- 1College of Pharmacy, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 2College of Basic Medical Science, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Basic and Application Research of Beiyao, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Ministry of Education, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
Background: Carthamus tinctorius L. has a long history of ethnomedicinal use for various ailments. This review focuses on the botany, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacological effects, and clinical applications of safflower, aiming to enhance current research in this field.
Methods: The study incorporated relevant scientific literature up to April 2025. It involved the collection of both Chinese and English studies on safflower from various databases, including PubMed, Elsevier, Web of Science, Springer, ScienceDirect, Wiley, ACS, and CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure). Additionally, doctoral and master’s dissertations were included in the analysis.
Results: From 1978 to April 2025, various active metabolites were identified, primarily comprising flavonoids, polyacetylenes, and alkaloids, with flavonoids being the predominant group. Extracts and metabolites derived from safflower have demonstrated a range of bioactivities, including antioxidant, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects. In clinical practice, the effective components of safflower have been utilized in the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, diabetes, hepatobiliary conditions, poor blood circulation, sudden deafness, and other ailments.
Conclusion: This review elucidates the research surrounding safflower in the domains of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacological activity, and clinical applications. Safflower is known to contain a diverse array of compounds, with flavonoids in particular demonstrating significant pharmacological activity. These compounds are extensively utilized in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries, positioning safflower as a promising candidate for development and application in the treatment of various diseases. Nonetheless, research on safflower remains limited, and many active metabolites have yet to be thoroughly investigated in terms of their phytochemical and pharmacological properties. To date, only a handful of active metabolites have been isolated and assessed for their biological activity, and there is a notable deficiency in research regarding their mechanisms of action. Therefore, comprehensive studies are imperative to enhance our understanding of safflower and to substantiate its therapeutic potential.
1 Introduction
Carthamus tinctorius L., commonly known as safflower, is an effective herbal medicine with a long history of use. Its cultivation is primarily concentrated in China, India, and Western European countries (Hamdan, 2024). Safflower is associated with the liver and heart meridians and is effective in alleviating pain, promoting blood circulation, and removing blood stasis (Wang L. et al., 2023). The plant contains a variety of chemical metabolites, predominantly flavonoids, alkaloids, polyacetylenes, and polysaccharides. As medical research advances, the clinical applications of safflower in specialized fields, such as gynecology and dermatology, have become increasingly prevalent and demonstrate significant therapeutic effects (Ren et al., 2023). This review provides a comprehensive synopsis and analysis of the botany, ethnomedicine, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic uses of safflower. Additionally, we address the limitations of previous studies and propose future research directions. Our aim is to provide a thorough analysis of safflower to assess its potential as a therapeutic agent and to recommend future research pathways that will support its ongoing development and application.
2 Botany
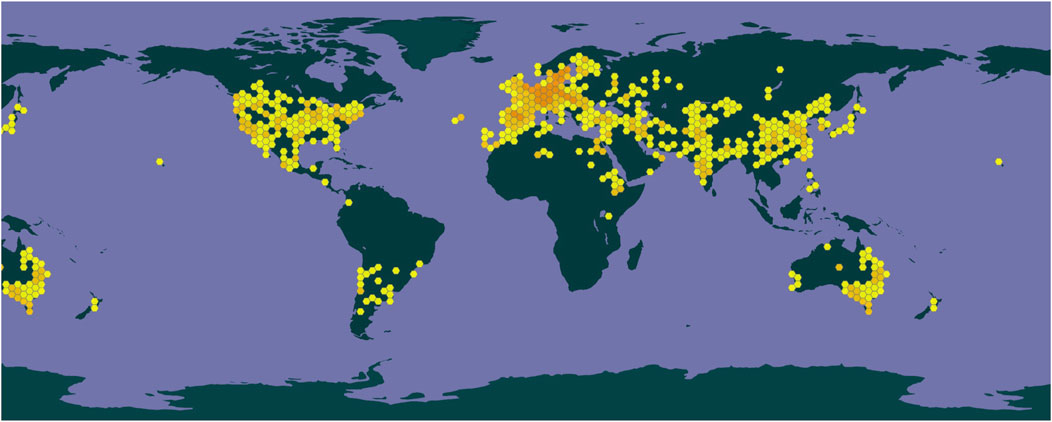
Safflower is highly adaptable and exhibits resistance to salt, drought, and cold conditions, making it widely cultivated across China. Fragments of the stigma, corolla, and filament are commonly observed, along with elongated tubular secretory cells that can reach diameters of up to 66 μm, with secretions varying in color from yellow-brown to reddish-brown, often located near the duct (Waki et al., 2021). The outer walls of the epidermal cells at the tips of the corolla lobes display a brief, tomentose extension (Wang et al., 2015). Prominent or slightly obtuse single-celled hairs with conical apexes emerge from both the stigma and the upper epidermal cells of the style. Pollen grains possess three germination pores and tooth-like protrusions on their outer walls, measure up to 60 μm in diameter, and are ellipsoidal, olive-shaped, or orbicular (Lu et al., 2025). Calcium oxalate crystals are found within the thin-walled cells and range in size from 2 μm to 6 μm. A depiction of safflower is presented in Figure 1. The genus Carthamus comprises approximately 85 species, primarily distributed in India, Spain, and Sweden, with one species found in China, specifically in Xinjiang and Yunnan provinces. The geographical distribution of safflower worldwide was obtained from the GBIF online database (www.gbif.org, shown in Figure 2).

Figure 1. Plant flower (A), leaves (B), and aerial part (C) (http://ppbc.iplant.cn/).
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Identification and selection of studies
The initial phase of our analysis involved systematically assessing all studies identified through keyword searches about Carthamus tinctorius L. Following the removal of duplicate entries, we conducted a preliminary review of titles and abstracts to evaluate their relevance based on the established inclusion criteria. A detailed examination of studies that satisfied these criteria was performed, encompassing a thorough analysis of the full text and an in-depth review of the reference lists to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the relevant literature.
3.2 Search strategy
We identified the studies independently using the following keywords: “Carthamus tinctorius L.,” “Carthamus tinctorius,” and “Safflower.” In addition, reported pharmacological activities and phytochemical compositions were searched as keywords. This study only includes results found before April 2025. The search was carried out in the electronic bibliographic databases, including PubMed, Elsevier, Web of Science, Springer, ScienceDirect, Wiley, ACS, and CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure).
3.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Our inclusion criteria encompassed all experimental studies investigating various aspects of Carthamus tinctorius L., including its botany, phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology, pharmacology, and clinical applications. Additionally, we incorporated Chinese doctoral and master’s dissertations and theses that detailed the properties of safflower. Editorials, conference abstracts, duplicate articles, review articles, and conference proceedings were excluded. Further exclusions were articles unrelated to the topic.
3.4 Others
ChemDraw 19.0 was used to redraw the chemical compounds. The PubChem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) was used to confirm the chemical classifications and structures. The whole procedure was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA statement (https://www.prisma-statement.org/).
4 Ethnopharmacology
The introduction of safflower to China dates back over 2,100 years. The earliest recorded application of safflower in China can be traced to the Han Dynasty, during which it was introduced from the western regions primarily as a dye. Its initial medicinal use occurred in the Eastern Han Dynasty, as documented in Zhongjing Zhang’s “Synopsis of the Golden Chamber” (《金匮要略》A.D.219). The “Natural History” (《博物志》A.D.232) notes that “it was born in the Liang and Han dynasties and the Western region and is now also grown in the Wei dynasty,” indicating that safflower was cultivated in Henan Province by at least as early as the Western Jin Dynasty. In Bao Cui’s “Ancient and Modern Annotations” (《古今注》A.D.278) from the Western Jin Dynasty, it is recorded that Artocarpus tonkinensis A. Chev. ex Gagnep., which has leaves resembling thistle and flowers akin to Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz., originated from the West, and the locals referred to it as “Yan Zhi” in Chinese. During the Northern Wei Dynasty, “Qi Min Yao Shu” (《齐民要术》A.D.533) documented the method for planting red safflower, stating, “The flower land needs to be well-ripened. Planting occurs in late February or early March. The flowers should be picked on cool days. Picking will be exhaustive, and a method for killing flowers to make rouge is also recorded.” This indicates that mature safflower cultivation techniques were established in China by the Northern Wei Dynasty. The term “safflower” first appeared in the Song Dynasty’s “Herbal Atlas,” (《本草图经》A.D.1061) which noted, “Now it is found everywhere. People plant it in gardens, sowing seeds in the ripe ground during winter for spring seedlings.” In the Ming Dynasty, Xiangjin Wang’s “Botanical Treatise” (《群芳谱》A.D.1621) recorded that “seeds are collected in May, pounded and decocted, mixed with vinegar, and combined with vegetables for consumption. It can also be used as car fat and for making candles.” Shizhen Li also recorded in the “Compendium of Materia Medica” (《本草纲目》A.D.1590) that “the seeds of safflower can be planted in February, August, and December after rainfall, similar to the method of planting hemp. The young leaves and seedlings are also edible, and the leaves resemble those of small thistle.” This indicates that safflower has been widely utilized throughout history for various purposes, including medicinal applications, dyes, culinary uses, and oil production (Zhou et al., 2014).
From a historical perspective, safflower seeds, packets, and garlands of florets were commonly found alongside mummies in ancient Egypt (Weiss, 1971). Additionally, safflower is consumed raw in various regions of Iran (Mohamadpour et al., 2012). Safflower dye has been utilized in Italian, French, and British cuisine for both flavoring and coloring purposes. The florets have been applied in diverse ways, serving as a dye, coloring agent, flavoring, rouge, potion, and unguent (Delshad et al., 2018). The significance of safflower dyes is particularly evident in the carpet-weaving industries of Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent (Dajue and Mündel, 1996). This specific application is reflected in the latter part of the binomial name, where plants or their derivatives are often designated with the term “tinctorius,” indicating their association with dyes (Guarrera, 2006). In Thailand, the aqueous extract of safflower flowers is widely used as a hair color promoter (Boonyaprapas and Chokchaijareonporn, 1996). In traditional Indian medicine, safflower is commonly employed for treating scabies, arthritis, and mastalgia.
This plant species is frequently used in the treatment of amenorrhea, gastric tumors, and wounds, whether of internal or external origin, according to Chinese folklore. Notably, Iranian traditional medicine recognizes safflower for treating skin patches, baldness, phlegm, and colic (Imami et al., 2010). The traditional applications of safflower in Persian medicine are documented in traditional Persian texts. The flower and seeds of safflower exhibit laxative effects, while its seed oil is utilized for conditions such as rheumatism and paralysis (Razi, 2000). Additionally, safflower facilitates the absorption of therapeutic agents by target tissues and promotes tissue contraction. It is also employed in the treatment of vitiligo, hyperpigmentation, psoriasis, oral ulcers, and for analgesic purposes.
The fruit and leaves of safflower are known to alleviate phlegm, serve as an antidote for scorpion stings, and address numbness in the limbs (Ibn, 2007). The seeds of safflower possess laxative properties and are believed to mitigate melancholic tendencies and enhance semen quality (Jorjani, 2012; Uosefi, 1999). Safflower has been utilized in Persian folk medicine for treating diabetes, phlegmatic fever, melancholia, and dropsy (Aghili Khorasani and Makhzan al-Adwiyyah, 2011). Additionally, various plants from the Compositae family are traditionally used as agents promoting abortion. The water extract of safflower is applied for painful menstruation as a sedative, serves as a laxative for constipation, and acts as an anti-inflammatory remedy in traditional medicine (Zargari, 1992). The dried floret of Carthamus tinctorius L., known as Carthami flos, has gained significant popularity due to its extensive applications in the treatment of coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, gynecological conditions, stroke, and hypertension (Chen et al., 2025).
5 Phytochemistry
The tubular flowers of safflower, which comprise a variety of chemical substances, are the primary sites of concentration of its active metabolites. The most prevalent of these include flavonoids, alkaloids, sterols, lignans, spermidine, alkyl diols, and polysaccharides. In addition to its tubular blossoms, the achenes are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, such as oleic acid and linoleic acid (Chen et al., 2023). The tocopherols and unsaturated fatty acids present in the seeds prevent the “three highs” (hypertension, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia) and possess anti-aging properties (Wang et al., 2021).
5.1 Flavonoids
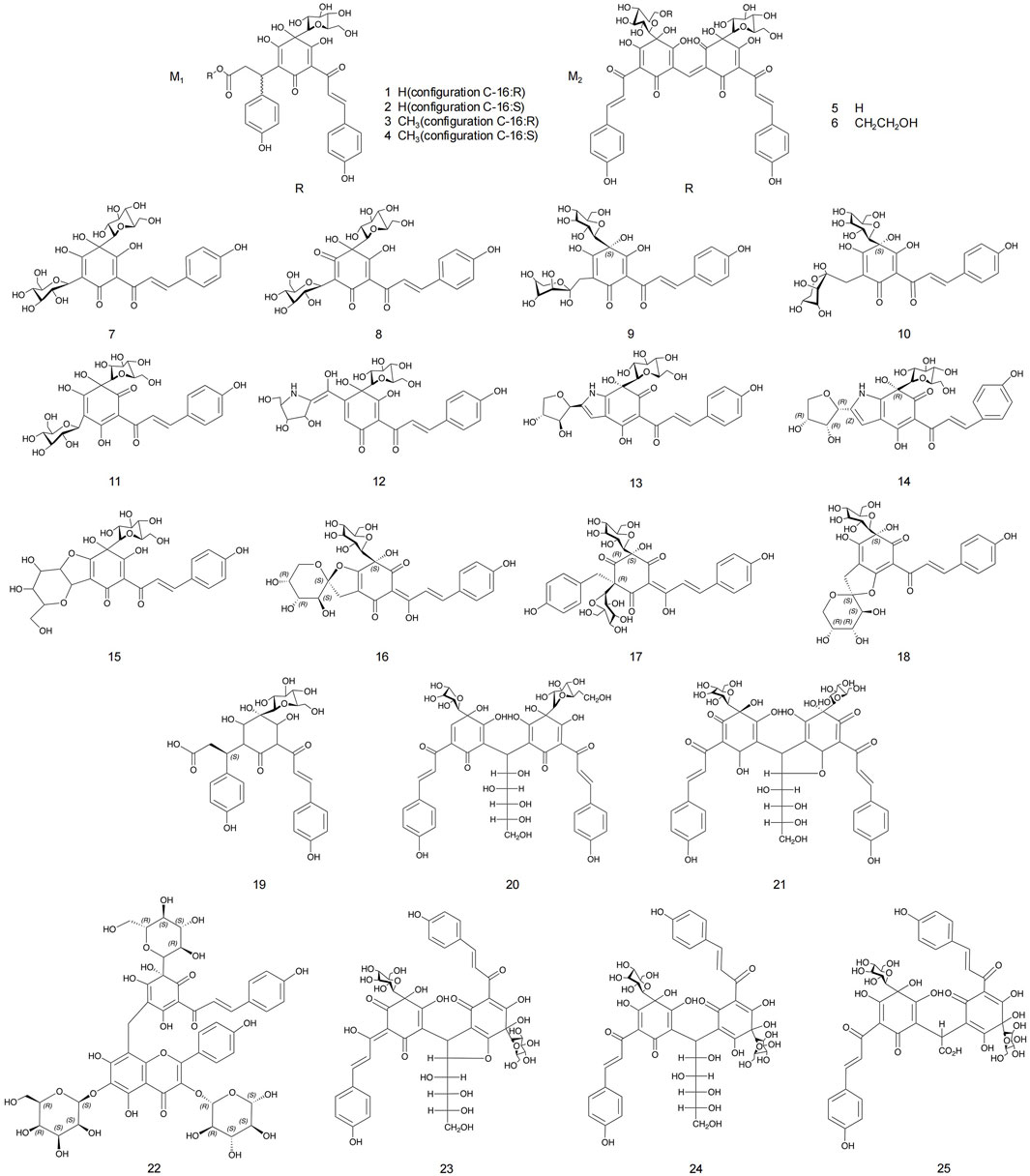
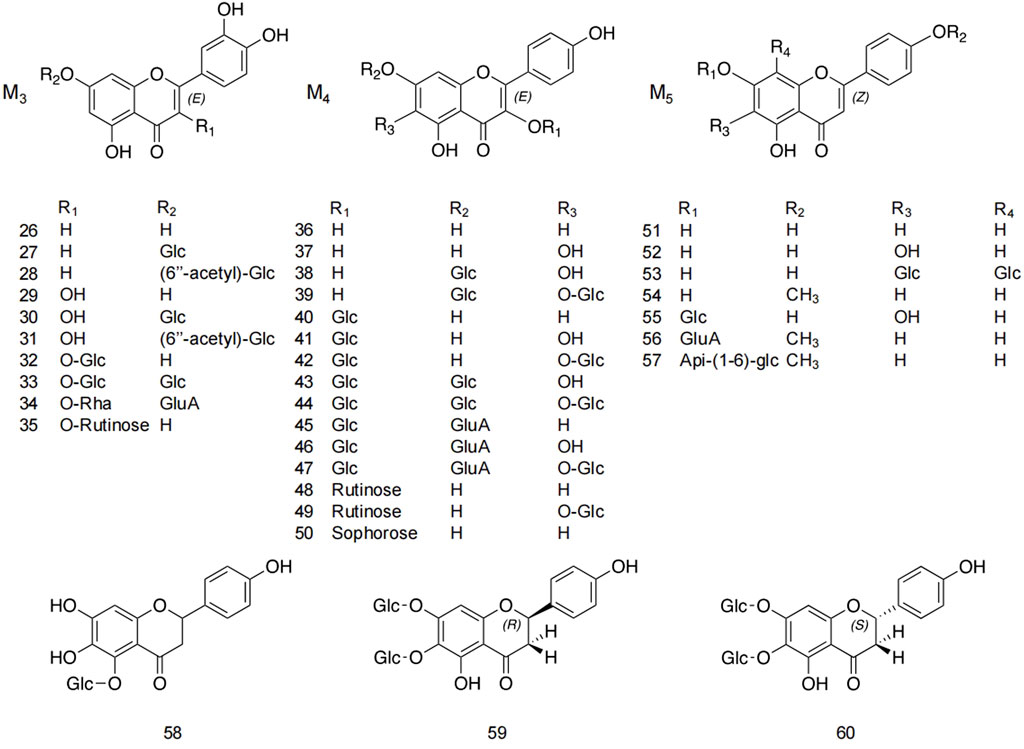
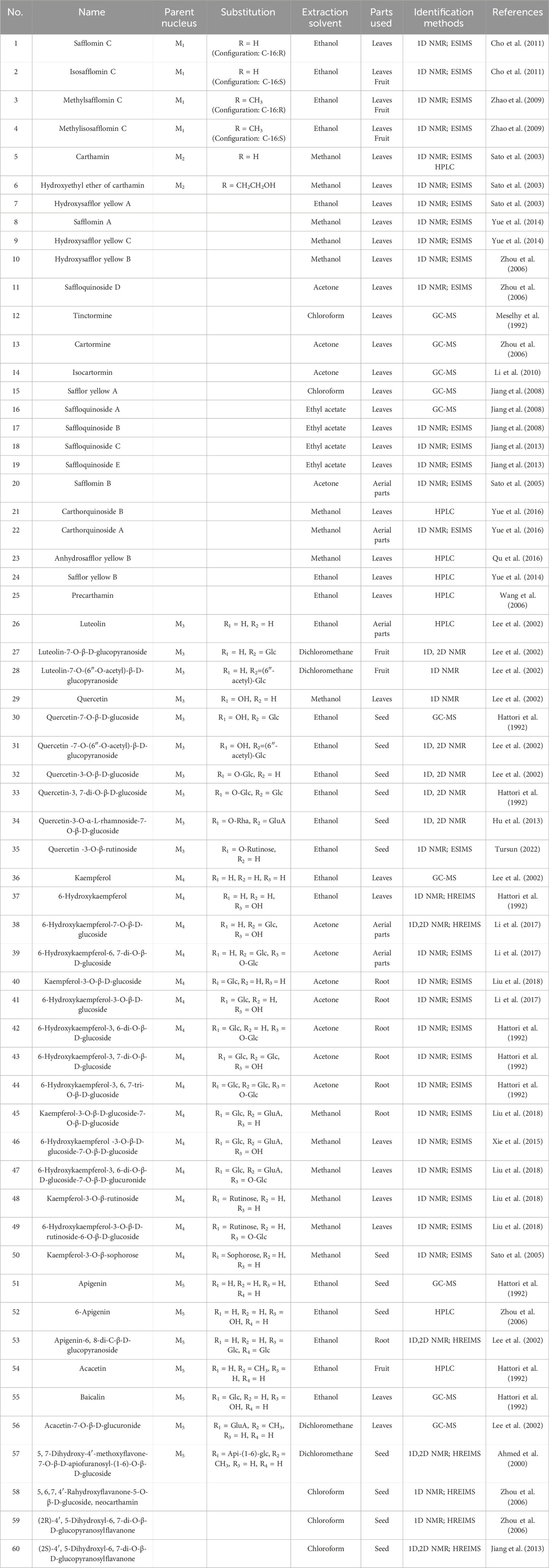
Flavonoids and flavonoid glycosides represent the most significant active metabolites in safflower and have been extensively studied within safflower research due to their close association with the pharmacological effects of this plant. The active flavonoid metabolites, known as quinone chalcone carbohydrates, encompass nearly all the safflower yellow (SY) and safflower red (SR) pigments found in safflower (Zhang J. et al., 2018). To date, 25 quinone chalcone carbohydrates have been isolated from safflower, predominantly existing as monomers, while a minority are found as bimolecular polymers. Their structures are illustrated in Figure 3. In addition to quinone chalcone carbohydrates, safflower contains flavonoid metabolites such as flavonols and dihydroflavonoids, which exhibit a range of pharmacological activities. Among these, flavonol glycosides are the most extensively studied metabolites, some of which demonstrate conformational relationships, with antioxidant activity being linked to the structure of the substituted glucose (Lee et al., 2002). Currently, 35 flavonoid metabolites have been extracted from safflower, with the primary flavonols in this category being kaempferol, apigenin, quercetin, and other derivatives. Figure 4 illustrates their specific architectures, while Table 1 provides a comprehensive list of the specific flavonoid metabolites.
5.2 Polyalkynes
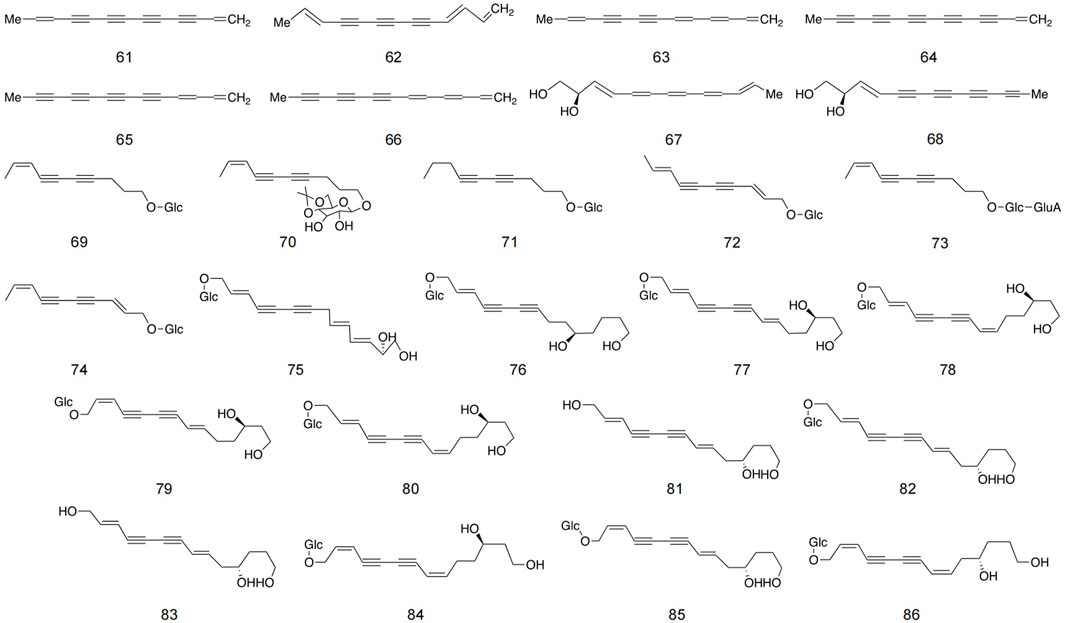
Polyalkyne metabolites in safflower are typically based on ten- and thirteen-carbon structures. The majority of glycosides in polyynes exist in an oily form, which readily aggregates in the air and is naturally unstable. However, once glycosides are formed, they transition into a powder state, thereby enhancing stability (Li et al., 2017). These metabolites is primarily located in stems, roots, blooms, and immature seeds infected by Epidermophyton (Zheng et al., 2019). Currently, 26 distinct polyynes have been isolated from safflower, with detailed structures and information provided in Figure 5 and Table 2.
5.3 Alkaloids and spermidines
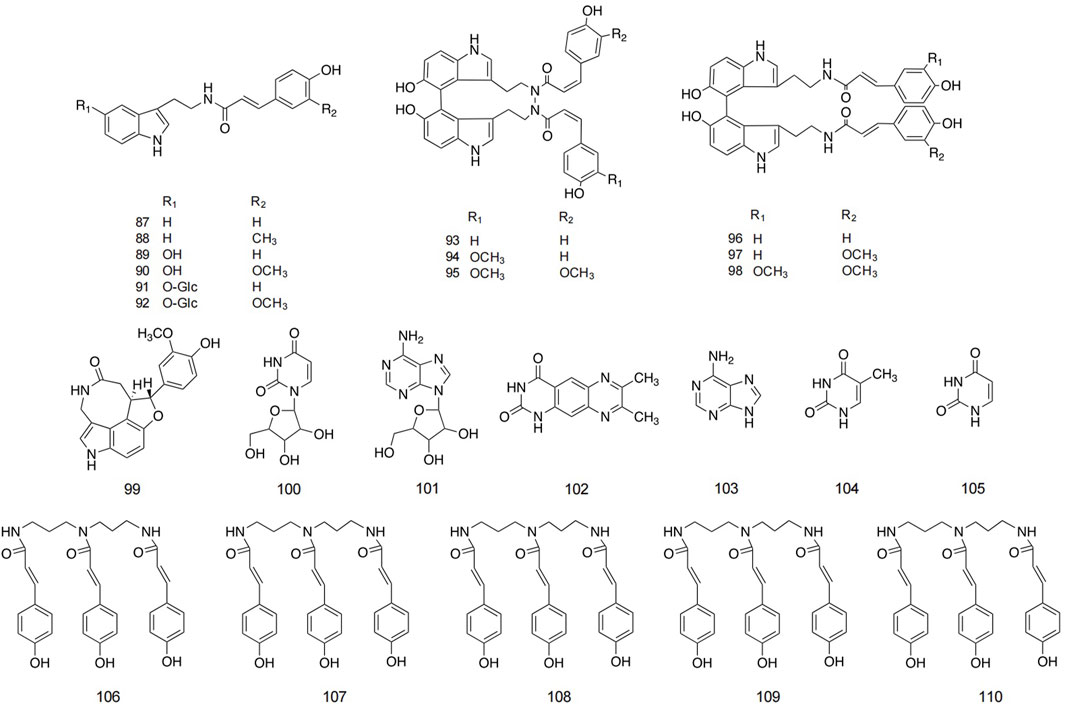
The alkaloid metabolites isolated from safflower are primarily derivatives of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), characterized by their lower polarity, and are predominantly found in safflower seeds. Additionally, a total of 13 and 11 alkaloids have been isolated from safflower oil and the dried flowers of safflower, respectively (Hao et al., 2010; Sakamura et al., 1980). Spermidine metabolites in safflower are spermidine derivatives with three coumaryl groups. Researchers successfully isolated five spermidine compounds from safflower by high-speed countercurrent chromatography (Jiang et al., 2014). Studies reported the preparation method for total spermine in safflower residue. The optimization method is to conduct three heating reflux extractions using 35 times the absolute volume of methanol, with each reflux extraction lasting for 2 h. The total extraction rate of four spermine compounds in safflower residue was 2.894 ± 0.011 mg/g (Zhao et al., 2014). Detailed structures and additional information are presented in Figure 6 and Table 3.
5.4 Lignans and sterols
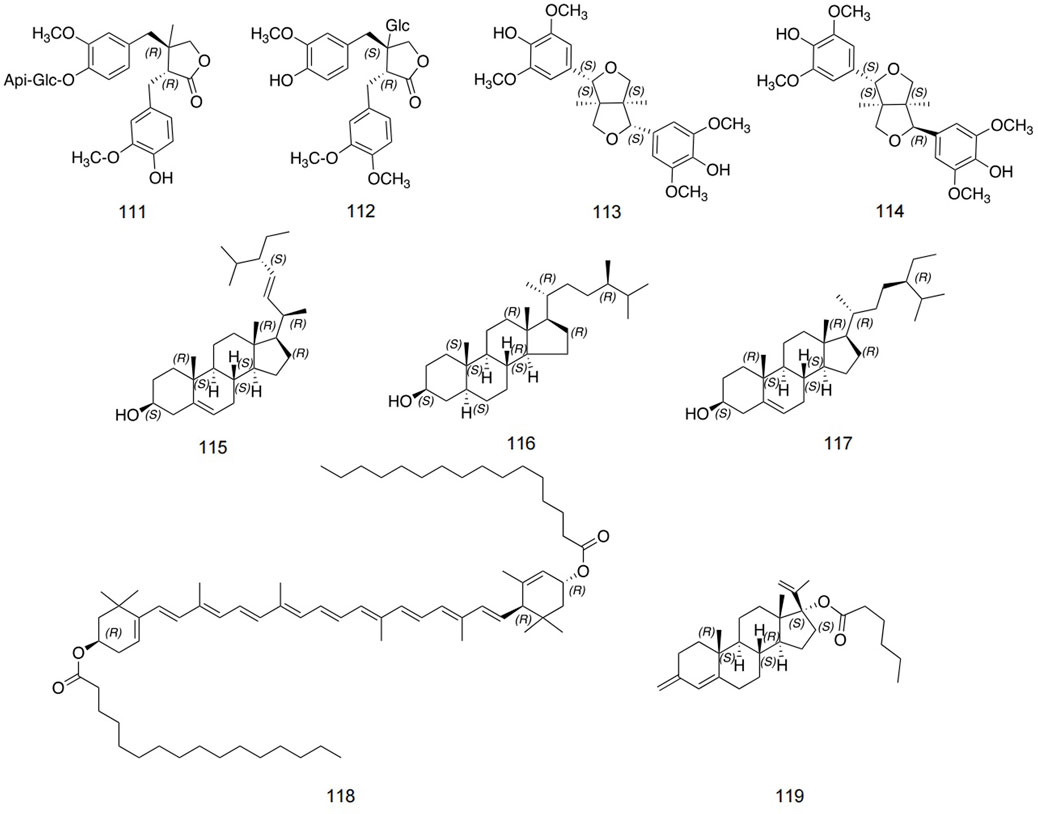
At present, few lignans have been found in safflower, including double tetrahydrofuran syringaresinol, lirioresinol A, and so on (Peng et al., 2017). Zhou et al. identified stigmasterol, campesterol, pregnane, and so on using IR, NMR, and MS analysis methods (Zhou et al., 2014). The detailed information is shown in Figure 7 and Table 4.
5.5 Other metabolites
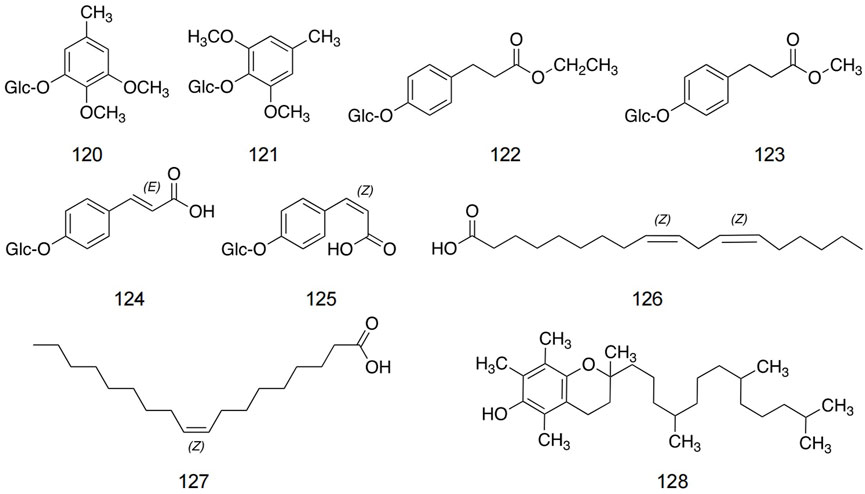
Zhou et al. (2008) found three new aromatic glycosides and three known aromatic glycosides. In addition, linoleic acid, oleic acid, and tocopherol are the main components in safflower seeds. The structures and detailed information of other metabolites in safflower are shown in Figure 8 and Table 5.
6 Pharmacological effects
The “Kaibao Materia Medica” (《开宝本草》A.D.973) asserts that safflower possesses the capability to activate blood circulation and promote menstruation and is primarily utilized for the treatment of menorrhagia, bruises, and injuries. According to contemporary pharmacological research, safflower has anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antioxidant, vascular, osteoporosis-preventative, and hepatoprotective properties. It also exhibits remarkable medicinal efficiency in regulating the functions of the neurological, motor, and cardiovascular systems (Kurt et al., 2025). The ensuing sections address each of these pharmacological effects. Figure 9 and Table 6 display the pharmacological properties of safflower and its active metabolites.
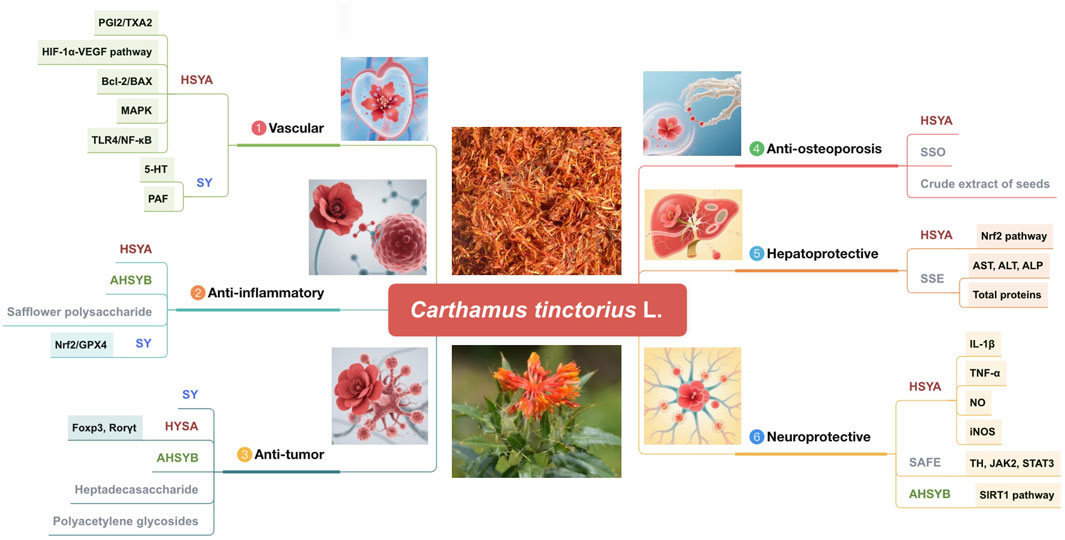
Figure 9. Pharmacological activities of the active metabolites of safflower (AHSYB, anhydroxysafflor yellow B; HSYA, hydroxysafflor yellow A; SAFE, safflower flavonoid extract; SSE, safflower seed extract; SSO, safflower seed oil; SY, safflower yellow).
6.1 Vascular effects
Recent pharmacological studies have demonstrated that SY, the active metabolite in safflower, significantly prolongs plasma prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time, reduces plasma fibrinogen content, and inhibits platelet aggregation induced by adenosine diphosphate (ADP) in rat models (Zhou et al., 2014). Additionally, SY significantly inhibits platelet aggregation induced by platelet-activating factor (PAF), 5-HT release, and increases intraplatelet free Ca2+ levels (Jiang et al., 2017). Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) has been shown to reduce ADP-induced platelet aggregation in a dose-dependent manner, achieving a maximum inhibition rate of 41.8%. The mechanism of action of HSYA may be attributed to its inhibition of thrombosis, reduction of platelet aggregation, and regulation of prostacyclin/prothrombin (PGI2/TXA2) as it significantly enhances blood rheological parameters such as whole blood viscosity, plasma viscosity, erythrocyte deformability, and aggregation, while having no significant effect on erythrocyte cumulative pressure (Li et al., 2017). Notably, safflower has been observed to prevent venous thrombosis but not arterial thrombosis, indicating that safflower may exhibit greater efficacy in venous thrombosis models, which are characterized by higher fibrin content in stasis-dependent thrombosis.
HSYA enhances vascular endothelial cell viability under hypoxic conditions by activating the HIF-1α-VEGF pathway and modulating the Bcl-2/Bax ratio (Yue et al., 2014). By preventing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, HSYA may also mitigate hypoxia-induced damage to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (Sun et al., 2013). A 4-week treatment of rats with safflower extract to study its effect on renal vascular hypertension showed that safflower extract inhibited hemodynamic alterations and vascular remodeling in 2K-1C hypertensive rats and had potent antioxidant activity (Bunbupha et al., 2018). Experiments on a rat model of left ventricular hypertrophy injected with different doses of HSYA found that HSYA at doses of 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg could inhibit cell apoptosis and metalloproteinase expression by enhancing the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax (Wang et al., 2013). The inflammatory response is the main cause of acute myocardial cell apoptosis, and HSYA reduces myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury by reducing autophagy and inhibiting the inflammatory response (Ye et al., 2020). Some studies have also established a model of cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury and found that HSYA inhibits the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and limits the output of mitochondrial cytochrome C (CytC) by regulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, thus helping to improve cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury (Huang et al., 2021). Recent findings revealed that HSYA exerted protective effects against ferroptosis in neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)-induced HUVECs and venous thromboembolism (VTE) mice. HSYA ameliorates VTE by depleting neutrophil extracellular traps through the inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, thus providing a novel therapeutic strategy for treating VTE (Yan et al., 2024). Modern pharmacological research indicates that safflower can dilate blood vessels, enhance microcirculation, increase blood flow, and stimulate uterine activity. Safflower injection has emerged as a popular therapeutic option, exhibiting sedative and analgesic properties (Wan et al., 2020).
6.2 Anti-inflammatory activities
Numerous studies have shown that the anti-inflammatory activity of safflower may be related to its flavonoid metabolites, which exhibit strong and effective anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in vivo. In vitro studies have shown that HSYA with anhydroxysafflor yellow B (AHSYB) inhibited a variety of inflammatory responses, including inhibition of PAF proliferation and asthma-related inflammatory responses in human bronchial smooth muscle cells (HBSMCs) (Guo et al., 2019). According to the research of Bacchetti et al., safflower polyphenol extract and HSYA from safflower had high antioxidant activity. They could also reduce the sensitivity of low-density lipoprotein to copper-induced lipid peroxidation and regulate the oxidative stress induced by tert-butyl hydrogen peroxide in human skin fibroblasts (HSFs), but at high concentrations, these extracts could promote oxidation (Bacchetti et al., 2020). In vivo studies have shown that the direct injection of HSYA (50 mg/kg, 75 mg/kg, and 112.5 mg/kg) into guinea pigs enhances the protective effect against ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma (Zheng et al., 1996).
Safflower extract inhibited ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats by reducing the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and attenuating the inflammatory response (Lu et al., 2019). AHSYB could protect against brain I/R injury by decreasing the expression of inflammatory cytokines in rats (Du et al., 2019). HSYA and SY inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and protect against myocardial ischemia in rats (Zhou et al., 2014). The therapeutic effect of HSYA on liver I/R injury was tested by constructing a mouse model, and the results showed that HSYA could reduce I/R-induced acute liver injury by directly attenuating macrophage activation under inflammatory conditions (Jiang et al., 2017). When the effects of HSYA treatment on microglia ischemia were examined in a mouse model, the results showed that HSYA inhibited the inflammatory response induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) (Li et al., 2017). HSYA was administered to rats with focal cerebral ischemia to see if it had neuroprotective effects, and the results of the study showed that HSYA is a promising drug for the treatment of stroke (Sun et al., 2013). Similarly, HSYA was injected into mice in three doses (26.7 mg/kg/day, 40 mg/kg/day, and 60 mg/kg/day). The results showed that HSYA reduced the loss of body weight, increased myeloperoxidase activity, and inhibited the inflammatory response in the lungs induced by bleomycin (Wu et al., 2013). Researchers established colitis models in mice via DSS and in Caco-2 cells via lipopolysaccharide. Further analyses revealed that SY could inhibit ferroptosis via the Nrf2/GPX4 axis in both in vivo and RSL3-induced Caco-2 cell models. Importantly, the antiferroptotic and protective effects of SY were nullified by Nrf2 knockout in vivo and by the use of ML385 in vitro. The effects of SY on ulcerative colitis (UC) are strongly associated with the Nrf2 pathway. SY might be a potential candidate for the treatment of UC, which provides an important reference for investigating the mechanisms of flavonoid compounds involved in preventing inflammatory diseases (Bian et al., 2024).
6.3 Antitumor activities
Safflower extracts have been shown to have a strong inhibitory effect on several types of cancer in both in vivo and in vitro tests. In one in vivo experiment, the anticancer effect of HSYA was investigated using a mouse model, and it was found that HSYA can effectively prevent the proliferation and migration of cancer cells and can induce apoptosis, a result that provides a scientific basis for an anticancer agent for human hepatic cell carcinoma (HCC) (Zhang S. M. et al., 2018). The proportion of FOXP3-expressing Tregs in the spleen and the expression of Foxp3 and Rorγt mRNA decreased following treatment with certain doses of HSYA. HSYA inhibited tumor growth without detrimental effects on the weight of the mice, indicating that HSYA may be suitable as a novel therapy for HCC patients (Ma et al., 2019). In an in vitro study, AHSYB was found to block the MCF-7 cell cycle and induce apoptosis (Qu et al., 2019). Similarly, in an experiment to observe the effect of safflower polysaccharide on the proliferation and metastasis of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, its inhibitory effect was found to increase in a dose-time-dependent manner (Luo et al., 2015). It has also been found that HSYA has an effect on angiogenesis in H22-bearing mice, and the results suggest that HSYA could significantly inhibit tumor growth by suppressing the secretion of angiogenic factors, indicating that HSYA is a candidate for the prevention and treatment of HCC (Yang et al., 2015). All these experimental results suggest that SY analogs, as flavonoid metabolites in safflower, are related to the antitumor process of safflower. Additionally, a highly branched heptadecasaccharide can target galectin-3 and inhibit pancreatic cancer cell growth (Hu et al., 2022). The polyacetylene glycoside (5R)-5-acetoxy-8,10,12-tetradecatriyne-1-O-β-D-glucopyranoside exhibited anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting LPS-induced NO production in RAW264.7 cells (Li et al., 2021).
6.4 Anti-osteoporosis activities
HSYA has the potential to prevent and treat glucocorticoid-induced intraocular pressure elevation (GCIOP) by promoting bone mineralization, osteoblast viability, and bone collagen expression and inhibiting bone resorption (Liu et al., 2018). Another study showed that a crude extract of seeds affected osteoblast differentiation and intracellular calcium ion concentration in MC3T3-E1 cells, suggesting that the crude extract of seeds has the ability to prevent osteoporosis and prevent bone loss (Jang et al., 2007). A study of the effects produced by safflower seed oil (SSO) on osteoporotic de-ovulated rats showed a potential role of SSO in ameliorating osteoporosis (Alam et al., 2006). The effect of safflower seed extract (SSE) on periodontal tissue regeneration was evaluated in a preclinical single-walled model in dogs and showed improved bone formation (Kim et al., 2002).
6.5 Hepatoprotective activities
Injection of HSYA into rat hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) showed inhibition of HSC activation and cell proliferation, suggesting it as a potential candidate for the prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis (Dong, 2019). The effect of HSYA on brain changes induced by lymphoretentive encephalopathy in rats, a test that supports the idea that HSYA can treat lymphoretentive encephalopathy (Pan et al., 2012). Hepatic fibrosis was significantly reduced in rats injected with carbon tetrachloride every 2 weeks (5 mg/kg) within 12 weeks, indicating that HSYA is a promising anti-fibrotic agent for chronic liver disease (Zhang S. M. et al., 2018). Additionally, Wu et al. explored a rat liver injury model induced by CCl4 through in vivo experiments and observed that safflower seed extract (SSE) could reduce the serum levels of AST, ALT, ALP, and total protein in model rats. Through HE staining analysis, it was determined that HSYA effectively alleviates liver injury by exerting a significant hepatoprotective effect via the Nrf2 pathway (Wu et al., 2013). Studies have shown that SSE tocopherol has strong hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity when administered at doses up to 2 g/kg in a rat model (Wu et al., 2013).
6.6 Neuroprotective activities
Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are neurodegenerative diseases. Safflower petal extracts have been shown to have free radical scavenging and neuroprotective effects (Abuova et al., 2022). Safflower flavonoid extract (SAFE) showed significant anti-PD effects, which might be due to the anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids (Lei et al., 2020). Molecular docking analysis revealed that key components of SAFE, such as kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside or AHSYB, can bind to proteins such as TH, JAK2, STAT3, and α7-nAChR (Ablat et al., 2022). Thus, SAFE is a potential drug candidate for PD prevention.
SY and HYSA can protect nerves by alleviating amyloid β1-42-induced glutamate cycle disorder in an AD rat model and by improving synaptic structural plasticity, leading to enhanced learning and memory (Hou et al., 2020). In particular, HYSA can partially inhibit the expression of NF-κB p65 and iNOS and downregulate the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and NO, leading to the suppression of inflammatory responses, the attenuation of LPS-induced midbrain neurotoxicity and neuroinflammation, and the alleviation of LPS-induced dopaminergic neuronal damage (Tiwari et al., 2018). HYSA and AHSYB may improve cell viability, decrease neuronal apoptosis, reduce infarct volume, improve neurological function, inhibit apoptosis, and reduce oxidative stress, which suggests that HYSA and AHSYB are potential drugs for the treatment of brain ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury via the SIRT1 pathway (Fangma et al., 2021).
7 Clinical applications
Safflower is known for its ability to activate blood circulation, disperse stasis, and relieve pain. In Western medicine, safflower is recognized for its uterine-stimulating effects and is widely used to treat gynecological conditions such as dysmenorrhea, abdominal masses, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, and pelvic stasis syndrome (Zhou et al., 2006). In 2013, Dong et al. summarized the medical records of patients who used SY at their institution, revealing that 59.32% of the 880 records pertained to cardiovascular issues, while 20.00% were related to cerebrovascular diseases (Dong et al., 2013). Notably, the combination of SY for injection with insulin and azithromycin yielded promising results. Concurrently, Li et al. demonstrated that blood-activating and stasis-transforming medications can exert myocardial protective effects through various pathways and targets (Li et al., 2017). Among these, safflower can decrease serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels by enhancing the body’s antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX).
Ovarian vein syndrome, also referred to as pelvic stasis syndrome, is a significant cause of gynecological pelvic pain, characterized by chronic discomfort, a marked increase in fatigue, and, in severe cases, symptoms indicative of neurological depletion. In Western medicine, surgical interventions for severe cases, such as total transabdominal hysterectomy or round ligament suspension, have been widely accepted (Zhou et al., 2014). However, patients, especially women, often find these treatments to be more distressing and may struggle to accept them. Due to their pharmacological effects, safflower and safflower-containing formulations have gained popularity in clinical treatments, providing significant benefits to female patients (Zhang S. M. et al., 2018). Dysmenorrhea, a prevalent gynecological condition, is primarily attributed to the weakening of qi and blood in the uterus due to blood stasis and qi stagnation, according to TCM (Zhang et al., 2011). The clinical application of Honghua injection for stimulating the “San Yin” acupoint may benefit patients with dysmenorrhea, as it can modulate sympathetic nerve fibers and relax the pelvic floor and uterine smooth muscles. This treatment is particularly effective for primary dysmenorrhea.
Diabetes mellitus is classified as a form of “thirst” in TCM, and is often characterized by abnormalities in blood glucose and lipid levels, with an irreversible onset leading to long-term complications such as renal failure (Qu et al., 2019). In clinical practice, Liu et al. treated patients with diabetic nephropathy for several years. When assessing the effects of safflower redox on type 2 diabetic nephropathy, using metformin and glibenclamide as positive control drugs, they found that SY significantly reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and increased SOD content in the body, thereby improving antioxidant capacity, lowering blood glucose levels in diabetic nephropathy patients, enhancing insulin resistance, and ultimately providing protective effects on the kidneys (Liu et al., 2018). Notably, a clinical trial conducted by Zhang et al. categorized the clinical applications of safflower and provided experimental evidence demonstrating its efficacy in reducing insulin resistance and renal oxidative stress. The study revealed that safflower inhibits the expression of growth factors in renal tubules, decreases renal interstitial fibrosis, and possesses anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, anticoagulant, and antioxidant properties. Moreover, it enhances blood viscosity, coagulation, and aggregation, which collectively contribute to improved renal blood perfusion. These effects are crucial in preventing the progression of kidney disease (Zhang S. M. et al., 2018).
In TCM theory, the liver and bile are considered cognate, with bile being closely associated with the liver. Wu et al. concluded that the metabolites extracted from safflower not only inhibit bile acid synthesis and promote the excretion of bile acids and bilirubin from the liver, but also alleviate jaundice, hepatomegaly, liver injury, and liver failure caused by bile stasis. The mechanism of action is related to the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and pregnane X receptor (PXR), which regulate bile synthesis and expression. On one hand, FXR activation downregulates cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1), thereby alleviating hepatocellular injury caused by bile acid accumulation. On the other hand, it controls the expression of related proteins, reduces hepatic uptake, and promotes the metabolism of bile acids and bile salts (Wu et al., 2013). Clinical trials have shown that oral treatment with safflower seed granules in postmenopausal women over a period of time had strong antioxidant and potential osteoprotective effects without hepatotoxicity (Cho et al., 2011).
Sudden deafness is a symptom of sudden sensorineural hearing loss, which has various causes and mechanisms and has been relatively under-researched clinically. SY and Ginkgo biloba extract may alleviate the symptoms of sudden deafness resulting from abnormal microcirculation in the ear, edema in the inner ear canal, and nutritional damage to the ear canal. Wang conducted a study on patients with sudden deafness by measuring their hearing, blood lipids, blood rheology, neutrophils, and lymphocytes following drug administration (Wang, 2020). The study confirmed that SY improves inner ear microcirculation in patients with sudden deafness by reducing blood lipids, decreasing capillary permeability, and inhibiting inflammatory exudation. The cost of SY is lower than that of Ginkgo biloba extract, known as “gold nadol” in Chinese, and its therapeutic effect is significant.
In addition to treating physical diseases, a recent survey of 752 Saudis who had previously tried safflower for depression and anxiety showed that 279 (37.1%) reported that safflower was effective, whereas 389 (51.73%) reported some improvement (Albaiz, 2022). Consistent with the survey, a systematic review of scientific articles published between 2010 and 2020 showed that safflower flower extracts have an anxiolytic effect as effective as diazepam (Meneses et al., 2023). Due to its nutritional and health benefits, many safflower products, such as painkillers, health drinks, skin lotions, tablets, and other nutritional supplements, are currently on the market. The combination of safflower and other ingredients is effective in the treatment of some diseases. It was reported that GuHong injection, composed of safflower and the chemical drug N-acetyl-L-glutamine, has great value in clinical settings for cerebrovascular diseases, such as ischemic stroke and related diseases (Wang Q. et al., 2023). A safflower and peach kernel herb pair is widely used in TCM for the treatment of liver fibrosis (Huang et al., 2023; Yuan et al., 2023).
8 Conclusion and perspective
Based on data gathered from both traditional and contemporary literary sources, this article outlines the historical applications, chemical constitution, and extensive pharmacological activities of safflower. Through years of contemporary research, primary metabolites such as polyalkynes, flavonoids, alkaloids, and polysaccharides have been identified, isolated, and their pharmacological properties confirmed. Pharmacological studies have substantiated the traditional uses of safflower, particularly in the management of dysmenorrhea and urinary tract infections (Adamska and Biernacka, 2021). To fully comprehend the mechanisms of action of safflower, further in-depth research on the intricate pharmacological effects of its metabolites, along with comprehensive analyses of all phytochemicals, is necessary.
Thin-layer chromatography and microscopy techniques are the only methods authorized by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia for the identification of safflower. Therefore, it is crucial to develop a reliable, precise, and scientifically valid identification technique to ensure the authenticity of the product. The majority of ost safflower medicinal materials are derived from wild sources. Consequently, attention should be directed towards developing large-scale cultivation methodologies to preserve the sources of safflower medicinal materials and minimize confusion between products and substitutes. A unified standard system and quality grade standards should be prioritized in research (Liao et al., 2019). Alkaloids and flavonoids are recognized as the primary pharmacologically active metabolites among several bioactive compounds identified in safflower, along with newly isolated metabolites. However, basic research on the pharmacological activities of safflower remains limited, primarily concentrating on the activities of the extracted components (Pu et al., 2019). Therefore, future research should strengthen the investigation of the biological activity of other chemical metabolites, and the interactions and structure–activity relationships between alkaloids and flavonoids. Additionally, clinical studies are necessary to effectively evaluate the efficacy, adverse reactions, and toxicity of safflower.
At present, research on safflower predominantly focuses on quinones, and the variety of safflower preparations utilized in clinical practice remains limited. The separation and investigation of other chemical components are insufficient, leading to an incomplete understanding of the effective components and a lack of depth in pharmacological mechanism research. It is essential to elucidate the pharmacological mechanisms of action to better guide clinical drug use and facilitate new drug development. Increasingly, there is recognition of the significance of the prevention of chronic diseases and the challenges posed by an aging population. Safflower possesses both dietary and medicinal properties (Snoke et al., 2022). Although the range of safflower products developed is currently limited, the safflower industry is experiencing significant growth. Various enterprises have transformed certain chemical components abundant in safflower into marketable products, including safflower tea, safflower pigment, safflower vinegar, and safflower seed oil (Nasiri et al., 2021). Moving forward, it is imperative to focus on the research and development of the safflower industry to create a broader array of products that contribute to human health.
Author contributions
HB: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. JY: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. RW: Funding Acquisition, Software, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81603418) and the Central Government Support for Local College Reform Projects (No. 2020YQ05).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AHSYB, anhydroxysafflor yellow B; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; CYP7A1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; CytC, cytochrome C; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; GSH-PX, glutathione peroxidase; HCC, hepatic cell carcinoma; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; HSFs, human skin fibroblasts; HSYA, hydroxysafflor yellow A; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MDA, malondialdehyde; OGD, oxygen-glucose deprivation; OVA, ovalbumin; PAF, platelet-activating factor; PXR, pregnane X receptor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; SR, safflower red; SSE, safflower seed extract; SSO, safflower seed oil;SY, safflower yellow; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine.
References
Ablat, N., Liu, R., Ablimit, M., Sun, Y., Xu, F., Zhao, X., et al. (2022). Preventive effects of a standardized flavonoid extract of safflower in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease rat model. Neuropharmacology 217, 109209. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109209
Abuova, Z., Turgumbayeva, A., Jumagaziyeva, A., Rakhimov, K., and Jussupkaliyeva, A. (2022). Study of component composition and antimicrobial activity of the ophthalmic emulsion based on the safflower flowers (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2022/3181270
Adamska, I., and Biernacka, P. (2021). Bioactive substances in safflower flowers and their applicability in medicine and health-promoting foods. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 1–23. doi:10.1155/2021/6657639
Ahmed, K. M., Marzouk, M. S., El-Khrisy, E. A. M., Abdel Wahab, S., and El-Din, S. S. (2000). ChemInform abstract: a new flavone diglycoside from Carthamus tinctorius seeds. Die Pharmazie 55 (8), 621–622. doi:10.1002/chin.200047189
Alam, M. R., Kim, S. M., Lee, J., Chon, S. K., Choi, S. J., Choi, I. H., et al. (2006). Effects of safflower seed oil in osteoporosis induced-ovariectomized rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 34, 601–612. doi:10.1142/S0192415X06004132
Albaiz, A. S. (2022). The use of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) in treating depression and anxiety. Cureus J. Med. Sci. 2 (14), e22278. doi:10.7759/cureus.22278
Bacchetti, T., Morresi, C., Bellachioma, L., and Ferretti, G. (2020). Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of Carthamus tinctorius, hydroxy safflor yellow A, and safflor yellow A. Antioxidants (Basel, Switz.) 9, 119. doi:10.3390/antiox9020119
Bian, W., Wei, L., and Wang, K. (2024). Carthamin yellow alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis by repairing the intestinal barrier and activating the Nrf2/GPX4 axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 141, 113020. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113020
Boonyaprapas, N., and Chokchaijareonporn, O. (1996). SamoonPrai maipeunban (herbal plants, in Thai). Thailand: Faculty of Pharmacy, Mahidol University.
Bunbupha, S., Wunpathe, C., Maneesai, P., Berkban, T., Kukongviriyapan, U., Kukongviriyapan, V., et al. (2018). Carthamus tinctorius L. extract improves hemodynamic and vascular alterations in a rat model of renovascular hypertension through Ang II-AT1R-NADPH oxidase pathway. Ann. Anat. 216, 82–89. doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2017.11.005
Chen, J., Guo, S., Hu, X., Wang, R., Jia, D., Li, Q., et al. (2023). Whole-genome and genome-wide association studies improve key agricultural traits of safflower for industrial and medicinal use. Hortic. Res. 10 (11), uhad197. doi:10.1093/hr/uhad197
Chen, Y., Lai, F., Xu, H., and He, Y. (2025). Chinese herb pairs for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: compatibility effects, pharmacological potential, clinical efficacy, and molecular mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 347, 119516. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2025.119516
Cho, S. H., Jang, J. H., Yoon, J. Y., Han, C. D., Choi, Y. S., and Choi, S. W. (2011). Effects of a safflower tea supplement on antioxidative status and bone markers in postmenopausal women. Nutr. Res. Pract. 5, 20–27. doi:10.4162/nrp.2011.5.1.20
Dajue, L., and Mündel, H. H. (1996). Safflower, Carthamus Tinctorius L. Italy: International Plant Genetic Resources Institute.
Delshad, E., Yousefi, M., Sasannezhad, P., Rakhshandeh, H., and Ayati, Z. (2018). Medical uses of Carthamus tinctorius L. (Safflower): a comprehensive review from Traditional Medicine to Modern Medicine. Electron. physician 10, 6672–6681. doi:10.19082/6672
Dong, H., Liu, Y., Zou, Y., Li, C. C., Li, L. B., Li, X. M., et al. (2013). Alteration of the ERK5 pathway by hydroxysafflor yellow A blocks expression of MEF2C in activated hepatic stellate cells in vitro: potential treatment for hepatic fibrogenesis. Pharm. Biol. 52, 435–443. doi:10.3109/13880209.2013.840850
Dong, Y. N. (2019). Analysis on use of safflower Yellow for injection in the People’s Hospital of Jizhou district, Tianjin in 2018. D&C 34, 2828–2832.
Du, S., Deng, Y., Yuan, H., and Sun, Y. (2019). Safflower yellow B protects brain against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through AMPK/NF-kB pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2019/7219740
Fangma, Y., Zhou, H., Shao, C., Yu, L., Yang, J., Wan, H., et al. (2021). Hydroxysafflor yellow A and anhydrosafflor yellow B protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating oxidative stress and apoptosis via the silent information regulator 1 signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 739864. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.739864
Guarrera, P. M. (2006). Household dyeing plants and traditional uses in some areas of Italy. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed 2, 9. doi:10.1186/1746-4269-2-9
Guo, X., Zheng, M., Pan, R., Zang, B., Gao, J., Ma, H., et al. (2019). Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) targets the platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor and inhibits human bronchial smooth muscle activation induced by PAF. Food Funct. 10, 4661–4673. doi:10.1039/c9fo00896a
Hamdan, Y. A. S. (2024). Genetic diversity assessment of Palestinian safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) utilizing DAMD molecular markers. Biotechnol. Lett. 46 (12), 1293–1302. doi:10.1007/s10529-024-03538-4
Hao, J., Li, F. S., Liu, Z. Z., and Zhang, P. C. (2010). Polyacetylenic chemical components in Carthamus tinctorius L. In Proceedings of 2010 China Pharmaceutical Congress and the 10th China Pharmacist Week, 2122–2130.
Hattori, M., Huang, X. L., Che, Q. M., Kawata, Y., Tezuka, Y., Kikuchi, T., et al. (1992). 6-Hydroxykaempferol and its glycosides from Carthamus tinctorius petals. Phytochemistry 31, 4001–4004. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)97572-1
Hou, J., Wang, C., Zhang, M., Ren, M., Yang, G., Qu, Z., et al. (2020). Safflower yellow improves the synaptic structural plasticity by ameliorating the disorder of glutamate circulation in aβ1-42-induced AD model rats. Neurochem. Res. 45 (8), 1870–1887. doi:10.1007/s11064-020-03051-w
Hu, C., Wu, S., He, F., Cai, D., Xu, Z., Ma, W., et al. (2022). Convergent synthesis and anti-pancreatic cancer cell growth activity of a highly branched heptadecasaccharide from Carthamus tinctorius. Angew. Chem. 134 (32). doi:10.1002/ange.202202554
Hu, X. J., Yin, S., Yuan, T. T., Wang, Y. J., Huang, Z. R., and Lu, Y. (2013). Chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Carthamus tinctorius L. J. Pharm. Pract. Serv. 31, 161–168.
Huang, L., Yu, Q., Peng, H., and Zhen, Z. (2023). The mechanism of peach kernel and safflower herb-pair for the treatment of liver fibrosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology: a review. Med. Balt. 102 (16), e33593. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000033593
Huang, P., Wu, S. P., Wang, N., Seto, S., and Chang, D. (2021). Hydroxysafflor yellow A alleviates cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by suppressing apoptosis via mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Phytomedicine 85, 153532. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153532
Imami, A., Taleb, A., and Khalili, H. (2010). PDR for herbal medicines. 1 ed. Tehran: Andisheh-Avar.
Jang, H. O., Park, Y. S., Lee, J. H., Seo, J. B., Koo, K. I., Jeong, S. C., et al. (2007). Effect of extracts from safflower seeds on osteoblast differentiation and intracellular calcium ion concentration in MC3T3-E1 cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 21, 787–797. doi:10.1080/14786410601133475
Jiang, J. S., Chen, Z., Yang, Y. N., Feng, Z. M., and Zhang, P. C. (2013). Two new glycoside compounds, named saffloquinoside C(1) and (-)-4-hydroxybenzoic acid-4-O-(6′-O-(2″-methylbutyryl)-β-D-glucopyranoside)(2), were isolated from the florets of Carthamus tinctorius. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 15, 427–432. doi:10.1080/10286020.2013.780046
Jiang, J. S., He, J., Feng, Z. M., and Zhang, P. C. (2017). Two new quinochalcones from the florets of Carthamus tinctorius. Org. Lett. 12, 1196–1199. doi:10.1021/ol902971w
Jiang, J. S., Lü, L., Yang, Y. J., Zhang, J. L., and Zhang, P. C. (2008). New spermidines from the florets of Carthamus tinctorius. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 10, 447–451. doi:10.1080/10286020801948540
Jiang, S., Shi, Z., Li, C., Ma, C., Bai, X., and Wang, C. Y. (2014). Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced liver injury by suppressing macrophage activation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 7, 2595–2608. doi:10.1155/2016/2816743
Kim, H. Y., Kim, C. S., Jhon, G. J., Moon, I. S., Choi, S. H., Cho, K. S., et al. (2002). The effect of safflower seed extract on periodontal healing of 1-wall intrabony defects in beagle dogs. J. Periodontol. 73, 1457–1466. doi:10.1902/jop.2002.73.12.1457
Kurt, C., Altaf, M. T., Liaqat, W., Nadeem, M. A., Çil, A. N., and Baloch, F. S. (2025). Oil content and fatty acid composition of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) germplasm. Foods 14 (2), 264. doi:10.3390/foods14020264
Lee, J. Y., Chang, E. J., Kim, H. J., Park, J. H., and Choi, S. W. (2002). Antioxidative flavonoids from leaves of Carthamus tinctorius. Arch. Pharm. Res. 25, 313–319. doi:10.1007/BF02976632
Lei, H., Ren, R., Sun, Y., Zhang, K., Zhao, X., Ablat, N., et al. (2020). Neuroprotective effects of safflower flavonoid extract in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced model of Parkinson’s disease may be related to its anti-inflammatory action. Molecules 25 (21), 5206. doi:10.3390/molecules25215206
Li, F., He, Z., and Ye, Y. (2017). Isocartormin, a novel quinochalcone C-glycoside from Carthamus tinctorius. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 7, 527–531. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2017.04.005
Li, F., He, Z. S., and Ye, Y. (2010). Flavonoids from Carthamus tinctorius. Chin. J. Chem. 20, 699–702. doi:10.1002/cjoc.20020200715
Li, X., Liu, J., Peng, C., Zhou, Q., Liu, F., Guo, L., et al. (2021). Polyacetylene glucosides from the florets of Carthamus tinctorius and their anti-inflammatory activity. Phytochemistry 187, 112770. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112770
Liao, H., Li, Y., Zhai, X., Zheng, B., Banbury, L., Zhao, X., et al. (2019). Comparison of inhibitory effects of safflower decoction and safflower injection on protein and mRNA expressions of iNOS and IL-1β in LPS-Activated RAW264.7 cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2019/1018274
Liu, L., Tao, W., Pan, W., Yang, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2018). Hydroxysafflor Yellow A promoted bone mineralization and inhibited bone resorption which reversed glucocorticoids-induced osteoporosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2018/6762146
Lu, D., Wang, L., Yu, Y., Li, L., Su, X., Sun, Y., et al. (2025). Genome-wide identification and functional analyses of the TCP gene family in Carthamus tinctorius L. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 12970. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-97743-4
Lu, Q. Y., Ma, J. Q., Duan, Y. Y., Cai, X. J., Feng, Y., Yang, Y. Q., et al. (2019). Carthamin yellow protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury with reduced reactive oxygen species release and inflammatory response. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 74, 228–234. doi:10.1097/fjc.0000000000000710
Luo, Z. B., Zeng, H. X., Ye, Y. Q., Liu, L. B., Li, S. J., Zhang, J. Y., et al. (2015). Safflower polysaccharide inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 11, 4611–4616. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.3310
Ma, Y., Feng, C., Wang, J., Chen, Z., Wei, P., Fan, A., et al. (2019). Hydroxyl safflower yellow A regulates the tumor immune microenvironment to produce an anticancer effect in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 17, 3503–3510. doi:10.3892/ol.2019.9946
Meneses, C., Valdes-Gonzalez, M., Garrido-Suárez, B. B., and Garrido, G. (2023). Systematic review on the anxiolytic and hypnotic effects of flower extracts in in vivo pre-clinical studies published from 2010 to 2020. Phytother. Res. 37 (5), 2144–2167. doi:10.1002/ptr.7830
Meselhy, M. R., Kadota, S., Momose, Y., Hattori, M., and Namba, T. (1992). Tinctormine, a novel Ca2+ antagonist N-containing Quin chalcone C-glycoside from Carthamus tinctorius L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 40, 3355–3357. doi:10.1248/cpb.40.3355
Mohamadpour, M., Khorsandi, L., and Mirhoseini, M. (2012). Toxic effect of Carthamus tinctorius L. (Safflower) extract in the mouse testis. 13th Royan congress on reproductive biomedicine and 7th Royan nursing and midwifery seminar. Tehran: Int J Fertil Steri.
Nasiri, K., Akbari, A., Nimrouzi, M., Ruyvaran, M., and Mohamadian, A. (2021). Safflower seed oil improves steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in rats with type II diabetes mellitus by modulating the genes expression involved in steroidogenesis, inflammation and oxidative stress. J. Ethnopharmaco. 275, 114139. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114139
Pan, Y., Zheng, D. Y., Liu, S. M., Meng, Y., Xu, H. Y., Zhang, Q., et al. (2012). Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuates lymphostatic encephalopathy-induced brain injury in rats. Phytother. Res. 26, 1500–1506. doi:10.1002/ptr.4594
Peng, X. R., Wang, X., Dong, J. R., Qin, X. J., Li, Z. R., Yang, H., et al. (2017). Rare hybrid dimers with anti-acetylcholinesterase activities from a safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) seed oil cake. J. Agr. food Chem. 65, 9453–9459. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03431
Pu, Z. J., Yue, S. J., Zhou, G. S., Yan, H., Shi, X. Q., Zhu, Z. H., et al. (2019). The comprehensive evaluation of safflowers in different producing areas by combined analysis of color, chemical compounds, and biological activity. Mol. (Basel, Switz.) 24 (18), 3381. doi:10.3390/molecules24183381
Qu, C., Wang, L. Y., Jin, W. T., Tang, Y. P., Jin, Y., Shi, X. Q., et al. (2016). Comparative analysis of the effects of hydroxysafflor yellow a and anhydrosafflor yellow B in safflower series of herb pairs using prep-HPLC and a selective knock-out approach. Molecules 21, 1480. doi:10.3390/molecules21111480
Qu, C., Zhu, W., Dong, K., Pan, Z., Chen, Y., Chen, X., et al. (2019). Inhibitory effect of hydroxysafflor yellow B on the proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 14, 187–197. doi:10.2174/1574891x14666190516102218
Ren, C., Xi, Z., Xian, B., Chen, C., Huang, X., Jiang, H., et al. (2023). Identification and characterization of CtUGT3 as the key player of astragalin biosynthesis in Carthamus tinctorius L. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 71 (43), 16221–16232. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05117
Sakamura, S., Terayama, Y., Kawakatsu, S., Ichihara, A. M., and Saito, H. (1980). Conjugated serotonins and phenolic constituents in safflower seed (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Agric. Biol. Chem. 44, 2951–2954. doi:10.1080/00021369.1980.10864416
Sato, K., Sugimoto, N., Ohta, M., Mori, T., Nakamura, N., and Kondo, K. (2003). Structure determination of minor red pigment in carthamus red colorant isolated by preparative LC/MS. Food Addit. Contam. 20, 1015–1022. doi:10.1080/02652030310001615177
Sato, S., Kusakari, T., Suda, T., Kasai, T., Kumazawa, T., Onodera, J. i., et al. (2005). Efficient synthesis of analogs of safflower yellow B carthamin and its precursor: two yellow and one red dimeric pigment in safflower petals. Tetrahedron 76, 131925–131931. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2005.07.080
Snoke, D. B., Angelotti, A., Borkowski, K., Cole, R. M., Newman, J. W., and Belury, M. A. (2022). Linoleate-Rich safflower oil diet increases linoleate-derived bioactive lipid mediators in plasma, and brown and white adipose depots of healthy mice. Metabolites 12, 743. doi:10.3390/metabo12080743
Sun, L., Yang, L., Fu, Y., Han, J., Xu, Y., Liang, H., et al. (2013). Capacity of HSYA to inhibit nitro tyrosine formation induced by focal ischemic brain injury. Nitric Oxide 88, 144–151. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2013.10.002
Tiwari, K., Gatto, C., and Wilkinson, B. (2018). Interrelationships among fatty acid composition, staphyloxanthin content, fluidity, and carbon flow in the Staphylococcus aureus membrane. Molecules 23 (5), 1201. doi:10.3390/molecules23051201
Tursun, E. (2022). Study on the chemical composition of safflower and acorn. Aral: Tarim University.
Uosefi, H. U. (1999). Riaz al-Advieh. 1st ed. Tehran: Institute of Meical History, Islamic Medicine and Complementary Medicine.
Waki, T., Terashita, M., Fujita, N., Fukuda, K., Kato, M., Negishi, T., et al. (2021). Identification of the genes coding for carthamin synthase, peroxidase homologs that catalyze the final enzymatic step of red pigmentation in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Plant cell physiol. 62 (10), 1528–1541. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcab122
Wan, X. H., Qin, Y. L., and Yan, T. (2020). Research progress on the pharmacological effects of honghua injection. Chin. J. Basic Med. Tradit. Chin. Med. 26, 429–431.
Wang, C., Zhang, D., Li, G., Liu, J., Tian, J., Fu, F., et al. (2006). Neuroprotective effects of safflower yellow B on brain ischemic injury. Exp. Brain Res. 241, 1195–1203. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0705-2
Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Mei, X., and Zhang, X. (2013). Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuates left ventricular remodeling after pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Pharm. Biol. 57, 31–35. doi:10.3109/13880209.2013.805791
Wang, J. J. (2020). Comparison of the therapeutic effects of safflower yellow pigment and Ginkgo Biloba extract on sudden deafness and exploration of the preliminary mechanism. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University.
Wang, L. W., Cui, X. Y., He, J. F., Duan, S., Liu, C. R., Shan, C. B., et al. (2021). Hydroxysafflor yellows alleviate thrombosis and acetaminophen-induced toxicity in vivo by enhancing blood circulation and poison excretion. Phytomedicine 87, 153579. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153579
Wang, X. P., Wang, P. F., Bai, J. Q., Gao, S., Wang, Y. H., Quan, L. N., et al. (2019). Investigating the effects and possible mechanisms of danshen-honghua herb pair on acute myocardial ischemia induced by isoproterenol in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 121, 109268. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109268
Wang, Y., Li, X., Zhang, Y., and Zhao, Y. (2015). Effect of hydroxy safflower yellow A on myocardial apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 165, 251–257. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.015
Wang, L., Ma, C., and Li, X. (2023). Hydroxysafflor yellows alleviate thrombosis and acetaminophen-induced toxicity in vivo by enhancing blood circulation and poison excretion. Phytomedicine 112, 154892. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154892
Wang, Q., Yang, Z., Guo, L., Li, Z., Liu, Y., Feng, S., et al. (2023). Chemical composition, pharmacology and pharmacokinetic studies of GuHong injection in the treatment of ischemic stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1261326. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1261326
Wu, S., Yue, Y., Tian, H., Li, Z., Li, X., He, W., et al. (2013). Carthamus red from Carthamus tinctorius L. Exerts antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect against CCl4-induced liver damage in rats via the Nrf2 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 218, 570–578. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.04.054
Wu, Y., Wang, L., Jin, M., and Zang, B. X. (2012). Hydroxysafflor yellow A alleviates early inflammatory response of bleomycin-induced mice lung injury. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 41, 515–522. doi:10.1248/bpb.35.515
Xie, X., Zhou, J. M., Sun, L., Zhang, H. D., Zhao, Y. W., Song, Y. L., et al. (2015). A new flavonol glycoside from the florets of Carthamus tinctorius L. Nat. Prod. Res. 33, 150–156. doi:10.1080/14786419.2015.1045905
Yan, Li, Gu, J. P., Ge, J. P., Kong, J., and Shang, L. C. (2024). HSYA ameliorates venous thromboembolism by depleting the formation of TLR4/NF-κB pathway-dependent neutrophil extracellular traps. Int. Immunopharmacol. 143, 113534. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113534
Yang, F., Li, J. M., Zhu, J. H., Wang, D., Chen, S. S., and Bai, X. Y. (2015). Hydroxysafflor yellow A inhibits angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma via blocking ERK/MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 898, 105–114. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.02.015
Ye, J., Lu, S., Wang, M., Ge, W., Liu, H., Qi, Y., et al. (2020). Hydroxysafflor yellow A protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome and activating autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 1170. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01170
Yuan, Y., Liu, H., and Meng, Q. (2023). The cardioprotective effects and mechanisms of astragalus-safflower herb pairs on coronary heart disease identified by network pharmacology and experimental verification. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 28 (5), 94. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2805094
Yue, S., Tang, Y., Xu, C., Li, S., Zhu, Y., and Duan, J. A. (2014). Two new quinchalcone C-glycosides from the florets of Carthamus tinctorius. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 2160–2171. doi:10.3390/ijms150916760
Yue, S. J., Qu, C., Zhang, P. X., Tang, Y. P., Jin, Y., Jiang, J. S., et al. (2016). Carthorquinosides A and B, quinochalcone C-Glycosides with diverse dimeric skeletons from Carthamus tinctorius. J. Nat. Prod. 79, 2644–2651. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00561
Zhang, J., Li, J., Song, H., Xiong, Y., Liu, D., and Bai, X. (2018a). Hydroxysafflor yellow A suppresses angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibition of p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 806–814. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.086
Zhang, S. M., Li, Z. Q., and Wang, G. Y. (2018b). Clinical observation of 94 cases of female infertility treated by integrated Chinese and Western medicine. Qinghai Med. J. 48, 59–60.
Zhang, Y., Guo, J., Dong, H., Zhao, X., Zhou, L., Li, X., et al. (2011). Hydroxysafflor yellow A protects against chronic carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 903, 438–444. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.04.015
Zhao, G., Gai, Y., Chu, W. J., Qin, G. W., and Guo, L. H. (2009). A novel compound N1, N5-(Z)-N10-(E)-tri-p-coumaroyl spermidine isolated from Carthamus tinctorius L. and acting by serotonin transporter inhibition. Eur. Neuro Psycho Pharmacol. 29, 749–758. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2009.06.009
Zhao, S., Lu, X., Xiao, C., Ning, Z., Zeng, H., Ding, X., et al. (2014). Diversified bioactivities of four types of naturally occurring Quin chalcones. Fitoterapia 118, 7–20. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2014.08.017
Zheng, H. Z., Xi, Z. H., and She, J. (1996). Research and application of modernization of traditional Chinese medicine, Vol. 3. Beijing: Xueyuan Press, 2057.
Zheng, M., Guo, X., Pan, R., Gao, J., Zang, B., and Jin, M. (2019). Hydroxysafflor yellow A alleviates ovalbumin-induced asthma in a Guinea pig model by attenuateing the expression of inflammatory cytokines and signal transduction. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 328. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00328
Zhou, X., Tang, L., Xu, Y., Zhou, G., and Wang, Z. (2014). Towards a better understanding of medicinal uses of Carthamus tinctorius L. in traditional Chinese medicine: a phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 151, 27–43. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.050
Zhou, Y. Z., Chen, H., Qiao, L., Xu, N., Cao, J. Q., and Pei, Y. H. (2008). Two new compounds from Carthamus tinctorius. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 10, 429–433. doi:10.1080/10286020801892425
Keywords: Carthamus tinctorius L., flavonoids, pharmacology, hydroxysafflor yellow A, ethnopharmacology
Citation: Bai H, Yang J and Wang R (2025) Carthamus tinctorius L.: a comprehensive review of its ethnomedicine, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1609299. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1609299
Received: 10 April 2025; Accepted: 22 July 2025;
Published: 21 August 2025.
Edited by:
Rajeev K. Singla, Sichuan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Roodabeh Bahramsoltani, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, IranHari Hariadi, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), Indonesia
Hao Deng, Fudan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Bai, Yang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rui Wang, d3JkeEBzaW5hLmNvbQ==
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
†ORCID: Haotian Bai, orcid.org/0000-0002-7158-7668; Jing Yang, orcid.org/0000-0002-9705-3883; Rui Wang, orcid.org/0000-0003-4770-3515
 Haotian Bai
Haotian Bai Jing Yang
Jing Yang Rui Wang
Rui Wang