Abstract
MDD is a complex mental illness shaped by the interplay between genetic vulnerability and environmental triggers. Its underlying pathophysiological processes are now understood to be influenced by epigenetic mechanisms. Growing evidence points to critical roles for DNA methylation, histone modification, and ncRNAs in driving transcriptional dysregulation within key brain regions implicated in MDD. These epigenetic alterations may underlie the persistent impairments in neuroplasticity following environmental stress exposure. NPs, renowned for their multi-target properties, have demonstrated promise in modulating epigenetic processes. However, a systematic synthesis of their regulatory roles, mechanisms, and therapeutic potential remains incomplete. This review aims to bridge this gap by integrating evidence from PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase databases to elucidate the role of epigenetic modifications in the pathogenesis and progression of MDD, dissect the mechanisms through which NPs exert antidepressant effects via epigenetic regulation, and highlight current research limitations while proposing strategies for translational applications in both preclinical and clinical settings.
1 Introduction
Major depressive disorder (MDD), is a psychiatric disorder characterized by persistent low mood, loss of interest, and cognitive dysfunction. Global epidemiological data show that MDD affects over 350 million people, with a lifetime prevalence rate as high as 15%–20%, and its disability rate ranks second among all diseases (Gore et al., 2011). The World Health Organization predicts that by 2030, MDD will become the leading contributor to the global disease burden, causing over one trillion dollars in economic losses annually (Malhi and Mann, 2018). Current clinical treatments mainly rely on first-line drugs such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), but there are significant limitations: approximately 30%–50% of patients do not respond to existing medications, and issues like delayed onset of action, side effects (sexual dysfunction, weight gain), and withdrawal syndromes are prominent (Gill et al., 2020; Rothmore, 2020). Moreover, traditional monoamine neurotransmitter theories have failed to fully explain the heterogeneity and recurrence mechanisms of MDD. Therefore, breaking through the current treatment framework to develop new antidepressants that feature rapid onset, high safety, and multi-target intervention has become an urgent need in the field of psychopharmacology.
Natural products (NPs), as a diverse pool of secondary metabolites derived from plants, microbes, and marine organisms, exhibit far greater structural complexity than synthetic compound libraries (Penner-Goeke and Binder, 2019). In the field of antidepressant research, flavonoids, terpenoids, and alkaloids have demonstrated a wide range of pharmacological activities, including the regulation of neuroplasticity and suppression of neuroinflammation (Caruso et al., 2022). Critically, NPs often act through multi-target synergistic mechanisms that mimic the body’s intrinsic self-healing processes, offering new insights into the complex pathophysiology of MDD (Zhang et al., 2020). However, the chemical complexity of NPs also poses challenges, such as potential toxicity and poorly defined mechanisms of action, which require systematic elucidation through modern pharmacological approaches.
Epigenetics refers to the regulation of gene expression without alterations in the underlying Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) sequence (Tsou et al., 2021). Major epigenetic mechanisms include DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs)-mediated regulation. These modifications play critical roles in controlling gene expression and influence cell differentiation, development, and function. In the context of MDD, the pathogenesis is believed to involve dysregulation of genes related to neurotransmitter synthesis, receptor signaling, transporter activity, and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis function. Recent evidence suggests that epigenetic mechanisms contribute significantly to the development and progression of MDD by modulating the expression and translation of these key genes (Buschdorf and Meaney, 2016; Karpova, 2014). Consequently, epigenetic-based strategies are increasingly recognized as promising targets for therapeutic intervention (Yuan et al., 2023). However, there remains a lack of comprehensive reviews that systematically explore the pathophysiological connections between epigenetic regulation and MDD, as well as the potential of NPs-based interventions to modulate these epigenetic pathways.
In this review, we systematically summarize and analyze the mechanisms by which epigenetic modifications contribute to MDD, and explore the potential and application prospects of NPs in antidepressant treatments through the regulation of these modifications. We hope that this review provides new insights and directions for the development of antidepressant drugs, thereby facilitating the creation of more effective and safer therapies for MDD.
2 Review methodology
This study adheres to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, conducting a systematic search of studies related to NPs intervening in MDD via epigenetic mechanisms. A systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and ScienceDirect for studies published from January 2000 to March 2025. The search strategy combined Medical Subject Headings terms and free-text words, including “epigenetic modification,” “DNA methylation,” “histone acetylation,” “non-coding RNA,” “natural products,” “antidepressant,” “depression,” “herb,” “herbal medicine,” “small-molecule drugs,” “flavonoids,” “terpenoids,” and “saponins,” connected through Boolean operators (AND/OR). Inclusion criteria were: ①original research articles published in English; ②studies based on animal or cellular models of MDD; ③investigations clearly exploring the molecular mechanisms by which NPs exert antidepressant effects through epigenetic pathways such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNA. Exclusion criteria included: ①non-English literature; ②reviews, conference abstracts, case reports, and other grey literature; ③duplicate publications; ④studies not involving NPs or failing to specify epigenetic regulatory mechanisms (e.g., those only describing behavioral outcomes or changes in monoamine neurotransmitters); ⑤interventions involving synthetic drugs or compounds not derived from natural sources. Two researchers independently conducted the literature screening, initially excluding studies that clearly did not meet the criteria based on titles and abstracts. Subsequently, they performed a full-text review of the remaining articles and resolved discrepancies through cross-checking. Ultimately, 189 articles were included for systematic analysis (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1
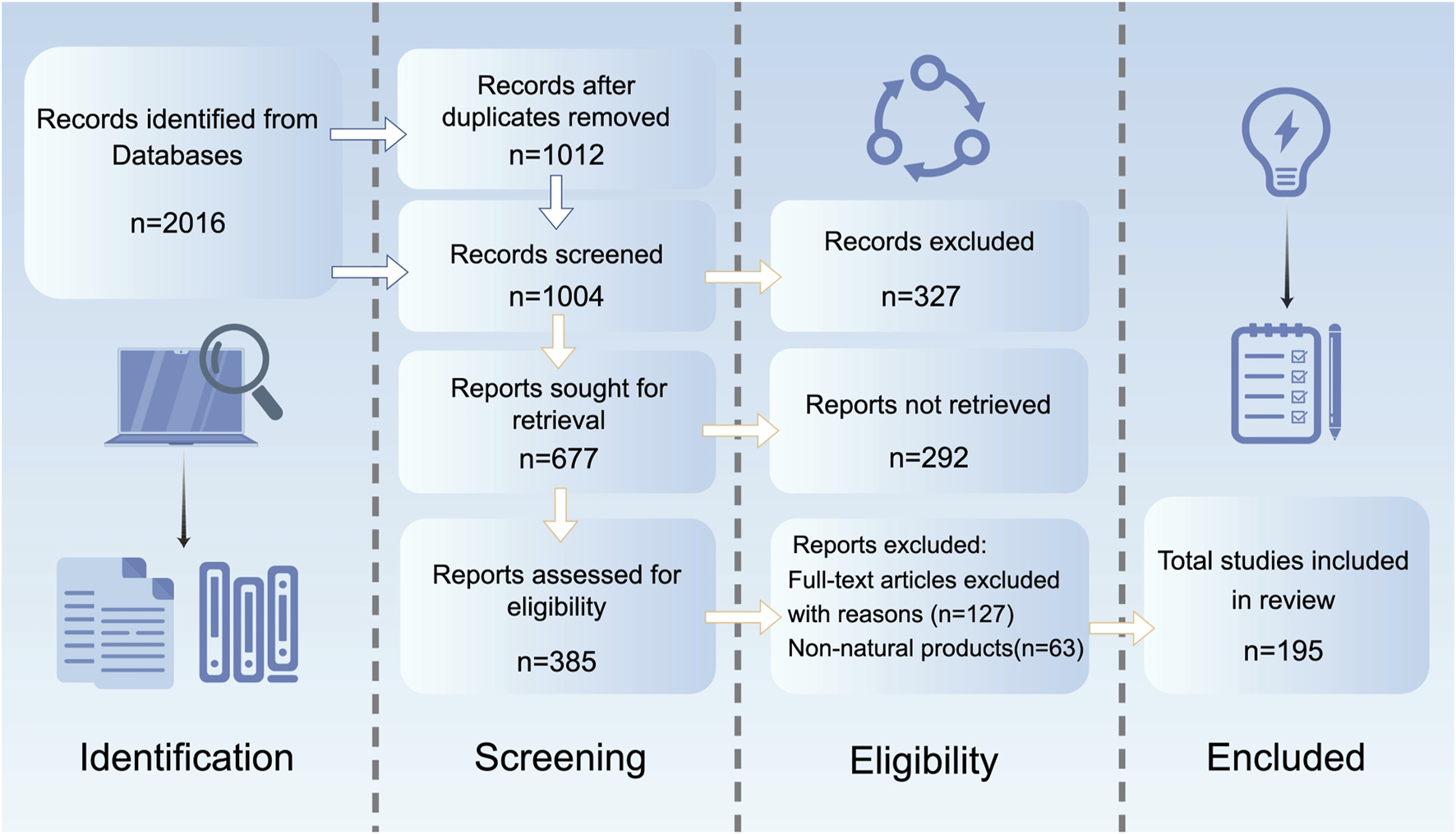
The literature search and screening flowchart.
3 Overview of epigenetic mechanisms
Epigenetic regulation refers to a group of mechanisms that control gene function without changing the nucleotide sequence of DNA. These mechanisms include, but are not limited to, chemical modifications such as DNA methylation, histone modification, and the actions of ncRNAs. These epigenetic changes can modulate gene transcription through structural changes in chromatin, and are often reversible and inheritable through cell divisions. They play essential roles in development, cellular function, and adaptive responses to environmental signals. As a result, epigenetic mechanisms are critical in maintaining genomic stability and influencing health and disease trajectories (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2
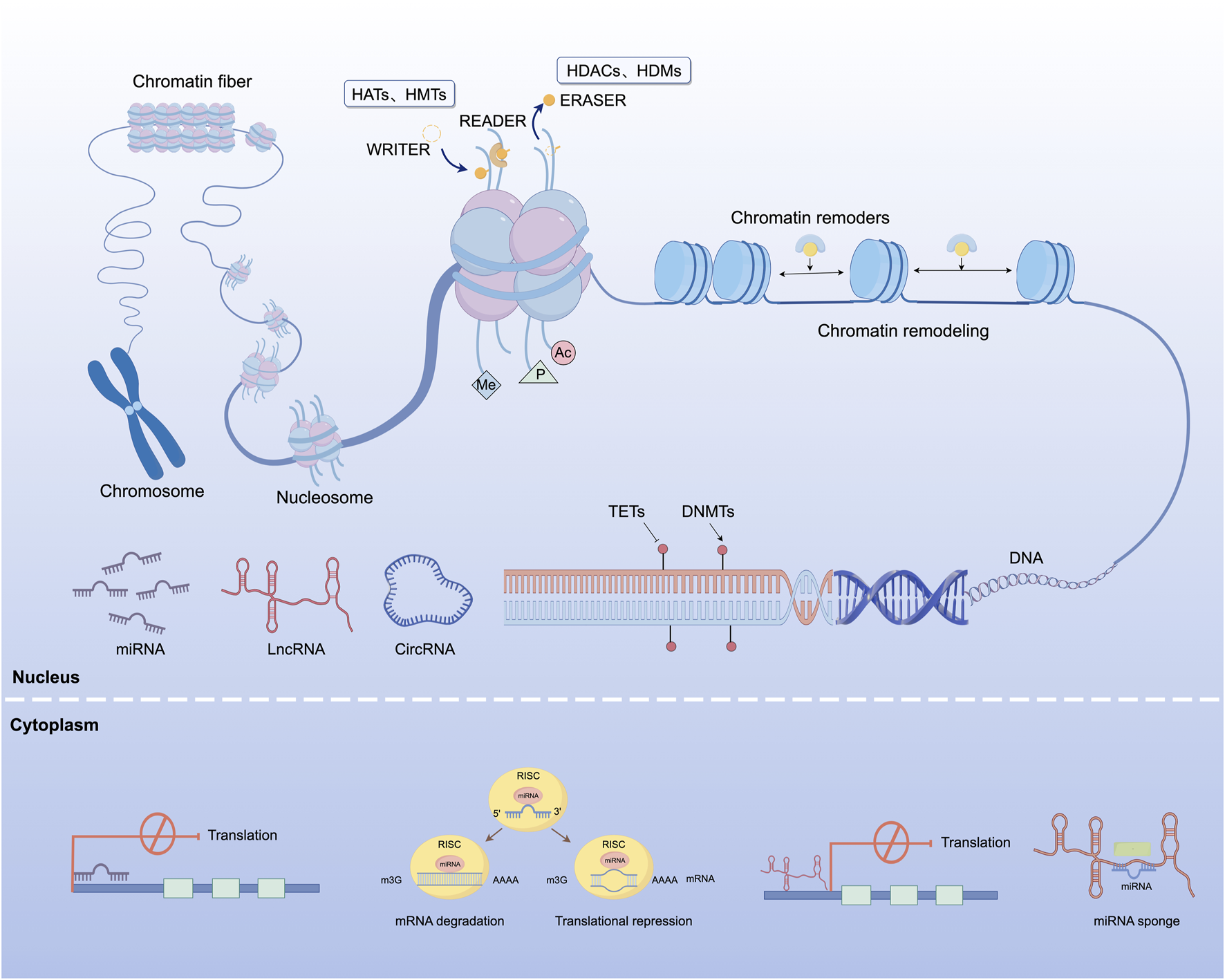
Overview of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms involved in gene expression. This figure illustrates the major epigenetic processes involved in transcriptional regulation. DNA methylation and demethylation are carried out by DNMTs and TETs, respectively. Histone modifications such as acetylation and methylation are catalyzed by HATs and HMTs, removed by HDACs and HDMs, and subsequently recognized by specific chromatin-binding regulatory proteins. Chromatin remodeling is mediated by adenosine triphosphate-dependent remodeling complexes that reposition nucleosomes and modulate chromatin accessibility. In the cytoplasm, ncRNAs including miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs contribute to post-transcriptional regulation through messenger RNA degradation, translational repression, and miRNA sequestration via competing endogenous RNA activity. These regulatory effects are predominantly mediated by the RISC. HATs, histone acetyltransferases; HMTs, histone methyltransferases; HDACs, histone deacetylases; HDMs, histone demethylases; DNMTs, DNA methyltransferases; TETs, ten-eleven translocation enzymes; miRNA, microRNA; lncRNA, long non-coding RNA; circRNA, circular RNA; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex.
3.1 DNA methylation
DNA methylation refers to the covalent addition of a methyl group to the 5-carbon position of cytosine within Cytosine-phosphate-Guanine (CpG) dinucleotides, catalyzed by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs). As a core mechanism of epigenetic regulation, this dynamic process is governed by the DNMT family. DNMT3a and DNMT3b are chiefly involved in establishing new DNA methylation marks, while DNMT1 preserves pre-existing methylation patterns during DNA replication. These enzymatic activities function in concert with demethylating regulators, notably the ten-eleven translocation (TET) protein family (Mattei et al., 2022). Within the genome, hypermethylation of CpG islands in promoter regions is typically associated with gene silencing. In contrast, methylation in gene bodies may facilitate transcriptional elongation, and methylation of repetitive elements plays a critical role in maintaining genomic stability (Jones, 2012).
In the brain, DNA methylation is highly dynamic and sensitive to factors such as aging, environmental exposures, and neuronal activity (Lister et al., 2013). During early embryonic development, DNA methylation plays a crucial role in the lineage commitment of neural progenitor cells. De novo methyltransferases such as DNMT3a and DNMT3b are essential for silencing pluripotency genes and activating lineage-specific programs. Loss of DNMT function impairs neural differentiation and disrupts epigenetic patterning (Smith and Meissner, 2013). These findings highlight DNA methylation as a key regulator of neurodevelopmental fate decisions. In the adult brain, particularly in the hippocampus, localized DNA methylation reprogramming contributes to learning and memory formation. Environmental stimuli or cognitive tasks can induce methylation changes at specific loci, regulating gene expression associated with synaptic plasticity and memory consolidation (Zocher et al., 2021). Environmental stressors such as chronic stress or nutrient deprivation can activate glucocorticoid receptor (GR) signaling pathways, which in turn promote the recruitment of DNMTs to stress-responsive gene promoters. For example, early-life adversity has been shown to increase methylation at the promoter of the GR gene nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 1 (NR3C1) in the hippocampus, thereby suppressing its expression and disrupting negative feedback regulation of the HPA axis (Bakusic et al., 2021).
3.2 Histone modification
Histones, the core components of chromatin, are responsible for packaging genomic DNA into compact chromatin structures. Histone modifications, which involve covalent chemical changes at specific amino acid residues such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination, play dynamic roles in regulating chromatin organization. These modifications influence chromatin condensation and DNA accessibility, thereby modulating gene expression patterns. They function as essential epigenetic mechanisms that control a wide range of physiological and developmental processes in eukaryotic cells. Among these modifications, histone acetylation and methylation have been the most extensively studied and are recognized as major regulators of transcriptional activity.
Among all histone modifications, acetylation is a highly dynamic mark that is closely associated with transcriptional activation. This process is catalyzed by lysine acetyltransferases (KATs), which transfer the acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to the ε-amino group of lysine residues on histones. This modification neutralizes the positive charge of histones, thereby weakening the electrostatic interactions between histones and DNA. As a result, chromatin structure becomes more relaxed, enhancing DNA accessibility and facilitating transcriptional initiation (Shvedunova and Akhtar, 2022). Histone acetylation predominantly occurs on lysine residues at the N-terminal tails of histones H3 and H4. Common modification sites include histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9ac), histone H3 lysine 14 acetylation (H3K14ac). These marks are strongly associated with transcriptionally active chromatin and are widely used as epigenetic indicators in functional studies (Kouzarides, 2007). In contrast to KAT-mediated acetylation, histone deacetylases (HDACs) remove acetyl groups from lysine residues, thereby strengthening histone-DNA interactions, promoting chromatin condensation, and repressing gene expression (D’Mello, 2020).
Histone methylation typically occurs on lysine and arginine residues and is catalyzed by histone methyltransferases (HMTs). The functional outcome of this modification depends on both the specific residue involved and the number of methyl groups added. Methylation can occur in the form of mono, di, or trimethylation, each with distinct regulatory effects on gene expression (Yang et al., 2020). For instance, trimethylation at histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) is associated with active gene promoters and facilitates transcription. In contrast, methylation at histone H3 lysine 27 methylation (H3K27me) and H3K27me3 is linked to gene repression and is typically enriched in heterochromatic regions and transcriptionally silent loci (Di Nisio et al., 2021).
3.3 NcRNAs
NcRNAs constitute a class of functionally diverse ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules that do not encode proteins but play critical regulatory roles, accounting for over 60% of the mammalian transcriptome. NcRNAs can be broadly classified according to their sequence length and biological function into three major types: long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs, typically exceeding 200 nucleotides), microRNAs (miRNAs, approximately 18–25 nucleotides), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) (Reik, 2007; Zaratiegui et al., 2007). These molecules dynamically regulate chromatin architecture, genomic stability, and post-transcriptional modifications through interactions with DNA, RNA, proteins, or chromatin complexes, thereby influencing cellular differentiation, development, and disease progression via epigenetic mechanisms. LncRNAs can recruit polycomb repressive complex 2 to deposit H3K27me3 marks at target gene promoters, leading to transcriptional silencing (Guo et al., 2021). MiRNAs bind to complementary seed sequences within the 3′untranslated regions (3′UTRs) of target mRNAs, mediating translational repression or degradation (Bartel, 2009). This enables miRNAs to fine-tune gene expression networks, as exemplified by region-specific miRNA ensembles in neurons that regulate local protein synthesis to modulate synaptic homeostasis and plasticity (Martins and Schratt, 2021). Owing to their covalently closed circular structure, circRNAs exhibit enhanced stability and function as miRNA sponges. By sequestering miRNAs (e.g., circRNA CDR1as binding miR-7), they relieve miRNA-mediated suppression of target mRNAs (Misir et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2016). Additionally, circRNAs interact with RNA-binding proteins to form novel regulatory circuits. For example, CDR1 as modulates synaptic plasticity through both miR-7 sponging and direct protein interactions (Mehta et al., 2022).
3.4 Chromatin remodeling
Unlike DNA methylation and histone modifications that regulate gene expression through chemical alterations of chromatin, chromatin remodeling primarily operates via physical restructuring of chromatin architecture. The core mechanism involves Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)-dependent chromatin remodelers that utilize energy from ATP binding/hydrolysis to modulate nucleosome positioning through sliding, eviction, or histone variant replacement, thereby regulating transcriptional accessibility. Depending on the specificity of different ATPase subunits, ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes are primarily classified into four categories: the switching defective/sucrose nonfermenting (SWI/SNF) family, interphase structure whirlpool (ISWI) family, inositol requiring protein 80 (INO80) family, and chromodomain helicase DNA-binding (CHD) family (Flaus et al., 2006). Chromatin remodeling complexes exhibit distinct regulatory mechanisms based on their subunit composition. SWI/SNF-family proteins mediate chromatin accessibility by displacing nucleosomes to create nucleosome-free regions, facilitating transcriptional activation (Whitehouse et al., 1999). ISWI-family complexes regulate nucleosomal spacing to maintain chromatin structural integrity (Ito et al., 1997), while CHD-family members coordinate transcriptional processes through nucleosome binding and interactions with transcription elongation and chromatin modification factors (Reyes et al., 2021); INO80-family remodelers specialize in histone variant exchange to dynamically modulate chromatin states (Papamichos-Chronakis et al., 2011). Additionally, chromatin remodeling activity is regulated by multiple mechanisms, including auto-inhibition, histone modifications, and auxiliary subunit functions (Wang et al., 2021).
4 Pathologic connection between epigenetic mechanisms and MDD
MDD arises from the complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social determinants, with epigenetics emerging as a pivotal regulatory layer elucidating its underlying mechanisms. Key epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation, histone post-translational modifications, chromatin remodeling, ncRNAs, and stress-responsive pathways, orchestrate fine-tuned regulation of gene expression without altering DNA sequences, thereby modulating brain structure and function. Accumulating evidence demonstrates that these mechanisms critically regulate neurodevelopment, synaptic plasticity, and adaptive responses to environmental stressors. In subsequent sections, we systematically dissect how specific epigenetic alterations contribute to MDD pathophysiology, with emphasis on their dynamic interplay and disease-specific roles (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3
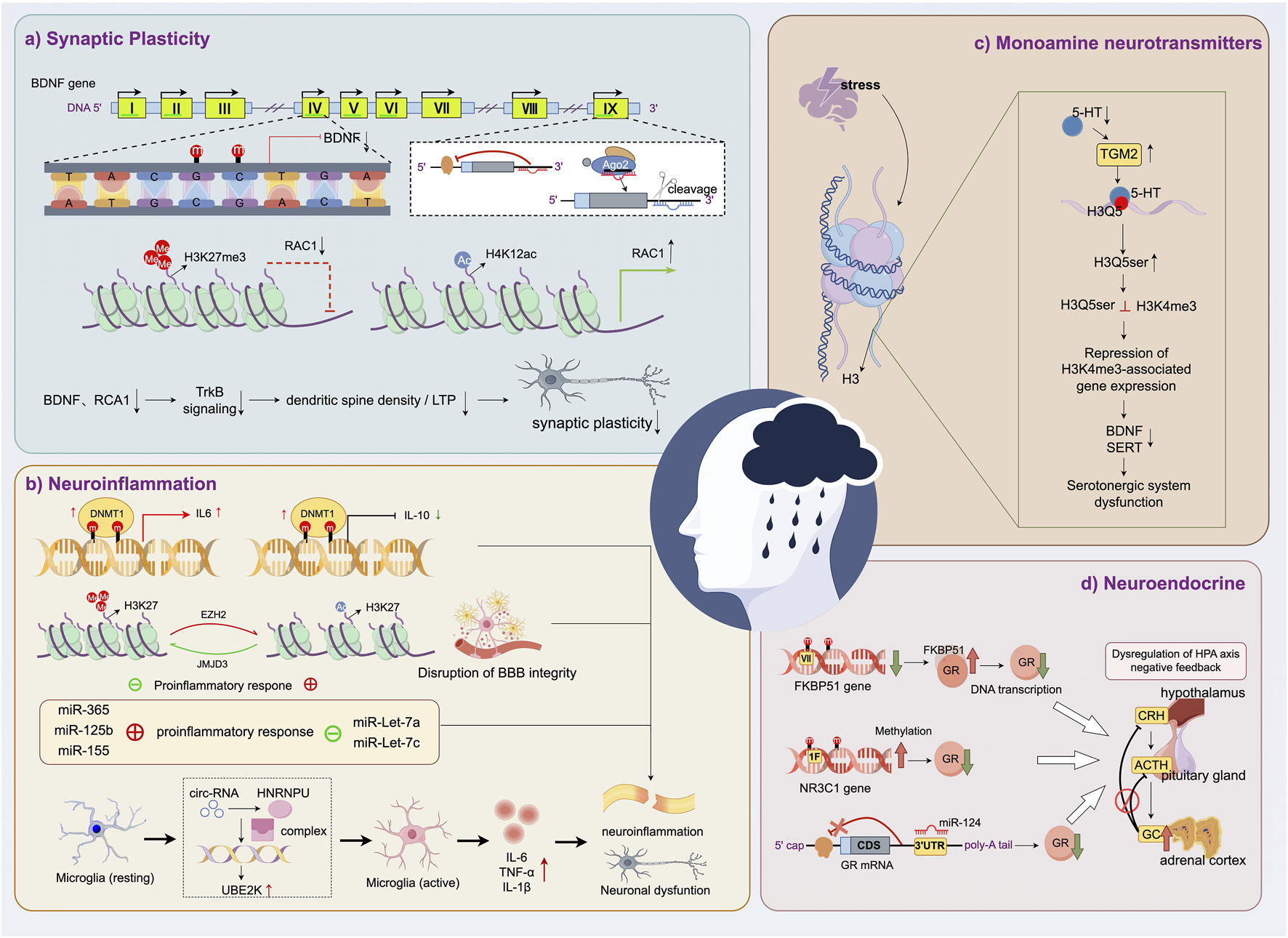
Epigenetic regulation of MDD-related pathophysiological mechanisms. (a) Synaptic plasticity is impaired by epigenetic downregulation of BDNF and RAC1. (b) Neuroinflammation is promoted through epigenetic control of cytokine expression and microglial activation. (b) Serotonergic dysfunction results from stress-induced disruption of histone serotonylation and gene repression. (d) HPA axis imbalance is driven by epigenetic regulation of glucocorticoid receptor signaling.
4.1 DNA methylation in MDD
4.1.1 Childhood adversity as a key factor in methylation-driven MDD risk
DNA methylation is increasingly recognized as a critical molecular bridge connecting environmental risk exposures with genetic vulnerability in MDD. Large-scale cohort studies demonstrate that childhood adversities (e.g., maltreatment, neglect, household dysfunction) confer elevated MDD risk through enduring methylation imprints. A landmark epigenome-wide association study investigating blood-derived DNA methylation patterns linking seven childhood adversity types (age 0–7) with adolescent depressive symptoms (mean age 10.6) revealed adversity-associated methylation alterations at 70 CpG sites. These loci collectively mediated 10%–73% of adversity-MDD symptom associations (Lussier et al., 2024). Hypermethylation at 39 CpG sites exhibited protective effects, suggesting DNA methylation may partially buffer psychological trauma through compensatory mechanisms, a finding highlighting novel directions for understanding MDD resilience.
4.1.2 Changes in DNMTs and TETs in MDD
The dynamic process of DNA methylation requires the involvement of DNMTs and TETs, with the expression levels and activities of these enzymes playing a crucial role in the DNA methylation process. Their activities also regulate mood behaviors and are closely related to the onset and progression of MDD. Animal experiments have found that chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) increases the levels of DNMT3a in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of mice, and overexpression of DNMT3a promotes depressive-like behaviors, while local administration of the DNMT inhibitor reverses such behaviors (LaPlant et al., 2010). A similar result was observed in a clinical study (Hodes et al., 2015). Previous studies have demonstrated that DNMTs also undergo stress-related expression changes in other key brain regions. In the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus, DNMT1/3a are upregulated in the chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) model, and their expression can be reversed by antidepressant treatment (Cheng et al., 2023). In contrast, the amygdala shows a distinct expression pattern. Postmortem analyses have revealed reduced DNMT1/3B mRNA levels in the amygdala of patients with MDD (Poulter et al., 2008). However, in animal models, DNMT1 expression is increased in the central nucleus of the amygdala following CSDS, with this change observed exclusively in female mice, suggesting a sex-specific regulatory mechanism in this region (Wright et al., 2017).
Furthermore, studies have shown that TET1 knockout mice exhibit resistance to chronic restraint stress, whereas TET2 knockout mice show hypersensitivity to stress (Cheng et al., 2018). When TET1 protein is overexpressed in the hippocampus of mice, it upregulates the expression levels of Delta-like canonical Notch ligand 3 and Notch1 proteins, promoting hippocampal neurogenesis and alleviating depressive-like behaviors (Shuang et al., 2024). Under stress conditions, abnormal expression and decreased nuclear translocation of TET2 lead to a reduction in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine levels and dysregulated gene expression, increasing susceptibility to MDD in mice (Zhang et al., 2021a). Additionally, the rapid antidepressant effect of ascorbic acid is mediated by the activation of DNA demethylation catalyzed by TET1 and TET2 (Han et al., 2022). Similarly, TET enzymes also exhibit region-specific roles in depression-like behavior. CSDS leads to a downregulation of TET1 expression exclusively in the NAc of susceptible mice, while selective deletion of TET1 in the NAc induces antidepressant-like effects. Mechanistically, TET1 deficiency relieves transcriptional repression of immune-related gene clusters via demethylation, resulting in the upregulation of genes that closely overlap with the expression profile of resilient mice. These findings suggest that TET1 in the NAc may function as a negative regulator of stress responses (Feng et al., 2017).
4.1.3 The methylation dysregulation of key genes associated with MDD
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a widely expressed neurotrophin critical for synaptic transmission and plasticity, plays pivotal roles in late-stage neurodevelopment and psychiatric disorder pathogenesis (Zelada et al., 2023). Clinical studies consistently report reduced BDNF expression and protein levels in peripheral blood and postmortem brain tissues of MDD patients, positioning BDNF deficiency as a key etiological factor (Gelle et al., 2021). The synthesis of BDNF in neurons, which is significantly diminished in MDD, is closely associated with elevated methylation levels in the BDNF promoter region, and given that the methylation status of the BDNF gene has been implicated as a crucial factor in the pathogenesis of MDD, it is increasingly recognized as a potential biomarker for the disorder. Li et al. identified elevated methylation levels at two CpG dinucleotides (BDNF133 and BDNF134) within exon VI of the BDNF gene in MDD patients relative to healthy controls (Li et al., 2021a). In contrast, a recent study demonstrated reduced pre-treatment methylation in the promoter region of exon IV in adolescents with MDD compared to non-affected individuals (Zwolińska et al., 2024). These discordant findings highlight the context-dependent nature of BDNF methylation patterns, suggesting substantial variability influenced by exon specificity, developmental stage, sex, environmental exposures. Consequently, the clinical utility of BDNF methylation as a MDD biomarker necessitates multi-faceted validation through large-scale, population-diverse cohort studies incorporating multi-omics approaches to account for these confounding variables. On the other hand, BDNF promoter methylation appears to be associated with brain structural alterations in MDD patients. Choi et al. found a significant negative correlation between the methylation status of the BDNF promoter region and the integrity of the right anterior corona radiata white matter, which is involved in emotional and cognitive control networks implicated in the pathophysiology of MDD. This suggests that BDNF gene methylation may contribute to the pathogenesis of MDD by regulating white matter structural integrity (Choi et al., 2015). Meanwhile, reduced cortical thickness in the prefrontal and occipital regions of MDD patients was associated with increased methylation levels at the BDNF promoter in these areas (Na et al., 2016).
NR3C1, a critical regulator of stress responses, modulates GR levels and HPA axis activity. Hyperactivation of the HPA axis and elevated glucocorticoid (GC) levels represent hallmark pathophysiological features of MDD. Experimental evidence reveals that two GC dinucleotide pairs within the human NR3C1 coding sequence are typically unmethylated under normal conditions. However, stress-induced methylation at these sites suppresses NR3C1 transcription, reduces GR mRNA levels, elevates cortisol concentrations, and impairs HPA axis negative feedback, ultimately driving HPA hyperactivation and depressive pathogenesis (Bustamante et al., 2016). In rodent models, the maternal tactile stimulation (licking/grooming) during postnatal day 1 reduces HPA reactivity and alleviates anxiety-like behaviors in offspring. This protective effect is mediated by demethylation of the NR3C1 exon 1–7 promoter in the hippocampus (Murgatroyd et al., 2015). Moreover, Early-life stress (e.g., childhood trauma, neglect) is a well-established risk factor for MDD (Nelson et al., 2017). Studies demonstrating that NR3C1 undergoes stress-induced epigenetic modifications, particularly DNA methylation, which confers lifelong MDD susceptibility (Keller et al., 2017). Adults with MDD and childhood maltreatment (CM) histories exhibit elevated NR3C1 promoter methylation, with methylation levels positively correlating with CM severity and subtype (Perroud et al., 2011).
FKBP5 encodes FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP51), a critical negative regulator of the GR signaling pathway. By interfering with GR nuclear translocation and function, FKBP51 modulates the activity of the HPA axis, thereby affecting the balance of the stress response. Dysregulation of the HPA axis is a core pathophysiological mechanism in MDD, and polymorphisms in the FKBP5 gene have been shown to confer increased vulnerability to MDD, particularly among individuals exposed to early-life trauma or chronic stress (Klengel et al., 2012). Epigenetically, methylation at specific CpG sites within intron 7 of FKBP5 (e.g., cg25563198 in the TSS1500 region) has been identified as a regulatory element of transcriptional activity. Hypomethylation in this region is associated with elevated FKBP5 expression, which enhances its inhibition of GR activity, leading to impaired negative feedback of the HPA axis, GC resistance, and prolonged stress responses (Tang et al., 2024). This epigenetic alteration may interact with specific risk genotypes such as rs1360780, further modulating gene-environment interactions in the development of depressive pathology. Collectively, the hypomethylation of FKBP5 intron 7 represents a crucial mechanism linking environmental stress exposure to HPA axis dysregulation and increased risk for MDD (Klinger-König et al., 2019).
The Solute Carrier Family 6 Member 4 (SLC6A4) gene encodes the serotonin (5-HT) transporter, which plays a key role in regulating 5-HT reuptake and neurotransmission. DNA methylation of the SLC6A4 promoter region has been consistently associated with reduced gene expression and 5-HT dysregulation, which are both implicated in the neurobiology of MDD. Kang et al. reported that individuals with more severe depressive symptoms and a history of childhood adversity showed significantly higher SLC6A4 methylation levels (Kang et al., 2013). Similarly, Bakusic et al. found that hypermethylation of both SLC6A4 and NR3C1 was associated with blunted cortisol reactivity following acute psychosocial stress in MDD patients (Bakusic et al., 2020). This functional attenuation of the HPA axis was especially evident during the recovery phase after social stress exposure. These findings suggest that hypermethylation of stress-related genes may contribute to the pathophysiology of MDD by impairing the dynamic regulation of the stress response. Furthermore, methylation of a specific CpG site in NR3C1 (CpG20) was predictive of poor symptom improvement over an 8-week follow-up, highlighting its potential as a biomarker for treatment response.
4.2 Histone modifications in MDD
4.2.1 Histone acetylation
Histone acetylation plays a critical role in regulating chromatin structure and gene transcription. In recent years, it has been widely investigated as a key epigenetic mechanism in the pathogenesis of MDD. In animal models, chronic stress significantly reduces histone acetylation levels in emotion-regulating brain regions such as the hippocampus. This loss of acetylation is often accompanied by downregulation of BDNF expression, impaired synaptic plasticity, and diminished stress resilience, ultimately leading to depression-like behaviors such as social withdrawal and anhedonia (Tsankova et al., 2007). Interestingly, some acetylation marks exhibit a gradual increase during the recovery phase, typically between 15 and 21 days following stress cessation (Montagud-Romero et al., 2016). This observation suggests that the dynamic restoration of histone acetylation may play a central role in the natural remission of depressive symptoms. In addition, metabolic agents such as metformin can enhance histone acetylation via the AMP-activated protein kinase/cAMP response element-binding protein (AMPK/CREB) signaling pathway, leading to increased BDNF expression and behavioral improvement (Fang et al., 2020). Moreover, some studies have shown that in the CSDS model, HDAC7 expression is downregulated in the NAc, leading to reduced histone deacetylation and a relative increase in histone acetylation levels (Qian et al., 2021). Another study reported that CSDS induces a delayed increase in H3K14ac in the mPFC of susceptible mice, with significant elevation observed at 24 h and 10 days after stress, returning to baseline by day 20 (Covington et al., 2015). These findings suggest that histone acetylation is regulated in a region-specific manner across different brain areas in response to stress.
Microglia, as the principal effector cells of neuroinflammation in the central nervous system (CNS), play a crucial role in the pathophysiology of MDD. Elevated expression of HDAC1 in microglia has been shown to suppress the transcription of anti-inflammatory genes such as IL-10 by reducing H3K9ac. At the same time, HDAC1 activity promotes the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), as well as the activation of the NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, thereby amplifying the neuroinflammatory cascade (Patnala et al., 2017). Elevated HDAC1 activity also promotes the polarization of microglia toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype, thereby strengthening the link between the inflammatory microenvironment and depression-like behaviors. Mechanistic studies have shown that the antidepressant fluoxetine alleviates depressive susceptibility in mice by suppressing HDAC1 expression, activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) signaling pathway, and reducing both eukaryotic elongation factor 2 activity and NLRP3 inflammasome expression. Notably, administration of enidone, a selective HDAC1 agonist, completely abolished the anti-inflammatory and antidepressant effects of fluoxetine, confirming the pivotal role of HDAC1 as an epigenetic therapeutic target (Li et al., 2021b).
4.2.2 Histone methylation
The function of histone methylation as a reversible epigenetic mark is highly dependent on the modification site. Among the many histone modifications, H3K4me3 is one of the most widely studied modifications. Early evidence from Uchida et al. demonstrated that H3K4me3 levels at the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor promoter were reduced in the ventral striatum of stress-susceptible mice, contributing to altered neurotrophic support in MDD (Uchida et al., 2011). Subsequent findings by Cruceanu et al. revealed excessive enrichment of H3K4me3 at the synapsin 1 (SYN1) promoter in MDD patients, leading to the overexpression of SYN1a and SYN1b and potentially disrupting synaptic plasticity (Cruceanu et al., 2013). More recently, Tseng et al. reported decreased H3K4me3 levels at promoters of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathway genes in MDD brains, correlating with MDD severity and implicating immune dysregulation as a potential mechanism (Tseng et al., 2023).
In contrast to H3K4me3, which activates gene transcription, other forms of histone methylation, such as histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) and H3K27me3, inhibit gene transcription (Li et al., 2021c; Wang et al., 2023). CSDS-induced MDD models demonstrated aberrantly increased H3K9me2/me3 levels in the NAc, resulting in transcriptional repression of target genes, which impairs neuroplasticity and reward circuitry function, linking to core depressive symptoms such as anhedonia (Pathak et al., 2017). Concurrently, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1), a small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) critical for cytoskeletal dynamics, exhibits reduced expression in the NAc, resulting in synaptic structural and functional alterations that are closely linked to depressive-like behaviors. Studies have shown that reduced expression of RAC1 in the NAc of mice exposed to CSDS is associated with increased levels of H3K27me3 (Golden et al., 2013). In stress-induced murine MDD models, Claudin-5 dysregulation was linked to elevated H3K27me3 at its promoter. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) catalyzed H3K27me3 deposition to repress Claudin-5, thereby compromising blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity, triggering neuroinflammation, and exacerbating depressive behaviors. EZH2 knockdown or antidepressant treatment reduced H3K27me3 levels, restored Claudin-5 expression, and rescued depressive-like phenotypes (Sun et al., 2024). More recently, polycomb group ring finger 1 (PCGF1), a component of the noncanonical polycomb repressive complex 1, was found to alleviate adolescent MDD by suppressing matrix metallopeptidase 10 (MMP10) transcription in hippocampal microglia. PCGF1 increased the enrichment of both H2AK119ub and H3K27me3 at the MMP10 promoter, thereby repressing nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells/mitogen-activated protein kinase (NF-κB/MAPK)-mediated inflammatory signaling and improving behavioral outcomes (Li et al., 2025). Collectively, these findings underscore that histone methylation, depending on site-specific patterns and the activity of HMTs, regulates key biological pathways in MDD, including synaptic plasticity, neuroimmune signaling, and BBB integrity.
4.2.3 Histone crotonylation
Histone crotonylation is a novel acyl modification mediated by crotonyl-CoA donors, strongly associated with transcriptional activation. Crotonyl-CoA hydratase (CDYL) suppresses this modification by hydrolyzing crotonyl-CoA. Pioneering work by Huang’s team revealed that CUMS significantly reduces H3K9 crotonylation levels in the prelimbic cortex of mice, concomitant with decreased expression of neuropeptide and synaptic loss. CDYL overexpression in the PL heightened susceptibility to depressive phenotypes, whereas CDYL suppression or crotonate supplementation rescued depressive-like behaviors (Liu et al., 2019a).
4.2.4 Histone monoaminylation
Histone monoaminylation is a recently identified form of epigenetic modification involving the covalent attachment of neurotransmitters such as 5-HT, dopamine, and histamine to the glutamine residue at position 5 of histone H3. This process is typically catalyzed by transglutaminase 2 and results in the formation of the composite mark H3K4me3Q5ser in the presence of H3K4 trimethylation. This dual modification enhances the recruitment of the transcription factor transcription factor IID (TFIID) to chromatin and concurrently suppresses demethylase activity, thereby sustaining the transcriptional activation of key genes (Farrelly et al., 2019).
Recent studies have shown that histone monoaminylation not only represents a downstream extension of neurotransmitter signaling but also directly regulates gene expression. In a CSDS model, stress-susceptible animals displayed dynamic changes in histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation and glutaminyl-serotonylation at glutamine 5 (H3K4me3Q5ser) levels within the dorsal raphe nucleus, characterized by a marked decrease during the acute phase and abnormal accumulation during the prolonged stress period. These alterations were closely associated with stress-induced behavioral phenotypes, suggesting that this epigenetic mark may contribute to the development of depression-like behaviors. Pharmacological intervention further demonstrated that chronic fluoxetine treatment significantly restored H3K4me3Q5ser levels, which was accompanied by an improvement in depressive-like behaviors. Moreover, virally mediated expression of the H3.3Q5A mutant, which blocks monoaminylation at the Q5 site, also reversed both transcriptional abnormalities and behavioral impairments induced by stress. These findings indicate that H3K4me3Q5ser functions not only as a state-dependent marker but also as an epigenetic regulator of mood-related plasticity. Consistent results have been observed in postmortem brain tissue from individuals with MDD. Patients who had not received antidepressant treatment exhibited significantly lower levels of H3K4me3Q5ser, whereas treated patients showed no significant difference compared to healthy controls. This suggests that H3K4me3Q5ser may serve as a potential biomarker for antidepressant responsiveness (Al-Kachak et al., 2024). Collectively, these findings support a critical epigenetic role for histone monoaminylation, particularly H3K4me3Q5ser, in modulating transcriptional plasticity under stress, which may partly explain the delayed therapeutic effects of conventional antidepressants.
4.3 NcRNAs in the epigenetic regulation of MDD
4.3.1 MiRNAs
Among ncRNAs, miRNAs constitute a pivotal epigenetic regulatory system and have emerged as master regulators of neuroplasticity and higher-order brain functions. Multiple studies have identified significant differences in miRNA expression profiles between individuals with MDD and healthy controls. These miRNA alterations are closely associated with the pathophysiological mechanisms of MDD, participating in its pathogenesis through multidimensional molecular pathways.
MiRNAs regulate key proteins involved in monoaminergic neurotransmitter metabolism, thereby modulating synaptic neurotransmitter homeostasis. Notably, miR-16-mediated targeted inhibition of the serotonin transporter (SERT) has been implicated in the pathological dysregulation of the monoaminergic system. CSDS downregulates miR-16 expression in the cerebrospinal fluid and raphe nuclei, leading to excessive SERT protein accumulation and enhanced synaptic 5-HT reuptake, which ultimately elicits depression-like phenotypes (Shao et al., 2018). After chronic treatment with SSRIs, miR-16 levels increase in the serotonergic dorsal raphe nucleus, while its expression decreases in the noradrenergic locus coeruleus and the hippocampus (Baudry et al., 2010; Launay et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2017).
miRNAs modulate stress responses by targeting GR–related signaling pathways, thereby contributing to a positive feedback loop that reinforces HPA axis dysregulation. Studies have shown that the upregulation of miR-124 in the hippocampus of mice exposed to CUMS is closely associated with the suppression of GR mRNA expression. miR-124 directly targets GR mRNA, inhibiting its translation and thereby modulating the negative feedback regulation of GC signaling. During the early phase of stress exposure (weeks 5–6), elevated miR-124 expression is considered a compensatory response to increased GC levels (Huang et al., 2019). Another study further demonstrated that in key emotion-regulating brain regions, including the basolateral amygdala, PFC and hippocampus, both miR-124 and its target gene FKBP5 were significantly upregulated and closely associated with depression-like behavior (Xu et al., 2017). Increased FKBP5 expression may disrupt GR stability and activity, thereby exacerbating HPA axis dysregulation and contributing to the development of depressive symptoms.
The dynamic homeostatic regulation of BDNF by miRNAs should not be overlooked. miRNAs can interfere with neurotrophic factor expression and downstream signaling pathways, altering neuronal plasticity and synaptic remodeling ability. Emerging evidence identifies miR-1, miR-10b, miR-155, and miR-191 as novel regulatory factors of BDNF, expanding the epigenetic network governing neurotrophin dynamics in MDD pathophysiology (Varendi et al., 2014). Furthermore, in a CUMS-induced murine MDD model, miR-155 levels were significantly elevated, whereas BDNF expression was markedly reduced. miR-155 directly binds to the 3′UTR of BDNF mRNA, inhibiting its translation and thereby diminishing BDNF protein levels (Huan et al., 2021). Additionally, Fiori et al. demonstrated significant upregulation of miR-204-5p, miR-320b, miR-323a-3p, and miR-331-3p in the anterior cingulate cortex and habenula of individuals with MDD. Notably, miR-323a-3p was found to directly target the 3′UTR of Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 4 (ERBB4) mRNA, suppressing its expression. ERBB4, a critical receptor tyrosine kinase in neuregulin signaling pathways, functionally intersects with BDNF-mediated synaptic plasticity. ERBB4 downregulation disrupts neurotrophin signaling cascades, contributing to depressive pathogenesis through impaired glutamatergic transmission and dendritic atrophy (Fiori et al., 2021).
MiRNAs are thought to influence the progression of MDD by targeting inflammation. For instance, miR-29a-5p has been shown to alleviate depression-like behaviors by promoting anti-inflammatory microglial M2 polarization in the PFC (Yang et al., 2024a). MiR-532-5p alleviates depression-like behaviors in CUMS-exposed mice by suppressing the expression of IL-6, interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), TNF-α, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 through inhibition of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway (Yan et al., 2020).
4.3.2 CircRNAs
The stable structure and tissue-specific expression patterns of circRNAs suggest their potential utility in neuropsychiatric disorders. Several circRNAs have been shown to regulate miRNA activity through a sponge-like mechanism, thereby indirectly modulating neurotransmitter-related pathways. For instance, circRNA derived from the DYM gene (circDYM) is downregulated in the plasma of patients with MDD and positively correlates with MDD severity. Functionally, circDYM inhibits microglial activation by sequestering miR-9, and its expression is upregulated following repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation treatment, highlighting its potential as both a diagnostic biomarker and a predictor of therapeutic response.
In addition, circHIPK3 and circTulp4 have been implicated in neuroinflammatory and neurodevelopmental processes, suggesting their involvement as epigenetic regulators in the pathogenesis of MDD. More recently, circ-UBE2K has been identified as significantly upregulated in the peripheral blood of MDD patients and in the brain tissue of MDD model mice. Predominantly expressed in microglia, circ-UBE2K binds to the nuclear protein heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U (HNRNPU), thereby enhancing the expression of its host gene, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 K (UBE2K). This interaction promotes aberrant microglial activation and neuroinflammation, contributing to the progression of MDD (Cai et al., 2024).
4.3.3 LncRNAs
lncRNAs exhibit sequence specificity and typically regulate gene expression through mechanisms such as chromatin remodeling, RNA splicing, and miRNA competition. Several lncRNAs display marked sex-specific expression patterns in female patients with MDD, particularly within the PFC. LINC00473 is significantly downregulated in female MDD patients, and its reduced expression disrupts the CREB signaling pathway, thereby impairing neuronal plasticity and stress resilience (Issler et al., 2020). In contrast, FEmale DepressiOn lncRNA (FEDORA) is significantly upregulated in depressed females, is enriched in both neurons and oligodendrocytes, and its overexpression induces depressive-like behaviors, synaptic dysfunction, and myelin abnormalities in female mice (Issler et al., 2022). Notably, neither lncRNA produced comparable effects in males, indicating a distinct sex-specific regulatory role. Additionally, plasma levels of FEDORA are positively associated with clinical response to ketamine.
4.4 Chromatin remodeling and MDD
Histone modifications regulate chromatin structure and gene expression through chemical alterations, whereas chromatin remodeling, an ATP-dependent mechanism involving nucleosome repositioning, directly governs chromatin accessibility. This dynamic process not only synergizes with histone modifications but may also independently perturb critical pathways in MDD. For instance, overexpression of the ACF complex and its subunit BAZ1A in the NAc is strongly associated with depressive-like behaviors. Animal studies demonstrate that CSDS upregulates the bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain/SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 complex in the NAc, promoting nucleosome clustering at transcription start sites to block gene transcription, particularly suppressing BDNF expression and increasing MDD susceptibility (Sun et al., 2015). In contrast, the homologous protein bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain 1B (BAZ1B) is thought to serve as an indicator of stress resilience, as it both enhances responses to rewarding stimuli and promotes adaptive responses to aversive stimuli. Although BAZ1B expression rapidly recovers post-stress exposure, persistent behavioral abnormalities suggest chromatin remodeling may induce long-term effects via downstream gene cascades (Bielawski et al., 2019). However, the roles of ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling complexes in MDD remain poorly understood, necessitating further investigation to elucidate their mechanistic contributions.
5 Epigenetic antidepressant molecular mechanisms of NPs
5.1 Flavonoids
Flavonoids are polyphenolic NPs characterized by a C6-C3-C6 backbone, widely distributed in fruits, vegetables, and medicinal plants. Based on structural variations, they are classified into six major subclasses: flavonols, flavanols, flavanones, flavones, isoflavones, and anthocyanins. Preclinical studies have identified specific flavonoids with antidepressant potential, demonstrating their ability to reverse depressive-like behaviors in rodent models of MDD.
Hesperidin, chemically identified as hesperetin 7-O-rutinoside, is a flavanone glycoside abundantly present in citrus fruits (Li et al., 2023b). Preclinical studies across diverse CNS disease models have demonstrated its potent pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects (Ikram et al., 2019; Muhammad et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2020). In lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced murine models, hesperidin upregulates miRNA-132 expression in the PFC. This upregulation suppresses hyperactivation of pro-inflammatory cytokines via negative feedback mechanisms, attenuating neuroinflammation and thereby exerting antidepressant-like effects (Li et al., 2016).
Quercetin, a flavonol ubiquitously distributed in fruits, vegetables, and traditional herbal medicines, exhibits multimodal pharmacological activities such as antidepressant, anticancer, gut microbiota-modulatory, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and HPA axis-modulating properties (Chen et al., 2022). In perimenopausal MDD models, quercetin ameliorates depressive-like behaviors by binding estrogen receptors, restoring KAT/HDAC homeostasis, and significantly enhancing H3K9ac in the hypothalamus. This epigenetic modulation alleviates MDD-related phenotypes via suppression of the endoplasmic reticulum stress inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha/X-box binding protein 1 (IRE1α/XBP1) pathway, reducing ferroptosis-associated lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction (Wang et al., 2024a).
Malvidin-3′-O-glucoside (Mal-gluc), a predominant anthocyanin in Vitis vinifera, displays antioxidant and anti-inflammatory bioactivities. It exerts antidepressant effects by downregulating HDAC2 expression in the NAc, thereby elevating histone acetylation at the RAC1 promoter to enhance its transcription and protein expression. RAC1, a critical small GTPase, improves dendritic spine morphology/function, enhances synaptic plasticity, and mitigates stress-induced synaptic deficits (Wang et al., 2018).
Isoliquiritin (ISL), a major flavonoid glycoside isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., exhibits broad-spectrum pharmacological actions encompassing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antidepressant, neuroprotective, angiogenic, and cardioprotective activities (Fu et al., 2025; Luo et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2021b). ISL upregulates miR-27a to suppress spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) translation, reducing SYK protein levels and inhibiting NF-κB pathway activation. This cascade ultimately attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation, Caspase-1 cleavage, and maturation of IL-1β/GSDMD with an N-terminal fragment, thereby ameliorating pyroptosis, neuroinflammation, and depressive symptomatology (Li et al., 2021d).
Genistein, a phytoestrogen derived from Glycine max (L.) Merr., belongs to the isoflavone class of compounds and exhibits both estrogen-like activity and a range of neuroprotective effects due to its unique chemical structure (Shete et al., 2024). In addition to its well-documented antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hormonal regulatory properties, Genistein has also been identified as a natural compound with epigenetic modulatory activity. It can influence gene transcription by inhibiting the expression of DNMTs (Sundaram et al., 2018). A recent study using a CUMS model in mice demonstrated that Genistein downregulates the expression of miR-221 and miR-222 in the PFC, thereby relieving the suppression of their target gene Connexin 43 (Cx43). This leads to the restoration of glial gap junction protein expression, enhancement of synaptic plasticity, and significant alleviation of depression-like behaviors (Shen et al., 2018).
5.2 Alkaloids
Alkaloids represent a class of nitrogen-containing organic compounds derived from plants, characterized by diverse chemical architectures and broad-spectrum bioactivities. These phytochemicals are ubiquitously distributed in roots, stems, leaves, and fruits across botanical species, with numerous alkaloids exhibiting marked pharmacological properties including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and neuromodulatory effects.
The genus Mahonia, a traditional medicinal plant in China, synthesizes over 150 chemical constituents, predominantly alkaloids such as protoberberines (e.g., berberine, palmatine, coptisine), bisbenzylisoquinolines (e.g., tetrahydroberberine), and aporphines (He and Mu, 2015). Emerging evidence identifies Mahonia alkaloids (MA) as potent antidepressant agents. Mechanistically, MA downregulates miR-205 expression to relieve its inhibitory effect on Cx43, thereby upregulating Cx43 levels. This cascade activates the CREB/BDNF signaling pathway, enhancing neuroplasticity and neuronal functionality. Notably, gap junction dysfunction is an important pathological feature of MDD (Xia et al., 2018). Cx43 is the major gap junction protein in astrocytes. MA restores the normal function of gap junctions and regulates neurosecretory function and synaptic activity through upregulation of Cx43, which then exerts antidepressant effects (He et al., 2022).
Of particular therapeutic interest is berberine, an antimicrobial alkaloid extracted from Mahonia species (e.g., Coptis chinensis Franch.), clinically employed for diarrheal management. Contemporary pharmacological studies reveal its multifaceted potential in cardiovascular, neurological, and psychiatric disorders. Experimental models demonstrate berberine’s capacity to suppress miR-34b-5p and miR-470-5p activity, which subsequently upregulates BDNF expression. This miRNA-mediated transcriptional modulation stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis while ameliorating depressive behaviors in murine models (Zhan et al., 2021).
5.3 Terpenoids
Terpenoids, a large class of NPs composed of isoprene units (C5H8), are widely distributed across plants, fungi, and marine organisms. Based on the number of isoprene units, they are classified into subclasses including monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), and others. Extensive research has demonstrated that terpenoids possess significant neurotherapeutic potential, exhibiting antidepressant, anxiolytic, and cognitive-enhancing effects. Their therapeutic mechanisms involve diverse molecular pathways, including reducing oxidative stress levels, antagonizing mitochondrial apoptosis, modulating inflammatory responses, regulating neurotransmitter homeostasis, promoting BDNF signaling cascades. These multifaceted actions collectively contribute to their efficacy in treating neurological disorders through precise molecular modulation.
Nerolidol (3,7,11-trimethyl-1,6,10-dodecatrien-3-ol), a naturally occurring sesquiterpenoid alcohol belonging to the monoterpenoid family, is predominantly isolated from essential oils of Aquilaria Lam. and other plant species (Lei et al., 2024). This compound demonstrates diverse pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, neuroprotective, anxiolytic, and hippocampal repair properties, and has been traditionally employed in herbal medicine to alleviate fatigue, enhance qi-blood circulation, and restore mental homeostasis. At the molecular level, Nerolidol exerts antidepressant effects by significantly reducing DNMT1 expression in the brains of CUMS-induced depressed mice. Through downregulation of DNMT1, it suppresses microglial activation and attenuates the release of proinflammatory cytokines, thereby alleviating neuroinflammation (Zhang et al., 2024b).
Geniposide, a bioactive iridoid glycoside extracted from the fruits of Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis, has garnered significant attention for its diverse pharmacological properties. Accumulating evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies supports its multifaceted biological activities, including neuroprotection, hepatoprotection, anti-inflammation, analgesia, antidepressant effects, cardioprotection, antioxidation, immune modulation, antithrombotic activity, and antitumor potential (Choi et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2024; Qin et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2024). A recent investigation elucidates a novel molecular mechanism underlying its antidepressant efficacy: Geniposide upregulates the expression of transcription factors CREB1 and lncRNA Six3os1, thereby enhancing synaptic protein synthesis (e.g., Htr3a and Htr2a), which ultimately modulates neuronal function and ameliorates MDD-related behaviors (Li et al., 2023a).
Genipin, a monoterpenoid compound extracted from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, functions as the aglycone of Geniposide. It is generated through deglycosylation in the intestine and liver, exhibiting pleiotropic bioactivities including antidepressant, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and neuroprotective effects. Distinct from Geniposide’s mechanism, Genipin inhibits DNMT1 activity to reduce DNA methylation at the BDNF promoter region, thereby alleviating prenatal stress-induced depressive-like behaviors through epigenetic regulation of neurotrophin synthesis (Ye et al., 2018).
Eucalyptol, a natural monoterpene predominantly derived from Eucalyptus robusta Sm. (Hoch et al., 2023). This aromatic compound, widely employed in food flavoring, perfumery, and pharmaceuticals, demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antimicrobial, and antioxidative properties (Yin et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2019). Crucially, recent studies have elucidated its antidepressant efficacy via miRNA-mediated epigenetic pathways. Eucalyptol suppresses the expression of miR-329 and miR-362, two miRNAs that target the mRNA of brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1-associated protein 3 (Baiap3) –a C2-domain containing protein critical for dense core vesicle (DCV) trafficking. By restoring Baiap3 expression, Eucalyptol enhances DCV-mediated 5-HT secretion, ultimately ameliorating depression-like phenotypes (Kim et al., 2021a).
Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid isolated from the flower and leaf tissues of Cannabis sativa L., has garnered significant attention for its therapeutic potential in mental health disorders due to its absence of psychoactive and hallucinogenic properties (Castillo-Arellano et al., 2023). This multifaceted compound modulates CNS function through diverse neurobiological mechanisms, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and protein homeostasis-regulating activities (Dash et al., 2021). In the context of antidepressant action, CBD reverses the upregulation of miR-16 and miR-135 in the PFC of CUMS-induced models, thereby alleviating depression-like behaviors through epigenetic normalization; second, it activates 5-HT1A receptors to counteract CUMS-induced transcriptional repression of the htr1a gene, ultimately enhancing serotonergic system function (Bright and Akirav, 2023).
Shanzhiside methylester (SM), a cyclohexenyl ether glycoside extracted from Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis, functions as a small-molecule glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist with potent anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antidepressive properties (Fan et al., 2016). SM exerts anti-depressant effects through multiple mechanisms, with epigenetic regulation serving as a critical pathway. SM binds to miRNA-155-5p, thereby inhibiting its targeting of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 (SOCS1) mRNA and upregulating SOCS1 protein expression. The upregulation of SOCS1 subsequently suppresses janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (JAK2/STAT3) signaling pathway activation, reduces proinflammatory cytokine production, and ultimately alleviates inflammatory responses and depressive behaviors (Sun et al., 2022).
Morroniside, a cyclohexenyl ether glycoside isolated from Cornus officinalis Siebold & Zucc., exhibits pleiotropic bioactivities including antioxidative, antiapoptotic, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects (Liu et al., 2021; Shi et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024a). Morroniside downregulates miRNA-409-3p expression, thereby derepressing BDNF transcription through the release of its 3′UTR binding site. This derepression activates the canonical BDNF/TrkB signaling cascade, which sequentially phosphorylates downstream effectors including Akt, ERK1/2, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, β-catenin, and CREB. The resultant upregulation of these kinases enhances neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity through multiple pathways, ultimately alleviating depressive-like phenotypes in rodent models (Qian et al., 2024).
5.4 Phenolic compounds
Phenolic compounds, a structurally diverse class of plant secondary metabolites characterized by hydroxyl (-OH) substituents on aromatic rings, encompass two major subclasses: phenolic acids and polyphenols. These bioactive molecules are ubiquitously present in plant tissues across various food matrices (fruits, vegetables, cereals) and medicinal herbs. Their multifaceted biological activities, including potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties, are primarily attributed to their redox-active phenolic hydroxyl groups, making them promising therapeutic targets for MDD.
Dihydrocaffeic acid (DHCA), a phenolic acid containing a catechol moiety and a propyl side chain, belongs to the phenolic acids subgroup within the polyphenol family. This bioactive compound, characterized by extremely low natural abundance, is primarily found in fermented food systems and selectively accumulated in coffee extracts as a metabolic derivative of caffeic acid (CAA) and chlorogenic acid metabolism. It has a variety of biological activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulation (Zieniuk, 2023). At the molecular level, DHCA exerts its antidepressant effects through epigenetic regulation of proinflammatory pathways. It directly inhibits DNMT1 activity, leading to hypomethylation of CpG dinucleotides in IL-6 gene introns 1 and 3. This epigenetic modification reduces IL-6 protein expression, thereby lowering peripheral inflammatory levels and exerting antidepressive effects (Wang et al., 2018).
CAA, 3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid, a natural hydroxycinnamic acid containing phenolic and acrylic functional groups, is ubiquitously distributed in various plant matrices including coffee beans, argan oil, barley, olive oil, and selected fruits. This bioactive compound exhibits prominent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and neuroprotective properties (Khan et al., 2021; Li et al., 2024; Pavlíková, 2022). CAA modulates the expression of epigenetic enzymes involved in DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation (including DNMT1, DNMT3a, and TET1-3), thereby affecting the transcription of BDNF and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) genes to exert antidepressant effects. Additionally, CAA downregulates COMT expression, elevates dopamine levels in the brain, and ameliorates depressive symptoms through dopaminergic neurotransmission enhancement (Hu et al., 2020).
Apple phenolic extracts (APEs), a complex mixture of polyphenolic compounds derived from Malus pumila Mill., exhibit pleiotropic bioactivities including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties (Cambeiro-Pérez et al., 2022). These bioactive components are primarily composed of chlorogenic acid, procyanidin B2, epicatechin, phloridzin, and phloretin (Feng et al., 2021). Its antidepressant mechanism involves the miR-22-3p/Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) axis. By downregulating the level of miR-22-3p, it upregulates the expression of the NAD+-dependent HDAC SIRT1, thereby enhancing cellular antioxidant capacity, inhibiting the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways, and reducing cell apoptosis, thus alleviating depressive symptoms (Ren et al., 2022).
Gastrodin (GAS), a phenolic glycoside isolated from the rhizomes of Gastrodia elata Bl., has emerged as a promising therapeutic candidate for inflammation-associated neurological disorders due to its remarkable efficacy and safety profile (Wang et al., 2024b). Mechanistically, GAS exerts anti-depressant effects through miRNA-mediated epigenetic regulation: It downregulates miR-107-3p expression, thereby upregulating its target gene karyopherin alpha 1, reducing the production of inflammatory factors, and alleviating inflammatory response and depressive-like behavior (Song et al., 2022).
Resveratrol, a polyphenolic found in plants such as Vitis vinifera L. and Reynoutria japonica Houtt., exhibits multiple biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects (Caruso et al., 2022; Ungurianu et al., 2023). As a SIRT1 activator, it regulates histone modifications through NAD+-dependent deacetylation, enhancing chromatin accessibility and promoting the transcriptional expression of neurotrophic factors like BDNF, highlighting its epigenetic antidepressant potential (Lagouge et al., 2006). Notably, resveratrol also upregulates the RNA-binding protein ELAV-like RNA binding protein 4 (ELAVL4), which stabilizes BDNF mRNA and improves neuroplasticity. In the CUMS model, resveratrol significantly restores neuronal morphology and dendritic spine density in the hippocampal cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) region (Ge et al., 2025). Further studies in a prenatal X-ray exposure-induced MDD model showed that resveratrol, by activating SIRT1, reverses the transcriptional repression of tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) 2, restores 5-HT synthesis, downregulates aging-associated epigenetic markers (p16/p21), and upregulates BDNF, thereby alleviating depression-like symptoms (Zhang et al., 2025).
Curcumin, a natural polyphenolic compound derived from Curcuma longa L., belongs to the diarylheptanoid class and is widely studied for its significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (Bhat et al., 2019; Pulido-Moran et al., 2016). A study using a LPS-induced MDD rat model found that preventive administration of curcumin (40 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, for 7 consecutive days) effectively reversed the abnormal upregulation of miR-146a-5p in the hippocampal CA1 region. This microRNA is primarily released by activated microglia through exosomes and plays a role in inflammatory signaling regulation. Overexpression of miR-146a-5p inhibits the phosphorylation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, leading to the downregulation of synaptic proteins, which results in reduced dendritic spine density and synaptic dysfunction, manifesting as prominent depression-like behaviors. Curcumin intervention restores synaptic density and function by inhibiting the miR-146a-5p/ERK signaling axis, thereby producing rapid and significant antidepressant effects (Fan et al., 2021).
5.5 Saponins
Saponins, a class of amphiphilic NPs, are characterized by hydrophobic triterpenoid or steroidal aglycone cores conjugated with hydrophilic oligosaccharide chains via glycosidic bonds. Their surface-active properties enable foam formation in aqueous solutions, earning them the name “saponins”. These compounds predominantly occur in medicinal plants of families Araliaceae, Fabaceae, Umbelliferae, and Campanulaceae, serving as core bioactive components in traditional antidepressant formulations. Beyond their well-established anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunoregulatory activities, recent studies reveal novel antidepressant mechanisms involving epigenetic regulation and neurotrophic factor signaling pathways.
Saikosaponin C (SSc), a triterpenoid saponin isolated from Bupleurum chinense Franch., exhibits multifaceted pharmacological activities including anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, antioxidant, immunoregulatory, and hepatoprotective effects (Li et al., 2018). SSc inhibits DNMT1 activity, leading to reduced methylation of the IL-6 gene intron region and subsequent downregulation of IL-6 expression. This process disrupts the activation of the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway, alleviating neuroinflammation by suppressing proinflammatory mediators, while enhancing synaptic plasticity ultimately ameliorates depression-like behaviors (Bai et al., 2023).
Ginsenoside Rb1 (Rb1), a major bioactive component of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer, is widely used for the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases. As one of the most abundant ginsenosides, Rb1 demonstrates multiple pharmacological activities including anti-fatigue, anti-inflammatory, immunoregulatory, neuroprotective, and antidepressant effects (Li et al., 2023c; Ni et al., 2022). Rb1 downregulates miR-134 expression, thereby relieves miR-134-mediated suppression of BDNF, activates BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway, enhances synaptic plasticity, and ultimately ameliorates depression-like behaviors (Wang et al., 2022).
5.6 Other types
Schisandrin B (SCHB), a major dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan isolated from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., is characterized by prominent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties (Ba et al., 2015; Luo et al., 2022). SCHB exerts therapeutic effects against MDD through a multifaceted molecular mechanism: it upregulates miR-124 expression, thereby suppressing NF-κB/TLR4/Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) and MAPK signaling pathways, which induces microglial M1 to M2 phenotypic conversion, reduces neuroinflammation, and ultimately ameliorates depression-like behaviors (Yang et al., 2024b).
Cinnamaldehyde (CA), 3-phenylprop-2-enal, a major bioactive aldehyde constituent of Cinnamomum cassia (L.) D. Don, has been traditionally employed for the management of MDD (Kim et al., 2021b). As a neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic agent (Bae et al., 2018; Mateen et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2016), CA alleviates CUMS-induced depressive-like behaviors in middle-aged rats (Yao et al., 2015). CA upregulates GR expression in the testes, suppresses miR-190b transcription, restores BDNF levels, thereby enhancing neural plasticity and improving depression-like behaviors. Notably, these epigenetic modifications also prevent intergenerational transmission of MDD through GR/miR-190b/BDNF axis regulation (Gao et al., 2022).
Sulforaphane (SFN), a natural isothiocyanate compound derived from cruciferous vegetables such as Brassica oleracea, is the precursor of glucoraphanin. As a natural HDAC inhibitor, SFN plays a critical role in epigenetic regulation and exhibits significant antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidepressant potential (Myzak et al., 2004). Animal studies have shown that SFN alleviates depression-like behaviors induced by CSDS by enhancing BDNF transcription. The underlying mechanism involves upregulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and downregulation of methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) in microglia, thereby relieving transcriptional repression of the BDNF promoter. Additionally, SFN promotes the shift of microglia from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory phenotype, further creating a microenvironment conducive to neuroprotection and synaptic plasticity (Tang et al., 2022).
Betaine is a natural trimethylamine compound widely found in Beta vulgaris L. (Zawieja and Chmurzynska, 2025). As a methyl donor, it regulates DNA methylation and neurotransmitter synthesis through one-carbon metabolism. In a rat model of hereditary generalized epilepsy with comorbid depression-like behaviors, maternal intake of a methyl-enriched diet containing betaine (15 g/kg) significantly alleviated depression-like behaviors in the offspring during adulthood. Mechanistically, this intervention upregulated the expression of DNMT1, hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1 (HCN1), and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) genes in the somatosensory cortex, hippocampus, and NAc, suggesting that betaine may enhance DNA methylation, block the binding of transcriptional repressors, relieve transcriptional repression of antidepressant-related genes, and enhance dopaminergic function in the midbrain-limbic system, thereby producing persistent antidepressant effects during critical periods of brain development (Sarkisova et al., 2023).
Trichostatin A (TSA), derived from the actinomycete Streptomyces hygroscopicus, is a hydroxamic acid compound and a classic HDACs inhibitor widely used in epigenetics research. TSA inhibits Class I and Class II HDACs, increasing histone acetylation levels, thereby modulating chromatin accessibility and activating the transcription of various genes involved in mood regulation. Studies have shown that TSA enhances H3K9/14 acetylation levels by inhibiting HDACs, directly activating BDNF promoter 1 transcription (Tian et al., 2010). In a repeated restraint stress model in male mice, TSA increased histone H3 acetylation levels, leading to the formation of transcriptionally active chromatin, which subsequently upregulated the expression of TPH in the midbrain. As the rate-limiting enzyme in 5-HT synthesis, increased TPH expression enhances 5-HT synthesis and neurotransmission, ultimately significantly reversing stress-induced mood depression (Kimijima et al., 2022). Another study demonstrated that the HDACs inhibitor TSA increased hippocampal H3K9, H4K5, and H4K12 acetylation levels, accompanied by a decrease in HDAC1/2/4/5 expression, restoring the transcriptional activity of antidepressant-related genes such as BDNF, and significantly reversing depression-like behaviors induced by the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist in mice (Zhu et al., 2021). In an Alzheimer’s disease model using amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 (APP/PS1) mice, TSA inhibited HDACs activity, increased histone acetylation levels, and downregulated Cystatin F-mediated microglial inflammation, significantly alleviating anxiety and depression-like behaviors in the APP/PS1 mice (Su et al., 2024) (Table 1).
TABLE 1
| Classification | Natural product | Chemical structure | Molecular formula | CAS number | Source | In vivo/in vitro | Modeling method | Main indicators | Antidepressant mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | Hesperidin |
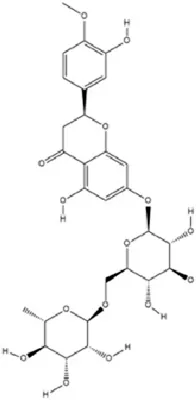
|
C28H34O15 | 520-26-3 | Peel of citrus fruits | In vivo | LPS | IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α↓; miRNA-132↑ | Upregulating miRNA-132 to suppress proinflammatory cytokines via negative feedback, thereby alleviating neuroinflammation | Li et al. (2016) |
| Flavonoids | Quercetin |
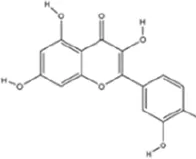
|
C15H10O7 | 117-39-5 | Vegetables, fruits, leafy vegetables, whole grains, red wine, tea, etc. | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: OVX and CUMS | N6-Acetyl-L-lysine↑; acetyl-H3K9↑ | Targeting ERα/ERβ restores HAT/HDAC balance to enhance H3K9ac levels, suppress IRE1α/XBP1 activity, and reduce ferroptosis/mitochondrial dysfunction | Wang et al. (2024a) |
| Flavonoids | Malvidin-3′-O-glucoside |
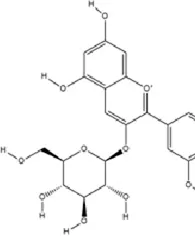
|
C23H25ClO12 | 7228-78-6 | Vitis vinifera | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: Repeated Social Defeat Stress, (RSDS) | Rac1, Histone acetylation↑; number of PSD-95 puncta, mEPSC frequency↓ | Reducing HDAC2 in the NAc elevates histone acetylation at the Rac1 promoter to enhance its transcription and expression | Wang et al. (2018) |
| Flavonoids | Isoliquiritin |
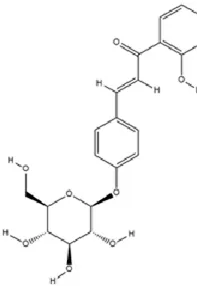
|
C21H22O9 | 5041-81-6 | Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CSDS and LPS | miR-27a, SKY↑; p-NF-κB, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α↓ | Upregulating miRNA-27a suppresses SYK translation, reducing NF-κB activity to inhibit NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β/GSDMD-N, alleviating pyroptosis/neuroinflammation and depression | Li et al. (2021c) |
| Flavonoids | Genistein |
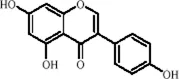
|
C15H10O5 | 446-72-0 | Glycine max (L.) Merr. | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CUMS | miR-221、miR-222 expression↓, Cx43 mRNA level↑ | down-regulating miR-221/222, thereby up-regulating Cx43 to restore gap-junction–mediated neuronal communication. | Shen et al. (2018) |
| Alkaloids | Berberine |
|
C20H18NO4+ | 2086-83-1 | Coptis chinensis Franch. | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CUMS | miR-34b-5p, miR-470-5p↓; BDNF↑ | Inhibiting miR-34b-5p/miR-470-5p upregulates BDNF expression to promote hippocampal neuron growth. | Zhan et al. (2021) |
| Alkaloids | Mahonia alkaloids | -- | -- | -- | phylum Berberiaceae [Mahonia bealei (Fort.) Carr.] | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: Reserpine-Induced Depression Model | miR-205↓; Cx43↑; BDNF, p-CREB↑; 5-HT, DA, NE↑; MAO↓ | inhibiting miR-205, upregulating Cx43 to restore gap junction function, and activating the CREB/BDNF signaling pathway | He et al. (2022) |
| Terpenoids | Nerolidol |
|
C15H26O | 7212-44-4 | Aquilaria Lam. | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CUMS | DNMT1↓; Iba-1↓; TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6↓ | Inhibiting DNMT1 to reduce microglial activation and neuroinflammation | Zhang et al. (2024b) |
| Terpenoids | Geniposide |
|
C17H24O10 | 24512-63-8 | Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CUMS | DNMT1↓; Htr3a, Htr2a↑ | Regulating the Creb1/Six3os1-synaptic protein axis to enhance synaptic plasticity | Li et al. (2023a) |
| Terpenoids | Genipin |
|
C11H14O5 | 6902-77-8 | Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis | In vivo | Prenatal Stress Model | DNMT1↓; BDNF↑ | Inhibiting DNMT1 activity, upregulating BDNF expression, enhancing synaptic plasticity, and promoting neuroprotection | Ye et al. (2018) |
| Terpenoids | Eucalyptol |
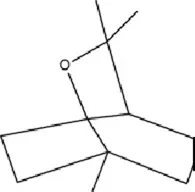
|
C10H18O | 470-82-6 | Eucalyptus robusta Sm. | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CUMS+ Ionizing Radiation | miR-329/362↓; Baiap3↑; 5-HT↑ | Inhibiting miR-329/362, restoring Baiap3 expression, promoting DCV trafficking of 5-HT, and increasing synaptic 5-HT levels to alleviate depressive behaviors. | Kim et al. (2021a) |
| Terpenoids | Cannabidiol |
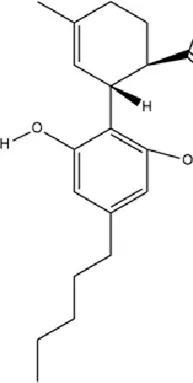
|
C21H30O2 | 13956-29-1 | Cannabis sativa L. | In vivo | UCMS | miR-16, miR-135↓; miR-16↑; htr1a↑ | Regulating the miR-16/miR-135-5-HT1A receptor axis in the vmPFC | Bright and Akirav (2023) |
| Terpenoids | Shanzhiside methylester | -- | -- | -- | Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CUMS | miRNA-155-5p↓; p-JAK2/p-STAT3↓, SOCS1↑, Iba1, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6↓ | inhibiting the miRNA-155-5p/SOCS1 axis to suppress the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and reduce inflammation | Sun et al. (2022) |
| Terpenoids | Morroniside |
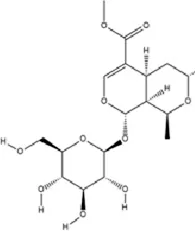
|
C17H26O11 | 25406-64-8 | Cornus officinalis Siebold & Zucc. | In vivo | Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (MCAO) combined with CUMS | miR-409-3p↓; BDNF↑; TrkB, p-AKT, p-ERK, p-GSK-3β, β-catenin, p-CREB↑ | Inhibiting miR-409-3p and activating the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway (including downstream molecules such as AKT, ERK, GSK-3β/β-catenin, and CREB) | Qian et al. (2024) |
| Phenolic compounds | Dihydrocaffeic acid |
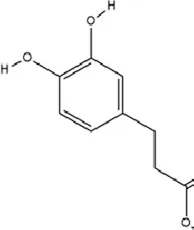
|
C9H10O4 | 1078-61-1 | Coffea | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: RSDS | DNMT1↓; IL-6↓ | Inhibiting DNA methylation in the intronic regions of the IL-6 gene reduces IL-6 production and attenuates peripheral inflammation | Wang et al. (2018) |
| Phenolic compounds | Caffeic acid |
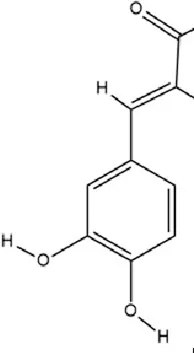
|
C9H8O4 | 331-39-5 | Coffea | In vivo | CUMS | Hippocampus: 5mC↓, 5hmC↑, BDNF promoter IV mRNA levels↑; PFC: COMT mRNA levels↓ | Modulating hippocampal DNA methylation (reducing 5mC and enhancing 5hmC) to restore BDNF expression, while suppressing excessive prefrontal hydroxymethylation (lowering 5hmC) | Hu et al. (2020) |
| Phenolic compounds | Apple Phenolic Extracts | -- | -- | -- | Malus pumila Mill. | In vivo | Lead exposure | miR-22-3p↓; SIRT1↑ | Activation of the miR-22-3p/SIRT1 signaling pathway synergistically exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects, thereby alleviating hippocampal damage | Ren et al. (2022) |
| Phenolic compounds | Gastrodin |
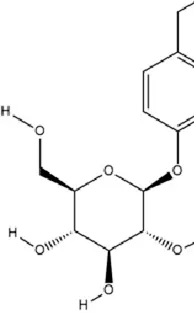
|
C13H18O7 | 62499-27-8 | Gastrodia elata Bl. | In vivo | LPS | miR-107-3p↓; KPNA1 ↓; IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-18, MCP-1↓ | Downregulation of miR-107-3p and upregulation of its downstream target gene KPNA1 alleviate neuroinflammation | Song et al. (2022) |
| Phenolic compounds | Resveratrol |
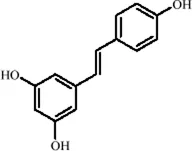
|
C14H12O3 | 501-36-0 | Vitis vinifera L. and Reynoutria japonica Houtt. | In vivo | CUMS | ELAVL4↑; BDNF↑ | Restoring hippocampal neuroplasticity and regulating the ELAVL4-Bdnf mRNA pathway | Ge et al. (2025) |
| Phenolic compounds | Resveratrol |
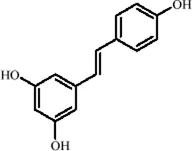
|
C14H12O3 | 501-36-0 | Vitis vinifera L. and Reynoutria japonica Houtt. | In vivo | Prenatal radiation depression model | SIRT1↑; TPH2↑; 5-HT level↑ | Activating SIRT1-mediated histone deacetylation to derepress the TPH2 promoter, thereby restoring 5-HT synthesis | Zhang et al. (2025) |
| Phenolic compounds | Curcumin |
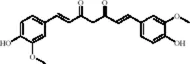
|
C17H19O6 | 458-37-7 | Curcuma longa L. | In vivo | LPS | miR-146a-5p↓; p-ERK↑ | Inhibiting miR-146a-5p overexpression, restoring ERK phosphorylation, reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, inhibiting neuronal apoptosis, salvaging synaptic loss | Fan et al. (2021) |
| Saponins | Saikosaponin C |
|
C48H78O17 | 20736-08-7 | Bupleurum chinense Franch. | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CSDS | DNMT1, p-STAT3/STAT3↓; IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β↓; PSD-95↓ | Inhibition of DNMT1-mediated IL-6 gene methylation reduces IL-6 expression, thereby inhibiting microglia activation and suppressing neuroinflammation; Promoting synaptic plasticity | Bai et al. (2023) |
| Saponins | Ginsenoside Rb1 |
|
C54H92O23 | 41753-43-9 | Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. | In vivo | CUMS | miR-134↓; BDNF, TrkB, p-Akt, p-ERK, p-GSK-3β (Ser9), β-catenin, p-CREB, PSD-95, GAP-43, NR2A/B, GluR1, CaMKII↑ | Blocking miR-134 boosts BDNF activity, activates its TrkB signaling pathway, improves synaptic plasticity | Wang et al. (2022) |
| Other types | Schisandrin B |
|
C23H28O6 | 61281-37-6 | Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. | In vitro | LPS | miR-124↑; NO, TNF-α↓; IL-10, Arg-1↑; iNOS, IBA-1↓; CD206, Arg-1↑ | Upregulating miR-124 inhibits NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, promotes microglial polarization from the M1 to M2 phenotype, and alleviates inflammatory responses | Yang et al. (2024b) |
| Other types | Cinnamaldehyde |
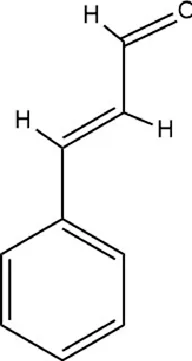
|
C9H8O | 14371-10-9 | Cinnamomum cassia (L.) D. Don | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CMS | GR↑; miR-190b↓; CORT↓; BDNF↑ | upregulateing GR, inhibiting miR-190b, and restoring BDNF expression in the hippocampus | Gao et al. (2022) |
| Other types | Sulforaphane |
|
C6H11NOS2 | 4478-93-7 | Cruciferous vegetables, such as Brassica oleracea | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: CSDS | Nrf2 protein↑; MeCP2↓; BDNF↑; TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6↓; IL-4, IL-10↑ | Activating Nrf2, suppressing MeCP2, and enhancing microglial BDNF transcription, restoring dendritic spine density and mitigating inflammation to promote stress resilience | Tang et al. (2022) |
| Other types | Betaine |
|
C5H11NO2 | 107-43-7 | Beta vulgaris L. | In vivo | Wistar Albino Glaxo Rijswijk (WAG/Rij) | DNMT1 mRNA↑; HCN1 mRNA↑; TH mRNA↑ | Through DNMT1-mediated DNA methylation reprogramming, transcriptionally up-regulating TH and HCN1, elevating mesolimbic dopaminergic tone, and suppressing cortical excitability | Sarkisova et al. (2023) |
| Other types | Trichostatin A |
|
C17H22N2O3 | 58880-19-6 | Streptomyces platensis | In vivo | Repeated restraint stress | HDAC↓; TPH↑; 5-HT↑ | Inhibiting HDAC, increasing histone acetylation, enhancing the transcription of TPH gene, boosting 5-HT synthesis and release | Kimijima et al. (2022) |
| Other types | Trichostatin A |
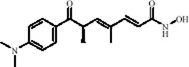
|
C17H22N2O3 | 58880-19-6 | Streptomyces platensis | In vivo | Male C57BL/6 mice | HDAC1/4/5↓ | Inhibiting HDACs, promoting histone acetylation, and regulating the expression of depression-related genes | Zhu et al. (2021) |
| Other types | Trichostatin A |
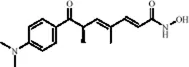
|
C17H22N2O3 | 58880-19-6 | Streptomyces platensis | In vivo and in vitro | In vivo: APP/PS1; in vitro: LPS-induced BV2 microglial cells | HDAC↓; CST7↓ | Inhibiting histone deacetylase activity, thereby increasing histone acetylation and down-regulating CST7 expression to suppress microglial inflammation | Su et al. (2024) |
| Other types | Sodium butyrate |
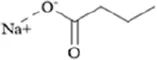
|
C4H7NaO2 | 156-54-7 | Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Roseburia spp., Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens | In vivo | Flinders Sensitive Line rats | TET1↑; BDNF P4 promoter 5hmC↑; BDNF P4 promoter 5 mC↓ BDNF↑ | Upregulating TET1 demethylates the BDNF promoter (5mC→5hmC), relieves epigenetic repression, boosts BDNF, and enhances neuroplasticity. | Wei et al. (2015) |
Summary of the antidepressant mechanisms of NPs via epigenetic modifications.
6 Toxicology and side effects
There is no bioactive compound on Earth that can simultaneously exhibit therapeutic activity and completely avoid non-specific off-target effects on normal physiological tissues (Guo et al., 2023). While NPs exhibit multi-component synergy, polytarget modulation, and epigenetic regulatory networks that offer unique advantages for MDD intervention, their complex composition simultaneously introduces potential toxicological liabilities.
The paradox of therapeutic selectivity versus systemic toxicity is exemplified by CBD, where its epigenetic modulatory effects in MDD are juxtaposed with significant safety concerns. In a clinical trial evaluating CBD’s antiepileptic properties, 12 out of 18 patients (66.7%) experienced at least one adverse event related to CBD during a 12-month treatment period with escalating doses ranging from 5 to 50 mg/kg/day. The most frequent adverse events were somnolence (44.4%, n = 8), ataxia (27.8%, n = 5), and diarrhea (22.2%, n = 4) (Hess et al., 2016). Preclinical studies further revealed dose-dependent toxicities. At 30 mg/kg, CBD caused testosterone depletionand spermatogonial cell loss in male mice, suggesting reproductive system vulnerability (Carvalho et al., 2018). Notably, 50 mg/kg CBD induced severe cardiovascular complications including hypotension and ventricular arrhythmias leading to sudden cardiac arrest in rodent models (Garberg et al., 2017).
CA demonstrates overall good tolerability with low acute toxicity, as evidenced by a wide oral LD50 range of 0.6–3.4 g/kg body weight in mice. Even at 20-fold higher than the effective dose (20 mg/kg), no significant behavioral or serum biochemical abnormalities were observed (Anand et al., 2010). However, chronic exposure to high doses induces dose-dependent adverse effects: marked weight loss in female rats and mice, along with histopathological alterations including esophageal squamous hyperplasia and nasal olfactory epithelial degeneration (Hooth et al., 2004). At suprapharmacological levels, CA also displays hepatotoxic potential characterized by glutathione depletion and micronucleus formation, implying genotoxic risk (Mereto et al., 1994). In the respiratory system, as an e-cigarette flavoring agent, CA causes pulmonary cytotoxicity via disruption of cellular proliferation/differentiation and induction of DNA damage in lung cells (Behar et al., 2016). Despite these findings, regulatory agencies including the Food and Drug Administration and the Council of Europe consider CA safe within the acceptable daily intake limit of 1.25 mg/kg.
In studies on the reproductive toxicity of CAA, it was found that high doses (5 and 150 mg/kg/day) affected embryo implantation, particularly when administered during the first 6 days of pregnancy, leading to reduced implantation rates. Additionally, the dose of 150 mg/kg/day also influenced fetal weight gain. The study did not observe significant maternal toxicity, teratogenic malformations, or developmental abnormalities in offspring. Meanwhile, the report proposed that the no-observed-adverse-effect level for CAA was determined to be 0.15 mg/kg/day (Liu et al., 2019b).
Geniposide, despite possessing multiple pharmacological activities, exhibits dose-dependent and duration-dependent toxicities upon high-dose or long-term administration. Studies have demonstrated that continuous administration of 300 mg/kg Geniposide induces severe hepatorenal toxicity in rats, manifesting as hepatic cellular swelling, necrosis, inflammatory infiltration, and renal tubular vacuolar degeneration. Notably, its hepatotoxicity is closely associated with the metabolic product Genipin, while thiol compounds in the liver play a crucial regulatory role in modulating its toxicity. Conversely, low-dose administration (60 mg/kg) or short-term treatment generally does not produce overt toxicity (Tian et al., 2018).
The translation challenges of NPs in drug development and clinical application primarily originate from their inherent duality of therapeutic efficacy and toxicological risks, particularly due to the coexistence of active components and endogenous toxins. Over half of natural extracts exhibit dose-dependent toxicities, manifesting not only in classical hepatorenal injuries but also emerging patterns such as cardiotoxicity and hematopoietic suppression. Furthermore, NPs exhibit diminished bioavailability due to significant first-pass metabolism and may cause delayed organ toxicity via accumulation effects. Therefore, future toxicological evaluations of NPs require continuous innovation, including advanced in vitro/in vivo assays to elucidate the mechanisms underlying hepato-renal injury. In the context of neuropsychiatric disorders, quantitative assessment of the dynamic equilibrium between antidepressant-active components and neurotoxic thresholds is critical to enable rational utilization of NPs through evidence-based frameworks.
7 Conclusions and prospects
MDD, as a multifaceted psychiatric disorder, presents two fundamental challenges to therapeutic intervention. First, conventional drugs such as SSRIs exhibit prolonged onset latency, marked interindividual variability in efficacy, high relapse rates post-withdrawal, and significant side effects including gastrointestinal disturbances and sexual dysfunction. Secondly, the heterogeneity of the disease itself means that its pathological mechanisms have not yet been fully elucidated, especially since the monoamine neurotransmitter hypothesis cannot explain all clinical phenomena. Recent advances in epigenetic regulation have emerged as a promising paradigm to overcome these limitations. Dysregulation of DNA methylation, histone acetylation, and ncRNA networks has been implicated in hippocampal synaptic plasticity remodeling, modulation of monoaminergic transmission, HPA axis balance, and microglia-mediated neuroinflammation, thereby illuminating the complex pathophysiology of MDD. Accordingly, this review systematically summarizes NPs-based interventions targeting epigenetic machinery, including flavonoids, alkaloids, and terpenoids, through mechanisms such as DNA methyltransferase inhibition, HDACs expression regulation, and miRNA-mRNA network modulation, which collectively enhance depressive-like behavior amelioration. Furthermore, it provides critical assessments of safety concerns related to hepatic and renal toxicity, emphasizing the necessity for precision-oriented approaches to balance epigenetic therapies’ benefits with systemic risk profiles.
Despite the promising antidepressant effects of NPs via epigenetic mechanisms in animal models, their clinical translation faces multiple challenges. First, safety remains a major concern in drug development. Most NPs exert their effects by inhibiting HDACs or DNMTs, which are widely expressed across tissues, and long-term use may lead to systemic side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances or immune activation due to off-target toxicity. Second, the lack of target specificity limits clinical applicability. Many NPs act on multiple epigenetic enzymes, which may enhance efficacy but also increase the risk of widespread, non-specific gene expression changes and associated adverse effects. Developing more selective NPs or derivatives is therefore essential to improve therapeutic precision and reduce unwanted effects.
Additionally, NPs often exhibit dose-dependent effects, and the effective dose range varies across experimental models. For example, low-dose curcumin promotes BDNF promoter demethylation, whereas high doses may induce global methylation dysregulation. This complexity makes it difficult to define an optimal therapeutic window. Furthermore, most NPs lack selective binding to specific epigenetic enzymes or gene loci, which may lead to off-target modulation of unrelated pathways. Structural optimization and ligand-directed targeting strategies may enhance specificity.
Finally, most current studies rely on chronic stress animal models, which do not fully replicate the complexity of human MDD. Disease-specific validation is still lacking, and clinical studies on epigenetically active NPs remain scarce. Further research using patient-derived neuronal models and early-phase clinical trials is needed to assess their safety and efficacy in humans. In summary, addressing safety concerns, optimizing dosing strategies, and improving epigenetic and disease specificity are critical prerequisites for the successful clinical translation of NPs as novel antidepressant therapies.
Pharmacokinetic limitations remain a major obstacle to the clinical translation of NPs. Compounds such as resveratrol and curcumin exhibit poor water solubility, low oral bioavailability, and limited BBB permeability, reducing their effectiveness in targeting epigenetic pathways in the brain. To overcome these issues, novel delivery systems such as nanoparticles, liposomes, and transdermal formulations have been explored. For example, quercetin-loaded chitosan-coated lipid carriers showed superior antidepressant and neuroprotective effects in an LPS-induced mouse model compared to free quercetin and fluoxetine (Zewail et al., 2025). Additionally, the lack of standardized formulations and consistent quality across NP extracts hinders clinical application. Future efforts should focus on improving formulation, optimizing delivery, and evaluating pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic relationships to enhance therapeutic potential.
To advance the clinical translation of NPs in epigenetic antidepressant therapy, a multidimensional strategy is required. Future research should focus on improving safety, optimizing dosing, enhancing target specificity, and validating disease relevance. From a pharmacokinetic perspective, advanced delivery systems, such as nanoparticles, targeted carriers, and transdermal technologies, are needed to improve brain bioavailability. Given the complex composition and variability of NPs, efforts should also be made to standardize extraction, ensure quality control, and develop consistent formulations. Mechanistically, multi-omics, single-cell sequencing, and spatial transcriptomics can help elucidate how NPs regulate epigenetic processes in specific brain regions and cell types. In particular, region- and cell-type-specific epigenetic interventions targeting areas such as the prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, or hippocampus may enhance therapeutic precision. Well-characterized NPs with favorable safety profiles should be prioritized for early clinical trials and evaluated in combination with existing antidepressants. Overall, bridging mechanistic insights with translational validation will be key to developing safe, precise, and feasible NP-based therapies for MDD.
Statements
Author contributions
YL: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. RS: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. XZ: Writing – review and editing. JS: Writing – review and editing. GZ: Writing – review and editing, Data curation. WZ: Writing – review and editing. JT: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. GZB20240036), the Key Project of the National Key Research and Development Program “Traditional Chinese Medicine Modernization Research” (Grant No. 2018YFC1707500), the Shandong Province Special Disease Prevention Project of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine (Grant No. YXH2019ZXY006), and the Graduate Education Quality Improvement and Innovation Project of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant No. YJSTZCX2025166).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
- MDD
Major depressive disorder
- NPs
Natural products
- SSRIs
Serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- HPA
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal
- CpG
Cytosine-phosphate-Guanine
- DNMTs
DNA methyltransferases
- TET
Ten-eleven translocation
- NR3C1
Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 1
- KATs
Lysine acetyltransferases
- H3K9ac
Histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation
- H3K14ac
Histone H3 lysine 14 acetylation
- HMTs
Histone methyltransferases
- H3K4me3
Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation
- H3K27me
Histone H3 lysine 27 methylation
- RNA
Ribonucleic acid
- ncRNAs
Non-coding RNAs
- lncRNAs
long non-coding RNAs
- miRNAs
microRNAs
- circRNAs
circular RNAs
- 3′UTRs
3′untranslated regions
- ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
- SWI/SNF
Switching defective/sucrose nonfermenting
- ISWI
Interphase structure whirlpool
- INO80
Inositol requiring protein 80
- CHD
Chromodomain helicase DNA-binding
- CSDS
Chronic social defeat stress
- NAc
Nucleus accumbens
- BDNF
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- GR
Glucocorticoid receptor
- GC
Glucocorticoid
- CM
Childhood maltreatment
- FKBP51
FKBP5 encodes FK506-binding protein 51
- SLC6A4
Solute carrier family 6 member 4
- 5-HT
Serotonin
- AMPK/CREB
AMP-activated protein kinase/cAMP response element-binding protein
- IL-6
interleukin-6
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- HDACs
Histone deacetylases
- PFC
Prefrontal cortex
- CNS
Central nervous system
- NLRP3
NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin
- SYN1
Synapsin 1
- TLR4
Toll-like receptor 4
- H3K9me2
histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation
- RAC1
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1
- GTPase
Guanosine triphosphatase
- PCGF1
Polycomb group ring finger 1
- MMP10
Matrix metallopeptidase 10
- NF-κB/MAPK
Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells/mitogen-activated protein kinase
- EZH2
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2
- BBB
Blood-brain barrier
- CDYL
Crotonyl-CoA hydratase
- CUMS
Chronic unpredictable mild stress
- TFIID
Transcription factor IID
- H3K4me3Q5ser
Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation and glutaminyl-serotonylation at glutamine5
- SERT
Serotonin transporter
- ERBB4
Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 4
- IL-1β
Interleukin-1 beta
- circDYM
Circular RNA derived from the DYM gene
- HNRNPU
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U
- UBE2K
ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 K
- FEDORA
FEmale DepressiOn lncRNA
- BAZ1B
Bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain 1B
- IRE1α/XBP1
Inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha/X-box binding protein 1
- Mal-gluc
Malvidin-3′-O-glucoside
- ISL
Isoliquiritin
- SYK
Spleen tyrosine kinase
- MA
Mahonia alkaloids
- Cx43
Connexin 43
- Baiap3
Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1-associated protein 3
- DCV
Dense core vesicle
- CBD
Cannabidiol
- SM
Shanzhiside methylester
- JAK2/STAT3
Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- SOCS1
Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1
- DHCA
Dihydrocaffeic acid
- CAA
Caffeic acid
- COMT
Catechol-O-methyltransferase
- APEs
Apple phenolic extracts
- SIRT1
Sirtuin 1
- GAS
Gastrodin
- ELAVL4
ELAV-like RNA binding protein 4
- SSc
Saikosaponin C
- Rb1
Ginsenoside Rb1
- SCHB
Schisandrin B
- MyD88
Myeloid differentiation primary response 88
- CA
Cinnamaldehyde
- LPS
Lipopolysaccharide
- CA1
Cornu ammonis 1
- TPH
Tryptophan hydroxylase
- ERK
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- SFN
Sulforaphane
- Nrf2
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- MeCP2
methyl-CpG binding protein 2
- HCN1
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1
- TH
Tyrosine Hydroxylase
- TSA
Trichostatin A
- APP/PS1
Amyloid Precursor Protein/Presenilin 1
References
1
Al-Kachak A. Di Salvo G. Fulton S. L. Chan J. C. Farrelly L. A. Lepack A. E. et al (2024). Histone serotonylation in dorsal raphe nucleus contributes to stress- and antidepressant-mediated gene expression and behavior. Nat. Commun.15, 5042. 10.1038/s41467-024-49336-4
2
Anand P. Murali K. Y. Tandon V. Murthy P. S. Chandra R. (2010). Insulinotropic effect of cinnamaldehyde on transcriptional regulation of pyruvate kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and GLUT4 translocation in experimental diabetic rats. Chemico-Biological Interact.186, 72–81. 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.03.044
3
Ba Q. Cui C. Wen L. Feng S. Zhou J. Yang K. (2015). Schisandrin B shows neuroprotective effect in 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease via inhibiting the negative modulation of miR-34a on Nrf2 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother.75, 165–172. 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.07.034
4
Bae W.-Y. Choi J.-S. Jeong J.-W. (2018). The neuroprotective effects of cinnamic aldehyde in an MPTP mouse model of parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19, 551. 10.3390/ijms19020551
5
Bai Z. Gao T. Zhang R. Lu Y. Tian J. Wang T. et al (2023). Inhibition of IL-6 methylation by Saikosaponin C regulates neuroinflammation to alleviate depression. Int. Immunopharmacol.118, 110043. 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110043
6
Bakusic J. Vrieze E. Ghosh M. Bekaert B. Claes S. Godderis L. (2020). Increased methylation of NR3C1 and SLC6A4 is associated with blunted cortisol reactivity to stress in major depression. Neurobiol. Stress13, 100272. 10.1016/j.ynstr.2020.100272
7
Bakusic J. Ghosh M. Polli A. Bekaert B. Schaufeli W. Claes S. et al (2021). Role of NR3C1 and SLC6A4 methylation in the HPA axis regulation in burnout. J. Affect. Disord.295, 505–512. 10.1016/j.jad.2021.08.081
8
Bartel D. P. (2009). MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell136, 215–233. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
9
Baudry A. Mouillet-Richard S. Schneider B. Launay J.-M. Kellermann O. (2010). MiR-16 targets the serotonin transporter: a new facet for adaptive responses to antidepressants. Science329, 1537–1541. 10.1126/science.1193692
10
Behar R. Z. Luo W. Lin S. C. Wang Y. Valle J. Pankow J. F. et al (2016). Distribution, quantification and toxicity of cinnamaldehyde in electronic cigarette refill fluids and aerosols. Tob. Control25, ii94–ii102. 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2016-053224
11
Bhat A. Mahalakshmi A. M. Ray B. Tuladhar S. Hediyal T. A. Manthiannem E. et al (2019). Benefits of curcumin in brain disorders. BioFactors45, 666–689. 10.1002/biof.1533
12
Bielawski T. Misiak B. Moustafa A. Frydecka D. (2019). Epigenetic mechanisms, trauma, and psychopathology: targeting chromatin remodeling complexes. Rev. Neurosci.30, 595–604. 10.1515/revneuro-2018-0055
13
Bright U. Akirav I. (2023). Cannabidiol modulates alterations in PFC microRNAs in a rat model of depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 2052. 10.3390/ijms24032052
14
Buschdorf J. P. Meaney M. J. (2016). Epigenetics/programming in the HPA axis. Compr. Physiol.6, 87–110. 10.1002/j.2040-4603.2016.tb00667.x
15
Bustamante A. C. Aiello A. E. Galea S. Ratanatharathorn A. Noronha C. Wildman D. E. et al (2016). Glucocorticoid receptor DNA methylation, childhood maltreatment and major depression. J. Affect. Disord.206, 181–188. 10.1016/j.jad.2016.07.038
16
Cai Y. Ji Y. Liu Y. Zhang D. Gong Z. Li L. et al (2024). Microglial circ-UBE2K exacerbates depression by regulating parental gene UBE2K via targeting HNRNPU. Theranostics14, 4058–4075. 10.7150/thno.96890
17
Cambeiro-Pérez N. Figueiredo-González M. Pérez-Gregorio M. R. Bessa-Pereira C. De Freitas V. Sánchez B. et al (2022). Unravelling the immunomodulatory role of apple phenolic rich extracts on human THP-1- derived macrophages using multiplatform metabolomics. Food Res. Int.155, 111037. 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111037
18
Caruso G. Torrisi S. A. Mogavero M. P. Currenti W. Castellano S. Godos J. et al (2022). Polyphenols and neuroprotection: therapeutic implications for cognitive decline. Pharmacol. Ther.232, 108013. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.108013
19
Carvalho R. K. Santos M. L. Souza M. R. Rocha T. L. Guimarães F. S. Anselmo-Franci J. A. et al (2018). Chronic exposure to cannabidiol induces reproductive toxicity in male Swiss mice. J. Appl. Toxicol.38, 1545. 10.1002/jat.3731
20
Castillo-Arellano J. Canseco-Alba A. Cutler S. J. León F. (2023). The polypharmacological effects of cannabidiol. Molecules28, 3271. 10.3390/molecules28073271
21
Chen S. Tang Y. Gao Y. Nie K. Wang H. Su H. et al (2022). Antidepressant potential of Quercetin and its glycoside derivatives: a comprehensive review and update. Front. Pharmacol.13, 865376. 10.3389/fphar.2022.865376
22
Cheng Y. Sun M. Chen L. Li Y. Lin L. Yao B. et al (2018). Ten-eleven translocation proteins modulate the response to environmental stress in mice. Cell Rep.25, 3194–3203.e4. 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.11.061
23
Cheng S. Wang W. Zhu Z. Zhao M. Li H. Liu D. et al (2023). Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor methylation in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in male mice. J. Neurochem.164, 624–642. 10.1111/jnc.15735
24
Choi S. Han K.-M. Won E. Yoon B.-J. Lee M.-S. Ham B.-J. (2015). Association of brain-derived neurotrophic factor DNA methylation and reduced white matter integrity in the anterior corona radiata in major depression. J. Affect. Disord.172, 74–80. 10.1016/j.jad.2014.09.042
25
Choi P. G. Park S.-H. Jeong H. Y. Kim H. S. Hahm J.-H. Seo H.-D. et al (2024). Geniposide attenuates muscle atrophy via the inhibition of FoxO1 in senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8. Phytomedicine123, 155281. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155281
26
Covington H. E. Maze I. Vialou V. Nestler E. J. (2015). Antidepressant action of HDAC inhibition in the prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience298, 329–335. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.04.030
27
Cruceanu C. Alda M. Nagy C. Freemantle E. Rouleau G. A. Turecki G. (2013). H3K4 tri-methylation in synapsin genes leads to different expression patterns in bipolar disorder and major depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol.16, 289–299. 10.1017/S1461145712000363
28
Dash R. Ali Md.C. Jahan I. Munni Y. A. Mitra S. Hannan Md.A. et al (2021). Emerging potential of cannabidiol in reversing proteinopathies. Ageing Res. Rev.65, 101209. 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101209
29
Di Nisio E. Lupo G. Licursi V. Negri R. (2021). The role of histone lysine methylation in the response of mammalian cells to ionizing radiation. Front. Genet.12, 639602. 10.3389/fgene.2021.639602
30
D’Mello S. R. (2020). Histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 in nervous system development. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. Neurosci. Neurogenesis50, 74–81. 10.1016/j.coph.2019.11.007
31
Fan H. Li T.-F. Gong N. Wang Y.-X. (2016). Shanzhiside methylester, the principle effective iridoid glycoside from the analgesic herb Lamiophlomis rotata, reduces neuropathic pain by stimulating spinal microglial β-endorphin expression. Neuropharmacology101, 98–109. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.09.010
32
Fan C. Li Y. Lan T. Wang W. Mao X. Yu S. Y. (2021). Prophylactic treatment of curcumin in a rat model of depression by attenuating hippocampal synaptic loss. Food Funct.12, 11202–11213. 10.1039/D1FO02676C
33
Fang W. Zhang J. Hong L. Huang W. Dai X. Ye Q. et al (2020). Metformin ameliorates stress-induced depression-like behaviors via enhancing the expression of BDNF by activating AMPK/CREB-mediated histone acetylation. J. Affect. Disord.260, 302–313. 10.1016/j.jad.2019.09.013
34
Farrelly L. A. Thompson R. E. Zhao S. Lepack A. E. Lyu Y. Bhanu N. V. et al (2019). Histone serotonylation is a permissive modification that enhances TFIID binding to H3K4me3. Nature567, 535–539. 10.1038/s41586-019-1024-7
35
Feng J. Pena C. J. Purushothaman I. Engmann O. Walker D. Brown A. N. et al (2017). Tet1 in nucleus accumbens opposes depression- and anxiety-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology42, 1657–1669. 10.1038/npp.2017.6
36
Feng S. Yi J. Li X. Wu X. Zhao Y. Ma Y. et al (2021). Systematic review of phenolic compounds in apple fruits: compositions, distribution, absorption, metabolism, and processing stability. J. Agric. Food Chem.69, 7–27. 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c05481
37
Fiori L. M. Kos A. Lin R. Théroux J.-F. Lopez J. P. Kühne C. et al (2021). miR-323a regulates ERBB4 and is involved in depression. Mol. Psychiatry26, 4191–4204. 10.1038/s41380-020-00953-7
38
Flaus A. Martin D. M. A. Barton G. J. Owen-Hughes T. (2006). Identification of multiple distinct Snf2 subfamilies with conserved structural motifs. Nucleic Acids Res.34, 2887–2905. 10.1093/nar/gkl295
39
Fu J. Cheng L. Zhang J. Sun R. Yu M. Wu M. et al (2025). Isoliquiritin targeting m5C RNA methylation improves mitophagy in doxorubicin-induced myocardial cardiotoxicity. Phytomedicine136, 156293. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156293
40
Gao Z. Chen T. Yu T. Zhang L. Zhao S. Gu X. et al (2022). Cinnamaldehyde prevents intergenerational effect of paternal depression in mice via regulating GR/miR-190b/BDNF pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin.43, 1955–1969. 10.1038/s41401-021-00831-0
41
Garberg H. T. Solberg R. Barlinn J. Martinez-Orgado J. Løberg E.-M. Saugstad O. D. (2017). High-dose cannabidiol induced hypotension after global hypoxia-ischemia in piglets. Neonatology112, 143–149. 10.1159/000471786
42
Ge H. Si L. Li C. Huang J. Sun L. Wu L. et al (2025). The antidepressant effect of resveratrol is related to neuroplasticity mediated by the ELAVL4-Bdnf mRNA pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci.26, 1113. 10.3390/ijms26031113
43
Gelle T. Samey R. A. Plansont B. Bessette B. Jauberteau-Marchan M.-O. Lalloué F. et al (2021). BDNF and pro-BDNF in serum and exosomes in major depression: evolution after antidepressant treatment. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry109, 110229. 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.110229
44
Gill H. Gill B. El‐Halabi S. Chen‐Li D. Lipsitz O. Rosenblat J. D. et al (2020). Antidepressant medications and weight change: a narrative review. Obesity28, 2064–2072. 10.1002/oby.22969
45
Golden S. A. Christoffel D. J. Hodes G. E. Heshmati M. Magida J. Davis K. et al (2013). Epigenetic regulation of RAC1 induces synaptic remodeling in stress disorders and depression. Nat. Med.19, 337–344. 10.1038/nm.3090
46
Gore F. M. Bloem P. J. Patton G. C. Ferguson J. Joseph V. Coffey C. et al (2011). Global burden of disease in young people aged 10–24 years: a systematic analysis. Lancet377, 2093–2102. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60512-6
47
Guo Y. Zhao S. Wang G. G. (2021). Polycomb gene silencing mechanisms: PRC2 chromatin targeting, H3K27me3 “readout” and phase separation-based compaction. Trends Genet.37, 547–565. 10.1016/j.tig.2020.12.006
48
Guo C. Huang Q. Wang Y. Yao Y. Li J. Chen J. et al (2023). Therapeutic application of natural products: NAD+ metabolism as potential target. Phytomedicine114, 154768. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154768
49
Han Q.-Q. Wu P.-F. Li Y.-H. Cao Y. Chen J.-G. Wang F. (2022). SVCT2–mediated ascorbic acid uptake buffers stress responses via DNA hydroxymethylation reprogramming of S100 calcium-binding protein A4 gene. Redox Biol.58, 102543. 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102543
50
He J.-M. Mu Q. (2015). The medicinal uses of the genus Mahonia in traditional Chinese medicine: an ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol.175, 668–683. 10.1016/j.jep.2015.09.013
51
He J. Li D. Wei J. Wang S. Chu S. Zhang Z. et al (2022). Mahonia Alkaloids (MA) ameliorate depression induced gap junction dysfunction by miR-205/Cx43 axis. Neurochem. Res.47, 3761–3776. 10.1007/s11064-022-03761-3
52
Hess E. J. Moody K. A. Geffrey A. L. Pollack S. F. Skirvin L. A. Bruno P. L. et al (2016). Cannabidiol as a new treatment for drug-resistant epilepsy in Tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia57, 1617–1624. 10.1111/epi.13499
53
Hoch C. C. Petry J. Griesbaum L. Weiser T. Werner K. Ploch M. et al (2023). 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol): a versatile phytochemical with therapeutic applications across multiple diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother.167, 115467. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115467
54
Hodes G. E. Pfau M. L. Purushothaman I. Ahn H. F. Golden S. A. Christoffel D. J. et al (2015). Sex differences in nucleus accumbens transcriptome profiles associated with susceptibility versus resilience to subchronic variable stress. J. Neurosci.35, 16362–16376. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1392-15.2015
55
Hooth M. J. Sills R. C. Burka L. T. Haseman J. K. Witt K. L. Orzech D. P. et al (2004). Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of microencapsulated trans-cinnamaldehyde in rats and mice. Food Chem. Toxicol.42, 1757–1768. 10.1016/j.fct.2004.07.002
56
Hu J. Cao S. Zhang Z. Wang L. Wang D. Wu Q. et al (2020). Effects of caffeic acid on epigenetics in the brain of rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress. Mol. Med. Rep.22, 5358–5368. 10.3892/mmr.2020.11609
57
Huan Z. Mei Z. Na H. Xinxin M. Yaping W. Ling L. et al (2021). lncRNA MIR155HG alleviates depression-like behaviors in mice by regulating the miR-155/BDNF axis. Neurochem. Res.46, 935–944. 10.1007/s11064-021-03234-z
58
Huang Y.-L. Zeng N.-X. Chen J. Niu J. Luo W.-L. Liu P. et al (2019). Dynamic changes of behaviors, dentate gyrus neurogenesis and hippocampal miR-124 expression in rats with depression induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress. Neural Regen. Res.15, 1150–1159. 10.4103/1673-5374.270414
59
Ikram M. Muhammad T. Rehman S. U. Khan A. Jo M. G. Ali T. et al (2019). Hesperetin confers neuroprotection by regulating Nrf2/TLR4/NF-κB signaling in an Aβ mouse model. Mol. Neurobiol.56, 6293–6309. 10.1007/s12035-019-1512-7
60
Issler O. van der Zee Y.Y. Ramakrishnan A. Wang J. Tan C. Loh Y.-H. E. et al (2020). Sex-specific role for the long non-coding RNA LINC00473 in depression. Neuron106, 912–926.e5. 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.03.023
61
Issler O. van der Zee Y.Y. Ramakrishnan A. Xia S. Zinsmaier A. K. Tan C. et al (2022). The long noncoding RNA FEDORA is a cell type– and sex-specific regulator of depression. Sci. Adv.8, eabn9494. 10.1126/sciadv.abn9494
62
Ito T. Bulger M. Pazin M. J. Kobayashi R. Kadonaga J. T. (1997). ACF, an ISWI-containing and ATP-utilizing chromatin assembly and remodeling factor. Cell90, 145–155. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80321-9
63
Jones P. A. (2012). Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet.13, 484–492. 10.1038/nrg3230
64
Kang H.-J. Kim J.-M. Stewart R. Kim S.-Y. Bae K.-Y. Kim S.-W. et al (2013). Association of SLC6A4 methylation with early adversity, characteristics and outcomes in depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry44, 23–28. 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.01.006
65
Karpova N. N. (2014). Role of BDNF epigenetics in activity-dependent neuronal plasticity. Neuropharmacology, BDNF regulation of synaptic structure. Funct. Plasticity76, 709–718. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.002
66
Keller J. Gomez R. Williams G. Lembke A. Lazzeroni L. Murphy G. M. et al (2017). HPA axis in major depression: cortisol, clinical symptomatology and genetic variation predict cognition. Mol. Psychiatry22, 527–536. 10.1038/mp.2016.120
67
Khan F. Bamunuarachchi N. I. Tabassum N. Kim Y.-M. (2021). Caffeic acid and its derivatives: antimicrobial drugs toward microbial pathogens. J. Agric. Food Chem.69, 2979–3004. 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07579
68
Kim H. Kim J. Lee H. Shin E. Kang H. Jeon J. et al (2021a). Baiap3 regulates depressive behaviors in mice via attenuating dense core vesicle trafficking in subsets of prefrontal cortex neurons. Neurobiol. Stress16, 100423. 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100423
69
Kim H. J. Kim H. Choi Y. Lee J.-H. Kim D. Lee S. K. et al (2021b). Cinnamomum verum-derived O-methoxycinnamaldehyde prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in mice via NFAT mRNA stability in T lymphocytes. Phytomedicine91, 153703. 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153703
70
Kimijima H. Miyagawa K. Kurokawa K. Mochida-Saito A. Takahashi K. Takeda H. et al (2022). Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, alleviates the emotional abnormality induced by maladaptation to stress in mice. Neurosci. Lett.766, 136340. 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136340
71
Klengel T. Mehta D. Anacker C. Rex-Haffner M. Pruessner J. C. Pariante C. M. et al (2012). Allele-specific FKBP5 DNA demethylation mediates gene–childhood trauma interactions. Nat. Neurosci.16, 33–41. 10.1038/nn.3275
72
Klinger-König J. Hertel J. Van der Auwera S. Frenzel S. Pfeiffer L. Waldenberger M. et al (2019). Methylation of the FKBP5 gene in association with FKBP5 genotypes, childhood maltreatment and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology44, 930–938. 10.1038/s41386-019-0319-6
73
Kouzarides T. (2007). Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell128, 693–705. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.005
74
Lagouge M. Argmann C. Gerhart-Hines Z. Meziane H. Lerin C. Daussin F. et al (2006). Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell127, 1109–1122. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.013
75
LaPlant Q. Vialou V. Covington H. E. Dumitriu D. Feng J. Warren B. et al (2010). Dnmt3a regulates emotional behavior and spine plasticity in the nucleus accumbens. Nat. Neurosci.13, 1137–1143. 10.1038/nn.2619
76
Launay J. M. Mouillet-Richard S. Baudry A. Pietri M. Kellermann O. (2011). Raphe-mediated signals control the hippocampal response to SRI antidepressants via miR-16. Transl. Psychiatry1, e56. 10.1038/tp.2011.54
77
Lei Y. Li M. Liu X. Zhang L. Zhang R. Cai F. (2024). Nerolidol rescues hippocampal injury of diabetic rats through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and regulation of MAPK/AKT pathway. BioFactors50, 1076–1100. 10.1002/biof.2058
78
Li M. Shao H. Zhang X. Qin B. (2016). Hesperidin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in mice by promoting the miRNA-132 pathway. Inflammation39, 1681–1689. 10.1007/s10753-016-0402-7
79
Li X. Li X. Huang N. Liu R. Sun R. (2018). A comprehensive review and perspectives on pharmacology and toxicology of saikosaponins. Phytomedicine50, 73–87. 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.174
80
Li L. Wang T. Chen S. Yue Y. Xu Z. Yuan Y. (2021a). DNA methylations of brain-derived neurotrophic factor exon VI are associated with major depressive disorder and antidepressant-induced remission in females. J. Affect. Disord.295, 101–107. 10.1016/j.jad.2021.08.016
81
Li W. Ali T. Zheng C. Liu Z. He K. Shah F. A. et al (2021b). Fluoxetine regulates eEF2 activity (phosphorylation) via HDAC1 inhibitory mechanism in an LPS-induced mouse model of depression. J. Neuroinflammation18, 38. 10.1186/s12974-021-02091-5
82
Li Y. Chen X. Lu C. (2021c). The interplay between DNA and histone methylation: molecular mechanisms and disease implications. EMBO Rep.22, e51803. 10.15252/embr.202051803
83
Li Y. Song W. Tong Y. Zhang X. Zhao J. Gao X. et al (2021d). Isoliquiritin ameliorates depression by suppressing NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis via miRNA-27a/SYK/NF-κB axis. J. Neuroinflammation18, 1. 10.1186/s12974-020-02040-8
84
Li B. Zhao Y. Zhou X. Peng C. Yan X. Zou T. (2023a). Geniposide improves depression by promoting the expression of synapse-related proteins through the Creb1/Six3os1 axis. Gene877, 147564. 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147564
85
Li X. Huang W. Tan R. Xu C. Chen X. Li S. et al (2023b). The benefits of hesperidin in central nervous system disorders, based on the neuroprotective effect. Biomed. & Pharmacother.159, 114222. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114222
86
Li Y. Li J. Yang L. Ren F. Dong K. Zhao Z. et al (2023c). Ginsenoside Rb1 protects hippocampal neurons in depressed rats based on mitophagy-regulated astrocytic pyroptosis. Phytomedicine121, 155083. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155083
87
Li X. Shang N. Kang Y. Sheng N. Lan J. Tang J. et al (2024). Caffeic acid alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in rats by resisting ferroptosis via Nrf2 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin.45, 248–267. 10.1038/s41401-023-01177-5
88
Li N. Du J. Yang Y. Zhao T. Wu D. Peng F. et al (2025). Microglial PCGF1 alleviates neuroinflammation associated depressive behavior in adolescent mice. Mol. Psychiatry30, 914–926. 10.1038/s41380-024-02714-2
89
Lister R. Mukamel E. A. Nery J. R. Urich M. Puddifoot C. A. Johnson N. D. et al (2013). Global epigenomic reconfiguration during mammalian brain development. Science341, 1237905. 10.1126/science.1237905
90
Liu Y. Li M. Fan M. Song Y. Yu H. Zhi X. et al (2019a). Chromodomain Y-like protein–mediated histone crotonylation regulates stress-induced depressive behaviors. Biol. Psychiatry85, 635–649. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.11.025
91
Liu Y. Qiu S. Wang L. Zhang N. Shi Y. Zhou H. et al (2019b). Reproductive and developmental toxicity study of caffeic acid in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol.123, 106–112. 10.1016/j.fct.2018.10.040
92
Liu H. Ou M.-X. Han Q.-Q. (2021). Microglial M2 polarization mediated the neuroprotective effect of morroniside in transient MCAO-induced mice. Front. Pharmacol.12, 784329. 10.3389/fphar.2021.784329
93
Liu L. Wu Q. Chen Y. Gu G. Gao R. Peng B. et al (2022). Updated pharmacological effects, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic potential of natural product geniposide. Molecules27, 3319. 10.3390/molecules27103319
94
Luo J. Li Z. Wang J. Weng Q. Chen S. Hu M. (2016). Antifungal activity of isoliquiritin and its inhibitory effect against peronophythora litchi Chen through a membrane damage mechanism. Molecules21, 237. 10.3390/molecules21020237
95
Luo W. Lin K. Hua J. Han J. Zhang Q. Chen L. et al (2022). Schisandrin B attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by targeting MyD88 and inhibiting MyD88‐dependent inflammation. Adv. Sci. (Weinh)9, 2202590. 10.1002/advs.202202590
96
Lussier A. A. Smith B. J. Fisher J. Luo M. Cerutti J. Schneper L. et al (2024). DNA methylation mediates the link between adversity and depressive symptoms. Nat. Ment. Health2, 1476–1485. 10.1038/s44220-024-00345-8
97
Ma Y. Li S. X. Zhou R. Y. Deng L. J. He W. Guo L. L. et al (2024). Geniposide improves depression-like behavior in prenatal stress male offspring through restoring HPA axis- and glucocorticoid receptor-associated dysfunction. Life Sci.340, 122434. 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122434
98
Malhi G. S. Mann J. J. (2018). Depression. Lancet392, 2299–2312. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31948-2
99
Martins H. C. Schratt G. (2021). MicroRNA-dependent control of neuroplasticity in affective disorders. Transl. Psychiatry11, 263. 10.1038/s41398-021-01379-7
100
Mateen S. Shahzad S. Ahmad S. Naeem S. S. Khalid S. Akhtar K. et al (2019). Cinnamaldehyde and eugenol attenuates collagen induced arthritis via reduction of free radicals and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Phytomedicine53, 70–78. 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.004
101
Mattei A. L. Bailly N. Meissner A. (2022). DNA methylation: a historical perspective. Trends Genet.38, 676–707. 10.1016/j.tig.2022.03.010
102
Mehta S. L. Chokkalla A. K. Bathula S. Arruri V. Chelluboina B. Vemuganti R. (2022). CDR1as regulates α-synuclein-mediated ischemic brain damage by controlling miR-7 availability. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids31, 57–67. 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.11.022
103
Mereto E. Brambilla-Campart G. Ghia M. Martelli A. Brambilla G. (1994). Cinnamaldehyde-induced micronuclei in rodent liver. Mutat. Research/Genetic Toxicol.322, 1–8. 10.1016/0165-1218(94)90027-2
104
Misir S. Wu N. Yang B. B. (2022). Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs. Cell Death Differ.29, 481–491. 10.1038/s41418-022-00948-7
105
Montagud-Romero S. Montesinos J. Pascual M. Aguilar M. A. Roger-Sanchez C. Guerri C. et al (2016). `Up-regulation of histone acetylation induced by social defeat mediates the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry70, 39–48. 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.04.016
106
Muhammad T. Ikram M. Ullah R. Rehman S. U. Kim M. O. (2019). Hesperetin, a citrus flavonoid, attenuates LPS-induced neuroinflammation, apoptosis and memory impairments by modulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Nutrients11, 648. 10.3390/nu11030648
107
Murgatroyd C. Quinn J. P. Sharp H. M. Pickles A. Hill J. (2015). Effects of prenatal and postnatal depression, and maternal stroking, at the glucocorticoid receptor gene. Transl. Psychiatry5, e560. 10.1038/tp.2014.140
108
Myzak M. C. Karplus P. A. Chung F.-L. Dashwood R. H. (2004). A novel mechanism of chemoprotection by sulforaphane: inhibition of histone deacetylase. Cancer Res.64, 5767–5774. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1326
109
Na K.-S. Won E. Kang J. Chang H. S. Yoon H.-K. Tae W. S. et al (2016). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promoter methylation and cortical thickness in recurrent major depressive disorder. Sci. Rep.6, 21089. 10.1038/srep21089
110
Nelson J. Klumparendt A. Doebler P. Ehring T. (2017). Childhood maltreatment and characteristics of adult depression: meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry210, 96–104. 10.1192/bjp.bp.115.180752
111
Ni X.-C. Wang H.-F. Cai Y.-Y. Yang D. Alolga R. N. Liu B. et al (2022). Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits astrocyte activation and promotes transfer of astrocytic mitochondria to neurons against ischemic stroke. Redox Biol.54, 102363. 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102363
112
Papamichos-Chronakis M. Watanabe S. Rando O. J. Peterson C. L. (2011). Global regulation of H2A.Z localization by the INO80 chromatin-remodeling enzyme is essential for genome integrity. Cell144, 200–213. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.021
113
Pathak S. S. Maitra S. Chakravarty S. Kumar A. (2017). Histone lysine demethylases of JMJD2 or KDM4 family are important epigenetic regulators in reward circuitry in the etiopathology of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology42, 854–863. 10.1038/npp.2016.231
114
Patnala R. Arumugam T. V. Gupta N. Dheen S. T. (2017). HDAC inhibitor sodium butyrate-mediated epigenetic regulation enhances neuroprotective function of microglia during ischemic stroke. Mol. Neurobiol.54, 6391–6411. 10.1007/s12035-016-0149-z
115
Pavlíková N. (2022). Caffeic acid and diseases—mechanisms of action. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 588. 10.3390/ijms24010588
116
Penner-Goeke S. Binder E. B. (2019). Epigenetics and depression. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci.21, 397–405. 10.31887/DCNS.2019.21.4/ebinder
117
Perroud N. Paoloni-Giacobino A. Prada P. Olié E. Salzmann A. Nicastro R. et al (2011). Increased methylation of glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) in adults with a history of childhood maltreatment: a link with the severity and type of trauma. Transl. Psychiatry1, e59. 10.1038/tp.2011.60
118
Poulter M. O. Du L. Weaver I. C. G. Palkovits M. Faludi G. Merali Z. et al (2008). GABAA receptor promoter hypermethylation in suicide brain: implications for the involvement of epigenetic processes. Biol. Psychiatry64, 645–652. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.05.028
119
Pulido-Moran M. Moreno-Fernandez J. Ramirez-Tortosa C. Ramirez-Tortosa Mc. (2016). Curcumin and health. Molecules21, 264. 10.3390/molecules21030264
120
Qian W. Yu C. Wang S. Niu A. Shi G. Cheng Y. et al (2021). Depressive-like behaviors induced by chronic social defeat stress are associated with HDAC7 reduction in the nucleus accumbens. Front. Psychiatry11, 586904. 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.586904
121
Qian L. Huang S. Liu X. Jiang Y. Jiang Y. Hu Y. et al (2024). Morroniside improves the symptoms of post-stroke depression in mice through the BDNF signaling pathway mediated by MiR-409-3p. Phytomedicine123, 155224. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155224
122
Qin T. Hasnat M. Wang Z. Hassan H. M. Zhou Y. Yuan Z. et al (2023). Geniposide alleviated bile acid-associated NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating SIRT1/FXR signaling in bile duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis. Phytomedicine118, 154971. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154971
123
Reik W. (2007). Stability and flexibility of epigenetic gene regulation in mammalian development. Nature447, 425–432. 10.1038/nature05918
124
Ren Y. Sun-Waterhouse D. Ouyang F. Tan X. Li D. Xu L. et al (2022). Apple phenolic extracts ameliorate lead-induced cognitive impairment and depression- and anxiety-like behavior in mice by abating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis via the miR-22-3p/SIRT1 axis. Food Funct.13, 2647–2661. 10.1039/D1FO03750A
125
Reyes A. A. Marcum R. D. He Y. (2021). Structure and function of chromatin remodelers. J. Mol. Biol. RNA Polym. II Transcr.433, 166929. 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166929
126
Rothmore J. (2020). Antidepressant‐induced sexual dysfunction. Med. J. Aust.212, 329–334. 10.5694/mja2.50522
127
Sarkisova K. Y. Fedosova E. A. Shatskova A. B. Rudenok M. M. Stanishevskaya V. A. Slominsky P. A. (2023). Maternal methyl-enriched diet increases DNMT1, HCN1, and TH gene expression and suppresses absence seizures and comorbid depression in offspring of WAG/Rij rats. Diagnostics13, 398. 10.3390/diagnostics13030398
128
Shao Q.-Y. You F. Zhang Y.-H. Hu L.-L. Liu W.-J. Liu Y. et al (2018). CSF miR-16 expression and its association with miR-16 and serotonin transporter in the raphe of a rat model of depression. J. Affect. Disord.238, 609–614. 10.1016/j.jad.2018.06.034
129
Shen F. Huang W. Xing B. Fang X. Feng M. Jiang C. (2018). Genistein improves the major depression through suppressing the expression of miR-221/222 by targeting connexin 43. Psychiatry Investig.15 (06.29), 919–925. 10.30773/pi.2018.06.29
130
Shete V. Mahajan N. M. Shivhare R. Akkewar A. Gupta A. Gurav S. (2024). Genistein: a promising phytoconstituent with reference to its bioactivities. Phytotherapy Res.38, 3935–3953. 10.1002/ptr.8256
131
Shi P. Zheng B. Zhang S. Guo Q. (2024). A review of the sources and pharmacological research of morroniside. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1423062. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423062
132
Shuang R. Gao T. Sun Z. Tong Y. Zhao K. Wang H. (2024). Tet1/DLL3/Notch1 signal pathway affects hippocampal neurogenesis and regulates depression-like behaviour in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol.968, 176417. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176417
133
Shvedunova M. Akhtar A. (2022). Modulation of cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.23, 329–349. 10.1038/s41580-021-00441-y
134
Smith Z. D. Meissner A. (2013). DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet.14, 204–220. 10.1038/nrg3354
135
Song J.-J. Li H. Wang N. Zhou X.-Y. Liu Y. Zhang Z. et al (2022). Gastrodin ameliorates the lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in mice by downregulating miR-107-3p. Front. Pharmacol.13, 1044375. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1044375
136
Su Q. Ren Y.-H. Liu G.-W. Gao Y.-P. Zhang J.-X. Zhang J.-N. et al (2024). Trichostatin A relieves anxiety-and depression-like symptoms in APP/PS1 mice. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1333235. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1333235
137
Sun H. Damez–Werno D. M. Scobie K. N. Shao N. Dias C. Rabkin J. et al (2015). ACF chromatin remodeling complex mediates stress–induced depressive–like behavior. Nat. Med.21, 1146–1153. 10.1038/nm.3939
138
Sun Z. Zhan H. Wang C. Guo P. (2022). Shanzhiside methylester protects against depression by inhibiting inflammation via the miRNA-155-5p/SOCS1 axis. Psychopharmacology239, 2201–2213. 10.1007/s00213-022-06107-7
139
Sun Z.-W. Wang X. Zhao Y. Sun Z.-X. Wu Y.-H. Hu H. et al (2024). Blood-brain barrier dysfunction mediated by the EZH2-Claudin-5 axis drives stress-induced TNF-α infiltration and depression-like behaviors. Brain, Behav. Immun.115, 143–156. 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.10.010
140
Sundaram M. K. Ansari M. Z. Al Mutery A. Ashraf M. Nasab R. Rai S. et al (2018). Genistein induces alterations of epigenetic modulatory signatures in human cervical cancer cells. ACAMC18, 412–421. 10.2174/1871520617666170918142114
141
Tang R. Cao Q. Hu S. He L. Du P. Chen G. et al (2022). Sulforaphane activates anti-inflammatory microglia, modulating stress resilience associated with BDNF transcription. Acta Pharmacol. Sin.43, 829–839. 10.1038/s41401-021-00727-z
142
Tang L. Zhao P. Pan C. Song Y. Zheng J. Zhu R. et al (2024). Epigenetic molecular underpinnings of brain structural-functional connectivity decoupling in patients with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord.363, 249–257. 10.1016/j.jad.2024.07.110
143
Tian F. Marini A. M. Lipsky R. H. (2010). Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A on epigenetic changes and transcriptional activation of Bdnf promoter 1 by rat hippocampal neurons. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.1199, 186–193. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05175.x
144
Tian J. Yi Y. Zhao Y. Li C. Zhang Y. Wang L. et al (2018). Oral chronic toxicity study of geniposide in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol.213, 166–175. 10.1016/j.jep.2017.11.008
145
Tsankova N. Renthal W. Kumar A. Nestler E. J. (2007). Epigenetic regulation in psychiatric disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci.8, 355–367. 10.1038/nrn2132
146
Tseng C.-C. Wang S.-C. Yang Y.-C. Fu H.-C. Chou C.-K. Kang H.-Y. et al (2023). Aberrant histone modification of TNFAIP3, TLR4, TNIP2, miR-146a, and miR-155 in major depressive disorder. Mol. Neurobiol.60, 4753–4760. 10.1007/s12035-023-03374-z
147
Tsou P.-S. Varga J. O’Reilly S. (2021). Advances in epigenetics in systemic sclerosis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.17, 596–607. 10.1038/s41584-021-00683-2
148
Uchida S. Hara K. Kobayashi A. Otsuki K. Yamagata H. Hobara T. et al (2011). Epigenetic status of Gdnf in the ventral striatum determines susceptibility and adaptation to daily stressful events. Neuron69, 359–372. 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.12.023
149
Ungurianu A. Zanfirescu A. Margină D. (2023). Sirtuins, resveratrol and the intertwining cellular pathways connecting them. Ageing Res. Rev.88, 101936. 10.1016/j.arr.2023.101936
150
Varendi K. Kumar A. Härma M.-A. Andressoo J.-O. (2014). miR-1, miR-10b, miR-155, and miR-191 are novel regulators of BDNF. Cell Mol. Life Sci.71, 4443–4456. 10.1007/s00018-014-1628-x
151
Wang J. Hodes G. E. Zhang H. Zhang S. Zhao W. Golden S. A. et al (2018). Epigenetic modulation of inflammation and synaptic plasticity promotes resilience against stress in mice. Nat. Commun.9, 477. 10.1038/s41467-017-02794-5
152
Wang L. Chen K. Chen Z. (2021). Structural basis of ALC1/CHD1L autoinhibition and the mechanism of activation by the nucleosome. Nat. Commun.12, 4057. 10.1038/s41467-021-24320-4
153
Wang G. An T. Lei C. Zhu X. Yang L. Zhang L. et al (2022). Antidepressant-like effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on potentiating synaptic plasticity via the miR-134–mediated BDNF signaling pathway in a mouse model of chronic stress-induced depression. J. Ginseng Res.46, 376–386. 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.03.005
154
Wang H. Fan Z. Shliaha P. V. Miele M. Hendrickson R. C. Jiang X. et al (2023). H3K4me3 regulates RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pause-release. Nature615, 339–348. 10.1038/s41586-023-05780-8
155
Wang D. Yu Z. Yao R. Zhang J. Cui W. Dai J. et al (2024a). Quercetin alleviates depressive-like behavior by modulating acetyl-H3K9 mediated ferroptosis pathway in hypothalamus of perimenopausal depression rat model. Biomed. Pharmacother.179, 117369. 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117369
156
Wang W. Wang Y. Wang F. Xie G. Liu S. Li Z. et al (2024b). Gastrodin regulates the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway to reduce neuroinflammation and microglial activation in an AD model. Phytomedicine128, 155518. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155518
157
Wei Y. B. Melas P. A. Wegener G. Mathé A. A. Lavebratt C. (2015). Antidepressant-like effect of sodium butyrate is associated with an increase in TET1 and in 5-hydroxymethylation levels in the bdnf gene. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol.18, pyu032–pyu032. 10.1093/ijnp/pyu032
158
Whitehouse I. Flaus A. Cairns B. R. White M. F. Workman J. L. Owen-Hughes T. (1999). Nucleosome mobilization catalysed by the yeast SWI/SNF complex. Nature400, 784–787. 10.1038/23506
159
Wright E. C. Johnson S. A. Hao R. Kowalczyk A. S. Greenberg G. D. Ordoñes Sanchez E. et al (2017). Exposure to extrinsic stressors, social defeat or bisphenol A, eliminates sex differences in DNA methyltransferase expression in the amygdala. J. Neuroendocrinol.29, jne.12475. 10.1111/jne.12475
160
Xia C.-Y. Wang Z.-Z. Yamakuni T. Chen N.-H. (2018). A novel mechanism of depression: role for connexins. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol.28, 483–498. 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.01.009
161
Xu J. Wang R. Liu Y. Liu D. Jiang H. Pan F. (2017). FKBP5 and specific microRNAs via glucocorticoid receptor in the basolateral amygdala involved in the susceptibility to depressive disorder in early adolescent stressed rats. J. Psychiatric Res.95, 102–113. 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2017.08.010
162
Yan X. Zeng D. Zhu H. Zhang Y. Shi Y. Wu Y. et al (2020). MiRNA-532-5p regulates CUMS-induced depression-like behaviors and modulates LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokine signaling by targeting STAT3. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat.16, 2753–2764. 10.2147/NDT.S251152
163
Yang W. Du W. W. Li X. Yee A. J. Yang B. B. (2016). Foxo3 activity promoted by non-coding effects of circular RNA and Foxo3 pseudogene in the inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis. Oncogene35, 3919–3931. 10.1038/onc.2015.460
164
Yang Y. Hu Z. Du X. Davies H. Huo X. Fang M. (2017). miR-16 and fluoxetine both reverse autophagic and apoptotic change in chronic unpredictable mild stress model rats. Front. Neurosci.11, 428. 10.3389/fnins.2017.00428
165
Yang C. Zhang J. Ma Y. Wu C. Cui W. Wang L. (2020). Histone methyltransferase and drug resistance in cancers. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.39, 173. 10.1186/s13046-020-01682-z
166
Yang J.-C. Zhao J. Chen Y.-H. Wang R. Rong Z. Wang S.-Y. et al (2024a). miR-29a-5p rescues depressive-like behaviors in a CUMS-induced mouse model by facilitating microglia M2-polarization in the prefrontal cortex via TMEM33 suppression. J. Affect. Disord.360, 188–197. 10.1016/j.jad.2024.05.156
167
Yang Y. Liu R. Sun Y. Wu B. He B. Jia Y. et al (2024b). Schisandrin B restores M1/M2 balance through miR-124 in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.76, 1352–1361. 10.1093/jpp/rgae079
168
Yao Y. Huang H.-Y. Yang Y.-X. Guo J.-Y. (2015). Cinnamic aldehyde treatment alleviates chronic unexpected stress-induced depressive-like behaviors via targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in mid-aged rats. J. Ethnopharmacol.162, 97–103. 10.1016/j.jep.2014.12.047
169
Ye D. Zhang L. Fan W. Zhang X. Dong E. (2018). Genipin normalizes depression-like behavior induced by prenatal stress through inhibiting DNMT1. Epigenetics13, 310–317. 10.1080/15592294.2018.1450033
170
Yin C. Liu B. Wang P. Li X. Li Y. Zheng X. et al (2020). Eucalyptol alleviates inflammation and pain responses in a mouse model of gout arthritis. Br. J. Pharmacol.177, 2042–2057. 10.1111/bph.14967
171
Yu N. Sun Y.-T. Su X.-M. He M. Dai B. Kang J. (2019). Eucalyptol protects lungs against bacterial invasion through attenuating ciliated cell damage and suppressing MUC5AC expression. J. Cell. Physiology234, 5842–5850. 10.1002/jcp.26359
172
Yuan M. Yang B. Rothschild G. Mann J. J. Sanford L. D. Tang X. et al (2023). Epigenetic regulation in major depression and other stress-related disorders: molecular mechanisms, clinical relevance and therapeutic potential. Sig Transduct. Target Ther.8, 309. 10.1038/s41392-023-01519-z
173
Zaratiegui M. Irvine D. V. Martienssen R. A. (2007). Noncoding RNAs and gene silencing. Cell128, 763–776. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.016
174
Zawieja E. Chmurzynska A. (2025). Betaine and aging: a narrative review of findings, possible mechanisms, research perspectives, and practical recommendations. Ageing Res. Rev.104, 102634. 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102634
175
Zelada M. I. Garrido V. Liberona A. Jones N. Zúñiga K. Silva H. et al (2023). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a predictor of treatment response in major depressive disorder (MDD): a systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 14810. 10.3390/ijms241914810
176
Zewail M. B. Nomier Y. A. E.Elesawy A. El-Dakroury W. A. (2025). Investigating the potential of quercetin-loaded chitosan-coated lipid carriers as an oral nanoplatform for depression management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.319, 145569. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145569
177
Zhan Y. Han J. Xia J. Wang X. (2021). Berberine suppresses mice depression behaviors and promotes hippocampal neurons growth through regulating the miR-34b-5p/miR-470-5p/BDNF axis. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat.17, 613–626. 10.2147/NDT.S289444
178
Zhang L. Zhang Z. Fu Y. Yang P. Qin Z. Chen Y. et al (2016). Trans-cinnamaldehyde improves memory impairment by blocking microglial activation through the destabilization of iNOS mRNA in mice challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Neuropharmacology110, 503–518. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.08.013
179
Zhang L. Song J. Kong L. Yuan T. Li W. Zhang W. et al (2020). The strategies and techniques of drug discovery from natural products. Pharmacol. & Ther. Youyou Tu 90th Birthd. Tribute216, 107686. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107686
180
Zhang Q. Hu Q. Wang J. Miao Z. Li Z. Zhao Y. et al (2021a). Stress modulates Ahi1-dependent nuclear localization of ten-eleven translocation protein 2. Hum. Mol. Genet.30, 2149–2160. 10.1093/hmg/ddab179
181
Zhang X.-H. Zhou C.-C. Li C.-Y. Hua Y. Li K. Wei P. et al (2021b). Isoliquiritin exert protective effect on telencephalon infarction injury by regulating multi-pathways in zebrafish model of ischemic stroke. Phytomedicine83, 153469. 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153469
182
Zhang C. Tong Q. Liu K. Mao T. Song Y. Qu Y. et al (2024a). Morroniside delays the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by promoting AMPK-mediated lipophagy. Phytomedicine129, 155703. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155703
183
Zhang G. Zhou X. Feng Q. Ke W. Pan J. Zhang H. et al (2024b). Nerolidol reduces depression-like behavior in mice and suppresses microglia activation by down-regulating DNA methyltransferase 1. NeuroReport35, 457–465. 10.1097/WNR.0000000000002029
184
Zhang Y. F. Xu Z. L. Wang C. Li J. Wu M. Y. Yi Y. Q. et al (2025). Resveratrol attenuates prenatal X-ray-induced microcephaly and adult depression via SIRT1-mediated senescence suppression and TPH2/5-HT pathway restoration in mice. Phytomedicine143, 156845. 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156845
185
Zhu X. Liu H. Liu Y. Chen Y. Liu Y. Yin X. (2020). The antidepressant-like effects of hesperidin in streptozotocin‐induced diabetic rats by activating Nrf2/ARE/Glyoxalase 1 pathway. Front. Pharmacol.11, 1325. 10.3389/fphar.2020.01325
186
Zhu L.-J. Sun Y.-Q. Wang S. Shi H.-J. Li N. (2021). Involvement of 5-HT1A receptor-mediated histone acetylation in the regulation of depression. NeuroReport32, 1049–1057. 10.1097/wnr.0000000000001693
187
Zhu D. Ni Y. Chen C. Dong Z. Wang L. Zhang W. (2024). Geniposide ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic mice by targeting AGEs-RAGE-dependent inflammatory pathway. Phytomedicine135, 156046. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156046
188
Zieniuk B. (2023). Dihydrocaffeic acid—is it the less known but equally valuable phenolic acid?Biomolecules13, 859. 10.3390/biom13050859
189
Zocher S. Overall R. W. Lesche M. Dahl A. Kempermann G. (2021). Environmental enrichment preserves a young DNA methylation landscape in the aged mouse hippocampus. Nat. Commun.12, 3892. 10.1038/s41467-021-23993-1
190
Zwolińska W. Bilska K. Tarhonska K. Reszka E. Skibińska M. Pytlińska N. et al (2024). Biomarkers of depression among adolescent girls: BDNF and epigenetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci.25, 3281. 10.3390/ijms25063281
Summary
Keywords
epigenetic modifications, depression, natural products, molecular mechanism, antidepressant
Citation
Lu Y, Shang R, Zhong X, Shi J, Zhang G, Zhao W and Teng J (2025) Pharmacological mechanism of natural antidepressants: the role of epigenetic modifications. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1616322. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1616322
Received
22 April 2025
Accepted
05 August 2025
Published
29 August 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Jiu Chen, Nanjing University, China
Reviewed by
Zhiting Gong, Dali University, China
Qian Wu, Johns Hopkins University, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Lu, Shang, Zhong, Shi, Zhang, Zhao and Teng.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Teng, 60170099@sdutcm.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.