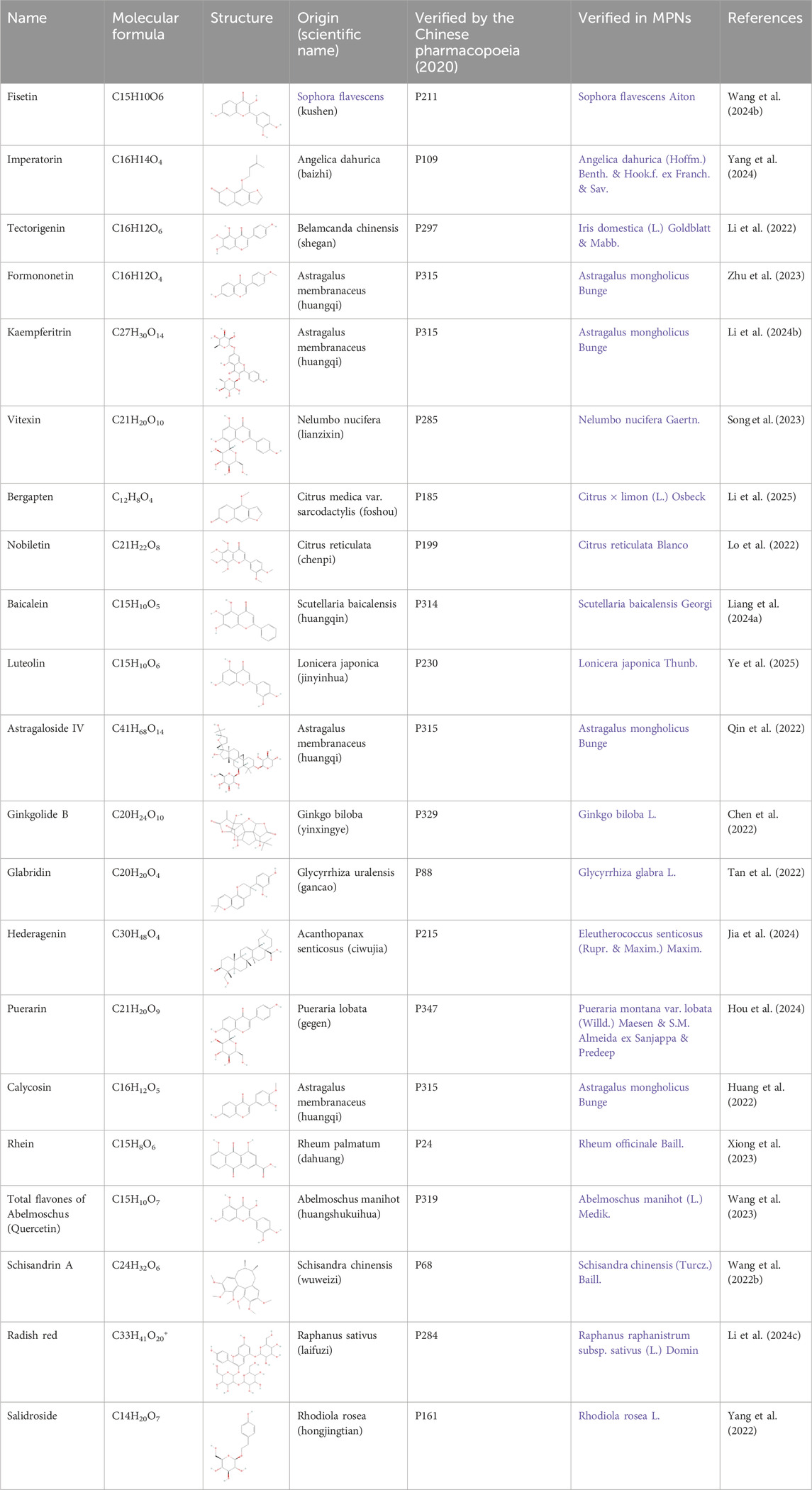
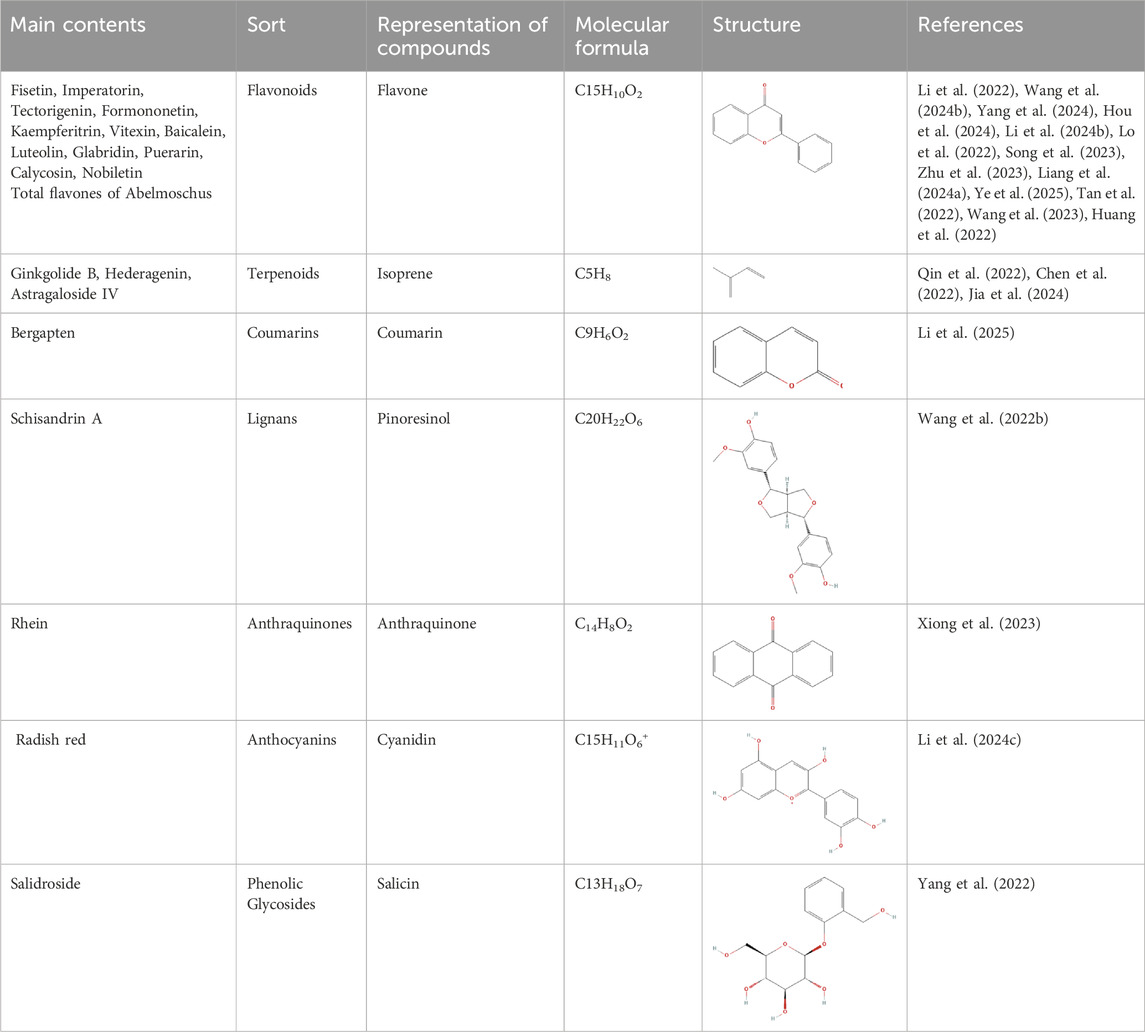
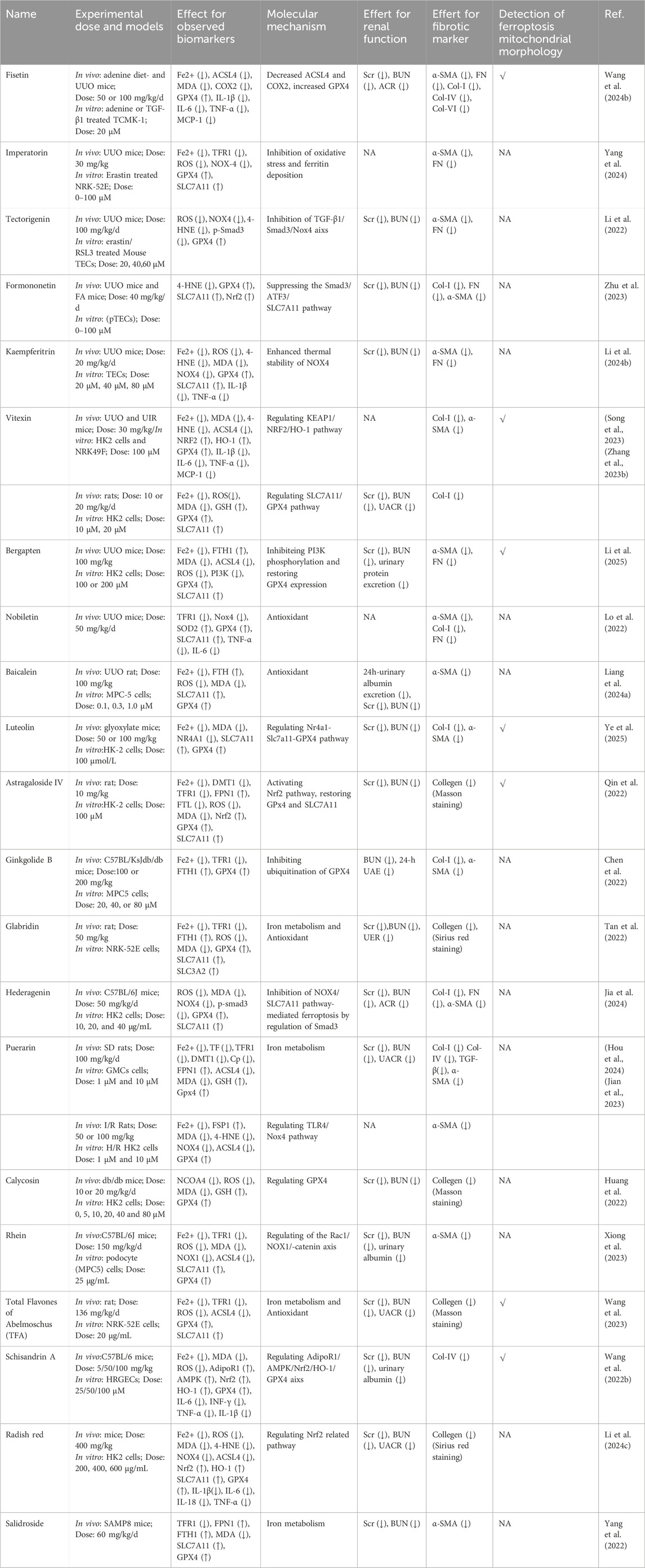
- Department of Nephrology and Institute of Nephrology, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
Background and purpose: Renal fibrosis is a common characteristic of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Studies have confirmed the role of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of various kidney diseases, making it a new research hotspot in the field of renal fibrosis. Monomers of Chinese herbal medicines (CHMs) can improve renal fibrosis by multi-target inhibition of ferroptosis. This review aimed to explore the roles and mechanisms of CHMs in renal fibrosis.
Methods: Using the keywords “ferroptosis”, “chronic kidney disease”, “renal fibrosis”, “Chinese herbal medicine”, “natural products”, “bioactive components”, and “herb”, we conducted an extensive literature search of several databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, CNKI, and Wanfang database, to identify studies reporting the role of CHM monomers in inhibiting ferroptosis and improving renal fibrosis. The names of the plants covered in the review have been checked through MPNS (http://mpns.kew.org). All monomers of CHMs were identified in the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China.
Results: In total, 21 monomers of CHMs were identified in this study, most of which were flavonoids, followed by terpenoids and coumarins. This review showed that monomers of CHMs inhibited ferroptosis and improved renal fibrosis through multi-target mechanisms. They maintained iron homeostasis by acting on NCOA4 and Nrf2 to reduce ferritinophagy. They also inhibited lipid peroxidation and regulated the antioxidant system by modulating ACSL4, NOX4, Nrf2, FSP1, and GPX4 and inhibiting Smad3 to improve renal fibrosis.
Conclusion: Monomers of CHMs effectively inhibited ferroptosis and prevented renal fibrosis in various animal models and cell models of CKD. However, further in-depth studies with better designs are needed to identify the exact targets of monomers of CHMs and improve the treatment of renal fibrosis and CKD.
1 Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major global health concern, affecting 8%–16% of the global population (Chen et al., 2019). In 2022, CKD was estimated to affect ∼850 million people globally (Kovesdy, 2011; Romagnani et al., 2025). The primary risk factors for CKD include glomerular diseases, diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and aging (Sui et al., 2020). CKD can advance to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), necessitating dialysis or kidney transplantation. By 2030, an estimated 5 million patients will need kidney replacement therapy worldwide, doubling the 2010 figures (Liyanage et al., 2015). The number of patients needing dialysis in China is rising rapidly, with 207,863 new cases in 2023, increasing the total number to 1 million (Webster et al., 2017). These statistics highlight the growing burden of CKD and the pressing need for effective treatments. Renal fibrosis is a common characteristic of CKD. It involves excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) in the interstitial space, disrupting normal kidney architecture and contributing to renal failure. Inhibiting the progression of renal fibrosis is essential for preserving renal function (Huang et al., 2023). However, effective treatments to decelerate the progression of CKD remain limited, and disease progression can be rarely reversed (Li S. et al., 2024).
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent form of programmed cell death, primarily characterized by the accumulation of intracellular lipid peroxides (Dixon et al., 2012). This form of cell death is strongly associated with iron overload, lipid peroxidation, and impaired antioxidant capacity (Zhang et al., 2022; Zhou L. et al., 2022). Previous studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between ferroptosis and kidney disease, suggesting that regulation of ferroptosis can serve as a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of kidney diseases (Li S. et al., 2024; Lai et al., 2024; Wang F. et al., 2024). Targeting ferroptosis with specific inhibitors, such as ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1) and liproxstatin-1 (Lip-1), promotes adaptive cell repair and mitigates fibrosis, highlighting ferroptosis inhibition as a promising strategy for mitigating renal fibrosis (Zhou L. et al., 2022; Balzer et al., 2022; Wang J. et al., 2022). However, the long-term off-target consequences of these inhibitors, particularly drug interactions and cumulative organ-specific toxicities, need further systematic assessments (Conrad et al., 2021). These concerns underscore the critical need for ferroptosis inhibitors with improved efficacy and optimized safety profiles.
The discovery of artemisinin for the treatment of malaria indicates that monomers of Chinese herbal medicines (CHMs) can effectively address complex health issues (Tu, 2011). Notably, monomers derived from CHMs exhibit superior biocompatibility and multi-target regulatory capacity compared to synthetic compounds, making them promising candidates for pharmacological intervention (Parkash et al., 2018). CHMs have long been used in clinical practice, and recent pharmacological studies have elucidated their nephroprotective mechanisms in CKD through multi-target modulation of ferroptosis and renal fibrosis (Gong et al., 2024). The main monomers of CHMs include flavonoid glycosides, triterpenoid derivatives, coumarin analogs, isoquinoline alkaloids, steroidal saponins, polyphenolic acids, and enzymatic cofactors. Previous studies have shown that CHM-derived monomers and their compounds exhibit significant therapeutic efficacy in treating various diseases while maintaining low toxicity and minimal side effects, making them invaluable candidates for modern drug development (Huang et al., 2024; Singh et al., 2024).
This review provides a comprehensive overview of monomer research methods and identifies key targets for regulating ferroptosis. It also discusses the effects and mechanisms of these targets on renal fibrosis, establishing a foundation for future studies on how monomers can enhance ferroptosis and mitigate renal fibrosis.
2 CKD and renal fibrosis
Renal fibrosis is a hallmark feature of the progression of CKD to ESKD, characterized by tubular atrophy, chronic interstitial inflammation, fibrosis, glomerulosclerosis, and vascular rarefaction (Yuan et al., 2022). Renal fibrosis can be caused by various conditions affecting the kidneys, including glomerular diseases, ischemia-reperfusion injury, diabetic nephropathy, and nephrotoxic agents (Han et al., 2024). Its severity is positively correlated with decreased renal function (Rayego-Mateos and Valdivielso, 2020; Risdon et al., 1968; Rodríguez-Iturbe et al., 2005). Renal fibrosis is a multifaceted pathological process driven by interactions between various renal cell types and multiple molecular pathways, such as the TGF-β/Smads, Wnt/β-catenin, and NF-κB pathways (Gu et al., 2024; Tan et al., 2014; Niu et al., 2025). This process is characterized by several pathological alterations, including ECM deposition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of renal tubular cells, fibroblast activation, immune cell infiltration, and renal cell apoptosis (Rayego-Mateos and Valdivielso, 2020). Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) is a main mediator of renal fibrosis, promoting ECM deposition by stimulating fibroblast proliferation and enhancing collagen synthesis (Lan, 2011). TGF-β activates Smad2/3 through TGF-β receptor I (TGF-βRI) and TGF-β receptor II (TGF-βRII). Activated Smad2/3 forms a complex with Smad4 and translocates to the nucleus, where it modulates the expression of genes associated with EMT of renal tubular epithelial cells (TEC) (Lovisa et al., 2015). Via EMT, epithelial cells can excessively produce collagen I (Col-I) and fibronectin (FN), thereby driving renal interstitial fibrosis (Xing et al., 2022; Yuan et al., 2019). Moreover, pathological conditions, such as renal ischemia, hypoxia, renal tubular epithelial cell injury, diabetes, and hypertension, exacerbate renal fibrosis (Naas et al., 2023; Nogueira et al., 2017; Qiu et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2020).
3 Ferroptosis in renal fibrosis
3.1 Core mechanisms of ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is a novel form of cell death that differs morphologically and biochemically from apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy. It was first identified by Dixon et al., in 2012 (Dixon et al., 2012). Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent lipid peroxidation mechanism, which plays a crucial role in cell survival and homeostasis (Liu et al., 2022; Jiang et al., 2021; Li J. et al., 2020; Ru et al., 2024). It is currently believed that ferroptosis is an important target for developing new therapeutic strategies (Stockwell, 2022).
3.1.1 Iron metabolism
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent form of cell death closely associated with impaired iron metabolism (Figure 1). Extracellular ferric iron (Fe3+) is internalized via transferrin (TF), which binds to transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1). Iron export is primarily mediated by ferroportin 1 (FPN1). Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3 (STEAP3) reduces Fe3+ to ferrous iron (Fe2+) in endosomes. Divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) facilitates the release of Fe2+ from endosomes into the cytoplasmic labile iron pool (LIP). Free Fe2+ in the LIP participates in the Fenton reaction (Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + ·OH + OH−), generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), particularly hydroxyl radicals. In pathological conditions, an imbalance between FPN1 and DMT1, such as FPN1 downregulation or DMT1 overexpression, leads to intracellular iron overload (Feng et al., 2020). Intracellular iron is stored in the form of ferritin, a complex with two major subunits: ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1) and ferritin light chain (FTL). FTH1 primarily maintains the structural integrity of the ferritin shell, while FTL is critically involved in iron storage and release. These subunits work synergistically to maintain intracellular iron homeostasis (Ru et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2020; Latunde-Dada, 2017). Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) facilitates ferritin degradation through ferritinophagy, thereby leading to the release of Fe2+ and increasing the burden of labile LIP. Additionally, NCOA4 mediates FTH1 autophagy, thereby modulating sensitivity to ferroptosis (Luo et al., 2025; Yu et al., 2024).
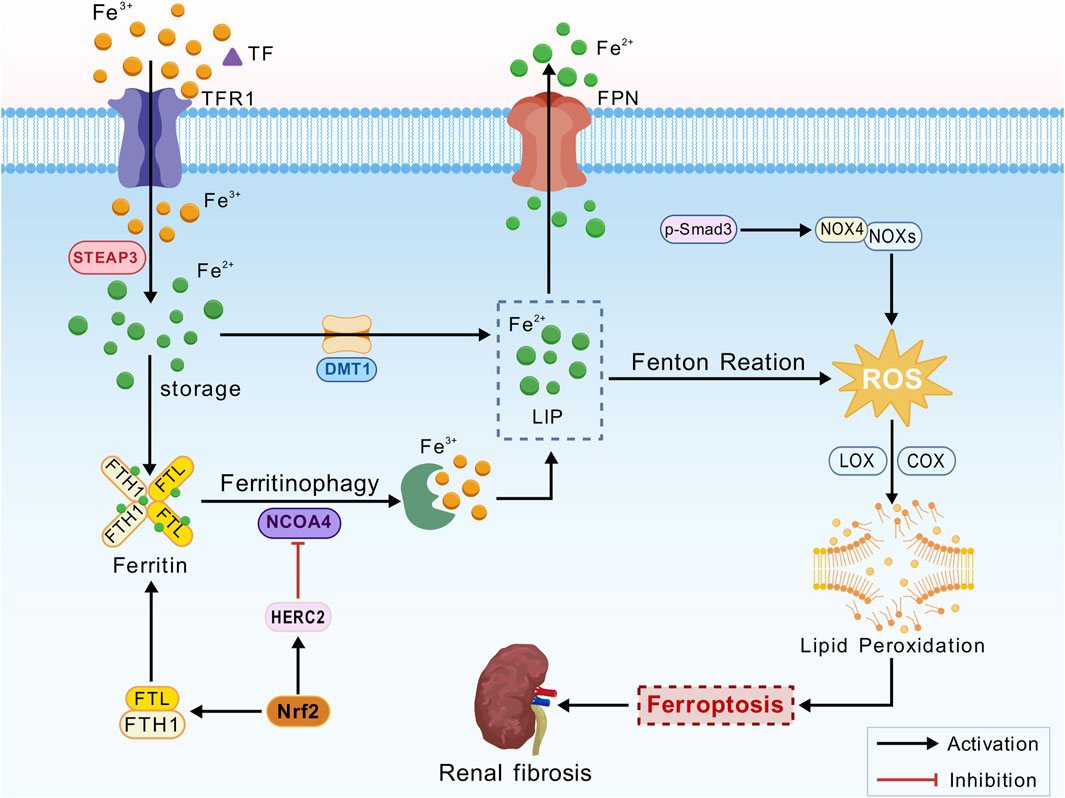
Figure 1. Iron metabolism mechanism. Transferrin (TF), transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1), ferroportin 1 (FPN1), six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3 (STEAP3), divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), labile iron pool (LIP), reactive oxygen species (ROS), ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1), ferritin light chain (FTL), nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), NADPH oxidases (NOXs), lipoxygenase (LOX), cyclooxygenase (COX), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), and phosphorylated Smad3 (p-Smad3).
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a critical transcription factor that plays a significant role in the kidneys, particularly in the context of oxidative stress and inflammation (Dächert et al., 2020). Activation of Nrf2 promotes iron storage, reduces iron uptake by cells, and limits ROS production (Han et al., 2024). Nrf2 could regulate iron homeostasis by controlling HERC2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase for NCOA4 and FBXL5, as well as VAMP8, thereby facilitating autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Furthermore, NRF2 modulates the transcription of FTL and FTH1, ensuring the safe storage of intracellular iron and limiting the accumulation of free Fe2+. This mechanism mitigates lipid peroxidation and suppresses ferroptosis via the Fenton reaction (Anandhan et al., 2023; Cheng et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2025). In the presence of iron overload, Fe2+ catalyzes ROS production via the Fenton reaction, generating highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (·OH). These radicals attack polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the cell membrane, initiating a lipid peroxidation chain reaction, membrane disruption, and ferroptosis (Bayir et al., 2023).
3.1.2 Lipid peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation is one of the essential factors driving ferroptosis and serving as a major cause of cell death (Figure 2) (Rochette et al., 2022). The oxidative metabolism of PUFAs is the central mechanism of ferroptosis. Acetyl-CoA, the initial substrate for fatty acid synthesis, is catalyzed by acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) to generate malonyl-CoA, providing precursors for lipid biosynthesis. Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) facilitates the conversion of free PUFAs, such as arachidonic acid (AA) and adrenic acid (AdA), into PUFA-CoA. These PUFA-CoA molecules are subsequently incorporated into the sn-2 position of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) by lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3), forming highly oxidation-sensitive PUFA-phospholipids (PUFA-PE), including AA-PE and AdA-PE. After the activation of NADPH oxidases (NOXs)-derived ROS, lipoxygenases (LOXs) and cyclooxygenases (COXs) directly oxidize PUFA-PE, leading to the production of lipid hydroperoxides (PUFA-OOH) (Lai et al., 2024; Lee et al., 2021).
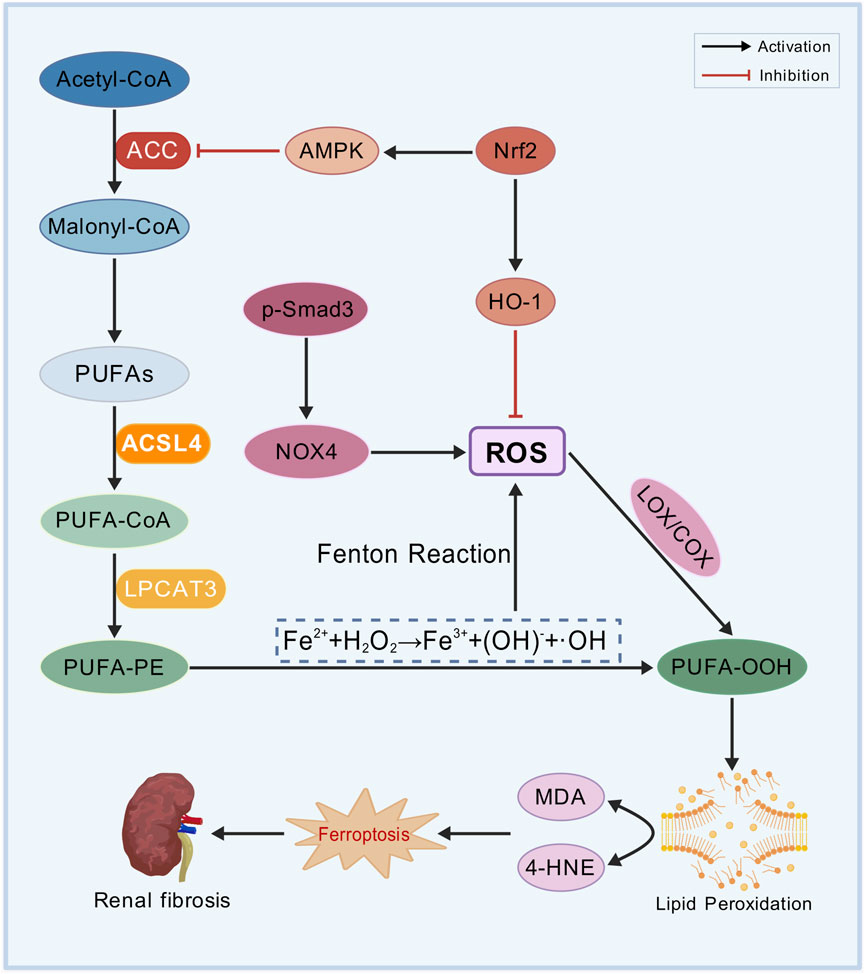
Figure 2. Lipid peroxidation mechanism. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4), arachidonic acid (AA), adrenic acid (AdA), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3), PUFA-phospholipids (PUFA-PE), NADPH oxidases (NOXs), reactive oxygen species (ROS), lipoxygenases (LOXs), cyclooxygenases (COXs), lipid hydroperoxides (PUFA-OOH), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), malondialdehyde (MDA), and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE).
NRF2 mitigates oxidative stress by activating antioxidant genes, such as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), to eliminate ROS. Additionally, NRF2 suppresses lipid peroxidation by inhibiting ACC via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) (Lu et al., 2023). PUFA-OOH undergoes non-enzymatic degradation to generate malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), both of which can represent the severity of ferroptosis. 4-HNE and MDA compromise the integrity of cell membranes, leading to protein cross-linking, DNA damage, and mitochondrial dysfunction, finally inducing ferroptosis in renal TECs (Stockwell, 2022; Tang et al., 2021; Zhang X. et al., 2023).
3.1.3 Antioxidant defense
The core regulatory mechanisms of ferroptosis include three major antioxidant systems, namely the Xc−/GSH/GPX4 pathway, the FSP1/CoQ10 pathway, and the Nrf2/ARE pathway (Figure 3).
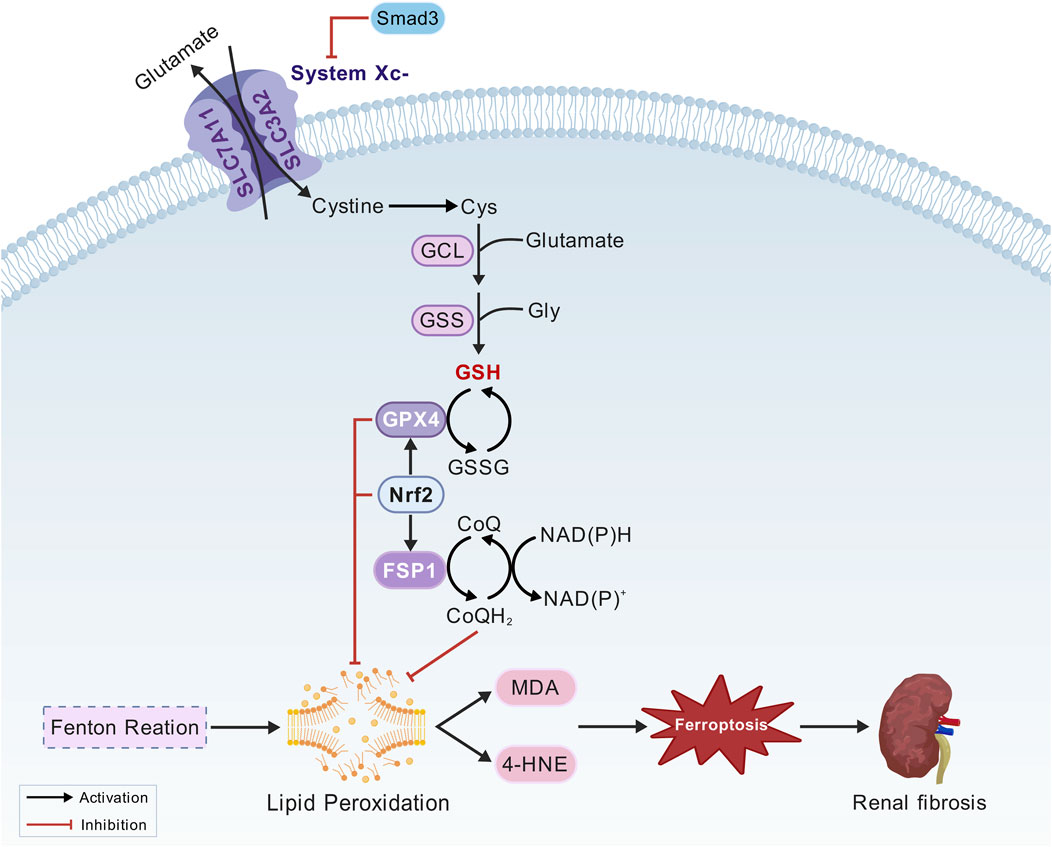
Figure 3. Oxidation system mechanism. Cystine/glutamate antiporter (System Xc−), glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11), solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2), glutathione (GSH), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (Smad3), ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1), coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), ubiquinol (CoQ10H2), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH).
3.1.3.1 The Xc-/GSH/GPX4 pathway
Inhibition of system Xc− and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) expression leads to insufficient GSH synthesis, resulting in excessive lipid peroxidation and ROS accumulation in the intracellular space. This process plays a crucial role in triggering ferroptosis (Liu et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023). The System Xc− is composed of solute carrier family members solute carrier family 7 member 11(SLC7A11) and solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2). It facilitates the transport of extracellular cystine into cells, where it is reduced to cysteine, a critical precursor for the synthesis of glutathione (GSH). As an antioxidant enzyme, GPX4 regulates ferroptosis and functions as a “scavenger” of lipid peroxides. It utilizes reduced glutathione to convert lipid hydroperoxides into their corresponding lipid alcohols, thereby mitigating lipid peroxidation and inhibiting ferroptosis. Therefore, GPX4 can regulate ferroptosis (Jia et al., 2020). Nrf2 can promote the expression of SLC7A11 and GPX4 under oxidative stress, thereby preventing ferroptosis (Dong et al., 2020; G et al., 2021). Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) induces ferroptosis by directly binding to the SLC7A11 promoter and suppressing its expression (Wang et al., 2020). Smad3, a central regulator of fibrosis, directly interacts with ATF3 and regulates its transcriptional activity (Shi et al., 2020).
3.1.3.2 The FSP1/CoQ10 pathway
Using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1) reduces coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) to its active form, ubiquinol (CoQ10H2). As a lipophilic antioxidant, ubiquinol directly neutralizes lipid radicals, establishing a GPX4-independent defense mechanism against ferroptosis (Bersuker et al., 2019; Doll et al., 2019). The discovery of FSP1 unveiled the complex regulation of ferroptosis and offered new directions for targeted therapy.
3.1.3.3 The Nrf2/ARE pathway
Nrf2 is a master regulator of cell defense systems involved in detoxification, antioxidant defense, and resolving inflammation and fibrosis (Murakami et al., 2023). Under oxidative stress, Nrf2 translocates to the nucleus and binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE), upregulating the expression of various antioxidant genes, including SLC7A11, GPX4, and HO-1. They are essential for reducing lipid hydroperoxides to their corresponding alcohols, thereby preventing the accumulation of lipid peroxides that trigger ferroptosis (Deng et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2021; Song and Long, 2020). By enhancing the expression of these protective factors, Nrf2 effectively prevents lipid peroxidation, thereby mitigating the oxidative damage in various pathological conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, chronic inflammation, and cancer (Li et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2025). Nrf2 also plays a crucial role in regulating iron homeostasis by modulating the expression of HERC2 and VAMP8. The latter is involved in the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes. This regulation highlights the significance of Nrf2 inhibition in triggering ferroptosis (Anandhan et al., 2023). Furthermore, previous studies have shown that FSP1, a key inhibitor of ferroptosis, partly relies on Nrf2 for its expression. Targeting both FSP1 and Nrf2 may represent a promising therapeutic strategy for renal ferroptosis (Kim et al., 2023).
3.2 The involvement of ferroptosis in renal fibrosis
The kidney is a crucial organ involved in iron filtration and reabsorption, thereby regulating iron metabolism. Rich in mitochondria and exhibiting high oxygen uptake, the kidney is highly susceptible to oxidative stress. In patients with CKD, decreased expression of saturated fatty acids in the kidney impairs the transfer of iron from cells to the extracellular space, while overexpression of iron-transfer factors leads to iron deposition in renal tubules (Packer, 2024). Furthermore, the kidney has high lipoxygenase expression, making it susceptible to lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Previous studies have demonstrated that ferroptosis is closely associated with renal fibrosis subsequent to glomerulonephritis, renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, diabetic nephropathy, and kidney stones in animal models (Ru et al., 2024; Du et al., 2022; Zhou Y. et al., 2022).
3.2.1 Renal tubular epithelial cell (TEC) injury induces ferroptosis-induced fibrosis
Accumulating evidence suggests that TECs plays diverse roles in renal repair or progression to CKD (Liu et al., 2018). TECs are involved in the kidney’s response to various harmful stimuli and also serve as the source of myofibroblasts (Kuppe et al., 2021). The activation of myofibroblasts and subsequent release of ECM are the core features of renal interstitial fibrosis. During renal fibrosis, TECs mediate the initial response to injury, initiating EMT, when myofibroblasts become the main effector cells (Hong et al., 2019).
TECs are rich in mitochondria and generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for cellular function through fatty acid oxidation (FAO) (Hwang and Chung, 2021). After renal TEC injury, mitochondrial dysfunction leads to the accumulation of mitochondrial ROS, which triggers ferroptosis (Su et al., 2023). Damaged TECs promote inflammation and fibrosis through several mechanisms, including EMT, the release of pro-inflammatory factors, and the activation of signaling pathways, such as the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway (Liu et al., 2018). This process is accompanied by intracellular iron accumulation and lipid peroxide generation, leading to cell death and decreased kidney function (Linkermann et al., 2014). The proximal tubule (PT), being a key site for substance transport and reabsorption, has high energy demands and is particularly susceptible to oxidative damage. Recent findings suggest that PT cells exhibit a unique pro-inflammatory function after injury, which significantly attenuates the mechanisms inhibiting ferroptosis (Ide et al., 2021).
3.2.2 Ferroptosis-inflammation-fibrosis
Ferroptosis not only directly affects the survival of renal TECs but also affects the inflammatory response by inducing macrophage polarization. Ferroptosis leads to macrophage polarization toward the M1 phenotype, releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which also aggravate renal inflammation and fibrosis. Studies have shown that macrophage polarization is closely associated with the severity of renal fibrosis, and inhibiting M1 polarization of macrophages can alleviate renal fibrosis (Tang et al., 2025).
Furthermore, ferroptosis promotes EMT by activating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, leading to excessive deposition of extracellular matrix components, such as collagen. Studies have observed decreased levels of ferritin (FTH) during EMT. During EMT, ferritin releases free iron ions that induce iron overload, resulting in excessive ROS generation and ferroptosis (Zhou L. et al., 2022). This study supports the notion that iron overload contributes to renal fibrosis. These findings highlight the significant role of the ferroptosis-inflammation-fibrosis cascade in the pathogenesis of renal fibrosis. In vivo and in vitro studies have shown that ferroptosis inhibitors can inhibit fibrosis by downregulating the TGF-β1/SMAD3 signaling pathway, inhibiting the activation of fibroblasts, downregulating the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and inhibiting macrophage chemotaxis (Wang J. et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022; Ikeda et al., 2014; Lyu et al., 2025). Various forms of EMT activation, including TGF-β stimulation, increase the susceptibility to ferroptosis, thereby forming a vicious cycle (Lyu et al., 2025; Schwab et al., 2024) (Figure 4).
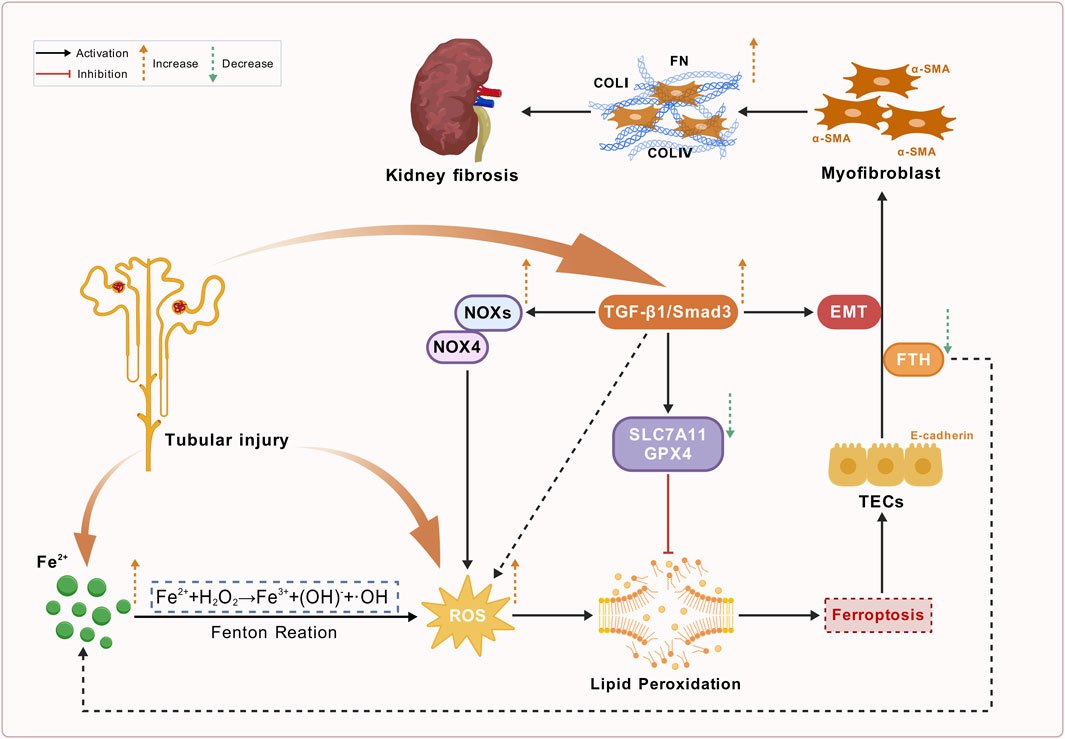
Figure 4. Schematic overview of renal fibrosis, ferroptosis, and TGF-β/Smad pathway activation in chronic kidney disease (CKD). This figure depicts the pathological mechanisms underlying renal fibrosis in CKD associated with ferroptosis. Tubular injury activates Fe2+ accumulation, leading to the Fenton reaction that generates reactive oxygen species (ROS). Increased ROS levels promote lipid peroxidation, which is inhibited by SLC7A11 and GPX4. Concurrently, the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling, which is activated by tubular injury, enhances ROS production by triggering NOXs/NOX4 and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This complex pathway leads to myofibroblast activation through ferroptosis, characterized by α-SMA activation and enhanced production of ECM components (e.g., COLI, COLIV and FN), exacerbating kidney fibrosis.
4 Monomers of CHMs protect against renal fibrosis by targeting ferroptosis
CHMs have been administered for more than 2000 years. A huge body of evidence suggests that CHMs monomers have great potential for treating renal fibrosis (Song et al., 2024). In this study, we conducted an extensive literature search in PubMed, Web of Science, CNKI, and Wanfang databases using keywords “ferroptosis”, “chronic kidney disease”, “renal fibrosis”, “Chinese herbal medicine”, “natural products”, “bioactive components”, and “herb” to identify studies reporting the role of CHM monomers in inhibiting ferroptosis and improving renal fibrosis. In total, 21 monomers and their roles, mechanisms, and targets in inhibiting ferroptosis and mitigating renal fibrosis were summarized (Table 1; Table 2; Table 3). The mechanisms and molecular targets of these monomers in inhibiting ferroptosis and alleviating renal fibrosis are summarized in Figure 5.
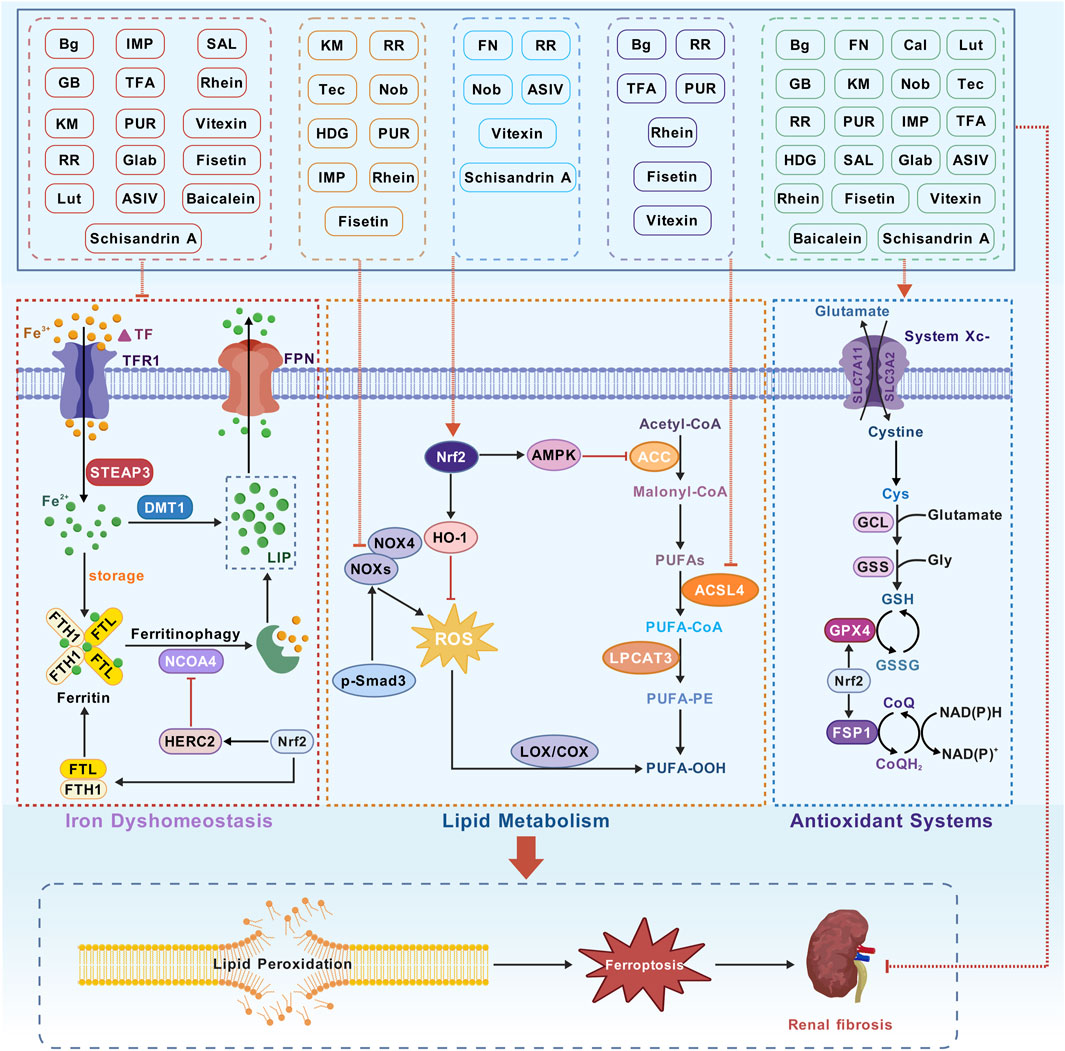
Figure 5. Monomer mechanism and target. Transferrin (TF), transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1), six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3 (STEAP3), divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), labile iron pool (LIP), ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1), ferritin light chain (FTL), nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4), Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4), lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3), PUFA-phospholipids (PUFA-PE), lipid hydroperoxides (PUFA-OOH), Cystine/glutamate antiporter (System Xc−), glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11), solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2), glutathione (GSH), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1).
4.1 Flavonoids
Fisetin, a compound extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Sophora flavescens (Kushen), and imperatorin (IMP), a compound derived from Angelica dahurica (Baizhi), exhibit significant nephroprotective effects and share common therapeutic properties, such as anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Wang B. et al. (2024) studied the effects of fisetin on ferroptosis and renal fibrosis in CKD models, induced by adenine diets and unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Their findings revealed that fisetin reduced serum creatinine (Scr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR). Furthermore, fisetin downregulated renal fibrosis markers, such as α-SMA, FN, Col-I and VI, and inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP-1. It also upregulated glutathione levels and the GSH/GSSG ratio while decreasing MDA levels, suggesting its protective role against oxidative stress. ACSL4 overexpression attenuated the protective effects of fisetin, indicating its potential to inhibit ferroptosis in kidney diseases. Similarly, treatment with IMP reversed the increases in α-SMA, FN, and TGF-β1 expression, restored E-cadherin expression, and reduced inflammatory infiltration. Additionally, IMP mitigated oxidative stress by restoring GPX4 and SLC7A11 expression, which were downregulated in the UUO model. IMP also effectively reversed erastin-induced ferroptosis by normalizing intracellular Fe2+ and ROS levels, emphasizing its ability to maintain redox homeostasis (Yang et al., 2024).
Both fisetin and IMP exhibited promising nephroprotective effects by modulating oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Their ability to regulate inflammatory responses and key signaling pathways make them potential therapeutic agents for treating renal fibrosis.
Puerarin (PUR), an isoflavone primarily extracted from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Pueraria lobata (Ge Gen), exhibits a wide range of pharmacological effects. For instance, it improves cardiovascular and cerebrovascular function, prevents osteoporosis, offers hepatoprotection and neuroprotection, and possesses hypoglycemic properties. Hou et al. (2024) investigated the therapeutic effects of puerarin on diabetic nephropathy. Puerarin reduced the levels of ACSL4, LDH, and MDA while upregulating GSH and GPX4, suggesting its protective role against HG-induced oxidative stress. These findings indicated that puerarin mitigated ferroptosis by modulating iron homeostasis and redox balance, thereby inhibiting ECM accumulation and decelerating the progression of diabetic nephropathy-associated renal fibrosis. In a separate study, puerarin attenuated renal fibrosis, and suppressed the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4), highlighting its potential to ameliorate I/R-induced ferroptosis and renal injury (Jian et al., 2023).
Tectorigenin (Tec), a bioactive isoflavone extracted from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Belamcanda chinensis (She Gan), exhibits a wide range of pharmacological activities, including antibacterial, antiviral, antitussive, expectorant, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and antitumor properties. Tec significantly ameliorated renal dysfunction and fibrosis, evidenced by decreased levels of Scr, BUN, and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1). Tec also downregulated collagen deposition and fibrotic markers, inhibited Smad3 phosphorylation and NOX4 expression, and restored GPX4 levels. These results suggested that Tec can protect the kidneys by inhibiting ferroptosis and modulating oxidative stress and the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathways (Li et al., 2022). Additionally, Kaempferitrin (KM) from Astragalus membranaceus was studied in a UUO mouse model, significantly lowering Fe2+, 4-HNE, MDA, and NOX4 levels in the kidney and increasing GSH, GPX4, and SLC7A11 expression (Li J. et al., 2024). This study suggests that KM ameliorates renal fibrosis by inhibiting NOX4-mediated ferroptosis in renal tubular cells. Besides, nobiletin (Nob) is a polymethoxyflavone derived from the TCM Citrus reticulata (Chenpi), which attenuated collagen deposition, inflammation, and renal ferroptosis by downregulating NOX4 expression in mice with UUO (Lo et al., 2022).
Vitexin and formononetin are phytochemicals derived from Nelumbo nucifera (lianzixin) and Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi), respectively. Both of them demonstrated significant nephroprotective properties. Vitexin has been widely recognized for its diverse pharmacological activities, including antiarrhythmic, antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, sedative, and hypoglycemic effects. Treatment with vitexin (30 mg/kg/day) significantly alleviated renal tubular injury and renal fibrosis and downregulated pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP-1) in mice with UUO. Mechanistically, vitexin enhanced the nuclear translocation of NRF2 and increased HO-1 mRNA expression by binding to KEAP1, thereby activating the KEAP1/NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway (Song et al., 2023). Furthermore, vitexin inhibited EMT, preserved mitochondrial integrity, and exhibited no adverse effects in ischemia-reperfusion injury and diabetic nephropathy (Song et al., 2023; Zhang S. et al., 2023). Notably, the nephroprotective effects of vitexin were weakened in NRF2-knockout mice, suggesting that vitexin inhibited ferroptosis by suppressing KEAP1-induced NRF2 degradation, thereby upregulatign GPX4 expression and suppressing lipid peroxidation.
Formononetin exerts renoprotective effects primarily by modulating the Nrf2/ARE and TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathways. Zhu et al. (2023) reported that formononetin attenuated UUO-induced renal injury by downregulating Fe2+ and 4-HNE levels, while upregulating SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression, demonstrating superior efficacy compared to valsartan. Furthermore, it inhibited the translocation of Smad3 and ATF3 in renal tubular epithelial cells treated with inducers of ferroptosis (RSL3 and erastin). Although Nrf2 expression was significantly reduced after exposure to RSL3 or erastin, formononetin restored the nuclear translocation of NRF2 in a dose-dependent manner.
Baicalein, a flavonoid extracted from Scutellaria baicalensis (Huangqin), exhibited significant therapeutic potential in the treatment of kidney diseases. Treatment with baicalein markedly attenuated renal injury and fibrosis in the mouse models of UUO. It reduced tubular capillary dilation, decreased interstitial space expansion, diminished inflammatory cell infiltration, alleviated perivascular exudation, and downregulated α-SMA expression. Furthermore, treatment with baicalein reduced the number of iron-positive cells and decreased ROS and MDA levels, while elevating the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as SOD, glutathione, and GSH. These protective effects are mediated partly by downregulating TGF-β1 and Smad2 expression (Liang GQ. et al., 2024).
Luteolin (Lut), a natural flavonoid derived from Lonicera japonica (Jinyinhua), possesses diverse pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, hypolipidemic, hypoglycemic, and immunomodulatory properties. Luteolin demonstrated renoprotective effects against calcium oxalate (CaOx)-induced renal injury and fibrosis by modulating oxidative stress and ferroptosis-related pathways. Specifically, it regulates the intracellular levels of GSH, MDA, and Fe2+, and restores the expression of key ferroptosis-associated proteins, such as SLC7A11 and GPX4. These mechanisms may be regulated by the orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1, suggesting the involvement of a gene-mediated pathway in the anti-fibrotic effects of luteolin (Ye et al., 2025).
Glabridin (Glab), derived from Glycyrrhiza uralensis (Gan cao), and total flavones of Abelmoschus manihot (TFA) were shown to significantly improve the management of diabetes and inhibit ferroptosis. Both compounds ameliorated renal fibrosis and suppressed ferroptosis by downregulation Fe2+, TFR1, and ROS levels, while concurrently upregulating the decreased levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4 (Tan et al., 2022) (Wang et al., 2023). Although Glab and TFA both regulate iron metabolism and suppress oxidative stress to inhibit ferroptosis-mediated fibrogenesis, their distinct molecular mechanisms remain incompletely characterized. Further studies are warranted to elucidate their precise mode of action and validate their translational potential in clinical practice.
Calycosin (Cal), derived from Astragalus membranaceus, protects against renal injury in diabetic nephropathy. It reverses the decrease in GPX4 expression and the increase in NCOA4 expression (Huang et al., 2022). This finding indicates that Cal may ameliorate diabetic nephropathy by regulating GPX4 and NCOA4 levels.
4.2 Terpenoids
Astragaloside IV (ASIV), extracted from Astragalus membranaceus (Huang Qi), has been demonstrated to mitigate Adriamycin (ADR)-induced renal damage. ASIV reduces reactive oxygen species and malondialdehyde levels, while enhancing antioxidant enzymes like GPX and SOD and reducing iron accumulation in kidneys by regulating FPN1, DMT1, TFR1, and FTL. Additionally, ASIV improves mitochondrial structure, increases oxidative stress proteins GPX4, Nrf2, and HO-1, and activates the PI3K/Akt pathway for protection against ADR-induced oxidative stress (Qin et al., 2022). Ginkgo biloba (GB), derived from Ginkgo biloba (Yin Xingye), exhibits pharmacological effects like vasodilation and antioxidant properties. Chen et al. (2022) showed that GB alleviates diabetic nephropathy in mice by reducing BUN and urinary albumin, thereby improving renal function. GB also mitigates renal histological damage by inhibiting GPX4 ubiquitination and lowering iron and ROS levels. HDG, extracted from Acanthopanax senticosus (Ciwujia), protects against ferroptosis and renal fibrosis by inhibiting NOX4 and p-Smad3 in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic nephropathy (DN) model (Jia et al., 2024).
4.3 Coumarins
Bergapten, a natural coumarin derivative, has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent for renal fibrosis. It modulates the expression of GPX4. Studies have indicated that treatment with bergapten can indirectly restore GPX4 levels, thus inhibiting lipid peroxidation and mitigating the progression of renal fibrosis. Bergapten exerts its protective effects by inhibiting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway, which regulates GPX4 expression. By inhibiting PI3K phosphorylation, bergapten upregulates GPX4 expression and enhances the antioxidant defense system in renal tubular epithelial cells. This restoration of GPX4 protects against ferroptosis and downregulates fibrotic markers, such as α-SMA and FN, in the kidney (Li et al., 2025).
4.4 Lignans
Schisandrin A (Sch A) is a prominent lignan compound primarily extracted from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis. Sch A has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent for renal fibrosis. Particularly, it can regulate iron metabolism-related proteins. Sch A can downregulate key ferroptosis markers, such as GPX4 and SLC7A11, suggesting its role in preserving cellular integrity and function in stress conditions. Furthermore, activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway by Sch A may contribute to its antioxidative effects, enhancing the resilience of the kidney against oxidative damage and subsequent fibrosis (Wang X. et al., 2022). Overall, this study underscores the potential of Sch A in treating renal fibrosis by inhibiting ferroptosis and oxidative stress, paving the way for future clinical applications.
4.5 Anthraquinones
Rhein is derived from Rheum palmatum (Da Huang), which possesses purgative, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, and lipid-lowering properties, improves vascular function, and preserves renal function. Recent studies have elucidated the mechanisms by which Rhein exerts its protective effects, notably through Rac1 inhibition. Rhein was shown to downregulate Rac1 expression, which correlates with decreased NOX1-mediated ROS production and downregulation of fibrosis markers, such as α-SMA and TGF-β (Xiong et al., 2023). Furthermore, inhibition of Rac1 activity by Rhein not only reduces oxidative stress but also affects downstream signaling pathways involved in EMT and renal fibrosis, such as the β-catenin pathway (Xiong et al., 2023). This finding suggests the ability of Rhein to inhibit Rac1, which finally improves renal fibrosis.
4.6 Other monomers
Radish red (RR) is an anthocyanin extracted from the red-fleshed root of Raphanus sativus L., chemically identified as pelargonidin-3-sophoroside-5-glucoside. RR possesses significant potential in the development of natural food colorants, functional antioxidants, and nutritionally fortified foods. The dried mature seeds of Raphanus sativus L., known as Raphanus sativus (Laifuzi), possess medicinal properties, promote digestion, relieve bloating, descend qi, and resolve phlegm. In the mice model of CKD, RR reduced the levels of LDH and kidney injury markers, including KIM-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL). RR exerted its protective effects by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway (Li Q. et al., 2024).
Salidroside (SAL), a phenylpropanoid glycoside, is primarily derived from the roots of various species of the Rhodiola genus, particularly Rhodiola rosea. This compound has garnered significant attention due to its diverse biological activities, which include antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective properties (Liang K. et al., 2024). SAL has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent in mitigating renal fibrosis, primarily through its ability to modulate iron metabolism. Studies have indicated that SAL can effectively regulate the expression of key iron transport proteins, including DMT1 and FPN1, which are crucial for iron uptake and export, respectively. Treatment with SAL significantly decreased iron accumulation in renal tissues, which was associated with reduced levels of TFR1 and increased ferritin expression, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis and fibrosis (Yang et al., 2022).
5 Clinical relevance and translational potential
Currently, the treatment of CKD is still based on controlling the etiology, such as poorly controlled diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, glomerular disease, and glomerulonephritis (Webster et al., 2017). The international standard of care for slowing the progression of CKD recommends the blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) antagonists, or direct renin blockers. However, RAAS blockade is not sufficient to halt the progression of CKD and renal fibrosis (Klinkhammer et al., 2017).
Great progress has been made in the prevention and treatment of renal fibrosis by regulating ferroptosis using CHMs. Compared to RAAS inhibitors (candesartan, irbesartan, and valsartan), CHMs (IMP (Yang et al., 2024), Tec (Li et al., 2022), formononetin (Zhu et al., 2023), and Nob (Lo et al., 2022)) have a comparable effect in ameliorating renal fibrosis in UUO kidney.
Astragalus membranaceus (Huang Qi) is one of the most widely used traditional CHMs. It has been used in treatment of various kidney diseases for many years (Fu et al., 2014). Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated that compared to monotherapy with RAAS inhibitors alone, Astragalus membranaceus combined with RAAS inhibitors can offer superior efficacy in the clinical treatment of DN (Lin et al., 2024). Four monomers from Astragalus membranaceus, including formononetin (Zhu et al., 2023), kaempferitrin (Li J. et al., 2024), calycosin (Huang et al., 2022) and astragaloside IV (Qin et al., 2022), markedly ameliorated renal fibrosis and ferroptosis similar to the ferroptosis inhibitor Fer-1. These findings suggest that monomers of Astragalus have great potential for clinical applications.
Several studies have reported the protective effects of Abelmoschus manihot in patients with CKD, without any noticeable side effects (Zhao et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2014; Li P. et al., 2020). TFA, a bioactive phytochemical complex derived from the Abelmoschus manihot, exerts significant anti-fibrotic activity in the experimental models of renal diseases. Wang et al. (2023) reported that TFA can attenuate renal fibrosis similar to dapagliflozin, an established first-line medication for CKD (Heerspink et al., 2020; KDIGO, 2024, 2024). Collectively, these findings position TFA as a promising therapeutic candidate for targeted anti-fibrotic therapy in progressive renal diseases.
Currently, there are no specific drugs for renal fibrosis. Monomers of CHMs possess multiple effects, multiple targets, and strong activity. They have become a recent focus of research and drug development (Song et al., 2024). However, research on the regulation of ferroptosis in renal fibrosis by CHMs is still in the preliminary stage. Future studies should explore the combination of monomers of CHMs to discover new drugs for the treatment of renal fibrosis.
6 Perspectives and conclusion
This review showed that CHM monomers can regulate iron homeostasis, inhibit lipid peroxidation, balance oxidative stress, and modulate EMT through their effects on relevant signaling pathways and molecular targets, thereby reducing Scr and BUN levels, mitigating proteinuria, protecting against pathological fibrosis, suppressing the inflammatory response, and reducing the expression of Col and FN in the kidneys. They can delay or reverse fibrosis in various animal models and cell models of CKD. Most monomers of CHMs can reduce Fe2+ load, possibly by improving iron transport through the regulation of TF, TFR, DMT1, and FPN1. They maintain iron reserves by stabilizing FTH1 and FTL and inhibit ferritinophagy by acting on NCOA4 and Nrf2, thereby maintaining iron homeostasis and inhibiting ferroptosis. Among them, IMP, GB, TFA, and RR can markedly reduce Fe2+ levels. Cal can inhibit NCOA4, thereby suppressing ferritinophagy and reducing Fe2+ levels. Fisetin, vitexin, Rhein, TFA, and RR can inhibit the target ACSL4, thereby improving lipid peroxidation. IMP, Tec, KM, Nob, HDG, RR, and PUR can significantly inhibit NOX4. This study found that many CHM monomers can upregulate GPX4 levels, and PUR can increase FSP1 levels. This study also found that FN, vitexin, Nob, ASIV, schisandrin A, and RR can increase Nrf2 levels and inhibit ferroptosis through several pathways. Additionally, Tec, FN, and HDG can regulate ferroptosis and fibrosis through Smad3. The results showed that FN is more effective than valsartan. The effects of ASIV and DFO were shown to be similar, and the effects of TFA were shown to be like those of dapagliflozin. These results emphasize the potential of CHM monomers in providing clinical benefits.
Most monomers mentioned in this study were flavonoids, which can strongly suppress ferroptosis and renal fibrosis. Flavonoids, such as formononetin, kaempferitrin, astragaloside IV, and calycosin, all are derived from Astragalus membranaceus, which can modulate Fe2+, Smad3/ATF3/SLC7A11, NOX4, Nrf2, GPX4, and NCOA4, lower Scr and BUN levels. We look forward to their combined use to enhance their efficacy for renal fibrosis.
In addition to deepening research on current hotspots, such as GPX4 and Nrf2, it is essential to investigate the monomers of CHMs that target key nodes in iron metabolism. These nodes include ferritin autophagy mediated by NCOA4, the lipid remodeling enzyme system ACSL4, and the novel antioxidant axis involving FSP1-CoQ10. Further studies on the exact mechanisms by which these monomers affect ferroptosis and fibrosis are necessary to promote their clinical application.
Some challenges faced by CHM monomers include poor water solubility, low bioavailability, and inadequate stability. Monomers like, bergapten and tectorigenin, exhibit low bioavailability due to poor aqueous solubility and rapid metabolism. For example, only high doses (50 mg/kg in UUO mice) of kaempferitrin can achieve therapeutic effects (Li J. et al., 2024), which may not be feasible in humans without optimized formulation. Although astragaloside IV is linked to Nrf2 activation (Qin et al., 2022), its specific targets in iron metabolism (e.g., hepcidin or transferrin receptor regulation) remain uncharacterized. Similarly, direct evidence linking schisandrin A, rhein, and their antioxidant properties to ferroptosis modulation in renal cells are lacking. Furthermore, no clinical trials have evaluated these monomers for renal fibrosis. Preclinical models (UUO or 5/6 nephrectomy) do not fully recapitulate human CKD heterogeneity, such as comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension) or drug-drug interactions.
In summary, CHM monomers possess significant potential for treating renal fibrosis. Advancements in technical methods can help develop more effective, targeted, and safe treatment options to address the challenges in the treatment of renal fibrosis. Future large-sized randomized controlled trials are needed to verify the efficacy and safety of CHM monomers, offering new hope for the treatment of CKD and renal fibrosis.
This review provides a comprehensive overview of monomer research methods and identifies key targets for regulating ferroptosis. The 21 CHM monomers can regulate iron homeostasis, inhibit lipid peroxidation, and regulate oxidative stress and EMT by affecting relevant signaling pathways and molecular targets, thereby delaying or reversing fibrosis. The majority of the herbal monomers mentioned in this study belong to flavonoids, which have strong potential in treating CKD and renal fibrosis.
Author contributions
KL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. MY: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YH: Data curation, Writing – original draft. TW: Methodology, Writing – original draft. GL: Writing – review and editing. LW: Supervision, Writing – original draft. XZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970641) and the Key R&D projects in Sichuan Province (2021YFS0372).
Acknowledgments
We thank all the consortium studies for making the summary association statistics data publicly available.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Anandhan, A., Dodson, M., Shakya, A., Chen, J., Liu, P., Wei, Y., et al. (2023). NRF2 controls iron homeostasis and ferroptosis through HERC2 and VAMP8. Sci. Adv. 9 (5), eade9585. doi:10.1126/sciadv.ade9585
Balzer, M. S., Doke, T., Yang, Y. W., Aldridge, D. L., Hu, H., Mai, H., et al. (2022). Single-cell analysis highlights differences in druggable pathways underlying adaptive or fibrotic kidney regeneration. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 4018. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-31772-9
Bayir, H., Dixon, S. J., Tyurina, Y. Y., Kellum, J. A., and Kagan, V. E. (2023). Ferroptotic mechanisms and therapeutic targeting of iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation in the kidney. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 19 (5), 315–336. doi:10.1038/s41581-023-00689-x
Bersuker, K., Hendricks, J. M., Li, Z., Magtanong, L., Ford, B., Tang, P. H., et al. (2019). The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 575 (7784), 688–692. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1705-2
Chen, J., Ou, Z., Gao, T., Yang, Y., Shu, A., Xu, H., et al. (2022). Ginkgolide B alleviates oxidative stress and ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 ubiquitination to improve diabetic nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 156, 113953. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113953
Chen, T. K., Knicely, D. H., and Grams, M. E. (2019). Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: a review. Jama 322 (13), 1294–1304. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.14745
Chen, X., Yu, C., Kang, R., and Tang, D. (2020). Iron metabolism in ferroptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 590226. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.590226
Cheng, H., Wang, P., Wang, N., Dong, W., Chen, Z., Wu, M., et al. (2023). Neuroprotection of NRF2 against ferroptosis after traumatic brain injury in mice. Antioxidants (Basel) 12 (3), 731. doi:10.3390/antiox12030731
Conrad, M., Lorenz, S. M., and Proneth, B. (2021). Targeting ferroptosis: new hope for as-yet-incurable diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 27 (2), 113–122. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2020.08.010
Dächert, J., Ehrenfeld, V., Habermann, K., Dolgikh, N., and Fulda, S. (2020). Targeting ferroptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 146 (2), 510–520. doi:10.1002/ijc.32496
Deng, H. F., Yue, L. X., Wang, N. N., Zhou, Y. Q., Zhou, W., Liu, X., et al. (2020). Mitochondrial iron overload-mediated inhibition of Nrf2-HO-1/GPX4 assisted ALI-induced nephrotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 624529. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.624529
Dixon, S. J., Lemberg, K. M., Lamprecht, M. R., Skouta, R., Zaitsev, E. M., Gleason, C. E., et al. (2012). Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149 (5), 1060–1072. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Doll, S., Freitas, F. P., Shah, R., Aldrovandi, M., da Silva, M. C., Ingold, I., et al. (2019). FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 575 (7784), 693–698. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1707-0
Dong, H., Qiang, Z., Chai, D., Peng, J., Xia, Y., Hu, R., et al. (2020). Nrf2 inhibits ferroptosis and protects against acute lung injury due to intestinal ischemia reperfusion via regulating SLC7A11 and HO-1. Aging (Albany NY) 12 (13), 12943–12959. doi:10.18632/aging.103378
Du, X., Dong, R., Wu, Y., and Ni, B. (2022). Physiological effects of ferroptosis on organ fibrosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 5295434. doi:10.1155/2022/5295434
Feng, H., Schorpp, K., Jin, J., Yozwiak, C. E., Hoffstrom, B. G., Decker, A. M., et al. (2020). Transferrin receptor is a specific ferroptosis marker. Cell Rep. 30 (10), 3411–3423. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.049
Fu, J., Wang, Z., Huang, L., Zheng, S., Wang, D., Chen, S., et al. (2014). Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (huangqi). Phytother. Res. 28 (9), 1275–1283. doi:10.1002/ptr.5188
Ge, M. H., Tian, H., Mao, L., Li, D. Y., Lin, J. Q., Hu, H. S., et al. (2021). Zinc attenuates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in contusion spinal cord injury by activating Nrf2/GPX4 defense pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 27 (9), 1023–1040. doi:10.1111/cns.13657
Gong, X. X., Cao, L. H., Ni, H. X., Zang, Z. Y., and Chang, H. (2024). Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy: from clinical evidence to potential mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 330, 118179. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118179
Gu, Y. Y., Liu, X. S., and Lan, H. Y. (2024). Therapeutic potential for renal fibrosis by targeting Smad3-dependent noncoding RNAs. Mol. Ther. 32 (2), 313–324. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.12.009
Han, Z., Luo, Y., Chen, H., Zhang, G., You, L., Zhang, M., et al. (2024). A deep insight into ferroptosis in renal disease: facts and perspectives. Kidney Dis. (Basel) 10 (3), 224–236. doi:10.1159/000538106
Heerspink, H. J. L., Stefánsson, B. V., Correa-Rotter, R., Chertow, G. M., Greene, T., Hou, F. F., et al. (2020). Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 383 (15), 1436–1446. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2024816
Hong, W., Zhang, G., Lu, H., Guo, Y., Zheng, S., Zhu, H., et al. (2019). Epithelial and interstitial Notch1 activity contributes to the myofibroblastic phenotype and fibrosis. Cell Commun. Signal 17 (1), 145. doi:10.1186/s12964-019-0455-y
Hou, B., Ma, P., Yang, X., Zhao, X., Zhang, L., Zhao, Y., et al. (2024). In silico prediction and experimental validation to reveal the protective mechanism of puerarin against excessive extracellular matrix accumulation through inhibiting ferroptosis in diabetic nephropathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 2), 117281. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117281
Huang, D., Shen, P., Wang, C., Gao, J., Ye, C., and Wu, F. (2022). Calycosin plays a protective role in diabetic kidney disease through the regulation of ferroptosis. Pharm. Biol. 60 (1), 990–996. doi:10.1080/13880209.2022.2067572
Huang, L., Luo, S., Tong, S., Lv, Z., and Wu, J. (2024). The development of nanocarriers for natural products. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 16 (3), e1967. doi:10.1002/wnan.1967
Huang, R., Fu, P., and Ma, L. (2023). Kidney fibrosis: from mechanisms to therapeutic medicines. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8 (1), 129. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01379-7
Hwang, S., and Chung, K. W. (2021). Targeting fatty acid metabolism for fibrotic disorders. Arch. Pharm. Res. 44 (9-10), 839–856. doi:10.1007/s12272-021-01352-4
Ide, S., Kobayashi, Y., Ide, K., Strausser, S. A., Abe, K., Herbek, S., et al. (2021). Ferroptotic stress promotes the accumulation of pro-inflammatory proximal tubular cells in maladaptive renal repair. Elife 10, e68603. doi:10.7554/eLife.68603
Ikeda, Y., Ozono, I., Tajima, S., Imao, M., Horinouchi, Y., Izawa-Ishizawa, Y., et al. (2014). Iron chelation by deferoxamine prevents renal interstitial fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction. PLoS One 9 (2), e89355. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089355
Jia, J., Tan, R., Xu, L., Wang, H., Li, J., Su, H., et al. (2024). Hederagenin improves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by regulating Smad3/NOX4/SLC7A11 signaling-mediated tubular cell ferroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 135, 112303. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112303
Jia, M., Qin, D., Zhao, C., Chai, L., Yu, Z., Wang, W., et al. (2020). Redox homeostasis maintained by GPX4 facilitates STING activation. Nat. Immunol. 21 (7), 727–735. doi:10.1038/s41590-020-0699-0
Jian, J., Wang, D., Xiong, Y., Wang, J., Zheng, Q., Jiang, Z., et al. (2023). Puerarin alleviated oxidative stress and ferroptosis during renal fibrosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury via TLR4/Nox4 pathway in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 38, e382523. doi:10.1590/acb382523
Jiang, X., Stockwell, B. R., and Conrad, M. (2021). Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 22 (4), 266–282. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
KDIGO 2024 (2024). KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 105 (4s), S117–s314. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018
Kim, J. W., Kim, M. J., Han, T. H., Lee, J. Y., Kim, S., Kim, H., et al. (2023). FSP1 confers ferroptosis resistance in KEAP1 mutant non-small cell lung carcinoma in NRF2-dependent and -independent manner. Cell Death Dis. 14 (8), 567. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06070-x
Klinkhammer, B. M., Goldschmeding, R., Floege, J., and Boor, P. (2017). Treatment of renal fibrosis-turning challenges into opportunities. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 24 (2), 117–129. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2016.11.002
Kovesdy, C. P. (2011)2022). Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: an update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 12 (1), 7–11. doi:10.1016/j.kisu.2021.11.003
Kuppe, C., Ibrahim, M. M., Kranz, J., Zhang, X., Ziegler, S., Perales-Patón, J., et al. (2021). Decoding myofibroblast origins in human kidney fibrosis. Nature 589 (7841), 281–286. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2941-1
Lai, W., Wang, B., Huang, R., Zhang, C., Fu, P., and Ma, L. (2024). Ferroptosis in organ fibrosis: from mechanisms to therapeutic medicines. J. Transl. Int. Med. 12 (1), 22–34. doi:10.2478/jtim-2023-0137
Lan, H. Y. (2011). Diverse roles of TGF-β/Smads in renal fibrosis and inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 7 (7), 1056–1067. doi:10.7150/ijbs.7.1056
Latunde-Dada, G. O. (2017). Ferroptosis: role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 1861 (8), 1893–1900. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.05.019
Lee, J. Y., Kim, W. K., Bae, K. H., Lee, S. C., and Lee, E. W. (2021). Lipid metabolism and ferroptosis. Biol. (Basel). 10 (3), 184. doi:10.3390/biology10030184
Li, B., Wang, Y., Jiang, X., Du, H., Shi, Y., Xiu, M., et al. (2023). Natural products targeting Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 164, 114950. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114950
Li, J., Cao, F., Yin, H. L., Huang, Z. J., Lin, Z. T., Mao, N., et al. (2020a). Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 11 (2), 88. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
Li, J., Yang, J., Xian, Q., Su, H., Ni, Y., and Wang, L. (2024b). Kaempferitrin attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal inflammation and fibrosis in mice by inhibiting NOX4-mediated tubular ferroptosis. Phytother. Res. 38 (6), 2656–2668. doi:10.1002/ptr.8191
Li, J., Yang, J., Zhu, B., Fan, J., Hu, Q., and Wang, L. (2022). Tectorigenin protects against unilateral ureteral obstruction by inhibiting Smad3-mediated ferroptosis and fibrosis. Phytother. Res. 36 (1), 475–487. doi:10.1002/ptr.7353
Li, L., Cai, W., Zhang, H., Tang, J., Yang, Y., Huang, Y., et al. (2025). Bergapten ameliorates renal fibrosis by inhibiting ferroptosis. Phytother. Res. 39 (3), 1355–1371. doi:10.1002/ptr.8425
Li, P., Lin, H., Ni, Z., Zhan, Y., He, Y., Yang, H., et al. (2020b). Efficacy and safety of abelmoschus manihot for IgA nephropathy: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Phytomedicine 76, 153231. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153231
Li, Q., Zheng, Y., Zhao, J., Wei, X., Shi, Z., Fan, H., et al. (2024c). Radish red attenuates chronic kidney disease in Obese mice through repressing oxidative stress and ferroptosis via Nrf2 signaling improvement. Int. Immunopharmacol. 143 (Pt 3), 113385. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113385
Li, S., Han, Q., Liu, C., Wang, Y., Liu, F., Pan, S., et al. (2024a). Role of ferroptosis in chronic kidney disease. Cell Commun. Signal 22 (1), 113. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01422-8
Liang, G. Q., Mu, W., and Jiang, C. B. (2024a). Baicalein improves renal interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting the ferroptosis in vivo and in vitro. Heliyon 10 (7), e28954. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28954
Liang, K., Ma, S., Luo, K., Wang, R., Xiao, C., Zhang, X., et al. (2024b). Salidroside: an overview of its promising potential and diverse applications. Pharm. (Basel) 17 (12), 1703. doi:10.3390/ph17121703
Lin, Y. Q., Yu, F., Chen, H. J., Deng, Y. R., Lin, J., Xu, Y., et al. (2024). Efficacy of astragalus combined with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers in the treatment of stage III diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren. Fail 46 (2), 2359033. doi:10.1080/0886022X.2024.2359033
Linkermann, A., Skouta, R., Himmerkus, N., Mulay, S. R., Dewitz, C., De Zen, F., et al. (2014). Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111 (47), 16836–16841. doi:10.1073/pnas.1415518111
Liu, B. C., Tang, T. T., Lv, L. L., and Lan, H. Y. (2018). Renal tubule injury: a driving force toward chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 93 (3), 568–579. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2017.09.033
Liu, J., Kang, R., and Tang, D. (2022). Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. Febs J. 289 (22), 7038–7050. doi:10.1111/febs.16059
Liu, Y., Wan, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhang, L., and Cheng, W. (2023). GPX4: the hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1878 (3), 188890. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188890
Liyanage, T., Ninomiya, T., Jha, V., Neal, B., Patrice, H. M., Okpechi, I., et al. (2015). Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet 385 (9981), 1975–1982. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61601-9
Lo, Y. H., Yang, S. F., Cheng, C. C., Hsu, K. C., Chen, Y. S., Chen, Y. Y., et al. (2022). GTP-binding protein 1-Like (GTPBP1l) regulates vascular patterning during zebrafish development. Biomedicines 10 (3), 3208. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10123208
Lovisa, S., LeBleu, V. S., Tampe, B., Sugimoto, H., Vadnagara, K., Carstens, J. L., et al. (2015). Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induces cell cycle arrest and parenchymal damage in renal fibrosis. Nat. Med. 21 (9), 998–1009. doi:10.1038/nm.3902
Lu, J., Zhao, Y., Liu, M., Lu, J., and Guan, S. (2021). Toward improved human health: nrf2 plays a critical role in regulating ferroptosis. Food Funct. 12 (20), 9583–9606. doi:10.1039/d1fo01036k
Lu, Q., Yang, L., Xiao, J. J., Liu, Q., Ni, L., Hu, J. W., et al. (2023). Empagliflozin attenuates the renal tubular ferroptosis in diabetic kidney disease through AMPK/NRF2 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 195, 89–102. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.12.088
Luo, C., Liang, H., Ji, M., Ye, C., Lin, Y., Guo, Y., et al. (2025). Autophagy induced by mechanical stress sensitizes cells to ferroptosis by NCOA4-FTH1 axis. Autophagy 21, 1263–1282. doi:10.1080/15548627.2025.2469129
Lyu, G., Liao, H., and Li, R. (2025). Ferroptosis and renal fibrosis: mechanistic insights and emerging therapeutic targets. Ren. Fail 47 (1), 2498629. doi:10.1080/0886022X.2025.2498629
Murakami, S., Kusano, Y., Okazaki, K., Akaike, T., and Motohashi, H. (2023). NRF2 signalling in cytoprotection and metabolism. Br. J. Pharmacol. doi:10.1111/bph.16246
Naas, S., Schiffer, M., and Schödel, J. (2023). Hypoxia and renal fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 325 (4), C999–c1016. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00201.2023
Niu, Z., Guo, J., Liu, X., Chen, M., Jin, Y., Yao, M., et al. (2025). Renal tubular epithelial-derived follistatin-like 1 protects against UUO-Induced renal fibrosis in mice via inhibiting NF-κB-mediated epithelial inflammation. Theranostics 15 (6), 2413–2427. doi:10.7150/thno.100969
Nogueira, A., Pires, M. J., and Oliveira, P. A. (2017). Pathophysiological mechanisms of renal fibrosis: a review of animal models and therapeutic strategies. Vivo 31 (1), 1–22. doi:10.21873/invivo.11019
Packer, M. (2024). Iron homeostasis, recycling and vulnerability in the stressed kidney: a neglected dimension of iron-deficient heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail 26 (7), 1631–1641. doi:10.1002/ejhf.3238
Parkash, J., Prasad, D. N., Shahnaz, M., and Dev, D. (2018). Herbs as traditional medicines: a review. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 8 (5), 146–150. doi:10.22270/jddt.v8i5.1910
Qin, L. Y., Guan, P., Wang, J. X., Chen, Y., Zhao, Y. S., Yang, S. C., et al. (2022). Therapeutic potential of astragaloside IV against adriamycin-induced renal damage in rats via ferroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 812594. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.812594
Qiu, D., Song, S., Chen, N., Bian, Y., Yuan, C., Zhang, W., et al. (2023). NQO1 alleviates renal fibrosis by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Signal 108, 110712. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110712
Rayego-Mateos, S., and Valdivielso, J. M. (2020). New therapeutic targets in chronic kidney disease progression and renal fibrosis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 24 (7), 655–670. doi:10.1080/14728222.2020.1762173
Risdon, R. A., Sloper, J. C., and De Wardener, H. E. (1968). Relationship between renal function and histological changes found in renal-biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerular nephritis. Lancet 2 (7564), 363–366. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90589-8
Rochette, L., Dogon, G., Rigal, E., Zeller, M., Cottin, Y., and Vergely, C. (2022). Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: two corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (1), 449. doi:10.3390/ijms24010449
Rodríguez-Iturbe, B., Johnson, R. J., and Herrera-Acosta, J. (2005). Tubulointerstitial damage and progression of renal failure. Kidney Int. Suppl. 68 (99), S82–S86. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.09915.x
Romagnani, P., Agarwal, R., Chan, J. C. N., Levin, A., Kalyesubula, R., Karam, S., et al. (2025). Chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 11 (1), 8. doi:10.1038/s41572-024-00589-9
Ru, Q., Li, Y., Chen, L., Wu, Y., Min, J., and Wang, F. (2024). Iron homeostasis and ferroptosis in human diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9 (1), 271. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01969-z
Schwab, A., Rao, Z., Zhang, J., Gollowitzer, A., Siebenkäs, K., Bindel, N., et al. (2024). Zeb1 mediates EMT/plasticity-associated ferroptosis sensitivity in cancer cells by regulating lipogenic enzyme expression and phospholipid composition. Nat. Cell Biol. 26 (9), 1470–1481. doi:10.1038/s41556-024-01464-1
Shi, Z., Zhang, K., Chen, T., Zhang, Y., Du, X., Zhao, Y., et al. (2020). Transcriptional factor ATF3 promotes liver fibrosis via activating hepatic stellate cells. Cell Death Dis. 11 (12), 1066. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03271-6
Singh, K., Gupta, J. K., Chanchal, D. K., Shinde, M. G., Kumar, S., Jain, D., et al. (2024). Natural products as drug leads: exploring their potential in drug discovery and development. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 398, 4673–4687. doi:10.1007/s00210-024-03622-6
Song, J., Wang, H., Sheng, J., Zhang, W., Lei, J., Gan, W., et al. (2023). Vitexin attenuates chronic kidney disease by inhibiting renal tubular epithelial cell ferroptosis via NRF2 activation. Mol. Med. 29 (1), 147. doi:10.1186/s10020-023-00735-1
Song, L., Zhang, W., Tang, S. Y., Luo, S. M., Xiong, P. Y., Liu, J. Y., et al. (2024). Natural products in traditional Chinese medicine: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets of renal fibrosis and state-of-the-art drug delivery systems. Biomed. Pharmacother. 170, 116039. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116039
Song, X., and Long, D. (2020). Nrf2 and ferroptosis: a new research direction for neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurosci. 14, 267. doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.00267
Stockwell, B. R. (2022). Ferroptosis turns 10: emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell. 185 (14), 2401–2421. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.003
Su, L., Zhang, J., Gomez, H., Kellum, J. A., and Peng, Z. (2023). Mitochondria ROS and mitophagy in acute kidney injury. Autophagy 19 (2), 401–414. doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2084862
Sui, Z., Wang, J., Cabrera, C., Wei, J., Wang, M., and Zuo, L. (2020). Aetiology of chronic kidney disease and risk factors for disease progression in Chinese subjects: a single-centre retrospective study in beijing. Nephrol. Carlt. 25 (9), 714–722. doi:10.1111/nep.13714
Tan, H., Chen, J., Li, Y., Li, Y., Zhong, Y., Li, G., et al. (2022). Glabridin, a bioactive component of licorice, ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by regulating ferroptosis and the VEGF/Akt/ERK pathways. Mol. Med. 28 (1), 58. doi:10.1186/s10020-022-00481-w
Tan, R. J., Zhou, D., Zhou, L., and Liu, Y. (2014). Wnt/β-catenin signaling and kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. Suppl. (2011) 4 (1), 84–90. doi:10.1038/kisup.2014.16
Tang, D., Chen, X., Kang, R., and Kroemer, G. (2021). Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 31 (2), 107–125. doi:10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1
Tang, Q., Xie, J., Wang, Y., Dong, C., and Sun, Q. (2025). Exosomes secreted by ATF3/Nrf2-mediated ferroptotic renal tubular epithelial cells promote M1/M2 ratio imbalance inducing renal interstitial fibrosis following ischemia and reperfusion injury. Front. Immunol. 16, 1510500. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1510500
Tu, Y. (2011). The discovery of artemisinin (Qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 17 (10), 1217–1220. doi:10.1038/nm.2471
Wang, B., Yang, L. N., Yang, L. T., Liang, Y., Guo, F., Fu, P., et al. (2024b). Fisetin ameliorates fibrotic kidney disease in mice via inhibiting ACSL4-mediated tubular ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 45 (1), 150–165. doi:10.1038/s41401-023-01156-w
Wang, F., Huang, X., Wang, S., Wu, D., Zhang, M., and Wei, W. (2024a). The main molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in chronic kidney disease. Cell Signal 121, 111256. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111256
Wang, J., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Cai, X., Huang, X., Fu, W., et al. (2022a). Ferroptosis, a new target for treatment of renal injury and fibrosis in a 5/6 nephrectomy-induced CKD rat model. Cell Death Discov. 8 (1), 127. doi:10.1038/s41420-022-00931-8
Wang, L., Liu, Y., Du, T., Yang, H., Lei, L., Guo, M., et al. (2020). ATF3 promotes erastin-induced ferroptosis by suppressing system Xc. Cell Death Differ. 27 (2), 662–675. doi:10.1038/s41418-019-0380-z
Wang, M. Z., Cai, Y. F., Fang, Q. J., Liu, Y. L., Wang, J., Chen, J. X., et al. (2023). Inhibition of ferroptosis of renal tubular cells with total flavones of abelmoschus manihot alleviates diabetic tubulopathy. Anat. Rec. Hob. 306 (12), 3199–3213. doi:10.1002/ar.25123
Wang, X., Li, Q., Sui, B., Xu, M., Pu, Z., and Qiu, T. (2022b). Schisandrin A from Schisandra chinensis attenuates ferroptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in diabetic nephropathy through mitochondrial damage by AdipoR1 ubiquitination. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 5411462. doi:10.1155/2022/5411462
Webster, A. C., Nagler, E. V., Morton, R. L., and Masson, P. (2017). Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 389 (10075), 1238–1252. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32064-5
Xing, J., He, Y. C., Wang, K. Y., Wan, P. Z., and Zhai, X. Y. (2022). Involvement of YTHDF1 in renal fibrosis progression via up-regulating YAP. FASEB J. 36 (2), e22144. doi:10.1096/fj.202100172RR
Xiong, D., Hu, W., Han, X., and Cai, Y. (2023). Rhein inhibited ferroptosis and EMT to attenuate diabetic nephropathy by regulating the Rac1/NOX1/β-Catenin axis. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 28 (5), 100. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2805100
Xu, X., Zhao, H., Zhang, J., Yan, H., Liu, X., Huo, J., et al. (2025). Interleukin-22 ameliorates alcohol-associated liver fibrosis via Nrf2-ARE signaling: mechanistic insights and clinical correlations. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 49, 102617. doi:10.1016/j.clinre.2025.102617
Yang, J. D., Lin, S. C., Kuo, H. L., Chen, Y. S., Weng, P. Y., Chen, C. M., et al. (2024). Imperatorin ameliorates ferroptotic cell death, inflammation, and renal fibrosis in a unilateral ureteral obstruction mouse model. Phytomedicine 135, 156066. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156066
Yang, S., Pei, T., Wang, L., Zeng, Y., Li, W., Yan, S., et al. (2022). Salidroside alleviates renal fibrosis in SAMP8 mice by inhibiting ferroptosis. Molecules 27 (22), 8039. doi:10.3390/molecules27228039
Ye, Z., Yang, S., Chen, L., Yu, W., Xia, Y., Li, B., et al. (2025). Luteolin alleviated calcium oxalate crystal induced kidney injury by inhibiting Nr4a1-mediated ferroptosis. Phytomedicine 136, 156302. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156302
Yu, X., Wang, S., Wang, X., Li, Y., and Dai, Z. (2024). Melatonin improves stroke by inhibiting autophagy-dependent ferroptosis mediated by NCOA4 binding to FTH1. Exp. Neurol. 379, 114868. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114868
Yuan, Q., Tan, R. J., and Liu, Y. (2019). Myofibroblast in kidney fibrosis: origin, activation, and regulation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1165, 253–283. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-8871-2_12
Yuan, Q., Tang, B., and Zhang, C. (2022). Signaling pathways of chronic kidney diseases, implications for therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7 (1), 182. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01036-5
Zhang, L., Li, P., Xing, C. Y., Zhao, J. Y., He, Y. N., Wang, J. Q., et al. (2014). Efficacy and safety of abelmoschus manihot for primary glomerular disease: a prospective, multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 64 (1), 57–65. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.01.431
Zhang, L., Liu, L., Bai, M., Liu, M., Wei, L., Yang, Z., et al. (2020). Hypoxia-induced HE4 in tubular epithelial cells promotes extracellular matrix accumulation and renal fibrosis via NF-κB. FASEB J. 34 (2), 2554–2567. doi:10.1096/fj.201901950R
Zhang, S., Zhang, S., Wang, H., and Chen, Y. (2023b). Vitexin ameliorated diabetic nephropathy via suppressing GPX4-mediated ferroptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 951, 175787. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175787
Zhang, X., Hou, L., Guo, Z., Wang, G., Xu, J., Zheng, Z., et al. (2023a). Lipid peroxidation in osteoarthritis: focusing on 4-hydroxynonenal, malondialdehyde, and ferroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 9 (1), 320. doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01613-9
Zhang, Y., Mou, Y., Zhang, J., Suo, C., Zhou, H., Gu, M., et al. (2022). Therapeutic implications of ferroptosis in renal fibrosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9, 890766. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2022.890766
Zhao, J., Tostivint, I., Xu, L., Huang, J., Gambotti, L., Boffa, J. J., et al. (2022). Efficacy of combined abelmoschus manihot and irbesartan for reduction of albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease: a multicenter randomized double-blind parallel controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Care 45 (7), e113–e115. doi:10.2337/dc22-0607
Zhao, P., Yin, S., Qiu, Y., Sun, C., and Yu, H. (2025). Ferroptosis and pyroptosis are connected through autophagy: a new perspective of overcoming drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 24 (1), 23. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-02217-2
Zhou, L., Xue, X., Hou, Q., and Dai, C. (2022a). Targeting ferroptosis attenuates interstitial inflammation and kidney fibrosis. Kidney Dis. (Basel) 8 (1), 57–71. doi:10.1159/000517723
Zhou, Y., Zhang, J., Guan, Q., Tao, X., Wang, J., and Li, W. (2022b). The role of ferroptosis in the development of acute and chronic kidney diseases. J. Cell Physiol. 237 (12), 4412–4427. doi:10.1002/jcp.30901
Zhu, B., Ni, Y., Gong, Y., Kang, X., Guo, H., Liu, X., et al. (2023). Formononetin ameliorates ferroptosis-associated fibrosis in renal tubular epithelial cells and in mice with chronic kidney disease by suppressing the Smad3/ATF3/SLC7A11 signaling. Life Sci. 315, 121331. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121331
Glossary
CKD chronic kidney disease
CHMs Chinese herbal medicines
Fer-1 ferrostatin-1
Lip-1 liproxstatin-1
EMT epithelial-mesenchymal transition
TGF-β1 Transforming growth factor-β1
TGF-βRI TGF-β receptor I
TGF-βRII TGF-β receptor II
TEC tubular epithelial cells
Col-I collagen I
TFR1 transferrin receptor 1
FPN1 ferroportin 1
STEAP3 Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3
DMT1 Divalent metal transporter 1
LIP labile iron pool
FTH1 ferritin heavy chain 1
FTL ferritin light chain
NCOA4 Nuclear receptor coactivator 4
Nrf2 Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
ACC acetyl-CoA carboxylase
ACSL4 Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4
AA arachidonic acid
AdA adrenic acid
PE phosphatidylethanolamine
LPCAT3 lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3
NOXs NADPH oxidases
LOXs lipoxygenases
COXs cyclooxygenases
PUFA-OOH production of lipid hydroperoxides
HO-1 heme oxygenase-1
AMPK AMP-activated protein kinase
MDA malondialdehyde
4- HNE 4-hydroxynonenal
GPX4 glutathione peroxidase 4
GSH glutathione
ATF3 activating transcription factor 3
NADPH nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
FSP1 ferroptosis suppressor protein 1
CoQ10 coenzyme Q10
ARE antioxidant response element
PT proximal tubule
FTH ferritin
MCP-1 monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
IMP imperatorin
UUO unilateral ureteral obstruction
Scr serum creatinine
BUN blood urea nitrogen
ACR albumin-to-creatinine ratio
PUR Puerarin
TLR4 Toll-like receptor 4
NOX4 NADPH oxidase 4
Tec Tectorigenin
KIM-1 kidney injury molecule-1
Nob nobiletin
Glab Glabridin
TFA total flavones of Abelmoschus manihot
ASIV Astragaloside IV
GB Ginkgo biloba
STZ streptozotocin
DN diabetic nephropathy
PI3K phosphoinositide 3-kinase
Sch A Schisandrin A
SAL Salidroside
DM diabetes mellitus
RAAS renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
AT1 angiotensin II receptor type 1
FN fibronectin
SLC7A11 solute carrier family 7 member 11
SLC3A2 solute carrier family 3 member 2
FAO fatty acid oxidation
ATP adenosine triphosphate
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine, ferroptosis, chronic kidney disease, renal fibrosis, monomers
Citation: Liu K, Yu M, He Y, Wang T, Li G, Wang L and Zhong X (2025) Inhibitory effects of herbal monomers on ferroptosis in renal fibrosis: a review and mechanistic study. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1610573. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1610573
Received: 12 April 2025; Accepted: 07 July 2025;
Published: 22 July 2025.
Edited by:
Yang Yang, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, ChinaReviewed by:
Javier Ventura-Juárez, Autonomous University of Aguascalientes, MexicoZhongyu Han, Southeast University, China
Yijian Deng, Southern Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yu, He, Wang, Li, Wang and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiang Zhong, emhvbmd4aWFuZ0B1ZXN0Yy5lZHUuY24=
 Kaixiang Liu
Kaixiang Liu Guisen Li
Guisen Li Xiang Zhong
Xiang Zhong