Abstract
Object:
The occurrence of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) poses a significant challenge in treating non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), limiting the clinical use of EGFR-TKIs. Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) demonstrate promise in preclinical settings. This study is aimed to design effective EGFR degraders by linking CRBN ligands with relatively lower molecular weights.
Methods:
Computational methods are employed to do the rational design for the PROTACs. Western blots are used to examine the expression of proteins including EGFR. Cell viability and colony-formation assays are conducted to evaluate the anti-proliferative effects of degraders to NSCLC cell lines, and apoptosis assays are assessed by Annexin V‐FITC/PI dual staining followed by flow cytometry. Female BALB/c nude mice bearing HCC827 xenografts are administered compound 14 (30 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection and the tumor volume and weights are measured.
Results:
We designed and synthesized a series of highly potent degraders based on the first‐generation EGFR‐TKI gefitinib and a cereblon (CRBN) ligand. Among these degraders, compound 14, with a relatively low molecular weight of 814.32 Da, exhibits notable activity against EGFRDel19 and EGFRL858R, with DC50 values of 0.26 nM and 20.57 nM, respectively, while showing no effect on EGFRwt. Additionally, downstream signaling pathways are significantly inhibited. Mechanistic studies indicate that EGFR degradation depends on the ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS). Furthermore, compound 14 markedly suppresses the growth of HCC827 cells and induces apoptosis, with a 96‐h IC50 value of 4.91 nM, while not affecting the viability of H1299, HeLa, and H1975 cells up to 1 μM. In the HCC827 cell-derived xenograft model, compound 14 demonstrates substantial anti-tumor activity and effectively reduces EGFRDel19 protein levels in vivo.
Conclusion:
With its low molecular weight and excellent in vitro and in vivo efficacy, compound 14 could serve as a promising lead for developing degrader-based therapies targeting mutated EGFR.
Introduction
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, also known as HER1 and ERBB1) is a transmembrane protein receptor that constitutes one of the four members of the ErbB family. Activation of EGFR leads to the initiation of a cascade of downstream signaling pathways and directly regulates cell proliferation and survival. Activating mutations in the EGFR gene are present in approximately 10%–35% of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, and in-frame deletion in exon 19 (LREA deletions) and substitutions in exon 21 (L858R) account for more than 85% of known EGFR alterations (Westover et al., 2018; Kobayashi and Mitsudomi, 2016). EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as first-generation gefitinib and erlotinib, second-generation afatinib, and third-generation osimertinib, provide significant clinical benefit in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC. However, the occurrence of acquired resistance limits the long-term efficacy of these TKIs. The acquired T790M mutation in exon 20 upon treatment with first- and second-generation TKIs leads to more than 60% resistance. Osimertinib, the third-generation EGFR TKI, irreversibly inhibits mutated EGFR alleles, including T790M, and presents impressive outcomes in EGFR-mutated NSCLC (Soria et al., 2018). However, numerous secondary EGFR mutations, such as C797, G796, L792, L718, and G724 site mutations, have evolved to evade inhibition and mediate resistance to osimertinib in NSCLC harboring EGFR T790M mutants (Thress et al., 2015; Zheng et al., 2017; Fuchs et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2017; Pisapia et al., 2019; Bersanelli et al., 2016; Peled et al., 2017). Hence, novel technologies and approaches to overcome therapeutic resistance to EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC are a priority.
Recently, proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) have emerged as a promising modality for targeted protein degradation (TPD) via the ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS). PROTACs are hetero-bifunctional molecules that are composed of a ligand for targeting the protein of interest (POI), an E3 ubiquitin ligase ligand, and a linker connecting these two ligands (Bekes et al., 2022). Different from traditional inhibitors based on occupancy-driven pharmacology, PROTACs induce protein degradation through an event-driven mechanism and are considered capable of therapeutically targeting a broad range of intractable proteins (Lai and Crews, 2017). Proteins that have evolved resistance mutations to targeted therapies are considered suitable PROTAC targets, and the design of specific PROTAC molecules against mutant EGFR proteins in EGFR mutant-driven NSCLC may be a promising strategy to eradicate the occurrence of secondary mutations.
In the past 10 years, multiple PROTACs targeting EGFRs have been reported. In 2018, a gefitinib-based PROTAC, compound 3, which recruits von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) to EGFR, was reported to effectively degrade both exon 19 deletion EGFR and the L858R mutation with DC50 (half-maximal degradation concentration) values of 11.7 nM and 22.3 nM, respectively (Burslem et al., 2018). In 2020, MS39, a VHL-recruiting EGFR degrader, and MS154, a cereblon (CRBN)-recruiting degrader, were discovered to degrade EGFRDel19 (DC50 = 5.0 nM and 11 nM, respectively) and the L858R point mutant EGFR (DC50 = 3.3 nM and 25 nM, respectively) (Cheng et al., 2020). Despite good degradation activity, these two gefitinib-based PROTACs have not displayed impressive IC50 values for cell proliferation, probably due to the poor cell permeability. Using the fourth-generation EGFR TKIs as the ligand, Zhang et al. (2020) discovered a CRBN-based PROTAC 2 and a VHL-based PROTAC 10, which have degraded EGFRDel19 with DC50 values of 45.2 nM and 34.8 nM, respectively, and showed selective cytotoxic activity in HCC827 cells harboring an exon 19 deletion EGFR mutant with IC50 values of 180 nM and 220 nM, respectively. Thereafter, by replacing the EGFR ligand part as a reversible EGFR TKI with a purine scaffold, they have reported a more promising degrader P3 with a DC50 value of 0.51 nM and an IC50 value of 0.76 nM in HCC827 cells (Zhao et al., 2020). In 2022, they found an osimertinib- and VHL-based covalent EGFRDel19 and EGFRL858R+T790M degrader, CP17, which exhibited excellent activities against EGFRDel19 in HCC827 cells with a DC50 value of 0.49 nM and an IC50 value of 1.6 nM (Zhao et al., 2022). In 2021, the degrader SIAIS125, based on the EGFR irreversible inhibitor canertinib and a CRBN ligand, has also degraded EGFRDel19 with a DC50 value of 100 nM and an IC50 value of 2.6 nM in PC9 cells (Qu et al., 2021). Shi et al. (2022) synthesized a dacomitinib- and VHL-based EGFRDel19 degrader, compound 13, with a DC50 value of 3.57 nM and an IC50 value of 6 nM in HCC827 cells. Notably, among these PROTACs, most PROTACs with promising degradation ability and cytotoxic activity have been designed to recruit VHL.
As is well known, one of the disadvantages of PROTACs is their poor cell or tissue permeability due to their large molecular weights (M.W.). Reducing the M.W. to below 1,000 Da can enhance permeability. Therefore, we aim to design effective EGFR degraders by linking CRBN ligands with relatively lower molecular weights. By using computational methods, we designed novel PROTACs based on the first-generation EGFR TKI gefitinib and a CRBN ligand. The most active compound, 14, has a molecular weight as low as 814.32 Da and potently and selectively degrades EGFRDel19 and EGFRL858R, but not the wild-type EGFR. This compound-induced degradation occurs in a dose- and time-dependent manner through the ubiquitin–proteasome system. Furthermore, compound 14 significantly inhibits the growth of HCC827 cells harboring the EGFRDel19 mutation, both in vitro and in vivo. The selective and potent EGFR degraders with low molecular weights reported here may serve as lead compounds for treating EGFR mutation-related diseases, such as lung cancer.
Materials and methods
Molecular modeling
The PDB files of the EGFR–gefitinib complex structure, 4I22, and the CRBN–thalidomide complex structure, 6BN7, were downloaded from the Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org/). Water and ions were removed from the structures, and only the proteins and ligands were retained. CoDockPP was used to perform docking between the EGFR–gefitinib complex and the CRBN–thalidomide complex (Kong et al., 2019). Site-constraint search was used with a distance constraint of 20 Å between the tethering atoms from each ligand (Figure 1). A knowledge-based scoring function was used to rank the binding poses. Finally, the top 100 energetically favorable poses were retained.
FIGURE 1
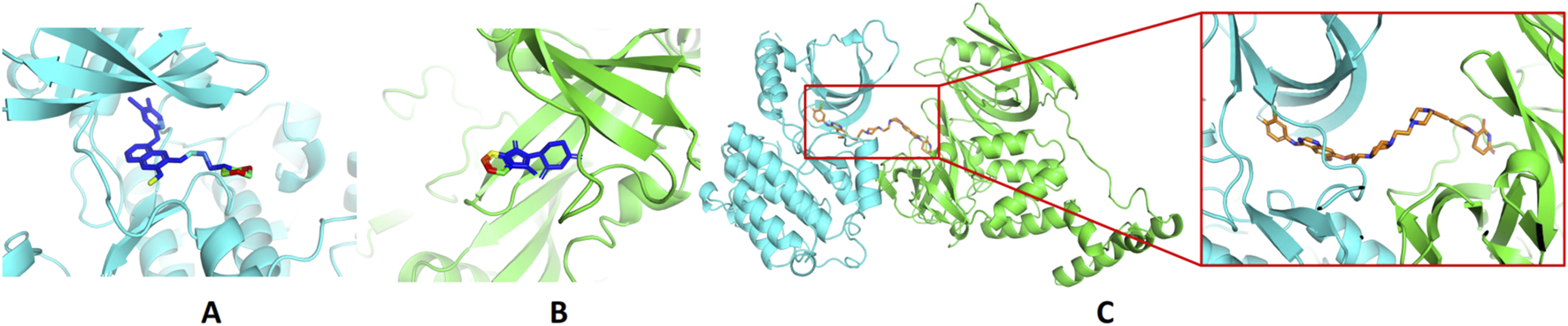
Design of EGFR PROTACs. (A) Binding of gefitinib with EGFR (PDB ID: 4I22). (B) Binding of thalidomide with CRBN (PDB ID: 6BN7). The proteins are shown in the cartoon model and compounds in the stick model. The compounds are colored by the solvent-accessible area, from blue to red indicating the increase in the solvent-accessible area. (C) The predicted ternary structures of EGFR, compound 14, and CRBN.
Cell lines and cell culture
HCC827 and H1975 cell lines were purchased from ATCC (United States) and cultured according to the manuals. Cells were grown in monolayers in appropriate media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% antibiotic/antimycotic solution. Ba/F3 cells stably expressing EGFRL858R were obtained by infection with lentivirus produced by co-transfection of pLVX-EGFRL858R, psPAX2, and pMD2.G into 293T cells, followed by selection with puromycin.
Cell viability and colony formation assays
Cells (5 × 103 for 48 h or 1 × 103 for 96 h) were seeded in 96-well plates, allowed to attach overnight, and then incubated with various concentrations of compounds for 48 h or 96 h. The viability of cells was determined using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; Dojindo), and IC50 was calculated using GraphPad Prism (version 6.0). For colony formation assays, cells (1 × 103 cells/well) seeded in 24-well plates were treated with different concentrations of compounds and replaced with fresh media with compounds every 4 days. After 7 days, the cells were washed with PBS, fixed with methanol, and stained with 0.1% crystal violet solution.
Western blot analysis
Cells at 70%–90% confluence were lysed in RIPA buffer with complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany). Lysates were quantified, separated on SDS-PAGE gels, and transferred onto PVDF membranes, followed by the blockade with 5% milk in TBS+ 0.1% Tween-20 buffer for 1 h at room temperature. The following primary antibodies were used: anti-EGFR (1:50000, ABclonal Technology, Wuhan, China), anti-pEGFR (Tyr1068, 1, Cell Signaling Technology, MA, United States), anti-AKT (1:10000, ABclonal Technology, Wuhan, China), anti-pAKT (1:10000, ABclonal Technology, Wuhan, China), and anti-β-actin (1:10000, ABclonal Technology, Wuhan, China). Protein bands were detected using Tanon High-signal ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Tanon Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The band density of the protein of interest was quantified using ImageJ.
Apoptosis assay
HCC827 cells incubated with control vehicle (DMSO), 10 nM of compound 14, or 10 nM of gefitinib for 48 h were collected, stained with FITC Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI), and analyzed using a BD FACSAria II Flow Cytometer. The percentage of apoptotic cells in total cells was designated as the apoptotic index.
In vivo xenograft research
Female BALB/c nude mice (5–6 weeks old) were purchased from Changzhou Cavens Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. (China) and housed under pathogen-free conditions. HCC827 cells (5 × 106) suspended in 150 μL PBS were inoculated subcutaneously on the left flank of the mouse. When tumor volume reached an average of 70–80 mm3, mice were randomly assigned to two groups (three mice in each group). Compound 14 (30 mg/kg, dissolved in 40% PEG 400 and 5% Tween-80) or vehicle (40% PEG 400 and 5% Tween-80) was administered to mice via intraperitoneal injection every 2 days for 21 days. The tumor volume was calculated as follows: tumor volume (mm3) = (length × width2)/2. All animal experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee for laboratory animals, The Nanjing Han & Zaenker Cancer Institute (File number: OGKQSPF/SQ-112).
Statistical analysis
All experiments were repeated at least three times independently with similar results, and the results are presented as the mean values ±standard deviation (SD). The significance of differences among groups was assessed using ordinary one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparisons tests using Prism 8 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001). p < 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results and discussion
Rational design of EGFR PROTACs
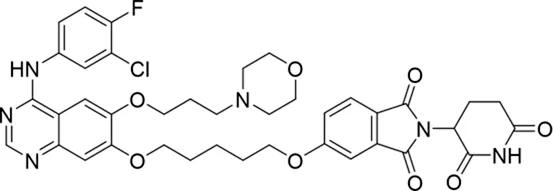
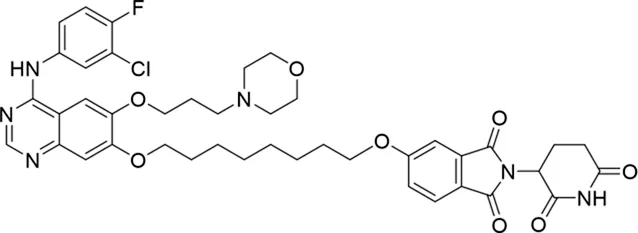
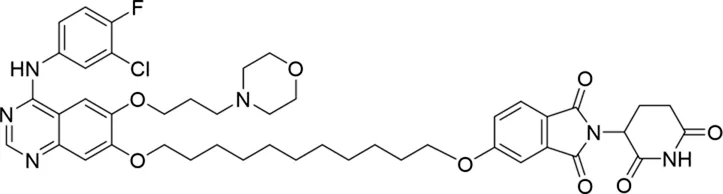
Molecular docking methods were used to predict the ternary complex structure of the POI-PROTAC-E3 ligase in previous studies (Pereira et al., 2023; Ignatov et al., 2023; Zaidman et al., 2020). In this study, computational methods were used for the rational design of PROTACs before conducting costly and time-consuming synthesis experiments. The complex structure of gefitinib with the L858R/T790M mutant EGFR (PDBID: 4I22) was chosen as the POI structure for docking (Gajiwala et al., 2013). By analyzing the solvent availability of the atoms in gefitinib, we selected the solvent-exposed methoxyl group as the attachment point (Figure 1A; Ribeiro et al., 2019). Considering synthesis feasibility, the carbon atom was removed, and the oxygen atom was used as a tethering atom to connect with potential linkers (Figure 1). For the E3 ligase part, the complex structure of thalidomide with CRBN (PDBID: 6BN7) was extracted and used for docking (Nowak et al., 2018). Accordingly, the solvent-available atoms from thalidomide were selected as the tethering atoms (Figure 1). Protein docking was performed using CoDockPP, setting a distance constraint of 20 Å between the tethering atoms from the warhead and the E3 ligand (Kong et al., 2019). The top 100 complex poses, ranked by a knowledge-based scoring function, were retained for further analysis (Supplementary Figure S1). For the top 100 poses, the distance distribution between the tethering atoms is shown in Supplementary Table S1. No pose satisfied with a distance of less than 7 Å, and the largest fraction of poses fell within an atom distance of 15 to 20 Å. We hypothesized that the ideal linker length should be tolerant, allowing as many energetically favorable poses as possible to stabilize the ternary structure. As the C–C bond length was approximately 1.5 Å, we designed and synthesized a series of compounds with different linker length composed of approximately 6–15 atoms, as shown in Table 1. Detailed information on the synthesis and characterization of the compounds is provided in the Supplementary Schemes.
TABLE 1
| ID | 2D structure | EGFR degradation (%)a |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
−6.6 ± 4.2 |
| 2 |
|
15.3 ± 5.9 |
| 3 |
|
7.0 ± 9.3 |
| 4 |
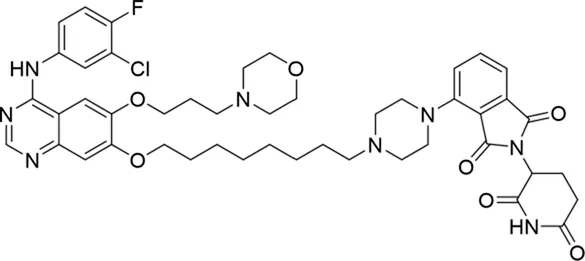
|
NA |
| 5 |
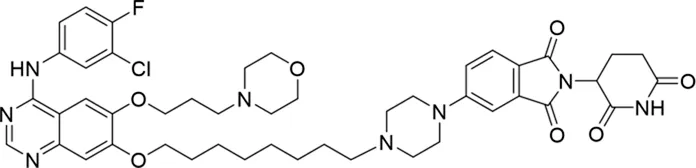
|
NA |
| 6 |
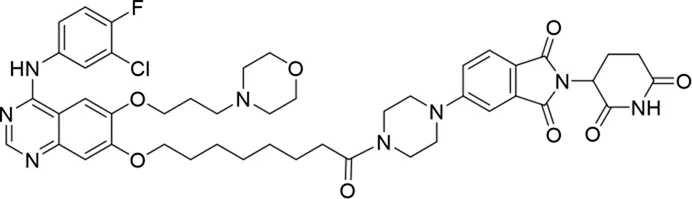
|
15.0 ± 4.0 |
| 7 |
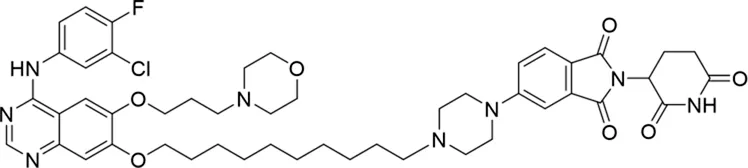
|
19.4 ± 15.1 |
| 8 |
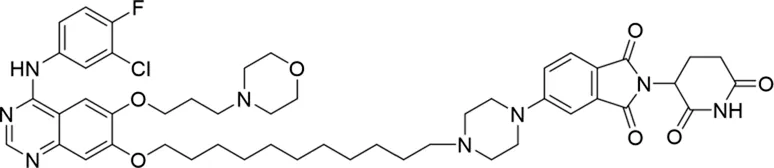
|
NA |
| 9 |
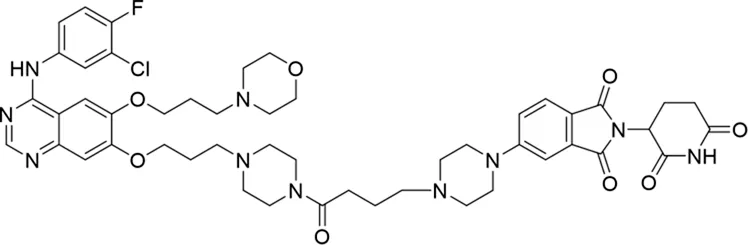
|
66.3 ± 22.7 |
| 10 |
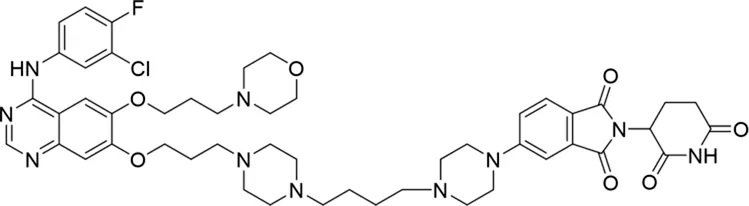
|
32.4 ± 17.1 |
| 11 |
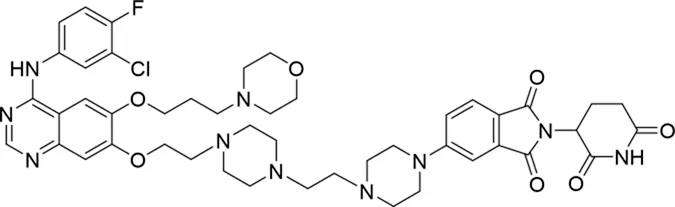
|
25.1 ± 11.2 |
| 12 |
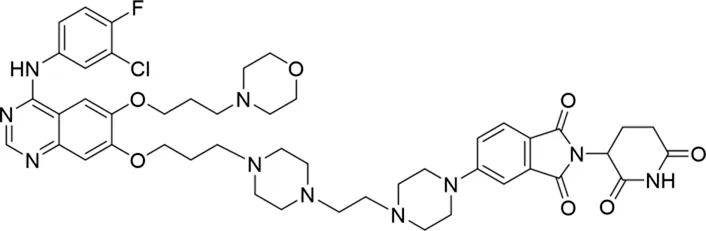
|
60.0 ± 6.9 |
| 13 |
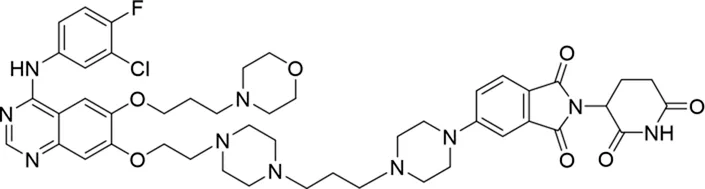
|
16.8 ± 10.5 |
| 14 |
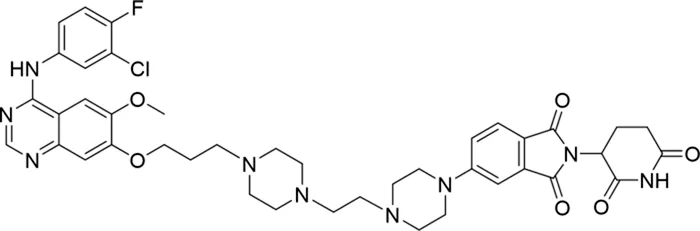
|
66.3 ± 3.5 |
| 15 |
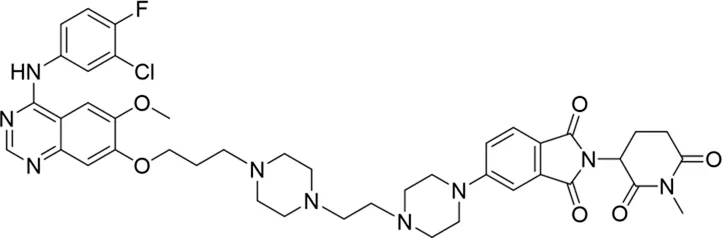
|
NA |
Degradation rates of EGFR under the treatment of compounds 1–15.
Average of two independent experiments at 10 nM in HCC827 for 24 h.
NA, not active.
Initial evaluation of degradation potency of compounds 1–15
The degradation rates of compounds 1–15 at 10 nM were evaluated in HCC827 (EGFRDel19) cells, as shown in Table 1. To connect the tethering atoms with different lengths of alkyl chains, we synthesized compounds 1–3. The short linker with six carbon atoms in compound 1 exhibited no degradation effect, consistent with the distance distribution of the tethering atoms. As shown in Supplementary Table S1, when the distance between the tethering atoms was less than 11 Å, only a limited number of energetically favorable protein–protein poses satisfied this distance condition. With an increased linker length, compounds 2 and 3 showed weak degradation activities. To reduce linker flexibility, piperazine and carbonyl groups were introduced into the compound design. Among these, compounds 6, 7, and 9–13, which featured sufficiently long and relatively rigid linkers, demonstrated significantly enhanced degradation activities.
Based on the binding mode of gefitinib with EGFR (PDBID: 4I22), limited interactions were observed between the morpholine ring and the protein (Gajiwala et al., 2013). Therefore, the extended morpholine ring, which was intended to improve solubility, was removed from compound 12 to reduce molecular weight. The resulting compound 14 exhibited comparable degradation activity to compound 12 (66.3% ± 3.5% for 14 versus 60.0% ± 6.9% for 12, Table 1) with significantly decreased molecular weight. Compound 15, which incorporated an extra methyl group on the glutarimide moiety of thalidomide in compound 14, completely lost its degradation ability (Table 1). It is reported that methylation at this position entirely disrupts the binding of thalidomide to cereblon (Fischer et al., 2014), implying that E3 ligase binding is essential for EGFR degradation. The predicted ternary structure of the most active molecule, compound 14, is illustrated in Figure 1C. Compound 14 presents an appropriate conformation to bind to the top 1 docking pose of EGFR and CRBN, indicating its potential to induce ternary structure formation.
Compounds 12 and 14 efficiently decrease EGFRDel19 and EGFRL858R proteins but not EGFRwt
We further evaluated the degradation potencies of compounds 12 and 14, which were identified as the most potent degraders in the primary study. Both compounds could efficiently degrade EGFRDel19 in HCC827 cell lines at 24 h treatment with a DC50 value of 1.944 nM for 12 (Dmax = 85.1%) and 0.261 nM for 14 (Dmax = 91.2%) (Figure 2A). Concordantly, the levels of both pEGFR and pAKT also markedly reduced upon EGFR degradation. Compound 14 also efficiently degraded EGFRL858R in Ba/F3 cells stably expressing the EGFRL858R mutant with a DC50 value of 20.57 nM (Figure 2B). However, neither compound degraded the EGFRWT protein in H1299, H460, and HeLa cell lines nor the EGFRL858R/T790M protein in the H1975 cell line, up to 1 μM (Figure 2C). We also compared the degradation efficacy of compound 14 and MS154 in both HCC827 and Ba/F3 cell lines. The results indicate that compound 14 showed remarkable improvements in the degradation of EGFRDel19 and EGFRL858R than MS154 (Supplementary Figure S2).
FIGURE 2
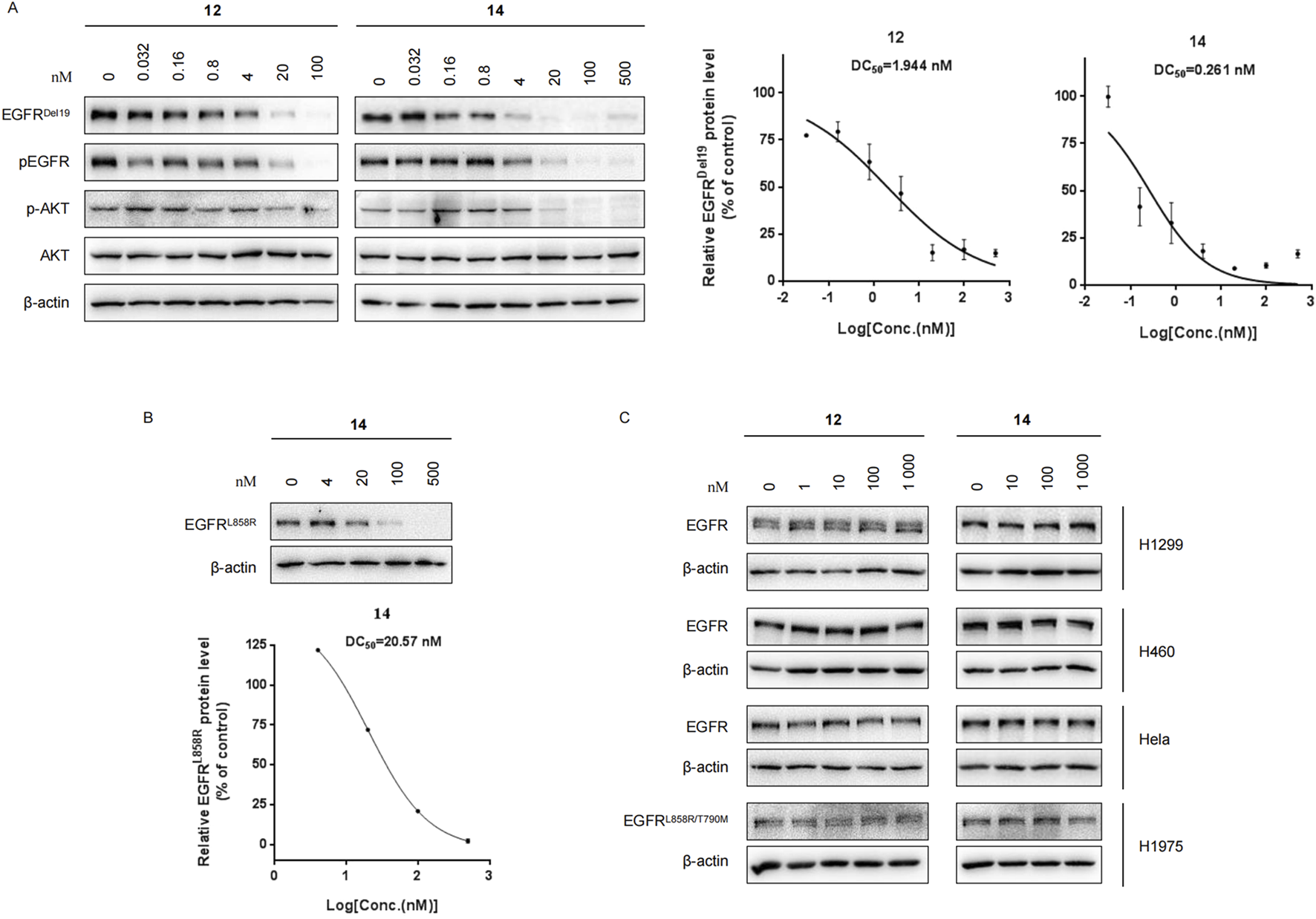
(A) Western blots of EGFRDel19, pEGFR, AKT, and pAKT in HCC827 cells with compound 12 or 14 for 24 h. The DC50 values were calculated using GraphPad Prism. (B) Western blots in Ba/F3 cells stably expressing the EGFRL858R mutant with compound 14 for 24 h. (C) Immunoblots of EGFR in H1299, H460, HeLa, and H1975 cells treated with compound 12 or 14 for 24 h.
Next, the levels of the EGFRDel19 protein in HCC827 cells incubated with compound 12 or 14 at a dose of 10 nM at multiple time points were examined (Figure 3). The degradation of EGFRDel19 could be observed as early as 2 h after treatment. Compound 14 decreased the half-life of the EGFRDel19 protein at 8.6 h and compound 12 at 6.8 h; however, compound 14 induced significantly greater degradation of EGFR, with a maximum degradation (Dmax) of 85% after 24 h of incubation (Figures 3A,B). Meanwhile, compound 14 led to more marked decreases in pEGFR and pAKT compared with compound 12. In addition, compound 14 mediated a sustained degradation of the EGFRDel19 protein over 96 h (Figure 3C). More interestingly, a reduction in the EGFRDel19 protein induced by an 8 h-incubation with 10 nM of compound 14 was constantly maintained for over 72 h, even after compound removal (Figure 3D).
FIGURE 3
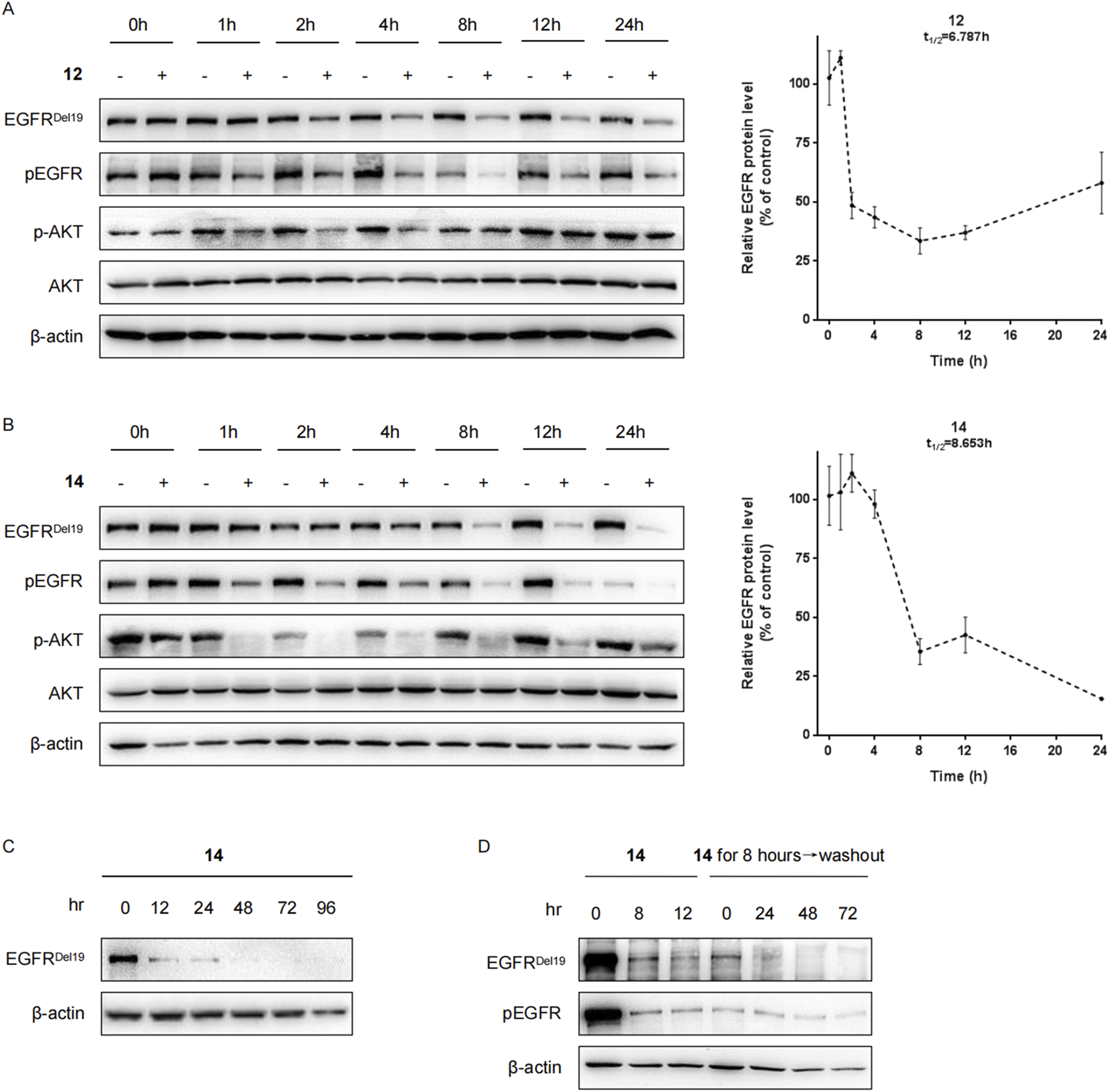
Compounds 12 and 14 time-dependently decreased the EGFR protein in HCC827 cells. (A) HCC827 cells were incubated with compound 12 (A) or 14 (B) at a final concentration of 10 nM for indicated times (1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, and 24 h). (C) HCC827 cells were incubated with compound 14 at a final concentration of 10 nM for indicated times (12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h). (D) After pretreatment for 8 h with 10 nM of compound 14, the media were washed out and replaced with fresh media without compound. After further incubation for the indicated times (24 h, 48 h, and 72 h), HCC827 cells were lysed for Western blot.
Furthermore, HCC827 cells were incubated with cycloheximide (CHX) with or without compound 14, and the levels of the EGFRDel19 protein were determined. As a result, after 4 h and 8 h of cycloheximide treatment, control DMSO-treated samples still retained approximately 70% and 55% of EGFR proteins, whereas, in the presence of compound 14, only 34.5% and 12.5% remained (Figure 4).
FIGURE 4
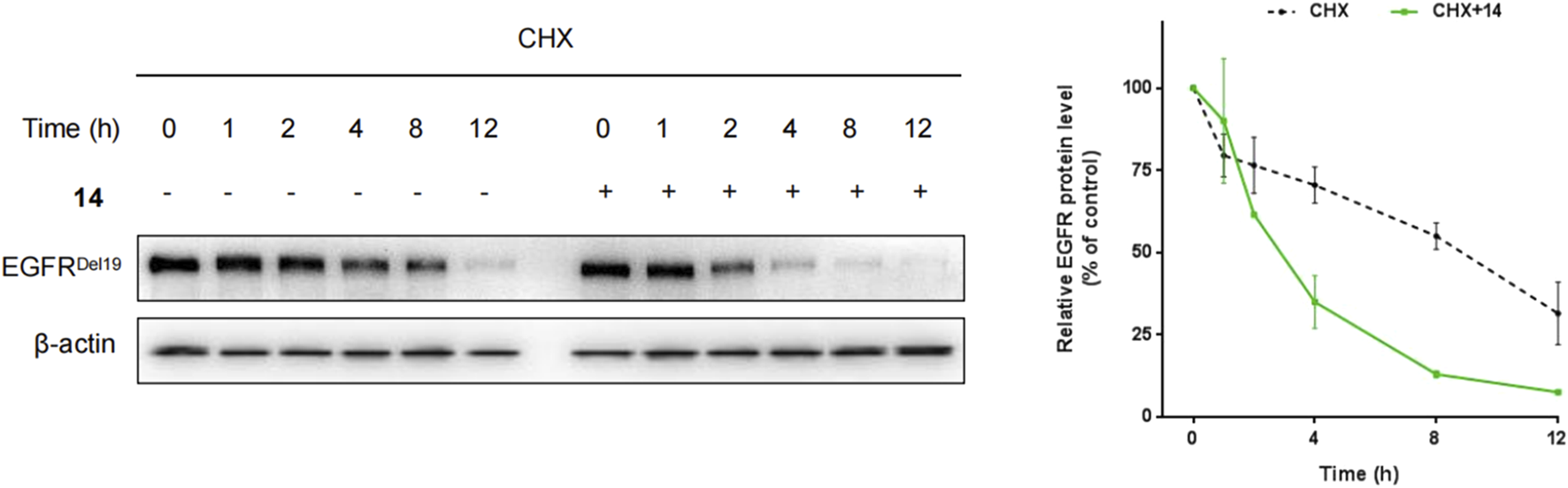
HCC827 cells were incubated with cycloheximide (100 μg/mL) only or cycloheximide (100 μg/mL) with compound 14 (10 nM) for indicated times.
Degradation of EGFRDel19 using the ubiquitination and proteasome-dependent system
To clarify whether these degradations were dependent on E3 ligase complex recruitment, HCC827 cells were pretreated with either the proteasome inhibitor MG132 or the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 for 2 h and continuously incubated with compound 14 for an additional 8 h. As shown in Figures 5A,B, both MG132 and MLN4924 restored EGFRDel19 degradation induced by compound 14, implying that EGFR degradation by compound 14 was dependent on the ubiquitination and neddylation system.
FIGURE 5
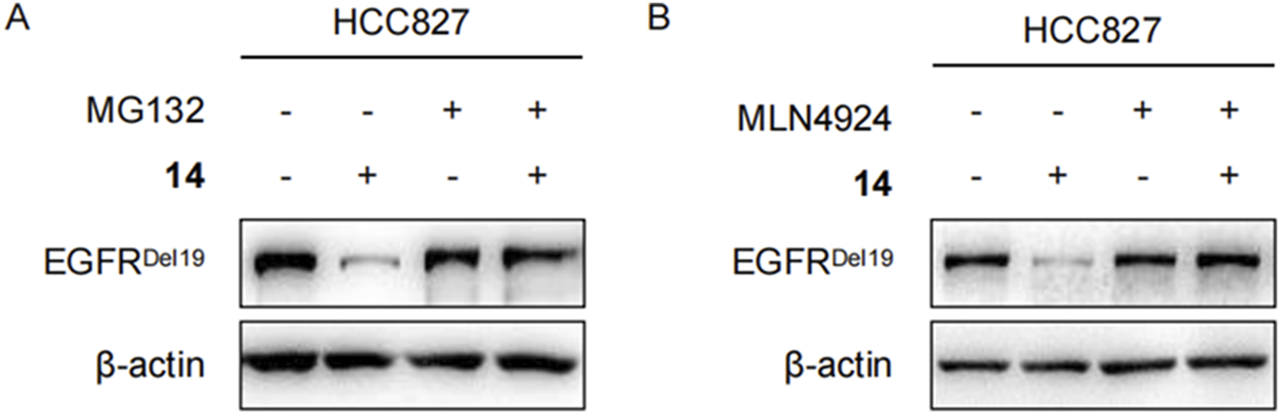
Compound 14 degraded EGFR via proteasome in HCC827 cells. Immunoblots of EGFR in HCC827 cells pretreated with DMSO, 2 μM of MG132 (A), and 5 μM of MLN4924 (B) for 2 h and then treated with 10 nM of 14 for 8 h.
Moreover, competitive binding experiments were conducted with either the CRBN ligand thalidomide (Figure 6A) or the EGFR ligand gefitinib (Figure 6B). Both thalidomide and gefitinib could completely rescue the EGFRDel19 reduction induced by compound 12 or 14 at 500 times the degrader dose, whereas a slight decrease in EGFRDel19 was still observed at 100 times the dose. These results suggested that compound 14 directly targeted EGFRDel19 and mediated EGFRDel19 degradation through the CRBN-dependent mechanism.
FIGURE 6
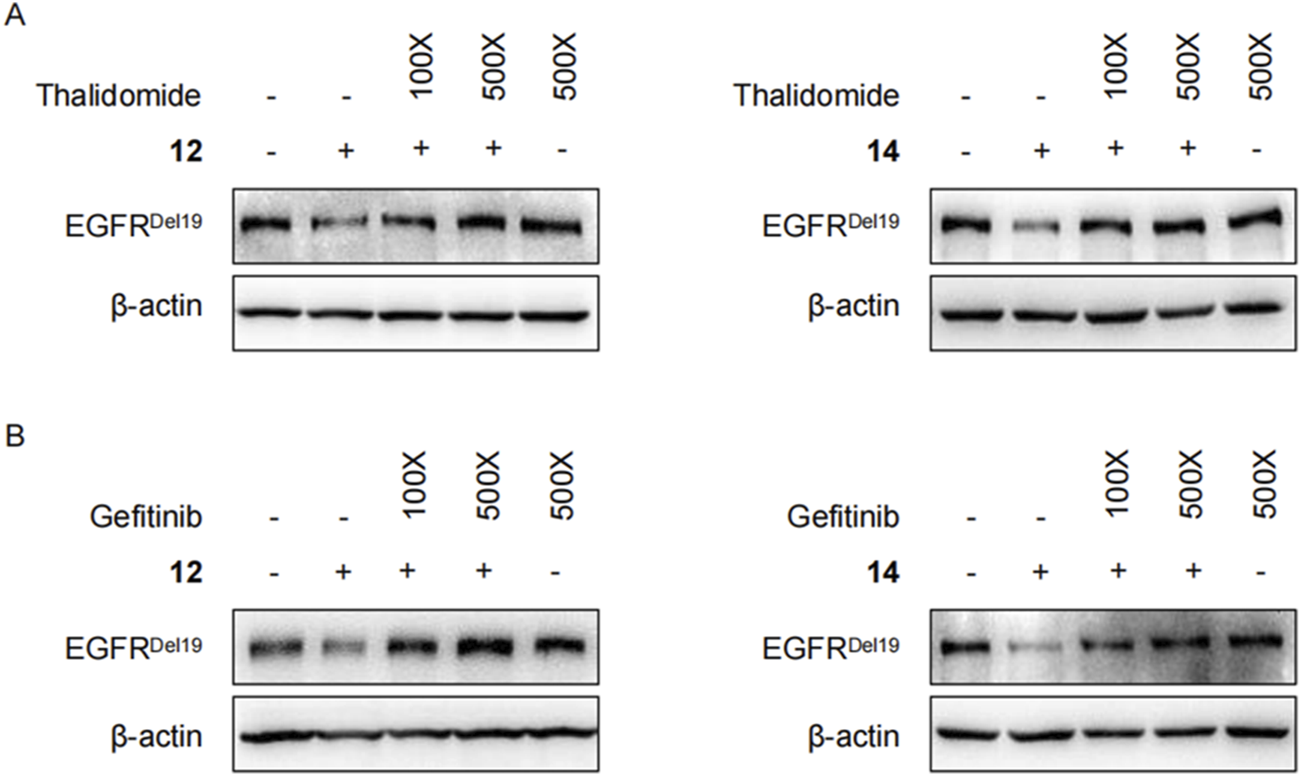
(A) Immunoblots of EGFR in HCC827 cells pretreated with thalidomide (1 μM or 5 μM) for 2 h and co-treated with 10 nM of compound 12 (left panel) or 14 (right panel) for 4 h. (B) Immunoblots of EGFR in HCC827 cells pretreated with gefitinib (1 μM or 5 μM) for 2 h and co-treated with 10 nM of compound 12 (left panel) or 14 (right panel) for 4 h.
Evaluation of cell viability of compounds
To study the biological effects of the decrease in PROTAC-mediated EGFRDel19 on cancer cell survival, HCC827 cells were treated with compound 12, compound 14, gefitinib, or thalidomide for 48 h or 96 h, and the number of viable cells was calculated using CCK-8 (Figure 7). With a 48 h-incubation, the IC50 values of compound 12, compound 14, and gefitinib were approximately 30.68 ± 6.15 nM, 8.29 ± 3.31 nM, and 4.74 ± 1.19 nM, respectively (Figure 7A). With a 96 h-incubation, the IC50 values of compound 12, compound 14, and gefitinib were approximately 25.64 ± 3.8 nM, 4.91 ± 0.78 nM, and 3.93 ± 1.4 nM, respectively (Figure 7A). In particular, compound 14 exhibited cytotoxic activity similar to that of gefitinib. Thalidomide had no influence on the viability of HCC827 cells up to 200 nM. To explore the prolonged efficacy, HCC827 cells were treated with 10 nM of compound 14 or gefitinib for 8 h, washed with PBS, and cultured with fresh media for an additional 24, 48, 72, or 96 h. Intriguingly, gefitinib-pretreated cells gradually continued to proliferate after the removal of compounds, whereas compound 14-pretreated cells almost completely stopped proliferating (Figure 7B), illustrating the distinct pharmacological mechanisms of compound 14 and gefitinib.
FIGURE 7
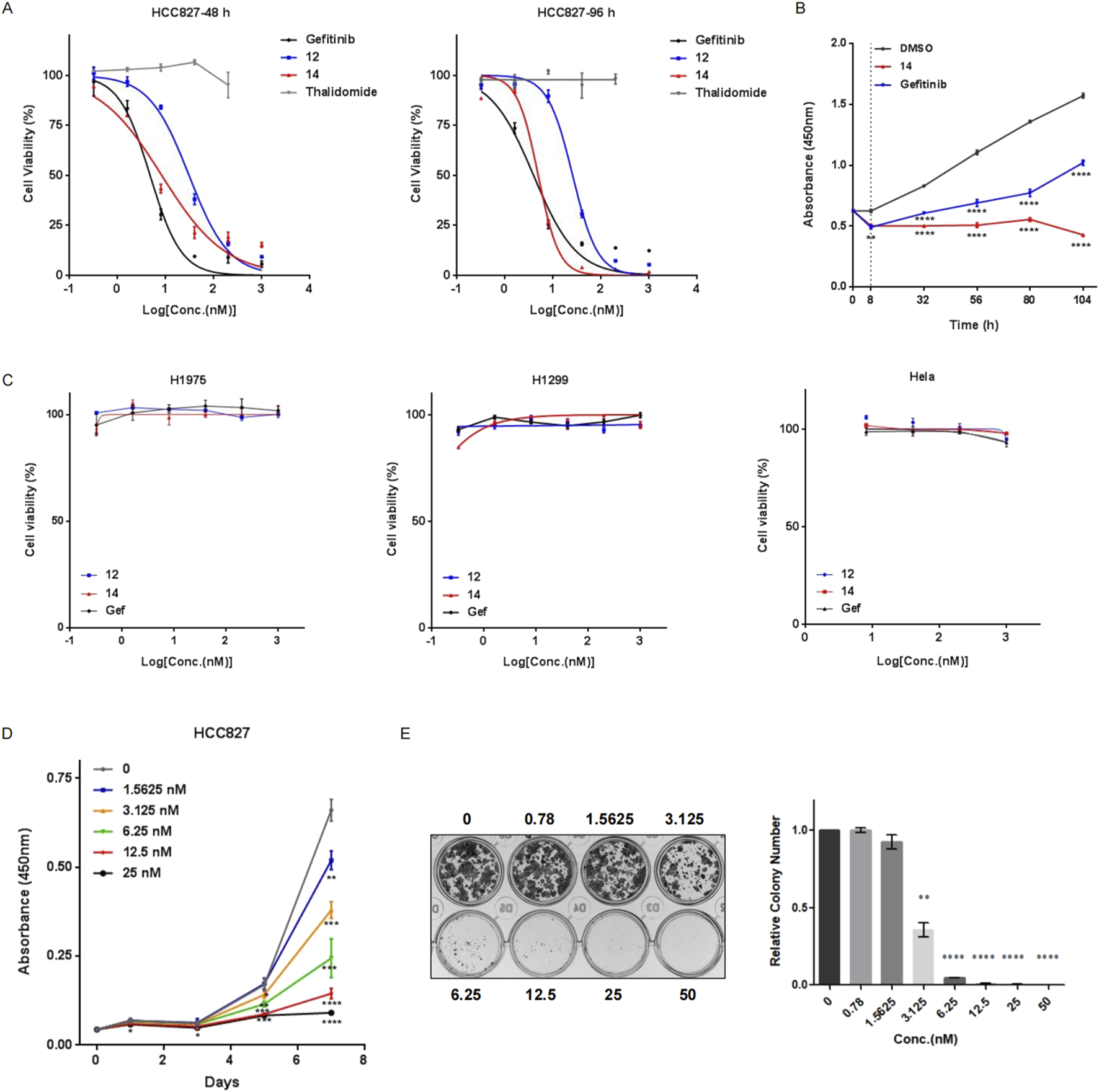
Compound 14 effectively inhibited cell viability of HCC827. (A) HCC827 cells were treated with various concentrations of compound 12, compound 14, gefitinib, or thalidomide for 48 h (left panel) or 96 h (right panel). (B) HCC827 cells were pretreated with compound 14 or gefitinib at 10 nM for 8 h, rinsed with PBS, and cultured for additional indicated times (24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h). Cell proliferation was measured using CCK-8. (C) H1975, H1299, and HeLa cells were treated with compound 12, compound 14, or gefitinib for 96 h. Proliferation (D) and colony-forming abilities (E) of HCC827 cells with different concentrations of compound 14 were examined. Results are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. p-values were calculated using the Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001)
In addition, compound 12, compound 14, and gefitinib did not affect the viability of H1299, HeLa, and H1975 cells up to 1 μM, suggesting high specificity of PROTACs toward the EGFRDel19 mutant (Figure 7C). Concordantly, compound 14 markedly attenuated the proliferation of HCC827 cells compared with control vehicle-treated cells (Figure 7D) and formed fewer and smaller colonies in HCC827 cells than the control in colony formation assays (Figure 7E).
Degradation of EGFRDel19 induces cell apoptosis in HCC827 cells
In the above study, numerous apoptotic cells were observed under the microscope following treatment with compound 14. Hence, we performed FACS analysis to further calculate the apoptotic cell population upon treatment with compound 14 or gefitinib in HCC827 cells. As expected, both gefitinib and compound 14 led to at least a two-fold increase in the number of apoptotic cells, and there was little difference between compound 14 and gefitinib (Figures 8A,B).
FIGURE 8
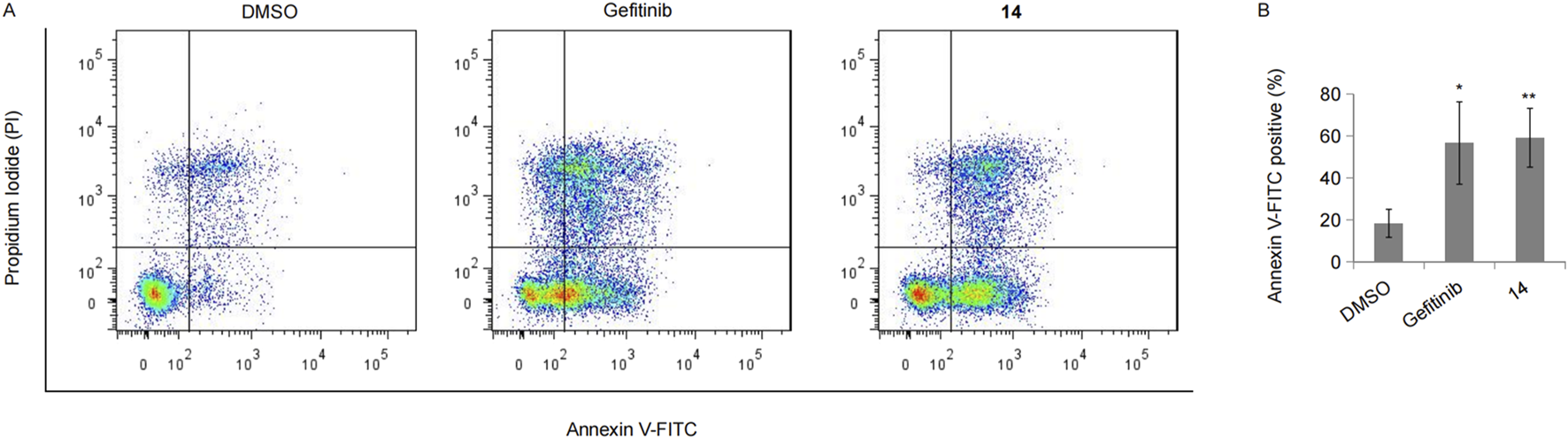
Compound 14 induced cell apoptosis. (A) HCC827 cells incubated with 10 nM of gefitinib or compound 14 for 48 h were double-stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI, and the representative result was shown. (B) The experiment was repeated three times, and data represented the average percentage of apoptotic cells (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; Student’s t-test).
In vivo anti-tumor activity of the compound
We evaluated the efficacy of compound 14 to inhibit the growth of HCC827 cells using a xenograft immunodeficient mouse model. As shown in Figure 9A, compound 14 (30 mg/kg) markedly suppressed the growth of implanted tumors. The mean volume of HCC827 tumors treated with compound 14 (56.58 ± 10.91 mm3) was noticeably decreased compared with that of control vehicle mice (350.86 ± 191.41 mm3) (Figure 9A, p < 0.05). Meanwhile, compound 14 effectively degraded the EGFRDel19 protein in vivo (Figure 9C). Furthermore, mice-bearing HCC827 xenografts were administered a one-time intraperitoneal injection of compound 14 at 30 mg/kg. Intriguingly, as shown in Figures 9D,E, one dose of compound 14 led to a mean tumor volume inhibition of 79% (P = 5.4E-05 versus vehicle control) 18 days after treatment, indicating the long-term effect for this compound. None of the mice showed signs of wasting (Figures 9B,F).
FIGURE 9
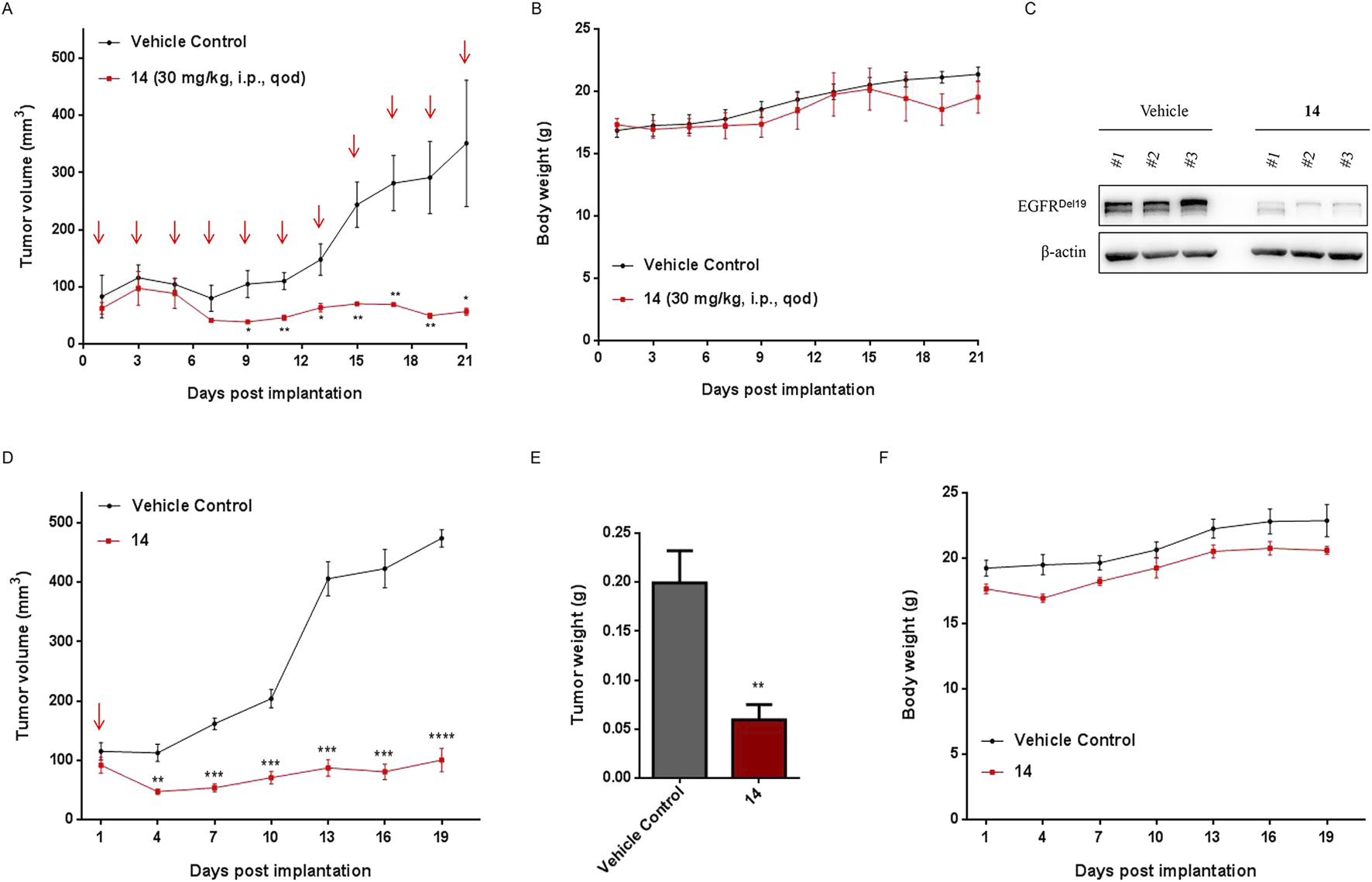
Compound 14 inhibited the growth of human tumor xenografts. Nude mice bearing established HCC827 human tumor xenograft were dosed with either vehicle or compound 14 (30 mg/kg) via an intraperitoneal injection every other day for 22 days. Tumor volumes (A) and mouse weights (B) were measured every other day and plotted against time. Each point represented the mean ± SD of three tumors. (C) The indicated proteins of dissected tumors were detected using Western blot. (D) Nude mice bearing established HCC827 human tumor xenograft were administered a one-time intraperitoneal injection of compound 14 (30 mg/kg). Tumor volumes, tumor weights (E), and mouse weights (F) were measured every 3 days and plotted against time. Each point represented the mean ± SD of three tumors. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Conclusions
In this study, a series of EGFR degraders were designed using computational methods based on gefitinib and thalidomide. Compound 14 was identified as a potent and selective degrader against both EGFRDel19 and EGFRL858R proteins, with DC50 values of 0.26 nM and 20.57 nM, respectively. No significant degradation of the wild-type EGFR was observed, even at a concentration of 1 μM. Compound 14 significantly reduced the viability of HCC827 cells while having no effect on EGFR wild-type cells, exhibiting a 96-h IC50 value of 4.91 nM, similar to the cytotoxic activity of gefitinib. Notably, cells pretreated with gefitinib showed a mild attenuation of proliferation after the compound was removed, whereas cells pretreated with compound 14 completely ceased proliferation, indicating the long-lasting effects of compound 14. The degradation of EGFRDel19 by compound 14 was confirmed to be dependent on ubiquitination and the proteasome pathway. In the HCC827 cell-derived xenograft model, compound 14 also demonstrated excellent anti-tumor efficacy in vivo. With a relatively low molecular weight of 814.32 Da and impressive in vitro and in vivo efficacy, compound 14 may serve as a lead for further development of drug-like EGFR degraders.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used. The animal study was approved by the Ethics Committee for laboratory animals, The Nanjing Han & Zaenker Cancer Institute (File number: OGKQSPF/SQ-112). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
LP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. YS: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. QL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. XY: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – original draft. WH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. WZ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review and editing. JK: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review and editing. P-CC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing – review and editing. SC: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review and editing. RK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The present study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62373172), the Youth Science and Technology Talent Program of Changzhou Health and Family Planning Commission (QN202106), the Youth Talent Development Plan of Changzhou Health Commission (CZQM2023006), and the Jiangsu Province Innovation Support Program (Soft Science Research) Special funding for research (BZ2023012).
Conflict of interest
Authors LP, YG, QL, and RK were employed by Primary Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Author JK was employed by Aqsens Health Oy.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1604661/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Bekes M. Langley D. R. Crews C. M. (2022). PROTAC targeted protein degraders: the past is prologue. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.21 (3), 181–200. 10.1038/s41573-021-00371-6
2
Bersanelli M. Minari R. Bordi P. Gnetti L. Bozzetti C. Squadrilli A. et al (2016). L718Q mutation as new mechanism of acquired resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol.11 (10), e121–e123. 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.05.019
3
Burslem G. M. Smith B. E. Lai A. C. Jaime-Figueroa S. McQuaid D. C. Bondeson D. P. et al (2018). The advantages of targeted protein degradation over inhibition: an RTK case study. Cell Chem. Biol.25 (1), 67–77. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.09.009
4
Chen K. Zhou F. Shen W. Jiang T. Wu X. Tong X. et al (2017). Novel mutations on EGFR Leu792 potentially correlate to acquired resistance to osimertinib in advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol.12 (6), e65–e68. 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.12.024
5
Cheng M. Yu X. Lu K. Xie L. Wang L. Meng F. et al (2020). Discovery of potent and selective epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) bifunctional small-molecule degraders. J. Med. Chem.63 (3), 1216–1232. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01566
6
Fischer E. S. Böhm K. Lydeard J. R. Yang H. Stadler M. B. Cavadini S. et al (2014). Structure of the DDB1-CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase in complex with thalidomide. Nature512 (7512), 49–53. 10.1038/nature13527
7
Fuchs V. Roisman L. Kian W. Daniel L. Dudnik J. Nechushtan H. et al (2021). The impact of osimertinib' line on clonal evolution in EGFRm NSCLC through NGS-based liquid biopsy and overcoming strategies for resistance. Lung Cancer153, 126–133. 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.12.039
8
Gajiwala K. S. Feng J. Ferre R. Ryan K. Brodsky O. Weinrich S. et al (2013). Insights into the aberrant activity of mutant EGFR kinase domain and drug recognition. Structure21 (2), 209–219. 10.1016/j.str.2012.11.014
9
Ignatov M. Jindal A. Kotelnikov S. Beglov D. Posternak G. Tang X. et al (2023). High accuracy prediction of PROTAC complex structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc.145 (13), 7123–7135. 10.1021/jacs.2c09387
10
Kobayashi Y. Mitsudomi T. (2016). Not all epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are created equal: perspectives for individualized treatment strategy. Cancer Sci.107 (9), 1179–1186. 10.1111/cas.12996
11
Kong R. Wang F. Zhang J. Wang F. Chang S. (2019). CoDockPP: a multistage approach for global and site-specific protein-protein docking. J. Chem. Inf. Model59 (8), 3556–3564. 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00445
12
Lai A. C. Crews C. M. (2017). Induced protein degradation: an emerging drug discovery paradigm. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.16 (2), 101–114. 10.1038/nrd.2016.211
13
Nowak R. P. DeAngelo S. L. Buckley D. He Z. Donovan K. A. An J. et al (2018). Plasticity in binding confers selectivity in ligand-induced protein degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol.14 (7), 706–714. 10.1038/s41589-018-0055-y
14
Peled N. Roisman L. C. Miron B. Pfeffer R. Lanman R. B. Ilouze M. et al (2017). Subclonal therapy by two EGFR TKIs guided by sequential plasma cell-free DNA in EGFR-mutated lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol.12 (7), e81–e84. 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.02.023
15
Pereira G. P. Jiménez-García B. Pellarin R. Launay G. Wu S. Martin J. et al (2023). Rational prediction of PROTAC-compatible protein-protein interfaces by molecular docking. J. Chem. Inf. Model63 (21), 6823–6833. 10.1021/acs.jcim.3c01154
16
Pisapia P. Rocco D. Pepe F. De Luca C. Battiloro C. Smeraglio R. et al (2019). EGFR exon 19 deletion switch and development of p.L792Q mutation as a new resistance mechanism to osimertinib: a case report and literature review. Transl. Cancer Res.8 (Suppl. 1), S64–S69. 10.21037/tcr.2018.09.13
17
Qu X. Liu H. Song X. Sun N. Zhong H. Qiu X. et al (2021). Effective degradation of EGFR(L858R+T790M) mutant proteins by CRBN-based PROTACs through both proteosome and autophagy/lysosome degradation systems. Eur. J. Med. Chem.218, 113328. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113328
18
Ribeiro J. Ríos-Vera C. Melo F. Schüller A. (2019). Calculation of accurate interatomic contact surface areas for the quantitative analysis of non-bonded molecular interactions. Bioinformatics35 (18), 3499–3501. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz062
19
Shi S. Du Y. Huang L. Cui J. Niu J. Xu Y. et al (2022). Discovery of novel potent covalent inhibitor-based EGFR degrader with excellent in vivo efficacy. Bioorg Chem.120, 105605. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105605
20
Soria J. C. Ohe Y. Vansteenkiste J. Reungwetwattana T. Chewaskulyong B. Lee K. H. et al (2018). Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.378 (2), 113–125. 10.1056/NEJMoa1713137
21
Thress K. S. Paweletz C. P. Felip E. Cho B. C. Stetson D. Dougherty B. et al (2015). Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat. Med.21 (6), 560–562. 10.1038/nm.3854
22
Westover D. Zugazagoitia J. Cho B. C. Lovly C. M. Paz-Ares L. (2018). Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann. Oncol.29 (Suppl. l_1), i10–i19. 10.1093/annonc/mdx703
23
Zaidman D. Prilusky J. London N. (2020). PRosettaC: Rosetta based modeling of PROTAC mediated ternary complexes. J. Chem. Inf. Model60 (10), 4894–4903. 10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00589
24
Zhang H. Zhao H. Y. Xi X. X. Liu Y. J. Xin M. Mao S. et al (2020). Discovery of potent epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) degraders by proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC). Eur. J. Med. Chem.189, 112061. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112061
25
Zhao H. Y. Yang X. Y. Lei H. Xi X. X. Lu S. M. Zhang J. J. et al (2020). Discovery of potent small molecule PROTACs targeting mutant EGFR. Eur. J. Med. Chem.208, 112781. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112781
26
Zhao H. Y. Wang H. P. Mao Y. Z. Zhang H. Xin M. Xi X. X. et al (2022). Discovery of potent PROTACs targeting EGFR mutants through the optimization of covalent EGFR ligands. J. Med. Chem.65 (6), 4709–4726. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01827
27
Zheng D. Hu M. Bai Y. Zhu X. Lu X. Wu C. et al (2017). EGFR G796D mutation mediates resistance to osimertinib. Oncotarget8 (30), 49671–49679. 10.18632/oncotarget.17913
Summary
Keywords
EGFRDe19, epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFRL858R, non-small-cell lung cancer, proteolysis-targeting chimeras, molecular docking
Citation
Piao L, Gao Y, Su Y, Li Q, Yuan X, He W, Zhao W, Kulpakko J, Cha P-C, Chang S and Kong R (2025) Targeted degradation of EGFR 19Del by PROTACs suppresses tumor growth in non-small-cell lung cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1604661. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1604661
Received
02 April 2025
Accepted
29 September 2025
Published
24 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Dongwen Lyu, Augusta University, United States
Reviewed by
Yufeng Xiao, University of Florida, United States
Zhengyu Wang, The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Piao, Gao, Su, Li, Yuan, He, Zhao, Kulpakko, Cha, Chang and Kong.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ren Kong, rkong@jsut.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.