- 1School of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Yunnan Key Laboratory of Pharmacology for Natural Products, Kunming Medical University, Yunnan, Kunming, China
- 2School of Pharmacy, Dali University, Dali, Yunnan, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Panzhihua Central Hospital, Sichuan, Panzhihua, China
In recent decades, the pharmacological properties of botanical drugs have been investigated with increasing depth, offering novel insights into their potential for enhancing healthcare. Berberine (BBR) is an alkaloid extracted from the roots, rhizomes and stem tubers of plants such as Coptis chinensis, Phellodendron amurense, Radix berberidis, and several other plants, which is used not only as an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agent, but also for the treatment of cancer and chronic diseases. BBR has demonstrated remarkable therapeutic efficacy in the management of disorders affecting the nervous, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems, characterized by its high safety profile and minimal adverse effects. Despite the substantial progress made in understanding BBR’s pharmacodynamics, its precise mechanisms of action remain incompletely elucidated and warrant further systematic investigation. This study provides an extensive review of the latest pharmacological findings related to berberine and its therapeutic advancements, offering strong evidence for future research and clinical implementation.
1 Introduction
In recent years, the pharmacological properties of botanical drugs have been explored and uncovered with increasing depth, opening new avenues for the advancement of healthcare systems. Botanical drugs have long been esteemed for their remarkable efficacy in preventing and treating diseases, positioning them as a crucial pillar of human health (Raskin et al., 2002). According to the World Health Organization, herbal remedies continue to serve as the primary source of healthcare for more than half of the global population, with particular significance in developing nations (Bodeker, 1996; Kim et al., 2020; Mei, 2024). The prominence of botanical drug is largely attributable to its high cultural acceptability, strong compatibility with the human body, and relatively low incidence of adverse effects (Yuan et al., 2023). However, the discovery and processing of plant-based medicinal products also face numerous challenges, including access restrictions, difficulties in material identification, and the conservation of wild species (Ge W. et al., 2024). Despite these hurdles, natural products in certain contexts continue to enjoy broad popularity worldwide due to their perceived ease of use, affordability, renewable resources, and relatively low toxicity in well-studied compounds (Newman and Cragg, 2020).
Among the myriad of natural phytochemicals, berberine (BBR) has garnered significant attention from scholars both domestically and internationally. As an isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from the traditional Chinese medicinal herbs Coptis chinensis and Phellodendron amurense, BBR is renowned for its heat-clearing, damp-drying, and detoxifying properties. It has been employed in Chinese medical practice for thousands of years in the treatment of various inflammatory diseases (Yu et al., 2017). Studies have shown that BBR has demonstrated exceptional antimicrobial efficacy in the treatment of intestinal infections, conjunctivitis, and suppurative otitis media. Additionally, it has shown significant therapeutic benefits in the management of chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension (Riu et al., 2020). Some natural antioxidant agents and their biological properties with anti-oxidative stress potentials in some tissues related to health (Gogebakan et al., 2012; Selamoglu Talas et al., 2008; Adnan et al., 2021; Das et al., 2024), BBR also has a certain antioxidant capacity (Salehi et al., 2019). Notably, BBR is characterized by a favorable safety profile, with only mild and infrequent gastrointestinal discomfort reported as side effects, rendering it an optimal treatment option for patients with limited financial resources (Nie et al., 2024). Despite significant progress in BBR research, a comprehensive and systematic elucidation of its exact pharmacological mechanisms and its role in disease treatment remains lacking. Current studies tend to focus on a specific pharmacological activity of BBR for particular diseases, and there is a lack of a comprehensive article that integrates the latest research findings to fully reveal its pharmacological mechanisms in disease treatment.
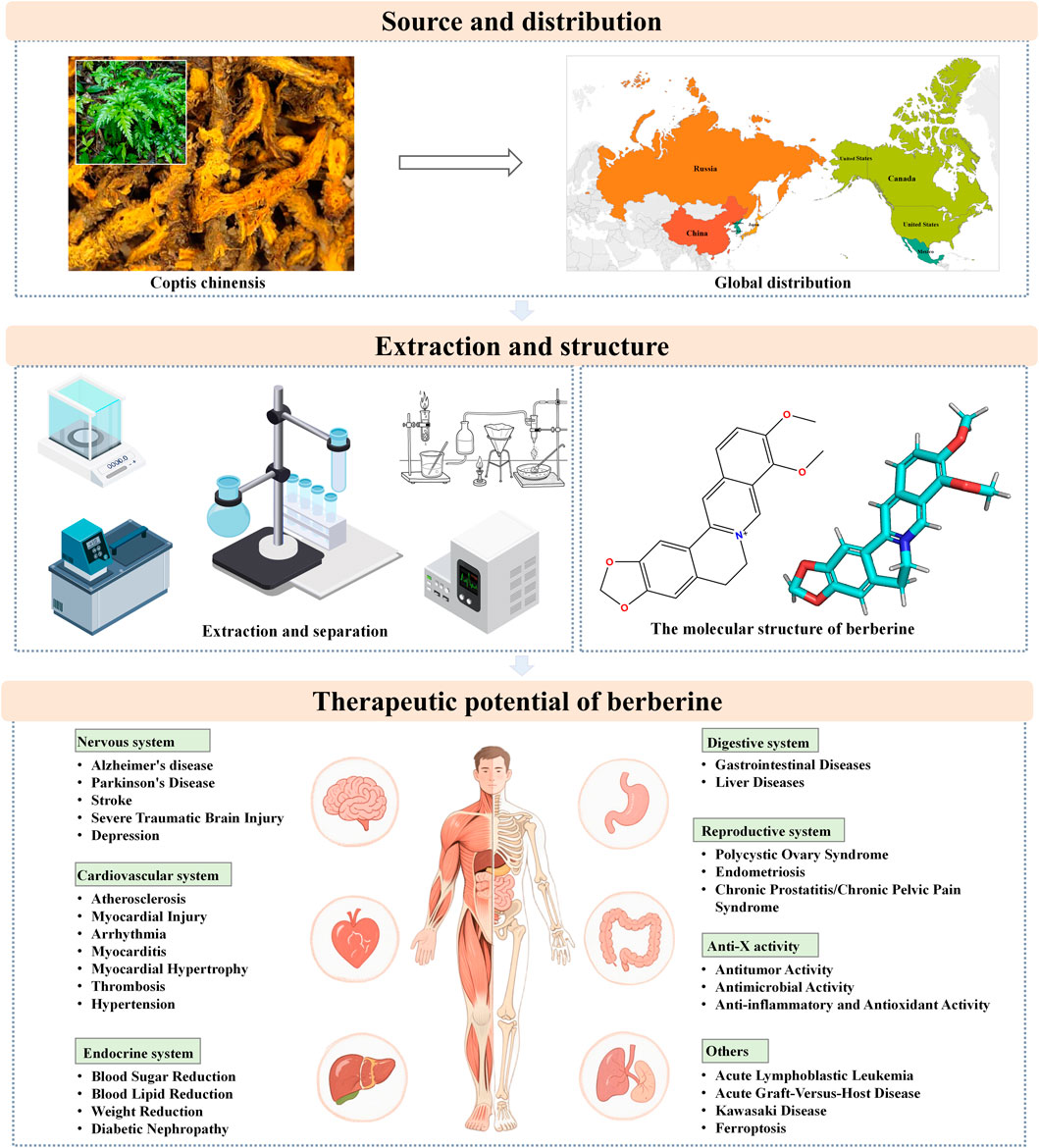
This study aims to provide an overview of the sources, chemical composition, and bioactive constituents of BBR, as well as its extraction and isolation methods. It comprehensively discusses the mechanisms underlying BBR’s protective effects in a range of diseases affecting the nervous, cardiovascular, endocrine, digestive, and reproductive systems (Figure 1). Additionally, the study summarizes BBR’s bioactivity in anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities, with the goal of providing robust evidence for its further research and clinical application. Through this review, a more comprehensive understanding of BBR’s clinical potential and pharmacological mechanisms across various diseases is presented, highlighting key areas such as neuroprotection, cardiovascular protection, glycemic and lipid-lowering effects, and anti-cancer properties.
2 Literature retrieval and screening methods
2.1 Language
The pharmacological mechanisms of action section of this review includes only studies originally written in English; other sections such as source, extraction and separation include Chinese studies.
2.2 Databases
PubMed databases were searched. The mesh terms used were berberine or umbellatine and pharmacological mechanism of action or mechanisms of pharmacological action or pharmacology or mechanism of action or mode of action or pharmacologic action or molecular mechanisms of pharmacological action. The mesh terms enabled the search and identification of in vivo and in vitro studies that were related to the objective of this review. Chinese studies were obtained through CNKI database.
2.3 Study selection
In this review, due to the lack of clinical studies of BBR, both in vitro and in vivo studies were considered in the final analysis. Only full texts were considered. Studies on BBR derivatives, novel delivery systems, and network pharmacological analysis were excluded.
2.4 Time frame
The studies included in the pharmacological mechanism of action section were mainly published from 2017 to 2024.
3 Source
BBR is an alkaloid compound extracted from the roots, rhizomes, and stem bulbs of plants belonging to the Berberidaceae, Ranunculaceae, and Papaveraceae families (such as Coptis chinensis, Phellodendron amurense, Radix berberidis, and several other plants). In addition, studies have shown that BBR can also be extracted from plants of the Zanthoxylum monophyllum (Stermitz and Sharifi, 1977). It is the principal alkaloid component in C. chinensis. In addition to being extracted from natural sources, BBR can also be synthetically produced through modern manufacturing processes (An et al., 2022). Studies have shown that there are 11 species and one subspecies of Coptis globally. Among these, six species are found in China, with another 6 to 8 species in Japan and the Russian Far East, and 4 species in North America (Chen, 2022).
4 The physical and chemical properties of berberine
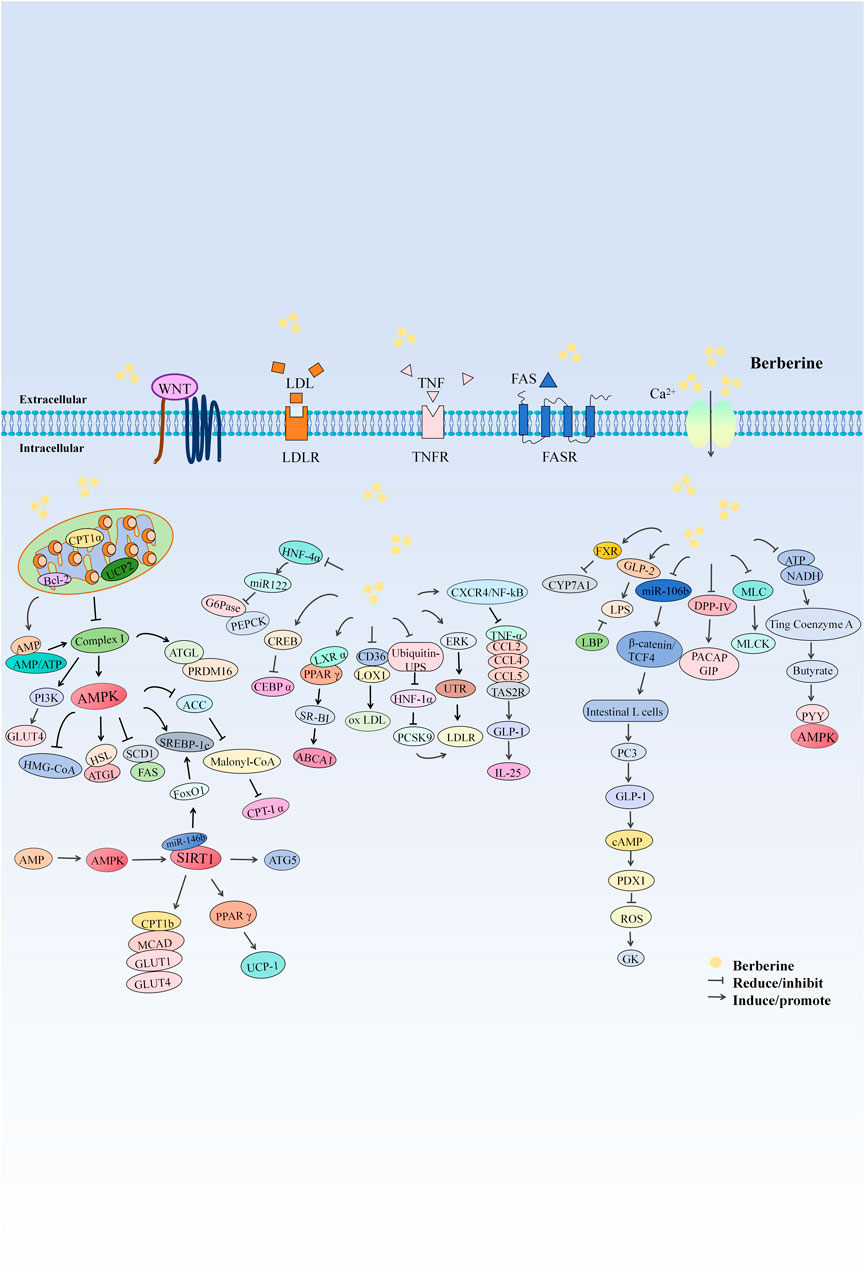
BBR is a yellow, needle-like crystalline compound that precipitates in ether. It is odorless, with an intensely bitter taste, and has a melting point of 145°C. It is readily soluble in hot water, sparingly soluble in cold water and ethanol, and insoluble in benzene, chloroform, and acetone. Classified as a quaternary ammonium compound and an isoquinoline alkaloid, its clinical applications are primarily in the form of hydrochloride and sulfate salts (Si et al., 2019). The chemical name of BBR is 5,6-dihydro-9,10- dimethoxybenzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo[5,6-á]quinolizine, with a molecular structure of C20H18NO4 and a molecular weight of 336.39 g/mol. Pharmacokinetic studies indicate that BBR exhibits a very low plasma drug concentration following oral administration, with extensive distribution throughout the body, rapid metabolism, and slow elimination (Hui and Mao, 2011). After oral intake, BBR is rapidly converted into phase I metabolites, which are subsequently conjugated with glucuronic acid or sulfate to form phase II metabolites. These metabolites are ultimately excreted through urine and bile. The main metabolic pathways of BBR include demethylation and glucuronidation, but the bioavailability of BBR itself is low (Wang K. et al., 2017).
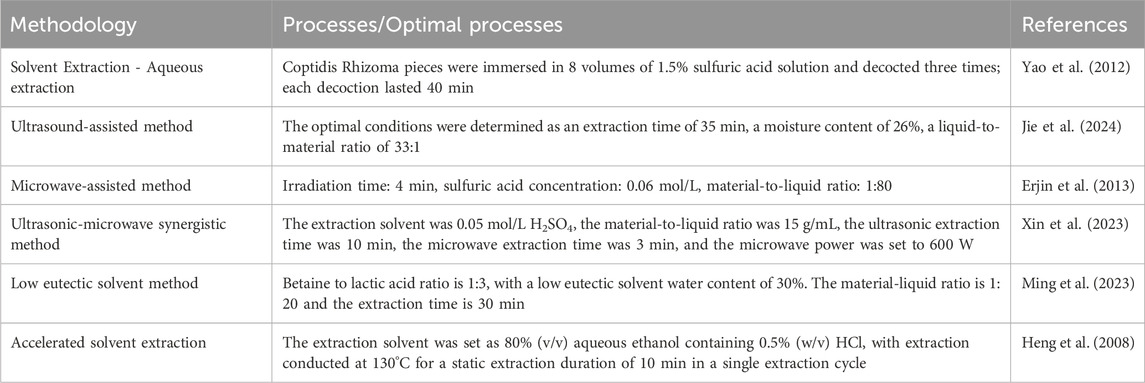
5 Extraction of berberine
The extraction methods commonly used in BBR include Solvent Extraction, Ultrasound-assisted method, Microwave-assisted method, Ultrasonic-microwave synergistic method, Low eutectic solvent method and Accelerated solvent extraction (Table 1).
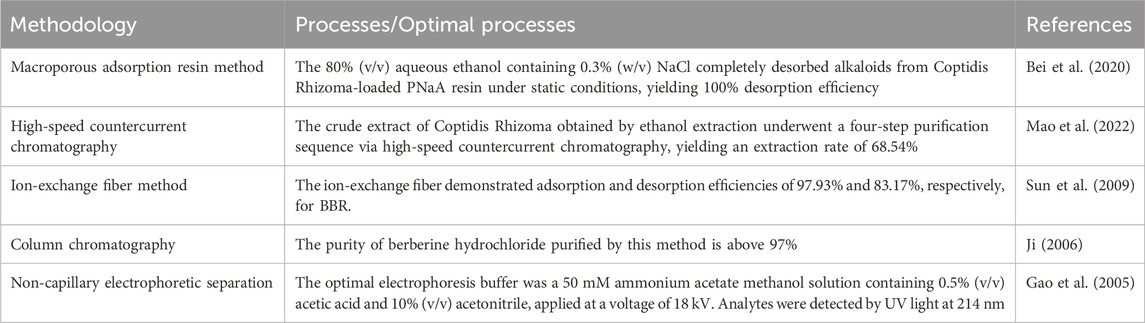
6 Separation of berberine
The separation methods commonly used in BBR include Macroporous adsorption resin method, High-speed countercurrent chromatography, Ion-exchange fiber method, Column chromatography and Non-capillary electrophoretic separation (Table 2).
7 Pharmacological mechanisms and disease treatment of berberine
7.1 Neuroprotective effects
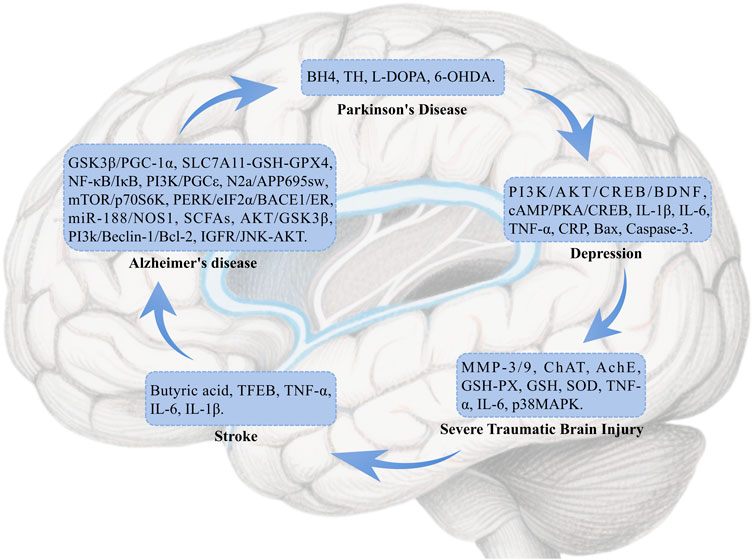
Neurological diseases are disorders that affect the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and muscles, encompassing conditions such as cerebrovascular diseases, neuroimmune diseases, infections, and others that can lead to motor, sensory, and cognitive impairments (Shayganfard, 2023). These diseases are caused by various factors, including genetics, infections, and trauma. This section explores the pharmacological mechanisms of BBR in treating Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Parkinson’s Disease (PD), stroke, traumatic brain injury (TBI), depression, and other related conditions (Figure 2).
7.1.1 Alzheimer’s disease
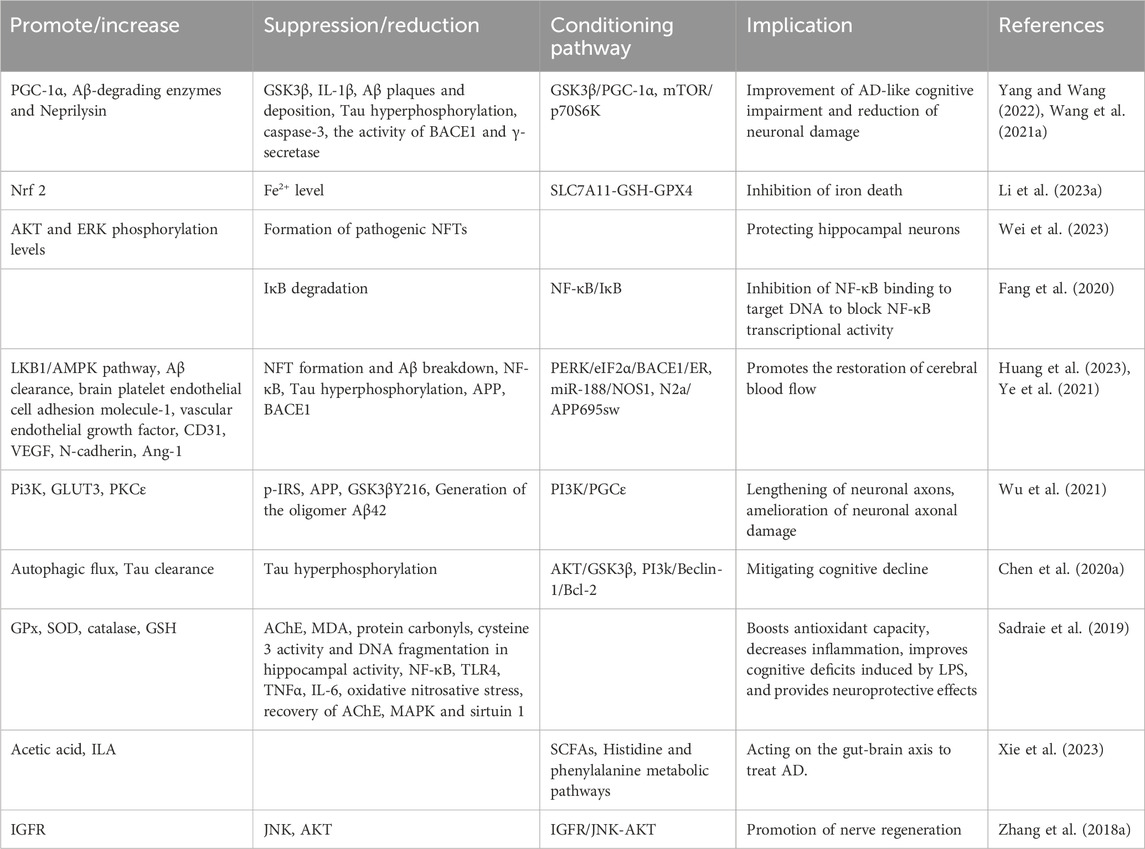
AD is a complex neurodegenerative disorder that induces a variety of cellular changes, including cholinergic system dysfunction, aggregation of β-amyloid proteins, hyperphosphorylation of Tau, dysregulation of metal homeostasis, and neuroinflammation. BBR enhances antioxidant activity through multiple pathways and targets, reduces inflammation-related biomarkers, promotes the formation of microvessels in the brain, and facilitates the creation of structurally intact and functionally competent new blood vessels. These actions help restore cerebral blood flow, regulate the gut-brain axis via short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and ultimately ameliorate AD-like cognitive impairments and spatial memory dysfunction (Patil et al., 2020) (Table 3).
7.1.2 Parkinson’s disease
BBR stimulates the biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin in the gut microbiota, increases dopamine and L-DOPA concentrations in both the blood and brain, enhances tyrosine hydroxylase activity to produce L-DOPA, and regulates the biosynthesis of phenylalanine, tyrosine, dopamine, and other intermediates, thus improving brain function and overall motor abilities in animals (Wang et al., 2021b). It also significantly depletes the number of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells in the substantia nigra and reduces dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the striatum, affecting PD (Kwon et al., 2010). BBR protects against 6-OHDA-induced cell death, attenuates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease-like behaviours and dopaminergic neuron loss in zebrafish by targeting cerebral mitochondria via mitophagy regulation (Wang L. et al., 2021).
7.1.3 Stroke
BBR may significantly increase the abundance of beneficial bacteria producing butyrate by modulating the gut microbiota, thereby enhancing butyrate levels. This action suppresses the activation of microglia and astrocytes in the brain of model mice and inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α), ultimately improving stroke outcomes (Duan et al., 2023). Additionally, BBR promotes the nuclear translocation of TFEB in neurons, increases autophagic flux, and enhances both autophagic activity and lysosomal function to mitigate ischemic injury and protect against ischemic stroke (Liu Y. et al., 2024).
7.1.4 Severe traumatic brain injury
BBR reduces cerebral edema and inhibits the expression of MMP-3/9 proteins, promoting ChAT activity and inhibiting AchE activity in mice with severe TBI. This results in a significant increase in the activities of GSH-PX, GSH, and SOD, exerting antioxidant effects. BBR also diminishes the levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 and generates neuroprotective effects by inducing the expression of SIRT1 and inhibiting p38 MAPK expression. These actions help restore learning and memory abilities in severe TBI mice (Wang and Zhang, 2018).
7.1.5 Depression
BBR improves depressive-like symptoms in chronic restraint stress mice by upregulating the phosphorylation and mRNA expression of PI3K and AKT, which subsequently increases the mRNA and protein expression/phosphorylation of CREB. This effect likely occurs through the PI3K/AKT/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway. Additionally, BBR regulates the mRNA expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, CRP, Bax, and Caspase-3, suppresses inflammation and cell apoptosis, and alleviates cell damage induced by corticosterone (Tang et al., 2024a). Further studies indicate that BBR improves diabetes and depression by activating the cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway (Tang et al., 2024b).
7.2 Cardiovascular protective effects
Cardiovascular diseases refer to conditions that affect the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels, including coronary heart disease, hypertension, myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, and others. These diseases often lead to circulatory disorders, manifesting symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, they may be life-threatening and represent a major global health issue (Feng et al., 2019). This section primarily discusses the therapeutic approaches of BBR in treating cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis (AS), myocardial injury, myocardial hypertrophy, and hypertension (Figure 3).
7.2.1 Atherosclerosis
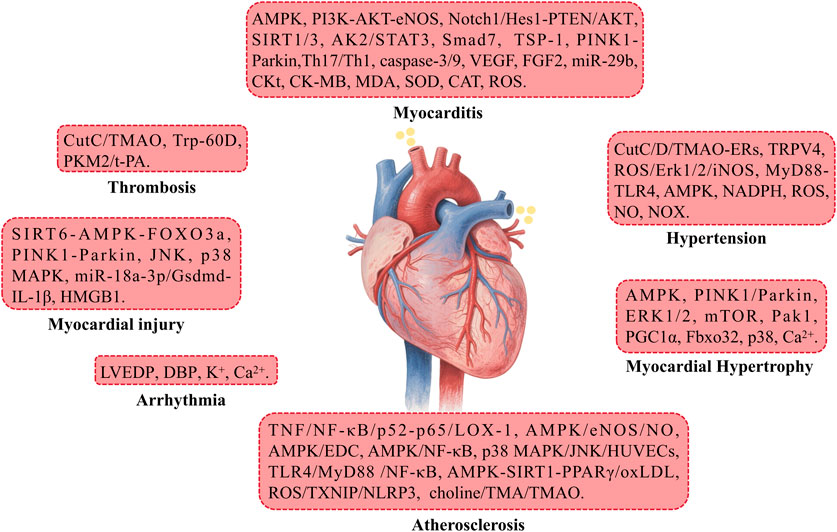
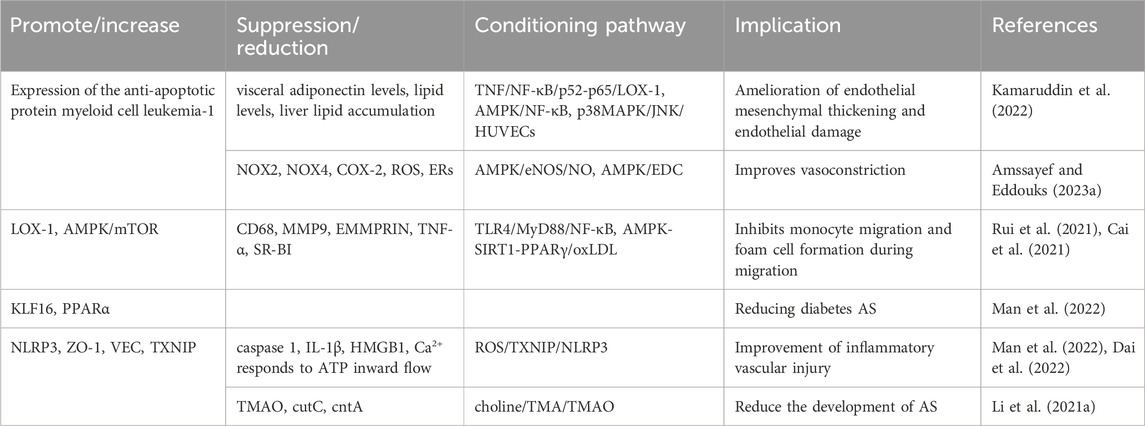
BBR plays a role in inhibiting atherosclerosis by improving endothelial dysfunction, suppressing smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, reducing monocyte adhesion, macrophage inflammation, cholesterol accumulation, foam cell formation, and platelet aggregation. Additionally, BBR prevents ischemia/reperfusion injury by increasing positive inotropic activity, enhancing the phosphorylation of Bad, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory mediators (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNFα), alleviating oxidative stress, lowering blood pressure, and providing protection against endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress (Table 4) (Feng et al., 2019).
7.2.2 Myocardial injury
BBR modulates several targets and signaling pathways to alleviate myocardial injury, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy. Specifically, BBR induces the expression of miR-181c-5p and miR-340-5p while inhibiting HMGB1 expression, thereby promoting the expression of miRNAs targeting HMGB1, effectively reducing cancer-related myocardial injury (Goto et al., 2024). BBR also activates the SIRT6-AMPK-FOXO3a signaling pathway, enhances PINK1-Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy to reduce oxidative stress, and preserves mitochondrial function. In a dose-dependent manner (Zhou et al., 2024), BBR inhibits CIH-induced myocardial remodeling, heart failure, and myocardial injury. Moreover, BBR upregulates miR-18a-3p to suppress miR-18a-3p-mediated Gsdmd activation, IL-1β secretion, and alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy (Yang et al., 2023). Additionally, BBR suppresses CVB3r replication by inhibiting the p38 MAPK and JNK pathways, thus reducing cardiac damage (Hashemzaei et al., 2017).
7.2.3 Arrhythmia
BBR increases cardiac output, reduces LVEDP and DBP, and prevents heart failure. It also prevents arrhythmias by decreasing the frequency of ventricular premature beats and tachycardia. Furthermore, BBR inhibits K+ and Ca2+ current activation, thus prolonging the effective refractory period of the atria and the action potential duration of atrial myocytes (Cai et al., 2021).
7.2.4 Myocarditis
BBR activates several signaling pathways, including AMPK, PI3K-AKT-eNOS, Notch1/Hes1-PTEN/AKT, AK2/STAT3, SIRT1, and Smad7, finely regulates the PINK1-Parkin pathways, and effectively reduces cell apoptosis and oxidative stress. It inhibits myocardial inflammation, promotes mitochondrial autophagy, and myocardial cell proliferation, significantly reducing I/R damage (Abudureyimu et al., 2020). Moreover, BBR inhibits the expression of caspase-3, upregulates VEGF, FGF2, and TSP-1 expression, and promotes ischemia-induced angiogenesis through the upregulation of miR-29b, reducing infarct area and improving heart function (Zhu et al., 2017). Furthermore, BBR suppresses Th17/Th1 cell differentiation, intracellular Ca2+ levels, caspase-9 and -3 activation, decreases CKt, CK-MB, and MDA levels, while increasing SOD, CAT, SIRT3 levels, upregulating SIRT1, and downregulating p66shc expression. This synergistically improves left ventricular function, mitigates cardiac toxicity, suppresses ROS production, apoptosis, mitochondrial damage, and cardiac fibrosis, comprehensively improving heart function (Hashemzaei et al., 2017).
7.2.5 Myocardial hypertrophy
BBR activates the AMPK signaling pathway to inhibit mitochondrial fission, upregulates PGC1α to stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis, restores autophagic flux, and interferes with the prevention of high glucose-induced myocardial hypertrophy. Additionally, BBR may regulate the mTOR pathway to suppress the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38, increase autophagy, alleviate ER stress, and activate the Pak1 pathway to inhibit Fbxo32 upregulation, lower myocardial cell Ca2+ concentration, reduce left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, upregulate PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy, and thus inhibit myocardial cell apoptosis and mitochondrial damage, improving heart failure and myocardial hypertrophy (Abudureyimu et al., 2020).
7.2.6 Thrombosis
BBR reduces thrombus formation by inhibiting CutC enzyme activity and decreasing TMAO production (Qu et al., 2024). It also improves thrombus formation by suppressing the expression of PKM2, thereby influencing the expression of tissue t-PA in the fibrinolytic system (Sun Z. et al., 2024).
7.2.7 Hypertension
BBR inhibits the biosynthesis of TMAO precursors in the gut microbiota by binding to and inhibiting the activity of CutC/D enzymes, downregulates the TMAO-endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway, and alleviates endothelial cell dysfunction, thereby improving vascular function. Simultaneously, BBR inhibits TRPV4 and MyD88-TLR4 signaling pathways, relaxes vascular smooth muscle, protects endothelial cells from damage, increases NO expression to promote vasodilation, and activates AMPK to inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress in endothelial cells, safeguarding vascular function. BBR also prevents NADPH oxidase expression and ROS production, increases NO bioavailability, forms stable free radicals with ROS-derived NADPH oxidase, and prevents NOX subunit assembly, thus improving hypertension (Cai et al., 2021; Qu et al., 2024; Yousefian et al., 2019; Wang Z. et al., 2024) Furthermore, BBR suppresses the ROS/Erk1/2/iNOS pathway to alleviate hypertension and sympathetic nervous excitation in double-kidney, one-kidney hypertension rat models (Tian H. et al., 2019).
7.3 Protective effects on the endocrine system
Endocrine disorders involve diseases that affect endocrine glands or tissues, leading to abnormal hormone secretion and triggering a range of symptoms. These disorders include diabetes, thyroid diseases, and pituitary tumors, often manifesting as metabolic disorders, growth abnormalities, and significantly impacting patient health and quality of life. This section discusses the activities of BBR in reducing blood sugar (Shrivastava et al., 2023), lowering blood pressure (Alruhaimi et al., 2024), and decreasing weight (Wang H. et al., 2024), among other effects (Figure 4).
7.3.1 Blood sugar reduction
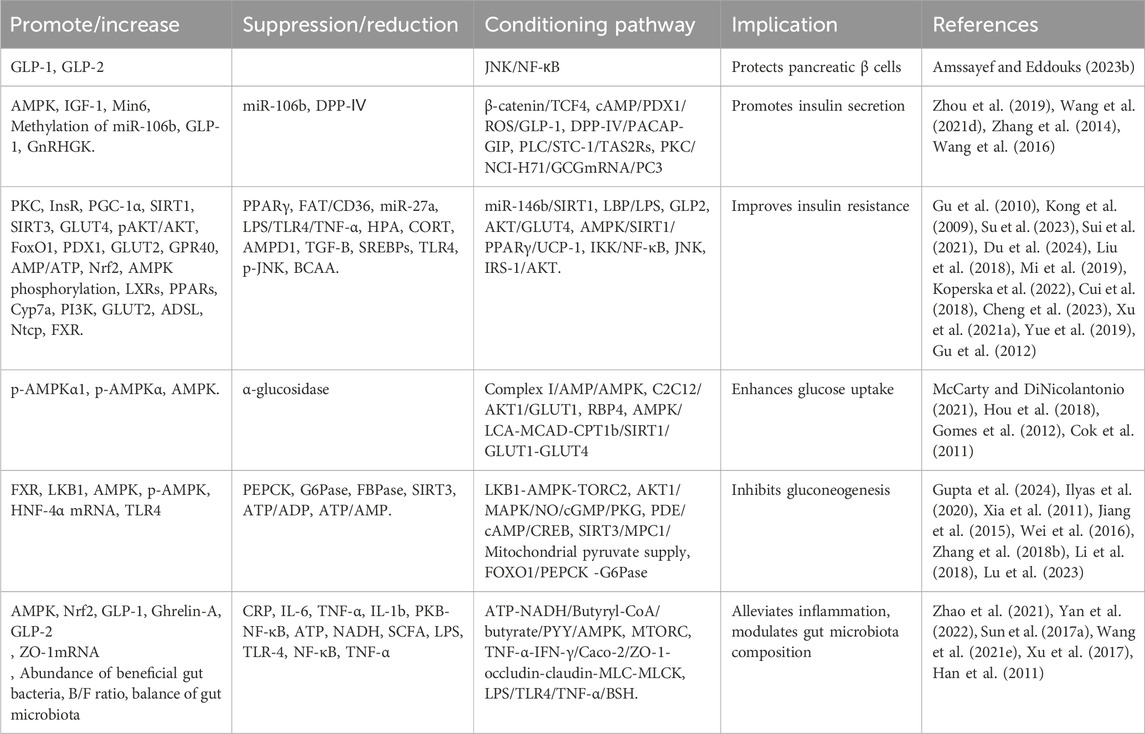
Numerous studies have confirmed the hypoglycemic activity of BBR and identified various mechanisms through which it lowers blood sugar. These include promoting insulin secretion, alleviating insulin resistance, inhibiting gluconeogenesis, enhancing glucose uptake, improving inflammation, and regulating gut microbiota disturbances. BBR also improves gut-brain communication, relieves intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction, and enhances intestinal permeability, thereby aiding in the amelioration of obesity and insulin resistance-related metabolic abnormalities (Table 5).
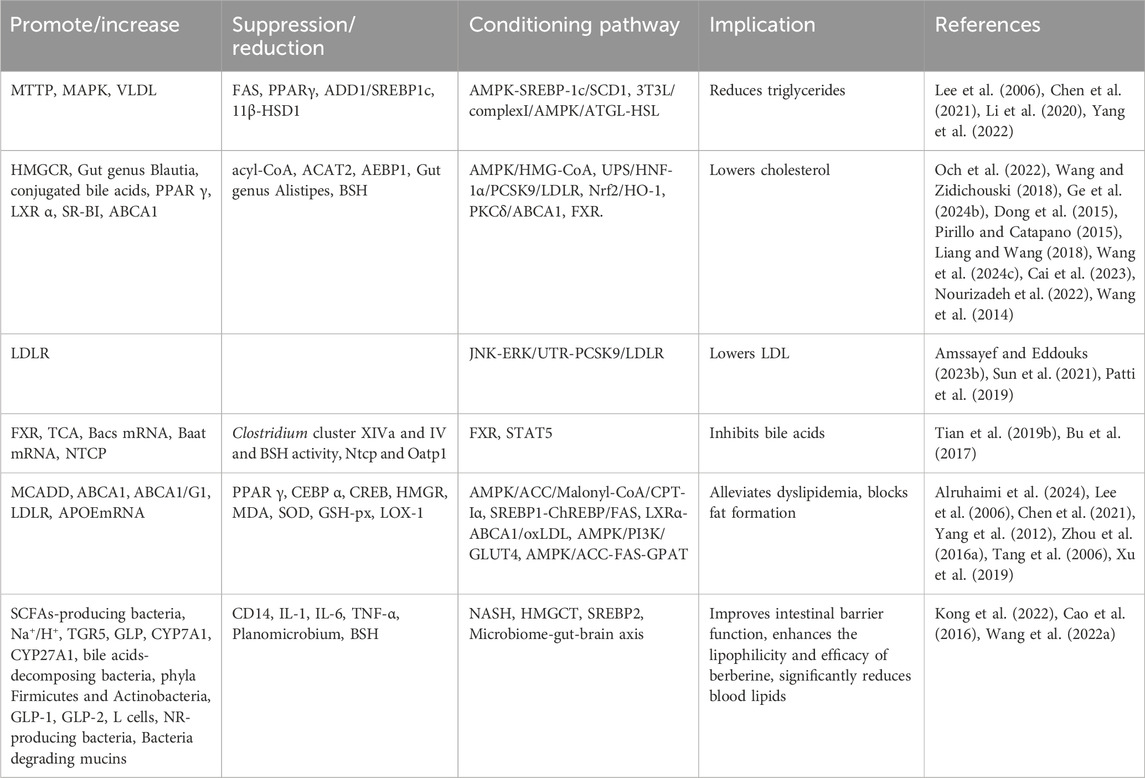
7.3.2 Blood lipid reduction
Elevated blood lipid levels are a common feature of lipid metabolism disorders such as obesity, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis. BBR can reduce blood lipid levels by inhibiting the progression of hyperlipidemia, reducing adipocyte differentiation, decreasing triglyceride (TG) accumulation, inhibiting the synthesis of total intracellular triglycerides; improving cholesterol esters (CE), inhibiting cholesterol synthesis, lowering cellular cholesterol levels; reducing circulating low-density lipoprotein and cholesterol levels, promoting bile acid uptake, and enhancing intestinal barrier function. These actions significantly lower blood lipid levels and alleviate dyslipidemia (Table 6).
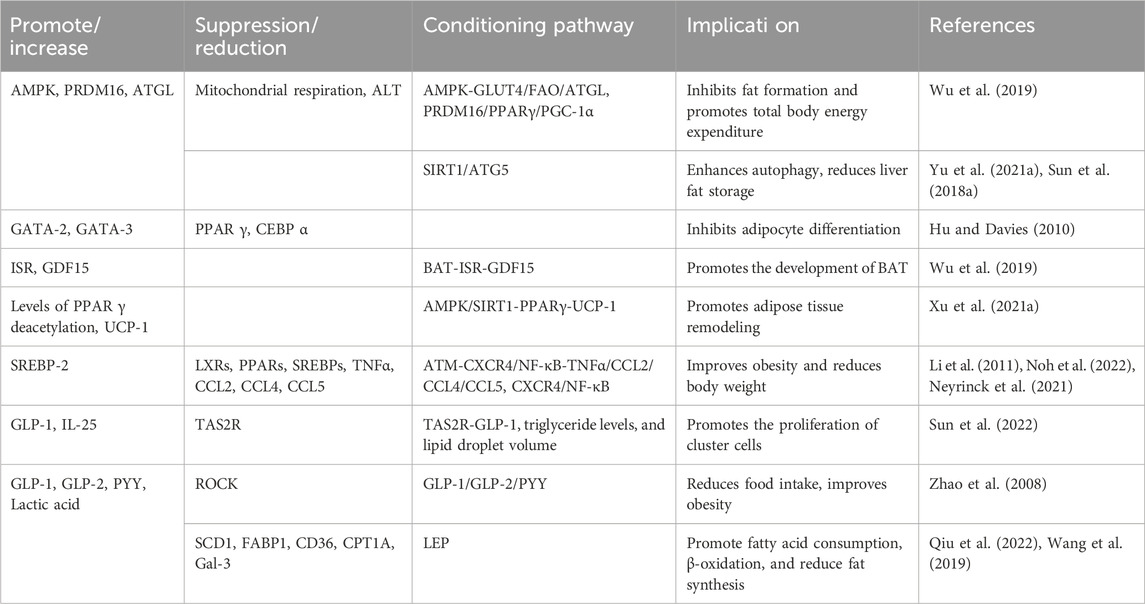
7.3.3 Weight reduction
In addition to its hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering effects, studies have found that BBR can effectively improve obesity and reduce body weight by reducing adipocyte formation, decreasing fat production, increasing fat breakdown, and promoting adipose tissue remodeling (Table 7).
7.3.4 Diabetic nephropathy
BBR lowers the expression and secretion of various inflammatory cytokines in the renal cortex and throughout the body, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and MCP-1. It also inhibits the expression of proteins related to the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, including TLR4, p65, and IKBα. These actions lead to reduced podocyte apoptosis, thickened glomerular basement membrane, enhanced kidney function, and ultimately, alleviated podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy models (Wu et al., 2024).
7.4 Protective effects on the digestive system
Diseases of the digestive system involve the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and gallbladder, with common ailments including gastritis, gastric ulcers, hepatitis, and cholecystitis. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These diseases affect nutrient absorption and digestion and may lead to severe complications such as bleeding and perforation (Zou et al., 2017). This paper briefly discusses the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and hepatitis with BBR (Figure 5).
7.4.1 Gastrointestinal diseases
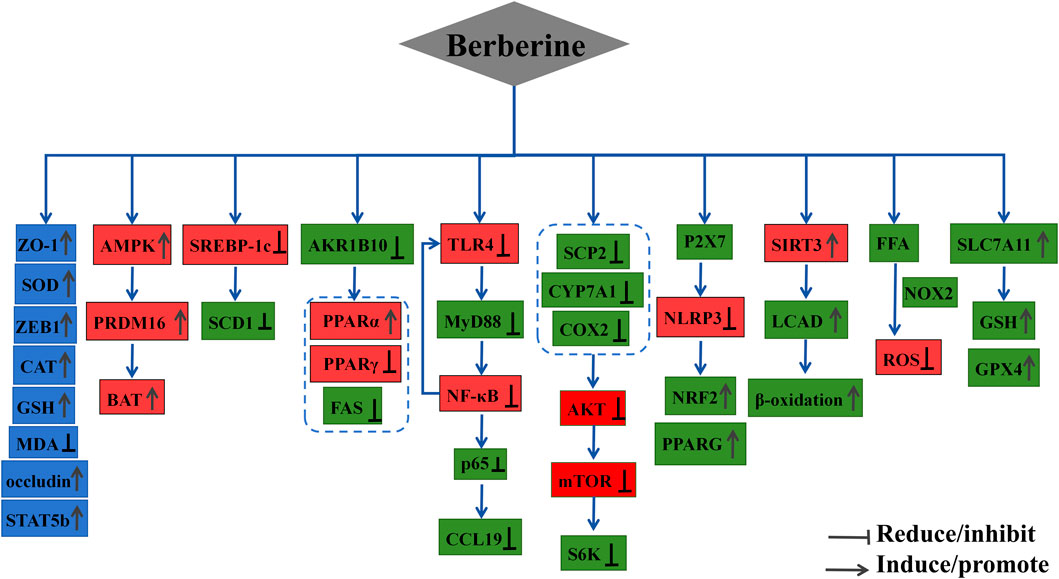
BBR enhances the expression of ZO-1, ZEB1, occludin, and STAT5b, improving intestinal barrier function (Han et al., 2024). Additionally, BBR treatment significantly increases SOD, CAT, and GSH levels, and reduces MDA levels, potentially protecting against oxidative stress in indomethacin-induced gastric tissue damage (Xu and Yang, 2024).
7.4.2 Liver diseases
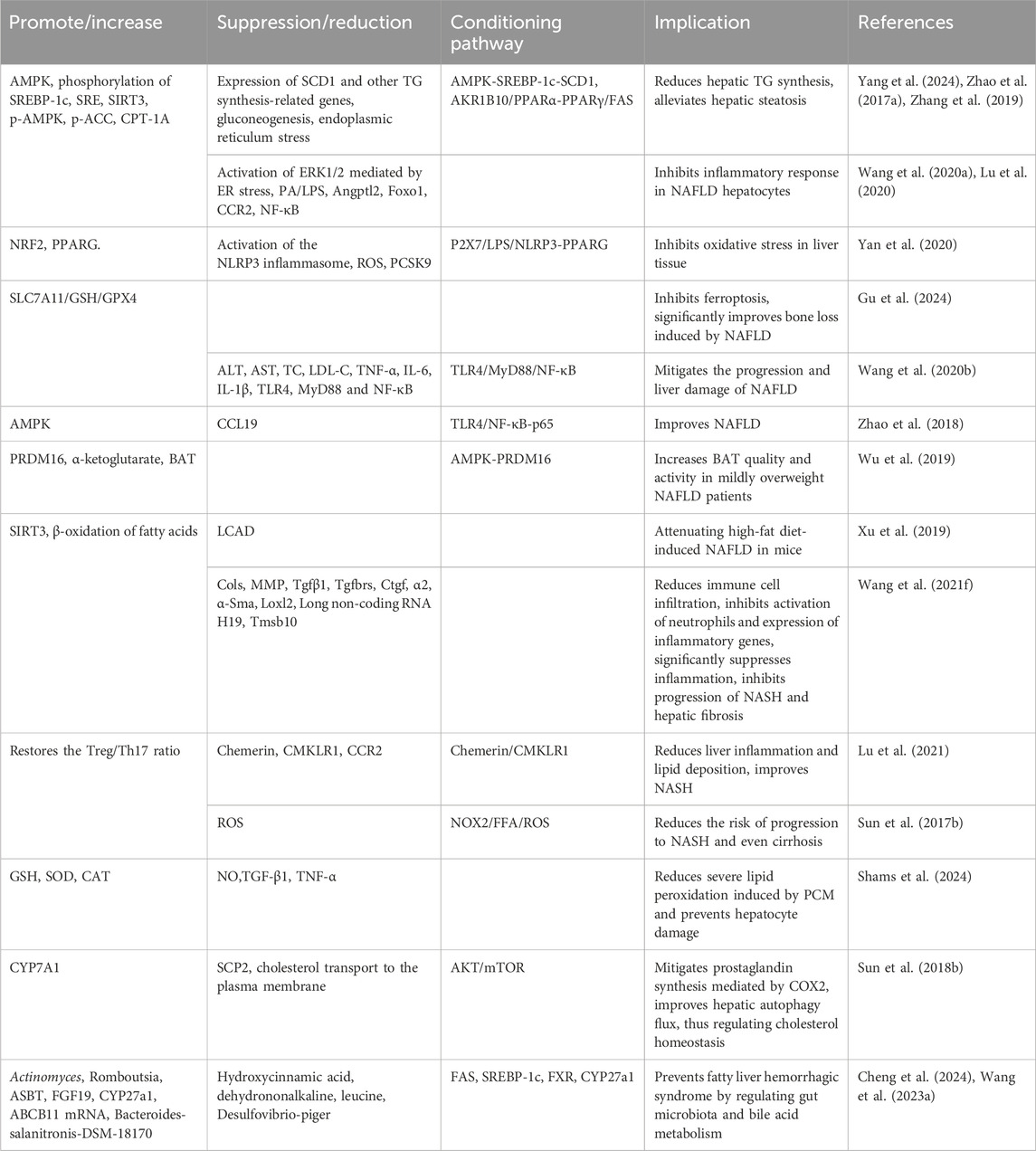
BBR reduces inflammation, oxidative reactions, and oxidative stress, enhances aerobic lipid metabolism and mitochondrial function, regulates gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism, alleviates hepatic steatosis, inhibits the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and liver fibrosis, and protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (Table 8).
7.5 Protective effects on the reproductive system
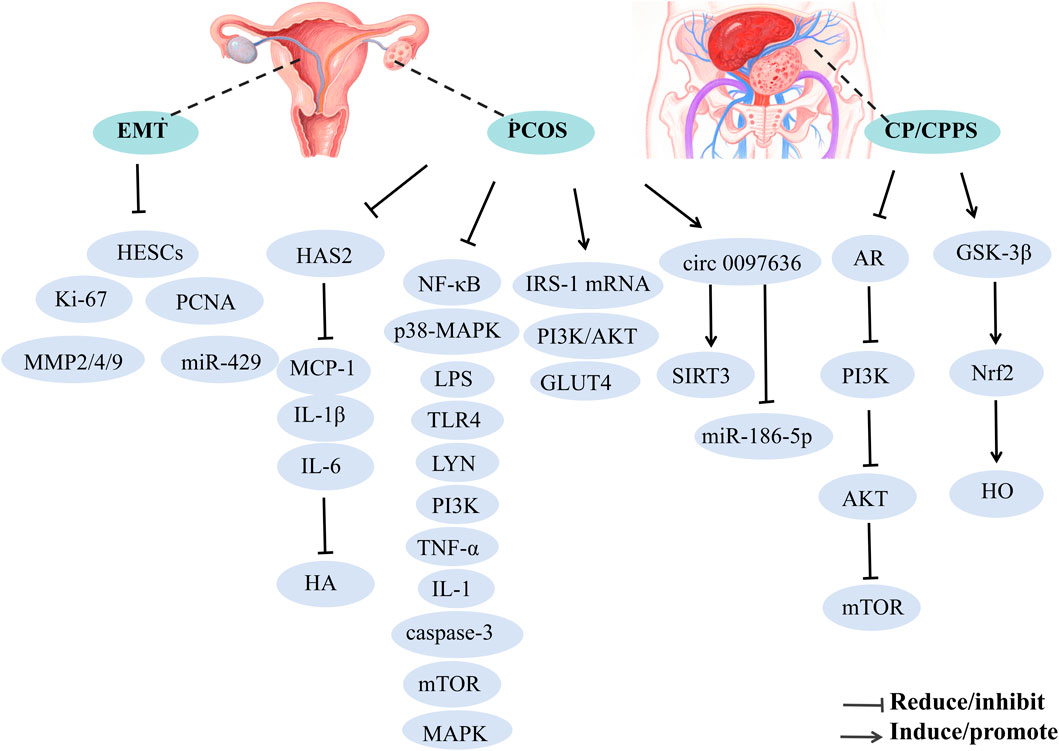
Reproductive system diseases affect the function and structure of reproductive organs, including conditions like male prostatitis, orchitis, female vaginitis, and uterine fibroids. These conditions can lead to pain, infertility, and menstrual disorders, severely affecting patient quality of life and reproductive health. This section briefly discusses the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) (Jin et al., 2024), endometriosis (EMT) (Gu and Zhou, 2021), and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) (Tian et al., 2024) with BBR (Figure 6).
7.5.1 Polycystic ovary syndrome
BBR has been shown to ameliorate symptoms associated with PCOS, such as oligo-ovulation, embryo damage, and hormonal dysregulation, thereby contributing to its therapeutic effects. The underlying mechanisms may include: (1) upregulation of LHCGR, CYP19A1 (Wang Z. et al., 2021), and circ 0097636/SIRT3 (Wang S. et al., 2024), alongside downregulation of HAS2/MCP-1-IL-1β-IL-6 (He et al., 2024), integrin αvβ3, LPAR3, miR-186-5p, which further enhance endometrial receptivity, reduce hyaluronic acid (HA) synthesis, restore ovarian morphology, and improve DHT-induced KGN cell damage; (2) BBR alleviates cell apoptosis via ROS/caspase-3-dependent pathways, while inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines and mitigate LPS-induced embryo damage during pre-implantation stages (Miao and Cui, 2022); (3) BBR modulates hormonal imbalance and insulin resistance in PCOS rats by downregulating p38-MAPK and NF-κB proteins in ovarian tissues and lowering serum LPS levels (Zhao F. et al., 2022); (4) BBR exerts beneficial effects on PCOS through activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway, including modification of serum hormone levels, restoration of ovarian morphological changes, improvement of insulin resistance, and enhancement of cell viability while inhibiting apoptosis (Yu J. et al., 2021); (5) BBR potentially alleviates PCOS pathology and insulin resistance (IR) by suppressing apoptosis and modulating the expression of TLR4, LYN, PI3K, AKT, NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, and caspase-3 (Shen HR. et al., 2021); (6) BBR enhances insulin sensitivity by increasing IRS-1 mRNA expression and decreasing mTOR mRNA levels, thereby improving therapeutic outcomes for PCOS (Kuang et al., 2020); (7) BBR may also mitigate PCOS by intervening in gut microbiota changes (Xin et al., 2024).
7.5.2 Endometriosis
BBR significantly inhibits the proliferation and colony formation of human endometrial stromal cells (HESCs) by reducing the expression of proliferative markers, including Ki-67 and PCNA, as well as matrix metalloproteinases (MMP2, MMP4, and MMP9). This effect is mediated through the downregulation of miR-429, suppressing HESCs' proliferation, invasion, and migration (Gu and Zhou, 2021).
7.5.3 Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome
BBH may alleviate symptoms of CP/CPPS by modulating gut microbiome signaling. Notably, butyrate-producing bacteria have been identified as key players, mediating the alleviation of CP/CPPS through the inhibition of the AR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and the activation of the GSK-3β-DUSP1-Nrf2-HO axis. Additionally, BBH mitigates prostatitis, suppresses lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress, reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines, and significantly lowers the prostate index in CP/CPPS rats (Tian et al., 2024).
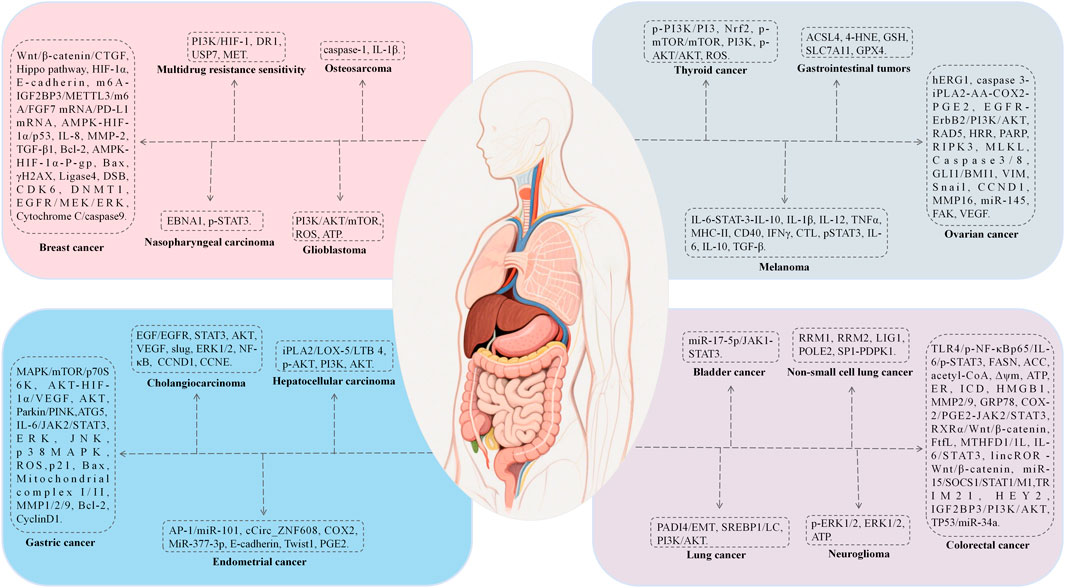
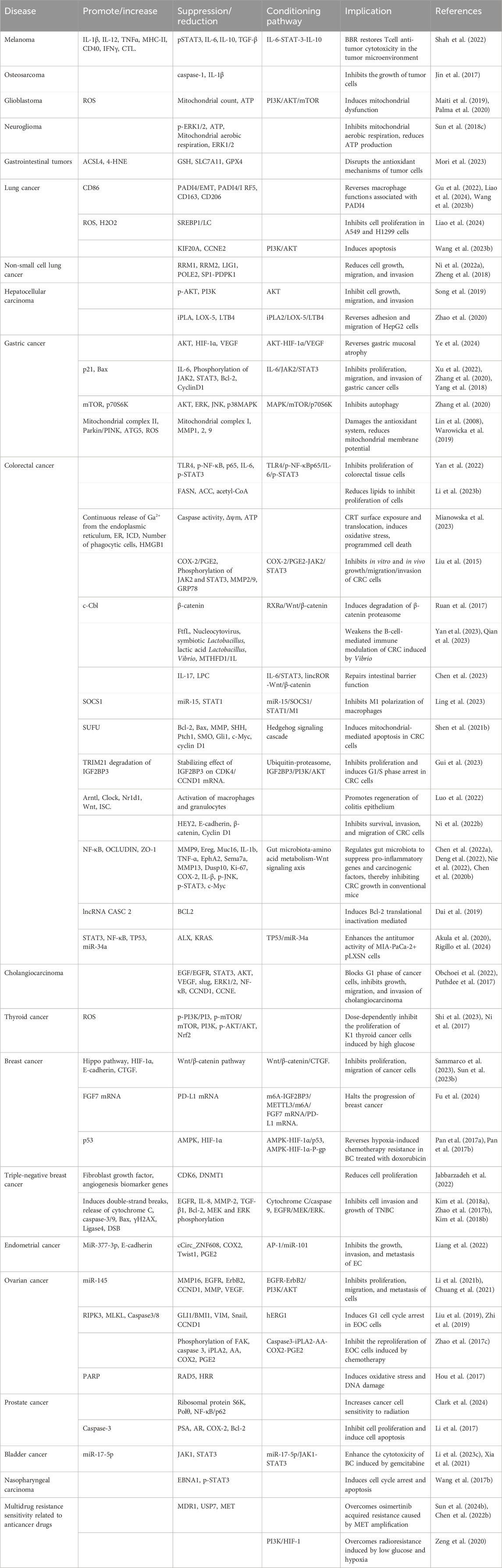
7.6 Antitumor activity
BBR exhibits extensive antitumor properties primarily through mechanisms that induce apoptosis and autophagy, inhibit tumor proliferation, metastasis, and invasion. The mechanisms include: (1) induction of apoptosis and autophagy via NRF2 degradation (Guan et al., 2020), activation of ATF6/GRP78 (La et al., 2017), and downregulation of the AKT/mTOR/GLUT1 signaling pathway (Guo et al., 2021), which reverses the Warburg effect; (2) inhibition of proliferation and metastasis by suppressing Topoisomerase I, DSBs, and MUS81-EME1 (Inoue et al., 2021), downregulating KRAS expression, and impeding KRAS-G4 replication, thereby delaying DNA synthesis (Wang KB. et al., 2022), disruption of claudin interactions and promotion of immune macrophage transformation (Cornelius et al., 2022; Shah et al., 2022); (3) modulation of molecular interactions by interacting with microRNAs to suppress cell proliferation and telomerase activity, and activating AMPK while inhibiting ACC to reduce fatty acid synthesis and vesicular secretion (Gu et al., 2020); (4) alleviation of oxidative stress by promoting Dicer expression, reducing DNA damage, and mitigating inflammation to suppress carcinogenesis (Wu et al., 2020); (5) reversal of exosome function by inhibiting the tumorigenic effects of colon cancer exosomes, reducing cell survival and metastasis in colorectal cancer (CRC) (Sun Q. et al., 2023).
We have summarized the pharmacological mechanisms of BBR against various tumors, including rhabdomyosarcoma, melanoma, glioma, lung cancer, breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and colorectal cancer (Figure 7; Table 9).
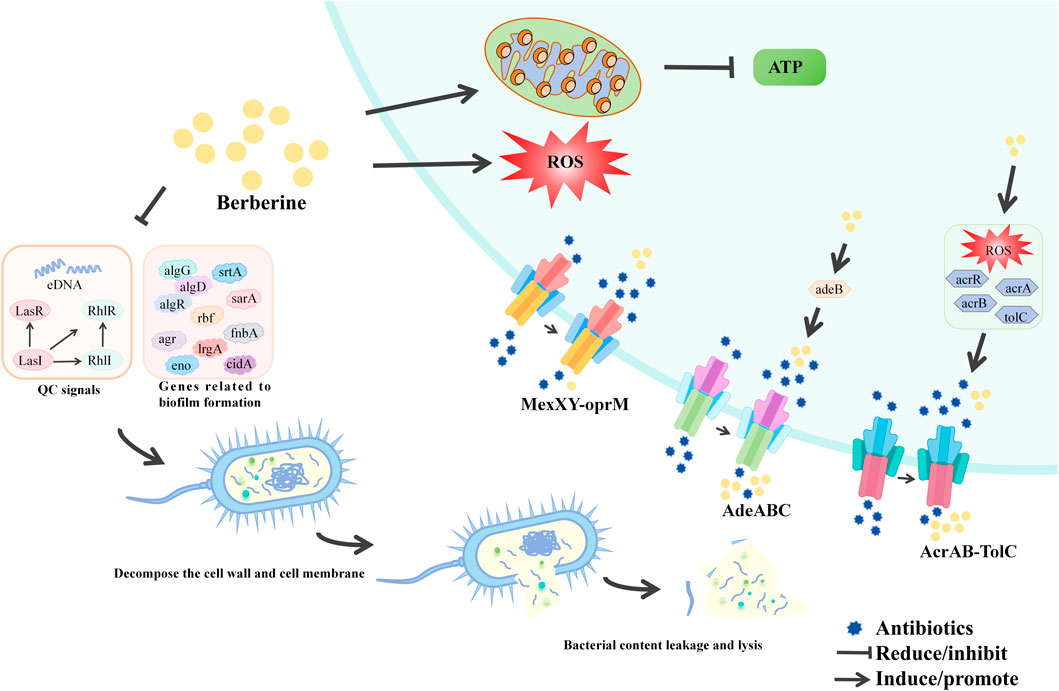
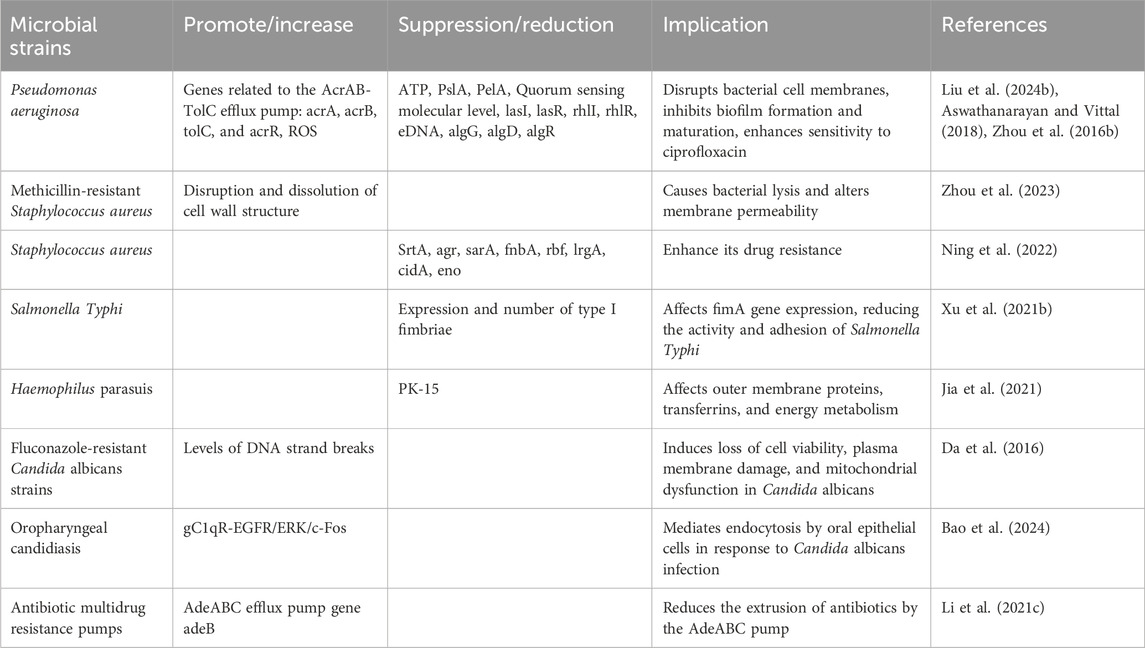
7.7 Antimicrobial activity
BBR exerts its antibiotic adjuvant effects through two main mechanisms. Firstly, it reduces the development of antibiotic resistance by inhibiting bacterial efflux pumps and biofilm formation. Secondly, BBR enhances antibiotic efficacy by interacting with host defense mechanisms and restoring the intestinal microbiota. The table below provides a brief overview of BBR’s antimicrobial activity according to bacterial species (Figure 8; Table 10).
7.8 Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity
BBR demonstrates multiple pharmacological actions, including the enhancement of antioxidant enzyme activity, direct scavenging of free radicals, and anti-inflammatory effects, all of which contribute to its potential therapeutic applications. The specific mechanisms underlying its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects may include: (1) the activation of endogenous antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, GPx), the stimulation of the AMPK, PI3K/AKT, and Nrf2 pathways, alleviation of oxidative stress, inhibition of NADPH oxidase, and reduction of ROS levels, thus preventing oxidative damage (Carrizzo et al., 2020); (2) direct scavenging of free radicals by donating electrons or hydrogen atoms, forming coordination bonds with metal ions via hydroxyl and methoxy groups, and effectively sequestering metals such as iron and copper, thereby amplifying BBR’s antioxidant activity (García-Muñoz et al., 2024); (3) activation of the antioxidant Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which alleviates cholesterol overload-induced oxidative stress and apoptotic cell death in mouse hepatocytes, suggesting that BBR may be a potential therapeutic agent for cholesterol-related cardiovascular diseases (Ye et al., 2022); (4) inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α), thereby reducing inflammation; suppression of NF-κB pathway activation, IKBα degradation, and MAPK pathway activation, while enhancing the STAT1 signaling pathway; BBR influences cellular physiological activities by directly interacting with the cell membrane through various mechanisms (Wang K. et al., 2024); (5) targeting IRGM1 to suppress the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (Meng et al., 2024), as well as inhibiting IL-17 secretion and expression through the IL-17 signaling pathway, exerting anti-inflammatory effects. This study also indicates that BBR reduces the expression of CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, and Th17+ lymphocytes, as well as the expression of inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17, contributing to its anti-inflammatory effect in the treatment of periodontitis (Li et al., 2024).
7.9 Other pharmacological mechanisms and disease treatments
7.9.1 Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
BBR induces autophagic cell death in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells through inactivation of the AKT/mTORC1 signaling pathway (Liu et al., 2020). Additionally, BBR significantly increases the expression of caspases (CASP3, CASP8, CASP9) and pro-apoptotic genes (BAX, BAK1, BIK), while downregulating anti-apoptotic genes (BCL2, BCL2L2, BNIP1, BNIP3), thereby inducing apoptosis in leukemia cells via intrinsic pathways (Okubo et al., 2017).
7.9.2 Acute graft-versus-host disease
BBR alleviates acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) by suppressing inflammation, remodeling the gut microbiota, and protecting the intestinal mucosal barrier. The specific mechanisms include: (1) reduction of GVHD-induced weight loss and GVHD index scores through the NF-κB pathway, alleviation of liver and intestinal damage, suppression of ALT and AST activity in the liver and intestines, and reduction of inflammation, oxidative stress, and NF-κB activation; (2) inhibition of inflammation and reduction of Th1 cell count, with downregulation of Th1 activation and alleviation of chronic GVHD (Wang M. et al., 2020); (3) remodeling the gut microbiota and protecting the intestinal mucosal barrier, significantly suppressing the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the expression of inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-1β, IL-18, IFN-γ, TNF-α, MCP-1, and IL-6) (Zhao Y. et al., 2022), thereby protecting against GVHD through inhibition of inflammasome activation by “Signal 1” and “Signal 2.”
7.9.3 Kawasaki Disease
BBR protects patients with Kawasaki Disease (KD) by mitigating inflammatory responses, inhibiting oxidative stress and ER stress, and reversing endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) proliferation. The mechanisms include: (1) accelerating the reduction of CRP, NLR, and PLR levels, thus alleviating inflammation (Fan et al., 2021); (2) reducing ROS production and the expression of ER stress-related proteins (e.g., ATF4, p-EIF2α, p-PERK, XBP1, p-IRE1, HSP90B1, HSPG2, DNAJC3, P4HB, and VCP), protecting KD-induced human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) from apoptosis and regulating the cell cycle, arresting cells in the G0/G1 phase; (3) BBR reverses impaired EPC proliferation during the acute phase of KD, by activating the PI3K/AKT/eNOS signaling pathway and increasing PI3K/AKT/eNOS mRNA levels, as well as protein levels of PI3K, p-AKT, eNOS, and p-eNOS (Xu et al., 2020; Xiao et al., 2014).
7.9.4 Ferroptosis
BBR inhibits ferroptosis by modulating Nrf2 transcription, activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway, and increasing the expression of GPX4, FPN1, and SLC7A11 (NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway). This reduces levels of iron, MDA, and ROS, stabilizing atherosclerotic plaques (Li X. et al., 2023). Moreover, BBR suppresses the interaction between Keap1 and Nrf2, partially preventing RSL3-induced ferroptosis through activation of Nrf2 signaling. Additionally, BBR alleviates neuronal ferroptosis in spinal cord injury rats via the AMPK-NRF2-HO-1 pathway, and regulates the Circ_0097636/MiR-186-5p/SIRT3 pathway to prevent dihydrotestosterone-induced granulosa cell damage and ferroptosis (Song et al., 2023).
8 Critical assessment
The research on BBR has advanced from the stage of “activity discovery” to the “deep waters” of clinical translation. However, its clinical transformative value is constrained by systemic methodological flaws, despite its biological activity being investigated across multiple systemic diseases.
The current clinical translation of BBR faces multi-dimensional and systematic limitations. At the model level, existing animal models are mostly simplified simulations of human diseases, making it difficult to reproduce the multi-dimensional characteristics of diseases, such as the superimposition of age-related pathologies and the dynamic interaction between the immune system, microbiota, and host. This leads to significant “model dependence” in mechanism conclusions, which are disconnected from clinical phenotypes. In terms of dose-effect, the oral bioavailability of BBR is extremely low (<1%), resulting in a contradiction between in vitro effectiveness and in vivo ineffectiveness. Moreover, high doses pose an oxidative stress risk, and the dose-effect relationship lacks a systematic assessment based on pharmacokinetics, which restricts the selection of clinical doses.
There are obvious hierarchical deficiencies in clinical evidence. Existing randomized controlled trials are mostly small-sample and short-term designs, making it difficult to support the long-term application value of BBR in chronic diseases. At the same time, there are issues such as racial bias and insufficient control of confounding factors, which weaken the universality of the conclusions. Additionally, there is insufficient research on the interaction between BBR and conventional drugs, affecting clinical guidance for combined medication. Mechanism research has long focused on classic pathways such as NF-κB and AMPK, lacking systematic integration across pathways and organs. The verification of causal relationships in the interaction between microbiota and host is also insufficient.
To overcome the aforementioned bottlenecks, the implementation of a “three-pronged breakthrough” strategy emphasizing multidisciplinary collaboration is essential. In terms of model innovation, efforts should focus on developing humanized organoids, immunocompetent tumor models, and multi-factor-induced composite models to reduce reliance on traditional models and better reflect human pathological features. Optimization of delivery systems should leverage nano-targeting technologies (Hsu et al., 2024), liposomes (Mianowska et al., 2023), solid dispersion techniques (Leimann et al., 2023), enteric-coated pellets, or prodrug strategies to enhance lesion-specific accumulation. These approaches should be integrated with pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling to more accurately define the effective dose range. In clinical research, there is a need to transition toward multicenter, large-sample, long-term follow-up randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that prioritize hard clinical endpoints. These trials should incorporate biomarker or microbiota profiling for patient stratification and enable a systematic evaluation of the safety profile of combination therapies.
9 Conclusion
This review’s emphasis on the “pharmacological effects” of BBR might have resulted in an insufficiently in depth exploration of its “hurdles in clinical applications”.
Specifically, problems like BBR’s low bioavailability and formulation constraints (for example, the formulation challenges arising from its poor solubility) were merely touched upon in the discussion. However, they were not systematically analyzed in light of current research efforts, such as the exploration of delivery systems including nanoformulations and prodrug modifications. As a consequence, it is arduous to comprehensively represent the bottlenecks in its translation from the laboratory to the clinical setting. Moreover, there is a dearth of comparative research on BBR and other natural products (such as berberine analogues), which precludes the clear demonstration of its distinctive advantages and limitations.
In conclusion, future research endeavors should prioritize overcoming the bottlenecks in clinical translation, such as optimizing the route of administration and conducting multi center RCTs. Additionally, efforts are needed to elucidate the core mechanisms of action, for example, by validating key targets through gene knockout or knock in techniques. Furthermore, it is essential to intensify research on long term safety and the applicability in special populations. These measures are crucial for facilitating BBR’s transition from a “focal point in basic research” to a “clinically efficacious drug.”
Author contributions
K-QF: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. FS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. Y-HZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. TC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. NS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. YZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. TY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. FT: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. WX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. ZY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Sichuan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2025ZNSFSC0684); the Medical Quality (Evidence-Based) Management study Project of the National Institute of Hospital Administration, National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (YLZLXZ24G039); Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Joint Project of Local Universities (202001BA070001-041), Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine study Projects (2023MS057; 2023MS207), Sichuan Provincial Hospital Association Young Pharmacist study Fund Project (22009; YP2202419), Key Project of Yunnan Key Laboratory of Pharmacology for Natural Products Open Fund (YKLPNP-K2302; YKLPNP-K2504), Key Project of Scientific Popularization study by the Chinese Pharmaceutica Association (CMEI2024KPYJ (JZYY)00427), Panzhihua Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology Project (2024ZD-S-28), Panzhihua Central Hospital Internal study Topic (202311).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the institutions involved in the design, writing, and funding of the research related to this article, as well as the people who made valuable comments on this article, and their contributions were crucial to the completion of this review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abudureyimu, M., Yu, W., Cao, R. Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, H., and Zheng, H. (2020). Berberine promotes cardiac function by upregulating PINK1/Parkin-Mediated mitophagy in heart failure. Front. Physiol. 11, 565751. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.565751
Adnan, M., Rasul, A., Hussain, G., Shah, M. A., Sarfraz, I., Nageen, B., et al. (2021). Physcion and physcion 8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside: natural anthraquinones with potential anticancer activities. Curr. Drug Targets 22 (5), 488–504. doi:10.2174/1389450121999201013154542
Akula, S. M., Ruvolo, P. P., and McCubrey, J. A. (2020). TP53/miR-34a-associated signaling targets SERPINE1 expression in human pancreatic cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 12 (3), 2777–2797. doi:10.18632/aging.102776
Alruhaimi, R. S., Siddiq, A. M., Ahmeda, A. F., Bin-Ammar, A., Kamel, E. M., Hassanein, E. H. M., et al. (2024). Berberine attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress and modulates lymphocyte E-NTPDase in acute hyperlipidemia. Drug Dev. Res. 85 (2), e22166. doi:10.1002/ddr.22166
Amssayef, A., and Eddouks, M. (2023a). Alkaloids as vasodilator agents: a review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 29 (24), 1886–1895. doi:10.2174/1381612829666230809094313
Amssayef, A., and Eddouks, M. (2023b). Alkaloids as promising agents for the management of insulin resistance: a review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 29 (39), 3123–3136. doi:10.2174/0113816128270340231121043038
An, N., Zhang, G., Li, Y., Yuan, C., Yang, F., Zhang, L., et al. (2022). Promising antioxidative effect of berberine in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 865353. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.865353
Aswathanarayan, J. B., and Vittal, R. R. (2018). Inhibition of biofilm formation and quorum sensing mediated phenotypes by berberine in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium. RSC Adv. 8 (63), 36133–36141. doi:10.1039/c8ra06413j
Bao, M., Bu, Q., Pan, M., Xu, R., Chen, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2024). Coptidis rhizoma extract alleviates oropharyngeal candidiasis by gC1qR-EGFR/ERK/c-fos axis-induced endocytosis of oral epithelial cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 331, 118305. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118305
Bei, L., Gu, X., Juan, S., and Bi, L. (2020). Purification of Alkaloids from Coptis chinensis Using Sodium Polyacrylate Resin. Ion Exchange and Adsorption. 36 (05), 415–422. doi:10.16026/j.cnki.iea.2020050415
Bodeker, G. C. (1996). At least 80% of the population of Most developing countries relies on traditional medicine as its primary source of health care. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2 (3), 323–326. doi:10.1089/acm.1996.2.323
Bu, P., Le, Y., Zhang, Y., and Cheng, X. (2017). Berberine-induced inactivation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 signaling promotes male-specific expression of a bile acid uptake transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 292 (11), 4602–4613. doi:10.1074/jbc.M116.757567
Cai, Y., Xin, Q., Lu, J., Miao, Y., Lin, Q., Cong, W., et al. (2021). A new therapeutic candidate for cardiovascular diseases: berberine. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 631100. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.631100
Cai, Y., Yang, Q., Yu, Y., Yang, F., Bai, R., and Fan, X. (2023). Efficacy and underlying mechanisms of berberine against lipid metabolic diseases: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1283784. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1283784
Cao, Y., Pan, Q., Cai, W., Shen, F., Chen, G. Y., Xu, L. M., et al. (2016). Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine improves steatohepatitis in high-fat diet-fed BALB/C mice. Arch. Iran. Med. 19 (3), 197–203. doi:10.0161903/AIM.008
Carrizzo, A., Izzo, C., Forte, M., Sommella, E., Di Pietro, P., Venturini, E., et al. (2020). A novel promising frontier for human health: the beneficial effects of nutraceuticals in cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (22), 8706. doi:10.3390/ijms21228706
Chen, H., Ye, C., Cai, B., Zhang, F., Wang, X., Zhang, J., et al. (2022a). Berberine inhibits intestinal carcinogenesis by suppressing intestinal pro-inflammatory genes and oncogenic factors through modulating gut microbiota. BMC Cancer 22 (1), 566. doi:10.1186/s12885-022-09635-9
Chen, H., Ye, C., Wu, C., Zhang, J., Xu, L., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Berberine inhibits high fat diet-associated colorectal cancer through modulation of the gut microbiota-mediated lysophosphatidylcholine. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 19 (7), 2097–2113. doi:10.7150/ijbs.81824
Chen, H., Zhang, F., Zhang, J., Zhang, X., Guo, Y., and Yao, Q. (2020b). A holistic view of berberine inhibiting intestinal carcinogenesis in conventional mice based on microbiome-metabolomics analysis. Front. Immunol. 11, 588079. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.588079
Chen, P., Li, Y., and Xiao, L. (2021). Berberine ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by decreasing the liver lipid content via reversing the abnormal expression of MTTP and LDLR. Exp. Ther. Med. 22 (4), 1109. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10543
Chen, Y., Chen, Y., Liang, Y., Chen, H., Ji, X., and Huang, M. (2020a). Berberine mitigates cognitive decline in an alzheimer's disease mouse model by targeting both tau hyperphosphorylation and autophagic clearance. Biomed. Pharmacother. 121, 109670. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109670
Chen, Z. (2022). Phylogeny and taxonomic revision of the genus coptis [D]. Jiangxi Agricultural University. doi:10.27177/d.cnki.gjxnu.2022.000441
Chen, Z., Vallega, K. A., Chen, H., Zhou, J., Ramalingam, S. S., and Sun, S. Y. (2022b). The natural product berberine synergizes with osimertinib preferentially against MET-Amplified osimertinib-resistant lung cancer via direct MET inhibition. Pharmacol. Res. 175, 105998. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105998
Cheng, J., Ma, X., Yan, G., Yu, Q., Huang, Z., Lin, G., et al. (2023). High fructose-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance could be alleviated by berberine via AMPD1 and ADSL. Food Chem. Toxicol. 175, 113731. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2023.113731
Cheng, X., Hu, Y., Kuang, J., Guo, X., Cao, H., Wu, H., et al. (2024). Berberine alleviates high-energy and low-protein diet-induced fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome in laying hens: insights from microbiome and metabolomics. Poult. Sci. 103 (8), 103968. doi:10.1016/j.psj.2024.103968
Chuang, T. C., Wu, K., Lin, Y. Y., Kuo, H. P., Kao, M. C., Wang, V., et al. (2021). Dual down-regulation of EGFR and ErbB2 by berberine contributes to suppression of migration and invasion of human ovarian cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 36 (5), 737–747. doi:10.1002/tox.23076
Clark, A., Villarreal, M. R., Huang, S. B., Jayamohan, S., Rivas, P., Hussain, S. S., et al. (2024). Targeting S6K/NFκB/SQSTM1/Polθ signaling to suppress radiation resistance in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 597, 217063. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217063
Cok, A., Plaisier, C., Salie, M. J., Oram, D. S., Chenge, J., and Louters, L. L. (2011). Berberine acutely activates the glucose transport activity of GLUT1. Biochimie 93 (7), 1187–1192. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2011.04.013
Cornelius, V., Droessler, L., Boehm, E., and Amasheh, S. (2022). Concerted action of berberine in the porcine intestinal epithelial model IPEC-J2: effects on tight junctions and apoptosis. Physiol. Rep. 10 (7), e15237. doi:10.14814/phy2.15237
Cui, H., Hu, Y., Li, J., and Yuan, K. (2018). Hypoglycemic mechanism of the berberine organic acid salt under the synergistic effect of intestinal flora and oxidative stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018 (1), 8930374. doi:10.1155/2018/8930374
Da, S. A., de Andrade, N. J., Da, S. C., Campos, R. d. S., Costa Silva, R. A., Freitas, D. D., et al. (2016). Berberine antifungal activity in fluconazole-resistant pathogenic yeasts: action mechanism evaluated by flow cytometry and biofilm growth inhibition in candida spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60 (6), 3551–3557. doi:10.1128/AAC.01846-15
Dai, L., Zhu, L., Ma, S., Liu, J., Zhang, M., Li, J., et al. (2022). Berberine alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome induced endothelial junction dysfunction through Ca(2+) signalling in inflammatory vascular injury. Phytomedicine 101, 154131. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154131
Dai, W., Mu, L., Cui, Y., Li, Y., Chen, P., Xie, H., et al. (2019). Long non-coding RNA CASC2 enhances berberine-induced cytotoxicity in colorectal cancer cells by silencing BCL2. Mol. Med. Rep. 20 (2), 995–1006. doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.10326
Das, G., Kameswaran, S., Ramesh, B., Bangeppagari, M., Nath, R., Das Talukdar, A., et al. (2024). Anti-aging effect of traditional plant-based food: an overview. Foods 13 (23), 3785. doi:10.3390/foods13233785
Deng, J., Zhao, L., Yuan, X., Li, Y., Shi, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). Pre-administration of berberine exerts chemopreventive effects in AOM/DSS-Induced colitis-associated carcinogenesis mice via modulating inflammation and intestinal microbiota. Nutrients 14 (4), 726. doi:10.3390/nu14040726
Dong, B., Li, H., Singh, A. B., Cao, A., and Liu, J. (2015). Inhibition of PCSK9 transcription by berberine involves down-regulation of hepatic HNF1α protein expression through the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 290 (7), 4047–4058. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.597229
Du, J., Zhu, Y., Yang, X., Geng, X., Xu, Y., Zhang, M., et al. (2024). Berberine attenuates obesity-induced insulin resistance by inhibitingmiR -27a secretion. Diabet. Med. 41 (7), e15319. doi:10.1111/dme.15319
Duan, H., Hu, J., Deng, Y., Zou, J., Ding, W., Peng, Q., et al. (2023). Berberine mediates the production of butyrate to ameliorate cerebral ischemia via the gut microbiota in mice. Nutrients 16 (1), 9. doi:10.3390/nu16010009
Erjin, Z., Fei, B., Chun, M., Yang, L., Hong, Z., et al. (2013). Study on Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Berberine from Coptis chinensis. Shandong Chemical Industry. Shandong Chem. Ind. 42 (08), 11–14. doi:10.19319/j.cnki.issn.1008-021x.2013.08.006
Fan, X., Guo, X., Li, Y., and Xu, M. (2021). Utilizing network pharmacology to explore the possible mechanism of coptidis rhizoma in Kawasaki disease. Front. Pediatr. 9, 708553. doi:10.3389/fped.2021.708553
Fang, Z., Tang, Y., Ying, J., Tang, C., and Wang, Q. (2020). Traditional Chinese medicine for anti-alzheimer's disease: berberine and evodiamine from Evodia rutaecarpa. Chin. Med. 15, 82. doi:10.1186/s13020-020-00359-1
Feng, X., Sureda, A., Jafari, S., Memariani, Z., Tewari, D., Annunziata, G., et al. (2019). Berberine in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Theranostics 9 (7), 1923–1951. doi:10.7150/thno.30787
Fu, W., Liu, L., and Tong, S. (2024). Berberine inhibits the progression of breast cancer by regulating METTL3-mediated m6A modification of FGF7 mRNA. Thorac. Cancer 15 (17), 1357–1368. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.15321
Gao, W. H., Lin, S. Y., Jia, L., Guo, X. K., Chen, X. G., and Hu, Z. D. (2005). Analysis of protoberberine alkaloids in several herbal drugs and related medicinal preparations by non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 28 (1), 92–97. doi:10.1002/jssc.200401863
García-Muñoz, A. M., Victoria-Montesinos, D., Ballester, P., Cerdá, B., and Zafrilla, P. (2024). A descriptive review of the antioxidant effects and mechanisms of action of berberine and silymarin. Molecules 29 (19), 4576. doi:10.3390/molecules29194576
Ge, Q., Yan, Y., Luo, Y., Teng, T., Cao, C., Zhao, D., et al. (2024b). Dietary supplements: clinical cholesterol-lowering efficacy and potential mechanisms of action. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 75 (4), 349–368. doi:10.1080/09637486.2024.2342301
Ge, W., Gao, Y., He, L., Jiang, Z., Zeng, Y., Yu, Y., et al. (2024a). Developing Chinese herbal-based functional biomaterials for tissue engineering. Heliyon 10 (6), e27451. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27451
Gogebakan, A., Talas, Z. S., Ozdemir, I., and Sahna, E. (2012). Role of propolis on tyrosine hydroxylase activity and blood pressure in nitric oxide synthase-inhibited hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 34 (6), 424–428. doi:10.3109/10641963.2012.665542
Gomes, A. P., Duarte, F. V., Nunes, P., Hubbard, B. P., Teodoro, J. S., Varela, A. T., et al. (2012). Berberine protects against high fat diet-induced dysfunction in muscle mitochondria by inducing SIRT1-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 1822 (2), 185–195. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.10.008
Goto, K., Fujiwara-Tani, R., Nukaga, S., Miyagawa, Y., Kawahara, I., Nishida, R., et al. (2024). Berberine improves cancer-derived myocardial impairment in experimental cachexia models by targeting high-mobility group Box-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (9), 4735. doi:10.3390/ijms25094735
Gu, J., Gao, F., and Zhao, T. Y. (2012). A preliminary investigation of the mechanisms underlying the effect of berberine in preventing high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in rats. J. physiology Pharmacol. official J. Pol. Physiological Soc. 63 (5), 505–513.
Gu, S., Song, X., Xie, R., Ouyang, C., Xie, L., Li, Q., et al. (2020). Berberine inhibits cancer cells growth by suppressing fatty acid synthesis and biogenesis of extracellular vesicles. Life Sci. 257, 118122. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118122
Gu, S., Wang, J., Yu, S., Zhang, S., Gao, T., Yan, D., et al. (2024). Berberine ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-induced bone loss by inhibiting ferroptosis. Bone 185, 117114. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2024.117114
Gu, W., Zhang, M., Gao, F., Niu, Y., Sun, L., Xia, H., et al. (2022). Berberine regulates PADI4-related macrophage function to prevent lung cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 110, 108965. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108965
Gu, Y., Zhang, Y., Shi, X., Li, X., Hong, J., Chen, J., et al. (2010). Effect of traditional Chinese medicine berberine on type 2 diabetes based on comprehensive metabonomics. Talanta 81 (3), 766–772. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2010.01.015
Gu, Y., and Zhou, Z. (2021). Berberine inhibits the proliferation, invasion and migration of endometrial stromal cells by downregulating miR-429. Mol. Med. Rep. 23 (6), 416. doi:10.3892/mmr.2021.12055
Guan, X., Zheng, X., Vong, C. T., Zhao, J., Xiao, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2020). Combined effects of berberine and evodiamine on colorectal cancer cells and cardiomyocytes in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 875, 173031. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173031
Gui, Z., Li, J., Li, J., Li, X., Chen, L., Ma, Z., et al. (2023). Berberine promotes IGF2BP3 ubiquitination by TRIM21 to induce G1/S phase arrest in colorectal cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 374, 110408. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110408
Si, G., Wei, W., Kun, Y., Zhi, S., et al. (2019). Biological Functions of Berberine and Its Application in Animal Production. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition. 31 (10), 4464–4472. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.5461.S.20190702.1136.058
Guo, X. H., Jiang, S. S., Zhang, L. L., Hu, J., Edelbek, D., Feng, Y. Q., et al. (2021). Berberine exerts its antineoplastic effects by reversing the warburg effect via downregulation of the Akt/mTOR/GLUT1 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 46 (6), 253. doi:10.3892/or.2021.8204
Gupta, M., Rumman, M., Singh, B., Mahdi, A. A., and Pandey, S. (2024). Berberine ameliorates glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia: an in vitro and in vivo study. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives Pharmacol. 397 (3), 1647–1658. doi:10.1007/s00210-023-02703-2
Han, J., Lin, H., and Huang, W. (2011). Modulating gut microbiota as an anti-diabetic mechanism of berberine. Med. Sci. Monit. 17 (7), A164–A167. doi:10.12659/msm.881842
Han, M., Guo, Y., Tang, S., Li, D., Wan, J., Zhu, C., et al. (2024). Effects of berberine hydrochloride on antioxidant response and gut microflora in the Charybdis japonica infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. BMC Microbiol. 24 (1), 287. doi:10.1186/s12866-024-03420-3
Hashemzaei, M., Entezari, H. R., Rezaee, R., Roohbakhsh, A., and Karimi, G. (2017). Regulation of autophagy by some natural products as a potential therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular disorders. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 802, 44–51. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.02.038
He, S., Li, H., Zhang, Q., Zhao, W., Li, W., Dai, C., et al. (2024). Berberine alleviates inflammation in polycystic ovary syndrome by inhibiting hyaluronan synthase 2 expression. Phytomedicine 128, 155456. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155456
Heng, Z., Jun, C., Xiu, G., Xiao, Z., Xian, L., Xiao, W., et al. (2008). Rapid Extraction of Alkaloids from Coptis chinensis by Accelerated Solvent Extraction. Analytical Laboratory 27 (11), 5–9.
Hou, D., Xu, G., Zhang, C., Li, B., Qin, J., Hao, X., et al. (2017). Berberine induces oxidative DNA damage and impairs homologous recombination repair in ovarian cancer cells to confer increased sensitivity to PARP inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 8 (10), e3070. doi:10.1038/cddis.2017.471
Hou, W. L., Yin, J., Alimujiang, M., Yu, X. Y., Ai, L. G., Bao, Y. Q., et al. (2018). Inhibition of mitochondrial complex I improves glucose metabolism independently ofAMPK activation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 22 (2), 1316–1328. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13432
Hsu, C. Y., Pallathadka, H., Gupta, J., Ma, H., Al-Shukri, H. H. K., Kareem, A. K., et al. (2024). Berberine and berberine nanoformulations in cancer therapy: focusing on lung cancer. Phytother. Res. 38 (8), 4336–4350. doi:10.1002/ptr.8255
Hu, Y., and Davies, G. E. (2010). Berberine inhibits adipogenesis in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice. Fitoterapia 81 (5), 358–366. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2009.10.010
Huang, J., Huang, N., Mao, Q., Shi, J., and Qiu, Y. (2023). Natural bioactive compounds in alzheimer's disease: from the perspective of type 3 diabetes mellitus. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15, 1130253. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2023.1130253
Hui, X., and Mao, C. (2011). Research progress on in vivo processes of orally administered protoberberine-type alkaloids. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 17 (14), 302–305. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2011.14.082
Ilyas, Z., Perna, S., Al-thawadi, S., Alalwan, T. A., Riva, A., Petrangolini, G., et al. (2020). The effect of berberine on weight loss in order to prevent obesity: a systematic review. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 127, 110137. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110137
Inoue, N., Terabayashi, T., Takiguchi-Kawashima, Y., Fujinami, D., Matsuoka, S., Kawano, M., et al. (2021). The benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, berberine and coptisine, act against camptothecin-resistant topoisomerase I mutants. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 7718. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-87344-2
Jabbarzadeh, K. P., Luo, S., Chen, Y., Jomhori, M., Imani, S., Xiang, S., et al. (2022). Pharmacotranscriptomic profiling of resistant triple-negative breast cancer cells treated with lapatinib and berberine shows upregulation of PI3K/Akt signaling under cytotoxic stress. Gene 816, 146171. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2021.146171
Ji, M. (2006). Extraction, separation, and content determination of berberine hydrochloride from Coptis chinensis. Int. Med. and Health Guid. News (24), 75–77.
Jia, Y., Hao, C., Yang, Q., Zhang, W., Li, G., Liu, S., et al. (2021). Inhibition of Haemophilus parasuis by berberine and proteomic studies of its mechanism of action. Res. Vet. Sci. 138, 62–68. doi:10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.06.004
Jiang, S., Dong, H., Li, J. B., Xu, L. J., Zou, X., Wang, K. F., et al. (2015). Berberine inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesisvia the LKB1-AMPK-TORC2 signaling pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. World J. Gastroenterology 21 (25), 7777–7785. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7777
Jie, L., Yue, L., Hui, L., Chang, Z., et al. (2024). Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction for coptis alkaloids. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 46 (6), 1818–1823.
Jin, H., Jin, X., Cao, B., and Wang, W. (2017). Berberine affects osteosarcoma via downregulating the caspase-1/IL-1β signaling axis. Oncol. Rep. 37 (2), 729–736. doi:10.3892/or.2016.5327
Jin, R., Chen, A., Ye, Y., Ren, Y., Lu, J., Xuan, F., et al. (2024). Effect of berberine combined with metformin on autophagy in polycystic ovary syndrome by regulating AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 91 (8), e23768. doi:10.1002/mrd.23768
Kamaruddin, N. A., Hakim, A. M., Tan, J. J., Lim, V., Fong, L. Y., Abd Ghafar, S. A., et al. (2022). Vascular protective effect and its possible mechanism of action on selected active phytocompounds: a review. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 3311228. doi:10.1155/2022/3311228
Kim, J. K., Kim, K. H., Shin, Y. C., Jang, B. H., and Ko, S. G. (2020). Utilization of traditional medicine in primary health care in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Health Policy Plan. 35 (8), 1070–1083. doi:10.1093/heapol/czaa022
Kim, S., Lee, J., You, D., Jeong, Y., Jeon, M., Yu, J., et al. (2018b). Berberine suppresses cell motility through downregulation of TGF-β1 in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 45 (2), 795–807. doi:10.1159/000487171
Kim, S., You, D., Jeong, Y., Yu, J., Kim, S. W., Nam, S. J., et al. (2018a). Berberine down-regulates IL-8 expression through inhibition of the EGFR/MEK/ERK pathway in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 50, 43–49. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.08.004
Kong, W., Zhang, H., Song, D., Xue, R., Zhao, W., Wei, J., et al. (2009). Berberine reduces insulin resistance through protein kinase C–dependent up-regulation of insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 58 (1), 109–119. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2008.08.013
Kong, Y., Li, L., Zhao, L., Yu, P., and Li, D. D. (2022). A patent review of berberine and its derivatives with various pharmacological activities (2016–2020). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 32 (2), 211–223. doi:10.1080/13543776.2021.1974001
Koperska, A., Wesołek, A., Moszak, M., and Szulińska, M. (2022). Berberine in non-alcoholic fatty liver Disease-A review. Nutrients 14 (17), 3459. doi:10.3390/nu14173459
Kuang, H., Duan, Y., Li, D., Xu, Y., Ai, W., Li, W., et al. (2020). The role of serum inflammatory cytokines and berberine in the insulin signaling pathway among women with polycystic ovary syndrome. PLoS One 15 (8), e0235404. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0235404
Kwon, I. H., Choi, H. S., Shin, K. S., Lee, B. K., Lee, C. K., Hwang, B. Y., et al. (2010). Effects of berberine on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells and a rat model of parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 486 (1), 29–33. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.038
La, X., Zhang, L., Li, Z., Yang, P., and Wang, Y. (2017). Berberine-induced autophagic cell death by elevating GRP78 levels in cancer cells. Oncotarget 8 (13), 20909–20924. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.14959
Lee, Y. S., Kim, W. S., Kim, K. H., Yoon, M. J., Cho, H. J., Shen, Y., et al. (2006). Berberine, a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant states. Diabetes 55 (8), 2256–2264. doi:10.2337/db06-0006
Leimann, F. V., de Souza, L. B., de Oliveira, B., Rossi, B. F., da Silva, P. S., Shiraishi, C. S. H., et al. (2023). Evaluation of berberine nanoparticles as a strategy to modulate acetylcholinesterase activity. Food Res. Int. 173 (Pt 1), 113295. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113295
Li, A., Liu, Q., Li, Q., Liu, B., Yang, Y., and Zhang, N. (2018). Berberine reduces pyruvate-driven hepatic glucose production by limiting mitochondrial import of pyruvate through mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1. EBioMedicine 34, 243–255. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.039
Li, D., Yu, P., Xiao, W., Wang, Z. Z., and Zhao, L. G. (2020). Berberine: a promising natural isoquinoline alkaloid for the development of hypolipidemic drugs. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 20 (28), 2634–2647. doi:10.2174/1568026620666200908165913
Li, G., Liu, X., Zhu, H., Huang, L., Liu, Y. L., Ma, C., et al. (2011). Berberine-improved visceral white adipose tissue insulin resistance associated with altered sterol regulatory element-binding proteins, liver X receptors, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors transcriptional programs in diabetic hamsters. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 34 (5), 644–654. doi:10.1248/bpb.34.644
Li, J., Zhang, S., Wu, L., Pei, M., and Jiang, Y. (2021b). Berberine inhibited metastasis through miR-145/MMP16 axis in vitro. J. Ovarian Res. 14 (1), 4. doi:10.1186/s13048-020-00752-2
Li, Q., Qing, L., Xu, W., Yang, Y., You, C., Lao, Y., et al. (2023c). Berberine affects the proliferation, migration, invasion, cell cycle, and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells T24 and 5637 by down-regulating the HER2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Arch. Esp. Urol. 76 (2), 152–160. doi:10.56434/j.arch.esp.urol.20237602.17
Li, S. Y., Li, Y., Wu, Z. H., Zhou, Z. J., Li, C. Y., Wu, T. T., et al. (2023b). Study on the mechanism of action of effective monomeric, berberine of xianglian pill in inhibiting human Colon cancer cells based on fatty acid synthase target. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 13 (6), 538–549. doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.05.008
Li, W., Jiao, R., Luo, S., Liu, Z., Song, J., and Chen, Z. (2024). Mechanism of action of coptidis rhizome in treating periodontitis based on network pharmacology and in vitro validation. BMC Oral Health 24 (1), 530. doi:10.1186/s12903-024-04311-9
Li, X., Chen, J., Feng, W., Wang, C., Chen, M., Li, Y., et al. (2023a). Berberine ameliorates iron levels and ferroptosis in the brain of 3 × Tg-AD mice. Phytomedicine 118, 154962. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154962
Li, X., Song, Y., Wang, L., Kang, G., Wang, P., Yin, H., et al. (2021c). A potential combination therapy of berberine hydrochloride with antibiotics against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11, 660431. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.660431
Li, X., Su, C., Jiang, Z., Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., et al. (2021a). Berberine attenuates choline-induced atherosclerosis by inhibiting trimethylamine and trimethylamine-N-oxide production via manipulating the gut microbiome. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 7 (1), 36. doi:10.1038/s41522-021-00205-8
Li, X., Zhang, A., Sun, H., Liu, Z., Zhang, T., Qiu, S., et al. (2017). Metabolic characterization and pathway analysis of berberine protects against prostate cancer. Oncotarget 8 (39), 65022–65041. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.17531
Liang, H., Liu, Y., Fu, L., Li, L., and Gong, N. (2022). Berberine inhibits the development of endometrial cancer through circ_ZNF608/miR-377-3p/COX2 axis. Autoimmunity 55 (7), 485–495. doi:10.1080/08916934.2021.2010050
Liang, H., and Wang, Y. (2018). Berberine alleviates hepatic lipid accumulation by increasing ABCA1 through the protein kinase C δ pathway. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 498 (3), 473–480. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.003
Liao, W., Zhang, R., Chen, G., Zhu, X., Wu, W., Chen, Z., et al. (2024). Berberine synergises with ferroptosis inducer sensitizing NSCLC to ferroptosis in p53-dependent SLC7A11-GPX4 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 176, 116832. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116832
Lin, J. P., Yang, J. S., Wu, C. C., Lin, S. S., Hsieh, W. T., Lin, M. L., et al. (2008). Berberine induced down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-1, -2 and -9 in human gastric cancer cells (SNU-5) in vitro. Vivo 22 (2), 223–230.
Ling, Q., Fang, J., Zhai, C., Huang, W., Chen, Y., Zhou, T., et al. (2023). Berberine induces SOCS1 pathway to reprogram the M1 polarization of macrophages via miR-155-5p in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 949, 175724. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175724
Liu, D., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Hou, L., Li, S., Tian, H., et al. (2018). Berberine modulates gut microbiota and reduces insulin resistance via the TLR4 signaling pathway. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 126 (8), 513–520. doi:10.1055/s-0043-125066
Liu, J., Liu, P., Xu, T., Chen, Z., Kong, H., Chu, W., et al. (2020). Berberine induces autophagic cell death in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by inactivating AKT/mTORC1 signaling. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 1813–1823. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S239247
Liu, L., Fan, J., Ai, G., Liu, J., Luo, N., Li, C., et al. (2019). Berberine in combination with cisplatin induces necroptosis and apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. Biol. Res. 52 (1), 37. doi:10.1186/s40659-019-0243-6
Liu, Q., Tang, Y., Jiang, S., Yu, X., Zhu, H., Xie, X., et al. (2024b). Mechanisms of action of berberine hydrochloride in planktonic cells and biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 193, 106774. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106774
Liu, X., Ji, Q., Ye, N., Sui, H., Zhou, L., Zhu, H., et al. (2015). Berberine inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via COX-2/PGE2 mediated JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. PLoS One 10 (5), e0123478. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0123478
Liu, Y., Guo, T., Zhang, Y., Tang, S. C., Zhao, X. M., He, H. Y., et al. (2024a). Berberine alleviates ischemic brain injury by enhancing autophagic flux via facilitation of TFEB nuclear translocation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 52 (01), 231–252. doi:10.1142/S0192415X24500101
Lu, M., Wang, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhang, C., Wang, H., Sha, W., et al. (2023). Berberine inhibits gluconeogenesis in spontaneous diabetic rats by regulating the AKT/MAPK/NO/cGMP/PKG signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 478 (9), 2013–2027. doi:10.1007/s11010-022-04604-z
Lu, Z., He, B., Chen, Z., Yan, M., and Wu, L. (2020). Anti-inflammatory activity of berberine in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via the Angptl2 pathway. BMC Immunol. 21 (1), 28. doi:10.1186/s12865-020-00358-9
Lu, Z., Lu, F., Wu, L., He, B., Chen, Z., and Yan, M. (2021). Berberine attenuates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating chemerin/CMKLR1 signalling pathway and Treg/Th17 ratio. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 394 (2), 383–390. doi:10.1007/s00210-020-01914-1
Luo, Z., Li, Z., Liang, Z., Wang, L., He, G., Wang, D., et al. (2022). Berberine increases stromal production of wnt molecules and activates Lgr5(+) stem cells to promote epithelial restitution in experimental colitis. BMC Biol. 20 (1), 287. doi:10.1186/s12915-022-01492-z
Maiti, P., Plemmons, A., and Dunbar, G. L. (2019). Combination treatment of berberine and solid lipid curcumin particles increased cell death and inhibited PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway of human cultured glioblastoma cells more effectively than did individual treatments. PLoS One 14 (12), e0225660. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0225660
Man, B., Hu, C., Yang, G., Xiang, J., Yang, S., and Ma, C. (2022). Berberine attenuates diabetic atherosclerosis via enhancing the interplay between KLF16 and PPARα in ApoE(-/-) mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 624, 59–67. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.07.072
Mao, Z., Xun, X., Jia, W., Sheng, R., Hong, S., and Ming, H. (2022). Separation of Coptis Alkaloids by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography and Preliminary Study on Their Antibacterial Activity. Animal Husb. and Veterinary Med. 54 (06), 132–138.
McCarty, M. F., and DiNicolantonio, J. J. (2021). Maintaining effective beta cell function in the face of metabolic syndrome-associated glucolipotoxicity—nutraceutical options. Healthcare 10 (1), 3. doi:10.3390/healthcare10010003
Mei, H. (2024). Discussion on the standardization of natural plant components and preparations. China Cosmet. (04), 80–85.
Meng, G., Li, P., Du, X., Feng, X., and Qiu, F. (2024). Berberine alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting inflammation through targeting IRGM1. Phytomedicine 133, 155909. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155909
Mi, J., He, W., Lv, J., Zhuang, K., Huang, H., and Quan, S. (2019). Effect of berberine on the HPA-Axis pathway and skeletal muscle GLUT4 in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 12, 1717–1725. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S211188
Mianowska, M., Zaremba-Czogalla, M., Zygmunt, A., Mahmud, M., Süss, R., and Gubernator, J. (2023). Dual role of vitamin C-Encapsulated liposomal berberine in effective Colon anticancer immunotherapy. Pharm. (Basel) 17 (1), 5. doi:10.3390/ph17010005
Miao, X., and Cui, W. (2022). Berberine alleviates LPS-Induced apoptosis, oxidation, and skewed lineages during mouse preimplantation development. Biol. Reprod. 106 (4), 699–709. doi:10.1093/biolre/ioac002
Ming, T., Yue, Z., Jia, L., Hui, W., Yan, H., Yi, W., et al. (2023). Optimization of Green Extraction Process for Alkaloids from Coptis chinensis Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine. 45 (9), 3014–3017.
Mori, S., Fujiwara-Tani, R., Gyoten, M., Nukaga, S., Sasaki, R., Ikemoto, A., et al. (2023). Berberine induces combined cell death in gastrointestinal cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (7), 6588. doi:10.3390/ijms24076588
Newman, D. J., and Cragg, G. M. (2020). Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 83 (3), 770–803. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285
Neyrinck, A. M., Sánchez, C. R., Rodriguez, J., Cani, P. D., Bindels, L. B., and Delzenne, N. M. (2021). Prebiotic effect of berberine and curcumin is associated with the improvement of obesity in mice. Nutrients 13 (5), 1436. doi:10.3390/nu13051436
Ni, J., Wang, F., Yue, L., Xiang, G. D., Zhao, L. S., Wang, Y., et al. (2017). The effects and mechanisms of berberine on proliferation of papillary thyroid cancer K1 cells induced by high glucose. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 56 (7), 507–511. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2017.07.007
Ni, L., Li, Z., Ren, H., Kong, L., Chen, X., Xiong, M., et al. (2022a). Berberine inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell growth through repressing DNA repair and replication rather than through apoptosis. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 49 (1), 134–144. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13582
Ni, L., Sun, P., Ai, M., Kong, L., Xu, R., and Li, J. (2022b). Berberine inhibited the formation of metastasis by intervening the secondary homing of colorectal cancer cells in the blood circulation to the lung and liver through HEY2. Phytomedicine 104, 154303. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154303
Nie, Q., Li, M., Huang, C., Yuan, Y., Liang, Q., Ma, X., et al. (2024). The clinical efficacy and safety of berberine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Transl. Med. 22 (1), 225. doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05011-2
Nie, Q., Peng, W. W., Wang, Y., Zhong, L., Zhang, X., and Zeng, L. (2022). β-catenin correlates with the progression of Colon cancers and berberine inhibits the proliferation of Colon cancer cells by regulating the β-catenin signaling pathway. Gene 818, 146207. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2022.146207
Ning, Y., Wang, X., Chen, P., Liu, S., Hu, J., Xiao, R., et al. (2022). Targeted inhibition of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation by a graphene oxide-loaded aptamer/berberine bifunctional complex. Drug Deliv. 29 (1), 1675–1683. doi:10.1080/10717544.2022.2079768
Noh, J., Jun, M., Yang, H., and Lee, B. C. (2022). Cellular and molecular mechanisms and effects of berberine on obesity-induced inflammation. Biomedicines 10 (7), 1739. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10071739
Nourizadeh, N., Vazifeh Mostaan, L., Saburi, E., and Hashemy, S. I. (2022). Modulatory effect of berberine on plasma lipoprotein (or lipid) profile: a review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 49 (11), 10885–10893. doi:10.1007/s11033-022-07623-7
Obchoei, S., Detarya, M., Boonnate, P., Saranaruk, P., Vaeteewoottacharn, K., Mahalapbutr, P., et al. (2022). Low dose berberine suppresses cholangiocarcinoma cell progression as a multi-kinase inhibitor. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev. 23 (10), 3379–3386. doi:10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.10.3379
Och, A., Och, M., Nowak, R., Podgórska, D., and Podgórski, R. (2022). Berberine, a herbal metabolite in the metabolic syndrome: the risk factors, course, and consequences of the disease. Molecules 27 (4), 1351. doi:10.3390/molecules27041351
Okubo, S., Uto, T., Goto, A., Tanaka, H., Nishioku, T., Yamada, K., et al. (2017). Berberine induces apoptotic cell death via activation of Caspase-3 and -8 in HL-60 human leukemia cells: nuclear localization and structure-activity relationships. Am. J. Chin. Med. 45 (7), 1497–1511. doi:10.1142/S0192415X17500811
Palma, T. V., Lenz, L. S., Bottari, N. B., Pereira, A., Schetinger, M. R. C., Morsch, V. M., et al. (2020). Berberine induces apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme U87MG cells via oxidative stress and independent of AMPK activity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47 (6), 4393–4400. doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05500-9
Pan, Y., Shao, D., Zhao, Y., Zhang, F., Zheng, X., Tan, Y., et al. (2017a). Berberine reverses hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in breast cancer through the inhibition of AMPK- HIF-1α. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 13 (6), 794–803. doi:10.7150/ijbs.18969
Pan, Y., Zhang, F., Zhao, Y., Shao, D., Zheng, X., Chen, Y., et al. (2017b). Berberine enhances chemosensitivity and induces apoptosis through dose-orchestrated AMPK signaling in breast cancer. J. Cancer 8 (9), 1679–1689. doi:10.7150/jca.19106
Patil, P., Thakur, A., Sharma, A., and Flora, S. J. S. (2020). Natural products and their derivatives as multifunctional ligands against alzheimer's disease. Drug Dev. Res. 81 (2), 165–183. doi:10.1002/ddr.21587
Patti, A. M., Giglio, R. V., Papanas, N., Rizzo, M., and Rizvi, A. A. (2019). Future perspectives of the pharmacological management of diabetic dyslipidemia. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 12 (2), 129–143. doi:10.1080/17512433.2019.1567328
Pirillo, A., and Catapano, AL. (2015). Berberine, a plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in vitro evidence to clinical studies. Atherosclerosis 243 (2), 449–61. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.09.032
Puthdee, N., Seubwai, W., Vaeteewoottacharn, K., Boonmars, T., Cha'on, U., Phoomak, C., et al. (2017). Berberine induces cell cycle arrest in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines via inhibition of NF-κB and STAT3 pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 40 (6), 751–757. doi:10.1248/bpb.b16-00428
Qian, Y., Kang, Z., Zhao, L., Chen, H., Zhou, C., Gao, Q., et al. (2023). Berberine might block colorectal carcinogenesis by inhibiting the regulation of B-cell function by Veillonella parvula. Chin. Med. J. Engl. 136 (22), 2722–2731. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000002752
Qiu, Y., Li, M., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, Y., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). Berberine treatment for weight gain in patients with schizophrenia by regulating leptin rather than adiponectin. Asian J. Psychiatry 67, 102896. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2021.102896
Qu, H., Zhang, Y., Shi, J., Zhao, Y. H., Gao, J., Gao, Z. Y., et al. (2024). Berberine decreases thrombosis potential induced by a high-choline diet by inhibiting CutC enzyme. Curr. Med. Chem. 31 (24), 3844–3856. doi:10.2174/0929867330666230524142632
Raskin, I., Ribnicky, D. M., Komarnytsky, S., Ilic, N., Poulev, A., Borisjuk, N., et al. (2002). Plants and human health in the twenty-first century. Trends Biotechnol. 20 (12), 522–531. doi:10.1016/s0167-7799(02)02080-2
Rigillo, G., Cappellucci, G., Baini, G., Vaccaro, F., Miraldi, E., Pani, L., et al. (2024). Comprehensive analysis of Berberis aristata DC. Bark extracts: in vitro and in silico evaluation of bioaccessibility and safety. Nutrients 16 (17), 2953. doi:10.3390/nu16172953
Rui, Z., Chang, X., Jing, Z., and Hong, Y. (2020). Research Progress on Chemical Constituents of Coptis chinensis and Pharmacological Effects of Berberine. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 45 (19), 4561–4573. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200527.202
Ruan, H., Zhan, Y. Y., Hou, J., Xu, B., Chen, B., Tian, Y., et al. (2017). Berberine binds RXRα to suppress β-catenin signaling in Colon cancer cells. Oncogene 36 (50), 6906–6918. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.296
Rui, R., Yang, H., Liu, Y., Zhou, Y., Xu, X., Li, C., et al. (2021). Effects of berberine on atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 764175. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.764175
Sadraie, S., Kiasalari, Z., Razavian, M., Azimi, S., Sedighnejad, L., Afshin-Majd, S., et al. (2019). Berberine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced learning and memory deficit in the rat: insights into underlying molecular mechanisms. Metab. Brain Dis. 34 (1), 245–255. doi:10.1007/s11011-018-0349-5
Salehi, B., Selamoglu, Z., Sener, B., Kilic, M., Kumar Jugran, A., de Tommasi, N., et al. (2019). Berberis plants-drifting from farm to food applications, phytotherapy, and phytopharmacology. Foods 8 (10), 522. doi:10.3390/foods8100522
Sammarco, A., Beffagna, G., Sacchetto, R., Vettori, A., Bonsembiante, F., Scarin, G., et al. (2023). Antitumor effect of berberine analogs in a canine mammary tumor cell line and in zebrafish reporters via Wnt/β-Catenin and hippo pathways. Biomedicines 11 (12), 3317. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11123317
Selamoglu Talas, Z., Ozdemir, I., Yilmaz, I., Gok, Y., and Orun, I. (2008). The investigation of the antioxidative properties of the novel synthetic organoselenium compounds in some rat tissues. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 233 (5), 575–579. doi:10.3181/0707-RM-191
Shah, D., Challagundla, N., Dave, V., Patidar, A., Saha, B., Nivsarkar, M., et al. (2022). Berberine mediates tumor cell death by skewing tumor-associated immunosuppressive macrophages to inflammatory macrophages. Phytomedicine 99, 153904. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153904
Shams, G., Allah, S. A., Ezzat, R., and Said, M. A. (2024). Ameliorative effects of berberine and selenium against paracetamol-induced hepatic toxicity in rats. Open Vet. J. 14 (1), 292–303. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i1.26
Shayganfard, M. (2023). Berberine: is it a promising agent for mental disorders treatment? Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 16 (3), 307–320. doi:10.2174/1874467215666220509213122
Shen, H. R., Xu, X., and Li, X. L. (2021a). Berberine exerts a protective effect on rats with polycystic ovary syndrome by inhibiting the inflammatory response and cell apoptosis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 19 (1), 3. doi:10.1186/s12958-020-00684-y
Shen, Z. Q., Wang, J., Tan, W. F., and Huang, T. M. (2021b). Berberine inhibits colorectal tumor growth by suppressing SHH secretion. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 42 (7), 1190–1194. doi:10.1038/s41401-020-00514-2
Shi, X. Z., Zhao, S., Wang, Y., Wang, M. Y., Su, S. W., Wu, Y. Z., et al. (2023). Antitumor activity of berberine by activating autophagy and apoptosis in CAL-62 and BHT-101 anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell lines. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 17, 1889–1906. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S406354
Shrivastava, S., Sharma, A., Saxena, N., Bhamra, R., and Kumar, S. (2023). Addressing the preventive and therapeutic perspective of berberine against diabetes. Heliyon 9 (11), e21233. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21233
Song, C., Li, D., Zhang, J., and Zhao, X. (2023). Berberine hydrochloride alleviates imatinib mesylate – induced cardiotoxicity through the inhibition of Nrf2-dependent ferroptosis. Food and Funct. 14 (2), 1087–1098. doi:10.1039/d2fo03331c
Song, L., Luo, Y., Wang, X., Almutairi, M. M., Pan, H., Li, W., et al. (2019). Exploring the active mechanism of berberine against HCC by systematic pharmacology and experimental validation. Mol. Med. Rep. 20 (5), 4654–4664. doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.10698
Stermitz, F. R., and Sharifi, I. A. (1977). Alkaloids of zanthoxylum monophyllum and Z. punctatum. Phytochemistry 16 (12), 2003–2006. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(77)80113-1
Su, N., Ting, L., Xue, C., and Ting, X. (1977). Separation and Purification of Berberine by Ion-Exchange Fiber. Chinese Journal of New Drugs. 18 (22), 2183–2188.
Su, X., Yang, D., Hu, Y., Yuan, Y., and Song, L. (2023). Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy. Open Life Sci. 18 (1), 20220648. doi:10.1515/biol-2022-0648
Sui, M., Jiang, X., Sun, H., Liu, C., and Fan, Y. (2021). Berberine ameliorates hepatic insulin resistance by regulating microRNA-146b/SIRT1 pathway. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 14, 2525–2537. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S313068
Sun, H., Liu, Q., Hu, H., Jiang, Y., Shao, W., Wang, Q., et al. (2018b). Berberine ameliorates blockade of autophagic flux in the liver by regulating cholesterol metabolism and inhibiting COX2-prostaglandin synthesis. Cell Death Dis. 9 (8), 824. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0890-5
Sun, H., Wang, N., Cang, Z., Zhu, C., Zhao, L., Nie, X., et al. (2017a). Modulation of microbiota-gut-brain axis by berberine resulting in improved metabolic status in high-fat diet-fed rats. Obes. Facts 9 (6), 365–378. doi:10.1159/000449507
Sun, L., He, M., Li, F., Wu, D., Zheng, P., Zhang, C., et al. (2024b). Oxyberberine sensitizes liver cancer cells to sorafenib via inhibiting NOTCH1-USP7-c-Myc pathway. Hepatol. Commun. 8 (4), e0405. doi:10.1097/HC9.0000000000000405
Sun, Q., Shan, R., Qi, T., and Yang, P. (2023a). Berberine reverses the tumorigenic function of Colon cancer cell-derived exosomes. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 260 (1), 75–85. doi:10.1620/tjem.2022.J119
Sun, R., Kong, B., Yang, N., Cao, B., Feng, D., Yu, X., et al. (2021). The hypoglycemic effect of berberine and berberrubine involves modulation of intestinal farnesoid X receptor signaling pathway and inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Drug Metabolism Dispos. 49 (3), 276–286. doi:10.1124/dmd.120.000215
Sun, S., Yang, Y., Xiong, R., Ni, Y., Ma, X., Hou, M., et al. (2022). Oral berberine ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity by activating TAS2Rs in tuft and endocrine cells in the gut. Life Sci. 311 (Pt A), 121141. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121141
Sun, Y., Xia, M., Yan, H., Han, Y., Zhang, F., Hu, Z., et al. (2018a). Berberine attenuates hepatic steatosis and enhances energy expenditure in mice by inducing autophagy and fibroblast growth factor 21. Br. J. Pharmacol. 175 (2), 374–387. doi:10.1111/bph.14079
Sun, Y., Yu, J., Liu, X., Zhang, C., Cao, J., Li, G., et al. (2018c). Oncosis-like cell death is induced by berberine through ERK1/2-mediated impairment of mitochondrial aerobic respiration in gliomas. Biomed. Pharmacother. 102, 699–710. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.132
Sun, Y., Yuan, X., Zhang, F., Han, Y., Chang, X., Xu, X., et al. (2017b). Berberine ameliorates fatty acid-induced oxidative stress in human hepatoma cells. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 11340. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11860-3
Sun, Y., Zhou, Q., Chen, F., Gao, X., Yang, L., Jin, X., et al. (2023b). Berberine inhibits breast carcinoma proliferation and metastasis under hypoxic microenvironment involving gut microbiota and endogenous metabolites. Pharmacol. Res. 193, 106817. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106817
Sun, Z., Zhao, T., Bai, X., Li, H., Gao, J., Hao, Y., et al. (2024a). Berberine targets PKM2 to activate the t-PA-Induced fibrinolytic system and improves thrombosis. Pharm. (Basel) 17 (9), 1219. doi:10.3390/ph17091219
Tang, L. Q., Wei, W., Chen, L. M., and Liu, S. (2006). Effects of berberine on diabetes induced by alloxan and a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 108 (1), 109–115. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2006.04.019
Tang, Y., Gao, Y., Nie, K., Wang, H., Chen, S., Su, H., et al. (2024b). Jiao-tai-wan and its effective component-berberine improve diabetes and depressive disorder through the cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 324, 117829. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117829
Tang, Y., Su, H., Nie, K., Wang, H., Gao, Y., Chen, S., et al. (2024a). Berberine exerts antidepressant effects in vivo and in vitro through the PI3K/AKT/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 170, 116012. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116012
Tian, H., Kang, Y. M., Gao, H. L., Shi, X. L., Fu, L. Y., Li, Y., et al. (2019a). Chronic infusion of berberine into the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension and sympathoexcitation via the ROS/Erk1/2/iNOS pathway. Phytomedicine 52, 216–224. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.206
Tian, Y., Cai, J., Gui, W., Nichols, R. G., Koo, I., Zhang, J., et al. (2019b). Berberine directly affects the gut microbiota to promote intestinal farnesoid X receptor activation. Drug Metabolism Dispos. 47 (2), 86–93. doi:10.1124/dmd.118.083691
Tian, Y. Q., Ren, X., Wang, J., Li, X., Yin, Y. S., Guo, Z. H., et al. (2024). Berberine hydrochloride alleviates chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome by modifying gut microbiome signaling. Asian J. Androl. 26 (5), 500–509. doi:10.4103/aja202427
Wang, C., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Guo, W., Long, C., Wang, J., et al. (2017b). Berberine inhibits the proliferation of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via an epstein-barr virus nuclear antigen 1-dependent mechanism. Oncol. Rep. 37 (4), 2109–2120. doi:10.3892/or.2017.5489
Wang, C., Wang, Y., Ma, S., Zuo, Z. Y., Wu, Y. B., Kong, W. J., et al. (2019). Berberine inhibits adipocyte differentiation, proliferation and adiposity through down-regulating galectin-3. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 13415. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-50103-5
Wang, C., Yang, Y., Chen, J., Dai, X., Xing, C., Zhang, C., et al. (2023a). Berberine protects against high-energy and low-protein diet-induced hepatic steatosis: modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism in laying hens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (24), 17304. doi:10.3390/ijms242417304
Wang, H., Chen, S., Tang, Y., Nie, K., Gao, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2024b). Berberine promotes lacteal junction zippering and ameliorates diet-induced obesity through the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 124, 155268. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155268
Wang, H., Zhang, H., Gao, Z., Zhang, Q., and Gu, C. (2022a). The mechanism of berberine alleviating metabolic disorder based on gut microbiome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12, 854885. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.854885
Wang, J., Dai, G., and Li, W. (2016). Berberine regulates glycemia via local inhibition of intestinal dipeptidyl peptidase-Ⅳ. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 45 (5), 486–492. doi:10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2016.09.06
Wang, J., Wei, L. R., Liu, Y. L., Ding, C. Z., Guo, F., Wang, J., et al. (2021d). Berberine activates the β-catenin/TCF4 signaling pathway by down-regulating miR-106b to promote GLP-1 production by intestinal L cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 15911, 174482. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174482
Wang, J., and Zhang, Y. (2018). Neuroprotective effect of berberine agonist against impairment of learning and memory skills in severe traumatic brain injury via Sirt1/p38 MAPK expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 17 (5), 6881–6886. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.8674
Wang, K., Feng, X., Chai, L., Cao, S., and Qiu, F. (2017a). The metabolism of berberine and its contribution to the pharmacological effects. Drug Metab. Rev. 49 (2), 139–157. doi:10.1080/03602532.2017.1306544
Wang, K., Yin, J., Chen, J., Ma, J., Si, H., and Xia, D. (2024e). Inhibition of inflammation by berberine: molecular mechanism and network pharmacology analysis. Phytomedicine 128, 155258. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155258
Wang, K. B., Liu, Y., Li, J., Xiao, C., Wang, Y., Gu, W., et al. (2022b). Structural insight into the bulge-containing KRAS oncogene promoter G-quadruplex bound to berberine and coptisine. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 6016. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33761-4
Wang, L., Jia, Z., Wang, B., and Zhang, B. (2020b). Berberine inhibits liver damage in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Turk J. Gastroenterol. 31 (12), 902–909. doi:10.5152/tjg.2020.19568
Wang, L., Sheng, W., Tan, Z., Ren, Q., Wang, R., Stoika, R., et al. (2021c). Treatment of parkinson's disease in Zebrafish model with a berberine derivative capable of crossing blood brain barrier, targeting mitochondria, and convenient for bioimaging experiments. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 249, 109151. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109151
Wang, M., Zhang, J., Zhao, H., Wan, D., and Jiang, Z. (2020c). Berberine combined with cyclosporine A alleviates acute graft-versus-host disease in murine models. Int. Immunopharmacol. 81, 106205. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106205
Wang, Q., Shen, W., Shao, W., and Hu, H. (2024c). Berberine alleviates cholesterol and bile acid metabolism disorders induced by high cholesterol diet in mice. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 719, 150088. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150088
Wang, Q., Wu, H., Wu, Q., and Zhong, S. (2023b). Berberine targets KIF20A and CCNE2 to inhibit the progression of nonsmall cell lung cancer via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 84 (5), 907–921. doi:10.1002/ddr.22061
Wang, S., Wang, Y., Qin, Q., Li, J., Chen, Q., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024d). Berberine protects against dihydrotestosterone-induced human ovarian granulosa cell injury and ferroptosis by regulating the Circ_0097636/MiR-186-5p/SIRT3 pathway. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 196 (8), 5265–5282. doi:10.1007/s12010-023-04825-y
Wang, Y., Liu, H., Zheng, M., Yang, Y., Ren, H., Kong, Y., et al. (2021e). Berberine slows the progression of prediabetes to diabetes in zucker diabetic fatty rats by enhancing intestinal secretion of glucagon-like Peptide-2 and improving the gut microbiota. Front. Endocrinol. 12, 609134. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.609134
Wang, Y., Tai, Y. L., Zhao, D., Zhang, Y., Yan, J., Kakiyama, G., et al. (2021f). Berberine prevents disease progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through modulating multiple pathways. Cells 10 (2), 210. doi:10.3390/cells10020210
Wang, Y., Tong, Q., Ma, S. R., Zhao, Z. X., Pan, L. B., Cong, L., et al. (2021b). Oral berberine improves brain dopa/dopamine levels to ameliorate parkinson's disease by regulating gut microbiota. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6 (1), 77. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00456-5
Wang, Y., Yi, X., Ghanam, K., Zhang, S., Zhao, T., and Zhu, X. (2014). Berberine decreases cholesterol levels in rats through multiple mechanisms, including inhibition of cholesterol absorption. Metabolism 63 (9), 1167–1177. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2014.05.013
Wang, Y., Zhou, X., Zhao, D., Wang, X., Gurley, E. C., Liu, R., et al. (2020a). Berberine inhibits free fatty acid and LPS-Induced inflammation via modulating ER stress response in macrophages and hepatocytes. PLoS One 15 (5), e0232630. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0232630
Wang, Y., and Zidichouski, J. A. (2018). Update on the benefits and mechanisms of action of the bioactive vegetal alkaloid berberine on lipid metabolism and homeostasis. Cholesterol 2018, 7173920–17. doi:10.1155/2018/7173920
Wang, Y. Y., Yan, Q., Huang, Z. T., Zou, Q., Li, J., Yuan, M. H., et al. (2021a). Ameliorating ribosylation-induced Amyloid-β pathology by berberine via inhibiting mTOR/p70S6K signaling. J. Alzheimers Dis. 79 (2), 833–844. doi:10.3233/JAD-200995
Wang, Z., Nie, K., Su, H., Tang, Y., Wang, H., Xu, X., et al. (2021g). Berberine improves ovulation and endometrial receptivity in polycystic ovary syndrome. Phytomedicine 91, 153654. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153654
Wang, Z., Shao, Y., Wu, F., Luo, D., He, G., Liang, J., et al. (2024a). Berberine ameliorates vascular dysfunction by downregulating TMAO-Endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway via gut microbiota in hypertension. Microbiol. Res. 287, 127824. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2024.127824
Warowicka, A., Popenda, Ł., Bartkowiak, G., Musidlak, O., Litowczenko-Cybulska, J., Kuźma, D., et al. (2019). Protoberberine compounds extracted from Chelidonium majus L. as novel natural photosensitizers for cancer therapy. Phytomedicine 64, 152919. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152919
Wei, S., Zhang, M., Yu, Y., Lan, X., Yao, F., Yan, X., et al. (2016). Berberine attenuates development of the hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetic mice and in palmitate-incubated HepG2 cells through suppression of the HNF-4α miR122 pathway. PLOS ONE 11 (3), e0152097. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0152097
Wei, W., Yao, J. X., Zhang, T. T., Wen, J. Y., Zhang, Z., Luo, Y. M., et al. (2023). Network pharmacology reveals that berberine May function against alzheimer's disease via the AKT signaling pathway. Front. Neurosci. 17, 1059496. doi:10.3389/fnins.2023.1059496
Wu, J., Li, K., Zhou, M., Gao, H., Wang, W., and Xiao, W. (2024). Natural compounds improve diabetic nephropathy by regulating the TLR4 signaling pathway. J. Pharm. Anal. 14 (8), 100946. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2024.01.014
Wu, L., Xia, M., Duan, Y., Zhang, L., Jiang, H., Hu, X., et al. (2019). Berberine promotes the recruitment and activation of brown adipose tissue in mice and humans. Cell Death and Dis. 10 (6), 468. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1706-y
Wu, N., Liu, W., Wang, J., Han, Y., Ye, Y., Liu, X., et al. (2021). Berberine ameliorates neuronal AD-like change via activating Pi3k/PGCε pathway. Biofactors 47 (4), 587–599. doi:10.1002/biof.1725
Wu, X., Chen, X., Liu, H., He, Z. W., Wang, Z., Wei, L. J., et al. (2020). Rescuing dicer expression in inflamed Colon tissues alleviates colitis and prevents colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Theranostics 10 (13), 5749–5762. doi:10.7150/thno.41894
Xia, X., Yan, J., Shen, Y., Tang, K., Yin, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2011). Berberine improves glucose metabolism in diabetic rats by inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis. PLoS ONE 6 (2), e16556. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016556
Xia, Y., Chen, S., Cui, J., Wang, Y., Liu, X., Shen, Y., et al. (2021). Berberine suppresses bladder cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting JAK1-STAT3 signaling via upregulation of miR-17-5p. Biochem. Pharmacol. 188, 114575. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114575
Xiao, M., Men, L. N., Xu, M. G., Wang, G. B., Lv, H. T., and Liu, C. (2014). Berberine protects endothelial progenitor cell from damage of TNF-α via the PI3K/AKT/eNOS signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 743, 11–16. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.09.024
Xie, M., Gu, S., Hong, Y., Liu, Y., Rong, X., Lu, W., et al. (2023). Study on the mechanism of Coptis chinensis franch. And its main active components in treating alzheimer's disease based on SCFAs using orbitrap fusion lumos tribrid MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 311, 116392. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116392
Xin, G., Zhang, L. Y., Qiu, H. R., Wang, Y. C., Sui, Y. H., Xue, B. G., et al. (2024). Investigation of the effects and mechanisms of berberine on a mouse model of polycystic ovary syndrome: based on intestinal flora analysis. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 59 (3), 215–226. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20231222-00272
Xin, X., Jing, W., Xin, L., Yi, S., and Yi, D. (2023). Optimization of ultrasonic-microwave synergistic extraction of berberine using response surface methodology. Light Industry Sci. Technol. 39 (05), 42–47.
Xu, C., Wang, F., Huang, F., Yang, M., He, D., and Deng, L. (2021b). Targeting effect of berberine on type I fimbriae of Salmonella typhimurium and its effective inhibition of biofilm. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 105 (4), 1563–1573. doi:10.1007/s00253-021-11116-1
Xu, J., and Yang, X. (2024). LC-MS-Based metabolomics reveals the mechanism of protection of berberine against indomethacin-induced gastric injury in rats. Molecules 29 (5), 1055. doi:10.3390/molecules29051055
Xu, J. H., Liu, X. Z., Pan, W., and Zou, D. J. (2017). Berberine protects against diet-induced obesity through regulating metabolic endotoxemia and gut hormone levels. Mol. Med. Rep. 15 (5), 2765–2787. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.6321
Xu, M., Qi, Q., Men, L., Wang, S., Li, M., Xiao, M., et al. (2020). Berberine protects kawasaki disease-induced human coronary artery endothelial cells dysfunction by inhibiting of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Vasc. Pharmacol. 127, 106660. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2020.106660
Xu, M., Ren, L., Fan, J., Huang, L., Zhou, L., Li, X., et al. (2022). Berberine inhibits gastric cancer development and progression by regulating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and downregulating IL-6. Life Sci. 290, 120266. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120266
Xu, X., Zhu, X., Bai, J., Xia, P., Li, Y., Lu, Y., et al. (2019). Berberine alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver induced by a high-fat diet in mice by activating SIRT3. FASEB J. 33 (6), 7289–7300. doi:10.1096/fj.201802316R
Xu, Y., Yu, T., Ma, G., Zheng, L., Jiang, X., Yang, F., et al. (2021a). Berberine modulates deacetylation of PPARγ to promote adipose tissue remodeling and thermogenesis via AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17 (12), 3173–3187. doi:10.7150/ijbs.62556
Yan, J., Fang, C., Yang, G., Li, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2023). Identification of FtfL as a novel target of berberine in intestinal bacteria. BMC Biol. 21 (1), 280. doi:10.1186/s12915-023-01778-w
Yan, S., Chang, J., Hao, X., Liu, J., Tan, X., Geng, Z., et al. (2022). Berberine regulates short-chain fatty acid metabolism and alleviates the colitis-associated colorectal tumorigenesis through remodeling intestinal flora. Phytomedicine 102, 154217. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154217
Yan, T., Yan, N., Wang, P., Xia, Y., Hao, H., Wang, G., et al. (2020). Herbal drug discovery for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 10 (1), 3–18. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2019.11.017
Yang, J., Yin, J., Gao, H., Xu, L., Wang, Y., Xu, L., et al. (2012). Berberine improves insulin sensitivity by inhibiting fat Store and adjusting adipokines profile in human preadipocytes and metabolic syndrome patients. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2012, 363845–363849. doi:10.1155/2012/363845
Yang, L., Cheng, C. F., Li, Z. F., Huang, X. J., Cai, S. Q., Ye, S. Y., et al. (2023). Berberine blocks inflammasome activation and alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via the miR-18a-3p/Gsdmd pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 51 (6), 49. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2023.5252
Yang, L., Yu, S., Yang, Y., Wu, H., Zhang, X., Lei, Y., et al. (2022). Berberine improves liver injury induced glucose and lipid metabolic disorders via alleviating ER stress of hepatocytes and modulating gut microbiota in mice. Bioorg. and Med. Chem. 55, 116598. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116598
Yang, M., and Wang, J. (2022). Berberine ameliorates cognitive disorder via GSK3β/PGC-1α signaling in APP/PS1 mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 68 (3), 228–235. doi:10.3177/jnsv.68.228
Yang, S., Cao, S. J., Li, C. Y., Zhang, Q., Zhang, B. L., Qiu, F., et al. (2024). Berberine directly targets AKR1B10 protein to modulate lipid and glucose metabolism disorders in NAFLD. J. Ethnopharmacol. 332, 118354. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118354
Yang, Y., Zhang, N., Li, K., Chen, J., Qiu, L., and Zhang, J. (2018). Integration of microRNA-mRNA profiles and pathway analysis of plant isoquinoline alkaloid berberine in SGC-7901 gastric cancers cells. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 12, 393–408. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S155993
Yao, T., Zhi, J., Don, S., Jian, Z., Shao, L., and Jian, F. (2012). Study on extraction and purification process of coptis alkaloids. Traditional Chinese drug research and clinical. Pharmacology 23 (2), 208–212.
Ye, C., Liang, Y., Chen, Y., Xiong, Y., She, Y., Zhong, X., et al. (2021). Berberine improves cognitive impairment by simultaneously impacting cerebral blood flow and β-Amyloid accumulation in an APP/tau/PS1 mouse model of alzheimer's disease. Cells 10 (5), 1161. doi:10.3390/cells10051161
Ye, X., Yang, C., Xu, H., He, Q., Sheng, L., Lin, J., et al. (2024). Exploring the therapeutic mechanisms of coptidis rhizoma in gastric precancerous lesions: a network pharmacology approach. Discov. Oncol. 15 (1), 211. doi:10.1007/s12672-024-01070-5
Ye, Z., Wang, Q., Dai, S., Ji, X., Cao, P., Xu, C., et al. (2022). The Berberis vulgaris L. extract berberine exerts its anti-oxidant effects to ameliorate cholesterol overloading-induced cell apoptosis in the primary mice hepatocytes: an in vitro study. Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 58 (10), 855–866. doi:10.1007/s11626-022-00737-z
Yousefian, M., Shakour, N., Hosseinzadeh, H., Hayes, A. W., Hadizadeh, F., and Karimi, G. (2019). The natural phenolic compounds as modulators of NADPH oxidases in hypertension. Phytomedicine 55, 200–213. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.08.002
Yu, J., Ding, C., Hua, Z., Jiang, X., and Wang, C. (2021b). Protective effects of berberine in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome mediated via the PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 47 (5), 1789–1803. doi:10.1111/jog.14730
Yu, M., Alimujiang, M., Hu, L., Liu, F., Bao, Y., and Yin, J. (2021a). Berberine alleviates lipid metabolism disorders via inhibition of mitochondrial complex I in gut and liver. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17 (7), 1693–1707. doi:10.7150/ijbs.54604
Yu, X., Xin, L., Yuan, L., and Yong, Z. (2017). Research Progress on Pharmacological Effects and Clinical Applications of Berberine. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 31 (06), 491–502.
Yuan, R., Tan, Y., Sun, P., Qin, B., and Liang, Z. (2023). Emerging trends and research foci of berberine on tumor from 2002 to 2021: a bibliometric article of the literature from WoSCC. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1122890. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1122890
Yue, S., Liu, J., Wang, A., Meng, X. T., Yang, Z. R., Peng, C., et al. (2019). Berberine alleviates insulin resistance by reducing peripheral branched-chain amino acids. Am. J. Physiology-Endocrinology Metabolism 316 (1), E73–E85. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00256.2018
Zeng, X., Wan, L., Wang, Y., Xue, J., Yang, H., and Zhu, Y. (2020). Effect of low dose of berberine on the radioresistance of cervical cancer cells via a PI3K/HIF-1 pathway under nutrient-deprived conditions. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 96 (8), 1060–1067. doi:10.1080/09553002.2020.1770358
Zhang, B., Pan, Y., Xu, L., Tang, D., Dorfman, R. G., Zhou, Q., et al. (2018b). Berberine promotes glucose uptake and inhibits gluconeogenesis by inhibiting deacetylase SIRT3. Endocrine 62 (3), 576–587. doi:10.1007/s12020-018-1689-y
Zhang, H. N., Sun, Y. J., He, H. Q., Li, H. Y., Xue, Q. L., Liu, Z. M., et al. (2018a). Berberine promotes nerve regeneration through IGFR-Mediated JNK-AKT signal pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 18 (6), 5030–5036. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.9508
Zhang, Q., Wang, X., Cao, S., Sun, Y., He, X., Jiang, B., et al. (2020). Berberine represses human gastric cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo by inducing cytostatic autophagy via inhibition of MAPK/mTOR/p70S6K and akt signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 128, 110245. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110245
Zhang, Q., Xiao, X., Li, M., Li, W., Yu, M., Zhang, H., et al. (2014). Berberine moderates glucose metabolism through the GnRH-GLP-1 and MAPK pathways in the intestine. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 14 (1), 188. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-14-188
Zhang, Y. P., Deng, Y. J., Tang, K. R., Chen, R. S., Liang, S., Liang, Y. J., et al. (2019). Berberine ameliorates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via activation of SIRT3/AMPK/ACC pathway. Curr. Med. Sci. 39 (1), 37–43. doi:10.1007/s11596-019-1997-3
Zhao, F., Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Gou, Y. J., and Yang, Y. Q. (2022a). Effects of berberine on LPS/NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways in PCOS model rats. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 38 (2), 181–186. doi:10.12047/j.cjap.6229.2022.029
Zhao, J., Li, Y., Sun, M., Yu, C. J., Li, J. Y., Wang, S. H., et al. (2021). Effect of berberine on hyperglycaemia and gut microbiota composition in type 2 diabetic goto-kakizaki rats. World J. Gastroenterology 27 (8), 708–724. doi:10.3748/wjg.v27.i8.708
Zhao, J., Wang, Y., Wu, X., Tong, P., Yue, Y., Gao, S., et al. (2018). Inhibition of CCL19 benefits non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB-p65 signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 18 (5), 4635–4642. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.9490
Zhao, L., Cang, Z., Sun, H., Nie, X., Wang, N., and Lu, Y. (2017a). Berberine improves glucogenesis and lipid metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Endocr. Disord. 17 (1), 13. doi:10.1186/s12902-017-0165-7
Zhao, W., Xue, R., Zhou, Z., Kong, W. J., and Jiang, J. D. (2008). Reduction of blood lipid by berberine in hyperlipidemic patients with chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 62 (10), 730–731. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2008.01.007
Zhao, Y., Cui, L., Pan, Y., Shao, D., Zheng, X., Zhang, F., et al. (2017c). Berberine inhibits the chemotherapy-induced repopulation by suppressing the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway and phosphorylation of FAK in ovarian cancer. Cell Prolif. 50 (6), e12393. doi:10.1111/cpr.12393
Zhao, Y., He, K., Zheng, H., Sun, M., Shi, T., Zheng, X., et al. (2020). Berberine inhibits the apoptosis-induced metastasis by suppressing the iPLA2/LOX-5/LTB4 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 13, 5223–5230. doi:10.2147/OTT.S243357
Zhao, Y., Huang, J., Li, T., Zhang, S., Wen, C., and Wang, L. (2022b). Berberine ameliorates aGVHD by gut microbiota remodelling, TLR4 signalling suppression and colonic barrier repairment for NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 26 (4), 1060–1070. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17158
Zhao, Y., Jing, Z., Lv, J., Zhang, Z., Lin, J., Cao, X., et al. (2017b). Berberine activates caspase-9/cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis to suppress triple-negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 95, 18–24. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.045
Zheng, F., Wu, J., Tang, Q., Xiao, Q., Wu, W., and Hann, S. S. (2018). The enhancement of combination of berberine and metformin in inhibition of DNMT1 gene expression through interplay of SP1 and PDPK1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 22 (1), 600–612. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13347
Zhi, D., Zhou, K., Yu, D., Fan, X., Zhang, J., Li, X., et al. (2019). hERG1 is involved in the pathophysiological process and inhibited by berberine in SKOV3 cells. Oncol. Lett. 17 (6), 5653–5661. doi:10.3892/ol.2019.10263
Zhou, F. F., Gu, X. M., Wang, L., and Lin, M. (2023). The mechanism of berberine on methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. Zhonghua Yu Fang. Yi Xue Za Zhi 57 (8), 1217–1221. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20230206-00081
Zhou, G., Yan, M., Guo, G., and Tong, N. (2019). Ameliorative effect of berberine on neonatally induced type 2 diabetic neuropathy via modulation of BDNF, IGF-1, PPAR-γ, and AMPK expressions. Dose-Response 17 (3), 1559325819862449. doi:10.1177/1559325819862449
Zhou, Q., Li, C., Yang, J., and Zhang, T. (2016a). Berberine is a potent agonist of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha. Front. Biosci. 21 (5), 1052–1060. doi:10.2741/4440
Zhou, X. Y., Ye, X. G., He, L. T., Zhang, S. R., Wang, R. L., Zhou, J., et al. (2016b). In vitro characterization and inhibition of the interaction between ciprofloxacin and berberine against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 69 (10), 741–746. doi:10.1038/ja.2016.15
Zhou, Z., Zhao, Q., Huang, Y., Meng, S., Chen, X., Zhang, G., et al. (2024). Berberine ameliorates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced cardiac remodelling by preserving mitochondrial function, role of SIRT6 signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 28 (12), e18407. doi:10.1111/jcmm.18407
Zhu, M. L., Yin, Y. L., Ping, S., Yu, H. Y., Wan, G. R., Jian, X., et al. (2017). Berberine promotes ischemia-induced angiogenesis in mice heart via upregulation of microRNA-29b. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 39 (7), 672–679. doi:10.1080/10641963.2017.1313853
Keywords: berberine, pharmacological properties, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic potential, application prospects
Citation: Fan K-Q, Zhang L, Song F, Zhang Y-H, Chen T, Cheng X, Su N, Zou Y, Yu T, Tan F, Xu W and Yan Z (2025) Pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential of berberine: a comprehensive review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1604071. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1604071
Received: 01 April 2025; Accepted: 23 July 2025;
Published: 14 August 2025.
Edited by:
Fabien Schultz, Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine (BNITM), GermanyReviewed by:
Zeliha Selamoglu, Niğde Ömer Halisdemir University, TürkiyeGiovanna Rigillo, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Italy
Ivan Kahwa, University Hospital Leipzig, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Fan, Zhang, Song, Zhang, Chen, Cheng, Su, Zou, Yu, Tan, Xu and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenhao Xu, NzQ3MDg1Mjg4QHFxLmNvbQ==; Zijun Yan, c3dhbGxvd3l6akAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ke-Qin Fan
Ke-Qin Fan Liangming Zhang3†
Liangming Zhang3† Yue-Hui Zhang
Yue-Hui Zhang Zijun Yan
Zijun Yan