- 1The Fourth Clinical Medical College of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2The Third Clinical Medical College of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3Hangzhou Third People’s Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
Background: Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a neuropathic pain and the most common complication of herpes zoster (HZ). Pharmacotherapy serves as the primary intervention for alleviating pain associated with PHN.
Methods: Electronic databases were systematically searched to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating pharmacotherapy for PHN. The network meta-analysis (NMA) based on the Bayesian framework was analyzed using R4.4.1 and Stata18.0 software.
Results: A total of 38 RCTs were included in the analysis, enrolling 8,621 participants. In the Risk of Bias 2.0 (RoB 2.0) tool, nine studies (24%) were assessed as having a high risk of bias, 15 studies (39%) were rated as having some concerns, and 14 studies (37%) were assessed as having a low risk of bias. The NMA results showed that the NGX-4010 8% capsaicin patch had a statistically significant effect in terms of pain intensity (MD = −9.20, 95% CI: [−12.0, −6.60]). The secondary outcomes showed a significant effect of hydromorphone in improving sleep quality (MD = −3.8, 95% CI: [−23.0, −15.0]) and decreasing pain questionnaire scores (MD = −13.0, 95% CI: [−28.0, 2.1]). Amitriptyline plus pregabalin demonstrated the highest probability of clinical superiority (SUCRA = 0.92). The AE incidence results showed that opioids were identified as having the highest cumulative ranking (SUCRA = 0.87).
Conclusion: The study showed that capsaicin patches and hydromorphone were more significant in relieving pain in PHN, whereas calcium channel modulators were more comprehensive in clinical management. The inclusion of more high-quality articles was needed to support this evidence due to quality bias in the literature.
1 Introduction
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a pathological neuralgia that results from direct damage to peripheral nerves during an HZ infection (Johnson and Rice, 2014). PHN is recognized as the most prevalent complication of HZ, primarily defined as persistent neuropathic pain lasting ≥3 months following lesion resolution (Forbes et al., 2016; Fornasari et al., 2022). The predominant pain characteristics observed in clinical settings are described as burning sensations, lancinating pain, or stabbing pain, accompanied by hyperalgesia and allodynia in the affected dermatomes, which are pathognomonic manifestations of neuropathic sensitization mechanisms (Schutzer-Weissmann and Farquhar-Smith, 2017). The severity of neuropathic pain has been observed to range from mild to severe, with manifestations categorized as persistent or intermittent patterns. These pain phenotypes have been significantly associated with the development of depressive symptoms, persistent fatigue, and sleep architecture disruption (Nahm et al., 2013; Colloca et al., 2017). From an epidemiological perspective, the global incidence of HZ has been established to range between three and five per 1,000 person-years, with progression to PHN documented in 5% to over 30% of HZ cases (Kawai et al., 2014). Moreover, a progressive elevation in PHN incidence has been epidemiologically correlated with advancing age (Sun et al., 2021; Gross et al., 2020). PHN prevalence rates reach as high as 75% in patients aged ≥70 years following acute HZ reactivation (Schmader, 2002). However, this severe chronic neuropathic pain syndrome has been recognized as imposing a substantial socioeconomic burden on healthcare systems globally (Schmader, 2002; Johnson et al., 2010; Corcuera-Munguia et al., 2023; Yin et al., 2021; Cuenca-Zaldívar et al., 2025). Clinically, the syndrome is accompanied by a significant deterioration in quality of life scores (Colloca et al., 2017). Therefore, the selection of therapeutic interventions for PHN is considered critically significant.
A wide variety of drugs are currently used to treat PHN, primarily calcium channel modulators (pregabalin, gabapentin), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and 5% lidocaine medicated plasters (Finnerup et al., 2015). However, it has been demonstrated in previous studies that therapeutic interventions for PHN have been evaluated solely through direct comparisons or conventional meta-analyses (Han et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2017), thereby restricting the ability of clinicians to formulate evidence-based therapeutic strategies based on hierarchical efficacy rankings.
The NMA is conducted by integrating both direct and indirect evidence from existing RCTs, thereby providing hierarchical rankings of various interventions based on the Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Area (SUCRA). Concurrently, transitivity is quantified through node-splitting tests to validate the consistency of evidence synthesis (Jansen and Naci, 2013), thereby establishing evidence-based therapeutic strategies for PHN.
Therefore, this study was designed to systematically compare the efficacy and safety of pharmacological interventions for PHN through a Bayesian framework-based NMA, which integrates clinical data from previous RCTs. The hierarchical differences between therapeutic agents were comprehensively analyzed to quantify comparative advantages in pain reduction, functional improvement, and safety profiles, thereby generating evidence-based recommendations for optimizing clinical decision-making in PHN management.
2 Methods
2.1 Protocol
This study was conducted by the guidelines of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (Cumpston et al., 2019; Shamseer et al., 2015; Hutton et al., 2015). The detailed protocol was prospectively registered in the international PROSPERO (registration number: CRD420250651348). Ethical approval and informed consent were not required because the analysis was based on previously published clinical studies.
2.2 Eligibility criteria
This study strictly adhered to the PICOS framework to define inclusion criteria (Izurieta et al., 2021): (1) Participants: Eligible patients were diagnosed with PHN, defined by the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) as persistent dermatomal pain lasting 30 days to 6 months or longer after lesion resolution. No restrictions were applied to age, sex, nationality, or other demographic factors. (2) Intervention: This study focuses on pharmacological interventions for pain management in PHN patients, primarily examining first-line therapeutic agents, including pregabalin, gabapentin, opioid analgesics, and topical capsaicin patch. (3) Comparators: Control groups were defined as receiving either placebo treatment or standard pharmacological interventions. (4) The primary outcomes encompassed pain intensity and analgesic response, evaluated through validated instruments, including the Visual Analog Scale (VAS), Numeric Rating Scale (NRS), and Average Daily Pain Score (ADPS). Secondary outcomes comprised the Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ) and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). Pain relief was judged by pain relief rate and clinical effectiveness rate. (5) Study designs: This study included only randomised controlled trials of the drug therapy for PHN.
2.3 Data sources and search strategy
Searches of the electronic literature were conducted in five major databases: The Cochrane Library, Web of Science, PubMed, MEDLINE, and Embase. The search strategy was implemented without restrictions on language, country of origin, or publication type. The retrieval timeframe spanned from the inception of each database to March 2025, ensuring maximal coverage of both historical and contemporary evidence. The search terms were “Neuralgia, Postherpetic,” “Herpes Zoster,” “Drug therapy,” and “randomized controlled trial.” The full literature search strategy is detailed in Supplementary Material S1.
2.4 Screening process
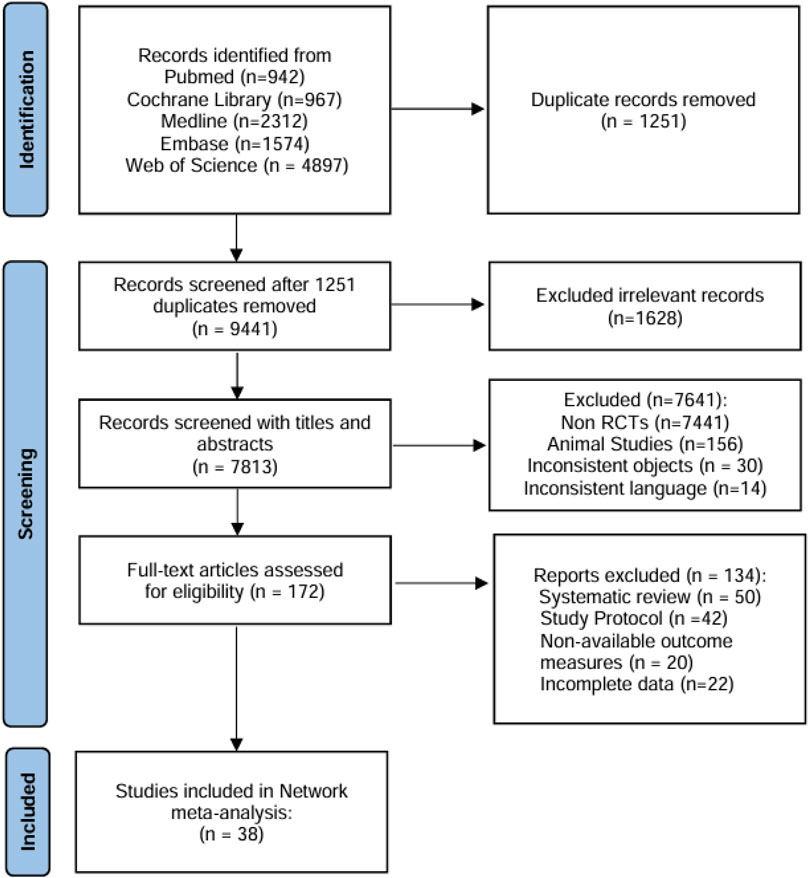
Two reviewers (GZ and XYF) independently screened the literature in the database based on predefined inclusion criteria. The retrieved bibliographic records were imported into NoteExpress, and duplicates were removed. Two reviewers (GZ and XYF) independently screened the titles and abstracts of the retrieved literature. At this stage, studies deemed irrelevant to the study objectives were excluded. The full text of the remaining articles was then further assessed for eligibility for inclusion in the NMA. Disagreements between the two reviewers were initially resolved through structured discussions. If consensus could not be reached, unresolved issues were referred to a third independent reviewer (ZZY) for arbitration until the three reviewers agreed.
2.5 Data extraction
Two reviewers (GZ and XYF) independently performed data extraction and extracted the following information: (1) General information: title, author, year of publication; (2) Study designs: sample size, randomisation, blinding, number of study groups, study duration, number of RCTs enrolled; (3) Intervention and control: drug therapy and control group; (4) Outcomes: primary and secondary outcome indicators, AEs, clinical effectiveness and conclusions.
2.6 Risk of bias assessment
The methodological quality of each included study was independently assessed using the Cochrane RoB 2.0 tool (Sterne et al., 2019), focusing on five critical domains: randomisation process, deviations from intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of the outcome, and selection of the reported result. This evaluation aimed to characterize potential biases as “low risks,” “some concerns,” or “high risks” based on predefined signaling questions and decision algorithms outlined in the tool. Two reviewers (GZ and XYF) independently evaluated each study for bias, resolving disagreements by consulting a third reviewer (ZZY).
2.7 Statistical analysis
Bayesian NMA was conducted using the GeMTC package (version 1.6-2) within the R Studio environment (version 4.4.1), and network evidence was mapped using STATA (18.0). Bayesian NMA under a random-effects model with vague prior information was implemented using Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods. Four parallel MCMC chains were simultaneously initiated, with 50,000 iterations per chain (20,000 burn-in iterations for adaptation and 30,000 posterior sampling iterations) to ensure convergence and minimize autocorrelation. Pooled analyses of all outcomes were performed using a random-effects model to account for inter-study heterogeneity. For continuous variables, treatment effects were expressed as mean difference (MD), whereas dichotomous outcomes were analysed as odds ratios (OR). 95% confidence intervals (CI) were used to analyse all data. Trace and kernel density plots were used to assess the convergence of the data, and sorted plots of the SUCRA were used to assess each outcome indicator for each intervention, with larger SUCRA values indicating that the treatment program was more effective. Model inconsistency was evaluated using the node-splitting method, which assesses discrepancies between direct and indirect evidence within closed-loop network structures. Statistical heterogeneity was quantified by the I2 statistic and Cochran’s Q test (threshold: I2 > 50%, p < 0.05), indicating substantial heterogeneity that required further heterogeneity analysis. An assessment of publication bias in outcome indicators by plotting funnel plots. Funnel plot asymmetry was further evaluated using Egger’s linear regression test (P < 0.05 indicating significant bias). A symmetrical distribution of effect estimates clustered uniformly around the null value (X = 0) was interpreted as no significant evidence of publication bias or small-study effects.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search
A total of 10,692 references were retrieved from five electronic databases, and 1,251 duplicates were removed. Subsequent title and abstract screening excluded 7,641 records deemed irrelevant to neuropathic pain interventions or lacking comparative effectiveness data for PHN therapies. After two reviewers (GZ and XYF) assessed the eligibility of full-text articles, 38 references were finally included for the NMA (Figure 1).
3.2 Study characteristics
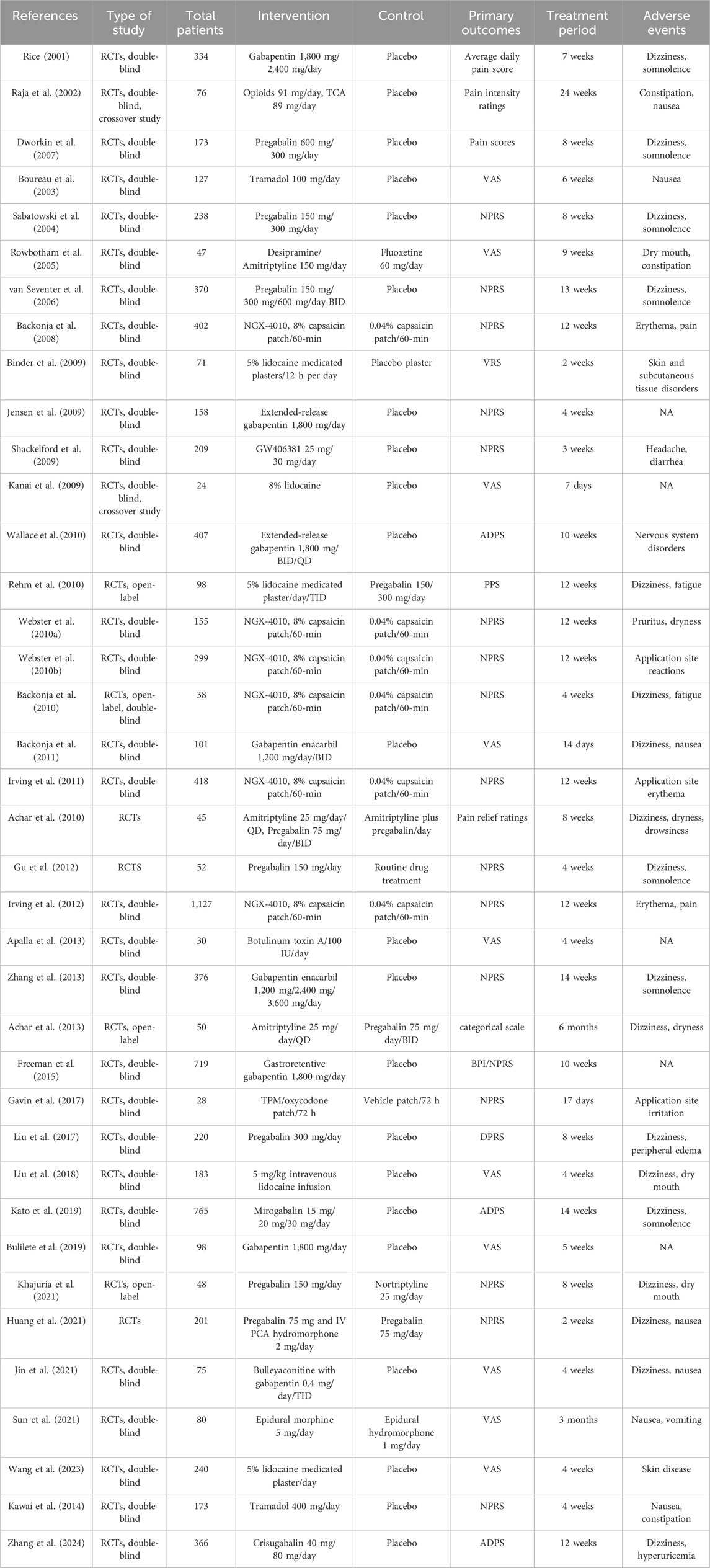
A total of 38 studies were included in the analysis, with 26 two-arm studies, nine three-arm studies, and three four-arm studies. The included studies were published over a time span of 2001-2024 and enrolled 8,621 participants with treatment durations ranging from 7 days to 6 months. In this study, the references included were both RCTs, and the specific characteristics of the references were shown in Table 1.
3.3 Risk of bias results
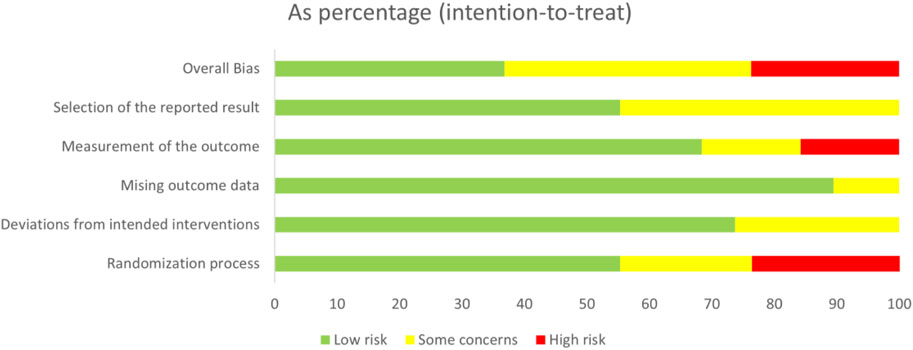
Among the 38 included RCTs, nine studies (24%) were assessed as having a high risk of bias, primarily attributed to unclear randomization processes, e.g., flaws in randomization, lack of blinding could lead to exaggerated efficacy, resulting in a spurious upgrading of the drug in the SUCRA rankings, and thus affecting the reliability of the SUCRA rankings. 15 studies (39%) were rated as having some concerns, primarily attributed to unclear outcome measurement protocols and the selective reporting of results. For example, the unpublished of negative results may have led to an underestimation of the placebo effect and thus a lower SUCRA ranking. 14 studies (37%) were assessed as having a low risk of bias. The results of the quality assessment of all studies were illustrated in Figure 2, which showed an overview of the judgments for each risk of bias item, indicated as a percentage of all included studies, and revealed a summary of the risk of bias by the two reviewers (GZ and XYF).
3.4 Statistical analysis results
3.4.1 Model convergence evaluation result
In the Bayesian framework constructed for this study, all Markov chains achieved stable convergence after 50,000 iterations, with trace plots shown with stationary trajectories and minimal autocorrelation. The Brooks-Gelman-Rubin diagnostic results demonstrated satisfactory model convergence, as evidenced by the median and 97.5th percentile of the potential scale reduction factor (PSRF) stabilized toward 1.0 after 20,000–30,000 iterations, with both univariate PSRF and multivariate PSRF (mPSRF) values remaining below 1.05 (Figure 3). Trace and density plots demonstrated robust convergence characteristics, with bandwidth parameters asymptotically approaching 0 and stabilized after 50,000 iterations, indicating stationary posterior distributions across all Markov chains (Supplementary Material S2).
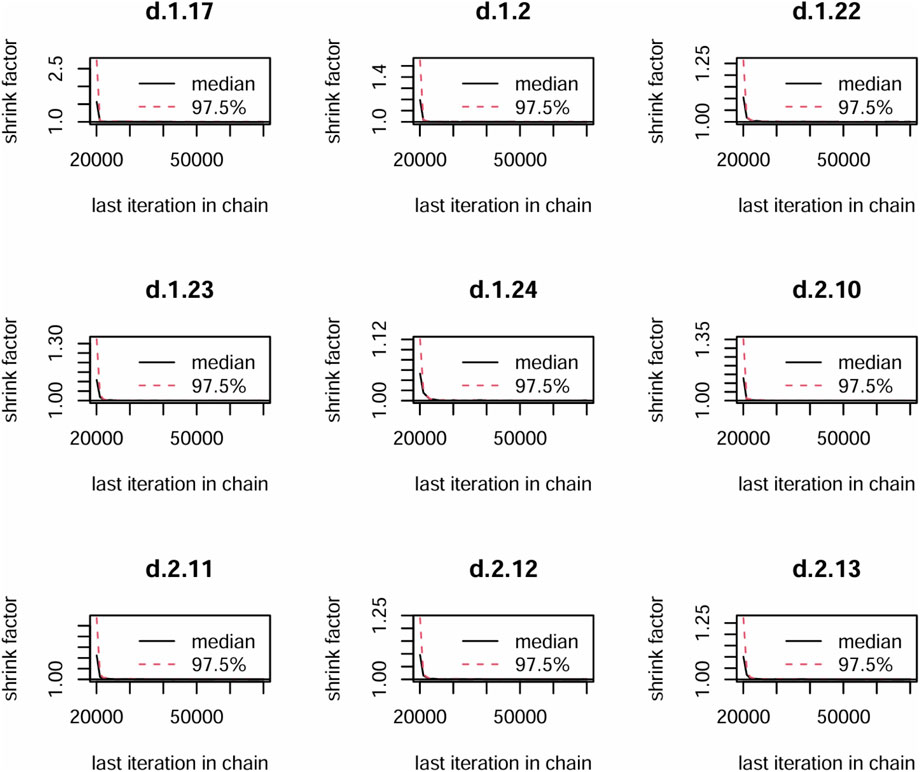
Figure 3. The Primary outcome convergence diagnostic map. 1 = Pregabalin, 2 = Placebo, 17 = 5% lidocaine medicated plasters, 22 = hydromorphone, 23 = Routine drug treatment, 24 = Nortriptyline, 10 = 8% lidocaine, 11 = TCAs, 12 = Gabapentin Enacarbil 1,200 mg, 13 = Gabapentin Enacarbil 2,400 mg.
3.4.2 Network evidence diagram
The specific network evidence maps were created for the different outcome data (Figure 4). Node sizes were weighted to reflect the patient cohort size within each intervention, while the thickness of the line was proportionally scaled to the cumulative sample size of participants involved in pairwise comparisons. Pain intensity outcomes were reported in 28 studies and involved 27 treatment modalities, which formed 11 closed loops. The SFMPQ outcomes were reported by 8 RCTs, which encompassed 15 distinct therapeutic modalities, and seven closed-loop comparisons were generated through the synthesis of direct and indirect evidence. Sleep quality outcomes were reported by 5 RCTs, which included seven different treatment modalities. A single closed-loop comparison was formed through the synthesis of direct and indirect evidence among the placebo, TCAs, and opioids. Clinical effective rates were reported by 27 RCTs, which included 32 distinct therapeutic modalities. Six therapeutic modalities failed to form closed-loop comparisons due to insufficient direct or indirect evidence for Bayesian network meta-analyses. AEs were reported by 29 RCTs, which included 32 distinct therapeutic modalities; eight therapeutic modalities failed to form closed-loop comparisons.
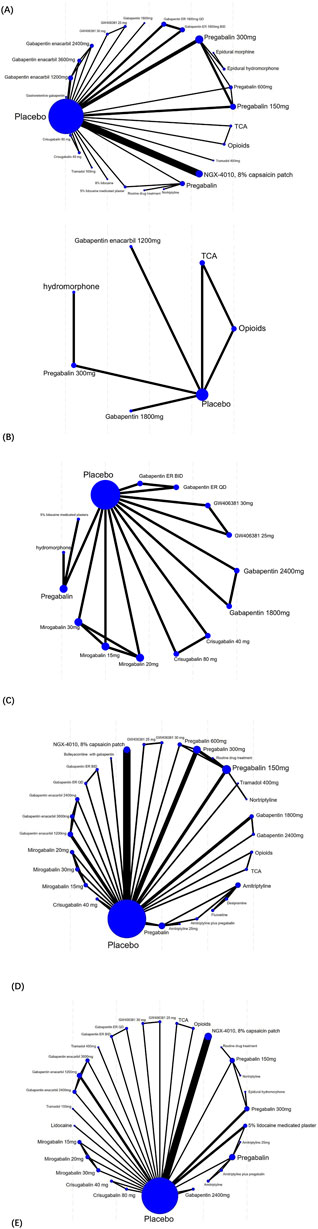
Figure 4. Network plot of included studies. ((A) for the pain intensity outcomes, (B) for the sleep quality outcomes, (C) for the SFMPQ outcomes, (D) for the clinical effective rates, (E) for the AEs).
3.4.3 Network meta-analysis results of pain scores
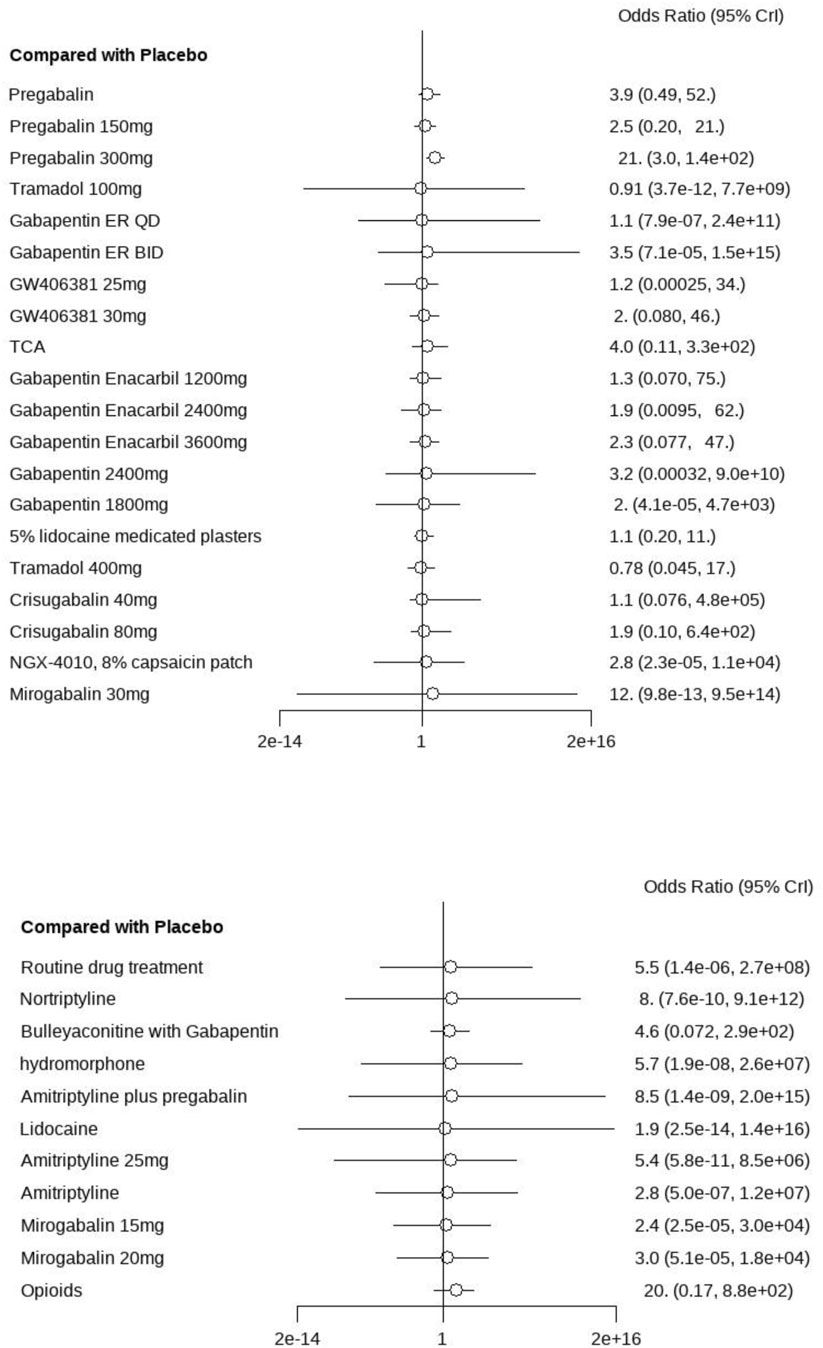
A total of 28 studies encompassing 6,946 patients diagnosed with PHN were included in this NMA. Compared with placebo, no statistically significant differences were observed for routine drug treatment (MD = 0.35, 95% CI: [−1.4, 2.1]) and Gabapentin 1,800 mg (MD = 0.30, 95% CI: [−1.0, 1.6]) in pain reduction outcomes, whereas all other therapeutic modalities demonstrated statistically significant efficacy. Forest plots were detailed in Supplementary Material S3. A comprehensive pairwise comparison matrix was constructed to evaluate all therapeutic interventions (Supplementary Material S4). Statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) were identified in 29 pairwise comparisons of interventions, as evidenced by non-overlapping 95% CI in pain reduction outcomes. A statistically significant reduction in pain intensity was demonstrated for the NGX-4010 8% capsaicin patch (MD = −9.20, 95% CI: [−12.0, −6.60]). The pain score results for all interventions were ranked according to SUCRA values, and the complete ranked effects were shown in Figure 5, the NGX-4010 8% capsaicin patch was identified as demonstrating the highest probability of superior efficacy (SUCRA = 0.98), followed by tramadol 100 mg (SUCRA = 0.93) and gastroretentive gabapentin (SUCRA = 0.88). The Consistency evaluation was performed, and the deviance information criterion (DIC) values demonstrated the absence of global inconsistency (consistency model DIC = 125.6, UME model DIC = 127.39). Local inconsistency evaluation was conducted using the node-splitting method. No statistically significant differences were observed between direct and indirect evidence comparisons across all intervention nodes (P > 0.1), indicating robust consistency in the network topology (Figure 6). Heterogeneity testing was performed, and I2 = 41%, P > 0.1, which suggested that there was no significant heterogeneity in the interventions between groups.
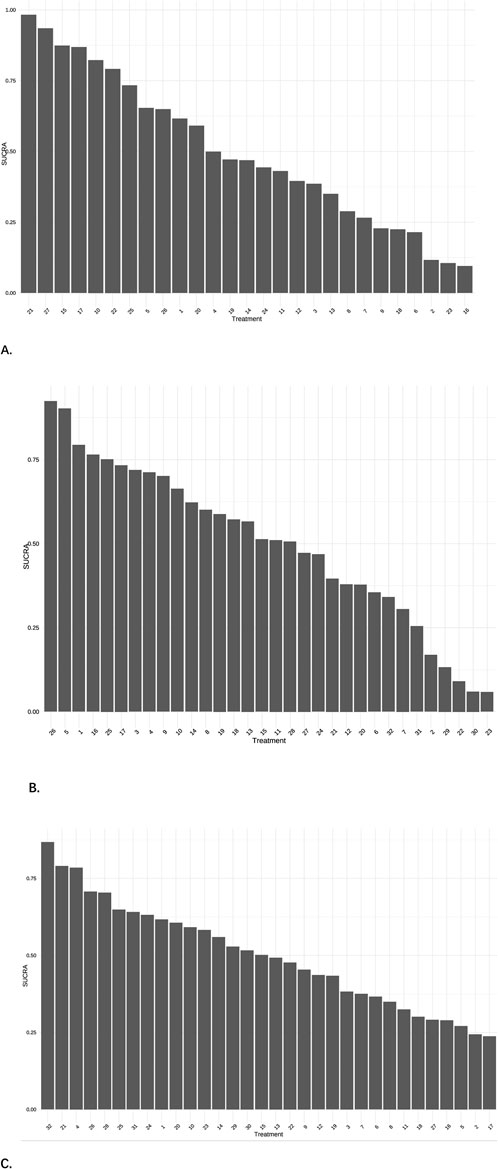
Figure 5. Cumulative probability plots. (A) The results of pain scores, 21 = NGX-4010, 8% capsaicin patch, 27 = Tramadol 100 mg, 15 = Gastroretentive Gabapentin. (B) The results of effective rate, 26 = Amitriptyline plus pregabalin, 5 = Pregabalin 600 mg, 1 = Pregabalin. (C) The results of AEs, 32 = Opioids, 21 = Mirogabalin 30 mg, 4 = Pregabalin 300 mg.
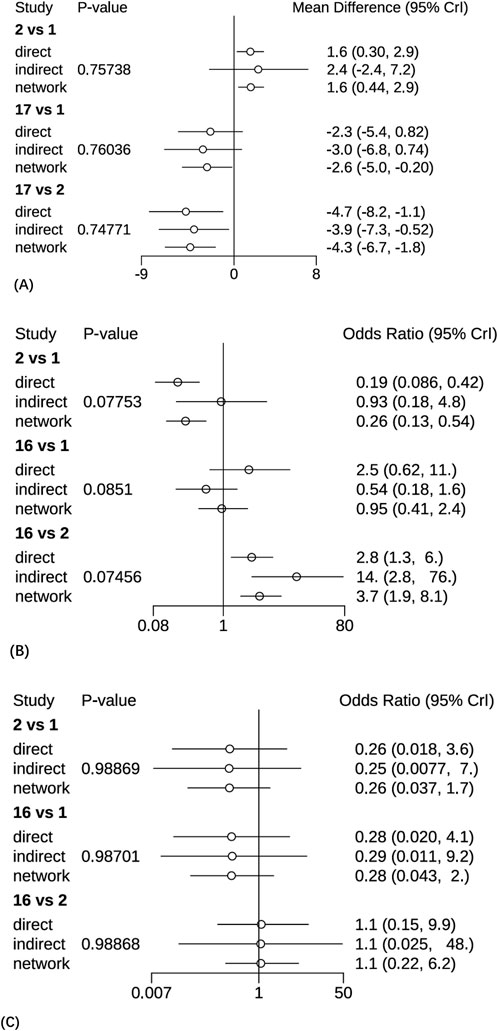
Figure 6. The Node-splitting methods for forest plots. (A) The pain intensity outcomes, 1 = Pregabalin, 2 = Placebo, 17 = 5% lidocaine medicated plasters. (B) The clinical effective rates, 1 = Pregabalin, 2 = Placebo, 16 = 5% lidocaine medicated plasters. (C) The AEs, 1 = Pregabalin, 2 = Placebo, 16 = 5% lidocaine medicated plasters.
3.4.4 Network meta-analysis results of the effective rate
A total of 27 studies involving 6,864 patients were included in this analysis. All interventions demonstrated statistically significant efficacy when compared to placebo (Supplementary Material S3), except for routine drug treatment (OR = 0.39, 95% CI: [0.073, 1.8]), nortriptyline (OR = 0.19, 95% CI: [0.0063, 1.8]), amitriptyline (OR = 0.42, 95% CI: [0.040, 3.0]), and fluoxetine (OR = 0.17, 95% CI: [0.0096, 2.2]). A pairwise comparison matrix was generated (Supplementary Material S4), and statistically significant differences were found in the 131 intervention comparisons evaluated. The clinical effective rate of nortriptyline (−4.03, 95% CI: [−8.01, −1.14]) for the treatment of PHN was remarkable. The efficacy hierarchy of all interventions was ranked based on the SUCRA values (Figure 5). Amitriptyline plus pregabalin demonstrated the highest probability of clinical superiority (SUCRA = 0.92), followed by pregabalin 600 mg (SUCRA = 0.90) and standard-dose pregabalin (SUCRA = 0.79). The Consistency evaluation was performed, and DIC values demonstrated the absence of global inconsistency (consistency model DIC = 136.1, UME model DIC = 134.93). No statistically significant differences were observed between direct and indirect evidence comparisons across all intervention nodes (P > 0.05), indicating robust consistency in the network topology (Figure 6). Heterogeneity testing was performed, and I2 = 0%, P > 0.05, which suggested that there was no significant heterogeneity in the interventions between groups.
3.4.5 Network meta-analysis results of SFMPQ scores
A total of eight studies involving 2,583 patients were included in this analysis. All interventions demonstrated statistically significant efficacy when compared to placebo (Supplementary Material S3). The results of SFMPQ for all interventions were ranked according to SUCRA values, and the complete ranked effects were shown in Supplementary Material S5. Hydromorphone was identified as demonstrating the highest probability of superior efficacy (SUCRA = 0.87), followed by 5% lidocaine medicated plasters (0.79) and Mirogabalin 30 mg (0.71). The Consistency evaluation was performed, and DIC values demonstrated the absence of global inconsistency (consistency model DIC = 44.08, UME model DIC = 44.06).
3.4.6 Network meta-analysis results of PSQI scores
A total of five studies involving 678 patients were included in this analysis. All interventions demonstrated statistically significant efficacy when compared to placebo (Supplementary Material S3), except Gabapentin 1,800 mg (MD = 11.0, 95% CI: [−5.8, 27.0]) and Opioids (MD = 0.088, 95% CI: [−13.0, 14.0]). The results of sleep quality for all interventions were ranked according to SUCRA values, and the complete ranked effects were shown in Supplementary Material S5. The improvement in sleep quality was most prominently demonstrated by hydromorphone (0.75), followed by gabapentin enacarbil 1,200 mg (0.61) and TCA (0.53). The Consistency evaluation was performed, and DIC values demonstrated the absence of global inconsistency (consistency model DIC = 21.94, UME model DIC = 21.98).
3.4.7 Network meta-analysis results of adverse events
A total of 29 studies encompassing 7,018 patients were systematically analyzed for AE incidence rates associated with pharmacological interventions. A significantly higher incidence of AEs was observed with opioids (OR = 20.0, 95% CI: [1.2, 4.3e+02]) compared to placebo, predominantly manifesting as constipation and nausea (Supplementary Material S3). No severe AEs were reported across the included studies. A pairwise comparison matrix was generated (Supplementary Material S4), and statistically significant differences were found in the 19 intervention comparisons evaluated. Opioids demonstrated a significantly higher incidence of AEs compared to other interventions (−3.28, 95% CI: [−7.13, 0.43]). The results of AE incidence rates for all interventions were ranked according to SUCRA values, and the complete ranked effects were shown in Figure 5. Opioids were identified as demonstrating the highest probability of superior efficacy (0.87), followed by Mirogabalin 30 mg (0.79) and Pregabalin 300 mg (0.78). The Consistency evaluation was performed, and DIC values demonstrated the absence of global inconsistency (consistency model DIC = 137.1, UME model DIC = 137.57). No statistically significant differences were observed between direct and indirect evidence comparisons across all intervention nodes (P > 0.05), indicating robust consistency in the network topology (Figure 6). Heterogeneity testing was conducted across intervention groups, these findings indicate significant heterogeneity in treatment effects between intervention arms (I2 pair = 84.01%, I2 cons = 64.27%). A network meta-regression analysis was conducted to explore sources of heterogeneity across intervention groups (Figure 7). The Rob assessment scores were incorporated into the model to evaluate their influence on the effect size (OR). Following the inclusion of Rob scores, the model heterogeneity was substantially reduced (I2 = 2%), indicating that methodological quality accounted for the majority of variability in the network. The model heterogeneity was substantially reduced (I2 = 2%), confirming that methodological quality stratification through Rob scoring was demonstrated to exert significant control over residual heterogeneity in the pooled estimates. However, the use of Rob as a covariate was mainly due to the significant impact of literature quality on heterogeneity. High risk of bias studies might exaggerate effect sizes, leading to increased heterogeneity, while low-quality studies might selectively report positive results, leading to a discrete distribution of effect sizes.
3.4.8 Network meta-analysis results of publication bias
Publication bias and small sample effect for the primary outcomes, clinical response rates, and AEs incidences were assessed using comparative-adjusted funnel plots, as detailed in Supplementary Material S6. A statistically significant risk of publication bias or small sample effect was identified for the clinical response rate through Egger’s regression test (P < 0.01), suggesting potential compromise in the reliability of pooled estimates.
4 Discussion
A systematic comparison of therapeutic efficacy and safety profiles among drug interventions for PHN was conducted through Bayesian NMA. The evaluated interventions included calcium channel modulators (pregabalin, gabapentin), TCAs (amitriptyline), 5% lidocaine medicated plasters, opioids, and capsaicin patches.
Significant advantages in pain relief were demonstrated by the NGX-4010 8% capsaicin patch. This therapeutic effect is mechanistically attributed to capsaicin’s role as a selective agonist of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor, which induces nociceptor defunctionalization through sustained calcium influx-mediated depolarization (Bode and Dong, 2011; Derry et al., 2013). Subsequent action potential initiation and propagation along C-fibers are attenuated due to TRPV1 receptor desensitization, thereby interrupting peripheral pain signaling pathways (Bley, 2004). After sustained exposure to capsaicin, TRPV 1-containing sensory axons might enter a prolonged period of inactivity, blocking pain transmission and leading to a reduced pain response. NGX-4010 8% capsaicin patch was a highly concentrated capsaicin skin patch that had been proven to relieve pain (Backonja et al., 2010; Backonja et al., 2008; Irving et al., 2011). Hydromorphone showed significant benefits in improved sleep quality and decreased SFMPQ scores. PHN could last for weeks or longer, severely disrupting the sleep and daily life of the patient (Colloca et al., 2017; Johnson et al., 2010). Hydromorphone is classified as a semi-synthetic derivative of morphine, analgesic effects being mediated through selective agonism of mu-opioid receptors within the central nervous system (CNS) (Quigley, 2002). Although hydromorphone had been used to treat severe pain, its current use in PHN was less (Mahler and Forrest, 1975; Dworkin et al., 2007). Huang2021’s study concluded that hydromorphone treatment of PHN resulted in a significant decrease in PSQI scores and greater improvement in the sleep of patients (Huang et al., 2021). Amitriptyline plus pregabalin had the highest clinical efficacy rate, this finding highlighted that optimization strategies for combination therapies would be a priority in future research agendas (Gonzalez-Alvarez et al., 2023; Martín Pérez et al., 2023). However, Opioids had the highest incidence of AEs, with the most common side effects reported as constipation and nausea. The analgesic effects of opioids were found to be effective and were gradually used in recent years for bursts of pain in patients with PHN (Portenoy et al., 1990; Arnér and Meyerson, 1988; Watson and Babul, 1998; Jadad et al., 1992). However, some elderly patients might not be able to tolerate the side effects of opioids, and caution should be exercised when using opioids.
The DIC values calculated for both consistency and inconsistency models were demonstrated to exhibit proximity, indicating robust agreement in model fit across the NMA framework (Ades et al., 2006). Heterogeneity tests were performed and found that the NMA for AE incidence indicated significant heterogeneity of interventions between groups, which was greatly reduced by network regressivity analysis with RoB as a covariate, and this indicated that the quality of the literature had a significant effect on heterogeneity. Publication bias and small-sample effects for clinical effectiveness rates were assessed using comparison-adjusted funnel plots. A statistically significant risk of publication bias or small-sample effect (P < 0.01) for clinical effectiveness rates was determined by the Egger regression test, which suggested that the reliability of the combined estimates may be compromised. Egger regression tests showed that asymmetry in clinical effectiveness rates might have an impact on pain intensity outcomes: (1) distortion of effect sizes and overestimation of pain relief: selective publication of positive results might lead to exaggerated drug efficacy, whereas the absence of negative results might lead to distorted safety assessments. (2) Decreased reliability of efficacy ranking: Publication bias caused an uneven evidence base for different drugs, which led to lower SUCRA rankings. However, publication bias also had an impact on the efficacy assessment of PHN drug treatment, so it was recommended to optimize the strategy of drug treatment in the clinic.
Ultimately, it was anticipated that the direct and indirect evidence synthesized through this investigation would be systematically leveraged to evaluate the comparative efficacy and safety of various drug interventions for PHN, thereby enabling the formulation of evidence-based therapeutic strategies to optimize pain management protocols for this neurological condition.
5 Limitations
There were some limitations in this study. Firstly, there were flaws in the study design, and a portion of the included RCTs had a high risk of bias in quality assessment, which might lead to an increase in the heterogeneity of the study results. Secondly, the Egger test indicated a publication bias or a small sample effect (P < 0.01) in the clinical effective rate, which might lead to unreliable results. Third, due to the limited amount of literature included in this study, certain interventions had a low number of cases in a certain efficacy indicator, which biased the results of the study. In conclusion, to be able to provide more scientific evidence, more high-quality RCTs are needed for further analysis in the future.
6 Conclusion
For pain management in PHN, capsaicin patches showed a statistically significant intervention on pain intensity, and hydromorphone was significant in improving sleep quality and reducing pain questionnaire scores. However, calcium channel modulators (pregabalin, gabapentin) were more relevant in the clinical management of PHN patients in terms of comprehensive treatment as well as improvement in quality of life.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZG: Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Software, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Methodology. YX: Validation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Investigation, Software, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Software, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Science and Technology Co-construction project of the National Demonstration Zone for Comprehensive Reform of Traditional Chinese Medicine (GZY-KJS-ZJ-2025-016). The trial sponsor is Hangzhou Third Hospital, Affiliated to the Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (No. 38, West Lake Road, Shangcheng District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province 310000, China, 86-571-87823126).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1614587/full#supplementary-material
References
Achar, A., Bisai, S., Biswas, R., Besra, M., Guharay, T., and Ghosh, T. (2013). Amitriptyline versus pregabalin in post herpetic neuralgia: a randomized clinical trial. Turkish J. Dermatology/Türk Dermatoloji Dergisi 7 (3), 145–149. doi:10.4274/tdd.1115
Achar, A., Chatterjee, G., Ray, T. G., and Naskar, B. (2010). Comparative study of clinical efficacy with amitriptyline, pregabalin, and amitriptyline plus pregabalin combination in postherpetic neuralgia. Indian J. Dermatology Venereol. & Leprology 76 (1), 63–65. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.58686
Ades, A. E., Sculpher, M., Sutton, A., Abrams, K., Cooper, N., Welton, N., et al. (2006). Bayesian methods for evidence synthesis in cost-effectiveness analysis. Pharmacoeconomics 24 (1), 1–19. doi:10.2165/00019053-200624010-00001
Apalla, Z., Sotiriou, E., Lallas, A., Lazaridou, E., and Ioannides, D. (2013). Botulinum toxin A in postherpetic neuralgia: a parallel, randomized, double-blind, single-dose, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. J. Pain 29 (10), 857–864. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e31827a72d2
Arnér, S., and Meyerson, B. A. (1988). Lack of analgesic effect of opioids on neuropathic and idiopathic forms of pain. Pain 33 (1), 11–23. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(88)90198-4
Backonja, M., Wallace, M. S., Blonsky, E. R., Cutler, B. J., Malan, P., Rauck, R., et al. (2008). NGX-4010, a high-concentration capsaicin patch, for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomised, double-blind study. Lancet Neurol. 7 (12), 1106–1112. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70228-X
Backonja, M. M., Canafax, D. M., and Cundy, K. C. (2011). Efficacy of gabapentin enacarbil vs placebo in patients with postherpetic neuralgia and a pharmacokinetic comparison with oral gabapentin. Pain Med. 12 (7), 1098–1108. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2011.01139.x
Backonja, M. M., Malan, T. P., Vanhove, G. F., and Tobias, J. K.C102/106 Study Group (2010). NGX-4010, a high-concentration capsaicin patch, for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double-blind, controlled study with an open-label extension. Pain Med. 11 (4), 600–608. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00793.x
Binder, A., Bruxelle, J., Rogers, P., Hans, G., Bösl, I., and Baron, R. (2009). Topical 5% lidocaine (lignocaine) medicated plaster treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational efficacy and safety trial. Clin. Drug Investig. 29 (6), 393–408. doi:10.2165/00044011-200929060-00003
Bley, K. R. (2004). Recent developments in transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 1 agonist-based therapies. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 13 (11), 1445–1456. doi:10.1517/13543784.13.11.1445
Bode, A. M., and Dong, Z. (2011). The two faces of capsaicin. Cancer Res. 71 (8), 2809–2814. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3756
Boureau, F., Legallicier, P., and Kabir-Ahmadi, M. (2003). Tramadol in post-herpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 104 (1–2), 323–331. doi:10.1016/s0304-3959(03)00020-4
Bulilete, O., Leiva, A., Rullán, M., Roca, A., and Llobera, J.PHN Group (2019). Efficacy of gabapentin for the prevention of postherpetic neuralgia in patients with acute herpes zoster: a double blind, randomized controlled trial. PLoS One 14 (6), e0217335. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0217335
Chen, N., Li, Q., Yang, J., Zhou, M., Zhou, D., and He, L. (2014). Antiviral treatment for preventing postherpetic neuralgia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014 (2), Cd006866. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006866.pub3
Colloca, L., Ludman, T., Bouhassira, D., Baron, R., Dickenson, A. H., Yarnitsky, D., et al. (2017). Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 3, 17002. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.2
Corcuera-Munguia, M., Gil-Prieto, R., Garcia-Carretero, R., and Gil-de-Miguel, A. (2023). Hospitalization burden related to Herpes zoster infection in Spain (2016-2019). Infect. Dis. Ther. 12 (1), 143–156. doi:10.1007/s40121-022-00717-6
Cuenca-Zaldívar, J. N., Del Corral-Villar, C., García-Torres, S., Araujo-Zamora, R., Gragera-Peña, P., Martínez-Lozano, P., et al. (2025). Fourteen-year retrospective cohort study on the impact of climatic factors on chronic musculoskeletal pain: a Spanish primary care analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 28 (3), e70125. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.70125
Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M. J., Chandler, J., Welch, V. A., Higgins, J. P., et al. (2019). Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 10 (10), Ed000142. doi:10.1002/14651858.ED000142
Derry, S., Sven-Rice, A., Cole, P., Tan, T., and Moore, R. A. (2013). Topical capsaicin (high concentration) for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (2), Cd007393. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007393.pub3
Dworkin, R. H., O’Connor, A. B., Backonja, M., Farrar, J. T., Finnerup, N. B., Jensen, T. S., et al. (2007). Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations. Pain 132 (3), 237–251. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.08.033
Finnerup, N. B., Attal, N., Haroutounian, S., McNicol, E., Baron, R., Dworkin, R. H., et al. (2015). Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 14 (2), 162–173. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70251-0
Forbes, H. J., Bhaskaran, K., Thomas, S. L., Smeeth, L., Clayton, T., Mansfield, K., et al. (2016). Quantification of risk factors for postherpetic neuralgia in herpes zoster patients: a cohort study. Neurology 87 (1), 94–102. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002808
Fornasari, D., Magni, A., Pais, P., Palao, T., Polati, E., and Sansone, P. (2022). Changing the paradigm in postherpetic neuralgia treatment: lidocaine 700 mg medicated plaster. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 26 (10), 3664–3676. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202205_28862
Freeman, R., Wallace, M. S., Sweeney, M., and Backonja, M. M. (2015). Relationships among pain quality, pain impact, and overall improvement in patients with postherpetic Neuralgia treated with gastroretentive Gabapentin. Pain Med. 16 (10), 2000–2011. doi:10.1111/pme.12791
Gavin, P. D., Tremper, L., Smith, A., Williams, G., and Brooker, C. (2017). Transdermal oxycodone patch for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Pain Manag. 7 (4), 255–267. doi:10.2217/pmt-2016-0067
Gonzalez-Alvarez, M. E., Sanchez-Romero, E. A., Turroni, S., Fernandez-Carnero, J., and Villafañe, J. H. (2023). Correlation between the altered gut microbiome and lifestyle interventions in chronic widespread pain patients: a systematic review. Med. Kaunas 59 (2), 256. doi:10.3390/medicina59020256
Gross, G. E., Eisert, L., Doerr, H. W., Fickenscher, H., Knuf, M., Maier, P., et al. (2020). S2k guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 18 (1), 55–78. doi:10.1111/ddg.14013
Gu, L.-L., Zhang, X-x., and Zhang, D-y. (2012). Efficacy and safety of pregabalin in patients with post-herpetic neuralgia. Chinese J. New Drugs 21 (16).
Han, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, N., He, L., Zhou, M., and Zhu, C. (2013). Corticosteroids for preventing postherpetic neuralgia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (3), Cd005582. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005582.pub4
Huang, Y., Xu, C., Zeng, T., Li, Z., Xia, Y., Tao, G., et al. (2021). Intravenous patient-controlled analgesia hydromorphone combined with pregabalin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a multicenter, randomized controlled study. Korean J. Pain 34 (2), 210–216. doi:10.3344/kjp.2021.34.2.210
Hutton, B., Salanti, G., Caldwell, D. M., Chaimani, A., Schmid, C. H., Cameron, C., et al. (2015). The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern Med. 162 (11), 777–784. doi:10.7326/M14-2385
Irving, G., Backonja, M., Rauck, R., Webster, L. R., Tobias, J. K., and Vanhove, G. F. (2012). NGX-4010, a capsaicin 8% dermal patch, administered alone or in combination with systemic neuropathic pain medications, reduces pain in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Clin. J. Pain 28 (2), 101–107. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e318227403d
Irving, G. A., Backonja, M. M., Dunteman, E., Blonsky, E. R., Vanhove, G. F., Lu, S. P., et al. (2011). A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled study of NGX-4010, a high-concentration capsaicin patch, for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Pain Med. 12 (1), 99–109. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2010.01004.x
Izurieta, H. S., Wu, X., Forshee, R., Lu, Y., Sung, H. M., Agger, P. E., et al. (2021). Recombinant zoster vaccine (Shingrix): real-world effectiveness in the first 2 years post-licensure. Clin. Infect. Dis. 73 (6), 941–948. doi:10.1093/cid/ciab125
Jadad, A. R., Carroll, D., Glynn, C. J., Moore, R. A., and McQuay, H. J. (1992). Morphine responsiveness of chronic pain: double-blind randomised crossover study with patient-controlled analgesia. Lancet 339 (8806), 1367–1371. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(92)91194-d
Jansen, J. P., and Naci, H. (2013). Is network meta-analysis as valid as standard pairwise meta-analysis? It all depends on the distribution of effect modifiers. BMC Med. 11, 159. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-159
Jensen, M. P., Chiang, Y. K., and Wu, J. (2009). Assessment of pain quality in a clinical trial of gabapentin extended release for postherpetic neuralgia. Clin. J. Pain 25 (4), 286–292. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e318192bf87
Jin, Y. Y., Qin, C. H., Duan, B. L., Huang, Y. Q., and Ma, K. (2021). Clinical efficacy of bulleyaconitine A combined with gabapentin on postherpetic neuralgia. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi 101 (43), 3575–3580. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210817-01867
Johnson, R. W., Bouhassira, D., Kassianos, G., Leplège, A., Schmader, K. E., and Weinke, T. (2010). The impact of herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia on quality-of-life. BMC Med. 8, 37. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-8-37
Johnson, R. W., and Rice, A. S. (2014). Clinical practice. Postherpetic neuralgia. N. Engl. J. Med. 371 (16), 1526–1533. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1403062
Kanai, A., Kumaki, C., Niki, Y., Suzuki, A., Tazawa, T., and Okamoto, H. (2009). Efficacy of a metered-dose 8% lidocaine pump spray for patients with post-herpetic neuralgia. Pain Med. 10 (5), 902–909. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00662.x
Kato, J., Matsui, N., Kakehi, Y., Murayama, E., Ohwada, S., and Sugihara, M. (2019). Mirogabalin for the management of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study in Asian patients. Pain 160 (5), 1175–1185. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001501
Kawai, K., Gebremeskel, B. G., and Acosta, C. J. (2014). Systematic review of incidence and complications of herpes zoster: towards a global perspective. BMJ Open 4 (6), e004833. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2014-004833
Khajuria, K., Gupta, S., Raj Dogra, D., Kumar, D., and Khajuria, V. (2021). Comparison of Pregabalin and nortriptyline on efficacy and safety in postherpetic Neuralgia. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 14 (7), 74–76. doi:10.22159/ajpcr.2021.v14i7.41872
Kim, H. J., Ahn, H. S., Lee, J. Y., Choi, S. S., Cheong, Y. S., Kwon, K., et al. (2017). Effects of applying nerve blocks to prevent postherpetic neuralgia in patients with acute herpes zoster: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean J. Pain 30 (1), 3–17. doi:10.3344/kjp.2017.30.1.3
Liu, H., Lu, F., Zhou, D., Yin, Y., Li, J., Yang, B., et al. (2018). The analgesic and emotional response to intravenous lidocaine infusion in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Clin. J. Pain 34 (11), 1025–1031. doi:10.1097/AJP.0000000000000623
Liu, Q., Chen, H., Xi, L., Hong, Z., He, L., Fu, Y., et al. (2017). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pregabalin for postherpetic neuralgia in a population of Chinese patients. Pain Pract. 17 (1), 62–69. doi:10.1111/papr.12413
Mahler, D. L., and Forrest, W. H. (1975). Relative analgesic potencies of morphine and hydromorphone in postoperative pain. Anesthesiology 42 (5), 602–607. doi:10.1097/00000542-197505000-00021
Martín Pérez, S. E., Martín Pérez, I. M. M., Sánchez-Romero, E. A., Sosa Reina, M. D. S., Muñoz Fernández, A. C., Alonso Pérez, J. L., et al. (2023). Percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (PENS) for infrapatellar saphenous neuralgia management in a patient with myasthenia gravis (MG). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20 (3), 2617. doi:10.3390/ijerph20032617
Nahm, F. S., Kim, S. H., Kim, H. S., Shin, J. W., Yoo, S. H., Yoon, M. H., et al. (2013). Survey on the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in Korea; multicenter study of 1,414 patients. Korean J. Pain 26 (1), 21–26. doi:10.3344/kjp.2013.26.1.21
Portenoy, R. K., Foley, K. M., and Inturrisi, C. E. (1990). The nature of opioid responsiveness and its implications for neuropathic pain: new hypotheses derived from studies of opioid infusions. Pain 43 (3), 273–286. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(90)90025-9
Quigley, C. (2002). Hydromorphone for acute and chronic pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (1), Cd003447. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003447
Raja, S. N., Haythornthwaite, J. A., Pappagallo, M., Clark, M. R., Travison, T. G., Sabeen, S., et al. (2002). Opioids versus antidepressants in postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 59 (7), 1015–1021. doi:10.1212/wnl.59.7.1015
Rehm, S., Binder, A., and Baron, R. (2010). Post-herpetic neuralgia: 5% lidocaine medicated plaster, pregabalin, or a combination of both? A randomized, open, clinical effectiveness study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 26 (7), 1607–1619. doi:10.1185/03007995.2010.483675
Rice, A. S. C., and Maton, S.Postherpetic Neuralgia Study Group (2001). Gabapentin in postherpetic neuralgia: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study. Pain 94 (2), 215–224. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(01)00407-9
Rowbotham, M. C., Reisner, L. A., Davies, P. S., and Fields, H. L. (2005). Treatment response in antidepressant-naïve postherpetic neuralgia patients: double-blind, randomized trial. J. Pain 6 (11), 741–746. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2005.07.001
Sabatowski, R., Gálvez, R., Cherry, D. A., Jacquot, F., Vincent, E., Maisonobe, P., et al. (2004). Pregabalin reduces pain and improves sleep and mood disturbances in patients with post-herpetic neuralgia: results of a randomised, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Pain 109 (1-2), 26–35. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.01.001
Schmader, K. E. (2002). Epidemiology and impact on quality of life of postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. Clin. J. Pain 18 (6), 350–354. doi:10.1097/00002508-200211000-00002
Schutzer-Weissmann, J., and Farquhar-Smith, P. (2017). Post-herpetic neuralgia - a review of current management and future directions. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 18 (16), 1739–1750. doi:10.1080/14656566.2017.1392508
Shackelford, S., Rauck, R., Quessy, S., Blum, D., Hodge, R., and Philipson, R. (2009). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a selective COX-2 inhibitor, GW406381, in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. J. Pain 10 (6), 654–660. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2009.01.328
Shamseer, L., Moher, D., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., et al. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. Bmj 350, g7647. doi:10.1136/bmj.g7647
Sterne, J. A. C., Savović, J., Page, M. J., Elbers, R. G., Blencowe, N. S., Boutron, I., et al. (2019). RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 366, l4898. doi:10.1136/bmj.l4898
Sun, X., Wei, Z., Lin, H., Jit, M., Li, Z., and Fu, C. (2021). Incidence and disease burden of Herpes zoster in the population aged ≥50 years in China: data from an integrated health care network. J. Infect. 82 (2), 253–260. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.12.013
van Seventer, R., Feister, H. A., Young, J. P., Stoker, M., Versavel, M., and Rigaudy, L. (2006). Efficacy and tolerability of twice-daily pregabalin for treating pain and related sleep interference in postherpetic neuralgia: a 13-week, randomized trial. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 22 (2), 375–384. doi:10.1185/030079906x80404
Wallace, M. S., Irving, G., and Cowles, V. E. (2010). Gabapentin extended-release tablets for the treatment of patients with postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study. Clin. Drug Investig. 30 (11), 765–776. doi:10.2165/11539520-000000000-00000
Wang, A., Li, H., Xie, Z., Li, L., Jiang, X., Guo, Q., et al. (2023). Randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical Study on the efficacy and safety of lidocaine patches in Chinese patients with postherpetic Neuralgia. Dermatol. Ther. (Heidelb). 13 (7), 1477–1487. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00938-8
Watson, C. P., and Babul, N. (1998). Efficacy of oxycodone in neuropathic pain: a randomized trial in postherpetic neuralgia. Neurology 50 (6), 1837–1841. doi:10.1212/wnl.50.6.1837
Webster, L. R., Malan, T. P., Tuchman, M. M., Mollen, M. D., Tobias, J. K., and Vanhove, G. F. (2010a). A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled dose finding study of NGX-4010, a high-concentration capsaicin patch, for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. J. Pain 11 (10), 972–982. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2010.01.270
Webster, L. R., Tark, M., Rauck, R., Tobias, J. K., and Vanhove, G. F. (2010b). Effect of duration of postherpetic neuralgia on efficacy analyses in a multicenter, randomized, controlled study of NGX-4010, an 8% capsaicin patch evaluated for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. BMC Neurol. 10, 92. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-10-92
Yin, D., Van Oorschot, D., Jiang, N., Marijam, A., Saha, D., Wu, Z., et al. (2021). A systematic literature review to assess the burden of herpes zoster disease in China. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 19 (2), 1–15. doi:10.1080/14787210.2020.1792290
Zhang, D., Lei, T., Qin, L., Li, C., Lin, X., Wang, H., et al. (2024). Efficacy and safety of crisugabalin (HSK16149) in adults with postherpetic neuralgia: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 160 (11), 1182–1191. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.3410
Zhang, L., Rainka, M., Freeman, R., Harden, R. N., Bell, C. F., Chen, C., et al. (2013). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess the efficacy and safety of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia (PXN110748). J. Pain 14 (6), 590–603. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2013.01.768
Keywords: postherpetic neuralgia, herpes zoster, network meta-analysis, randomized controlled trial, drug thearpy
Citation: Guo Z, Xia Y and Zhang Z (2025) Efficacy and safety of different medications compared for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1614587. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1614587
Received: 19 April 2025; Accepted: 24 June 2025;
Published: 30 July 2025.
Edited by:
Hiram Tendilla-Beltrán, Center for Research and Advanced Studies-IPN (Cinvestav), MexicoReviewed by:
Mohammed Abu El-Hamd, Sohag University, EgyptEleuterio A. Sánchez Romero, Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda, Spain
Copyright © 2025 Guo, Xia and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zuyong Zhang, MjAxNjgwMjhAemNtdS5lZHUuY24=
 Zhen Guo1
Zhen Guo1 Yunfan Xia
Yunfan Xia Zuyong Zhang
Zuyong Zhang