- 1Institute of Vascular Disease, Shanghai TCM-Integrated Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
Thromboembolism is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Current methods of treating thromboembolism include anticoagulant therapy, thrombolytic therapy, and surgical removal of the thrombus. All of these treatments have some drawbacks, such as an increased risk of bleeding, limitation to fresh thrombus, and a high recurrence rate. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find effective and safe drugs for the treatment of thromboembolism. In recent years, it has been found that many natural active herbal monomers exhibit distinct advantages in treating this condition. In this review, the therapeutic effects of effective active monomers from natural herbs on thromboembolism, including flavonoids, polyphenols, alkaloids, terpenoids, saponins, and organic acids, were described. Furthermore, their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, inhibition of platelet aggregation and antithrombotic effects through nuclear factor NF-κB, ERK1/2, PI3K, Akt and other signaling pathways were systematically summarized. Altogether, this review provides a comprehensive summary of promising therapeutic candidate drugs for the treatment of thromboembolic diseases and aims to guide future preclinical and clinical research for novel, safe and effective antithrombotic therapies.
1 Introduction
Thromboembolic diseases refer to a series of diseases caused by vascular obstruction due to thrombosis or thrombus embolization, such as ischemic stroke, acute myocardial infarction, and deep vein thrombosis. The American Society of Hematology reports that VTE occurs in 1–2 individuals per 1,000 each year, or ∼300,000 to 600,000 events in the United States annually (Ortel et al., 2020), and acute venous and arterial thromboses account for the most common causes of death in developed countries (Ashorobi et al., 2025).
Current treatments for thromboembolism include anticoagulant therapy, thrombolytic therapy, mechanical thrombectomy, inferior vena cava filter placement, and other methods for treating thrombus (Sagris et al., 2022). However, all of these treatments have some drawbacks. Conventional antithrombotic therapy is primarily based on three classes of drugs: anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and thrombolytics. Anticoagulants, such as the vitamin K antagonist warfarin, heparins, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) that inhibit Factor Xa or thrombin, are effective in preventing further expansion and propagation of the thrombus but carry a significant bleeding risk, require monitoring, and show a limited effect on the dissolution of thrombi that have already formed (Helin et al., 2019; Gailani and Gruber, 2024). Thrombolytic drugs such as recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA) can rapidly dissolve thrombi but are limited to the acute phase of thrombosis (fresh thrombus formed within 3–4.5 h). Their short therapeutic window, high risk of bleeding complications, and limited patient suitability further restrict their use (Montalvan Ayala et al., 2022; Khedr et al., 2023). Surgical mechanical debridement and inferior vena cava filter placement can remove thrombus directly through catheters, but they are invasive, costly, and only suitable for large vessel obstructions due to the risks of infection or vascular damage (Goldhaber et al., 2021). Notably, a major limitation of these synthetic drugs is that they typically target a single molecule or pathway, which, while potent, contributes to their narrow therapeutic index and risk of side effects. Therefore, the search for new drugs for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic diseases is urgent and necessary (Kim et al., 2021). Many natural herbal monomers, as reviewed herein, exhibit a multi-target approach (Mu et al., 2023; Yin et al., 2023). These natural compounds can simultaneously exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiplatelet, and anticoagulant effects, potentially offering a broader therapeutic window and a more favorable safety profile by modulating the entire thrombotic milieu rather than a single step. This review, therefore, aims to systematically evaluate these natural compounds to highlight their mechanisms in comparison to conventional therapies and identify promising candidates for future drug development.
An increasing number of studies have found that natural medicinal plants and their active monomers are widely used in a variety of diseases and have strong therapeutic potential. The efficacy of natural active herbal monomers in the treatment of thromboembolism is remarkable, effectively avoiding toxic side effects, reducing recurrence rates and improving the prognosis. Natural products have always been the cornerstone of modern drug discovery, providing lead compounds for many first-line clinical drugs (Newman and Cragg, 2020). Faced with the limitations of existing antithrombotic drugs, the search for new active monomers from medicinal herbs represents a promising frontier. However, despite numerous preclinical studies, translating these findings into clinical applications remains a challenge. Therefore, a systematic review of preclinical evidence is crucial for identifying the most promising drug candidates, elucidating their mechanisms of action, and providing a solid foundation for designing rigorous clinical trials in the future. Hence, the therapeutic effects of effective active monomers of natural herbal on thromboembolism, the molecular mechanisms and the research progress of related targets are reviewed. Therefore, this review aims to provide a scientific basis for the rational development of natural herbal monomers as complementary or alternative therapies, and to promote their translation from basic research to future clinical applications.
2 Natural herbal agents with effects on thromboembolism
Natural active herbal monomers mainly include flavonoids, polyphenols, terpenoids, alkaloids, saponins and organic acids (The chemical structure and molecular formula of representative compounds were shown in Figure 1; Table 1) which have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiplatelet and antithrombotic effects and are considered as potential drugs for the treatment of thromboembolic diseases (Mu et al., 2023; Yin et al., 2023).
2.1 Flavonoids
Flavonoids have a basic structural unit of 2-phenylchromone, including puerarin, quercetin, baicalein, baicalin, luteolin, kaempferol, naringenin, anthocyanins, apigenin and breviscapine, with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial effects, cardiovascular protection and thrombosis prevention (Chen et al., 2023).
2.1.1 Puerarin
Puerarin is an isoflavone isolated from the roots of Pueraria lobata, which has a variety of pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, inhibition of apoptosis (Jiang et al., 2022). A previous study found that in vitro puerarin and its metabolite daidzein inhibited adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and collagen-induced platelet aggregation, thereby exerting antithrombotic effects (as shown in Table 2) (Choo et al., 2002). A recent study found that in vitro pretreatment of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with puerarin for 1 h significantly attenuated oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) induced tissue factor (TF) expression, enhanced protein kinase B (Akt) phosphorylation and nitric oxide (NO) production, and inhibited extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and nuclear factor Kappa B (NF-κB) activation, suggesting that puerarin has anticoagulant effects and is a potential drug for coronary artery disease and thrombosis prevention (Deng et al., 2017). It has also been shown that Gegen Qinlian pills (the main ingredient is Pueraria lobata, each gram of Gegen Qinlian pills contains 2.78 mg of pueraria lobata) through modulation of the HMGB1/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway decreased tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in plasma and high mobility group protein 1 (HMGB1) in lung tissue, and thereby inhibiting carrageenan induceed pulmonary, hepatic, and caudal thrombosis and increased caudal blood flow (Wei et al., 2022).
2.1.2 Quercetin
Quercetin, a flavonoid widely distributed in nature and the human diet and particularly abundant in onions, exhibits potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant bioactivities (Singh et al., 2021; Qi et al., 2022). It has been shown that quercetin inhibited thrombin and coagulation factor Xa (FXa) activity in a thrombin-induced acute thromboembolism model in mice, thereby inhibiting thrombus formation (Choi et al., 2016). It has also been shown that quercetin inhibited ferric chloride (FeCl3)-induced carotid artery thrombosis in mice, and inhibited platelet aggregation and platelet dense granule secretion, improved carotid blood flow, and thus exerted antiplatelet and thrombopreventive effects (Mosawy et al., 2013; Oh et al., 2021). It was found that quercetin and two of its methylated metabolites, isorhamnetin and tamarixetin, inhibited arterial thrombosis caused by laser injury in mice and interacted with aspirin to enhance antiplatelet effects (as shown in Table 2) (Stainer et al., 2019). A clinical trial reported that isoquercetin at a dose of 1 g day-1 for 56 days significantly reduced D-dimer, P-selectin, and platelet-dependent fibrin production in cancer patients compared to placebo, suggesting that supplementation with isoquercetin prevents hypercoagulability and thrombosis in cancer patients (Manjunath and Thimmulappa, 2022). A multicenter, double-blind phase Ⅲ trial is now evaluating isoquercetin 1 g day-1 for primary VTE prophylaxis in metastatic pancreatic cancer (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06861088, accessed 9 July 2025). Consistent benefits were already reported in the CATIQ phase Ⅱ study, where isoquercetin 1,000 mg day-1 reduced D-dimer and platelet-dependent fibrin formation across 72 patients with advanced solid tumours (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02195232).
2.1.3 Baicalein and baicalin
Baicalein and baicalin are typical flavonoids extracted from the plant Scutellaria baicalensis, which have a variety of medicinal properties such as anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antibacterial and hypoglycemic effects (Zhao et al., 2022). It was shown that a deep vein thrombosis model was prepared by incompletely ligating the inferior vena cava (IVC) of rats, and baicalein was found to inhibit thrombosis by promoting the migration of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and angiogenesis through SIRT1/NF-κB signaling (Xie et al., 2025). It was found that baicalin inhibited FeCl3-induced arterial thrombosis, significantly prolonged the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and plasminogen time (PT), decreased the ratio of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 to tissue-type plasminogen activator (PAI-1/t-PA), and inhibited the activities of thrombin and coagulation factor FXa, inhibited thrombin-catalyzed fibrin polymerization and platelet function, thereby exerting antithrombotic effects (as shown in Table 2) (Lee et al., 2015).
2.1.4 Luteolin
Luteolin is a flavonoid polyphenolic compound that are widely found in fruits, vegetables, flowers and herbs such as honeysuckle and Perilla, and exhibit a variety of pharmacological activities including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antitumor activities (Zhu et al., 2024). It was shown that luteolin exhibited potent antithrombotic activity by inhibiting IgG-like receptor glycoprotein VI (GPVI) and thereby inhibiting FeCl3-induced mesenteric artery thrombosis, inhibiting collagen and convulxin-induced platelet aggregation and adhesion, and decreasing oxidative stress (Ye et al., 2023). It has also been shown that luteolin inhibited FeCl3-induced carotid artery thrombosis, suppressed oxidative stress, inhibited thrombin activity, prolonged APTT and PT, and reduced thrombosis (as shown in Table 2) (Choi et al., 2015a).
2.1.5 Kaempferol
Kaempferol is a flavonoid found in the tea plant (Camelia sinensis) with pharmacological activities such as hepatoprotective, antibacterial and antidiabetic properties (Periferakis et al., 2022). It was shown that kaempferol inhibited thrombus formation in three animal models of thrombosis (collagen-adrenaline and thrombin-induced acute thromboembolism model and FeCl3-induced carotid artery thrombosis model) and significantly suppressed the activity of prothrombin and coagulation factor FXa and inhibited the formation of fibrin polymers (Choi et al., 2015b). It has also been shown that kaempferol reduced cerebral infarct size and promoted neovascularization and vascular remodeling in a rat cerebral thrombotic stroke model through the HIF-1α/VEGF-A/Notch1 pathway, suggesting that kaempferol has therapeutic potential for the treatment of ischemic stroke (Zhang et al., 2025). In addition, it was found that kaempferol inhibited collagen-induced platelet activation, aggregation and adhesion by inhibiting nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase and protecting src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 (SHP-2) from oxidative inactivation in vitro, suggesting that kaempferol has therapeutic potential for the prevention and treatment of thrombosis and cardiovascular diseases (as shown in Table 2) (Wang et al., 2015).
2.1.6 Naringenin
Naringenin belongs to the polyphenol flavanone family, mainly found in citrus fruits such as grapefruit and medicinal plants, with bioactivities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective and anti-cancer properties (Motallebi et al., 2022). It was reported that naringin was found to inhibit FeCl3-induced carotid artery thrombosis in rats by inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and cyclic nucleotide signaling, without affecting bleeding time. In addition, it was found that naringenin dose-dependently inhibited ADP induced platelet aggregation and adhesion, and inhibited platelet α-granule secretion, fibrinogen binding, and intracellular calcium mobilization in vitro, indicating that naringin has antithrombotic effects (as shown in Table 2) (Huang et al., 2021).
2.1.7 Anthocyanin
Anthocyanins are a class of water-soluble flavonoids, widely found in food and plants, such as red cabbage microgreen, blueberry, blackcurrant, mulberry, cherry, black elderberry, black soybean, chokeberry and jaboticaba peel, which have been shown to improve cardiovascular disease and cognitive ability, and prevent neurodegenerative diseases (Mattioli et al., 2020; Avula et al., 2023). A clinical study showed that 320 mg of anthocyanins daily for 28 consecutive days significantly inhibited ADP-induced platelet aggregation and reduced the risk of thrombosis by lowering mean platelet volume (MPV), mean cellular hemoglobin (MCH) and fibrinogen levels in healthy subjects compared with placebo controls (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: ACTRN12615000293561) (Gaiz et al., 2022). In another clinical study, a patient with metabolic syndrome (MetS) took 320 mg of anthocyanins twice daily for 28 consecutive days. It turns out that in comparison with the placebo control group, his fasting blood glucose, triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were reduced, and the ADP-induced platelet activation and p-selectin levels were inhibited, thereby decreasing cardiovascular risk factors and reducing thrombogenicity in a MetS population (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: ACTRN12615000293561) (Aboonabi et al., 2020).
2.1.8 Apigenin
Apigenin is a natural flavonoid, and present principally as glycosylated in significant amount in vegetables (parsley, celery, onions) fruits (oranges), herbs (chamomile, thyme, oregano, basil), and plant-based beverages (tea, beer, and wine), with a variety of biological activities including anti-inflammatory, antiviral and anticancer properties (Liu et al., 2024). It was reported that apigenin inhibited thrombosis by repressing arachidonic acid (AA) metabolism, thereby inhibiting collagen-induced platelet aggregation and adhesion. Furthermore, apigenin was found to enhance the effect of aspirin on platelet aggregation (Navarro-Nunez et al., 2008).
2.1.9 Breviscapine
Breviscapine is a flavonoid compound extracted from Erigeron breviscapus, a plant of the Asteraceae family, which has the effects of increasing blood flow, improving microcirculation, dilating blood vessels, reducing blood viscosity, promoting fibrinolysis, inhibiting platelet aggregation and thrombosis, etc. (Wen et al., 2021). It was shown that breviscapine exerted its anticoagulant effect by reducing clotting time (CT) and prothrombin time (PT), inhibiting platelet factor III (PF3) activity, and decreasing euglobulin cleavage time (ELT) (Wang et al., 2003).
2.2 Polyphenols
The central feature of polyphenols is the presence of one or more benzene rings (aromatic rings) and hydroxyl groups attached to the benzene rings. Polyphenols include curcumin, epicatechin, paeonol, resveratrol, magnolol and honokiol, which have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties.
2.2.1 Curcumin
Curcumin, derived from the rhizome of the spice turmeric (Curcuma longa L.), is a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, thromboprophylactic, and cardiovascular protective properties (Keihanian et al., 2018; Abd El-Hack et al., 2021). A previous study reported that curcumin promoted venous thrombus resolution in mice by modulating the miR-499-mediated PTEN/VEGF/Ang-1 signaling pathway (Wang T. et al., 2021). Curcumin was found to reduce miR-21 expression by down-regulating specificity protein 1 (Sp1) and up-regulating phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, decreasing inflammatory factors and lung thrombus volume in an acute pulmonary embolism model in rats, thereby alleviating pulmonary thromboembolism (Liang et al., 2021). It has also been shown that curcumin reduced cerebral infarct volume and edema volume and increased glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) levels in a dose-dependent manner in a rat thromboembolic stroke model, thereby ameliorating cerebral embolism and protecting cerebral nerves (as shown in Table 3) (Dohare et al., 2008). Other studies also found that curcumin inhibited GPVI-mediated platelet activation by inhibiting spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) and phospholipase Cγ2 (PLCγ2) enzyme activities in vitro (Mayanglambam et al., 2010).
2.2.2 Epicatechin
Epicatechin is derived from the herb catechu (Acacia catechu (L. f.) Willd.) and is a flavanol compound (Si et al., 2021). A study found that epicatechin inhibited platelet aggregation induced by ADP, thrombin, epinephrine, and collagen, and reduced clot lysis time (CLT) in vitro, indicating that epicatechin may have anticoagulant and cardiovascular preventive effects (Sinegre et al., 2019). Other studies have found that epigallocatechin-3-gallate promotes deep vein thrombosis resolution by regulating EPCs iron death via the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway (as shown in Table 3) (Li et al., 2025).
2.2.3 Paeonol
Paeonol is a natural active compound extracted from the root bark of peony (Paeonia suffruticosa), which has anti-inflammatory, prevention of cardiovascular disease, neuroprotective effects as well as other bioactive properties (Zhang L. et al., 2019). It was shown that paeonol promoted thrombus resolution by up-regulating the levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and increasing the expression level of vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF165) (Ye et al., 2016). It has also been found that paeonol combined with, geranylgeranyl-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural inhibited the inflammatory response, the coagulation cascade, and thus thrombosis in the AA-induced thrombus model in zebrafish, and the antithrombotic activity was most pronounced when the ratio was 4:3:3, indicating powerful prophylactic effect against thrombus (as shown in Table 3) (Lin et al., 2024).
2.2.4 Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a phenolic substance isolated from Veratrum grandiflorum, which has cardiovascular disease prevention, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-aging properties (Breuss et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2021). It was found that resveratrol inhibited inflammatory responses and thrombosis through inhibition of the HIF-1α/NLRP3 pathway in the model of stagnant deep vein thrombosis prepared by complete IVC ligation in rats (Fei et al., 2022). Similarly, in another study, resveratrol was found to improve EPCs function and promote venous thrombus resolution by upregulating adhesion plaque kinase (FAK) and inhibiting miR-138 in mice (Zhang et al., 2018). It was also found that resveratrol promoted neovascularization through inhibition of miR-542-3p and upregulation of angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) in rats, thereby promoting venous thrombus resolution (as shown in Table 3) (Lu et al., 2019). In brief, resveratrol not only prevented thrombosis but also promoted venous thrombus resolution.
2.2.5 Magnolol and honokiol
Magnolol and honokiol are natural phenolic lignans isolated from Magnolia officinalis, which has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, neuroprotective, and cardiovascular protective effects (Zhang J. et al., 2019). It was reported that magnolol exerted cardiovascular modulatory effects especially strong therapeutic potential against atherosclerosis, thrombosis, hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy (Yuan et al., 2020). It was shown that magnolol inhibited platelet aggregation induced by collagen, AA, and thrombin, and suppressed the expression of thromboxane B2 (TXB2) and intracellular calcium mobilization, thereby exerting an antiplatelet effect (Teng et al., 1988). It was found that honokiol decreased electric current induced carotid thrombosis model in rats by upregulation of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha (6-keto-PGF1α). In a mouse model of mesenteric microvessel thrombosis induced by fluorescein sodium, honokiol downregulated Ca2+ mobilization and phosphorylation of LYN proto-oncogene (Lyn), PLCγ2, protein kinase C alpha (PKCα), mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPKs) and Akt to inhibite thrombosis (as shown in Table 3) (Lee et al., 2017).
2.3 Alkaloids
The core feature of alkaloids is the nitrogenous heterocyclic structure. Alkaloids include berberine, capsaicin, and ligustrazine, with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, anticancer and other pharmacological activities.
2.3.1 Berberine
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from the Chinese herb Coptis chinensis Franch and other berberis plants, which is used in the treatment of many diseases such as cancer and digestive, metabolic, cardiovascular, and neurological diseases (Song et al., 2020). It was also found that berberine inhibited FeCl3-induced carotid thrombosis by inhibiting pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme 2 (PKM2) to activate the t-PA-induced fibrinolytic system (Sun et al., 2024). Similarly, berberine inhibited ADP-induced platelet activation and keratin-induced thrombosis in mice by inhibiting the PI3Kβ/Rasa3/Rap1 pathway (Wang C. et al., 2021). In addition, integrated metabolomics and molecular docking revealed that berberine, the major metabolite of berberine in vivo, inhibited keratine-induced thrombosis in the tail of mice by modulating the catalytic cycle of vitamin K (Wang et al., 2023). It was also shown that berberine inhibited thrombosis induced by intraperitoneal injection of carrageenan by promoting the degradation of phenylacetic acid through modulation of the intestinal flora (as shown in Table 4) (Zhang H. J. et al., 2024). Berberine inhibited FeCl3-induced carotid artery thrombosis by increasing Genus Lactobacillus levels, remodeling the intestinal microbiota, and inhibiting trimethylamine N-oxide generation (Xie et al., 2021). Furthermore, the APLABE-PCI study is prospectively assessing whether adjunctive berberine (0.3–0.6 g day-1) enhances platelet inhibition in patients receiving dual antiplatelet therapy post-PCI (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03378934).
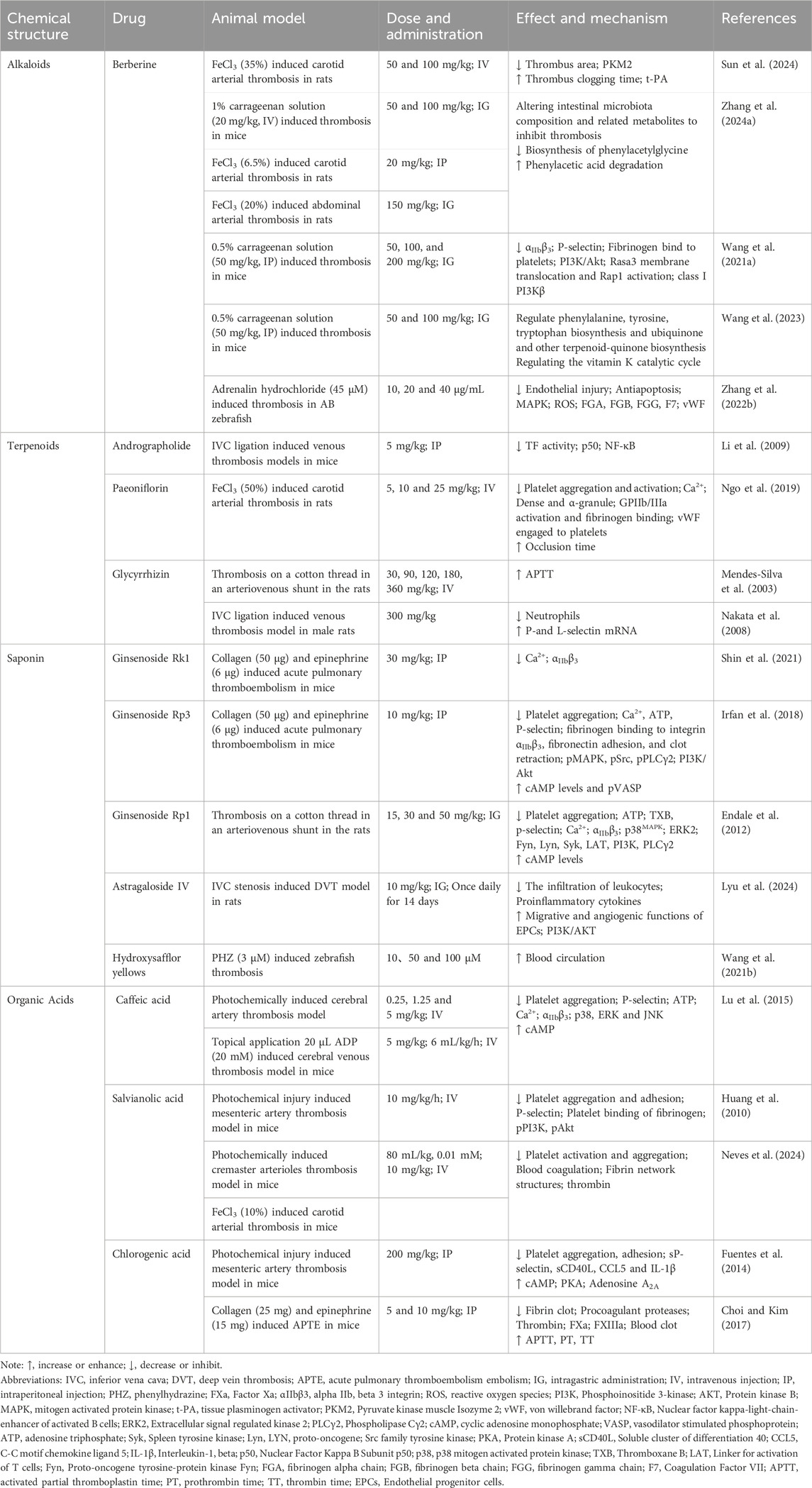
Table 4. Alkaloids, terpenoids, saponin and organic acids are used in the treatment of thromboembolism.
2.3.2 Capsaicin
Capsaicin, also known as capsaicin, is a vanillylamide alkaloid derived from plants of the genus Capsicum, with antioxidant, antitumor, antiulcer and analgesic effects (Wang Y. et al., 2021; Zhang W. et al., 2024). Capsaicin has been found to inhibit the formation of collagen fibers, which may inhibit blood clot formation (Perumal et al., 2015). Capsaicin was found to reduce mortality in acute pulmonary thromboembolism models prepared using ADP-induced mice and thromboembolism models prepared using collagen and sodium AA. Moreover, in vitro experiments revealed that capsaicin significantly inhibited platelet aggregation. In addition, capsaicin inhibited thrombosis more strongly than aspirin and indomethacin (Wang et al., 1985). In short, capsaicin exhibited antithrombotic effects by inhibiting platelet aggregation and collagen fibers.
2.3.3 Ligustrazine
Ligustrazine, also known as tetramethylpyrazine, is an alkaloid extracted from the Chinese medicine Ligusticum chuanxiong with pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties (Lin et al., 2022). It has been shown that tetramethylpyrazine inhibited ADP-induced platelet aggregation, reduced P-selectin secretion and glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa expression, and decreased the release of inflammatory mediators soluble cluster of differentiation 40 (sCD40L) and Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) by stimulating the production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), the phosphorylation of vasodilator-stimulated phosphorylated protein ser157 (VASPser157), and the dephosphorylation of Akt, indicating that tetramethylpyrazine has antiplatelet and thrombotic diseases prevention effects (Guan et al., 2022). Tetramethylpyrazine was found to protect endothelial cells and inhibit adrenaline-induced thrombosis in zebrafish by activating the MAPK signaling pathway, attenuating oxidative stress, and resisting cell apoptosis (Zhang Y. et al., 2022). In brief, ligustrazine prevented thrombosis by inhibiting platelet aggregation and protecting endothelial cells.
2.4 Terpenoids
Terpenoids are isoprene-based natural products with fundamental roles in the metabolism of all organisms, including andrographolide, paeoniflorin, tanshinone and glycyrrhizin (Bergman et al., 2019).
2.4.1 Andrographolide
Andrographolide is a diterpenoid extracted from Andrographis paniculata with pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, and antihyperglycemia (Li et al., 2022; Zeng et al., 2022). Andrographolide was found to inhibit p50 and TF expression in a mouse deep vein thrombosis model prepared by complete IVC ligation, thereby inhibiting thrombosis (as shown in Table 4) (Li et al., 2009). It was also shown that andrographolide inhibited thrombin-induced platelet aggregation by inhibiting the ERK1/2 pathway in a concentration- and time-dependent manner in vitro, indicating that andrographolide has antiplatelet effects and may prevent thrombosis-related diseases (Thisoda et al., 2006).
2.4.2 Paeoniflorin
Paeoniflorin is a water-soluble monoterpene glucoside extracted from the root of the plant Paeonia lactiflora, with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects (Zhang and Wei, 2020; Zhang X. X. et al., 2022). It was shown that paeoniflorin inhibited shear stress-induced platelet aggregation and FeCl3-induced carotid artery thrombosis by inhibiting vascular hemophilic factor (vWF)-platelet glycoprotein Ib (GPIb) interaction (Ngo et al., 2019). It has also been shown that in a deep vein thrombosis model prepared by incomplete IVC ligation in rats, an aqueous extract of Paeonia lactiflora, the main component of which is paeoniflorin, inhibited inflammation by suppressing glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) activity, thereby inhibiting thrombosis (as shown in Table 4) (Lu et al., 2021). In brief, paeoniflorin exerted antithrombotic effects through antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory pathways.
2.4.3 Tanshinone
Tanshinone is a lipophilic diterpene isolated from the rhizome of Salvia miltiorrhiza, which possesses a variety of pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiapoptosis (Subedi and Gaire, 2021). Tanshinone IIA was shown to prevent thrombosis by inhibiting platelet activation through downregulation of CD36 and MKK4/JNK2 signaling pathways (Wang et al., 2020). It was found that tanshinone inhibited thrombin-induced platelet activation, aggregation, and adhesion through downregulation of the Akt/ERK and cSrc/RhoA pathways in vitro. Moreover, it was found that tanshinone inhibited the carotid thrombosis induced by FeCl3 in vivo, indicating that tanshinone had antithrombotic activity (Zhang Y. et al., 2024).
2.4.4 Glycyrrhizin
Glycyrrhizin is an oleanane-type pentacyclic triterpenoid compound extracted from the roots and stems of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch, a leguminous plant, which is known for its antiviral, immunomodulatory, and hepatoprotective effects (Mou et al., 2024). A previous study found that glycyrrhizin could exert antithrombotic effects by inhibiting the activity of thrombin (Mendes-Silva et al., 2003). In another study, glycyrrhizin was found to inhibit venous thrombosis by inhibiting the adhesion of neutrophils to the venous endothelium in a rat deep vein thrombosis model prepared by ligating the IVC (as shown in Table 4) (Nakata et al., 2008).
2.5 Saponin
Saponins are compounds consisting of glycosides (ligands) and sugar chains linked by glycosidic bonds, and are natural products from a wide range of sources, with pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, and antithrombotic (Reichert et al., 2019).
2.5.1 Ginsenosides
Ginsenoside is the main active ingredient of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius and Panax notoginseng, belonging to the triterpenoid saponin class of compounds, with more than 40 components, including Rg (protopanaxatriol (PPT)-type within Rg-series), Rb (protopanaxadiol (PPD)-type, Rb-series), and Rh (low-glycosylated Rb-metabolite), according to their aglycone skeleton and sugar number (Figure 2) (Liu et al., 2021; Miao et al., 2022). It was shown that ginsenoside-Rk1 dose-dependently inhibited collagen and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation, Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum, granule release, and integrin αIIbβ3 without any cytotoxic effects (Shin et al., 2021). It has also been shown that ginsenoside-Rp3 suppressed collagen, ADP, and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation through inhibition of the MAPK pathway and cyclic nucleotide signaling, and that ginsenoside-Rp3 also inhibited thrombus formation in an acute pulmonary thromboembolism model (Irfan et al., 2018). In addition, ginsenoside-RP1 was found to repress collagen, thrombin or ADP-induced platelet activation and aggregation and thrombosis by inhibiting GPVI, tyrosine phosphorylation and MAPK signaling pathways (Endale et al., 2012). It has also been found that ginsenoside-Rk3 inhibited collagen-induced platelet aggregation and exerted antithrombotic effects by up-regulating cAMP and PI3K/MAPK pathways (as shown in Table 4) (Kwon et al., 2023). These findings underscored multifaceted antithrombotic mechanisms and therapeutic potential of ginsenosides. Hereafter, ginsenosides are grouped as Rb-series (PPD-type, e.g., Rb1), Rg-series (PPT-type, e.g., Rg1), and Rh-series (deglycosylated metabolites, e.g., Rh2).
2.5.2 Astragaloside IV
Astragaloside IV is a cyclic terpene triterpenoid saponin extracted from the Chinese herb Astragalus, which possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties (Zhang et al., 2020). It was shown that astragaloside IV inhibited deep vein thrombosis by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling, suppressing inflammation, and promoting neovascularization in a deep vein thrombosis model prepared by incompletely IVC ligation in rats, indicating that astragaloside IV had antithrombotic activity (as shown in Table 4) (Lyu et al., 2024).
2.5.3 Dioscin
Dioscin is a saponin compound extracted from the plant Dioscoreaceae with cardiovascular protective effects (Li et al., 2021). It was found that a mixture of total steroidal saponins (one of the main components is diosgenin) extracted from the rhizomes of the plant Dioscorea spp. exerted an antithrombotic effect by inhibiting platelet aggregation in a deep vein thrombosis model prepared by IVC ligating in rats, indicating that dioscin had antithrombotic activity (Li et al., 2010).
2.5.4 Hydroxysafflor yellows
Hydroxysafflor yellows are mainly derived from the plant safflower (Carthamus tinctorius Safflower) and belongs to the monochalcone glycosides. It was found that hydroxy saffron yellow inhibited phenylhydrazine-induced thrombosis in zebrafish by enhancing blood circulation and toxic excretion, indicating that hydroxysafflor had antithrombotic activity (as shown in Table 4) (Wang L. W. et al., 2021).
2.6 Organic acids
2.6.1 Caffeic acid
Caffeic acid is a common phenolic acid found in coffee and many fruits and vegetables, known for its antioxidant properties (Calabrese et al., 2024). It was shown that caffeic acid not only inhibited photochemical damage-induced thrombosis in mouse cerebral arteries, but also reduced platelet deposition and prolonged vascular occlusion, while caffeic acid also inhibited ADP induced cerebral venous thrombosis and platelet adherence in mice, and reduced the thrombus/vein area ratio. In addition, in vitro experiments in this study showed that caffeic acid also inhibited ADP-induced platelet aggregation, p-selectin expression, ATP release, Ca2+ mobilization, and integrin αIIbβ3 activation, and reduced p38, ERK, and JNK activation, and increased cAMP levels, thereby inhibiting thrombosis (as shown in Table 4) (Lu et al., 2015). It has also been shown that caffeic acid inhibited collagen-induced platelet aggregation, thromboxane A2 (TXA2) production, and Ca2+ mobilization in a concentration-dependent manner, increased cAMP and cGMP levels, and increased the phosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R), thereby preventing collagen-induced platelet aggregation and reducing the risk of thrombosis (Lee et al., 2014). Recent studies have shown that caffeic acid inhibited thrombin-induced clot retraction and decreased cAMP levels in platelets, inhibited phosphorylation of Akt and ERK, as well as enhanced phosphorylation of VASP, reducing intracellular Ca2+ mobilization, ATP release, p-selectin expression, and binding of fibrinogen to integrin αIIbβ3, thereby attenuating platelet activation and inhibiting thrombosis (Nam et al., 2020). In short, caffeic acid inhibited thrombosis by blocking platelet activation and multiple signaling pathways.
2.6.2 Salvianolic acid
Salvianolic acid is a water-soluble, weakly acidic drug extracted from the roots and rhizomes of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, family Labiatae, with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-tumor effects (He et al., 2023). It has been shown that salvinorin A dose-dependently inhibited ADP, thrombin, collagen-induced platelet aggregation, P-selectin expression, and fibrinogen binding through inhibition of the PI3K pathway, and also inhibited photochemically induced carotid thrombosis (Huang et al., 2010). Salvianolic acid B was found to dose-dependently inhibit thrombin, ADP, and collagen-induced platelet activation and aggregation, and to reduce FeCl3-induced carotid artery thrombosis and photochemical injury-induced thrombosis of small arteries of the raphe in mice (as shown in Table 4) (Neves et al., 2024). In, brief, salvianolic acid inhibited platelet aggregation and thrombosis in multiple models.
2.6.3 Chlorogenic acid
Chlorogenic acid is widely found in plant foods and is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antiviral activities (Singh et al., 2023). It was shown that chlorogenic acid inhibited ADP, collagen, and AA-induced platelet aggregation and adhesion in a dose-dependent manner through modulation of the A2A receptor, adenylate cyclase, and cAMP/PKA signaling pathways, and inhibited the expression of inflammatory mediators (sCD40L, CCL5, and IL-1β) by inhibiting thrombus in photochemically injured mouse mesenteric arteries (Fuentes et al., 2014). A mouse model of acute thromboembolism induced by collagen and epinephrine revealed that chlorogenic acid inhibited thrombosis by inhibiting the activities of procoagulant protease, thrombin, activated FXa, and activated factor XIII (FXIIIa) and delaying APTT, PT, and thrombin time (as shown in Table 4) (Choi and Kim, 2017).
2.7 Synthesis of mechanisms: novel targets and synergistic effects
A key advantage of the herbal monomers discussed is their ability to modulate a wide array of targets, encompassing both established and novel antithrombotic pathways. Many compounds, such as baicalin and kaempferol, inhibit thrombin and Factor Xa, which are the targets of conventional DOACs, suggesting they can improve upon existing mechanisms (Choi et al., 2015b; Lee et al., 2015). Similarly, compounds like caffeic acid and berberine interfere with platelet activation pathways involving PI3K, which are also targeted by synthetic drugs (Lu et al., 2015; Wang C. et al., 2021).
More importantly, this review highlights that natural products often engage novel or upstream targets not typically addressed by current pharmaceuticals. For instance, puerarin, curcumin, and resveratrol have been shown to suppress thrombosis by inhibiting inflammation through the NF-κB and NLRP3 signaling pathways (Deng et al., 2017; Liang et al., 2021; Fei et al., 2022). This approach targets the root causes of thrombus formation, representing a potentially more holistic treatment strategy. Furthermore, several compounds promote thrombus resolution, a mechanism distinct from prevention. Paeonol and epigallocatechin-3-gallate, for example, facilitate neovascularization and endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) function to actively resolve existing clots (Ye et al., 2016; Li et al., 2025).
The therapeutic potential of these natural monomers likely stems from their synergistic, multi-target action. A single compound can simultaneously inhibit platelet aggregation, reduce coagulation, suppress inflammation, and promote clot resolution, as summarized. This pleiotropic activity could lead to a more effective antithrombotic outcome with a potentially lower risk of bleeding compared to single-target synthetic drugs, making them highly attractive candidates for the development of the next-generation of antithrombotic therapies.
3 Conclusion and future perspectives
Due to the rising incidence of thromboembolic diseases and the defect of existing treatments, seeking new treatments and drugs is urgent and necessary. Natural plant herbs and their active monomers have shown unique advantages in the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic diseases. The antithrombotic mechanism of natural herbal monomers mainly focuses on the inhibition of platelet aggregation or thrombin activity, inhibition of procoagulant protease, prothrombin, activated FXa, and activated FXIIIa activities, and prolonged APTT, PT, and PT. In addition, some active ingredients can also inhibit inflammatory factors in thrombus, suppress the adhesion between leukocytes, platelets and endothelial cells, and promote neovascularization in thrombus to promote thrombus resolution, and have a multi-target synergistic effect. This review systematically summarizes the antithrombotic potential of various active monomers from Chinese herbs demonstrated in preclinical models. The vast majority of these findings have not yet entered clinical trials, highlighting the core purpose of this study: to comprehensively evaluate and screen promising natural drug candidates before initiating expensive and complex clinical research.
However, despite the significant antithrombotic potential of natural herbal monomers, most of the current studies have been limited to ex vivo experiments and rat or mouse models, with a lack of clinical trials, and still face many challenges. In addition, the low activity and poor bioavailability of the monomeric portion of natural active herbs require optimization of the structure or modification of the dosage form to improve activity and bioavailability. Existing antithrombotic drugs, such as warfarin and novel oral anticoagulants, are effective but still face challenges of bleeding risk and narrow therapeutic windows. The herbal monomers revealed in this review act through multiple targets and pathways—such as inhibiting platelet activation, regulating the coagulation cascade, and exerting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. This synergistic action could translate into a lower risk of bleeding and superior therapeutic outcomes, offering new approaches to overcome current clinical dilemmas (Atanasov et al., 2021).
Nanoparticles and liposomes can be developed to enhance the bioavailability of natural herbal monomers in the future. Combining artificial intelligence large models, single-cell omics, molecular docking and other technologies for target prediction, to clarify the new mechanisms by which natural herbal monomers and others regulate thrombus. Adopt a prevention-first treatment strategy, expand the natural herbal monomers obtained from food, and reduce the incidence of thrombus and protect the cardiovascular system through early intervention. The ultimate goal of this review is to pave the way for future clinical research. We propose that the next step should be to select one or two of the most promising compounds based on the evidence presented here (e.g., resveratrol, salvianolic acid B), conduct more standardized animal model studies, and ultimately design rigorous, scientific, small-scale Phase I or II clinical trials to evaluate their safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy in humans. At the same time, expanding the scope of research from treatment to prevention—especially for active ingredients derived from everyday foods (such as quercetin and anthocyanins)—could offer safe and convenient new strategies for the primary prevention of thrombotic diseases through dietary supplements or functional foods.
In conclusion, this review is not just a compilation of past research but also a roadmap for future studies. We have clearly identified the hurdles to be overcome in moving from preclinical evidence to clinical application and have proposed specific strategies to address them. We believe this work provides a valuable reference for the development of safer, more effective, next-generation antithrombotic drugs derived from nature and holds significant translational value.
Author contributions
Z-YN: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing, Software, Resources, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology, Visualization, Investigation, Conceptualization, Validation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Project administration. J-QZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Software, Investigation. Y-J-YS: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. J-QX: Writing – original draft, Project administration, Writing – review and editing, Validation, Formal Analysis. Y-BC: Resources, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. L-CZ: Project administration, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Resources, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. LL: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Software, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Resources, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82204737), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 24ZR1465300), the Health Commission of Shanghai Municipality (ZY (2021-2023)-0203-04), Future Plan for Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Development of Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (WLJH2021ZY-ZYY007; WL-HBBD-2021001K), Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project of Hongkou District Health Commission (HKZYY-2024-06), Medical Research Project of Hongkou District Health Commission (HW 2402-03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abd El-Hack, M. E., El-Saadony, M. T., Swelum, A. A., Arif, M., Abo Ghanima, M. M., Shukry, M., et al. (2021). Curcumin, the active substance of turmeric: its effects on health and ways to improve its bioavailability. J. Sci. Food Agric. 101 (14), 5747–5762. doi:10.1002/jsfa.11372
Aboonabi, A., Meyer, R. R., Gaiz, A., and Singh, I. (2020). Anthocyanins in berries exhibited anti-atherogenicity and antiplatelet activities in a metabolic syndrome population. Nutr. Res. 76, 82–93. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2020.02.011
Ashorobi, D., Ameer, M. A., and Fernandez, R. (2025). “Thrombosis,” in StatPearls. (Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing).
Atanasov, A. G., Zotchev, S. B., Dirsch, V. M., International Natural Product Sciences, T., and Supuran, C. T. (2021). Natural products in drug discovery: advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20 (3), 200–216. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-00114-z
Avula, B., Katragunta, K., Osman, A. G., Ali, Z., John Adams, S., Chittiboyina, A. G., et al. (2023). Advances in the chemistry, analysis and adulteration of anthocyanin rich-berries and fruits: 2000-2022. Molecules 28 (2), 560. doi:10.3390/molecules28020560
Bergman, M. E., Davis, B., and Phillips, M. A. (2019). Medically useful plant terpenoids: biosynthesis, occurrence, and mechanism of action. Molecules 24 (21), 3961. doi:10.3390/molecules24213961
Breuss, J. M., Atanasov, A. G., and Uhrin, P. (2019). Resveratrol and its effects on the vascular system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (7), 1523. doi:10.3390/ijms20071523
Calabrese, E. J., Pressman, P., Hayes, A. W., Baldwin, L., Agathokleous, E., Dhawan, G., et al. (2024). Caffeic acid: numerous chemoprotective effects are mediated via hormesis. J. Diet. Suppl. 21 (6), 842–867. doi:10.1080/19390211.2024.2410776
Chen, S., Wang, X., Cheng, Y., Gao, H., and Chen, X. (2023). A review of classification, biosynthesis, biological activities and potential applications of flavonoids. Molecules 28 (13), 4982. doi:10.3390/molecules28134982
Choi, J. H., and Kim, S. (2017). Investigation of the anticoagulant and antithrombotic effects of chlorogenic acid. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 31 (3), e21865. doi:10.1002/jbt.21865
Choi, J. H., Kim, Y. S., Shin, C. H., Lee, H. J., and Kim, S. (2015a). Antithrombotic activities of luteolin in vitro and in vivo. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 29 (12), 552–558. doi:10.1002/jbt.21726
Choi, J. H., Park, S. E., Kim, S. J., and Kim, S. (2015b). Kaempferol inhibits thrombosis and platelet activation. Biochimie 115, 177–186. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2015.06.001
Choi, J. H., Kim, K. J., and Kim, S. (2016). Comparative effect of quercetin and Quercetin-3-O-beta-d-Glucoside on fibrin polymers, blood clots, and in rodent models. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 30 (11), 548–558. doi:10.1002/jbt.21822
Choo, M. K., Park, E. K., Yoon, H. K., and Kim, D. H. (2002). Antithrombotic and antiallergic activities of daidzein, a metabolite of puerarin and daidzin produced by human intestinal microflora. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25 (10), 1328–1332. doi:10.1248/bpb.25.1328
Deng, H. F., Wang, X. L., Sun, H., and Xiao, X. Z. (2017). Puerarin inhibits expression of tissue factor induced by oxidative low-density lipoprotein through activating the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway and inhibiting activation of ERK1/2 and NF-κB. Life Sci. 191, 115–121. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2017.10.018
Dohare, P., Garg, P., Jain, V., Nath, C., and Ray, M. (2008). Dose dependence and therapeutic window for the neuroprotective effects of curcumin in thromboembolic model of rat. Behav. Brain Res. 193 (2), 289–297. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.06.012
Endale, M., Lee, W. M., Kamruzzaman, S. M., Kim, S. D., Park, J. Y., Park, M. H., et al. (2012). Ginsenoside-Rp1 inhibits platelet activation and thrombus formation via impaired glycoprotein VI signalling pathway, tyrosine phosphorylation and MAPK activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 167 (1), 109–127. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01967.x
Fei, J., Qin, X., Ma, H., Zhang, X., Wang, H., Han, J., et al. (2022). Resveratrol ameliorates deep vein thrombosis-induced inflammatory response through inhibiting HIF-1α/NLRP3 pathway. Inflammation 45 (6), 2268–2279. doi:10.1007/s10753-022-01689-y
Fuentes, E., Caballero, J., Alarcon, M., Rojas, A., and Palomo, I. (2014). Chlorogenic acid inhibits human platelet activation and thrombus formation. PLoS One 9 (3), e90699. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090699
Gailani, D., and Gruber, A. (2024). Targeting factor XI and factor XIa to prevent thrombosis. Blood 143 (15), 1465–1475. doi:10.1182/blood.2023020722
Gaiz, A., Kundur, A. R., Nikbakht, E., Vugic, L., Colson, N., Shibeeb, S., et al. (2022). Anthocyanin supplementation alleviates antithrombotic risk by inhibiting platelet activity in humans. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 28 (2), 44–49.
Goldhaber, S. Z., Magnuson, E. A., Chinnakondepalli, K. M., Cohen, D. J., and Vedantham, S. (2021). Catheter-directed thrombolysis for deep vein thrombosis: 2021 update. Vasc. Med. 26 (6), 662–669. doi:10.1177/1358863X211042930
Guan, B., Gao, J., Tan, Y., Ma, X., and Shi, D. (2022). Antiplatelet activity of tetramethylpyrazine via regulation of the P2Y12 receptor downstream signaling pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 7941039. doi:10.1155/2022/7941039
He, G., Chen, G., Liu, W., Ye, D., Liu, X., Liang, X., et al. (2023). Salvianolic acid B: a review of pharmacological effects, safety, combination therapy, new dosage forms, and novel drug delivery routes. Pharmaceutics 15 (9), 2235. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15092235
Helin, T. A., Joutsi-Korhonen, L., Asmundela, H., Niemi, M., Orpana, A., and Lassila, R. (2019). Warfarin dose requirement in patients having severe thrombosis or thrombophilia. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 85 (8), 1684–1691. doi:10.1111/bcp.13948
Hu, H., Zhang, X. X., Wang, Y. Y., and Chen, S. Z. (2005). Honokiol inhibits arterial thrombosis through endothelial cell protection and stimulation of prostacyclin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 26 (9), 1063–1068. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00164.x
Huang, Z. S., Zeng, C. L., Zhu, L. J., Jiang, L., Li, N., and Hu, H. (2010). Salvianolic acid A inhibits platelet activation and arterial thrombosis via inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J. Thromb. Haemost. 8 (6), 1383–1393. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03859.x
Huang, M., Deng, M., Nie, W., Zou, D., Wu, H., and Xu, D. (2021). Naringenin inhibits platelet activation and arterial thrombosis through inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-Kinase and cyclic nucleotide signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 722257. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.722257
Irfan, M., Jeong, D., Kwon, H. W., Shin, J. H., Park, S. J., Kwak, D., et al. (2018). Ginsenoside-Rp3 inhibits platelet activation and thrombus formation by regulating MAPK and cyclic nucleotide signaling. Vasc. Pharmacol. 109, 45–55. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2018.06.002
Jiang, Z., Cui, X., Qu, P., Shang, C., Xiang, M., and Wang, J. (2022). Roles and mechanisms of puerarin on cardiovascular disease:a review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 147, 112655. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112655
Keihanian, F., Saeidinia, A., Bagheri, R. K., Johnston, T. P., and Sahebkar, A. (2018). Curcumin, hemostasis, thrombosis, and coagulation. J. Cell Physiol. 233 (6), 4497–4511. doi:10.1002/jcp.26249
Khedr, E. M., Abdelwarith, A., Moussa, G., and Saber, M. (2023). Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rTPA) management for first onset acute ischemic stroke with covid -19 and non-covid -19 patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 32 (4), 107031. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2023.107031
Kim, K. A., Choi, S. Y., and Kim, R. (2021). Endovascular treatment for lower extremity deep vein thrombosis: an overview. Korean J. Radiol. 22 (6), 931–943. doi:10.3348/kjr.2020.0675
Kwon, H. W., Shin, J. H., Rhee, M. H., Park, C. E., and Lee, D. H. (2023). Anti-thrombotic effects of ginsenoside Rk3 by regulating cAMP and PI3K/MAPK pathway on human platelets. J. Ginseng Res. 47 (6), 706–713. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2023.04.006
Lee, D. H., Kim, H. H., Cho, H. J., Bae, J. S., Yu, Y. B., and Park, H. J. (2014). Antiplatelet effects of caffeic acid due to Ca(2+) mobilizationinhibition via cAMP-dependent inositol-1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor phosphorylation. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 21 (1), 23–37. doi:10.5551/jat.18994
Lee, W., Ku, S. K., and Bae, J. S. (2015). Antiplatelet, anticoagulant, and profibrinolytic activities of baicalin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 38 (5), 893–903. doi:10.1007/s12272-014-0410-9
Lee, T. Y., Chang, C. C., Lu, W. J., Yen, T. L., Lin, K. H., Geraldine, P., et al. (2017). Honokiol as a specific collagen receptor glycoprotein VI antagonist on human platelets: functional ex vivo and in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 7, 40002. doi:10.1038/srep40002
Li, Y. D., Ye, B. Q., Zheng, S. X., Wang, J. T., Wang, J. G., Chen, M., et al. (2009). NF-kappaB transcription factor p50 critically regulates tissue factor in deep vein thrombosis. J. Biol. Chem. 284 (7), 4473–4483. doi:10.1074/jbc.M806010200
Li, H., Huang, W., Wen, Y., Gong, G., Zhao, Q., and Yu, G. (2010). Anti-thrombotic activity and chemical characterization of steroidal saponins from Dioscorea zingiberensis C.H. wright. Fitoterapia 81 (8), 1147–1156. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2010.07.016
Li, X., Liu, S., Qu, L., Chen, Y., Yuan, C., Qin, A., et al. (2021). Dioscin and diosgenin: insights into their potential protective effects in cardiac diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 274, 114018. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114018
Li, X., Yuan, W., Wu, J., Zhen, J., Sun, Q., and Yu, M. (2022). Andrographolide, a natural anti-inflammatory agent: an Update. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 920435. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.920435
Li, D., Mao, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Tang, H., Huang, H., et al. (2025). Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate promotes recanalization in deep vein thrombosis by modulating endothelial progenitor cell ferroptosis through the Nrf2 pathway. Phytother. Res. 39 (3), 1632–1644. doi:10.1002/ptr.8457
Liang, D., Wen, Z., Han, W., Li, W., Pan, L., and Zhang, R. (2021). Curcumin protects against inflammation and lung injury in rats with acute pulmonary embolism with the involvement of microRNA-21/PTEN/NF-κB axis. Mol. Cell Biochem. 476 (7), 2823–2835. doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04127-z
Lin, J., Wang, Q., Zhou, S., Xu, S., and Yao, K. (2022). Tetramethylpyrazine: a review on its mechanisms and functions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 150, 113005. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113005
Lin, S., Ma, H., Zhang, S., Fan, W., Shen, C., Chen, J., et al. (2024). The combination of paeonol, diosmetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from trichosanthis pericarpium alleviates arachidonic acid-induced thrombosis in a zebrafish model. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1332468. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1332468
Liu, M. Y., Liu, F., Gao, Y. L., Yin, J. N., Yan, W. Q., Liu, J. G., et al. (2021). Pharmacological activities of ginsenoside Rg5 (review). Exp. Ther. Med. 22 (2), 840. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10272
Liu, S., Zheng, X., Luo, Z., Tang, C., Hu, Y., Peng, Q., et al. (2024). The synthesis and bioactivity of apigenin derivatives. Fitoterapia 179, 106228. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106228
Lu, Y., Li, Q., Liu, Y. Y., Sun, K., Fan, J. Y., Wang, C. S., et al. (2015). Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid on ADP-Induced thrombus formation and platelet activation involves mitogen-activated protein kinases. Sci. Rep. 5, 13824. doi:10.1038/srep13824
Lu, Z., Wang, S., Zhu, X., Yuan, X., Zhan, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2019). Resveratrol induces endothelial progenitor cells angiogenesis via MiR-542-3p by targeting Angiopoietin-2 and involves in recanalization of venous thrombosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 7675–7683. doi:10.12659/MSM.917013
Lu, Z., Ye, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, X., Ding, Q., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Aqueous extract of paeoniae Radix rubra prevents deep vein thrombosis by ameliorating inflammation through inhibiting GSK3β activity. Phytomedicine 92, 153767. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153767
Lyu, X., Yi, Z., He, Y., Zhang, C., Zhu, P., and Liu, C. (2024). Astragaloside IV induces endothelial progenitor cell angiogenesis in deep venous thrombosis through inactivation of PI3K/AKT signaling. Histol. Histopathol. 39 (9), 1149–1157. doi:10.14670/HH-18-704
Manjunath, S. H., and Thimmulappa, R. K. (2022). Antiviral, immunomodulatory, and anticoagulant effects of quercetin and its derivatives: potential role in prevention and management of COVID-19. J. Pharm. Anal. 12 (1), 29–34. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2021.09.009
Mattioli, R., Francioso, A., Mosca, L., and Silva, P. (2020). Anthocyanins: a comprehensive review of their chemical properties and health effects on cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 25 (17), 3809. doi:10.3390/molecules25173809
Mayanglambam, A., Dangelmaier, C. A., Thomas, D., Damodar Reddy, C., Daniel, J. L., and Kunapuli, S. P. (2010). Curcumin inhibits GPVI-Mediated platelet activation by interfering with the kinase activity of Syk and the subsequent activation of PLCgamma2. Platelets 21 (3), 211–220. doi:10.3109/09537100903528269
Mendes-Silva, W., Assafim, M., Ruta, B., Monteiro, R. Q., Guimaraes, J. A., and Zingali, R. B. (2003). Antithrombotic effect of glycyrrhizin, a plant-derived thrombin inhibitor. Thromb. Res. 112 (1-2), 93–98. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2003.10.014
Miao, L., Yang, Y., Li, Z., Fang, Z., Zhang, Y., and Han, C. C. (2022). Ginsenoside Rb2: a review of pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects. J. Ginseng Res. 46 (2), 206–213. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2021.11.007
Montalvan Ayala, V., Rojas Cheje, Z., and Aldave Salazar, R. (2022). Controversies in cerebrovascular disease: high or low doses of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator to treat acute stroke? A literature review. Neurol. Engl. Ed. 37 (2), 130–135. doi:10.1016/j.nrl.2018.04.003
Mosawy, S., Jackson, D. E., Woodman, O. L., and Linden, M. D. (2013). Treatment with quercetin and 3',4'-dihydroxyflavonol inhibits platelet function and reduces thrombus formation in vivo. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 36 (1), 50–57. doi:10.1007/s11239-012-0827-2
Motallebi, M., Bhia, M., Rajani, H. F., Bhia, I., Tabarraei, H., Mohammadkhani, N., et al. (2022). Naringenin: a potential flavonoid phytochemical for cancer therapy. Life Sci. 305, 120752. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120752
Mou, Y., Liao, W., Li, Y., Wan, L., Liu, J., Luo, X., et al. (2024). Glycyrrhizin and the related preparations: an inspiring resource for the treatment of liver diseases. Am. J. Chin. Med. 52 (2), 315–354. doi:10.1142/S0192415X24500149
Mu, K., Liu, Y., Liu, G., Ran, F., Zhou, L., Wu, Y., et al. (2023). A review of hemostatic chemical components and their mechanisms in traditional Chinese medicine and ethnic medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 307, 116200. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116200
Nakata, N., Kira, Y., Yabunaka, Y., and Takaoka, K. (2008). Prevention of venous thrombosis by preoperative glycyrrhizin infusion in a rat model. J. Orthop. Sci. 13 (5), 456–462. doi:10.1007/s00776-008-1259-x
Nam, G. S., Park, H. J., and Nam, K. S. (2020). The antithrombotic effect of caffeic acid is associated with a cAMP-dependent pathway and clot retraction in human platelets. Thromb. Res. 195, 87–94. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.07.024
Navarro-Nunez, L., Lozano, M. L., Palomo, M., Martinez, C., Vicente, V., Castillo, J., et al. (2008). Apigenin inhibits platelet adhesion and thrombus formation and synergizes with aspirin in the suppression of the arachidonic acid pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56 (9), 2970–2976. doi:10.1021/jf0723209
Neves, M. A. D., Ni, T. T., Mackeigan, D. T., Shoara, A. A., Lei, X., Slavkovic, S., et al. (2024). Salvianolic acid B inhibits thrombosis and directly blocks the thrombin catalytic site. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 8 (4), 102443. doi:10.1016/j.rpth.2024.102443
Newman, D. J., and Cragg, G. M. (2020). Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 83 (3), 770–803. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285
Ngo, T., Kim, K., Bian, Y., Noh, H., Lim, K. M., Chung, J. H., et al. (2019). Antithrombotic effects of paeoniflorin from Paeonia suffruticosa by selective inhibition on shear stress-induced Platelet aggregation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (20), 5040. doi:10.3390/ijms20205040
Oh, T. W., Do, H. J., Jeon, J. H., and Kim, K. (2021). Quercitrin inhibits platelet activation in arterial thrombosis. Phytomedicine 80, 153363. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153363
Ortel, T. L., Neumann, I., Ageno, W., Beyth, R., Clark, N. P., Cuker, A., et al. (2020). American society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Blood Adv. 4 (19), 4693–4738. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001830
Periferakis, A., Periferakis, K., Badarau, I. A., Petran, E. M., Popa, D. C., Caruntu, A., et al. (2022). Kaempferol: antimicrobial properties, sources, clinical, and traditional applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (23), 15054. doi:10.3390/ijms232315054
Perumal, S., Dubey, K., Badhwar, R., George, K. J., Sharma, R. K., Bagler, G., et al. (2015). Capsaicin inhibits collagen fibril formation and increases the stability of collagen fibers. Eur. Biophys. J. 44 (1-2), 69–76. doi:10.1007/s00249-014-1002-9
Qi, W., Qi, W., Xiong, D., and Long, M. (2022). Quercetin: its antioxidant mechanism, antibacterial properties and potential application in prevention and control of toxipathy. Molecules 27 (19), 6545. doi:10.3390/molecules27196545
Reichert, C. L., Salminen, H., and Weiss, J. (2019). Quillaja saponin characteristics and functional properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 10, 43–73. doi:10.1146/annurev-food-032818-122010
Sagris, M., Tzoumas, A., Kokkinidis, D. G., Korosoglou, G., Lichtenberg, M., and Tzavellas, G. (2022). Invasive and pharmacological treatment of deep vein thrombosis: a scoping review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 28 (10), 778–786. doi:10.2174/1381612828666220418084339
Shih, C. Y., and Chou, T. C. (2012). The antiplatelet activity of magnolol is mediated by PPAR-β/γ. Biochem. Pharmacol. 84 (6), 793–803. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2012.06.022
Shin, J. H., Kwon, H. W., Irfan, M., Rhee, M. H., and Lee, D. H. (2021). Ginsenoside Rk1 suppresses platelet mediated thrombus formation by downregulation of granule release and αIIbβ3 activation. J. Ginseng Res. 45 (4), 490–497. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2020.11.001
Si, H., Lai, C. Q., and Liu, D. (2021). Dietary epicatechin, A novel anti-aging bioactive small molecule. Curr. Med. Chem. 28 (1), 3–18. doi:10.2174/0929867327666191230104958
Sinegre, T., Teissandier, D., Milenkovic, D., Morand, C., and Lebreton, A. (2019). Epicatechin influences primary hemostasis, coagulation and fibrinolysis. Food Funct. 10 (11), 7291–7298. doi:10.1039/c9fo00816k
Singh, P., Arif, Y., Bajguz, A., and Hayat, S. (2021). The role of quercetin in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 166, 10–19. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.05.023
Singh, A. K., Singla, R. K., and Pandey, A. K. (2023). Chlorogenic acid: a dietary phenolic acid with promising pharmacotherapeutic potential. Curr. Med. Chem. 30 (34), 3905–3926. doi:10.2174/0929867329666220816154634
Song, D., Hao, J., and Fan, D. (2020). Biological properties and clinical applications of berberine. Front. Med. 14 (5), 564–582. doi:10.1007/s11684-019-0724-6
Stainer, A. R., Sasikumar, P., Bye, A. P., Unsworth, A. J., Holbrook, L. M., Tindall, M., et al. (2019). The metabolites of the dietary flavonoid Quercetin possess potent antithrombotic activity, and interact with aspirin to enhance antiplatelet effects. TH Open 3 (3), e244–e258. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1694028
Subedi, L., and Gaire, B. P. (2021). Tanshinone IIA: a phytochemical as a promising drug candidate for neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 169, 105661. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105661
Sun, Z., Zhao, T., Bai, X., Li, H., Gao, J., Hao, Y., et al. (2024). Berberine targets PKM2 to activate the t-PA-Induced fibrinolytic System and improves thrombosis. Pharm. (Basel) 17 (9), 1219. doi:10.3390/ph17091219
Teng, C. M., Chen, C. C., Ko, F. N., Lee, L. G., Huang, T. F., Chen, Y. P., et al. (1988). Two antiplatelet agents from Magnolia officinalis. Thromb. Res. 50 (6), 757–765. doi:10.1016/0049-3848(88)90336-2
Thisoda, P., Rangkadilok, N., Pholphana, N., Worasuttayangkurn, L., Ruchirawat, S., and Satayavivad, J. (2006). Inhibitory effect of Andrographis paniculata extract and its active diterpenoids on platelet aggregation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 553 (1-3), 39–45. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.09.052
Wang, J. P., Hsu, M. F., Hsu, T. P., and Teng, C. M. (1985). Antihemostatic and antithrombotic effects of capsaicin in comparison with aspirin and indomethacin. Thromb. Res. 37 (6), 669–679. doi:10.1016/0049-3848(85)90196-3
Wang, Y., Yang, X., Liu, H., and Tang, X. (2003). Study on effects of Erigeron breviscapus extract on anticoagulation. Zhong Yao Cai 26 (9), 656–658.
Wang, S. B., Jang, J. Y., Chae, Y. H., Min, J. H., Baek, J. Y., Kim, M., et al. (2015). Kaempferol suppresses collagen-induced platelet activation by inhibiting NADPH oxidase and protecting SHP-2 from oxidative inactivation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 83, 41–53. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.01.018
Wang, H., Zhong, L., Mi, S., Song, N., Zhang, W., and Zhong, M. (2020). Tanshinone IIA prevents platelet activation and down-regulates CD36 and MKK4/JNK2 signaling pathway. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 20 (1), 81. doi:10.1186/s12872-019-01289-z
Wang, C., Cheng, Y., Zhang, Y., Jin, H., Zuo, Z., Wang, A., et al. (2021a). Berberine and its main metabolite berberrubine inhibit Platelet activation through suppressing the class I PI3Kβ/Rasa3/Rap1 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 734603. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.734603
Wang, L. W., Cui, X. Y., He, J. F., Duan, S., Liu, C. R., Shan, C. B., et al. (2021b). Hydroxysafflor yellows alleviate thrombosis and acetaminophen-induced toxicity in vivo by enhancing blood circulation and poison excretion. Phytomedicine 87, 153579. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153579
Wang, T., Guan, R., Xia, F., Du, J., and Xu, L. (2021c). Curcumin promotes venous thrombi resolve process in a mouse deep venous thrombosis model via regulating miR-499. Microvasc. Res. 136, 104148. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104148
Wang, Y., Zhou, Y., and Fu, J. (2021d). Advances in antiobesity mechanisms of capsaicin. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 61, 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2021.08.012
Wang, C., Yuan, Z., Xie, J., Lei, Y., Li, Y., Huang, J., et al. (2023). Integrated metabolomics and molecular docking reveal berberrubine inhibits thrombosis by regulating the vitamin K catalytic cycle in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 938, 175436. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175436
Wei, X., Zhang, B., Wei, F., Ding, M., Luo, Z., Han, X., et al. (2022). Gegen Qinlian pills alleviate carrageenan-induced thrombosis in mice model by regulating the HMGB1/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling. Phytomedicine 100, 154083. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154083
Wen, L., He, T., Yu, A., Sun, S., Li, X., Wei, J., et al. (2021). Breviscapine: a review on its phytochemistry, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic effects. Am. J. Chin. Med. 49 (6), 1369–1397. doi:10.1142/S0192415X21500646
Xie, Z., Liu, X., Huang, X., Liu, Q., Yang, M., Huang, D., et al. (2021). Remodelling of gut microbiota by Berberine attenuates trimethylamine N-oxide-induced platelet hyperreaction and thrombus formation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 911, 174526. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174526
Xie, J., Liao, Y., and Wang, D. (2025). Baicalin promotes migration and angiogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells but impedes thrombus formation via SIRT1/NF-κB signaling in a rat model of deep vein thrombosis. Histol. Histopathol. 40 (4), 547–554. doi:10.14670/HH-18-799
Ye, S., Liu, X., Mao, B., Yang, L., and Liu, N. (2016). Paeonol enhances thrombus recanalization by inducing vascular endothelial growth factor 165 via ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 13 (6), 4853–4858. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.5135
Ye, Y., Yang, L., Leng, M., Wang, Q., Wu, J., Wan, W., et al. (2023). Luteolin inhibits GPVI-mediated platelet activation, oxidative stress, and thrombosis. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1255069. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1255069
Yin, Q., Zhang, X., Liao, S., Huang, X., Wan, C. C., and Wang, Y. (2023). Potential anticoagulant of traditional chinese medicine and novel targets for anticoagulant drugs. Phytomedicine 116, 154880. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154880
Yuan, Y., Zhou, X., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Teng, X., and Wang, S. (2020). Cardiovascular modulating effects of magnolol and Honokiol, two polyphenolic compounds from traditional Chinese medicine-magnolia Officinalis. Curr. Drug Targets 21 (6), 559–572. doi:10.2174/1389450120666191024175727
Zeng, B., Wei, A., Zhou, Q., Yuan, M., Lei, K., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Andrographolide: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches. Phytother. Res. 36 (1), 336–364. doi:10.1002/ptr.7324
Zhang, L., and Wei, W. (2020). Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of paeoniflorin and total glucosides of paeony. Pharmacol. Ther. 207, 107452. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107452
Zhang, Y., Du, X., Li, W., Sang, H., Qian, A., Sun, L., et al. (2018). Resveratrol improves endothelial progenitor cell function through miR-138 by targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) and promotes thrombus resolution in vivo. Med. Sci. Monit. 24, 951–960. doi:10.12659/msm.906116
Zhang, J., Chen, Z., Huang, X., Shi, W., Zhang, R., Chen, M., et al. (2019a). Insights on the multifunctional activities of magnolol. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 1847130. doi:10.1155/2019/1847130
Zhang, L., Li, D. C., and Liu, L. F. (2019b). Paeonol: pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. Int. Immunopharmacol. 72, 413–421. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.033
Zhang, J., Wu, C., Gao, L., Du, G., and Qin, X. (2020). Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: a research review on the pharmacological effects. Adv. Pharmacol. 87, 89–112. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2019.08.002
Zhang, L. X., Li, C. X., Kakar, M. U., Khan, M. S., Wu, P. F., Amir, R. M., et al. (2021). Resveratrol (RV): a pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 143, 112164. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112164
Zhang, X. X., Zuo, J. Q., Wang, Y. T., Duan, H. Y., Yuan, J. H., and Hu, Y. H. (2022a). Paeoniflorin in Paeoniaceae: distribution, influencing factors, and biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 980854. doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.980854
Zhang, Y., Ma, C., He, L., Liao, L., Guo, C., Wang, C., et al. (2022b). Tetramethylpyrazine protects endothelial injury and antithrombosis via antioxidant and antiapoptosis in HUVECs and zebrafish. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2232365. doi:10.1155/2022/2232365
Zhang, H. J., Fu, J., Yu, H., Xu, H., Hu, J. C., Lu, J. Y., et al. (2024a). Berberine promotes the degradation of phenylacetic acid to prevent thrombosis by modulating gut microbiota. Phytomedicine 128, 155517. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155517
Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., Fan, J., Feng, Z., and Song, X. (2024b). Pharmacological activity of capsaicin: mechanisms and controversies (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 29 (3), 38. doi:10.3892/mmr.2024.13162
Zhang, Y., Xin, G., Zhou, Q., Yu, X., Feng, L., Wen, A., et al. (2024c). Elucidating the distinctive regulatory effects and mechanisms of active compounds in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge via network pharmacology: unveiling their roles in the modulation of platelet activation and thrombus formation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 484, 116871. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2024.116871
Zhang, S., Liu, C., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., Yang, H., et al. (2025). Kaempferol promotes angiogenesis through HIF-1α/VEGF-A/Notch1 pathway in ischemic stroke rats. Neurochem. Int. 185, 105953. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2025.105953
Zhao, Z., Nian, M., Qiao, H., Yang, X., Wu, S., and Zheng, X. (2022). Review of bioactivity and structure-activity relationship on baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone) and wogonin (5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone) derivatives: structural modifications inspired from flavonoids in Scutellaria baicalensis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 243, 114733. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114733
Keywords: thromboembolism, thrombosis, antithrombosis, natural herbal monomers, small molecule compounds
Citation: Nie Z-Y, Zhang J-Q, Shen Y-J-Y, Xi J-Q, Cao Y-B, Zhang L-C and Li L (2025) Natural active herbal monomers for the treatment of thromboembolic diseases: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1607415. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1607415
Received: 07 April 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 03 September 2025.
Edited by:
Simone Brogi, University of Pisa, ItalyReviewed by:
Merten Prüser, Heidelberg University Hospital, GermanyIrma Guadalupe Quintal, Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán, Mexico
Asma Haffouz, Centre of Biotechnology of Sfax, Tunisia
Muttia Amalia, Jakarta Veterans National Development University, Indonesia
Emma Ozon, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Copyright © 2025 Nie, Zhang, Shen, Xi, Cao, Zhang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ling Li, bGluZ2xpX3oxNjNAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Li-Chao Zhang, Y2hhbmdoYWlza2luQDE2My5jb20=; Yong-Bing Cao, eWJjYW9AdmlwLnNpbmEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhou-Yu Nie
Zhou-Yu Nie Jia-Qi Zhang
Jia-Qi Zhang Yuan-Jia-Yi Shen1
Yuan-Jia-Yi Shen1 Jia-Qi Xi
Jia-Qi Xi Yong-Bing Cao
Yong-Bing Cao Ling Li
Ling Li



