- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 3State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Background: Sufentanil-induced cough (SIC) is prevalent in anesthesia practice. A variety of interventions have been employed to prevent SIC. However, the optimal intervention remains elusive.
Methods: A comprehensive search of the literature was conducted on the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library (CENTRAL) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases. The search was limited to publications prior to July 5, 2025. A network meta-analysis (NMA) was conducted using the R software. A Bayesian framework was employed for this NMA. Comparisons of competing models based on the deviance information criterion (DIC) were used to select the optimal model for NMA. The primary outcome is the overall incidence of SIC. The secondary outcomes included the incidence of mild SIC and moderate to severe SIC.
Results: The NMA included 37 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 5,105 patients and 18 interventions. Pairwise meta-analysis results indicate that the intervention group significantly decreases the overall incidence of SIC (7.6% vs. 34.8%; OR 0.13; 95% CI 0.09 to 0.18; P < 0.0001; I2 = 53.0%), the incidence of mild SIC (4.0% vs. 13.0%; OR 0.28; 95% CI 0.22 to 0.35; P = 0.369; I2 = 5.7%), and the incidence of moderate to severe SIC (3.4% vs. 21.7%; OR 0.13; 95% CI 0.10 to 0.16; P = 0.040; I2 = 30.6%). NMA results suggested that nalbuphine, dezocine, and butorphanol significantly reduced the overall incidence of SIC, as well as the incidence of mild and moderate-to-severe SIC. Additionally, remifentanil and esketamine were effective in reducing both the overall incidence of SIC and the incidence of moderate to severe SIC. The use of a mechanical dropper was also effective in reducing the incidence of moderate to severe SIC.
Conclusion: Three pharmacological interventions—nalbuphine, dezocine, and butorphanol significantly reduced the overall incidence of SIC, as well as the incidence of mild and moderate-to-severe SIC. Additionally, remifentanil and esketamine were effective in reducing the overall incidence of SIC and the incidence of moderate to severe SIC. The application of a mechanical dropper was also effective in reducing the incidence of moderate to severe SIC. The remaining interventions indicated a trend toward reducing SIC incidence; however, this was not statistically significant.
Systematic Review: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024581866 , PROSPERO (CRD42024581866)
Introduction
Sufentanil is a potent mu-opioid receptor agonist characterized by rapid action, strong analgesic properties, prolonged duration, stable hemodynamics, and a high therapeutic index, making it an optimal choice for opioid analgesia during the induction of general anesthesia (Xue et al., 2008). SIC is prevalent in anesthesia practice, with some studies indicating an incidence rate as high as 64.7% (Xie et al., 2024). Coughs can vary in severity, with mild cases being self-limiting. However, severe cough may elevate the risk of aspiration pneumonia (Smith and Houghton, 2013) and postoperative nausea and vomiting (Peringathara and Robinson, 2016). In severe cases, it can elevate intracranial, intraocular, and intraabdominal pressures, potentially leading to various adverse effects in patients with high-risk comorbidities (Schug et al., 1992). Consequently, implementing effective interventions to prevent sufentanil-induced cough (SIC) in clinical settings is crucial for saving lives, improving quality of life, enhancing patient satisfaction, and optimizing healthcare resource utilization (Liu et al., 2023).
Various interventions have been suggested for the prevention of SIC, including pretreatment with drugs like dizocin (Liu et al., 2015), esketamine (Gao et al., 2024), nalmefene (Xie et al., 2024), and remifentanil (Zhang et al., 2024), as well as extended administration of induction drugs (Liu et al., 2019). Despite various interventions, the most effective intervention for preventing SIC remains uncertain.
Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis that integrates existing randomized controlled trials and available interventions to assess the efficacy of various interventions in preventing SIC for clinical reference.
Methods
Study protocol
This systematic review was designed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses extension statement for reviews incorporating NMA. The protocol of this review has been published in PROSPERO (ID: CRD42024581866). The PRISMA NMA checklist is available in the Supplementary Table S1.
Search strategy
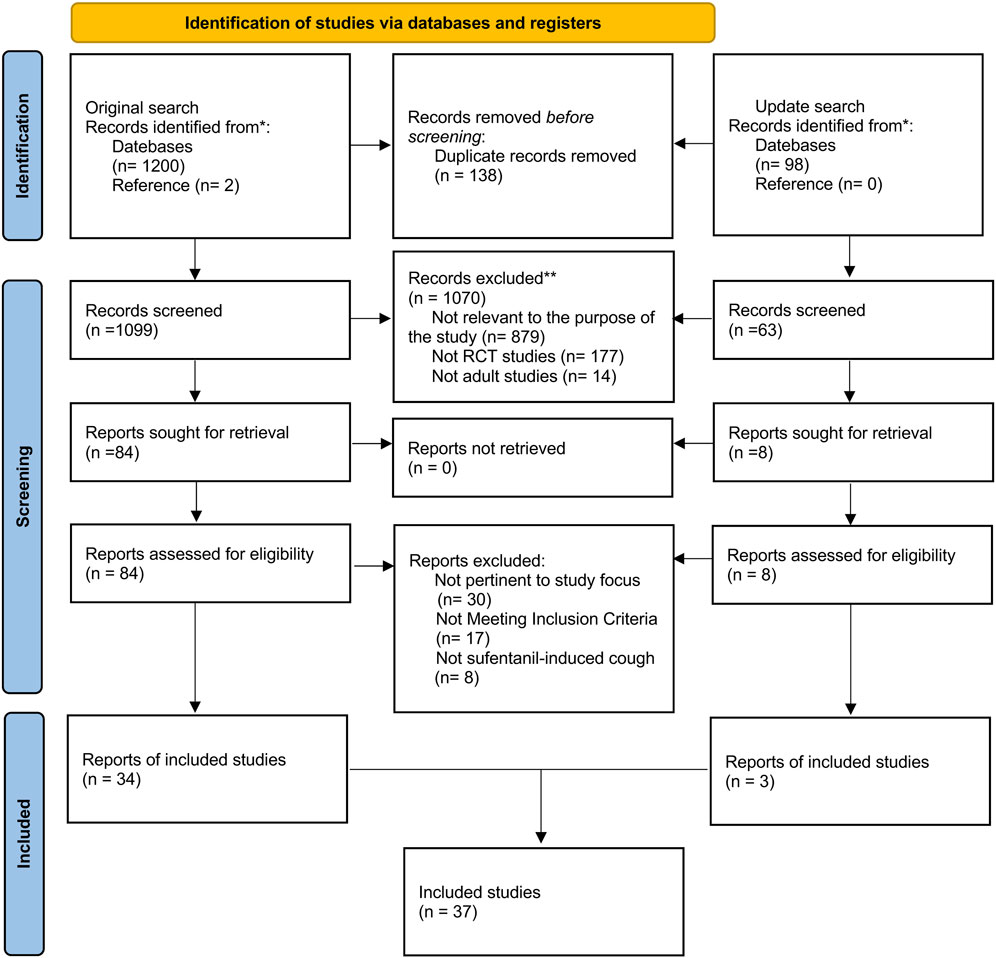
The search process was shown in PRISMA_2020_flow_diagram (Figure 1). Two researchers (H.L. and Y.W.H.) exhaustively searched studies published from inception to August 22, 2024, without language restriction in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library (CENTRAL), and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) database. To ensure the inclusion of the most recent evidence, an updated systematic search was conducted, extending the original search window to July 5, 2025. The search formula was developed jointly by two independent researchers. W.H.M. was responsible for resolving any disputes during the process. Synonym searches and similar terms from critical meta-analysis determined the search terms for this NMA. Based on different databases, we would appropriately change the retrieval strategy, such as Mesh word and Publication Type and other limitations. In addition, we conducted a reference list search to enhance comprehensiveness (details in Supplementary Table S2).
Study selection
The retrieved articles were managed by two researchers (H.L. and Y.W.H.) using EndNote X9 (Thomson Reuters, NY, USA). The process was as follows: first, we excluded all duplicates and incomplete studies. Subsequently, the titles, keywords, and abstracts were subjected to a review process, during which they were classified as “low correlation”, “moderate correlation” and “high correlation” in accordance with the established inclusion criteria. The investigators excluded all “low correlation” studies and examined the full text of the remaining studies, which were defined as “moderate correlation”, as well as all studies with “high correlation”. Finally, two reviewers identified the included literature based on the full text. When the results of the two researchers differed, the opinion of one researcher (W.H.M.) was used to reach a consensus. Figure 1 shows a screening process to illustrate the number of excluded studies at each stage.
Eligibility criteria
For the inclusion of this NMA, studies had to meet the following criteria: published randomized controlled trials; at least two different interventions should be compared; at least one of four clinical outcomes (overall incidence of SIC, mild severity of SIC, moderate severity of SIC, and severe severity of SIC) should be evaluated; study participants are adults. The exclusion criteria were detailed as follows: non-randomized controlled trials; articles that did not compare at least two different interventions; and articles that did not evaluate at least one of four clinical outcomes; data could not be extracted from articles.
Data extraction
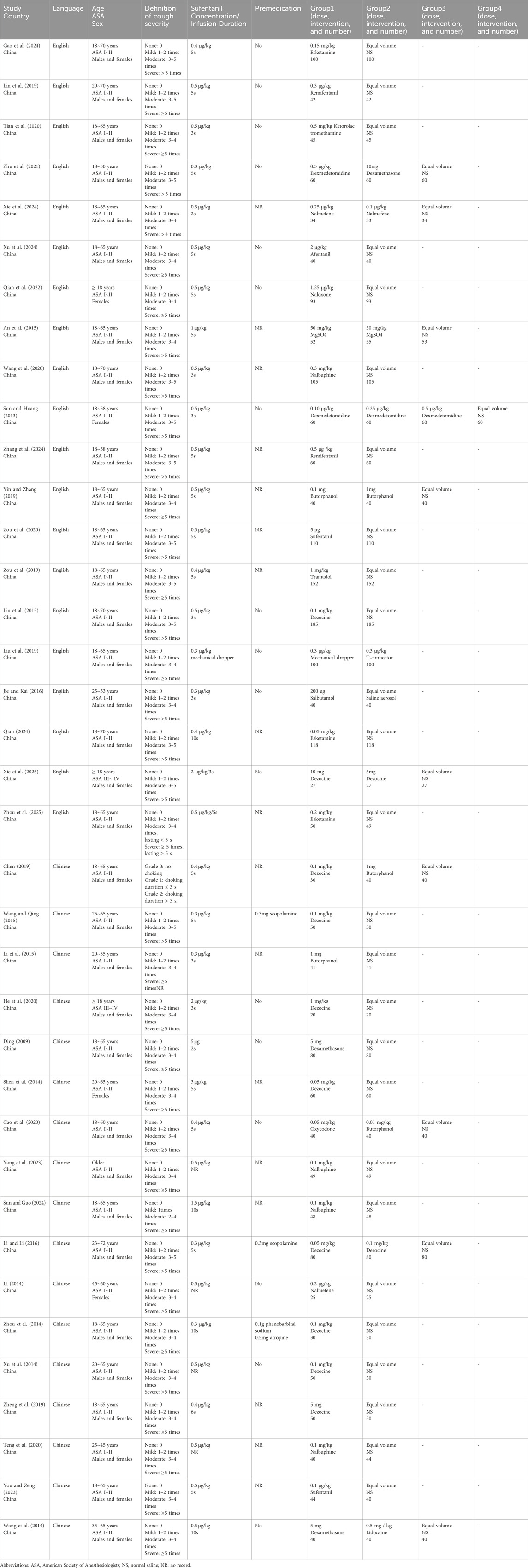
Two investigators (H.L. and Y.W.H.) were independently responsible for data extraction, and W.H.M. and Y.W. adjudicated all disputes. We extracted the following data based on the characteristics of the included studies: Author, National, Year of publication, Language, Definition of cough severity, Age, ASA classification, Sex, Premedication, and Group information (Table 1). H.L. and Y.W.H. extracted and summarized the research data in Excel 2019, and W.H.M. was responsible for confirming the accuracy of the research data.
Risk of bias assessment
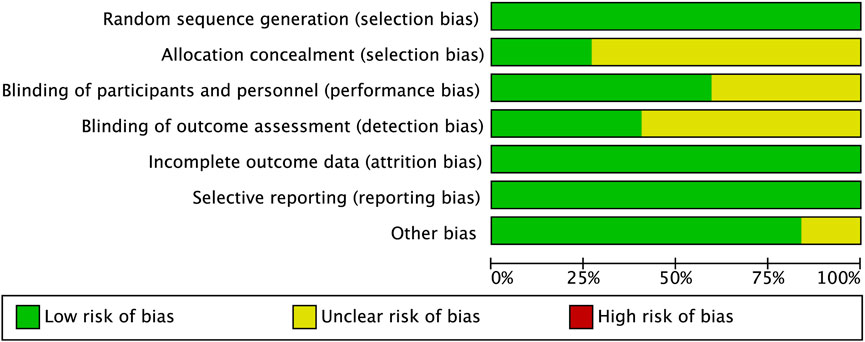
Two investigators (Z.Z.Z. and L.F.D.) independently assessed the risk of bias for each trial using Review Manager 5.4 (RevMan, The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom) according to the criteria outlined in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Based on the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool, RCT was defined as high risk, low risk, and unclear. The risk of bias summary is shown in Figure 2 and the Supplementary Figure S1.
Outcomes
The primary outcome is the overall incidence of SIC. The secondary outcomes include the incidence of mild SIC and the incidence of moderate to severe SIC.
Statistical analysis for pairwise meta-analysis
Two investigators (H.L. and Y.W.H.) are responsible for the statistical methodology. Meta packages of R (version 4.2.3) were applied to perform the pairwise meta-analysis of direct evidence by using random-effects models or fixed-effects models. For the pairwise meta-analysis, heterogeneity between studies was estimated by the I-squared (I2) test and Cochran’s Q test. According to the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook, when moderate or high heterogeneity (I2 > 50% and P < 0.05) was observed, a random-effects model was used; otherwise, a fixed-effects model was used. Furthermore, we chose meta packages of R (version 4.2.3) to generate funnel plots to assess publication bias. Evaluation methods include the plot of effect size centered at comparison-specific pooled effect and the Egger’s test to evaluate small sample effect. Where asymmetries were present, Duval and Tweedie’s trim-and-fill procedure was applied to estimate bias-corrected effects. When researchers disagree on the biased analysis of the same study, another researcher (W.H.M.) will make the decision.
Statistical analysis for network meta-analysis
Two investigators (H.L. and Y.W.H.) are responsible for the statistical methodology. We constructed a network graph to evaluate the overall arrangement of the network evidence base. A network graph consists of nodes and lines. The nodes depict what we regarded as individual interventions. Meanwhile, the lines connecting different nodes represent the direct comparisons between the relevant interventions, and their thicknesses are proportional to the number of RCTs that studied the respective direct comparison.
For the NMA, the analysis was carried out in a Bayesian framework. The network estimates are obtained using the Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation method. For the analysis results of this study, two-tailed tests with P < 0.05 were defined as statistically significant. The metafor package (3.8.1) generated the NMA forest plot. Then, the DIC and potential scale reduced factor (PSRF) were calculated. DIC is widely used in the selection of Bayesian models. In general, a smaller DIC indicates a better fit for the model (Spiegelha et al., 2002). As for the PSRF, closer to 1, it means that the results have good convergence, and the consistency model can be considered robust (Supplementary Table S3). We evaluated the consistency between direct and indirect evidence through both local and global approaches. Analysis of heterogeneity and node-splitting methods, along with Q statistics to assess homogeneity and consistency, were applied for this purpose.
To rank the interventions, we reported the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) scores. For the outcomes in this NMA, a larger value of SUCRA means a better effect. Finally, meta-regression and subgroup analyses were conducted based on the duration of sufentanil injection, dosage of sufentanil injection, and ASA classification, and leave-one-out sensitivity analyses was employed to identify outliers and explore potential sources of heterogeneity.
Certainty assessment of the evidence
Two independent investigators (H.L. and L.F.D.) assessed the quality of the evidence by using the standard Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) method. The NMA findings were evaluated comprehensively in terms of risk of bias, indirectness, inconsistency, imprecision, and publication bias according to the GRADE methodology (Brignardello-Petersen et al., 2020). Additionally, the GRADE published framework was used to guide the development of summary of findings (SoF) tables to report comparative results for the NMA (Yepes-Nuñez et al., 2019).
Results
Literature search findings
A total of 1,202 studies were identified through initial searches of five databases and the reference list: PubMed (106), Embase (307), Web of Science (362), Cochrane Library (CENTRAL) (70), CNKI (355), and a reference list (2). Duplicate and ineligible trials were removed, followed by the exclusion of all trials categorized as “low correlation”, resulting in the inclusion of 84 RCTs. Following a joint screening of the full text of 84 trials by two reviewers, 34 trials (Xie et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2015; Gao et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2019; Tian et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2024; Qian et al., 2022; An et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2020; Sun and Huang, 2013; Yin and Zhang, 2019; Zou et al., 2019; Zou et al., 2020; Chen, 2019; Wang and Qing, 2015; Li et al., 2015) involving 4,689 patients were deemed eligible. An updated search identified three additional eligible studies (Qian et al., 2024; Xie et al., 2025; Zhou et al., 2025). In total, 37 studies involving 5,105 patients were included in the NMA. The search process is illustrated in the PRISMA 2020 flow diagram (Figure 1).
Studies and patient characteristics
The intervention group comprised 2,815 patients undergoing pharmacological management or mechanical dropper, whereas the control group included 2,295 patients receiving normal saline. Eighteen distinct interventions were analyzed, comprising dezocine, nalbuphine, butorphanol, alfentanil, oxycodone, remifentanil, esketamine, ketorolac tromethamine, nalmefene, magnesium sulfate, salbutamol, dexmedetomidine, sufentanil, lidocaine, dexamethasone, naloxone, tramadol, and mechanical dropper (flow rate at 1 mL/s). Among them, dezocine (10 articles), butorphanol (5 articles), nalbuphine (3 articles), sufentanil (3 articles), esketamine (3 articles), dexamethasone (3 articles), dexmedetomidine (2 articles), nalmefene (2 articles), and remifentanil (2 articles) were discussed in more than 2 studies.
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of the enrolled studies. All included studies reported the overall incidence of SIC. All studies reported on cough severity; however, two studies (Chen, 2019; Sun and Guo, 2024) were excluded due to discrepancies in the definition of cough severity, leading to a final inclusion of 35 articles for the analysis of SIC severity. To minimize bias due to varying definitions of moderate and severe SIC across studies, we will evaluate the incidence of mild SIC (1-2 instances of coughing) and the incidence of moderate to severe SIC (more than 2 instances of coughing).
Assessment of risk of bias, consistency, and certainty of the evidence
The risk of bias assessments for 37 RCTs is shown in Figure 2 and the Supplementary Figure S1. Funnel plots were generated to assess the publication bias of the studies (Supplementary Figure S2). Moreover, the results of Egger’s test indicated that all outcomes had a risk of publication bias (Supplementary Table S5). Bias-corrected meta-analysis by trim-and-fill was performed separately for all outcomes (Supplementary Figures S2, S3).
No global or local inconsistencies were detected in any of the results (Supplementary Table S3; Supplementary Figure S6). The certainty of the evidence from the NMA was evaluated using the GRADE methodology (Supplementary Table S4). The absence of direct randomized controlled trial comparisons among certain interventions is noted. Consequently, inconsistency tests were not feasible. All indirect evidence was downgraded for inconsistency. Finally, the certainty of all evidence was between high and very low.
Pairwise meta-analysis
During the initial phase of data analysis, a pairwise meta-analysis was conducted to compare the intervention group with the control group. The findings indicate that the intervention group significantly decreases the overall incidence of SIC (7.6% vs. 34.8%; OR 0.13; 95% CI 0.09 to 0.18; P < 0.0001; I2 = 53.0%), the incidence of mild SIC (4.0% vs. 13.0%; OR 0.28; 95% CI 0.22 to 0.35; P = 0.369; I2 = 5.7%), and the incidence of moderate to severe SIC (3.4% vs. 21.7%; OR 0.13; 95% CI 0.10 to 0.16; P = 0.040; I2 = 30.6%). Significant heterogeneity was observed in the primary outcome (I2 = 53.0%) (Supplementary Figure S3). Consequently, after excluding outliers (Yin and Zhang, 2019; Qian et al., 2024; Ding, 2009; Xu et al., 2014), heterogeneity was substantially reduced (Supplementary Figure S3). Meta-regression analysis and 留一法 were performed however, the source of the heterogeneity could not be identified (Supplementary Table S3). The funnel plots and results from Egger’s test demonstrate the presence of publication bias across all outcomes. A bias-corrected meta-analysis was conducted utilizing the trim-and-fill method for all outcomes, confirming the effectiveness of the intervention group in preventing SIC (Supplementary Figures S2, S3).
Network meta-analysis
Network plot for the overall incidence of SIC is shown in Figure 3. Network plots for the incidence of mild SIC and moderate to severe SIC are shown in Supplementary Figure S4. We did not detect global inconsistency and therefore used the consistency model for network estimation. Effect model selection based on DIC results (Supplementary Table S3). The pooled effect sizes derived from the network estimation and the SUCRA values and the ranking of the interventions for some outcomes are presented in Figures 4, 5, and Supplementary Figure S5.
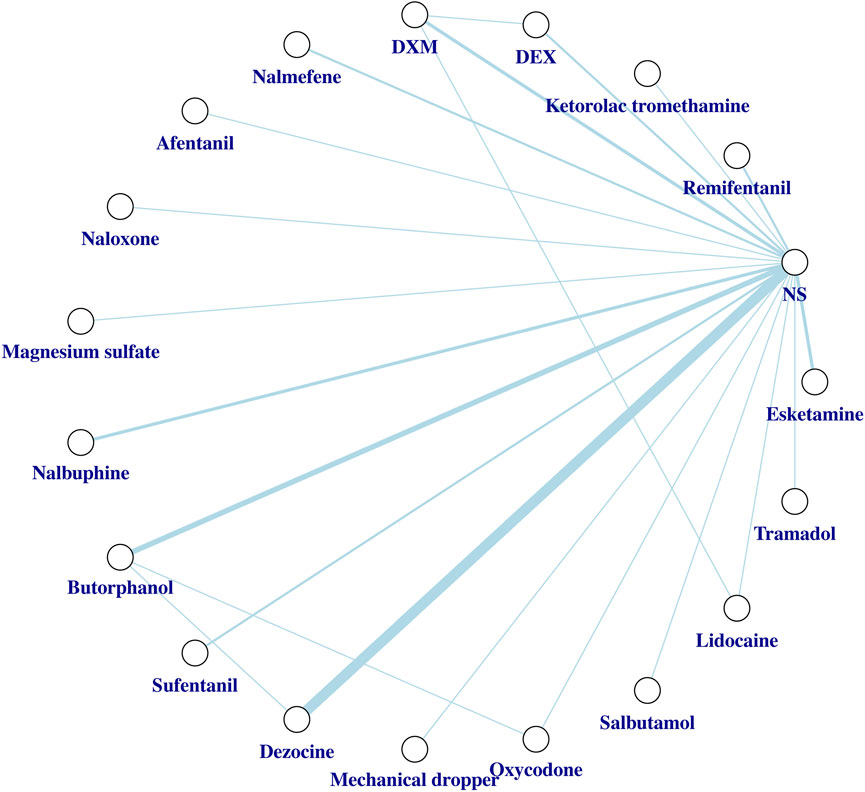
Figure 3. Network plot of the network meta-analysis for the overall incidence of SIC. Network meta-analysis plot comparing different interventions. Each node represents what we consider to be a single intervention. The lines represent direct comparisons between interventions, and their thickness is proportional to the number of clinical trials included in each comparison. Abbreviations: DEX, Dexmedetomidine; DXM, Dexamethasone; NS, normal saline; SIC, sufentanil-induced cough.
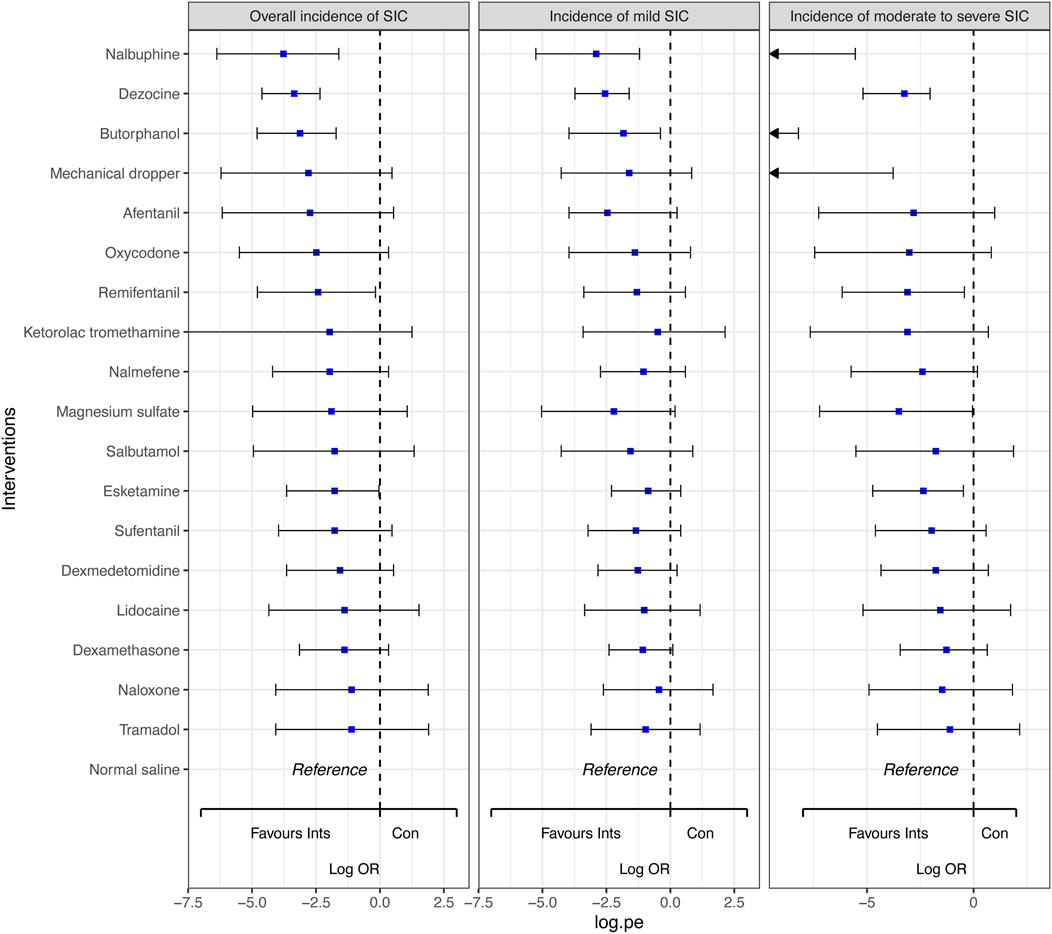
Figure 4. Forest plots for the outcomes with the comparative network effect sizes of all interventions. Blue squares represent the estimated network effect sizes. Black bars represent the 95% credible intervals (95% CrIs). Abbreviations: SIC, sufentanil-induced cough.
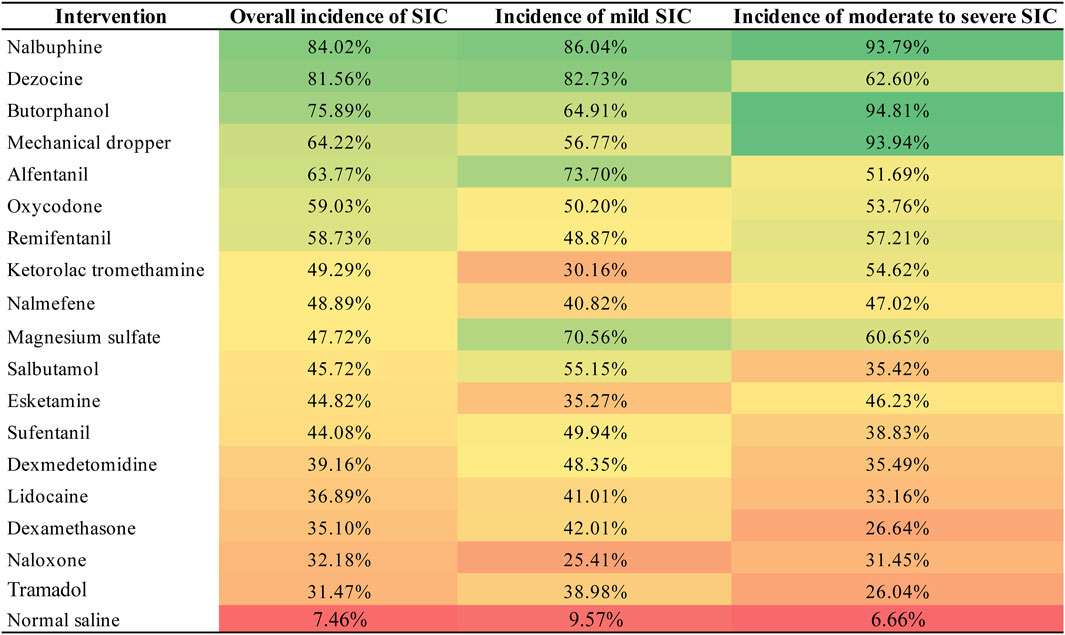
Figure 5. Heat map of surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) values of each intervention for the outcomes. “Heat map” of surface under every intervention’s cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) values for all outcomes. Values can range from 0% to 100%, and the higher the percentage, the greater the likelihood that the intervention is ranked first or in the top ranks. The highest SUCRA values are green, lowest ones are red. Abbreviations: SIC, sufentanil-induced cough.
In comparison to normal saline, dezocine (OR 0.03, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.10; high-quality evidence), nalbuphine (OR 0.02, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.20; high-quality evidence), butorphanol (OR 0.04, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.18; high-quality evidence),remifentanil (OR 0.09, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.84; moderate-quality evidence), and esketamine (OR 0.17, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.96; moderate-quality evidence) significantly decreased the overall incidence of SIC. Similarly, dezocine (OR 0.08, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.20; high-quality evidence), nalbuphine (OR 0.06, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.30; high-quality evidence), and butorphanol (OR 0.16, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.68; moderate-quality evidence) significantly reduced the incidence of mild SIC. Dezocine, nalbuphine, butorphanol, mechanical dropper, remifentanil, magnesium sulfate and esketamine significantly reduced the incidence of moderate to severe SIC. While the other interventions indicated a trend in decreasing the incidence of SIC, the results were not statistically significant.
Discussion
Sufentanil, a fentanyl analogue, is an opioid analgesic with high selectivity for the μ-receptor site (Monk et al., 1988). It is commonly utilized for inducing general anesthesia in clinical settings because of its reliable analgesic effectiveness, lack of histamine release, and minimal effects on hemodynamics (Xu et al., 2024). Coughing is a prevalent side effect associated with sufentanil during the induction of general anesthesia. Coughing serves as a defensive reflex (Yin et al., 2017), with receptors extensively located throughout the bronchial tree and present in lesser quantities in regions including the ear, paranasal sinuses, pleura, diaphragm, pericardium, and esophagus (Andrani et al., 2019; Polverino et al., 2012). Coughing results from the activation of a complex reflex arc, serving to prevent foreign objects from entering the respiratory tract and to clear excessive bronchial secretions, thereby playing a crucial protective role for the airways and lungs (Andrani et al., 2019). The increase in pressure within the coelomic cavity due to coughing, which encompasses intracranial, intraocular, and intra-abdominal pressure, may result in significant negative consequences for critically ill patients (Tian et al., 2020; Sun and Huang, 2013).
The mechanism of the Opioid-induced cough (OIC) is complex and currently not well understood. Various hypotheses have been proposed by researchers, including the receptor hypothesis, vagal excitation hypothesis, β-arrestin signaling pathway, citric acid, and opioid receptor hypothesis, among others (Chen et al., 2020). Moreover, OIC is influenced by several factors, including the types of opioids, dosage, concentration, and the individual physical conditions of patients (El Baissari et al., 2014; Shu et al., 2016). Various interventions are currently employed to prevent SIC in clinical settings. The absence of direct comparisons among various interventions presents challenges for clinical physicians in selecting the most effective therapeutic drug for patients undergoing general anesthesia. Consequently, we have produced the initial article on the prevention of SIC as an NMA to serve as a reference for future clinical research.
The study comprised 18 intervention measures. Traditional pair-wise meta-analyses demonstrated that these interventions effectively reduce the incidence and severity of SIC. The NMA results indicated that pre-treatment with dezocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol significantly decreases the overall incidence of SIC, as well as the incidence of mild and moderate to severe SIC. Remifentanil and a mechanical dropper are effective solely in reducing the incidence of moderate to severe SIC. No significant statistical significance was observed for the remaining intervention measures. The three drugs that are efficacious in preventing all SIC outcomes—dezocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol—are all mixed agonist-antagonists (Ye et al., 2022; Gunion et al., 2004; Commiskey et al., 2005). This sparks our curiosity. Previous studies have identified dezocine as a partial agonist of mu receptors. The role of kappa-receptors remains a subject of debate (Wang et al., 2017). Liu et al. (2014) suggest that dezocine acts as an antagonist of kappa-receptors, whereas Wang et al. (2018) propose it functions as a partial agonist. Nalbuphine exhibits solely antagonist effects at mu-receptors, while it demonstrates an activating agonist effect at kappa receptors (Gunion et al., 2004). Butorphanol functions as a partial agonist at mu-receptors and as an agonist at kappa-receptors (Ji et al., 2020). Future research necessitates a deeper investigation into the occurrence mechanisms of OIC and the mechanisms of drug action. In addition, some research indicates that combination therapies, including ketamine with dexmedetomidine (Saleh et al., 2014), ketamine with dexamethasone (Safavi et al., 2013), and dexmedetomidine with midazolam (Yu et al., 2012), may improve the preventive effects of monotherapy for OIC. At present, there is a lack of research assessing the efficacy of combination therapy in the prevention of SIC.
The dosage of the intervention medication requires careful consideration. The absence of consensus regarding the dosage of intervention drugs for SIC prevention leads to variability in the dosages of the same intervention drugs utilized in this study. Table 1. Li and Li (2017) reported no significant difference in the effectiveness of preventing SIC between the low-dose dexmedetomidine group (0.05 mg/kg) and the high-dose group (0.1 mg/kg). However, the high-dose group exhibited a greater incidence of adverse reactions. Xie et al. (2024) found that the incidence of SIC in the low-dose nalmefene group (0.25 μg/kg) was 30.3%, compared to 14.7% in the high-dose group. Previous studies (Cheng et al., 2016; Pandey et al., 2005; Zhou et al., 2019) on the impact of intervention drug dosages on OIC (69, 70, 71) also indicate a correlation between the dosage of pretreatment drugs and their preventive effects. In summary, there is still a significant gap regarding the optimal dosage of SIC preventive medications, and future research should focus more on the impact of drug dosage on the effectiveness of SIC prevention.
This study represents the inaugural NMA utilizing randomized controlled trials to compare the efficacy of various interventions in the prevention of SIC. The preventive effects of 18 interventions were analyzed and compared through traditional pairwise comparisons and NMA, addressing gaps in direct comparisons of specific interventions. Simultaneously, this study presents certain limitations. Different doses of the same drug utilized in various studies may introduce biases in the research outcomes. Secondly, the number of articles on specific intervention measures is restricted, and additional RCT studies are required in the future to address this. Ultimately, the constraints of meta-analysis permit the extraction of only a restricted volume of data from the selected articles. The analysis of our results focused solely on effectiveness, neglecting factors such as dosage variations, adverse effects, timing of drug administration, and cost-benefit considerations.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that pretreatment with dezocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol significantly reduced the overall incidence of SIC, as well as the incidence of mild and moderate-to-severe SIC. Additionally, remifentanil and mechanical dropper were effective in reducing the incidence of moderate to severe SIC. The remaining interventions indicated a trend toward reducing SIC incidence; however, this was not statistically significant. Future research should prioritize the conduct of additional high-quality randomized controlled trials to enhance current results and establish the optimal dosage of intervention medications.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
HL: Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – original draft. YH: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Software. LD: Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – original draft, Data curation. TW: Writing – review and editing, Data curation. RL: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. YW: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition. WM: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2025A1515010380) and the Basic Research Program of Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (Grant No. 2025A03J3582).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1619920/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
SIC, sufentanil-induced cough; NMA, network meta-analysis; DIC, deviance information criterion; SUCRA, surface under the cumulative ranking curve; PSRF, potential scale reduced factor; OIC, opioid-induced cough; GRADE, Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation.
References
An, L.-J., Gui, B., Su, Z., Zhang, Y., and Liu, H.-L. (2015). Magnesium sulfate inhibits sufentanil-induced cough during anesthetic induction. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 8 (8), 13864–13868. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26550339/
Andrani, F., Aiello, M., Bertorelli, G., Crisafulli, E., and Chetta, A. (2019). Cough, a vital reflex. mechanisms, determinants and measurements. Acta Biomed. 89 (4), 477–480. doi:10.23750/abm.v89i4.6182
Brignardello-Petersen, R., Izcovich, A., Rochwerg, B., Florez, I. D., Hazlewood, G., Alhazanni, W., et al. (2020). GRADE approach to drawing conclusions from a network meta-analysis using a partially contextualised framework. BMJ 371, m3907. doi:10.1136/bmj.m3907
Cao, L., Li, M., and Huang, X. (2020). Effect comparison of Oxycodone and Butorphanol in preventing sufentanil-induced cough. China Modern Medicine 27 (18), 13–16.
Chen, H. (2019). Effect of dizocine and butorphanol on cough induced by sufentanil. Chin. J. Clin. Electron. Ed. 13 (11), 837–840.
Chen, R., Tang, L. H., Sun, T., Zeng, Z., Zhang, Y. Y., Ding, K., et al. (2020). Mechanism and management of fentanyl-induced cough. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 584177. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.584177
Cheng, X.-Y., Lun, X.-Q., Li, H.-B., and Zhang, Z.-J. (2016). Butorphanol suppresses fentanyl-induced cough during general anesthesi a induction: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Medicine 95 (26), e3911. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000003911
Commiskey, S., Fan, L.-W., Ho, I. K., and Rockhold, R. W. (2005). Butorphanol: effects of a prototypical agonist-antagonist analgesic on kappa-opioid receptors. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 98 (2), 109–116. doi:10.1254/jphs.crj05001x
Ding, H. (2009). Clinical observation of dexamethasone in suppressing sufentanil-induced cough. Guide China Med. 7 (08), 288–289.
El Baissari, M. C., Taha, S. K., and Siddik-Sayyid, S. M. (2014). Fentanyl-induced cough--pathophysiology and prevention. Middle East J. Anaesthesiol. 22 (5), 449–456. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25137861/
Gao, L., Zhang, Z., Zhu, Y., Lu, X., Tian, Y., and Wei, L. (2024). Effect of pretreatment with a small dose of esketamine on sufentanil-induced cough during anesthesia induction: a randomized controlled trial. Bmc Anesthesiol. 24 (1), 116. doi:10.1186/s12871-024-02501-0
Gunion, M. W., Marchionne, A. M., and Anderson, C. T. M. (2004). Use of the mixed agonist–antagonist nalbuphine in opioid based analgesia. Acute Pain 6 (1), 29–39. doi:10.1016/j.acpain.2004.02.002
He, L., Shao, K., Zhao, Y., Wu, P., Ma, J., and Yao, Y. (2020). Pre-injection of dezocine to prevent sufentanil-induced cough reflex during induction of general anesthesia for cardiovascular surgery: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled study. Tongfang Knowledge Network (Beijing) Technology Co., Ltd. doi:10.16563/j.cnki.1671-6272.2020.12.008
Ji, J., Lin, W., Vrudhula, A., Xi, J., Yeliseev, A., Grothusen, J. R., et al. (2020). Molecular interaction between butorphanol and κ-Opioid receptor. Anesth. Analgesia 131 (3), 935–942. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000005017
Jie, L., and Kai, L. (2016). Effects of pre-inhalation of salbutamol on cough reflex induced by sufentanil. Atlantis Press, 237–239.
Li, J., and Li, K. (2016). “Effects of pre-inhalation of salbutamol on cough reflex induced by sufentanil,” in Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Mechatronics, Control and Automation Engineering (Dordrecht: Atlantis Press), 2352–5401. doi:10.2991/mcae-16.2016.56
Li, Y. (2014). Effects of low-dose nalmefene on the use of sufentanil during general anesthesia induction. J. North Pharm. 11 (05), 41.
Li, Y., and Li, Y. (2017). Comparative study of intravenous different dose of dezocine premedication on sufentanil-induced cough. J. Clin. Pulm. Med. 22 (12), 2219–2222.
Li, G., Yu, H., Wang, L., Ren, S., Zeng, J., and Ren, P. (2015). Effects of intravenous butorphanol premedication on sufentanyl-induced cough. Chin. Archives General Surg. Electron. Ed. 9, 389–390.
Lin, W., Sun, J., and Fu, S. (2019). A small dose of remifentanil pretreatment suppresses sufentanil-induced cough during general anesthesia induction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Bmc Anesthesiol. 19 (1), 164. doi:10.1186/s12871-019-0836-1
Liu, R., Huang, X.-P., Yeliseev, A., Xi, J., and Roth, B. L. (2014). Novel molecular targets of dezocine and their clinical implications. Anesthesiology 120 (3), 714–723. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000000076
Liu, X.-S., Xu, G.-H., Shen, Q.-Y., Zhao, Q., Cheng, X.-Q., Zhang, J., et al. (2015). Dezocine prevents sufentanil-induced cough during general anesthesia induction: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacol. Rep. 67 (1), 52–55. doi:10.1016/j.pharep.2014.08.004
Liu, M., Li, Z., Wang, S., Liu, Y., Zhong, X., He, R., et al. (2019). Application via mechanical dropper alleviates sufentanil-induced cough: a prospective, randomized, single-blinded trial. Trials 20, 170. doi:10.1186/s13063-019-3274-y
Liu, J., Ma, D., and Xie, Z. (2023). Anesthesiology and perioperative science: a journal for meeting the un met medical and scientific needs. Anesthesiol Perioper Sci 1 (1), 1. doi:10.1007/s44254-023-00008-4
Monk, J. P., Beresford, R., and Ward, A. (1988). Sufentanil. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 36 (3), 286–313. doi:10.2165/00003495-198836030-00003
Pandey, C. K., Raza, M., Ranjan, R., Singhal, V., Kumar, M., Lakra, A., et al. (2005). Intravenous lidocaine 0.5 mg·kg-1 effectively suppresses fentanyl-indu ced cough. Can. J. Anesth 52 (2), 172–175. doi:10.1007/BF03027724
Peringathara, B., and Robinson, S. (2016). Fentanyl-induced cough is a risk factor for postoperative nausea and vomiting. Br. J. Anaesth. 117 (2), 269. doi:10.1093/bja/aew207
Polverino, M., Polverino, F., Fasolino, M., Andò, F., Alfieri, A., and De Blasio, F. (2012). Anatomy and neuro-pathophysiology of the cough reflex arc. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 7 (1), 5. doi:10.1186/2049-6958-7-5
Qian, Y., Huang, Z., Wang, G., Han, J., Zhou, D., Ding, H., et al. (2022). Low-dose naloxone for prophylaxis of sufentanil-induced choking and postoperative nausea and vomiting. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1050847. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1050847
Qian, J., Peng, Y., Mao, Y., Ji, F., Shan, X., Cheng, J., et al. (2024). Inhibitory effect of low-dose esketamine on cough induced by sufentanil during the induction of anesthesia and postoperative impact on mental health status: a prospective, single-center, randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 24 (1), 471. doi:10.1186/s12871-024-02864-4
Safavi, M., Honarmand, A., and Khalighinejad, F. (2013). A comparison of the effect of pretreatment with intravenous dexamethas one, intravenous ketamine, and their combination, for suppression of r emifentanil-induced cough: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-control led clinical trial. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2 (1), 60. doi:10.4103/2277-9175.115808
Saleh, A. J., Zhang, L., Hadi, S. M., and Ouyang, W. (2014). A priming dose of intravenous ketamine-dexmedetomidine suppresses fent anyl-induced coughing: a double-blind, randomized, controlled study. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 119 (4), 333–337. doi:10.3109/03009734.2014.968270
Schug, S. A., Zech, D., and Grond, S. (1992). Adverse effects of systemic opioid analgesics. Drug Saf. 7 (3), 200–213. doi:10.2165/00002018-199207030-00005
Shen, J., Hou, L., and Shen, X. (2014). Effects of intravenous dezocine premedication on sulfentanil-induced cough. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 12 (10), 10–11.
Shuying, L., Ping, L., Juan, N., and Dong, L. (2016). Different interventions in preventing opioid-induced cough: a meta-ana lysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 34, 440–447. doi:10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.05.034
Smith, J. A., and Houghton, L. A. (2013). The oesophagus and cough: laryngo-pharyngeal reflux, microaspiration a nd vagal reflexes. Cough 9 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/1745-9974-9-12
Spiegelhalter, D. J., Best, N. G., and Carlin, B. P. (2002). Van Der Linde A: Baybsian Measures of Model Complexity and Fit. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodo logy 64 (4), 583–639. doi:10.1111/1467-9868.00353
Sun, Y., and Guo, X. (2024). Preventive effect of nalbuphine hydrochloride on cough induced by sufentanil during induction of general anesthesia and its effect on hemodynamics. Chin. J. Drug Abuse Prev. Treat. 30 (01), 15–17+22. doi:10.15900/j.cnki.zylf1995.2024.01.004
Sun, S., and Huang, S.-Q. (2013). Effects of pretreatment with a small dose of dexmedetomidine on sufentanil-induced cough during anesthetic induction. J. Anesth. 27 (1), 25–28. doi:10.1007/s00540-012-1470-y
Teng, Y., Zhao, J., and Wu, H. (2020). Analysis on effect of nabulphine for prevention of cough induced by sufentanyl general anaesthesia. Chongqing Medicine 49 (03), 439–442.
Tian, Z., Hu, B., Miao, M., Zhang, L., Wang, L., and Chen, B. (2020). Ketorolac tromethamine pretreatment suppresses sufentanil-induced cough during general anesthesia induction: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Bmc Anesthesiol. 20 (1), 205. doi:10.1186/s12871-020-01124-5
Wang, H., and Qing, E. (2015). Effect of intravenous dezocine premedication on sufentanil-induced cough. J. Chin. Pract. Diagnosis Ther. 29 (08), 825–826. doi:10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2015.08.037
Wang, Y.-X., Mao, X.-F., Li, T.-F., Gong, N., and Zhang, M.-Z. (2017). Dezocine exhibits antihypersensitivity activities in neuropathy throug h spinal μ-opioid receptor activation and norepinephrine reuptake inhi bition. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 43137. doi:10.1038/srep43137
Wang, Y.-H., Chai, J.-R., Xu, X.-J., Ye, R.-F., Zan, G.-Y., Liu, G. Y.-K., et al. (2018). Pharmacological characterization of dezocine, a potent analgesic actin g as a κ partial agonist and μ partial agonist. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 14087. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-32568-y
Wang, J., Duan, J., Wang, Q., and Lu, Y. (2020). Pretreatment with nalbuphine prevents sufentanil-induced cough during the anesthesia induction: a randomized controlled trial. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 16, 281–286. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S247437
Wang, J., Hou, Q., and Ma, Y. (2014). Clinical observation on the efficacy of dexamethasone and lidocaine in inhibiting cough induced during sufentanil general anesthesia induction[J]. Chinese General Practice (30), 3620–3622. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2014.30.024
Xie, W., He, H., Hong, J., Feng, C., Li, W., and Li, Y. (2024). Effect of preadministration of nalmefene on sufentanil-induced cough during induction of general anesthesia in patients undergoing breast surgery: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 18, 1865–1874. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S462710
Xie, C.-M., He, L.-X., Shen, M.-Q., and Yao, Y.-T.Evidence in Cardiovascular Anesthesia EICA Group (2025). The evidence in cardiovasc anesthesia EG: Effecacy comparison of two doses of dezocine on preventing sufentanil-induced cough in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. Medicine 104 (6), e41416. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000041416
Xu, Q., Zhou, D., and Xiong, S. (2014). The clinical observation of preinjection dezocine during induction of general anesthesia with sufentanil on different injection speed on induced cough reflex. J. Clin. Med. Pract. 18 (16), 137–139.
Xu, Q., Zou, X., Wu, J., Duan, G., Lan, H., and Wang, L. (2024). Low-dose alfentanil inhibits sufentanil-induced cough during anesthesia induction: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 18, 1603–1612. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S464823
Xue, F. S., Xu, Y. C., Liu, Y., Yang, Q. Y., Liao, X., Liu, H. P., et al. (2008). Different small-dose sufentanil blunting cardiovascular responses to l aryngoscopy and intubation in children: a randomized, double-blind com parison. Br. J. Anaesth. 100 (5), 717–723. doi:10.1093/bja/aen032
Yang, J., Pang, L., Zhang, Z., and Zhang, J. (2023). Clinical efficacy of nalbuphine in reducing sufentanil-induced cough in elderly patients during general anesthesia induction. Chinese Journal of Gerontology 43 (18), 4417–4419.
Ye, R.-R., Jiang, S., Xu, X., Lu, Y., Wang, Y.-J., and Liu, J.-G. (2022). Dezocine as a potent analgesic: overview of its pharmacological charac terization. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 43 (7), 1646–1657. doi:10.1038/s41401-021-00790-6
Yepes-Nuñez, J. J., Li, S. A., Guyatt, G., Jack, S. M., Brozek, J. L., Beyene, J., et al. (2019). Development of the summary of findings table for network meta-analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 115, 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.04.018
Yin, F., and Zhang, T. (2019). A small dose of butorphanol prevents sufentanil-induced cough during general anesthesia induction. J. Craniofacial Surg. 30 (8), 2499–2501. doi:10.1097/SCS.0000000000005967
Yin, N., Xia, J., Cao, Y.-Z., Lu, X., Yuan, J., and Xie, J. (2017). Effect of propofol combined with opioids on cough reflex suppression i n gastroscopy: study protocol for a double-blind randomized controlled trial. BMJ Open 7 (9), e014881. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014881
You, Y., and Zeng, M. (2023). Study of the inhibitory effect of small-dose sufentanil preconditioning on cough myofibrillation during induction of general anesthesia with etomidate and sufentanil. Heilongjiang Med. J. 47 (24), 2949–2951.
Yu, J., Lu, Y., Dong, C., Zhu, H., and Xu, R. (2012). Premedication with intravenous dexmedetomidine–midazolam suppresses fe ntanyl-induced cough. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 181 (4), 517–520. doi:10.1007/s11845-012-0807-8
Zhang, J., Zhang, D., Liu, Y., Yu, W., Lin, Y., Hua, F., et al. (2024). Effects of remifentanil pretreatment on sufentanil-induced cough suppression during the induction of general anesthesia. J. Perianesth Nurs. 40, 90–94. doi:10.1016/j.jopan.2024.03.015
Zheng, X., Ren, Y., Han, X., and Mao, S. (2019). Effects of intravenous pre-injection of dezocine and midazolam mixture on sufentanil-induced cough reflex. Tongfang Knowledge Network (Beijing) Technology Co., Ltd. doi:10.15991/j.cnki.41-1361/r.2019.01.011
Zhou, T., Yu, C., and Chen, J. (2014). Clinical observation of dezocine pretreatment in suppressing sufentanil-induced cough. Anhui Med. Pharm. J. 18 (09), 1772–1773.
Zhou, W., Zhang, D., Tian, S., Yang, Y., Xing, Z., Ma, R., et al. (2019). Optimal dose of pretreated-dexmedetomidine in fentanyl-induced cough s uppression: a prospective randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 19 (1), 89. doi:10.1186/s12871-019-0765-z
Zhou, X., Guo, C., Liu, B., Guan, Y., Wang, S., and Ji, J. (2025). Prevention of sufentanil-induced cough during induction of general anesthesia by low-dose esketamine. BMC Anesthesiol. 25 (1), 14. doi:10.1186/s12871-024-02852-8
Zhu, W., Cao, X., Li, X., Liu, Y., and Cheng, Z. (2021). Effect comparison of dexmedetomidine and dexamethasone on suppressing sufentanil-induced cough during general anesthesia induction in patients with gynecological tumors. Cancer Res. Clin. 33 (3), 184–188. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn115355-20200804-00432
Zou, Y., Ling, Y., Kong, G., Tang, Y., Huang, Q., Zhang, L., et al. (2019). Effect of tramadol pretreatment on sufentanil-induced cough. J. Perianesthesia Nurs. 34 (6), 1181–1186. doi:10.1016/j.jopan.2019.01.013
Keywords: cough, dezocine, NMA (network meta-analysis), RCT, randomized controlled trial, sufentanil
Citation: Liu H, He Y, Ding L, Zhang Z, Wu T, Li R, Wang Y and Ma W (2025) Different interventions in preventing sufentanil-induced cough: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1619920. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1619920
Received: 09 May 2025; Accepted: 08 October 2025;
Published: 19 November 2025.
Edited by:
Yonggang Zhang, Sichuan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Maohua Wang, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, ChinaYiling Qian, Wuxi People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, He, Ding, Zhang, Wu, Li, Wang and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wuhua Ma, dHVlc2RheW1vcm5pbmdnekAxMjYuY29t; Yong Wang, d2FuZ3lvbmdAZ3p1Y20uZWR1LmNu
 Hao Liu1,2
Hao Liu1,2 Zhengze Zhang
Zhengze Zhang Wuhua Ma
Wuhua Ma