- 1Suzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Suzhou, China
- 2School of Physical Education and Sports Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, China
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shenzhen Longhua District Central Hospital, Shenzhen, China
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Changzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changzhou, China
Ischemic stroke (IS) continues to be a major contributor to global mortality and long - term disability. Buyang Huanwu Decoction (BHD), a traditional Chinese medicine formula, has shown effectiveness in reducing brain injury and promoting post - stroke recovery through experimental researches and clinical trials. The neuroprotective mechanisms of BHD against cerebral ischemic injury involve multiple pathways, such as suppression of inflammation, reduction of oxidative stress, inhibition of apoptosis, regulation of autophagy, and enhancement of mitochondrial function. Moreover, BHD presents therapeutic potential by boosting neuroplasticity, enhancing angiogenesis, reducing excitotoxicity, optimizing brain energy metabolism, and regulating gut microbiota. Considering the current scarce effective treatments for IS, exploring BHD’s therapeutic potential and its mechanism holds substantial clinical significance. This review systematically organizes recent research advancements on BHD’s application in IS management and its underlying mechanisms, providing useful insights for future research and clinical practice.
1 Introduction
Stroke is a leading cause of death and long-term disability worldwide, owing to its high incidence and devastating sequelae (GBD 2016 Stroke Collaborators, 2019). IS, which is most often due to thrombotic vessel occlusion, comprises the majority of stroke cases and results in cerebral ischemia and hypoxia (Campbell et al., 2019). Current treatments—thrombolysis, antiplatelet therapy, and neuroprotective agents—face well-known limitations: a narrow therapeutic window, patient ineligibility or drug insensitivity, and significant post-treatment complications (Cheng et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2025). More than two-thirds of stroke survivors sustain persistent neurological deficits—manifesting as motor, cognitive (including language), sensory, and cardiopulmonary impairments (Crichton et al., 2016; Benjamin et al., 2018). Conventional therapeutic interventions, including pharmacotherapy, rehabilitation therapy, and secondary prevention, have shown very limited efficacy (Tg et al., 2020). Consequently, there is an urgent need to identify more effective therapeutic strategies.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been widely used as an adjunctive therapy for post-stroke sequelae in China, featuring multi-target effects and low side effects (Hu et al., 2018; Zhang W.-W. et al., 2018). Studies have demonstrated that combining TCM treatment with conventional therapies can improve neurological symptoms and activities of daily living in stroke patients (Cai et al., 2019; Gao et al., 2021). BHD, a classic TCM formula, was first recorded in Yilin Gaicuo (Corrections of Errors in Medical Works) by Wang Qingren in the Qing Dynasty, and is used for treating post-stroke sequelae due to qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome. The formula consists of seven ingredients: Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi), Angelica sinensis (Danggui), Paeonia lactiflora var. chinensis (Chishao), Lumbricus (Dilong), Persicae Semen (Taoren), Carthami Flos (Honghua), and Ligusticum chuanxiong (Chuanxiong) in a ratio of 120:6:4.5:3:3:3:3. BHD is widely used in clinical practice to promote the recovery of neurological and motor functions, benefiting patients with post-stroke sequelae, with no reported adverse reactions (Gao et al., 2021; Shao et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). In addition, in experimental stroke models, BHD can reduce cerebral infarct volume, improve neurological prognosis, and inhibit oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis (Cai et al., 2007; She et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024). However, the specific mechanisms underlying the role of BHD in stroke recovery remain incompletely elucidated.
This formula contains several bioactive components, including astragaloside IV and isoflavonoids from Astragalus membranaceus, paeoniflorin from Paeonia lactiflora, Hydroxy-safflor yellow A from Carthami Flos, and ligustrazine from Ligusticum chuanxiong. Studies have shown that these components exert multiple neuroprotective effects, such as promoting neurogenesis, inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation, preventing thrombosis, protecting the blood-brain barrier, and modulating apoptosis following cerebral ischemia (Fu et al., 2014; Jiang et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021; 2025). BHD, as an organic combination based on TCM theory, exhibits multi-component, multi-pathway, and multi-target effects. The interactions between its components may involve synergistic, antagonistic, or sensitizing effects. Numerous studies have demonstrated that BHD has a certain degree of neuroprotective effect in ischemic stroke, and its mechanisms are complex and diverse. The therapeutic efficacy results from the combined action of its ingredients. For example, Ligusticum chuanxiong, a key “guide” herb, increases the distribution of other ingredients in the brain; Astragalus membranaceus slows down the metabolism of paeoniflorin, maintaining its activity; and ligustrazine enhances the transmembrane transport of paeoniflorin, highlighting the scientific and rational compatibility of this formula (Zheng et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2021). Although the research on the individual active components provides important insights into the pharmacological basis of BHD’s therapeutic effects, the essence of TCM formulas lies in their “holistic view.” A TCM formula is an organic whole formulated under the guidance of TCM theory, and its efficacy arises from the combined effects of multiple components, pathways, and targets. The components may exhibit complex interactions, such as synergy, antagonism, or sensitization, rather than a simple additive effect of individual components. Therefore, this study will focus on the overall effects of the entire BHD formula, rather than isolating the targets of single components. It aims to systematically summarize the network pharmacology map of BHD’s multi-mechanistic, synergistic treatment of stroke, providing valuable references for its clinical application and offering direction for future research.
2 The mechanisms of BHD in the treatment of ischemic stroke
Extensive preclinical studies demonstrate that BHD effectively attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. In this review, we synthesize these findings to elucidate BHD’s molecular mechanisms—focusing on the principal pathways and targets that underlie its neuroprotective actions (Figure 1).
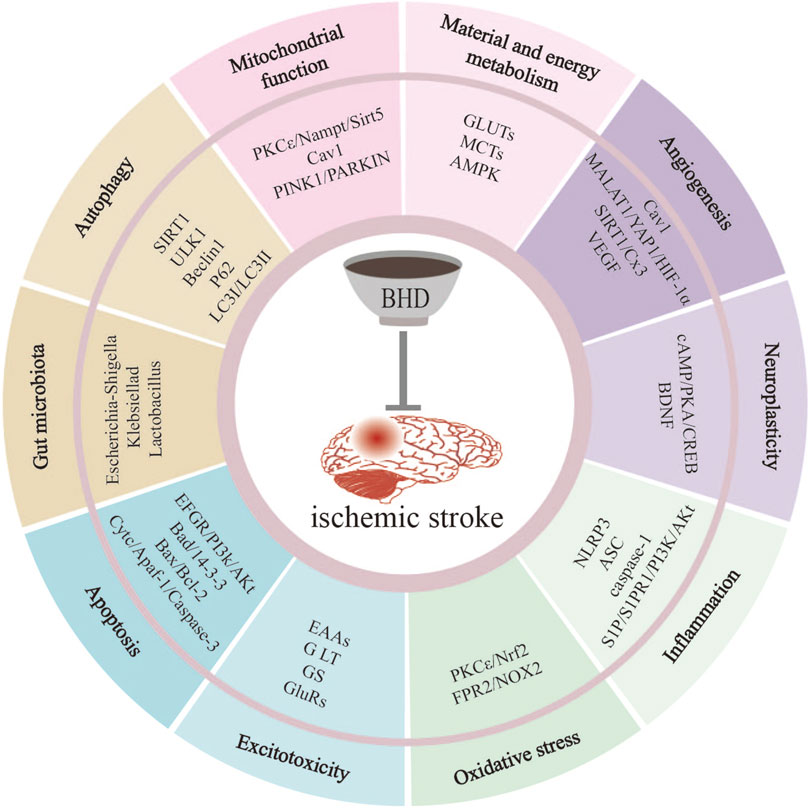
Figure 1. BHD mitigates IS-induced injury through multiple pathways. These pathways include suppression of inflammation, reduction of oxidative stress, inhibition of apoptosis, regulation of autophagy, improvement of mitochondrial function, promotion of neuroplasticity, promotion of angiogenesis, inhibition of excitotoxicity, regulation of material and energy metabolism, regulation of gut microbiota.
2.1 Suppression of inflammation
Neuroinflammation is a critical target for mitigating post-stroke damage and promoting recovery (Iadecola and Anrather, 2011; Kl et al., 2019). Neuronal necrosis following ischemic stroke releases damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and pro-inflammatory mediators, which activate microglia and astrocytes and recruit peripheral immune cells into the cerebral ischemic penumbra (Shi et al., 2019). Activated glia and infiltrating leukocytes then amplify local inflammation via overproduction of cytokines—a response tightly connected to systemic immune alterations (Iadecola et al., 2020; Simats and Liesz, 2022).
Importantly, pyroptosis—a caspase-1-dependent form of inflammatory cell death—has emerged as a major driver of ischemic stroke pathology, primarily through activation of the canonical Nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat-containing pyrin domain 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome (Adamczak et al., 2014; Tan et al., 2014). A growing body of evidence indicates that NLRP3 inflammasome activation markedly amplifies neuroinflammation and exacerbates I/R injury (Li J. et al., 2023). Studies have shown that pre-treatment with 7 days of BHD significantly enhances the brain’s tolerance to subsequent ischemia/reperfusion damage, as evidenced by a reduction in infarct volume and an improvement in neurological function scores 24 h post-reperfusion. This pharmacological preconditioning effect is likely associated with the downregulation of key NLRP3 inflammasome components (ASC, pro-caspase-1) and pyroptosis effectors (active caspase-1, IL-1β) (Figure 2) (She et al., 2019). Notably, astragaloside IV and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A may be key active ingredients of BHD in suppressing pyroptosis (Hou et al., 2024). Since NLRP3 inflammasome components are expressed across multiple cell types in the ischemic brain and drive pyroptosis (Fann et al., 2014; Jorgensen and Miao, 2015), targeting NLRP3-mediated inflammation presents a promising avenue for therapeutic intervention in ischemic stroke. Future research should explore the potential application of BHD’s preconditioning advantage in clinical high-risk populations.
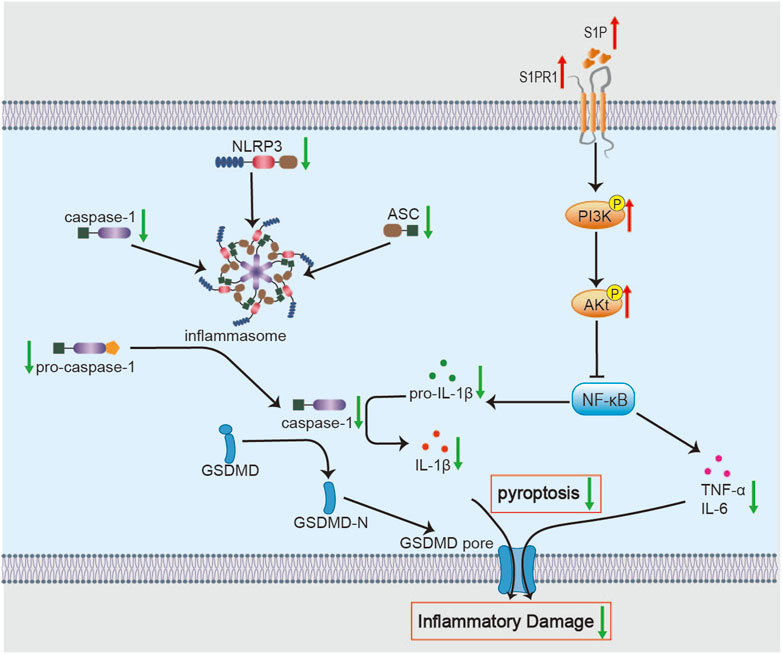
Figure 2. Molecular mechanisms of BHD in suppressing neuroinflammation. BHD alleviates neuroinflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway and its downstream molecules via activation of the S1P/S1PR1/PI3K/Akt axis. Concurrently, this inhibition suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and the activity of downstream pyroptosis effectors, thereby reducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and attenuating inflammatory tissue damage.
Notably, the role of neuroinflammation—and BHD’s modulation of it—is stage-dependent. In the acute phase, BHD primarily suppresses deleterious, excessive inflammation to mitigate secondary injury. As the disease advances into the recovery phase, the inflammatory response assumes a more complex, dual role. Studies show that BHD promotes polarization of microglia toward an M2 phenotype and astrocytes toward an A2 phenotype in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)/R rats during recovery, thereby facilitating synaptogenesis and neurite outgrowth (Li et al., 2024c). Moreover, Liu W demonstrated that in the permanent MCAO (pMCAO) mouse model, BHD treatment consistently promoted long-term neurological recovery, with improvements in neurological deficits and reduced infarct volume observed on days 7 and 14 post-stroke. The recovery benefits were closely related to the activation of the Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P)/Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 1 (S1PR1)/Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/Protein Kinase B (PKB, Akt) survival and repair signaling pathway (Liu W. et al., 2023). The PI3K/Akt/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling cascade is a core regulator of post-ischemic neuroinflammation (Li L. et al., 2023; Li J. et al., 2024). Upstream, S1P activates S1PR1 to promote Akt phosphorylation, thereby exerting neuroprotective effects in ischemic models (Hasegawa et al., 2010). As a bioactive sphingolipid, S1P/S1PR1 signaling mitigates inflammatory injury and supports neural repair (Nakamura et al., 2021; Zaibaq et al., 2022). These results implicate S1P/S1PR1 as a potential direct target of BHD. Moreover, most evidence derives from whole-brain homogenates in rodent models. Future work should validate these mechanisms in isolated cell populations—such as microglia and neurons—to delineate cell-type–specific effects of BHD.
In addition to local inflammation, ischemic stroke induces systemic immunosuppression, which profoundly affects recovery. Initially, DAMPs and cytokines leak into the circulation via a disrupted blood-brain barrier, provoking transient systemic immune activation. This phase swiftly gives way to sustained immunosuppression, heightening the risk of complications such as stroke-associated pneumonia (Iadecola et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2023). Concomitant splenic atrophy and lymphocyte apoptosis further exacerbate secondary neural damage (Yu H. et al., 2021). Fu R found that BHD reduces splenic T-cell apoptosis at 3 days post-MCAO/R, ameliorating both cerebral injury and systemic immunosuppression—possibly via the Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2)/IL-1β/Fas ligand-Fas receptor (FasL-Fas) axis. Moreover, quercetin from safflower may contribute to this process by inhibiting peripheral immune cell recruitment (Zhang et al., 2022). Yet, direct evidence for AIM2 dependence is lacking (Fu et al., 2024). However, it remains necessary to verify whether BHD exerts this effect specifically via AIM2. Notably, Roth S reported that AIM2 inhibition did not alter neurological outcomes within 24 h post-stroke, suggesting that timing critically influences AIM2’s role (Roth et al., 2021). Accordingly, future studies should dissect the temporal and spatial dynamics of BHD’s effects on splenic immune subsets and map the communication pathways of key immune mediators between brain and spleen.
2.2 Reduction of oxidative stress
ATP depletion after ischemia leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The resulting increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) and decrease in superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity exacerbate oxidative injury, damaging organelles and compromising neuronal viability (Liu et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2018; Kamal et al., 2023).
Li C showed that BHD scavenges ROS in isolated cerebral cells from MCAO/R rats and preserves neuronal membrane fluidity (Li, 2012). In in vivo experiments, BHD enhances the antioxidant defense capability in MCAO/R rats on day 3, restores mitochondrial membrane potential, reduces neuronal death, and decreases infarct size. Mechanistically, BHD upregulates protein kinase C epsilon (protein kinase Cε, PKCε), promoting nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) nuclear translocation and the subsequent induction of antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1) (Yin et al., 2023). Nrf2, the master regulator of antioxidant defense, maintains redox balance by driving both basal and inducible expression of enzymes that neutralize ROS and electrophiles (Figure 3) (Zhang et al., 2021). Notably, compared to edaravone—an ROS scavenger that acts via direct chemical quenching—BHD uniquely restores endogenous antioxidant capacity through enzyme induction (Dickmeiß et al., 2025; Lee et al., 2025). This highlights BHD’s antioxidative stress effect during the acute phase of cerebral ischemia. This effect may be mediated by astragaloside IV and Quercetin through the activation of the Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway (Li et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2022). Future work should identify the intermediate signaling factors that link BHD to PKCε activation and investigate Nrf2-independent mechanisms of mitochondrial protection.
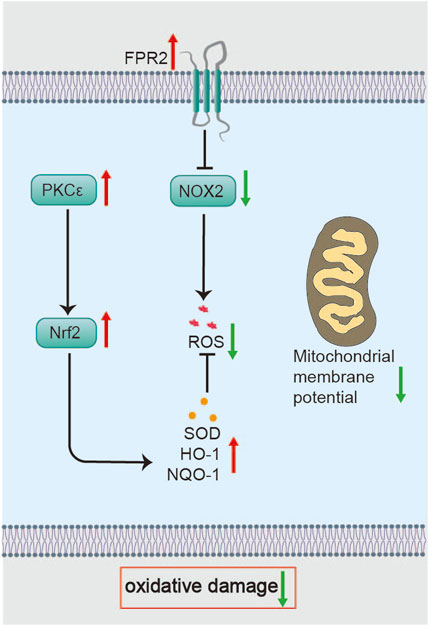
Figure 3. Molecular mechanisms of BHD in restoring mitochondrial function. BHD regulates mitochondrial dynamics via the PKCε/Nampt/Sirt5 axis and restores mitochondrial function, potentially involving Cav-1-mediated effects on MQC processes.
Additionally, Wu F proposed that BHD might exert its antioxidative effects in the acute phase of ischemic stroke through the Formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2)/NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) signaling pathway (Wu et al., 2021). FPR2—a neuroprotective GPCR abundant in the brain—when deficient, worsens I/R injury (Sa et al., 2016; Bisicchia et al., 2018). Since NOX2 is a primary source of ROS, its inhibition dampens oxidative bursts (Figure 3) (Khayrullina et al., 2015). Therefore, BHD is an effective remedy for combating oxidative stress in the acute phase. Nonetheless, it remains unclear whether BHD directly modulates NOX2 activity or acts upstream via FPR2.
2.3 Inhibition of apoptosis
Cerebral I/R activates complex apoptotic cascades, which are central to neuronal loss and ensuing neurological deficits. These cascades consist of the intrinsic (mitochondria-mediated) pathway—driven by mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization and calpain activation—and the extrinsic pathway, triggered by death receptors in response to cytokines and chemokines (Tuo et al., 2022). In the intrinsic pathway, injury-induced mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) releases cytochrome c into the cytosol. Cytochrome c then associates with apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) to form the apoptosome, which initiates the caspase cascade and orchestrates programmed cellular disassembly (Glover et al., 2024). Members of the B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family tightly regulate MOMP: anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 prevents cytochrome c release, whereas pro-apoptotic Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) facilitates membrane permeabilization (Shore and Nguyen, 2008; Soriano and Scorrano, 2011).
Liu F reported that BHD suppresses Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) and Tau overexpression in H2O2-stressed neuronal cells, concomitantly downregulating caspase-3 activity and reducing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio (Liu et al., 2019). CDK5 can trigger apoptosis by phosphorylating Bcl-2 family members at the mitochondrial membrane or directly modifying executioner caspases such as caspase-3 and caspase-7 (García-Sáez, 2012; Maitra and Vincent, 2022). Nevertheless, Liu et al. did not confirm a causal link between CDK5 inhibition and downstream apoptotic markers, underscoring the need for in vivo validation. In a separate study, Song C demonstrated that serum from BHD-treated MCAO/R rats protects Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion (OGD/R)-injured brain microvascular endothelial cells—enhancing viability, reducing TUNEL positivity, lowering Bax and caspase-3 levels, and increasing Bcl-2. They further showed that BHD suppresses glycolysis-driven histone H3 lactylation to downregulate Apaf-1 transcription (Song et al., 2024). However, the multifaceted composition of medicated serum raises the possibility of confounding by non-BHD factors. Notably, Paeoniflorin and Amygdalin may be key active components of BHD in mediating its anti-apoptotic effects (Zhang Y. et al., 2015; Kimura et al., 2025).
Chen et al. used proteomic analysis to find that, after 14 days of BHD intervention in the MCAO/R model, BHD significantly alleviated neuronal apoptosis. Mechanistic studies suggest that this effect might be mediated through the activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/PI3K/Akt signaling axis, which then regulates downstream Bcl-2-associated death promoter (Bad) and 14-3-3 protein signaling (Figure 4) (Chen et al., 2020). In this paradigm, Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Bad fosters its sequestration by 14-3-3 proteins, thereby blocking Bax activation, cytochrome c release, and caspase-3 induction (Datta et al., 2000; Nomura et al., 2015). Therefore, BHD may directly enhance the intrinsic pro-survival signaling network in the recovery phase after cerebral ischemia, providing a stable cellular environment for neuronal repair. However, the cell type-specificity of this signaling pathway (such as its effect on neurons, astrocytes, or oligodendrocytes) and the indispensability of each signaling node (e.g., EGFR, PI3K) in mediating BHD’s effects still require experimental validation using cell-specific knockout models.
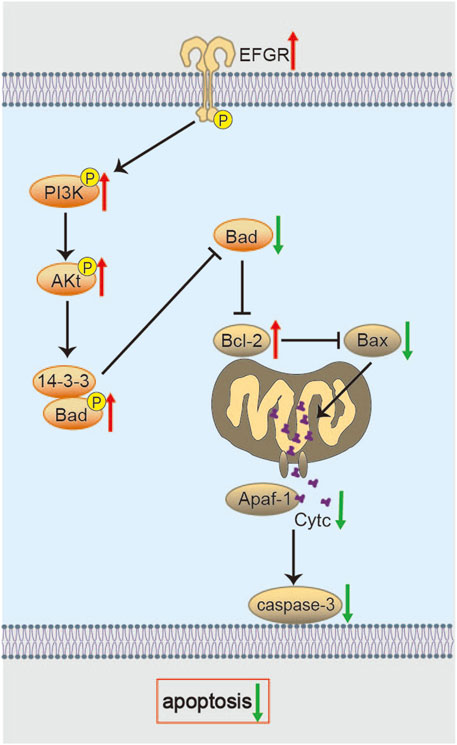
Figure 4. Molecular mechanisms of BHD in suppressing oxidative stress. BHD restores mitochondrial membrane potential and enhances antioxidant enzymes via the PKCε/Nrf2 axis, while potentially reducing ROS generation through FPR2/NOX2 signaling to alleviate oxidative damage.
2.4 Regulation of autophagy
Autophagy can protect neurons during cerebral ischemia by removing damaged organelles and misfolded proteins (Dugbartey, 2024; Newton et al., 2024), and it remains crucial for restoring cellular homeostasis during reperfusion (Liu S. et al., 2023). Nevertheless, the protective role of autophagy in I/R injury remains context-dependent (Aghaei et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2019), as excessive or prolonged dysregulation can be detrimental (Gao et al., 2012; Sun et al., 2018). Therefore, precise temporal regulation of autophagy is required at each post-ischemic stage. Studies have shown that after 2 h of ischemia and 3 days of reperfusion, the levels of Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) II/I and Beclin 1 autophagy related gene (Beclin-1) in the ischemic penumbra of MCAO/R rats were significantly elevated (Shu et al., 2016; Pan et al., 2020). However, in a 1.5-h ischemia MCAO/R model, the levels of Beclin-1 and LC3 II in the ischemic penumbra were significantly reduced at 24 h and 7 days post-surgery (Wu et al., 2018). These differences might be attributed to variations in ischemia and reperfusion times in the models.
Zhao Y found that BHD reduced Beclin-1 and LC3-II levels in the ischemic penumbra at day 3 post-MCAO/R, with no changes in the ischemic core or contralateral hemisphere. However, assessing only Beclin-1 and LC3-II risks conflating reduced autophagosome formation with impaired autophagic flux (Zhao et al., 2021). In contrast, Li H reported that by day 5 post-reperfusion, BHD not only reduced infarct size but also elevated Beclin-1 and LC3-II, decreased Sequestosome 1 (p62), and upregulated Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) in the penumbra (Li et al., 2021). Given that SIRT1 directly deacetylates autophagy regulators such as Beclin-1 and Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1) complex components (Thapa et al., 2024), these findings suggest a SIRT1-dependent mechanism—though direct evidence for SIRT1’s necessity in BHD-induced autophagy remains lacking. Future work should employ SIRT1 loss-of-function models (e.g., genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition) to verify its role in BHD-induced autophagy and neurogenesis, and use co-immunoprecipitation or proximity assays to confirm direct SIRT1–Beclin-1/ULK1 interactions. Because autophagy dynamics evolve over time, comprehensive flux mapping at days 1, 3, 5, and 7 post-ischemia—using metrics such as p62 degradation rates, LC3-II puncta quantification, and mRFP-GFP-LC3 reporter assays—is essential for delineating BHD’s temporal effects. Qin B also demonstrated that BHD enhances autophagy in OGD/R-injured neural stem cells—upregulating Beclin-1 and LC3-II while reducing p62 (Qin et al., 2021). However, without full flux measurements or identification of upstream receptors and signaling intermediates, the mechanistic basis remains unclear. Integrating transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic analyses in both in vitro and in vivo models will be crucial to pinpoint the precise molecular targets of BHD in autophagy regulation.
Overall, a principal function of BHD may be to restore autophagic homeostasis: it can attenuate excessive autophagic flux in the acute phase to prevent autophagy-dependent cell death, while in the subacute phase it can promote basal autophagy to facilitate clearance of damaged organelles and proteins, thereby supporting cellular repair and survival. This dynamic adaptation to the evolving post-stroke pathological milieu may be a key advantage of multi-herb formulas such as BHD. Future studies using serial time-point analyses are essential to validate this temporally specific regulation and to define the optimal therapeutic window for BHD intervention.
2.5 Improvement of mitochondrial function
Mitochondrial quality control (MQC)—the suite of processes that preserve mitochondrial morphology, dynamics, and function—underlies organelle homeostasis and supports neuronal survival (Tian et al., 2022). Mitochondrial disruption during cerebral I/R has emerged as a key pathological driver that determines the extent of neuronal damage following stroke (Rutkai et al., 2019). Dysregulation of MQC mechanisms, including impaired mitophagy, altered fusion/fission balance, and defective biogenesis, exacerbates mitochondrial dysfunction and contributes to neuronal death following IS (Song et al., 2022; Tian et al., 2022). Restoring MQC has therefore emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy to mitigate secondary brain damage and enhance neurological recovery after IS (Yang et al., 2021).
Studies demonstrate that BHD restores mitochondrial membrane potential and NAD+/NADH ratios, reduces infarct volume, and mitigates neuronal injury in MCAO/R model rats (Yin et al., 2024). Additionally, Liu Z found that, after 7 days of BHD treatment in MCAO/R rats, BHD regulated mitochondrial dynamics through the PKCε/nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt)/Sirtuin 5 (Sirt5) signaling axis. By modulating the expression of mitochondrial fission proteins (Drp1, Fis1) and fusion proteins (Mfn2, Opa1), BHD restored mitochondrial function and alleviated ischemia-reperfusion injury (Figure 5) (Liu et al., 2025). Notably, Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission might be activated by Ligustilide, a component of BHD (Wu et al., 2022). PKCε is a neuroprotective kinase that supports mitochondrial integrity. Downstream, Nampt elevates NAD+/NADH ratios and enhances neuronal survival after ischemia (Gomes et al., 2011; Morris-Blanco et al., 2016). Nampt’s elevation of NAD+ levels activates Sirt5 (Beaudoin et al., 2012), and Sirt5 overexpression in turn promotes mitochondrial fusion and limits organelle degradation (Polletta et al., 2015; Zou et al., 2018). However, the precise post-translational modifications through which BHD-induced Sirt5 activation alters fission/fusion machinery have not been defined. Studies in purified neuronal cultures are required to confirm these effects and rule out non-neuronal contributions.
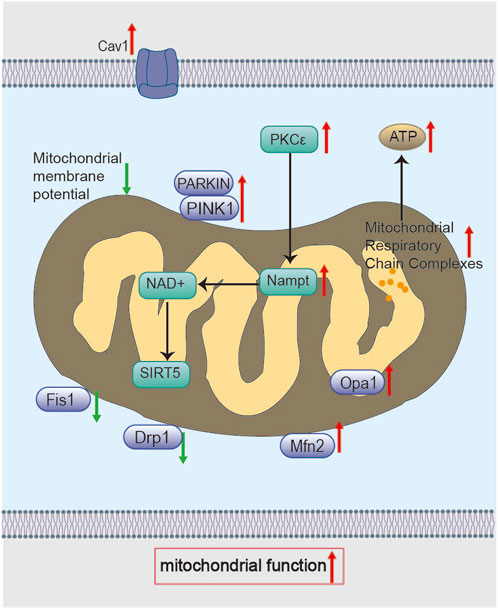
Figure 5. Molecular mechanisms of BHD in restoring mitochondrial function. BHD modulates the PKCε/Nampt signaling axis through Cav-1, elevates NAD+ levels, and activates Sirt5, which in turn upregulates the expression of mitochondrial fusion proteins (Mfn2, Opa1) and suppresses the expression of fission proteins (Drp1, Fis1), thereby regulating mitochondrial dynamics. In addition, BHD promotes mitophagy via the PINK1/Parkin pathway. Collectively, these mechanisms restore mitochondrial membrane potential, improve respiratory chain function, and enhance ATP production.
Furthermore, Xu Y’s study reported that BHD preserved mitochondrial morphology, protected respiratory chain function (including complex activities, ATP content, and ATPase activity), regulated mitochondrial dynamics (Drp1, Fis1, Mfn2, Opa1), improved mitophagy (via the PINK1/Parkin pathway), and promoted mitochondrial biogenesis in MCAO/R rats 7 days post-intervention (Figure 5). They further demonstrated that Caveolin-1 (Cav-1) deficiency aggravates MQC disruption and diminishes BHD’s neuroprotection after ischemia (Xu et al., 2023). Cav-1 depletion likely impairs mitophagy and biogenesis, culminating in mitochondrial dysfunction (Bosch et al., 2011; Jiang et al., 2022). Cav-1 may facilitate the recruitment of fission/fusion proteins and mediate lipid trafficking within mitochondria (Xiao et al., 2022), but these mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Therefore, Cav-1 is a critical MQC regulator and a potential therapeutic target in ischemic stroke. Intriguingly, Chen X observed decreased Cav-1 levels after BHD treatment (Chen et al., 2020), a discrepancy that may arise from species differences, sampling timepoints, or brain regions analyzed.
These findings collectively suggest that the multi-targeted regulation of mitochondrial homeostasis is one of the key mechanisms through which BHD exerts its therapeutic effects during the recovery phase. Given the dynamic nature of mitochondrial remodeling, static measurements at a single timepoint are insufficient. Future investigations should leverage single-cell sequencing or spatial transcriptomics at multiple post-ischemic intervals to chart Cav-1’s spatiotemporal dynamics.
2.6 Promotion of neuroplasticity
Enhancing neuroplasticity is vital for functional recovery after ischemic stroke (Marques et al., 2019; Du et al., 2024). Early investigations showed that BHD stimulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in the cortex and dentate gyrus of MCAO/R rats (Sun et al., 2007; Gao et al., 2009). Additionally, BHD significantly improved neurological scores and preserved synaptic ultrastructural integrity in pMCAO rats, although it did not reduce infarct volume (Pan et al., 2017). However, electrophysiological studies are required to establish whether these structural improvements translate into enhanced neural circuit function.
Li M et al. suggested that after 30 days of intervention in MCAO/R rats, BHD may promote neurite outgrowth and synaptogenesis via the AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)/cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB) pathway, a process associated with its ability to polarize microglia toward the M2 phenotype and astrocytes toward the A2 phenotype during stroke recovery (Li M. et al., 2024). This mechanism is supported at the compositional level: astragaloside IV, a key component of BHD, has been identified as an effective AMPK activator that drives M2 microglial polarization and facilitates axonal remodeling (Li et al., 2024c). Furthermore, after 7 days of intervention in MCAO/R rats, BHD ameliorated local pathology, increased dendritic spine density, and reduced neuronal apoptosis through the Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (cAMP)/Protein Kinase A (PKA)/CREB signaling axis (Figure 6) (Mo et al., 2024). Given that cAMP/PKA modulates growth, differentiation, metabolism, and cell survival (Khan et al., 2021). Activation of the PKA-CREB pathway positively influences learning and memory (Bae et al., 2019). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a key CREB transcriptional target, promotes new synapse formation (Jiang et al., 2023). In summary, BHD synergistically activates CREB—a key transcription factor—through multiple signaling pathways during stroke recovery, thereby efficiently promoting neuroplasticity. Future studies should validate the crosstalk among these pathways at a cell-specific level and clarify which specific components in BHD initiate these upstream signals. Additionally, it is essential to identify the specific effector genes regulated by CREB that are influenced by BHD and to evaluate whether these structural changes enable new neurons to functionally integrate into existing neural networks.
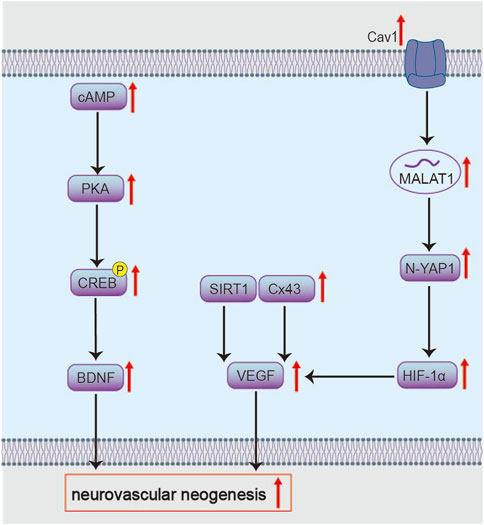
Figure 6. Molecular mechanisms of BHD in inhibiting apoptosis. BHD potentially inhibits Bad via the EGFR/PI3K/Akt/Bad/14-3-3 axis and modulates Bcl-2/Bax to control Cyt c release and caspase-3 activation, thereby suppressing apoptosis.
Kong X reported that on days 7 and 21 after intervention in MCAO/R model rats, BHD may promote the proliferation, migration, and differentiation of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) by upregulating the expression of C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 4 (CXCR4) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) (Kong et al., 2014). However, direct evidence linking these factors to NPCs migration is lacking. Furthermore, VEGF’s dual role—in promoting angiogenesis and increasing blood-brain barrier permeability—raises concerns about potential exacerbation of edema (Zhang et al., 2002). Future investigations should clarify how BHD modulates VEGF signaling to balance neurogenesis and vascular integrity, and employ long-term lineage tracing to confirm functional incorporation of migrating NPCs.
Notably, extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from BHD-preconditioned Neural Stem Cells (NSCs) significantly accelerated neurological recovery in MCAO/R rats and enhanced NSCs proliferation/differentiation more effectively than BHD alone (Long et al., 2023). Beyond utilizing single-cell sequencing to investigate EV secretion mechanisms in NSCs stimulated by BHD’s active constituents, future efforts should focus on developing nano-delivery systems to efficiently deliver BHD’s holistic therapeutic profile rather than isolated components.
2.7 Promotion of angiogenesis
Reconstituting collateral blood flow via cerebral angiogenesis is vital for ischemic stroke recovery. In the infarcted region, angiogenesis drives microvascular sprouting and vascular remodeling—key steps in tissue repair (Ma et al., 2018). Over time, these new vessels deliver oxygen and nutrients to the neurovascular niche, fostering neuronal survival and regeneration (Arai et al., 2009).
BHD also targets Cav-1, potentially activating the Wnt signaling pathway and mediating effects through the metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)/Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1)/hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) axis (Figure 6). This mechanism alleviates acute neurological deficits and pathological damage in MCAO/R mice, while promoting neural regeneration during recovery, increasing cortical blood flow and microvascular density in ischemic brain tissue (Chen et al., 2024; OuYang et al., 2025). The lncRNA MALAT1 is highly expressed in neural cells and participates in post-ischemic processes such as cell death, inflammation, and angiogenesis (Lipovich et al., 2012). Its neuroprotective and regulatory roles in pathological damage following cerebral ischemia have been confirmed in MCAO mouse models (Zhang et al., 2017). MALAT1 relies on Cav-1 for exosome internalization (Cooper et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2019). MALAT1 increases YAP1 nuclear translocation; YAP1 binds to and stabilizes HIF-1α protein, enhancing HIF-1α′s transcriptional activity to co-activate genes like VEGF, thereby promoting angiogenesis (Zhang X. et al., 2018; Sarkar et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020). Functionally, this axis alleviates neurological deficits, enhances cortical perfusion, and increases microvascular density. Future studies should dissect the mechanisms of Cav-1–mediated exosome uptake and directly test MALAT1’s role in orchestrating YAP1/HIF-1α activity. It is worth noting that calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside from Radix Astragali may be a mediator through which BHD modulates Cav-1 (Fu et al., 2014).
Experimental evidence demonstrates that BHD upregulates VEGF and angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1), improving microvascular density (MVD). These pro-angiogenic effects are attenuated by Gap26, a connexin 43 (Cx43) inhibitor (Zhou et al., 2022). This indicates that Cx43 mediates BHD’s pro-angiogenic action via VEGF and Ang-1 (Figure 6). Cx43 is widely distributed in perivascular end-feet of astrocytes and vascular cells, providing structural and functional support for metabolic homeostasis within the neurovascular unit (McConnell et al., 2017; Bello et al., 2020). Studies have confirmed the pro-angiogenic role of Cx43 in endothelial cells, and phosphorylated Cx43 mediates the protective effects of erythropoietin on ischemic neurovascular unit injury (Koepple et al., 2021; Yu W. et al., 2021). Although the specific molecular interplay between Cx43 and VEGF/Ang-1 warrants further investigation.
Furthermore, BHD promotes post-stroke angiogenesis by targeting the SIRT1/VEGF signaling pathway (Figure 6) (Zheng et al., 2018; Tang et al., 2023). Tetramethylpyrazine, a component from Ligusticum chuanxiong, has been reported as a key active constituent potentially responsible for activating the SIRT1/VEGF pathway (Shu et al., 2024). SIRT1 binds the VEGF promoter to upregulate its transcription (Zhang H. et al., 2015). Upon secretion, VEGF engages VEGFR2 on endothelial cells to initiate pro-angiogenic signaling (Shibuya and Claesson-Welsh, 2006). Yet, VEGF also increases vascular permeability and edema by loosening endothelial junctions (Weis and Cheresh, 2005), posing a therapeutic paradox. Future studies should delineate how BHD balances VEGF’s angiogenic and permeability effects over acute and recovery phases, and identify the downstream mediators responsible for beneficial outcomes.
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) transplantation holds considerable promise for treating ischemic brain injury (Shen et al., 2012; Miyamoto et al., 2013). Studies show BHD-preconditioned MSCs secrete exosomes with elevated VEGF and miR-126—and reduced miR-221/miR-222—thereby upregulating VEGF and Ki-67 in recipient tissue and augmenting cerebrovascular density (Yang et al., 2015). Optimizing BHD’s modulation of MSC exosome cargo may enhance the clinical efficacy of MSC-based therapies.
2.8 Inhibition of excitotoxicity
Mitigating excitotoxicity is an essential strategy for treating ischemic stroke (Chamorro et al., 2016). After ischemia, ATP depletion causes membrane depolarization and calcium overload. Simultaneously, excessive release of glutamate (GLU) and aspartate (ASP) from presynaptic terminals overstimulates NMDA and AMPA receptors, allowing massive Ca2+ and Na+ influx. This ionic imbalance drives ROS production, lipid peroxidation, and cytoskeletal breakdown, culminating in neuronal death (Belov Kirdajova et al., 2020; Choi, 2020; Baranovicova et al., 2023).
A study by Wang L et al. demonstrated that a 7-day intervention with BHD reduced elevated levels of glutamate (GLU) and aspartate (ASP) in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of MCAO/R model rats, while increasing the levels of inhibitory amino acids—glycine (Gly), taurine (Tau), and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (Wang et al., 2013). Nonetheless, how BHD modulates brain amino acid pools is unknown. Since the glutamate–glutamine cycle in astrocytes critically maintains excitatory–inhibitory balance and supports neuronal viability during ischemia (Stelmashook et al., 2011), future work should test whether BHD acts by enhancing astrocytic glutamine synthetase or glutamate uptake.
Glutamate transporter-1 (GLT-1) mediates over 90% of synaptic glutamate uptake into astrocytes for conversion to glutamine by glutamine synthetase (GS) (Zou et al., 2010; Krzyżanowska et al., 2014). During ischemia, GLT-1 and GS are downregulated, worsening excitotoxicity (Krzyżanowska et al., 2014). BHD was shown to increase the level of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide 38 (PACAP38) in the subacute phase of MCAO/R model rats. PACAP38 promotes the upregulation of GLT-1 and GS expression in the hippocampal region—an effect that can be blocked by a PACAP38 inhibitor (Ding et al., 2015). However, the study did not assess resulting changes in infarct size or neurological outcomes. Moreover, as GLT-1 is astrocyte-specific, it remains to be determined whether BHD’s action is directly astrocytic or mediated via other cell types.
Glutamate not only mediates fast synaptic transmission via ionotropic receptors (iGluRs) but also activates metabotropic receptors (mGluRs) that modulate intracellular signaling (Bodzęta et al., 2021). In ischemia, mGluR1 signaling worsens neuronal injury (Yawata et al., 2008), highlighting glutamate receptor modulation as an anti-excitotoxic strategy (Shen et al., 2022). Research by Zhao L et al. confirmed that BHD downregulated both the mRNA expression of mGluR1 and glutamate levels in the striatum during the acute phase of cerebral I/R model rats. This was accompanied by improved behavioral scores and reduced cerebral infarct volume 3 days after I/R (Zhao et al., 2012). However, the pathways by which BHD decreases glutamate release and mGluR1 expression—and whether it selectively targets specific receptor subtypes—remain unknown.
2.9 Regulation of material and energy metabolism
Proper energy metabolism is essential for neuronal survival. After ischemic stroke, reduced perfusion and tissue damage disrupt metabolic homeostasis, instigating calcium overload, neuroinflammation, mitochondrial failure, and excitotoxic cascades (Zhou et al., 2021; Awasthi et al., 2024). Thus, restoring metabolic balance is a key therapeutic goal (Villa et al., 2013).
Studies indicate that BHD modulates post-ischemic energy metabolism disturbances through multiple mechanisms. On one hand, BHD has been shown to upregulate the expression of glucose transporters (GLUTs) and monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) in the ischemic cortex of MCAO/R rats during the recovery phase (Li M. et al., 2024), suggesting its potential to enhance glucose and lactate transport. However, further quantification of actual metabolic flux changes using techniques such as isotopic tracing is still required. Moderate glycolysis during hypoxia maintains glial and neuronal viability, and the resulting lactate can drive angiogenesis (Bouzat and Oddo, 2014; Zeng et al., 2021; Dong et al., 2022). Moreover, Tian F report that BHD activates AMPK in ischemic brain, suggesting a role in sustaining glycolytic metabolism and perfusion (Tian et al., 2024). Moreover, based on preliminary evidence from metabolomics and functional validation, BHD may correct post-ischemic cerebral energy metabolism dysfunction by modulating the SIRT1/AMPK axis to promote glucose uptake, activate glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and restore mitochondrial respiratory function (Hu et al., 2025). Confirming AMPK’s direct involvement will require targeted AMPK inhibition studies.
Regarding neurometabolic balance, Wang R further link BHD’s neuroprotection to sphingolipid and inositol phosphate metabolism (Wang et al., 2024). Together, untargeted metabolomics (Tang et al., 2022) and multi-omics analyses (Zhou et al., 2023) converge on altered purine, glycerophospholipid, glycosphingolipid, and glutamate pathways in the ischemic hippocampus. Notably, post-IS glutamate accumulation triggers delayed neuronal degeneration and death cascades (Krzyżanowska et al., 2014; Lai et al., 2014). However, key enzymes and transporters mediating these shifts remain unvalidated. To translate these findings, future work should pair proteomic target confirmation with analysis of human stroke specimens to establish robust metabolic biomarkers of BHD efficacy.
2.10 Regulation of gut microbiota
Alterations in gut microbiota composition strongly influence ischemic stroke pathophysiology and recovery (Zhang et al., 2023). Evidence suggests gut dysbiosis plays a critical role in IS (Peh et al., 2022), primarily mediated via the gut-brain axis through pro-inflammatory immune responses and the accumulation of microbial metabolites (Singh et al., 2016). Notable metabolites include short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), tryptophan catabolites, and bile acids (BAs) (Peng et al., 2018; Peng et al., 2018).
In humans, IS patients exhibit reduced gut microbiota diversity with increased abundance of Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidaceae, and Bifidobacteriaceae, alongside decreased Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Eubacterium, Faecalibacterium, and Roseburia (Peh et al., 2022). Reduced SCFA levels, particularly acetate, correlate with poor 3-month outcomes in a case-control study of 140 acute IS (AIS) patients (Tan et al., 2021). In rodent models, stroke disrupts gut physiology—slowing motility and promoting bacterial overgrowth (Durgan et al., 2019). Transplanting dysbiotic microbiota from stroke donors into germ-free mice increases infarct size and neurological deficits upon MCAO (Singh et al., 2016; Xia et al., 2019).
Targeting Enterobacteriaceae in MCAO mice reduces systemic inflammation and hippocampal injury, whereas higher Lactobacillus levels associate with reduced apoptosis and smaller infarcts in stroke rats (Wanchao et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2021). BHD similarly enriches beneficial taxa (e.g., Lactobacillus) and suppresses pathogenic genera (e.g., Escherichia–Shigella, Klebsiella) in the MCAO gut microbiome. These alterations may modulate hippocampal metabolism (Tang et al., 2022), yet the causal chain linking microbial shifts and neuroprotection remains to be firmly established.
Recent investigations on individual active constituents of BHD have provided more direct experimental evidence for the proposed causal links. Calycosin has been reported to modulate gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism, thereby activating intestinal FXR signaling, which in turn upregulates tight junction proteins (ZO-1, Occludin) in both the colon and brain, ultimately attenuating neuroinflammatory injury in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion models (Zhou et al., 2025). Similarly, astragaloside IV, despite its low oral bioavailability, has been shown in several animal studies to exert protective effects by reshaping gut microbiota composition, restoring intestinal barrier integrity (reducing plasma LPS leakage), and regulating serum metabolic profiles, particularly amino acid metabolism and the PPAR signaling pathway. In addition, astragaloside IV can activate the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway, thereby maintaining tight junction proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells and mitigating blood–brain barrier disruption (Li et al., 2018; Li Z. et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2018).
Collectively, these findings suggest that BHD and its constituents may act through a multilayered network: initially by modulating gut microbiota, subsequently altering microbial metabolites and systemic endotoxin burden, and ultimately strengthening intestinal and blood–brain barriers while suppressing systemic and central inflammation to facilitate brain tissue repair. It should be emphasized, however, that most of the current evidence is derived from animal studies or single-compound interventions, and is insufficient to establish a complete causal chain in the context of the whole formula. To substantiate the pathway of “BHD → gut microbiota/metabolite modulation → barrier restoration → neuroprotection,” future studies should employ formula-level causal experiments (e.g., fecal microbiota transplantation, germ-free animal models, supplementation or inhibition of key strains/metabolites, barrier function assays), and further compare the interactions and potential synergy between isolated compounds and the full decoction.
3 Conclusion and perspectives
BHD is a classical TCM formula for ischemic stroke that embodies the principles of “multi-component, multi-target, and holistic regulation.” Clinical reports and preclinical studies suggest that BHD can improve neurological outcomes and functional recovery with a generally acceptable safety profile (Shao et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). However, high-quality, large-scale randomized trials remain limited. Mechanistic work to date indicates that BHD exerts synergistic neuroprotective effects across multiple biological processes, including attenuation of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, modulation of apoptosis and autophagy, promotion of neurovascular repair, reprogramming of cerebral energy metabolism, and regulation of gut microbiota composition.
A key finding that emerges from this systematic review is the multifunctional role of several core signaling pathways—such as PI3K/Akt, SIRT1, and AMPK—in mediating the pleiotropic effects of BHD. Rather than acting in isolation, these pathways form a complex, interconnected network that is dynamically engaged across different pathological contexts. For instance, the PI3K/Akt axis is recruited to suppress neuroinflammation, inhibit neuronal apoptosis, and promote angiogenesis. Similarly, SIRT1 activation contributes to the regulation of autophagy, energy metabolism, and vascular repair. This context-dependent multiplexing of core pathways underscores a fundamental advantage of polypharmacological agents like BHD: the ability to synchronously modulate multiple disease-relevant processes through a limited set of highly leveraged signaling hubs. Future research should prioritize mapping the cross-talk between these hubs and delineating how their engagement varies by cell type and temporal phase after stroke.
Importantly, available evidence supports a stage-dependent view of BHD’s actions that aligns with the evolving pathology after cerebral ischemia. In the acute phase, BHD primarily exerts neuroprotective effects by swiftly countering the initial damage cascade. This is achieved through robustly inhibiting neuroinflammation (e.g., via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome), alleviating oxidative stress (e.g., via activating the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway), and reducing excitotoxicity and apoptosis, thereby stabilizing the ischemic penumbra and limiting infarct expansion.During the subacute and recovery phases, BHD’s role strategically shifts from protection to reconstruction and repair. Its mechanisms pivot towards promoting neurovascular remodeling (e.g., via enhancing angiogenesis through VEGF signaling and synaptogenesis via CREB activation), regulating metabolic reprogramming (e.g., via SIRT1/AMPK axis), and restoring systemic homeostasis (e.g., via modulating peripheral immunity and gut microbiota). This multi-faceted approach underpins its efficacy in facilitating long-term neurological and functional recovery. These stage-specific patterns are supported mainly by animal and in vitro data; translation to defined clinical time windows requires further validation. Current evidence suggests that BHD’s therapeutic effects likely arise from the synergy among: (1) direct actions of brain-penetrant compounds on neuronal and glial targets; (2) peripheral immunomodulation that mitigates systemic inflammation and secondary brain injury; and (3) remodeling of the gut microbiome and production of neuroactive metabolites that influence brain function via the gut-brain axis. This multi-pathway model aligns well with the holistic philosophy of TCM and helps explain how BHD can coordinate restorative responses across multiple organ systems.
Several critical gaps must be addressed to advance BHD toward evidence-based, precision use. First, mechanistic studies have largely traced isolated signaling nodes; the crosstalk among pathways, the cell-type specificity of effects (neurons versus microglia, astrocytes, endothelial cells, etc.), and the temporal dynamics across defined post-ischemic windows remain incompletely characterized. Second, although multiple bioactive constituents (for example, astragaloside IV and paeoniflorin) have been identified (Liu et al., 2022), the net therapeutic effect likely arises from complex interactions (synergy, additivity, or antagonism) among many compounds; rigorous dissection of these interactions is lacking. Third, practical translational challenges—bioavailability, brain delivery, formulation standardization, and optimized dosing/time-window—require targeted solutions.
To address these gaps we recommend a coordinated, hypothesis-driven research agenda combining mechanistic precision and translational relevance. Key experimental approaches should include: (1) targeted pharmacokinetics and BBB penetration studies using labeled compounds to quantify brain exposure and metabolite formation; (2) cell-type-specific interventions, such as conditional (cell-specific) knockouts or genetic fate-tracing, to determine which cell populations mediate particular effects; (3) single-cell and spatial omics across multiple post-ischemic time points to resolve spatiotemporal pathway activation; (4) metabolic flux analyses (stable isotope tracing) to quantify changes in glucose/lactate/TCA flux and link transporter expression to functional metabolism; (5) gut-brain causal experiments, including germ-free models and fecal microbiota transplantation, to test whether microbiota shifts mediate neuroprotection; and (6) combinatorial pharmacology (fractionation, reconstitution, and systems pharmacology) to map synergy/antagonism among constituent groups. Parallel development of brain-targeted delivery platforms (e.g., nanoparticle or exosome carriers) should be pursued to improve CNS bioavailability where appropriate.
In summary, BHD represents a promising multi-target therapeutic strategy for ischemic stroke whose biological rationale is increasingly supported by preclinical data. Realizing its translational potential will depend on combining modern mechanistic tools with rigorous pharmacology and carefully timed clinical studies to define which components act where and when—and thereby to optimize formulations, delivery, and patient selection.
Author contributions
YQ: Visualization, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. SH: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SM: Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Resources. SP: Resources, Writing – review and editing, Investigation. YH: Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Resources. GL: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review and editing. TC: Resources, Writing – review and editing, Investigation. FZ: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review and editing. HD: Writing – review and editing, Resources, Investigation. XY: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review and editing. XW: Writing – review and editing, Resources, Investigation. ZL: Writing – review and editing, Resources, Investigation. JD: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review and editing. FH: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition. LL: Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81301128, 81771500), the Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (XZR2023086, XZR2024250), the Science and Technology Development Plan of Suzhou (SKYD2023156, SYW2025055), the Suzhou Health Youth Backbone Talent ‘National Tutorial System’ Training Project (Qngg2022024), the Suzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Youth Research Project (KY24007), the Suzhou Science, Education, and Health Strengthening Project (ZDXM2024012), the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX24_3371, KYCX25_3517), and the Basic Research Project of Shenzhen Science, Technology and Innovation Commission (JCYJ20240813152959014).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1620533/full#supplementary-material
References
Adamczak, S. E., de Rivero Vaccari, J. P., Dale, G., Brand, F. J., Nonner, D., Bullock, M. R., et al. (2014). Pyroptotic neuronal cell death mediated by the AIM2 inflammasome. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 34, 621–629. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2013.236
Aghaei, M., Motallebnezhad, M., Ghorghanlu, S., Jabbari, A., Enayati, A., Rajaei, M., et al. (2019). Targeting autophagy in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury: a novel therapeutic strategy. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 16768–16778. doi:10.1002/jcp.28345
Arai, K., Jin, G., Navaratna, D., and Lo, E. H. (2009). Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes: neurovascular injury and angiogenic recovery after stroke. FEBS J. 276, 4644–4652. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07176.x
Awasthi, V. A., Dhankar, V., and Singh, S. (2024). Novel therapeutic targets for reperfusion injury in ischemic stroke: understanding the role of mitochondria, excitotoxicity and ferroptosis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 156, 107413. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2024.107413
Bae, H. J., Sowndhararajan, K., Park, H.-B., Kim, S.-Y., Kim, S., Kim, D. H., et al. (2019). Danshensu attenuates scopolamine and amyloid-β-induced cognitive impairments through the activation of PKA-CREB signaling in mice. Neurochem. Int. 131, 104537. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2019.104537
Baranovicova, E., Kalenska, D., Kaplan, P., Kovalska, M., Tatarkova, Z., and Lehotsky, J. (2023). Blood and brain metabolites after cerebral ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 17302. doi:10.3390/ijms242417302
Beaudoin, G. M. J., Lee, S.-H., Singh, D., Yuan, Y., Ng, Y.-G., Reichardt, L. F., et al. (2012). Culturing pyramidal neurons from the early postnatal mouse hippocampus and cortex. Nat. Protoc. 7, 1741–1754. doi:10.1038/nprot.2012.099
Bello, C., Smail, Y., Sainte-Rose, V., Podglajen, I., Gilbert, A., Moreira, V., et al. (2020). Role of astroglial connexin 43 in pneumolysin cytotoxicity and during pneumococcal meningitis. PLOS Pathog. 16, e1009152. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009152
Belov Kirdajova, D., Kriska, J., Tureckova, J., and Anderova, M. (2020). Ischemia-triggered glutamate excitotoxicity from the perspective of glial cells. Front. Cell Neurosci. 14, 51. doi:10.3389/fncel.2020.00051
Benjamin, E. J., Virani, S. S., Callaway, C. W., Chamberlain, A. M., Chang, A. R., Cheng, S., et al. (2018). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 137, e67–e492. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558
Bisicchia, E., Sasso, V., Catanzaro, G., Leuti, A., Besharat, Z. M., Chiacchiarini, M., et al. (2018). Resolvin D1 halts remote neuroinflammation and improves functional recovery after focal brain damage via ALX/FPR2 receptor-regulated MicroRNAs. Mol. Neurobiol. 55, 6894–6905. doi:10.1007/s12035-018-0889-z
Bodzęta, A., Scheefhals, N., and MacGillavry, H. D. (2021). Membrane trafficking and positioning of mGluRs at presynaptic and postsynaptic sites of excitatory synapses. Neuropharmacology 200, 108799. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108799
Bosch, M., Marí, M., Herms, A., Fernández, A., Fajardo, A., Kassan, A., et al. (2011). Caveolin-1 deficiency causes cholesterol-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptotic susceptibility. Curr. Biol. 21, 681–686. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2011.03.030
Bouzat, P., and Oddo, M. (2014). Lactate and the injured brain: friend or foe? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 20, 133–140. doi:10.1097/MCC.0000000000000072
Cai, G., Liu, B., Liu, W., Tan, X., Rong, J., Chen, X., et al. (2007). Buyang huanwu decoction can improve recovery of neurological function, reduce infarction volume, stimulate neural proliferation and modulate VEGF and Flk1 expressions in transient focal cerebral ischaemic rat brains. J. Ethnopharmacol. 113, 292–299. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2007.06.007
Cai, Y., Zhang, C. S., Liu, S., Wen, Z., Zhang, A. L., Guo, X., et al. (2019). Add-on effects of Chinese herbal medicine for post-stroke spasticity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 734. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00734
Campbell, B. C. V., De Silva, D. A., Macleod, M. R., Coutts, S. B., Schwamm, L. H., Davis, S. M., et al. (2019). Ischaemic stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 5, 70. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0118-8
Chamorro, Á., Dirnagl, U., Urra, X., and Planas, A. M. (2016). Neuroprotection in acute stroke: targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol. 15, 869–881. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00114-9
Chen, X., Chen, H., He, Y., Fu, S., Liu, H., Wang, Q., et al. (2020). Proteomics-guided study on buyang huanwu decoction for its neuroprotective and neurogenic mechanisms for transient ischemic stroke: involvements of EGFR/PI3K/akt/bad/14-3-3 and Jak2/Stat3/cyclin D1 signaling cascades. Mol. Neurobiol. 57, 4305–4321. doi:10.1007/s12035-020-02016-y
Chen, B., Xu, Y., Tian, F., Liu, Y., Yi, J., Ouyang, Y., et al. (2024). Buyang huanwu decoction promotes angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia through modulating caveolin-1-mediated exosome MALAT1/YAP1/HIF-1α axis. Phytomedicine 129, 155609. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155609
Cheng, R., Luo, X., Wu, X., Wang, Z., Chen, Z., Zhang, S., et al. (2024). Artificial microglia nanoplatform loaded with anti-RGMa in acoustic/magnetic feld for recanalization and neuroprotection in acute ischemic stroke. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11, e2410529. doi:10.1002/advs.202410529
Choi, D. W. (2020). Excitotoxicity: still hammering the ischemic brain in 2020. Front. Neurosci. 14, 579953. doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.579953
Cooper, D. R., Wang, C., Patel, R., Trujillo, A., Patel, N. A., Prather, J., et al. (2018). Human adipose-derived stem cell conditioned media and exosomes containing MALAT1 promote human dermal fibroblast migration and ischemic wound healing. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 7, 299–308. doi:10.1089/wound.2017.0775
Crichton, S. L., Bray, B. D., McKevitt, C., Rudd, A. G., and Wolfe, C. D. A. (2016). Patient outcomes up to 15 years after stroke: survival, disability, quality of life, cognition and mental health. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 87, 1091–1098. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2016-313361
Datta, S. R., Katsov, A., Hu, L., Petros, A., Fesik, S. W., Yaffe, M. B., et al. (2000). 14-3-3 proteins and survival kinases cooperate to inactivate BAD by BH3 domain phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 6, 41–51. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(05)00012-2
Dickmeiß, J., Henning, Y., Stahlke, S., Weber, T., Theiss, C., and Matschke, V. (2025). Differential protective effects of edaravone in cerebellar and hippocampal ischemic injury models. Cerebellum 24, 49. doi:10.1007/s12311-025-01804-3
Ding, W., Yu, P., Liu, W., Zhou, L., Guan, L. I., and Lin, R. (2015). Buyang huanwu decoction increases the expression of glutamate transporter-1 and glutamate synthetase in association with PACAP-38 following focal ischemia. Biomed. Rep. 3, 651–656. doi:10.3892/br.2015.478
Dong, X., Zhang, Q., Yu, X., Wang, D., Ma, J., Ma, J., et al. (2022). Metabolic lactate production coordinates vasculature development and progenitor behavior in the developing mouse neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 25, 865–875. doi:10.1038/s41593-022-01093-7
Du, Y.-T., Pan, Z.-G., Chen, B.-C., and Sun, F.-Y. (2024). Carotid artery transplantation of brain endothelial cells enhances neuroprotection and neurorepair in ischaemic stroke rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 45, 2487–2496. doi:10.1038/s41401-024-01339-z
Dugbartey, G. J. (2024). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of cell damage and cell death in ischemia-reperfusion injury in organ transplantation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 51, 473. doi:10.1007/s11033-024-09261-7
Durgan, D. J., Lee, J., McCullough, L. D., and Bryan, R. M. (2019). Examining the role of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in stroke. Stroke 50, 2270–2277. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025140
Fann, D. Y.-W., Santro, T., Manzanero, S., Widiapradja, A., Cheng, Y.-L., Lee, S.-Y., et al. (2014). Intermittent fasting attenuates inflammasome activity in ischemic stroke. Exp. Neurol. 257, 114–119. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.04.017
Fu, S., Gu, Y., Jiang, J.-Q., Chen, X., Xu, M., Chen, X., et al. (2014). Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside regulates nitric oxide/caveolin-1/matrix metalloproteinases pathway and protects blood-brain barrier integrity in experimental cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 155, 692–701. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.06.015
Fu, R., Guo, Y., Zhao, L., Cheng, X., Qin, X., Xu, W., et al. (2024). Buyang huanwu decoction alleviates stroke-induced immunosuppression in MCAO mice by reducing splenic T cell apoptosis triggered by AIM2 inflammasome. J. Ethnopharmacol. 333, 118474. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118474
Gao, J., Lu, F., and Zhu, C. (2009). Effects of buyang huanwu decoction on cell proliferation and differentiation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of aged rats following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. NEURAL Regen. Res. 4, 390–395. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2009.05.011
Gao, L., Jiang, T., Guo, J., Liu, Y., Cui, G., Gu, L., et al. (2012). Inhibition of autophagy contributes to ischemic postconditioning-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. PLoS One 7, e46092. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046092
Gao, L., Xiao, Z., Jia, C., and Wang, W. (2021). Effect of Buyang Huanwu decoction for the rehabilitation of ischemic stroke patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 19, 79. doi:10.1186/s12955-021-01728-6
García-Sáez, A. J. (2012). The secrets of the bcl-2 family. Cell Death Differ. 19, 1733–1740. doi:10.1038/cdd.2012.105
GBD 2016 Stroke Collaborators (2019). Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 18, 439–458. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30034-1
Glover, H. L., Schreiner, A., Dewson, G., and Tait, S. W. G. (2024). Mitochondria and cell death. Nat. Cell Biol. 26, 1434–1446. doi:10.1038/s41556-024-01429-4
Gomes, L. C., Di Benedetto, G., and Scorrano, L. (2011). During autophagy mitochondria elongate, are spared from degradation and sustain cell viability. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 589–598. doi:10.1038/ncb2220
Hasegawa, Y., Suzuki, H., Sozen, T., Rolland, W., and Zhang, J. H. (2010). Activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 by FTY720 is neuroprotective after ischemic stroke in rats. Stroke 41, 368–374. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.568899
Hou, Y., Yan, Z., Wan, H., Yang, J., Ding, Z., and He, Y. (2024). A combination of astragaloside IV and hydroxysafflor yellow a attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via NF-κB/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway. Brain Sci. 14, 781. doi:10.3390/brainsci14080781
Hu, J., Pang, W.-S., Han, J., Zhang, K., Zhang, J.-Z., and Chen, L.-D. (2018). Gualou guizhi decoction reverses brain damage with cerebral ischemic stroke, multi-component directed multi-target to screen calcium-overload inhibitors using combination of molecular docking and protein-protein docking. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 33, 115–125. doi:10.1080/14756366.2017.1396457
Hu, Z., Deng, N., Li, Y., Bai, Y., Lan, X., Xiong, T., et al. (2025). Buyang huanwu decoction improves energy metabolism disorders after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion by regulating the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway to promote glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Chin. Med. 20, 108. doi:10.1186/s13020-025-01163-5
Iadecola, C., and Anrather, J. (2011). The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat. Med. 17, 796–808. doi:10.1038/nm.2399
Iadecola, C., Buckwalter, M. S., and Anrather, J. (2020). Immune responses to stroke: mechanisms, modulation, and therapeutic potential. J. Clin. Invest. 130, 2777–2788. doi:10.1172/JCI135530
Jiang, H., Li, J., Wang, L., Wang, S., Nie, X., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). Total glucosides of paeony: a review of its phytochemistry, role in autoimmune diseases, and mechanisms of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 258, 112913. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.112913
Jiang, Y., Krantz, S., Qin, X., Kim, Y.-M., Zimnicka, H., Bae, m., et al. (2022). Caveolin-1 controls mitochondrial damage and ROS production by regulating fission - fusion dynamics and mitophagy. Redox Biol. 52, 102304. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102304
Jiang, Y., Liu, Q., Zhao, Y., Wang, C., and Sun, M. (2023). Activation of CREB-BDNF pathway in pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus improves the neurological outcome of mice with ischemic stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 60, 1766–1781. doi:10.1007/s12035-022-03174-x
Jorgensen, I., and Miao, E. A. (2015). Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol. Rev. 265, 130–142. doi:10.1111/imr.12287
Kamal, F. Z., Lefter, R., Jaber, H., Balmus, I.-M., Ciobica, A., and Iordache, A.-C. (2023). The role of potential oxidative biomarkers in the prognosis of acute ischemic stroke and the exploration of antioxidants as possible preventive and treatment options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 6389. doi:10.3390/ijms24076389
Khan, R., Kulasiri, D., and Samarasinghe, S. (2021). Functional repertoire of protein kinases and phosphatases in synaptic plasticity and associated neurological disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 16, 1150–1157. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.300331
Khayrullina, G., Bermudez, S., and Byrnes, K. R. (2015). Inhibition of NOX2 reduces locomotor impairment, inflammation, and oxidative stress after spinal cord injury. J. Neuroinflammation 12, 172. doi:10.1186/s12974-015-0391-8
Kimura, K., Liu, Y.-H., and Hsieh, C.-L. (2025). Amygdalin’s neuroprotective effects on acute ischemic stroke in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 345, 119621. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2025.119621
Kl, L., B, F., and Bh, C. (2019). Post-stroke inflammation-target or tool for therapy? Acta neuropathol. 137, 693–714. doi:10.1007/s00401-018-1930-z
Koepple, C., Zhou, Z., Huber, L., Schulte, M., Schmidt, K., Gloe, T., et al. (2021). Expression of Connexin43 stimulates endothelial angiogenesis independently of gap junctional communication in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 7400. doi:10.3390/ijms22147400
Kong, X., Su, X., Zhu, J., Wang, J., Wan, H., Zhong, M., et al. (2014). Neuroprotective effect of buyang huanwu decoction on rat ischemic/reperfusion brain damage by promoting migration of neural precursor cells. Rejuvenation Res. 17, 264–275. doi:10.1089/rej.2013.1468
Krzyżanowska, W., Pomierny, B., Filip, M., and Pera, J. (2014). Glutamate transporters in brain ischemia: to modulate or not? Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 35, 444–462. doi:10.1038/aps.2014.1
Lai, T. W., Zhang, S., and Wang, Y. T. (2014). Excitotoxicity and stroke: identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 115, 157–188. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.006
Lee, J., Yeo, J. H., Kim, S. S., Lee, J. M., and Yeo, S. G. (2025). Production and role of free radicals and reactive oxygen species after facial nerve injury. Antioxidants (Basel) 14, 436. doi:10.3390/antiox14040436
Li, C. (2012). Buyang huanwu decoction enhances cell membrane fluidity in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neural Regen. Res. 7, 1605–1610. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.21.001
Li, H., Wang, P., Huang, F., Jin, J., Wu, H., Zhang, B., et al. (2018). Astragaloside IV protects blood-brain barrier integrity from LPS-induced disruption via activating Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 340, 58–66. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2017.12.019
Li, H., Peng, D., Zhang, S.-J., Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., and Guan, L. (2021). Buyang huanwu decoction promotes neurogenesis via sirtuin 1/autophagy pathway in a cerebral ischemia model. Mol. Med. Rep. 24, 791. doi:10.3892/mmr.2021.12431
Li, J., Xu, P., Hong, Y., Xie, Y., Peng, M., Sun, R., et al. (2023a). Lipocalin-2-mediated astrocyte pyroptosis promotes neuroinflammatory injury via NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Neuroinflammation 20, 148. doi:10.1186/s12974-023-02819-5
Li, L., Jiang, W., Yu, B., Liang, H., Mao, S., Hu, X., et al. (2023b). Quercetin improves cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by promoting microglia/macrophages M2 polarization via regulating PI3K/akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 168, 115653. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115653
Li, Z., Hu, E., Zheng, F., Wang, S., Zhang, W., Luo, J., et al. (2023c). The effects of astragaloside IV on gut microbiota and serum metabolism in a mice model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 121, 155086. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155086
Li, J., Dong, S., Quan, S., Ding, S., Zhou, X., Yu, Y., et al. (2024a). Nuciferine reduces inflammation induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the PI3K/akt/NF-κB pathway. Phytomedicine 125, 155312. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155312
Li, M., Li, M.-Z., Lin, Z.-Y., Zhuang, Y.-M., Wang, H.-Y., Jia, J.-T., et al. (2024b). Buyang Huanwu decoction promotes neurovascular remodeling by modulating astrocyte and microglia polarization in ischemic stroke rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 323, 117620. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117620
Li, M.-C., Jia, J.-T., Wang, Y.-X., Zhuang, Y.-M., Wang, H.-Y., Lin, Z.-Y., et al. (2024c). Astragaloside IV promotes cerebral tissue restoration through activating AMPK- mediated microglia polarization in ischemic stroke rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 334, 118532. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118532
Lipovich, L., Dachet, F., Cai, J., Bagla, S., Balan, K., Jia, H., et al. (2012). Activity-dependent human brain coding/noncoding gene regulatory networks. Genetics 192, 1133–1148. doi:10.1534/genetics.112.145128
Liu, F., Lu, J., Manaenko, A., Tang, J., and Hu, Q. (2018). Mitochondria in ischemic stroke: new insight and implications. Aging Dis. 9, 924–937. doi:10.14336/AD.2017.1126
Liu, F., Chen, N., Hu, Y., Xu, Y., and Zhu, Y. (2019). Effects of thin recipe of Buyang Huanwu decoction on CDK5 and apoptotic factors in an oxidative stress cell model. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 35, 1758–1764. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2019.12.026
Liu, J., Xu, L., and Zhan, X. (2020). LncRNA MALAT1 regulates diabetic cardiac fibroblasts through the hippo-YAP signaling pathway. Biochem. Cell Biol. 98, 537–547. doi:10.1139/bcb-2019-0434
Liu, S., Zheng, Q., Yue, P., Yang, M., Shuai, S., Liu, X., et al. (2021). Effect and mechanism of phthalides from Ligusticum chuanxiong on oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced MDCK-MDR1 cell injury. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 52, 2958–2966. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.10.012
Liu, W., Zeng, K., Zhou, X., Zhang, Y., and Nie, C. (2022). Comparative study on brain pharmacokinetics of buyang huanwu decoction in normal and cerebral ischemia rats using brain microdialysis combined with LC-MS/MS. Chin. Herb. Med. 14, 630–637. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2022.03.007
Liu, S., Yao, S., Yang, H., Liu, S., and Wang, Y. (2023a). Autophagy: regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 14, 648. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06154-8
Liu, W., Zhou, X., Zeng, K., Nie, C., Huang, J., Zhu, L., et al. (2023b). Study on the action mechanism of buyang huanwu decoction against ischemic stroke based on S1P/S1PR1/PI3K/akt signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 312, 116471. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116471
Liu, Z., Yin, M., Li, J., Wang, J., Jin, X., Zhou, X., et al. (2025). Buyang huanwu decoction restores the balance of mitochondrial dynamics after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion through calcium overload reduction by the PKCε-nampt-Sirt5 axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 338, 119003. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.119003
Long, J., Gu, C., Zhang, Q., Liu, J., Huang, J., Li, Y., et al. (2023). Extracellular vesicles from medicated plasma of buyang huanwu decoction-preconditioned neural stem cells accelerate neurological recovery following ischemic stroke. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1096329. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1096329
Ma, J., Zhang, L., Niu, T., Ai, C., Jia, G., Jin, X., et al. (2018). Growth differentiation factor 11 improves neurobehavioral recovery and stimulates angiogenesis in rats subjected to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Brain Res. Bull. 139, 38–47. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.02.011
Maitra, S., and Vincent, B. (2022). Cdk5-p25 as a key element linking amyloid and tau pathologies in alzheimer’s disease: mechanisms and possible therapeutic interventions. Life Sci. 308, 120986. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120986
Marques, B. L., Carvalho, G. A., Freitas, E. M. M., Chiareli, R. A., Barbosa, T. G., Di Araújo, A. G. P., et al. (2019). The role of neurogenesis in neurorepair after ischemic stroke. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 95, 98–110. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.12.003
McConnell, H. L., Kersch, C. N., Woltjer, R. L., and Neuwelt, E. A. (2017). The translational significance of the neurovascular unit. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 762–770. doi:10.1074/jbc.R116.760215
Miyamoto, M., Kuroda, S., Zhao, S., Magota, K., Shichinohe, H., Houkin, K., et al. (2013). Bone marrow stromal cell transplantation enhances recovery of local glucose metabolism after cerebral infarction in rats: a serial 18F-FDG PET study. J. Nucl. Med. 54, 145–150. doi:10.2967/jnumed.112.109017
Mo, J., Liao, W., Du, J., Huang, X., Li, Y., Su, A., et al. (2024). Buyang huanwu decoction improves synaptic plasticity of ischemic stroke by regulating the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 335, 118636. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118636
Morris-Blanco, K. C., Dave, K. R., Saul, I., Koronowski, K. B., Stradecki, H. M., and Perez-Pinzon, M. A. (2016). Protein kinase C epsilon promotes cerebral ischemic tolerance via modulation of mitochondrial Sirt5. Sci. Rep. 6, 29790. doi:10.1038/srep29790
Nakamura, N., Honjo, M., Yamagishi, R., Kurano, M., Yatomi, Y., Watanabe, S., et al. (2021). Neuroprotective role of sphingolipid rheostat in excitotoxic retinal ganglion cell death. Exp. eye Res. 208, 108623. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2021.108623
Newton, K., Strasser, A., Kayagaki, N., and Dixit, V. M. (2024). Cell death. Cell 187, 235–256. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.11.044
Nomura, M., Shimizu, S., Sugiyama, T., Narita, M., Ito, T., Matsuda, H., et al. (2015). 14-3-3 interacts directly with and negatively regulates pro-apoptotic bax. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 6753. doi:10.1074/jbc.A114.207880
OuYang, Y., Yi, J., Chen, B., Zeng, F., Chen, X., Yang, H., et al. (2025). Mechanism of buyang huanwu decoction mediating Cav1-regulated wnt pathway to promote neural regeneration in cerebral ischemic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 339, 119121. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.119121
Pan, R., Cai, J., Zhan, L., Guo, Y., Huang, R.-Y., Li, X., et al. (2017). Buyang huanwu decoction facilitates neurorehabilitation through an improvement of synaptic plasticity in cerebral ischemic rats. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 17, 173. doi:10.1186/s12906-017-1680-9
Pan, G., Jin, L., Shen, W., Zhang, J., Pan, J., Cheng, J., et al. (2020). Treadmill exercise improves neurological function by inhibiting autophagy and the binding of HMGB1 to Beclin1 in MCAO juvenile rats. Life Sci. 243, 117279. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117279
Peh, A., O’Donnell, J. A., Broughton, B. R. S., and Marques, F. Z. (2022). Gut microbiota and their metabolites in stroke: a double-edged sword. Stroke 53, 1788–1801. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.036800
Peng, J., Xiao, X., Hu, M., and Zhang, X. (2018). Interaction between gut microbiome and cardiovascular disease. Life Sci. 214, 153–157. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2018.10.063
Polletta, L., Vernucci, E., Carnevale, I., Arcangeli, T., Rotili, D., Palmerio, S., et al. (2015). SIRT5 regulation of ammonia-induced autophagy and mitophagy. Autophagy 11, 253–270. doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1009778
Qin, B., Peng, D., Wan, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, Q., and Guan, L. (2021). Buyang Huanwutang promoted proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells via regulating autophagy following OGD/R injury. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 27, 9–18. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20211002
Roth, S., Cao, J., Singh, V., Tiedt, S., Hundeshagen, G., Li, T., et al. (2021). Post-injury immunosuppression and secondary infections are caused by an AIM2 inflammasome-driven signaling cascade. Immunity 54, 648–659.e8. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.02.004
Rutkai, I., Merdzo, I., Wunnava, S. V., Curtin, G. T., Katakam, P. V., and Busija, D. W. (2019). Cerebrovascular function and mitochondrial bioenergetics after ischemia-reperfusion in male rats. Cereb. Blood Flow Metabolism 39, 1056–1068. doi:10.1177/0271678X17745028
Sa, V., F, B., Pm, H., J, R., M, P., Dn, G., et al. (2016). Formyl-peptide receptor 2/3/lipoxin A4 receptor regulates neutrophil-platelet aggregation and attenuates cerebral inflammation: impact for therapy in cardiovascular disease. Circulation 133, 2169–2179. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.020633
Sarkar, S., Chakraborty, D., Bhowmik, A., and Ghosh, M. K. (2019). Cerebral ischemic stroke: cellular fate and therapeutic opportunities. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 24, 435–450. doi:10.2741/4727
Shao, L., She, Y., Yong, S., Chen, B., Yi, J., Li, Y., et al. (2022). An evidence-based evaluation of Buyang Huanwu decoction for the treatment of the sequelae of stroke: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytomedicine 104, 154312. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154312
She, Y., Shao, L., Zhang, Y., Hao, Y., Cai, Y., Cheng, Z., et al. (2019). Neuroprotective effect of glycosides in buyang huanwu decoction on pyroptosis following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 242, 112051. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.112051
She, Y., Shao, L., Jiao, K., Sun, R., Lang, T., Long, H., et al. (2023). Glycosides of buyang huanwu decoction inhibits pyroptosis associated with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion through Nrf2-mediated antioxidant signaling pathway both in vivo and in vitro. Phytomedicine 120, 155001. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155001
Shen, L. H., Ye, M., Ding, X. S., Han, Q., Zhang, C., Liu, X. F., et al. (2012). Protective effects of MCI-186 on transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells in rat ischemic stroke model. Neuroscience 223, 315–324. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.08.001
Shen, Z., Xiang, M., Chen, C., Ding, F., Wang, Y., Shang, C., et al. (2022). Glutamate excitotoxicity: potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Biomed. Pharmacother. 151, 113125. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113125
Shi, K., Tian, D.-C., Li, Z.-G., Ducruet, A. F., Lawton, M. T., and Shi, F.-D. (2019). Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet. Neurology 18, 1058–1066. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30078-X
Shibuya, M., and Claesson-Welsh, L. (2006). Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp. Cell Res. 312, 549–560. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.11.012
Shore, G. C., and Nguyen, M. (2008). Bcl-2 proteins and apoptosis: choose your partner. Cell 135, 1004–1006. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.029
Shu, S., Li, C.-M., You, Y.-L., Qian, X.-L., Zhou, S., and Ling, C.-Q. (2016). Electroacupuncture ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulation of autophagy and apoptosis. Evid.-based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2016, 7297425. doi:10.1155/2016/7297425
Shu, M.-Q., Dai, Y.-Y., Song, L.-J., Ma, D., Liu, K.-X., Miao, Z.-Y., et al. (2024). Tetramethylpyrazine regulates angiogenesis of endothelial cells in cerebral ischemic stroke injury via SIRT1/VEGFA signaling pathway. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 49, 162–174. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20231116.303
Simats, A., and Liesz, A. (2022). Systemic inflammation after stroke: implications for post-stroke comorbidities. EMBO Mol. Med. 14, e16269. doi:10.15252/emmm.202216269
Singh, V., Roth, S., Llovera, G., Sadler, R., Garzetti, D., Stecher, B., et al. (2016). Microbiota dysbiosis controls the neuroinflammatory response after stroke. J. Neurosci. 36, 7428–7440. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1114-16.2016
Song, M., Zhou, Y., and Fan, X. (2022). Mitochondrial quality and quantity control: Mitophagy is a potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 59, 3110–3123. doi:10.1007/s12035-022-02795-6
Song, C., Fang, X., Fang, N., and Hu, F. (2024). Buyang huanwu decoction suppresses ischemic stroke by suppressing glycolysis and cell apoptosis in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells. Brain Res. Bull. 215, 111032. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111032
Soriano, M. E., and Scorrano, L. (2011). Traveling bax and forth from mitochondria to control apoptosis. Cell 145, 15–17. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.025
Stelmashook, E. V., Isaev, N. K., Lozier, E. R., Goryacheva, E. S., and Khaspekov, L. G. (2011). Role of glutamine in neuronal survival and death during brain ischemia and hypoglycemia. Int. J. Neurosci. 121, 415–422. doi:10.3109/00207454.2011.570464
Sun, J., Bi, Y., Guo, L., Qi, X., Zhang, J., Li, G., et al. (2007). Buyang huanwu decoction promotes growth and differentiation of neural progenitor cells: using a serum pharmacological method. J. Ethnopharmacol. 113, 199–203. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2007.05.018
Sun, B., Ou, H., Ren, F., Huan, Y., Zhong, T., Gao, M., et al. (2018). Propofol inhibited autophagy through Ca2+/CaMKKβ/AMPK/mTOR pathway in OGD/R-induced neuron injury. Mol. Med. 24, 58. doi:10.1186/s10020-018-0054-1
Tan, M.-S., Tan, L., Jiang, T., Zhu, X.-C., Wang, H.-F., Jia, C.-D., et al. (2014). Amyloid-β induces NLRP1-dependent neuronal pyroptosis in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 5, e1382. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.348
Tan, C., Wu, Q., Wang, H., Gao, X., Xu, R., Cui, Z., et al. (2021). Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in acute ischemic stroke and the subsequent risk for poor functional outcomes. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 45, 518–529. doi:10.1002/jpen.1861
Tang, R., Yi, J., Lu, S., Chen, B., and Liu, B. (2022). Therapeutic effect of buyang huanwu decoction on the gut microbiota and hippocampal metabolism in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12, 873096. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.873096
Tang, H., Wen, J., Qin, T., Chen, Y., Huang, J., Yang, Q., et al. (2023). New insights into Sirt1: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of cerebral ischemic stroke. Front. Cell Neurosci. 17, 1228761. doi:10.3389/fncel.2023.1228761
Tg, H., Ds, R., Ig, W., Pl, S., A, M., D, H., et al. (2020). Clinical practice guideline to improve locomotor function following chronic stroke, incomplete spinal cord injury, and brain injury. J. Neurologic Phys. Ther. 44, 49–100. doi:10.1097/NPT.0000000000000303
Thapa, R., Moglad, E., Afzal, M., Kumar, G., Bhat, A. A., Hassan Almalki, W., et al. (2024). The role of sirtuin 1 in ageing and neurodegenerative disease: a molecular perspective. Ageing Res. Rev. 102, 102545. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2024.102545
Tian, H., Chen, X., Liao, J., Yang, T., Cheng, S., Mei, Z., et al. (2022). Mitochondrial quality control in stroke: from the mechanisms to therapeutic potentials. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 26, 1000–1012. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17189
Tian, F., Yi, J., Liu, Y., Chen, B., Wang, X., Ouyang, Y., et al. (2024). Integrating network pharmacology and bioinformatics to explore and experimentally verify the regulatory effect of buyang huanwu decoction on glycolysis and angiogenesis after cerebral infarction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319, 117218. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117218
Tuo, Q.-Z., Zhang, S.-T., and Lei, P. (2022). Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med. Res. Rev. 42, 259–305. doi:10.1002/med.21817
Villa, R. F., Gorini, A., Ferrari, F., and Hoyer, S. (2013). Energy metabolism of cerebral mitochondria during aging, ischemia and post-ischemic recovery assessed by functional proteomics of enzymes. Neurochem. Int. 63, 765–781. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.10.004
Wanchao, S., Chen, M., Zhiguo, S., Futang, X., and Mengmeng, S. (2018). Protective effect and mechanism of lactobacillus on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Braz J. Med. Biol. Res. 51, e7172. doi:10.1590/1414-431x20187172
Wang, L., Huang, Y., Wu, J., Lv, G., Zhou, L., and Jia, J. (2013). Effect of buyang huanwu decoction on amino acid content in cerebrospinal fluid of rats during ischemic/reperfusion injury. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 86, 143–150. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.046
Wang, C., Qu, Y., Suo, R., and Zhu, Y. (2019). Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates angiogenesis following oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 23, 2970–2983. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14204
Wang, Y., Liu, X., Hu, T., Li, X., Chen, Y., Xiao, G., et al. (2021). Astragalus saponins improves stroke by promoting the proliferation of neural stem cells through phosphorylation of akt. J. Ethnopharmacol. 277, 114224. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114224
Wang, R., Ren, J., Li, S., Bai, X., Guo, W., Yang, S., et al. (2022). Efficacy evaluation of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in the treatment of ischemic stroke in the recovery period: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 975816. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.975816
Wang, H., Zhang, S., Xie, L., Zhong, Z., and Yan, F. (2023). Neuroinflammation and peripheral immunity: focus on ischemic stroke. Int. Immunopharmacol. 120, 110332. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110332
Wang, R.-J., Ma, G.-C., Yu, S., Zhang, M., and Pu, S.-B. (2024). UPLC-MS based metabonomics revealed the protective effects of buyang huanwu decoction on ischemic stroke rats. Toxicol. Res. 13, tfae052. doi:10.1093/toxres/tfae052
Wang, Z., Liu, Z., Hao, Y., Zhu, Z., Hong, J., Cui, L., et al. (2025). Hydroxysafflor yellow a promotes the proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells with neural regenerative effects in ischemic stroke. Phytomed, Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 144, 156905. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156905
Weis, S. M., and Cheresh, D. A. (2005). Pathophysiological consequences of VEGF-induced vascular permeability. Nature 437, 497–504. doi:10.1038/nature03987
Wu, M., Zhang, H., Kai, J., Zhu, F., Dong, J., Xu, Z., et al. (2018). Rapamycin prevents cerebral stroke by modulating apoptosis and autophagy in penumbra in rats. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 5, 138–146. doi:10.1002/acn3.507
Wu, W., Qiu, C., Feng, X., Tao, X., Zhu, Q., Chen, Z., et al. (2020). Protective effect of paeoniflorin on acute cerebral infarction in rats. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 21, 702–709. doi:10.2174/1389201021666191224151634
Wu, F., Liu, Y., Gao, Y., Yang, K., and Liu, W. (2021). Buyang Huanwutang alleviated oxidative stress following cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion in rats by formyl peptide receptor 2. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 27, 9–15. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20211838
Wu, Q., Liu, J., Mao, Z., Tian, L., Wang, N., Wang, G., et al. (2022). Ligustilide attenuates ischemic stroke injury by promoting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission via activation of AMPK. Phytomed, Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 95, 153884. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153884
Xia, G.-H., You, C., Gao, X.-X., Zeng, X.-L., Zhu, J.-J., Xu, K.-Y., et al. (2019). Stroke dysbiosis index (SDI) in gut microbiome are associated with brain injury and prognosis of stroke. Front. Neurol. 10, 397. doi:10.3389/fneur.2019.00397
Xiao, J., Zhao, T., Fang, W., Chen, Y., Wu, H., Li, P., et al. (2022). Caveolin-1 signaling-driven mitochondrial fission and cytoskeleton remodeling promotes breast cancer migration. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 152, 106307. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2022.106307
Xu, N., Kan, P., Yao, X., Yang, P., Wang, J., Xiang, L., et al. (2018). Astragaloside IV reversed the autophagy and oxidative stress induced by the intestinal microbiota of AIS in mice. J. Microbiol. (Seoul. Korea) 56, 838–846. doi:10.1007/s12275-018-8327-5
Xu, K., Gao, X., Xia, G., Chen, M., Zeng, N., Wang, S., et al. (2021). Rapid gut dysbiosis induced by stroke exacerbates brain infarction in turn. Gut 70, 1486–1494. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323263
Xu, Y., Chen, B., Yi, J., Tian, F., Liu, Y., Ouyang, Y., et al. (2023). Buyang huanwu decoction alleviates cerebral ischemic injury through modulating caveolin-1-mediated mitochondrial quality control. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1137609. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1137609
Yang, J., Gao, F., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., and Zhang, D. (2015). Buyang huanwu decoction (BYHWD) enhances angiogenic effect of mesenchymal stem cell by upregulating VEGF expression after focal cerebral ischemia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 56, 898–906. doi:10.1007/s12031-015-0539-0
Yang, J.-L., Mukda, S., and Chen, S.-D. (2018). Diverse roles of mitochondria in ischemic stroke. Redox Biol. 16, 263–275. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2018.03.002
Yang, M., Linn, B. S., Zhang, Y., and Ren, J. (2019). Mitophagy and mitochondrial integrity in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1865, 2293–2302. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.05.007
Yang, M., He, Y., Deng, S., Xiao, L., Tian, M., Xin, Y., et al. (2021). Mitochondrial quality control: a pathophysiological mechanism and therapeutic target for stroke. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 14, 786099. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2021.786099
Yang, P., Zhang, Y., and Liu, J. (2025). Ischaemic stroke in 2024: progress on multiple fronts. Lancet Neurol. 24, 7–8. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00473-3
Yawata, I., Takeuchi, H., Doi, Y., Liang, J., Mizuno, T., and Suzumura, A. (2008). Macrophage-induced neurotoxicity is mediated by glutamate and attenuated by glutaminase inhibitors and gap junction inhibitors. Life Sci. 82, 1111–1116. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2008.03.010
Yin, M., Liu, Z., Wang, J., and Gao, W. (2023). Buyang huanwu decoction alleviates oxidative injury of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion through PKCε/Nrf2 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 303, 115953. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115953
Yin, M., Liu, Z., Yin, J. X., Zhou, X., and Gao, Y. (2024). Effects of buyang huanwu decoction on mitochondrial oxidative damage and PKCε⁃nampt pathway in rats following cerebral ischemia⁃reperfusion. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 46, 79–86. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2024.01.014
Yu, H., Cai, Y., Zhong, A., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., and Xu, S. (2021a). The “dialogue” between central and peripheral immunity after ischemic stroke: focus on spleen. Front. Immunol. 12, 792522. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.792522
Yu, W., Jin, H., Sun, W., Nan, D., Deng, J., Jia, J., et al. (2021b). Connexin43 promotes angiogenesis through activating the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway under chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 41, 2656–2675. doi:10.1177/0271678X211010354
Zaibaq, F., Dowdy, T., and Larion, M. (2022). Targeting the sphingolipid rheostat in gliomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 9255. doi:10.3390/ijms23169255
Zeng, M., Zhou, H., He, Y., Wang, Z., Shao, C., Yin, J., et al. (2021). Danhong injection alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by improving intracellular energy metabolism coupling in the ischemic penumbra. Biomed. Pharmacother. 140, 111771. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111771
Zhang, Z. G., Zhang, L., Tsang, W., Soltanian-Zadeh, H., Morris, D., Zhang, R., et al. (2002). Correlation of VEGF and angiopoietin expression with disruption of blood-brain barrier and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 22, 379–392. doi:10.1097/00004647-200204000-00002
Zhang, H., He, S., Spee, C., Ishikawa, K., and Hinton, D. R. (2015a). SIRT1 mediated inhibition of VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling by resveratrol and its relevance to choroidal neovascularization. Cytokine 76, 549–552. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2015.06.019
Zhang, Y., Li, H., Huang, M., Huang, M., Chu, K., Xu, W., et al. (2015b). Paeoniflorin, a monoterpene glycoside, protects the brain from cerebral ischemic injury via inhibition of apoptosis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 43, 543–557. doi:10.1142/S0192415X15500342
Zhang, X., Tang, X., Liu, K., Hamblin, M. H., and Yin, K.-J. (2017). Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies in ischemic stroke. J. Neurosci. 37, 1797–1806. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3389-16.2017
Zhang, W.-W., Xu, F., Wang, D., Ye, J., and Cai, S.-Q. (2018a). Buyang huanwu decoction ameliorates ischemic stroke by modulating multiple targets with multiple components: in vitro evidences. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 16, 194–202. doi:10.1016/S1875-5364(18)30047-5
Zhang, X., Li, Y., Ma, Y., Yang, L., Wang, T., Meng, X., et al. (2018b). Yes-associated protein (YAP) binds to HIF-1α and sustains HIF-1α protein stability to promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell glycolysis under hypoxic stress. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 37, 216. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0892-2
Zhang, Q., Liu, J., Duan, H., Li, R., Peng, W., and Wu, C. (2021). Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: an important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress. J. Adv. Res. 34, 43–63. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.023
Zhang, L., Ma, J., Yang, F., Li, S., Ma, W., Chang, X., et al. (2022). Neuroprotective effects of quercetin on ischemic stroke: a literature review. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 854249. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.854249
Zhang, S., Jin, M., Ren, J., Sun, X., Zhang, Z., Luo, Y., et al. (2023). New insight into gut microbiota and their metabolites in ischemic stroke: a promising therapeutic target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 162, 114559. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114559
Zhao, L.-D., Wang, J.-H., Jin, G.-R., Zhao, Y., and Zhang, H.-J. (2012). Neuroprotective effect of buyang huanwu decoction against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats--time window and mechanism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 140, 339–344. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.01.026
Zhao, Y., Ma, X., Yu, W., Zhang, Z., Wang, W., Zhou, X., et al. (2021). Protective effect of buyang huanwu decoction on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by alleviating autophagy in the ischemic penumbra. eCAM 2021, 9937264. doi:10.1155/2021/9937264
Zheng, X.-W., Shan, C.-S., Xu, Q.-Q., Wang, Y., Shi, Y.-H., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Buyang huanwu decoction targets SIRT1/VEGF pathway to promote angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front. Neurosci. 12, 911. doi:10.3389/fnins.2018.00911
Zhou, X., Chen, H., Wang, L., Lenahan, C., Lian, L., Ou, Y., et al. (2021). Mitochondrial dynamics: a potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 13, 721428. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2021.721428
Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y.-X., Yang, K.-L., Liu, Y.-L., Wu, F.-H., Gao, Y.-R., et al. (2022). Connexin 43 mediated the angiogenesis of buyang huanwu decoction via vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 after ischemic stroke. Chin. J. Physiol. 65, 72–79. doi:10.4103/cjp.cjp_94_21
Zhou, H., Lin, B., Yang, J., Wei, X., Fu, W., Ding, Z., et al. (2023). Analysis of the mechanism of buyang huanwu decoction against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion by multi-omics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 305, 116112. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.116112
Zhou, Y., Song, W., Wang, Y., Li, S., Shan, C., Dong, J., et al. (2025). Calycosin regulates gut microbiota-bile acid-FXR axis to protect rats from cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1000, 177707. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177707
Zou, J., Wang, Y.-X., Dou, F.-F., Lü, H.-Z., Ma, Z.-W., Lu, P.-H., et al. (2010). Glutamine synthetase down-regulation reduces astrocyte protection against glutamate excitotoxicity to neurons. Neurochem. Int. 56, 577–584. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2009.12.021
Zou, R., Shi, W., Tao, J., Li, H., Lin, X., Yang, S., et al. (2018). SIRT5 and post-translational protein modifications: a potential therapeutic target for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury with regard to mitochondrial dynamics and oxidative metabolism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 818, 410–418. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.11.005
Keywords: ischemic stroke, Buyang Huanwu decoction, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, neuroprotection
Citation: Qin Y, Hu S, Mawen S, Pan S, Huai Y, Liang G, Chen T, Zhao F, Dong H, Yao X, Wu X, Lv Z, Deng J, Huang F and Luo L (2025) Neuroprotective mechanisms of Buyang Huanwu decoction in ischemic stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1620533. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1620533
Received: 29 April 2025; Accepted: 30 August 2025;
Published: 23 September 2025.
Edited by:
Carla Denise Bonan, Pontifical Catholic University of Rio Grande do Sul, BrazilReviewed by:
Yang Jiang, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaChang Zhou, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Qin, Hu, Mawen, Pan, Huai, Liang, Chen, Zhao, Dong, Yao, Wu, Lv, Deng, Huang and Luo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fei Huang, c3podWFuZ2ZlaUAxMjYuY29t; Li Luo, bHVvbGlAc3VkYS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yuanyuan Qin1†
Yuanyuan Qin1† Shiman Mawen
Shiman Mawen Shanyao Pan
Shanyao Pan Yaping Huai
Yaping Huai Ting Chen
Ting Chen Xue Wu
Xue Wu Zhigang Lv
Zhigang Lv Jiao Deng
Jiao Deng Li Luo
Li Luo