Abstract
Acute Lung Injury (ALI) is a severe and progressive condition characterized by hypoxic respiratory failure, often triggered by multiple contributing factors. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates and can advance to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in severe cases. The pathogenesis of ALI involves a complex interplay of pathological mechanisms, including immune-inflammatory responses, disruption of the alveolar-capillary barrier, damage to mesenchymal stem cell organelles, metabolic dysregulation, ferroptosis, and alterations in gut microbiota. From the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the development of ALI is primarily attributed to the invasion of toxic pathogens, which result in lung dysfunction. TCM treatment strategies, which emphasize heat-clearing, detoxification, promoting blood circulation, and resolving stasis, have demonstrated promising clinical efficacy. This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the pathogenesis of ALI and explores the therapeutic mechanisms of TCM compounds and bioactive monomers with potential therapeutic benefits. The goal is to establish a solid theoretical foundation for the clinical application of TCM in ALI treatment and to further validate its scientific rationale.
1 Introduction
ALI is characterized by decreased lung volume, reduced lung compliance, and an imbalance in the ventilation-perfusion ratio, which leads to clinical syndromes such as diffuse pulmonary interstitial edema and pulmonary edema. These conditions are primarily caused by lung infections (both bacterial and viral), as well as intrapulmonary or extrapulmonary factors, including lung contusion and sepsis, circulatory disorders associated with extracorporeal circulation, and immune system metabolic dysfunction. The underlying pathological mechanisms involve inflammation of the alveolar and pulmonary parenchyma, damage to the alveolar-capillary membrane, increased vascular permeability, and neutrophil recruitment (Dong et al., 2024; Mokrá, 2020). Clinically, ALI manifests as severe hypoxemia, changes in pulmonary function due to increased alveolar capillary membrane permeability, pulmonary edema, and respiratory failure.
From the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), ALI is classified under the categories of “sudden asthma” and “out of the syndrome” with pathogenic factors including heat, toxins, phlegm, and blood stasis. These factors often result from external pathogenic invasions affecting the lungs, internal phlegm accumulation, and subsequent impairment of lung qi, leading to symptoms such as coughing, sputum production, constipation, and irritability. A summary of the common etiology, pathogenesis, and pathological characteristics of ALI from an integrated Chinese and Western medicine perspective is provided in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Etiological categorization | Specific causes | Pathogenesis in traditional Chinese medicine | Pathology in western medicine | Document source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infectious agent | Bacteria, Virus | Pathogenic factors such as wind-cold or wind-heat enter the body through the mouth and nose, invading the lungs. This disrupts the lung’s functions of dispersing and descending qi, leading to qi stagnation and impaired distribution of body fluids. Over time, this results in the production of phlegm, which obstructs the lungs, further exacerbating respiratory dysfunction | Viral infections and bacterial proliferation in the lungs lead to the release of metabolites, which initiate inflammatory responses and cause subsequent tissue damage | McKelvey et al. (2024) |
| Pyemia | Internal deficiency of vital qi, accumulation of toxic heat, obstruction of qi circulation, and the formation of blood stasis | The body becomes susceptible to external infections, resulting in an imbalanced inflammatory response and weakened immune function | Zeng (2019), Van der Poll et al. (2017) | |
| Non-infectious Factor | Hemorrhagic shock induced by mechanical trauma | / | Pulmonary vascular protein leakage, neutrophil recruitment, and overexpression of proinflammatory factors, among other pathophysiological changes, lead to persistent and severe hypoxemia | Hao (2023) |
| The perfusion of the extracorporeal circulation system is compromised | Reperfusion following ischemic events | / | The imbalance between SOD and MDA in lung tissue led to the release and accumulation of oxygen free radicals within mitochondria, consequently increasing pulmonary vascular permeability and resulting in pulmonary edema, hypoxemia, and pulmonary hypertension | Shen et al. (2019) |
| Metabolic dysfunction within the immune system | Septicemia | The invasion of exogenous pathogens results in blood stasis and obstruction, internal accumulation of heat-toxin, and qi-yin deficiency | Bacterial toxins multiply in the bloodstream and spread systemically, causing toxic alterations in various tissues and organs. These alterations include pulmonary cellular turbidity, focal necrosis, and infiltration of inflammatory cells | Wang and Wang (2023), Xu Y. et al. (2024) |
Etiology, Pathogenesis and pathological Characteristics of ALI from an Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine Perspective.
The current treatment landscape for ALI remains limited, with conventional therapies primarily comprising protective mechanical ventilation, glucocorticoid therapy, and fluid management. However, these approaches are often accompanied by significant side effects. For example, glucocorticoids can suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, potentially leading to osteoporosis and other adverse effect (Schäcke et al., 2002). Similarly, mechanical ventilation, particularly when administered at high pressures or volumes, can aggravate ALI (Del Sorbo et al., 2011). In contrast, TCM offers a promising alternative, with a long-standing history in treating ALI, and has shown unique therapeutic benefits (Zhang et al., 2021; Jiang N. et al., 2021).
Recent years have seen an increase in research exploring the role of TCM in preventing and treating ALI. However, most existing reviews predate 2022 and do not incorporate the latest findings from the past 2 years (Liu Y. et al., 2024; Zhang, 2020). This paper aims to address this gap by providing a comprehensive review of significant advancements in ALI research over the past 5 years, with particular focus on recent discoveries related to its pathogenesis and molecular mechanism. Special attention is given to the pharmacological mechanisms and clinical application research of TCM in treating ALI since 2022, as well as the clinical efficacy of newly identified TCM formulations and their active components. By integrating the latest insights from both traditional Chinese and Western medicine, this review seeks to offer innovative strategies and perspectives for the holistic treatment of ALI.
2 Mechanisms of ALI pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of ALI is highly complex, involving a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including immune cell disfunction, alterations in cytokine profiles, disruption of the alveolar gas-blood barrier, organelle dysfunction, and ferroptosis. While classical mechanisms such as oxidative stress and inflammatory responses have been extensively discussed (Su et al., 2012), this review will briefly summarize these fundamental aspects while highlighting recent advancements and novel insights in ALI research over the past 5 years.
2.1 Dynamic alterations in immune cell composition and functionality
Dysregulation of the inflammatory response is a pivotal factor in ALI pathogenesis, encompassing not only aberrant expression of inflammatory factors but also intricate alterations in immune cell phenotypes and functions. Recent advances in cutting-edge technologies, such as single-cell sequencing, spatial transcriptomics, and spatial metabolomics, have enabled researchers to analyze the dynamic changes in cell types, migration patterns, and complex interaction networks within the lung microenvironment with unprecedented precision (Yu Y. et al., 2024; Wang Y. et al., 2024). These breakthroughs have significantly enhanced our understanding of ALI’s pathological mechanisms and provided novel directions for developing precision treatment strategies. This sections reviews recent progress on lung immune cell lineages in ALI, focusing on functional changes, underlying mechanisms, and their implications for disease progression.
2.1.1 Alveolar macrophages
As the primary innate immune effector cells in the lung, alveolar macrophages play a critical role in ALI. Upon pathogen invasion, they promote the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which polarize neutrophils and mononuclear macrophages, and activating effector T cells. In the early stages of ALI, intratracheal administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces necrosis of alveolar macrophages and releases IL-1α, compromising the integrity of pulmonary endothelial cells (PEC) and facilitating neutrophil extravasation, thus exacerbating ALI progression (Dagvadorj et al., 2015). Macrophage polarization enhances the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12) and chemokines (e.g., CCL8, IL-23), as well as oxidative stress factors like COX-2 and iNOS, all of which contribute to lung injury (Chen et al., 2020). Additionally, macrophages activate the NLRP3 inflammasome by upregulating key enzymes in the glycolysis signaling pathway, including HK1 and PKM2, which accelerate pyroptosis (Luo et al., 2022). Myeloid cells also express triggering receptor 1 (TREM-1), which reprograms macrophage metabolism, enhances glycolytic activity, activates the NLRP3 inflammasome, and triggers an inflammatory response in ALI (Zhong, 2023). The process of panoptosis in macrophages during ALI is regulated by the ZBP1 transcription factor. Knockdown of ZBP1 reduces key markers of inflammation and cell death (e.g., Caspase-3 p17/19, Caspase-1 p20, GSDMD p35, and Phospho-MLKL), thereby alleviating ALI in septic mice (Sun, 2024).
2.1.2 Neutrophils
In ALI, capillary endothelial and epithelial cells sustain significant damage, while alveolar macrophages are activated to release cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β) and chemokines, recruiting neutrophils into the lungs (Bhatia et al., 2012). Infiltrating neutrophils degranulate, releasing bactericidal proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines, further exacerbating the inflammatory response (Aulakh, 2018). External stimuli can activate neutrophils, leading to the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and proteases. This process activates the NLRP3 inflammasome, releasing inflammatory mediators and aggravating lung tissue injury (Li et al., 2018; Lin and Fessler, 2021; Lefrançais et al., 2018). In LPS-induced ALI models, Glycoprotein VI (GPVI) promotes neutrophil recruitment, platelet-neutrophil complexes and NETs, which subsequently trigger an inflammatory response (Burkard et al., 2023). The interaction between protein and fibrinogen in serum, via β-integrin on neutrophil surfaces, induces degranulation, abnormal neutrophil aggregation, and increased vascular permeability, contributing to ALI development (Soehnlein et al., 2008).
2.1.3 T lymphocytes
T cells are pivotal in ALI pathogenesis. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) suppress the proliferation and differentiation of lung fibroblasts during LPS-induced lung inflammation (Tan et al., 2019; Seyran et al., 2023). Th17 cells, a subset of T helper cells, contribute significantly to host defense by secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-17A/F, IL-21, and IL-22) (Sakaguchi et al., 2016). At the molecular level, upregulation of IL-10 expression and inhibition of IL-35, RAGE, and Caspase-1 expression can attenuate T cells differentiation and mitigate ALI (Xie et al., 2021). In sepsis-induced ALI patients, elevated plasma nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (NAMPT) levels induce T cells pyroptosis and immune dysfunction, which can be alleviated by the NAMPT inhibitor FK886 (Zheng, 2020).
2.1.4 Other immune cells
Eosinophils, derived from bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells, play a role in immune regulation and allergic responses. Reduced eosinophil levels increase the risk of lung inflammation and mortality (Grisaru-Tal and Rothenberg, 2022). Conversely, IL-33-induced eosinophilia can mitigate the inflammatory response associated with Staphylococcus aureus lung infections (Krishack et al., 2021). Additionally, Natural killer (NK) lymphocytes can significantly alleviate inflammatory cell infiltration in lung immune injury and reduce the expression of IFN-γ expression in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (Li et al., 2012).
2.2 Abnormal immune cytokines
2.2.1 Interleukins and tumor necrosis factor
In ALI and ARDS, inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 play a central role by mediating Cytidine monophosphate kinase 2 (CMPK2) (Chen D. S., 2022; Wang et al., 2021). IL-10 and IL-18 are critical in lung infections, compromising cell membrane integrity, stimulating alveolar neutrophils to produce chemokines, and promoting fibrosis via TGF-β and SMAD4 activation. This leads to production of pro-fibrotic proteins (e.g., ZO-1, MUC2) and fibroblast markers (e.g., FGF-1, αSMA) in epithelial cell, resulting in mesenchymal transformation and extracellular matrix collagen accumulation (Wang K. et al., 2022; Kandikattu et al., 2023). IL-33 induces neutrophil infiltration, increases alveolar endothelial barrier permeability and triggers alveolar epithelial cell death (Zou et al., 2023).
2.2.2 Cell chemokines
Chemokines LCN2 and CCN3 regulate inflammatory responses in ALI. LCN2 enhances M2-type macrophage proportions via IL-6 and TNF-α (Zheng, 2023), while CCN3 promotes NF-κB p65, TGF-β1, TGF-βRⅡ, and p-Smad2/3 expression, increasing IL-6 and TNF-α production (Zhu et al., 2020). Knockdown of CCL2 reduces mononuclear macrophage recruitment and increases neutrophil expression, mitigating viral-induced lung injury (Lai et al., 2017). The CRTH2 receptor antagonist CT-133 improves macrophage and neutrophil infiltration, inhibits pulmonary vascular permeability, and suppresses inflammatory factor expression (Hussain et al., 2019).
2.2.3 Other factors
Interferon (IFN) inhibits inflammatory responses to bacterial and viral infections and associated ALI (Verma et al., 2022). Inflammatory mediators activate the NLRP3 inflammasome in polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and alveolar macrophages (AMs) (Cui et al., 2024). Heat shock protein HSP70 promotes lung inflammation in ALI mice but reduces CD36 receptor expression (Chen Y., 2022).
2.3 Impaired alveolar gas-blood barrier
In ALI, the alveolar-capillary barrier’s function is compromised, increasing capillary permeability and protein leakage into alveoli (Esquivel-Ruiz et al., 2021). Apoptosis plays a key role in this process; modulation of apoptotic genes (e.g., Caspase-3, Caspase-8) can enhance cell viability and mitigates inflammation (Yang et al., 2021; Ju et al., 2018; Li X. et al., 2019). The pulmonary intravascular glycocalyx, composed of hyaluronan (HA), heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG), Syndecan-1, and Glypican-1, degrades during ALI, reducing lung surface protein expression (e.g., VE-Cadherin, Occludin, VCAM-1, E-selectin) (Chen et al., 2021; Cao et al., 2023). Alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis disrupts barrier integrity via the DAPK1 ligand pathway (Wang Y. et al., 2020). Cytoskeletal protein stability is crucial for barrier maintenance, facilitating intracellular signaling, tight junctions, and alveolar permeability (Yang et al., 2023). Inhibition of MMP-9 degradation, stabilization of endothelial cytoskeletal proteins, and Rho kinase pathway-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling have been shown to alleviate lung injury (Müller et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2016).
2.4 Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as a promising therapeutic avenue for ALI due to their self-renewal capacity, multidirectional differentiation potential, and ability to modulate inflammation and fibrosis. Exosomes derived from bone marrow-derived MSCs (BM-MSCs) have been shown to inhibit several key inflammatory proteins, such as p65, IKKβ, p-IκBα, p-IκBβ, Caspase-1, GSDMD, and NLRP3, thereby suppressing macrophage pyroptosis (Xiao et al., 2020; Liu P. et al., 2024). Human placental MSCs (hPMSCs) protect the alveolar epithelial barrier through the ACE2/Ang (1–7) axis, downregulating TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-10 levels, and alleviating endothelial injury (Yu W. et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2020). Human umbilical cord MSCs (hUC-MSCs) promote Trem2 expression, inhibit the NRF2/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway, and reduce the release of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β (Che et al., 2024). Overall, MSCs show considerable potential in the treatment of ALI, particularly in terms of protecting the alveolar barrier, modulating inflammatory responses, and exerting anti-fibrotic effects. Future research will aim to optimize MSC-based therapies, enhancing their efficacy and safety for clinical application.
2.5 Abnormal organelle function
2.5.1 Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)
Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) has been recognized as a significant contributor to ALI pathogenesis (Mo and Hu, 2019). ERS can induce M1 macrophage polarization, disrupting the balance between M1 and M2 macrophages and driving excessive inflammation. Specifically, the IRE-1/XBP-1 signaling pathway activated by ERS, leads to lung epithelial cell death and NLRP3 inflammasome activation, thereby accelerating ALI progression (Zhao et al., 2020; Uddin and Barabutis, 2019).
2.5.2 Abnormal mitochondrial function
Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a central role in ALI, with mitochondrial autophagy, dynamic imbalance, and metabolic dysfunction contributing to disease progression (Zong et al., 2024). This section focuses on mitochondrial autophagy and dynamic imbalance, while mitochondrial metabolic abnormalities are addressed in Section 2.7.
2.5.2.1 Mitochondrial autophagy
Mitochondrial autophagy, or mitophagy, is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing inflammation by removing damaged mitochondria. Disruption of mitophagy can lead to release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), which activates Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9), triggering inflammation. Elevated mitophagy, induced by deficiency in serine-activated protein kinase 3 (MMK3), enhances histone deacetylase activity and exacerbates lung injury (Tan and Chen, 2020). The PINK1/PARKIN pathway is pivotal in mitophagy regulation, where NLRP3 upregulates PINK1 expression, promoting mitophagy. However, inhibition of PINK1 abolishes this effect. PARKIN-mediated degradation of PARIS increases PGC-1α expression, promoting mitochondrial biogenesis and offering protection against hyperoxia-induced damage (Um and Yun, 2017).
2.5.2.2 Mitochondrial dynamic imbalance
Imbalance between mitochondrial fusion and fission also contribute to ALI. In LPS-induced ALI models, fusion proteins Mfn1/2 and OPA1 are downregulated, while fission proteins Drp1 and Fis1 are upregulated, disrupting mitochondrial function and morphology (Shi et al., 2021). Additionally, activation of the Panx1 gene triggers the CAN-DRP1 signaling pathway, inducing mitochondrial dynamic imbalance, disrupting tight junctions, and promoting apoptosis, all of which contribute to ALI (Xu, 2023).
2.6 Iron death (ferroptosis)
Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death characterized by lipid peroxidation, exacerbates ALI by causing oxidative damage to the alveolar membrane. In LPS-induced ALI models, elevated Fe2+ levels, decreased expression of ferroptosis markers (SLC7A11, GPX4), and increased lipid peroxidation (measured by propylene glycol) are observed in bronchial epithelial cells (Cai et al., 2022a). In sepsis-induced ALI, reduced GPX4 expression and increased MDA and Fe2+ levels further worsen lung injury (Cao et al., 2022; Long et al., 2020). Conversely, silencing mixed lineage kinase 3 (MLK3) mitigates LPS-induced epithelial damage by inhibiting p53-mediated ferroptosis (Liu et al., 2020). Furthermore, deficiency in the UTX/UTY protein family alleviates LPS-induced ALI by blocking ferroptosis in alveolar epithelia through NRF2 activation (Peng et al., 2021).
2.7 Metabolic disorders
Metabolic dysregulation plays a crucial role in ALI and ARDS, with altered sugar, lipid, amino acid, and glutathione metabolism being key contributors to disease progression (He et al., 2024).
2.7.1 Sugar metabolism
During M1-type macrophage polarization, hexokinase (HK) transitions from the low-affinity isoform HK4 to the high-affinity isoform HK2, which exhibits enhanced catalytic activity (Bustamante and Pedersen, 1977). HK2 binds to mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC), localizing to the outer mitochondrial membrane (Wang et al., 2014). Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) inhibit HK2 binding to VDAC (Colquhoun, 2002), acting as anti-inflammatory agents that promote the conversion from the M1 to the M2 phenotype (Kawano et al., 2019). HK2 expression correlated with the SLC7A11/GPX4 axis, and HK2 deficiency results in increased macrophage death (Tan et al., 2022). PKM2, upregulated in M1 macrophages, regulates the Warburg effect by translocating to the nucleus and binding HIF-1α, promoting the inflammatory metabolic response that exacerbates lung injury (Yu et al., 2021; Christofk et al., 2008; Wang J. et al., 2022). Reducing PKM2 activity enhances the Warburg effect, further driving lung injury (Li et al., 2021). Nrf2 is a key regulator of glucose metabolism, and its knockdown reduces the expression of glycolytic genes, inhibiting the glycolytic pathway (Osburn et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2018).
2.7.2 Lipid metabolism
Phospholipid hydroperoxides, derived from PUFAs, are key products of lipid peroxidation and play a significant role in ALI. Fatty acyl-CoA synthase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) participates in lipid biosynthesis and catalyzes the conversion of PUFAs to PUFA-PLS, compromising plasma membrane integrity (Wang Y. et al., 2022). HIF-1α binds to the ACSL4 promoter and negatively regulates its transcription, while activating Nrf2 to enhance glycolysis (Li et al., 2024). Some hydroperoxides, along with free PUFAs, act as substrates for lipid signaling. The esterification of PUFAs to acyl-CoA by long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase and their subsequent incorporation into membrane phospholipids contributed to ALI pathogenesis by activating toll-like receptors, thereby exacerbating inflammation (Zou et al., 2019; Imai et al., 2008).
2.7.3 Amino acid and glutathione metabolism
Glutathione (GSH), an important antioxidant, plays a crucial role in reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and preventing oxidative damage (Xie et al., 2016). GSH synthesis depends on the cystine/glutamate antiporter system, which exchanges extracellular cystine for intracellular glutamate, a precursor for GSH synthesis. Under the catalytic activity of GPX4, GSH reduces lipid hydroperoxides to non-toxic alcohols, with its depletion leading to increased oxidative stress and cell death (Yang et al., 2014). Fatty acid-binding proteins derived from glutathione can mitigate ALI by modulating inflammatory responses and inhibiting Grx1 expression (Guo Y. et al., 2021).
2.7.4 Mitochondrial metabolism disorder
Mitochondria are central to cellular energy metabolism, and their dysfunction contributes significantly to ALI. Pathological mitochondrial changes, such as shrinkage, altered membrane density, and compromised membrane integrity, are common in ALI. Inhibition of Mucin-1 dimerization disrupts mitochondrial function by downregulation GPX4, GSH and SOD expression, leading to lipid peroxide accumulation and mitochondrial damage. Targeted mitochondrial antioxidants, such as MitoQ, can reduce mitochondrial ROS, inhibit ferroptosis, and alleviate ALI (Kufe, 2020; Wang Y. M. et al., 2022; Zhan et al., 2022; Bock and Tait, 2020).
2.7.5 Other regulatory mechanisms
Exosome, small vesicles containing RNA and proteins, serve as important mediators of intracellular communication, immune responses, and cellular regulation (Wang and Zhu, 2019; Jiang et al., 2019; Tavasolian et al., 2021). In ALI, exosomes derived from alveolar macrophages have been shown to regulate the Hippo signaling pathway via tRNA-derived fragments, participating in LPS-induced ALI (Wang W. et al., 2022).
2.8 Intestinal bacteria factor
The intestinal microbiota, comprising bacteria like Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus, plays a critical role in immune modulation (Zhou et al., 2020). Disruption of the gut microbiota can lead to systemic inflammation, contributing to ALI. Research suggests that the TLR-endoplasmic reticulum stress-ROS signaling pathway, activated by intestinal barrier dysfunction with gut microbiota, exacerbates lung injury by promoting systemic inflammatory responses (Gong et al., 2022).
3 Study on mechanism of TCM treatment of ALI
3.1 Compounds
Recent studies on the use of TCM for ALI have largely focused on therapies aimed at clearing heat and detoxifying, regulating fu-organs, and resolving blood stasis. Over the past 3 years, a significant body of clinical research has emerged in investigating TCM compound treatments for ALI (Gasmi et al., 2024; Ren, 2020; Li and Liang, 2019; Guo J. et al., 2021). These studies have helped to deepen our understanding of the mechanisms through which TCM influences ALI, establishing a foundation for evaluating the clinical efficacy of TCM-based therapies and supporting the development of novel therapeutic agents in the future.
3.1.1 Heat clearance and detoxification
The development of ALI is closely linked to the accumulation of pathogenic heat, which invades the lungs, cause fluid injury, depletes qi, and obstructs lung qi. Therefore, heat-clearing prescriptions are a key therapeutic approach in TCM for treating ALI (Lu et al., 2020). Studies have demonstrated that TCM formulas like Shenlian and Retong Fang markedly reduced mRNA levels of inflammatory factors (IL-6, IL-18 and MCP-1) and decrease protein levels of CD68, SP-A, and CC16 in rat lung tissue with ALI (Yang et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2010).
The Wenqing Decoction has been found to inhibit the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, reducing levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, RAGE, and various phosphorylated proteins (PI3K, AKT, p-PI3K, p-AKT) (Xie et al., 2024). Chaihuqingwen and Zukamu Granules have also proven effective by inhibiting phosphorylation of NLRP3, TLR4, NF-κBp65, and IκBα in rat lung tissue, along with caspase-1 mRNA and protein expression, thus modulating inflammatory responses (Zhou et al., 2023; Yu C. et al., 2024).
The Qingfeilitan Formula reduces mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and MDA in alveolar lavage fluid, while increasing the activity of antioxidants like SOD and GSH-Px, providing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects (Diao et al., 2022). Similarly, Qingfei Paidu Decoction inhibits macrophage polarization, downregulates IL-6, TNF-α, MIP-2, MCP-1, upregulates IL-10, and reduces nuclear translocation of key inflammatory mediators (TAK1, IKK, and p65) (Ye et al., 2023).
Additionally, some formulas like Yindan Jiedu Capsule, Xuanfei Baidu Decoction and Tanreqing target various inflammatory pathways, including the MAPK/NF-κB and NF-κB signaling pathways, offering broad anti-inflammatory effects (Feng et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023; Hu et al., 2022). Shufengjiedu Capsule prevents macrophage apoptosis by increasing A2A adenosine receptor expression and inhibiting NF-κB phosphorylation (Cai et al., 2022b). Maxingshigan Decoction has been found to reduce lung inflammation, enhance antioxidant activity, and regulate key inflammatory pathways including MAPK/NF-κB pathway (Hou et al., 2023).
Qingjie Huagong Formula has shown promise in improving lung and pancreatic and lung tissue pathology in SAP-ALI rat models, inhibiting the PI3K/AKT1 signaling pathway (Feng et al., 2024). Gegen Qinlian Decoction has been found to reduce lung inflammation, enhance antioxidant activity, and suppress C3, C5a, and IL-17 expression (Li W. et al., 2022).
3.1.2 The catharsis category of promoting bowel clearance and pulmonary Detoxification (Tongfu)
The Tongfu approach, known for its cathartic properties, is crucial in managing ALI. Tongfu Formula, in particular, inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, IL-18), STING pathway components (p-STING, STING) and inflammasome proteins (NLRP3, ASC) in mice with sepsis-induced ALI (Huo and Yue, 2024). Similarly, Tongfu Xiefei Enema Solution reduces mRNA expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and p38 MAPK, as well as the protein expression of p38, p-MLC/MLC2, and MLCK, contributing to improved ALI outcomes (Ma et al., 2024).
Tingli Dazao Xiefei Decoction and Xuanbai Chengqi Decoction demonstrate efficacy in reducing inflammation by regulating the PI3K, mTOR, HIF-1α, and p-AKT/AKT pathways, while also inhibiting glycolysis in lung tissue (Zhang et al., 2023; Wang S. et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2021). Research into lung-intestinal co-treatment for ALI has shown that the Dachengqi Decoction alleviates inflammation by regulating the NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway (Kou et al., 2022).
3.1.3 Enhancing blood circulation and resolving blood stasis
TCM formulas aimed at enhancing blood circulation and resolving blood stasis, such as Huoxue Huayu Decoction, play a significant role in treating ALI by activating qi and promoting blood flow. These formulas help mitigate lung damage and enhance the expression of tight junction proteins (ZO-1, Occludin, AQP-1, AQP-5) in the lung gas-blood barrier (Qin et al., 2025).
Qidong Huoxue Yin inhibits apoptosis in lung epithelial cells and reduces inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and chemokines in mice with ALI (Zheng et al., 2021). Xuebijing Injection mitigates inflammatory infiltration in ALI by antagonizing neutrophils and other immune cells (Zheng and Zhang, 2024). Other formulas, such as Qilongtian Capsule and Mailuo Yin regulate the NF-κB pathway and suppress inflammation by reducing the phosphorylation of MyD88, IκBα, and NF-κB (Luo et al., 2024; Miao et al., 2022).
3.1.4 Other formulas
Formulas like Xiaoxuming Decoction, traditionally used for stroke treatment, have shown potential in alleviating lung inflammation associated with ALI (Pei et al., 2023). Research indicates that Xiaoxuming decoction reduces levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 in LPS-induced cells and mitigates pyroptosis by inhibiting key inflammasome proteins (USP9X, NLRP3, IL-1β, Caspase-1) (Xiang et al., 2022; Xiang et al., 2021).
Similarly, both Jiegeng Decoction and Compound Houttuynia mixture reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory responses by inhibiting ROS production, mitochondrial membrane potential polarization, and the expression of inflammatory mediators, apoptotic proteins (Cleaved Caspase 3, Bax, Bcl2) and pyrogenic proteins (p-NF-κB,NLRP3, ASC, Cleaved-Caspase 1 and Cleaved-GSDMD) (Li, 2023; Wei, 2024). Further details are provided in Table 2, Figure 1.
TABLE 2
| Principles of TCM | Herb/Compound | Signal pathway | Dose | Index detection | Constitution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Clearance and Detoxification | Shenlian Fang | / | 8.64 g/kg | IL-6, IL-18, IL-1α, MCP-1, SP-A, CC16↓ | Panax ginseng C. A. Mey., Coptis chinensis Franch., Setaria italica (L.) Beauv., Citrus reticulata Blanco, Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn., Poria cocos (Schw.)Wolf, et al. |
| Retong Fang | / | 1 g/kg | TNF-α, IL-6, IL-18, IL-1α↓ | Arnebia euchroma (Royle) Johnst., Eschenbachia blinii (H.Lév.) Brouillet, Gentiana macrophylla Pall., et al. | |
| Wenqing Yin | PI3K/AKT | 10.8 g/kg | TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, RAGE, PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT, p-AKT↓ | Angelica sinensis (Oliv.)Diels, Paeonia lactiflora Pall., Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort., Coptis chinensis Franch., et al. | |
| Chaihuqingwen Granule | TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 | 8 g/kg | TLR4, NLRP3, NF-κB p65, p-IκBα↓ | Bupleurum chinense DC., Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.)Bge., Lonicera japonica Thunb., Coix lacryma-jobi L.var.mayuen (Roman.) Stapf, et al. | |
| Zukamu Granule | NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD | 2.34 g/kg | NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1, Cleaved-caspase-1 p20, IL-1β, IL-18↓ | Rheum palmatum L., Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., Mentha haplocalyx Briq., et al. | |
| Qingfeilitan Formula | TNF-α,Toll-Like | 10 mg/mL | TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β↓; SOD, GSH-Px↑ | Gypsum Fibrosum, Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim., et al. | |
| Qingfei Paidu Decoction | TAK1/IKK/NF-κB | / | IL-6, TNF-α, MIP-2, MCP-1, TAK1, IKK p-p65↓; IL-10↑ | Ephedra sinica Stapf, Prunus armeniaca L.var.ansu Maxim., Poria cocos (Schw.)Wolf, Bupleurum chinense DC., et al. | |
| Yindan Jiedu Capsule | NF-κB | 30% medicated serum | IκBα/p-IκBα, p65, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, NO↓ | Morus alba L., Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, Descurainia Sophia (L.)Webb. ex Prantl., Lonicera japonica Thunb., Scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl., et al. | |
| Xuanfei baidu Decoction | MAPK/NF-κB | 0.5 mg/mL; 2.16 g/kg | p-IKKα, p-NF-κB, p-IκBα, p-p38, p-Erk, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, PGC-1α, LC3B, Nrf1, JC-1, NLRP1, NLRP3, Caspase11↓; Mfn1, Mfn2, ATP↑ | Ephedra sinica Stapf, Prunus armeniaca L.var.ansu Maxim., Gypsum Fibrosum, Coix lacryma-jobi L.var.mayuen (Roman.)Stapf, Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.)DC., et al. | |
| Tanreqing | HMGB1/NF-κB/SNHG1 | 4 mL/kg | p-p65, p-p38, HMGB1, SNHG1, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-18, MCP-1, ROS↓ | Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, Selenarctos thibetanus (G. Cuvier), Capra hircus L | |
| Shufeng Jiedu Capsule | A2A/NF-κB | 0.5 mg/mL | A2A, p-IκB/IκB, p-p65/p65, Cc3, Bax/Bcl-2↓; PKA↑ | Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc., Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.)Vahl, Isatis indigotica Fort., Bupleurum chinense.DC, Dahurian Patrinia, Verbena officinalis L.,Phragmites communis Trin., Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch | |
| Maxingshigan Decoction | MAPK/NF-κB | 5.4 g/kg | IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, p38MAPK, JNK, ERK1/2↓; MDA, SOD, GSH↑ | Prunus armeniaca L.var.ansu Maxim., Gypsum Fibrosum, Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc., Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch | |
| Qingjie Huagong Formula | PI3K/AKT1 | 4.5 g/kg | TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6↓ | Bupleurum chinense DC., Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge., et al. | |
| Gegenqinlian Decoction | MAPK/NF-κB | 1.25 g/kg | TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, C3, C5a,IL-17↓ | Pueraria lobata (Willd.)Ohwi, Coptis chinensis Franch., Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., et al. | |
| The Catharsis Category of Promoting Bowel Clearance and Pulmonary Detoxification (Tongfu) | Tongfu Formula | mtDNA-STING-NLRP3 | 9.9 g/kg | IL-6, IL-1β, IL-18, p-STING, STING, NLRP3, ASC mRNA and protein ↓ | Rheum palmatum L., Prunus persica (L.) Batsch, Paeonia lactiflora Pall., et al. |
| Tongfu Xiefei Enema Solution | p38 MAPK/MLCK | 7.37 g/kg | TNF-1α, IL-1β, p38 MAPK mRNA and p38, p-MLC/MLC2 MLCK protein↓ | Ephedra sinica Stapf, Prunus armeniaca L.var.ansu Maxim., Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim., et al. | |
| Tingli dazao xiefei Decoction | PTEN/PI3K/AKT | 5.85 g/kg | IL-6, TNF-α, STAT3, SOC3, PI3K, AKT, p-AKT, PTEN↓ | Descurainia Sophia (L.) Webb.ex, Prantl., Ziziphus jujuba Mill | |
| Xuanbai Cheng Qi Decoction | NLRP3 inflammasome | 9 g/kg | NLRP3, Cleaved-Caspase1, GSDMD-N, IL-1β, pro-IL-1β, CXCL1, CXCL10, TNF-α, NLRP3, NF-κB P65 mRNA↓ | Gypsum Fibrosum, Rheum palmatum L.,Prunus armeniaca L.var.ansu Maxim., et al. | |
| Dachengqi Decoction | NF-κB/NLRP3 | 5 g/kg | p-p65/p65, p-IκBα/IκBα, NLRP3, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β↓ | Rheum palmatum L., Magnolia officinalis Rehd.et Wils., Citrus aurantium L., et al. | |
| Enhancing blood circulation and resolving blood stasis | Huoxue Huayu Decoction | ZO-1/Occludin | 7.2 g/kg | ZO-1, Occludin, AQP-1, AQP-5↑ | A.membranaceus (Fisch.)Bge., Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.)Nannf., Angelica sinensis (Oliv.)Diels., et al. |
| Qidong Huoxue Yin | iRhom2/TACE | 8 mL/kg | iRhom2, TACE, TNF-α, IL-6↓ | A.membranaceus (Fisch.)Bge., Angelica sinensis (Oliv.)Diels, Rheum palmatum L., et al. | |
| Xuebijing Injection | FPRs/NLRP3 | 12 mL/kg | FPR1, FPR2, NLRP3, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α↓ | Carthamus tinctorius L., Paeonia lactiflora Pall., Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort., Angelica sinensis (Oliv.)Diels., et al. | |
| Qilongtian Capsule | TLR4/NF-κB | 0.35 g/kg | TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, TLR4, NF-κBP65, NLRP3, MyD88 IκBα, NF-κBP65↓; IκBα↑ | Rhodiola crenulata (Hook. f. et Thoms.) H. Ohba, Panax notoginseng (Burk.)F. H.Chen, Pheretima aspergillum (E.Perrier) | |
| Mailuo Yin | TLR4/NF-κB | 1.25 μL/mL; 7.5 mL/kg | TLR4, MyD88, p-p65, p65, p-IκBα, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, MPO↓ | Lonicera japonica Thunb., Achyranthes bidentata BL., Scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl., Dendrobium nobile Lindl | |
| Others | Xiaoxuming Decoction | USP9X/NLRP3/Caspase-1/Pro Caspase-1 | 10 mg/L | USP9X, NLRP3, IL-1β, Pro-IL-1β, Caspase-1, Pro-Caspase-1↓ | Ephedra sinica Stapf, Panax ginseng C. A.Mey., Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi., et al. |
| Jiegeng Decoction | / | 250 mg/kg | TLR4, p-IKKβ, p-IKKα and p-IκBα↓ | Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A.DC., Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch | |
| Compound Houttuynia mixture | TLR7/MyD88/NF-κB | 5.46 g/kg; 87.4 mg/mL | TRAF6, IRF7, MyD88↓ | Houttuynia cordata Thunb., Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, Isatis indigotica Fort., et al. |
Summary of TCM Compounds for the prevention and treatment of ALI.
FIGURE 1
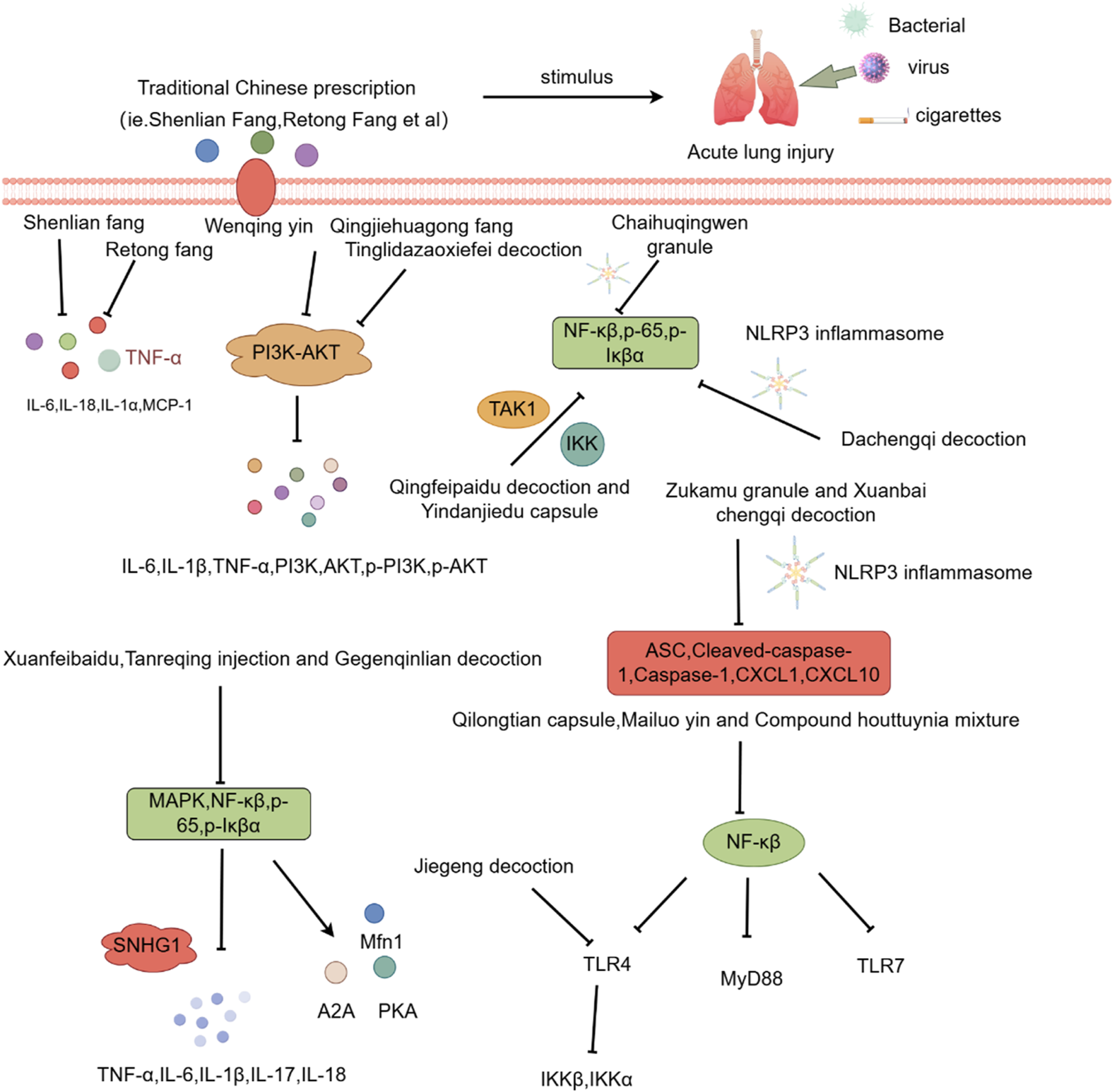
Investigation into the mechanism of TCM Compound in treating ALI.
3.2 Monomer components
This section systematically investigates the effects of monomer components with clinical therapeutic potential for treating ALI. These monomers have demonstrated diverse mechanisms of action, suggesting their promise as effective treatments for ALI.
3.2.1 Tanshinone ⅡA
Tanshinone ⅡA, when combined with carvedilol and simvastatin, is commonly used to treat cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease and heart failure (Shao et al., 2022). Recent research has shown that tanshinone ⅡA can mitigate ALI by inhibiting key signaling molecules, including ROCK2, NF-κB, Pro-caspase, P65, and IκBα, all of which play roles in inflammation and cell death (Liu J. et al., 2022).
3.2.2 Artemisinin
Known for its broad therapeutic potential against conditions like tumors, rheumatoid arthritis, and skin inflammation (Zhao et al., 2024; Liu Y. J. et al., 2022), artemisinin has also shown promise in ALI treatment. Studies suggest it alleviates lung injury by suppressing inflammatory factors, myeloperoxidase (MPO), malondialdehyde (MDA), and other oxidative stress markers. Additionally, it reduces the expression of p-AKT and HO-1 proteins, contributing to its protective effects on the lung injury (Ji et al., 2023).
3.2.3 Glycyrrhizin
Glycyrrhizin, and its derivatives, have been shown to reduce serum inflammatory markers and transaminase levels in viral hepatitis (Guo, 2024). In ALI, glycyrrhizin helps by inhibiting ROS production in LPS-induced cells, downregulating p-PI3K and p-AKT protein levels, and reducing the formation of NLRP3 inflammasome. These actions help protect against ALI by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation (Wang K. et al., 2020).
3.2.4 Andrographolide
Primarily used to treat bacterial pneumonia and other inflammatory conditions (Xu, 2016; Song, 2022), andrographolide has been shown to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation, reducing inflammatory factor and alleviating lung epithelial cell damage (Qin et al., 2024).
3.2.5 Huperzine-A
Typically used in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia (Wang et al., 2023; Lu et al., 2021), huperzine-A also exhibits nti-inflammatory effects in ALI. It reduces levels of IL-6, MDA, and ROS, while increasing SOD levels, which contribute to its therapeutic effects in lung injury (Shi et al., 2024).
3.2.6 Cepharanthine
Although primarily used to treat leukopenia in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, cepharanthine has shown potential in treating ALI by improving immune function and reducing inflammation (Ge et al., 2023). Stephanolin, a related compound, has been shown to reduce viral RNA and virus production, suggesting its potential in viral-induced ALI (Fan et al., 2020).
3.2.7 Chloroquine
As a 4-aminoquinoline antimalarial drug, chloroquine is alsoused to treat autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. It works by improving lysosomal pH, inhibiting autophagosome-lysosome fusion, and enhancing CXCR4 expression, thereby reducing inflammation and alleviating ALI (Yan et al., 2013).
3.2.8 Total paeony glycosides
These compounds inhibit mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) oxidative stress and block NLRP3 inflammasome activation. This significantly contributes to the treatment of ALI by reducing inflammation and cellular damage (Xu Y. J. et al., 2024).
3.2.9 Diacerein
As a derivative of rhein, diacerein is commonly used for degenerative joint diseases. Recently, diacerein has demonstrated potential in treating ALI by reducing the Sphk1/S1P axis and inhibiting GSK-3β, STAT3, and Caspase-3. It also increases BCL-2 protein expression, which plays a role in cell survival and inflammation regulation (Youssef et al., 2022). Further details are provided in Table 3, Figure 2.
TABLE 3
| Monomer compounds | CAS | Molecular formula | In vivo and in vitro models | Pertinent pharmacological targets | Investigation of the relevant mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
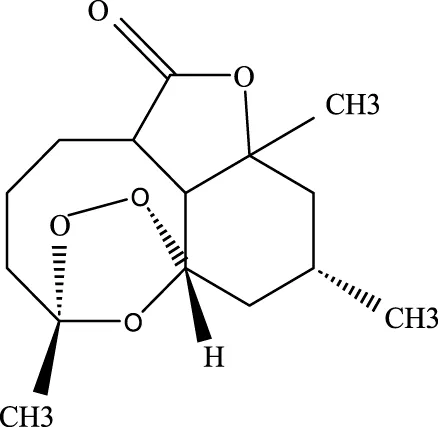
Artemisinin |
63968–64-9 | C15H22O5 | Ischemia-reperfusion modeling | TNF-a, IL-6, IL-1β, MDA, MPO, p-AKT, HO-1↓ | Artemisinin has the potential to suppress the expression of inflammatory responses, thereby mitigating ALI. |
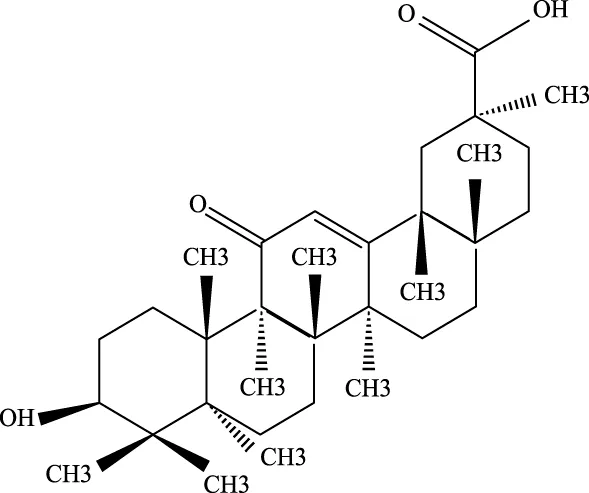
Glycyrrhetinic Acid |
471–53-4 | C30H46O4 | Intraperitoneal administration of LPS at a dose of 10 mg/kg | ROS, p-PI3K, p-AKT, Cleaved Caspase-1 and NLRP3 ↓ | Glycyrrhizic acid and its derivatives mitigate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in LPS-induced cells, downregulate the protein levels of phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (p-PI3K) and phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT), reduce the expression of cleaved Caspase-1 and NLRP3, and inhibit the formation of NLRP3 inflammasomes, thereby providing protection against ALI. |
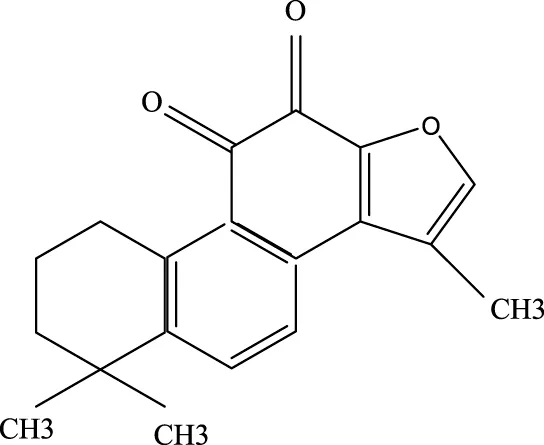
Tanshinone IIA |
568–72-9 | C19H18O3 | LPS was used to induce RLE-6TN cells. The sepsis model was established through cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) | ROCK2, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, Caspase, pro-caspase, P65, IkBα↓ | TIIA improved sepsis-induced lung injury by downregulating ROCK2 and further inactivating the NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro |
Andrographis |
5508–58-7 | C20H30O5 | CLP mouse model | TNF-α, IL-1β↓ | Andrographis suppresses the activation and release of inflammasomes, consequently inhibiting the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, which is beneficial for the treatment of ALI. |
Huperzine A |
102518–79-6 | C15H18NO2 | Intratracheal administration of LPS at a dose of 5 mg/kg | IL-6, MDA, ROS↓; SOD↑ | Huperzine A can decrease the concentrations of IL-6, MDA, and ROS while increasing the concentration of SOD, thereby contributing to the treatment of ALI. |
Cepharanthine |
481–49-2 | C37H38N2O6 | / | / | Cepharanthine tablets significantly decrease viral RNA levels and inhibit viral replication, thereby mitigating acute lung injury |
Chloroquine |
54–05-7 | C18H26ClN3 | Infection with the H5N1 influenza virus | PH, CXCR4↑ | Chloroquine elevates lysosomal pH, inhibits the fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes, degrades lysosomal proteins, upregulates the expression of CXCR4 in vivo, thereby alleviating ALI. |
White Paeony |
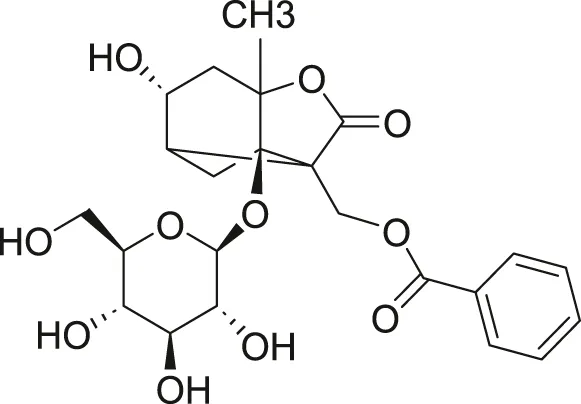
39011–90-0 | C23H28O11 | Intratracheal administration of LPS at a dose of 50 ng/mL | IL-1β, IL-18, IL-6, TNF-α, ASC, NLRP3↓ | Total paeony glycosides capsules may ameliorate ALI in mice through the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation |
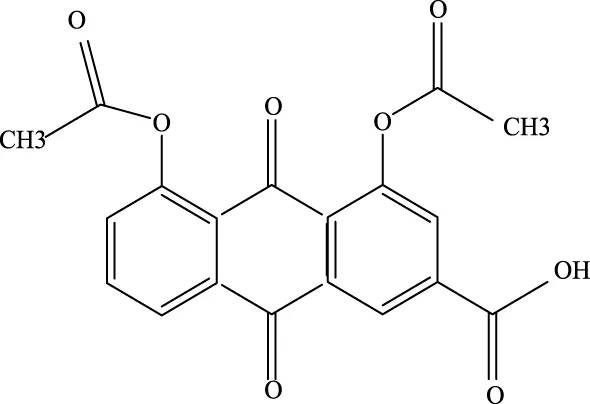 Diacerein Diacerein |
13739–02-1 | C19H12O8 | Intraperitoneal injection of LPS at 5 mg/kg | Sphk1/S1P, GSK-3β, STAT3, Caspase-3↓; BCL-2↑ | Diacerein can modulate the Sphk1/S1P axis, reduce the levels of GSK-3β, STAT3, and Caspase-3, while increasing the expression of BCL-2 protein, thereby contributing to the treatment of acute lung injury |
Investigation into the mechanism of monomer components in the treatment of ALI.
FIGURE 2
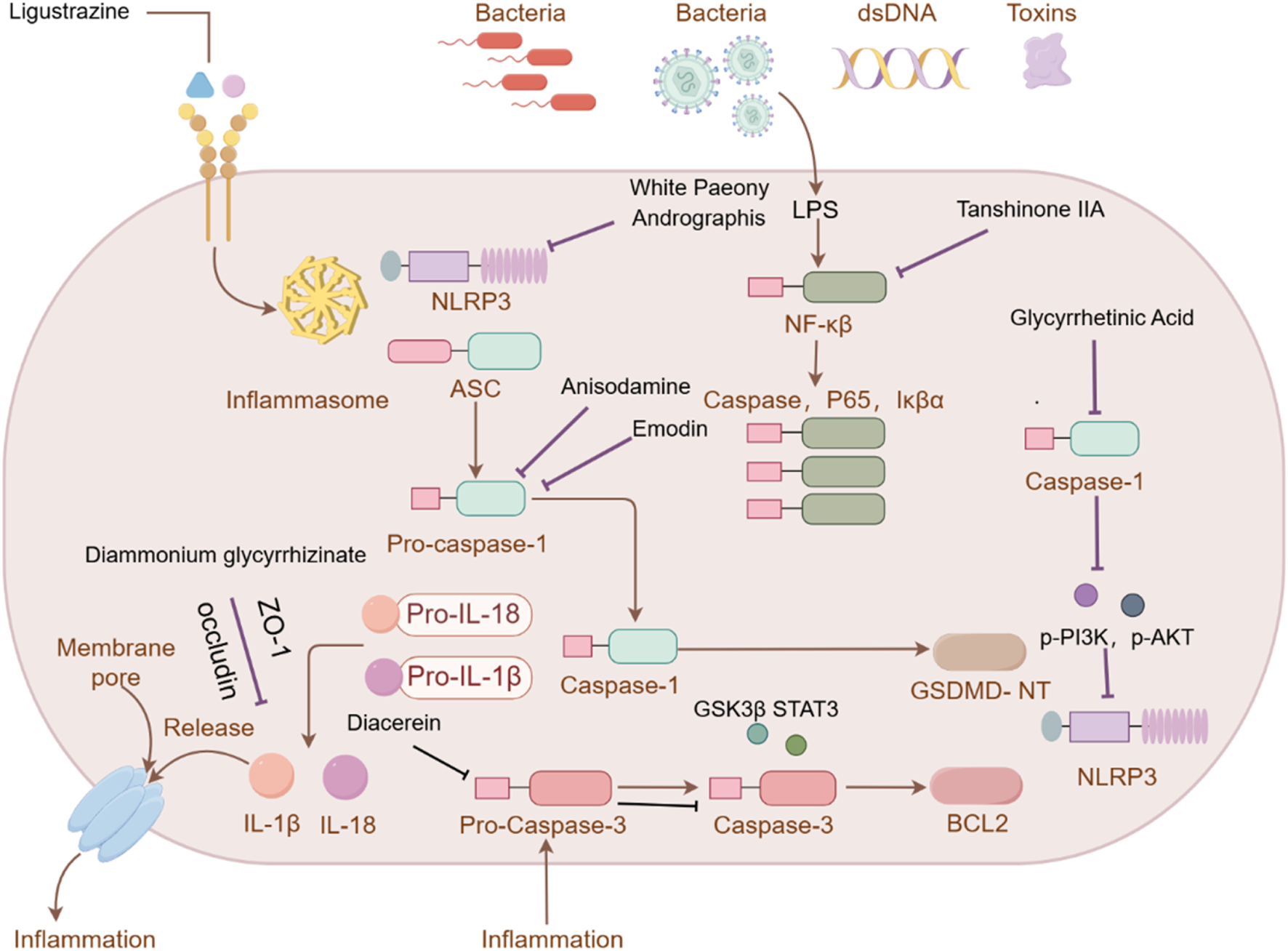
Investigation into the targets of TCM monomers and derivatives for the treatment of ALI.
4 Clinical research on the treatment of acute lung injury with Traditional Chinese Medicine
4.1 The significance and current status of clinical research
The application progress of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the clinical treatment of acute lung injury (ALI) is substantial, demonstrating promising therapeutic potential. As research advances from cell culture to clinical trials, findings from basic studies are increasingly being translated into clinical practice. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) serve as a critical methodology for evaluating the efficacy of TCM interventions in ALI. These trials provide valuable evidence and a scientific foundation for understanding the potential benefits of TCM in managing ALI (Zheng et al., 2024).
In recent years, a growing number of high-quality clinical studies have demonstrated the notable efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in treating acute lung injury (ALI). Particularly within an integrated treatment framework combining both TCM and Western medicine, this approach has been shown to effectively alleviate clinical symptoms, modulate inflammatory responses, improve oxygenation function, and significantly reduce patient mortality rates.
4.2 Clinical evidence of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in treatment
4.2.1 Clinical application of compound preparations
4.2.1.1 Baofeijiejiong mixture
A randomized controlled study involving 60 patients with acute lung injury (ALI) caused by sepsis demonstrated that the integration of traditional Chinese and Western medicine treatments—specifically Pulmonary Protective and Baofeijiejiong mixture—significantly reduced the 7-day mortality rate among ALI patients compared to treatment with Western medicine alone. Furthermore, this integrative approach enhanced the overall efficacy of Western medical treatment. Following the intervention, notable improvements were observed in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) symptom scores, including symptoms such as fever, dyspnea, and sputum production. Inflammatory markers, such as IL-8 and TNF-α, showed a marked decrease, while organ function indicators, including SOFA and APACHE II scores, significantly improved. Additionally, levels of biomarkers such as white blood cell count, C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin (PCT) were also reduced. Importantly, this therapeutic strategy decreased the need for invasive mechanical ventilation, thereby lowering the incidence of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) in patients with sepsis-induced ALI (Su, 2015).
4.2.1.2 Dachengqi Decoction
In a clinical study involving 68 patients with acute lung injury (ALI), administration of Dachengqi Decoction via nasogastric feeding demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) syndrome score of Yangming Fu in postoperative ALI patients, thereby effectively alleviating clinical symptoms such as profuse sweating, abdominal distension, and pain. Laboratory analyses revealed that following treatment, levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-1 (IL-1) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were markedly decreased, while the alveolar-arterial oxygen pressure difference P (Aa)o2 improved significantly. Additionally, the duration of mechanical ventilation was notably shortened (Li Y. et al., 2022).
4.2.1.3 Yiqihuoxuexiezhuo formula
Professor Chao Enxiang, a master of traditional Chinese medicine, formulated a therapeutic regimen aimed at tonifying qi, resolving turbidity, and promoting blood circulation. This formula demonstrated significant efficacy in a randomized controlled trial involving 60 patients with acute lung injury. In the study, patients were randomly assigned to either the control group, which received standard Western medical treatment (including lung-protective ventilation strategies), or the experimental group, which received the same standard treatment supplemented with the TCM formula. The results indicated that following treatment, the experimental group exhibited marked improvements in oxygenation-related parameters, including heart rate, arterial partial pressure of oxygen, and Sao2 levels. Additionally, biomarkers such as white blood cell count, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin showed notable reductions, while levels of inflammatory cytokines—including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8—decreased significantly. These findings provide strong evidence supporting the clinical application of the qi-tonifying, turbidity-resolving, and blood-circulation-promoting formula in the management of acute lung injury (Ren, 2020).
4.2.1.4 Tongfu Xiefei Formula
A study involving 40 patients with acute lung injury caused by phlegm-heat congestion syndrome revealed that Tongfu Xiefei Formula could effectively reduce the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (Paco2), significantly increase the oxygenation index, and simultaneously decrease levels of DAO, MDA, NO, and inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby demonstrating a therapeutic effect on acute lung injury (Cheng, 2020).
4.2.1.5 Qingwen Badu Yin
A randomized controlled trial conducted on 70 patients indicated that the addition of Qingwen Badu Yin to conventional treatment resulted in increased arterial partial pressure of oxygen (Pao2) and oxygenation index (Pao2/Fio2) compared to baseline measurements. Additionally, Paco2 levels were reduced after treatment, with more pronounced improvements observed in the treatment group (P < 0.05). Furthermore, serum levels of PCT, IL-6, TNF-α, and CRP were significantly decreased, and scores on the SOFA, APACHE II, and Murray lung injury scales were notably improved (Xu A. P. et al., 2024).
4.2.1.6 Shengjiang Lifei Decoction
In a randomized controlled trial involving 60 patients, the treatment group received Shengjiang Lifei Decoction in conjunction with standard Western medical therapy. Following a seven-day treatment period, both groups exhibited improvements in Pao2, PaCo2, and oxygenation index compared to pre-treatment values, with greater therapeutic effects observed in the treatment group. Moreover, the duration of mechanical ventilation and ICU length of stay were shorter in the treatment group than in the control group. No adverse reactions were reported in either group throughout the treatment period, confirming that Shengjiang Lifei Decoction can enhance pulmonary function and alleviate clinical symptoms in patients with sepsis-induced ARDS, with favorable safety profile (Li G. C. et al., 2019).
4.2.2 Clinical application of Traditional Chinese Medicine injections
4.2.2.1 Shenfu Injection
In a randomized controlled trial involving 50 patients with acute lung injury (ALI), treatment with Shenfu Injection led to a significant reduction in levels of inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). Additionally, prothrombin time was shortened, and D-dimer levels were markedly decreased compared to baseline (Zhang et al., 2022).
4.2.2.2 Xuebijing Injection
As one of the most widely prescribed traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) injections in current clinical practice, Xuebijing Injection has demonstrated notable therapeutic efficacy in managing ALI. Clinical evidence indicates that following intervention with Xuebijing Injection, multiple clinical and physiological parameters showed significant improvement. These include Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome scores, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) scores, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores, Murray Lung Injury scores, plateau pressure, and driving pressure (ΔP). Furthermore, levels of inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, interleukin-6, heparin-binding protein, white blood cell count, neutrophil count, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and D-dimer were significantly reduced. Concurrently, pulmonary function indices—including arterial oxygen partial pressure (Pao2), oxygenation index (Pao2/Fio2), and static lung compliance—as well as immune function indicators such as CD3+, CD4+, and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio were notably elevated (Ding et al., 2024).
4.2.2.3 Reduning Injection
Clinical investigations have revealed that Reduning Injection can substantially enhance cellular immune function in patients. The treatment group exhibited higher levels of CD3+, CD4+, and CD4+/CD8+ compared to the control group. The short-term overall effective rate in the treatment group reached 90.91%, significantly surpassing the 68.18% observed in the control group. More importantly, during a six-month follow-up period, the survival rate in the treatment group was 67.50%, compared to 56.67% in the control group, indicating sustained clinical benefits (Li et al., 2020).
4.2.3 Clinical applications of monomers derived from Traditional Chinese Medicine and their derivatives
TCM monomers and their derivatives are diverse in nature, with complex structures and a broad range of pharmacological activities. Recent studies have increasingly highlighted the significant potential of these monomers and their combinations (i.e., component-based TCM) in treating ALI, offering safer and more effective therapeutic options for clinical use. While several reviews have extensively explored the mechanisms and clinical applications of TCM monomers in preventing and treating ALI, this paper aims to provide a deeper analysis by focusing specifically on the clinical applications of these monomers and their derivatives.
Although most studies on the efficacy of TCM monomers in treating ALI is still in the preclinical stage, their therapeutic potential is being reevaluated for both prevention and treatment, whether as individual monomers or in synthetic formulations. The primary objective of this section is to investigate the mechanisms through which these TCM monomers act in ALI treatment, thus laying a scientific foundation for their future clinical applications. Several TCM monomers have shown promising results in treating ALI, demonstrating their potential to modulate immune responses, reduce inflammation, and improve lung function.
4.2.3.1 Ligustrazine
This compound has been shown to reverse macrophage polarization, reduce pyroptosis, and exert anti-ALI effects (Jiang R. et al., 2021). Clinical studies indicate that tetramethylpyrazine injection, which contain ligustrazine, significantly improve patients’ Pao2/Fio2 ratios and respiratory rates. It also reduces systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and lowers APACHE II scores, as along with decreasing levels of IL-6, C-reactive protein (CRP), nitric oxide (NO). These effects help alleviate ALI symptoms and promote recovery (Liu et al., 2019).
4.2.3.2 Diammonium glycyrrhizinate
This compound mitigates LPS-induced ALI by improving vascular endothelial barrier function (Liu et al., 2021). When combined with Astragalus injection, diammonium glycyrrhizinate significantly increases Po2/Fio2 ratios in patients, while also markedly reducing lactate (Lac), CRP, lung injury scores, APACHE-Ⅱ scores, and SIRS scores (Li et al., 2020).
4.2.3.3 Anisodamine
Preclinical studies suggest that anisodamine inhibits inflammasome activation, thereby suppressing macrophage pyroptosis (Zhang et al., 2024). In a clinical study involving 78 patients who developed ALI after lung cancer surgery, intravenous administration of anisodamine over 48 h reduce the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and procalcitonin (PCT). Additionally, it improves lung compliance, Pao2, and oxygenation indices, demonstrating its protective effects against ALI following thoracotomy for lung cancer (Du et al., 2017).
4.2.3.4 Diacerein
Through randomized, double-blind clinical trials, it was demonstrated that Diacerein can inhibit the secretion of IL-1β on the surface of human neutrophils during viral replication and downregulate the expression levels of NLRP3, Caspase-1, and GSDMD (Carmo et al., 2024). According to the World Clinical Trial Database, a study involving 40 patients with COVID-19 was conducted using diacerein as an intervention. Serum samples collected 10 days after treatment were analyzed for changes in biomarkers such as IL-1β, IL-8, IL-6, C-reactive protein and troponin. However, the results of this trial have not yet been disclosed (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São, 2022). Further details are provided in Table 4.
TABLE 4
| Monomer species | CAS | Molecular formula | Case | Appropriate clinical evaluation metrics | Clinical research |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
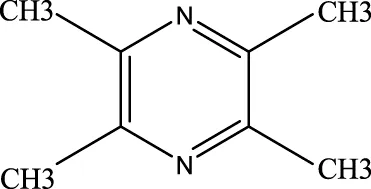
Ligustrazine |
1124–11-4 | C8H12N2 | 55 | SIRS, APACHEⅡ score, IL-6, C-protein, NO↓ | Ligustrazine can decrease the incidence of lung injury and improve patients’ respiratory rates |
Diammonium glycyrrhizinate |
79165–06-3 | C42H65NO16 | 60 | Lac, CRP, lung injury score, APACHE-Ⅱ, SIRS↓ | Diammonium glycyrrhizinate can enhance the PO2/FiO2 ratio while reducing lactate (Lac), C-reactive protein (CRP), lung injury score, APACHE-II score, and SIRS score |
Anisodamine |
55869–99-3 | C17H23NO3 | 78 | TNF-α, IL-6, hs-CRP, PCT↓ | Anisodamine reduces the expression of hs-CRP, and PCT while enhancing lung compliance, PaO2 levels, and the oxygenation index |
Diacerein |
13739–02-1 | C19H12O8 | 40 | IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, C-reactive protein | / |
Clinical applications of monomeric components in the treatment of ALI.
5 Discussion
According to the theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), acute lung injury (ALI) can be categorized under syndromes such as “asthma syndrome” and “sudden asthma”. Its etiology primarily involves pathological changes including deficiency of vital energy and accumulation of pathogenic toxins in the lungs. Consequently, clinical treatment strategies emphasize replenishing qi, nourishing Yin, clearing heat, and detoxifying (Xie et al., 2008). The pathogenesis of ALI involves a complex interplay of multiple pathophysiological mechanisms. Key pathogenic processes include excessive inflammatory response, disruption of the alveolar-capillary barrier, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. During the initial phase of lung injury—triggered by factors such as infection, trauma, or aspiration—pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) activate alveolar macrophages and neutrophils, resulting in the release of substantial amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. These cytokines further recruit additional immune cells, leading to an inflammatory cascade (Vora et al., 2021). Concurrently, activated neutrophils secrete proteases, including elastase, along with reactive oxygen species (ROS), which directly damage alveolar epithelial and vascular endothelial cells. This results in the degradation of tight junction proteins, such as ZO-1 and Occludin, increased vascular permeability, and the development of pulmonary edema (Yu L. C. et al., 2024). Moreover, dysfunction and apoptosis of alveolar type II epithelial cells (AT2) impair surfactant production, thereby exacerbating alveolar collapse. Recent studies have also indicated that cellular metabolic reprogramming, mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and regulated cell death pathways like ferroptosis and pyroptosis are not mere consequences but are central drivers of ALI progression, modulating apoptotic and autophagic pathways (Wang et al., 2025; Taheri et al., 2024). These mechanisms interact synergistically, forming a self-amplifying cycle that culminates in impaired gas exchange and respiratory failure.
Although significant progress has been made in the clinical and experimental research on TCM for ALI, there are still many issues worthy of in-depth exploration. Firstly, the quintessential strength of TCM lies in its holistic regulation and personalized treatment based on syndrome differentiation. Therapeutic principles such as clearing heat and resolving phlegm, or promoting blood circulation to unblock meridians, do not merely suppress excessive inflammatory responses but also aim to improve microcirculation and promote tissue repair. This multi-target, systematic approach contrasts sharply with the single-target interventions often prioritized in Western medicine. However, a critical gap remains: most current studies focuses on the mechanisms of single herbs or monomer components, while the synergistic effects arising from the complex interplay of components within a formula—governed by the principles of “sovereign, minister, assistant, and messenger” — are poorly understood. Bridging this gap is essential to elucidating the material basis of TCM efficacy. Secondly, while the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms of certain TCM monomers (such as artemisinin and tanshinone IIA) have been well-characterized, translating these findings into clinical practice requires overcoming significant hurdles, such as optimizing dosage for a precise therapeutic window that balances efficacy with safety, and developing novel drug delivery systems to improve bioavailability at the target site.
The rapid evolution of multi-omics technologies presents a paradigm-shifting opportunity for TCM pharmacology. An integrated multi-omics analysis, combining genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, can provide an unbiased, panoramic view of the body’s response to TCM interventions. This approach allows us to move beyond a one-molecule-one-target framework and instead map the complex interaction network through which TCM components modulate the genome, transcriptome, and proteome, thus revealing the multi-level regulatory landscape of TCM. Network pharmacology, as a computational method, further helps to deconstruct this complexity by identifying core targets and pathways, providing a robust theoretical basis for clinical applications (Wang Z. Y. et al., 2022). Furthermore, the combination of cutting-edge technologies, such as single-cell technology and spatial omics technology, has brought new opportunities and challenges to dissect the mechanism of TCM in modulating cellular and spatial heterogeneity (Chen et al., 2022). Through these technologies, we can pinpoint how specific TCM formulas regulate distinct cell populations (e.g., macrophage subtypes, endothelial cells) within the lung microenvironment and understand the spatial distribution of key proteins, thereby offering a more comprehensive explanation of TCM’s therapeutic mechanisms. This is a key direction for future work.
TCM compound prescriptions are the cornerstone of clinical TCM practice. However, due to the complex chemical composition of medicinal materials used in these formulations and the influence of multiple factors—including the origin of raw materials, processing methods of decoction pieces, and production techniques—the quality control of TCM faces significant challenges, often summarized as “uncertain efficacy and imprecise dosage”. This has become a major bottleneck for modernization, industrialization, and internationalization of TCM (Sun et al., 2017). Therefore, it is imperative to establish a multi-dimensional quality control system. This system should integrate qualitative and quantitative dual-standards, spectroscopic-effect relationship analyses, network pharmacology- and metabolomics-based identification of quality markers (Q-markers), and the combination of multi-component quantification with bioactivity assays. Only through such a comprehensive quality evaluation system can we ensure the consistency and reliability of TCM preparations (Lu et al., 2024).
In the management of ALI, an integrative model combining TCM and Western medicine holds immense untapped potential. Western medicine provides objective, quantifiable biomarkers and rapid, life-sustaining interventions. In contrast, TCM emphasizes individualized treatment and holistic regulation, which can be highly beneficial for alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life (Yu et al., 2023). However, a significant challenge lies in reconciling their different diagnostic and therapeutic philosophies within the rigid framework of conventional randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The “one-size-fits-all” design of RCTs often conflicts with the personalized nature of TCM syndrome differentiation, potentially masking the true efficacy of a formula when applied to a heterogeneous patient population. Thus, future clinical trial designs should incorporate biomarker-guided patient stratification or adaptive designs that allow for treatment adjustments based on TCM pattern diagnosis. Merging TCM’s holistic and individualized approach with Western medicine’s precise and emergency care models represents the most promising path forward for optimizing patient outcomes in ALI (Li et al., 2025).
Finally, conventional pharmacokinetics, which focuses on systemic drug exposure, often overlooks the critical role of the gut. Many TCM components have low oral bioavailability and exert their effects by modulating the gut microbiota or being transformed into active metabolites by it. Therefore, it is essential to investigate the “substance-effect” relationship within the intestinal lumen, clarifying how TCM components and their gut microbial metabolites interact to produce therapeutic effects or adverse reactions. This will provide a more complete picture of the multi-target interaction profiles of TCM and enhance the safety and efficacy of its clinical application (Zhu et al., 2024).
6 Conclusion
In conclusion, this review has systematically summarized the multifaceted pathogenesis of ALI and highlighted the significant therapeutic potential of TCM, acting through multi-component, multi-target, and multi-pathway mechanisms. While promising, the translation of TCM from bench to bedside requires a concerted effort to address existing challenges. Future efforts should prioritize the accumulation of high-quality clinical evidence through innovatively designed multicenter, international collaborations to achieve broader recognition from the mainstream medical community. Clinically, integrating TCM syndrome differentiation with modern diagnostic biomarkers can enable a more personalized and precise application of therapies, creating a synergistic effect that offers more comprehensive treatment for ALI patients. Mechanistically, the application of multi-omics and systems biology approaches is crucial for elucidating the complex pharmacological basis of TCM’s efficacy. Additionally, exploring the novel therapeutic potential of existing TCM components and strengthening evidence-based research on integrative medicine will not only elevate therapeutic outcomes but also enhance the scientific rigor and validation of TCM, providing a more reliable foundation for clinical decision-making in the fight against ALI.
Statements
Author contributions
JW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. ZY: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. XZ: Writing – original draft. SW: Investigation, Software, Writing – review and editing. LJ: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Validation, Writing – review and editing. BZ: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. BT: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. AY: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The present research was supported from the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (No. ZXS004R4-1, No. ZD2021CY001), the Shuguang Hospital Research Funding Project (SG3915) and the Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Budget Project (2021LK075).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Aulakh G. K. (2018). Neutrophils in the lung: the first responders. Cell Tissue Res.371 (3), 577–588. 10.1007/s00441-017-2748-z
2
Bhatia M. Zemans R. L. Jeyaseelan S. (2012). Role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol.46 (5), 566–572. 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0392TR
3
Bock F. J. Tait S. W. (2020). Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.21 (2), 85–100. 10.1038/s41580-019-0173-8
4
Burkard P. Schonhart C. Vögtle T. Köhler D. Tang L. Johnson D. et al (2023). A key role for platelet GPVI in neutrophil recruitment, migration, and NETosis in the early stages of acute lung injury. Blood142 (17), 1463–1477. 10.1182/blood.2023019940
5
Bustamante E. Pedersen P. L. (1977). High aerobic glycolysis of rat hepatoma cells in culture: role of mitochondrial hexokinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.74 (9), 3735–3739. 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3735
6
Cai J. Wang Y. L. Sheng X. D. Zhang L. Lv X. (2022b). Shufeng jiedu capsule inhibits inflammation and apoptosis by activating A2AAR and inhibiting NF-κB to alleviate LPS-induced ALI. J. Ethnopharmacol.298, 115661. 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115661
7
Cai J. Xu G. Lin Y. Zhou B. Luo Z. Yu S. et al (2022a). Inhibition of TRPV4 attenuates ferroptosis against LPS-induced ALI via Ca2+ pathway. Turk J. Biol.46 (6), 465–474. 10.55730/1300-0152.2632
8
Cao J. Ding C. Huang J. Chen Y. Chen Y. (2023). Pulmonary vascular endothelial glycocalyx degradation contributes to acute lung injury in experiencing heatstroke. Shock59 (6), 966–972. 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002130
9
Cao Z. Qin H. Huang Y. Zhao Y. Chen Z. Hu J. et al (2022). Crosstalk of pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2-related mechanisms in sepsis-induced lung injury in a mousemodel. Bioengineered13 (3), 4810–4820. 10.1080/21655979.2022.2033381
10
Carmo H. R. P. Castillo A. R. Bonilha I. Gomes E. I. L. Barreto J. Moura F. A. et al (2024). Diacerein reduces inflammasome activation and SARS-CoV-2 virus replication: a proof-of-concept translational study. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1402032. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1402032
11
Che J. Wang H. Dong J. Wu Y. Zhang H. Fu L. et al (2024). Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell‐derived exosomes attenuate neuroinflammation and oxidative stress through the NRF2/NF‐κB/NLRP3 pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther.30 (3), e14454. 10.1111/cns.14454
12
Chen D. S. (2022). Research on the mechanism of CMPK2 regulating TNF-α affecting acute lung injury in sepsis. Zhejiang: Chin. People's lib. Army Navy Mil. Med. Univ.10.26998/d.cnki.gjuyu.2022.000218
13
Chen J. Luo P. Wang C. Yang C. Bai Y. He X. et al (2022). Integrated single-cell transcriptomics and proteomics reveal cellular-specific responses and microenvironment remodeling in aristolochic acid nephropathy. JCI Insight7 (16), e157360. 10.1172/jci.insight.157360
14
Chen J. D. Gong D. Yi Y. H. Chen Y. (2021). The role of vascular endothelial glycocalyx in the pathological mechanism, diagnosis and treatment of sepsis-related acute lung injury. Med. J. People's Liberation Army46 (04), 398–403. 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.04.13
15
Chen X. Tang J. Shuai W. Meng J. Feng J. Han Z. (2020). Macrophage polarization and its role in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflamm. Res.69 (9), 883–895. 10.1007/s00011-020-01378-2
16
Chen Y. (2022). Heat shock protein 70 promotes pulmonary inflammatory response in mice with acute lung injury. Anhui: Bengbu medical college. 10.26925/d.cnki.gbbyc.2022.000141
17
Cheng L. (2020). “Clinical and experimental research on the treatment of sepsis-related acute respiratory distress syndrome with tongfu xiefei formula,”. Jiangsu: Nanjing University of Chinese medicine. 10.27253/d.cnki.gnjzu.2020.000256
18
Christofk H. R. Vander H. M. G. Harris M. H. Ramanathan A. Gerszten R. E. Wei R. et al (2008). The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature452 (7184), 230–233. 10.1038/nature06734
19
Colquhoun A. (2002). Gamma-linolenic acid alters the composition of mitochondrial membrane subfractions, decreases outer mitochondrial membrane binding of hexokinase and alters carnitine palmitoyltransferase I properties in the walker 256 rat tumour. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1583 (1), 74–84. 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00162-2
20
Cui A. F. Shao Y. Y. Wang H. D. Song J. Y. Wang Y. (2024). Immune cells and cytokines in the research progress in the treatment of acute lung injury. J. Of Clin. Med. Pract.33 (02), 114–117. 10.16047/j.cnki.cn14-1300/r.2024.02.005
21
Dagvadorj J. Shimada K. Chen S. Jones H. D. Tumurkhuu G. Zhang W. et al (2015). Lipopolysaccharide induces alveolar macrophage necrosis via CD14 and the P2X7 receptor leading to interleukin-1α release. Immunity42 (4), 640–653. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.03.007
22
Del Sorbo L. Goffi A. Ranieri V. M. (2011). Mechanical ventilation during acute lung injury: current recommendations and new concepts. Presse Med.40, 569–583. 10.1016/j.lpm.2011.05.028
23
Diao Y. Ding Q. Xu G. Li Y. Li Z. Zhu H. et al (2022). Qingfei litan decoction against acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome: the potential roles of anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects. Front. Pharmacol.13, 857502. 10.3389/fphar.2022.857502
24
Ding W. C. Chen J. Ye Y. Sun Z. R. Nie S. N. (2024). The clinical efficacy of xuebijing injection in the treatment of patients with pulmonary blood stasis syndrome in sepsis-related acute respiratory distress syndrome. Chin. Herb. Med.55 (19), 6645–6654. 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2024.19.018
25
Dong J. Liu W. Liu W. Wen Y. Q. Liu Q. G. Wang H. T. et al (2024). Acute lung injury: a view from the perspective of necroptosis. Inflamm. Res.73 (6), 997–1018. 10.1007/s00011-024-01879-4
26
Du N. Wang M. Zhang Y. F. Sun X. Ren H. Liu D. P. (2017). The protective effect of anisodamine on acute lung injury after thoracotomy for lung cancer. Mod. Oncol. Med.25 (23), 3770–3772. 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2017.23.012
27
Esquivel-Ruiz S. González-Rodríguez P. Lorente J. A. Pérez-Vizcaíno F. Herrero R. Moreno L. (2021). Extracellular vesicles and alveolar epithelial-capillary barrier disruption in acute respiratory distress syndrome: pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential. Front. Physiol.12, 752287. 10.3389/fphys.2021.752287
28
Fan H. H. Wang L. Q. Liu W. L. An X. P. Liu Z. D. He X. Q. et al (2020). Repurposing of clinically approved drugs for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in a 2019-novel coronavirus-related coronavirus model. Chin. Med. J.133 (09), 1051–1056. 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000797
29
Feng M. C. Luo F. Tang X. P. Li K. Zhu X. D. Zhang B. Y. (2024). The therapeutic effect and mechanism of qingjie huagong formula on acute lung injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis model. Chin. J. Pharmacol.40 (05), 975–983. 10.12360/CPB202308016
30
Feng Y. Zhu B. Liu Y. Liu Y. Zhou G. Yang L. et al (2022). Yindan jiedu granules exhibit anti-inflammatory effect in patients with novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. Phytomedicine95, 153784. 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153784
31
Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São (2022). Study design of the diacerein effect on inflammatory response in patients with Covid-19: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial, Editor P. Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São (Brazil).
32
Gasmi A. Gasmi A. Tippairote T. Mujawdiya P. K. Menzel A. Lysiuk R. et al (2024). Traditional Chinese medicine as the preventive and therapeutic remedy for COVID-19. Curr. Med. Chem.31 (21), 3118–3131. 10.2174/0929867330666230331084126
33
Ge Z. Xia Z. J. Ma K. (2023). Reusing old drugs: scopolamine - a typical case of clinical off-indication application. Chin. J. Ration. Drug Use Explor.20 (07), 26–28. 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3327.2023.07.008
34
Gong H. Chen Y. Chen M. Li J. Zhang H. Yan S. et al (2022). Advanced development and mechanism of sepsis-related acute respiratory distress syndrome. Front. Med. (Lausanne)9, 1043859. 10.3389/fmed.2022.1043859
35
Grisaru-Tal S. M. E. Rothenberg M. E. (2022). Eosinophil-lymphocyte interactions in the tumor microenvironment and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Immunol.23 (9), 1309–1316. 10.1038/s41590-022-01291-2
36
Guo J. Zhu J. Wang Q. Wang J. Jia Y. (2021). Comparative efficacy of seven kinds of Chinese medicine injections in acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol.12, 627751. 10.3389/fphar.2021.627751
37
Guo X. Q. (2024). Comparison of clinical effects of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate and diammonium glycyrrhizinate combined with shuganning in the treatment of viral hepatitis. Clin. Ration. Drug Use (35), 11–14. 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2024.35.003
38
Guo Y. Liu Y. Zhao S. Xu W. Li Y. Zhao P. et al (2021). Oxidative stress-induced FABP5 S-glutathionylation protects against acute lung injury by suppressing inflammation in macrophages. Nat. Commun.12 (1), 7094. 10.1038/s41467-021-27428-9
39
Hao J. D. (2023). The role of NLRP3 in estrogen-mediated alleviation of intestinal lymph fluid-induced lung injury following hemorrhagic shock. Hebei: Hebei North University. 10.27767/d.cnki.ghbbf.2023.000047
40
He Y. T. Huang W. Liu S. T. Xie W. P. Kong H. (2024). The mechanism and research progress of ferroptosis in acute lung injury. J. Clin. Pulmonol.29 (12), 1906–1912.
41
Hou W. Q. Liu D. L. Hai Y. Liu X. F. Dong J. Q. Su J. et al (2023). Maxing shigan decoction alleviates the inflammatory response of LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Clin. Pharmacol. Chin. Med.39 (3), 1–7. 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20230220.002
42
Hu C. Li J. Tan Y. Liu Y. Bai C. Gao J. et al (2022). Tanreqing injection attenuates macrophage activation and the inflammatory response via the lncRNA-SNHG1/HMGB1 axis in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Front. Immunol.13, 820718. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.820718
43
Huo Y. Yue D. (2024). Effect of anti-inflammatory tongfu formula on mtDNA-STING-NLRP3 signaling pathway in sepsis-induced acute lung injury rats. Chin. J. Emerg. Med.44 (04), 323–329. 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2024.04.008
44
Hussain M. Xu C. Wu X. Lu M. Tang L. Wu F. et al (2019). A CRTH2 antagonist, CT-133, suppresses NF-κB signalling to relieve lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol.854, 79–91. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.053
45
Imai Y. Kuba K. Neely G. G. Yaghubian-Malhami R. Perkmann T. van Loo G. et al (2008). Identification of oxidative stress and toll-like receptor 4 signaling as a key pathway of acute lung injury. Cell133 (2), 235–249. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.043
46
Ji T. Chen M. Liu Y. Jiang H. Li N. He X. (2023). Artesunate alleviates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion induced acute lung injury via up-regulating AKT and HO-1 signal pathway in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol.122, 110571. 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110571
47
Jiang L. Gu Y. Du Y. Liu J. (2019). Exosomes: diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic delivery vehicles for cancer. Mol. Pharm.16 (8), 3333–3349. 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00409
48
Jiang N. Li Z. Luo Y. Jiang L. Zhang G. Yang Q. et al (2021). Emodin ameliorates acute pancreatitis-induced lung injury by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neutrophil recruitment. Exp. Ther. Med.22 (2), 857. 10.3892/etm.2021.10289
49
Jiang R. Xu J. Zhang Y. Zhu X. Liu J. Tan Y. (2021). Ligustrazine alleviate acute lung injury through suppressing pyroptosis and apoptosis of alveolar macrophages. Front. Pharmacol.12, 680512. 10.3389/fphar.2021.680512
50
Ju M. Liu B. He H. Gu Z. Liu Y. Su Y. et al (2018). MicroRNA-27a alleviates LPS-Induced acute lung injury in mice via inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis through modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Cell Cycle17 (16), 2001–2018. 10.1080/15384101.2018.1509635
51
Kandikattu H. K. Upparahalli Venkateshaiah S. Kumar S. Yadavalli C. S. Mishra A. (2023). IL-18-mediated neutrophil recruitment promotes acute lung injury in inflammation-mediated chronic pancreatitis. Mol. Immunol.155, 100–109. 10.1016/j.molimm.2023.01.012
52
Kawano A. Ariyoshi W. Yoshioka Y. Hikiji H. Nishihara T. Okinaga T. (2019). Docosahexaenoic acid enhances M2 macrophage polarization via the p38 signaling pathway and autophagy. J. Cell Biochem.120 (8), 12604–12617. 10.1002/jcb.28527
53
Kou Y. L. Wang W. B. Yan S. G. Li J. T. Shi J. Hui Y. (2022). Mechanism of lung and intestine combination therapy in treatment of acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammatory response based on NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway and alveolar macrophage activation. China J. Chin. Materia Medica47 (1), 151–158. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211027.401
54
Krishack P. A. Hollinger M. K. Kuzel T. G. Decker T. S. Louviere T. J. Hrusch C. L. et al (2021). IL-33-mediated eosinophilia protects against acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol.64 (5), 569–578. 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0166OC
55
Kufe D. W. (2020). MUC1-C in chronic inflammation and carcinogenesis; emergence as a target for cancer treatment. Carcinogenesis41 (9), 1173–1183. 10.1093/carcin/bgaa082
56
Lai C. Wang K. Zhao Z. Zhang L. Gu H. Yang P. et al (2017). C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) mediates acute lung injury induced by lethal influenza H7N9 virus. Front. Microbiol.8, 587. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00587
57
Lefrançais E. Mallavia B. Zhuo H. Calfee C. S. Looney M. R. (2018). Maladaptive role of neutrophil extracellular traps in pathogen-induced lung injury. JCI Insight3 (3), e98178. 10.1172/jci.insight.98178
58
Li F. Zhu H. Sun R. Wei H. Tian Z. (2012). Natural killer cells are involved in acute lung immune injury caused by respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Virol.86 (4), 2251–2258. 10.1128/jvi.06209-11
59
Li G. C. Tian Z. Y. Zhang F. H. Hao H. Kong L. (2019). Clinical study on the treatment of sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome with shengxia lifei decoction. Chin. J. Acute Med.28 (08), 1321–1323. 10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2019.08.002
60
Li H. Zhou X. Tan H. Hu Y. Zhang L. Liu S. et al (2018). Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to the pathogenesis of acid-aspiration-induced ALI/ARDS. Oncotarget9 (2), 1772–1784. 10.18632/oncotarget.22744
61
Li J. Wang M. Xie Y. Li S. Yu X. Li F. et al (2025). A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study of the use of traditional Chinese medicine for treating patients with mild/moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Evid. Based Med.18 (2), e70023. 10.1111/jebm.70023
62
Li M. Zhao S. Liu Y. Wang Q. Chen Y. Zhou Y. (2024). Pathological characteristics of ferroptosis in kidney tissues in type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic kidney disease. Dis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes.17, 4105–4113. 10.2147/DMSO.S489536
63
Li M. H. (2023). “Investigation on the mechanism of quality markers of jiejing decoction in pedicting and improving acute lung injury,”. Jilin: Jilin agricultural university. 10.27163/d.cnki.gjlnu.2023.000920
64
Li W. Ding Z. Chen Y. Wang Y. Peng M. Li C. et al (2022). Integrated pharmacology reveals the molecular mechanism of gegen qinlian decoction against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Front. Pharmacol.13, 854544. 10.3389/fphar.2022.854544
65
Li W. Q. Wu S. Qiu C. H. (2020). Clinical effect of redu ning injection in the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by sepsis. Contemp. Chin. Med.27 (19), 57–60.
66
Li X. Jamal M. Guo P. Jin Z. Zheng F. Song X. et al (2019). Irisin alleviates pulmonary epithelial barrier dysfunction in sepsis-induced acute lung injury via activation of AMPK/SIRT1 pathways. Biomed. and Pharmacother.118, 109363. 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109363
67
Li X. N. Yang S. Q. Li M. Li X. S. Tian Q. Xiao F. et al (2021). Formaldehyde induces ferroptosis in hippocampal neuronal cells by upregulation of the warburg effect. Toxicology448, 152650. 10.1016/j.tox.2020.152650
68
Li Y. Tang T. T. Geng Y. (2022). The influence of dachengqi decoction combined with basic treatment on inflammatory indicators and prognosis in patients with lung injury caused by sepsis. Chin. J. Acute Med.31 (03), 443–446. 10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2022.03.018
69
Li Z. Huang H. Chen F. K. Huang K. G. Liang Y. Y. Qiu W. Y. et al (2020). Study on the lung-protective effects of diammonium glycyrrhizinate and astragalus injection on acute lung injury. World Comb. traditional Chin. West. Med. Mag.8 (10), 1025–1027. 10.13935/j.carolcarrollnkiSJZX.2013.10.030
70
Li Z. Pan H. Yang J. Chen D. Wang Y. Zhang H. et al (2023). Xuanfei baidu formula alleviates impaired mitochondrial dynamics and activated NLRP3 inflammasome by repressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways in LPS-induced ALI and inflammation models. Phytomedicine108, 154545. 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154545
71
Li Z. Y. Liang Q. (2019). Clinical observation on the treatment of acute lung injury in sepsis with chemical Fiber capsules. World J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med.14 (03), 403–406. 10.13935/j.cnki.sjzx.190327
72
Lin W. C. Fessler M. B. (2021). Regulatory mechanisms of neutrophil migration from the circulation to the airspace. Cell Mol. Life Sci.78 (9), 4095–4124. 10.1007/s00018-021-03768-z
73
Liu J. Wu Y. H. Zhang Z. L. Li P. (2022). Tanshinone IIA improves sepsis-induced acute lung injury through the ROCK2/NF-κB axis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.446, 116021. 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116021
74
Liu M. M. Zhou J. Ji D. Yang J. Huang Y. P. Wang Q. (2021). Diammonium glycyrrhizinate lipid ligand ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by modulating vascular endothelial barrier function. Exp. Ther. Med.21 (4), 303. 10.3892/etm.2021.9734
75
Liu P. Feng Y. Li H. Chen X. Wang G. Xu S. et al (2020). Ferrostatin-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett.25, 10–14. 10.1186/s11658-020-00205-0
76
Liu P. Yang S. Shao X. Li C. Wang Z. Dai H. et al (2024). Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury by inhibiting alveolar macrophage pyroptosis. Stem Cells Transl. Med.13 (4), 371–386. 10.1093/stcltm/szad094
77
Liu W. B. Jiang X. H. Xia Y. F. (2019). Clinical efficacy study of ligustrazine injection in the treatment of acute lung injury. Mod. Med. Health35 (15), 2363–2364. 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2019.15.034
78
Liu Y. Wang X. Chen Y. Zhou L. Wang Y. Li L. et al (2024). Pharmacological mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine against acute lung injury: from active ingredients to herbal formulae. Phytomedicine135, 155562. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155562
79
Liu Y. J. Li X. Liu F. Li Y. (2022). Research progress on the antiangiogenic mechanism and clinical application of artemisinin and its derivatives,28(08),148–153. 10.13862/j.cn43-1446/r.2022.08.033
80
Long W. Xu L. H. Cheng Y. Wang R. (2020). Ferroptosis involved in sepsis-associated acute lung injury in mice. Southwest Natl. Def. Med.30 (08), 725–728. 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2020.08.007
81
Lu X. K. Li D. W. Song T. Q. Ding X. Q. Feng W. G. J. Li J. (2021). Observation on the therapeutic effect of huperzine A tablets combined with butylphthalide soft capsules on cognitive function in patients with mild alzheimer's disease. J. BeiHua Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed.22 (01), 62–64. 10.11713/j.issn.1009-4822.2021.01.012
82
Lu Y. Cheng W. Q. Niu K. J. Yu H. J. Wang Y. F. (2024). Research review on quality evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine compound preparations based on multidimensional integration strategy. Chin. Herb. Med.55 (22), 7847–7856. 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2024.22.027
83
Lu Y. Zhang P. P. Wang D. Q. Li Z. J. (2020). Discussion on pathogenesis and pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Chin. J. Acute Med.29 (02), 280–282. 10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X
84
Luo R. Li X. Wang D. (2022). Reprogramming macrophage metabolism and its effect on NLRP3 inflammasome activation in sepsis. Front. Mol. Biosci.9, 917818. 10.3389/fmolb.2022.917818
85
Luo W. Ruan Z. L. Yuan C. F. Li W. Y. Xia Y. B. Qian C. et al (2024). Based on the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway, the mechanism by which qilongtian capsules reduce the polarization of M1 macrophages and inhibit the inflammatory response in acute lung injury was investigated. Chin. Herb. Med.47 (9), 2345–2349. 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2024.09.034
86
Ma M. Wang K. Yang Y. H. Yue M. R. Ren Q. N. Chen Y. H. et al (2024). Influence of tongfu xiefei guanchang solution on intestinal barrier and intestinal flora of rats with acute lung injury based on p38 MAPK/MLCK signaling pathway. Chin. J. traditional Chin. Med.49 (21), 5919–5931. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240802.707
87
McKelvey M. Uddin M. B. Palani S. Shao S. Sun K. (2024). IL-10 counteracts IFN-γ to alleviate acute lung injury in a viral-bacterial superinfection model. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol.71 (1), 110–120. 10.1165/rcmb.2023-0437OC
88
Miao J. Shen J. Yan C. Ren J. Liu H. Qiao Y. et al (2022). The protective effects of mai-luo-ning injection against LPS-induced acute lung injury via the TLR4/NF-κB signalling pathway. Phytomedicine104, 154290. 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154290
89
Mo X. Hu R. C. (2019). Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in respiratory diseases. J. Clin. Pathological Sci.39 (10), 2281–2287. 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2019.10.028
90
Mokrá D. (2020). Acute lung injury - from pathophysiology to treatment. Physiol. Res.69 (Suppl. 3), 353–366. 10.33549/physiolres.934602
91
Müller M. T. Schempp R. Lutz A. Felder T. Felder E. Miklavc P. et al (2019). Interaction of microtubules and actin during the post-fusion phase of exocytosis. Sci. Rep.9 (1), 11973. 10.1038/s41598-019-47741-0
92
Osburn W. O. Wakabayashi N. Misra V. Nilles T. Biswal S. Trush M. A. et al (2006). Nrf2 regulates an adaptive response protecting against oxidative damage following diquat-mediated formation of superoxide anion. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.454 (1), 7–15. 10.1016/j.abb.2006.08.005
93
Pei X. T. Peng L. Chen W. D. (2023). Research progress on the historical evolution, effective components, pharmacological effects and clinical application of xiaoxuming decoction. J. liaoning Univ. traditional Chin. Med.25 (10), 120–124. 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2023.10.024
94
Peng J. Fan B. Bao C. Jing C. (2021). JMJD3 deficiency alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting alveolar epithelial ferroptosis in a Nrf2-dependent manner. Mol. Med. Rep.24 (5), 807. 10.3892/mmr.2021.12447
95
Qin L. Xiang Y. Li H. Li M. Qi X. R. (2025). Effects of yiqi huoxue formula on pulmonary Qi-blood barrier function in rats with acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. J. Beijing Univ. Chin. Med.47 (12), 1702–1709. 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2024.12.010
96
Qin Y. Li W. Liu J. Wang F. Zhou W. Xiao L. et al (2024). Andrographolide ameliorates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by promoting autophagy in alveolar macrophages via the RAGE/PI3K/AKT/Mtor pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol.139, 112719. 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112719
97
Ren Y. (2020). Qi xie turbidity qi and the prevention and treatment of acute lung injury (ALI) clinical research. Guangzhou: Guangzhou university of Chinese medicine. 10.27044/d.cnki.ggzzu.2020.000464
98
Sakaguchi R. Chikuma S. Shichita T. Morita R. Sekiya T. Ouyang W. et al (2016). Innate-like function of memory Th17 cells for enhancing endotoxin-induced acute lung inflammation through IL-22. Int. Immunol.28 (5), 233–243. 10.1093/intimm/dxv070
99
Schäcke H. Döcke W. D. Asadullah K. (2002). Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther.96 (1), 23–43. 10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00297-8
100
Seyran M. Melanie S. Philip S. Amiq G. Fabian B. (2023). Allies or enemies? The effect of regulatory T cells and related T lymphocytes on the profibrotic environment in bleomycin-injured lung mouse models. Clin. Exp. Med.23 (4), 1075–1088. 10.1007/s10238-022-00945-7
101
Shao H. Fang C. Huang Y. Ye Y. Tong R. (2022). Sodium tanshinone ⅡA sulfonate injection as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine95, 153879. 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153879
102
Shen J. Y. Zhang E. Y. Hu J. (2019). Research progress on acute lung injury and lung protective strategies by cardiopulmonary bypass. Chin. J. Clin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.26 (02), 186–191. 10.7507/1007-4848.201805007
103
Shi J. Chen W. Tang J. Zhang C. Qi M. Zheng X. et al (2024). Huperzine A protected against ferroptosis via activating PI3K/Akt signaling in lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol.983, 177004. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177004
104
Shi J. Yu T. Song K. Du S. He S. Hu X. et al (2021). Dexmedetomidine ameliorates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in vivo and in vitro by preserving mitochondrial dynamic equilibrium through the HIF-1a/HO-1 signaling pathway. Redox Biol.41, 101954. 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101954
105
Soehnlein O. Oehmcke S. Ma X. Rothfuchs A. G. Frithiof R. van Rooijen N. et al (2008). Neutrophil degranulation mediates severe lung damage triggered by streptococcal M1 protein. Eur. Respir. J.32 (2), 405–412. 10.1183/09031936.00173207
106
Song J. (2022). Clinical effect and pharmacological study of andrographolide dispersible tablets in the treatment of acute periodontitis with wind-heat syndrome in the upper jiao. Chin. J. Pract. Med.17 (22), 141–143. 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2022.22.043
107
Su C. F. Kao S. J. Chen H. I. (2012). Acute respiratory distress syndrome and lung injury: pathogenetic mechanism and therapeutic implication. World J. Crit. Care Med.1 (2), 50–60. 10.5492/wjccm.v1.i2.50
108
Su Y. J. (2015). Clinical research on the treatment of acute lung injury caused by sepsis with baofei jiejiong mixture. Sichuan: ChengDu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
109
Sun T. T. Ma X. H. Li X. X. Zhang L. H. Li X. Q. Yu F. (2017). Discussion on research status and development ideas of biopotency for Chinese materia medica. Chin. Herb. Med.48 (09), 1906–1911. 10.11656/j.issn.1673-9043.2023.03.16
110
Sun Z. J. (2024). Down-regulation of SP1 inhibits ZBP1-induced pan-apoptosis of alveolar macrophages and alleviates sepsis lung injury. Jiangxi: Nanchang university. 10.27232/d.cnki.gnchu.2024.004392
111
Taheri P. Dave D. D. Dash R. K. Sharma G. P. Clough A. V. Jacobs E. R. et al (2024). Mitochondrial function in lungs of rats with different susceptibilities to hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury. J. Appl. Physiol.137 (2), 233–253. 10.1152/japplphysiol.00243.2024
112
Tan P. Li M. Liu Z. Li T. Zhao L. Fu W. (2022). Glycolysis-related LINC02432/hsa-miR-98–5p/HK2 axis inhibits ferroptosis and predicts immune infiltration, tumor mutation burden, and drug sensitivity in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Front. Pharma13, 937413. 10.3389/fphar.2022.937413
113
Tan S. Y. Chen S. (2020). Progress in research on mitophagy and pulmonary diseases. J. Basic Med. Clin.40 (6), 842–846. 10.16352/j.issn.1001-6325.2020.06.024
114
Tan W. Zhang C. Liu J. Miao Q. (2019). Regulatory T-cells promote pulmonary repair by modulating T helper cell immune responses in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Immunology157 (2), 151–162. 10.1111/imm.13060
115
Tavasolian F. Hosseini A. Z. Rashidi M. Soudi S. Abdollahi E. Momtazi-Borojeni A. A. et al (2021). The impact of immune cell-derived exosomes on immune response initiation and immune system function. Curr. Pharm. Des.27 (2), 197–205. 10.2174/1381612826666201207221819
116
Uddin M. A. Barabutis N. (2019). P53: the endothelium defender. J. Cell Biochem.120 (7), 10952–10955. 10.1002/jcb.28511
117
Um J. H. Yun J. (2017). Emerging role of mitophagy in human diseases and physiology. BMB Rep.50 (6), 299–307. 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.6.056
118
Van der Poll T. Van de Veerdonk F. L. Scicluna B. P. Netea M. G. (2017). The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Immunol.17 (7), 407–420. 10.1038/nri.2017.36
119
Verma A. K. McKelvey M. Uddin M. B. Palani S. Niu M. Bauer C. et al (2022). IFN-γ transforms the transcriptomic landscape and triggers myeloid cell hyperresponsiveness to cause lethal lung injury. Front. Immunol.13, 1011132. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1011132
120
Vora S. M. Lieberman J. Wu H. (2021). Inflammasome activation at the crux of severe COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol.21 (11), 694–703. 10.1038/s41577-021-00588-x
121
Wang H. Wang S. Huang S. (2021). MiR-494-3p alleviates acute lung injury through regulating NLRP3 activation by targeting CMPK2. Biochem. Cell Biol.99 (3), 286–295. 10.1139/bcb-2020-0243
122
Wang J. Yang P. Yu T. Gao M. Liu D. Zhang J. et al (2022). Lactylation of PKM2 suppresses inflammatory metabolic adaptation in pro-inflammatory macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Sci.18 (16), 6210–6225. 10.7150/ijbs.75434
123
Wang K. Wang M. Liao X. Gao S. Hua J. Wu X. et al (2022). Locally organised and activated Fth1(hi) neutrophils aggravate inflammation of acute lung injury in an IL-10-dependent manner. Nat. Commun.13 (1), 7703. 10.1038/s41467-022-35492-y
124
Wang K. Zhang Y. Cao Y. Shi Z. Lin Y. Chen Y. et al (2020). Glycyrrhetinic acid alleviates acute lung injury by PI3K/AKT suppressing macrophagic Nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.532 (4), 555–562. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.044
125
Wang L. Xiong H. Wu F. Zhang Y. Wang J. Zhao L. et al (2014). Hexokinase 2-mediated warburg effect is required for PTEN-and p53-deficiency-driven prostate cancer growth. Cell Rep.8 (5), 1461–1474. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.053
126
Wang P. Li H. Wu W. (2025). Anti-inflammatory effects of esomeprazole in septic lung injury by mediating endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr.57 (2-3), 173–182. 10.1007/s10863-025-10055-0
127
Wang S. Lin F. Zhang C. Gao D. Qi Z. Wu S. et al (2024). Xuanbai chengqi decoction alleviates acute lung injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Ethnopharmacol.319, 117227. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117227
128
Wang W. Zhu L. Li H. Ren W. Zhuo R. Feng C. et al (2022). Alveolar macrophage-derived exosomal tRF-22-8BWS7K092 activates hippo signaling pathway to induce ferroptosis in acute lung injury. Int. Immunopharmacol.107, 108690. 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108690
129
Wang X. H. Wang L. Chang S. Chen H. N. Cui X. L. (2023). Clinical research of huperzine A tablets combined with oxiracetam capsules in the treatment of vascular cognitive impairment after cerebral infarction. Chin. Med.18 (11), 1642–1646. 10.3760/j.issn.1673-4777.2023.11.010
130
Wang Y. Han Q. Liu L. Wang S. Li Y. Qian Z. et al (2024). Natural hydrogen gas and engineered microalgae prevent acute lung injury in sepsis. Mater Today Bio28, 101247. 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101247
131
Wang Y. Yang Y. Chen L. Xiong W. Song L. Li B. et al (2020). Death-associated protein kinase 1 mediates ventilator-induced lung injury in mice by promoting alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis. Anesthesiology133 (4), 905–918. 10.1097/ALN.0000000000003464
132
Wang Y. Zhang M. Bi R. Su Y. Quan F. Lin Y. et al (2022). ACSL4 deficiency confers protection against ferroptosis-mediated acute kidney injury. Redox Biolo51, 102262. 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102262
133
Wang Y. M. Gong F. C. Qi X. Zheng Y. J. Zheng X. T. Chen Y. et al (2022). Mucin 1 inhibits ferroptosis and sensitizes vitamin E to alleviate sepsis‐induced acute lung injury through GSK3β/Keap1‐Nrf2‐GPX4 pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2022 (1), 2405943. 10.1155/2022/2405943
134
Wang Z. Wang Z. (2023). The role of macrophages polarization in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front. Immunol.14, 1209438. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1209438
135
Wang Z. W. Zhu X. (2019). Exosomal miR-19b-3p communicates tubular epithelial cells and M1 macrophage. Cell Death Dis.10 (10), 762. 10.1038/s41419-019-2008-0
136
Wang Z. Y. Wang X. Zhang D. Y. Hu Y. J. Li S. (2022). Pharmacology of traditional chinese medicine network:development in the new era under the guidance of the guidelines. Chin. J. Traditional Chin. Med.47 (01), 7–17. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210914.702
137
Wei H. L. (2024). Research on the efficacy and mechanism of compound houttuynia cordata mixture against H3N2 influenza virus. Jiangsu: Yangzhou university. 10.27441/d.cnki.gyzdu.2024.001188
138
Wu L. Ramirez S. H. Andrews A. M. Leung W. Itoh K. Wu J. et al (2016). Neuregulin1‐β decreases interleukin‐1β‐induced RhoA activation, myosin light chain phosphorylation, and endothelial hyperpermeability. J. Neurochem.136 (2), 250–257. 10.1111/jnc.13374
139
Xiang Y. Cai M. Li X. Bao X. Cai D. (2021). Protective effect of xiao-xu-ming Decoction-mediated inhibition of ROS/NLRP3 axis on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in vitro and in vivo. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med.2021, 8257495. 10.1155/2021/8257495
140
Xiang Y. J. Cai D. F. Wang P. Yu J. W. Cai M. Li X. T. (2022). Study on the mechanism of xiaoxuming Decoction's intervention in acute lung injury by down-regulating USP9X to regulate NLRP3 ubiquitination levels. Shanghai J. Traditional Chin. Med.56 (03), 48–55. 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2022.2105105
141
Xiao K. He W. Guan W. Hou F. Yan P. Xu J. et al (2020). Mesenchymal stem cells reverse EMT process through blocking the activation of NF-κB and hedgehog pathways in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Cell Death Dis.11 (10), 863. 10.1038/s41419-020-03034-3
142
Xie K. Chen Y. Q. Chai Y. S. Lin S. H. Wang C. J. Xu F. (2021). HMGB1 suppress the expression of IL-35 by regulating naïve CD4+ T cell differentiation and aggravating caspase-11-dependent pyroptosis in acute lung injury. Int. Immunopharmacol.91, 107295. 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107295
143
Xie L. Zhang G. Wu Y. Hua Y. Ding W. Han X. et al (2024). Protective effects of wenqingyin on sepsis-induced acute lung injury through regulation of the receptor for advanced glycation end products pathway. Phytomedicine129, 155654. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155654
144
Xie Y. Hou W. Song X. Yu Y. Huang J. Sun X. et al (2016). Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ.23 (3), 369–379. 10.1038/cdd.2015.158
145
Xie Y. B. Liang Z. J. Huang W. Q. (2008). Progress in traditional Chinese medicine treatment of acute lung injury. J. Pract. Clin. Med. (03), 113–114+118. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=0YYC1NNgyEC98QcSjp0tLGKNxj9iEbQ9aq6uYMEMkkvrqlWFKp7zvihfcNmJIpE2RvE3aul_qz88sNvQ1mwWOQXti6Kf5X5Qu0n7NghjU3RyYuB2ST-bhf9eYF7ebEA-v8ILpm_JG2fX8e74_6Or-v0-aKWpWPPGk24l5M80f-Pl_F8C7zA9ng==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
146
Xu A. P. He X. L. You S. (2024). Clinical observation of qingwen badu decoction in the treatment of sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Hebei J. Traditional Chin. Med.46 (06), 932–935.
147
Xu G. R. (2016). Evaluation of the therapeutic effect of andrographolide dropping pills in the treatment of 85 cases of sore throat caused by upper respiratory tract infection. Chin. J. Mod. Med.26 (07), 104–107. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2016.07.024
148
Xu M. Li X. Ma C. Lü Y. Ma X. Ma X. et al (2020). Effect of human placental mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on pulmonary vascular endothelial permeability and lung injury repair in mice with acute lung injury. Chin. J. Reparative Reconstr. Surg.34 (3), 387–392. 10.7507/1002-1892.201909070
149
Xu Q. C. (2023). Research on the role and mechanism of Pannexin1 in regulating mitochondrial dynamics in acute lung injury caused by sepsis. Wu han: Wu Han University. 10.27379/d.cnki.gwhdu.2023.000365
150
Xu Y. Xin J. Sun Y. Wang X. Sun L. Zhao F. et al (2024). Mechanisms of sepsis-induced acute lung injury and advancements of natural small molecules in its treatment. Pharm. (Basel)17 (4), 472. 10.3390/ph17040472
151
Xu Y. J. Wang X. L. Mu W. Q. Wen J. C. Wang Y. Xiu Y. et al (2024). Mechanism of total glucosides of white paeony capsules in ameliorating acute lung injury based on NLRP3 inflammasome. ZhongGuo Zhong Yao Za Zhi49 (10), 2754–2765. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240202.703
152
Yan Y. Zou Z. Sun Y. Li X. Xu K. F. Wei Y. et al (2013). Anti-malaria drug chloroquine is highly effective in treating Avian influenza A H5N1 virus infection in an animal model. Cell Res.23 (2), 300–302. 10.1038/cr.2012.165
153
Yang Q. Xu H. R. Xiang S. Y. Zhang C. Ye Y. Shen C. X. et al (2021). Resolvin conjugates in tissue regeneration 1 promote alveolar fluid clearance by activating alveolar epithelial sodium channels and Na, K-ATPase in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.379 (2), 156–165. 10.1124/jpet.121.000712
154
Yang S. Qin H. L. Li Y. X. Wang X. Zhang R. T. Yang J. (2023). Research progress on traditional Chinese medicine in prevention and treatment of alveolar-capillary barrier dysfunction. Chin. Herb. Med.54 (15), 5075–5087. 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2023.15.031
155
Yang W. S. SriRamaratnam R. Welsch M. E. Shimada K. Skouta R. Viswanathan V. S. et al (2014). Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell156 (1), 317–331. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010
156
Yang Y. M. Qu S. Q. Chen L. N. Deng S. Q. Zhang Y Zheng Z. Y. (2022). Protective effect of Shenlian prescription on acute lung injury induced by particulate matter exposure in rats. Chin. J. Exp. Formulas Chin. Med.28 (20), 37–44. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20221405
157
Ye X. L. Tian S. S. Tang C. C. Jiang X. R. Liu D. Yang G. Z. et al (2023). Cytokine storm in acute viral respiratory injury: role of qing-fei-pai-du decoction in inhibiting the infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages through TAK1/IKK/NF-[Formula: see text]B pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med.51 (05), 1153–1188. 10.1142/S0192415X23500532
158
Youssef N. S. Elzaitony A. S. Baky N. A. A. (2022). Diacerein attenuate LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ER stress and apoptosis: impact on the crosstalk between SphK1/S1P, TLR4/NFκB/STAT3, and NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathways. Life Sci.308, 120915. 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120915
159
Yu C. Li Y. Li Y. Li S. Zeng F. Yu J. et al (2024). A novel mechanism for regulating lung immune homeostasis: zukamu granules alleviated acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and regulating Th17/Treg cytokine balance. J. Ethnopharmacol.324, 117831. 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117831
160
Yu H. Bai Y. Qiu J. He X. Xiong J. Dai Q. et al (2021). Pseudomonas aeruginosa PcrV enhances the nitric oxide-mediated tumoricidal activity of tumor-associated macrophages via a TLR4/PI3K/AKT/mTOR-glycolysis-nitric oxide circuit. Front. Oncol.11, 736882. 10.3389/fonc.2021.736882
161
Yu L. C. He R. Wang D. X. Qi D. (2024). Activated Clec4n(hi) neutrophils aggravate lung injury in an endothelial IGFBP7-dependent manner. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol.71 (1), 66–80. 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0017OC
162
Yu W. Lv Y. Xuan R. Han P. Xu H. Ma X. et al (2024). Human placental mesenchymal stem cells transplantation repairs the alveolar epithelial barrier to alleviate lipopolysaccharides-induced acute lung injury. Biochem. Pharmacol.229, 116547. 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116547
163
Yu Y. Li Y. Zhou L. Cheng X. Gong Z. (2024). Hepatic stellate cells promote hepatocellular carcinoma development by regulating histone lactylation: novel insights from single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics analyses. Cancer Lett.604, 217243. 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217243
164
Yu Y. J. Zhou Z. Y. Lv L. Jin X. Y. Wang Z. Q. Liu Y. Y. et al (2023). Discussion of traditional chinese medicine and western medicine treatment of pulmonary nodules. J. Tianjin Univ. Of Traditional Chin. Med.42 (03), 366–374.
165
Zeng Y. (2019). The characteristics and evolutionary features of TCM syndrome elements in sepsis resulting from pulmonary infection. Beijing: Beijing university of traditional Chinese medicine.
166
Zhan P. Lu X. Li Z. Wang W. J. Peng K. Liang N. N. et al (2022). Mitoquinone alleviates bleomycin-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting mitochondrial ROS-dependent pulmonary epithelial ferroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol.113, 109359. 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109359
167
Zhang B. Luo L. Xiong S. Xiao Y. Zhang T. Xiang T. (2024). Anisodamine hydrobromide ameliorates acute lung injury via inhibiting pyroptosis in murine sepsis model. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol.46 (5), 662–671. 10.1080/08923973.2024.2386331
168
Zhang C. (2020). Omics method screening for the reuse of old drugs against highly pathogenic avian influenza virus and research on immune response and lung injury in COVID-19 patients (doctoral dissertation). Anhui: University of Science and Technology of China. 10.27517/d.cnki.gzkju.2020.001129
169
Zhang C. Li X. Gao D. Zhu H. Wang S. Tan B. et al (2023). Network pharmacology and experimental validation of the anti-inflammatory effect of tingli dazao xiefei decoction in acute lung injury treatment. J. Inflamm. Res.16, 6195–6209. 10.2147/JIR.S433840
170
Zhang C. Wang X. Wang C. He C. Ma Q. Li J. et al (2021). Qingwenzhike prescription alleviates acute lung injury induced by LPS via inhibiting TLR4/NF-kB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Front. Pharmacol.12, 790072. 10.3389/fphar.2021.790072
171
Zhang G. M. Li F. A. Tong L. (2010). The protective effect of pretreatment with the hot pain formula on endotoxin-induced lung injury in rats. Chin. J. Exp. formulas Chin. Med.16 (15), 129–131. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2010.15.049
172
Zhang H. Hu P. P. Wang Z. L. Liu Y. J. Jin Q. F. (2022). The influence of shenfu injection on the levels of inflammatory factors and coagulation function in patients with septic lung injury undergoing mechanical ventilation. Chin. Foreign Med.41 (6), 17–21. 10.16662/j.carolcarrollnki.1674-0742.2022.06.017
173
Zhang H. S. Du G. Y. Zhang Z. G. Zhou Z. Sun H. L. Yu X. Y. et al (2018). NRF2 facilitates breast cancer cell growth via HIF1ɑ-mediated metabolic reprogramming. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.95, 85–92. 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.12.016
174
Zhao Y. Jiang Y. Chen L. Zheng X. Zhu J. Song X. et al (2020). Inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-associated IRE-1/XBP-1 pathway alleviates acute lung injury via modulation of macrophage activation. J. Thorac. Dis.12 (3), 284–295. 10.21037/jtd.2020.01.45
175
Zhao Y. T. Zhang H. Y. Cao Y. J. Li J. D. Yin X. D. Wang P. R. (2024). Research progress on the role and mechanism of artemisinin and its derivatives in skin diseases. Clin. Med. World45 (6), 575–582. 10.13683/j.wph.2024.06.002
176
Zheng J. S. Qian J. L. Jiang N. Wei Y. He H. D. Ma C. F. et al (2021). The effect of qidong huoxue yin on the iRhom2/TACE signaling pathway in alveolar macrophages of mice with acute lung injury. J. zhejiang Univ. Chin. Med.45 (05), 530–536. 10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2021.05.018
177
Zheng Q. (2020). Research on the role and mechanism of NAMPT regulating pyroptosis of T lymphocytes in immunosuppression of traumatic sepsis. Zhejiang: Huazhong university of science and technology. 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2020.002090
178
Zheng W. W. Zhang Z. B. (2024). The effect of xuebijing injection combined with ulinastatin injection in the treatment of sepsis complicated with acute lung injury and its influence on the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-Κb signaling pathway. J. Transl. Med.13 (02), 259–263. 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3097.2024.02.021
179
Zheng X. (2023). Investigation on the effect of LCN2 on macrophage polarization in severe hypothermia acute lung injury based on RNA-seq. Anhui: Anhui Medical University. 10.26921/d.cnki.ganyu.2023.000720
180
Zheng Y. Liu Y. Ye C. Ming L. Wanru C. (2024). Effectiveness and safety of qidong huoxue decoction in treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized, controlled trial. J. Tradit. Chin. Med.44 (2), 381–387. 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.02.003
181
Zhong W. J. (2023). Research on the role and mechanism of TREM-1 mediating macrophage inflammation and prognosis in acute lung injury. Hunan: Central south university. 10.27661/d.cnki.gzhnu.2023.000764
182
Zhou B. Yuan Y. Zhang S. Guo C. Li X. Li G. et al (2020). Intestinal flora and disease mutually shape the regional immune system in the intestinal tract. Front. Immunol.11, 575. 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00575
183
Zhou Y. Li Q. X. Liao Z. Z. Liu Y Ouyang Y. Jiang W. J. et al (2023). Anti-inflammatory effect and component analysis of Chaihu Qingwen granules. J. Ethnopharmacol.317, 116763. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116763
184
Zhu H. Wang S. Shan C. Li X. Tan B. Chen Q. et al (2021). Mechanism of protective effect of xuan-bai-cheng-qi decoction on LPS-induced acute lung injury based on an integrated network pharmacology and RNA-sequencing approach. Respir. Res.22 (1), 188. 10.1186/s12931-021-01781-1
185
Zhu H. P. Huang H. Y. Wu D. M. Dong N. Dong L. Chen C. S. et al (2020). Regulatory mechanism of NOV/CCN3 in the inflammation and apoptosis of lung epithelial alveolar cells upon lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Mol. Med. Rep.21 (4), 1872–1880. 10.3892/mmr.2019.10655
186
Zhu L. J. He Z. R. Wang C. Y. Lu D. Y. Yang J. L. Jia W. W. et al (2024). Development history and frontier research progress of pharmacokinetics of traditional chinese medicine. J. GuangZhou Univ. Chin. Med.41 (10), 2746–2757. 10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2024.10.034
187
Zong Y. Li H. Liao P. Chen L. Pan Y. Zheng Y. et al (2024). Mitochondrial dysfunction: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target Ther.9 (1), 124. 10.1038/s41392-024-01839-8
188
Zou L. Dang W. Tao Y. Zhao H. Yang B. Xu X. et al (2023). The Il-33/St2 axis promotes acute respiratory distress syndrome by natural killer T cells. Shock59 (6), 902–911. 10.1097/shk.0000000000002114
189
Zou Y. Palte M. J. Deik A. A. Li H. Eaton J. K. Wang W. et al (2019). A GPX4-dependent cancer cell state underlies the clear-cell morphology and confers sensitivity to ferroptosis. Nat. Commun.10 (1), 1617. 10.1038/s41467-019-09277-9
Summary
Keywords
acute lung injury, pathogenesis, treatment, Traditional Chinese Medicine, bioactive compounds
Citation
Wang J, Yan Z, Zhang X, Wang S, Jiao L, Zhu B, Tan B and Yang A (2025) Exploring the pathogenesis of acute lung injury and its treatment through Traditional Chinese Medicine: a state-of-the-art review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1592458. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1592458
Received
12 March 2025
Accepted
07 July 2025
Published
31 July 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Marcello Iriti, University of Milan, Italy
Reviewed by
Quansheng Feng, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
omali Y El-khawaga, Mansoura University, Egypt
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wang, Yan, Zhang, Wang, Jiao, Zhu, Tan and Yang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Aidong Yang, aidongy@126.com; Bo Tan, tbot@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.