzapine-342979.
Naber, D., Baker, R. A., Eramo, A., Forray, C., Hansen, K., Sapin, C., et al. (2018). Long-term effectiveness of aripiprazole once-monthly for schizophrenia is maintained in the QUALIFY extension study. Schizophrenia Res. 192, 205–210. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2017.04.013
Naber, D., Hansen, K., Forray, C., Baker, R. A., Sapin, C., Beillat, M., et al. (2015). Qualify: a randomized head-to-head study of aripiprazole once-monthly and paliperidone palmitate in the treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Res. 168, 498–504. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2015.07.007
Németh, G., Laszlovszky, I., Czobor, P., Szalai, E., Szatmári, B., Harsányi, J., et al. (2017). Cariprazine versus risperidone monotherapy for treatment of predominant negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia: a randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 389, 1103–1113. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30060-0
Nomenclatorul Medicamentelor Pentru uz Uman (2024). Available online at: https://nomenclator.anm.ro/medicamente.
Patel, K. R., Cherian, J., Gohil, K., and Atkinson, D. (2014). Schizophrenia: overview and treatment options. P&T 39 (9), 638–645.
PDSP (2019). PDSP database. Available online at: https://pdsp.unc.edu/databases/kidb.php.
Pillinger, T., McCutheon, R. A., Vano, L., Mizuno, Y., Arumuham, A., Hindley, G., et al. (2020). Comparative effects of 18 antipsychotics on metabolic function in patients with schizophrenia, predictors of metabolic dysregulation, and association with psychopathology: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 7, 64–77. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30416-X
Procyshyn, R. M., Bezchlibnyk-Butler, K. Z., and Jeffries, J. J. (2019). Clinical handbook of psychotropic drugs. 23rd edition. Boston, MA: Hogrefe Publishing.
Procyshyn, R. M., Bezchlibnyk-Butler, K. Z., and Kim, D. D. (2023). Clinical handbook of psychotropic drugs. 25th edition. Newburyport, MA: Hogrefe Publishing.
Scorza, F. A., de Almeida, A.-C. G., Scorza, C. A., Cysneiros, R. M., and Finsterer, J. (2021). Sudden death in schizophrenia: pay special attention and develop preventive strategies. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 37 (1), 1633–1634. doi:10.1080/03007995.2021.1937089
Stahl, S. M. (2021). Stahl’s essential psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific basis and practical applications -. 5th ed. 978-1-108-83857-3.
Stahl, S. M., and Djokic, G. (2023). Comparing the pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of antipsychotics: choosing an antipsychotic and dosing a long-acting injectable. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 73, 108–118. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2023.04.015
Switaj, P., Anczewska, M., Chrostek, A., Sabariego, C., Cieza, A., Bickenbach, J., et al. (2012). Disability and schizophrenia: a systematic review of experienced psychosocial difficulties. BMC Psychiatry 12, 193. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-12-193
Union Register of Medicinal Products (2024). Available online at: https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h479.htm.
Severity-of-adverse-drug-reactions (2024). Available online at: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/drugs/adverse-drug-reactions/severity-of-adverse-drug-reactions
Keywords: schizophrenia, antipsychotics, functionality, AFI, LAI
Citation: Marinescu G-C, Ifteni PI, Teodorescu A and Georgescu R (2025) The antipsychotics functional index (AFI) in schizophrenia. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1591763. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1591763
Received: 11 March 2025; Accepted: 20 June 2025;
Published: 02 July 2025; Corrected: 18 July 2025.
Edited by:
Ciria Hernandez, University of Michigan, United StatesReviewed by:
Ahmed Naguy, Kuwait Centre for Mental Health, KuwaitJustin Faden, Rowan University School of Osteopathic Medicine, United States
Copyright © 2025 Marinescu, Ifteni, Teodorescu and Georgescu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gabriel-Cristian Marinescu, ZHJtYXJpbmVzY3VnYWJyaWVsQHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==; Petru Iulian Ifteni, cGV0cnVfaWZ0ZW5pQHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==; Radu Georgescu, cmFkdS5nZW9yZ2VzY3VAZWxlYXJuLnVtZmNsdWoucm8=
 Gabriel-Cristian Marinescu
Gabriel-Cristian Marinescu Petru Iulian Ifteni
Petru Iulian Ifteni Andreea Teodorescu
Andreea Teodorescu Radu Georgescu
Radu Georgescu