Abstract
Background/Objectives:
Primary open-angle glaucoma is a major global cause of vision loss, severely impacting quality of life. Although the need for effective treatments is widely recognized, the efficacy and safety of antioxidants remain uncertain. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of antioxidants in treating patients with primary open-angle glaucoma.
Methods:
We reviewed studies from PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science published up to 30 November 2024. Eligible studies included adults aged 18–80 years with primary open-angle or normal-tension glaucoma, comparing antioxidant treatment with placebo or comparing a combination of topical treatment and antioxidants with topical treatment alone. Only randomized controlled trials and crossover trials were included. Studies involving secondary glaucoma, ocular inflammation, trauma, or severe systemic disease were excluded, as were nonhuman studies. Of the 518 studies, 15 (2.9%) met the final criteria. Data abstraction and quality assessment followed established guidelines for rigor and transparency. The study outcomes—intraocular pressure, visual field deterioration, ocular blood circulation, blood pressure, and adverse effects—were chosen to evaluate the efficacy and safety of antioxidant treatments in primary open-angle glaucoma.
Results:
Analysis of 15 studies showed that antioxidant supplementation reduces intraocular pressure, improves visual field mean deterioration, and enhances ocular blood circulation in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. No significant differences were observed in blood pressure or adverse effects between the treatment and placebo groups.
Conclusion:
This meta-analysis highlights the potential role of antioxidants as a safe and effective therapeutic option for patients with primary open-angle glaucoma.
1 Introduction
Glaucoma is a group of diseases characterized by pathological elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP), progressive optic nerve damage, and visual field defects (Stein et al., 2021), making it the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide (Steinmetz et al., 2021). By 2040, an estimated 111.8 million individuals aged 40–80 years will be affected globally (Tham et al., 2014). Glaucoma is classified into primary, secondary, and congenital subtypes. Primary glaucoma is further categorized into primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) and primary angle-closure glaucoma (PACG) based on the anatomical structure of the anterior chamber angle. POAG is characterized by an open anterior chamber angle with increased resistance to aqueous humor outflow through the trabecular meshwork. In contrast, PACG results from angle closure due to iridotrabecular contact, obstructing aqueous outflow (Jayaram et al., 2023). Additionally, optic nerve damage and visual field loss may occur without elevated IOP, a subtype known as normal-tension glaucoma (NTG), which is considered a variant of POAG (Leung and Tham, 2022). POAG is the most prevalent form of glaucoma, accounting for approximately 74%–90% of all cases, predominantly affecting individuals aged >40 years (Quigley and Broman, 2006; Tham et al., 2014; Jin, 2022). POAG is characterized by the progressive loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and their axons, leading to optic nerve atrophy. The pathogenesis of POAG is multifactorial, with elevated IOP identified as a primary risk factor (Weinreb and Khaw, 2004). Increased IOP induces lamina cribrosa deformation, which disrupts the axonal transport of neurotrophic factors, ultimately causing RGC death due to insufficient trophic support. In addition to IOP, reduced ocular blood flow and localized ischemia at the optic nerve head contribute to chronic ischemic damage and cellular dysfunction (Weinreb et al., 2014; Weinreb and Khaw, 2004). Although IOP control remains fundamental in slowing glaucoma progression (Weinreb and Khaw, 2004; Lusthaus and Goldberg, 2019), some patients experience continued disease progression despite effective IOP management (Almasieh and Levin, 2017; Oliver et al., 2002). This indicates that, beyond IOP regulation, interventional strategies targeting other pathological mechanisms warrant further exploration (Weinreb et al., 2014; Jayaram et al., 2023; Bou Ghanem et al., 2024).
Recent studies have highlighted the pivotal role of oxidative stress (OS) in the pathogenesis and progression of POAG (Evangelho et al., 2019; Kwon et al., 2009). Antioxidants may hold potential value in slowing the progression of POAG by scavenging free radicals and alleviating oxidative damage (Kwon et al., 2009; Boccaccini et al., 2023). Increasing evidence exists that OS levels are elevated in patients with glaucoma (Hondur et al., 2017; Li et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019). In several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies, researchers have investigated the potential benefits of antioxidants, including vitamins, coenzyme Q10, and flavonoids, in POAG management (Sabaner et al., 2021; Shim et al., 2012; Parisi et al., 2014; Ramdas et al., 2018). However, inconsistencies in findings across these studies have made the true efficacy of antioxidants in POAG unclear. Therefore, this study aimed to systematically review the existing literature to assess the therapeutic potential of antioxidants in patients with POAG.
2 Methods
2.1 Study protocol and registration
In this systematic review, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy of antioxidants versus placebo and antioxidants combined with topical treatment versus topical treatment alone in alleviating symptoms in patients with POAG. The study protocol was registered in PROSPERO (Registration No. CRD42025629951). The study design adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines (Moher et al., 2009) to ensure methodological rigor.
2.2 Search strategy and eligibility criteria
A comprehensive literature search was conducted in the PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases to identify RCTs evaluating antioxidant treatment in patients with POAG, including studies published up to 30 November 2024. The search strategy was tailored to each database, applied without language restrictions, and excluded nonhuman studies. The search terms included “primary open-angle glaucoma,” “normal-tension glaucoma,” “antioxidants,” and “randomized controlled trials.” Specific antioxidant subtypes, such as vitamins, coenzyme Q10, and flavonoids, were also considered (detailed search strategies and keywords are provided in Supplementary Material 1). To enhance the comprehensiveness of this review, the reference lists of relevant studies were screened. All identified studies were managed using EndNote 20. After duplicate removal, titles, abstracts, and full texts were screened and assessed according to predefined eligibility criteria.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Age 18–80 years; (2) Diagnosis of POAG or NTG in at least one eye, confirmed by glaucomatous optic disc or retinal nerve fiber layer abnormalities and/or visual field defects consistent with glaucoma, with the exclusion of other ocular or systemic neurological conditions that could cause visual field defects; (3) Studies comparing antioxidant treatment with placebo or studies comparing a combination of topical treatment and antioxidants with topical treatment alone and (4) RCTs.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Secondary glaucoma (e.g., pseudoexfoliative or pigmentary glaucoma), angle-closure glaucoma, or congenital glaucoma; (2) History of chronic or recurrent ocular inflammation, ocular trauma, glaucoma surgery (except uncomplicated cataract surgery performed at least 6 months prior), severe or progressive retinal disease, or severe cardiovascular, renal, or pulmonary disease; (3) Pregnancy or lactation; (4) Animal or in vitro studies; and (5) Studies that were withdrawn, as well as reviews, meta-analyses, case reports, protocols, conference abstracts, book chapters, and non-English literature.
2.4 Data collection and quality assessment
Two independent reviewers screened the titles, abstracts, and full texts to identify eligible studies. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion or, if necessary, consultation with a third reviewer. One reviewer conducted data extraction, which was independently verified by another reviewer. Any discrepancies were addressed through discussion. The extracted data included study characteristics such as the first author, publication year, country, glaucoma type, sample size, sex, age, intervention details, outcomes, and follow-up duration.
The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk-of-Bias tool, which evaluates the following seven domains: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants, blinding of outcome assessors, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other biases. Each domain was rated as low, high, or unclear risk, and an overall risk assessment was assigned to each study.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The clinical efficacy and safety of antioxidant treatments for POAG were assessed using the following outcome measures: IOP, mean visual field deterioration, ocular blood circulation, blood pressure, and adverse effects. Meta-analyses were performed for IOP, mean visual field deterioration, ocular blood circulation, and blood pressure by analyzing score changes before and after the intervention. Because most studies did not report significant differences in adverse effects between groups, a comprehensive meta-analysis was not feasible; therefore, only a descriptive analysis of adverse effects was conducted. Due to variations in intervention methods across studies, subgroup analyses were performed to compare antioxidant treatment with placebo, as well as the combination of topical treatment and antioxidants with topical treatment alone. Additional subgroup analyses were conducted based on different ocular blood flow measurement sites, including the optic nerve head, superior temporal disc rim, inferior temporal disc rim, superior temporal peripapillary retina, and inferior temporal peripapillary retina.
Data analyses were conducted using Review Manager 5.4. For continuous data measured on the same scale, the mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) was calculated. The standardized mean difference (SMD), with 95% CIs, was used when data were reported on different scales. Heterogeneity among studies was assessed using the I2 statistic, interpreted according to the Cochrane Handbook, with 0%–40%, 30%–60%, 50%–90%, and 75%–100% indicating minimal, moderate, substantial, and considerable heterogeneity, respectively. A fixed-effects model was applied for all analyses. The experimental group comprised participants who received antioxidants alone or in combination with topical treatment, whereas the control group included those who received either a placebo or topical treatment alone. To account for differences in measurement time points across studies, the final recorded time point from each study was used in the analysis.
2.6 Quality of evidence
The quality of evidence was assessed using the GRADE scoring system (Balshem et al., 2011). According to GRADE methodology, evidence from RCTs is initially classified as high quality but may be downgraded due to factors such as imprecision, inconsistency, indirectness, or publication bias. The evidence was categorized into the following two subgroups based on treatment type: (1) antioxidant treatment versus placebo and (2) a combination of topical treatment and antioxidants versus topical treatment alone.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of included studies
Overall, 518 relevant studies were identified through the search strategy. After removing 218 duplicate articles, 300 articles underwent title and abstract screening. Of these, 258 were excluded due to reviews, nonhuman studies, retrospective studies, protocols, case reports, or failure to meet the inclusion criteria. Following this initial screening, 42 articles proceeded to full-text review. Secondary screening led to the exclusion of several studies: four studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria, 10 conference abstracts, four studies lacking reported outcome data, four studies with inappropriate control groups, four non-English studies, and one study for which the full text was not accessible. Ultimately, 15 studies (Harris et al., 2018; Jabbarpoor Bonyadi et al., 2014; Garcia-Medina et al., 2015; Guo et al., 2014; Hao et al., 2018; Mahdiani et al., 2024; Ohguro et al., 2012; Ohguro et al., 2013; Parisi et al., 2014; Park et al., 2011; Quaranta et al., 2003; Sari et al., 2016; Yoshida et al., 2013; Vetrugno et al., 2012; Zhong et al., 2010) met the inclusion criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. The study screening and selection process is illustrated in Figure 1. The major characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1.
FIGURE 1
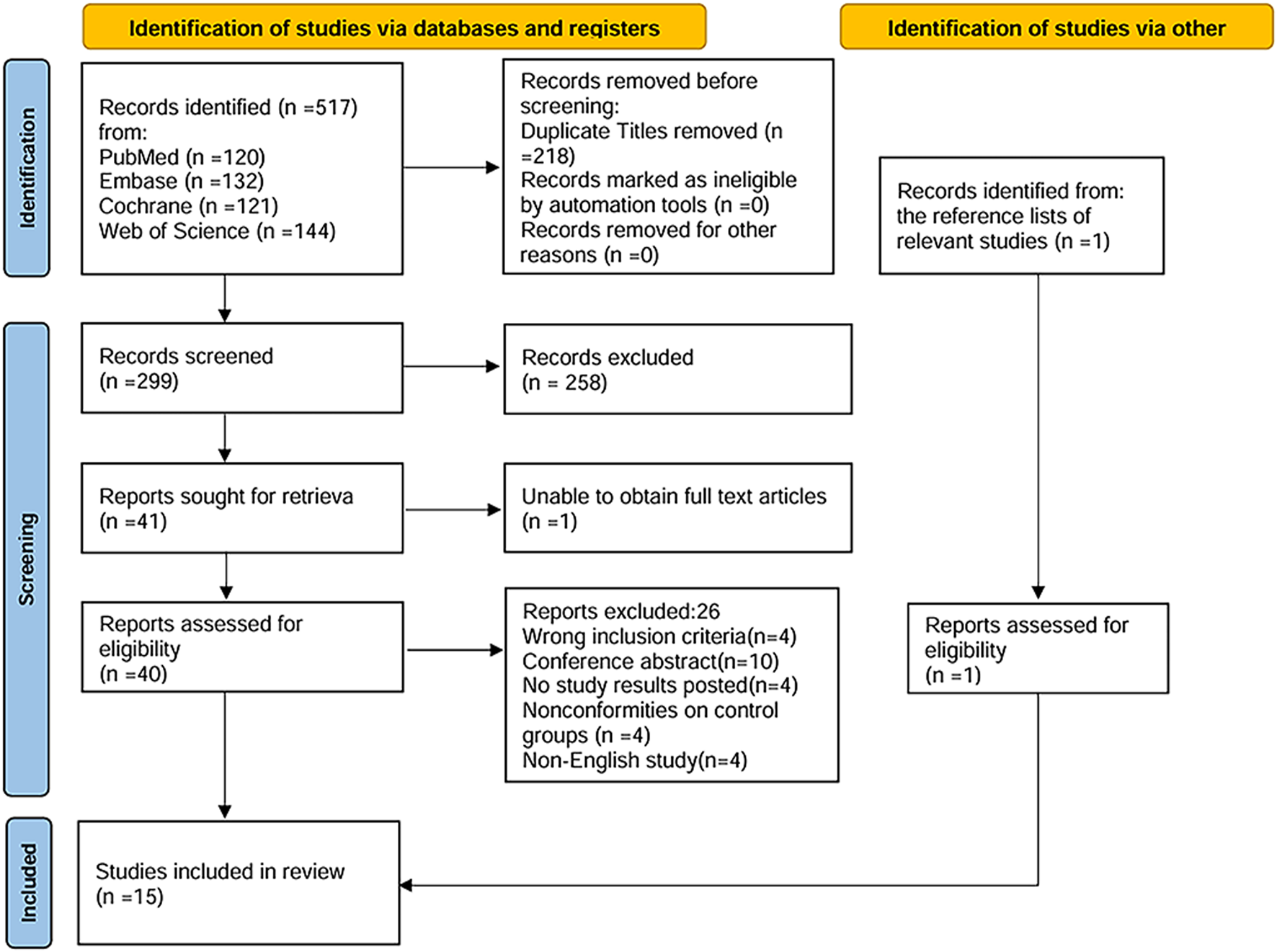
Flow diagram of literature search and selection process according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses statement.
TABLE 1
| Study | Study design | Country and participants | Sample description | Intervention | Outcome and duration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Control | Case | Control | ||||
| Harris et al. (2018) | Cross over trial | USA OAG |
42 (24/18) 67.1 ± 10.9 |
42 (24/18) 67.1 ± 10.9 |
Four soft gels daily of dietary supplement→ washout→ four soft gels daily of placebo | Four soft gels daily of placebo→ washout→ four soft gels daily of dietary supplement | HR, BP, IOP, and ocular blood flow 1 month |
| Bou Ghanem et al. (2014) | RCT | Iran POAG |
17 (10/7) 66.3 ± 9.5 |
17 (11/6) 67.6 ± 8.3 |
Topical timolol 0.5% two times daily, and dorzolamide 2% three times daily One saffron capsule daily |
Topical timolol 0.5% two times daily, and dorzolamide 2% three times daily One placebo capsule daily |
IOP 4 weeks |
| Garcia-Medina et al. (2015) | RCT | Spain POAG |
54 (21/33) 60.76 ± 12.21 |
63 (28/35) 63.14 ± 10.76 |
Topical antiglaucoma medications, one antioxidant-containing capsule after breakfast from Monday to Friday | Topical antiglaucoma medications | VF, RNFL parameters, and GCC parameters 2 years |
| Guo et al. (2014) | Cross over trial | China NTG |
28 (16/12) 63.7 ± 6.5 |
28 (16/12) 63.7 ± 6.5 |
A capsule containing 40 mg of ginkgo biloba three times a day→washout→Identical placebo capsules three times daily | Identical placebo capsules three times daily→washout→a capsule containing 40 mg of ginkgo biloba three times a day | VF, IOP, BP, contrast sensitivity, and side effects 4 weeks |
| Hao et al. (2018) | RCT | China POAG |
58 (28/30) 58.3 ± 12.3 |
50 (26/24) 58.3 ± 12.3 |
Artificial tear solution, Puerarin 2 mg/kg | Artificial tear solution, placebo 2 mg/kg | IOP, VA, TBUT, VF defect, inflammation score, corneal erosion, subjective discomfort, and side effects 6 months |
| Mahdiani et al. (2024) | RCT | Iran POAG |
20 (11/9) 56.88 ± 11.38 |
20 (7/13) 55.17 ± 14.6 |
Topical medications: 15 mg crocin tablet every day | Topical medications, identical placebo tablet every day | IOP, BCVA, CDR, and RNFL thickness 4 months |
| Ohguro (2012) | RCT | Japan OAG |
20 (13/7) 60.35 ± 7.22 |
20 (10/10) 63.20 ± 14.78 |
Take two capsules containing BCAC once a day | Take two placebo capsules once a day | IOP, VF, BP, PR, and ocular blood flow 2 years |
| Ohguro et al. (2013) | RCT | Japan OAG |
12 (8/4) 61.42 ± 6.95 |
9 (6/3) 64.78 ± 14.39 |
Prostaglandin analogs, two capsules containing BCAC once a day | Prostaglandin analogs, two capsules containing a placebo once a day | IOP, VF, BP, and PR 2 years |
| Parisi et al. (2014) | RCT | Spain OAG |
22 52.8 ± 5.46 |
21 52.1 ± 5.22 |
β-blocker monotherapy, coenzyme Q10, and vitamin E | β-blocker monotherapy | PERG, VEP, and IOP 12 months |
| Park et al. (2011) | RCT | Korea NTG |
15 (7/8) 18–80 |
15 (4/11) 18–80 |
80 mg GBE orally two times a day | Placebo orally two times a day | IOP, VF, and ocular blood flow 4 weeks |
| Quaranta et al. (2003) | Cross over trial | Italy NTG |
27 (16/11) 70.4 ± 6.5 |
27 (16/11) 70.4 ± 6.5 |
A capsule containing 40 mg of ginkgo biloba three times a day→washout→Identical placebo capsules three times daily | Identical placebo capsules three times daily→washout→a capsule containing 40 mg of ginkgo biloba three times a day | VF and side effects 4 weeks |
| Sari et al. (2016) | RCT | Indonesia POAG |
20 (6/14) 54.63 ± 4.34 |
20 (8/12) 54.92 ± 4.26 |
40 mg GBE two times daily | Identical placebo two times daily | IOP, VF, RNFL thickness, CDR, and OS marker 6 months |
| Yoshida et al. (2013) | RCT | Japan OAG |
19 (NA) | 19 (NA) | Take two capsules containing BCAC once a day | Take two placebo capsules once a day | Levels of ET-1 concentration, NO, AOPP and antioxidant activities 2 years |
| Vetrugno et al. (2012) | RCT | Italy POAG |
52 (25/27) 63.5 ± 7.62 |
45 (23/22) 67.4 ± 6.37 |
Antiglaucoma medication, one supplement tablet two times a day | Antiglaucoma medication | IOP 3 weeks |
| Zhong et al. (2010) | RCT | China POAG |
20 (10/10) 63.00 ± 14.45 |
20 (11/9) 64.83 ± 13.03 |
Two tablets containing 40 mg of flavonoids orally three times a day | Two placebo tablets orally three times a day | IOP, CDR, VF, BP, PR and VA 6 months |
Summary of the included studies.
RCT, randomized control trial; OAG, open-angle glaucoma; POAG, primary open-angle glaucoma; NTG, normal tension glaucoma; IOP, intraocular pressure; VF, visual field; RNFL, retinal nerve fiber layer; GCC, ganglion cell complex; VA, visual acuity; BCVA, best-corrected visual acuity; CDR, cup-to-disc ratio; PERG, pattern electroretinogram; VEP, visual-evoked potential; TBUT, tear film break-up time; NO, nitric oxide; AOPP, advanced oxidation protein products; OS, oxidative stress; BP, blood pressure; HR, heart rate; PR, pulse rate; NA, not applicable; Sample description: sample size (male/female); age (mean ± SD, or median [minimum–maximum]).
3.2 Risk of bias
The risk of bias in the 15 included RCTs was assessed using the Cochrane Risk-of-Bias tool (Higgins et al., 2011); the results are summarized in Figure 2. Two studies met all assessment criteria and were classified as having a low risk of bias. Twelve studies exhibited an unclear risk due to uncertainties in one or more domains. One study was deemed to have a high risk of bias due to the lack of blinding in a specific domain.
FIGURE 2
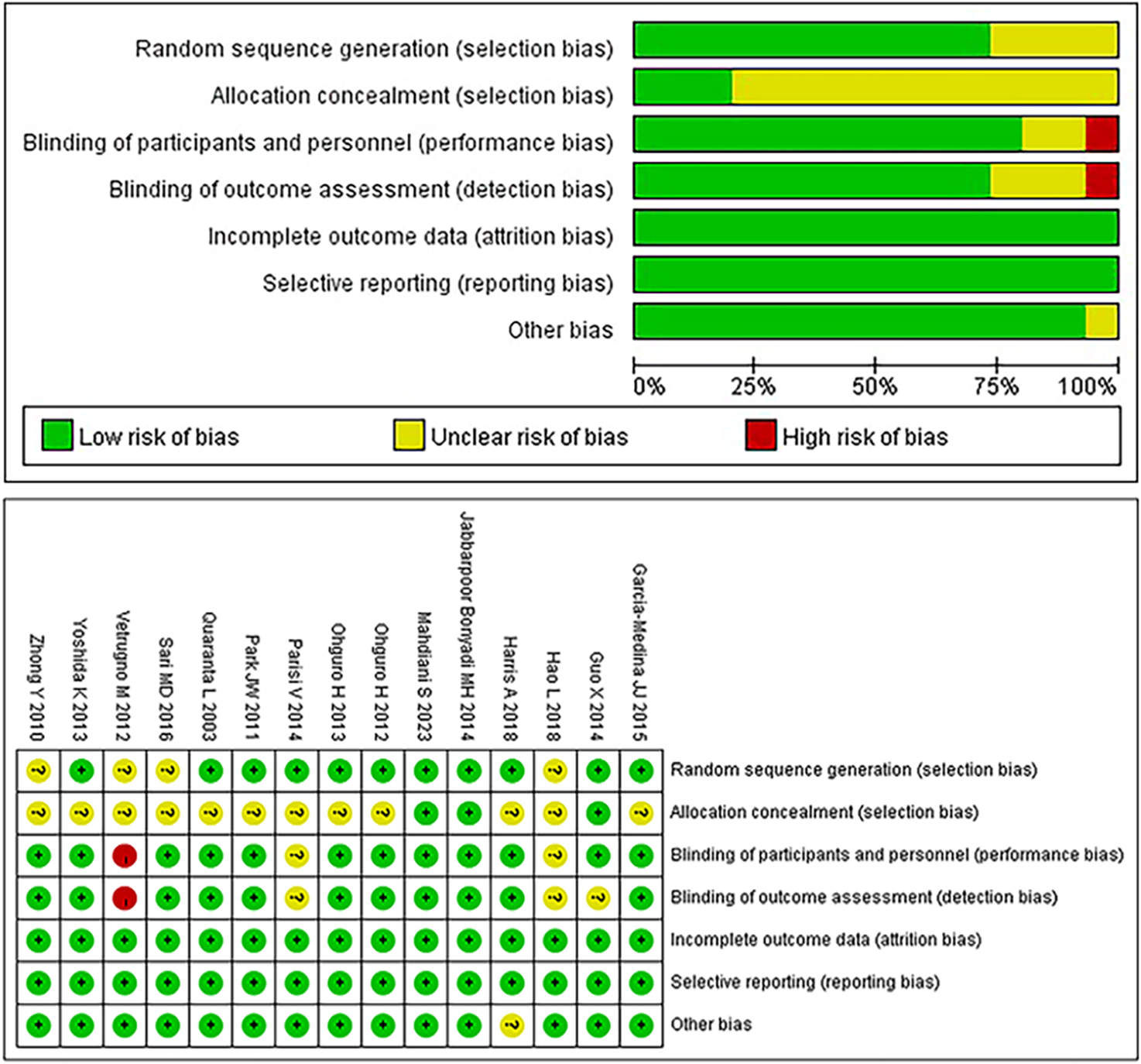
Bias risk of the included studies (Cochrane Collaboration tool).
3.3 Meta-analysis
The meta-analysis included 15 studies, and the results for each outcome measure are detailed below.
3.3.1 Intraocular pressure
Eight studies assessing the effect of antioxidants on IOP in patients with POAG were included in the analysis. The overall heterogeneity among the studies was 22%. Subgroup analysis revealed that, compared to placebo, antioxidant treatment did not result in a statistically significant reduction in IOP (MD -0.61 [−1.29, 0.07]; P = 0.08; I2 = 39%; PI2 = 0.18). However, the combination of topical treatment and antioxidants was associated with a significantly greater reduction in IOP than in topical treatment alone (MD -1.26 [−2.25, −0.27], P = 0.01, I2 = 0%, PI2 = 0.39). The overall pooled analysis indicated that the experimental group (n = 240) had a significantly lower IOP than the control group (n = 222) (MD -0.82 [−1.38, −0.26], P = 0.004; I2 = 22%, PI2 = 0.25; Figure 3). Notably, sensitivity analysis excluding one study (Vetrugno et al., 2012) with high risk of bias demonstrated consistent results (MD -0.74 [−1.32, −0.16], P = 0.01; I2 = 23%, PI2 = 0.25), suggesting relative robustness of the findings.
FIGURE 3
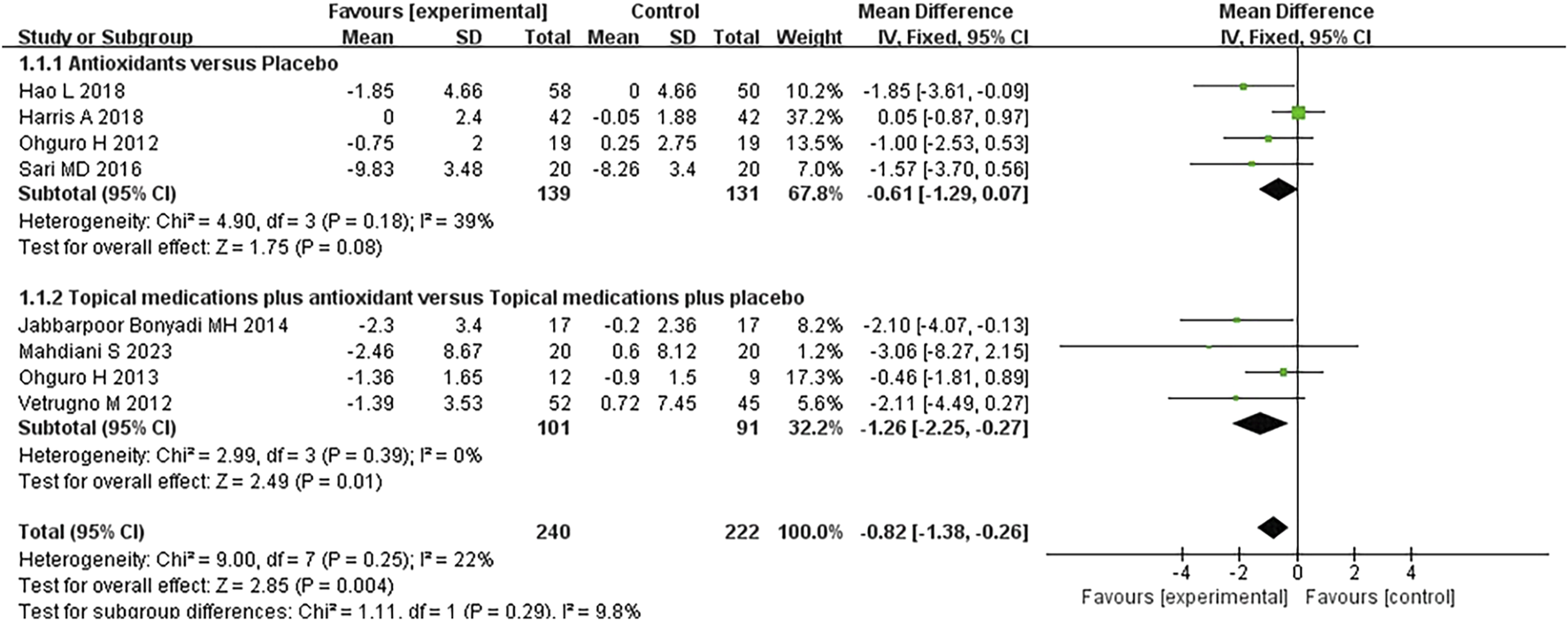
Meta-analysis plot of intraocular pressure (mmHg) in the experimental and control groups.
3.3.2 Visual field
Seven studies assessed the visual field in patients with POAG. When analyzing the first and second phases of the crossover trial separately, a meta-analysis of the mean visual field deterioration (endpoint value minus baseline value) indicated a statistically significant improvement in the experimental group compared to the control group (MD −0.45 [−0.49, −0.42], P < 0.00001). Subgroup analysis revealed that antioxidants alone were more effective than placebo (MD −0.45 [−0.49, −0.42], P < 0.00001, I2 = 54%, PI2 = 0.04), whereas combined topical treatment with antioxidants showed no significant difference compared to topical treatment alone (MD −0.13 [−0.70, 0.95], P = 0.76, I2 = 79%, PI2 = 0.03). The overall heterogeneity in the effect of antioxidants on mean visual field deterioration across all studies was moderate (I2 = 60%, PI2 = 0.01; Figure 4). Further investigation of this heterogeneity identified the study by Quaranta et al. (2003), where the authors reported results as mean ±2 SD, as a potential source of substantial heterogeneity. Excluding this study reduced the heterogeneity to 31% (MD -0.45 [−0.48, −0.42], P < 0.00001, I2 = 31%, PI2 = 0.19; Figure 5).
FIGURE 4
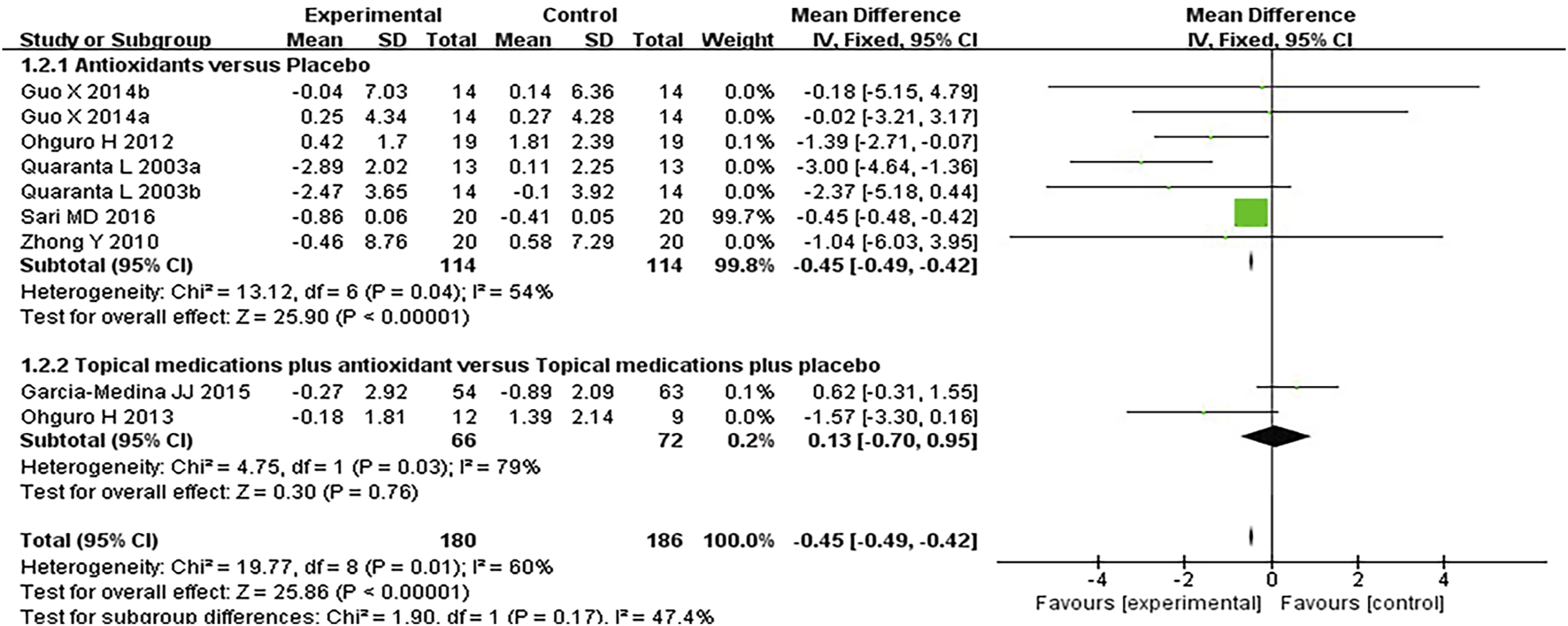
Meta-analysis plot of visual field mean deterioration (dB) in the experimental and control groups.
FIGURE 5
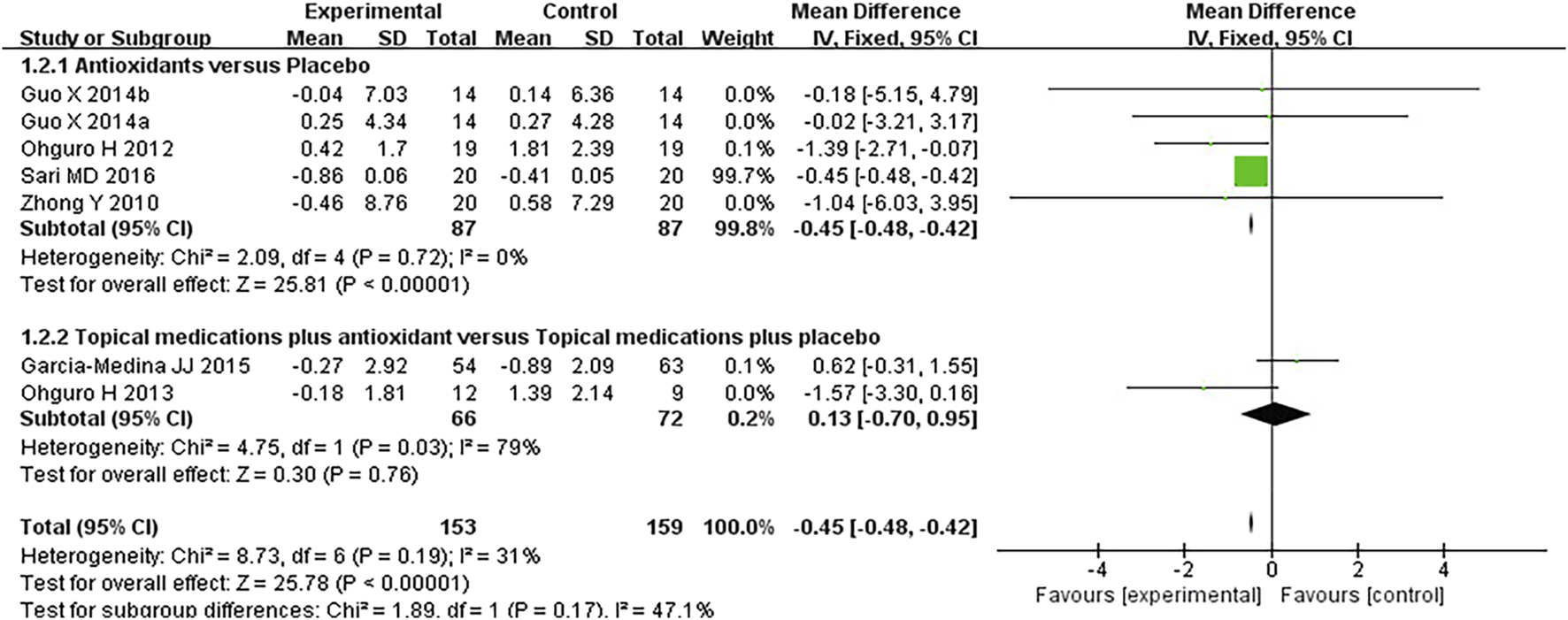
Meta-analysis plot of visual field mean deterioration (dB) in the experimental and control groups.
3.3.3 Ocular blood circulation
Three studies assessing the effect of antioxidants on retinal blood flow in patients with POAG were analyzed; the studies together comprised 12 subgroups, and the measured parameters were as follows: optic nerve head, superior temporal disc rim, inferior temporal disc rim, superior temporal peripapillary retina, and inferior temporal peripapillary retina. Compared to placebo, antioxidants significantly improved blood flow in the optic nerve head (SMD 0.55 [0.06, 1.03], P = 0.03, I2 = 0%, PI2 = 0.81), superior temporal disc rim (SMD 0.52 [0.03, 1.01], P = 0.04, I2 = 58%, PI2 = 0.12), inferior temporal disc rim (SMD 0.81 [0.31, 1.31], P = 0.001, I2 = 0%, PI2 = 0.56), and inferior temporal peripapillary retina (SMD 0.53 [0.21, 0.86], P = 0.001, I2 = 0%, PI2 = 0.39), except for the superior temporal peripapillary retina (SMD 0.29 [-0.03, 0.61], P = 0.08, I2 = 51%, PI2 = 0.13). The pooled analysis indicated that the experimental group (n = 254) exhibited significantly higher retinal blood flow than the control group (n = 254) (SMD 0.49 [0.32, 0.67]; P < 0.00001; I2 = 8%; PI2 = 0.36; Figure 6).
FIGURE 6
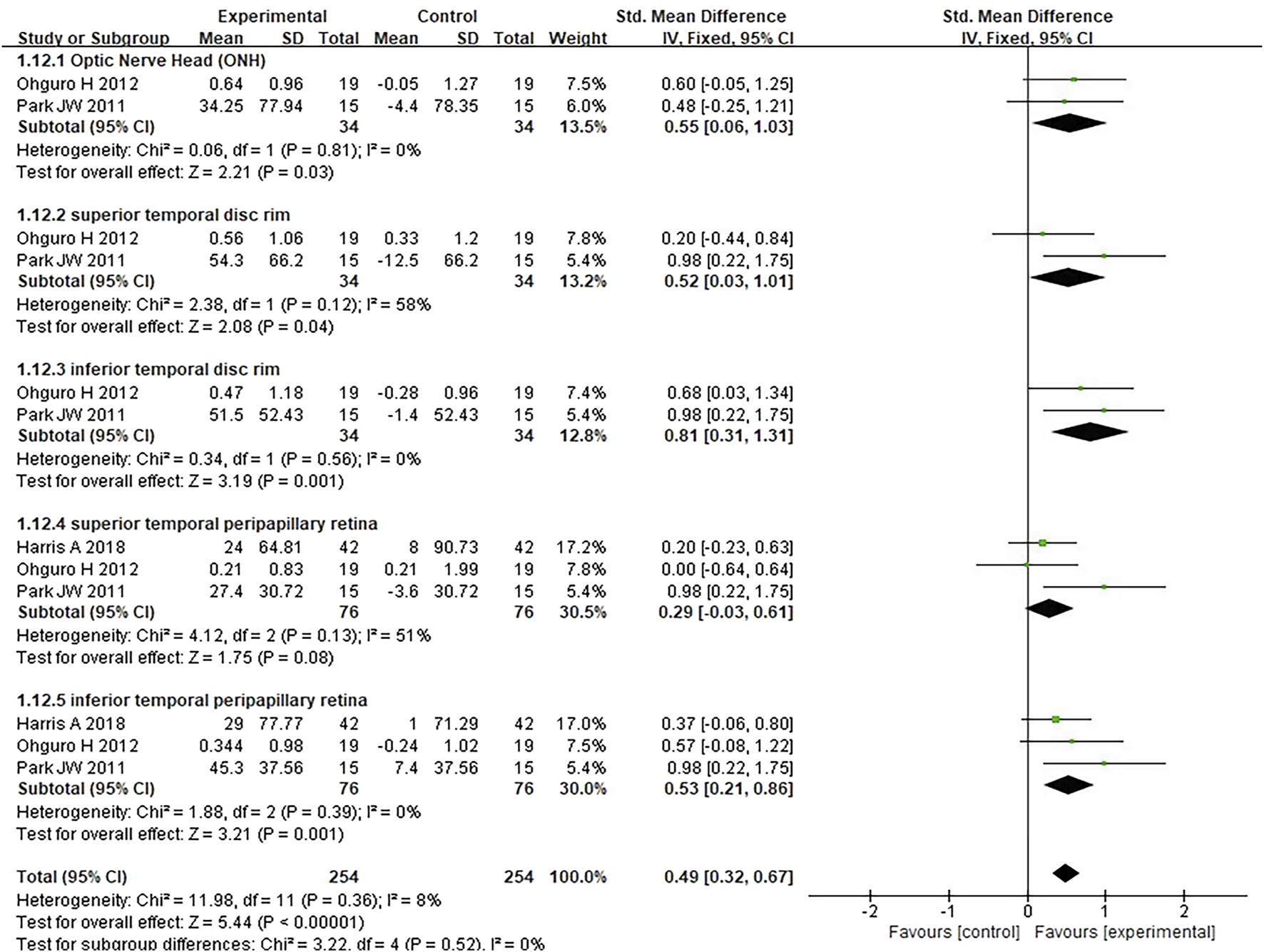
Meta-analysis plot of ocular blood circulation in the experimental and control groups.
3.3.4 Blood pressure
Six studies where systolic and diastolic blood pressure data were reported were included in the analysis, with separate assessments conducted for the first and second phases of the crossover trials. Seven subgroups were included in this meta-analysis. The forest plots for systolic and diastolic blood pressure indicated no statistically significant differences between the experimental and control groups for either systolic blood pressure (MD 0.57 [−1.85, 2.98], P = 0.64, I2 = 0%, PI2 = 1.00) or diastolic blood pressure (MD 0.29 [−1.62, 2.21], P = 0.76, I2 = 0%, PI2 = 0.97) (Figures 7, 8).
FIGURE 7
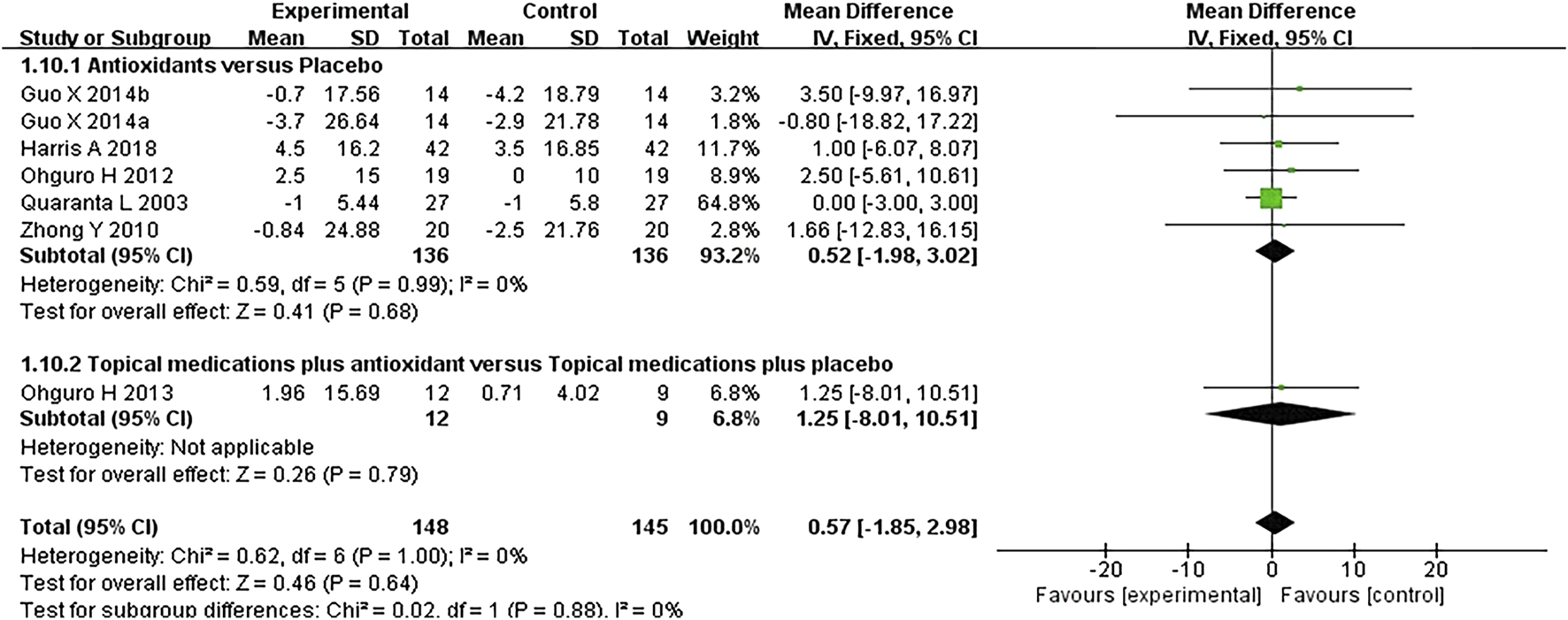
Meta-analysis plot of systolic blood pressure (mmHg) in the experimental and control groups.
FIGURE 8
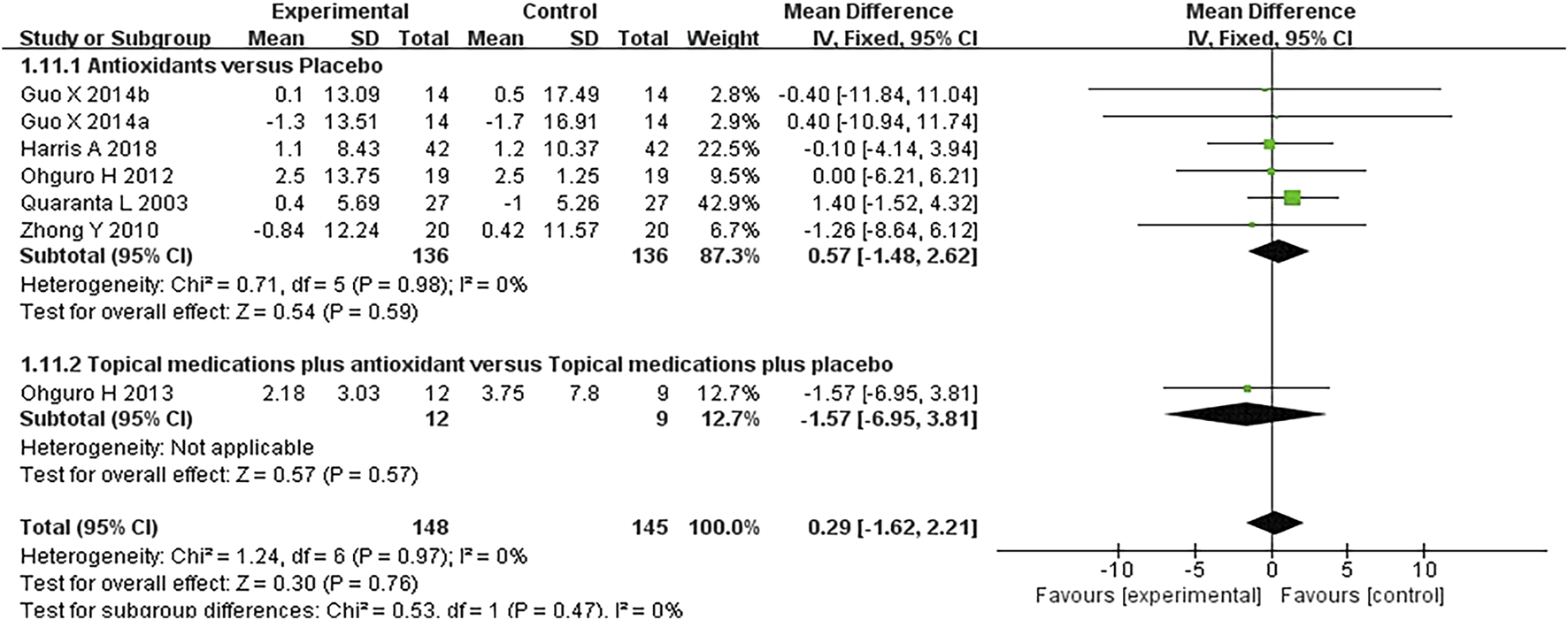
Meta-analysis plot of diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) in the experimental and control groups.
3.4 Adverse effects
In seven of the studies, the adverse effects of treatment were assessed. Guo et al. (2014) identified two drug-related adverse events during the placebo phase, whereas Mahdiani et al. (2024) reported nine and seven cases during the antioxidant and placebo phases, respectively. No adverse events occurred during treatment in the other studies. No statistically significant differences were observed in adverse effects between the treatment and placebo groups. Adverse events reported by the studies are presented in Table 2.
TABLE 2
| Study | Intervention | Adverse events (test Group) | Adverse events (control Group) | Causality assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harris et al. (2018) | 4 capsule of antioxidant supplement per day | None | None | — |
| Jabbarpoor Bonyadi et al. (2014) | Saffron extract 30 mg/day | None | None | — |
| Garcia-Medina et al. (2015) | 1 capsule of antioxidant supplement per day | None | None | — |
| Guo et al. (2014) | Ginkgo biloba 120 mg/day | None | Gastric discomfort (n = 1), urticaria (n = 1) | Possibly unrelated |
| Hao et al. (2018) | Puerarin 2 mg/kg | None | None | — |
| Mahdiani et al. (2024) | Crocin 15 mg/day | Epiphora (n = 2); Increased IOP (n = 1); Nausea (n = 1); Shortness of breath (n = 1); Increased heart rate (n = 1); Red light sensitivity (n = 1); Reduced visibility (n = 2) | Floaters and brown spots in the eye (n = 2); Burning eyes (n = 1); Increased IOP (n = 3); Reduced visibility (n = 1) | Possibly related |
| Ohguro et al. (2012) | Black currant anthocyanins 50 mg/day | None | None | — |
| Ohguro et al. (2013) | Black currant anthocyanins 50 mg/day | not reported | not reported | — |
| Park et al. (2011) | Ginkgo biloba 160 mg/day | None | None | — |
| Quaranta et al. (2003) | Ginkgo biloba 120 mg/day | None | None | — |
| Sari et al. (2016) | Ginkgo biloba 80 mg/day | not reported | not reported | — |
| Yoshida et al. (2013) | Black currant anthocyanins 50 mg/day | not reported | not reported | — |
| Vetrugno et al. (2012) | Forskolin 30 mg + rutin 400 mg | not reported | not reported | — |
| Zhong et al. (2010) a | Erigeron breviscapus 240 mg/day | None | None | — |
| Parisi et al. (2014) | Topical eye drops containing Coenzyme Q10 (100 mg) and Vitamin E TPGS (500 mg), 2drops/day | None | None | — |
Adverse events reported by the studies.
Study included in this review used a dose higher than the recommended daily amount.
Across the 15 included studies, Guo et al. (2014) identified two drug-related adverse events (AEs) during the placebo phase, whereas Mahdiani et al. (2024) reported nine and seven AEs during the antioxidant and placebo phases, respectively. Nine studies reported no occurrence of AEs during treatment, while four studies did not document treatment-emergent AEs. No statistically significant differences were observed in AEs between the treatment and placebo groups. AEs reported by the studies are presented in Table 2. Notably, in the study by Zhong et al., the administered metabolite dosage exceeded the recommended daily allowance; however, no AEs were observed in any participant throughout the 6-month trial period.
3.5 Level of evidence
The quality of evidence was assessed using the GRADE approach. Two overall assessments were performed as follows: (1) a comparison of antioxidants with placebo (Figure 9) and (2) a comparison of combined topical treatment with antioxidants versus topical treatment alone (Figure 10). The overall quality of evidence ranged from “very low” to “low.” The primary factors contributing to evidence downgrading were the risk of bias and the small sample size.
FIGURE 9
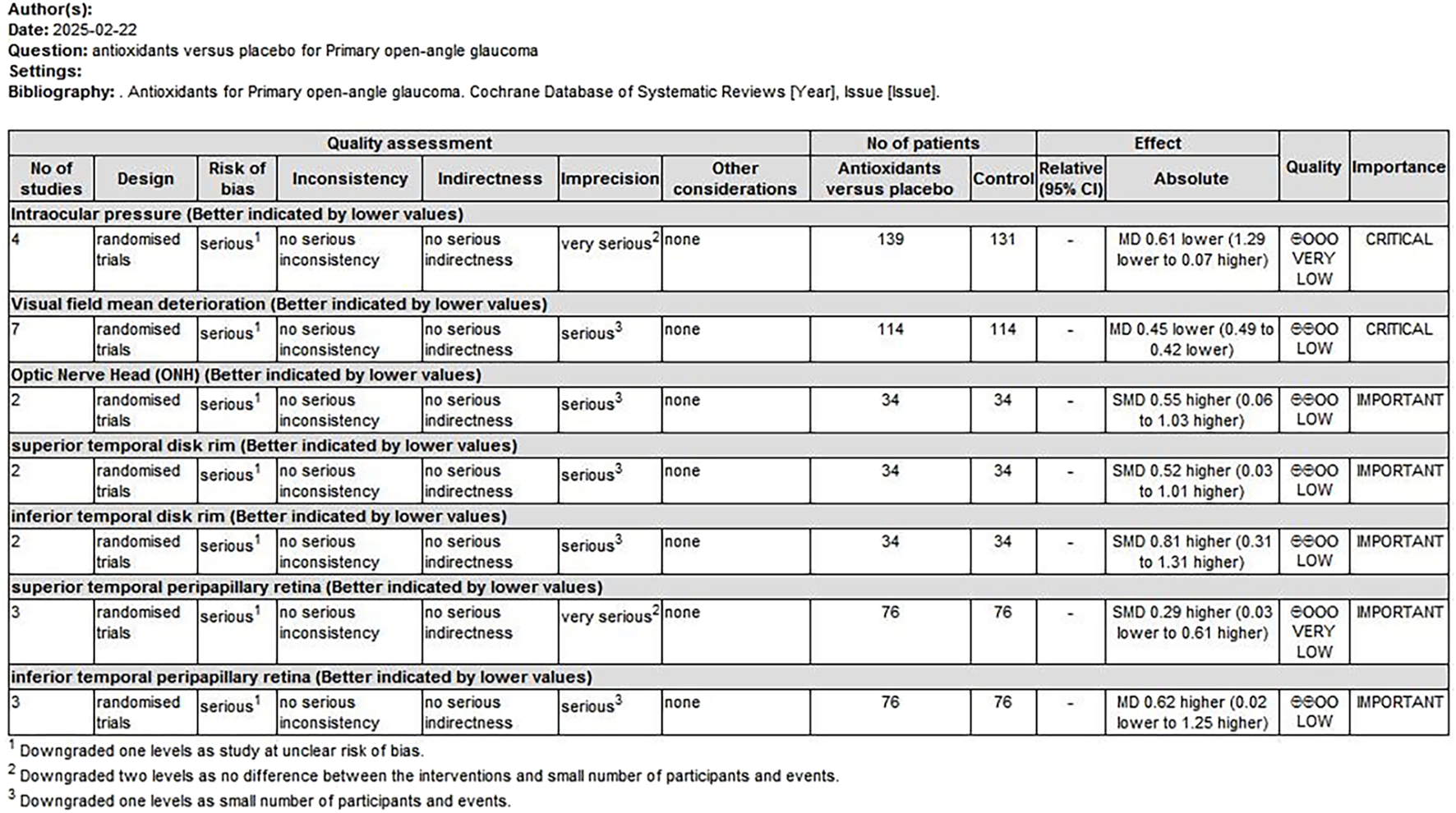
Antioxidant treatment compared to placebo for treating POAG. POAG, primary open-angle glaucoma.
FIGURE 10
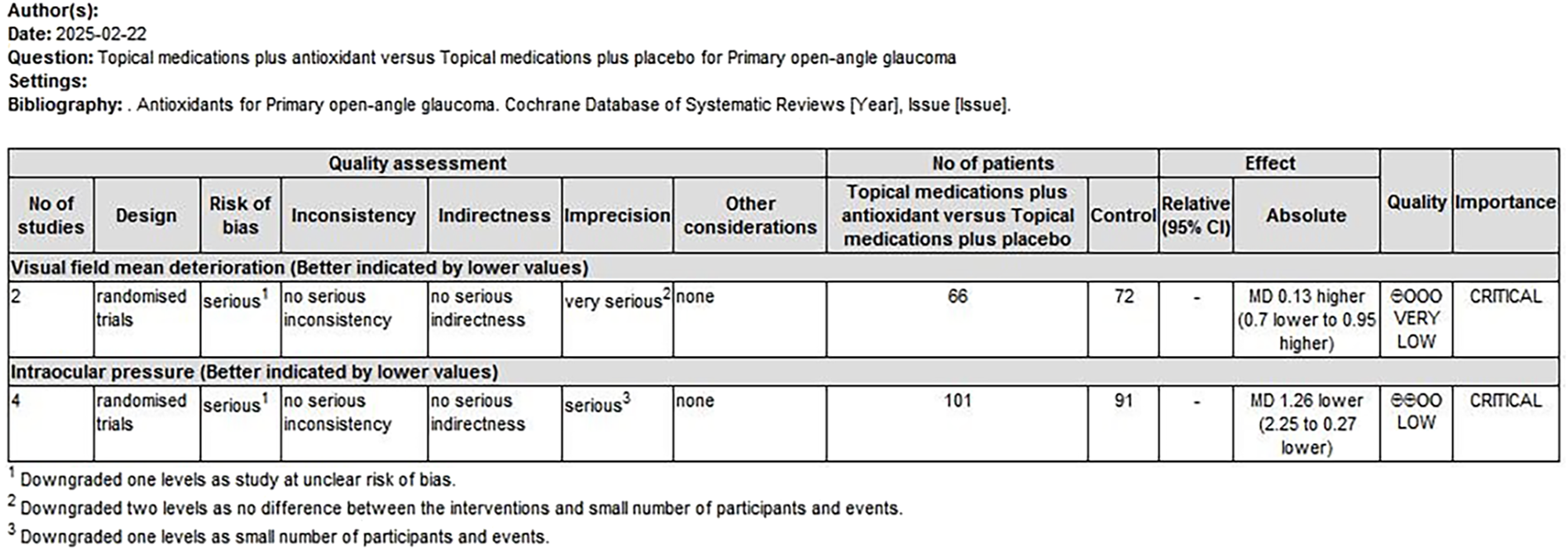
Combination of topical treatment with antioxidants compared to topical treatment alone for treating POAG. POAG, primary open-angle glaucoma.
4 Discussion
Antioxidants have been widely studied for their potential to enhance ocular health in patients with glaucoma; however, their specific effects on POAG have not been systematically evaluated. The results of our meta-analysis indicate that antioxidant treatment significantly reduces IOP in patients with POAG and leads to statistically significant improvements in mean visual field deterioration and ocular blood circulation. Conversely, we found no significant differences in blood pressure or adverse effects between antioxidant and placebo treatments. The quality of evidence supporting significant outcome differences, as assessed using the GRADE scoring system, ranged from grade D to C for both comparisons: antioxidants versus placebo and antioxidants combined with topical treatment versus topical treatment alone. The strength of evidence was rated at level 2 allocation concealment methods or blinding were not indicated in all of the studies, and the overall quality of the evidence was limited due to inadequate study design and small sample sizes, contributing to the downgrading of evidence levels. These preliminary findings suggest that antioxidant supplementation may offer adjunctive benefits in POAG. However, the low certainty of evidence (GRADE: D to C) underscores the need for large-scale, rigorously designed RCTs to validate these effects before clinical recommendations can be established.
OS is broadly defined as an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the efficacy of antioxidant defense mechanisms. This imbalance results in damage to macromolecules such as DNA, proteins, and lipids, ultimately triggering apoptosis. OS is a common pathological mechanism underlying various neurodegenerative diseases, including glaucoma (Nita and Grzybowski, 2016; Tezel, 2006; Aruoma, 1998; Andersen, 2004). There is increasing evidence from both animal models and clinical studies that OS is present in the ocular tissues of experimental glaucoma models and patients with clinical glaucoma (Jassim et al., 2021; Benoist d'Azy et al., 2016). OS plays a pivotal role in the progression of glaucoma through a dual mechanism. Firstly, OS directly disrupts the structure and function of the trabecular meshwork, obstructing aqueous humor outflow and thereby contributing to pathological elevation of IOP (Izzotti et al., 2006; Vernazza et al., 2020; Chrysostomou et al., 2013). Secondly, OS-induced vascular alterations compromise the autoregulation of optic nerve blood flow, leading to localized ischemia (Izzotti et al., 2006; Raaz et al., 2014; Chrysostomou et al., 2013). These mechanisms act synergistically: elevated IOP exacerbates compression of the optic nerve microvasculature, intensifying ischemia, while ischemia promotes ROS accumulation, further amplifying oxidative stress. This self-perpetuating cycle collectively accelerates retinal ganglion cell (RGC) degeneration.
IOP control has long been the foundation of POAG management. Studies linking OS to glaucoma pathogenesis further indicate that antioxidants could mitigate neuronal degeneration and slow disease progression. By scavenging free radicals, antioxidants can reduce OS, enhance trabecular meshwork function, facilitate aqueous humor outflow, and lower IOP. This reduction in IOP can, in turn, minimize RGC damage, inhibit optic nerve atrophy, and preserve visual field function. Additionally, studies have indicated that antioxidants, including vitamin E and coenzyme Q10, can modulate the ocular redox state, influencing aqueous humor dynamics (Martucci and Nucci, 2019; Engin et al., 2007; Ozates et al., 2019). Antioxidants may also enhance retinal blood flow by improving ocular microcirculation and reducing local ischemic damage. By inhibiting ROS production and enhancement of vascular endothelial function, antioxidants promote ocular blood circulation, optimize blood supply to the optic nerve, and mitigate ischemic injury (Jabbehdari et al., 2021). These findings indicate that antioxidants exert multifaceted protective effects in POAG management by improving IOP regulation, preserving visual field function, and enhancing ocular blood circulation, ultimately contributing to delayed disease progression.
Although antioxidants have shown promising potential in significantly reducing IOP, improving mean visual field deterioration, and enhancing ocular blood circulation, their integration into clinical practice requires caution. First, IOP control remains the cornerstone of glaucoma management. While observed reductions in IOP may reach statistical significance, current guidelines indicate that a clinically meaningful decrease generally requires a ≥20% reduction from baseline (Gedde et al., 2021; Augusto et al., 2021). Consequently, antioxidant monotherapy may have limited efficacy, and combination therapy with conventional IOP-lowering medications may provide additional benefits.
A major limitation of the current evidence is the considerable heterogeneity in antioxidant interventions across the included trials, with substantial variations observed in antioxidant types and inconsistent reporting of metabolite preparation details, dosage regimens, and administration routes in original studies (see Table 3) Additionally, some studies evaluated antioxidants as adjuncts to conventional IOP-lowering therapies, whereas others administered them as monotherapy. These clinical and methodological variations make it challenging to determine whether the observed effects can be attributed to any specific metabolite, dosage, or regimen. Consequently, the pooled results should be interpreted as reflecting the average effect of antioxidants as a class, rather than the precise efficacy of a particular preparation. This heterogeneity also limits the generalizability of the findings, especially in clinical practice, where treatment decisions require drug-specific evidence regarding optimal dosage and duration. Future research should therefore focus on rigorously designed RCTs that directly compare different antioxidants using standardized dosages, uniform treatment courses, and objective biological endpoints to identify potentially superior metabolites or regimens, thereby providing more precise evidence for clinical application. Methodologically, several studies lacked adequate reporting of key design elements, including randomization procedures, allocation concealment, and blinding methods, which may introduce bias and undermine the internal validity of the results. Future clinical trials should rigorously adhere to the CONSORT guidelines to improve methodological quality and ensure transparent reporting of critical trial metabolites.
TABLE 3
| Study | Botanical drug/Antioxidant | Taxonomic validation (POWO/MPNS) | Pharmacopeial standard | Reported composition | Complete details in original study? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harris et al. (2018) | Antioxidant blend | N/A (non-botanical) | — | Blend of ingredients | Yes (full composition listed) |
| Jabbarpoor Bonyadi et al. (2014) | Saffron extract | Crocus sativus L. [Iridaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:436688-1) | Crocus sativus L., stigmas (Ph. Eur. 11) | 30 mg saffron stigma extract | Partial (no active compound quantification) |
| Garcia-Medina et al. (2015) | Synthetic antioxidants | N/A (non-botanical) | — | Blend of ingredients | Yes (full composition listed) |
| Guo et al. (2014) | Ginkgo leaf extract | Ginkgo biloba L. [Ginkgoaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:262125-1) | Ginkgo Folium (Ph. Eur. 11) | 40 mg extract (24% flavonol glycosides, 6% terpene lactones) | Yes (EGb761 standard) |
| Hao et al. (2018) | Puerarin | Pueraria montana var. Lobata (Willd.) (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:967441-1) | None | Puerarin 2 mg/kg (≥98% purity) | Yes (purity specified) |
| Mahdiani et al. (2024) | Crocin | Crocus sativus L. [Iridaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:436688-1) | Crocus sativus L., stigmas (Ph. Eur. 11) | 15 mg crocin (≥90% purity by HPLC) | Yes (analytical validation) |
| Ohguro et al. (2012) | Black currant anthocyanins | Ribes nigrum L. [Grossulariaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:792873-1) | None | 50 mg anthocyanins | Yes (doses specified) |
| Ohguro et al. (2013) | Black currant anthocyanins | Ribes nigrum L. [Grossulariaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:792873-1) | None | 50 mg anthocyanins | Yes (doses specified) |
| Park et al. (2011) | Ginkgo leaf extract | Ginkgo biloba L. [Ginkgoaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:262125-1) | Ginkgo Folium (Ph. Eur. 11) | 80 mg extract (19.2 mg flavonol glycosides) | Yes (standardized extract) |
| Quaranta et al. (2003) | Ginkgo leaf extract | Ginkgo biloba L. [Ginkgoaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:262125-1) | Ginkgo Folium (Ph. Eur. 11) | 40 mg extract (24% flavonol glycosides, 6% terpene lactones) | Yes (EGb761 standard) |
| Sari et al. (2016) | Ginkgo leaf extract | Ginkgo biloba L. [Ginkgoaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:262125-1) | Ginkgo Folium (Ph. Eur. 11) | 40 mg extract (24% flavonol glycosides, 6% terpene lactones) | Yes (EGb761 standard) |
| Yoshida et al. (2013) | Black currant anthocyanins | Ribes nigrum L. [Grossulariaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:792873-1) | None | 50 mg anthocyanins | Yes (doses specified) |
| Vetrugno et al. (2012) | Forskolin + rutin | Coleus hadiensis (Forssk.) A.J.Paton [Lamiaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:77201104-1) + Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott [Fabaceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:1119529-2) |
None | Forskolin 15 mg + rutin 200 mg | Yes (ratios provided) |
| Zhong et al. (2010) | Erigeron breviscapus extract | Erigeron breviscapus (Vaniot) Hand.-Mazz. [Asteraceae] (POWO: urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:203633-1) | None | 40 mg scutellarin (≥85% purity) | Yes (pharmacopeial standard) |
| Parisi et al. (2014) | Coenzyme Q10 + Vitamin E | N/A (synthetic) | — | Topical eye drops containing Coenzyme Q10 (100 mg) and Vitamin E TPGS (500 mg) | Yes (doses specified) |
Detailed information on botanical drug/antioxidant preparations in included studies.
5 Conclusion
Antioxidants significantly reduce IOP, slow visual field deterioration, and enhance ocular blood circulation in patients with POAG. These findings indicate that antioxidants could be an effective adjunct therapy for POAG management. However, current evidence requires further validation through large-scale, high-quality RCTs to ensure the robustness and reliability of these findings. Furthermore, future studies should incorporate standardized functional and structural assessment metrics to more comprehensively evaluate the clinical utility of antioxidants in the management of POAG.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JB: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Conceptualization. YY: Validation, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Methodology, Software. GC: Validation, Software, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. CH: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. CZ: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Validation. XL: Visualization, Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2024NSFC0726).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1625735/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
IOP, intraocular pressure; POAG, primary open-angle glaucoma; PACG, primary angle-closure glaucoma; NTG, normal-tension glaucoma; RGCs, retinal ganglion cells; OS, oxidative stress; RCTs, randomized controlled trials; MD, mean difference; CIs, confidence intervals; SMD, standardized mean difference; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
References
1
Almasieh M. Levin L. A. (2017). Neuroprotection in glaucoma: animal models and clinical trials. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci.3, 91–120. 10.1146/annurev-vision-102016-061422
2
Andersen J. K. (2004). Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: cause or consequence?Nat. Med.10 (Suppl. l), S18–S25. 10.1038/nrn1434
3
Aruoma O. I. (1998). Free radicals, oxidative stress, and antioxidants in human health and disease. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc.75, 199–212. 10.1007/s11746-998-0032-9
4
Augusto A. B. Luca B. Alessandro B. Joao B. B. Chiara B. Andrei B. et al (2021). European Glaucoma society terminology and guidelines for glaucoma, 5th edition. Br. J. Ophthalmol.105, 1–169. 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2021-egsguidelines
5
Balshem H. Helfand M. Schunemann H. J. Oxman A. D. Kunz R. Brozek J. et al (2011). GRADE guidelines: 3. rating the quality of evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol.64, 401–406. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.015
6
Benoist D'azy C. Pereira B. Chiambaretta F. Dutheil F. (2016). Oxidative and anti-oxidative stress markers in chronic glaucoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One11, e0166915. 10.1371/journal.pone.0166915
7
Boccaccini A. Cavaterra D. Carnevale C. Tanga L. Marini S. Bocedi A. et al (2023). Novel frontiers in neuroprotective therapies in glaucoma: molecular and clinical aspects. Mol. Aspects Med.94, 101225. 10.1016/j.mam.2023.101225
8
Bou Ghanem G. O. Wareham L. K. Calkins D. J. (2024). Addressing neurodegeneration in glaucoma: mechanisms, challenges, and treatments. Prog. Retin. Eye Res.100, 101261. 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2024.101261
9
Chrysostomou V. Rezania F. Trounce I. A. Crowston J. G. (2013). Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in glaucoma. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol.13, 12–15. 10.1016/j.coph.2012.09.008
10
Engin K. N. Engin G. Kucuksahin H. Oncu M. Engin G. Guvener B. (2007). Clinical evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of alpha-tocopherol against glaucomatous damage. Eur. J. Ophthalmol.17, 528–533. 10.1177/112067210701700408
11
Evangelho K. Mogilevskaya M. Losada-Barragan M. Vargas-Sanchez J. K. (2019). Pathophysiology of primary open-angle glaucoma from a neuroinflammatory and neurotoxicity perspective: a review of the literature. Int. Ophthalmol.39, 259–271. 10.1007/s10792-017-0795-9
12
Garcia-Medina J. J. Garcia-Medina M. Garrido-Fernandez P. Galvan-Espinosa J. Garcia-Maturana C. Zanon-Moreno V. et al (2015). A two-year follow-up of oral antioxidant supplementation in primary open-angle glaucoma: an open-label, randomized, controlled trial. Acta Ophthalmol.93, 546–554. 10.1111/aos.12629
13
Gedde S. J. Vinod K. Wright M. M. Muir K. W. Lind J. T. Chen P. P. et al (2021). Primary open-angle glaucoma Preferred practice Pattern®. Ophthalmology128, 71–150. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.10.022
14
Guo X. Kong X. Huang R. Jin L. Ding X. He M. et al (2014). Effect of Ginkgo biloba on visual field and contrast sensitivity in Chinese patients with normal tension glaucoma: a randomized, crossover clinical trial. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.55, 110–116. 10.1167/iovs.13-13168
15
Hao L. Lu D. Zhao X. Liu X. (2018). Clinical importance of puerarin for nursing of patients with glaucoma. Biomed. Research-tokyo29, 3034–3036. 10.4066/biomedicalresearch.29-17-3960
16
Harris A. Gross J. Moore N. Do T. Huang A. Gama W. et al (2018). The effects of antioxidants on ocular blood flow in patients with glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol.96, e237–e241. 10.1111/aos.13530
17
Higgins J. P. Altman D. G. Gotzsche P. C. Juni P. Moher D. Oxman A. D. et al (2011). The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ343, d5928. 10.1136/bmj.d5928
18
Hondur G. Göktas E. Yang X. Al-Aswad L. Auran J. D. Blumberg D. M. et al (2017). Oxidative stress-related molecular biomarker candidates for glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.58, 4078–4088. 10.1167/iovs.17-22242
19
Izzotti A. Bagnis A. Saccà S. C. (2006). The role of oxidative stress in glaucoma. Mutat. Research/Reviews Mutat. Res.612, 105–114. 10.1016/j.mrrev.2005.11.001
20
Jabbarpoor Bonyadi M. H. Yazdani S. Saadat S. (2014). The ocular hypotensive effect of saffron extract in primary open angle glaucoma: a pilot study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med.14, 399. 10.1186/1472-6882-14-399
21
Jabbehdari S. Chen J. L. Vajaranant T. S. (2021). Effect of dietary modification and antioxidant supplementation on intraocular pressure and open-angle glaucoma. Eur. J. Ophthalmol.31, 1588–1605. 10.1177/1120672120960337
22
Jassim A. H. Fan Y. Pappenhagen N. Nsiah N. Y. Inman D. M. (2021). Oxidative stress and hypoxia modify mitochondrial homeostasis during glaucoma. Antioxid. Redox Signal35, 1341–1357. 10.1089/ars.2020.8180
23
Jayaram H. Kolko M. Friedman D. S. Gazzard G. (2023). Glaucoma: now and beyond. Lancet402, 1788–1801. 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)01289-8
24
Jin J. (2022). Screening for primary open-angle glaucoma. JAMA327, 2030. 10.1001/jama.2022.7531
25
Kwon Y. H. Fingert J. H. Kuehn M. H. Alward W. L. (2009). Primary open-angle glaucoma. N. Engl. J. Med.360, 1113–1124. 10.1056/NEJMra0804630
26
Leung D. Y. L. Tham C. C. (2022). Normal-tension glaucoma: current concepts and approaches-A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol.50, 247–259. 10.1111/ceo.14043
27
Li S. Shao M. Li Y. Li X. Wan Y. Sun X. et al (2020). Relationship between oxidative stress biomarkers and visual field progression in patients with primary angle closure glaucoma. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2020, 2701539. 10.1155/2020/2701539
28
Lusthaus J. Goldberg I. (2019). Current management of glaucoma. Med. J. Aust.210, 180–187. 10.5694/mja2.50020
29
Mahdiani S. Shokoohi-Rad S. Sepahi S. Motamedshariaty V. S. Mohajeri S. A. Sahebkar A. (2024). Crocin supplementation in primary open angle glaucoma: a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Med. Drug Discov.21, 100169. 10.1016/j.medidd.2023.100169
30
Martucci A. Nucci C. (2019). Evidence on neuroprotective properties of coenzyme Q10 in the treatment of glaucoma. Neural Regen. Res.14, 197–200. 10.4103/1673-5374.244781
31
Moher D. Liberati A. Tetzlaff J. Altman D. G. Group P. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ339, b2535. 10.1136/bmj.b2535
32
Nita M. Grzybowski A. (2016). The role of the reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress in the pathomechanism of the age-related ocular diseases and other pathologies of the anterior and posterior eye segments in adults. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2016, 3164734. 10.1155/2016/3164734
33
Ohguro H. Ohguro I. Katai M. Tanaka S. (2012). Two-year randomized, placebo-controlled study of black currant anthocyanins on visual field in glaucoma. Ophthalmologica228, 26–35. 10.1159/000335961
34
Ohguro H. Ohguro I. Yagi S. (2013). Effects of black currant anthocyanins on intraocular pressure in healthy volunteers and patients with glaucoma. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther.29, 61–67. 10.1089/jop.2012.0071
35
Oliver J. E. Hattenhauer M. G. Herman D. Hodge D. O. Kennedy R. Fang-Yen M. et al (2002). Blindness and glaucoma: a comparison of patients progressing to blindness from glaucoma with patients maintaining vision. Am. J. Ophthalmol.133, 764–772. 10.1016/s0002-9394(02)01403-4
36
Ozates S. Elgin K. U. Yilmaz N. S. Demirel O. O. Sen E. Yilmazbas P. (2019). Evaluation of oxidative stress in pseudo-exfoliative glaucoma patients treated with and without topical coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E. Eur. J. Ophthalmol.29, 196–201. 10.1177/1120672118779486
37
Parisi V. Centofanti M. Gandolfi S. Marangoni D. Rossetti L. Tanga L. et al (2014). Effects of coenzyme Q10 in conjunction with vitamin E on retinal-evoked and cortical-evoked responses in patients with open-angle glaucoma. J. Glaucoma23, 391–404. 10.1097/IJG.0b013e318279b836
38
Park J. W. Kwon H. J. Chung W. S. Kim C. Y. Seong G. J. (2011). Short-term effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on peripapillary retinal blood flow in normal tension glaucoma. Korean J. Ophthalmol.25, 323–328. 10.3341/kjo.2011.25.5.323
39
Quaranta L. Bettelli S. Uva M. G. Semeraro F. Turano R. Gandolfo E. (2003). Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on preexisting visual field damage in normal tension glaucoma. Ophthalmology110, 359–362. 10.1016/S0161-6420(02)01745-1
40
Quigley H. A. Broman A. T. (2006). The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br. J. Ophthalmol.90, 262–267. 10.1136/bjo.2005.081224
41
Raaz U. Toh R. Maegdefessel L. Adam M. Nakagami F. Emrich F. C. et al (2014). Hemodynamic regulation of reactive oxygen species: implications for vascular diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal20, 914–928. 10.1089/ars.2013.5507
42
Ramdas W. D. Schouten J. Webers C. a. B. (2018). The effect of vitamins on glaucoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients10, 359. 10.3390/nu10030359
43
Sabaner M. C. Dogan M. Altin S. S. Balaman C. Yilmaz C. Omur A. et al (2021). Ginkgo Biloba affects microvascular morphology: a prospective optical coherence tomography angiography pilot study. Int. Ophthalmol.41, 1053–1061. 10.1007/s10792-020-01663-3
44
Sari M. D. Sihotang A. D. Lelo A. (2016). Ginkgo biloba extract effect on oxidative stress marker malonildialdehyde, redox enzyme gluthation peroxidase, visual field damage, and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in primary open angle glaucoma. 9, 158–166.
45
Shim S. H. Kim J. M. Choi C. Y. Kim C. Y. Park K. H. (2012). Ginkgo biloba extract and bilberry anthocyanins improve visual function in patients with normal tension glaucoma. J. Med. Food15, 818–823. 10.1089/jmf.2012.2241
46
Stein J. D. Khawaja A. P. Weizer J. S. (2021). Glaucoma in adults-screening, Diagnosis, and management: a review. Jama325, 164–174. 10.1001/jama.2020.21899
47
Steinmetz J. D. Bourne R. R. A. Briant P. S. Flaxman S. R. Taylor H. R. B. Jonas J. B. et al (2021). Causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: the Right to Sight: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob. Health9, e144–e160. 10.1016/s2214-109x(20)30489-7
48
Tang B. Li S. Cao W. Sun X. (2019). The association of oxidative stress status with open-angle glaucoma and exfoliation glaucoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ophthalmol.2019, 1803619. 10.1155/2019/1803619
49
Tezel G. (2006). Oxidative stress in glaucomatous neurodegeneration: mechanisms and consequences. Prog. Retin Eye Res.25, 490–513. 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2006.07.003
50
Tham Y.-C. Li X. Wong T. Y. Quigley H. A. Aung T. Cheng C.-Y. (2014). Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology121, 2081–2090. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.05.013
51
Vernazza S. Tirendi S. Bassi A. M. Traverso C. E. Saccà S. C. (2020). Neuroinflammation in primary open-angle glaucoma. J. Clin. Med.9, 3172. 10.3390/jcm9103172
52
Vetrugno M. Uva M. G. Russo V. Iester M. Ciancaglini M. Brusini P. et al (2012). Oral administration of forskolin and rutin contributes to intraocular pressure control in primary open angle glaucoma patients under maximum tolerated medical therapy. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther.28, 536–541. 10.1089/jop.2012.0021
53
Weinreb R. N. Khaw P. T. (2004). Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet363, 1711–1720. 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16257-0
54
Weinreb R. N. Aung T. Medeiros F. A. (2014). The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: a review. Jama311, 1901–1911. 10.1001/jama.2014.3192
55
Yoshida K. Ohguro I. Ohguro H. (2013). Black currant anthocyanins normalized abnormal levels of serum concentrations of endothelin-1 in patients with glaucoma. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther.29, 480–487. 10.1089/jop.2012.0198
56
Zhong Y. Xiang M. Ye W. Cheng Y. Jiang Y. (2010). Visual field protective effect of Erigeron breviscapus (vant.) Hand. Mazz. extract on glaucoma with controlled intraocular pressure: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Drugs R. D.10, 75–82. 10.2165/11539090-000000000-00000
Summary
Keywords
antioxidants, primary open-angle glaucoma, normal-tension glaucoma, meta-analysis, randomized controlled trials
Citation
Bao J, Yu Y, Chen G, Hu C, Zhao C and Li X (2025) Effect of antioxidants on primary open-angle glaucoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1625735. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1625735
Received
16 May 2025
Accepted
25 August 2025
Published
05 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Silvia Bisti, University of L'Aquila, Italy
Reviewed by
Anna Maria Bassi, University of Genoa, Italy
Arturo Bravo Nuevo, Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine (PCOM), United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Bao, Yu, Chen, Hu, Zhao and Li.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiang Li, jeannelxiang@cdutcm.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.