- 1Jinling Clinical Medical College, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, Jinling Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
- 3Department of Breast Surgery, Nantong Maternal and Child Healthcare, Nantong, China
Background: Plant-derived active substances are increasingly recognized as potential adjuvant therapies in breast cancer treatment, with emerging evidence suggesting their positive impact on both treatment outcomes and quality of life (QoL). This study aims to evaluate the effects of fifteen active substances—soy capsules, Helixor A, Viscum album [L.] extracts, Withania somnifera, Paullinia cupana, P. ovata husk, ginseng, curcumin, Jollab, ginger, fermented soybean extract, mistletoe extract, robuvit®, peppermint extract, and Chlorella extract—on QoL in patients with breast cancer (BC).
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed across PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science up to January 2025. The primary outcomes of interest included QoL, fatigue, pain, physical functioning, nausea, and role and emotional functioning. Statistical analyses were carried out using StataMP 15.1 software. Treatment efficacy was assessed using Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) probabilities. Additionally, cluster analysis was conducted to examine the multidimensional effects of natural extracts across these seven clinical outcomes.
Results: After screening, 18 eligible studies were included, encompassing 2062 patients and evaluating 15 substances. The analysis incorporated patient-reported outcomes from multiple trials: QoL (11 studies), fatigue (10 studies), pain (8 studies), physical functioning (8 studies), nausea (7 studies), role functioning (7 studies), and emotional functioning (7 studies). Based on SUCRA values, Withania somnifera was identified as the most effective treatment for enhancing QoL (99.4%) (SMD = 4.66, 95% CI: 3.47–5.85), physical functioning (100.0%) (SMD = 7.78, 95% CI: 6.61–8.96), role functioning (100.0%) (SMD = 8.10, 95% CI: 6.89–9.32), and emotional functioning (100.0%) (SMD = 5.71, 95% CI: 4.81 to 6.61) were more effective than the standard treatment. Moreover, Withania somnifera was found to be the most promising option for reducing fatigue (99.9%), pain (100.0%), and nausea (98.6%).
Conclusion: The network meta-analysis indicates that Withania somnifera was effective in enhancing quality of life and contributed to a reduction in therapeutic side effects in BC patients. Our findings support the therapeutic potential of plant bioactive substances in breast cancer care; however, further clinical validation of their efficacy is warranted.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD420251006422.
Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most prevalent malignant cancers affecting women globally. The risk factors for BC include, but are not limited to, hormonal status, ionizing radiation, obesity, and genetic factors (Smolarz, Nowak, and Romanowicz, 2022; Fan et al., 2014). According to statistical data from 2022, the global incidence of new breast cancer cases was estimated at approximately 2.309 million, making it the second most common cancer. Additionally, around 666,000 global breast cancer deaths placed it fourth in mortality rates, posing a substantial risk to the health of women worldwide (Bray et al., 2024). Common treatment modalities for BC include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and hormone therapy. In recent years, targeted therapy and immunotherapy have contributed to longer survival rates for patients. However, patients undergoing these treatments may experience a high risk of adverse effects, including pain, cardiovascular disease, and diarrhea (Strijbos et al., 2024; García-Aranda and Redondo, 2019; Jerusalem, Lancellotti, and Kim, 2019), leading them to explore adjuvant therapeutic methods aimed at improving quality of life and reducing side effects. The application of plant bioactive substances in the treatment of breast cancer is increasingly gaining attention (Liang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020).
Plant bioactive substances can be derived from a variety of natural plants, including Green Tea, Red Clover, Boswellia serrata, and Cimicifuga racemosa, through advanced techniques such as ultrasound-assisted extraction, decoction extraction, and solvent extraction (Dostal et al., 2015; Ferraris et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2019; Valente et al., 2024). The therapeutic role of plant bioactive substances in breast cancer (BC) management has gained increasing prominence, primarily due to their ability to enhance treatment efficacy while mitigating the toxic side effects associated with conventional therapies in breast cancer patients (Wang et al., 2022; Valente et al., 2024). Research by J. Chen et al. demonstrated that Salvia miltiorrhiza effectively mitigated skin flap ischemia and prevented necrosis following mastectomy procedures (Chen et al., 2010). Furthermore, a study by Hamidian and colleagues revealed that prophylactic administration of ginseng supplementation may provide cardioprotective benefits against doxorubicin-induced early-onset cancer therapeutics-related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD) and mitigate the decline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in breast cancer patients undergoing treatment (Hamidian et al., 2023a). Additionally, research has suggested that isopropanolic black cohosh extract may prolong disease-free survival in breast cancer patients (Henneicke-von Zepelin et al., 2007).
However, most studies focus on the effects of individual plant bioactive substances on breast cancer (BC) patients without directly comparing different plant extracts (Brooker et al., 2006; Khosropanah et al., 2023; Kedzierska et al., 2012). The outcomes of various clinical studies exhibit significant heterogeneity, and there is a limited number of evidence-based medicine studies available in this area (Chung et al., 2015). Therefore, determining the optimal therapeutic approach within complex treatment regimens for BC patients is a critical clinical priority. Network Meta-Analysis (NMA) is an advanced statistical method that simultaneously compares the effects of multiple interventions, integrating both direct and indirect evidence to quantitatively evaluate and rank interventions within a complex treatment network (Chang et al., 2022; Shehab et al., 2025). In this article, we will use network meta-analysis to compare the therapeutic effects of different plant active substance in breast cancer patients, in order to provide effective evidence-based support for clinical decision-making.
Methods
This meta-analysis was rigorously conducted in accordance with the Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The research protocol has been formally registered with the PROSPERO registry under ID: CRD420251006422.
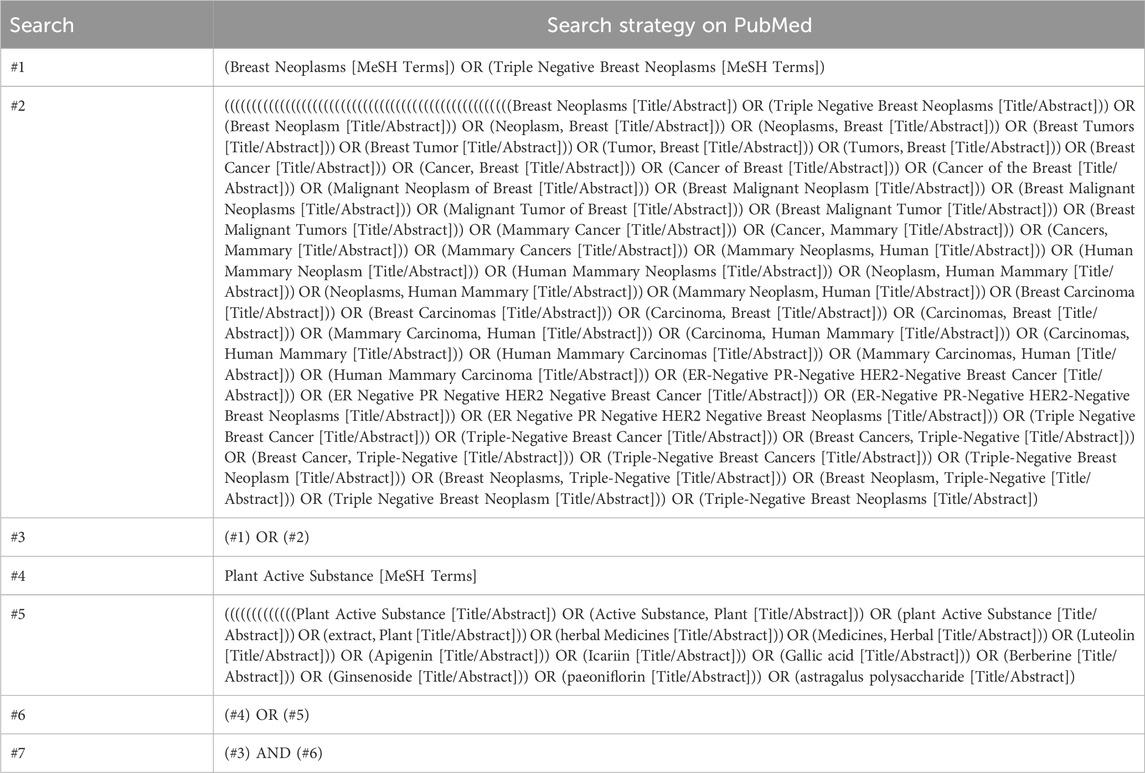
Search strategy
Investigators conducted a comprehensive search across four major electronic databases (PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Web of Science), spanning from the inception of each database until January 2025. Additionally, a manual search was performed by including references from the relevant literature. The search strategy was designed around intervention methods, utilizing specific search terms such as Breast Neoplasms, Plant Active Substances, Luteolin, Apigenin, Icariin, Gallic Acid, Berberine, Ginsenoside, Paeoniflorin, and Astragalus Polysaccharide. The detailed search methodologies are outlined in Table 1, with PubMed serving as an example. The process of study selection, data extraction, and evaluation of the risk of bias was rigorously carried out by two independent researchers.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The following inclusion criteria were applied: (1) All participants were diagnosed with breast cancer (BC) through pathological and histological examination; (2) Studies in which the intervention group received treatment utilizing various plant active substances; (3) A comparison of the intervention measures with inactive controls, including placebos, standard care (such as surgical treatment, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, or other therapies), no treatment, or habitual diet.
Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Non-randomized controlled trials (RCTs); (2) Non-therapeutic clinical research, conference papers, animal or cell experiments, case studies, or review articles; (3) Literature lacking experimental data; (4) Articles that could not be fully accessed.
Data extraction and management
Two investigators independently reviewed the titles and abstracts of all documents, systematically excluding those that clearly did not meet the established inclusion criteria. Any discrepancies were resolved through discussion, and in cases of persistent disagreement, a third author was consulted for further evaluation to reach a consensus. The following data were recorded from the included randomized controlled trials (RCTs): (1) the first author; (2) publication year; (3) participant characteristics (e.g., sample size, age); (4) intervention measures; (5) statistical results, including the pooled effect estimates for each comparison across all outcomes.
Quality assessment
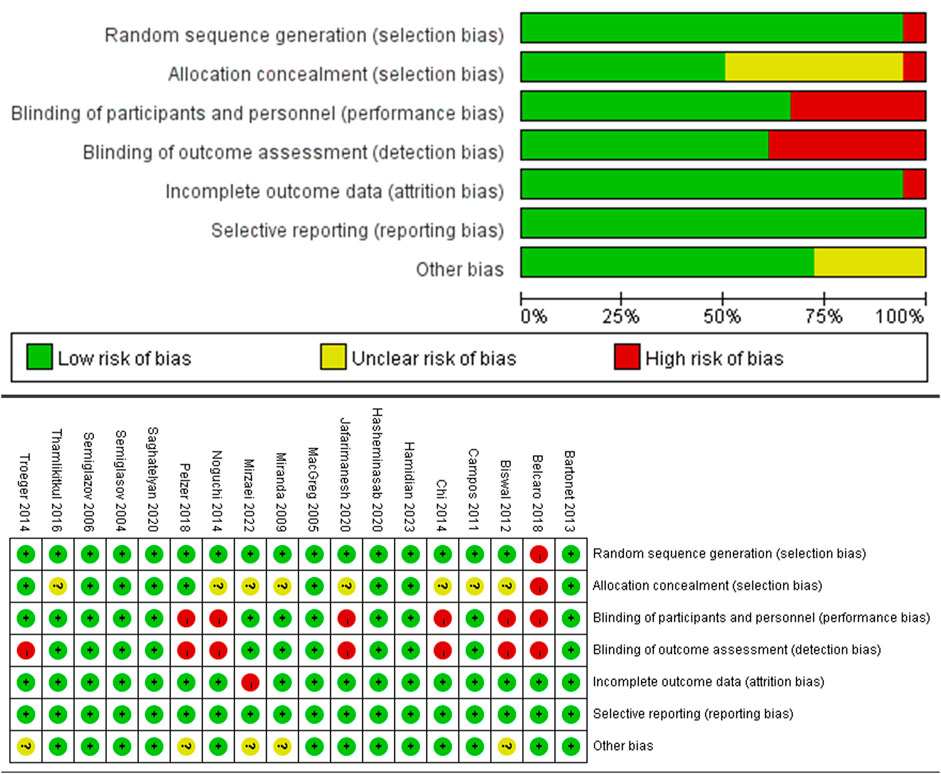
Two independent researchers evaluated the quality of the included studies using the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool (version 5.4.1.0) for assessing the risk of bias. The risk of bias was categorized into seven domains: (1) randomization method; (2) allocation concealment; (3) blinding of both researchers and participants; (4) blinding of outcome assessment; (5) completeness of outcome data; (6) selective reporting; (7) other sources of bias. Discrepancies in opinion among researchers were resolved through deliberative discussion. If necessary, a third investigator joined the discussion to reach a consensus. Trials were categorized into three levels based on the number of components with a potential high risk of bias (ROB): high risk (five or more), moderate risk (three or four), and low risk (two or fewer) (Higgins et al., 2011).
Statistical analysis
Plant active substances were regarded as the intervention measure, with all variables being continuous and expressed as means with standard deviations (SD) (Li and Chen, 2021). To address heterogeneity in outcome measurement units across studies, continuous variables were analyzed using 95% confidence intervals (CI) and standardized mean differences (SMD). A random-effects model was applied to account for potential variations among the included studies (Jackson, Riley, and White, 2011).
Stata MP 15.1 software was used for the analysis, in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines for network meta-analysis (NMA) (Shamseer et al., 2015). A Bayesian framework, incorporating Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation, was used for the network meta-analysis (NMA). To evaluate the consistency between direct and indirect comparisons, researchers conducted a node-splitting analysis, with a p-value threshold of >0.05 indicating statistical consistency (Supplemenatry Tables S1-S3) (Salanti, Ades, and Ioannidis, 2011). Network diagrams were generated using Stata software. In this graphical representation, nodes represent distinct intervention groups (including different natural extracts and control groups), while connecting lines indicate direct comparisons between these interventions. The visualization parameters were scaled according to study availability, with both node size and line thickness being proportional to the number of studies for each respective intervention or comparison (Chaimani et al., 2013).
The hierarchy of interventions was quantified using P scores, which serve as the frequentist counterpart to the Bayesian surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) values. These scores estimate the probability that a treatment is superior to competing interventions, averaged across all comparisons. Ranging from 0 to 1, a P score of 1 represents the highest probability of being the optimal treatment, while a score of 0 indicates the lowest probability. Although P scores and SUCRA values can be interpreted as percentage estimates of treatment effectiveness or acceptability, their clinical interpretation requires caution, as they do not necessarily reflect clinically significant differences between interventions (Marotta et al., 2020). To assess potential small-study effects and publication bias in the network meta-analysis, we constructed a network funnel plot and evaluated its symmetry through visual inspection (Khera et al., 2016).
Results
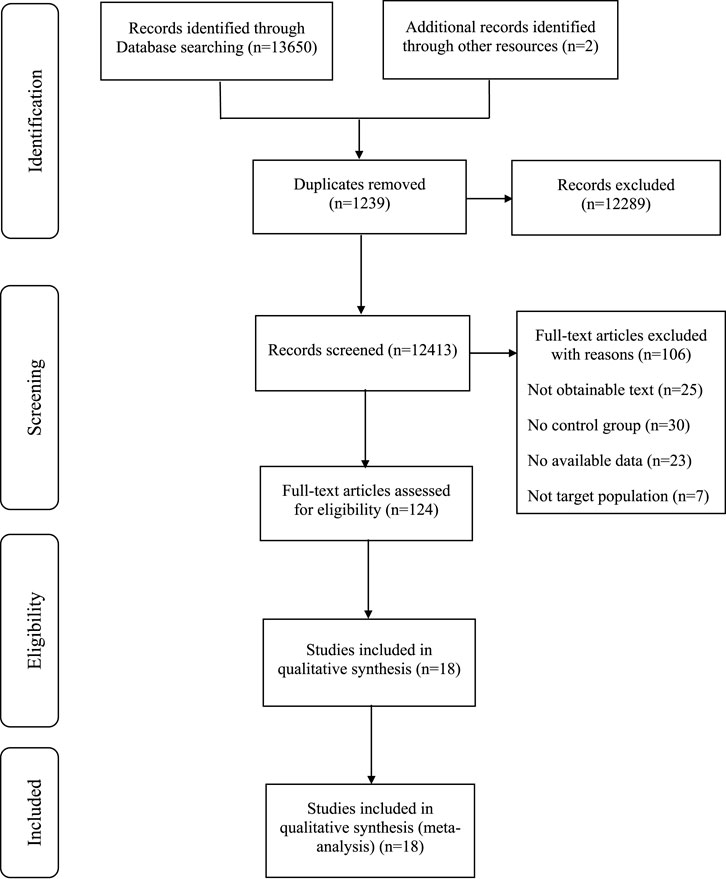
A total of 13,650 articles were collected from electronic databases, supplemented by two additional articles obtained through manual searches. Following the removal of 1,239 duplicate articles using a reference management tool, the titles and abstracts of the remaining 12,413 articles were screened, resulting in the exclusion of 112,289 articles. The remaining 124 articles underwent a comprehensive review, resulting in the exclusion of 106 articles for reasons such as being non-randomized controlled trials, containing incomplete data or outcome measures, failing to meet inclusion criteria, or not adhering to the specified interventions of this review. Ultimately, 18 articles met the eligibility criteria and were included in the final analysis of the study (MacGregor et al., 2005; Tröger et al., 2014; Pelzer, Tröger, and Nat, 2018; Biswal et al., 2013; da Costa Miranda et al., 2009; Hasheminasab et al., 2020; Hamidian et al., 2023b; Saghatelyan et al., 2020; Mirzaei et al., 2022; Thamlikitkul et al., 2017; de Oliveira Campos et al., 2011; Chi et al., 2014; Semiglazov et al., 2006; Belcaro et al., 2018; Jafarimanesh et al., 2020; Noguchi, Maruyama, and Yamada, 2014; Semiglasov et al., 2004; Barton et al., 2013) (Figure 1).
All 18 articles included in the analysis were randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Among these, 10 were rated as having a low risk of bias, 8 as having a moderate risk, and none as having a high risk, suggesting that the overall quality of the studies was acceptable. Further details are presented in Figure 2, which provides a visual representation of the risk-of-bias assessment for the included RCTs.
This study analyzed 18 randomized controlled trials involving a total of 2,062 breast cancer patients. The control groups received various interventions, including soy capsules, peppermint extract, Viscum album [L.] extracts, Withania somnifera, Paullinia cupana, P. ovate husk, ginseng, curcumin, and chlorella extract. Among the studies, 11 used quality of life as an outcome measure, 10 assessed fatigue, 8 evaluated pain severity, 8 assessed physical functioning, 7 measured nausea, 7 reported role functioning, and 7 included emotional functioning as outcome measures (Table 2). A forest plot summarizing pooled effect sizes across outcomes to enhance visual interpretation, which has been included in the Supplementary Material (Supplementary Table S4).
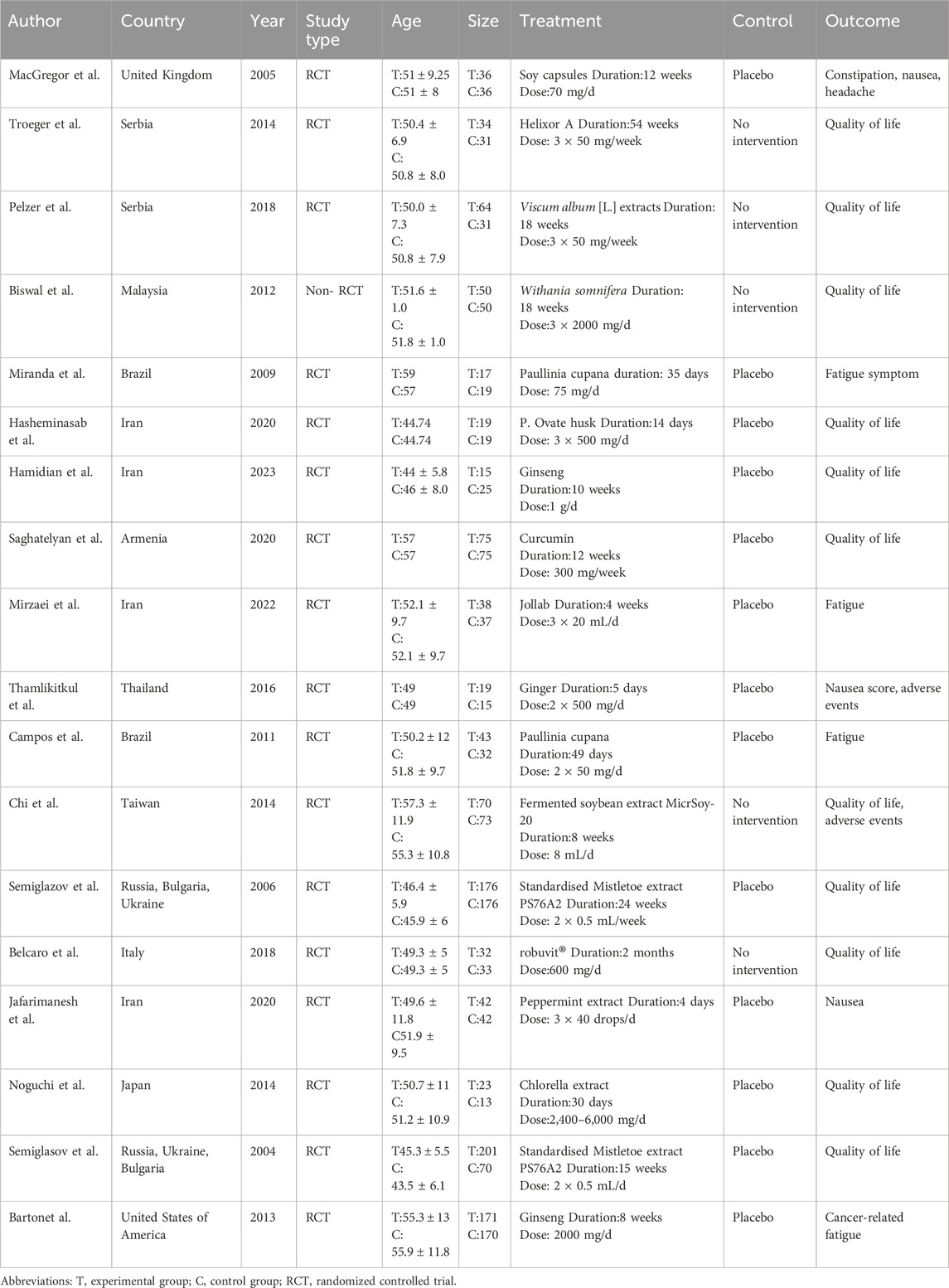
Table 2. Characteristics of included network meta-analysis. Study characteristics included in network meta-analysis.
Network meta-analysis
The full NMA figure will be shown in Figures 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A and 9A.
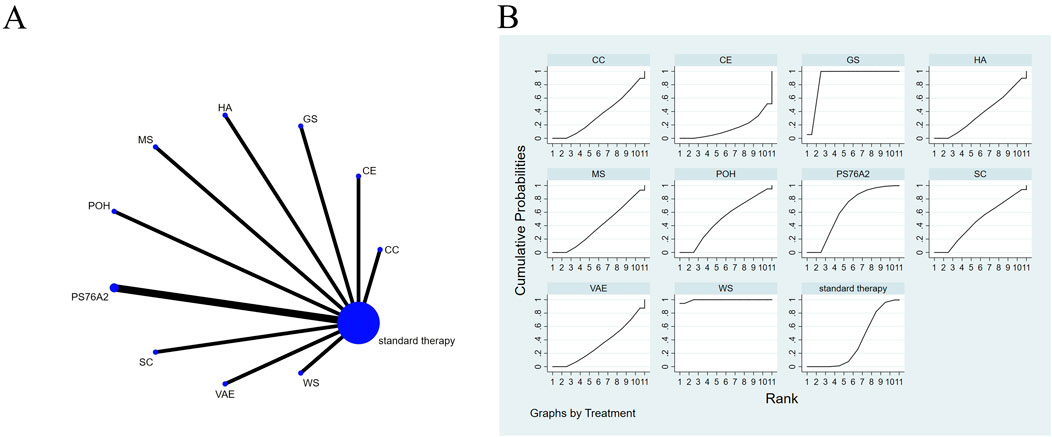
Figure 3. The evidence of plant active substance in influencing quality of life. (A), network graph of the Quality of Life. (B), the SUCRA plot for Quality of Life. Abbreviations: WS, Withania somnifera; VAE, Viscum album [L.] extracts; SC, soy capsules; PS76A2, an aqueous mistletoe extract standardised to the galactoside-specific mistletoe lectin; POH, P. ovate husk; MS, fermented soybean extract MicrSoy; HA, Helixor A; GS, ginseng; CE, Chlorella extract; CC, curcumin.

Figure 4. The evidence of plant active substance in influencing fatigue. (A), network graph of the fatigue. (B), the SUCRA plot for fatigue. Abbreviations: WS, Withania somnifera; VAE, Viscum album fatigue [L.] extracts; PS76A2, an aqueous mistletoe extract standardised to the galactoside-specific mistletoe lectin; PC, Paullinia cupana; MS-20, fermented soybean extract MicrSoy20; JA, Jollab; HA, Helixor A; GS, ginseng.
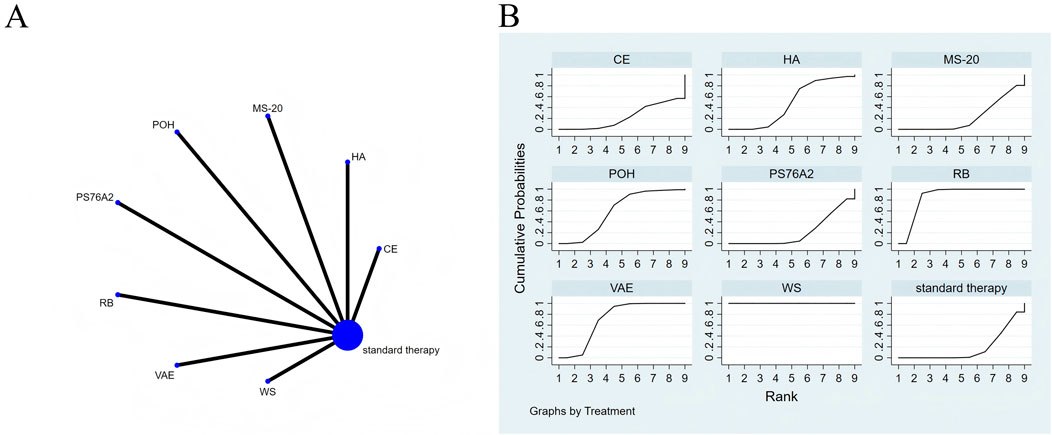
Figure 5. The evidence of plant active substance in influencing pain. (A), network graph of the pain. (B), the SUCRA plot for pain. Abbreviations: WS, Withania somnifera; VAE, Viscum album [L.] extracts; RB, robuvit® (a natural supplement extracted from the French oak wood); PS76A2, an aqueous mistletoe extract standardised to the galactoside-specific mistletoe lectin; POH, P. ovate husk; MS-20, fermented soybean extract MicrSoy20; HA, Helixor A; CE, Chlorella extract.
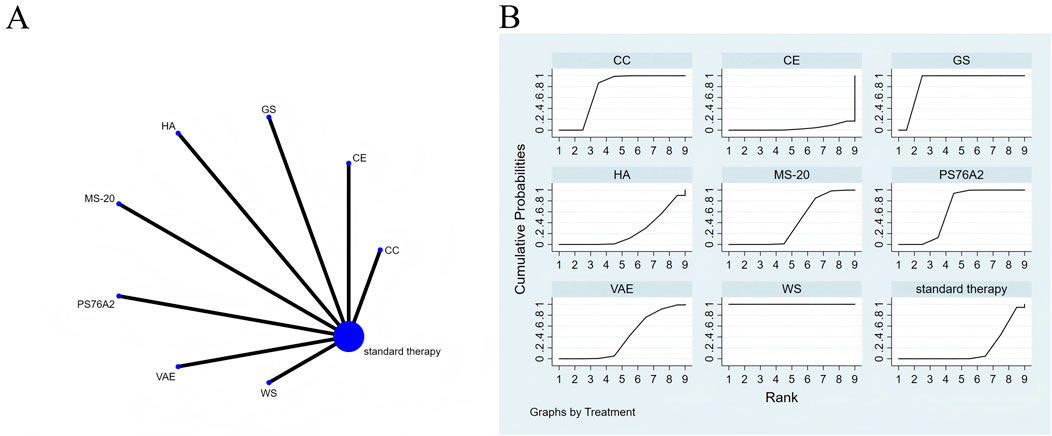
Figure 6. The evidence of plant active substance in influencing physical functioning. (A), network graph of the physical functioning. (B), the SUCRA plot for physical functioning. Abbreviations: WS, Withania somnifera; VAE, Viscum album [L.] extracts; PS76A2, an aqueous mistletoe extract standardised to the galactoside-specific mistletoe lectin; MS-20, fermented soybean extract MicrSoy20; HA, Helixor A; GS, ginseng; CE, Chlorella extract; CC, curcumin.

Figure 7. The evidence of plant active substance in influencing nausea. (A), network graph of the nausea. (B), the SUCRA plot for nausea. Abbreviations: WS, Withania somnifera; VAE, Viscum album [L.] extracts; PS76A2, an aqueous mistletoe extract standardised to the galactoside-specific mistletoe lectin; PEP, Peppermint; MS-20, fermented soybean extract MicrSoy20; GI, ginger.
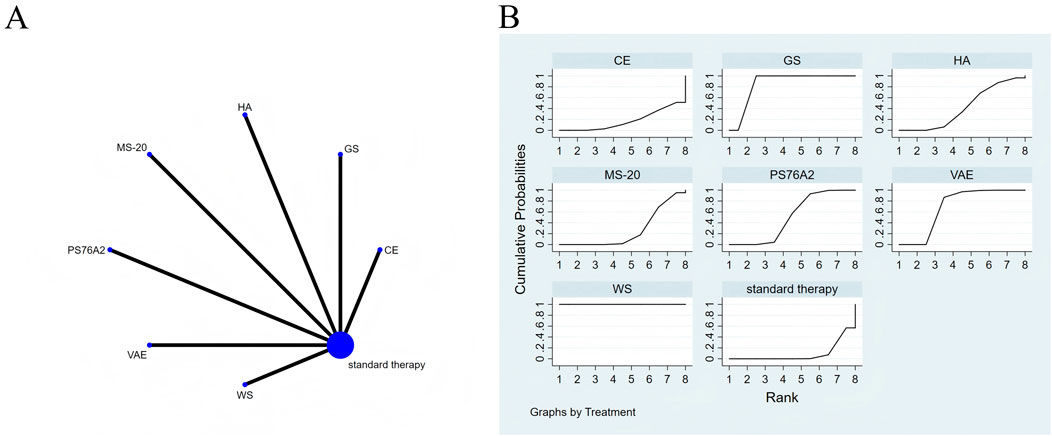
Figure 8. The Evidence of Plant Active Substance in Influencing role functioning. (A), network graph of the role functioning. (B), the SUCRA plot for role functioning. Abbreviations: WS, Withania somnifera; VAE, Viscum album [L.] extracts; PS76A2, an aqueous mistletoe extract standardised to the galactoside-specific mistletoe lectin; MS-20, fermented soybean extract MicrSoy20; HA, Helixor A; GS, ginseng; CE, Chlorella extract.

Figure 9. The Evidence of Plant Active Substance in Influencing emotional functioning. (A), network graph of the emotional functioning. (B), the SUCRA plot for emotional functioning. Abbreviations: WS, Withania somnifera; VAE, Viscum album [L.] extracts; PS76A2, an aqueous mistletoe extract standardised to the galactoside-specific mistletoe lectin; MS-20, fermented soybean extract MicrSoy20; HA, Helixor A; GS, ginseng; CE, Chlorella extract.
Effects of natural extract on quality of life
The results of the network meta-analysis are illustrated in Figure 3A. Consistency and inconsistency tests were performed for all direct and indirect comparisons across the studies, with all p-values exceeding 0.05, indicating that the effect consistency across the studies is satisfactory.
The results of the network NMA indicate that Withania somnifera (SMD = 4.66, 95% CI: 3.47–5.85) and ginseng (SMD = 3.16, 95% CI: 1.83–4.50) were more effective than the standard treatment in improving quality of life, with specific details provided in Supplementary Table S5. In the hierarchy of probability for enhancing quality of life through various plant active substances, Withania somnifera emerged as the most efficacious, boasting the highest SUCRA value of 99.4%, as depicted in Figure 3B.
Effects of natural extracts on fatigue
The results of the network meta-analysis are illustrated in Figure 4A. Consistency and inconsistency tests were performed for all direct and indirect comparisons across the studies, with all p-values exceeding 0.05, indicating that the effect consistency across the studies is satisfactory.
The results of the network meta-analysis showed that, relative to the control group’s routine measures, Withania somnifera (SMD = −6.12, 95% CI: −8.94 to −3.30) was superior to the control group in reducing fatigue (Supplementary Table S6). In terms of alleviating fatigue, Withania somnifera was ranked first in the SUCRA analysis, indicating the highest probability of being the most effective intervention among the evaluated options (SUCRA: 99.9%, as shown in Figure 4B).
Effects of natural extracts on pain
The network meta-analysis diagram is shown in Figure 5A. All p-values for the indirect and direct comparisons between studies underwent tests for consistency and inconsistency, with all p-values exceeding 0.05, indicating that the consistency of effects among the studies is acceptable.
The results of the network NMA indicate that, compared to standard treatment, Withania somnifera (SMD = −6.60, 95% CI: −7.62 to −5.59), robuvit® (SMD = −1.48, 95% CI: −2.04 to −0.93), Viscum album [L.] extracts (SMD = −0.91, 95% CI: −1.37 to −0.45), and P. ovate husk (SMD = −0.66, 95% CI: −1.32 to −0.01) were more effective in reducing pain than the control group (Supplementary Table S7). In terms of probability rankings among different plant active substances for reducing pain, Withania somnifera ranked first in SUCRA (SUCRA = 100.0%, as shown in Figure 5B).
Effects of natural extracts on physical functioning
All direct and indirect comparisons across the included studies were assessed for consistency and inconsistency. The resulting p-values were all above 0.05, suggesting that the consistency of effects among the studies was statistically acceptable (Figure 6A).
The NMA results indicate that, in improving physical functioning, Withania somnifera (SMD = 7.78, 95% CI: 6.61–8.96), ginseng (SMD = 2.49, 95% CI: 1.62–3.35), curcumin (SMD = 0.99, 95% CI: 0.56–1.42), PS76A2 (SMD = 0.70, 95% CI: 0.48–0.92), and fermented soybean extract MicrSoy20 (SMD = 0.29, 95% CI: 0.02–0.55) were superior to the control group (standard treatment), with details presented in Supplementary Table S8. Regarding probability rankings among different plant active substances for improving physical functioning, St. John’s Wort extract ranked first in SUCRA (SUCRA = 100.0%, as shown in Figure 6B).
Effects of natural extracts on nausea
Consistency and inconsistency were evaluated for all direct and indirect comparisons across the studies. Since all p-values exceeded 0.05, the consistency of effects across the studies was deemed acceptable (Figure 7A).
The NMA results demonstrated that both Withania somnifera (SMD = −1.63, 95% CI: −2.22 to −1.04) and peppermint (SMD = −1.03, 95% CI: −1.62 to −0.44) were significantly more effective in reducing nausea compared to standard treatment, with additional details outlined in Supplementary Table S9. Regarding the probability rankings of plant active substances for reducing nausea, Withania somnifera achieved the highest SUCRA value (98.6%), ranking first, as illustrated in Figure 7B.
Effects of natural extracts on role functioning
Figure 8A presents the network meta-analysis evidence diagram. Tests for consistency and inconsistency were performed on all direct and indirect comparisons, with all p-values exceeding 0.05, indicating that the consistency of effects across the studies was statistically acceptable.
According to the NMA, Withania somnifera (SMD = 8.10, 95% CI: 6.89–9.32), ginseng (SMD = 2.68, 95% CI: 1.78–3.57), Viscum album [L.] extracts (SMD = 0.91, 95% CI: 0.45–1.37), and PS76A2 (SMD = 0.50, 95% CI: 0.29–0.72) showed superior efficacy in improving role functioning compared to standard treatment (see Supplementary Table S10 for details). In the probability ranking of plant active substances for enhancing role functioning, Withania somnifera emerged as the top intervention with a SUCRA value of 100.0%, as depicted in Figure 8B.
Effects of natural extracts on emotional functioning
The network meta-analysis evidence is presented in Figure 9A. Consistency and inconsistency assessments were conducted for all direct and indirect comparisons across the studies, and all resulting p-values exceeded 0.05, indicating acceptable consistency in the effects among the included studies.
According to the NMA, Withania somnifera (SMD = 5.71, 95% CI: 4.81–6.61), ginseng (SMD = 2.70, 95% CI: 1.80–3.60), PS76A2 (SMD = 0.52, 95% CI: 0.30–0.74), and Viscum album [L.] extracts (SMD = 0.52, 95% CI: 0.07–0.96) showed superior efficacy in enhancing emotional functioning compared to standard treatment (see Supplementary Table S11 for details). In the probability ranking of plant active substances for improving emotional functioning, Withania somnifera emerged as the top intervention with a SUCRA value of 100.0%, as depicted in Figure 9B.
Publication bias test
To assess potential publication bias, individual funnel plots were constructed for each outcome measure. Upon visual examination, the funnel plots did not show substantial evidence of publication bias (Wallace et al., 2009). Further details are provided in Figure 10.
Discussion
This study evaluated the effects of several natural compounds on overall quality of life, mental health, and adverse reactions in individuals recovering from breast cancer. The analysis included 18 randomized controlled trials involving a substantial cohort of 2,062 breast cancer (BC) patients and examined the effects of fifteen distinct natural substances. The findings indicated that extracts from Withania somnifera were effective in enhancing quality of life, while also contributing to reductions in fatigue, pain, and nausea. Furthermore, Withania somnifera was associated with improvements in physical functioning, role functioning, and emotional functioning. In conclusion, the study underscores Withania somnifera as a beneficial natural option for reducing adverse reactions and improving mental health and overall quality of life in breast cancer patients.
This study demonstrates that Withania somnifera offers comparative benefits in enhancing quality of life compared to other plant-based substances. Withania somnifera (Indian ginseng or Ashwagandha) is a plant widely used in traditional medicine and is renowned for its diverse biological activities. Its active constituents, such as withaferin A and withanolides, are considered crucial to its pharmacological effects (Singh et al., 2021; Hassannia et al., 2020; Lem et al., 2022). These compounds have been shown to modulate various signaling pathways, including NF-κB, JAK-STAT, and AP-1, thereby reducing cancer-associated inflammation (White et al., 2016; Taniguchi and Karin, 2018). Furthermore, Withania somnifera improves reproductive system function by reducing infertility, enhancing spermatogenesis, and promoting sexual behavior in both male and female subjects (Nasimi Doost Azgomi et al., 2018). Studies have reported that Withania somnifera (WS) improves semen quality, enhances levels of vitamins E, C, and A, and promotes fertility. These beneficial effects are attributed to WS’s rich composition of alkaloids, ergostane steroids, and essential amino acids, which collectively enhance detoxification processes, reduce oxidative stress, and restore testosterone secretion (Ahmad et al., 2010). Withaferin A has been shown to mitigate oxidative stress by preserving the activity and levels of key antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase, and the non-enzymatic antioxidant glutathione (GSH), while reducing thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS). Catalase plays a critical role in cellular homeostasis by decomposing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and its deficiency or dysregulation is implicated in various age-related complication (Nandi et al., 2019). Furthermore, Withaferin A reduced myeloperoxidase (MPO) and nitrotyrosine levels and enhanced Nrf2 signaling in acute pancreatitis, highlighting its antioxidant role. Given that MPO elevation predicts diabetes and cardiovascular risk, MPO suppression could improve outcomes in aging patients (Giovannini et al., 2010).
Breast cancer patients often experience symptoms such as nausea, pain, and fatigue during their treatment (Qi et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2022). Withania somnifera has shown promise in alleviating chemotherapy-induced fatigue and improving the quality of life for breast cancer patients (Biswal et al., 2013). Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and IFN-γ, contribute to the promotion of neuropathic pain (Koch et al., 2007), whereas the inhibition of these cytokines or the administration of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 has been shown to alleviate neuropathic pain in animal models (Laumet et al., 2020; Kumar, Sharma, and Garg, 2022). In rat models, treatment with Withania somnifera root extract significantly reduced IFN-γ levels while increasing IL-10 expression following SNI-induced neuropathic pain. The analgesic effects of Withania somnifera (WS) against both postoperative and neuropathic pain appear to be mediated by its bioactive compounds, particularly withanolides (Lim et al., 2018; Orrù et al., 2014).
Breast cancer significantly impacts the mental and psychological health of patients, particularly during the initial diagnosis and the first year following treatment. Psychological distress is most pronounced during this period (Dinapoli et al., 2021; Fortin et al., 2021). Research indicates that Withania somnifera offers a range of potential benefits for mental and psychological health. The root extract of Withania somnifera, known as glycowithanolides, has demonstrated anxiolytic and antidepressant effects in rat models, supporting its potential use as a mood stabilizer (Pathak et al., 2021). Studies have found that Withania somnifera can be used to promote physical and mental health, restore vitality, and treat various central nervous system disorders, including epilepsy, stress, and neurodegenerative diseases (Kulkarni and Dhir, 2008). Clinical trials suggest that W. somnifera extract enhances cognitive function—including task performance, executive function, attention, and reaction time—in individuals with cognitive impairment, such as older adults with mild cognitive decline and those with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, or bipolar disorder. Additionally, it demonstrates good tolerability, high adherence, and minimal side effects (Ng et al., 2020).
We conducted a statistical analysis of adverse events across the included 18 studies. The findings indicate that the plant extract is both safe and effective. The most frequently reported adverse reaction was injection and infusion site reactions. Other adverse events included mild to moderate nausea, febrile temperature, flatulence and gastritis, all of which resolved without sequelae (Supplementary Table S12).
Overall, our study has clinical implications. Withania somnifera has demonstrated superior efficacy in improving the overall quality of life, including physical and functional status, among breast cancer patients, while reducing side effects such as nausea, pain, and fatigue. Additionally, it has shown significant effects in enhancing mental wellbeing. These findings provide valuable insights for breast cancer patients considering plant-based active substances. However, the notably high effect sizes observed for Withania somnifera (e.g., SMD >5) warrant careful interpretation. While these estimates suggest a potent intervention effect, their clinical plausibility must be critically evaluated. It is important to consider whether these values may have been influenced by small-study effects, a common source of bias in meta-analyses wherein smaller studies tend to yield larger effect sizes. Future research with larger, rigorously designed trials is needed to validate these findings and clarify the true magnitude of the intervention’s benefit.
Strengths and limitations
Our study has several notable strengths. It includes 18 research articles involving a substantial cohort of 2,062 patients, providing a robust sample size. The research evaluates 15 distinct natural extracts, adheres to stringent inclusion criteria, systematically identifies all relevant studies that meet predefined conditions, and follows established guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses in its reporting. Additionally, Breast cancer (as well as other forms of cancer) exhibits high incidence and aggressive phenotypes in countries near the equator and in the Southern Hemisphere. We searched regional databases—including SCIELO, ARC, NRF, and AJOL—that focus on geographic areas with high breast cancer prevalence; however, no eligible clinical studies meeting our inclusion criteria were identified.
However, our study also has several inevitable limitations: (1) The prior treatments received by patients undergoing natural extract therapy may influence the evaluation of post-treatment outcomes; (2) There are variations in the doses of natural extracts used across different studies, with a lack of consensus on standardized intervention doses; (3) Variations in the techniques for preparing plant-based active substances and insufficient descriptions of these methods may introduce bias; (4) The impact on patients’ quality of life may also be influenced by factors such as social support systems, which some studies did not consider or report. (5)The inability to perform subgroup analyses due to the limited number of included studies represents a notable limitation of this review, as it restricts the exploration of potential sources of heterogeneity and the examination of differential effects across patient populations or intervention characteristics. (6)The clinical applicability of SUCRA rankings requires cautious interpretation, particularly due to heterogeneity in dosage regimens, pharmaceutical formulations, and treatment durations across included studies.
The conclusion indicates that the effectiveness of plant-based active substances in treating breast cancer is not sufficiently supported by robust clinical evidence, primarily due to the lack of direct comparative data for certain treatments. Consequently, the findings of this study should be interpreted with caution, highlighting the critical need for more comprehensive and detailed research in this area.
Conclusion
The results of the network meta-analysis (NMA) indicate that Withania somnifera is an effective natural product for improving the quality of life, reducing side effects, and promoting mental health in breast cancer patients. Therefore, we recommend the integration of Withania somnifera alongside standard treatment to enhance the overall quality of life in these patients. Our study provides valuable insights into the potential of plant-based active substances to improve quality of life, mitigate side effects, and support mental health in breast cancer patients. However, the limitations of the initial study design resulted in indirect comparisons for certain treatments, which may diminish the strength of the evidence presented. Consequently, there is a pressing need for more rigorous, high-quality randomized controlled trials to further validate the efficacy and safety of natural extracts in the treatment of breast cancer.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
LW: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal Analysis. XX: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. MG: Conceptualization, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. YD: Validation, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis. HD: Resources, Writing – original draft. SH: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Investigation. LH: Writing – original draft. YS: Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Data curation. JG: Writing – review and editing, Data curation, Supervision. ZY: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Resources.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1622479/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmad, M. K., Mahdi, A. A., Shukla, K. K., Islam, N., Rajender, S., Madhukar, D., et al. (2010). Withania somnifera improves semen quality by regulating reproductive hormone levels and oxidative stress in seminal plasma of infertile males. Fertil. Steril. 94 (3), 989–996. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.04.046
Barton, D. L., Liu, H., Dakhil, S. R., Linquist, B., Sloan, J. A., Nichols, C. R., et al. (2013). Wisconsin ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) to improve cancer-related fatigue: a randomized, double-blind trial, N07C2. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 105 (16), 1230–1238. doi:10.1093/jnci/djt181
Belcaro, G., Dugall, M., Cotellese, R., Feragalli, B., Cianchetti, E., and Cesarone, M. R. (2018). Supplementation with robuvit® in post-mastectomy post-radiation arm lymphedema. Minerva Chir. 73 (3), 288–294. doi:10.23736/s0026-4733.18.07667-8
Biswal, B. M., Sulaiman, S. A., Ismail, H. C., Zakaria, H., and Musa, K. I. (2013). Effect of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) on the development of chemotherapy-induced fatigue and quality of life in breast cancer patients. Integr. Cancer Ther. 12 (4), 312–322. doi:10.1177/1534735412464551
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74 (3), 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Brooker, S., Martin, S., Pearson, A., Bagchi, D., Earl, J., Gothard, L., et al. (2006). Double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase II trial of IH636 grape seed proanthocyanidin extract (GSPE) in patients with radiation-induced breast induration. Radiother. Oncol. 79 (1), 45–51. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2006.02.008
Chaimani, A., Higgins, J. P., Mavridis, D., Spyridonos, P., and Salanti, G. (2013). Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA. PLoS One 8 (10), e76654. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076654
Chang, E., Josan, A. S., Purohit, R., Patel, C. K., and Xue, K. (2022). A network meta-analysis of retreatment rates following bevacizumab, ranibizumab, aflibercept, and laser for retinopathy of prematurity. Ophthalmology 129 (12), 1389–1401. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2022.06.042
Chen, J., Lv, Q., Yu, M., Zhang, X., and Gou, J. (2010). Randomized clinical trial of Chinese herbal medications to reduce wound complications after mastectomy for breast carcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 97 (12), 1798–1804. doi:10.1002/bjs.7227
Chi, K. H., Chiou, T. J., Li, C. P., Chen, S. Y., and Chao, Y. (2014). MS-20, a chemotherapeutical adjuvant, reduces chemo-associated fatigue and appetite loss in cancer patients. Nutr. Cancer 66 (7), 1211–1219. doi:10.1080/01635581.2014.951731
Chung, V. C., Wu, X., Hui, E. P., Ziea, E. T., Ng, B. F., Ho, R. S., et al. (2015). Effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine for cancer palliative care: overview of systematic reviews with meta-analyses. Sci. Rep. 5, 18111. doi:10.1038/srep18111
da Costa Miranda, V., Trufelli, D. C., Santos, J., Campos, M. P., Nobuo, M., da Costa Miranda, M., et al. (2009). Effectiveness of guaraná (Paullinia cupana) for postradiation fatigue and depression: results of a pilot double-blind randomized study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 15 (4), 431–433. doi:10.1089/acm.2008.0324
de Oliveira Campos, M. P., Riechelmann, R., Martins, L. C., Hassan, B. J., Casa, F. B., and Del Giglio, A. (2011). Guarana (Paullinia cupana) improves fatigue in breast cancer patients undergoing systemic chemotherapy. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 17 (6), 505–512. doi:10.1089/acm.2010.0571
Dinapoli, L., Colloca, G., Di Capua, B., and Valentini, V. (2021). Psychological aspects to consider in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 23 (3), 38. doi:10.1007/s11912-021-01049-3
Dostal, A. M., Samavat, H., Bedell, S., Torkelson, C., Wang, R., Swenson, K., et al. (2015). The safety of green tea extract supplementation in postmenopausal women at risk for breast cancer: results of the Minnesota Green Tea Trial. Food Chem. Toxicol. 83, 26–35. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2015.05.019
Fan, L., Strasser-Weippl, K., Li, J. J., St Louis, J., Finkelstein, D. M., Yu, K. D., et al. (2014). Breast cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15 (7), e279–e289. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70567-9
Ferraris, C., Ballestra, B., Listorti, C., Cappelletti, V., Reduzzi, C., Scaperrotta, G. P., et al. (2020). Red clover and lifestyle changes to contrast menopausal symptoms in premenopausal patients with hormone-sensitive breast cancer receiving tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 180 (1), 157–165. doi:10.1007/s10549-020-05534-4
Fortin, J., Leblanc, M., Elgbeili, G., Cordova, M. J., Marin, M. F., and Brunet, A. (2021). The mental health impacts of receiving a breast cancer diagnosis: a meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 125 (11), 1582–1592. doi:10.1038/s41416-021-01542-3
García-Aranda, M., and Redondo, M. (2019). Immunotherapy: a challenge of breast cancer treatment. Cancers (Basel) 11 (12), 1822. doi:10.3390/cancers11121822
Giovannini, S., Onder, G., Leeuwenburgh, C., Carter, C., Marzetti, E., Russo, A., et al. (2010). Myeloperoxidase levels and mortality in frail community-living elderly individuals. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 65 (4), 369–376. doi:10.1093/gerona/glp183
Hamidian, M., Foroughinia, F., Haghighat, S., Attar, A., and Haem, E. (2023a). Protective effects of Panax ginseng against doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in patients with non-metastatic breast cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 29 (6), 1306–1316. doi:10.1177/10781552221118530
Hamidian, M., Foroughinia, F., Yousefi, M., Haghighat, S., and Haem, E. (2023b). Effects of Panax ginseng on health-related quality of life in patients with non-metastatic breast cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial ginseng for HRQOL in breast cancer. Nutr. Cancer 75 (6), 1429–1437. doi:10.1080/01635581.2023.2181735
Hasheminasab, F. S., Hashemi, S. M., Dehghan, A., Sharififar, F., Setayesh, M., Sasanpour, P., et al. (2020). Effects of a Plantago ovata-based herbal compound in prevention and treatment of oral mucositis in patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy: a double-blind, randomized, controlled crossover trial. J. Integr. Med. 18 (3), 214–221. doi:10.1016/j.joim.2020.02.008
Hassannia, B., Logie, E., Vandenabeele, P., Vanden Berghe, T., and Vanden Berghe, W. (2020). Withaferin A: from ayurvedic folk medicine to preclinical anti-cancer drug. Biochem. Pharmacol. 173, 113602. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.08.004
Henneicke-von Zepelin, H. H., Meden, H., Kostev, K., Schröder-Bernhardi, D., Stammwitz, U., and Becher, H. (2007). Isopropanolic black cohosh extract and recurrence-free survival after breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 45 (3), 143–154. doi:10.5414/cpp45143
Higgins, J. P., Altman, D. G., Gøtzsche, P. C., Jüni, P., Moher, D., Oxman, A. D., et al. (2011). The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 343, d5928. doi:10.1136/bmj.d5928
Jackson, D., Riley, R., and White, I. R. (2011). Multivariate meta-analysis: potential and promise. Stat. Med. 30 (20), 2481–2498. doi:10.1002/sim.4172
Jafarimanesh, H., Akbari, M., Hoseinian, R., Zarei, M., and Harorani, M. (2020). The effect of peppermint (Mentha piperita) extract on the severity of nausea, vomiting and anorexia in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: a randomized controlled trial. Integr. Cancer Ther. 19, 1534735420967084. doi:10.1177/1534735420967084
Jerusalem, G., Lancellotti, P., and Kim, S. B. (2019). HER2+ breast cancer treatment and cardiotoxicity: monitoring and management. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 177 (2), 237–250. doi:10.1007/s10549-019-05303-y
Kedzierska, M., Olas, B., Wachowicz, B., Glowacki, R., Bald, E., Czernek, U., et al. (2012). Effects of the commercial extract of aronia on oxidative stress in blood platelets isolated from breast cancer patients after the surgery and various phases of the chemotherapy. Fitoterapia 83 (2), 310–317. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2011.11.007
Khera, R., Murad, M. H., Chandar, A. K., Dulai, P. S., Wang, Z., Prokop, L. J., et al. (2016). Association of pharmacological treatments for obesity with weight loss and adverse events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama 315 (22), 2424–2434. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.7602
Khosropanah, A., Mehri Ardestani, M., Rostami, N., Hashemi, F., Pasalar, M., Hunter, J., et al. (2023). Effects of chicory and fumitory on hot flashes among breast cancer survivors: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J. Integr. Complement. Med. 29 (1), 31–41. doi:10.1089/jicm.2022.0624
Koch, A., Zacharowski, K., Boehm, O., Stevens, M., Lipfert, P., von Giesen, H. J., et al. (2007). Nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokines correlate with pain intensity in chronic pain patients. Inflamm. Res. 56 (1), 32–37. doi:10.1007/s00011-007-6088-4
Kulkarni, S. K., and Dhir, A. (2008). Withania somnifera: an Indian ginseng. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 32 (5), 1093–1105. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.09.011
Kumar, P., Sharma, R., and Garg, N. (2022). Withania somnifera - a magic plant targeting multiple pathways in cancer related inflammation. Phytomedicine 101, 154137. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154137
Laumet, G., Bavencoffe, A., Edralin, J. D., Huo, X. J., Walters, E. T., Dantzer, R., et al. (2020). Interleukin-10 resolves pain hypersensitivity induced by cisplatin by reversing sensory neuron hyperexcitability. Pain 161 (10), 2344–2352. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001921
Lem, F. F., Yong, Y. S., Goh, S., Chin, S. N., and Chee, F. T. (2022). Withanolides, the hidden gem in Physalis minima: a mini review on their anti-inflammatory, anti-neuroinflammatory and anti-cancer effects. Food Chem. 377, 132002. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.132002
Li, D., and Chen, P. (2021). Effects of aquatic exercise and land-based exercise on cardiorespiratory fitness, motor function, balance, and functional Independence in stroke Patients-A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Brain Sci. 11 (8), 1097. doi:10.3390/brainsci11081097
Liang, J., Zhang, X. L., Yuan, J. W., Zhang, H. R., Liu, D., Hao, J., et al. (2019). Cucurbitacin B inhibits the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by altering the biomechanical properties of cells. Phytother. Res. 33 (3), 618–630. doi:10.1002/ptr.6250
Lim, D. W., Kim, J. G., Lim, E. Y., and Kim, Y. T. (2018). Antihyperalgesic effects of ashwagandha (Withania somnifera root extract) in rat models of postoperative and neuropathic pain. Inflammopharmacology 26 (1), 207–215. doi:10.1007/s10787-017-0389-1
MacGregor, C. A., Canney, P. A., Patterson, G., McDonald, R., and Paul, J. (2005). A randomised double-blind controlled trial of oral soy supplements versus placebo for treatment of menopausal symptoms in patients with early breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 41 (5), 708–714. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2005.01.005
Marotta, N., Demeco, A., Moggio, L., Marinaro, C., Pino, I., Barletta, M., et al. (2020). Comparative effectiveness of breathing exercises in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 41, 101260. doi:10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101260
Mirzaei, H., Gharehgozlou, R., Heydarirad, G., Fahimi, S., Ghafari, S., Mosavat, S. H., et al. (2022). Efficacy and safety of Jollab (a saffron-based beverage) on cancer-related fatigue in breast cancer patients: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Complement. Med. Res. 29 (6), 437–445. doi:10.1159/000525775
Nandi, A., Yan, L. J., Jana, C. K., and Das, N. (2019). Role of catalase in oxidative stress- and age-associated degenerative diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 9613090. doi:10.1155/2019/9613090
Nasimi Doost Azgomi, R., Zomorrodi, A., Nazemyieh, H., Fazljou, S. M. B., Sadeghi Bazargani, H., Nejatbakhsh, F., et al. (2018). Effects of Withania somnifera on reproductive system: a systematic review of the available evidence. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 4076430. doi:10.1155/2018/4076430
Ng, Q. X., Loke, W., Foo, N. X., Tan, W. J., Chan, H. W., Lim, D. Y., et al. (2020). A systematic review of the clinical use of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) to ameliorate cognitive dysfunction. Phytother. Res. 34 (3), 583–590. doi:10.1002/ptr.6552
Noguchi, N., Maruyama, I., and Yamada, A. (2014). The influence of chlorella and its hot water extract supplementation on quality of life in patients with breast cancer. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 704619. doi:10.1155/2014/704619
Orrù, A., Marchese, G., Casu, G., Casu, M. A., Kasture, S., Cottiglia, F., et al. (2014). Withania somnifera root extract prolongs analgesia and suppresses hyperalgesia in mice treated with morphine. Phytomedicine 21 (5), 745–752. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2013.10.021
Pathak, P., Shukla, P., Kanshana, J. S., Jagavelu, K., Sangwan, N. S., Dwivedi, A. K., et al. (2021). Standardized root extract of Withania somnifera and Withanolide A exert moderate vasorelaxant effect in the rat aortic rings by enhancing nitric oxide generation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 278, 114296. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114296
Pelzer, F., Tröger, W., and Nat, D. R. (2018). Complementary treatment with mistletoe extracts during chemotherapy: safety, neutropenia, fever, and quality of life assessed in a randomized study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 24 (9-10), 954–961. doi:10.1089/acm.2018.0159
Qi, Y., Li, H., Guo, Y., Cao, Y., and Wong, C. L. (2024). Symptom clusters in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: a systematic review. J. Clin. Nurs. 33 (12), 4554–4567. doi:10.1111/jocn.17479
Saghatelyan, T., Tananyan, A., Janoyan, N., Tadevosyan, A., Petrosyan, H., Hovhannisyan, A., et al. (2020). Efficacy and safety of curcumin in combination with paclitaxel in patients with advanced, metastatic breast cancer: a comparative, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 70, 153218. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153218
Salanti, G., Ades, A. E., and Ioannidis, J. P. (2011). Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64 (2), 163–171. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.03.016
Semiglasov, V. F., Stepula, V. V., Dudov, A., Lehmacher, W., and Mengs, U. (2004). The standardised mistletoe extract PS76A2 improves QoL in patients with breast cancer receiving adjuvant CMF chemotherapy: a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicentre clinical trial. Anticancer Res. 24 (2c), 1293–1302.
Semiglazov, V. F., Stepula, V. V., Dudov, A., Schnitker, J., and Mengs, U. (2006). Quality of life is improved in breast cancer patients by standardised mistletoe extract PS76A2 during chemotherapy and follow-up: a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicentre clinical trial. Anticancer Res. 26 (1B), 1519–1530.
Shamseer, L., Moher, D., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., et al. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. Bmj 350, g7647. doi:10.1136/bmj.g7647
Shehab, M., Alrashed, F., Alsayegh, A., Aldallal, U., Ma, C., Narula, N., et al. (2025). Comparative efficacy of biologics and small molecule in ulcerative colitis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 23 (2), 250–262. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2024.07.033
Singh, N., Yadav, S. S., Rao, A. S., Nandal, A., Kumar, S., Ganaie, S. A., et al. (2021). Review on anticancerous therapeutic potential of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal. J. Ethnopharmacol. 270, 113704. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113704
Smolarz, B., Nowak, A. Z., and Romanowicz, H. (2022). Breast cancer-epidemiology, classification, pathogenesis and treatment (Review of literature). Cancers (Basel) 14 (10), 2569. doi:10.3390/cancers14102569
Strijbos, B. T. M., Janssen, L., Voogd, A. C., Zwaans, W. A. R., Roumen, R. M. H., and Maaskant-Braat, A. J. G. (2024). Persistent pain after breast cancer treatment, an underreported burden for breast cancer survivors. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 31 (10), 6753–6763. doi:10.1245/s10434-024-15682-2
Taniguchi, K., and Karin, M. (2018). NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 18 (5), 309–324. doi:10.1038/nri.2017.142
Thamlikitkul, L., Srimuninnimit, V., Akewanlop, C., Ithimakin, S., Techawathanawanna, S., Korphaisarn, K., et al. (2017). Efficacy of ginger for prophylaxis of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in breast cancer patients receiving adriamycin-cyclophosphamide regimen: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Support Care Cancer 25 (2), 459–464. doi:10.1007/s00520-016-3423-8
Tröger, W., Zdrale, Z., Tišma, N., and Matijašević, M. (2014). Additional therapy with a mistletoe product during adjuvant chemotherapy of breast cancer patients improves quality of life: an open randomized clinical pilot trial. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 430518. doi:10.1155/2014/430518
Valente, I. V. B., Garcia, D., Abbott, A., Spruill, L., Siegel, J., Forcucci, J., et al. (2024). The anti-proliferative effects of a frankincense extract in a window of opportunity phase ia clinical trial for patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 204 (3), 521–530. doi:10.1007/s10549-023-07215-4
Wallace, B. C., Schmid, C. H., Lau, J., and Trikalinos, T. A. (2009). Meta-analyst: software for meta-analysis of binary, continuous and diagnostic data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 9, 80. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-9-80
Wang, C., Huang, Q., Liang, C. L., Zhang, Y. W., Deng, D. H., Yu, Y., et al. (2019). Effect of cimicifuga racemosa on menopausal syndrome caused by LHRH-a in breast cancer. J. Ethnopharmacol. 238, 111840. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.111840
Wang, S., Long, S., Deng, Z., and Wu, W. (2020). Positive role of Chinese herbal medicine in cancer immune regulation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 48 (7), 1577–1592. doi:10.1142/s0192415x20500780
Wang, Z., Tu, C., Pratt, R., Khoury, T., Qu, J., Fahey, J. W., et al. (2022). A presurgical-window intervention trial of isothiocyanate-rich broccoli sprout extract in patients with breast cancer. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 66 (12), e2101094. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202101094
White, P. T., Subramanian, C., Motiwala, H. F., and Cohen, M. S. (2016). Natural withanolides in the treatment of chronic diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 928, 329–373. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-41334-1_14
Keywords: breast cancer, plant active substance, network meta-analysis, quality of life, randomized controlled trials
Citation: Wang L, Xu X, Guo M, Dong Y, Ding H, Hao S, Huo L, Song Y, Gu J and Yu Z (2025) Systematic review and network meta-analysis of the effects of plant active substance on quality of life in breast cancer patients. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1622479. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1622479
Received: 03 May 2025; Accepted: 30 October 2025;
Published: 28 November 2025.
Edited by:
Jean Christopher Chamcheu, Louisiana State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Cassiano Merussi Neiva, São Paulo State University, BrazilArpana Parihar, Advanced Materials and Processes Research Institute (CSIR), India
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Xu, Guo, Dong, Ding, Hao, Huo, Song, Gu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenghong Yu, MTMzMjc4MDAxODJAMTg5LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Lu Wang
Lu Wang Xiaofan Xu
Xiaofan Xu Mengmeng Guo3
Mengmeng Guo3 Yanxu Dong
Yanxu Dong Shuai Hao
Shuai Hao Jun Gu
Jun Gu