- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Postdoctoral Mobile Station of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
- 4Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Shaoxing Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Shaoxing, China
Endometriosis (EMs) is a prevalent benign gynecological disorder characterized by dysmenorrhea and infertility, significantly impacting women’s health and quality of life. Currently, the pathogenesis of EMs remains incompletely elucidated. There are various side effects of drug treatment, while surgical interventions involve a certain degree of tissue trauma. Therefore, novel therapeutic drugs and clinical strategies should be developed. Apoptosis, a programmed cell death pathway, maintains tissue homeostasis, and its dysregulation is linked to various diseases and pathological complexities. Accumulating evidence suggests that abnormal apoptosis is intricately linked to the development and progression of EMs and that targeted promotion of cell apoptosis may contribute to the prevention and treatment of EMs. Natural metabolites, with their biological properties such as multipathway and multitarget effects, exhibit unique advantages in treating EMs, possibly by regulating apoptosis. This paper reviews the relationship between apoptosis and EMs. It systematically summarizes the latest progress of natural metabolites in treating EMS by regulating apoptosis, offering an innovative strategy for treating EMs.
1 Introduction
Endometriosis (EMs) constitutes a prevalent chronic gynecological disorder characterized by the presence of functional endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterine cavity (Crump et al., 2024). Affecting 6%–10% of women of reproductive age (Zondervan et al., 2020), it typically presents with dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain, and infertility. Epidemiological surveys have shown that the prevalence of EMs increases to approximately 30% among infertile patients and reaches up to 45% among those with chronic pelvic pain (Mounsey et al., 2006). In addition, although EMs is a benign disease, it exhibits typical features of malignant tumors, such as progressive and invasive growth, estrogen-dependent growth, and a tendency to recur and metastasize (Steinbuch et al., 2024). Various pathogenic mechanisms have been proposed for the development of EMs, including genetics, hormones, and immune factors. (Burney and Giudice, 2019; Saunders and Horne, 2021; Taylor et al., 2021; Vannuccini et al., 2022). In recent years, spontaneous apoptosis of the endometrium has been recognized as essential for maintaining its normal structure and function, whereas aberrant apoptosis promotes the development and progression of EMs (Yang et al., 2024).
Apoptosis, a distinct type of programmed cell death, is critical for eliminating damaged or unwanted cells (Zhong et al., 2024). Apoptosis is also pivotal in maintaining cellular homeostasis of tissues. Dysregulation of this process has been linked to diverse diseases and pathologies (Bertheloot et al., 2021), including neurodegenerative disorders, ischemic injuries, autoimmune diseases, and various types of cancer (Elmore, 2007). Under normal conditions, apoptosis destroys ectopic and eutopic endometrial cells before they form necrotic tissues, thereby preventing cell migration and accumulation (Agic et al., 2009; Taniguchi et al., 2011; Kobayashi et al., 2024). This underscores the critical role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of EMs. Related studies have confirmed that in women with EMs, the eutopic endometrium shows increased expression of anti-apoptotic factors and decreased expression of pro-apoptotic factors, compared with the endometrium of healthy women (Harada et al., 2007). Such differences might facilitate the survival of refluxed endometrial cells within the abdominal cavity, thereby driving the progression of EMs. The potential of modulating apoptosis as a promising therapeutic approach for EMs has now been widely recognized. Therefore, an increasing number of studies are focusing on developing drugs to ameliorate EMs by promoting apoptosis.
In recent years, natural metabolites have emerged as an integral part of new drug development, especially those derived from plants. Natural metabolites treat EMs through a variety of molecular mechanisms, including pro-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and antioxidant effects (Meresman et al., 2021). Systematic reviews and meta-analyses have further confirmed their efficacy, safety, and tolerability of natural metabolites, positioning them as a promising option for EMs. Numerous studies have indicated that natural metabolites are derived from a wide range of fruits and vegetables. Traditional Chinese medicinal plants are more suitable for long-term complementary and alternative therapies due to their low medication cost, fewer side effects, and higher safety profile (Xu et al., 2022). However, a large number of natural metabolites, such as quercetin, ginsenosides, curcumin, naringenin, and baicalein, show considerable potential to induce apoptosis. In light of this, this paper delves into the pathological mechanisms of apoptosis in EMs and explores natural metabolites targeting apoptosis for the treatment of EMs. Additionally, it discusses the limitations and challenges of this therapy. The aim is to provide novel strategies for developing therapeutic agents against EMs and meaningful references for related research.
2 Search strategy and selection criteria
We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, and SinoMed databases using “endometriosis”, “apoptosis”, “natural compounds”, “natural products”, “Chinese herbal monomers”, “Chinese herbal extracts”, and related MeSH terms as keywords. Studies published between January 2004 and December 2024 were included, and the reference lists of eligible articles were further screened to identify additional relevant literature. Initially, 985 articles were identified through initial database searches. Subsequently, studies potentially affected by selection bias, detection bias, reporting bias, or other bias sources were excluded. Finally, 79 studies were considered eligible for inclusion in this review.
3 Major molecular mechanisms of apoptosis
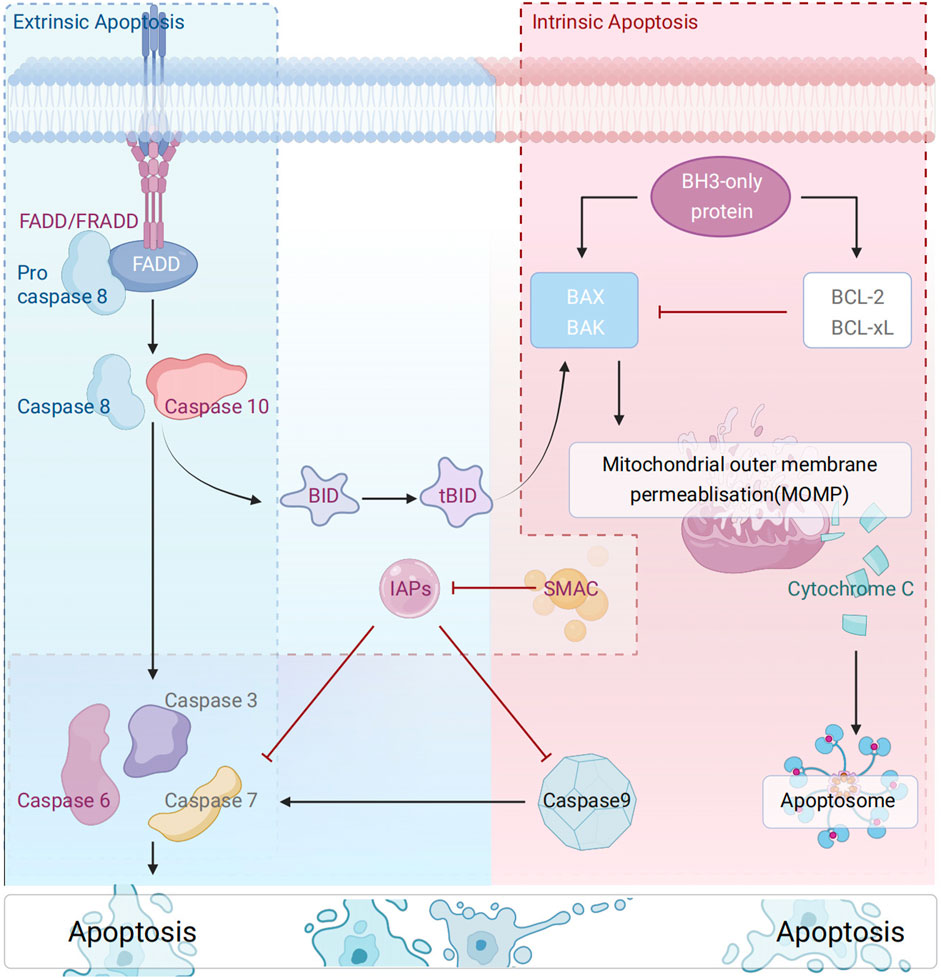
Apoptosis, a programmed death mechanism precisely regulated by genes, is central to the maintenance of organismal homeostasis (Mustafa et al., 2024). It is associated with a series of cellular morphological and functional changes, including cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation (accompanied by characteristic DNA fragmentation), plasma membrane blebbing, and the formation of phagocytotrophic apoptotic bodies (Bortner and Cidlowski, 2002; Dejas et al., 2023). Current studies have clearly defined two core apoptotic pathways: the mitochondria-dependent intrinsic pathway and the death receptor-mediated extrinsic pathway (Chinnaiyan, 1999; Dlamini et al., 2004; Yuan and Ofengeim, 2024). As confirmed by previous studies, the former is mediated by the dynamic homeostasis of the Bcl-2 family mediating the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition. Conversely, the latter activates the caspase cascade via the DISC complex; the two pathways ultimately converge at the co-activation of effector caspases (e.g., caspase-3/7) and the amplification of MOMP-dependent signaling, thus forming a sophisticated programmed cell death network (Figure 1).
The mitochondrial pathway is the central route of intrinsic apoptosis, whose progression is governed by the delicate balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family (Kale et al., 2018). Functionally, Bcl-2 family proteins are classified into three subgroups: (1) anti-apoptotic proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, Bcl-W), (2) pro-apoptotic pore-forming proteins (e.g., Bax, Bak, Bok), (3) pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins (e.g., Bad, Bid, Bik, Bim, Bmf, etc.) (Kim et al., 2009)., BH3-only proteins (key mediators of the mitochondrial pathway) regulate BAX/BAK activation through a dual mechanism: (1) direct activators (e.g., BID, BIM, PUMA) (Wei et al., 2000); (2) indirect regulators (e.g., BAD) (Wei et al., 2000; Czabotar et al., 2009; Huang K. et al., 2019).: Notably, recent studies have suggested that all BH3-only proteins can indirectly activate BAX/BAK by antagonizing BCL-xL/MCL-1 (Antignani and Youle, 2006), a hypothesis that warrants further validation and exploration. Furthermore, studies have shown that BAX/BAK activation and oligomerization during intrinsic apoptosis drive the formation of the mitochondrial outer membrane permeability transition pore (mPTP), triggering the release of mitochondrial contents (Ehrmann et al., 2023). This, in turn, activated and amplified apoptotic signaling. In the cytoplasm, SMAC (Second Mitochondrial Activator of Caspases)/OMI (also known as HtrA2) synergistically enhances apoptotic signaling by binding to X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) (Brentnall et al., 2013; Jost and Vucic, 2020). Additionally, stimuli such as DNA damage, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and mitotic defects can activate this apoptotic cascade (Nuñez et al., 1990; Zou et al., 1997; Czabotar et al., 2014).
The extrinsic apoptotic pathway is initiated by the activation of death receptors (e.g., Fas/TNF-R1/DR4-5), which recruit adaptor proteins such as FADD (Fas-associated death domain protein)/TRADD (TNF receptor-associated death domain protein) (Nagata, 2018). Among them, FADD recruits procaspase-8 (cysteine precursor-8) to form a death-induced signaling complex (DISC) at the plasma membrane surface (Han et al., 2023). This facilitates the initiation of the apoptotic execution program. The phosphorylation status of RADD, a TNF-R1-specific adaptor protein, dictates the direction of apoptotic signaling. The execution of these processes is intricately linked to the TNF receptor superfamily, the core regulatory hub of extrinsic apoptosis. The TNF receptor superfamily specifically activates cysteine proteases of the caspase family via ligand-receptor binding, particularly the caspase-8 signaling axis (Chipuk et al., 2006; Hughes et al., 2016). In apoptosis, beyond the caspase-dependent pathway, mitochondrial outer membrane permeability (MOMP) leads to the release of apoptosis-inducing factor AIF (a mitochondrial oxidoreductase). AIF directly induces DNA fragmentation and chromatin condensation via the caspase-independent pathway, serving as a key node connecting the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. This factor directly induces DNA breaks and chromatin condensation through the caspase-independent pathway. Additionally, AIF serves as a key hub connecting the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways (Lorenzo et al., 1999; Kuan et al., 2021).
Apoptosis can be subdivided into extrinsic and intrinsic types. Extrinsic pathway: The process commences with the binding of the death receptor to the receptor, resulting in the activation of the intracellular domain, or DD, of the death ligand. Through the activity of the adaptive molecules FADD and TRADD, a connection is established with the DED domain of the Caspase-8 proenzyme, resulting in the formation of the DISC complex. The proenzyme Caspase-8 undergoes self-catalysis to produce active Caspase-8. The stimulation of downstream effectors Caspase-3, -6, and -7 by Caspase-8 results in substrate breakage and triggers cellular death. Intrinsic pathway: Internal cellular injury causes apoptosis of Bcl-2 family members, including Bad, which enhances the porosity of the mitochondrial outer membrane and facilitates the release of cytochrome c (Cytc) from the intermembrane gap of the mitochondria. The released Cytc engages with Apaf-1 and Caspase9 proenzymes in the cytoplasm to create an apoptotic complex that autonomously catalyzes the activation of Caspase9. The activation of downstream effectors Caspase-3, -6, and -7 by Caspase-9 results in substrate breakage and triggers cellular death.
4 Apoptosis in the pathogenesis of EMs
Studies have shown that the endometrium achieves cyclic proliferation and shedding through tightly regulated cell proliferation and apoptosis mechanisms, which are crucial for maintaining normal physiological functions. Therefore, apoptosis is pivotal in maintaining the cyclic structural and functional stability of endometrial cells (Doroftei et al., 2021). However, aberrant apoptosis—characterized by decreased susceptibility of endometrial cells to apoptosis—enhances their ability to grow at ectopic sites. This may further promote the development and progression of EMs (Depalo et al., 2009). Consequently, the apoptotic mechanism is intricately tightly linked to EM pathogenesis, underscoring the importance of investigating the role of apoptosis in EMs.
Bcl-2 and Bax, key proteins of the mitochondrial pathway, are involved in regulating morphological and functional changes in the normal endometrium. The ratio of these two factors determines the kinetics of endometrial cell apoptosis (Johnson et al., 2005). Their aberrant expression leads to dysregulation of apoptosis in endometrial cells. The Bcl-2/Bax expression ratio in the ectopic endothelial tissues of patients is significantly elevated, interfering with mitochondrial cytochrome C release. This, in turn, blocks the activation of the caspase protease cascade, reducing the apoptosis rate and facilitating the survival, implantation, and infiltration of ectopic endometrium (Junqi and Yan, 2008; Chen et al., 2019). Concurrently, oxidative stress induced by excessive mitochondrial ROS is critical for apoptosis in EMs cells (Rossi et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2019; Assaf et al., 2022). PGC-1α and PGC-1β, which inhibit estrogen receptor β (ERβ) activation, promote Nrf2 expression. In EMs, sustained Nrf2 activation induces mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, leading to excessive oxidative stress that may affect apoptosis. As a result, apoptosis is also affected (Haider and Knöfler, 2009; Liao et al., 2019).
Pro-apoptotic receptors and their ligands on endometrial cell surfaces are also pivotal in the pathogenesis of EMs (Gogacz et al., 2017). Fas functions as a death receptor on activated cell surfaces, regulating NK cells and lymphocytes to induce apoptosis (Garcia-Velasco et al., 1999). Conversely, further studies have shown a stage-dependent decrease in Fas ligand (FasL) expression in the ectopic endometrium of EMs patients (Bellezza et al., 2018). The Fas-FasL axis may also enable ectopic endometrial cells to evade immune surveillance, thereby promoting disease progression. Furthermore, it has been confirmed that apoptosis in EMs cells is positively regulated by p53. In contrast, endometriotic cells exhibit a Warburg effect, which increased glycolysis suppresses apoptosis by inhibiting excessive ROS production (Leonte et al., 2023). In addition, under hypoxic conditions, aberrant autophagy in EMs impedes apoptosis. Collectively, multiple biological mechanisms have been implicated in EM-associated apoptosis and disease progression, including the classical mitochondrial pathway, mitochondrial oxidative stress, Fas receptor-mediated apoptosis, and hypoxic stress.
5 Role of natural metabolites in apoptosis in EMs
Building on the established role of apoptosis in EMs pathogenesis, an expanding body of research has identified numerous natural metabolites with chemopreventive and therapeutic potential for EMs via apoptotic targeting. These apoptosis-promoting natural metabolites encompass a diverse array of plant-derived metabolites including terpenes, polyphenol quinones, phenylpropanoids, and alkaloids. Interestingly, by regulating MAPK, NF-κB, Nrf2, and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways as well as their unique molecular mechanisms to induce apoptosis, such natural metabolites exhibit multi-target and multi-pathway characteristics. Herein, we summarize naturally occurring apoptosis promoters and discuss their biological significance in EMs (Figure 2).
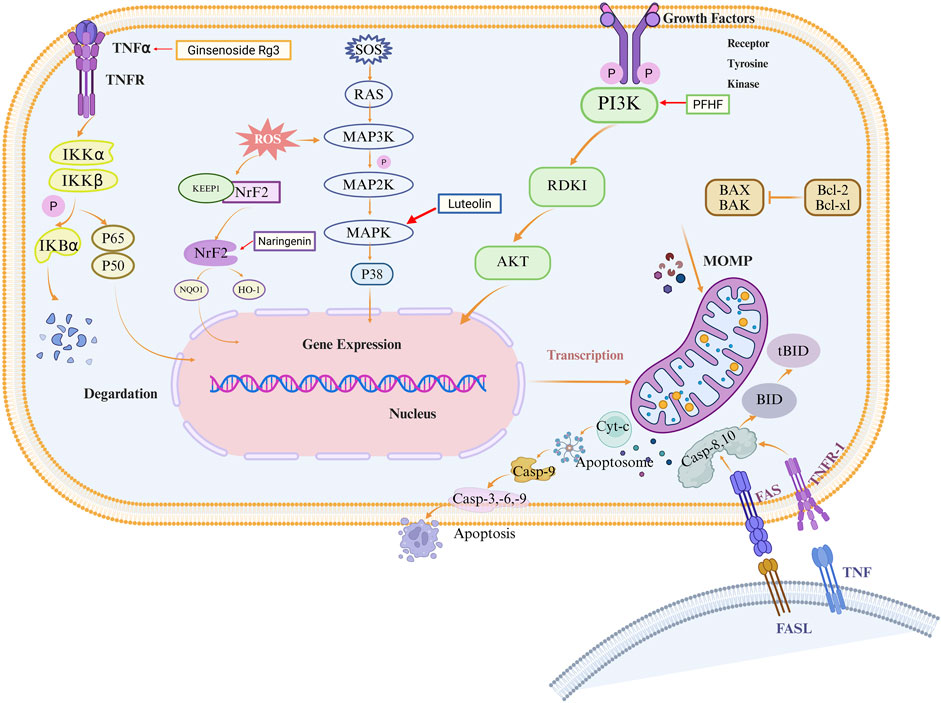
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of natural metabolites’ molecular mechanisms for the prevention and treatment of EMs by promoting apoptosis. Natural metabolites such as polyphenols, terpenes, quinones, phenylpropanoids, alkaloids, etc., mediate multiple signaling pathways such as MAPK, NF-κB, Nrf2, and PI3K/AKT, which induce intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis in EMs cells.
5.1 Polyphenols
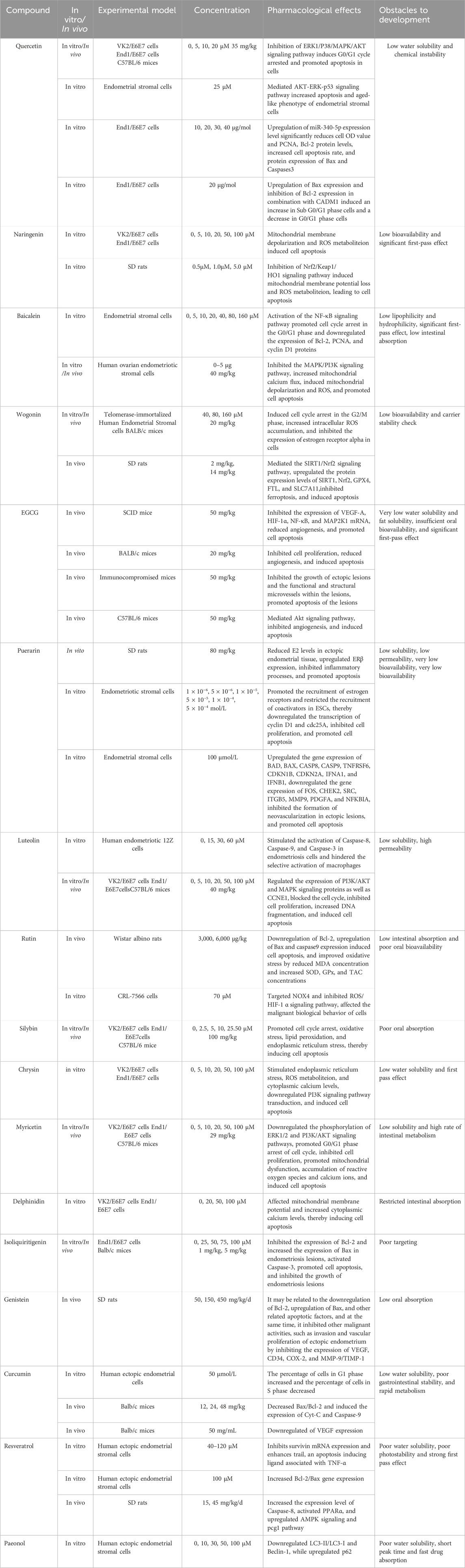
Polyphenols, primarily derived from natural metabolites, are a group of phytochemicals containing hydroxyl groups and one or more aromatic rings, including flavonoids, tannins, phenolic acids, and anthocyanins (Goel et al., 2023). There is growing evidence that polyphenols from medicinal plants exert therapeutic effects through multiple biological activities such as free radical scavenging, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and pro-apoptotic activities (Wu et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022). Table 1 summarizes the mechanisms by which curcumin, resveratrol, quercetin, naringenin, baicalein, wogonin, and other polyphenolic metabolites improve endometriosis via apoptosis induction.
5.1.1 Flavonoids
Flavonoids are ubiquitously distributed in nature, predominantly existing in a glycosylated form in numerous medicinal plants, vegetables, and fruits (Bouyahya et al., 2021; Elham et al., 2021). Contemporary studies have confirmed their diverse pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and cardiovascular protective effects (Fischer et al., 1997; Huang T. et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2021). Regarding the treatment of EMs, several flavonoids, such as quercetin, naringenin, baicalein, and wogonin, exert therapeutic effects by inducing apoptosis, primarily through cell cycle arrest induction, endoplasmic reticulum stress activation, ferroptosis inhibition, and mitochondrial function disruption, thereby triggering apoptosis (Figure 3).
5.1.1.1 Quercetin
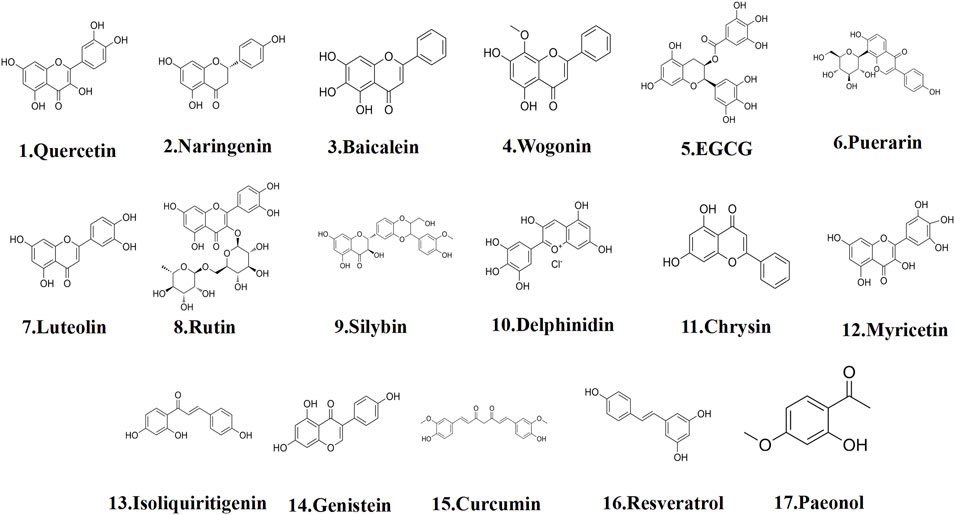
Quercetin, a major dietary flavonol, is isolated from Sophora japonica L. (syn. Sophora japonica L.), is widely distributed in various common fruits and vegetables, such as Allium cepa L. (onion) and Brassica oleracea var. botrytis (cauliflower) (Ranganathan et al., 2015). As reported, it features various apoptotic effects in obesity, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, and a variety of tumor cells (Bishayee et al., 2013; Maciejczyk and Surowiak, 2013). Unsurprisingly, quercetin shows a significant pro-apoptotic potential to act as an apoptosis inducer in EMs. For example, Park et al. (Qingjing et al., 2023) observed in vitro experiments that 20 μM quercetin maximally blocked the cell cycle in a dose-dependent manner. This further resulted in a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, DNA breaks, and reactive oxygen species production. Concurrently, an in vivo study revealed that CCND1 mRNA expression was substantially reduced after intraperitoneal injection (35 mg/kg) of quercetin. This stalled the cell cycle in the G0/G1 period and increased End1/E6E7 apoptosis, as compared to the blank group (Park et al., 2019a). Further studies have found that quercetin at a concentration of 25 μM could significantly enhance apoptosis and senescence-like phenotypes. It promoted the dedifferentiation of endometrial stromal cells in both control and endometriotic EMs. The underlying mechanisms involve two aspects: one is attenuating the phosphorylation of multiple signaling molecules in the AKT and ERK1/2 pathways, and the other is increasing the phosphorylation levels of p53 and the total amount of p53 (Delenko et al., 2024). In addition, quercetin might inhibit the proliferation of End1/E6E7 cells and promote cell apoptosis by upregulating miR-340-5p (Papari et al., 2020). Another in vitro study utilizing the identical cell model as the research object demonstrated that quercetin (20 μg/mol) promoted the expression of Bax and inhibited the expression of Bcl-2, This led to an increase in Sub G0/G1 phase cells and a decrease in G0/G1 phase cells, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis (Jin et al., 2020). Nonetheless, certain investigations have indicated that the limited aqueous solubility and chemical instability of quercetin considerably restrict its absorption efficacy (Alizadeh and Ebrahimzadeh, 2022). Consequently, we can clarify the mechanism of pleiotropy by concentrating on the optimization of delivery systems and the resolution of toxicity mechanisms, while also integrating multi-omics techniques (e.g., transcriptomics and metabolomics) to elucidate pleiotropy and enhance the clinical application of quercetin-based versatile collaboration systems. In conclusion, quercetin may provide innovative ideas and targets as a treatment for EMs. Most current studies focus on in vitro and in vivo studies. However, the lack of clinical trials in humans precludes the elucidation of quercetin’s in vivo mechanisms.
5.1.1.2 Naringenin
Naringenin (from Ruta graveolens L.) is predominantly found in Citrus paradisi Macfadyen (grapefruit) and Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck (sweet orange), and it constitutes a major phytochemical metabolite (Kawaii et al., 1999). It is a phytoestrogen featuring multiple effects, such as blocking the cell cycle, inducing ROS production, and inducing apoptosis (Lim et al., 2017). With research deepening, researchers focused on EMs and found that in the VK2/E6E7 and End1/E6E7 cell lines, naringenin targeted the MAPK and PI3K pathways in a dose-dependent manner. It upregulated pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bak via mitochondrial membrane potential depolarization, an increase in ROS production, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. As a result, it inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis (Park et al., 2017). In addition, naringenin significantly inhibited the expression of Nrf2 and its downstream effector molecules (NQO1, HO-1, etc.), causing a dose-dependent loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and inducing apoptosis (Kapoor et al., 2019). Naringenin, similar to quercetin, is characterized by low bioavailability and a pronounced first-pass effect (Cai et al., 2023). However, these problems may be solved by nanotechnology (e.g., liposomes), novel drug modifications, etc., in anticipation of its optimal clinical application (Vakilzadeh et al., 2021). Collectively, these results suggest naringenin’s pro-apoptotic potential in human EMs. However, evidence is mostly from in vitro studies, lacking in vivo data. It is anticipated to overcome current bottlenecks in molecular development and emerge as a promising natural drug candidate that have both therapeutic efficacy and safety.
5.1.1.3 Baicalein
Baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone), a flavonoid metabolite, is isolated from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (Lamiaceae) (Krawczyk et al., 2016). This metabolite exhibits multiple pharmacological properties multiple pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, antiallergic, antioxidant, and cytoprotective effects (Kim et al., 2005). A recent study revealed that treatment of human endometrial stromal cells with baicalein (40 µM) for 48 h resulted in a significant increase in the number of cells in the G0/G1 phase, as well as a significant decrease in the number of cells in the S phase and G2/M phase. Furthermore, the protein expression of Bcl-2, PCNA, and Cyclin D1 in the cells also decreased significantly. Activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway inhibits stromal cell viability, potentially inducing apoptosis (Jin et al., 2017). Existing studies have shown that iron accumulation can affect the expression of macrophage apoptosis genes and related proteins (HMOX1, FTH1, FTL) in ectopic tissues. Conversely, baicalein (20 µM) may increase the expression of GPX4, significantly inhibit ferroptosis, and then restore the phagocytosis of THP-1 cells, or induce apoptosis through this pathway (Yi et al., 2022). Due to its significant anti-inflammatory properties, baicalein reduced pro-inflammatory factor expression in ihOESCs. Additionally, it promoted apoptosis in these cells, increased mitochondrial calcium flux, and induced mitochondrial depolarization and ROS production (Park et al., 2024). Existing delivery systems can address its poor lipophilicity and hydrophilicity, significant first-pass effect, and lower intestinal absorption of baicalein due to the molecular structure of baicalein (Huang et al., 2014; Yu et al., 2017). Therefore, future studies should also integrate more precise delivery strategies to promote the efficient transformation of baicalein from natural metabolite to clinical drug.
5.1.1.4 Wogonin
Wogonin (WG), derived from the same source as baicalein, has been shown to possess anti-tumor, anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory, and pro-apoptotic properties in distinct studies (Li-Weber, 2009; Wu et al., 2016). WG constitutes one of the active ingredients in Wenjing Tang (a classic formula for treating EMs), which may treat endometriosis by modulating inflammation and endocrine secretion (Liu et al., 2021). In vitro studies confirmed that Treating THESC cells with WG (40 μM, 80 µM) for 24 h significantly inhibited cell proliferation, induced G2/M phase arrest in T-HESC cells, increased intracellular ROS accumulation, and inhibited the expression of estrogen receptor. Further, in vivo studies indicated that WG (20 mg/kg) notably reduced the size of ectopic lesions, decreased the proliferating cells, and increased the rate of apoptotic cells (Ferella et al., 2018). In addition, WG significantly ameliorated the histopathological damage of ectopic endometrial tissue and reduced the serum levels of E2, P, IL-1β, and IL-6 (Xiaoying et al., 2023). In contrast to the extensively studied baicalein, research on wogonin has primarily focused on conventional nanoparticulate formulations, with stability posing a more significant challenge (Yu et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2022). Collectively, both in vivo and in vitro experiments have convincingly demonstrated its therapeutic effects. Its increased clinical application is eagerly anticipated, which will help elucidate the safety and efficacy of this treatment.
5.1.1.5 Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), found in Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze, demonstrates a variety of antioxidant, anti-angiogenic, and pro-apoptotic pharmacological effects (Zaveri, 2006; Khan and Mukhtar, 2008). Upon intraperitoneal injection of EGCG (50 mg/kg), it significantly downregulated the levels of VEGF-A and HIF-1α mRNA while up-regulating the levels of NF-κB and MAP2K1 mRNA, thereby promoting apoptosis in the foci and further reducing microvessel size and density resulting in a significant reduction of endometriotic foci, with a much smaller glandular epithelium, and an eccentrically distributed endometrium (Xu et al., 2009). In recent studies related to mouse models, this effect was also verified by EGCG (Ricci et al., 2013). While EGCG can effectively inhibit the occurrence and development of EMs, its bioavailability remains suboptimal. In response, the prodrug of EGCG (pro-EGCG, EGCG octaacetate) has been developed to improve the stability and bioavailability of EGCG in vivo. Findings from previous studies indicated that both EGCG and pro-EGCG significantly inhibited the growth of endometrial implants, disrupted the functional and structural microvasculature within the lesions, and promoted lesion apoptosis. Notably, pro-EGCG demonstrated a more potent effect (Wang et al., 2013). Using in vitro and in vivo gene knockdown assays and microvascular network imaging, recent research revealed distinct mechanisms of action between the two metabolites. While EGCG targeted the Akt pathway, pro-EGCG inhibited angiogenesis and exhibited stronger pro-apoptotic activities through the EGF/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway (Hung et al., 2024). These characteristics suggest that pro-EGCG may represent a novel anti-angiogenic therapeutic strategy for EMs. It holds promise for combination with existing clinical anti-angiogenic agents to enhance treatment efficacy.
5.1.1.6 Puerarin
Puerarin, a phytoestrogenic isoflavonoid metabolite isolated from Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi, has demonstrated therapeutic potential in the management of cardiovascular diseases, alcohol use disorder, and neurodegenerative conditions (Atteritano et al., 2007). As observed, puerarin (80 mg/kg) not only reduced E2 levels in serum and ectopic endometrial tissue but also promoted E2 metabolism by up-regulating 17β-HSD2 expression and down-regulating 17β-HSD1 expression. It reduced ER binding in E2 endometrial cells, interfered with the binding of E2-ER complexes to transcriptional regulatory proteins as well as initiated gene transcription, and thus inhibited the growth of ectopic endometrial lesions (Dassen et al., 2007; Yu et al., 2015). Meanwhile, it revealed that puerarin inhibited the above proliferation, which might be achieved partially by promoting co-inhibitor recruitment of the estrogen receptor, as well as restricting coactivator recruitment in endometrial cells, and down-regulating the transcription of cyclin D1 and cdc25A (Ji et al., 2013). In addition, puerarin could upregulate Erβ expression, inhibit the inflammatory process, and promote its apoptosis (Yu et al., 2015). Moreover, another in vivo study showed that puerarin could inhibit the formation of neovascularization in ectopic lesions, reduce the blood supply to the ectopic lesions, and promote apoptosis by modulating gene expression of EMs-related oncogenes, cell cycle, and apoptosis factors, thus inhibiting the tumor-like malignant behavior of EMs endothelial cells (Chaoqin et al., 2009). Puerarin has been shown to have low solubility and low permeability, which has led to its extremely low oral bioavailability (Li et al., 2014). Future research should focus on structural modification, the development of penetration enhancers to promote its conversion from a natural metabolite to a clinical drug, and systematic toxicological evaluations in order to fully utilize its therapeutic potential for the treatment of EMs.
5.1.1.7 Other flavonoids
In addition to the above flavonoid metabolites, several other natural metabolites associated with EMs apoptosis exist in nature, such as rutin, luteolin, total flavonoids of Polygala fallax Hemsl (PFHF), silibinin, delphinidin, chrysin, myricetin, isoglycoside (ISL), etc. All these have been shown to affect the apoptotic process in endometriosis in different ways. Rutin (from S. japonica L.) induced apoptosis by down-regulating Bcl-2 and up-regulating the expression of Bax and Caspase 9. It ameliorated oxidative stress and thus induced apoptosis by decreasing the concentration of MDA while elevating the concentration of SOD, GPx, and TAC (Talebi et al., 2021). In addition, rutin also inhibited endometriotic cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and promoted apoptosis via a mechanism possibly related to targeting NOX4 and blocking ROS/HIF-1α signaling (Haoran et al., 2023). Similarly, luteolin (from R. odorata L.)inhibited the growth of 12Z human endometriotic cells and induced intrinsic apoptosis through activation of Caspase-3, Caspase-8, and Caspase-9 (Khazaei et al., 2016). Further in vivo studies confirmed that luteolin dose-dependently increased cell cycle arrest, enhanced DNA breaks, and induced apoptosis, thereby inhibiting the development of EMs (Park et al., 2019c). Moreover, C. Zhong et al. observed that 0.6 mg/mL PFHF significantly affected the malignant biological behaviors of human ectopic endometrial stromal cells after 24 h of treatment, which might induce apoptosis of EESCs through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (Zhong et al., 2023). Derived from Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn, silymarin (from S. marianum), exerts pro-apoptotic, anti-proliferative, oxidative stress-inducing, and lipid peroxidation effects on human endometriosis cell lines by targeting the MAPK signaling pathway to induce endoplasmic reticulum stress (Ham et al., 2019). Similarly, chrysin induced programmed cell death through the aforementioned stress response (Ryu et al., 2019). Myricetin, a flavonoid metabolite derived from Morella rubra (Lour.), exhibits antiproliferative, antioxidant, and oxidative stress-inducing effects (Xie and Zheng, 2017). In vivo, studies of EMs have uncovered that it reduced lesion size in a mouse model of EMs by inhibiting Ccne1. In vitro, it induced apoptosis through inhibition of cell proliferation and cell cycle progression, as well as loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and accumulation of reactive oxygen species and calcium ions (Park et al., 2020). Concurrently, delphinidin (from Vaccinium myrtillus L.) exerted comparable effects on human endometrial cells. It modulated mitochondrial membrane potential and elevated cytoplasmic calcium levels in VK2/E6E7 and End1/E6E7 cells, ultimately triggering apoptosis (Park et al., 2019b). In contrast, another Isoliquiritigenin (ISL) isolated from Glycyrrhiza glabra L. could reduce the size of lesions, downregulate serum levels of inflammatory cytokines, inhibit the progression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and induce apoptosis (Gai et al., 2015; Hsu et al., 2020). In addition, Genistein (Gen), an isoflavone metabolite derived from Glycine max (L.) Merr., inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces apoptosis (Hillman et al., 2007) This pro-apoptotic effect occurs in a dose-dependent manner, thereby slowing the progression of EMs. Interestingly, its mechanism of action might not involve the NF-κB signaling pathway. Instead, it could be associated with down-regulating Bcl-2, up-regulating the expression and activity of apoptotic factors such as Bax, and suppressing the invasion and angiogenesis of ectopic endometrium. This was achieved by inhibiting the expression of proteins such as VEGF, CD34, COX-2, and MMP-9/TIMP-1 (Huixing et al., 2014). Overall, most flavonoids are dependent on nano-delivery (e.g., PLGA, liposomes) or structural modifications (e.g., glycosylation, hydroxyethylation) due to poor solubility, first-pass effect, or limited intestinal metabolism (Li et al., 2023). Moreover, most of the available data are based on in vitro or short-term animal experiments, lacking long-term toxicology and metabolite safety assessment. We look forward to optimizing the perfect combination of the above substances with the existing formulation technology, which can be used in combination with existing drugs to expand the limits of their clinical applications (Liu F. et al., 2020). Undoubtedly, a variety of flavonoids can fully utilize their apoptosis-inducing ability in the treatment of EMs, which may provide more drug sources for the treatment of EMs and fully utilize their biological properties.
5.1.2 Non-flavonoids
Curcumin is a natural polyphenolic metabolite extracted from Curcuma longa L. (Patel et al., 2020). Multiple studies have validated curcumin’s potential as an effective treatment modality for EMs. This highlights its ability to trigger programmed cell death in endometriotic tissues (Kamal et al., 2021). Cao et al. (Cao H. et al., 2017) showed that 50 μmol/L curcumin increased apoptosis rates in human endometriotic and endometrial stromal cells in vitro following 24 h treatment. Further studies revealed that intraperitoneal injection of curcumin (12, 24, and 48 mg/kg) decreased the expression of the anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 and downregulated the expression of Bcl-2 mRNA in endometrial cells of BALB/c mice (Yu and Shah, 2007; Liang et al., 2009). This could increase the Baw/Bcl-2 ratio, induce the expression of cytochrome c, Caspase 9, and p53, and accelerate apoptosis in EMs (Anto et al., 2002). Additionally, curcumin could abrogate EMs by inhibiting NF-κB translocation and MMP-3 expression (Jana et al., 2012). In contrast, resveratrol, a polyphenolic metabolite derived from Reynoutria japonica Houtt., exhibits potent apoptosis-inducing activity (Bhardwaj et al., 2007; van Ginkel et al., 2007). It was confirmed that resveratrol (50 mg/mL) caused a significant increase in apoptotic cells in ectopic lesions, while significantly reducing the volume and weight of endometriotic lesions (Taguchi et al., 2016). Conversely, resveratrol could cause apoptosis in endometriotic stromal cells by inhibiting survivin mRNA expression and enhancing TNF-α-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), an apoptosis-inducing ligand associated with TNF-α (Kolahdouz-Mohammadi et al., 2020). Resveratrol induced apoptosis by down-regulating Bcl-2 expression and decreasing the Bcl-2/Bax ratio in EuESCs and CESCs(Chen et al., 2021; Gołąbek-Grenda et al., 2023). Additionally, it promoted apoptosis by increasing the expression level of Caspase-8 through upregulation of signaling pathways such as AMPK and PCG1 (Zhang et al., 2019). Concurrently, the therapeutic potential of paeonol (from Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) might be attributed to its antioxidant, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties (Erekat, 2018). A study showed that paeonol induced autophagy in ectopic endometrial stromal cells by down-regulating HIF-α. Hypoxia-induced autophagy was ameliorated by paeonol through down-regulating LC3 and Beclin-1 and up-regulating P62 (Pang et al., 2021), suggesting that paeonol inhibits autophagy-mediated cell death in the development of EMs. In addition, paeonol dose-dependently reduced the cell viability, proliferation, migration, and invasion of ectopic endometrial stromal cells. It also promoted apoptosis, thereby inhibiting the malignant biological behavior of the cells (Bolton and Dunlap, 2017). In conclusion, polyphenolic natural metabolites show promise as apoptosis inducers for EMs but face clinical translation barriers due to physicochemical properties (solubility/stability) and metabolic complexity. In the future, it is necessary to combine structural optimization and targeted delivery technologies, and strengthen the safety and dose-toxicity correlation studies of nanocarriers (Kong et al., 2024).
5.2 Terpenoids
Terpenoids, as a common class of metabolites in nature, are extensively found in a variety of medicinal plants (Baunach et al., 2015; Lu X. et al., 2023). Their specific typology is primarily shaped by the number of their carbon atoms in monoterpenes, diterpenes, triterpenes, etc. (Figure 4) (Huang et al., 2023). Terpenoids have demonstrated significant potential in the treatment of endometriosis by virtue of their ability to induce apoptosis in multiple ways. Table 2 summarizes their multiple core mechanisms, such as mitochondrial apoptosis pathway regulation and ferroptosis regulation, which trigger cell apoptosis. Moreover, representative metabolites like ginsenosides and pachymic acid can achieve therapeutic synergy through the above-mentioned multi-target synergistic regulatory network.
5.2.1 Ginsenoside Rg3
Ginsenoside Rg3, a terpenoid metabolite obtained from Panax ginseng C.A.Mey., exhibits multiple pharmacological effects including immunomodulation, fatigue alleviation, cardiomyocyte protection, and anti-diabetic and anti-cancer activities (Liu X. et al., 2020). It significantly inhibited endometrial stromal cells’ proliferation and induced apoptosis to inhibit EMs by inducing cell cycle blockade (Liqing et al., 2018). Similarly, low-to-medium concentrations (0.625 × 10−4 mol/L) enhance apoptosis, whereas medium-to-high concentrations (1.25 × 10−4 mol/L, 1.25 × 10−4 mol/L) induced G1-phase arrest and inhibit mitosis (Shaohui and Zhaoai, 2019). An in-depth study of the mechanism suggested that it might, on the one hand, act on the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to downregulate the expression of VEGF, p-Akt, and p-mTOR, inhibit angiogenesis, and promote cell apoptosis (Cao Y. et al., 2017). On the other hand, it might be closely related to the conventional NF-κB signaling pathway, decreasing the expression of NF-κB p65, IL-8, cIAP-2 mRNA, and VEGF, upregulating the expression of Caspases 3, and increasing the rate of apoptosis in endometrial stromal cells (Huang et al., 2020). In summary, ginsenoside Rg3 has the potential to serve as a precise natural lead compound for the treatment of EMs. The advancement of ginsenoside Rg3 as a medicinal pharmaceutical encounters numerous obstacles: The compound’s inadequate water solubility results in diminished bioavailability, evidenced by a total bioavailability of merely 2.63% in rat studies (Xie et al., 2005), making it difficult to reach an effective therapeutic concentration. In addition, its potential toxicity should not be ignored, and high doses may cause gastrointestinal discomfort and hepatotoxicity (Kim et al., 2018). Future development of innovative drug delivery methods is essential to enhance bioavailability and minimize toxicity, accompanied by comprehensive clinical trials to assess their effectiveness and safety.
5.2.2 Tanshinone IIA
Tanshinone IIA (from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) has multiple anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities (Long et al., 2019). Intraperitoneal injection of Tanshinone IIA (30 mg/kg) significantly improved the symptoms of EMs, while reducing the volume of ectopic tissues in rats. This was achieved by inhibiting the TGF-β/SMADS signaling pathway, down-regulating the expression of cytokines, such as VEGF, MMP9, Bcl2, and TGF-β1, and up-regulating the expression of apoptotic proteins, such as Bax and Caspase 9 (Jianghong et al., 2016; Zhongling et al., 2021). In addition, it was also observed to decrease 14-3-3ζ, a key protein for maintaining cellular homeostasis, thereby promoting apoptosis (Wan et al., 2015). Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate (STS), a derivative of Tanshinone IIA, overcomes its water solubility limitation (Zhou et al., 2019). STS shranks lesions and activated p53, Sav1, and CCN1. Meanwhile, it inhibited factors such as HAS2 and GM-CSF, which in turn induced apoptosis (Luo et al., 2020). Despite its therapeutic potential, Tanshinone IIA faces clinical development challenges due to poor water solubility, leading to low oral bioavailability (Zhang et al., 2012). However, this challenge is expected to be addressed through novel formulations, such as solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN), which can significantly improve the bioavailability of tanshinone IIA.
5.2.3 Triptonoterpene
Triptonoterpene is a major diterpenoid metabolite derived from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. (Zhang et al., 2021). Data showed that the cell activity of Triptonoterpene (20 and 40 μg/mL) was significantly reduced upon treatment of the in situ mesenchymal endometrial cells for 48 h in a dose-dependent manner. Subsequent studies found that it inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis by increasing KISS-1 mRNA expression. This led to reduced Ki67 and Pro-Caspase3 levels while boosting Cleaved-Caspase3 and Bax protein expression (Xiao et al., 2002; Liling et al., 2021). Additionally, network pharmacological analysis of the main active substance in triptonoterpene revealed that it could act on several key signaling pathways of EMs. Meanwhile, it could also target the core of the treatment of EMs and give full play to its therapeutic effects (Dongfang et al., 2024). However, it's their physicochemical properties that lead to their limited absorption and distribution in the body. Meanwhile, the toxicity of triptonoterpene should not be ignored, as high doses may cause gastrointestinal discomfort, skin rash, central nervous system depression, and hematologic toxicity (Sun et al., 2013). Future research should focus on developing innovative drug delivery systems with precise dosage control to enhance their bioavailability and mitigate toxicity and conducting more extensive clinical trials to determine their safety and efficacy in humans.
5.2.4 Other terpenoids
In nature, numerous terpenoid metabolites are closely associated with the apoptosis of EMs cells. Lin et al. (Lin et al., 2024) demonstrated that pachymic acid (from Wolfiporia cocos F.A.Wolf) could reduce the volume of ectopic endometrium, inhibit cell proliferation, attenuate inflammatory responses, and regulate ferroptosis. It also might decrease the levels of MDA, TNF-α, and IL-6, inhibit ACSL4 and PTGS2 protein expression, and contribute to the expression of GSH. Moreover, the effect of a high dose of pachymic acid (7.0 mg/kg) seemed to be more pronounced. Picroside II, an iridoid glycoside metabolite derived from Picris hieracioides L., reduced adhesions in SD rats, inhibited angiogenesis and fibrosis, attenuated M2 macrophage polarization, and promoted apoptosis in ectopic endometrium. This might be achieved by inhibiting Bax, Bcl-2, VEGF, and TGF-β expression, remarkably decreasing the number of CD206+ macrophages (Jun et al., 2020). Chen et al. (Chen et al., 2022) demonstrated that Betulinic Acid (BA) is isolated from Betula pendula Roth, targets genes associated with estrogen receptor β (ERβ), including superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), nuclear respiratory factor-1 (NRF1), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1). It could inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, enhance oxidative stress, impair mitochondrial function, and promote the apoptosis of endometrial ectopic cells (Xiang et al., 2020). Meanwhile, as a natural antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, neroli oil had been found to significantly increase SOD and CAT levels after injection in model rats, thereby delaying the progression of EMs (Canday et al., 2024). Nerol (from Citrus L.) is the main natural metabolite of neroli oil, triggers mitochondrial dysfunction, and induces apoptosis by enhancing Ca2+ and oxidative stress (Tian et al., 2018). These findings suggest that neroli oil may serve as an apoptosis inducer for treating EMs. The terpene metabolite crocin extracted from Crocus sativus L. promoted apoptosis of ectopic endometrial cells. Meanwhile, it also inhibited the release of cellular inflammatory factors such as VFP, IL-6, TNF-α, etc., relieved symptoms, and slowed down the process (Liu et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2021). Curcumol (from Curcuma longa L.), a common terpenoid natural metabolite, was observed to induce apoptosis of endometrial stromal cells via a mechanism tightly linked to the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. As a result, it inhibits Bcl-2 protein expression, activates Bax and Caspase-3, and suppresses inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, thereby affecting the malignant biological behavior of the cells and reducing lesion size (Li et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2022). In contrast to curcumol, the action mechanism of dehydrocostus lactone (from Dolomiaea souliei var. cinerea) in treating EMs might be achieved through inhibition of the Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways. This increased the expression of Caspase-3, Caspase-8, and Caspase-9, and reduced the metabolism of pain-related neurotrophic factors such as BDNF, NGF, NT3, and NT4/5. Moreover, the expression levels of macrophage M2 markers as well as IL-10, VEGF, MMP-2, and MMP-9 were impeded, and apoptosis in 12Z human endometriotic cells was induced (Woo et al., 2019). In addition, ursolic acid (UA) is a member of terpenoids derived from Osmanthus fragrans Lour. (Song et al., 2012), increased Caspase-3 activity and inhibited the secretion of COX-2, PGE2, and VEGF in a dose-dependent manner, aiming to achieve the pharmacological activity of inhibiting angiogenesis and cell proliferation while promoting apoptosis (Li et al., 2020). However, most terpenoids face development barriers due to poor water solubility and rapid hepatic/gastrointestinal metabolism. Several approaches have been applied to address these issues, such as the preparation of liposomes, the development of terpenoid-loaded nanoparticles, and other innovative drug delivery systems (Cahova et al., 2017). In addition, further studies in animal models are needed to clarify subacute/chronic toxicity, molecular mechanisms, and structural modifications for developing novel therapies based on sesquiterpene lactones or derivatives.
5.3 Quinones
Quinoid metabolites, naturally abundant in nature, comprise benzoquinones, naphthoquinones, anthraquinones, and phenanthrenequinones, with anthraquinones and their derivatives being particularly prevalent (Gomes de Carvalho et al., 2023). Emodin is a natural anthraquinone found in the Rheum palmatum L. and exhibits antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, and anticancer effects (Zheng et al., 2020). Emodin induces apoptosis and inhibites invasion of ectopic endothelial and stromal cells via the downregulation of Bcl-2 expression, upregulation of Bax expression, and activating the Caspase-3 pathway (Zheng et al., 2016). Meanwhile, rhubarb-peach kernel herbal pair exerts anti-EMs effects by activating the p53 apoptotic signaling pathway, with emodin proposed as the key pro-apoptotic component (Liao et al., 2023). However, Zhang et al. (Yu and Hong, 2018) reported that shikonin, a naphthoquinone metabolite isolated from Lithospermum erythrorhizon Siebold and Zucc., enhances apoptosis in ectopic endometrial cells. This effect attenuated endometrial infiltration by modulating the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and accelerating ectopic cell apoptosis. The optimal efficacy was observed at a high shikonin concentration (5.6 mg/kg) (Hong and Yu, 2019). Collectively, these study results suggest that quinone-derived natural metabolites may fully activate the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis and show great potential for the treatment of EMs. However, quinone metabolites generally have clinical translation barriers such as poor water solubility, significant first-pass metabolism, and insufficient evidence of safety. Future research needs to focus on delivery system innovation (nano-delivery technology, colon-targeted delivery), optimization of structural modifications, establishment of humanized transgenic animal models, and simultaneous assessment of pharmacodynamic and metabolic regulatory effects and compound safety (Figure 5).
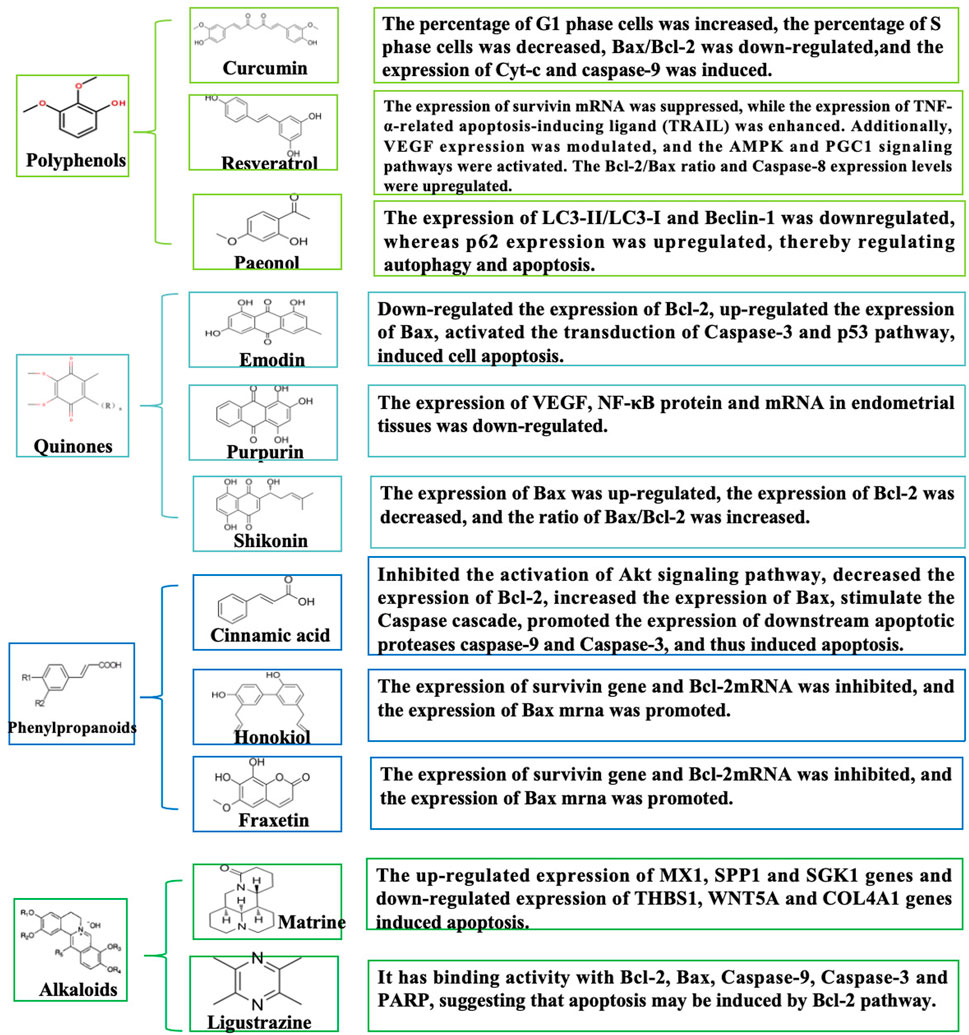
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of the mechanism of quinones, phenylpropanoids, and alkaloids in the treatment of EMs by promoting apoptosis.
5.4 Phenylpropanoids
Phenylpropanoid metabolites have good biological activities in antioxidant, antitumor, endocrine, and other areas due to their structural uniqueness (Falcone Ferreyra et al., 2012). Among many phenylpropanoid metabolites, cinnamic acid, honokiol, and fraxetin can play a good role in EMs by inducing apoptosis. Cinnamic acid (from Cinnamomum cassia (L.) J. Presl) induces apoptosis in EESCs by downregulating Bcl-2 expression and upregulating Bax, thereby triggering the Caspase cascade reaction to promote downstream apoptotic proteases (Caspase-9 and Caspase-3). This process may also involve inhibition of the Akt signaling pathway (Hongli et al., 2021). Similarly, honokiol, a lignan metabolite obtained from Magnolia officinalis Rehder and E.H.Wilson, induces apoptosis by suppressing survivin and Bcl-2 mRNA levels while enhancing Bax mRNA expression (Wang et al., 2016). Furthermore, it was demonstrated that fraxetin (from Fraxinus chinensis Roxb.) disrupts calcium buffer homeostasis between mitochondria and ER and promotes intrinsic apoptosis during endometriosis (Ham et al., 2024). Most studies of phenylpropanoid analogs have focused on mitochondrial apoptosis, and the multiple interactions induced by phenylpropanoid metabolites have been under-analyzed, which may provide innovative paths for future studies. Most studies on phenylpropanoid compounds focus on mitochondrial apoptosis, and their clinical translation is limited by the triple dilemma of “absorption-metabolism-toxicity”, which requires breakthroughs in delivery technology innovation (e.g., smart nanocarriers), metabolic pathway regulation, and precise clinical trial design. Future research should prioritize establishing a standardized quality control system (e.g., USP certification) and developing a multi-omics biomarker network to facilitate their efficient translation from bench to clinic.
5.5 Alkaloids
Alkaloids, as a class of nitrogen-containing natural metabolites, exhibit diverse and remarkable biological activities (Qiu et al., 2014). As previously reported, alkaloidal natural metabolites such as matrine and ligustrazine have demonstrated potent apoptosis-inducing mechanisms, thereby inhibiting the progression of EMs. Specifically, the matrine metabolite from Sophora flavescens Ait., demonstrated a dose-dependent promotion of apoptosis in ectopic stromal cells, after which RNA-seq was used to identify differentially expressed genes. The most significantly differentially expressed upregulated genes included MX1, SPP1, and SGK1, and the downregulated genes included THBS1, WNT5A, and COL4A1 (Dandan, 2023). Ligustrazine, the main bioactive metabolite from Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Apiaceae), exhibits significant efficacy in enhancing microcirculation, antithrombotic activity, sedation, and antioxidant defense (Qinglin et al., 2021). Further in vitro experiments showed that ligustrazine might inhibit the progression of EMs by down-regulating UBOX5-AS1 to inhibit EMs cells invasion, induce apoptosis, and mediate the activation of MMP-9/TIMP-3 signaling (Hongfang et al., 2023). Additionally, network pharmacological studies have revealed that ligustrazine, one of the main drug targets of Jiawei Foshou San (JFS), had binding activity with Bcl-2, Bax, Caspase-9, Caspase-3, and PARP in molecular docking experiments. This could possibly induce apoptosis through the Bcl-2 pathway and exert a positive effect (Wei et al., 2019). The primary obstacles to the clinical translation of alkaloids include dose-dependent organ toxicity (liver and kidney toxicity, neurotoxicity), low water solubility, first-pass metabolism, and multi-metabolite interference. Further integration of structural biology, nanotechnology, and computational toxicology is expected to break through the Activity-Toxicity-Delivery barrier of alkaloids and facilitate their transformation toward precision and intelligent drug development.
6 Clinical trials of natural metabolites for the treatment of EMs
The potential therapeutic efficacy of natural metabolites has been investigated in clinical trials, with some results have confirmed their effectiveness and safety (Table 3). However, these trials still exhibit significant limitations that compromise the reproducibility and generalizability of findings. First of all, the sample size of most clinical trials is small, which may cause the research results to be greatly affected by individual differences, limiting the statistical reliability of the research and making it difficult to obtain results with strong promotional value. Second, different trials have used varying administration methods (oral, local infiltration, sublingual, etc.) and dose regimens, making it hard to compare results between studies and affecting the stability of treatment effects. At the same time, the active ingredients of natural metabolites may be subject to extraction purity and stability, further affecting their controllability in the trial addition. The treatment cycles of trials varied widely, ranging from short-term (4 weeks) to long-term (1 year). This may lead to the long-term effect of clinical symptom improvement not being evaluated accurately, and it also makes the judgment of lesion progression more variable. Finally, although most trials use a Visual Analog Scale (VAS) to assess pain relief, the criteria for measuring lesion growth, hormone levels, quality of life, and other indicators have not been unified, making direct data comparison between different studies difficult. In order to further evaluate the value of natural metabolites in the treatment of EMs, future trials should consider several points to increase the sample size and improve the statistical power. The mode of administration and dose regimen were unified for cross-trial comparison. In addition, long-term observation indicators, including lesion progression, hormone level changes, and quality of life improvement, were set to comprehensively evaluate the clinical benefits of natural metabolites.
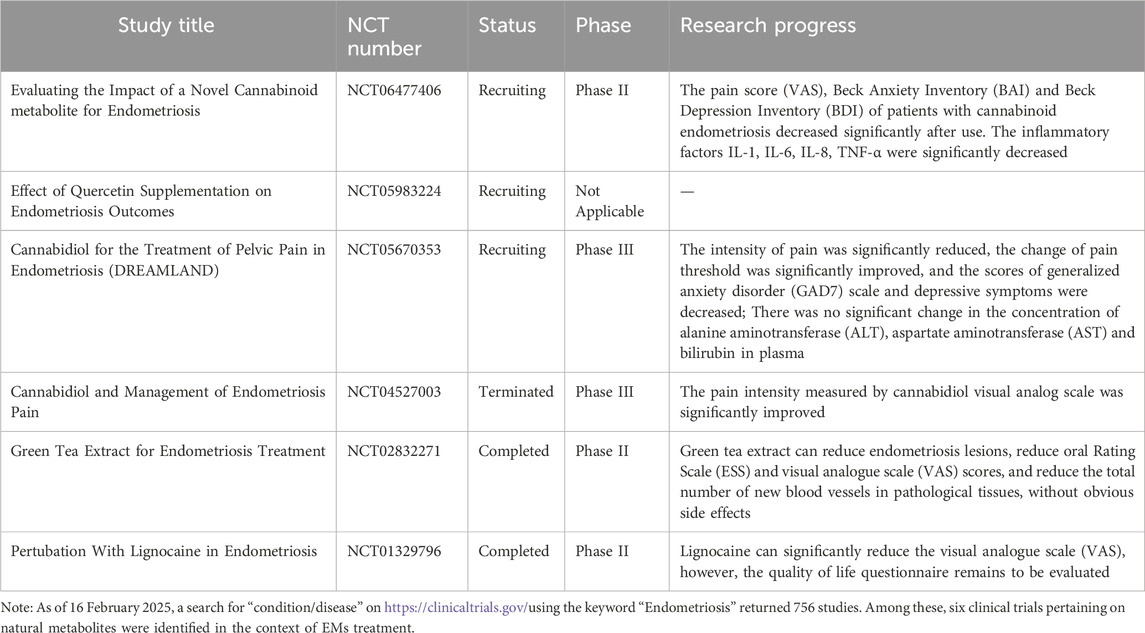
Table 3. Clinical trials of traditional natural metabolites for treating EMs registered on ClinicalTrials.gov.
7 Discussion
EMs is a benign gynecological disorder characterized by the abnormal implantation of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterine cavity. The incidence of this disease has been rising steadily over the years. Statistics show that approximately 176 million women worldwide suffer from the disease (Swift et al., 2024). EMs can not only cause dysmenorrhoea, chronic pelvic pain, and infertility in women but also lead to mental health imbalances and affect the social functioning of the patient (Nnoaham et al., 2011). Considering EMs as an estrogen-dependent disease, the most common and effective pharmacological treatment is to inhibit the growth of intrinsic estrogen by altering gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GRH) (Giudice, 2010). However, these treatments are associated with significant side effects, are limited long-term applicability, and result in delayed conception (Lu J. et al., 2023). Therefore, new drugs and clinical strategies should be urgently developed to treat the disease based on innovative molecular mechanisms.
Apoptosis is a tightly regulated process of cell death, controlled by various stress modalities and complex molecular signaling pathways. Studies have indicated that aberrant apoptosis significantly contributes to the development and progression of EMs (Depalo et al., 2009) and that targeting apoptosis may provide novel targets, strategies, and pathways for the prevention and treatment of EMs. This paper presents a systematic and comprehensive review of the potential mechanisms of action of natural metabolites that ameliorate EMs by inducing apoptosis. It is confirmed that an increasing number of natural metabolites have been found to possess pro-apoptotic properties, which may hold promise for treating EMs. However, existing studies have certain limitations, particularly in the assessment of evidence quality and comparative analysis of results across different studies, which require further investigation. First, a variety of natural metabolites can induce apoptosis in EMs through overlapping signaling pathways. However, their differences in molecular regulation deserve further comparison. For example, quercetin and luteolin both modulate the MAPK signaling pathway, but quercetin induces apoptosis by inhibiting the ERK/P38/MAPK/AKT signaling axis, leading to DNA fragmentation, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, and ROS accumulation. Luteolin, on the other hand, induced cell cycle arrest and promotes apoptosis mainly through the PI3K/AKT/MAPK signaling pathway. The primary distinction between the two lies in their specific molecular targets for inducing cell death, suggesting differential efficacy at distinct pathological stages of EMs. Meanwhile, naringenin, wogonin, and pachymic acid can modulate the Nrf2 pathway. Naringenin inhibites the Nrf2/Keap1/HO-1 signaling pathway, leading to enhanced oxidative stress, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, and induction of apoptosis. Conversely, wogonin might inhibit ferroptosis and increase the percentage of apoptotic cells in EMs models by activating the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Pachymic acid mediated AMPK/GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling pathway, reduces inflammatory response, regulates ferroptosis, and induces apoptosis of endometrial stromal cells. Although all of them can induce apoptosis, differences in their core molecular mechanisms may influence their clinical application strategies. It is worth noting that different compounds interact with the Nrf2 pathway via distinct mechanisms. It is expected that with further research, we can further clarify its mechanism of action. Meanwhile, metabolites such as curcumin and triptonoterpene, which are natural metabolites that mediate the NF-κB signaling pathway, have distinctive mechanisms in regulating apoptosis. Triptonoterpene induces apoptosis through the NF-κB and/or Rho-ROCK pathways, whereas curcumin not only activates the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway but also downregulates the expression of Bcl-2 and upregulates Bax and Bad by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. This mechanistic divergence suggests that curcumin may exert dual anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic effects, whereas triptonoterpene tends to induce apoptosis directly. Second, despite numerous studies highlighting the potential pro-apoptotic effects of natural compounds in EMs treatment, these findings must be interpreted with caution. Current research relies heavily on in vitro cellular models and in vivo animal experiments. However, in vitro experiments, constrained by artificially simulated environments and simplified cellular models, fail to adequately recapitulate the complex pathological milieu of the human body, particularly in domains such as drug metabolism, immune regulation, and endocrine interventions. Notably, certain natural metabolites like flavonoids (e.g., naringenin, silibinin, luteolin) and quinones (e.g., shikonin) have been categorized as pan-assay interference compounds (PAINS), metabolites susceptible to false-positive results in high-throughput screening, in vitro experiments. These PAINS compounds often often interact non-specifically with multiple targets, potentially leading to misleading “false activity” findings. For instance, flavonoids such as naringenin and silibinin are prone to non-specific interactions with diverse proteins due to the presence of functional groups such as phenolic hydroxyl moieties and conjugated double bonds in their structures, thereby compromising the physiological activation status of signaling pathways. Concurrently, Bolz et al. (Bolz et al., 2021) demonstrated that PAINS metabolites exhibit pronounced binding promiscuity and target non-selectivity in protein databases, which substantially exacerbates the misinterpretation of their “broad-spectrum activity” in vitro assays. Therefore, when interpreting the effects of such natural metabolites on EMs, it is critical to emphasize that “effective in vitro” does not equate to “clinically reliable”. In the absence of target validation and structural modifications, these metabolites are likely to be “chemical level disruptors” rather than genuine therapeutic candidates. Additionally, current studies are mainly based on in vitro cellular experiments and in vivo animal models. However, the translation of these experimental results to the clinic remains challenging. Information on the underlying molecular mechanisms is provided in the in vitro experiments, but the effects of drug metabolism, immune system effects, and endocrine modulation on the foci of EMs are neglected. For instance, quercetin exhibits significant pro-apoptotic effects in cell culture experiments, but its bioavailability may be reduced by metabolic processes in vivo. Although animal models can more comprehensively mimic the pathological process of EMs, physiological differences between species may lead to differences in drug efficacy. For example, curcumin demonstrates efficacy in mouse models, but its poor solubility and low bioavailability in human physiology limit its clinical utility. Meanwhile, the current number of clinical trials for natural compounds is limited, and there is a lack of systematic randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to verify their therapeutic efficacy and safety. Consequently, future studies should prioritize well-designed clinical trials to assess the true efficacy of these metabolites and to determine optimal therapeutic dosages.
To advance the clinical translation of natural compounds for EMs therapy, future research should focus on the following directions. First, during the screening of natural compounds, a PAINS screening filter should be integrated to identify and exclude potential interfering compounds using computational chemistry and structural biology approaches—before candidates enter animal or clinical trials. Meanwhile, although numerous studies have validated their efficacy, inconsistencies remain in evidence regarding specific mechanisms of action, key targets, and optimal dosing regimens. This suggests that we should pay more attention to the standardization of experimental conditions in subsequent studies, including the uniform selection of cell lines and standardization of dosage and cycle of drug administration. At the same time, strengthening the strategy of combined medication with different natural metabolites may improve the therapeutic effect through a synergistic effect. Secondly, drug delivery system optimization is critical. At present, the bioavailability of most natural metabolites is low. Nanotechnology (lipid nanocarrier, microemulsion technology, etc.) can be used to improve their stability, absorption rate, and pharmacokinetic characteristics, so as to improve their therapeutic effect. At this stage, the research on apoptosis of EMs induced by natural metabolites mainly involves in vitro cell experiments and in vivo animal experiments. Future efforts should prioritize multicenter RCTs to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of natural metabolites in EMs patients, accompanied by long-term follow-up to assess drug impacts on adverse reactions, recurrence rates, and quality of life. In summary, natural metabolites demonstrate promising pro-apoptotic potential in EMs therapy. However, current studies still lack in-depth comparative analysis and systematic evidence assessment, as well as systematic assessment of PAINS risk. Future studies should integrate critical PAINS mechanism-based evaluation, optimize drug delivery techniques, strengthen combination therapy strategies, and promote the development of clinical trials to enhance the practical application value of natural metabolites in the treatment of EMs.
8 Conclusion
This paper systematically summarizes the potential mechanisms by which diverse natural metabolites induce apoptosis in EMs therapy. Researches have shown that the effectiveness of these natural metabolites in treating EMs has been demonstrated in vitro and in vivo experiments. Various natural metabolites such as quercetin, luteolin, and naringin can regulate key signaling pathways (such as MAPK, Nrf2, NF-κB) to promote cell apoptosis, exhibiting multi-target and multi-pathway characteristics, providing new ideas and strategies for the treatment of EMs. However, current researches still have limitations, especially in terms of PAINS metabolites and clinical translation. Future researches should prioritize PAINS risk assessment, bioavailability enhancement, and advancement of multi-center randomized controlled trials to validate clinical efficacy and safety profiles.
Author contributions
YY: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition. YZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. MG: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. YW: Supervision, Writing – original draft. SL: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft. YG: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project was funded by the Heilongjiang PhD General Funding Project (LBH-Z23035) and the Heilongjiang Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Classics Popularization Research Special Topic (ZYW2024121).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1624569/full#supplementary-material
References
Agic, A., Djalali, S., Diedrich, K., and Hornung, D. (2009). Apoptosis in endometriosis. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest 68 (4), 217–223. doi:10.1159/000235871
Alizadeh, S. R., and Ebrahimzadeh, M. A. (2022). Quercetin derivatives: drug design, development, and biological activities, a review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 229, 114068. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.114068
Antignani, A., and Youle, R. J. (2006). How do bax and bak lead to permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18 (6), 685–689. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2006.10.004
Anto, R. J., Mukhopadhyay, A., Denning, K., and Aggarwal, B. B. (2002). Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) induces apoptosis through activation of caspase-8, BID cleavage and cytochrome c release: its suppression by ectopic expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl. Carcinogenesis 23 (1), 143–150. doi:10.1093/carcin/23.1.143
Assaf, L., Eid, A. A., and Nassif, J. (2022). Role of AMPK/mTOR, mitochondria, and ROS in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Life Sci. 306, 120805. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120805
Atteritano, M., Marini, H., Minutoli, L., Polito, F., Bitto, A., Altavilla, D., et al. (2007). Effects of the phytoestrogen genistein on some predictors of cardiovascular risk in osteopenic, postmenopausal women: a two-year randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92 (8), 3068–3075. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-2295
Baunach, M., Franke, J., and Hertweck, C. (2015). Terpenoid biosynthesis off the beaten track: unconventional cyclases and their impact on biomimetic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 54 (9), 2604–2626. doi:10.1002/anie.201407883
Bellezza, I., Giambanco, I., Minelli, A., and Donato, R. (2018). Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1865 (5), 721–733. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.02.010
Bertheloot, D., Latz, E., and Franklin, B. S. (2021). Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol. Immunol. 18 (5), 1106–1121. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-00630-3
Bhardwaj, A., Sethi, G., Vadhan-Raj, S., Bueso-Ramos, C., Takada, Y., Gaur, U., et al. (2007). Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and overcomes chemoresistance through down-regulation of STAT3 and nuclear factor-kappab-regulated antiapoptotic and cell survival gene products in human multiple myeloma cells. Blood 109 (6), 2293–2302. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-02-003988
Bishayee, K., Ghosh, S., Mukherjee, A., Sadhukhan, R., Mondal, J., and Khuda-Bukhsh, A. R. (2013). Quercetin induces cytochrome-c release and ROS accumulation to promote apoptosis and arrest the cell cycle in G2/M, in cervical carcinoma: signal Cascade and drug-DNA interaction. Cell Prolif. 46 (2), 153–163. doi:10.1111/cpr.12017
Bolton, J. L., and Dunlap, T. (2017). Formation and biological targets of quinones: cytotoxic versus cytoprotective effects. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 30 (1), 13–37. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00256
Bortner, C. D., and Cidlowski, J. A. (2002). Cellular mechanisms for the repression of apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 42, 259–281. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.42.083101.143836
Bouyahya, A., Chamkhi, I., Benali, T., Guaouguaou, F. E., Balahbib, A., El Omari, N., et al. (2021). Traditional use, phytochemistry, toxicology, and pharmacology of Origanum majorana L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 265, 113318. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113318
Brentnall, M., Rodriguez-Menocal, L., De Guevara, R. L., Cepero, E., and Boise, L. H. (2013). Caspase-9, caspase-3 and caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol. 14, 32. doi:10.1186/1471-2121-14-32
Burney, R. O., and Giudice, L. C. (2019). Reprint of: pathogenesis and pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 112 (4 Suppl. 1), e153–e161. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2019.08.083
Cahova, M., Bratova, M., and Wohl, P. (2017). Parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease: the role of the gut microbiota. Nutrients 9 (9), 987. doi:10.3390/nu9090987
Cai, J., Wen, H., Zhou, H., Zhang, D., Lan, D., Liu, S., et al. (2023). Naringenin: a flavanone with anti-inflammatory and anti-infective properties. Biomed. Pharmacother. 164, 114990. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114990
Canday, M., Yurtkal, A., Makav, M., and Kuru, M. (2024). Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiangiogenic, and therapeutic efficacy of neroli oil in rats with endometriotic lesions. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 50 (3), 516–525. doi:10.1111/jog.15866
Cao, H., Wei, Y. X., Zhou, Q., Zhang, Y., Guo, X. P., and Zhang, J. (2017a). Inhibitory effect of curcumin in human endometriosis endometrial cells via downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor. Mol. Med. Rep. 16 (4), 5611–5617. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7250
Cao, Y., Ye, Q., Zhuang, M., Xie, S., Zhong, R., Cui, J., et al. (2017b). Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits angiogenesis in a rat model of endometriosis through the VEGFR-2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. PLoS One 12 (11), e0186520. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186520
Chaoqin, Y., Jin, Y., Jie, H., Qiaoling, Z., and Wei, S. (2009). Regulatory mechanism of malignant behavior of endometriosis mediated by puerarin. J. Chin. Integr. Med. 7 (01), 41–47. doi:10.3736/jcim20090106
Chen, C., Zhou, Y., Hu, C., Wang, Y., Yan, Z., Li, Z., et al. (2019). Mitochondria and oxidative stress in ovarian endometriosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 136, 22–34. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.03.027
Chen, H., Li, R., Zhao, F., Luan, L., Han, T., and Li, Z. (2022). Betulinic acid increases lifespan and stress resistance via insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Front. Nutr. 9, 960239. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.960239
Chen, Z., Wang, C., Lin, C., Zhang, L., Zheng, H., Zhou, Y., et al. (2021). Lipidomic alterations and PPARα activation induced by resveratrol lead to reduction in lesion size in endometriosis models. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 9979953. doi:10.1155/2021/9979953
Chinnaiyan, A. M. (1999). The apoptosome: heart and soul of the cell death machine. Neoplasia 1 (1), 5–15. doi:10.1038/sj.neo.7900003
Chipuk, J. E., Bouchier-Hayes, L., and Green, D. R. (2006). Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: the innocent bystander scenario. Cell Death Differ. 13 (8), 1396–1402. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401963
Crump, J., Suker, A., and White, L. (2024). Endometriosis: a review of recent evidence and guidelines. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 53 (1-2), 11–18. doi:10.31128/ajgp/04-23-6805
Czabotar, P. E., Colman, P. M., and Huang, D. C. (2009). Bax activation by bim? Cell Death Differ. 16 (9), 1187–1191. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.83
Czabotar, P. E., Lessene, G., Strasser, A., and Adams, J. M. (2014). Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15 (1), 49–63. doi:10.1038/nrm3722
Dandan, L. (2023). Exploring the mechanism of the effect of matrine on the proliferation and apoptosis of primary stromal cells in endometriosis based on RNA seq. 硕士: Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Dassen, H., Punyadeera, C., Kamps, R., Delvoux, B., Van Langendonckt, A., Donnez, J., et al. (2007). Estrogen metabolizing enzymes in endometrium and endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 22 (12), 3148–3158. doi:10.1093/humrep/dem310
Dejas, L., Santoni, K., Meunier, E., and Lamkanfi, M. (2023). Regulated cell death in neutrophils: from apoptosis to NETosis and pyroptosis. Semin. Immunol. 70, 101849. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2023.101849
Delenko, J., Xue, X., Chatterjee, P. K., Hyman, N., Shih, A. J., Adelson, R. P., et al. (2024). Quercetin enhances decidualization through AKT-ERK-p53 signaling and supports a role for senescence in endometriosis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 22 (1), 100. doi:10.1186/s12958-024-01265-z
Depalo, R., Cavallini, A., Lorusso, F., Bassi, E., Totaro, I., Marzullo, A., et al. (2009). Apoptosis in normal ovaries of women with and without endometriosis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 19 (6), 808–815. doi:10.1016/j.rbmo.2009.09.024
Dlamini, Z., Mbita, Z., and Zungu, M. (2004). Genealogy, expression, and molecular mechanisms in apoptosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 101 (1), 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2003.08.005
Dongfang, L., Xiaolan, K., Yinghua, Y., Fangfang, X., Bo, L., and Aihua, W. (2024). Analysis of the mechanism of triptolide in treating endometriosis using network pharmacology combined with molecular docking technology. Mod. Chin. Med. 44 (02), 110–117. doi:10.13424/j.cnki.mtcm.2024.02.019
Doroftei, B., Ilie, O. D., Balmus, I. M., Ciobica, A., Maftei, R., Scripcariu, I., et al. (2021). Molecular and clinical insights on the complex interaction between oxidative stress, apoptosis, and endobiota in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Diagn. (Basel) 11 (8), 1434. doi:10.3390/diagnostics11081434
Ehrmann, J. F., Grabarczyk, D. B., Heinke, M., Deszcz, L., Kurzbauer, R., Hudecz, O., et al. (2023). Structural basis for regulation of apoptosis and autophagy by the BIRC6/SMAC complex. Science 379 (6637), 1117–1123. doi:10.1126/science.ade8873
Elham, A., Arken, M., Kalimanjan, G., Arkin, A., and Iminjan, M. (2021). A review of the phytochemical, pharmacological, pharmacokinetic, and toxicological evaluation of Quercus infectoria galls. J. Ethnopharmacol. 273, 113592. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113592
Elmore, S. (2007). Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 35 (4), 495–516. doi:10.1080/01926230701320337
Erekat, N. S. (2018). Autophagy precedes apoptosis among at risk cerebellar purkinje cells in the shaker mutant rat: an ultrastructural study. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 42 (2), 162–169. doi:10.1080/01913123.2018.1424744
Falcone Ferreyra, M. L., Rius, S. P., and Casati, P. (2012). Flavonoids: biosynthesis, biological functions, and biotechnological applications. Front. Plant Sci. 3, 222. doi:10.3389/fpls.2012.00222
Ferella, L., Bastón, J. I., Bilotas, M. A., Singla, J. J., González, A. M., Olivares, C. N., et al. (2018). Active compounds present inRosmarinus officinalis leaves andScutellaria baicalensis root evaluated as new therapeutic agents for endometriosis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 37 (6), 769–782. doi:10.1016/j.rbmo.2018.09.018
Fischer, C., Speth, V., Fleig-Eberenz, S., and Neuhaus, G. (1997). Induction of zygotic polyembryos in wheat: influence of auxin polar transport. Plant Cell 9 (10), 1767–1780. doi:10.1105/tpc.9.10.1767
Gai, Q. Y., Jiao, J., Luo, M., Wei, Z. F., Zu, Y. G., Ma, W., et al. (2015). Establishment of hairy root cultures by Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated transformation of Isatis tinctoria L. for the efficient production of flavonoids and evaluation of antioxidant activities. PLoS One 10 (3), e0119022. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119022
Garcia-Velasco, J. A., Arici, A., Zreik, T., Naftolin, F., and Mor, G. (1999). Macrophage derived growth factors modulate fas ligand expression in cultured endometrial stromal cells: a role in endometriosis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 5 (7), 642–650. doi:10.1093/molehr/5.7.642
Giudice, L. C. (2010). Clinical practice. Endometriosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 362 (25), 2389–2398. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1000274
Goel, H., Kumar, R., Tanwar, P., Upadhyay, T. K., Khan, F., Pandey, P., et al. (2023). Unraveling the therapeutic potential of natural products in the prevention and treatment of leukemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 160, 114351. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114351
Gogacz, M., Gałczyński, K., Wojtaś, M., Winkler, I., Adamiak, A., Romanek-Piva, K., et al. (2017). Fas-related apoptosis of peritoneal fluid macrophages in endometriosis patients: understanding the disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 3175394. doi:10.1155/2017/3175394
Gołąbek-Grenda, A., Kaczmarek, M., Juzwa, W., and Olejnik, A. (2023). Natural resveratrol analogs differentially target endometriotic cells into apoptosis pathways. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 11468. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-38692-8
Gomes de Carvalho, N. K., Wellisson da Silva Mendes, J., and Martins da Costa, J. G. (2023). Quinones: biosynthesis, characterization of (13) C spectroscopical data and pharmacological activities. Chem. Biodivers. 20 (12), e202301365. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202301365
Guo, Z. L., Li, M. X., Li, X. L., Wang, P., Wang, W. G., Du, W. Z., et al. (2021). Crocetin: a systematic review. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 745683. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.745683
Haider, S., and Knöfler, M. (2009). Human tumour necrosis factor: physiological and pathological roles in placenta and endometrium. Placenta 30 (2), 111–123. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2008.10.012
Ham, J., Kim, J., Bazer, F. W., Lim, W., and Song, G. (2019). Silibinin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction suppress growth of endometriotic lesions. J. Cell Physiol. 234 (4), 4327–4341. doi:10.1002/jcp.27212
Ham, J., Park, W., Song, J., Kim, H. S., Song, G., Lim, W., et al. (2024). Fraxetin reduces endometriotic lesions through activation of ER stress, induction of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis, and generation of ROS. Phytomedicine 123, 155187. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155187
Han, J. H., Tweedell, R. E., and Kanneganti, T. D. (2023). Evaluation of caspase activation to assess innate immune cell death. J. Vis. Exp. 191. doi:10.3791/64308
Haoran, W., Weiwei, R., Juan, W., and Shasha, L. (2023). Rutin participates in the proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of endometriosis cells by targeting nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 to regulate reactive oxygen species/hypoxia inducible factor-1 α signaling. Maternal Child Health Care China 38 (16), 3093–3099. doi:10.19829/j.zgfybj.issn.1001-4411.2023.16.039
Harada, T., Taniguchi, F., Izawa, M., Ohama, Y., Takenaka, Y., Tagashira, Y., et al. (2007). Apoptosis and endometriosis. Front. Biosci. 12, 3140–3151. doi:10.2741/2302
Hillman, G. G., Wang, Y., Che, M., Raffoul, J. J., Yudelev, M., Kucuk, O., et al. (2007). Progression of renal cell carcinoma is inhibited by genistein and radiation in an orthotopic model. BMC Cancer 7, 4. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-7-4
Hong, T., and Yu, Z. (2019). Effects of comfrey extract at different concentrations on inflammatory factors and apoptotic genes in rats with endometriosis. J. Mod. Integr. Chin. West. Med. 28 (11), 1155–1158. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2019.11.004
Hongfang, T., Muling, Z., and Yedi, Z. (2023). Effect of ligustrazine on cell invasion and apoptosis in endometriosis. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 39 (04), 503–507. doi:10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2023.04.010
Hongli, H., Lanfang, W., Jie, L., and Jiangxia, Y. (2021). Effect and mechanism of cinnamic acid pretreatment on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Electron. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Dis. Chin. West. Med. 9 (10), 32–34+54. doi:10.16282/j.cnki.cn11-9336/r.2021.10.047
Hsu, Y. W., Chen, H. Y., Chiang, Y. F., Chang, L. C., Lin, P. H., and Hsia, S. M. (2020). The effects of isoliquiritigenin on endometriosis in vivo and in vitro study. Phytomedicine 77, 153214. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153214
Huang, K., O'Neill, K. L., Li, J., Zhou, W., Han, N., Pang, X., et al. (2019a). BH3-only proteins target BCL-xL/MCL-1, not BAX/BAK, to initiate apoptosis. Cell Res. 29 (11), 942–952. doi:10.1038/s41422-019-0231-y
Huang, M. Y., Chen, Y. C., Lyu, W. Y., He, X. Y., Ye, Z. H., Huang, C. Y., et al. (2023). Ginsenoside Rh2 augmented anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy by reinvigorating CD8(+) T cells via increasing intratumoral CXCL10. Pharmacol. Res. 198, 106988. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106988
Huang, R., Chen, S., Zhao, M., Li, Z., and Zhu, L. (2020). Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates endometriosis by inhibiting the viability of human ectopic endometrial stromal cells through the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Hum. Reprod. 49 (1), 101642. doi:10.1016/j.jogoh.2019.101642
Huang, T., Liu, Y., and Zhang, C. (2019b). Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability enhancement of baicalin: a review. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 44 (2), 159–168. doi:10.1007/s13318-018-0509-3
Huang, Y., Zhang, B., Gao, Y., Zhang, J., and Shi, L. (2014). Baicalein-nicotinamide cocrystal with enhanced solubility, dissolution, and oral bioavailability. J. Pharm. Sci. 103 (8), 2330–2337. doi:10.1002/jps.24048
Hughes, M. A., Powley, I. R., Jukes-Jones, R., Horn, S., Feoktistova, M., Fairall, L., et al. (2016). Co-operative and hierarchical binding of c-FLIP and Caspase-8: a unified model defines how c-FLIP isoforms differentially control cell fate. Mol. Cell 61 (6), 834–849. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.023
Huixing, C., Xiaoxing, P., Lanying, W., and Yanze, J. (2014). Expression of Caspase-8 and NF kB in endometriosis of rats after gen treatment. Maternal Child Health Care China 29 (11), 1759–1762. doi:10.7620/zgfybj.j.issn.1001-4411.2014.11.44
Hung, S. W., Gaetani, M., Li, Y., Tan, Z., Zheng, X., Zhang, R., et al. (2024). Distinct molecular targets of ProEGCG from EGCG and superior inhibition of angiogenesis signaling pathways for treatment of endometriosis. J. Pharm. Anal. 14 (1), 100–114. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2023.09.005
Jana, S., Paul, S., and Swarnakar, S. (2012). Curcumin as anti-endometriotic agent: implication of MMP-3 and intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 83 (6), 797–804. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.12.030
Ji, M., Liu, Y., Yang, S., Zhai, D., Zhang, D., Bai, L., et al. (2013). Puerarin suppresses proliferation of endometriotic stromal cells in part via differential recruitment of nuclear receptor coregulators to estrogen receptor-α. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 138, 421–426. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.07.006
Jianghong, L., Ruili, L., and Xiaofei, C. (2016). Therapeutic effect of tanshinone IIA on endometriosis rats. J. Emerg. Traditional Chin. Med. 25 (04), 612–615. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2016.04.014
Jin, T., Li, Y., Min, S., Xueling, L., and Shuwei, Z. (2020). Effect of quercetin combined with CADM1 on cell proliferation and apoptosis in endometriosis. Explor. Ration. Drug Use China 17 (04), 95–99.
Jin, Z., Huang, J., and Zhu, Z. (2017). Baicalein reduces endometriosis by suppressing the viability of human endometrial stromal cells through the nuclear factor-κB pathway in vitro. Exp. Ther. Med. 14 (4), 2992–2998. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4860
Johnson, M. C., Torres, M., Alves, A., Bacallao, K., Fuentes, A., Vega, M., et al. (2005). Augmented cell survival in eutopic endometrium from women with endometriosis: expression of c-myc, TGF-beta1 and bax genes. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 3, 45. doi:10.1186/1477-7827-3-45
Jost, P. J., and Vucic, D. (2020). Regulation of cell death and immunity by XIAP. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 12 (8), a036426. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a036426
Jun, L., Qianqing, W., Wisdom, G., Li, L., Mingfei, G., and Beibei, C. (2020). Picroside II reduces the expression of M2 macrophages and regulates pelvic adhesion and endometrial cell apoptosis in rats with endometriosis. Immunol. J. 36 (11), 994–1000. doi:10.13431/j.cnki.immunol.j.20200153
Junqi, M., and Yan, D. (2008). Study on apoptosis-related genes in patients with EMs. Chin. J. Maternal Child Clin. Med. (05), 35–39. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5250.2008.05.010
Kale, J., Osterlund, E. J., and Andrews, D. W. (2018). BCL-2 family proteins: changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ. 25 (1), 65–80. doi:10.1038/cdd.2017.186
Kamal, D. A. M., Salamt, N., Yusuf, A. N. M., Kashim, M., and Mokhtar, M. H. (2021). Potential health benefits of curcumin on female reproductive disorders: a review. Nutrients 13 (9), 3126. doi:10.3390/nu13093126
Kapoor, R., Sirohi, V. K., Gupta, K., and Dwivedi, A. (2019). Naringenin ameliorates progression of endometriosis by modulating Nrf2/Keap1/HO1 axis and inducing apoptosis in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 70, 215–226. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.05.003
Kawaii, S., Tomono, Y., Katase, E., Ogawa, K., and Yano, M. (1999). HL-60 differentiating activity and flavonoid content of the readily extractable fraction prepared from citrus juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 47 (1), 128–135. doi:10.1021/jf9805101
Khan, N., and Mukhtar, H. (2008). Multitargeted therapy of cancer by green tea polyphenols. Cancer Lett. 269 (2), 269–280. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.04.014
Khazaei, M. R., Rashidi, Z., Chobsaz, F., and Khazaei, M. (2016). Apoptosis induction of human endometriotic epithelial and stromal cells by noscapine. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 19 (9), 940–945. doi:10.22038/ijbms.2016.7593
Kim, D. H., Cho, K. H., Moon, S. K., Kim, Y. S., Kim, D. H., Choi, J. S., et al. (2005). Cytoprotective mechanism of baicalin against endothelial cell damage by peroxynitrite. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 57 (12), 1581–1590. doi:10.1211/jpp.57.12.0008
Kim, H., Lee, J. H., Kim, J. E., Kim, Y. S., Ryu, C. H., Lee, H. J., et al. (2018). Micro-/nano-sized delivery systems of ginsenosides for improved systemic bioavailability. J. Ginseng Res. 42 (3), 361–369. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2017.12.003
Kim, H., Tu, H. C., Ren, D., Takeuchi, O., Jeffers, J. R., Zambetti, G. P., et al. (2009). Stepwise activation of BAX and BAK by tBID, BIM, and PUMA initiates mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell 36 (3), 487–499. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.09.030
Kobayashi, H., Imanaka, S., Yoshimoto, C., Matsubara, S., and Shigetomi, H. (2024). Molecular mechanism of autophagy and apoptosis in endometriosis: current understanding and future research directions. Reprod. Med. Biol. 23 (1), e12577. doi:10.1002/rmb2.12577
Kolahdouz-Mohammadi, R., Delbandi, A. A., Khodaverdi, S., Arefi, S., Arablou, T., and Shidfar, F. (2020). The effects of resveratrol treatment on Bcl-2 and bax gene expression in endometriotic compared with non-endometriotic stromal cells. Iran. J. Public Health 49 (8), 1546–1554. doi:10.18502/ijph.v49i8.3900
Kong, Y., Chen, X., Liu, F., Tang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). Ultrasmall polyphenol-NAD(+) nanoparticle-mediated renal delivery for mitochondrial repair and anti-inflammatory treatment of AKI-to-CKD progression. Adv. Mater 36 (30), e2310731. doi:10.1002/adma.202310731
Krawczyk, N., Banys-Paluchowski, M., Schmidt, D., Ulrich, U., and Fehm, T. (2016). Endometriosis-associated malignancy. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 76 (2), 176–181. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1558239
Kuan, K. K. W., Gibson, D. A., Whitaker, L. H. R., and Horne, A. W. (2021). Menstruation dysregulation and endometriosis development. Front. Reprod. Health 3, 756704. doi:10.3389/frph.2021.756704
Leonte, D., Ungureanu, D., and Zaharia, V. (2023). Flavones and related compounds: synthesis and biological activity. Molecules 28 (18), 6528. doi:10.3390/molecules28186528
Li, C., Dai, T., Chen, J., Chen, M., Liang, R., Liu, C., et al. (2023). Modification of flavonoids: methods and influences on biological activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 63 (31), 10637–10658. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2083572
Li, H., Dong, L., Liu, Y., Wang, G., Wang, G., and Qiao, Y. (2014). Biopharmaceutics classification of puerarin and comparison of perfusion approaches in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 466 (1-2), 133–138. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.03.014
Li, J., Zeng, Z., Chang, Y., Li, M., Wu, Q., Chen, P., et al. (2020). Suppressive effects of ursolic acid on human endometriotic stromal cells survival. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest 85 (1), 72–81. doi:10.1159/000502258
Li, M., Zheng, Y., Zhao, J., Liu, M., Shu, X., Li, Q., et al. (2022). Polyphenol mechanisms against gastric cancer and their interactions with gut microbiota: a review. Curr. Oncol. 29 (8), 5247–5261. doi:10.3390/curroncol29080417
Li, N., Liu, T. H., Yu, J. Z., Li, C. X., Liu, Y., Wu, Y. Y., et al. (2019). Curcumin and curcumol inhibit NF-κB and TGF-β (1)/Smads signaling pathways in CSE-treated RAW246.7 cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 3035125. doi:10.1155/2019/3035125
Liang, Y. J., Hao, Q., Wu, Y. Z., Wang, Q. L., Wang, J. D., and Hu, Y. L. (2009). Aromatase inhibitor letrozole in synergy with curcumin in the inhibition of xenografted endometrial carcinoma growth. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 19 (7), 1248–1252. doi:10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181b33d76
Liao, T. L., Lee, Y. C., Tzeng, C. R., Wang, Y. P., Chang, H. Y., Lin, Y. F., et al. (2019). Mitochondrial translocation of estrogen receptor β affords resistance to oxidative insult-induced apoptosis and contributes to the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 134, 359–373. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.01.022
Liao, Z., Lei, Y., Peng, L., Fu, X., Wang, W., and Yang, D. (2023). Network pharmacology prediction and experimental verification of rhubarb-peach kernel promoting apoptosis in endometriosis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23 (1), 291. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-04084-8
Liling, L., Shaoxuan, W., Weihong, T., Yanming, J., Lihong, P., blessings, P. b.a., et al. (2021). Effect of upregulation of KISS-1 expression by Tripterygium wilfordii glycosides on proliferation and apoptosis of endometrial stromal cells in endometriosis. Chin. Archives Traditional Chin. Med. 39 (11), 192–196. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2021.11.045
Lim, W., Park, S., Bazer, F. W., and Song, G. (2017). Naringenin-induced apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer cells is mediated via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways. J. Cell Biochem. 118 (5), 1118–1131. doi:10.1002/jcb.25729
Lin, L., Benling, M., Bing, H., Yi, Z., and Min, X. (2024). Effect of pachymic acid regulating AMPK/GSK-3 β/Nrf2 signaling pathway on ferroptosis of endometrial stromal cells in endometriosis rats. Hunan J. Traditional Chin. Med. 40 (06), 175–182. doi:10.16808/j.cnki.issn1003-7705.2024.06.040
Liqing, S., Zhaoai, L., Liyan, H., and Miao, L. (2018). Effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on the growth and apoptosis of endometrial cells. Chin. Drugs Clin. Pract. 18 (09), 1497–1500+1658. doi:10.11655/zgywylc2018.09.010
Liu, F., Sun, L., You, G., Liu, H., Ren, X., and Wang, M. (2020a). Effects of astragalus polysaccharide on the solubility and stability of 15 flavonoids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 143, 873–880. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.148
Liu, X., Mi, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Hou, J., Jiang, S., et al. (2020b). Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes regression from hepatic fibrosis through reducing inflammation-mediated autophagy signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 11 (6), 454. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2597-7
Liu, Y., Qin, X., and Lu, X. (2018). Crocin improves endometriosis by inhibiting cell proliferation and the release of inflammatory factors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 106, 1678–1685. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.108
Liu, Y. N., Hu, X. J., Liu, B., Shang, Y. J., Xu, W. T., and Zhou, H. F. (2021). Network pharmacology-based prediction of bioactive compounds and potential targets of wenjing decoction for treatment of endometriosis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 4521843. doi:10.1155/2021/4521843
Li-Weber, M. (2009). New therapeutic aspects of flavones: the anticancer properties of scutellaria and its main active constituents wogonin, baicalein and baicalin. Cancer Treat. Rev. 35 (1), 57–68. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2008.09.005
Long, G., Zijing, X., Dan, Z., and Yuguang, Z. (2019). Research progress on pharmacological activity of tanshinone metabolites in the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Asia-Pacific Tradit. Med. 15 (02), 190–192.
Lorenzo, H. K., Susin, S. A., Penninger, J., and Kroemer, G. (1999). Apoptosis inducing factor (AIF): a phylogenetically old, caspase-independent effector of cell death. Cell Death Differ. 6 (6), 516–524. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400527
Lu, J., Ling, X., Liu, L., Jiang, A., Ren, C., Lu, C., et al. (2023a). Emerging hallmarks of endometriosis metabolism: a promising target for the treatment of endometriosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1870 (1), 119381. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2022.119381
Lu, X., Huang, L., Scheller, H. V., and Keasling, J. D. (2023b). Medicinal terpenoid UDP-Glycosyltransferases in plants: recent advances and research strategies. J. Exp. Bot. 74 (5), 1343–1357. doi:10.1093/jxb/erac505
Luo, M., Cai, X., Yan, D., Liu, X., and Guo, S. W. (2020). Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate restrains fibrogenesis through induction of senescence in mice with induced deep endometriosis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 41 (3), 373–384. doi:10.1016/j.rbmo.2020.04.006
Maciejczyk, A., and Surowiak, P. (2013). Quercetin inhibits proliferation and increases sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin and paclitaxel. Ginekol. Pol. 84 (7), 590–595. doi:10.17772/gp/1609
Meresman, G. F., Götte, M., and Laschke, M. W. (2021). Plants as source of new therapies for endometriosis: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. Hum. Reprod. Update 27 (2), 367–392. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmaa039
Mounsey, A. L., Wilgus, A., and Slawson, D. C. (2006). Diagnosis and management of endometriosis. Am. Fam. Physician 74 (4), 594–600. doi:10.1002/psb.1398
Mustafa, M., Ahmad, R., Tantry, I. Q., Ahmad, W., Siddiqui, S., Alam, M., et al. (2024). Apoptosis: a comprehensive overview of signaling pathways, morphological changes, and physiological significance and therapeutic implications. Cells 13 (22), 1838. doi:10.3390/cells13221838
Nagata, S. (2018). Apoptosis and clearance of apoptotic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 36, 489–517. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053010
Nnoaham, K. E., Hummelshoj, L., Webster, P., d'Hooghe, T., de Cicco Nardone, F., de Cicco Nardone, C., et al. (2011). Impact of endometriosis on quality of life and work metaboliteivity: a multicenter study across ten countries. Fertil. Steril. 96 (2), 366–373.e368. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.05.090
Nuñez, G., London, L., Hockenbery, D., Alexander, M., McKearn, J. P., and Korsmeyer, S. J. (1990). Deregulated Bcl-2 gene expression selectively prolongs survival of growth factor-deprived hemopoietic cell lines. J. Immunol. 144 (9), 3602–3610. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.144.9.3602
Pang, C., Wu, Z., Xu, X., Yang, W., Wang, X., and Qi, Y. (2021). Paeonol alleviates migration and invasion of endometrial stromal cells by reducing HIF-1α-regulated autophagy in endometriosis. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 26 (9), 485–495. doi:10.52586/4961
Papari, E., Noruzinia, M., Kashani, L., and Foster, W. G. (2020). Identification of candidate microRNA markers of endometriosis with the use of next-generation sequencing and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Fertil. Steril. 113 (6), 1232–1241. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.01.026
Park, S., Lim, W., Bazer, F. W., and Song, G. (2017). Naringenin induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress by regulating MAPK and AKT signal transduction pathways in endometriosis cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 23 (12), 842–854. doi:10.1093/molehr/gax057
Park, S., Lim, W., Bazer, F. W., Whang, K. Y., and Song, G. (2019a). Quercetin inhibits proliferation of endometriosis regulating cyclin D1 and its target microRNAs in vitro and in vivo. J. Nutr. Biochem. 63, 87–100. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.09.024
Park, S., Lim, W., and Song, G. (2019b). Delphinidin induces antiproliferation and apoptosis of endometrial cells by regulating cytosolic calcium levels and mitochondrial membrane potential depolarization. J. Cell Biochem. 120 (4), 5072–5084. doi:10.1002/jcb.27784
Park, S., Lim, W., You, S., and Song, G. (2019c). Ameliorative effects of luteolin against endometriosis progression in vitro and in vivo. J. Nutr. Biochem. 67, 161–172. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.02.006
Park, S., Song, G., and Lim, W. (2020). Myricetin inhibits endometriosis growth through cyclin E1 down-regulation in vitro and in vivo. J. Nutr. Biochem. 78, 108328. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108328
Park, W., Jang, H., Kim, H. S., Park, S. J., Lim, W., Song, G., et al. (2024). Therapeutic efficacy and anti-inflammatory mechanism of baicalein on endometriosis progression in patient-derived cell line and mouse model. Phytomedicine 130, 155469. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155469
Patel, S. S., Acharya, A., Ray, R. S., Agrawal, R., Raghuwanshi, R., and Jain, P. (2020). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of curcumin in prevention and treatment of disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 60 (6), 887–939. doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1552244
Qingjing, Z., Xiaoling, W., and Wenhui, J. (2023). Quercetin affects the proliferation and apoptosis of endometriosis cells by regulating miR-340-5p. Chin. J. Birth Health and Hered. 31 (07), 1360–1365. doi:10.13404/j.cnki.cjbhh.2023.07.039
Qinglin, Z., Ziqiong, Z., Ziwen, J., and Mingjun, X. (2021). Effect of Linc00261 regulating miR-139-3p on adhesion, invasion, and apoptosis of ectopic endometrial cells in mice with endometriosis. J. Guangxi Med. Univ. 38 (07), 1325–1331. doi:10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2021.07.012
Qiu, S., Sun, H., Zhang, A. H., Xu, H. Y., Yan, G. L., Han, Y., et al. (2014). Natural alkaloids: basic aspects, biological roles, and future perspectives. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 12 (6), 401–406. doi:10.1016/s1875-5364(14)60063-7
Ranganathan, S., Halagowder, D., and Sivasithambaram, N. D. (2015). Quercetin suppresses twist to induce apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. PLoS One 10 (10), e0141370. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0141370
Ricci, A. G., Olivares, C. N., Bilotas, M. A., Bastón, J. I., Singla, J. J., Meresman, G. F., et al. (2013). Natural therapies assessment for the treatment of endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 28 (1), 178–188. doi:10.1093/humrep/des369
Rossi, A., Pizzo, P., and Filadi, R. (2019). Calcium, mitochondria and cell metabolism: a functional triangle in bioenergetics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1866 (7), 1068–1078. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.10.016
Ryu, S., Bazer, F. W., Lim, W., and Song, G. (2019). Chrysin leads to cell death in endometriosis by regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and cytosolic calcium level. J. Cell Physiol. 234 (3), 2480–2490. doi:10.1002/jcp.26770
Saunders, P. T. K., and Horne, A. W. (2021). Endometriosis: etiology, pathobiology, and therapeutic prospects. Cell 184 (11), 2807–2824. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.041
Shaohui, C., and Zhaoai, L. (2019). Study on the mechanism of ginsenoside Rg3 promoting apoptosis of endometriosis stromal cells. Chin. Drugs Clin. Pract. 19 (05), 715–717. doi:10.11655/zgywylc2019.05.007
Song, Y. H., Jeong, S. J., Kwon, H. Y., Kim, B., Kim, S. H., and Yoo, D. Y. (2012). Ursolic acid from Oldenlandia diffusa induces apoptosis via activation of caspases and phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35 (7), 1022–1028. doi:10.1248/bpb.b110660
Steinbuch, S. C., Lüß, A. M., Eltrop, S., Götte, M., and Kiesel, L. (2024). Endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer: from molecular pathologies to clinical relevance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (8), 4306. doi:10.3390/ijms25084306
Sun, L., Li, H., Huang, X., Wang, T., Zhang, S., Yang, J., et al. (2013). Triptolide alters barrier function in renal proximal tubular cells in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 223 (1), 96–102. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.08.014
Swift, B., Taneri, B., Becker, C. M., Basarir, H., Naci, H., Missmer, S. A., et al. (2024). Prevalence, diagnostic delay and economic burden of endometriosis and its impact on quality of life: results from an eastern mediterranean population. Eur. J. Public Health 34 (2), 244–252. doi:10.1093/eurpub/ckad216
Taguchi, A., Koga, K., Kawana, K., Makabe, T., Sue, F., Miyashita, M., et al. (2016). Resveratrol enhances apoptosis in endometriotic stromal cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 75 (4), 486–492. doi:10.1111/aji.12489
Talebi, H., Farahpour, M. R., and Hamishehkar, H. (2021). The effectiveness of rutin for prevention of surgical induced endometriosis development in a rat model. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 7180. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86586-4
Taniguchi, F., Kaponis, A., Izawa, M., Kiyama, T., Deura, I., Ito, M., et al. (2011). Apoptosis and endometriosis. Front. Biosci. Elite Ed. 3 (2), 648–662. doi:10.2741/e277
Taylor, H. S., Kotlyar, A. M., and Flores, V. A. (2021). Endometriosis is a chronic systemic disease: clinical challenges and novel innovations. Lancet 397 (10276), 839–852. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00389-5
Tian, J., Gan, Y., Pan, C., Zhang, M., Wang, X., Tang, X., et al. (2018). Nerol-induced apoptosis associated with the generation of ROS and Ca(2+) overload in saprotrophic fungus Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102 (15), 6659–6672. doi:10.1007/s00253-018-9125-z
Vakilzadeh, H., Varshosaz, J., and Soghrati, S. (2021). Enhanced solubility and permeability of naringenin across non-everted sacs of rat small intestine by lipid nanocapsules. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 15 (1), 55–69. doi:10.2174/1872210514666200731181130
van Ginkel, P. R., Sareen, D., Subramanian, L., Walker, Q., Darjatmoko, S. R., Lindstrom, M. J., et al. (2007). Resveratrol inhibits tumor growth of human neuroblastoma and mediates apoptosis by directly targeting mitochondria. Clin. Cancer Res. 13 (17), 5162–5169. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-07-0347
Vannuccini, S., Clemenza, S., Rossi, M., and Petraglia, F. (2022). Hormonal treatments for endometriosis: the endocrine background. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 23 (3), 333–355. doi:10.1007/s11154-021-09666-w
Wan, L., Zou, Y., Wan, L. H., Wang, L. Q., Huang, M. Z., Wu, J., et al. (2015). Tanshinone IIA inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of ectopic endometrial stromal cells of adenomyosis via 14-3-3ζ downregulation. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 292 (6), 1301–1309. doi:10.1007/s00404-015-3766-2
Wang, C. C., Xu, H., Man, G. C., Zhang, T., Chu, K. O., Chu, C. Y., et al. (2013). Prodrug of green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (Pro-EGCG) as a potent anti-angiogenesis agent for endometriosis in mice. Angiogenesis 16 (1), 59–69. doi:10.1007/s10456-012-9299-4
Wang, Y., Jiang, L. L., Wu, J. F., and Liu, Z. (2016). Protective effect of honokiol against endometriosis in rats via attenuating survivin and Bcl-2: a mechanistic study. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 62 (1), 1–5. doi:10.14715/cmb/2016.62.1.1
Wang, Y., Nie, X. B., Liu, S. J., Liu, J., and Bian, W. H. (2022). Curcumol attenuates endometriosis by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 28, e934914. doi:10.12659/msm.934914
Wei, J., Zhao, B., Zhang, C., Shen, B., Zhang, Y., Li, C., et al. (2019). Jiawei foshou san induces apoptosis in ectopic endometrium based on systems pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental evidence. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2360367. doi:10.1155/2019/2360367
Wei, M. C., Lindsten, T., Mootha, V. K., Weiler, S., Gross, A., Ashiya, M., et al. (2000). tBID, a membrane-targeted death ligand, oligomerizes BAK to release cytochrome c. Genes Dev. 14 (16), 2060–2071. doi:10.1101/gad.14.16.2060
Woo, J. H., Ahn, J. H., Jang, D. S., and Choi, J. H. (2019). Effect of dehydrocostus lactone isolated from the roots of Aucklandia lappa on the apoptosis of endometriotic cells and the alternative activation of endometriosis-associated macrophages. Am. J. Chin. Med. 47 (6), 1289–1305. doi:10.1142/s0192415x19500666
Wu, M., Luo, Q., Nie, R., Yang, X., Tang, Z., and Chen, H. (2021). Potential implications of polyphenols on aging considering oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy, and gut microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 61 (13), 2175–2193. doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1773390
Wu, X., Zhang, H., Salmani, J. M., Fu, R., and Chen, B. (2016). Advances of wogonin, an extract from Scutellaria baicalensis, for the treatment of multiple tumors. Onco Targets Ther. 9, 2935–2943. doi:10.2147/ott.S105586
Xiang, D., Zhao, M., Cai, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Yao, H., et al. (2020). Betulinic acid inhibits endometriosis through suppression of estrogen receptor β signaling pathway. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 11, 604648. doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.604648
Xiao, Y. H., Chen, D. P., Yan, J. H., and Yokoyama, Y. (2002). Mechanism of action of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycoside on experimental endometriosis. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 23 (1), 63–67. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(01)00353-7
Xiaoying, H., Jianfa, W., Ying, W., and Lingli, J.Liuzhou (2023). Effect of wogonin regulating the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway on ferroptosis in rats with endometriosis. J. Zunyi Med. Univ. 46 (10), 943–949. doi:10.14169/j.cnki.zunyixuebao.2023.0141
Xie, H. T., Wang, G. J., Sun, J. G., Tucker, I., Zhao, X. C., Xie, Y. Y., et al. (2005). High performance liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric determination of ginsenoside Rg3 and its metabolites in rat plasma using solid-phase extraction for pharmacokinetic studies. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 818 (2), 167–173. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.12.028
Xie, J., and Zheng, Y. (2017). Myricetin protects keratinocyte damage induced by UV through IκB/NFκb signaling pathway. J. Cosmet. Dermatol 16 (4), 444–449. doi:10.1111/jocd.12399
Xu, D., Wu, L., and Chen, Q. (2022). Editorial: bone and cartilage diseases-the role and potential of natural products. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 938303. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.938303
Xu, H., Lui, W. T., Chu, C. Y., Ng, P. S., Wang, C. C., and Rogers, M. S. (2009). Anti-angiogenic effects of green tea catechin on an experimental endometriosis mouse model. Hum. Reprod. 24 (3), 608–618. doi:10.1093/humrep/den417
Yang, B., Dong, Y., Xu, Z., Li, X., Wang, F., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Improved stability and pharmacokinetics of wogonin through loading into PASylated ferritin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 216, 112515. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112515
Yang, Y., Li, L. L., Qi, Y. X., and Liu, D. J. (2024). Research progress of caspase in endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 31 (6), 1496–1507. doi:10.1007/s43032-023-01425-3
Yang, Y., Yuan, Y., Ma, X., and Xing, F. (2019). Ca2+ channel subunit a 1D inhibits endometriosis cell apoptosis and mediated by prostaglandin E2. Ginekol. Pol. 90 (12), 669–674. doi:10.5603/gp.2019.0115
Yi, Z. H., Li, S. Q., Ke, J. Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, M. Z., Li, J., et al. (2022). Baicalein relieves ferroptosis-mediated phagocytosis inhibition of macrophages in ovarian endometriosis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 44 (12), 6189–6204. doi:10.3390/cimb44120422
Yu, H., Chang, J. S., Kim, S. Y., Kim, Y. G., and Choi, H. K. (2017). Enhancement of solubility and dissolution rate of baicalein, wogonin and oroxylin A extracted from Radix scutellariae. Int. J. Pharm. 528 (1-2), 602–610. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.06.068
Yu, J., Zhao, L., Zhang, D., Zhai, D., Shen, W., Bai, L., et al. (2015). The effects and possible mechanisms of puerarin to treat endometriosis model rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 269138. doi:10.1155/2015/269138
Yu, Z., and Hong, T. (2018). Experimental study on the effect of shikonin on endometrial cell apoptosis in rats with endometriosis. J. Liaoning Univ. Traditional Chin. Med. 20 (09), 50–53. doi:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2018.09.013
Yu, Z., and Shah, D. M. (2007). Curcumin down-regulates Ets-1 and Bcl-2 expression in human endometrial carcinoma HEC-1-A cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 106 (3), 541–548. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.05.024
Yuan, J., and Ofengeim, D. (2024). A guide to cell death pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 25 (5), 379–395. doi:10.1038/s41580-023-00689-6
Zaveri, N. T. (2006). Green tea and its polyphenolic catechins: medicinal uses in cancer and noncancer applications. Life Sci. 78 (18), 2073–2080. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2005.12.006
Zhang, C., Ju, J., Wu, X., Yang, J., Yang, Q., Liu, C., et al. (2021). Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycoside ameliorated TNBS-induced colitis in rats via regulating Th17/Treg balance in intestinal mucosa. J. Inflamm. Res. 14, 1243–1255. doi:10.2147/jir.S293961
Zhang, L., Li, D. C., and Liu, L. F. (2019). Paeonol: pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. Int. Immunopharmacol. 72, 413–421. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.033
Zhang, Y., Jiang, P., Ye, M., Kim, S. H., Jiang, C., and Lü, J. (2012). Tanshinones: sources, pharmacokinetics and anti-cancer activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13 (10), 13621–13666. doi:10.3390/ijms131013621
Zheng, Q., Wang, J., Li, W., Chen, X., Chen, S., and Chen, L. (2020). Emodin reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human endometrial stromal cells by inhibiting ILK/GSK-3β pathway. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 3663–3672. doi:10.2147/dddt.S262816
Zheng, Q., Xu, Y., Lu, J., Zhao, J., Wei, X., and Liu, P. (2016). Emodin inhibits migration and invasion of human endometrial stromal cells by facilitating the mesenchymal-epithelial transition through targeting ILK. Reprod. Sci. 23 (11), 1526–1535. doi:10.1177/1933719116645192
Zhong, C., Ju, G., Yang, S., Zhao, X., Chen, J., and Li, N. (2023). Total flavonoids of Polygala fallax hemsl induce apoptosis of human ectopic endometrial stromal cells through PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest 88 (4), 197–213. doi:10.1159/000530104
Zhong, G., Wang, X., Zhang, Q., Zhang, X., Fang, X., Li, S., et al. (2024). Exploring the therapeutic implications of natural compounds modulating apoptosis in vascular dementia. Phytother. Res. 38 (11), 5270–5289. doi:10.1002/ptr.8316
Zhongling, M., Xin, L., and Yufeng, W. (2021). The intervention effect of tanshinone IIA on endometriosis rats and its impact on the TGF - β/smads signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Materia Medica 37 (05), 21–26. doi:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2021.05.004
Zhou, Z. Y., Zhao, W. R., Zhang, J., Chen, X. L., and Tang, J. Y. (2019). Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate: a review of pharmacological activity and pharmacokinetics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 109362. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109362
Zhu, W., Wang, Z., Sun, Y., Yang, B., Wang, Q., and Kuang, H. (2021). Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of genus syringa: a comprehensive review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 266, 113465. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113465
Zondervan, K. T., Becker, C. M., and Missmer, S. A. (2020). Endometriosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 382 (13), 1244–1256. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1810764
Zou, H., Henzel, W. J., Liu, X., Lutschg, A., and Wang, X. (1997). Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell 90 (3), 405–413. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80501-2
Glossary
AMPK AMP-activated Protein Kinase
APAF-1 Apoptotic peptidase-activating factor 1
Bax BCL2-Associated X protein
Bcl-2 B-cell lymphoma/leukemia-2
Caspases Cysteine-requiring aspartate protease
CCNE1 Cyclin E1
DED Death effector domain
DISC Death-inducing signaling complex
EMs Endometriosis
ER Endoplasmic reticulum
ERK1/2 Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
FADD Fas-associated death domain
FTH1 Ferritin Heavy Chain 1
FTL Ferritin Light Chain
FOX Forkhead box
GM-CSF Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
GSK-3β Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
GPX4 Glutathione Peroxidase 4
HNF-1β Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1 beta
HO-1 Heme Oxygenase-1
IhOESCs Immortalized human ovarian endometriotic stromal cell lines
LC3 Microtubule-associated Protein Light Chain 3
MAPK Mitogen-activated protein kinase
MDA Malondialdehyde
MLKL Mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase
MMP-9 Matrix metalloproteinase-9
mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin
NF-κB Nuclear Factor kappa-B
NOX4 Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase 4
NRF2 Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
NQO1 Quinone Oxidoreductase 1
PAINS Pan-assay interference compoundss
PCNA Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen
PGC-1α Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α
PI3K/AKT Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Protein Kinase B
RIPK Receptor-interacting protein kinase
ROS Reactive oxygen species
SMAC Second Mitochondrial Activator of Caspases
TGF-β1 Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor I
Keywords: natural plant metabolites, apoptosis, endometriosis, clinical translation, signaling pathways
Citation: Yu Y, Zhu Y, Gao M, Wang Y, Li S and Gou Y (2025) Research progress on natural plant metabolites targeting apoptosis for endometriosis prevention and treatment: a systematic review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1624569. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1624569
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 09 July 2025.
Edited by:
Irina Ielciu, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hatieganu, RomaniaReviewed by:
Yi Chen, Chongqing University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaWenfei Zheng, Yichang Central People’s Hospital, China
Mujde Canday, Kafkas University, Türkiye
Ramiro Cabrera Carranco, Instituto Doyenne, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Zhu, Gao, Wang, Li and Gou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shiying Li, bGlzaGl5aW5nOTRAcXEuY29t; Ying Gou, aGxqX3p5eV9neUAxNjMuY29t
 Yang Yu
Yang Yu Yufei Zhu
Yufei Zhu Mengyao Gao3
Mengyao Gao3 Yu Wang
Yu Wang Shiying Li
Shiying Li Ying Gou
Ying Gou