- 1Department of Dermatology, Hejin Wang Xiaobo Dermatology Clinic, Hejin, China
- 2Department of Dermatology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (Xibei Hospital), Xi’an, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore campus, Lahore, Pakistan
- 4Department of Emergency, XD Group Hospital, Xi’an, China
The current study aims to develop chitosan transdermal patches containing AgNPs synthesized and characterized from C. esculenta to reduce inflammation. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were prepared utilizing the C. esculenta extract and characterized through Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), zeta potential measurements, and particle size analysis. The AgNPs were incorporated into chitosan-based transdermal patches, which were assessed for physicochemical properties, dermal compatibility, and anti-inflammatory effectiveness. In vitro protein denaturation and in vivo carrageenan-induced paw edema models evaluated anti-inflammatory efficacy. Characterization verified that the AgNPs were stable and spherical. The transdermal patches were biocompatible, had uniform thickness, and were extremely adhesive. The anti-inflammatory effects of AgNP-loaded patches were found to be superior to those of diclofenac sodium in in vivo studies, while in vitro studies revealed a notable inhibition of protein denaturation (p < 0.05). The current study offers new evidence that transdermal drug delivery systems derived from C. esculenta can effectively and sustainably manage inflammation.
1 Introduction
Nanotechnology is employed in the fabrication of various functioning systems at the molecular level. These systems exhibit specific electrical, physical, and optical features, making them valuable in a wide array of domains such as biology and material science (Bamrungsap et al., 2012). Nanotechnology involves the synthesis of nanoparticles (NPs) in the size range of 10–1,000 nm, in which active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is entrapped or encapsulated, thus experiencing many advancements in science due to its invaluable applications in medicine, catalysis, material science, and drug delivery (Mohanraj and Chen, 2007). Previously, various metal NPs and their complexes in the form of oxides, sulfides, fluorides, hydroxides, chlorides, and phosphates have been formulated and employed in various applications (Paramasivam et al., 2017; Ramos et al., 2017; Rasouli et al., 2018). Various physical, chemical, and biological methods can be employed in the synthesis of nanomaterials. As these conventional methods include the use of toxic materials, green alternative approaches have been explored to minimize the use of toxic materials (Adeyemi et al., 2022; Câmara et al., 2022). Some of these approaches require NP synthesis by employing the plant extract, which is simple, ecofriendly, sustainable, non-hazardous, and cost effective (Bharadwaj et al., 2021; Gupta et al., 2023).
Nanoparticles can be synthesized from a variety of sources, including noble metals like silver, platinum, palladium, gold, titanium dioxide, and zinc oxide. Ionic silver has taken the place of silver (Ag) to formulate the bulk coins and is currently employed for the formulation of colloidal silver NPs (Chandoliya et al., 2024; El-Seedi et al., 2024). It is also utilized as the silver nitrate to present the antimicrobial properties. Silver NPs exhibit enhanced antimicrobial effects due to an increased surface area, which can interact with the microbial species efficiently. Silver is the widely used element of choice for NP synthesis in the fields of medicine, living organisms, and biological systems. Thus, the combination of reducing agents with silver to form NPs with better activity and efficacy is an area of interest (K. Singh et al., 2014). Physical and chemical methods are commonly employed for the synthesis of NP with more stability as colloidal dispersion in organic solvents or water. However, chemical methods employed for the NP synthesis use noxious chemicals that affect plants, animals, and the overall environment. Thus, there is a need to explore new approaches to synthesize the NPs in a pollution-free environment to ensure a pollution-free and healthy environment.
Nanobiotechnologists are striving to explore new green approaches to replace the existing hazardous NP synthesis techniques. Green biology involves attractive domains such as green technology, green engineering, green polymerization, silver chemistry, wastewater treatment, bio-composites, and particle technology (Kharissova et al., 2009). Green chemistry for silver NP synthesis is ecofriendly, simple, less time consuming, cost effective, and favors the large-scale production of NPs by utilizing a common capping, reducing, and stabilizing agent (Lade and Patil, 2017). Green approaches to NP formulation include natural products, table sugar, polyphenols, glucose, amino acids, and plant extracts. Plant leaf extracts are widely utilized for the reduction of AgNO3 to Ag, as they contain various functional groups such as carboxylic acid, aliphatic amine, amines, alkanes, alkynes, alcohol, nitro-compound, saturated aldehyde, phenols, and glutathione (Balavandy et al., 2014; B. Kumar et al., 2015). Protective foods include the green leafy vegetables harboring a spectrum of bioactive compounds and micronutrients that boost the immune system and prevent diseases. The distinctive therapeutic index of bioactive compounds present in the leafy vegetables has been emphasized in various studies (Anand et al., 2019; Mehmood and Zeb, 2020).
Colocasia esculenta (C. esculenta) Shott, generally recognized as “taro,” is an annual herbaceous plant of the Araceae family (Goncalves et al., 2013). It is referred to as tabbia, cocoyam, dasheen, or eddoe in different parts of the world (Dilek and Bilgiçli, 2021). C. esculenta is native to Southeast Asia and cultivated in the tropical and subtropical regions (Chand et al., 2021). Depending upon its genotype, its leaves are heart shaped with or without blotches, lines, and spots. Its color varies from light green to dark purple. C. esculenta exhibits various medicinal properties such as antidiabetic, antioxidative (Sudhakar et al., 2020), anticancer (Pereira et al., 2021), anti-inflammatory (Baro et al., 2023), anti-hypersensitive (Esposito et al., 2024), and antimicrobial (Sudhakar et al., 2020). Its leaves contain various sugars (glucose, fructose, and sucrose, etc.), vitamins (thiamin, niacin, and riboflavin), and minerals (iron, potassium, calcium, and copper) to cause rapid oxidation, explaining their enhanced potential as reducing agents (K. K. P. Kumar et al., 2019).
In the current study, we formulated the NPs from C. esculenta by reacting them with AgNO3 and adopting green synthesis. Formulated NPs were characterized for shape, particle size, zeta potential, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and FTIR analysis. Optimized NP formulations were then integrated into transdermal patches synthesized from chitosan. NP-harboring patches were analyzed for physical character, adhesion, skin irritation, moisture content, thermal analysis, and sensitization. These patches were also subjected to in vivo anti-inflammatory studies and toxicity studies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
C. esculenta plant leaves were procured from the local market of Lahore, Pakistan. The plant material was authenticated and verified under voucher No. GC.Herb.Bot.4184 by comparison of the morphological features with authenticated specimens in the herbarium by the taxonomist at the Department of Botany, Government College University, Lahore, Pakistan. Silver nitrate (AgNO3), acetic acid, glutaraldehyde, glycerol, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), ortho-phosphoric acid, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4), and methanol (HPLC grade) were procured from Sigma-Aldrich Co., St Louis, MO, USA. Low-molecular weight chitosan (CAS No: 9012-76-4), with a molecular weight of 50–190 kDa, ∼75%–85% degree of acetylation, and purity >98%, was also procured from Sigma-Aldrich (USA). All other reagents and materials used in this study were of analytical grade.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Formulation of C. esculenta extract
C. esculenta leaves were washed with Milli-Q water to detach dust and attached impurities. Leaves were subjected to air drying under shade at room temperature (25 °C) for 3–4 days. Afterward, 40 g of dried leaves was sliced into small pieces and boiled in 500 mL of distilled water while stirring continuously via a magnetic stirrer at 60 °C for 30 min. The resulting mixture was cooled to room temperature (25 °C), filtered through Whatman No. 1 filter paper, and subjected to vacuum filtration assembly to acquire the clear extract. The pH of the prepared extract was recorded (∼6.8–7.0), and it was stored in amber-colored bottles at 4 °C for further use (K. K. P. Kumar et al., 2019).
2.2.2 Preparation of C. esculenta extract-based AgNPs
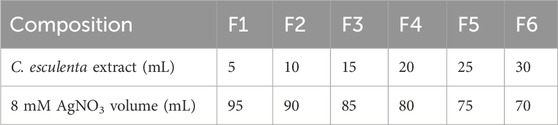
Silver NPs were prepared according to the method described by Lade and Patil (2017) with small modifications. The aqueous AgNO3 solution (8 mM) and varying concentrations of aqueous extract of C. esculenta were mixed in Erlenmeyer flasks to synthesize the silver nanoparticles, as shown in Table 1. The pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to ∼8.0 with 0.1 M NaOH, and reactions were carried out at 70 °C in the water bath for different time intervals (30 min, 45 min, and 60 min) with continuous stirring. The color of the mixture changed from pale yellow to brown, indicating the Ag+ reduction to Ag° nanoparticles. The colloidal solution was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min. The NP pellet was harvested and rinsed twice with distilled water, followed by freeze-drying in a benchtop freeze dryer (LYO60B-1 PT Bioevopeak, China). The NP pellet was then stored at 4 °C for further use.
2.2.3 Preparation of silver NP-containing chitosan patches
Varying concentrations (1%–3%, w/v) of chitosan (CS) were dissolved in 1%–2% acetic acid solution (v/v) individually to make the CS solutions to achieve the desired thickness and mechanical properties of the patch. The solution was stirred under magnetic stirring for several hours (12–24 h) to achieve the complete dissolution of the CS in the solution. Polyethylene glycol (PEG-400, 1%–2% v/v) was added to the CS solution as a plasticizer to enhance the mechanical properties and flexibility of the formulated patch. Similarly, 100–300 mg of PVP-k30 was added to enhance the mechanical strength, skin adhesion, and stability of the prepared patch. Subsequently, 5% (w/v) of C. esculenta-derived AgNP product (lyophilized powder redispersed in distilled water) was mixed into the CS solution. The resulting mixture was poured into the casting molds or Petri dishes to generate the thin layer. The solution was then dried in the drying oven under controlled conditions at 30 °C–40 °C for 24 h. After drying, the formed patches/films from the molds were peeled off carefully (Sabbagh and Kim, 2022). Various formulations of patches manufactured with C. esculenta AgNPs are presented in Table 2. Regarding quantification in the final patch, it contained AgNPs (5% w/v) as per the formulation shown in Table 2. The AgNP concentration was kept uniform based on the controlled batch conditions and the synthesis protocol, ensuring a consistent AgNP concentration across the patches.
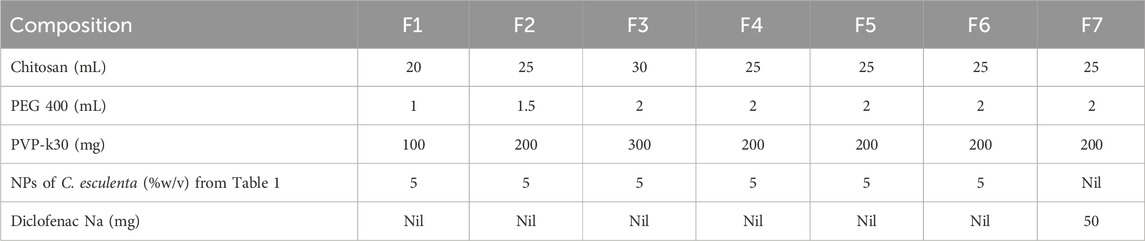
Table 2. Composition of different formulations of chitosan-based transdermal patches with varying concentrations of C. esculenta extract-based NPs (Mean ± standard deviation (SD)).
2.2.4 Characterization of C. esculenta AgNPs and CS transdermal patches
2.2.4.1 FTIR spectral analysis
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, JASCO FT/IR 6300 spectrometer) analysis was performed to analyze the chemical structure and functional groups of the C. esculenta plant extract and interactions of different functional groups during the formation of C. esculenta-AgNPs and C. esculenta-AgNP-loaded transdermal patches. Samples were prepared in KBr pressed pellets, and spectra were recorded in the 4,000–400 cm−1 range with a spectral resolution of 4 cm−1 from the average of 100 spectra in the absorbance mode.
2.2.4.2 UV spectrophotometry
UV–visible spectroscopy was conducted with a VWR UV-1600PC UV/Vis spectrophotometer. Samples were evaluated in the 400–900 nm spectral range.
2.2.4.3 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
SEM studies of C. esculenta extract AgNPs and prepared transdermal patches were conducted to analyze the surface morphology. Samples were prepared as a fine powder and coated with gold to be analyzed using SEM (Quanta FEG250) at a high voltage (20 kV) of electron beam to analyze the surface morphology.
2.2.4.4 Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies
XRD studies of the dried extract of C. esculenta and prepared AgNPs of the C. esculenta extract were performed by using XRD (X-Pert, PAN analytical, Netherlands), and diffractograms were detailed at 2θ = 5–70° to analyze the crystalline or amorphous nature of the samples.
2.2.4.5 Zeta potential and particle size analysis
Light scattering studies were performed with a He–Ne laser operating at a wavelength of 633 nm at 25 °C by using a ZETASIZER (Nano ZS; ZEN3600, Malvern). The intensity size distributions were acquired from the evaluation of the correlation functions by the Multiple Narrow Modes algorithm. The prepared samples (AgNPs, AgNPs 200, 300, and 400) were diluted 1:20 with distilled water to remove the primary charge, followed by ultrasound for 10 min to prevent agglomeration. A 2-mL aliquot of the sample was transferred in disposable cuvettes of 10 mm diameter. The experiment was repeated three times to analyze the repeatability of the results. Both surface charge and stability of the particles were determined by measuring the zeta potentials (SZ-100, Horiba Scientific, Kyoto, Japan). Formulated NPs were diluted with deionized water (1/10, w/v) and transferred into the measurement cell for analysis (n = 5).
2.2.5 Characterization of C. esculenta AgNP-loaded chitosan patches
All prepared formulations of C. esculenta AgNPs loaded CS patches were characterized for the below mentioned parameters:
2.2.5.1 Physical appearance
The physical appearance of formulated patches was analyzed to check the irregularities in the form of wrinkles, air bubbles, or roughness. Color uniformity across the entire patch was also ensured, as discoloration of the patch may lead to degradation. Similarly, patches were also observed for the cloudiness, as it is a sign of material change. The batch number and expiry date were also monitored.
2.2.5.2 Thickness uniformity
Prepared patches were subjected to thickness measurement by employing an electronic caliper with a thickness count of 0.01 mm. Thickness uniformity was ensured by measuring the thickness at three different positions of the film, and the average thickness of the measured readings was taken.
2.2.5.3 Adhesive properties
Adhesiveness of the patch was evaluated, and even distribution of the adhesive layer over the patch was ensured to eradicate the chance of defect or lump formation on the patch. Peel adhesion and tackiness were also evaluated by the gentle pressing of the patch on the clean surface.
2.2.5.4 Moisture content
Prepared patches were subjected to a moisture test to evaluate the moisture content present in the patches, as excess moisture can affect the drug stability and appearance of the patch.
2.2.5.5 Skin irritation and sensitization tests
Skin irritation caused by patch application can be evaluated by the Draize patch test. Skin irritation causes visible changes in the skin, such as erythema, edema, or redness, after multiple applications of the patch over the skin.
2.2.5.6 Uniformity of weight
The weight of the prepared patch was measured after cutting the patch into multiple pieces of 1 × 1 cm2 size each, and the average weight of the patch was calculated.
2.2.5.7 Folding endurance
The folding endurance of the patches was measured manually. Briefly, a patch strip of 2 × 2 cm2 size was folded at the same point repeatedly until broken, and the folding endurance was calculated by counting the number of folds a patch film could withstand until it was broken.
2.2.5.8 Tensile strength
Prepared patches were also subjected to tensile strength measurement using a Universal Testing Machine (UTM 100-500KN, Testometric Inc., UK). The apparatus consisted of 5N load cells and operated at room temperature. A 4 × 1 cm2 sample of the test film was prepared and placed between the lower and upper cell grips, followed by force application. The force was increased gradually until the film was broken. Tensile strength was measured in Kg and expressed as follows:
2.2.6 Ex vivo permeation study
Ex vivo investigations of prepared patches and nanoparticles were conducted on the skin of rats. The procedure to extract the rat skin received approval from the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (Ref. no: PHM.Eth/Lhr-05/08-24). Male Sprague–Dawley rats weighing 200–250 g were sacrificed via cervical dislocation. Hairs of rats were excised from the dorsal area utilizing an electric trimmer, followed by skin excision surgically. Skin was rinsed with a 0.9% sodium chloride solution and stored at −20 °C ± 1 °C. The rat’s skin was subsequently positioned between the donor and receptor compartments of the Franz diffusion cell. The phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) was filled in the recipient compartment, and the temperature was set at 37 °C ± 2 °C. The receiving medium was agitated at 100 revolutions per minute. The donor partition was filled with a nanoparticle patch exhibiting 5 mg of the drug. Subsequently, 2-mL aliquots were collected at designated time intervals (0.5 h, 1 h, 1.5 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 16 h, and 24 h), and the medium was replenished with fresh buffer to preserve the sink conditions. The samples were subjected to UV–Vis spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 425 nm for further analysis (Nawaz et al., 2022).
2.2.7 In vitro anti-inflammatory study (egg albumin denaturation study)
The in vitro anti-inflammatory effect was assessed through a protein denaturation test utilizing egg albumin. We performed the egg albumin denaturation assay following the protocol described in previously conducted studies (Abbas et al., 2021; Mizushima and Kobayashi, 1968) with minor modifications. This method involved mixing a test sample (2 mL) with a concentration of 100–400 g/mL, egg albumin (0.2 mL), and phosphate buffer saline, pH = 6.5 (2.8 mL). The reaction mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 20 min, followed by heating at 70 °C for 5 min. When the temperature dropped to room temperature, the absorbance was assessed at 660 nm using a spectrophotometer. Phosphate buffer served as the control, while diclofenac Na was employed as the standard drug. Percentage inhibition was calculated using the following equation:
where AC is the absorption of the control, and AS is the absorption of the test sample.
2.2.8 In vivo anti-inflammatory studies
2.2.8.1 Animals
The subjects employed for in vivo anti-inflammatory studies were female Wistar rats (140–190 g). Animals were acquired from the laboratory Animal Services Division of the Central Drug Research Institute. Subjects were reserved in a polyacrylic cage (22.5 × 37.5 cm) under the standard housing environment with humidity 60%–65% and room temperature 24°C–27°C. Water and food were provided ad libitum, but food was restricted 1 h prior to the behavioral studies. The anti-inflammatory study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (Ref. no: PHM.Eth/Lhr-05/08-24), and studies were conducted according to the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA) guidelines regarding the care of experimental subjects.
2.2.8.2 Paw edema induced by carrageenan
Experimental subjects were categorized into four groups (n = 5). Group I of the experimental subjects was considered as a normal control without induced edema by carrageenan. 0.1 mL of 1% carrageenan in normal saline was administered via the sub-plantar route in the left-hand paw of the subjects of groups II, III and IV. Measurements of the paw volume were taken with the plethysomometer at 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h after administering the carrageenan. Group II of the experimental subjects received the normal saline 3 mL/kg body weight, intraperitoneal, and is referred to as the saline control, while Group III received the C. esculenta plant extract NPs 5% w/v in the transdermal patch. Group IV received the transdermal patch loaded with diclofenac Na (8 mg/film) for the treatment of paw edema caused by carrageenan administration. The formula employed to calculate the % paw edema inflammation is as follows:
Furthermore, blood samples from the experimental subjects were also subjected to the hematological analysis to assess the hematological parameters, including, hemoglobin concentration, platelet count, red blood cell count, and white blood cells count, via an automated hematology analyzer (Sysmex KX-21). Blood samples were analyzed within 2 hours of collection from the subjects.
2.2.9 Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed by GraphPad Prism v. 9.0 (GraphPad Software, USA), and data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test was selected to compare multiple formulations in the evaluation of physicochemical parameters of transdermal patches. In addition, a paired t-test was employed to compare results before and after treatment for Group II, while one-way ANOVA was used for intergroup comparison in the evaluation of biochemical parameters. An unpaired t-test was applied to compare the control with the treatment groups. Results were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Synthesis of C. esculenta AgNPs
C. esculenta AgNP synthesis is generally divided into three phases: nucleation, nuclei conversion into seeds, and, eventually, seed growth into nanocrystals (Abbas et al., 2021). To formulate C. esculenta AgNPs, C. esculenta extract was added to synthesize AgNPs. Ag+ ions in AgNO3 were reduced to Ag atoms by the reducing ingredients in the plant extract, depicted by the change of color from green to bright reddish-brown upon stirring. In addition, C. esculenta AgNPs are favorable for the calorimetric analysis due to their bright color and high molar absorbance (Figure 1a).
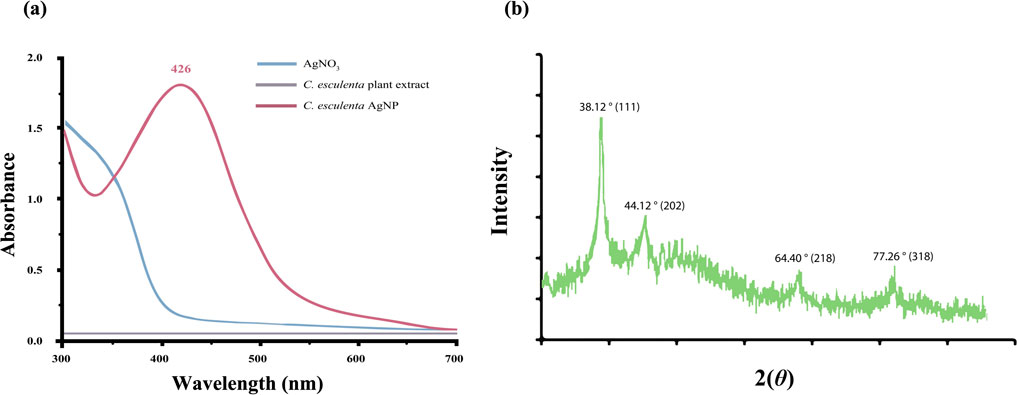
Figure 1. (a) UV analysis of synthesized C. esculenta AgNPs and (b) XRD analysis of C. esculenta AgNPs.
3.2 UV spectrophotometry
UV spectrophotometry was employed to analyze the optical characteristics depending upon the size effects to confirm the synthesis of metal NPs. The color of C. esculenta AgNPs was evaluated using UV–Vis. Various color changes were observed during the synthesis of C. esculenta AgNPs, and specific absorption was shown by C. esculenta extract and synthesized C. esculenta AgNPs (Figure 1a). Ag ions were reduced by the extract of C. esculenta and assessed by UV–Vis spectroscopy. No peak for silver salt and plant extract was observed in the range of 380–460 nm, but an obvious peak appeared for the synthesized AgNPs in the range of 380–460 nm without any noise, indicating the surface plasmon resonance characteristic of the aggregated and spherical AgNPs. Results revealed the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) bands in the visible region (∼426 nm) showing the synthesis of AgNPs as shown in Figure 1a. As AgNPs derived from different plant extracts exhibit different absorption peaks, their SPR bands are usually found in the absorption range of 350–450 nm (Beg et al., 2018; Francis et al., 2019).
3.3 Effect of silver nitrate concentration
AgNO3 concentration affects the synthesis of AgNPs (Figure 2a) and the SPR peak position. According to the UV spectrum, the highest peak appeared at the AgNO3 concentration of 8 mM, expressing the optimal formulation concentration of AgNO3 to synthesize the AgNPs. Due to the increase in Ag salt concentration, a portion of Ag+ ions is reduced to Ag atoms with the plant extracts, which in turn serves as a starting point of nucleation. Consequently, the remaining Ag+ is reduced, leading to the generation of more AgNPs and increased absorbance. NP size was increased due to the formation of clusters by the growth of individual nuclei, causing a red shift in the absorption peaks of the UV spectrum toward higher wavelengths. Results revealed that the SPR peak position remained unchanged by an increase in Ag+ within the AgNO3 concentration range of 2–8 mM. However, previous studies described the competition and aggregation effect of NPs contributed toward the shifting of the SPR band, which was not affected by increased concentration of Ag+ (Zaheer, 2018). In addition, AgNO3 concentration (10 mM) caused aggregation of the NPs due to the increased collision frequency of the Ag+ ions. Exposure to a high concentration of AgNO3 led to the deposition of silver salts on AgNPs, leading to the appearance of an unclear surface (Park et al., 2012). These results showed that 8 mM of AgNO3 is the optimum concentration to synthesize the C. esculenta AgNPs, avoiding any aggregation between the particles.

Figure 2. (a) Effect of AgNO3 concentration on the synthesis of C. esculenta AgNPs; (b) effect of C. esculenta extract concentration on the synthesis of C. esculenta AgNPs; (c) effect of reaction time on the synthesis of C. esculenta AgNPs.
3.4 Effect of the C. esculenta extract concentration
The concentration of C. esculenta extract affects the absorbance (Figure 2b). An increased extract concentration increases the absorbance, leading to increased production of AgNPs due to secondary reduction of Ag+ ions (Satpathy et al., 2018). The nucleation process is facilitated by the higher concentration of reducing agents. One study demonstrated that decreased concentration of extract resulted in the synthesis of a low number of AgNPs, and some of them exhibited anisotropic and irregular nanostructures (Sathishkumar et al., 2010). To achieve the optimum yield of C. esculenta AgNPs, 15 mL of C. esculenta extract was found to be appropriate in size (˂100 nm) and morphology.
3.5 Effect of the reaction time
C. esculenta AgNP synthesis was accomplished within 30 min of the reaction at 70 °C. A slow rate of NP nucleation with unchanged absorption peaks was observed with a rise in reaction time (Figure 2c). In addition, the width and position of SPR peaks also remained constant, showing that increased reaction time does not alter the morphology and size of the AgNPs. However, decreased absorption intensity was observed with an extension of reaction time up to 60 min. This decrease in absorption intensity is attributed to instability and aggregation of nanosilver (S. P. Singh et al., 2021). Mittal et al. revealed that maximum absorption occurred after 12 h of reaction time, followed by aggregation of particles after 24 h, by employing Syzygium cumini fruit extracts in the synthesis of AgNPs (Mittal et al., 2014). Based on the use of C. esculenta for the synthesis of AgNPs, the time expenditure can be minimized to within 45 min.
3.6 FTIR spectral analysis of C. esculenta AgNP
FTIR analysis revealed the identification of phytochemicals of the extract involved in the coating of AgNPs by depicting the molecular vibrations (bending, twisting, and stretching of the chemical bonds) of the sample in particular infrared regions (Mondal et al., 2023). The FTIR spectra of AgNO3 yield various peaks at 734 cm−1, 817 cm−1, and 1,384 cm−1 due to the bending and asymmetric stretching vibrations of nitrate ions. C. esculenta plant extract showed significant absorption at the range from 443–586 cm−1, 1,031 cm−1, 1,112 cm−1, 1,313–1,633 cm−1, and 2,401–3,832 cm−1 due to C-C or C-O bending, C-O or C-O-C stretching, C-H bending, and C = O stretching and O–H and N–H stretching, respectively (Figure 3a). These absorption peaks identified the presence of polysaccharide, phenolic, and flavonoid compounds within C. esculenta extract. However, the spectra of AgNP formulated by employing C. esculenta plant extract showed various significant and minor shifts within the absorption peaks. The reductions in the nitrate peaks at 734 cm−1, 817 cm−1, and 1,384 cm−1 confirm the proper consumption of AgNO3 (Figure 3a). Furthermore, the shifting of plant extract peaks from 1,031 cm−1, 1,122 cm−1, and 1,633 cm−1 to 1,047 cm−1, 1,390 cm−1, and 1,624 cm−1 indicates interaction between phytochemicals and Ag ions, as shown in Figure 3b. The appearance of new characteristic peaks at 596 cm−1, 713 cm−1, 846 cm−1, 1,047 cm−1, 1,390 cm−1, and 1,624 cm−1 confirmed the binding of phytochemicals with nanoparticles. Broadening of the O-H and N-H bands at 3,217 cm−1 and 3,394 cm−1 provides evidence of the stabilization of phytochemicals due to the generation of hydrogen bonding and hence provides proper capping of these chemicals.
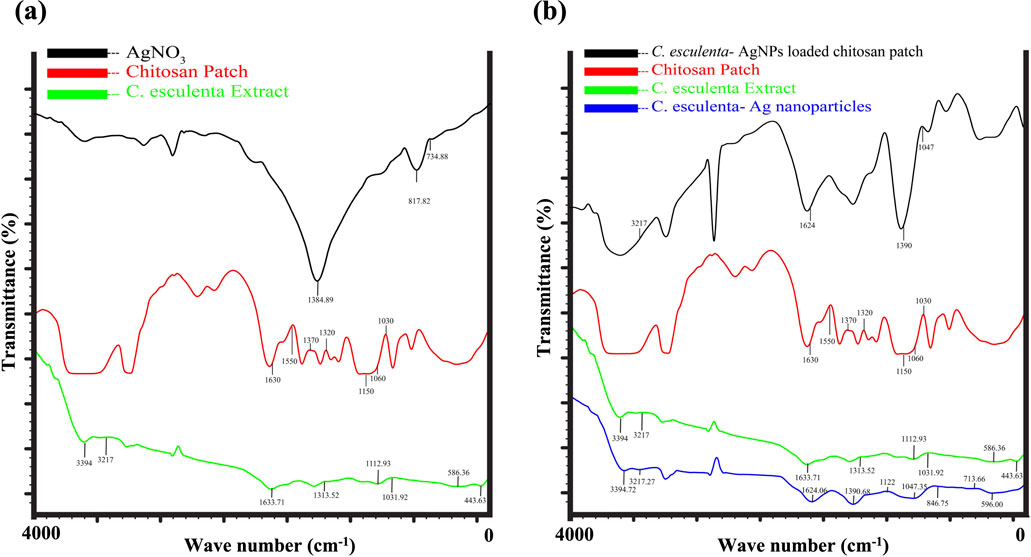
Figure 3. TIR analysis of (a) FTIR analysis of AgNO3, CS patch, and C. esculenta extract (b) C. esculenta Ag-NPs loaded CS patch, Formulated CS patch, C. esculenta extract and C. esculenta Ag-NPs.
3.7 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
SEM was employed to explore the morphology of AgNPs, as morphology plays an important role in the characteristics and potential applications of NPs in biomedicine and nanotechnology. Spherical aggregated clusters of AgNPs were observed (Figure 4a) in the SEM images, and these results are in concordance with the previous studies (Arya et al., 2024; Okaiyeto et al., 2021).
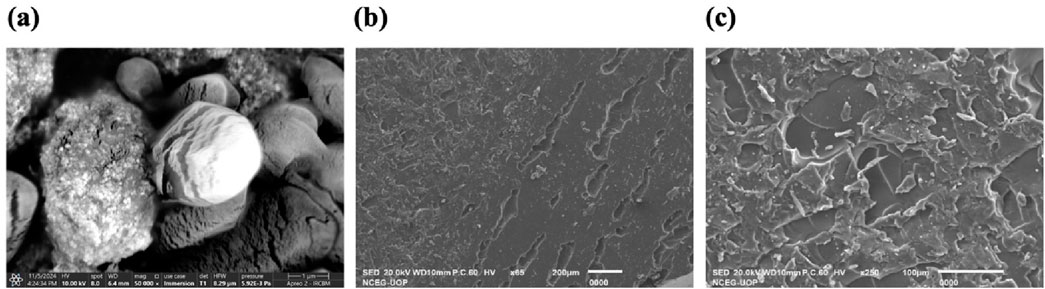
Figure 4. SEM analysis of (a) C. esculenta AgNPs; (b) formulated CS patch; (c) C. esculenta AgNP-loaded CS patch.
3.8 Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies
XRD analysis of the prepared C. esculenta AgNPs demonstrated distinct diffraction peaks at 2θ values of 38.12°, 44.12°, 64.40°, and 77.26°, corresponding to the 111, 202, 218, and 318 lattice planes, respectively (Figure 1a). These results are the property of the face-centered cubic (FCC) structure of the metallic silver and are consistent with JCPDS file No. 04-0783. These intense and sharp peaks verify the crystallinity of the nanoparticles and preferential growth direction in the 111 plane (Ryu et al., 2022; Yi et al., 2014).
3.9 Zeta potential and particle size analysis
The zeta potential, particle size, and polydispersity index (PDI) of C. esculenta AgNPs were investigated. The size distribution of AgNPs was measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS), and the particle size of AgNPs was evaluated to be 90.17 ± 12.65 nm with a PDI value of 0.281 ± 0.07, which shows the polydispersity (Figure 5). The measured zeta potential value was −31.6 ± 1.26 mV, indicating the surface charge to deliver the strong repulsion between nanoparticles and minimize the agglomeration risk. This value suggests that the nanoparticles exhibit a stable electrical double layer and colloidal stability. In addition, the low PDI (0.281 ± 0.07) indicates the uniform size distribution, reduced aggregation and sedimentation, and enhanced colloidal stability. These findings confirmed that C. esculenta-mediated AgNPs exhibit dispersion stability in the aqueous media (José Pochapski et al., 2021; Riaz et al., 2021). Particles are considered stable with the zeta potential values below −30 mV or exceeding +30 mV (Chinni et al., 2021). In this regard, C. esculenta AgNPs may avoid particle aggregation and retain stability in solution owing to the electrostatic repulsion between the nanoparticles.
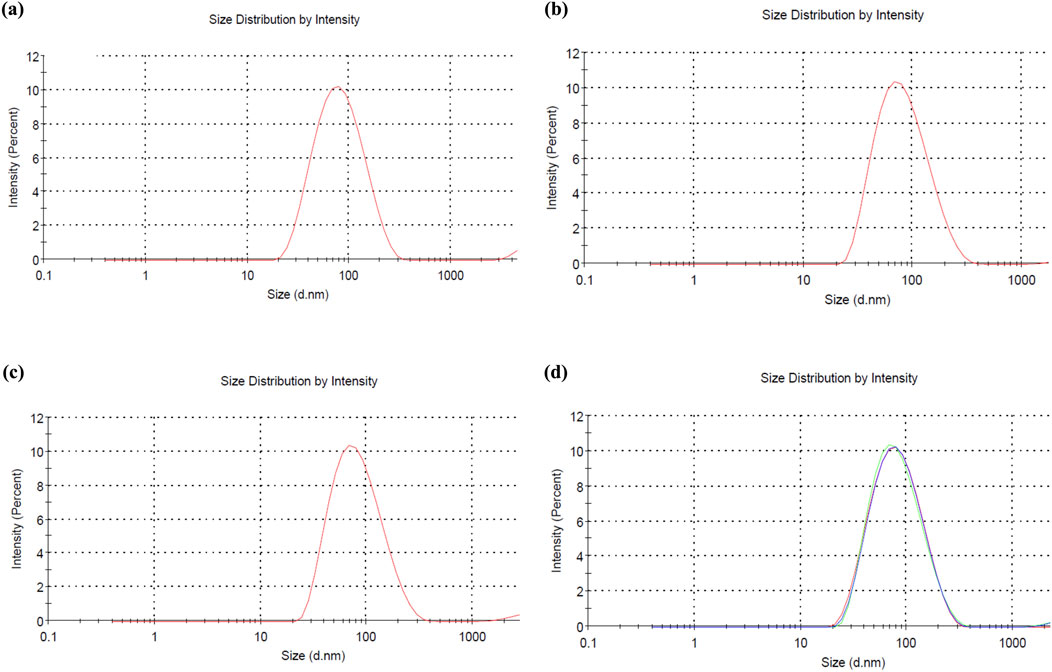
Figure 5. Size analysis of (a) F1 formulation of C. esculenta AgNPs, (b) F2 formulation of C. esculenta AgNPs, (c) F3 formulation of C. esculenta AgNPs, and (d) collective size of all formulations of C. esculenta AgNPs.
3.10 Characterization of C. esculenta AgNPs loaded CS patches
3.10.1 FTIR spectral analysis of CS transdermal patches
FTIR analysis was performed to verify the successful integration of C. esculenta AgNP into CS transdermal patches. The spectral analysis of C. esculenta AgNP, the chitosan patch, and the C. esculenta AgNP-loaded chitosan patch demonstrated notable differences. Significant absorption peaks in C. esculenta AgNP were observed at 596 cm−1, 713 cm−1, 846 cm−1, 1,047 cm−1, 1,390 cm−1, 1,624 cm−1, 3,217 cm−1, and 3,394 cm−1, indicative of metal–ligand vibrations and biomolecule capping. The CS patch displayed peaks at 580 cm−1, 837 cm−1, 1,082 cm−1, 1,647 cm−1, and 3,331–3,468 cm−1, corresponding to the CS and PEG functional groups employed in the patch formation, as summarized in Figure 3A. Upon the incorporation of C. esculenta AgNP into the patch, novel peaks appeared at 569 cm−1, 650 cm−1, 840 cm−1, 945 cm−1, 1,099 cm−1, 1,377 cm−1, 1,639 cm−1, and 2,156 cm−1, signifying Ag-polymer interactions. Displacements in O–H or N–H stretching (3,427 cm−1) and the emergence peaks at 3,716 cm−1, 3,867 cm−1, and 3,992 cm−1 validated the augmentation of hydrogen bonding and molecular reconfiguration. The absence of peaks at 1,251 cm−1, 1,296 cm−1, and 1,357 cm−1 in the CS patch spectrum indicates an interaction with C. esculenta AgNP, altering the polymer matrix. The spectral alterations provide compelling evidence that silver nanoparticles were effectively integrated into the chitosan-PEG patch, establishing stable interactions with the polymer’s functional groups (Alven and Aderibigbe, 2024).
3.10.2 Physical appearance
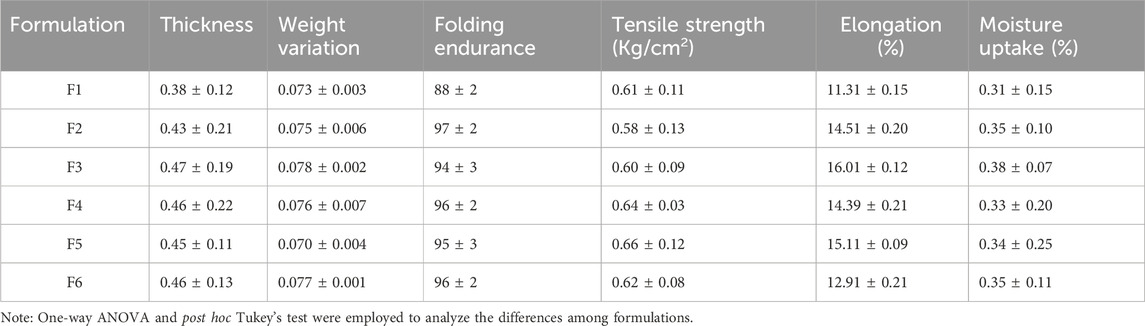
Different concentrations of ingredients were employed to formulate the patches (F1-F6), as mentioned in Table 3. The physical appearance of the formulated chitosan patch and the C. esculenta AgNP-loaded chitosan patch was assessed by visual inspection of the prepared patches (Figures 6a,b). All formulated patches had a non-sticky, homogeneous, opaque, flexible, and smooth nature. In addition, the formulated patches exhibited even distribution of adhesive layer to diminish the lump formation. Furthermore, formulated patches exhibited the acceptable pH range (5.2–5.9). Therefore, the prepared transdermal patches are user friendly, as they will cause no irritation to the skin.
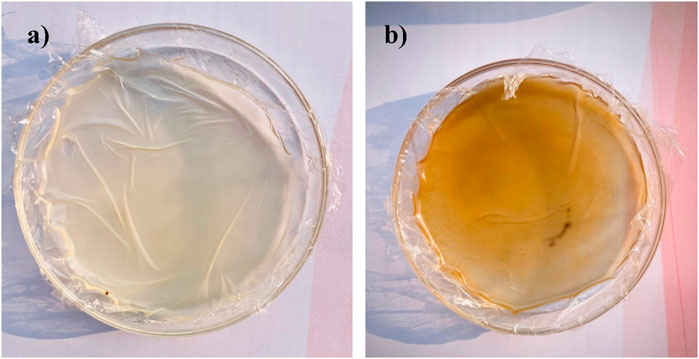
Figure 6. Physical appearance of (a) formulated chitosan patch and (b) C. esculenta AgNP-loaded chitosan patch.
3.10.3 Thickness uniformity
The thickness uniformity of the patches was observed by using the digital calipers, and the average thickness was investigated (Table 3). Chitosan concentration has an impact on the overall thickness of the patch, as it may result in a denser and more robust formulation of the matrix system of the polymer. The results suggest the optimum thickness uniformity in all prepared transdermal patches with the thickness order: F-1 < F-2 < F-3. However, no significant difference in thickness was observed in the formulations F4, F5, and F6.
3.10.4 Moisture content
The moisture absorption profile of the prepared patches was investigated (Table 3) and showed the moisture absorption of the formulated patches in the order of F-3 > F-2 > F-1; however, formulations F-4 to F-6 have comparable moisture content due to similar CS concentrations. All formulations showed the moisture absorption in the acceptable range and retained an appropriate shape and texture.
3.10.5 Uniformity of weight
The weight uniformity of the drug-loaded patches (1 × 1 cm2) was evaluated according to the lower SD values (Table 3). Patch weights were found to be uniform, as the thickness uniformity of the patches ensured the weight uniformity. As the concentration of the CS changes, achieving a uniform layer is difficult, and hence, the uniformity of weight may change accordingly.
3.10.6 Folding endurance
All prepared transdermal patches exhibit favorable film properties and folding endurance, as shown in Table 3. The folding endurance of the prepared transdermal patches was found to be in the order of F-1 < F-2 > F-3, with the F2 formulation showing more folding endurance (97 ± 2). In addition, F4 and F6 exhibited the same folding endurance with value 96 ± 2, while F5 showed lesser folding endurance with value 95 ± 3. These results indicate that the folding endurance of the prepared patches increased with the corresponding increase in the CS concentration initially due to an increase in the elasticity and flexibility of the patch. However, as the concentration of CS increases above a certain value, it may decrease folding endurance due to the formation of a very rigid structure that reduces overall flexibility.
3.10.7 Tensile strength
The tensile strength of the formulated patches was determined (Table 3) by employing the fabricated apparatus according to previous studies. Tensile strength was measured in triplicate, and the average was calculated. The tensile strength of the prepared patches increased with increased CS proportion, indicating that tensile strength can be increased with a high concentration of the polymer in the formulation.
3.10.8 SEM analysis of transdermal patches
The surface morphology of the CS transdermal patches and CS patches (Figure 4b) loaded with C. esculenta AgNPs was analyzed using SEM to assess the impact of nanoparticle incorporation. Figure 4c displays the SEM image of the CS-based patch prior to C. esculenta AgNP incorporation, showing a smooth and uniform surface. The lack of particulate matter indicates a uniform polymeric structure, typical of a well-constructed CS-PEG film.
Figure 4c depicts the chitosan patch post-loading with C. esculenta AgNPs, revealing notable surface alterations. The formerly smooth surface now displays dispersed nanoparticle clusters, validating the successful integration of C. esculenta AgNPs into the polymeric matrix. The irregular and diverse morphology indicates significant interactions between C. esculenta AgNPs and CS, potentially affecting release dynamics and mechanical characteristics. These observations validate that nanoparticle incorporation modifies the patch morphology, shifting from a smooth surface to a rougher texture due to AgNP distribution, thereby validating the effective fabrication of a nanoparticle-loaded chitosan patch for prospective biomedical applications.
3.10.9 Skin irritation and sensitization tests
A skin irritation test was done with the F4 formulation. A transdermal patch was employed on the skin of the experimental subjects, and subjects were examined after 24 h and 72 h. There was no sign of erythema and edema over the skin of experimental subjects. The primary irritancy index (PII) for the control patches and medicated patches was <2, while the PII for the formalin-treated group was 5.67 ± 0.52, indicating high irritation of the skin. Formulations with PII<2 are considered a non-irritant according to the Draize patch test. Therefore, patches formulated in this study were safe and non-irritant when applied to the skin for the specific time of application (Supplementary Figure S1).
These results demonstrate that the formulated transdermal patches (F4) are non-irritant and present good skin compatibility. The absence of any adverse reaction and irritation suggests that these patches are safe and reliable for prolonged application over the skin and are a suitable option for their intended transdermal drug delivery applications.
3.11 Ex vivo permeation
Using Franz diffusion cells and rat skin, an ex vivo permeation study was conducted on C. esculenta extract, C. esculenta AgNP, C. esculenta AgNP-loaded CS patches, and a control drug (diclofenac Na). Compared to the C. esculenta AgNP, the permeation of the CS patches loaded with C. esculenta AgNP was found to be significantly greater (ANOVA; p < 0.05). As a permeation enhancer, chitosan increases drug penetration by reversibly changing skin proteins and lipids (Nawaz and Wong, 2017). The results of the ex vivo permeation study are summarized in Figure 7b.
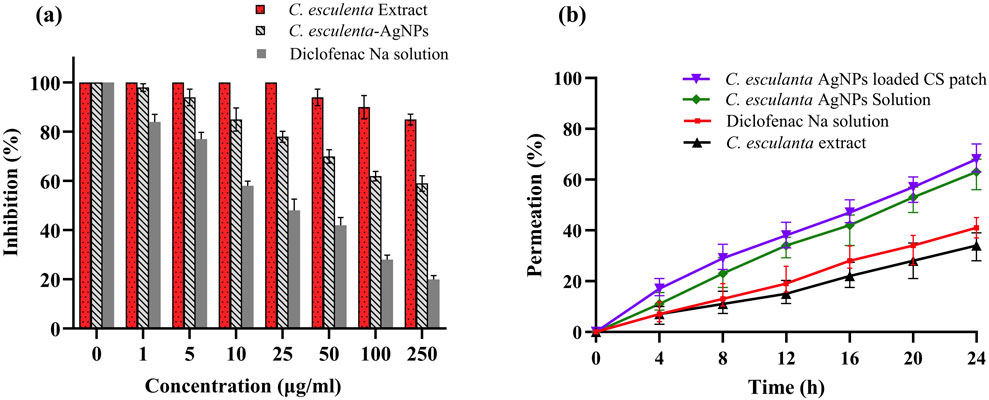
Figure 7. Protein denaturation effects of (a) control (diclofenac Na), C. esculenta extract, and C. esculenta AgNPs and (b) ex vivo permeation of C. esculenta extract, control (diclofenac Na), C. esculenta AgNP solution, and C. esculenta AgNP-loaded CS patches.
3.12 Egg albumin denaturation study
Protein denaturation is a recognized contributor to inflammation, and credible literature verifies the association between inflammatory and arthritic conditions and the denaturation of tissue proteins (OPIE, 1962; Williams et al., 2008). The results presented in Figure 7A indicate that C. esculenta crude extracts and their subsequent fractions demonstrate minimal inhibition of egg albumin denaturation. In contrast, C. esculenta AgNP exhibited the highest potency (80.1%, p < 0.001), followed by diclofenac Na (59.3%, p < 0.01), and C. esculenta crude extracts (15.1%, p < 0.01) at a concentration of 250 μg/mL, in a dose-dependent manner relative to the control. The results align with those reported by Chandra et al. (2012), demonstrating a concentration-dependent inhibition of egg albumin denaturation by experimental coffee extracts and standard diclofenac sodium. Other researchers demonstrated that the methanol extract of Enicostemma axillare, at concentrations ranging from 100 to 500 μg/mL, significantly safeguards against heat-induced protein denaturation (Leelaprakash and Mohan Dass, 2011). Our results indicate that C. esculenta AgNP (p < 0.001) demonstrates significant inhibition of serum albumin denaturation, followed by diclofenac Na (p < 0.001), and the crude extract of C. esculenta AgNP (p < 0.01), with percentage inhibitions of 80.1%, 59.3%, and 15.1%, respectively, at a concentration of 250 μg/mL compared to the control. Diclofenac sodium (p < 0.0001) demonstrated significant inhibition of egg albumin denaturation at a concentration of 250 μg/mL.
3.13 In vivo anti-inflammatory studies
3.13.1 Determination of hematological parameters
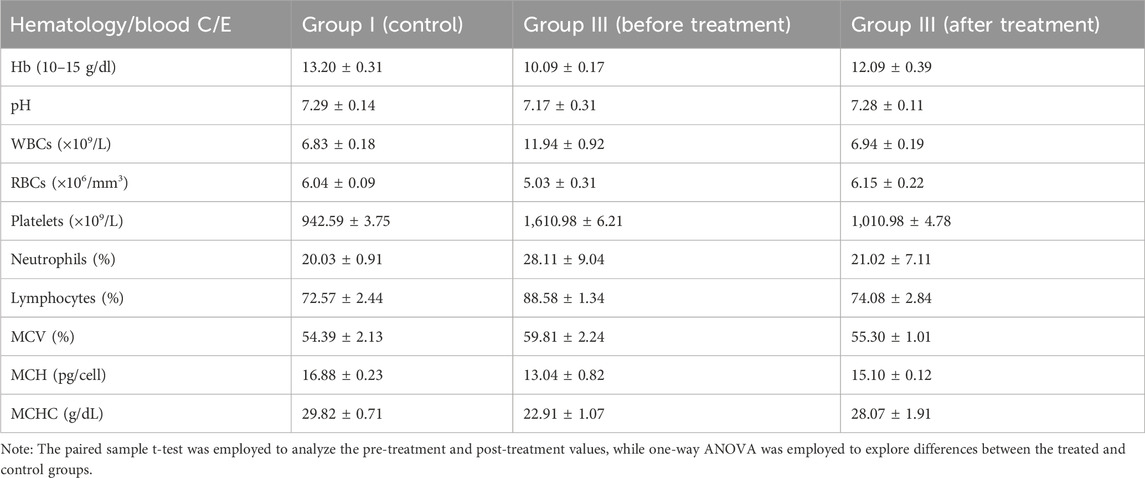
The hematological parameters were assessed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory potential of the C. esculenta AgNP-loaded CS patches. The notable decrease in WBC count from 11.94 ± 0.92 × 109/L prior to treatment to 6.94 ± 0.19 × 109/L post-treatment signifies a reduction in systemic inflammation, given that elevated WBC levels are generally linked to an inflammatory response. Furthermore, neutrophil levels, essential in acute inflammation, exhibited a significant reduction from 28.11% ± 9.04% to 21.02% ± 7.11% following treatment, thereby corroborating the resolution of inflammation in the treatment group. The RBC count, initially lower before treatment (5.03 ± 0.31 × 106/mm3), rose to 6.15 ± 0.22 × 106/mm3 post-treatment, indicating enhanced hematological stability, presumably attributable to diminished oxidative stress and inflammation-related hemolysis. The platelet count, significantly elevated prior to treatment (1,610.98 ± 6.21 × 109/L), decreased to 1,010.98 ± 4.78 × 109/L following treatment, signifying a reduction in inflammatory and pro-thrombotic activity, given the pivotal role of platelets in immune responses and inflammation. Furthermore, the slight fluctuations noted in MCV, MCH, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) indicate that the treatment did not negatively impact erythrocyte morphology or hemoglobin levels. The hematological parameters are presented in Table 4.
3.13.2 Carrageenan-induced paw edema measurements
The anti-inflammatory effects of the prepared nanoparticle-loaded patches are illustrated in Supplementary Figure S2. Female Sprague–Dawley rats were employed in this study due to the prevalence of inflammation being 3–5 times higher in females than in males. C. esculenta is extensively documented as a potential anti-inflammatory agent owing to the presence of phenolic and flavonoid compounds (Sudhakar et al., 2020). The anti-inflammatory efficacy of C. esculenta phytochemicals was augmented by their transformation into nanoparticles to improve skin permeation. The results indicated that the highest percentage of inhibition in paw volume was recorded with patches containing nanoparticles (ANOVA; p < 0.05). Patches significantly suppress inflammation and edema relative to the control group. Diclofenac Na-loaded patches also diminish edema volume relative to the control, albeit to a lesser extent than the C. esculenta AgNP-loaded chitosan patches. This resulted from increased penetration of phytochemicals into skin layers due to enhanced skin permeation. The elevated concentration of nanoparticles in the deeper dermal layers aids in mitigating skin infections and inflammation.
The nanoparticle-infused patches administer the requisite quantity of anti-inflammatory agents at the target location with greater efficiency. Consequently, the topical administration of natural compounds via nanoparticles embedded in patches enhances the management of inflammation. The findings of anti-inflammatory studies are encapsulated in Table 5. The findings indicate that the treatment effectively reduced inflammatory responses and aided in restoring hematological homeostasis in the experimental model.
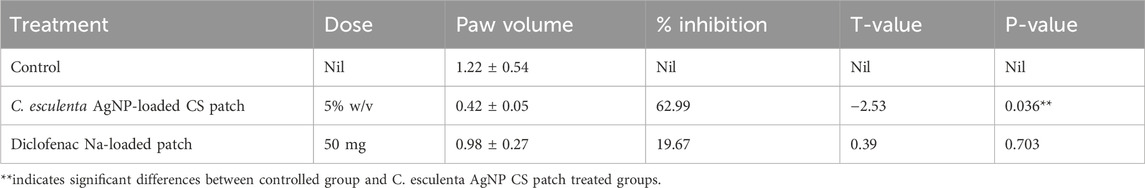
Table 5. Comparative study of different formulations on carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats (n = 5).
The anti-inflammatory effect found in the study is predominantly due to the silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Several studies described that AgNPs exhibit anti-inflammatory characteristics as they inhibit the pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6 and TNF-α), modulate the NF-κ signaling pathway, and suppress the reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Gopinath et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2014). AgNPs may release some silver ions (Ag+); they typically act synergistically and may contribute to the anti-inflammatory effect. In our study, C. esculenta-mediated AgNPs incorporated into the CS patches exerted an active anti-inflammatory effect.
In the present study, the CS-based matrix played a pivotal role in the transdermal mechanism as CS is a bioadhesive, biocompatible, and permeation-enhancing polymer, having the ability to open the tight junctions present in the skin, thus facilitating the paracellular transport. CS also promotes the intimate contact between skin and the applied patch, thus enhancing the absorption through the skin.
AgNPs may penetrate the upper layer of the skin more efficiently, owing to their nano-size, further facilitating the skin permeability. These factors demonstrate the efficient and sustained transdermal delivery of the active constituents via a combination of NP-assisted penetration and polymer-aided permeation enhancement.
4 Conclusion
The present research successfully demonstrated the green production of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using C. esculenta extract, which were then integrated into CS-based transdermal patches for anti-inflammatory purposes. The synthesized AgNPs were characterized by studies that confirmed their stability, spherical form, and good physicochemical properties. Transdermal patches showed great potential as an effective medication delivery system due to their high levels of biocompatibility, mechanical integrity, and sustained drug release patterns. The in vivo and in vitro studies demonstrated that the anti-inflammatory effects of the patches loaded with AgNPs were significantly stronger than those of the usual diclofenac sodium formulations. Superior efficacy in moderating inflammatory responses is shown by the considerable suppression of protein denaturation and reduction in carrageenan-induced paw edema, which are both caused by AgNPs. In addition, the chitosan matrix allowed for better drug dispersion, which was confirmed by the ex vivo permeation experiments, which led to improved transdermal penetration. Additional evidence of the formulation’s safety is the lack of skin irritation and sensitization.
These results highlight the possibility of AgNPs derived from C. esculenta as a greener, more sustainable substitute for current anti-inflammatory treatments. To determine the therapeutic feasibility of these new transdermal patches, additional research is needed to examine their long-term toxicity, clinical translation, and the anti-inflammatory pathways from a molecular perspective.
5 Limitations
The present study utilized zeta potential studies for stability, SEM for surface morphology, and dynamic light scattering (DLS) for size and PDI measurement. However, nanoscale imaging studies, such as atomic force microscopy (AFM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), could provide better insights for the evaluation of surface topography and NP morphology.
6 Future perspectives
Although C. esculenta-mediated AgNPs exhibit significant anti-inflammatory potential, the immunomodulatory role of C. esculenta-mediated AgNPs has yet to be mechanistically explored. The LPS-induced macrophage model, which uses RAW 264.7 cells to assess TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β concentration, will assist in elucidating the cellular pathways involved in future studies. These assays would enlighten the understanding of the biological activity of the AgNPs and complement the current findings. While the colloidal stability of AgNPs was not assessed in PBS or FBS due to solid-state patch formulation, C. esculenta-AgNP stability under physiological conditions may be investigated in future research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (Ref. no: PHM.Eth/Lhr-05/08-24). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XW: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. WW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. AE: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. MM: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Methodology. NA: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. IN: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. YS: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. TB: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore campus, for providing laboratory access to conduct this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used for language improvement purposes only.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1611507/full#supplementary-material
References
Abbas, M. W., Hussain, M., Qamar, M., Ali, S., Shafiq, Z., Wilairatana, P., et al. (2021). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Peganum harmala extracts: an in vitro and in vivo study. Mol. Basel, Switz. 26 (19), 6084. doi:10.3390/molecules26196084
Adeyemi, J. O., Oriola, A. O., Onwudiwe, D. C., and Oyedeji, A. O. (2022). Plant extracts mediated metal-based nanoparticles: synthesis and biological applications. Biomolecules 12 (Issue 5), 627. doi:10.3390/biom12050627
Alven, S., and Aderibigbe, B. A. (2024). Chitosan-Based scaffolds incorporated with silver nanoparticles for the treatment of infected wounds. Pharmaceutics 16 (3), 327. doi:10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS16030327
Anand, U., Jacobo-Herrera, N., Altemimi, A., and Lakhssassi, N. (2019). A comprehensive review on medicinal plants as antimicrobial therapeutics: potential avenues of biocompatible drug discovery. Metabolites 9 (11), 258. doi:10.3390/metabo9110258
Arya, A., Kumar Tyagi, P., Bhatnagar, S., Kumar Bachheti, R., Bachheti, A., and Ghorbanpour, M. (2024). Biosynthesis and assessment of antibacterial and antioxidant activities of silver nanoparticles utilizing Cassia occidentalis L. seed. Sci. Rep. 14, 7243. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57823-3
Balavandy, S. K., Shameli, K., Biak, D. R. B. A., and Abidin, Z. Z. (2014). Stirring time effect of silver nanoparticles prepared in glutathione mediated by green method. Chem. Central J. 8 (1), 11. doi:10.1186/1752-153X-8-11
Bamrungsap, S., Zhao, Z., Chen, T., Wang, L., Li, C., Fu, T., et al. (2012). Nanotechnology in therapeutics: a focus on nanoparticles as a drug delivery system. Nanomedicine 7 (8), 1253–1271. doi:10.2217/nnm.12.87
Baro, M. R., Das, M., Kalita, A., Das, B., and Sarma, K. (2023). Exploring the anti-inflammatory potential of Colocasia esculenta root extract in in-vitro and in-vivo models of inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 303, 116021. doi:10.1016/J.JEP.2022.116021
Beg, M., Maji, A., Mandal, A. K., Das, S., Jha, P. K., and Hossain, M. (2018). Spectroscopic investigation on interaction of biogenic, Croton bonplandianum leaves extract mediated potential bactericidal silver nanoparticles with human hemoglobin and human serum albumin. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 36 (3), 711–723. doi:10.1080/07391102.2017.1294505
Bharadwaj, K. K., Rabha, B., Pati, S., Sarkar, T., Choudhury, B. K., Barman, A., et al. (2021). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extracts as beneficial prospect for cancer theranostics. Molecules 26 (21), 6389. doi:10.3390/molecules26216389
Câmara, J. S., Perestrelo, R., Berenguer, C. V., Andrade, C. F. P., Gomes, T. M., Olayanju, B., et al. (2022). Green extraction techniques as advanced sample preparation approaches in biological, food, and environmental matrices: a review. Molecules 27 (9), 2953. doi:10.3390/molecules27092953
Chand, N., Suthar, S., Kumar, K., and Tyagi, V. K. (2021). Enhanced removal of nutrients and coliforms from domestic wastewater in cattle dung biochar-packed colocasia esculenta-based vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland. J. Water Process Eng. 41, 101994. doi:10.1016/J.JWPE.2021.101994
Chandoliya, R., Sharma, S., Sharma, V., Joshi, R., and Sivanesan, I. (2024). Titanium dioxide nanoparticle: a comprehensive review on synthesis, applications and toxicity. Plants 13 (21), 2964. doi:10.3390/plants13212964
Chandra, S., Chatterjee, P., Dey, P., and Bhattacharya, S. (2012). Evaluation of in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of coffee against the denaturation of protein. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2 (1), S178–S180. doi:10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60154-3
Chinni, S. V., Gopinath, S. C. B., Anbu, P., Fuloria, N. K., Fuloria, S., Mariappan, P., et al. (2021). Characterization and antibacterial response of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using an ethanolic extract of Coccinia indica leaves. Crystals 11 (2), 97. doi:10.3390/CRYST11020097
Dilek, N. M., and Bilgiçli, N. (2021). Effect of taro [Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott] flour and different shortening ratio on physical and chemical properties of gluten-free cookie. J. Food Process. Preserv. 45 (11). doi:10.1111/jfpp.15894
El-Seedi, H. R., Omara, M. S., Omar, A. H., Elakshar, M. M., Shoukhba, Y. M., Duman, H., et al. (2024). Updated review of metal nanoparticles fabricated by green chemistry using natural extracts: biosynthesis, mechanisms, and applications. Bioengineering 11 (11), 1095. doi:10.3390/bioengineering11111095
Esposito, T., Pisanti, S., Mauro, L., Mencherini, T., Martinelli, R., and Aquino, R. P. (2024). Activity of Colocasia esculenta (taro) corms against gastric adenocarcinoma cells: Chemical study and molecular characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (1), 252. doi:10.3390/IJMS25010252/S1
Francis, S., Nair, K. M., Paul, N., Koshy, E. P., and Mathew, B. (2019). Catalytic activities of green synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 9, 97–104. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2019.02.042
Goncalves, R. F., Silva, A. M. S., Silva, A. M., Valentao, P., Ferreres, F., Gil-Izquierdo, A., et al. (2013). Influence of taro (Colocasia esculenta L. Shott) growth conditions on the phenolic composition and biological properties. Food Chem. 141 (4), 3480–3485. doi:10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2013.06.009
Gopinath, P., Gogoi, S. K., Sanpui, P., Paul, A., Chattopadhyay, A., and Ghosh, S. S. (2010). Signaling gene cascade in silver nanoparticle induced apoptosis. Colloids Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 77 (2), 240–245. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.01.033
Gupta, D., Boora, A., Thakur, A., and Gupta, T. K. (2023). Green and sustainable synthesis of nanomaterials: recent advancements and limitations. Environ. Res. 231, 116316. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.116316
José Pochapski, D., Carvalho dos Santos, C., Wosiak Leite, G., Helena Pulcinelli, S., and Valentim Santilli, C. (2021). Zeta potential and colloidal stability predictions for inorganic nanoparticle dispersions: effects of experimental conditions and electrokinetic models on the. Langmuir 15 (45), 48. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02056
Kharissova, O. V., Kharisov, B. I., Garcia, T. H., and Méndez, U. O. (2009). A review on less-common nanostructures. Synthesis React. Inorg. Metal-Organic Nano-Metal Chem. 39 (10), 662–684. doi:10.1080/15533170903433196
Kumar, B., Smita, K., Cumbal, L., Debut, A., Camacho, J., Hernández-Gallegos, E., et al. (2015). Pomosynthesis and biological activity of silver nanoparticles using Passiflora tripartita fruit extracts. Adv. Mater. Lett. 6 (2), 127–132. doi:10.5185/amlett.2015.5697
Kumar, K. K. P., Dinesh, N. D., and Murari, S. K. (2019). Microwave assisted green synthesis of ZnO and Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles as antifungal and antibacterial agents using Colocasia esculenta leaf extract. Int. J. Nanoparticles 11 (3), 239–263. doi:10.1504/IJNP.2019.102624
Lade, B. D., and Patil, A. S. (2017). Silver nano fabrication using leaf disc of Passiflora foetida linn. Appl. Nanosci. Switz. 7 (5), 181–192. doi:10.1007/s13204-017-0558-y
Leelaprakash, G., and Mohan Dass, S. (2011). Invitro anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of enicostemma axillare. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 3 (3), 189–196.
Liu, X., Hao, W., Lok, C.-N., Wang, Y. C., Zhang, R., and Wong, K. K. Y. (2014). Dendrimer encapsulation enhances anti-inflammatory efficacy of silver nanoparticles. J. Pediatr. Surg. 49 (12), 1846–1851. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.09.033
Mehmood, A., and Zeb, A. (2020). Effects of different cooking techniques on bioactive contents of leafy vegetables. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 22, 100246. doi:10.1016/j.ijgfs.2020.100246
Mittal, A. K., Bhaumik, J., Kumar, S., and Banerjee, U. C. (2014). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: elucidation of prospective mechanism and therapeutic potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 415, 39–47. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2013.10.018
Mizushima, Y., and Kobayashi, M. (1968). Interaction of anti-inflammatory drugs with serum proteins, especially with some biologically active proteins. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 20 (3), 169–173. doi:10.1111/J.2042-7158.1968.TB09718.X
Mohanraj, V. J., and Chen, Y. (2007). Nanoparticles - a review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 5 (1), 561–573. doi:10.4314/tjpr.v5i1.14634
Mondal, M. S., Paul, A., and Rhaman, M. (2023). Recycling of silver nanoparticles from electronic waste via green synthesis and application of AgNPs-chitosan based nanocomposite on textile material. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 13798–15. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-40668-7
Nawaz, A., Farid, A., Safdar, M., Latif, M. S., Ghazanfar, S., Akhtar, N., et al. (2022). Formulation development and ex-vivo permeability of curcumin hydrogels under the influence of natural chemical enhancers. Gels 8, 384. doi:10.3390/gels8060384
Nawaz, A., and Wong, T. W. (2017). Microwave as skin permeation enhancer for transdermal drug delivery of chitosan-5-fluorouracil nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 157, 906–919. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2016.09.080
Okaiyeto, K., and Hoppe, H. (2021). Plant-based synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Salvia officinalis: characterization and its antiplasmodial activity. SpringerK Okaiyeto, H Hoppe, AI OkohJournal Clust. Sci. 2021⋅Springer 32 (1), 101–109. doi:10.1007/s10876-020-01766-y
Opie, E. L. (1962). On the relation of necrosis and inflammation to denaturation of proteins. J. Exp. Med. 115 (3), 597–608. doi:10.1084/jem.115.3.597
Paramasivam, G., Kayambu, N., Rabel, A. M., Sundramoorthy, A. K., and Sundaramurthy, A. (2017). Anisotropic noble metal nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functionalization and applications in biosensing, bioimaging, drug delivery and theranostics. Acta Biomater. 49, 45–65. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.066
Park, Y., Noh, H. J., Han, L., Kim, H.-S., Kim, Y.-J., Choi, J. S., et al. (2012). Artemisia capillaris extracts as a green factory for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activities. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 12 (9), 7087–7095. doi:10.1166/jnn.2012.6575
Pereira, P. R., Mattos, É. B. de A., Corrêa, A. C. N. T. F., Vericimo, M. A., and Paschoalin, V. M. F. (2021). Anticancer and immunomodulatory benefits of taro (Colocasia esculenta) corms, an underexploited tuber crop. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (1), 1–33. doi:10.3390/ijms22010265
Ramos, A. P., Cruz, M. A. E., Tovani, C. B., and Ciancaglini, P. (2017). Biomedical applications of nanotechnology. Biophys. Rev. 9, 79–89. doi:10.1007/s12551-016-0246-2
Rasouli, R., Barhoum, A., and Uludag, H. (2018). A review of nanostructured surfaces and materials for dental implants: surface coating, patterning and functionalization for improved performance. Biomaterials Sci. 6 (6), 1312–1338. doi:10.1039/c8bm00021b
Riaz, M., Mutreja, V., Sareen, S., Ahmad, B., Faheem, M., Zahid, N., et al. (2021). Exceptional antibacterial and cytotoxic potency of monodisperse greener AgNPs prepared under optimized pH and temperature. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 2866–11. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-82555-z
Ryu, S., Nam, S. H., and Baek, J. S. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) of Angelica Gigas fabricated by hot-melt extrusion technology for enhanced antifungal effects. Materials 15 (20), 7231. doi:10.3390/MA15207231
Sabbagh, F., and Kim, B. S. (2022). Recent advances in polymeric transdermal drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 341, 132–146. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.11.025
Sathishkumar, M., Sneha, K., and Yun, Y. S. (2010). Immobilization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Curcuma longa tuber powder and extract on cotton cloth for bactericidal activity. Bioresour. Technol. 101 (20), 7958–7965. doi:10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2010.05.051
Satpathy, S., Patra, A., Ahirwar, B., Hussain, D., and Hussain, M. D. (2018). Antioxidant and anticancer activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of tubers of Pueraria tuberosa. Taylor & FrancisS Satpathy 46 (Suppl. 3), S71–S85. doi:10.1080/21691401.2018.1489265
Singh, K., Panghal, M., Kadyan, S., Chaudhary, U., and Yadav, J. P. (2014). Green silver nanoparticles of Phyllanthus amarus: as an antibacterial agent against multi drug resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Nanobiotechnology 12 (1), 40–49. doi:10.1186/s12951-014-0040-x
Singh, S. P., Mishra, A., Shyanti, R. K., Singh, R. P., and Acharya, A. (2021). Silver nanoparticles synthesized using Carica papaya leaf extract (AgNPs-PLE) causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human prostate (DU145) cancer cells. Biol. Trace Elem. es. 199 (4), 1316–1331. doi:10.1007/S12011-020-02255-Z
Sudhakar, P., Thenmozhi, V., Srivignesh, S., and Dhanalakshmi, M. (2020). Colocasia esculenta (L.) schott: pharmacognostic and pharmacological review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochemistry 9 (4), 1382–1386. doi:10.22271/PHYTO.2020.V9.I4S.11937
Williams, L. A. D., O’Connar, A., Latore, L., Dennis, O., Ringer, S., Whittaker, J. A., et al. (2008). The in vitro anti-denaturation effects induced by natural products and non-steroidal compounds in heat treated (immunogenic) bovine serum albumin is proposed as a screening assay for the detection of anti-inflammatory compounds, without the use of animals, in the early stages of the drug discovery process. West Indian Med. J. 57 (4), 327–331.
Yi, Z., Xu, X., Fang, Q., Wang, Y., Li, X., Tan, X., et al. (2014). Fabrication of silver nanosheets on quartz glass substrates through electroless plating approach. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 114 (2), 485–493. doi:10.1007/S00339-013-7813-1
Keywords: C. esculenta extract, green synthesis, anti-inflammatory, transdermal patches, ex vivo permeation
Citation: Wang X, Wang W, Ejaz A, Mehmood M, Ahmad N, Nazir I, Shahzad Y and Bai T (2025) Green synthesis of Colocasia esculenta-based silver nanoparticles: characterization and transdermal delivery for anti-inflammatory applications. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1611507. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1611507
Received: 23 May 2025; Accepted: 18 July 2025;
Published: 14 August 2025.
Edited by:
Peng Liu, Central South University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yihua Yang, Xuzhou Medical University, ChinaSurendra Gulla, University at Buffalo, United States
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Ejaz, Mehmood, Ahmad, Nazir, Shahzad and Bai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tianshuo Bai, YnRzaHVvQHNpbmEuY29t
 Xiaobo Wang1
Xiaobo Wang1 Nadeem Ahmad
Nadeem Ahmad Imran Nazir
Imran Nazir Yasser Shahzad
Yasser Shahzad Tianshuo Bai
Tianshuo Bai