Abstract
She Medicine, a traditional therapeutic system from China’s She ethnic group, shows promise in cancer treatment. This paper provides a comprehensive review of She medicinal herbs, focusing on their anticancer activities and underlying mechanisms. Compared to widely studied traditional medicines (e.g., Traditional Chinese Medicine), She Medicine exhibits unique ethnopharmacological traits, such as localized plant usage and multi-target mechanisms involving apoptosis induction, immune modulation, and tumor microenvironment regulation. Key herbs like Pimpinella diversifolia and Melastoma dodecandrum showing significant anticancer potential due to their bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, quercetin, and gallic acid. For example, homoharringtonine (HT), a She-derived alkaloid, targets Smad3/TGF-β pathways in non-small cell lung cancer and synergizes with chemotherapy in leukemia treatment, as evidenced by preliminary clinical trials. However, challenges persist, including resource shortages, insufficient mechanistic studies, and a lack of quality control standards. Future research should integrate multi-omics and bioengineering approaches to standardize She Medicine and bridge its traditional use with modern therapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors. Overall, She medicinal herbs hold great promise for cancer treatment and warrant further exploration to unlock their full potential in modern medicine.
1 Introduction
The She people, one of China’s ancient ethnic minorities, primarily inhabit the mountainous regions of southeastern provinces, such as Fujian, Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Jiangxi (Liu et al., 2017; Chen, 2019). Jingning She Autonomous County in Lishui City, Zhejiang Province, as the only She Autonomous County in the country, serves as the core area for the inheritance of She Culture. She medicine emerged in the long process of the She people adapting to their natural environment and their relentless struggle for survival and health (Lin Y., 2023; Lin H., 2023). Unlike mainstream Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), She Medicine retains distinct ethnopharmacological practices, such as the use of alcohol-based remedies for rapid therapeutic penetration and localized herbs like Melastoma dodecandrum for gastrointestinal bleeding. The field of diagnosis and treatment in She Medicine is extensive, covering trauma, rheumatic pain, and infections (Rajath et al., 2024; Roshan et al., 2023; Folk-lore and Medicine, 1939). A 1999 survey of She practitioners revealed a focus on bone injuries (50%) and snake bites (17%), reflecting adaptations to local environmental challenges (Lei et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2016). She doctors also treat dysentery, syphilis, and eye diseases, demonstrating broad therapeutic scope (ДВ and ЛВ, 2023).
She medicine employs both medicinal and non-medicinal therapies. Medicinal treatments include oral and external applications, with innovations in dosage forms such as alcohol-based patches for arthritis (Li et al., 2015; Xue and O’Brien, 2003; Liu et al., 2019). While early She medicine relied on single-herb formulas, modern practices increasingly use compound formulations, though a unified theoretical framework remains underdeveloped (Lei et al., 2014; Gedif and Hahn, 2002; Sharma T. et al., 2022). The Asteraceae family dominates She Medicine, with 37 species used holistically, maximizing resource utility (Lei et al., 2014; Da Silva et al., 2023). This contrasts with TCM’s emphasis on roots and rhizomes, highlighting She’s ecological adaptation. Globally, rising cancer mortality underscores the urgency for innovative therapies. She Medicine’s unique bioactive compounds—such as homoharringtonine in leukemia and Scutellaria baicalensis flavonoids—offer multi-target mechanisms complementary to synthetic drugs (e.g., paclitaxel) and immune therapies. However, challenges like resource scarcity and insufficient clinical validation hinder its integration into modern oncology (Singh S et al., 2021; Sharma et al., 2024; Huang et al., 2024).
2 Anticancer potential of She medicine herbal drugs
2.1 Common anti-cancer She medicinal herbs
Cold tea is one of the most commonly used traditional medicines among the She people. Modern studies have shown that the active ingredients of cold tea, in addition to volatile oils, include flavonoids, coumarins, anthraquinones, and other non-volatile compounds, with flavonoids being the dominant component. Modern pharmacological studies suggest that the anticancer effects of flavonoids in cold tea are closely linked to their ability to induce apoptosis and inhibit angiogenesis. In She medicine, cold tea is primarily used to treat conditions caused by food stagnation, such as fullness, chronic gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers leading to bloating, gastric pain, and acid reflux, as well as playing a crucial role in the prevention and treatment of colds and influenza (Liu et al., 2013; Samanta, 2022; Luo et al., 2024). Diren, derived from the whole plant Melastomadodecandrum (Lour.), is known for its sweet and astringent taste. Modern clinical studies have confirmed that Diren has notable hemostatic effects, particularly in treating gastrointestinal bleeding. Studies show that Diren is rich in polysaccharides, flavonoids, amino acids, phenols, and both macro and trace elements, contributing to its hemostatic, antioxidant, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and hypoglycemic effects. Flavonoid compounds from Diren have demonstrated apoptosis-inducing and immune-modulatory properties, enhancing its potential as an adjunct therapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Further reports highlight its antitumor, hypoglycemic, and hypolipidemic properties, while showing no toxic side effects on normal cells (Zheng et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2016; Yao et al., 2021). Jinxian Diao Hulu: Many bioactive compounds, such as dandelion terpenes, flavonoids, and sterols, These compounds contribute to its anti-tumor, immune regulating, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral properties, and no toxicity has been observed. It is used clinically to treat febrile seizures, pneumonia, and various cancers in children (Gezici and Şekeroğlu, 2019; Chang et al., 2013). Xiaoye Rong 1934: a shrub commonly used in She medicine in Eastern and Southeastern China, is used to treat various conditions such as infantile malnutrition, indigestion, diarrhea, hernia, gout, and joint pain. The plant has been widely studied for its phytochemical components, and research has begun to explore its potential antitumor effects through pathways such as oxidative stress inhibition and immune modulation (Li et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2022). Tu Mu Xiang: Tu Mu Xiang, also known as “Hong Mu Xiang” or “Nan Wu Wei Zi Gen,” is a common herbal remedy among the She people of Fujian province. Research has shown that its source plants include multiple species from the Magnoliaceae family, particularly the roots and stems of Schisandra chinensis. These compounds exert anticancer activity by modulating apoptosis pathways and suppressing metastasis-related signaling (Yang et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2022). Scutellaria baicalensis: Commonly used in She medicine for its multiple pharmacological effects, particularly anticancer properties. The key component baicalin has been shown to induce apoptosis in cancer cells, inhibit tumor angiogenesis, and reduce metastasis (Liu Y. et al., 2024). Panax notoginseng: Known for its effects on blood circulation and pain relief, it has demonstrated significant potential in anticancer therapy by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting the proliferation and invasion of cancer cells (Hawthorne et al., 2022). Lonicera japonica: Widely used for its anti-inflammatory and detoxifying properties, its active ingredients, such as chlorogenic acid and quercetin, show anticancer activity by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis (Ma et al., 2024; Park et al., 2017). Ganoderma lucidum: This popular herb enhances immunity and exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties through its polysaccharide content (Cör et al., 2018; Sohretoglu and Huang, 2018). Hedyotis diffusa: An important part of She medicine, its active ingredients are widely used for their anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidant effects, particularly in the treatment of liver and stomach cancers (Figure 1) (Shao et al., 2011).
FIGURE 1

Anticancer activity and mechanisms of She medicinal herbs. The figure illustrates the anticancer activity and mechanisms of She medicinal herbs. It provides an overview of the medicinal components, therapeutic potential, and molecular mechanisms involved. The figure highlights the geographical distribution of She culture, which is centered in specific regions known for the use of these herbs. Key anticancer components, including polysaccharides, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds, are shown as vital bioactive substances within the herbs. The development of She medicinal herbs for cancer treatment is discussed, with an emphasis on the importance of standardized collection, processing, preparation, and storage methods to maximize their efficacy. Additionally, the figure lists major types of She medicinal herbs, such as Shiliangcha, Diren, Xiaoyerong 1934, Shuren, Jinxian Diaohulu, and Tumu Xiang, each noted for their unique medicinal properties. The medicinal parts of these herbs, such as the whole herb, root, flower, fruit, and stem, are also illustrated. Finally, the figure depicts the anticancer mechanisms of these herbs, highlighting the roles of compounds like HHT (Homoharringtonine) and Cephalotaxus in triggering apoptosis in cancer cells through various molecular pathways, including the regulation of BCL-XL, caspase 9, and the alternative splicing of mRNAs. This information underscores the potential of She medicinal herbs in cancer therapy.
In comparison with conventional therapies such as paclitaxel or platinum-based chemotherapy, these She medicinal herbs provide multi-targeted mechanisms—including apoptosis regulation, immune modulation, and microenvironment adjustment—highlighting their potential as complementary or alternative options in integrative cancer therapy.
2.2 Main medicinal parts and efficacy of She medicine anti-cancer herbs
From the perspective of medicinal parts, Asteraceae family herbs in She Medicine most frequently utilize the whole plant with 37 species falling into this category, followed by root and rhizome, flower, fruit and seed, and stem wood types (Sharma M. et al., 2022). There are 20 species with two or more medicinal parts, including Artemisia lactiflora Wall. ex DC. and Eupatorium japonicum Thunb. This reflects the traditional emphasis on maximizing pharmacological utility by using multiple plant parts (Lei et al., 2014; Yarnell, 2015). For example, Rubus chingii (Eastern raspberry) has dry roots that are used in She medicine to treat wind pain, improve vision, expel toxins, and soothe nausea. It is applied for treating conditions such as tuberculosis and spinal cord compression (Sheng et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2019) Di Ren: A commonly used herb in She medicine, the whole plant is used. It is sweet and slightly cool, containing polysaccharides and flavonoids. It has hemostatic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. The highest concentration of active compounds is found in the leaves (Sze et al., 2010). Shi Liang Cha: Derived from the dry leaves of Lyonia species, it has a cooling, slightly bitter, and pungent nature. It is used in treating wind-heat symptoms, with significant antioxidant and anti-tumor effects. It is clinically applied for diseases like colds and diarrhea (Ma et al., 2017). Di Jin Ju: The whole plant is used and is beneficial for activating blood flow and expelling wind, and it treats gastric pain. This herb has been used in She communities for generations (Wali et al., 2022). The use of whole plants or multiple parts enhances the synergistic efficacy of She Medicine. This holistic approach differs from modern single-compound therapies by preserving the complex phytochemical interactions essential for therapeutic effects.
3 Anticancer activity and mechanisms of She medicine herbs
3.1 Active ingredients and their biological activities
Flavonoids, triterpenes, alkaloids, and polyphenols found in She medicine exhibit a wide range of biological functions, including anticancer properties. For example, flavonoids in Shiliang tea may be the basis of its cardiovascular protection, antibacterial, antiviral and anticancer activities (Wang et al., 2020; Li and Jiang, 2018). Anthraquinone compounds such as rhein methyl ether and rhein-8-O-β-D-glucoside contribute to antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and potentially cytotoxic effects in cancer cells. Harringtonine (HT), a natural alkaloid from Cephalotaxus, has shown strong efficacy against leukemia and is currently used in the treatment of acute leukemia and lymphoma (Luo et al., 2004). The study of HT derivatives showed that ht1 enhanced the antiproliferative activity of HL-60 cells, with an IC50 value approximately 2,000 times lower than that of HT itself (Ochi et al., 2022; Sakamoto et al., 2018). These results highlight the importance of chemical modification in enhancing bioactivity. In Sanjiaofeng dew, extraction efficiency of active ingredients like flavonoids is influenced by solid-liquid ratios and microwave irradiation time, which are critical factors in maximizing anticancer efficacy during preparation. These components induce tumor cell apoptosis and inhibit proliferation by modulating key signaling pathways (Abotaleb et al., 2018; Raina et al., 2020).
3.2 Progress in chemical constituents and anticancer research
In recent years, notable advances have been made in the phytochemical investigation of She medicine herbs. For example, the flavonoids in the extract of Liquidambar sanjiaoensis are essential for anti-cancer and immune regulation (Luo et al., 2004). The pharmacological effects of Di Ren and San Jiao Feng Lu are directly related to the contents of flavonoids and phenols. By analyzing the content of gallic acid and quercetin in different parts of Rehmannia glutinosa, the researchers determined the best harvest time of Rehmannia glutinosa (Yue-ling et al., 2017). Its extracts, rich in quercetin and gallic acid, show significant variability across plant parts and seasons, affecting therapeutic efficacy (Engström et al., 2015). Quercetin, a key flavonoid, reduces oxidative stress and inhibits tumor cell proliferation through cell cycle arrest (Xie et al., 2011). Its concentration reached its peak in early May, making it a critical compound for maximizing anticancer activity during harvesting (Xie et al., 2012).
3.3 Extraction and analysis of active ingredients
Many herbs in she medicine contain bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, saponins, quinones and terpenes, considered core contributors to their anticancer activity198,199. For example, astragaloside IV from Astragalus enhances immune responses and suppresses tumor progression (Zhou et al., 2017). The chemical constituents of Euphorbia officinalis, including flavonoids and quercetin, have been proved to inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells (Engström et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2021). Quercetin not only regulates the cell cycle but also significantly increases the apoptosis rate of malignant cells. Researchers have employed advanced analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to identify and quantify bioactive ingredients in Camellia and other She herbs. Emerging tools including single-cell sequencing, network pharmacology, and molecular docking are increasingly used to uncover the intricate anticancer mechanisms of She herbal medicines (Huang et al., 2024; Qi and Zou, 2023; Ni et al., 2025; Jiao et al., 2021).
3.4 Anticancer mechanism
At the cellular level, the components of She medicine can induce tumor cell apoptosis by modulating apoptosis-related genes and activating intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways (Yang et al., 2023a; Yang et al., 2023b). For example, triptolide activates caspase enzymes and suppresses Bcl-2 expression to initiate programmed cell death (Davis and Salton, 1975; Safarzadeh et al., 2014; Lefkowitz, 1975). In AML, homoquercetin upregulates MCL-1 and ROS levels, activates Bax, and promotes mitochondrial release of cytochrome c to trigger apoptosis (Figure 2). At the molecular level, HT showed anti-cancer effect on gefitinib resistant NSCLC cell lines by targeting Smad3 and TGF-β signaling pathways. It also regulates alternative splicing of Bcl-x and caspase-9 through a PP1-dependent mechanism (Cao et al., 2015; Qin et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2021; Gao et al., 2007). At the tissue level, She medicine inhibits tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. This is achieved through comprehensive regulation of the tumor microenvironment, such as downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and restoring intestinal microbiota balance (Yang W. et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023a). Immunocytochemical and pathway studies have shown that She medicines enhance immune surveillance and counteract tumor immune evasion by modulating the infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages and T-cell subtypes. They also inhibit key pathways like NF-κB, offering mechanistic insights into their immunomodulatory effects (Ding et al., 2025). Some She medicines, such as Astragalus and Codonopsis, stimulate macrophage and T cell activity, amplifying antitumor immune responses (Patanapongpibul and Chen, 2019). With the integration of single-cell transcriptomics, bioinformatics, and experimental validation, researchers can now delineate She medicine’s impact on immune cell subtypes within the tumor microenvironment, providing robust evidence for its immunotherapeutic value (Yang et al., 2023b; Liang et al., 2024; Qian et al., 2024; Yu and Pan, 2024; Luo et al., 2023).
FIGURE 2
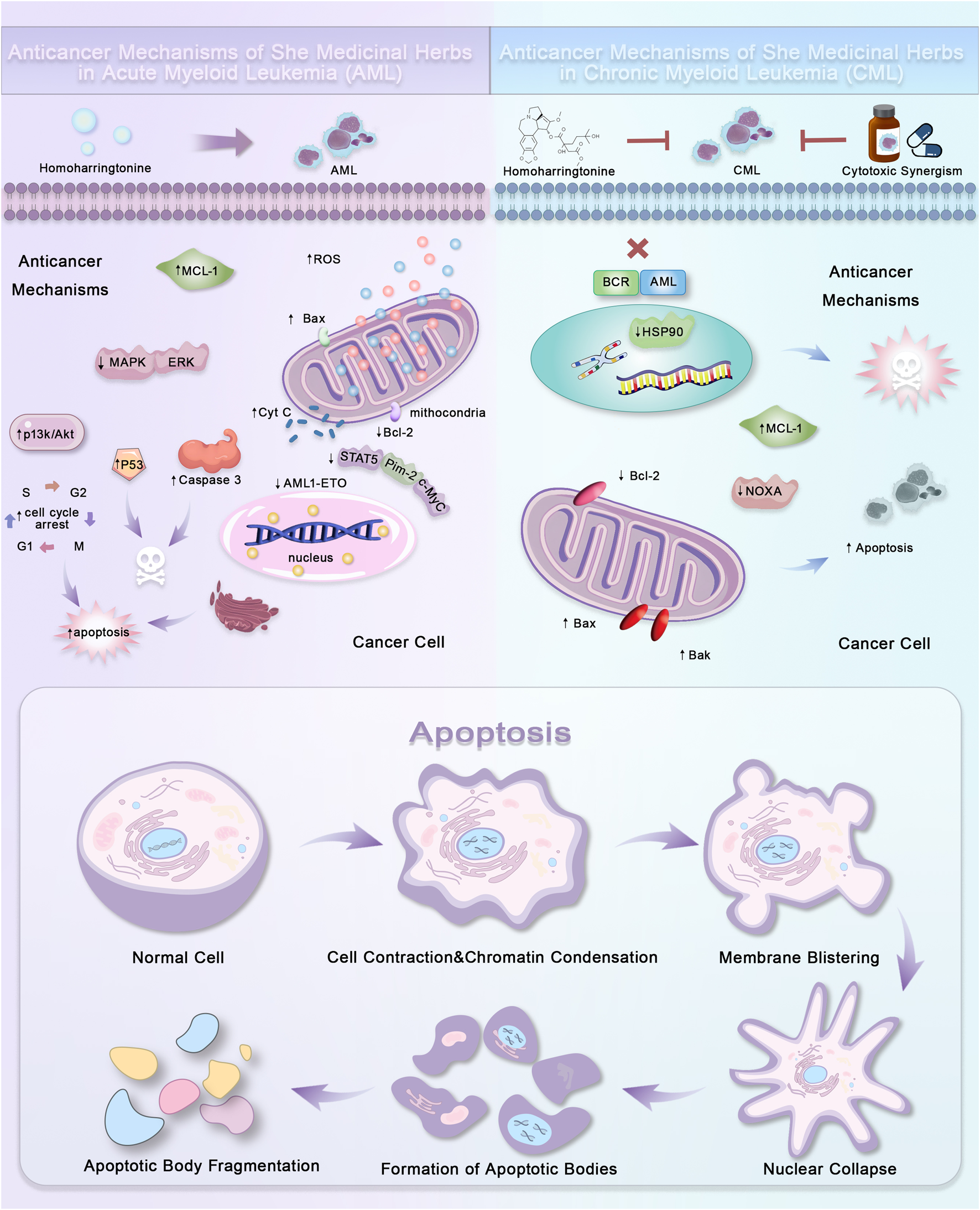
Anticancer mechanisms of She medicinal herbs in acute and chronic myeloid leukemia. The figure illustrates the anticancer mechanisms of She medicinal herbs in the treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). In AML, Homoharringtonine induces apoptosis by upregulating MCL-1 and ROS, activating Bax, and promoting mitochondrial release of cytochrome c, which triggers a cascade of apoptotic events through p53 activation, caspase 3 and 9, and cell cycle arrest. In CML, Homoharringtonine works in synergy with cytotoxic agents to inhibit BCR-ABL fusion proteins, modulate HSP90, and downregulate Bcl-2 and MCL-1, leading to Bax, Bak, and NOXA activation and apoptosis. The figure also shows the typical apoptotic morphological changes, including cell contraction, chromatin condensation, membrane blistering, apoptotic body fragmentation, and nuclear collapse, which occur during the cancer cell death process. These findings underscore the therapeutic potential of She medicinal herbs in leukemia treatment by targeting key apoptotic pathways.
3.5 Related research and technological innovation
Genetic analysis of ITS2 sequences in raspberry and related species revealed distinct molecular markers, offering new insights into Rubus taxonomy and the evolutionary basis of anticancer activity in She herbal species (Song et al., 2012). A new she medicine crushing device was designed to improve processing efficiency and standardization, ensuring uniform quality for research and clinical use (Thapliyal et al., 2024). The device enhances purity and consistency, which are essential for reproducibility in pharmacological studies. Simultaneously, bioactive scaffolds are being used to deliver She herbal extracts to tumor tissues with enhanced targeting and controlled release, forming a novel strategy for She medicine-based anticancer drug delivery systems (Jia et al., 2024; Li et al., 2024). In summary, She medicine presents a promising approach to cancer therapy through its chemically diverse components and multi-target mechanisms.
4 Clinical applications and case studies
4.1 Combination chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Numerous clinical studies suggest that She medicinal herbs can be used as adjuncts to chemotherapy drugs to improve their efficacy (Wang et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2018; Murasawa et al., 2023). For instance, extracts from Bai Ji (Radix Bletillae) and Tripterygium wilfordii L. have been shown to significantly enhance the efficacy of standard chemotherapeutic regimens while concurrently reducing drug resistance and toxicity (Zhou et al., 2023b). In advanced cancer patients, She medicine is often employed to alleviate cancer-related symptoms, such as pain and fatigue, and to improve appetite and sleep quality, ultimately enhancing patients’ overall quality of life (Mystakidou et al., 2007). The use of golden-thread gourds (Cocculus trilobus) in She folk medicine has demonstrated empirical effectiveness in tumor management. Recent studies conducted by Chinese research institutions have confirmed its anticancer activity, particularly by inducing apoptosis in liver cancer and leukemia cell lines (Mystakidou et al., 2007; Dai et al., 2013). Mechanistic investigations suggest involvement of caspase-3 activation and modulation of mitochondrial pathways, indicating that this herb holds promise as a supplementary treatment. These findings align with a growing body of literature that supports the integrative use of traditional medicine in reducing chemotherapy side effects and enhancing clinical response.
4.2 Classic cases
In traditional She medicine, many She medicinal herbs are widely used not only for cancer but also for a variety of other chronic and inflammatory conditions. One notable example is the externally applied formula “She Medicine Twelve-Hour Ointment,” which exemplifies the distinctive therapeutic approach of She ethnomedicine and offers insights for translational applications in modern integrative medicine (Yu et al., 2016). Research has shown that the ointment possesses favorable stability and reproducibility during preparation, and exhibits significant analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity. The clinical application of this ointment in musculoskeletal pain, soft tissue injuries, and even localized cancer-related pain syndromes underscores the need for further exploration into topical She herbal therapeutics.
5 Challenges and limitations in the anti-cancer research of She medicine herbal drugs
While She medicine exhibits promising therapeutic potential in oncology, several critical limitations hinder its further development and clinical translation. Compared with other ethnic medicinal systems in China, She medicine research has progressed relatively slowly. For example, despite the identification of active components in the fruits and seeds of Schisandra sphenanthera, research on its roots and stems remains insufficient (Huang et al., 2021). This gap underscores the need for comprehensive, plant-part-specific analyses using modern tools such as LC-MS/MS and multi-omics approaches. The absence of standardized quality control frameworks is another major barrier. Since most She herbal drugs are sourced from the wild, there is considerable batch-to-batch variability in chemical composition, which can directly affect clinical efficacy and reproducibility (Li et al., 2013).
Additionally, soil pollution and the intrinsic genetic variability of medicinal plants may result in heavy metal accumulation and introduce safety concerns. Current studies reveal regional differences in She medicine safety profiles, attributable to ecological, climatic, and processing disparities. These would help analyze adverse event variability, and provide robust data to support the development of unified safety standards, risk control measures, and regulatory guidelines (Nyame et al., 2024). Establishing a comprehensive quality assurance system that encompasses cultivation practices, harvesting protocols, processing techniques, and formulation standards is essential for promoting the safe and standardized clinical application of She medicine in cancer therapy.
6 The future direction of She medicine in cancer research
She medicine represents a promising frontier in integrative oncology, offering multi-target, plant-based therapeutic strategies that complement modern cancer treatments. To fully harness its potential, future research should focus on comprehensive investigations into its active compounds and mechanisms of action through advanced methodologies such as single-cell RNA sequencing, multi-omics analysis, and spatial transcriptomics (Luo et al., 2023; Li G. et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2022). Although preliminary studies have identified a range of bioactive flavonoids, alkaloids, and terpenes, their precise pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics remain incompletely understood.
Standardized extraction protocols, quality control frameworks, and pharmacological validation are essential prerequisites for clinical application. AI-based analytical tools, including machine learning algorithms and predictive pharmacology models, will facilitate the screening and prioritization of effective compounds, while optimizing extraction processes and formulation development (Ye et al., 2023; Li W. et al., 2023).
To evaluate anticancer efficacy, preclinical models such as orthotopic liver, breast, and gastric cancer animal models should be employed. These models allow for the identification of biomarkers responsive to She medicine and support subsequent validation in clinical studies (Qin et al., 2023; Ramirez-Hernandez et al., 2024). High-throughput screening and Box–Behnken response surface methodology have already proven useful in optimizing prescriptions, as demonstrated in the case of the Snake Medicine Twelve-Hour Ointment (Liu DSK. et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2021).
The integration of she medicine with modern drug discovery platforms holds transformative potential. For instance, the traditional use of Taxus plants by She communities has stimulated the development of anti-leukemic agents. Current studies are investigating their metabolic pathways, biosynthesis, and target-specific interactions (Shao et al., 2021). Computer-aided drug design (CADD), molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations are being applied to structurally optimize She herbal compounds and predict their interactions with tumor-associated targets, thereby accelerating the discovery of low-toxicity derivatives (Nascimento et al., 2022).
Furthermore, targeted drug delivery systems such as flavonoid-loaded nanoparticles, liposomes, and ADCs are being developed to improve She medicine’s bioavailability, targeting accuracy, and safety profile. These technologies support the clinical translation of She herbal compounds and facilitate the transition from laboratory to bedside (Zhu et al., 2024; Rajendran et al., 2025; Zhu et al., 2025; Patra et al., 2018; Rajendran et al., 2025; Soroudi et al., 2024; Xi et al., 2024). A population-based cohort study has been conducted to assess biomarker changes before and after She medicine treatment, and meta-analyses are being employed to explore patterns of disease progression and response (Wu et al., 2024).
7 Conclusion
As a vital component of traditional Chinese medicine, She herbal medicine holds increasing importance in the field of cancer research and treatment. It not only draws from a rich foundation of ethnopharmacological knowledge, but also contains a diverse range of bioactive compounds with demonstrated anticancer potential. Through multi-target mechanisms—such as inhibiting cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, modulating immune responses, and suppressing angiogenesis—She medicine provides a novel and holistic approach to anticancer drug discovery. However, several key limitations remain. The identification and characterization of active ingredients require deeper investigation, and the lack of standardized quality control protocols continues to hinder clinical translation. Future research should leverage advanced biotechnological platforms, including multi-omics, AI-assisted compound screening, and molecular pharmacology, to clarify mechanisms of action and identify therapeutic targets. Moreover, the efficacy and safety of She medicinal herbs must be rigorously validated through preclinical animal models and well-designed clinical trials.
Statements
Author contributions
YM: Formal Analysis, Validation, Data curation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Software, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Resources. YC: Software, Writing – review and editing, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Resources, Conceptualization, Validation, Project administration, Methodology, Formal Analysis. QL: Formal Analysis, Resources, Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. RC: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Software, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JZ: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. HS: Investigation, Software, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Data curation. MW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Resources, Data curation, Validation. JM: Writing – original draft, Project administration, Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Formal Analysis. CL: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Data curation, Software, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the 2024 Research Project of Ningde Normal University (Project No. 2024Y08). Additional funding has been provided by the Startup Fund for Advanced Talents of Ningde Normal University (2023Y21) and the Educational Research Projects for Young and Middle-aged Teachers in Fujian Province (JZ230060).
Acknowledgments
Thanks to JX and RC for their work during the early stages of the manuscript; however, they were not fully involved during the revision process and are therefore not listed as co-authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. We employed ChatGPT-4.0 primarily for language refinement, aiming to improve the clarity and flow of the paper. The tool was used exclusively for correcting grammar and optimizing language, with no involvement in the creation of academic content. As such, the use of this tool adheres to academic ethical guidelines and does not undermine the integrity or originality of the research.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abotaleb M. Samuel S. Varghese E. Varghese S. Kubatka P. Liskova A. et al (2018). Flavonoids in cancer and apoptosis. Cancers11, 28. 10.3390/cancers11010028
2
Cao W. Liu Y. Zhang R. Zhang B. Wang T. Zhu X. et al (2015). Homoharringtonine induces apoptosis and inhibits STAT3 via IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signal pathway in Gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells. Sci. Rep.5, 8477. 10.1038/srep08477
3
Chang H.-W. Chuang L.-Y. Guleria S. Yasmin S. (2013). Natural products: bioactivity, biochemistry, and biological effects in cancer and disease therapy. Sci. World J.2013, 713480. 10.1155/2013/713480
4
Chen J. (2019). “The status quo and inheritance of the traditional handmade silverware of the She nationality in the Eastern Fujian Region,” in Proceedings of the 5th international conference on arts, design and contemporary education (ICADCE 2019). Moscow: Atlantis Press. 10.2991/icadce-19.2019.20
5
Cör D. Knez Ž. Knez Hrnčič M. (2018). Antitumour, antimicrobial, antioxidant and antiacetylcholinesterase effect of Ganoderma Lucidum terpenoids and polysaccharides: a review. Molecules23, 649. 10.3390/molecules23030649
6
Dai X.-Z. Yin H.-T. Sun L.-F. Hu X. Zhou C. Zhou Y. et al (2013). Potential therapeutic efficacy of curcumin in liver cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev.14, 3855–3859. 10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.6.3855
7
Da Silva L. C. N. Sahal D. Panda S. K. (2023). Editorial: developing medicines (drugs) derived from the Asteraceae—an opportunity in ethnopharmacology, volume II. Front. Pharmacol.14, 1285815. 10.3389/fphar.2023.1285815
8
Davis R. H. Salton M. R. (1975). Some properties of a D-alanine carboxypeptidase in envelope fractions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect. Immun.12, 1065–1069. 10.1128/iai.12.5.1065-1069.1975
9
Ding C. Wang J. Wang J. Niu J. Xiahou Z. Sun Z. et al (2025). Heterogeneity of cancer-associated fibroblast subpopulations in prostate cancer: implications for prognosis and immunotherapy. Transl. Oncol.52, 102255. 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102255
10
Engström M. T. Pälijärvi M. Salminen J.-P. (2015). Rapid fingerprint analysis of plant extracts for ellagitannins, gallic acid, and quinic acid derivatives and Quercetin-Kaempferol- and myricetin-based flavonol glycosides by UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem.63, 4068–4079. 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00595
11
Folk-lore and medicine (1939). Folk-lore and medicine. Nature143, 111–112. 10.1038/143111c0
12
Gao S. P. Mark K. G. Leslie K. Pao W. Motoi N. Gerald W. L. et al (2007). Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Invest117, 3846–3856. 10.1172/JCI31871
13
Gedif T. Hahn H.-J. (2002). Herbalists in Addis Ababa and Butajira, central Ethiopia: mode of service delivery and traditional pharmaceutical practice. Ethiop. J. Health Dev.16, 183–189. 10.4314/ejhd.v16i2.9810
14
Gezici S. Şekeroğlu N. (2019). Current perspectives in the application of medicinal plants against cancer: novel therapeutic agents. ACAMC19, 101–111. 10.2174/1871520619666181224121004
15
Hawthorne B. Lund K. Freggiaro S. Kaga R. Meng J. (2022). The mechanism of the cytotoxic effect of Panax notoginseng extracts on prostate cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother.149, 112887. 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112887
16
Huang S. Zhang D. Li Y. Fan H. Liu Y. Huang W. et al (2021). Schisandra sphenanthera: a comprehensive review of its botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications. Am. J. Chin. Med.49, 1577–1622. 10.1142/S0192415X21500749
17
Huang W.-B. Qin S.-Y. Zou J.-B. Li X. Kang W.-L. Yuan P.-W. (2024). Efficacy of Juanbi capsule on ameliorating knee osteoarthritis: a network pharmacology and experimental verification-based study. Tradit. Med. Res.9, 33. 10.53388/TMR20230829002
18
Jia Q.-P. Li Q. Boucetta H. Xu Z.-P. Zhang L.-X. (2024). Biomimetic-smart materials for osteochondral regeneration and repair. Microstructures4, 4. 10.20517/microstructures.2023.84
19
Jiao X. Jin X. Ma Y. Yang Y. Li J. Liang L. et al (2021). A comprehensive application: molecular docking and network pharmacology for the prediction of bioactive constituents and elucidation of mechanisms of action in component-based Chinese medicine. Comput. Biol. Chem.90, 107402. 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107402
20
Kim T.-H. Zaslawski C. Kwon S. Kang J. W. (2016). Korean medicine in general practice: current status, challenges, and vision in clinical evidence. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med.2016, 3269474. 10.1155/2016/3269474
21
Lefkowitz R. J. (1975). Identification of adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors with radiolabeled beta-adrenergic antagonists. Biochem. Pharmacol.24, 1651–1658. 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90001-5
22
Lei H. X. Li J. L. Zheng S. M. Fan L. H. Li S. F. Cheng W. L. et al (2014). Resources and application of she’s nationality wild medicinal plants. China J. Chin. Materia Medica39, 3180–3183. 10.4268/cjcmm20141635
23
Li G. Jin Q. Xia F. Fu S. Zhang X. Xiao H. et al (2023a). Smart stimuli-responsive carrier-free nanoassembly of SN38 prodrug as efficient chemotherapeutic nanomedicine. Acta Mater. Medica2. 10.15212/AMM-2023-0003
24
Li H. Wang S. Yang Z. Meng X. Niu M. (2024). Nanomaterials modulate tumor-associated macrophages for the treatment of digestive system tumors. Bioact. Mater.36, 376–412. 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.03.003
25
Li M. Wang A. Zhang Y. Han T. Guan L. Fan D. et al (2022). A comprehensive review on ethnobotanical, phytochemical and pharmacological aspects of Rhus chinensis mill. J. Ethnopharmacol.293, 115288. 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115288
26
Li W. Dong B. Wang H. Yuan J. Qian H. Zheng L. et al (2023b). Artificial intelligence promotes shared decision-making through recommending tests to febrile pediatric outpatients. World J. Emerg. Med.14, 106–111. 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.033
27
Li X. Chen H. Jia W. Xie G. (2013). A metabolomics-based strategy for the quality control of traditional Chinese medicine: Shengmai injection as a case study. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med.2013, 836179–8. 10.1155/2013/836179
28
Li Y. Jiang J.-G. (2018). Health functions and structure–activity relationships of natural anthraquinones from plants. Food Funct.9, 6063–6080. 10.1039/C8FO01569D
29
Li Y. Li R. Ouyang Z. Li S. (2015). Herb network analysis for a famous TCM doctor’s prescriptions on treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med.2015, 451319–9. 10.1155/2015/451319
30
Liang Y. Zhang R. Biswas S. Bu Q. Xu Z. Qiao L. et al (2024). Integrated single-cell transcriptomics reveals the hypoxia-induced inflammation-cancer transformation in NASH-Derived hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Prolif.57, e13576. 10.1111/cpr.13576
31
Lin H. (2023a). Evaluation on the protection and development of intangible cultural heritage in she township, Jingning from the perspective of ecological civilization. Sustainability15, 2330. 10.3390/su15032330
32
Lin Y. (2023b). The writing of youth in Zhejiang original opera “Sheshan Dawn”. JHASS7, 909–912. 10.26855/jhass.2023.05.005
33
Liu D. S. K. Puik J. R. Venø M. T. Mato Prado M. Rees E. Patel B. Y. et al (2024b). MicroRNAs as bile-based biomarkers in pancreaticobiliary cancers (MIRABILE): a cohort study. Int. J. Surg.110, 6518–6527. 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001888
34
Liu S. Chen G. Huang H. Lin W. Guo D. Zhao S. et al (2017). Patrilineal background of the She minority population from Chaoshan Fenghuang Mountain, an isolated mountain region, in China. Genomics109, 284–289. 10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.05.002
35
Liu Y. Ahmed S. Long C. (2013). Ethnobotanical survey of cooling herbal drinks from southern China. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine9, 82. 10.1186/1746-4269-9-82
36
Liu Y. Gao Z. Zhao Y. Kong L. Ji X. Wu J. et al (2024a). Exploring bioactive constituents and pharmacological effects of Scutellaria baicalensis georgi: a review. Nat. Product. Commun.19, 1934578X241266692. 10.1177/1934578X241266692
37
Liu Z. Zheng Z. Guo X. Qi L. Gui J. Fu D. et al (2019). AttentiveHerb: a novel method for traditional medicine prescription generation. IEEE Access7, 139069–139085. 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941503
38
Lu Z. Chen H. Lin C. Ou G. Li J. Xu W. (2022). Ethnobotany of medicinal plants used by the Yao people in Gongcheng County, Guangxi, China. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine18, 49. 10.1186/s13002-022-00544-6
39
Luo C. Y. Tang J. Y. Wang Y. P. (2004). Homoharringtonine: a new treatment option for myeloid leukemia. Hematology9, 259–270. 10.1080/10245330410001714194
40
Luo Q. Luo L. Zhao J. Wang Y. Luo H. (2024). Biological potential and mechanisms of Tea’s bioactive compounds: an updated review. J. Adv. Res.65, 345–363. 10.1016/j.jare.2023.12.004
41
Luo S. Wang L. Xiao Y. Cao C. Liu Q. Zhou Y. (2023). Single-cell RNA-sequencing integration analysis revealed immune cell heterogeneity in five human autoimmune diseases. BIOI4, 4. 10.15212/bioi-2023-0012
42
Ma P. Yuan L. Jia S. Zhou Z. Xu D. Huang S. et al (2024). Lonicerae japonicae flos with the homology of medicine and food: a review of active ingredients, anticancer mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, quality control, toxicity and applications. Front. Oncol.14, 1446328. 10.3389/fonc.2024.1446328
43
Ma S. Lv Q. Zhou H. Fang J. Cheng W. Jiang C. et al (2017). Identification of traditional she medicine Shi-Liang tea species and closely related species using the ITS2 barcode. Appl. Sci.7, 195. 10.3390/app7030195
44
Murasawa S. Kageyama K. Usutani M. Asari Y. Kinoshita N. Nakada Y. et al (2023). Biochemical evaluation by confirmatory tests after unilateral adrenalectomy for primary aldosteronism. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst.2023, 5732812. 10.1155/2023/5732812
45
Mystakidou K. Parpa E. Tsilika E. Pathiaki M. Gennatas K. Smyrniotis V. et al (2007). The relationship of subjective sleep quality, pain, and quality of life in advanced cancer patients. Sleep30, 737–742. 10.1093/sleep/30.6.737
46
Nascimento IJDS De Aquino T. M. Da Silva-Júnior E. F. (2022). The new era of drug discovery: the power of computer-aided DrugDesign (CADD). LDDD19, 951–955. 10.2174/1570180819666220405225817
47
Ni G. Sun Y. Jia H. Xiahou Z. Li Y. Zhao F. et al (2025). MAZ-mediated tumor progression and immune evasion in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: targeting tumor microenvironment and PCLAF+ subtype-specific therapy. Transl. Oncol.52, 102280. 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102280
48
Nyame L. Hu Y. Xue H. Fiagbey E. D. K. Li X. Tian Y. et al (2024). Variation of adverse drug events in different settings in Africa: a systematic review. Eur. J. Med. Res.29, 333. 10.1186/s40001-024-01934-0
49
Ochi A. Yoritate M. Miyamoto T. Usui K. Yusakul G. Putalun W. et al (2022). Harringtonine Ester derivatives with enhanced antiproliferative activities against HL-60 and HeLa cells. J. Nat. Prod.85, 345–351. 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00888
50
Park K. I. Park H. Nagappan A. Hong G. E. Yumnam S. Lee H. J. et al (2017). Polyphenolic compounds from Korean Lonicera japonica Thunb. induces apoptosis via AKT and caspase cascade activation in A549 cells. Oncol. Lett.13, 2521–2530. 10.3892/ol.2017.5771
51
Patanapongpibul M. Chen Q.-H. (2019). Immune modulation of Asian folk herbal medicines and related chemical components for cancer management. CMC26, 3042–3067. 10.2174/0929867324666170705112644
52
Patra J. K. Das G. Fraceto L. F. Campos E. V. R. Rodriguez-Torres M. D. P. Acosta-Torres L. S. et al (2018). Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol16, 71. 10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8
53
Qi R. Zou Q. (2023). Trends and potential of machine learning and deep learning in drug study at single-cell level. Research6, 0050. 10.34133/research.0050
54
Qian S. Long Y. Tan G. Li X. Xiang B. Tao Y. et al (2024). Programmed cell death: molecular mechanisms, biological functions, diseases, and therapeutic targets. MedComm5, e70024. 10.1002/mco2.70024
55
Qin M. Gao Y. Guo S. Lu X. Zhao Q. Ge Z. et al (2023). Establishment and evaluation of animal models of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. World J. Emerg. Med.14, 349–353. 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.088
56
Qin M. Wang T. Xu B. Ma Z. Jiang N. Xie H. et al (2015). Novel hydrazone moiety-bearing aminopyrimidines as selective inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutant. Eur. J. Med. Chem.104, 115–126. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.09.031
57
Raina R. Hussain A. Sharma R. (2020). Molecular insight into apoptosis mediated by flavones in cancer. World Acad. Sci. J. 10.3892/wasj.2020.47
58
Rajath M. AshwinKumar S. Bharathi A. A. (2024). Review on the use of Kukkuta(Hen) in Sarpavisha (snake poison) Chikitsa as folklore medicine. EPRA, 409–412. 10.36713/epra17844
59
Rajendran A. Rajan R. A. Balasubramaniyam S. Elumalai K. (2025). Nano delivery systems in stem cell therapy: transforming regenerative medicine and overcoming clinical challenges. Nano TransMed4, 100069. 10.1016/j.ntm.2024.100069
60
Ramirez-Hernandez D. Lezama-Martinez D. Velazco-Bejarano B. Valencia-Hernandez I. Lopez-Sanchez P. Fonseca-Coronado S. et al (2024). The beneficial effects of swimming training preconditioning on reducing vascular reactivity in chronic myocardial infarction: independent of NO production. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst.25, 14703203241294029. 10.1177/14703203241294029
61
Roshan M. Kavithalaya K. Mozhi P. A. (2023). Documentation of siddha paediatric external therapies. Int. J. Health Sci. Res.13, 73–84. 10.52403/ijhsr.20230411
62
Safarzadeh E. Sandoghchian Shotorbani S. Baradaran B. (2014). Herbal medicine as inducers of apoptosis in cancer treatment. Adv. Pharm. Bull.4, 421–427. 10.5681/APB.2014.062
63
Sakamoto S. Miyamoto T. Usui K. Tanaka H. Morimoto S. (2018). Sodium-periodate-mediated harringtonine derivatives and their antiproliferative activity against HL-60 acute leukemia cells. J. Nat. Prod.81, 34–40. 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00541
64
Samanta S. (2022). Potential bioactive components and health promotional benefits of tea (Camellia sinensis). J. Am. Nutr. Assoc.41, 65–93. 10.1080/07315724.2020.1827082
65
Shao F. Wilson I. W. Qiu D. (2021). The research progress of taxol in taxus. CPB22, 360–366. 10.2174/1389201021666200621163333
66
Shao J. Gong G. Trombetta L. (2011). “An evidence-based perspective of Hedyotis diffusa or Oldenlandia diffusa (spreading hedyotis) for cancer patients,” in Evidence-based anticancer materia medica. Evidence-based anticancer complementary and alternative medicine. Editor ChoW. C. S. (Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands), 179–192. 10.1007/978-94-007-0526-5_9
67
Sharma A. N. Dewangan H. K. Upadhyay P. K. (2024). Comprehensive review on herbal medicine: emphasis on current therapy and role of phytoconstituents for cancer treatment. Chem. Biodivers.21, e202301468. 10.1002/cbdv.202301468
68
Sharma M. Sharma M. Bithel N. Sharma M. (2022b). Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and nutritional potential of MedicinalPlants from asteraceae family. J. Mt. Res.17. 10.51220/jmr.v17i2.7
69
Sharma T. Sharma P. Chandel P. Singh S. Sharma N. Naved T. et al (2022a). Circumstantial insights into the potential of traditional Chinese medicinal plants Asa therapeutic approach in rheumatoid arthritis. CPD28, 2140–2149. 10.2174/1381612828666220324124720
70
Sheng J.-Y. Wang S.-Q. Liu K.-H. Zhu B. Zhang Q.-Y. Qin L.-P. et al (2020). Rubus chingii hu: an overview of botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. Chin. J. Nat. Med.18, 401–416. 10.1016/S1875-5364(20)30048-0
71
Singh S K. Singh R. Chopra C. (2021). “Traditional medicine: recognize potential cancer treatments of herbal origin,” Modern cancer therapies and traditional medicine: an integrative approach to combat cancers (United Kingdom: Bentham Science), 252–267. 10.2174/9789814998666121010015
72
Sohretoglu D. Huang S. (2018). Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides as an anti-cancer agent. ACAMC18, 667–674. 10.2174/1871520617666171113121246
73
Song J. Shi L. Li D. Sun Y. Niu Y. Chen Z. et al (2012). Extensive pyrosequencing reveals frequent intra-genomic variations of internal transcribed spacer regions of nuclear ribosomal DNA. PLoS ONE7, e43971. 10.1371/journal.pone.0043971
74
Soroudi S. Jaafari M. R. Arabi L. (2024). Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) mediated mRNA delivery in cardiovascular diseases: advances in genome editing and CAR T cell therapy. J. Control. Release372, 113–140. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.06.023
75
Sze S. C. W. Tong Y. Ng T. B. Cheng C. L. Y. Cheung H. P. (2010). Herba epimedii: anti-oxidative properties and its medical implications. Molecules15, 7861–7870. 10.3390/molecules15117861
76
Thapliyal S. Vishnoi R. Murti Y. Kumar R. Chavan N. Rawat P. et al (2024). Exploring anticancer properties of the phytoconstituents and comparative analysis of their chemical space parameters with USFDA ‐approved synthetic anticancer agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des.103, e14561. 10.1111/cbdd.14561
77
Wali R. Khan M. F. Mahmood A. Mahmood M. Qureshi R. Ahmad K. S. et al (2022). Ethnomedicinal appraisal of plants used for the treatment of gastrointestinal complaints by tribal communities living in Diamir district, Western Himalayas, Pakistan. PLoS ONE17, e0269445. 10.1371/journal.pone.0269445
78
Wang C.-Z. Calway T. Yuan C.-S. (2012). Herbal medicines as adjuvants for cancer therapeutics. Am. J. Chin. Med.40, 657–669. 10.1142/S0192415X12500498
79
Wang H. Wang R. Huang D. Li S. Gao B. Kang Z. et al (2021). Homoharringtonine exerts anti-tumor effects in hepatocellular carcinoma through activation of the Hippo pathway. Front. Pharmacol.12, 592071. 10.3389/fphar.2021.592071
80
Wang H. Yang D. Li L. Yang S. Du G. Lu Y. (2020). Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of Rhein, an anthraquinone compound, and its applications in treating arthritis: a review. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect10, 445–452. 10.1007/s13659-020-00272-y
81
Wang Z. Qi F. Cui Y. Zhao L. Sun X. Tang W. et al (2018). An update on Chinese herbal medicines as adjuvant treatment of anticancer therapeutics. BST12, 220–239. 10.5582/bst.2018.01144
82
Wu Z. Shang G. Zhang K. Wang W. Fan M. Lin R. (2024). A nomogram incorporating treatment data for predicting overall survival in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a population-based cohort study. Int. J. Surg.110, 2178–2186. 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001080
83
Xi W. Zhang Y. Zhang Z. Chen Y. Huang X. Mou H. et al (2024). Integrating Cu/Cux O ternary nanocomposites with multi-walled carbon nanotubes enabling a high-performance nonenzymatic amperometric glucose sensor. Microstructures4, 4. 10.20517/microstructures.2023.79
84
Xie J.-H. Jin M.-L. Morris G. A. Zha X.-Q. Chen H.-Q. Yi Y. et al (2016). Advances on bioactive polysaccharides from medicinal plants. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.56, S60–S84. 10.1080/10408398.2015.1069255
85
Xie Z. Huang H. Zhao Y. Shi H. Wang S. Wang T. T. Y. et al (2012). Chemical composition and anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects of the leaf and whole-plant samples of diploid and tetraploid Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino. Food Chem.132, 125–133. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.10.043
86
Xie Z. Zhao Y. Chen P. Jing P. Yue J. Yu L. (2011). Chromatographic fingerprint analysis and rutin and Quercetin compositions in the leaf and whole-plant samples of Di- and tetraploid Gynostemma pentaphyllum. J. Agric. Food Chem.59, 3042–3049. 10.1021/jf104329v
87
Xue C. C. O’Brien K. A. (2003). AttentiveHerb: a novel method for traditional medicine prescription generation in a comprehensive guide to Chinese medicine. Singapore: World Sci.19–46. 10.1142/9789812794987_0002
88
Yang M. Wang F. Liang H. Ji G. Lian Y. Zou C. et al (2023a). Accurate gingival segmentation from 3D images with artificial intelligence: an animal pilot study. Med. Adv.24 (1), 14–29. 10.1186/s40510-023-00465-4
89
Yang M. Wang F. Liang H. Ji G. Lian Y. Zou C. et al (2023b). Single‐cell RNA sequencing reveals distinct immune cell subsets in phalangeal and soft‐tissue recurrence of giant cell tumor of bone. Med. Adv.1, 14–29. 10.1002/med4.10
90
Yang S. Shan L. Luo H. Sheng X. Du J. Li Y. (2017). Rapid classification and identification of chemical components of Schisandra Chinensis by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS combined with data post-processing. Molecules22, 1778. 10.3390/molecules22101778
91
Yang W. Ma Y. Xu H. Zhu Z. Wu J. Xu C. et al (2023c). Mulberry biomass-derived nanomedicines mitigate colitis through improved inflamed mucosa accumulation and intestinal microenvironment modulation. Research6,0188. 10.34133/research.0188
92
Yang Y. Chen X. Luan F. Wang M. Wang Z. Wang J. et al (2021). Euphorbia helioscopia L.: a phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Phytochemistry184, 112649. 10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112649
93
Yao Q. Wang Y. Dong Z. Lai C. Chang B. Gong Q. et al (2021). Dichondra repens J.R.Forst. and G.Forst.: a review of its traditional uses, chemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and applications. Front. Pharmacol.11, 608199. 10.3389/fphar.2020.608199
94
Yarnell E. (2015). Synergy in herbal medicines: part 1. J. Restorat Med.4, 60–73. 10.14200/jrm.2015.4.0104
95
Ye H. Ye Y. Wang Y. Tong T. Yao S. Xu Y. et al (2023). Automated assessment of necrosis tumor ratio in colorectal cancer using an artificial intelligence‐based digital pathology analysis. Med. Adv.1, 30–43. 10.1002/med4.9
96
Yu G. Luo Z. Wang W. Li Y. Zhou Y. Shi Y. (2019). Rubus chingii Hu: a review of the phytochemistry and pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol.10, 799. 10.3389/fphar.2019.00799
97
Yu X. Pan S. (2024). Role and mechanism of cGAS-STING pathway in cardiovascular system. Rev. Cardiovasc Med.25, 135. 10.31083/j.rcm2504135
98
Yuan H. Ma Q. Ye L. Piao G. (2016). The traditional medicine and modern medicine from natural products. Molecules21, 559. 10.3390/molecules21050559
99
Yue-ling M. Yu-jie C. Ding-rong W. Ping C. Ran X. (2017). HPLC determination of quercetin in three plant drugs from genus sedum and conjecture of the best harvest time. PJ9, 725–728. 10.5530/pj.2017.6.114
100
Zhang F. Zhai J. Weng N. Gao J. Yin J. Chen W. (2022). A comprehensive review of the main lignan components of Schisandra chinensis (North Wu wei zi) and Schisandra sphenanthera (South Wu wei zi) and the lignan-induced drug-drug interactions based on the inhibition of cytochrome P450 and P-Glycoprotein activities. Front. Pharmacol.13, 816036. 10.3389/fphar.2022.816036
101
Zhang X. Qiu H. Li C. Cai P. Qi F. (2021). The positive role of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy for cancer. BST15, 283–298. 10.5582/bst.2021.01318
102
Zheng W.-J. Ren Y.-S. Wu M.-L. Yang Y.-L. Fan Y. Piao X.-H. et al (2021). A review of the traditional uses, phytochemistry and biological activities of the melastoma genus. J. Ethnopharmacol.264, 113322. 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113322
103
Zhou H. Jing S. Liu Y. Wang X. Duan X. Xiong W. et al (2023a). Identifying the key genes of epstein–barr virus‐regulated tumour immune microenvironment of gastric carcinomas. Cell Prolif.56, e13373. 10.1111/cpr.13373
104
Zhou H. Zhang M. Cao H. Du X. Zhang X. Wang J. et al (2023b). Research progress on the synergistic anti-tumor effect of natural anti-tumor components of Chinese herbal medicine combined with chemotherapy drugs. Pharmaceuticals16, 1734. 10.3390/ph16121734
105
Zhou L. Liu Z. Wang Z. Yu S. Long T. Zhou X. et al (2017). Astragalus polysaccharides exerts immunomodulatory effects via TLR4-mediated MyD88-dependent signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep.7, 44822. 10.1038/srep44822
106
Zhu A. Jiang Y. Pan L. Li J. Huang Y. Shi M. et al (2025). Cell inspired delivery system equipped with natural membrane structures in applications for rescuing ischemic stroke. J. Control. Release377, 54–80. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.11.013
107
Zhu C. Wu Q. Sheng T. Shi J. Shen X. Yu J. et al (2024). Rationally designed approaches to augment CAR-T therapy for solid tumor treatment. Bioact. Mater.33, 377–395. 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.11.002
108
Zhu X. Yao Q. Yang P. Zhao D. Yang R. Bai H. et al (2022). Multi-omics approaches for in-depth understanding of therapeutic mechanism for traditional Chinese medicine. Front. Pharmacol.13, 1031051. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1031051
109
Дв З. Лв Б. (2023). Doctors-advocates in the fight against syphilis, contagious skin diseases and leprosy in Russia (late 19th – early 20th centuries). A view from the twenty-first century. Дерматовенерология Косметология, 92–107. 10.34883/PI.2023.9.1.018
Summary
Keywords
She medicine, anticancer herbs, flavonoids, quercetin, cancer research
Citation
Miao Y, Chen Y, Lan Q, Chen R, Zhuang J, Shi H, Wang M, Miao J and Lin C (2025) The anticancer activity and mechanisms of She medicine herbs. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1610301. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1610301
Received
11 April 2025
Accepted
13 June 2025
Published
17 July 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Sujit Nair, Phytoveda Pvt. Ltd., India
Reviewed by
Hong Kwan Kim, Sungkyunkwan University, Republic of Korea
Bizhar Ahmed Tayeb, University of Szeged, Hungary
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Miao, Chen, Lan, Chen, Zhuang, Shi, Wang, Miao and Lin.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yisheng Chen, casenablerbq@hotmail.com; Miao Wang, 19233539174@163.com, wangm2516@163.com; Jianhui Miao, mjoenlacauzk@hotmail.com; Chengshou Lin, ishiiorwin2r@hotmail.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.