Abstract
Objectives:
The ARMANI trial demonstrated that ramucirumab plus paclitaxel (switch maintenance group) significantly prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival in patients with advanced HER2-negative gastric cancer (GC) and gastroesophageal junction cancer (GEJC) compared to continued first-line oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy (control group). However, its cost-effectiveness remained unclear. This study aimed to evaluate its cost-effectiveness from the Chinese and United States (US) healthcare system perspective.
Methods:
A partitioned survival model was developed to compare the total costs, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) of switch maintenance group versus control group over a 10-year time horizon. Survival data were sourced from the ARMANI trial. Cost and utility were derived from open-access databases and published literature. The robustness of the results was verified through one-way sensitivity analysis and probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA). Additionally, subgroup analysis and scenario analysis were conducted.
Results:
The switch maintenance group yielded incremental gains of 0.15 QALYs in China and 0.16 QALYs in the US, with corresponding incremental costs of $56,738.32 and $185,250.55, resulting in ICERs of $373,219.84/QALY and $1,193,220.74/QALY, respectively. For the PD-L1 CPS ≥5 subgroup, incremental QALYs increased to 0.24 and 0.25, with incremental costs rising to $62,741.24 and $206,107.13, yielding ICERs of $266,259.94/QALY and $835,740.90/QALY, respectively. One-way sensitivity analysis revealed that the utility of PFS, the price of ramucirumab, and patient body weight were the most influential factors on the ICER, with consistent results observed from both Chinese and US perspectives. To be cost-effective in a 50% of chance, ramucirumab would need to reduce its price to 14.2% of the original price ($0.743 per mg) in China and 13.92% ($2.088 per mg) in the US, respectively.
Conclusion:
Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel is unlikely to be cost-effective compared to continuing oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for patients with advanced HER2-negative GC or GEJC in China and US.
Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC), including gastroesophageal junction cancer (GEJC), is a major global health burden (Cao et al., 2020). It ranks as the fifth most diagnosed malignancy and the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Approximately 1 million new cases are reported each year, with the majority occurring in east Asia (Smyth et al., 2020). China accounts for 44% of the global GC incidence (He et al., 2024). In the United States (US), the incidence and mortality rates of GC have been steadily declining (Thrift and El-Serag, 2020). However, GC exhibits the lowest 5-year overall survival (OS) rate among all cancers, posing significant implications for the US healthcare system (Thrift and El-Serag, 2020). Due to the high proportion of late-stage diagnoses, the prognosis for advanced GC remains poor (Smyth et al., 2020), with a five-year survival rate of less than 10% in metastatic cases (Yang et al., 2020).
Beyond its clinical impact, GC imposes a heavy financial burden. In China, newly diagnosed patients face an average annual out-of-pocket expense of $5,368, consuming 63.80% of their household income from the preceding year (Zhang et al., 2020). Despite improved therapeutic efficacy in GC treatment, the associated healthcare burden and costs have risen substantially in US, with average hospital expenses surging from $75,341 per patient in 2003 to $91,385 per patient in 2014 (Liu et al., 2018).
The standard first-line treatment for advanced GC includes a fluoropyrimidine combined with a platinum-based chemotherapy (National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2024; Lordick et al., 2022). Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) mediated signaling and angiogenesis contribute to the pathogenesis of gastric cancer (Wang et al., 2024). Inhibition of VEGFR-2 has been demonstrated to reduce tumor growth and neovascularization (Jung et al., 2002). Ramucirumab, a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody VEGFR-2 antagonist, blocks ligand binding and receptor-mediated pathway activation in endothelial cells (Coudert et al., 2012; Hu et al., 2019). Based on the great progress made in the RAINBOW trial, ramucirumab plus paclitaxel was approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the second-line treatment of advanced GC (Wilke et al., 2014). The Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) guidelines (Wang et al., 2024) and National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines (National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2024) recommend ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as the preferred second-line treatment for advanced Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2)-negative GC. However, despite the significant advances demonstrated in the RAINBOW trial, the median OS remains less than 10 months (Wilke et al., 2014). Switch maintenance therapy, which involves an early transition to a non-cross-resistant regimen (Lee and Chung, 2014), has shown clinical benefits in other cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (Coudert et al., 2012; Hu et al., 2019). Therefore, ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as switch maintenance or early second-line therapy for patients with HER2-negative GC who have received standard fluoropyrimidine combined with a platinum-based chemotherapy induction deserves further study.
The phase III ARMANI trial (NCT02934464) evaluated ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as a switch maintenance therapy (switch maintenance group) compared to continuing first-line oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy (control group). The study showed significant improvements in clinical outcomes. The switch maintenance group had longer median progression-free survival (PFS) (8.8 vs. 6.1 months; Hazard ratio [HR] = 0.61) and OS (15.8 vs. 12.7 months; HR = 0.75). Additionally, the disease control rate was higher (85% vs. 54%) (Randon et al., 2024).
Although ramucirumab plus paclitaxel has shown promising clinical benefits, the high cost of ramucirumab raises concerns about affordability, especially in resource-limited settings (Saito et al., 2017; Li et al., 2020). Pharmacoeconomic studies can help clinical decision makers and patients allocate resources rationally and improve the overall efficiency of medical resource allocation (Liu et al., 2020). However, no cost-effectiveness analysis has assessed ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as a first-line switch maintenance therapy. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as first-line switch maintenance therapy or early second-line treatment for GC from the perspective of the Chinese and US healthcare system.
Materials and methods
This study was conducted in accordance with the Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS 2022) Statement (Supplementary Table S1) (Husereau et al., 2022). Institutional review board approval or patient consent was not required as this analysis utilized publicly available data and modeling techniques.
Patients and interventions
Our study simulated a patient population aligned with the ARMANI trial. These patients had histologically confirmed advanced HER2-negative gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer, with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1. All patients were assumed to have achieved disease control after 3 months of first-line FOLFOX (folinic acid, fluorouracil, oxaliplatin) or CAPOX (capecitabine, oxaliplatin) therapy. For the Chinese perspective, patient weight was 69 kg with a body surface area (BSA) of 1.74 m2; for the US perspective, weight was 75 kg with a BSA of 1.80 m2. Other key baseline characteristics mirrored those of patients in the ARMANI study.
Patients were randomly assigned to the switch maintenance group or the control group. Patients assigned to the switch maintenance group received intravenous ramucirumab 8 mg/kg on days 1 and 8, and paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15, once every 28 days until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, withdrawal of informed consent, or patient death. Patients in the control group continued to receive FOLFOX or CAPOX and received fluorouracil therapy alone (capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil) after a maximum of 24 weeks of treatment. After disease progression, 58% of patients in the switch maintenance group and 56% of patients in the control group received subsequent systemic therapy (Randon et al., 2024). Based on the CSCO guidelines (Wang et al., 2024) and the NCCN guidelines (National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2024), intravenous injection of irinotecan 150 mg/m2 on the first day of a 21-day cycle as the subsequent treatment for patients was chosen for disease progression. For patients who did not receive antitumor systemic therapy after disease progression, we assumed they received best supportive care (BSC).
Model structure
A partitioned survival model was developed by TreeAge Pro 2019. The model consisted of three mutually exclusive health states: PFS, progressive disease (PD), and death (Figure 1). All patients were assumed to begin in the PFS state and could transition to PD or death following treatment. Patient survival proportions were estimated using the area under the curve (AUC) of OS data from ARMANI, while PFS proportions were derived from PFS AUC. The PD proportion was calculated by subtracting the PFS proportion from the OS proportion. The model time horizon was set at 10 years, based on the assumption that more than 99% of patients would die within this period. The cycle length was 28 days, in alignment with the treatment regimen. The outcomes of the model were total cost, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER). The ICER was calculated to compare the cost-effectiveness of the switch maintenance group and control group. Combining the recommendations of the WHO-CHOICE guidelines (Bertram et al., 2021) and the China guidelines for pharmacoeconomic evaluations (Liu et al., 2020), the willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold for China was set at $38,042.49 per QALY, which is three times the per capita GDP of China in 2023 (Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China, 2025). Consistent with other studies (Su et al., 2021; Chiang et al., 2021), $150,000 per QALY was used as the WTP threshold from the US perspective.
FIGURE 1
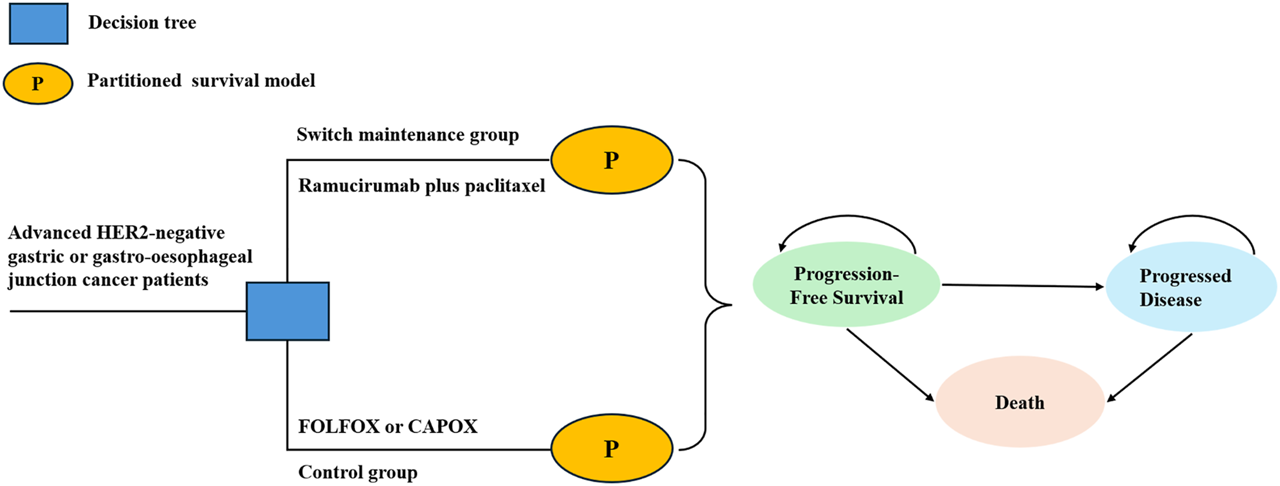
Structure of decision tree and partitioned survival model.
Clinical data
Referring to the method of Guyot (Guyot et al., 2012), the WebPlotDigitizer program (version 4.6, https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer/) was used to extract the survival data of OS and PFS from the Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves reported in the ARMANI study. The survHE, IPDfromKM, and flexsurv packages in R 4.4.2 were used to reconstruct the KM curves based on individual patient data (IPD). These data were used to fit various parametric survival models, including Exponential, Weibull, Gompertz, Log-logistic, Log-normal (Supplementary Table S2). Optimal models were selected by minimizing Akaike information criteria (AIC), Bayesian information criteria (BIC) and visual inspection (Table 1) (Williams et al., 2017). The fitting results are shown in Supplementary Figure S1–S10.
TABLE 1
| Parameter | Baseline value | Range | Distribution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-logistic OS survival model of switch maintenance group | shape = 2.309, scale = 13.051 | — | — | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Log-logistic OS survival model of control group | shape = 1.891, scale = 9.593 | — | — | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Log-logistic PFS survival model of switch maintenance group | shape = 2.061, scale = 6.767 | — | — | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Log-logistic PFS survival model of control group | shape = 1.697, scale = 3.579 | — | — | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Log-logistic OS survival model of switch maintenance group in PD-L1-CPS≥5 patients | shape = 2.386, scale = 15.518 | — | — | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Log-normal OS survival model of control group in PD-L1-CPS≥5 patients | meanlog = 2.376, sdlog = 0.805 | — | — | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Log-normal PFS survival model of switch maintenance group in PD-L1-CPS≥5 patients | meanlog = 2.0989, sdlog = 0.7146 | — | — | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Log-normal PFS survival model of control group in PD-L1-CPS≥5 patients | meanlog = 1.802, sdlog = 0.856 | — | — | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Cost from the chinese perspective | ||||
| Enhanced CT per unit | 23.693 | 10.659–106.647 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| Blood biochemistry per unit | 63.814 | 33.253–93.564 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| Blood routine per unit | 1.930 | 1.425–3.622 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| Urine routine per unit | 0.594 | 0.287–2.553 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| Injection administration | 0.802 | 0.158–0.643 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| Intravenous injection | 0.713 | 0.356–1.564 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| Cost of terminal care | 1,506.51 | 1,205.21–1,807.81 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| Cost of BSC per cycle | 267.78 | 214.22–321.34 | Gamma | Zhou et al. (2025) |
| Ramucirumab/mg | 5.23 | 4.186–6.279 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Paclitaxel/mg | 0.280 | 0.224–0.335 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Ondansetron/mg | 0.360 | 0.288–0.433 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Dexamethasone/mg | 0.018 | 0.0148–0.0221 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Diphenhydramine/mg | 0.103 | 0.0823–0.123 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Capecitabine/mg | 0.000653 | 0.000522–0.000783 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Calcium folinate/mg | 0.0355 | 0.0284–0.0426 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Oxaliplatin/mg | 0.881 | 0.705–1.058 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| 5-Fluorouracil/mg | 0.0183 | 0.0146–0.0220 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Irinotecan/mg | 0.0955 | 0.0764–0.115 | Gamma | Shanghai sunshine procurement all. (2025) |
| Cost from the US perspective | ||||
| Enhanced CT per unit | 530.79 | 424.63–636.95 | Gamma | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2025) |
| Blood biochemistry per unit | 10.56 | 8.45–12.67 | Gamma | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2025) |
| Blood routine per unit | 7.77 | 6.22–9.32 | Gamma | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2025) |
| Urine routine per unit | 3.17 | 2.54–3.80 | Gamma | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2025) |
| Injection administration | 13.91 | 11.13–16.69 | Gamma | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2025) |
| Intravenous injection | 223.30 | 178.64–267.96 | Gamma | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2025) |
| Cost of terminal care | 19,247.03 | 15,397.62–23,096.44 | Gamma | Zhu et al. (2023) |
| Cost of BSC per cycle | 2,262.59 | 1,810.07–2,715.11 | Gamma | Zhu et al. (2023) |
| Ramucirumab/mg | 15 | 12–18 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| Paclitaxel/mg | 0.2882 | 0.23056–0.34584 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| Ondansetron/mg | 0.1056 | 0.08448–0.12672 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| Dexamethasone/mg | 0.02255 | 0.01804–0.02706 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| Diphenhydramine/mg | 0.0602 | 0.04816–0.07224 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| Capecitabine/mg | 0.002 | 0.0016–0.0024 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| Calcium folinate/mg | 0.07026 | 0.056208–0.084312 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| Oxaliplatin/mg | 0.6 | 0.48–0.72 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| 5-Fluorouracil/mg | 0.01027 | 0.008216–0.012324 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| Irinotecan/mg | 0.3 | 0.24–0.36 | Gamma | IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation. (2025) |
| AEs management costs from Chinese perspective | ||||
| Neutropenia | 136.792 | 109.418–164.147 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 1,097.008 | 8,77.607–1,316.410 | Gamma | Pike et al. (2012) |
| Hypertension | 17.824 | 14.261–21.387 | Gamma | Qiu et al. (2023) |
| AEs management costs from US perspective | ||||
| Neutropenia | 18,360.82 | 14,688.66–22,032.98 | Gamma | Stenehjem et al. (2023) |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 14,184.2 | 11,347.36–17,021.04 | Gamma | Stenehjem et al. (2023) |
| Hypertension | 19,272.01 | 15,417.61–23,126.41 | Gamma | Zhang et al. (2021) |
| Utility | ||||
| PFS | 0.797 | 0.64–0.96 | Beta | Tsuchiya et al. (2002) |
| PD | 0.577 | 0.46–0.69 | Beta | Holden et al. (2011) |
| Disutility | ||||
| Neutropenia | 0.2 | 0.16–0.24 | Beta | Nafees et al. (2017) |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 0.16 | 0.128–0.192 | Beta | Swinburn et al. (2015) |
| Hypertension | 0.04 | 0.032–0.048 | Beta | Nafees et al. (2017) |
| Risk of serious AEs in switch maintenance group | ||||
| Neutropenia (%) | 26.24 | 20.99–31.49 | Beta | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Peripheral neuropathy (%) | 6 | 4.80–7.20 | Beta | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Hypertension (%) | 6 | 4.80–7.20 | Beta | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Risk of serious AEs in control group | ||||
| Neutropenia (%) | 9.63 | 7.70–11.56 | Beta | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Peripheral neuropathy (%) | 7 | 5.60–8.40 | Beta | Randon et al. (2024) |
| Others | ||||
| Weight of Chinese patients (kg) | 69 | 55.2–82.88 | Gamma | Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. (2021) |
| Weight of US patients (kg) | 75 | 60–90 | Gamma | Luo et al. (2024) |
| BSA of Chinese patients (m2) | 1.74 | 1.392–2.088 | Gamma | Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China (2021) |
| BSA of US patients (m2) | 1.8 | 1.44–2.16 | Gamma | Li et al. (2021) |
| Discount rate in China (%) | 5 | 0–8 | Fixed | Liu et al. (2020) |
| Discount rate in US (%) | 3 | 0–8 | Fixed | Sanders et al. (2016) |
Base-case model parameter.
Abbreviations: OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; CT, computed tomography; AE, adverse event; PD, progressed disease; BSC, best supportive care; US, united states; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; CPS, combined positive score.
Costs and utilities
This study was conducted from the perspective of the Chinese and US healthcare system, considering only direct medical costs, including drug costs, drug injections costs, examination costs, management costs of each adverse events (AEs), BSC cost, and terminal care costs. We assumed that AEs occurred exclusively during the first model cycle (Su et al., 2021). Given that grade <3 AEs generally have minimal clinical impact and are managed either expectantly or with supportive care, only grade ≥3 AEs with an incidence >5% were incorporated into the model to maintain methodological simplicity. The included AEs encompassed peripheral neuropathy, hypertension, and neutropenia. The cost of drugs was obtained from the Shanghai Sunshine pharmaceutical procurement network (Shanghai sunshine procurement all, 2025) and Red Book® (IBM Micromedex IBM Corporation, 2025), and the cost of examinations, terminal care, drug injections and management costs of each AE were obtained from Medicare Physician Fee Schedule and published studies (Qiu et al., 2023; Tang et al., 2022; Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, 2025). Given price variations across multiple manufacturers, the median price was applied as the drug cost parameter. All Chinese costs were adjusted to 2023 values using the China Consumer Price Index (CPI) and are presented in USD ($1 = ¥7.0467). All US cost were adjusted to 2023 dollars using Tom’s Inflation Calculator (Medical-care inflation, 2025). Waste of medication was not considered in our study. The detailed cost data are shown in Table 1.
Health utility values for PFS and PD states were derived from published studies, with values set at 0.797 for PFS from TOGA trial (Tsuchiya et al., 2002), 0.577 for PD from National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) (Holden et al., 2011), and a utility of 0 for death. The disutility of AEs was also incorporated into the model. The disutility values for peripheral neuropathy, neutropenia, and hypertension were 0.16, 0.2, and 0.04, respectively, as reported in published studies (Swinburn et al., 2015; Nafees et al., 2017). All costs and utilities were discounted at an annual rate of 5% for the Chinese perspective and 3% for the US perspective (Liu et al., 2020; Sanders et al., 2016).
Sensitivity analysis
Both one-way sensitivity analysis and probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) were conducted to assess the robustness of the results. One-way sensitivity analysis evaluated the impact of individual parameters on model outcomes by varying each parameter within a range of ±20% from its baseline value while keeping all other variables constant. Tornado diagram was used to present the results of one-way sensitivity analysis. For the discount rate, we followed the recommendations of the China guidelines for pharmacoeconomic evaluations and varied it between 0% 8% (Liu et al., 2020). PSA was performed using a Monte Carlo simulation with 5,000 iterations, where each parameter was randomly sampled from predefined distributions. Results from the PSA were represented by an incremental cost-effectiveness scatter plot and a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC), illustrating the probability of the treatment being cost-effectiveness at different WTP thresholds. Gamma distributions were assumed for cost, weight, and body surface area, while beta distributions were used for utility and probability parameters.
Scenarios analysis
To further assess the cost-effectiveness of ramucirumab, we employed the quartile range method to analyze various pricing scenarios where the price of ramucirumab was reduced to 75%, 50%, and 25% of its original price. This analysis aimed to observe the impact on the ICER and the probability of cost-effectiveness acceptability.
Subgroup analysis
Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) may act on VEGFR2 to promote cancer cell angiogenesis and metastasis (Choi et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2021). Therefore, the expression of PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) significantly impacts the efficacy of ramucirumab. Based on this rationale, we conducted a subgroup analysis in patients with PD-L1 CPS ≥5.
Results
Base-case analysis and subgroup analysis
The base-case analysis results are presented in Table 2. In the overall population from the Chinese perspective, the switch maintenance group provided an additional 0.15 QALYs compared to the control group, but incurred incremental costs of $56,738.52, yielding an ICER of $373,219.84 per QALY. For the PD-L1 CPS ≥5 subgroup, the switch maintenance group provided an additional 0.24 QALYs with incremental costs of $62,741.24, resulting in an ICER of $266,259.94 per QALY. In both the overall population and PD-L1 CPS ≥5 subgroup, the ICERs substantially exceeded China’s current WTP threshold ($38,042.49 per QALY).
TABLE 2
| Parameters | Overall population | PD–L1 CPS ⩾5 population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese perspective | United States perspective | Chinese perspective | United States perspective | |||||
| Switch maintenance group | Control group | Switch maintenance group | Control group | Switch maintenance group | Control group | Switch maintenance group | Control group | |
| Total cost ($) | 69,852.42 | 13,114.09 | 256,611.11 | 713,60.56 | 75,556.47 | 12,815.23 | 276,370.43 | 70,263.30 |
| Incremental costs ($) | 56,738.52 | – | 185,250.55 | – | 62,741.24 | – | 206,107.13 | – |
| Overall QALYs | 0.89 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 0.76 | 1.02 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 0.80 |
| Incremental QALYs | 0.15 | – | 0.16 | – | 0.24 | – | 0.25 | – |
| ICER ($/QALY) | 373,219.84 | 1,193,220.74 | 266,259.94 | 835,740.90 | ||||
The cost and outcome results of the base-case analysis.
Abbreviations: CPS, combined positive score; ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; QALYs, quality-adjusted life-years.
The bold font represents the ratio of incremental costs to incremental QALYs between the two treatment groups.
From the US perspective, the switch maintenance group provided an additional 0.16 QALYs in the overall population versus control, with incremental costs of $185,250.55, yielding an ICER of $1,193,220.74 per QALY. In the PD-L1 CPS ≥5 subgroup, it provided 0.25 additional QALYs at incremental costs of $206,107.13, resulting in an ICER of $835,740.90 per QALY. All ICERs significantly exceeded the US WTP threshold ($150,000.00 per QALY) across both overall populations and subgroup populations.
Sensitivity analysis
The results of the tornado diagram are shown in Figure 2. In the overall population, the top three influential parameters of the ICER were the utility of PFS, the price of ramucirumab, and patient weight. In the PD-L1 CPS ≥5 population, the top three influential parameters were body weight, the price of ramucirumab, and the utility of PD. Other parameters, such as the discount rate, incidence of AEs, and disutility values, had slight impacts on the ICER. These hierarchical patterns remained consistent in both Chinese and US perspectives. However, no single parameter factors could reduce the ICER below current WTP threshold in China and US. This is consistent with our results in base-case analysis.
FIGURE 2
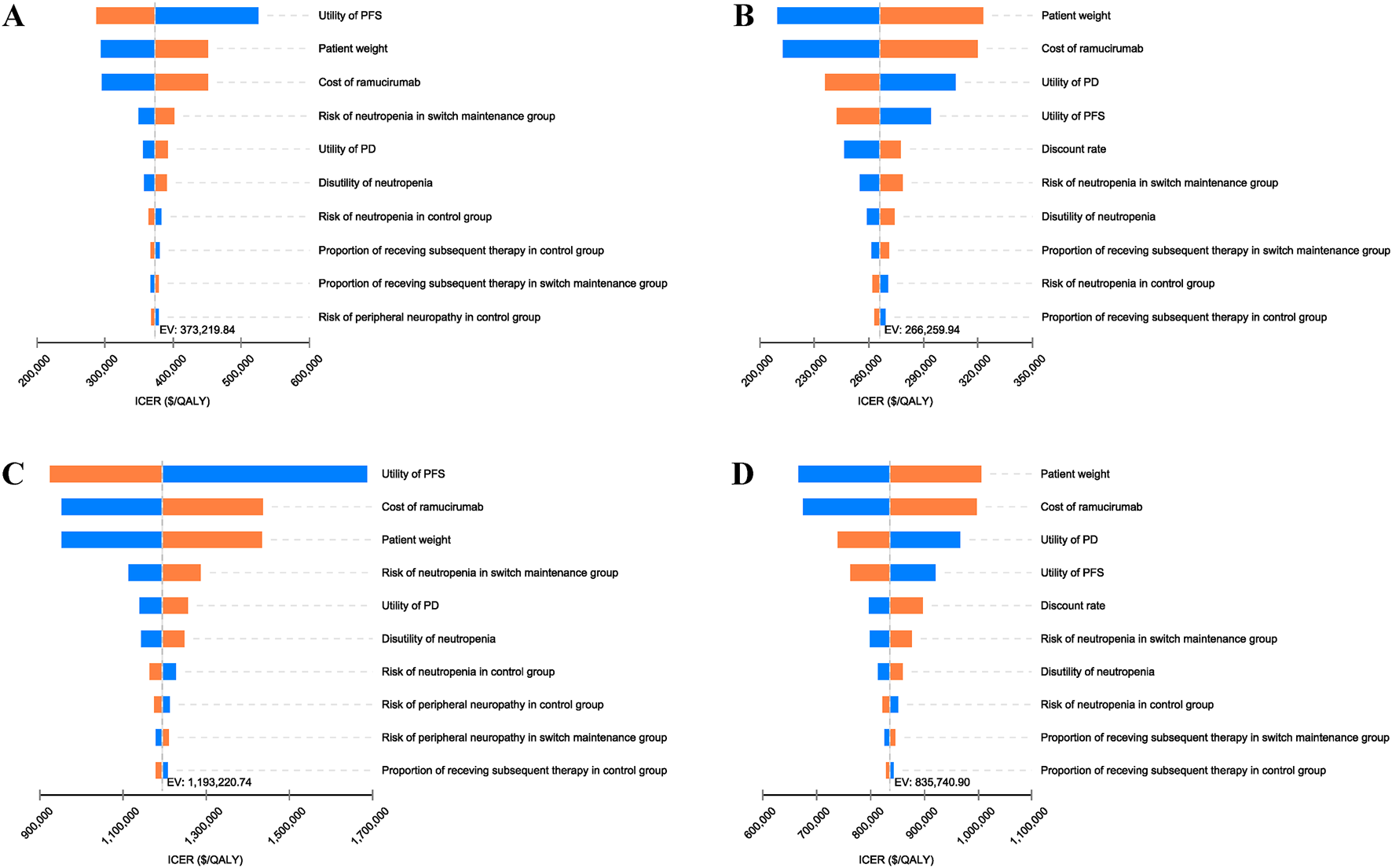
Tornado diagram of one-way sensitivity analysis of switch maintenance group versus control group. (A) Overall population from Chinese perspective, (B) PD-L1 CPS ⩾5 population from Chinese perspective, (C) Overall population from United States perspective, (D) PD-L1 CPS ⩾5 population from United States perspective. ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; PD, progressive disease; PFS, Progression-free survival.
The results of the PSA are shown in Figures 3, 4. The scatter plots demonstrated that none of the 5,000 Monte Carlo iterations yielded ICERs below current WTP thresholds in either China or US perspectives—consistent across both the overall population and PD-L1 CPS ≥5 subgroup. Furthermore, the CEAC demonstrated that the acceptable probability of full-price ramucirumab-based switch maintenance regimen was 0% in both China and the US in the overall population and the PD-L1 CPS ≥5 subgroup.
FIGURE 3
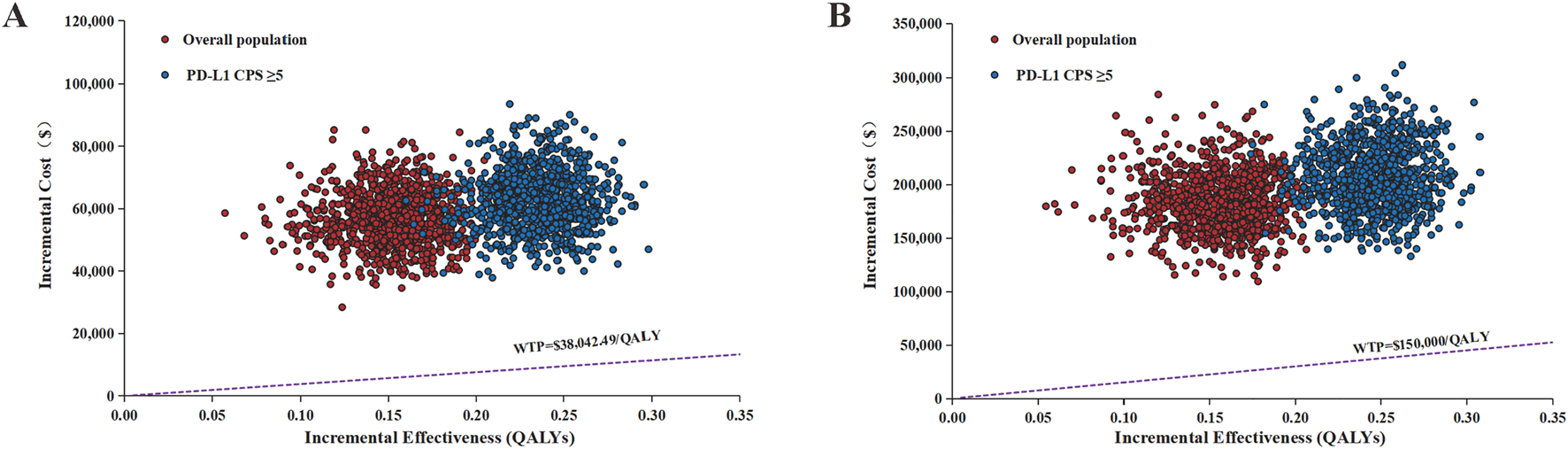
Incremental cost-effectiveness scatter plot of switch maintenance group versus control group. (A) Chinese perspective (B) United States perspective. QALYs, quality-adjusted life years; WTP, willingness-to-pay.
FIGURE 4
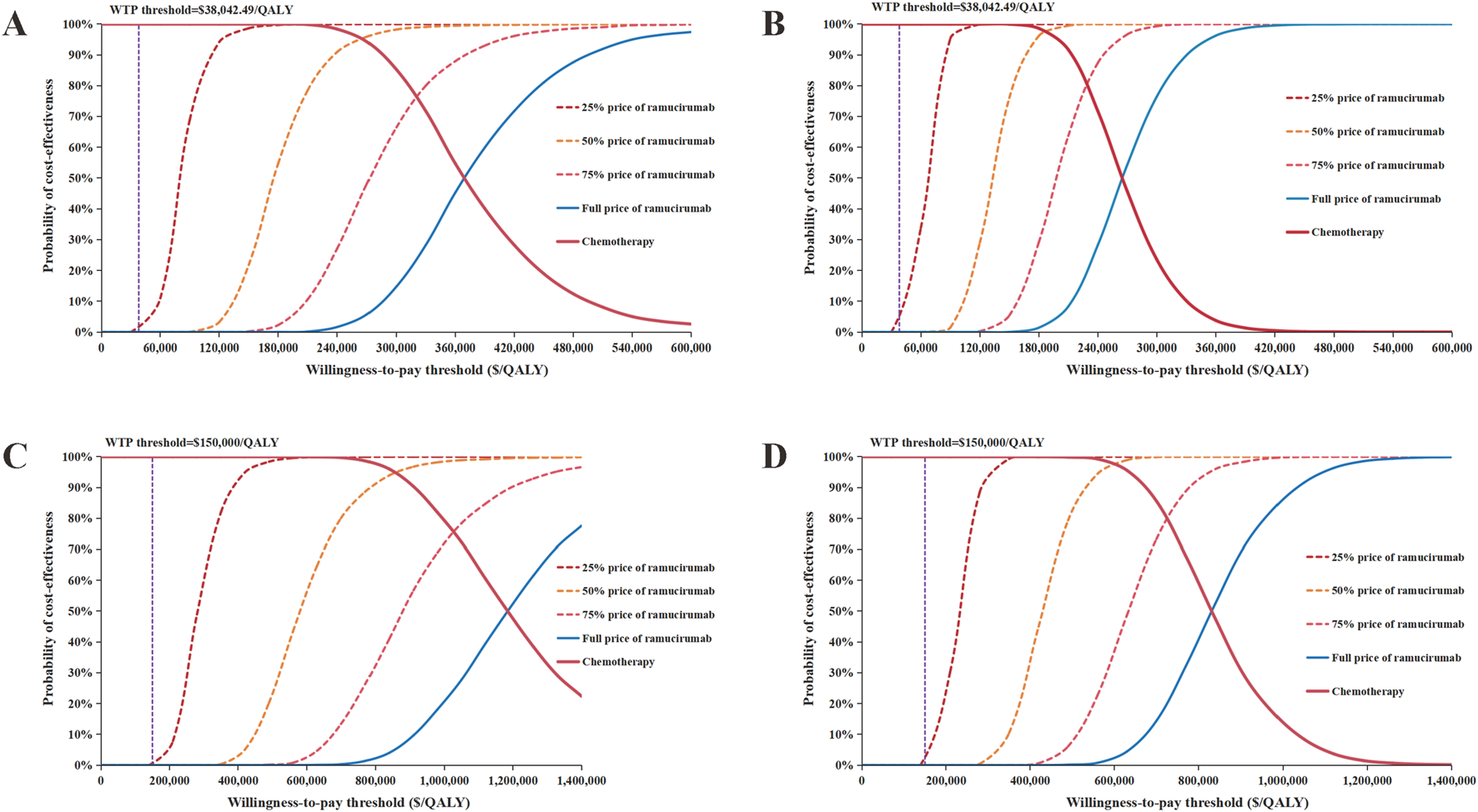
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve of different ramucirumab prices. (A) Overall population from Chinese perspective, (B) PD-L1 CPS ⩾5 population from Chinese perspective, (C) Overall population from United States perspective, (D) PD-L1 CPS ⩾5 population from United States perspective. Abbreviations: QALYs, quality-adjusted life years; WTP, willingness-to-.pay.
Scenario analysis
The results of the scenario analysis are shown in Figure 4 and Table 3. The CEACs demonstrated that at current WTP thresholds in both China and the US, the switch maintenance therapy showed no cost-effectiveness advantage over the control group even with a 75% reduction in ramucirumab price. Further analysis revealed that when the cost of ramucirumab dropped to $0.743/mg (14.2% of the current price) in China and $2.088/mg (13.92% of the current price) in the US for the overall population, the probability of ramucirumab being cost-effective will increase to 50%.
TABLE 3
| Parameter | Perspective | Ramucirumab price/mg ($) | Total costs ($) | QALYs | ICER($/QALY) | Cost-effectiveness probability (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall population | ||||||
| 100% price of ramucirumab | China | 5.2322 | 69,852.42 | 0.89 | 373,219.84 | 0 |
| United States | 15 | 256,611.11 | 0.91 | 1,193,220.74 | 0 | |
| 75% price of ramucirumab | China | 3.9242 | 55,044.13 | 0.89 | 275,812.24 | 0 |
| United States | 11.25 | 209,632.44 | 0.91 | 890,625.58 | 0 | |
| 50% price of ramucirumab | China | 2.6161 | 40,234.72 | 0.89 | 178,397.19 | 0 |
| United States | 7.5 | 162,653.77 | 0.91 | 588,030.42 | 0 | |
| 25% price of ramucirumab | China | 1.3081 | 25,426.44 | 0.89 | 80,989.59 | 0 |
| United States | 3.75 | 115,675.11 | 0.91 | 285,435.26 | 0 | |
| PD-L1 CPS ⩾5 population | ||||||
| 100% price of ramucirumab | China | 5.2322 | 75,556.47 | 1.02 | 266,259.94 | 0 |
| United States | 15 | 276,370.43 | 1.05 | 835,740.90 | 0 | |
| 75% price of ramucirumab | China | 3.9242 | 59,820.01 | 1.02 | 199,477.88 | 0 |
| United States | 11.25 | 226,670.71 | 1.05 | 634,214.22 | 0 | |
| 50% price of ramucirumab | China | 2.6161 | 44,082.34 | 1.02 | 132,690.71 | 0 |
| United States | 7.5 | 176,971.00 | 1.05 | 432,687.54 | 0 | |
| 25% price of ramucirumab | China | 1.3081 | 28,345.88 | 1.02 | 65,908.65 | 0 |
| United States | 3.75 | 127,271.28 | 1.05 | 231,160.86 | 0 | |
Results of scenarios analysis of ramucirumab at different prices.
Abbreviations: ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; QALY, quality-adjusted life years; US, United State.
Discussion
For patients with HER2-negative advanced GC or GEJC, fluoropyrimidine and platinum-based chemotherapy remains the first-line treatment (National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2024; Lordick et al., 2022). However, the OS with first-line treatment rarely exceeds 12 months, and only 40%–50% of patients in clinical trials qualify for subsequent anticancer therapies (Janjigian et al., 2024), highlighting an urgent need to optimize upfront treatment strategies. The ARMANI trial offers a promising therapeutic approach for this population. However, the high cost of ramucirumab poses a serious challenge to patient accessibility, and a thorough evaluation of the economic feasibility of this regimen is needed.
The analysis results underscore that, under current WTP threshold in China and US, the ramucirumab plus paclitaxel regimen lacks cost-effectiveness compared to continuing oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in HER2-negative advanced GC or GEJC patients—a conclusion consistent across both the overall population and the PD-L1 CPS ≥5 population. The one-way sensitivity analysis revealed that utility of PFS and PD, patient weight, and the price of ramucirumab significantly influenced model outcomes. However, no single parameter adjustment could reduce the ICER below current WTP threshold in China or US, a finding consistent across both the overall population and the PD-L1 CPS ≥5 population, thereby validating the robustness of our analysis.
Our findings align with existing cost-effectiveness analyses of the regimen of ramucirumab plus paclitaxel. Li and his colleagues evaluated ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel as a second-line therapy for advanced GC or GEJC within Chinese healthcare system (Li et al., 2020). Their study concluded that when the price of ramucirumab exceeded $1.6667 per mg, the probability of the ICER surpassing WTP threshold in China ($26,021.9 per QALY) was 100%. A Japanese study reported an ICER of $2,417,664.31/QALY for ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus paclitaxel monotherapy, far exceeding WTP threshold in Japan of $674,536.26 per QALY (Saito et al., 2017). Additionally, NICE concluded that ramucirumab plus paclitaxel lacks cost-effectiveness for advanced GC after prior chemotherapy (Büyükkaramikli et al., 2017). The lacks of cost-effectiveness of the ramucirumab plus paclitaxel regimen may be primarily attributed to the sustained administration of ramucirumab, which substantially elevates treatment costs. In the aforementioned studies, ramucirumab was administered at 8 mg/kg on days 1 and 8 of each 28-day cycle, with no predefined treatment duration limit.
Scenario analysis further sheds light on the economic toxicity of ramucirumab under real-world pricing policies. Ramucirumab was approved for marketing by National Medical Products Administration in 2022, but it has not been included in China’s National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL), which increases the financial pressure on patients. Nevertheless, our results suggest that even if ramucirumab were included in the NRDL (with an average price reduction of 63% after negotiation in 2024 according to the National Healthcare Security Administration (China’s National Healthcare Security Administration, 2024)), ramucirumab plus paclitaxel would still not be cost-effective. To achieve cost-effectiveness, ramucirumab would require price reductions to 14.2% of full price ($0.743/mg) in China. As a high-burden country for GC, China reported approximately 509,000 new GC cases and 400,000 deaths in 2022 (Xia et al., 2022)—the highest global incidence—necessitating policymakers to implement aggressive strategies to alleviate patient financial toxicity and broaden access to this promising therapy. Furthermore, China is currently the second-largest pharmaceutical market globally and dominates the GC treatment space in the Asia-Pacific region, with a revenue share of 27.1% in 2024 (Grand view research, 2025). The manufacturer must reduce the price of ramucirumab or optimize its dosing regimen, for example, by exploring the feasibility of reducing the dose and shortening the duration of treatment, to increase the economic feasibility of ramucirumab and cover more patients who can benefit from it.
Despite declining incidence and mortality of GC in the US, its substantial treatment costs continue to impose significant burdens on the US healthcare system (Thrift and El-Serag, 2020). This economic burden largely stems from exorbitant drug pricing—US pharmaceutical costs in 2022 averaged nearly threefold higher than those in other OECD nations (Mulcahy et al., 2024). Such pricing threatens patient’s access to quality hospital care, making healthcare affordability and accessibility top priorities for most Americans (American Hospital Association, 2024). On 12 May 2025, the White House issued the Executive Order “Most Favored Nation Pricing for Prescription Drugs Delivered to American Patients,” projected to reduce US drug prices by 59% (The White House, 2025). Nevertheless, our analysis demonstrates that even with a 75% price reduction for ramucirumab, the ramucirumab plus paclitaxel remains lacks cost-ineffectiveness in the US perspective. Consequently, alongside advocating for policy interventions, future clinical trials should prioritize dose optimization and alternative administration strategies. The positive effects of proving that lower doses or less intensive schedules retain therapeutic activity include reduced toxicity and large price reductions, leading to better cost-effectiveness and greater access to treatments that improve survival (Tannock et al., 2025).
Our study has some limitations. First, drug prices from a Chinese perspective were sourced from the Shanghai Sunshine Pharmaceutical Procurement Network. Given the regional variations in drug pricing across different areas of China, the ICER values in this study may not be directly generalizable to other Chinese regions. Nevertheless, the large differences between ICER and WTP thresholds suggest that the conclusions drawn from our study remain robust across different regions. Second, manually extracting data points from the KM curves reported in the ARMANI trial using the WebPlotDigitizer for curve reconstruction could lead to uncontrolled methodological biases. Third, since the ARMANI trial enrolled a predominantly Caucasian population, extrapolating its findings to assess the cost-effectiveness of switch maintenance therapy in China may introduce uncertainty due to inherent heterogeneity between the study populations. Fourth, as the ARMANI trial did not specify post-progression treatment regimens or their proportions, we assumed intravenous irinotecan as the standard subsequent therapy for all patients based on NCCN and CSCO guidelines. However, real-world treatment pathways are often more complex and heterogeneous. Despite the limitations of our study, the finding that the ICER of the ramucirumab plus paclitaxel regimen is tenfold higher than current WTP threshold in China and US suggests that these limitations are unlikely to reverse the conclusions. Thus, our results still offer critical economic insights for policymakers, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and healthcare providers.
This study highlights several key directions for further investigation. First, future research should focus on identifying patient subgroups that may benefit cost-effectively from switch maintenance therapy through the exploration of additional tumor biomarkers such as CLDN18.2 or mismatch repair status. Second, alternative ramucirumab dosing strategies warrant exploration, including reduced-dose regimens or treatment duration limitations (Tannock et al., 2025). Finally, comparative cost-effectiveness analyses of switch maintenance therapy should be conducted across diverse healthcare systems and socioeconomic contexts to assess generalizability.
Conclusion
In summary, for Chinese and US patients with previously treated advanced HER2-negative GC or GEJC—whether in the overall population or the PD-L1 CPS ⩾5 population—the ramucirumab plus paclitaxel regimen lacks cost-effectiveness as first-line switch maintenance therapy compared to continuing oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Ramucirumab would need to reduce its price to 14.2% of the original price ($0.743/mg) in China and 13.92% of the original price ($2.088/mg) in the US, to have a 50% probability of being cost-effective.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JFL: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft. ZL: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review and editing. QD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. JYL: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review and editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1616826/full#supplementary-material
References
1
American Hospital Association (2024). Drug prices and shortages jeopardize patient access to quality hospital care. Available online at: https://www.aha.org/news/blog/2024-05-22-drug-prices-and-shortages-jeopardize-patient-access-quality-hospital-care (Accessed August 05, 2025).
2
Bertram M. Y. Lauer J. A. Stenberg K. Edejer T. T. T. (2021). Methods for the economic evaluation of health care interventions for priority setting in the health system: an update from WHO CHOICE. Int. J. Health Policy Manag.10 (11), 673–677. 10.34172/ijhpm.2020.244
3
Büyükkaramikli N. C. Blommestein H. M. Riemsma R. Armstrong N. Clay F. J. Ross J. et al (2017). Ramucirumab for treating advanced gastric cancer or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma previously treated with chemotherapy: an evidence Review Group perspective of a NICE single technology appraisal. Pharmacoeconomics35 (12), 1211–1221. 10.1007/s40273-017-0528-y
4
Cao X. Zhang M. Li N. Zheng B. Liu M. Song X. et al (2020). First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric cancer, gastroesophageal junction cancer, and esophageal adenocarcinoma: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol.15, 17588359231171038. 10.1177/17588359231171038
5
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (2025). Medicare physician fee schedule. Available online at: https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician (Accessed July 29, 2025).
6
Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China (2025). China’s Gdp Grows by 5.2% year-on-year in 2023. Beijing, China: China Physical Fitness Surveillance Center. Available online at: https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01&zb=A0201&sj=2023 (Accessed February 11, 2025).
7
Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China (2021). The fifth national physical fitness monitoring bulletin. China Institute of Sport Science. Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/guoqing/2023-03/12/content_5745851.htm (Accessed February 11, 2025).
8
Chiang C. L. Chan S. K. Lee S. F. Wong I. O. Choi H. C. (2021). Cost-effectiveness of pembrolizumab as a second-line therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open4 (1), e2033761. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33761
9
China's National Healthcare Security Administration (2024). Transcript of the national healthcare security Administration's press conference on the adjustment of the national basic medical insurance, work-related injury insurance and maternity insurance drug catalog in 2024. Available online at: https://www.nhsa.gov.cn/art/2024/11/28/art_14_14889.html (Accessed February 11, 2025).
10
Choi D. H. Lee J. Lim H. Y. Kang W. K. Jang J. Y. Jeon Y. et al (2023). Effect of ramucirumab plus paclitaxel in advanced gastric cancer according to the status of programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression. J. Gastrointest. Oncol.14 (6), 2324–2333. 10.21037/jgo-23-418
11
Coudert B. Ciuleanu T. Park K. Wu Y. L. Giaccone G. Brugger W. et al (2012). Survival benefit with erlotinib maintenance therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) according to response to first-line chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol.23 (2), 388–394. 10.1093/annonc/mdr125
12
Grand view research (2025). Stomach cancer treatment market size, share & trends analysis report by treatment type (standard chemotherapy), by disease indication, by route of administration, by drug class, by region, and segment forecasts. Available online at: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/stomach-cancer-gastric-cancer-market#:∼:text=The%20stomach%20cancer%20treatment%20market%20in%20China%20dominated,with%20a%20revenue%20share%20of%2027.1%25%20in%202024 (Accessed March 30, 2025).
13
Guyot P. Ades A. E. Ouwens M. J. Welton N. J. (2012). Enhanced secondary analysis of survival data: reconstructing the data from published kaplan-Meier survival curves. BMC Med. Res. Methodol.12, 9. 10.1186/1471-2288-12-9
14
He F. Wang S. Zheng R. Gu J. Zeng H. Sun K. et al (2024). Trends of gastric cancer burdens attributable to risk factors in China from 2000 to 2050. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 44, 101003. 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.101003
15
Holden J. Garrett Z. Stevens A. (2011). NICE guidance on trastuzumab for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic gastric cancer. Lancet. Oncol.12 (1), 16–17. 10.1016/s1470-2045(10)70276-x
16
Hu J. Hu J. Liu X. Li L. Bai X. (2019). Efficacy and toxicities of combination maintenance therapy in the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: an up-to-date meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep.39 (6). 10.1042/BSR20182464
17
Husereau D. Drummond M. Augustovski F. de Bekker-Grob E. Briggs A. H. Carswell C. et al (2022). Consolidated health economic evaluation reporting standards 2022 (CHEERS 2022) statement: updated reporting guidance for health economic evaluations. Value Health25 (1), 3–9. 10.1016/j.jval.2021.11.1351
18
IBM Micromedex; IBM Corporation (2025). RED BOOK online. Available online at: http://www.micromedexsolutions.com (Accessed August 05, 2025).
19
Janjigian Y. Y. Ajani J. A. Moehler M. Shen L. Garrido M. Gallardo C. et al (2024). First-Line nivolumab plus chemotherapy for advanced gastric, gastroesophageal junction, and esophageal adenocarcinoma: 3-year Follow-Up of the phase III CheckMate 649 trial. J. Clin. Oncol.42 (17), 2012–2020. 10.1200/JCO.23.01601
20
Jung Y. D. Mansfield P. F. Akagi M. Takeda A. Liu W. Bucana C. D. et al (2002). Effects of combination anti-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapies on the growth of gastric cancer in a nude mouse model. Eur. J. Cancer38 (8), 1133–1140. 10.1016/s0959-8049(02)00013-8
21
Lee J. E. Chung C. U. (2014). Update on the evidence regarding maintenance therapy. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. Seoul.76 (1), 1–7. 10.4046/trd.2014.76.1.1
22
Li S. Peng L. Tan C. Zeng X. Wan X. Luo X. et al (2020). Cost-effectiveness of ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as a second-line therapy for advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal cancer in China. PLoS One15 (5), e0232240. 10.1371/journal.pone.0232240
23
Li W. Bai R. Qian L. Chen N. Zhao Y. Han F. et al (2021). Cost-effectiveness of icotinib versus whole-brain irradiation with or without chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC patients with brain metastases. Asia Pac J. Clin. Oncol.17 (2), e40–e47. 10.1111/ajco.13291
24
Liu D. Mehta D. Kaur S. Kumar A. Parikh K. Chawla L. et al (2018). Decreasing mortality and hospitalizations with rising costs related to gastric cancer in the USA: an epidemiological perspective. J. Hematol. Oncol.11 (1), 138. 10.1186/s13045-018-0682-5
25
Liu G. Hu S. Wu J. Wu J. Dong Z. Li H. (2020). China guidelines for pharmacoeconomic evaluations. Beijing China Mark.
26
Lordick F. Carneiro F. Cascinu S. Fleitas T. Haustermans K. Piessen G. et al (2022). Gastric cancer: ESMO clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol.33 (10), 1005–1020. 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.07.004
27
Luo X. Cai T. Wu J. Li X. Wang X. Ma H. (2024). Cost-effectiveness of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy vs. chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced biliary tract cancer in China and the US. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1393559. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1393559
28
Medical-care inflation (2025). Tom’s inflation calculator. Available online at: https://www.halfhill.com/inflation_js.html (Accessed July 15, 2025).
29
Mulcahy A. W. Schwam D. Lovejoy S. L. (2024). International prescription drug price comparisons: estimates using 2022 data. Rand Health Q.11 (3), 5.
30
Nafees B. Lloyd A. J. Dewilde S. Rajan N. Lorenzo M. (2017). Health state utilities in non-small cell lung cancer: an international study. Asia Pac J. Clin. Oncol.13 (5), e195–e203. 10.1111/ajco.12477
31
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2024). NCCN Clinical Practice guidelines in Oncology: gastric cancer. Available online at: https://www.nccn.org/login?ReturnURL=https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/gastric.pdf (Accessed September 02, 2025).
32
Pike C. T. Birnbaum H. G. Muehlenbein C. E. Pohl G. M. Natale R. B. (2012). Healthcare costs and workloss burden of patients with chemotherapy-associated peripheral neuropathy in breast, ovarian, head and neck, and nonsmall cell lung cancer. Chemother. Res. Pract.2012, 913848. 10.1155/2012/913848
33
Qiu Y. Zha J. Ma A. Zhou T. (2023). Cost-effectiveness analysis of niraparib maintenance therapy in Chinese patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol.174, 175–181. 10.1016/j.ygyno.2023.05.010
34
Randon G. Lonardi S. Fassan M. Palermo F. Tamberi S. Giommoni E. et al (2024). Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as switch maintenance versus continuation of first-line oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced HER2-negative gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ARMANI): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.25 (12), 1539–1550. 10.1016/S1470-2045(24)00580-1
35
Saito S. Muneoka Y. Ishikawa T. Akazawa K. (2017). Cost-effectiveness of Paclitaxel + ramucirumab combination therapy for advanced gastric cancer progressing after first-line chemotherapy in Japan. Clin. Ther.39 (12), 2380–2388. 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.10.017
36
Sanders G. D. Neumann P. J. Basu A. Brock D. W. Feeny D. Krahn M. et al (2016). Recommendations for conduct, methodological practices, and reporting of cost-effectiveness analyses: Second panel on cost-effectiveness in health and medicine. Jama316 (10), 1093–1103. 10.1001/jama.2016.12195
37
Shanghai sunshine procurement all-in-one. Shanghai sunshine Pharmaceutical Purchasing Network (2025). Available online at: https://www.smpaa.cn/gzfw/index.shtml (Accessed March 27, 2025).
38
Smyth E. C. Nilsson M. Grabsch H. I. van Grieken N. C. Lordick F. (2020). Gastric cancer. Lancet396 (10251), 635–648. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
39
Stenehjem D. Lubinga S. J. Wu A. Betts K. A. (2023). Adverse event costs associated with first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the United States: an analysis of clinical trials of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm.29 (9), 1054–1064. 10.18553/jmcp.2023.29.9.1054
40
Su D. Wu B. Shi L. (2021). Cost-effectiveness of atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab vs sorafenib as first-line treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open4 (2), e210037. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0037
41
Swinburn P. Shingler S. Acaster S. Lloyd A. Bonthapally V. (2015). Health utilities in relation to treatment response and adverse events in relapsed/refractory hodgkin lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma56 (6), 1839–1845. 10.3109/10428194.2014.970542
42
Tang W. X. Shao R. J. Wang J. Scherrer E. Ma A. X. Aguiar-Ibáñez R. (2022). Cost-effectiveness of pembrolizumab versus carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma after first-line treatment in China. Value Health Reg. Issues27, 99–107. 10.1016/j.vhri.2021.04.007
43
Tannock I. F. de Vries E. G. E. Fojo A. Buyse M. Moja L. (2025). Dose optimisation to improve access to effective cancer medicines. Lancet Oncol.26 (3), e171–e180. 10.1016/S1470-2045(24)00648-X
44
The White House (2025). Delivering most-favored-nation prescription drug pricing to American patients. Available online at: https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/2025/05/delivering-most-favored-nation-prescription-drug-pricing-to-american-patients/ (Accessed August 05, 2025).
45
Thrift A. P. El-Serag H. B. (2020). Burden of gastric cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.18 (3), 534–542. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.045
46
Tsuchiya A. Ikeda S. Ikegami N. Nishimura S. Sakai I. Fukuda T. et al (2002). Estimating an EQ-5D population value set: the case of Japan. Health Econ.11 (4), 341–353. 10.1002/hec.673
47
Wang F. H. Zhang X. T. Tang L. Wu Q. Cai M. Y. Li Y. F. et al (2024). The Chinese society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO): Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer. Cancer Commun. (Lond).44 (1), 127–172. 10.1002/cac2.12516
48
Wilke H. Muro K. Van Cutsem E. Oh S. C. Bodoky G. Shimada Y. et al (2014). Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): a double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.15 (11), 1224–1235. 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70420-6
49
Williams C. Lewsey J. D. Mackay D. F. Briggs A. H. (2017). Estimation of survival probabilities for use in cost-effectiveness analyses: a comparison of a multi-state modeling survival analysis approach with partitioned survival and markov decision-analytic modeling. Med. Decis. Mak.37 (4), 427–439. 10.1177/0272989X16670617
50
Xia C. Dong X. Li H. Cao M. Sun D. He S. et al (2022). Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin. Med. J. Engl.135 (5), 584–590. 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002108
51
Yang L. Ying X. Liu S. Lyu G. Xu Z. Zhang X. et al (2020). Gastric cancer: epidemiology, risk factors and prevention strategies. Chin. J. Cancer Res.32 (6), 695–704. 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2020.06.03
52
Yang Y. Xia L. Wu Y. Zhou H. Chen X. et al (2021). Programmed death ligand-1 regulates angiogenesis and metastasis by participating in the c-JUN/VEGFR2 signaling axis in ovarian cancer. Cancer Commun. (Lond).41 (6), 511–527. 10.1002/cac2.12157
53
Zhang K. Yin J. Huang H. Wang L. Guo L. Shi J. et al (2020). Expenditure and financial burden for stomach cancer diagnosis and treatment in China: a multicenter Study. Front. Public Health8, 310. 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00310
54
Zhang X. Wang J. Shi J. Jia X. Dang S. Wang W. (2021). Cost-effectiveness of atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab vs sorafenib for patients with unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open4 (4), e214846. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4846
55
Zhou Z. Yang Y. Chen S. You M. (2025). Cost-effectiveness analysis of first-line cadonilimab plus chemotherapy in HER2-negative advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Front. Immunol.16, 1575627. 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1575627
56
Zhu Y. Liu K. Zhu H. Wu H. (2023). Immune checkpoint inhibitors plus chemotherapy for HER2-negative advanced gastric/gastroesophageal junction cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol.16, 17562848231207200. 10.1177/17562848231207200
Summary
Keywords
ramucirumab, paclitaxel, gastric cancer, gastro-oesophageal junction cancer, cost-effectiveness
Citation
Luo J, Li Z, Du Q and Liu J (2025) Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as switch maintenance in patients with advanced HER2-negative gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1616826. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1616826
Received
23 April 2025
Accepted
18 August 2025
Published
12 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Adina Turcu-Stiolica, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, Romania
Reviewed by
Ramon Mohanlal, Independent Researcher, New York, NY, United States
Xueqiong Cao, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Luo, Li, Du and Liu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiong Du, dujoan-88@163.com; Jiyong Liu, liujiyong@fudan.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.