- 1Department of Oncology, Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang, Guizhou, China
- 3Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine Internal Medicine, Eye Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
Objective: This review aimed to determine the therapeutic effects and safety of oral curcumin compared with other comparators for human health and wellbeing outcomes.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library were searched from their inception to 18 June 2024. The Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews-2 checklist, and Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation system were used to assess the methodological and evidence quality for each meta-analysis, respectively. The results are presented in a narrative review.
Results: We included 25 studies. The overall methodological quality was relatively poor, and there is considerable room for improvement. The findings suggest that curcumin has potentially positive effects on lipid profiles, blood pressure, inflammatory markers and oxidative stress, musculoskeletal diseases, emotional and cognitive function, ulcerative colitis, liver and kidney function, primary dysmenorrhea or premenstrual syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, COVID-19, painful statues, and HR-QOL. However, for many diseases, the conclusions remain uncertain.
Conclusion: The available evidence suggests that curcumin is a safe medicinal agent that improves multiple clinical outcomes; however, the scientific quality of published studies needs to be improved.
1 Introduction
Curcumin, a natural compound derived from the rhizome of the turmeric plant (Curcuma Longa), has garnered significant attention for its health-promoting properties over the years (Ayub et al., 2024). It is particularly popular among residents of India and Southeast Asian countries (Kasprzak-Drozd et al., 2024). The present studies have found that curcumin has various pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory (Zhang et al., 2025), antioxidant (Nirgude et al., 2025), and immune response modulation (Gouda et al., 2024). These properties have promoted the exploration of its use as a potential drug for treating various chronic diseases. For instance, curcumin has demonstrated significant beneficial effects in musculoskeletal diseases (Jamali et al., 2020), gastrointestinal diseases (Ben-Horin et al., 2024), and mood or anxiety disorders (Asadi et al., 2020). Additionally, curcumin targets multitude signaling pathways and exerts cellular-level effects, making it a versatile supplement for various health conditions.
Specifically, curcumin’s antioxidant properties are attributed to scavenging free radicals and enhancing endogenous antioxidant defenses (Wang et al., 2024a). The anti-inflammatory benefits of curcumin are associated with pain reduction (Zhang et al., 2024) and mucosal protective effects in ulcerative colitis (Sadeghi et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2024b). Curcumin has been proven to inhibit cholesterol production and adipogenesis, thereby regulating lipid profiles and aiding in weight management (Shao et al., 2012). Furthermore, curcumin compounds have been shown to have actions similar to antidiabetic agents, reducing insulin resistance (Li et al., 2020), and interacting with the gut microbiota (Gu et al., 2024). Moreover, clinical practice guidelines have acknowledged the therapeutic value of curcumin, particularly in managing osteoarticular pain, making it among the most prescribed supplements for this condition (Liu et al., 2018; Mobasheri et al., 2024).
In recent decades, the popularity of curcumin supplements has surged, driven by widespread promoting in folk media, and the growing use of turmeric dietary supplements. In fact, turmeric has become the best-selling botanical dietary supplement in the United States (Panknin et al., 2023). The medicinal therapeutic value, diverse functionality, and rapid development of curcumin have driven considerable growth in the number of clinical trials worldwide (Yeung et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2022). However, despite the abundance of clinical studies and mechanistic research supporting the health benefits of curcumin, there is a lack of high-quality integrated studies to determine which health effects are most strongly supported by evidence.
In evidence-based healthcare settings, systematic reviews and meta-analyses are vital for developing clinical practice guidelines and guiding clinical decision-making (Weissgerber, 2021). In particular, umbrella review serves as an effective method to assess the scientific quality of published systematic reviews and to summarize clinical evidence reported in domain-specific meta-analyses (Aromataris et al., 2015). This approach has been successfully applied to other natural products and dietary agents, including berberine (Li et al., 2023), anthocyanins (Sandoval-Ramírez et al., 2022), and tea (Keller and Wallace, 2021). Given the extensive research on curcumin’s health benefits and the need for a comprehensive synthesis of the available evidence, our review aimed to systematically identify and evaluate the therapeutic efficacy and safety of oral curcumin than any comparator for several human health and wellbeing outcomes. We hypothesize that curcumin will demonstrate significant therapeutic benefits across multiple health domains, supported by high-quality evidence from well-conducted systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
2 Materials and methods
The umbrella review is a novel method for deliberately searching, integrating and appraising available evidence on specific exposures and health outcomes among systematic reviews and/or meta-analyses (Aromataris et al., 2015). To provide a comprehensive evaluation of the therapeutic effect of curcumin, therefore, we only included systematic reviews with meta-analyses.
2.1 Screening and search strategy
We searched PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane Library from their inception to 18 June 2024, using medical subject headings and keywords, including “curcumin,” “turmeric,” “curcuma,” “curcuminoids,” “systematic reviews,” and “meta-analysis.” We only included English-language articles when searching these databases. Furthermore, we manually searched the references of the eligible articles to identify additional studies that may meet the inclusion criteria. The specific search methods are described in Supplementary Table S1. Two independent reviewers (Q.X. and J.W.) removed duplicates and screened the records based on titles and abstracts. Then, the potentially eligible records were downloaded for further evaluation. Any disagreements during the screening period, were resolved through discussion with a third reviewer (Y.W.).
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The selected articles were eligible if they were meta-analyses that conducted a systematic review approach. The details of the inclusion criteria for our review were as follows: (1) Participants: adults aged ≥18 years, including patients and healthy participants; (2) interventions: curcumin alone or as a supplement on health outcomes; (3) controls: placebo, routine care, and others; (4) outcomes: any reported health outcomes, for example, metabolic indicators, gastrointestinal disorders, and musculoskeletal diseases; (5) study design: systematic review and meta-analyses based on randomized controlled studies (RCTs). We excluded preclinical studies, primary studies, genetic research, and conference abstracts. We also excluded studies on intravenous and topical administration, because of the potential differences in the mechanisms of action. If multiple meta-analyses were performed on the same intervention and outcome, we preferred the most recent, largest, and updated meta-analysis (Khan et al., 2019).
2.3 Data extraction
Two reviewers (Q.X. and R.Z.) independently extracted and cross-checked the data, including the first author, publication year, country, sample size, number of primary RCTs for meta-analysis, interventions, treatment duration, dosage, registration number, and health-related outcomes. In case of disagreements, the third reviewer (Z.Y.L.) was consulted for judgment.
2.4 Quality assessment of included studies
We referred to the relevant literature and used the Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR)-2 checklist, the revised version of which was officially published by the AMSTAR Working Group in 2017, for methodological quality assessment (Shea et al., 2017). AMSTAR-2 checklist includes 16 items covering selecting topics, design, registration, data extraction, statistical analysis, and discussion of meta-analyses. Specifically, ‘Yes’ (Y), ‘Partial Yes’ (PY), or ‘No’ (N) were used to answer item-related questions. The AMSTAR-2 checklist classified the methodological quality into four levels: high, moderate, low, and critically low levels.
We used the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) framework to assess the quality of evidence for each outcome (Guyatt et al., 2011). The GRADE system provides explicit criteria for grading the quality of evidence, including the risk of bias (RoB), inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and publication bias. We created an evidence map exhibiting the plausible benefits and the certainty of evidence for each intervention. The certainty of the evidence was assessed using the GRADE methodology (GRADEpro GDT) (https://gdt.gradepro.org/app/) and categorized evidence as high, moderate, low or very low credibility. Finally, the two reviewers (J.W. and Z.Z.G.) cross-checked the quality assessment and reached a consensus. Any disagreements were resolved by a third reviewer (Y.W.).
2.5 Statistical analysis
We extracted the necessary data (for example, estimated effects and 95% confidence interval (CI) for meta-analyses, p-values) directly from meta-analyses for narrative review. I2 statistics were used to assess heterogeneity between studies. Funnel plots, Egger’s test, and Begg’s test were used to assess publication bias. Statistical significance was set at two-sided p < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Findings of study screening
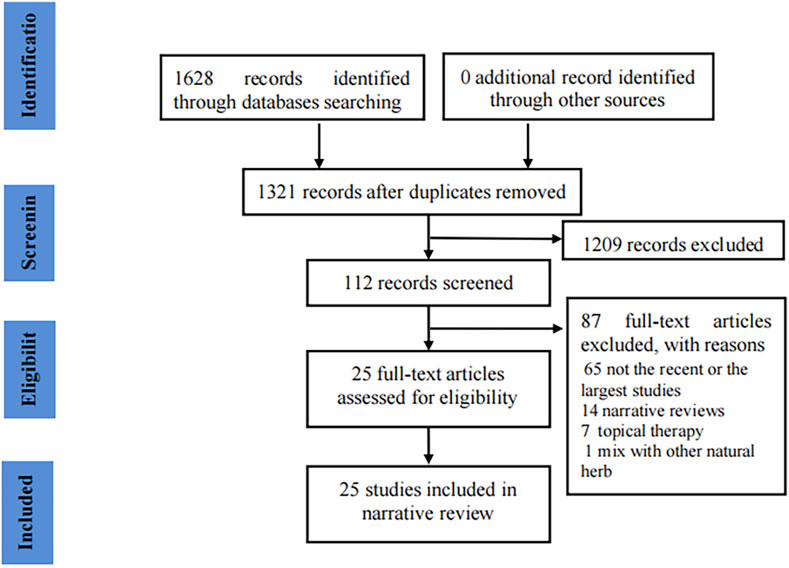
Initially, we obtained 1,628 records through a literature search. After removing 307 duplicates, 1,209 records were excluded by screening titles and abstracts. We screened the full-text of 112 meta-analyses and finally included 25 articles (Dehzad et al., 2023a; Dehzad et al., 2023d; Dehzad et al., 2023c; Dehzad et al., 2024; Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024; Fathi et al., 2024; Sharifipour et al., 2024; Sahebkar and Henrotin, 2016; Ng et al., 2018; Sarraf et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2019; Sadeghian et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021a; Wang et al., 2021b; Zeng et al., 2021; Beba et al., 2022; Emami et al., 2022; Malekmakan et al., 2022; Shen et al., 2022; Tian et al., 2022; Yin et al., 2022; Dehzad et al., 2023b; Kou et al., 2023; Mirzaei Dahka et al., 2023; Shafiee et al., 2023) in our review (Figure 1 presents the flow chart of the study selection).
3.2 Research characteristics
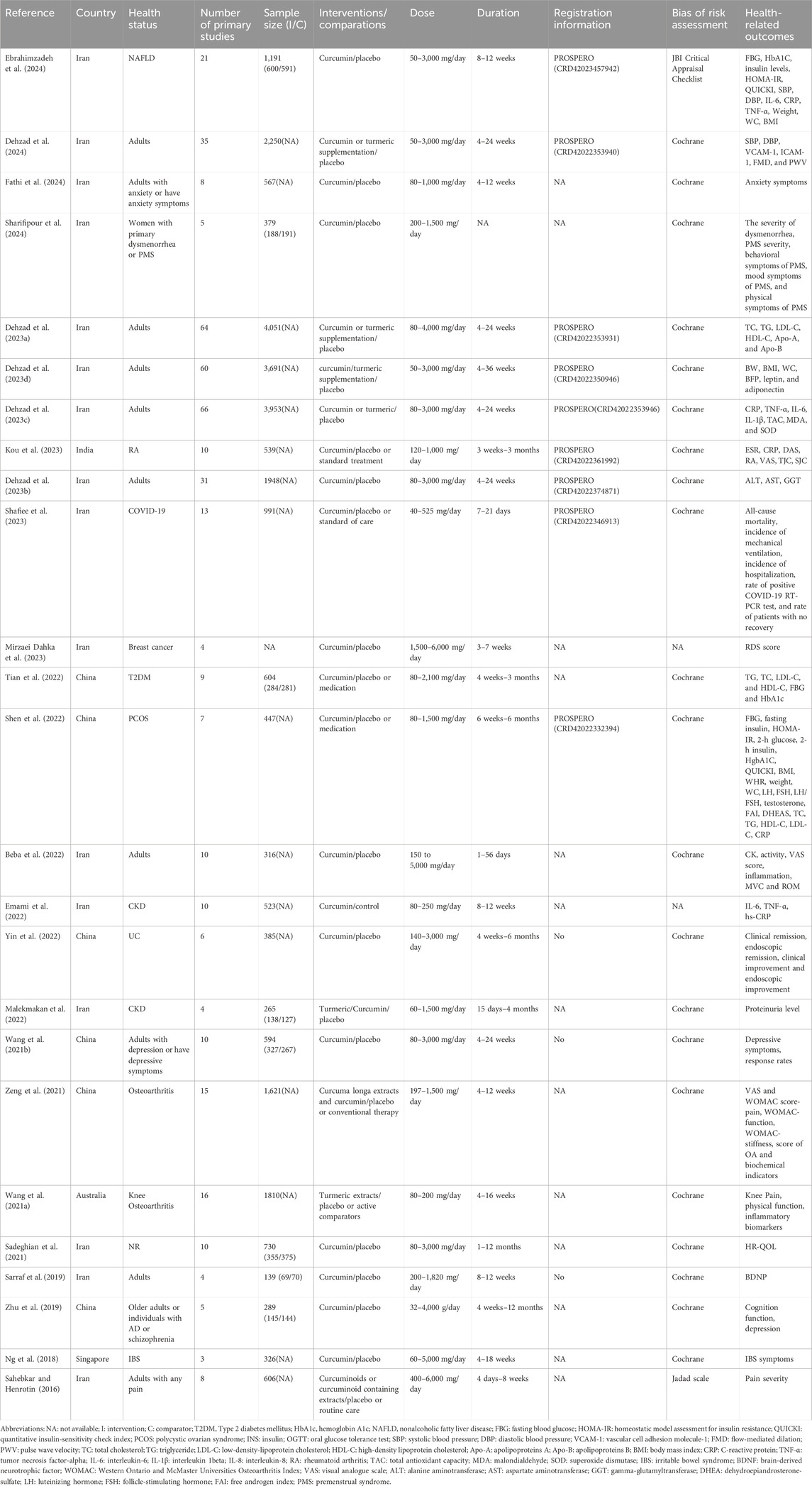
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of the included meta-analyses. The articles were published between 2016 and 2024. The meta-analyses were from six regions: 16 from Iran, six from China, and the remaining were from Australia, Singapore, and India. Only nine meta-analyses were registered on the PROSPERO platform and reported their registration number, but the remaining reviews failed to provide registration details. The number of primary clinical trials in the meta-analyses ranged from 3 to 66, and the number of participants ranged from 139 to 4,051. The Cochrane RoB assessment tool was the most commonly used to evaluate methodological quality, with one review each in the Jadad score and JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist, and two articles that did not report the tool used to assess methodological quality. Sixteen meta-analyses included only placebo-controlled trials, and the other meta-analyses included placebo, routine care, or medication as comparators. The curcumin dose varied considerably across the original studies, ranging from 50 to 6,000 mg. The treatment duration of curcumin interventions ranged from 1 day to 12 months in the meta-analyses.
3.3 Methodological quality
Most meta-analyses (n = 19, 76%) were classified as very low quality, with the remaining as low quality (n = 3, 12%) and moderate quality (n = 3, 12%). No articles were rated as high-quality. Table 2 provides the assessment results of the included meta-analyses.
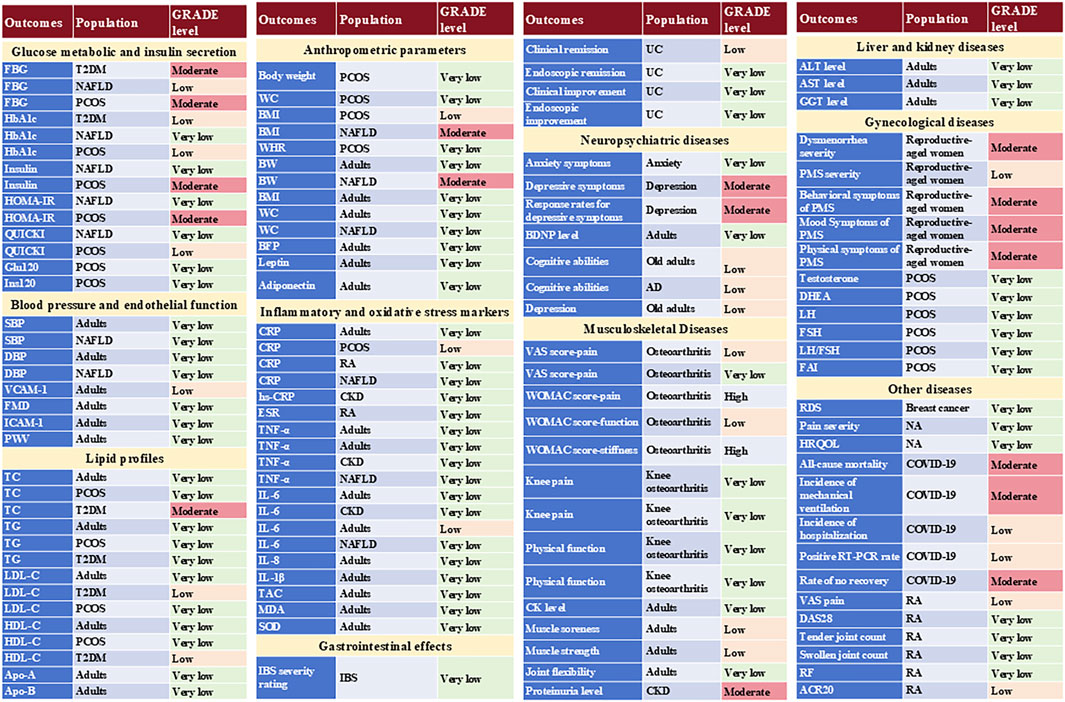
According to the GRADE, 82.79% (n = 101) of outcomes were rated as very low to low certainty, indicating limited confidence in the real word. The remaining 13.93% (n = 17) and 3.28% (n = 4) of the outcomes had moderate or high levels of confidence levels, respectively (Supplementary Table S2). The GRADE was impacted by the risk of bias, inconsistency (high heterogeneity), and imprecision (small sample size). Additionally, the limited number of available studies precluded a comprehensive assessment of publication bias, which could have exerted an indeterminate influence on the conclusions.
3.4 Therapeutic efficacy and safety of curcumin
Supplementary Table S2 lists meta-analyses evaluating the effect of curcumin on each human outcome, as reported in the included systematic reviews. These results are more simply presented in Figure 2.
3.4.1 Metabolic indicators
3.4.1.1 Glucose metabolic and insulin secretion
Three meta-analyses have evaluated the effects of curcumin on glucose metabolism and insulin levels (Shen et al., 2022; Tian et al., 2022; Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024). In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), curcumin significantly reduced blood glucose levels (WMD: 8.85 mg/dL; 95%CI: 14.4, −3.29 mg/dL; I2 = 41.2%) and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) (WMD: 0.54%; 95%CI: 0.81, −0.27; I2 = 65.2%) when compared with control treatment (Tian et al., 2022). In patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), the meta-analysis indicated that curcumin significantly reduced fasting blood glucose (FBG) (WMD: 2.83; 95%CI: 4.61, −1.06; I2 = 51.3%), homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (WMD: 0.52; 95%CI: 0.84, −0.20; I2 = 82.8%), but not including HbA1c (WMD: 0.17; 95%CI: 0.44, 0.11, I2 = 92.4%), insulin levels (WMD: 0.14; 95%CI: 1.03, 0.76; I2 = 83.0%) and quantitative insulin-sensitivity check index (QUICKI) (WMD: 0.01; 95%CI: 0.00, 0.01; I2 = 96.2%) compared with placebo (Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024). In patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), curcumin reduced FBG (WMD: 3.618; 95%CI: 5.165, −2.071; I2 = 20.4%), and insulin levels (WMD: 1.834; 95%CI: 2.701, −0.968; I2 = 8.4%) (Shen et al., 2022). Moreover, it observed improvement on QUICKI (WMD: 0.011, 95%CI: 0.005, 0.017; I2 = 39.6%) and HOMA-IR (WMD: 0.565; 95%CI: 0.779, −0.351; I2 = 0.0%), but not including blood glucose at 2 h after oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) (WMD: 0.063, 95%CI: 2.307, 2.181; I2 = 87.4%), insulin at 2 h after OGTT (WMD: 12.445; 95%CI: 44.384, 19.494; I2 = 0.0%) and HbA1c (WMD = −0.042, 95%CI: 0.471, 0.387, I2 = 56.8%) (Shen et al., 2022).
3.4.1.2 Blood pressure and endothelial function
Two meta-analyses evaluated the effects of curcumin on blood pressure and endothelial function (Dehzad et al., 2024; Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024). For the effect on blood pressure, one meta-analysis demonstrated that curcumin/turmeric supplementation has a beneficial effect on regulating systolic blood pressure (SBP) (WMD: −2.02 mmHg; 95% CI: −2.85, −1.18; I2 = 96.7%), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (WMD: −0.82 mmHg; 95% CI: −1.46, −0.18; I2 = 93.2%) in adult population when compared to placebo (Dehzad et al., 2024). However, another meta-analysis indicated that curcumin failed to reduce SBP (WMD: −0.93; 95% CI: −2.36, 0.50; I2 = 83.4%) and DBP (WMD: −1.37; 95% CI: −3.09, 0.35; I2 = 90.5%) in patients with NAFLD compared to placebo (Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024). Regarding endothelial function, curcumin/turmeric supplementation reduced the levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (WMD: −39.19 ng/mL; 95% CI: −66.15, −12.23; I2 = 73%), and flow-mediated dilation (WMD: 2.00%; 95% CI: 1.07, 2.94; I2 = 79.5%), but did not significantly change ICAM-1 (WMD: 17.05 ng/mL; 95%CI: 80.79, 46.70; I2 = 94.1%), or pulse wave velocity (WMD: −79.53 cm/s; 95%CI: −210.38, 51.33; I2 = 99.7%) in the adult population compared to placebo (Dehzad et al., 2024).
3.4.1.3 Lipid profiles
Three meta-analyses evaluated the effects of curcumin on lipid profiles (Shen et al., 2022; Tian et al., 2022; Dehzad et al., 2023a). Compared to placebo, one meta-analysis found that curcumin/turmeric supplementation improved lipid indices, including total cholesterol (TC) (WMD: 3.99 mg/dL; 95% CI: 5.33, −2.65; I2 = 97.0%), triglyceride (TG) (WMD: 6.69 mg/dL; 95% CI: 7.93, −5.45; I2 = 95.7%), low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (WMD: 4.89 mg/dL; 95% CI: 5.92, −3.87; I2 = 95.6%), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (WMD:1.80 mg/dL; 95%CI:1.43, 2.17; I2 = 95.0%) in adults. However, it has non-significant effects on apolipoproteins-A (WMD:1.58 mg/dL; 95% CI: 3.49, 6.56, I2 = 64.4%) or apolipoproteins B (WMD:1.35 mg/dL; 95% CI: 9.74, 12.44; I2 = 83.4%) (Dehzad et al., 2023a). For patients with T2DM, compared to controls, curcumin significantly reduced TG (WMD: 18.97 mg/dL; 95%CI: 36.47, −1.47; I2 = 80.5%), TC (WMD: 8.91 mg/dL; 95% CI: 14.18, −3.63; I2 = 28.9%), but not including LDL-C (WMD: 4.01 mg/dL; 95% CI: 10.96, 2.95; I2 = 49.7%) and HDL-C (WMD: 0.32 mg/dL; 95%CI: 0.74, 1.37; I2 = 19.1%) (Tian et al., 2022). For patients with PCOS, curcumin significantly reduced TC (WMD: 15.591; 95% CI: 27.908, −3.273; I2 = 68.9%), but were not identified TG (WMD: 8.889; 95% CI: 27.246, 9.468; I2 = 91.5%), LDL-C (WMD: 6.427; 95%CI: 17.343, 4.489; I2 = 78.8%) and HDL-C (WMD:3.713; 95% CI: 0.786, 8.211; I2 = 81.3%) compared to the control group (Shen et al., 2022).
3.4.2 Anthropometric measurements
Three meta-analyses evaluated the effect of curcumin on anthropometric measurements among different settings (Shen et al., 2022; Dehzad et al., 2023d; Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024). Compared to placebo, we found that supplementation with curcumin/turmeric significantly reduced body weight (WMD: 0.82 kg; 95% CI: 1.30, −0.35; I2 = 78.7%), body mass index (BMI) (WMD: 0.30 kg/m2; 95% CI: 0.53, −0.06; I2 = 94.7%), waist circumference (WMD: 1.31 cm; 95%CI: 1.94, −0.69; I2 = 78.5%), body fat percentage (WMD: 0.88%; 95% CI: 1.51, −0.25; I2 = 86.2%), leptin (WMD: 4.46 ng/mL; 95%CI: 6.70, −2.21; I2 = 96.1%), and increased adiponectin (WMD:2.48 μg/mL; 95% CI: 1.34, 3.62; I2 = 96.3%) in adults (Dehzad et al., 2023d). In patients with NAFLD, curcumin supplementation also significantly reduced body weight (WMD: 0.81; 95% CI: 1.28, −0.35; I2 = 0.0%) and BMI (WMD: 0.35; 95% CI: 0.57, −0.13; I2 = 0.0%), but had no significant effect on waist circumference (WMD: 01.80; 95% CI: 3.61, 0.02; I2 = 87.2%) when compared to placebo (Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024). Regarding PCOS patients, curcumin reduced BMI (WMD: 0.267; 95% CI: 0.450, −0.084; I2 = 0.0%) compared to controls. However, there were non-significant effects on body weight (WMD: 0.924; 95% CI: 2.009, 0.162; I2 = 45.2%), waist circumference (WMD: 1.475, 95%CI: 4.519, 1.570; I2 = 81.6%), and waist-hip ratio (WMD: 0.024; 95% CI: 0.048, 0.000; I2 = 0.0%) (Shen et al., 2022).
3.4.3 Inflammatory and oxidative stress markers
Six meta-analyses evaluated the effect of curcumin on inflammatory and oxidative stress markers (Beba et al., 2022; Emami et al., 2022; Dehzad et al., 2023c; Kou et al., 2023; Shen et al., 2022; Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024). Compared to placebo, curcumin/turmeric supplementation significantly reduced C-reactive protein (CRP) level (WMD: 0.58 mg/L; 95%CI: 0.74, −0.41; I2 = 98.9%), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) level (WMD: 3.48 pg/mL; 95%CI: 4.38, −2.58; I2 = 99.4%), interleukin-6(IL-6) level (WMD: 1.31 pg/mL; 95%CI: 1.58, −0.67; I2 = 88.2%) but failed to affect interleukin 1beta (IL-1β) level (WMD: 0.46 pg/mL; 95% CI: 1.18, 0.27; I2 = 75.8%) in adults (Dehzad et al., 2023c). In adult with delayed-onset muscle soreness, curcumin supplementation reduced TNF-α levels compared to placebo (WMD: 0.22 pg/mL; 95%CI: 0.33, −0.10; I2 = 93.2%), but did not affect IL-6 (WMD: 0.05 pg/mL; 95% CI: 0.14, 0.04; I2 = 46.9%) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) levels (WMD: 0.33 pg/mL; 95% CI: 1.39, 0.73; I2 = 85.6%) (Beba et al., 2022). For patients with PCOS, curcumin reduced CRP levels (WMD: 0.785; 95%CI: 1.553, −0.017; I2 = 23.9%) compared to placebo (Shen et al., 2022). In patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), curcumin significantly reduced the ESR (MD: 29.47; 95%CI: 54.05, −4.88; I2 = 99%) and CRP levels (MD: 0.93; 95%CI: 1.33, −0.53; I2 = 89%) as compared to the control group (Kou et al., 2023). In chronic kidney disease receiving hemodialysis, when compared with placebo, curcumin had a non-significant effect on IL-6 (SMD:0.24%; 95% CI: 0.14, 0.62; I2 = 97.1%), TNF-a (SMD:0.11; 95% CI: 0.19, 0.40; I2 = 95.9%) or hs-CRP (SMD: 0.17%; 95%CI: 0.36, 0.03; I2 = 79.6%) (Emami et al., 2022). However, compared with placebo, curcumin supplementation had a non-significant effect on IL-6 (WMD: 1.67; 95%CI: 3.80, 0.47; I2 = 81.3%), TNF-a (WMD: 2.58; 95%CI: 6.21, 1.06; I2 = 98.6%) and CRP levels (WMD: 2.59; 95% CI: 5.45, 0.26; I2 = 99.4%) in patients with NAFLD (Ebrahimzadeh et al., 2024).
Regaarding antioxidants, intake of curcumin/turmeric supplementation significantly increased total antioxidant capacity (WMD:0.21 mmol/L; 95% CI: 0.08, 0.33; I2 = 99.6%), and decreased malondialdehyde levels (WMD: 0.33 μmol/L; 95%CI: 0.53, −0.12; I2 = 99.6%) and superoxide dismutase activity (WMD:20.51 u/L; 95%CI: 7.35, 33.67; I2 = 95.4%) (Dehzad et al., 2023c).
3.4.4 Gastrointestinal disorders
Two meta-analyses have explored the effects of curcumin on gastrointestinal disorders (Ng et al., 2018; Yin et al., 2022). For patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), curcumin had a beneficial albeit not statistically significant effect on IBS severity ratings compared to placebo (SMD: 0.466; 95% CI: 1.113, 0.182; I2 = 85.22%) (Ng et al., 2018). Regarding patients with ulcerative colitis, adjuvant curcumin therapy was effective in inducing clinical remission (RR: 2.10; 95%CI: 1.13, 3.89; I2 = 80%), but not in inducing clinical improvement (RR: 1.62; 95% CI: 1.00, 2.61; I2 = 64%), endoscopic remission (RR: 4.17; 95% CI: 0.63, 27.71; I2 = 80%), and endoscopic improvement (RR: 4.13; 95% CI:0.20, 87.07; I2 = 79%) (Yin et al., 2022).
3.4.5 Neuropsychiatric diseases
Four meta-analyses have explored the effects of curcumin on neuropsychiatric diseases (Sarraf et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2021b; Fathi et al., 2024). The meta-analysis indicated that compared to placebo, curcumin might contribute to alleviating anxiety symptoms (SMD: 1.56; 95%CI: 2.48, −0.64; I2 = 95.6%) (Fathi et al., 2024), reduce depressive symptoms (SMD: 0.32; 95%CI: 0.50, −0.13; I2 = 15%), and improve clinical response rates (OR: 3.20; 95% CI: 1.28, 7.99; I2 = 35%) in patients with psychological disorders (Wang et al., 2021b). One study analyzed the effects of curcumin on neurotransmitters. The results suggested that curcumin significantly increased the serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in adults (WMD:1789.38 pg/mL; 95%CI: 722.04, 2,856.71; I2 = 83.5%)compared to the placebo (Sarraf et al., 2019). In older adults who received curcumin, cognitive function (SMD: 0.33; 95% CI:0.05, 0.62; I2 = 0%)was significantly improved, but not for depression (SMD: 0.29; 95% CI: 0.64, 0.05; I2 = 0%) compared to placebo (Zhu et al., 2019). However, in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, there was a trend towards worse performance in cognitive status (SMD: 0.90; 95%CI: 1.48, −0.32; I2 = 0%) when treated with curcumin compared to placebo (Zhu et al., 2019).
3.4.6 Musculoskeletal diseases
Three meta-analyses have evaluated the effects of curcumin on the musculoskeletal diseases (Wang et al., 2021a; Zeng et al., 2021; Beba et al., 2022). In patients with osteoarthritis, compared with placebo, Curcuma longa extract and curcumin reduced visual analog scale (VAS) (WMD: 11.55; 95%CI: 14.3, −9.06; I2 = 0%) and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) scores-pain (SMD: 0.66, 95% CI: 0.88, −0.43; I2 = 34%), WOMAC scores-function (SMD: 0.79; 95% CI: 1.27, −0.31; I2 = 75%), and WOMAC scores-stiffness (SMD: 0.35; 95%CI: 0.57, −0.12; I2 = 26%) (Zeng et al., 2021). When compared to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), Curcuma longa extract and curcumin had similar effects on joint pain (WMD: 0.34; 95%CI: 1.25, 0.57; I2 = 0%) (Zeng et al., 2021). In knee osteoarthritis, compared to placebo, turmeric extract also significantly reduced knee pain (SMD: 0.82; 95%CI: 1.17, −0.47; I2 = 86.23%) and improved physical function (SMD: 0.75; 95% CI: 1.18, −0.33; I2 = 90.05%), but had similar effects as NSAIDs (Wang et al., 2021a). Furthermore, one meta-analysis evaluated the effects on adults with delayed-onset muscle soreness, the results found that curcumin supplementation reduced creatine kinase activity level (WMD: 65.98IU/L; 95% CI: 99.53, −32.44; I2 = 86.8%), and muscle soreness (WMD: 0.56; 95%CI: 0.84, −0.27; I2 = 61.2%) compared to the placebo group (Beba et al., 2022). Moreover, curcumin supplementation also significantly improved muscle strength (WMD:3.10 nm; 95% CI:1.45, 4.75; I2 = 0.0%) and affected joint flexibility (WMD: 6.49°, 95% CI: 3.91, 9.07; I2 = 71.7%) (Beba et al., 2022).
3.4.7 Liver and kidney diseases
Two studies evaluated the effects of curcumin on liver and kidney functions (Malekmakan et al., 2022; Dehzad et al., 2023b). One meta-analysis suggested that oral turmeric supplementation significantly reduced the proteinuria levels (SMD: 0.72; 95% CI: 1.10, −0.35; I2 = 46.2%) in patients with chronic kidney disease compared to placebo (Malekmakan et al., 2022). Regarding liver function, curcumin/turmeric supplementation reduced blood alanine aminotransferase level (WMD: 4.09 U/L, 95%CI: 6.49, −1.70; I2 = 95.8%) and aspartate aminotransferase level (WMD: 3.81 U/L; 95%CI: 5.71, −1.91; I2 = 96.3%) but not gamma-glutamyltransferase level (WMD: 12.78 U/L; 95%CI: 28.20, 2.64; I2 = 98.0%) in adults (Dehzad et al., 2023b).
3.4.8 Gynecological disorders
Two meta-analyses evaluated the effects of curcumin on gynecological disorders (Shen et al., 2022; Sharifipour et al., 2024). Regarding patients with PCOS, curcumin had a non-significant effect on improving testosterone (T) level (WMD: 0.128; 95%CI: 0.383, 0.127; I2 = 98.6%), dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (WMD: 8.239; 95% CI: 30.260, 13.781; I2 = 62.3%), luteinizing hormone (LH) (WMD: 0.003; 95%CI: 0.007, 0.000; I2 = 0.0%) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (WMD: 0.002; 95%CI: 0.024, 0.029; I2 = 0.0%) compared to placebo (Shen et al., 2022). Compared to the control group, there failed to observed that curcumin improve LH/FSH (WMD: 0.114; 95%CI: 0.311, 0.084; I2 = 0.0%) and ameliorating free androgen index (WMD: 0.245; 95% CI: 1.138, 0.647; I2 = 30.0%) (Shen et al., 2022). As for reproductive-aged women with primary dysmenorrhea or premenstrual syndrome (PMS), curcumin intake significantly reduced the severity of dysmenorrhea (MD: 1.25; 95% CI: 1.52, −0.98; I2 = 31%) and the overall score of PMS (SMD: 1.41; 95% CI: 1.81, −1.02; I2 = 0%) than placebo (Sharifipour et al., 2024). Furthermore, curcumin also significantly reduced behavioral symptoms (MD: 12.90; 95% CI: 17.82, −7.99; I2 = 0%), mood symptoms (MD: 17.61; 95% CI: 22.75, −12.46; I2 = 0%) and physical disorders (MD: 19.65; 95% CI: 25.50, −13.80; I2 = 0%) of PMS patients (Sharifipour et al., 2024).
3.4.9 Other diseases
In patients with COVID-19, curcumin reduced the risk of all-cause mortality (RR: 0.37; 95% CI: 0.21, 0.65; I2 = 0%), and patients with no recovery status (RR: 0.55; 95% CI: 0.43, 0.69; I2 = 0%) but did no effect on the incidence of mechanical ventilation (RR: 0.23; 95% CI: 0.05, 1.07; I2 = 0%), hospitalization (RR: 0.17; 95% CI: 0.02, 1.40; I2 = 0%), and the rate of a positive viral polymerase chain reaction test (RR: 0.55; 95% CI: 0.40, 0.77; I2 = 32%) when compared to the control group (Shafiee et al., 2023). For RA, curcumin was beneficial for DAS28 (MD: 1.20; 95% CI: 1.85, −0.55; I2 = 92%), rheumatoid factor (MD: 24.15; 95% CI: 36.47, −11.83; I2 = 97%), VAS pain (MD: 5.32; 95% CI: 9.42, −1.22; I2 = 19%), swollen joint count (MD: 5.33; 95% CI: 9.90, −0.76; I2 = 98%) and tender joint count (MD: 6.33; 95%CI: 10.86, −1.81; I2 = 98%) compared to control group, but not including ACR-20 (MD:0.96; 95% CI:0.39, 1.52; I2 = 0%) (Kou et al., 2023). Moreover, one meta-analysis assessed the therapeutic effect of curcumin on the severity of radiation dermatitis in patients with breast cancer, and the results indicated that curcumin supplementation significantly reduced the radiation dermatitis severity score compared to the placebo group (WMD: 0.50; 95% CI: 0.72, −0.27; I2 = 95.7%) (Mirzaei Dahka et al., 2023). Regarding analgesic effects, one meta-analysis suggested that curcumin significantly reduced the pain severity (SMD: 0.57; 95%CI: 1.1, −0.03; I2 = 86%) in patients with painful statues (Sahebkar and Henrotin, 2016). Furthermore, oral curcumin had a strong positive impact on HR-QOL (SMD: 2.46; 95% CI: 1.30, 3.63; I2 = 97.4%) compared with placebo (Sadeghian et al., 2021).
3.5 Safety
Eight studies reported adverse events (Zhu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2021a; Wang et al., 2021b; Zeng et al., 2021; Malekmakan et al., 2022; Shen et al., 2022; Yin et al., 2022; Kou et al., 2023), including gastrointestinal symptoms, such as bloating, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea and constipation, and other symptoms including headache, dizziness, rash and hot flushes. However, there were no serious adverse events.
4 Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first review to assess the methodological quality and evidence of available meta-analyses on curcumin. Our review included 25 studies that evaluated the therapeutic and preventive effects of curcumin on diverse diseases. The findings suggested that curcumin has potential effects on lipid profiles, blood pressure, inflammatory markers and oxidative stress, musculoskeletal diseases, emotional and cognitive function, ulcerative colitis, liver and kidney function, primary dysmenorrhea or PMS, RA, COVID-19, and painful statues as well as HR-QOL. However, for many of the diseases the conclusions are still uncertain.
The biological activity of curcumin has been well confirmed, and it is expected to increase the clinical applicability of curcumin by revealing its mechanism of action in different diseases. In clinical trials, curcumin as an effective antihyperglycaemic agent, has been found to improve insulin resistance and reduce insulin and blood glucose levels. Numerous studies have revealed that curcumin induces PPAR-γ activation to regulate glucose metabolism (Jiménez-Flores et al., 2014). Additionally, studies revealed that curcumin could prevent hyperglycemia by promoting insulin secretion, improving β-cell function, and inhibiting β-cell apoptosis (Gu et al., 2024). Curcumin/turmeric can reduce blood pressure by inducing eNOS protein expression, enhancing antioxidant capacity by restoring glutathione, and decreasing the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (Ramaswami et al., 2004; Nakmareong et al., 2011). Curcumin/turmeric can also improve endothelial vasorelaxation response to acetylcholine, increase NO bioavailability, and induce several antioxidant enzyme genes expressions through activation of the Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathways (Aggarwal and Sung, 2009; Rungseesantivanon et al., 2010; Suphim et al., 2010). The exact mechanism by which curcumin/turmeric may affect body measurements has not been fully determined. However, curcumin’s effects on anthropometric aspects have been associated with downregulation of the Janus kinase enzyme and inhibition of adipocyte differentiation (Dehzad et al., 2023d). Curcumin is effectively used in obesity treatment because it is a lipophilic molecule that rapidly penetrates cell membranes and may be associated with lipid metabolism, gut microbiota and anti-inflammatory potential (Kasprzak-Drozd et al., 2022).
A recent study found that curcumin exerts beneficial effects on gastrointestinal disorders. This may be related to the regulation of the ‘brain-gut axis’ and restoration of the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier (Yu et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2017). Notably, curcumin has been found to modulate neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine, which may account for its antidepressant effects (Spanoudaki et al., 2024). Curcumin also improves cognitive function. The neuroprotective properties of curcumin act by inducing cAMP response element-binding protein and, subsequently, BDNF activation (Gomez-Pinilla and Nguyen, 2012). These interactions may contribute to mental and neurological health.
Curcumin has potential therapeutic effects on bone, joint and muscle disorders. This may help modulate inflammatory processes and metabolic pathways, thereby reducing symptoms and potentially slowing disease progression (Maouche et al., 2024). Curcumin, a promising antiviral drug for COVID-19, has been revealed to have high inhibitory activity against this virus (Al-Doori et al., 2021). Meanwhile, computer simulations and molecular docking indicated that the monomer has a good ability to bind to coronavirus and host targets, thus blocking the virus-host binding site (Jena et al., 2021). Therefore, the use of curcumin as an antiviral and anti-inflammatory substance may improve the containment of the damage caused by COVID-19 patients.
Curcumin has potential protective effects on the liver and kidney functions. The mechanism by which curcumin attenuates proteinuria can be explained by referring to recent investigations regarding its anti-inflammatory enhanced autophagy effects (Fan et al., 2020). Given that curcumin is a potent antioxidant, its protective effect on liver function may be related to its free radical scavenging properties. The therapeutic effects of curcumin in radiodermatitis have been associated with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, as well as the ability to stimulate the regeneration of skin epithelial cells and promote wound healing (Kasprzak-Drozd et al., 2024). Curcumin is widely used in most countries globally. Given its multidirectional effects, it is used for health-promoting purposes. Moreover, further mechanistic studies are needed to explore the effects of curcumin on various signaling cascades in the body.
Although many experts believe that natural remedies may be safer than conventional medicine, patients are still susceptible to adverse reactions to other ingredients. There is a need for certainty when combined with other therapies. Moreover, suitable dosages and contraindications of curcumin need to be explored. There is also a need to study the mechanisms that have revealed the mechanism of action of curcumin on different diseases. There is also a need to explore the mechanism underlying the effects of curcumin on different diseases.
Since the methodological quality assessed using the AMSTAR-2 checklist and the certainty of the outcome effects assessed using the GRADE grading were mostly very low to low, there is a need to improve the quality of future studies. We recommend that researchers make their studies public in advance. This could encourage researchers to comply with the protocol and reduce various biases (Sideri et al., 2018). It can also avoid unnecessary duplication and optimize limited resources (Booth et al., 2011). The protocol could be registered and published on platforms such as PROSPERO (https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/), OSF REGISTRIES (https: //osf.io/registries? viewonly=). The included primary studies are an important guarantee for the evaluation of evidence, and comprehensive search strategies, as well as reasonable inclusion criteria, an important guarantee for reliability. To improve the accuracy of the meta-analysis results, the following suggestions are made: Choosing multiple search methods and databases, tracing back references, retrieving registry information, consulting with experts in the relevant fields, and searching grey literature to ensure that the relevant literature is not missed.
Furthermore, it is necessary to explain the rationale and reasons for the inclusion of studies, which can provide reviewers and readers with a clearer understanding of whether the processes involved were justified. It is also important to note that authors need to provide a list of excluded literature and reasons, thus avoiding bias in meta-analyses. Furthermore, commercially funded studies are more likely to reach conclusions in favor of the sponsor’s product than independently funded studies (DeAngelis and Fontanarosa, 2008). Therefore, authors must keep detailed records of the funding sources for each study facilitate the judgement of whether funding could lead to a conflict of interest. The investigation and discussion of potential publication bias for the meta-analysis included in this overview needs to be improved. The funnel plot, Egger’s test, Begg’s test, and Macaskill’s can all be used to detect publication bias (Hayashino et al., 2005). Consequently, it is important to strengthen the quality of the systematic reviews to make more confident recommendations. Hence, future reviews should be rigorously reported following the PRISMA guidelines (Page et al., 2021) and use the best practice methods. Finally, given the heterogeneities and the inconsistencies, we suggest that future studies focus on resolving the existing ambiguities concerning the impact of turmeric/curcumin on health outcomes and clinical biomarkers in the high-quality human trials.
4.1 Strengths and limitations
This umbrella review has some strengths and limitations. For instance, our review synthesizes evidence based on clinical practice, and the findings improve our knowledge of the validity of curcumin in clinical settings. It is worth highlighting that we used a rigorous study design, including use the latest versions of AMSTAR-2 and the GRADE system, to assess methodological quality and quality of evidence. As a result, we synthesized up-to-date comprehensive evidence, which will help guide the integration of adjunctive curcumin use into clinical practice to address general health and wellbeing, as well as therapeutic disease management. For example, healthcare experts may recommend that patients take curcumin as needed to prevent or treat diseases. However, there remains a gap betwwenn evidence and clinical practice, and future research should explore the reasons and mechanisms in different populations. Most of the studies failed to register their protocols, which could impair the transparency and credibility of the evidence. Second, we searched only English databases, which may have limited access to some available evidence. We obtained evidence synthesized by existing reviews, where details of the original trials may have been omitted, and studies included in different reviews may have overlapped. Third, there was significant heterogeneity regarding participants, interventions and assessment of outcomes, which may have affected the stability and accuracy of the findings. Finally, not all included studies were of high quality, which could introduce potential bias.
5 Conclusion
This umbrella review provides up-to-date evidence for the effect of curcumin on diverse clinical outcomes in humans. Oral curcumin has been found to be safe and therapeutic for human health and wellbeing, with potential benefits for osteoarthritis, blood sugar, lipids, and blood pressure. Curcumin has also been associated with improvements in dysmenorrhea and polycystic ovary syndrome; inflammatory status, including RA, COVID-19, and radiation dermatitis; liver and kidney function; and gastrointestinal and psychological disorders. In summary, while curcumin has demonstrated potential therapeutic benefits across various health domains, its clinical application is still fraught with challenges. In the future, more high-quality studies are needed to determine the effects of curcumin on different populations and to determine the availability of personalized, effective interventions to optimize curcumin use in clinical and healthcare settings.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
QX: Writing – original draft. HL: Writing – original draft. RZ: Writing – review and editing. ZG: Writing – review and editing. JW: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Validation. YW: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. ZL: Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82405373) and Major Research Project of Science and Technology Innovation Project of China Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine (CI2021A01803).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1601204/full#supplementary-material
References
Aggarwal, B. B., and Sung, B. (2009). Pharmacological basis for the role of curcumin in chronic diseases: an age-old spice with modern targets. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 30 (2), 85–94. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2008.11.002
Al-Doori, A., Ahmed, D., Kadhom, M., and Yousif, E. J. (2021). Herbal medicine as an alternative method to treat and prevent COVID-19. Baghdad J. Biochem. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2 (01), 1–20. doi:10.47419/bjbabs.v2i01.25
Aromataris, E., Fernandez, R., Godfrey, C. M., Holly, C., Khalil, H., and Tungpunkom, P. (2015). Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 13 (3), 132–140. doi:10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055
Asadi, S., Gholami, M. S., Siassi, F., Qorbani, M., and Sotoudeh, G. (2020). Beneficial effects of nano-curcumin supplement on depression and anxiety in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 34 (4), 896–903. doi:10.1002/ptr.6571
Ayub, H., Islam, M., Saeed, M., Ahmad, H., Al-Asmari, F., Ramadan, M. F., et al. (2024). On the health effects of curcumin and its derivatives. Food Sci. Nutr. 12 (11), 8623–8650. doi:10.1002/fsn3.4469
Beba, M., Mohammadi, H., Clark, C. C. T., and Djafarian, K. (2022). The effect of curcumin supplementation on delayed-onset muscle soreness, inflammation, muscle strength, and joint flexibility: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 36 (7), 2767–2778. doi:10.1002/ptr.7477
Ben-Horin, S., Salomon, N., Karampekos, G., Viazis, N., Lahat, A., Ungar, B., et al. (2024). Curcumin-QingDai combination for patients with active ulcerative colitis: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 22 (2), 347–356.e6. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.05.023
Booth, A., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Moher, D., Petticrew, M., and Stewart, L. (2011). An international registry of systematic-review protocols. Lancet 377 (9760), 108–109. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60903-8
DeAngelis, C. D., and Fontanarosa, P. B. (2008). Impugning the integrity of medical science: the adverse effects of industry influence. JAMA 299 (15), 1833–1835. doi:10.1001/jama.299.15.1833
Dehzad, M. J., Ghalandari, H., Amini, M. R., and Askarpour, M. (2023a). Effects of curcumin/turmeric supplementation on lipid profile: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 75, 102955. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2023.102955
Dehzad, M. J., Ghalandari, H., Amini, M. R., and Askarpour, M. (2023b). Effects of curcumin/turmeric supplementation on liver function in adults: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 74, 102952. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2023.102952
Dehzad, M. J., Ghalandari, H., and Askarpour, M. (2024). Curcumin/turmeric supplementation could improve blood pressure and endothelial function: a grade-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 59, 194–207. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.12.009
Dehzad, M. J., Ghalandari, H., Nouri, M., and Askarpour, M. (2023c). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin/turmeric supplementation in adults: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cytokine 164, 156144. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156144
Dehzad, M. J., Ghalandari, H., Nouri, M., and Askarpour, M. (2023d). Effects of curcumin/turmeric supplementation on obesity indices and adipokines in adults: a grade-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 37 (4), 1703–1728. doi:10.1002/ptr.7800
Ebrahimzadeh, A., Mohseni, S., Safargar, M., Mohtashamian, A., Niknam, S., Bakhoda, M., et al. (2024). Curcumin effects on glycaemic indices, lipid profile, blood pressure, inflammatory markers and anthropometric measurements of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 80, 103025. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2024.103025
Emami, E., Heidari-Soureshjani, S., and Sherwin, C. M. (2022). Anti-inflammatory response to curcumin supplementation in chronic kidney disease and hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Avicenna J. Phytomed 12 (6), 576–588. doi:10.22038/AJP.2022.20049
Fan, H.-Y., Wang, X.-K., Li, X., Ji, K., Du, S.-H., Liu, Y., et al. (2020). Curcumin, as a pleiotropic agent, improves doxorubicin-induced nephrotic syndrome in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 250, 112502. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.112502
Fathi, S., Agharloo, S., Falahatzadeh, M., Bahraminavid, S., Homayooni, A., Faghfouri, A. H., et al. (2024). Effect of curcumin supplementation on symptoms of anxiety: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 62, 253–259. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2024.05.017
Gomez-Pinilla, F., and Nguyen, T. T. J. (2012). Natural mood foods: the actions of polyphenols against psychiatric and cognitive disorders. Nutr. Neurosci. 15 (3), 127–133. doi:10.1179/1476830511Y.0000000035
Gouda, M. M., Balaya, R. D. A., Modi, P. K., Kadri, S., Chanderasekaran, J., Balnadupete, A., et al. (2024). Impact of curcumin on the IL-17a-mediated p53-fibrinolytic system: mouse proteomics and integrated human fibrosis scRNAseq insights. Inflammation. doi:10.1007/s10753-024-02167-3
Gu, Y., Niu, Q., Zhang, Q., and Zhao, Y. (2024). Ameliorative effects of curcumin on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Molecules 29 (12), 2934. doi:10.3390/molecules29122934
Guyatt, G., Oxman, A. D., Akl, E. A., Kunz, R., Vist, G., Brozek, J., et al. (2011). GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64 (4), 383–394. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026
Hayashino, Y., Noguchi, Y., and Fukui, T. (2005). Systematic evaluation and comparison of statistical tests for publication bias. J. Epidemiol. 15 (6), 235–243. doi:10.2188/jea.15.235
Jamali, N., Adib-Hajbaghery, M., and Soleimani, A. (2020). The effect of curcumin ointment on knee pain in older adults with osteoarthritis: a randomized placebo trial. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 20 (1), 305. doi:10.1186/s12906-020-03105-0
Jena, A. B., Kanungo, N., Nayak, V., Chainy, G. B. N., and Dandapat, J. (2021). Catechin and curcumin interact with S protein of SARS-CoV2 and ACE2 of human cell membrane: insights from computational studies. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 2043. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-81462-7
Jiménez-Flores, L. M., López-Briones, S., Macías-Cervantes, M. H., Ramírez-Emiliano, J., and Pérez-Vázquez, V. (2014). A PPARγ, NF-κB and AMPK-dependent mechanism may be involved in the beneficial effects of curcumin in the diabetic db/db mice liver. Molecules 19 (6), 8289–8302. doi:10.3390/molecules19068289
Kasprzak-Drozd, K., Niziński, P., Hawrył, A., Gancarz, M., Hawrył, D., Oliwa, W., et al. (2024). Potential of curcumin in the management of skin diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (7), 3617. doi:10.3390/ijms25073617
Kasprzak-Drozd, K., Oniszczuk, T., Gancarz, M., Kondracka, A., Rusinek, R., and Oniszczuk, A. (2022). Curcumin and weight loss: does it work? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (2), 639. doi:10.3390/ijms23020639
Keller, A., and Wallace, T. C. (2021). Tea intake and cardiovascular disease: an umbrella review. Ann. Med. 53 (1), 929–944. doi:10.1080/07853890.2021.1933164
Khan, S. U., Khan, M. U., Riaz, H., Valavoor, S., Zhao, D., Vaughan, L., et al. (2019). Effects of nutritional supplements and dietary interventions on cardiovascular outcomes: an umbrella review and evidence map. Ann. Intern Med. 171 (3), 190–198. doi:10.7326/M19-0341
Kou, H., Huang, L., Jin, M., He, Q., Zhang, R., and Ma, J. (2023). Effect of curcumin on rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 14, 1121655. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1121655
Li, P., Ding, L., Cao, S., Feng, X., Zhang, Q., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). Curcumin metabolites contribute to the effect of curcumin on ameliorating insulin sensitivity in high-glucose-induced insulin-resistant HepG2 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 259, 113015. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113015
Li, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, Q., Ma, J., Li, X., Yan, J., et al. (2023). Berberine and health outcomes: an umbrella review. Phytother. Res. 37 (5), 2051–2066. doi:10.1002/ptr.7806
Liu, X., Eyles, J., McLachlan, A. J., and Mobasheri, A. (2018). Which supplements can I recommend to my osteoarthritis patients? Rheumatol. Oxf. 57 (Suppl. l_4), iv75–iv87. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/key005
Malekmakan, L., Hamidianjahromi, A., Sayadi, M., and Rezazadeh, M. H. (2022). Efficacy and safety of turmeric dietary supplementation on proteinuria in CKD: a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCT. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 16 (3), 153–161. doi:10.52547/ijkd.6772
Maouche, A., Boumediene, K., and Baugé, C. (2024). Bioactive compounds in osteoarthritis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic roles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (21), 11656. doi:10.3390/ijms252111656
Mirzaei Dahka, S., Afsharfar, M., Tajaddod, S., Sohouli, M. H., Shekari, S., Bakhshi Nafouti, F., et al. (2023). Impact of curcumin supplementation on radiation dermatitis severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev. 24 (3), 783–789. doi:10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.3.783
Mobasheri, A., Spring-Charles, A., Gamaleri, F. C., McSwan, J., Garg, M., and Sethi, V. S. (2024). Evidence-based opinions from multidisciplinary experts on use of naturopathic herbal remedies in pain management. J. Pain Res. 17, 599–608. doi:10.2147/JPR.S432090
Nakmareong, S., Kukongviriyapan, U., Pakdeechote, P., Donpunha, W., Kukongviriyapan, V., Kongyingyoes, B., et al. (2011). Antioxidant and vascular protective effects of curcumin and tetrahydrocurcumin in rats with L-NAME-induced hypertension. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 383 (5), 519–529. doi:10.1007/s00210-011-0624-z
Ng, Q. X., Soh, A. Y. S., Loke, W., Venkatanarayanan, N., Lim, D. Y., and Yeo, W.-S. (2018). A meta-analysis of the clinical use of curcumin for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). J. Clin. Med. 7 (10), 298. doi:10.3390/jcm7100298
Nirgude, S., Desai, S., Ravindran, F., Mhatre, A., Mahadeva, R., Sharma, S., et al. (2025). Global transcriptome profiling of ST09 treated breast cancer cells identifies miR-197-5p/GPX3 antioxidant axis as a regulator of tumorigenesis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 148, 114127. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114127
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 134, 103–112. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.02.003
Panknin, T. M., Howe, C. L., Hauer, M., Bucchireddigari, B., Rossi, A. M., and Funk, J. L. (2023). Curcumin supplementation and human disease: a scoping review of clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (5), 4476. doi:10.3390/ijms24054476
Ramaswami, G., Chai, H., Yao, Q., Lin, P. H., Lumsden, A. B., and Chen, C. (2004). Curcumin blocks homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction in porcine coronary arteries. J. Vasc. Surg. 40 (6), 1216–1222. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2004.09.021
Rungseesantivanon, S., Thenchaisri, N., Ruangvejvorachai, P., and Patumraj, S. (2010). Curcumin supplementation could improve diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction associated with decreased vascular superoxide production and PKC inhibition. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 10, 57. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-10-57
Sadeghi, N., Mansoori, A., Shayesteh, A., and Hashemi, S. J. (2020). The effect of curcumin supplementation on clinical outcomes and inflammatory markers in patients with ulcerative colitis. Phytother. Res. 34 (5), 1123–1133. doi:10.1002/ptr.6581
Sadeghian, M., Rahmani, S., Jamialahmadi, T., Johnston, T. P., and Sahebkar, A. (2021). The effect of oral curcumin supplementation on health-related quality of life: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Affect Disord. 278, 627–636. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.09.091
Sahebkar, A., and Henrotin, Y. (2016). Analgesic efficacy and safety of curcuminoids in clinical practice: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain Med. 17 (6), 1192–1202. doi:10.1093/pm/pnv024
Sandoval-Ramírez, B.-A., Catalán, Ú., Llauradó, E., Valls, R.-M., Salamanca, P., Rubió, L., et al. (2022). The health benefits of anthocyanins: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies and controlled clinical trials. Nutr. Rev. 80 (6), 1515–1530. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuab086
Sarraf, P., Parohan, M., Javanbakht, M. H., Ranji-Burachaloo, S., and Djalali, M. (2019). Short-term curcumin supplementation enhances serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adult men and women: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Res. 69, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2019.05.001
Shafiee, A., Athar, M. M. T., Shahid, A., Ghafoor, M. S., Ayyan, M., Zahid, A., et al. (2023). Curcumin for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 37 (3), 1167–1175. doi:10.1002/ptr.7724
Shao, W., Yu, Z., Chiang, Y., Yang, Y., Chai, T., Foltz, W., et al. (2012). Curcumin prevents high fat diet induced insulin resistance and obesity via attenuating lipogenesis in liver and inflammatory pathway in adipocytes. PLoS One 7 (1), e28784. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028784
Sharifipour, F., Siahkal, S. F., Qaderi, K., Mohaghegh, Z., Zahedian, M., and Azizi, F. (2024). Effect of curcumin on dysmenorrhea and symptoms of premenstrual syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean J. Fam. Med. 45 (2), 96–104. doi:10.4082/kjfm.23.0184
Shea, B. J., Reeves, B. C., Wells, G., Thuku, M., Hamel, C., Moran, J., et al. (2017). AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 358, j4008. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4008
Shen, W., Qu, Y., Jiang, H., Wang, H., Pan, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Therapeutic effect and safety of curcumin in women with PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 1051111. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1051111
Sideri, S., Papageorgiou, S. N., and Eliades, T. (2018). Registration in the international prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO) of systematic review protocols was associated with increased review quality. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 100, 103–110. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.01.003
Spanoudaki, M., Papadopoulou, S. K., Antasouras, G., Papadopoulos, K. A., Psara, E., Vorvolakos, T., et al. (2024). Curcumin as a multifunctional spice ingredient against mental disorders in humans: current clinical studies and bioavailability concerns. Life (Basel) 14 (4), 479. doi:10.3390/life14040479
Suphim, B., Prawan, A., Kukongviriyapan, U., Kongpetch, S., Buranrat, B., and Kukongviriyapan, V. (2010). Redox modulation and human bile duct cancer inhibition by curcumin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 48 (8-9), 2265–2272. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.05.059
Tian, J., Feng, B., and Tian, Z. (2022). The effect of curcumin on lipid profile and glycemic status of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 8278744. doi:10.1155/2022/8278744
Wang, J., Ghosh, S. S., and Ghosh, S. (2017). Curcumin improves intestinal barrier function: modulation of intracellular signaling, and organization of tight junctions. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 312 (4), C438–C445. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00235.2016
Wang, Y., Wang, S., Ma, C., Qi, W., Lv, J., Zhang, M., et al. (2024a). Nrf2 depletion enhanced curcumin therapy effect in gastric cancer by inducing the excessive accumulation of ROS. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 30165. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-81375-1
Wang, Y., Zhou, D., Zhang, X., Qing, M., Li, X., Chou, Y., et al. (2024b). Curcumin promotes renewal of intestinal epithelium by miR-195-3p. J. Ethnopharmacol. 320, 117413. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117413
Wang, Z., Singh, A., Jones, G., Winzenberg, T., Ding, C., Chopra, A., et al. (2021a). Efficacy and safety of turmeric extracts for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 23 (2), 11. doi:10.1007/s11926-020-00975-8
Wang, Z., Zhang, Q., Huang, H., and Liu, Z. (2021b). The efficacy and acceptability of curcumin for the treatment of depression or depressive symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect Disord. 282, 242–251. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.12.158
Weissgerber, T. L. (2021). Training early career researchers to use meta-research to improve science: a participant-guided “learn by doing” approach. PLoS Biol. 19 (2), e3001073. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3001073
Yeung, A. W. K., Horbańczuk, M., Tzvetkov, N. T., Mocan, A., Carradori, S., Maggi, F., et al. (2019). Curcumin: total-scale analysis of the scientific literature. Molecules 24 (7), 1393. doi:10.3390/molecules24071393
Yin, J., Wei, L., Wang, N., Li, X., and Miao, M. (2022). Efficacy and safety of adjuvant curcumin therapy in ulcerative colitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 289, 115041. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115041
Yu, Y., Wu, S., Li, J., Wang, R., Xie, X., Yu, X., et al. (2015). The effect of curcumin on the brain-gut axis in rat model of irritable bowel syndrome: involvement of 5-HT-dependent signaling. Metab. Brain Dis. 30 (1), 47–55. doi:10.1007/s11011-014-9554-z
Zeng, L., Yu, G., Hao, W., Yang, K., and Chen, H. (2021). The efficacy and safety of Curcuma longa extract and curcumin supplements on osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 41 (6). doi:10.1042/BSR20210817
Zhang, J., Huang, Y., Xu, J., Zhao, R., Xiong, C., Habu, J., et al. (2022). Global publication trends and research hotspots of curcumin application in tumor: a 20-year bibliometric approach. Front. Oncol. 12, 1033683. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1033683
Zhang, M.-W., Sun, X., Xu, Y.-W., Meng, W., Tang, Q., Gao, H., et al. (2024). Curcumin relieves oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain via reducing inflammation and activating antioxidant response. Cell Biol. Int. 48 (6), 872–882. doi:10.1002/cbin.12153
Zhang, X., Zhang, H., Wang, J., Chen, Y., Lin, J., Wang, Q., et al. (2025). Curcumin attenuates ulcerative colitis via regulation of Sphingosine kinases 1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biofactors 51 (1), e70001. doi:10.1002/biof.70001
Keywords: curcumin, metabolic indicators, health outcomes, evidence, meta-analysis, umbrella review
Citation: Xu Q, Lian H, Zhou R, Gu Z, Wu J, Wu Y and Li Z (2025) Curcumin and multiple health outcomes: critical umbrella review of intervention meta-analyses. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1601204. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1601204
Received: 29 March 2025; Accepted: 26 May 2025;
Published: 05 June 2025.
Edited by:
Mohamed T. El-Saadony, Zagazig University, EgyptReviewed by:
Ahmed M. Saad, Zagazig University, EgyptFawze Alnadari, Research and Development Center of Jiangsu Tianmeijian Nature Bioengineering Co. Ltd., China
Dina Mostafa Mohammed, National Research Centre, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Lian, Zhou, Gu, Wu, Wu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiao Wu, MTQ4MTUwNjg1M0BxcS5jb20=; Yu Wu, d3k3MTNAdmlwLnNpbmEuY29t; Zhongyu Li, bHp5NjgxYmpAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Qin Xu1†
Qin Xu1† Zhenzhen Gu
Zhenzhen Gu Zhongyu Li
Zhongyu Li