- 1School of Basic Medical, Luoyang Polytechnic, Luoyang, China
- 2Henan Provincial Engineering Research Center for Key Biomaterials in Immunology Technology, Luoyang, China
- 3Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Shenzhen, China
Neurological diseases, including stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and diabetic neuropathy, pose a significant global health burden. The rising incidence of these diseases, driven by factors including an aging population, lifestyle changes, and environmental influences, has intensified the urgent need for effective neuroprotective therapies. Rutin, a natural flavonoid glycoside widely distributed in various plants including buckwheat, citrus fruits, and onions, has garnered significant attention as a promising neuroprotective agent. This review comprehensively evaluates the current research on rutin’s multifaceted neuroprotective mechanisms, which encompass antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, antidepressant, anticonvulsant, and analgesic effects, as well as its role in enhancing neural signal transduction, improving learning and memory, and protecting the blood-brain barrier. However, despite its broad spectrum of neuroprotective effects and favorable safety profile, the clinical application of rutin is currently limited by its relatively low bioavailability. To address this limitation and fully harness rutin’s therapeutic potential, future research should prioritize the development of innovative formulations designed to enhance its bioavailability.
1 Introduction
The nervous system includes the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). It is reported that common neurological diseases worldwide include stroke, neonatal encephalopathy, migraine, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD) and diabetic neuropathy (Guo X et al., 2025). The common clinical manifestations of nervous system diseases include disturbance of consciousness, cognitive impairment, headache, vertigo, visual impairment, hearing impairment, motor impairment, somatosensory impairment and balance disorder. With the growth and aging of the global population, as well as the increase of risk factors such as environment, metabolism and lifestyle, the number of people suffering from stroke, AD, meningitis and other neurological diseases and deaths from these diseases has increased significantly (Mead et al., 2023; Calabrese et al., 2024; Mckee and Daneshvar, 2015).
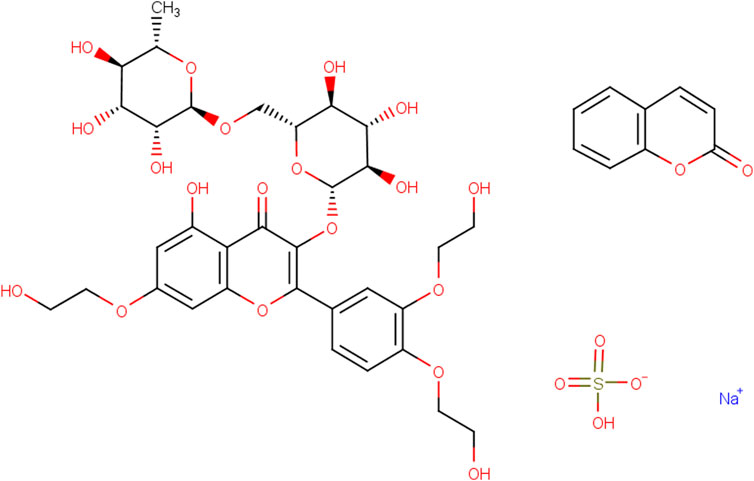
Rutin (Rut), a natural flavonoid glycoside, is a light yellow or light green crystalline powder (Figure 1). It widely exists in Rut leaves, tobacco leaves, jujubes, apricots, orange peel, tomatoes, buckwheat flowers and other plants (Forouzanfar et al., 2025a; Nicola et al., 2024; Shimazu et al., 2021). The content of Rut in the flower buds of Sophora japonica is high up to 20% and Sophora japonica is often used as raw material for industrial extraction of Rut (Saafan et al., 2023). Rut has a variety of pharmacological effects such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antihypertensive, maintaining vascular elasticity and neuroprotection (Mani et al., 2025; Abdullah et al., 2025; Jang et al., 2014). Due to its high pharmacological activity, less adverse drug reactions and wide range of targets, Rut is used to treat nervous system diseases (Chekuri et al., 2025; Forouzanfar et al., 2025b). Thus, Rut has a variety of neuroprotective mechanisms, including antioxidant effect, inhibition of neuronal apoptosis, improvement of learning and memory ability, protection of blood-brain barrier (BBB), which can be used as an effective drug for the treatment of nervous system diseases (Hai et al., 2024; Faysal et al., 2025; Xinghua et al., 2023; Xianchu et al., 2022). Rut also could pass through the BBB to improve the function of the hypothalamus pituitary adrenal axis by regulating the levels of monoamine neurotransmitters and brain-derived neurotrophic factors (BDNF) in the body, and exert neuroprotective effects on GABAergic, glutamatergic and cholinergic nervous systems (Motamedshariaty et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2021; Ji et al., 2024). As a safe and efficient new plant medicine, Rut has significant biological activity and has a wide application prospect in the medical field. This article will discuss the research progress of Rut neuroprotective effect based on the neuroprotective mechanisms.
2 Neuroprotective mechanisms of Rut
2.1 Antioxidant
Under physiological conditions, reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by the body can be eliminated by antioxidant systems such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH PX) in the body. The process of generation and elimination is in dynamic balance to maintain the stability of the internal environment (Song et al., 2018; Nkpaa and Onyeso, 2018; Aldian et al., 2025). Under pathological conditions, the rate of ROS generation by the body is far higher than the rate of endogenous elimination, resulting in a large amount of ROS accumulation, so that DNA, protein, lipid and other macromolecular compounds in the cell are in a state of peroxidation and cannot play their normal physiological functions (Andonova et al., 2025; de Carvalho et al., 2025).
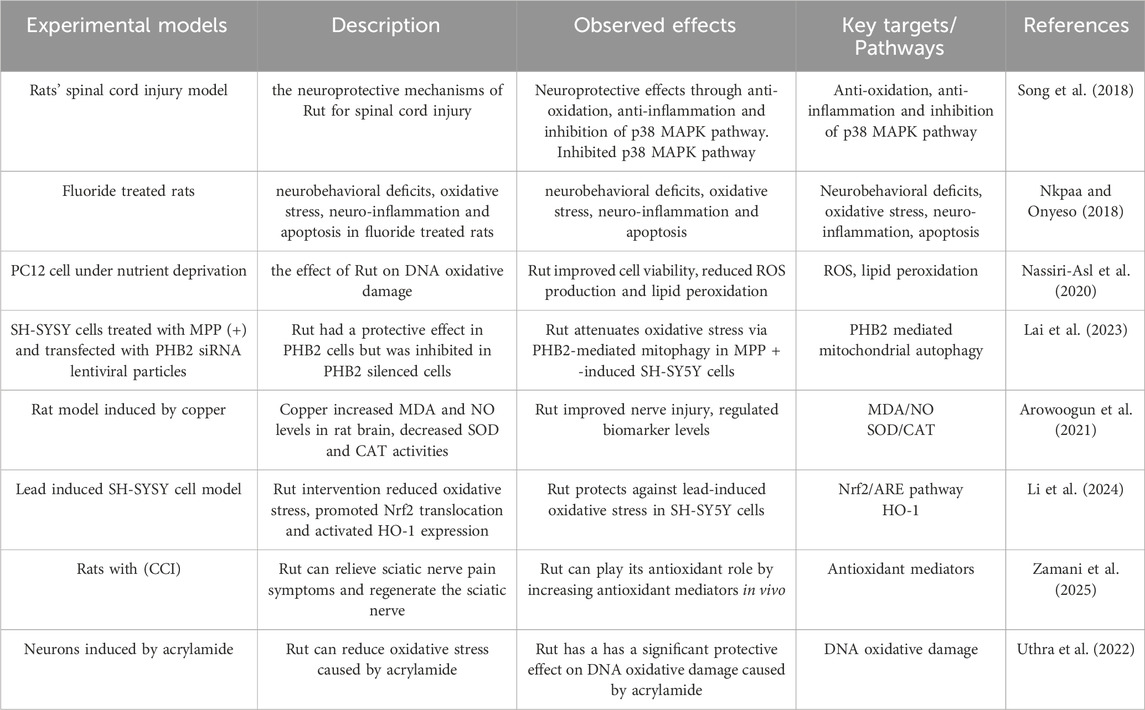
Nassiri-Asl M studied the effect of Rut on DNA oxidative damage in cultured rat pheochromocytoma cells (PC12) under nutrient deprivation. The results showed that Rut could improve the viability of PC12 cells under nutrient deprivation, reduce ROS production and lipid peroxidation (Nassiri-Asl et al. 2020). Lai X transfected Prohibitin 2 (PHB2) siRNA lentiviral particles into SH-SYSY cells treated with matrix metalloproteinase (MPP) (+) and found that Rut had a protective effect in PHB2 cells, but was inhibited in PHB2 silenced cells, suggesting that Rut may play its neuroprotective role by reducing oxidative damage and the depolarization level of mitochondrial membrane potential through PHB2 mediated mitochondrial autophagy (Lai et al. 2023). Arowoogun J established a rat model induced by copper. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO) in rat brain increased, and the activities of SOD and catalase (CAT) decreased, damaging neurons. Rut administration can improve nerve injury and regulate the levels of these biomarkers, suggesting that Rut can play a neuroprotective role by participating in antioxidant pathways and inhibiting oxidative stress (Arowoogun et al. 2021). Li F established the lead induced SH-SYSY cell model. After Rut intervention, it significantly reduced the oxidative stress of cells, promoted the translocation of nuclear factor red cell 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, and then activated the expression of antioxidant substances including Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and knocked out Nrf2 by small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection to reduce the protective effect of Rut on lead induced cells, suggesting that Rut alleviated lead induced oxidative stress by activating Nrf2/ARE pathway in SH-SY5Y cells and played its antioxidant role (Li et al. 2024). Zamani K have studied that Rut can effectively relieve the symptoms of abnormal sciatic nerve pain in rats with chronic constrictive injury (CCI) and regenerate the sciatic nerve, suggesting that Rut can play its antioxidant role by increasing antioxidant mediators in vivo (Zamani et al. 2025). Uthra C studied the effect of Rut on oxidative damage of neurons induced by acrylamide, and found that Rut can reduce oxidative stress caused by acrylamide, suggesting that Rut plays its antioxidant role and has a significant protective effect on DNA oxidative damage caused by acrylamide (Uthra et al. 2022) (Figure 2; Table 1).

Figure 2. This figure illustrates the mechanisms of oxidative stress regulation and neuronal damage by Rut. In the presence of stressors such as heavy metals, nutrient deprivation, MPP(+), DNA fragmentation and lipid peroxidation, NOX and mitochondrial complex I PHB2 contribute to the generation of ROS. The imbalance of the antioxidant system, including decreased levels of GSH, NRF2, NQO1, HO-1 and increased levels of MDA, NO, CAT and SOD results in impaired neuronal function. Rut treatment modulates oxidative damage and neuronal injury by bidirectionally regulating key factors of the redox system, including upregulating antioxidant markers (GSH, NRF2, NQO1, HO-1) while downregulating oxidative stress indicators (MDA, NO). The figure highlights the role of Rut in modulating oxidative stress.
2.2 Anti-inflammatory
Inflammatory response is a crucial factor in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Excessive neuroinflammation can exacerbate the damage to nerve cells, thereby further promoting the occurrence of neurological diseases (Taşlı et al. 2018). Neuroinflammatory response is one of the important triggers of neurodegenerative diseases. As the main immune cells in the CNS, microglia play a crucial role in maintaining brain homeostasis, including synaptic remodeling, BBB regulation, and neuroinflammation regulation (Hao et al. 2016; Sreelatha et al. 2024). When an inflammatory response occurs, microglia are immediately activated, and the activated microglia mainly have two states: M1 type and M2 type. M1 type microglia can cause local or widespread central nervous system damage by releasing cytotoxic substances and inflammatory factors, while M2 type microglia play a neuroprotective role by secreting anti-inflammatory mediators and neurotrophic factors (Sui et al. 2022; Jasim et al. 2025; Meimei et al. 2024). Therefore, targeting the selective activation of microglia, studying their functions and related inflammatory signaling pathways is of great significance for the treatment of nervous system inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases.
Xu PX found that Rut exerts neuroprotective effects by reducing the levels of oligomeric Aβ, inhibiting the activation of glial cells, and decreasing the production of inflammatory cytokines, thereby alleviating memory impairment in AD transgenic mice (Xu et al., 2014). Khan MM observed that administration of Rut resulted in a decrease in the number of dopamine D2 receptors in the striatum due to an increase in glutathione and its dependent enzymes (glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase), dopamine, and its metabolite 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, demonstrating the neuroprotective effect of Rut on PD (Khan et al. 2012). In addition, Javed H observed a reduction in “neuroinflammation” in a rat model of “Alzheimer’s type sporadic dementia”, and observed that Rut intervention alleviated impaired proliferation of hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) cells and protected mice from morphological changes in the CA3 region, reversing cognitive deficits and improving memory ability in it (Javed et al. 2012). In cell experiments, Rut can inhibit the secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis alpha, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and alleviate lipopolysaccharide induced neuronal inflammation (Lee et al. 2024). In addition, it was found that Rut can also downregulate the expression of M1 type markers inducible nitric oxide synthase and CD86 in BV-2 microglia by regulating the Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4)/NF-κB signaling pathway, and increase the expression of M2 type markers arginase 1 (Arg1) and CD206, thereby promoting the transformation of BV-2 cells from M1 to M2 type and exerting anti-inflammatory effects at the cellular level (Hu et al. 2023) (Figure 3; Table 2).

Figure 3. This figure reveals important factors in anti-inflammatory signaling pathway of Rut in the CNS microenvironment. Rut regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-1β, COX2, iNOS and TNF-α by acting on signaling pathways such as TLR4/NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome. Rut can also promote the clearance of A β peptide, maintain the stability of β-catenin, and protect the tight junctions between cells from damage. In microglia, Rut may alleviate inflammatory response and promote tissue repair by regulating its polarization state (M1 to M2 transition).
2.3 Anti-apoptotic effect
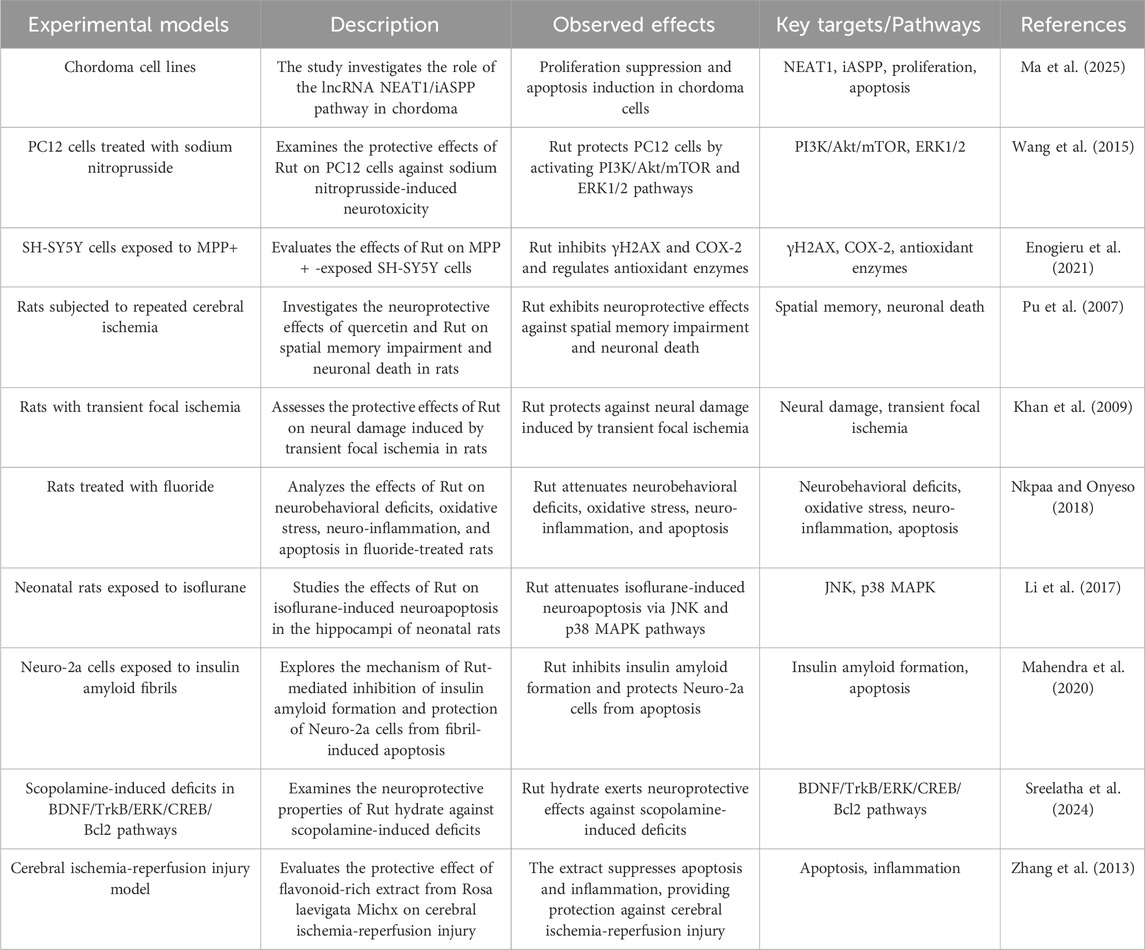
Apoptosis is an autonomous programmed cell death controlled by apoptotic genes. It is one of the types of programmed cell death, and its purpose is to maintain the stability of the human environment. The physiological process of apoptosis involves the activation, expression and regulation of a series of genes, such as the pro apoptotic gene B-cell lymphoma-2 associated X protein (Bax), cystainaspartate protease (Caspase), anti apoptotic gene B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), tumor suppressor gene Tumor Protein 53 (p53) and myelocytomatosis oncogene (c-Myc) (Ma et al. 2025). Rut can reduce sodium nitroprusside induced injury to PC12 neurons by activating extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK), reduce apoptosis triggered by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) producing NO, and protect neurons (Wang et al. 2015). Rut has a protective effect on SH-SYSY cells treated with 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine ion (MPP (+)), which can inhibit cell apoptosis and reduce cell oxidative damage (Enogieru et al. 2021). Bilateral common carotid artery ligation and middle cerebral artery occlusion are common models for establishing cerebral ischemia in mice. Rut can not only improve the survival rate of mice after bilateral common carotid artery ligation, but also significantly reduce brain edema and the number of apoptotic neurons (Pu et al. 2007). Khan MM have shown that Rut can inhibit the apoptosis of ischemic nerve cells by reducing the expression of p53, preventing the morphological changes of nerve cells and improving the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes (Khan et al. 2009). Ischemic stroke, also known as cerebral infarction, refers to a cerebrovascular disease in which cerebral blood supply insufficiency is caused by stenosis or occlusion of cerebral blood supply arteries (carotid artery and vertebral artery), and ischemic necrosis of brain tissue is caused by cerebral ischemia and hypoxia, especially apoptosis of neurons after ischemia. Nkpaa KW studied Rut attenuates fluoride induced toxicity in the cerebrum and striatum of rats via mechanisms involving neuro-inflammation and anti-apoptosis in rats. Rut may be used as a neuroprotective agent against induced neurotoxicity through anti-apoptosis pathway (Nkpaa and Onyeso, 2018). In addition, Rut can significantly avoid the production of ROS and inhibit cell apoptosis through two different mechanism pathways (p38MAPK and JNK signaling pathway) (Li et al. 2017). Rut decreases the insulin amyloid fibrils-induced Neuro-2a cytotoxicity by reducing ROS levels which in turn downregulates Bax and upregulates Bcl-2 and pBad proteins (Mahendra et al. 2020). Rut can alleviate the neuronal injury in AD-like learning and memory impairment rat model by inhibiting reduce the neuronal apoptosis rate and the expression of apoptosis related proteins Bax in hippocampus (Sreelatha et al. 2024). Rut also significantly inhibit the activation of MAPK signaling pathway induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion, reduce the expression of apoptosis related proteins and the occurrence of apoptosis, indicating that Rut can play an anti apoptotic role in reducing nerve injury by inhibiting MAPK signaling pathway (Zhang et al. 2013) (Figure 4; Table 3).

Figure 4. This figure shows the apoptotic signaling cascades triggered by Rut in nerve cells. Rut initiates the extrinsic apoptotic pathway through interaction with the Fas receptor, culminating in Caspase-8 activation. In parallel, Rut stimulates the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway by upregulating the tumor suppressor protein P53, which subsequently enhances the expression of the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bak. The subsequent activation of Bax and Bak facilitates the release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria, thereby activating the Caspase cascade involving Caspase-9 and Caspase-3. Additionally, Rut downregulates the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL, thereby potentiating the apoptotic response. The convergence of these pathways leads to Caspase-3 activation, which is pivotal in executing apoptosis.
2.4 Antidepressant effect
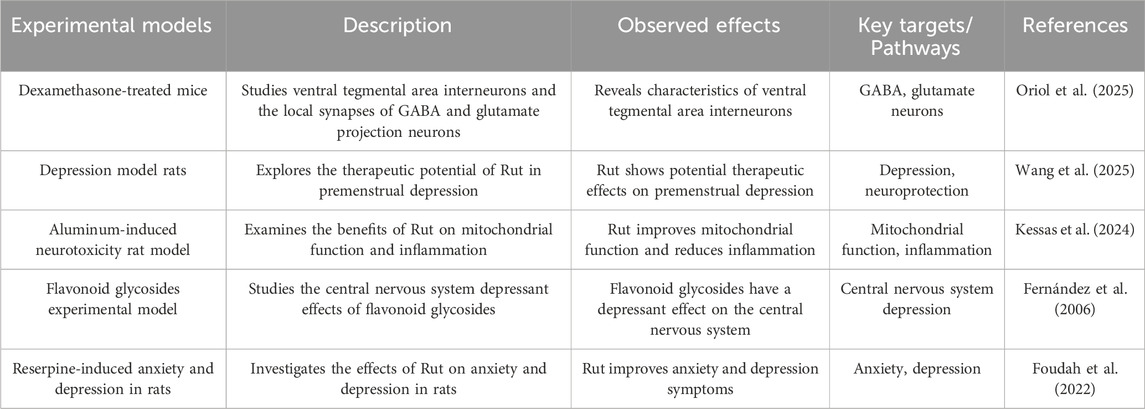
The hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis is associated with a variety of emotional and cognitive disorders. The HPA axis is hyperactive in patients with major depression, and the onset of the disease is closely related to the increase of cortisol content and the decrease of the activity of mineralocorticoid receptor and glucocorticoid receptor. Excessive content of endothelin in the body will stimulate hypothalamic atrophy and cause anxiety and emotional tension (Sălcudean et al. 2025). Schloms L found that Rut can effectively prevent the changes of adrenocorticotropic hormone in plasma and cortisol in serum of depression model mice, significantly reduce the cortisol level in adrenal H295R cells, and show antidepressant effect in open field test, forced swimming test and sucrose preference test (Schloms et al. 2014). Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid, which can cause the death of hippocampal CA3 neurons, and then cause learning and memory disorders. The water maze test showed that the escape latency of Rut pretreatment group was significantly lower than that of dexamethasone group, and Rut pretreatment could effectively change the morphological damage of CA3 area caused by dexamethasone. This study suggests that Rut may regulate the activity of HPA axis by affecting the glucocorticoid level in vivo, and then participate in neuroprotection and play an antidepressant role (Tongjaroenbuangam et al. 2011).
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. The balance between GABA and excitatory neurotransmission is essential for the normal function of the brain. The study found that the content of GABA in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue samples of patients with depression decreased, the function of GABAR was defective, and the expression of GABA synthase GAD67 was downregulated. For GABA deficiency in depression, there are benzodiazepines that can enhance the function of GABAAR γ 2 subunit and tetrahydroperone preparations that act on GABAA receptor (Oriol et al. 2025). Wang X found Rut alleviated depressed mood, memory impairment and social impairment, ameliorated hippocampal neuronal damage and reduces GABA and acetylcholine (ACh) levels in depressed rats (Wang et al. 2025). In addition, Kessas K found that 200 mg/kg Rut intervened the aluminum poisoning model rats, and the GABA content in the brain tissue was significantly increased. Therefore, it is speculated that Rut can exert antidepressant effect by affecting GABAergic system (Kessas et al. 2024). The CNS and behavioral activity of Rut were tested by pore plate and thiopental sodium induced sleep time and motor activity in mice. Rut can inhibit the CNS by intraperitoneal administration. Studies have confirmed that Rut cannot have inhibitory activity of CNS due to the participation of GABA A receptor (Fernández et al. 2006). Foudah AI found that 14 days of treatment with Rut showed a modest antidepressant effect in reserpine-induced anxiety and depression in rats. Rut has shown antidepressant effects by reducing antioxidant activity and acetylcholinesterase (Foudah et al. 2022) (Figure 5; Table 4).

Figure 5. This figure illustrates the diverse neuroprotective effects of Rut and its underlying molecular mechanisms. Rut exhibits antidepressant effects by modulating the CA3 region and the HPA axis, as well as influencing GABA and GAD67. It demonstrates anticonvulsant properties through interactions with Glu, AMPA, NMDA receptors, and components like GluA1, GluA2, IL-1R1, and TLR4. Rut’s analgesic effects are linked to its interaction with CB1, CRIP1a, MAPK, and NF-κB pathways. The compound enhances neural signaling by regulating BDNF, GDNF, ERα, and ERβ. Additionally, rutin improves learning and memory skills via NGF, TrkA, TrkB, and CREB. The figure also highlights Rut’s role in protecting the BBB by modulating miR-124, MMP-9, BACE1, and APP. Furthermore, it shows Rut’s influence on GAD67 and Aβ in the context of neurological protection. Overall, this diagram provides a comprehensive overview of rutin’s multifaceted neuroprotective and neuromodulatory effects.
2.5 Anticonvulsant effect
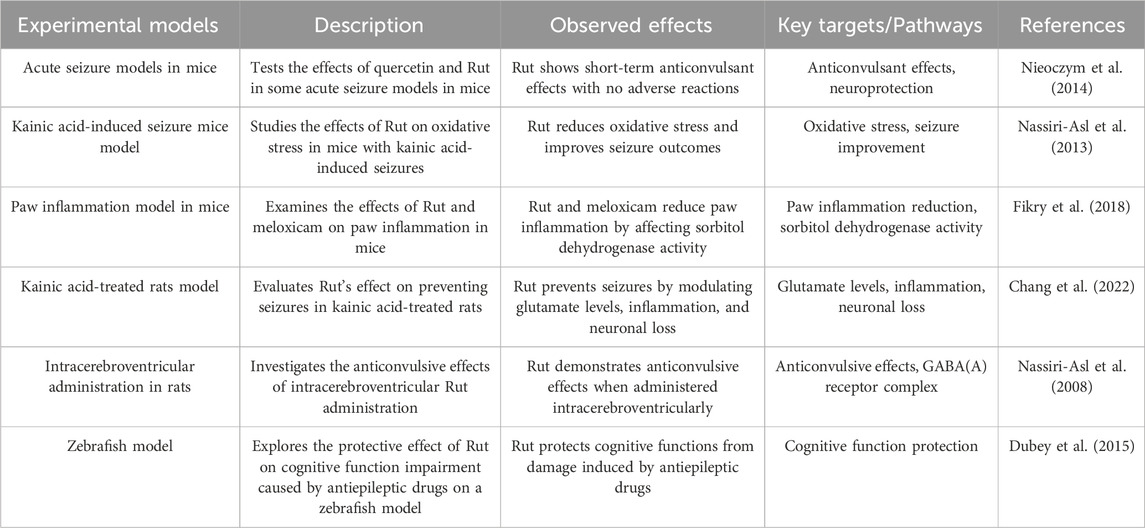
Researchers conducted behavioral tests on psychomotor convulsion model mice, including motor coordination test, muscle strength test and long-term memory test, and found that Rut intervention mice had short-term anticonvulsant effect and Rut had no adverse reactions (Nieoczym et al. 2014). Nassiri-Asl M found that in the kainic acid-induced seizure rat model, Rut pretreatment can significantly reduce the severity of seizures and reverse hippocampal neuron loss (Nassiri-Asl et al. 2013). In addition, Researchers found that Rut can also regulate the level of glutamate, reduce the expression of glutaminase and NMDA receptor subunit glun2b, and increase the expression of excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT), glutamine synthetase (GS) and AMPA receptor subunit GluA1 and GluA2 (Fikry et al. 2018).
Rut can also inhibit activated astrocytes, downregulate inflammatory molecules such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), high mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1), interleukin-1 receptor 1 (IL-1r1) and toll like receptor 4 (TLR-4), and upregulate the protein expression of anti-inflammatory molecule interleukin-10 (IL-10). In conclusion, the results suggest that Rut can reduce kainic acid-treated seizures and neuron loss by reducing glutamatergic hyperfunction and inhibiting IL-1r1/TLR4 related neuroinflammatory cascade (Chang et al. 2022). The effect of Rut injected into lateral ventricle on mild clonic seizures (MCS) and generalized tonic clonic seizures (GTC) induced by pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) was dose-dependent, and its mechanism was to increase the number of seizures. In addition, flumazenil pretreatment can eliminate the anticonvulsant effect of Rut during two seizures. These results indicate that Rut has anticonvulsant effect in the brain, which may be the positive allosteric regulation of GABA (a) receptor complex through the interaction at the benzodiazepine site (Nassiri-Asl et al. 2008). The convulsions of zebrafish were induced by benzotetrazole, and the behavior of zebrafish was studied, including latency, movement effect, color effect, fish cohesion, light/dark experiment. Antiepileptic drugs were used to interfere with the regional activities of fish, and Rut was used to treat them. It was found that the behavioral response of zebrafish returned to normal. These results indicate that Rut has a positive effect on the swimming behavior of zebrafish. Rut can increase the latency of zebrafish moving in the light room, suggesting that Rut plays its neuroprotective role by alleviating convulsive reaction (Dubey et al. 2015).
The anticonvulsant effect of Rut is closely related to its anti-inflammatory and cognitive improvement properties. Rut can inhibit activated astrocytes, downregulate the expression of inflammatory molecules (such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, etc.), and upregulate the expression of anti-inflammatory molecule IL-10, so as to improve cognitive ability. These mechanisms suggest that Rut exerts its neuroprotective effect against seizures by regulating the level of neurotransmitters, inhibiting neuroinflammation and improving cognitive ability (Figure 5; Table 5).
2.6 Analgesic effect
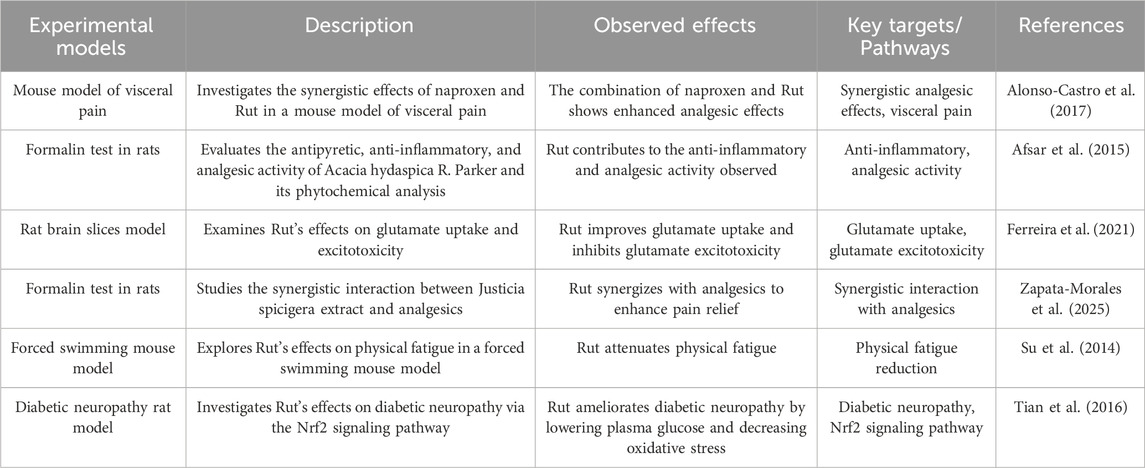
The generation of pain depends on pain signals uploaded to the CNS. Neurotransmitters and ion channels regulate the electrical activities of primary afferent nerves. Ionic glutamate receptors are coupled with ion channels and play an important role in mediating the transmission of pain signals in the CNS and PNS. Activation of glutamate receptors can induce the increase of NO and cGMP, and participate in the pain neuron response caused by peripheral inflammation (Alonso-Castro et al. 2017).
The antinociceptive effect of Rut in acetic acid-induced writhing test in mice was given 60 min before intraperitoneal injection of acetic acid. In the writhing test, the dose-response curve and the experimental effective dose 50 (ED50) of Rut in different dose combinations were measured. The results showed that Rut participated in two different mechanisms and had protective effect on writhing injury (Afsar et al. 2015). Rut has an effect on formalin induced paw inflammation in mice. Rut can significantly improve the licking time of mice on the first day, and has a good inhibitory effect on formalin induced paw inflammation pain in mice (Ferreira et al. 2021). In addition, studies have confirmed that Rut has peripheral and central antinociceptive activities. Zapata-Morales JR found that Rut synergistically produces analgesic effect by regulating opioid system, paracetamol and non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs by down regulating p38 MAPK NF-κB and prostaglandins (Zapata-Morales JR et al. 2025). Su KY found that Rut significantly increased the expression of CB1 cannabinoid receptor interacting proteins A (crip1a) in the brain of mice (Su et al. 2014). Crip1a is an auxiliary protein of CB1 and can regulate the tension inhibition of voltage dependent calcium channels mediated by CB1 receptors. Tian R found that Rut had significant inhibitory effects on mechanical hyperalgesia, thermal hyperalgesia and cold hyperalgesia in diabetic rats, and the mechanism was related to inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and reducing the production of IL-6 and TNF-α in dorsal root ganglion (Tian et al. 2016).
The analgesic effect of Rut is induced by enhancing the antioxidant pool, reducing the levels of inflammatory factors (such as TNF-α) and IL-1β, inhibiting the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and regulating MAPK, NF-κB and Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathways (Figure 5; Table 6).
2.7 Enhance neural signal transduction
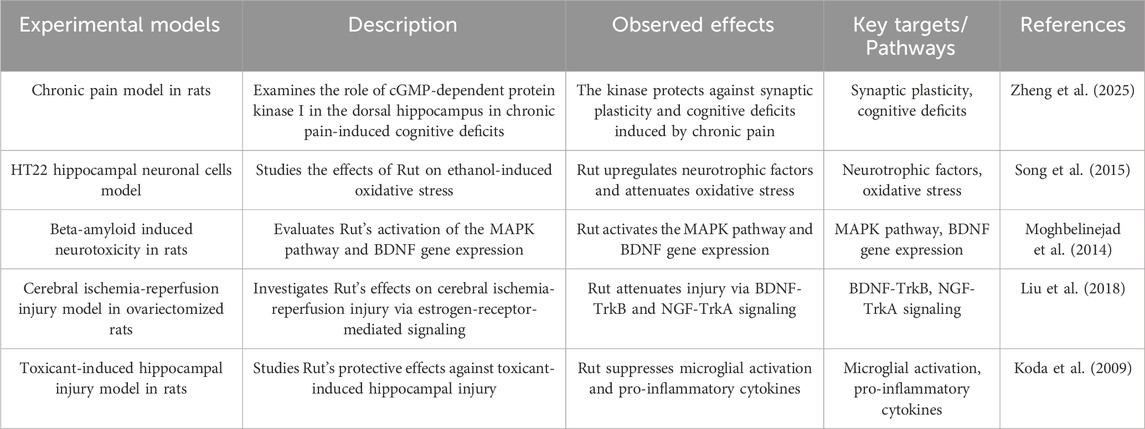
Nerve regulation refers to the excitation, inhibition, or regulation of neurons or nerve signal transduction in the CNS, intestinal nervous system, and autonomic nervous system through various forms of stimulation enhancement. These may help to strengthen new nerve connections and enhance neural plasticity, and neurotrophic factors regulate nerve survival and proliferation in the nervous system (Zheng et al. 2025). Song K found that Rut pretreatment prevented the ethanol-induced decrease in protein level expression of nerve growth factor, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and BDNF in HT22 cells (Song et al. 2015). Flavonoids improve the mechanism of DPN enhancing neurotrophic signal transduction. BDNF is associated with neurogenesis, neuronal maturation, survival and synaptic plasticity in vivo. BDNF combines with its receptor tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) to activate downstream signaling pathways, including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT and mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), and plays its growth promoting role (Moghbelinejad et al. 2013). Liu H Found that Rut can enhance Erα ERβ, BDNF, The levels of nerve growth factor (NGF), tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA), TrkB and cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein (p-CREB) in ovariectomized rats were measured and the cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in ovariectomized rats was improved. It has been improved that level of BDNF decreased in the hippocampus of depression patients and animal models (Liu et al. 2018). Koda T Found that Rut can improve memory damage induced by aβ25-35 by regulating BDNF signaling pathway in hippocampus (including Akt, ERK and CREB), and quantitative analysis of its crude extract found that Rut is a high content compound in Lespedeza, suggesting that Rut may participate in memory protection as the main component of Lespedeza in the process of up regulating BDNF signaling pathway in hippocampus (Koda et al. 2009) (Figure 5; Table 7).
2.8 Improve learning and memory ability
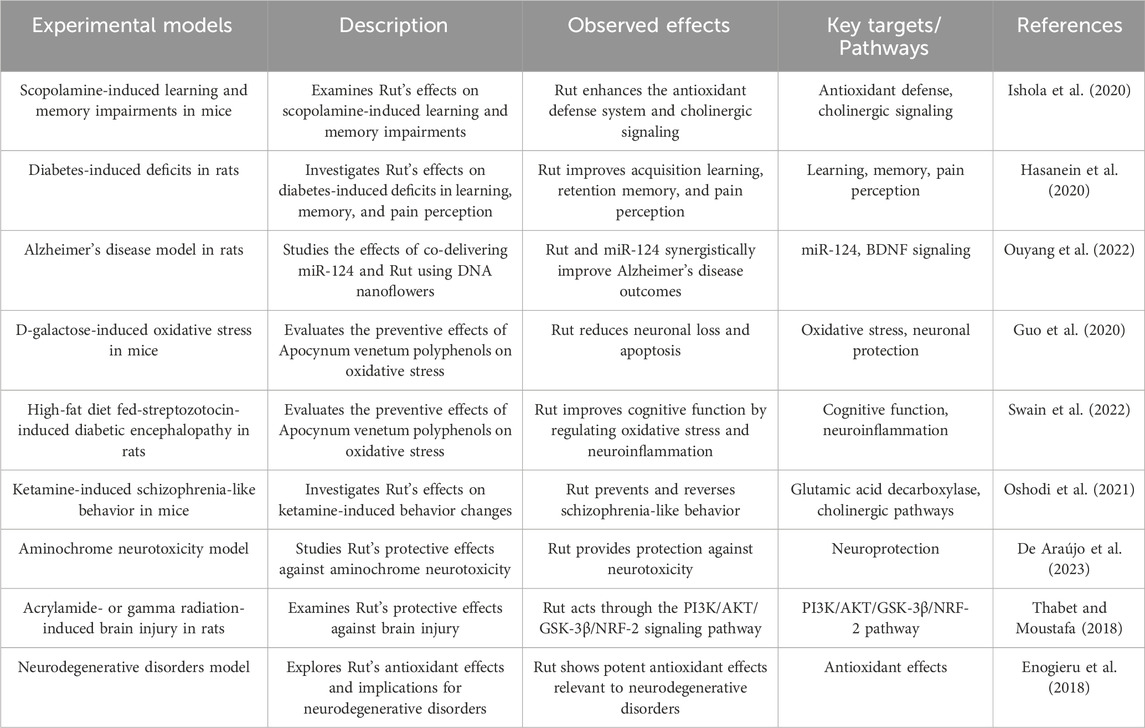
Ishola IO’s study found that Rut pretreatment can significantly reduce scopolamine induced nitrosation/oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase activity in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of mice. Rut can restore cognitive function of scopolamine induced amnesia by enhancing antioxidant defense system and cholinergic system (Ishola et al. 2020). Rut can reverse the learning and memory impairment of diabetic rats. 50 mg/kg Rut has obvious hypoglycemic effect on diabetic rats and non-diabetic rats, and long-term oral administration of Rut can induce cognitive enhancement in diabetic rats. Therefore, Rut is considered as a potential treatment for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (Hasanein et al. 2020). Studies have found that Rut can improve the energy metabolism of microglia in the brain of AD mice, increase the expression level of phagocytic receptors, and then restore and enhance the phagocytosis and clearance of a β by microglia, and improve ad related pathological and cognitive damage (Ouyang et al. 2022). Rut can also improve the spatial learning and memory ability of aging mice by inhibiting D-galactose-induced neuronal loss and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons (Guo et al. 2020). Studies have found that Rut can improve the cognitive function of SAMP8 mice fed with high-fat diet, and its mechanism is related to reducing the level of brain a β related protein and improving neuroinflammation (Swain et al. 2022). In the experiment of schizophrenic mice, Rut can prevent and treat ketamine induced spatial learning and memory impairment and improve their social ability by up regulating the expression of GAD67 in the striatum and prefrontal cortex (Oshodi et al. 2021).
Rut contains lecithin, triglyceride and other components that can directly promote the development of nervous system and brain cell activity, enhance children’s intellectual development and delay the cognitive decline of the elderly (De Araújo et al., 2023). At the same time, Rut can regulate capillary permeability, improve cerebral microcirculation and metabolic environment, and provide stable nutritional support for the brain (Thabet and Moustafa, 2018). In addition, Rut can enhance neuroprotective effect by promoting energy metabolism of microglia, which may have intervention effect on Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases (Enogieru et al. 2018) (Figure 5; Table 8).
2.9 Protect blood brain barrier
BBB is a kind of barrier composed of vascular endothelial cells, basement membrane and astrocytes, which is located in the cerebrovascular system. Its main function is to limit the damage of external substances to the brain, only allow nutrients, oxygen and other essential substances to pass through, filter out harmful substances and protect the brain from harmful substances (Zhang et al. 2025).
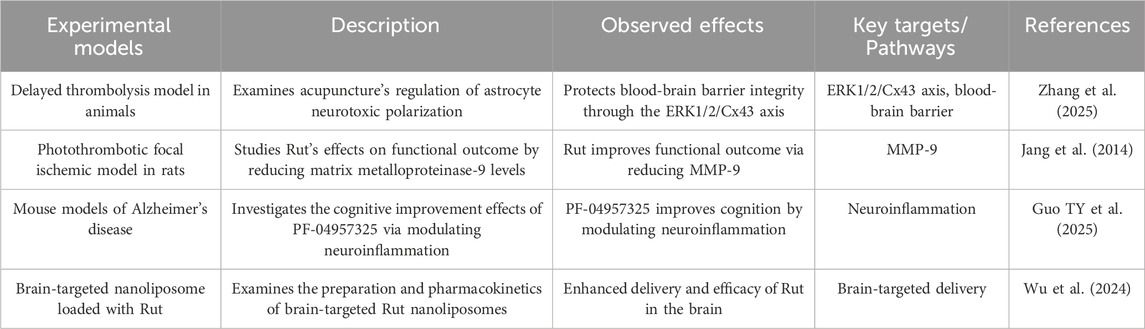
Rut can reduce the damage of BBB caused by cerebral thrombosis and local ischemia, and improve acute ischemic stroke. The mechanism is partly through inhibiting the expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) (Jang et al., 2014). Rut can cooperate with miR-124 to inhibit the expression of BACE1 and app, thus strongly inhibiting the production of Aβ. The nano system can promote the long-term circulation of miR-124 in vivo, promote its BBB permeability and neuron targeting, and significantly increase the content of miR-124 in hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice, which has good therapeutic effect in vivo. This biologically derived therapeutic system shows the prospect of being used as a biocompatible nanodrug in the treatment of ad (Guo TY et al., 2025). Rut liposomes were prepared by film dispersion method, and the preparation conditions were optimized by response surface methodology. Then transferrin (TF) was introduced into liposomes through covalent modification to prepare TF Rut liposomes, indicating that TF Rut lip has brain targeting, which may improve the efficacy of Rut in the treatment of brain diseases (Wu et al. 2024) (Figure 5; Table 9).
3 Discussion and perspectives
Rut is emerging as a highly promising neuroprotective agent, demonstrating a wide array of mechanisms that equip it to address multiple facets of neurological disorders. Its antioxidant properties are particularly vital in the context of neurological diseases, many of which are underpinned by oxidative stress. The hydroxyl groups on the flavonoid core of Rut are key to its antioxidant properties. The conjugated system formed by the benzene rings and oxygen atoms in the structure enables Rut to stabilize free radicals and scavenge reactive oxygen species such as superoxide anions, hydroxyl radicals, and peroxyl radicals, thereby reducing oxidative damage to the body. The glycosidic moiety influences its antioxidant activity by enhancing its solubility in water and facilitating its transport and absorption within biological systems, allowing it to exert antioxidant effects in both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments (Agarwal et al. 2025; L Suraweera et al. 2020). In the fields of neuroinflammation, Rut’s role is equally significant. It can inhibit the activity of inflammatory mediators such as cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase. Its structural components interact with key enzymes and signaling molecules involved in the inflammatory response, blocking inflammatory signaling pathways and reducing the production and release of inflammatory cytokines like interleukins and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Additionally, its antioxidant properties help mitigate oxidative stress-induced inflammation (Habtemariam, 2016; Budzynska et al. 2019). Moreover, Rut also can regulate the delicate balance of apoptosis-related genes, it can interact with a variety of signaling pathways and molecular targets during development. It also can regulate cell cycle related proteins, induce cell cycle arrest and prevent cell proliferation. It promotes cell apoptosis by activating apoptosis signaling pathway. This is crucial for preserving neuronal integrity and function (Wen and Hu, 2024; Zhang et al. 2021).
Beyond these mechanisms, Rut has shown antidepressant, anticonvulsant, and analgesic effects. These multifaceted effects can be attributed to its ability to regulate the HPA axis, which is often dysregulated in stress-related disorders, as well as its modulation of neurotransmitter systems and inflammatory responses (Chen et al. 2022). Rut can alleviate symptoms associated with depression and anxiety while also providing relief in seizure disorders and pain conditions by enhancing GABAergic transmission or modulating the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Emudainohwo et al., 2023). Rut’s impact on neural signal transduction is another key aspect of its neuroprotective profile. It can upregulate neurotrophic factor BDNF, which plays a crucial role in supporting the survival and growth of neurons, enhancing synaptic plasticity, and promoting neurogenesis (Çelik et al. 2020). The activation of downstream signaling pathways like PI3K/AKT and MAPK by BDNF further amplifies, Rut’s beneficial effects on learning and memory (Ola et al. 2015). Moreover, Rut has been found to protect the BBB by inhibiting the expression and activity of MMP-9 (Sun et al. 2025).
Despite these extensive and promising neuroprotective effects, Rut’s journey to clinical application faces some challenges, such as its relatively low bioavailability, chemically unstable under certain conditions, including light, heat, and pH, pharmacokinetic limitations, interact with other medication could either reduce Rut’s effectiveness or increase the risk of adverse effects and its safety profile with long-term use or at high doses (Ozkan et al. 2020; Goyal and Verma et al., 2023). These limitations have dampened their therapeutic potential in humans despite its efficacy in preclinical models. However, the development of advanced drug delivery systems, nano systems or liposomes with brain targeting properties, Genetic engineering and metabolic engineering techniques and combine with other bioactive substances could markedly enhance Rut’s bioavailability. These innovative formulations could facilitate the efficient delivery of Rut across the BBB to target tissues, thereby maximizing its therapeutic effects (Malekpour et al. 2025).
In conclusion, Rut boasts a multitude of neuroprotective mechanisms that position it as a versatile and potent therapeutic agent for neurological disorders. While further research is needed to optimize its delivery and overcome its bioavailability limitations, the existing evidence underscores Rut’s immense potential. With continued scientific efforts, Rut could evolve into a cornerstone of neuroprotective therapy, offering new hope for patients suffering from a wide spectrum of neurological diseases.
Author contributions
ZC: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Software, Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration. WS: Data curation, Project administration, Validation, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Software, Investigation, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Zhongyuan Scholar Workstation Project (234400510005).
Acknowledgments
The mechanism figures of this paper were drawn by Figdraw, thank you to Home for Researchers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdullah, H. A., Moawed, F. S., Ahmed, E. S., Abdel Hamid, F. F., and Haroun, R. A. (2025). Iron chelating, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic activities of hesperidin and/or rutin against induced-ferroptosis in heart tissue of rats. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 39, 3946320251331873. doi:10.1177/03946320251331873
Afsar, T., Khan, M. R., Razak, S., Ullah, S., and Mirza, B. (2015). Antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of Acacia hydaspica R. Parker and its phytochemical analysis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 15, 136. doi:10.1186/s12906-015-0658-8
Agarwal, S., Kaushik, S., Saha, H., Paramanick, D., Mazhar, M., Basist, P., et al. (2025). Therapeutic potential of traditional herbal plants and their polyphenols in alleviation of mercury toxicity. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 6. doi:10.1007/s00210-025-03807-7
Aldian, D., Harisa, L. D., Tomita, H., Tian, K., Takashima, S., Iwasawa, A., et al. (2025). Insights into rutin and quercetin biotransformations in ruminants revealed by molecular networking. J. Anim. Sci., skaf154. doi:10.1093/jas/skaf154
Alonso-Castro, A. J., Rangel-Velázquez, J. E., Isiordia-Espinoza, M. A., Villanueva-Solís, L. E., Aragon-Martinez, O. H., and Zapata-Morales, J. R. (2017). Synergism between naproxen and rutin in a mouse model of visceral pain. Drug Dev. Res. 78 (5), 184–188. doi:10.1002/ddr.21391
Andonova, T., Muhovski, Y., Naimov, S., Apostolova, E., Mladenova, S., Dincheva, I., et al. (2025). Potentillae argenteae herba-antioxidant and DNA-protective activities, and microscopic characters. Antioxidants (Basel) 14 (4), 487. doi:10.3390/antiox14040487
Arowoogun, J., Akanni, O. O., Adefisan, A. O., Owumi, S. E., Tijani, A. S., and Adaramoye, O. A. (2021). Rutin ameliorates copper sulfate-induced brain damage via antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 35 (1), e22623. doi:10.1002/jbt.22623
Budzynska, B., Faggio, C., Kruk-Slomka, M., Samec, D., Nabavi, S. F., Sureda, A., et al. (2019). Rutin as neuroprotective agent: from bench to Bedside. Curr. Med. Chem. 26 (27), 5152–5164. doi:10.2174/0929867324666171003114154
Calabrese, E. J., Pressman, P., Hayes, A. W., Dhawan, G., Kapoor, R., Agathokleous, E., et al. (2024). RUTIN, a widely consumed flavonoid, that commonly induces hormetic effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 187, 114626. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2024.114626
Çelik, H., Kandemir, F. M., Caglayan, C., Özdemir, S., Çomaklı, S., Kucukler, S., et al. (2020). Neuroprotective effect of rutin against colistin-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rat brain associated with the CREB/BDNF expressions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47 (3), 2023–2034. doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05302-z
Chang, A., Chang, Y., and Wang, S. J. (2022). Rutin prevents seizures in kainic acid-treated rats: evidence of glutamate levels, inflammation and neuronal loss modulation. Food Funct. 13 (20), 10401–10414. doi:10.1039/d2fo01490d
Chekuri, S., Sirigiripeta, S. R., Thupakula, S., Vyshnava, S. S., Ayesha, S., Karamthote Cheniya, S. B., et al. (2025). Rutin isolated from Acalypha indica L.: a comprehensive analysis of its antibacterial and anticancer activities. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 765, 151833. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151833
Chen, S., Tang, Y., Gao, Y., Nie, K., Wang, H., Su, H., et al. (2022). Antidepressant potential of quercetin and its glycoside derivatives: a comprehensive review and update. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 865376. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.865376
De Araújo, F. M., Frota, A. F., de Jesus, L. B., Cuenca-Bermejo, L., Ferreira, K. M. S., Santos, C. C., et al. (2023). Protective effects of flavonoid rutin against aminochrome neurotoxicity. Neurotox. Res. 41 (3), 224–241. doi:10.1007/s12640-022-00616-1
de Carvalho, L. S., Meccatti-Domiciano, V. M., da Silva, L. R. D., Marcucci, M. C., Carvalho, C. A. T., Abu Hasna, A., et al. (2025). Psidium guajava L. hydroethanolic extract as endodontic irrigant: phytochemical analysis, antioxidant activity, antimicrobial action and biocompatibility. PeerJ 13, e19301. doi:10.7717/peerj.19301
Dubey, S., Ganeshpurkar, A., Bansal, D., and Dubey, N. (2015). Protective effect of rutin on impairment of cognitive functions of due to antiepileptic drugs on zebrafish model. Indian J. Pharmacol. 47 (1), 86–89. doi:10.4103/0253-7613.150357
Emudainohwo, J. O. T., Ben-Azu, B., Adebayo, O. G., Aduema, W., Uruaka, C., Ajayi, A. M., et al. (2023). Normalization of HPA Axis, cholinergic neurotransmission, and inhibiting brain oxidative and inflammatory dynamics are associated with the adaptogenic-like effect of rutin against psychosocial defeat stress. J. Mol. Neurosci. 73 (1), 60–75. doi:10.1007/s12031-022-02084-w
Enogieru, A. B., Haylett, W., Hiss, D., and Ekpo, O. (2021). Inhibition of γH2AX, COX-2 and regulation of antioxidant enzymes in MPP+-exposed SH-SY5Y cells pre-treated with rutin. Metab. Brain Dis. 36 (7), 2119–2130. doi:10.1007/s11011-021-00746-z
Enogieru, A. B., Haylett, W., Hiss, D. C., Bardien, S., and Ekpo, O. E. (2018). Rutin as a potent antioxidant: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 27, 6241017. doi:10.1155/2018/6241017
Faysal, M., Al Amin, M., Zehravi, M., Sweilam, S. H., Arjun, UVNV, Gupta, J. K., et al. (2025). Therapeutic potential of flavonoids in neuroprotection: brain and spinal cord injury focus. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 27. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40014123. doi:10.1007/s00210-025-03888-4
Fernández, S. P., Wasowski, C., Loscalzo, L. M., Granger, R. E., Johnston, G. A., Paladini, A. C., et al. (2006). Central nervous system depressant action of flavonoid glycosides. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 539 (3), 168–176. Epub 2006 Apr 6. PMID: 16698011. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.04.004
Ferreira, R. S., Teles-Souza, J., Dos Santos Souza, C., Pereira, É. P. L., de Araújo, F. M., da Silva, A. B., et al. (2021). Rutin improves glutamate uptake and inhibits glutamate excitotoxicity in rat brain slices. Mol. Biol. Rep. 48 (2), 1475–1483. Epub 2021 Jan 25. PMID: 33492574. doi:10.1007/s11033-021-06145-y
Fikry, E. M., Hasan, W. A., and Mohamed, E. G. (2018). Rutin and meloxicam attenuate paw inflammation in mice: affecting sorbitol dehydrogenase activity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 32 (2). Epub 2018 Jan 5. PMID: 29315975. doi:10.1002/jbt.22029
Forouzanfar, F., Pourbagher-Shahri, A. M., and Ahmadzadeh, A. M. (2025b). Rutin attenuates complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain in rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 28 (3), 332–339. PMID: 39906613; PMCID: PMC11790188. doi:10.22038/ijbms.2024.81572.17655
Forouzanfar, F., Sahranavard, T., Tsatsakis, A., Iranshahi, M., and Rezaee, R. (2025a). Rutin: a pain-relieving flavonoid. Inflammopharmacology 33, 1289–1301. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39961908. doi:10.1007/s10787-025-01671-8
Foudah, A. I., Alqarni, M. H., Alam, A., Devi, S., Salkini, M. A., and Alam, P. (2022). Rutin improves anxiety and reserpine-induced depression in rats. Molecules 27 (21), 7313. PMID: 36364141; PMCID: PMC9654015. doi:10.3390/molecules27217313
Goyal, J., and Verma, P. K. (2023). An overview of biosynthetic pathway and therapeutic potential of rutin. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 23 (14), 1451–1460. PMID: 36698235. doi:10.2174/1389557523666230125104101
Guo, H., Kuang, Z., Zhang, J., Zhao, X., Pu, P., and Yan, J. (2020). The preventive effect of Apocynum venetum polyphenols on D-galactose-induced oxidative stress in mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 19 (1), 557–568. Epub 2019 Nov 29. PMID: 31897099; PMCID: PMC6923744. doi:10.3892/etm.2019.8261
Guo, T. Y., Zhang, M., Lv, Y. L., Qiu, N. Z., Chen, R. M., Zhang, F. F., et al. (2025). Cognitive improvement effects of PF-04957325, a phosphodiesterase-8 inhibitor, in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease via modulating neuroinflammation. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2, pyaf028. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40312965. doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyaf028
Guo, X., Liu, X., Lin, J., Huang, Z., Lin, S., Zhang, M., et al. (2025). Global, regional, and national burden of four major neurological diseases in women from 1990 to 2021. Front. Public Health 13, 1561216. PMID: 40270724; PMCID: PMC12014452. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2025.1561216
Habtemariam, S. (2016). Rutin as a natural therapy for Alzheimer's disease: insights into its mechanisms of action. Curr. Med. Chem. 23 (9), 860–873. doi:10.2174/0929867323666160217124333
Hai, J. J., Liang, W., Sun, D., Yin, P., Han, B., and Qu, X. (2024). Rutin attenuates distraction spinal cord injury by inhibiting microglial inflammation through downregulation of P38 MAPK/NF-κB/STAT3 pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 19, 6027–6040. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39699845. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-04659-7
Hao, G., Dong, Y., Huo, R., Wen, K., Zhang, Y., and Liang, G. (2016). Rutin inhibits neuroinflammation and provides neuroprotection in an experimental rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage, possibly through suppressing the RAGE-NF-κb inflammatory signaling pathway. Neurochem. Res. 41 (6), 1496–1504. Epub 2016 Feb 11. PMID: 26869040. doi:10.1007/s11064-016-1863-7
Hasanein, P., Emamjomeh, A., Chenarani, N., and Bohlooli, M. (2020). Beneficial effects of rutin in diabetes-induced deficits in acquisition learning, retention memory and pain perception in rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 23 (7), 563–574. Epub 2018 Oct 15. PMID: 30321127. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2018.1533269
Hu, Y., Jia, K., Zhou, Y., Chen, L., Wang, F., Yi, X., et al. (2023). Rutin hydrate relieves neuroinflammation in zebrafish models: involvement of NF-κB pathway as a central network. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 141, 109062. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37678480. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2023.109062
Ishola, I. O., Olubodun-Obadun, T. G., Ojulari, M. A., and Adeyemi, O. O. (2020). Rutin ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairments through enhancement of antioxidant defense system and cholinergic signaling. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 36, 53–61. doi:10.1515/dmpt-2020-0118
Jang, J. W., Lee, J. K., Hur, H., Kim, T. W., Joo, S. P., and Piao, M. S. (2014). Rutin improves functional outcome via reducing the elevated matrix metalloproteinase-9 level in a photothrombotic focal ischemic model of rats. J. Neurol. Sci. 339 (1-2), 75–80. Epub 2014 Jan 24. PMID: 24507948. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2014.01.024
Jasim, M. H., Saadoon Abbood, R., Sanghvi, G., Roopashree, R., Uthirapathy, S., Kashyap, A., et al. (2025). Flavonoids in the regulation of microglial-mediated neuroinflammation; focus on fisetin, rutin, and quercetin. Exp. Cell Res. 447 (2), 114537. Epub 2025 Mar 25. PMID: 40147710. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2025.114537
Javed, H., Khan, M. M., Ahmad, A., Vaibhav, K., Ahmad, M. E., Khan, A., et al. (2012). Rutin prevents cognitive impairments by ameliorating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in rat model of sporadic dementia of Alzheimer type. Neuroscience 210, 340–352. Epub 2012 Mar 6. PMID: 22441036. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.02.046
Ji, Y., Ma, Y., Ma, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, X., Jin, D., et al. (2024). Rutin prevents pyroptosis and M1 microglia via Nrf2/Mac-1/caspase-1-mediated inflammasome axis to improve POCD. Int. Immunopharmacol. 127, 111290. Epub 2023 Dec 7. PMID: 38064815. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111290
Kessas, K., Lounis, W., Chouari, Z., Vejux, A., Lizard, G., and Kharoubi, O. (2024). Benefits of rutin on mitochondrial function and inflammation in an aluminum-induced neurotoxicity rat model: potential interest for the prevention of neurodegeneration. Biochimie 222, 1–8. Epub 2024 Feb 24. PMID: 38408719. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2024.02.010
Khan, M. M., Ahmad, A., Ishrat, T., Khuwaja, G., Srivastawa, P., Khan, M. B., et al. (2009). Rutin protects the neural damage induced by transient focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 1292, 123–135. Epub 2009 Jul 22. PMID: 19631195. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.07.026
Khan, M. M., Raza, S. S., Javed, H., Ahmad, A., Khan, A., Islam, F., et al. (2012). Rutin protects dopaminergic neurons from oxidative stress in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. Neurotox. Res. 22 (1), 1–15. Epub 2011 Dec 23. PMID: 22194158. doi:10.1007/s12640-011-9295-2
Koda, T., Kuroda, Y., and Imai, H. (2009). Rutin supplementation in the diet has protective effects against toxicant-induced hippocampal injury by suppression of microglial activation and pro-inflammatory cytokines: protective effect of rutin against toxicant-induced hippocampal injury. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 29 (4), 523–531. Epub 2009 Jan 21. PMID: 19156514. doi:10.1007/s10571-008-9344-4
Lai, X., Zhang, Y., Wu, J., Shen, M., Yin, S., and Yan, J. (2023). Rutin attenuates oxidative stress via PHB2-mediated mitophagy in MPP+-Induced SH-SY5Y cells. Neurotox. Res. 41 (3), 242–255. Epub 2023 Feb 4. PMID: 36738374. doi:10.1007/s12640-023-00636-5
Lee, G. B., Kim, Y., Lee, K. E., Vinayagam, R., Singh, M., and Kang, S. G. (2024). Anti-inflammatory effects of quercetin, rutin, and troxerutin result from the inhibition of NO production and the reduction of COX-2 levels in RAW 264.7 cells treated with LPS. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 196 (12), 8431–8452. Epub 2024 Aug 3. PMID: 39096472. doi:10.1007/s12010-024-05003-4
Li, F., Zhang, L., Zhang, X., Fang, Q., Xu, Y., and Wang, H. (2024). Rutin alleviates Pb-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death via activating Nrf2/ARE system in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurotoxicology 104, 1–10. Epub 2024 Jul 18. PMID: 39032614. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2024.07.010
Li, W., Li, D. Y., Zhao, S. M., Zheng, Z. J., Hu, J., Li, Z. Z., et al. (2017). Rutin attenuates isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis via modulating JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in the hippocampi of neonatal rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 13 (5), 2056–2064. Epub 2017 Mar 2. PMID: 28565808; PMCID: PMC5443216. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4173
Liu, H., Zhong, L., Zhang, Y., Liu, X., and Li, J. (2018). Rutin attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in ovariectomized rats via estrogen-receptor-mediated BDNF-TrkB and NGF-TrkA signaling. Biochem. Cell Biol. 96 (5), 672–681. Epub 2018 Feb 8. PMID: 29420916. doi:10.1139/bcb-2017-0209
Liu, Y., Liu, Q., Yang, Z., Li, R., Huang, Z., Huang, Z., et al. (2021). Trihydroxyethyl rutin provides neuroprotection in rats with cervical spinal cord hemi-contusion. Front. Neurosci. 15, 759325. PMID: 34867167; PMCID: PMC8637531. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021.759325
L Suraweera, T., Rupasinghe, H. P. V., Dellaire, G., and Xu, Z. (2020). Regulation of nrf2/ARE pathway by dietary flavonoids: a friend or foe for cancer management? Antioxidants (Basel) 9 (10), 973. PMID: 33050575; PMCID: PMC7600646. doi:10.3390/antiox9100973
Ma, Z., Wang, L., Ji, Z., and Li, H. (2025). Exploring the lncRNA NEAT1/iASPP pathway in chordoma: mechanisms of proliferation suppression and apoptosis induction. Discov. Med. 37 (195), 727–736. PMID: 40287808. doi:10.24976/Discov.Med.202537195.63
Mahendra, V. P., Yogendra Prasad, K., Ganesan, P., and Kumar, R. (2020). Mechanism of rutin mediated inhibition of insulin amyloid formation and protection of Neuro-2a cells from fibril-induced apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47 (4), 2811–2820. Epub 2020 Apr 2. PMID: 32240467. doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05393-8
Malekpour, M., Ebrahiminezhad, A., Karimi, Z., Saadi, M. I., and Berenjian, A. (2025). Current strategies for rutin nano-formulation; a promising bioactive compound with increased efficacy. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 48, 877–898. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40148481. doi:10.1007/s00449-025-03156-y
Mani, R., Babu, S. V., Murugesan, N., Duraisamy, R., and Thayumanavan, P. (2025). A comparative study of quercetin/rutin loaded PEG polymeric nanoparticles: controlled drug release and its biological activity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 39 (5), e70269. PMID: 40269608. doi:10.1002/jbt.70269
Mckee, A. C., and Daneshvar, D. H. (2015). The neuropathology of traumatic brain injury. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 127, 45–66. PMID: 25702209; PMCID: PMC4694720. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-52892-6.00004-0
Mead, G. E., Sposato, L. A., Sampaio Silva, G., Yperzeele, L., Wu, S., Kutlubaev, M., et al. (2023). A systematic review and synthesis of global stroke guidelines on behalf of the World Stroke Organization. Int. J. Stroke 18 (5), 499–531. Epub 2023 Mar 1. PMID: 36725717; PMCID: PMC10196933. doi:10.1177/17474930231156753
Meimei, C., Fei, Z., Wen, X., Huangwei, L., Zhenqiang, H., Rongjun, Y., et al. (2025). Taxus chinensis (Pilg.) Rehder fruit attenuates aging behaviors and neuroinflammation by inhibiting microglia activation via TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 337 (Pt 3), 118943. Epub 2024 Oct 15. PMID: 39413938. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118943
Moghbelinejad, S., Nassiri-Asl, M., Farivar, T. N., Abbasi, E., Sheikhi, M., Taghiloo, M., et al. (2014). Rutin activates the MAPK pathway and BDNF gene expression on beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 224 (1), 108–113. Epub 2013 Oct 20. PMID: 24148604. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.10.010
Motamedshariaty, V. S., Amel Farzad, S., Nassiri-Asl, M., and Hosseinzadeh, H. (2014). Effects of rutin on acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity. Daru 22 (1), 27. PMID: 24524427; PMCID: PMC3927829. doi:10.1186/2008-2231-22-27
Nassiri-Asl, M., Ghorbani, A., Salehisar, S., Asadpour, E., and Sadeghnia, H. R. (2020). Effect of rutin on oxidative DNA damage in PC12 neurons cultured in nutrients deprivation condition. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 23 (3), 390–395. PMID: 32440327; PMCID: PMC7229504. doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2020.31832.7657
Nassiri-Asl, M., Naserpour Farivar, T., Abbasi, E., Sadeghnia, H. R., Sheikhi, M., Lotfizadeh, M., et al. (2013). Effects of rutin on oxidative stress in mice with kainic acid-induced seizure. J. Integr. Med. 11 (5), 337–342. PMID: 24063781. doi:10.3736/jintegrmed2013042
Nassiri-Asl, M., Shariati-Rad, S., and Zamansoltani, F. (2008). Anticonvulsive effects of intracerebroventricular administration of rutin in rats. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 32 (4), 989–993. Epub 2008 Jan 19. PMID: 18262708. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.01.011
Nicola, M. A., Attaai, A. H., Abdel-Raheem, M. H., Mohammed, A. F., and Abu-Elhassan, Y. F. (2024). Neuroprotective effects of rutin against cuprizone-induced multiple sclerosis in mice. Inflammopharmacology 32 (2), 1295–1315. Epub 2024 Mar 21. PMID: 38512652; PMCID: PMC11006763. doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01442-x
Nieoczym, D., Socała, K., Raszewski, G., and Wlaź, P. (2014). Effect of quercetin and rutin in some acute seizure models in mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 54, 50–58. Epub 2014 May 22. PMID: 24857758. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.05.007
Nkpaa, K. W., and Onyeso, G. I. (2018). Rutin attenuates neurobehavioral deficits, oxidative stress, neuro-inflammation and apoptosis in fluoride treated rats. Neurosci. Lett. 682, 92–99. Epub 2018 Jun 13. PMID: 29908257. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.023
Ola, M. S., Ahmed, M. M., Ahmad, R., Abuohashish, H. M., Al-Rejaie, S. S., and Alhomida, A. S. (2015). Neuroprotective effects of rutin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat retina. J. Mol. Neurosci. 56 (2), 440–448. Epub 2015 May 1. PMID: 25929832. doi:10.1007/s12031-015-0561-2
Oriol, L., Chao, M., Kollman, G. J., Dowlat, D. S., Singhal, S. M., Steinkellner, T., et al. (2025). Ventral tegmental area interneurons revisited: GABA and glutamate projection neurons make local synapses. Elife 13, RP100085. PMID: 40238649; PMCID: PMC12002793. doi:10.7554/eLife.100085
Oshodi, T. O., Ben-Azu, B., Ishola, I. O., Ajayi, A. M., Emokpae, O., and Umukoro, S. (2021). Molecular mechanisms involved in the prevention and reversal of ketamine-induced schizophrenia-like behavior by rutin: the role of glutamic acid decarboxylase isoform-67, cholinergic, Nox-2-oxidative stress pathways in mice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 48 (3), 2335–2350. Epub 2021 Apr 3. PMID: 33811574. doi:10.1007/s11033-021-06264-6
Ouyang, Q., Liu, K., Zhu, Q., Deng, H., Le, Y., Ouyang, W., et al. (2022). Brain-penetration and neuron-targeting DNA nanoflowers Co-delivering miR-124 and rutin for synergistic therapy of Alzheimer's disease. Small 18 (14), e2107534. Epub 2022 Feb 19. PMID: 35182016. doi:10.1002/smll.202107534
Ozkan, G., Kostka, T., Esatbeyoglu, T., and Capanoglu, E. (2020). Effects of lipid-based encapsulation on the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of phenolic compounds. Molecules 25 (23), 5545. PMID: 33256012; PMCID: PMC7731217. doi:10.3390/molecules25235545
Pu, F., Mishima, K., Irie, K., Motohashi, K., Tanaka, Y., Orito, K., et al. (2007). Neuroprotective effects of quercetin and rutin on spatial memory impairment in an 8-arm radial maze task and neuronal death induced by repeated cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 104 (4), 329–334. Epub 2007 Aug 1. PMID: 17666865. doi:10.1254/jphs.fp0070247
Saafan, S. M., Mohamed, S. A., Noreldin, A. E., El Tedawy, F. A., Elewa, Y. H. A., Fadly, R. S., et al. (2023). Rutin attenuates D-galactose-induced oxidative stress in rats' brain and liver: molecular docking and experimental approaches. Food Funct. 14 (12), 5728–5751. PMID: 37282615. doi:10.1039/d2fo03301a
Sălcudean, A., Bodo, C. R., Popovici, R. A., Cozma, M. M., Păcurar, M., Crăciun, R. E., et al. (2025). Neuroinflammation-A crucial factor in the pathophysiology of depression-A comprehensive review. Biomolecules 15 (4), 502. PMID: 40305200; PMCID: PMC12024626. doi:10.3390/biom15040502
Schloms, L., Smith, C., Storbeck, K. H., Marnewick, J. L., Swart, P., and Swart, A. C. (2014). Rooibos influences glucocorticoid levels and steroid ratios in vivo and in vitro: a natural approach in the management of stress and metabolic disorders? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 58 (3), 537–549. Epub 2013 Sep 11. PMID: 24022885. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201300463
Shimazu, R., Anada, M., Miyaguchi, A., Nomi, Y., and Matsumoto, H. (2021). Evaluation of blood-brain barrier permeability of polyphenols, anthocyanins, and their metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69 (39), 11676–11686. Epub 2021 Sep 23. PMID: 34555897. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c02898
Song, H. L., Zhang, X., Wang, W. Z., Liu, R. H., Zhao, K., Liu, M. Y., et al. (2018). Neuroprotective mechanisms of rutin for spinal cord injury through anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation and inhibition of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase pathway. Neural Regen. Res. 13 (1), 128–134. PMID: 29451217; PMCID: PMC5840978. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.217349
Song, K., Na, J. Y., Kim, S., and Kwon, J. (2015). Rutin upregulates neurotrophic factors resulting in attenuation of ethanol-induced oxidative stress in HT22 hippocampal neuronal cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 95 (10), 2117–2123. Epub 2014 Oct 31. PMID: 25251136. doi:10.1002/jsfa.6927
Sreelatha, I., Choi, G. Y., Lee, I. S., Inturu, O., Lee, H. S., Park, Y. N., et al. (2024). Neuroprotective properties of rutin hydrate against scopolamine-induced deficits in BDNF/TrkB/ERK/CREB/Bcl2 pathways. Neurol. Int. 16 (5), 1094–1111. PMID: 39452684; PMCID: PMC11510686. doi:10.3390/neurolint16050082
Su, K. Y., Yu, C. Y., Chen, Y. W., Huang, Y. T., Chen, C. T., Wu, H. F., et al. (2014). Rutin, a flavonoid and principal component of saussurea involucrata, attenuates physical fatigue in a forced swimming mouse model. Int. J. Med. Sci. 11 (5), 528–537. PMID: 24693223; PMCID: PMC3970108. doi:10.7150/ijms.8220
Sui, C., Wu, Y., Zhang, R., Zhang, T., Zhang, Y., Xi, J., et al. (2022). Rutin inhibits the progression of osteoarthritis through CBS-mediated RhoA/ROCK signaling. DNA Cell Biol. 41 (6), 617–630. Epub 2022 May 19. PMID: 35588172. doi:10.1089/dna.2021.1182
Sun, Z. W., Sun, Z. X., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., Xie, F., Wang, X., et al. (2025). Rutin ameliorates stress-induced blood‒brain barrier dysfunction and cognitive decline via the endothelial HDAC1‒Claudin-5 axis. Fluids Barriers CNS. 22 (1), 35. PMID: 40176114; PMCID: PMC11967129. doi:10.1186/s12987-025-00639-8
Swain, S. K., Chandra Dash, U., and Sahoo, A. K. (2022). Hydrolea zeylanica improves cognitive impairment in high-fat diet fed-streptozotocin-induced diabetic encephalopathy in rats via regulating oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neurotransmission in brain. Heliyon 8 (11), e11301. PMID: 36387425; PMCID: PMC9640967. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11301
Taşlı, N. G., Çimen, F. K., Karakurt, Y., Uçak, T., Mammadov, R., Süleyman, B., et al. (2018). Protective effects of Rutin against methanol induced acute toxic optic neuropathy: an experimental study. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 11 (5), 780–785. PMID: 29862175; PMCID: PMC5957028. doi:10.18240/ijo.2018.05.10
Thabet, N. M., and Moustafa, E. M. (2018). Protective effect of rutin against brain injury induced by acrylamide or gamma radiation: role of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β/NRF-2 signalling pathway. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 124 (2), 185–193. Epub 2017 Sep 14. PMID: 28906145. doi:10.1080/13813455.2017.1374978
Tian, R., Yang, W., Xue, Q., Gao, L., Huo, J., Ren, D., et al. (2016). Rutin ameliorates diabetic neuropathy by lowering plasma glucose and decreasing oxidative stress via Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 771, 84–92. Epub 2015 Dec 10. PMID: 26688570. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.12.021
Tongjaroenbuangam, W., Ruksee, N., Chantiratikul, P., Pakdeenarong, N., Kongbuntad, W., and Govitrapong, P. (2011). Neuroprotective effects of quercetin, rutin and okra (Abelmoschus esculentus Linn.) in dexamethasone-treated mice. Neurochem. Int. 59 (5), 677–685. Epub 2011 Jun 29. PMID: 21740943. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2011.06.014
Uthra, C., Reshi, M. S., Jaswal, A., Yadav, D., Shrivastava, S., Sinha, N., et al. (2022). Protective efficacy of rutin against acrylamide-induced oxidative stress, biochemical alterations and histopathological lesions in rats. Toxicol. Res. (Camb) 11 (1), 215–225. PMID: 35237426; PMCID: PMC8882811. doi:10.1093/toxres/tfab125
Wang, R., Sun, Y., Huang, H., Wang, L., Chen, J., and Shen, W. (2015). Rutin, A natural flavonoid protects PC12 cells against sodium nitroprusside-induced neurotoxicity through activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR and ERK1/2 pathway. Neurochem. Res. 40 (9), 1945–1953. Epub 2015 Aug 9. PMID: 26255195. doi:10.1007/s11064-015-1690-2
Wang, X., Xia, X., Song, X., Zhou, Y., Ma, M., Ren, Y., et al. (2025). Therapeutic potential of rutin in premenstrual depression: evidence from in vivo and in vitro studies. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1525753. PMID: 39877393; PMCID: PMC11772486. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1525753
Wen, X., and Hu, J. (2024). Targeting STAT3 signaling pathway in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease with compounds from natural products. Int. Immunopharmacol. 141, 112936. Epub 2024 Aug 19. PMID: 39163684. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112936
Wu, C., Zhang, J., Yang, S., Peng, C., Lv, M., Liang, J., et al. (2024). Preparation and pharmacokinetics of brain-targeted nanoliposome loaded with rutin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (21), 11404. PMID: 39518957; PMCID: PMC11546852. doi:10.3390/ijms252111404
Xianchu, L., Huan, P., Kang, L., Beiwang, D., and Ming, L. (2022). Protective effect of rutin against diabetes-associated cognitive decline in rats. Pak J. Pharm. Sci. 35 (3), 769–775. PMID: 35791475. doi:10.36721/PJPS.2022.35.3.REG.769-775.1
Xinghua, L., Yingying, H., Shuai, W., and Guangping, L. (2023). Anti-aging effect of rutin in Caenorhabditis elegans and D-gal-induced aging mouse model. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 513 (1), 350–354. Epub 2023 Dec 8. PMID: 38066322. doi:10.1134/S1607672923700515
Xu, P. X., Wang, S. W., Yu, X. L., Su, Y. J., Wang, T., Zhou, W. W., et al. (2014). Rutin improves spatial memory in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice by reducing Aβ oligomer level and attenuating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Behav. Brain Res. 264, 173–180. Epub 2014 Feb 7. PMID: 24512768. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2014.02.002
Zamani, K., Fakhri, S., Kiani, A., Abbaszadeh, F., and Farzaei, M. H. (2025). Rutin engages opioid/benzodiazepine receptors towards anti-neuropathic potential in a rat model of chronic constriction injury: relevance to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39912904. doi:10.1007/s00210-025-03842-4
Zapata-Morales, J. R., Alonso-Castro, A. J., González-Rivera, M. L., González Prado, H. I., Barragán-Gálvez, J. C., Hernández-Flores, A., et al. (2025). Synergistic interaction between Justicia spicigera extract and analgesics on the formalin test in rats. Pharm. (Basel) 18 (2), 187. PMID: 40006001; PMCID: PMC11859130. doi:10.3390/ph18020187
Zhang, M., Hu, G., Shao, N., Qin, Y., Chen, Q., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) as a target for Alzheimer's disease: flavonoids and phenols. Inflammopharmacology 29 (5), 1317–1329. Epub 2021 Aug 4. PMID: 34350508. doi:10.1007/s10787-021-00861-4
Zhang, S., Qi, Y., Xu, Y., Han, X., Peng, J., Liu, K., et al. (2013). Protective effect of flavonoid-rich extract from Rosa laevigata Michx on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppression of apoptosis and inflammation. Neurochem. Int. 63 (5), 522–532. Epub 2013 Sep 4. PMID: 24012531. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.08.008
Zhang, Z. H., Gu, Y., Huang, Z., Liu, X. Y., Xu, W. T., Zhang, X. C., et al. (2025). Acupuncture regulates astrocyte neurotoxic polarization to protect blood-brain barrier integrity in delayed thrombolysis through mediating ERK1/2/Cx43 axis. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 18, 604–618. PMID: 40292080; PMCID: PMC12022658. doi:10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.04.005
Zheng, X. X., Wang, F., Ding, H., Li, H. T., Yang, X. J., Li, X. C., et al. (2025). cGMP-dependent protein kinase I in the dorsal hippocampus protects against synaptic plasticity and cognitive deficit induced by chronic pain. Pain. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40310865. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003624
Glossary
AD Alzheimer’s disease
ARE Antioxidant response element
Arg1 Arginase 1
Aβ Amyloid-beta
Bax B-cell lymphoma-2 associated X protein
BBB blood-brain barrier
Bcl-2 anti apoptotic gene B-cell lymphoma-2
BDNF brain-derived neurotrophic factor
CAT catalase
CNS Central nervous system
COX-2 cyclooxygenase-2
CREB cAMP response element binding protein
DG dentate gyrus
ERK extracellular signal regulated kinase
GABA Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
GDNF glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor
GSH-PX glutathione peroxidase
HO-1 Heme Oxygenase-1
IL-10 interleukin-10
IL-1β interleukin-1β
IL-6 interleukin-6
iNOS inducible nitric oxide synthase
JNK c-Jun N-terminal kinase
LPS Lipopolysaccharide
MAPK mitogen activated protein kinas
MDA malondialdehyde
MMP-9 matrix metalloproteinase-9
MPP(+) 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion
NF-κB nuclear factor kappa B
NGF nerve growth factor
Nrf2 nuclear factor red cell 2 related factor 2
PCC pheochromocytoma cells
P-CREB cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein
PHB2 Prohibitin 2
PI3K phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
RhoA/ROCK Ras homolog family member A/Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase
ROS reactive oxygen species
Rut Rutin
SOD superoxide dismutase
TLR4 Toll-like receptor 4
TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-α
TrkA tropomyosin receptor kinase A
TrkB tropomyosin receptor kinase B
Keywords: rutin, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective effects, mechanisms, medicinal potential
Citation: Chunmei Z and Shuai W (2025) Molecular mechanisms of neuroprotective effect of rutin. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1599167. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1599167
Received: 26 March 2025; Accepted: 19 May 2025;
Published: 03 June 2025.
Edited by:
Francisco Lopez-Munoz, Camilo José Cela University, SpainReviewed by:
Paramita Basu, University of Pittsburgh, United StatesDoaa abdelsatar Madkour, University of Sadat City, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Chunmei and Shuai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhang Chunmei, MTg3MDQwNzk5NEBxcS5jb20=
 Zhang Chunmei
Zhang Chunmei Wang Shuai3
Wang Shuai3