Abstract
Background:
Liver injury is a multifaceted condition marked by oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Schisandra chinensis, a traditional Chinese medicinal herb with a history of use spanning over 2,000 years, exhibits significant hepatoprotective, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects. This study aims to review the therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms of Schisandra chinensis in mitigating liver injury in animal models.
Methods:
A systematic review was conducted across eight databases. The methodological quality of the studies was assessed using the Sycle’s RoB tool. Sensitivity and subgroup analyses were performed in cases of high heterogeneity. Publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s test and funnel plots. A meta-analysis was carried out using Stata 18.0.
Results:
A total of 54 animal studies were included in this review. The results indicated that bioactive compounds in Schisandra chinensis significantly reduced levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) [standardized mean difference = −4.74, 95% confidence interval (−5.42, −4.06), p < 0.001, I2 = 90.8%], aspartate aminotransferase (AST) [SMD = −5.10, 95% CI (−5.84, −4.37), p < 0.001, I2 = 91.7%], and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). Additionally, Schisandra chinensis decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) levels while increasing superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH). Additionally, the results revealed a significant reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines, including Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). Subgroup analysis suggested that variations in animal species, drugs, modeling methods, and dosages may contribute to the observed heterogeneity.
Conclusion:
Schisandra chinensis demonstrates significant therapeutic effects in liver injury, likely due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic properties. However, further research is needed to validate its efficacy and safety.
Systematic Review Registration:
https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2025-2-0084/, identifier INPLASY202520084.
1 Introduction
Liver injury is characterized by hepatocellular damage, inflammatory reactions, reduced liver function, and the development of fibrosis (Tujios et al., 2022). The worldwide burden of liver injury has risen dramatically, making it the 11th leading cause of death globally (Devarbhavi et al., 2023). The etiology of liver injury is diverse, encompassing metabolic disorders, viral infections and toxin exposure, all of which trigger hepatocyte damage and fibrosis through oxidative stress, inflammatory cascades, and apoptosis (Taru et al., 2024). Despite significant advancements in the therapeutic management of hepatic injury, identifying safe and effective natural compounds for the prevention and treatment of hepatic injury remains crucial.
Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., commonly known as Wu Wei Zi, is the dried mature fruit of the Schisandra genus. Its medicinal use dates back to the Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220 AD), as recorded in the Shennong Bencao Jing (Divine Farmer’s Materia Medica), where it was documented to have astringent, qi-tonifying, fluid-generating, kidney-nourishing, and heart-calming properties according to Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theories. Modern pharmacological studies have revealed that Schisandra chinensis exhibits anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antitussive, and antiasthmatic properties (Yang et al., 2022), making it clinically valuable for treating disorders of the central nervous system (Li et al., 2023a), cardiovascular system (Shi et al., 2021), digestive system (Zhang et al., 2024), and endocrine system (Guo et al., 2025).
Meanwhile, Schisandra chinensis is a hepatoprotective herb, the renowned Ming Dynasty pharmacologist Li Shizhen explicitly noted in the Bencao Gangmu (Compendium of Materia Medica) that Schisandra chinensis used to treat liver deficiency syndromes. According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the standard preparation consists of 3–9 g of dried berries, typically decocted in water for oral administration or processed into pills or powders. Research has revealed that the chemical composition of Schisandra chinensis fruit primarily consists of lignan compounds (e.g., Schisandrin A, Schisandrin B, Schisandrin C, Schisandrol A, and Schisandrol B), polysaccharides, and other bioactive constituents. These components are known to exhibit a range of pharmacological activities, including hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic effects (Yang et al., 2022).
Many studies have demonstrated that Schisandra chinensis exhibits hepatoprotective effects in various murine models of liver injury. Furthermore, pharmaceutical agents derived from its Schisandra chinensis—such as bifendate (DDB) and bicyclol—have been extensively applied in clinical practice (Zhu et al., 2019). Extensive experimental studies have demonstrated that the bioactive ingredients of Schisandra chinensis can mitigate liver injury through multiple-target mechanisms, such as the nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway (Zhao et al., 2022), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway (Yan et al., 2025), and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated proptosis pathway (Bing et al., 2025).
While numerous studies have investigated the hepatoprotective effects of Schisandra chinensis, its precise molecular mechanisms and clinical translational potential remain unclear. A systematic review and meta-analysis are crucial for consolidating existing evidence and enhancing the reliability of these findings (Siddaway et al., 2019). Current evidence suggests no systematic evaluation exists regarding the therapeutic efficacy of Schisandra chinensis for hepatic injury. Therefore, this work attempts to systematically assess the protective effects and underlying mechanisms of Schisandra chinensis in models of liver injury.
2 Methods
The systematic review and meta-analysis were carried out in strict accordance with the PRISMA guidelines, ensuring a rigorous and transparent methodology (Page et al., 2021).
2.1 Search strategy
A comprehensive systematic search was performed across eight major databases: PubMed, Web of Science, Embase and Cochrane Library, CNKI, WANFANG, VIP, CBM, covering studies from their inception to January 2025. The search terms included “Acute Liver Injury,” “Chemically Induced Liver Toxicity,” and “Toxic Hepatitis,” as well as “Schisandra chinensis,” “schizandrol,” “schizandrin,” “schisantherin,” “gomisin,” and “Bay Starvine”. A detailed description of the search strategies employed for each database is provided in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Following the PICO principle, the inclusion criteria were defined as follows: (1) participants: rats/mice with liver injury induced by drugs, alcohol, or chemical reagents; (2) intervention: extracts of Schisandra chinensis, lignans, Schizandrin, Schisandrin, Schizandrol, or other extracts from Schisandra chinensis with clearly defined administration time and dosages; (3) comparison: the control group received an equal volume of placebo solution (e.g., 0.9% saline, 1% carboxymethylcellulose, or vehicle-matched solvent); (4) outcomes: AST, ALT, ALP, SOD, GSH, and MDA levels; (5) papers: controlled in vivo experiments.
Studies meeting the following criteria were excluded: (1) non-original research literature, such as human clinical trials, case reports, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews; (2) non-holistic animal model studies, such as cell culture, isolated liver perfusion, or liver sectioning experiments; (3) conference abstracts, editorials, and letter articles not published in full text; (4) models that did not induce liver injury; (5) studies lacking relevant outcomes; (6) studies that did not have a concurrent control group (e.g., using only blank controls) or mismatched baseline data for the control group; (7) lack of sample sizes, margins of error, and statistical results (e.g., SD or SEM).
2.3 Data extraction
The retrieved literature was managed using NoteExpress (Version 9.0). After removing duplicates, two authors (Bo-Han Lv and Bo-Hao Huang) independently screened the studies and evaluated them according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. To reach a consensus, any discrepancies were addressed by consulting the corresponding author (Wen-Liang Lv). Basic study information was recorded using Excel 2019, including:
1. The first author’s name and the publication year;
2. Type of animal model, sample size per group, body weight, and sex;
3. Liver injury modeling methods;
4. Drug type and dosage, with a particular focus on the highest administered dose, as well as the administration time and duration.
5. Inclusion of more than two active Schisandra ingredients as therapeutic agents in the study
If the study data were presented in graphical format, the authors were contacted to request the original numerical values. If the original data were unavailable, we used the digitization software GetData Graph Digitizer 2.26 to extract values from the graphs. When data were provided as standard error of the mean (SEM), we converted them into standard deviation (SD) using the formula SD = SEM × , where n represents the number of animals per group.
2.4 Risk of bias assessment
Two investigators, Fei-Yang Xiong and Dong-Jie Wu, independently conducted a methodological quality assessment using SYRCLE’s Risk of Bias Tool (Hooijmans et al., 2014), which evaluates ten methodological aspects across various bias categories, including selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, reporting bias, and other biases. The evaluation system utilized three distinct symbols: “×” denoting minimal bias risk, “√” representing significant bias concerns, and “?” Signifying an indeterminate risk status due to inadequate data documentation. Discrepancies in assessment outcomes were resolved through consultation with a third evaluator, Bo-Hao Huang.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The statistical analyses were performed using Stata 18.0. The standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to evaluate pooled outcome measures. Heterogeneity was assessed with the I2 statistic. A random-effects model was applied when I2 > 50% and p < 0.05; otherwise, a fixed-effects model was employed. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on variables such as animal species, model induction methods, treatment agents, and dosages to explore sources of heterogeneity. Sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the robustness of the results. Subgroup analyses for AST, ALT, SOD, MDA, and GSH were based on therapeutic drugs, mouse strains, modeling methods, and dosages. In studies with more than 10 studies, publication bias was assessed using funnel plots and Egger’s test. A symmetrical distribution of data points on the funnel plot indicated a low risk of publication bias, while asymmetry suggested potential bias. Egger’s test with p < 0.05 was considered indicative of significant publication bias.
3 Results
3.1 Study selection
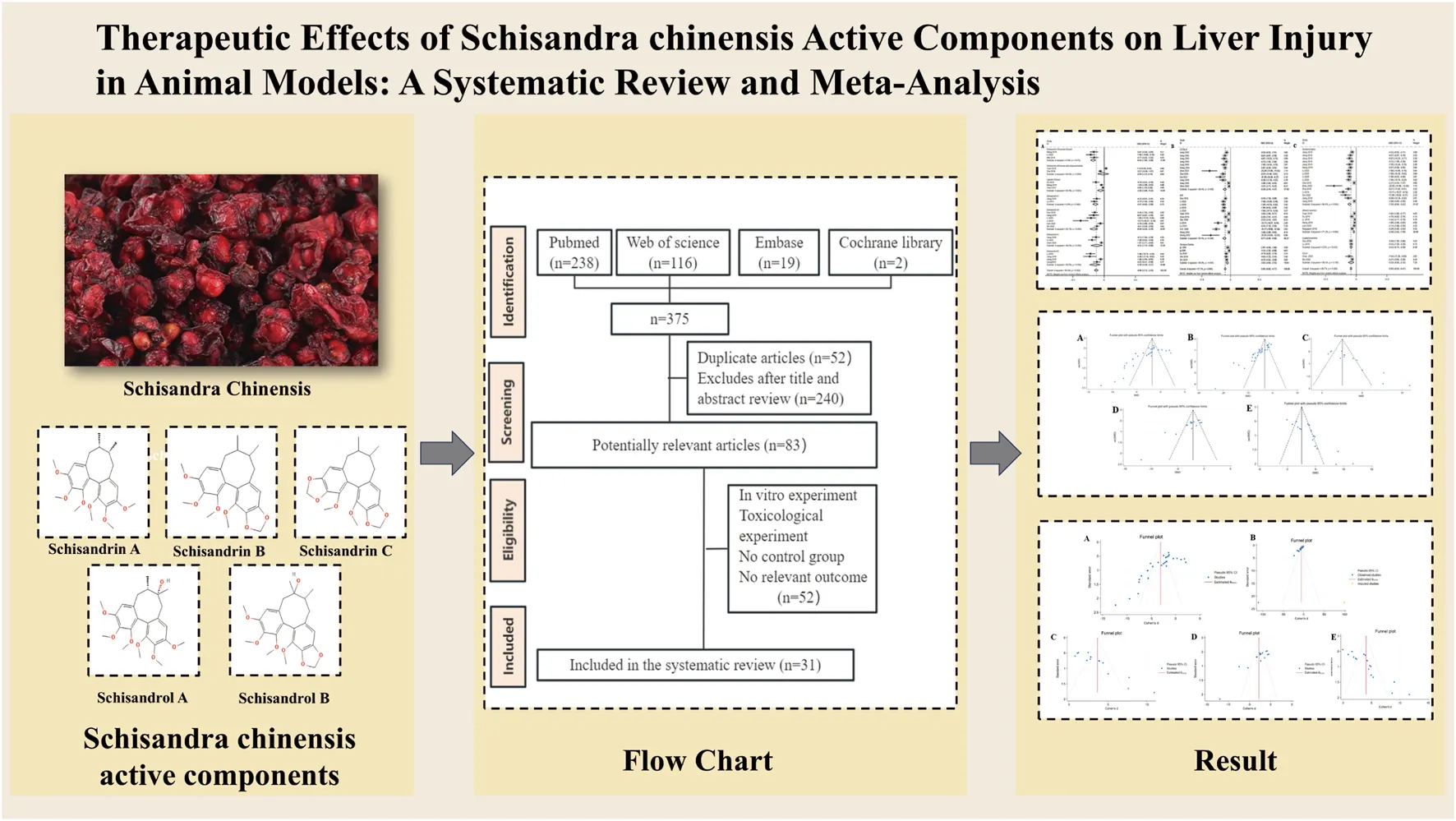
The initial database search identified 1,102 articles. After removing duplicates and reviewing articles, 792 records were excluded following a detailed screening of titles and abstracts. Subsequently, the remaining 310 articles underwent a full-text review, which was conducted independently by Bo-Hao Huang and Fei-Yang Xiong to ensure accuracy and consistency. After this rigorous assessment, 54 studies comprising 1,314 animals were selected for the final analysis. Details of the study selection process are depicted in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1
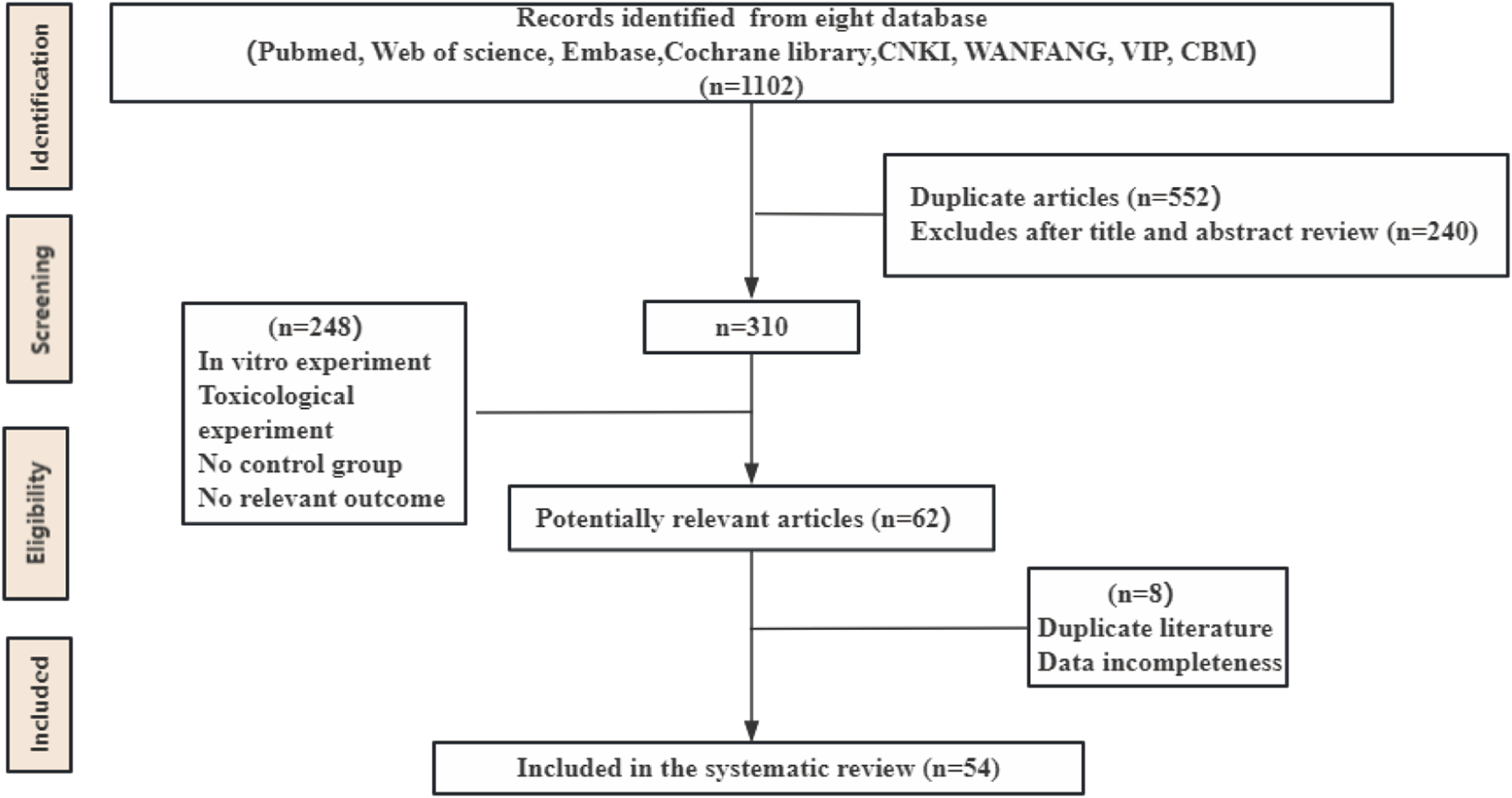
Flow diagram of database searches and study selection.
3.2 Study characteristics
Supplementary Table S2 provides an overview of the key features of the included studies, including: (1) first author, (2) publication year, (3) animal species, sample size per group, weight, and sex; (4) Model establishment method; (5) Interventional drug and dosage; (6) Mechanism of action; (7) Primary outcome measures.
Specifically, in this systematic review, 13 studies used C57BL/6 mice (Wang et al., 2014b; Jiang et al., 2015a, 2015b, 2016; Li et al., 2018; Nagappan et al., 2018; Zhai et al., 2018; Yan et al., 2021; Dai et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2023; Lin et al., 2024, p. 38), six studies used Sprague-Dawley rats (Chen et al., 2017a; Ip et al., 1996; Shi et al., 2022; Su et al., 2019; Wei et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2014; Dai et al., 2022).
20 studies used ICR mice (Che et al., 2019a; Gao et al., 2016; Kim et al., 2008; Li et al., 2014a, 2020; Lu et al., 2014; Shan et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2014c; Yuan et al., 2018; Li et al., 2014b; Wang et al., 2014a; Li et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2020a; Guo et al., 2024; Che et al., 2019b; Wang et al., 2020b; Wang et al., 2019a, 2019b; Zhao et al., 2006), five study used Kunming rats (Chang et al., 2024; ZHOU et al., 2018; Yao et al., 2014; Sun, 2019; Yan et al., 2009), one study used BALB/c mice (Lam et al., 2023), and one study used Wistar rats (Teraoka et al., 2012).
The drugs used to establish liver injury animal models include: aflatoxin B (Ip et al., 1996), CdCl (Ip et al., 1996), Acetaminophen (Che et al., 2019a; Jiang et al., 2016, 2015a; 2015b; Li et al., 2014a, 2020; Wang et al., 2014b; Zhai et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2022; Yan et al., 2009; Che et al., 2019b; Dai et al., 2022; Qiu et al., 2018), CCl4 (Teraoka et al., 2012; Xie et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2023), d-galactosamine (Gao et al., 2016; Li et al., 2013; Lu et al., 2014; Yan et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2011; ZHOU et al., 2018; Yao et al., 2014; Xu and Liu, 2011; Sun, 2019; Wang et al., 2020b, 2019a; Sun et al., 2021), ethanol solution (Lam et al., 2023; Li et al., 2018; Nagappan et al., 2018; Su et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2014c; Yuan et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2014; Li et al., 2014b; Wang et al., 2014a, 2019b), Concanavalin A (Shan et al., 2019; Li et al., 2013), Senecionine (Chang et al., 2024), Cyclophosphamide (Chen et al., 2017a), Cyclosporin A (Wei et al., 2021), LPS/D-GalN (Kim et al., 2008), lithocholic acid (Lin et al., 2024), dictamine (Chang et al., 2024), and pirarubicin (Shi et al., 2022).
The Schisandra chinensis extracts and active components used in the included studies were as follows: Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus extract (Chen et al., 2017a; Ip et al., 1996; Li et al., 2013, 2020; Wang et al., 2014b; Wei et al., 2021; ZHOU et al., 2018; Qiu et al., 2018; Yan et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2006), Schisandra lignans (Su et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2014c; Xie et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2014; Yao et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2020a; An et al., 2014), Schisandrin A (Gao et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2014; Teraoka et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2020b, Wang et al., 2019a), Schisandrin B (Zhu and Wang, 2012; Li et al., 2014a, 2020; Jiang et al., 2015b; Gao et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2021; Shi et al., 2022; Lam et al., 2023), Schisandrin C (Chen et al., 2023; Jiang et al., 2015b; Dai et al., 2022), Schisandrol A (Jiang et al., 2015b; Li et al., 2020; Yan et al., 2021), Schisandrol B (Jiang et al., 2016; 2015a; 2015b; Li et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2024; Li et al., 2013), Schisantherin A (Li et al., 2018; Chang et al., 2024), Schisandra acid polysaccharides (Yuan et al., 2018; Che et al., 2019a), Schisandra polysaccharides (Shan et al., 2019; Xu et al., 2014; Li et al., 2014b; Chen et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2014a; Xu et al., 2011; Xu and Liu, 2011; Guo et al., 2024; Che et al., 2019b; Sun, 2019; Wang et al., 2019b), Schisandra essential oil (Zhai et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2022), Gomisin A (Kim et al., 2008; Teraoka et al., 2012), and Gomisin N (Nagappan et al., 2018).
3.3 Evaluation of the methodological quality of selected studies
The quality of the included studies was independently evaluated by two researchers (Fei-Yang Xiong and Zi-Wen Zhuo) using SYRCLE’s Risk of Bias Tool (Hooijmans et al., 2014) across ten domains. The summarized risk of bias for each study is presented in the figure below. Forty-eight studies were assessed with a risk of bias score of 5, while four studies scored 6, and two studies scored 4.
Among the 54 included studies, all adequately reported on animal inclusion and handled incomplete outcome data appropriately, ensuring comprehensive reporting of expected results. All randomized outcome-assessment studies were judged to be at low risk of bias. However, it should be noted that none of the included studies provided explicit descriptions regarding the implementation of allocation concealment or experimenter blinding procedures. Regarding other bias domains, all studies were evaluated as having low risk for incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other potential sources of bias (Figure 2; Supplementary Table S3).
FIGURE 2
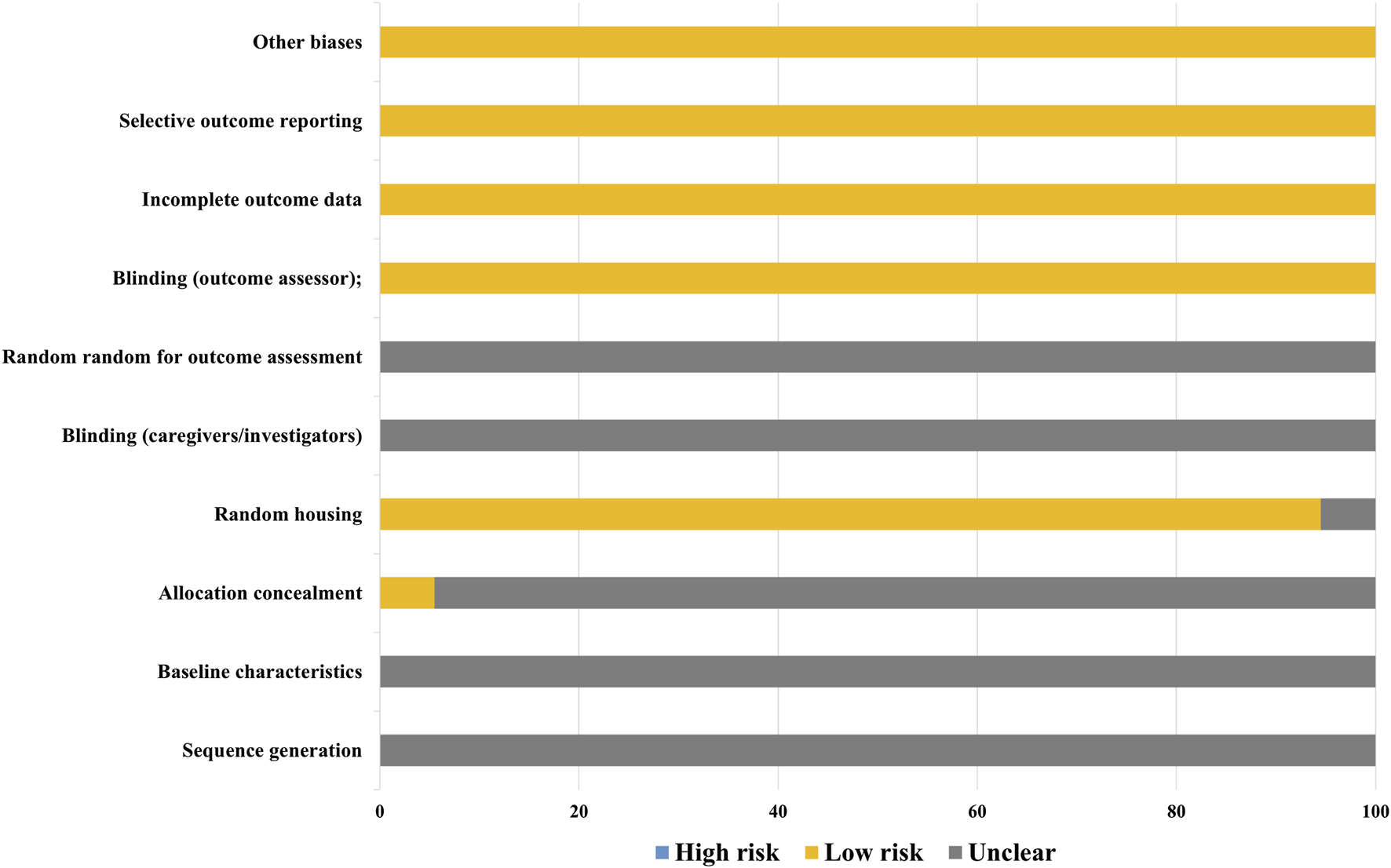
Risk of bias.
3.4 Efficacy of Schisandra chinensis in treating liver injury
3.4.1 Liver function
The levels of ALT and AST are widely recognized as the most reliable markers for detecting liver injury. A total of 46 studies, involving 1,150 animals, evaluated the effects of Schisandra chinensis on AST levels. According to the random-effects model, ALT levels were significantly lower in the experimental group, indicating Schisandra chinensis contributes to liver function improvement [SMD = −4.74, 95% CI (−5.42, −4.06), p < 0.001, I2 = 90.8%] (Figure 3A).
FIGURE 3
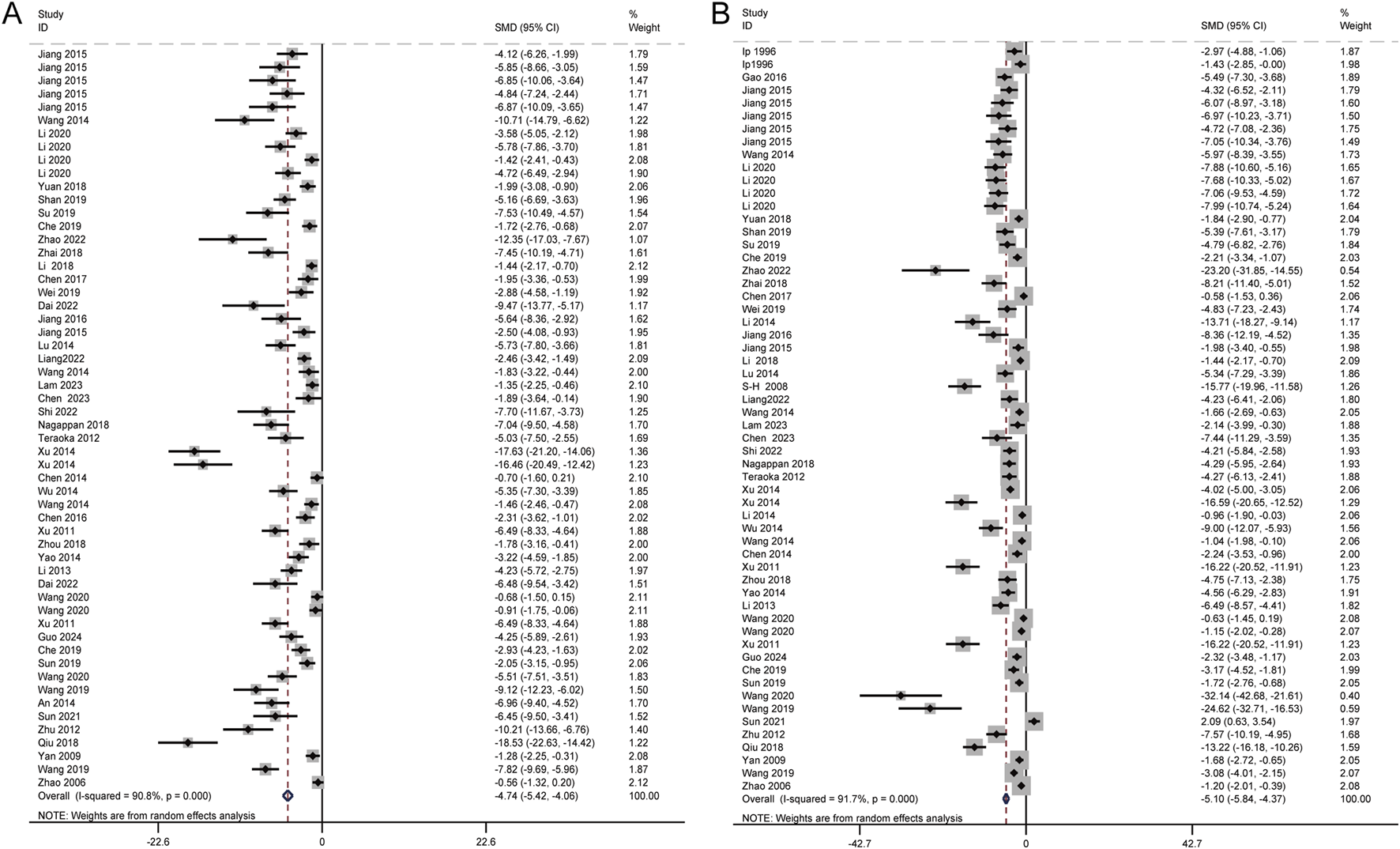
Forest plot (effect size and 95% CI) summarizing the effects of the Schisandra chinensis active ingredient on AST (A) and ALT (B).
Similarly, 50 studies, including 1,184 animals, assessed the effects of Schisandra chinensis on ALT levels. The random-effects analysis revealed a significant reduction in ALT levels in the experimental group compared to the model group, suggesting a hepatoprotective effect of Schisandra chinensis [SMD = −5.10, 95% CI (−5.84, −4.37), p < 0.001, I2 = 91.7%] (Figure 3B).
Additionally, six studies involving 52 animals assessed the effects of Schisandra chinensis on ALP levels. A random-effects analysis suggested that, compared to the model group, the active components of Schisandra chinensis might reduce ALP levels [SMD = −3.11, 95% CI (−4.86, −1.37), p < 0.001, I2 = 87.0%] (Figure 4).
FIGURE 4
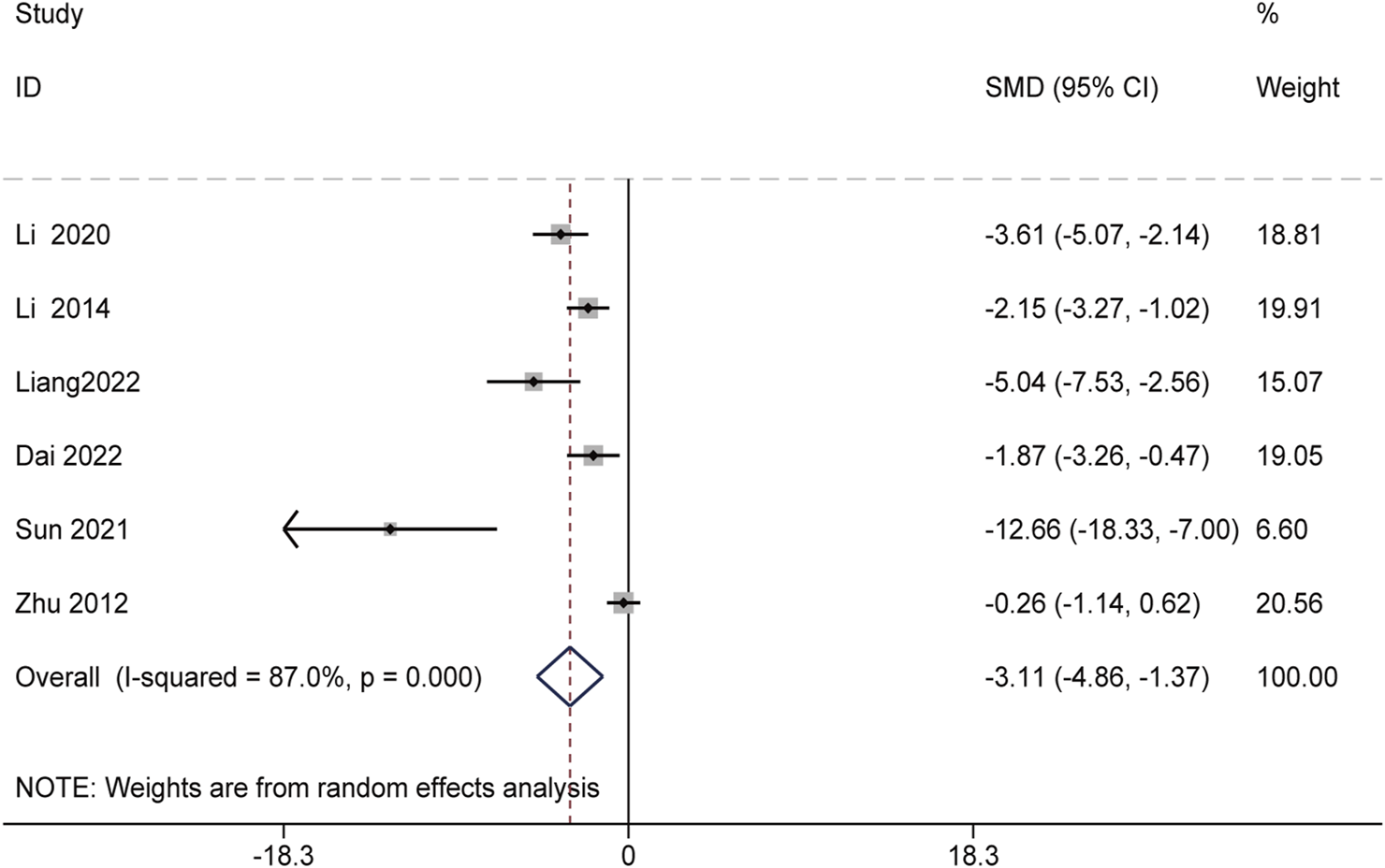
Forest plot (effect size and 95% CI) summarizing the effects of the Schisandra chinensis active ingredient on ALP.
3.4.2 Oxidative stress
To investigate the regulatory effects of Schisandra chinensis on oxidative stress, 17 studies involving 466 animals assessed its impact on SOD levels. The results indicated that Schisandra chinensis significantly increased SOD levels [SMD = 4.37, 95% CI (3.38, 5.37), p < 0.001, I2 = 89.3%] (Figure 5A). Additionally, 26 studies involving 658 animals evaluated its effects on MDA levels, showing that Schisandra chinensis reduced MDA levels [SMD = −3.42, 95% CI (−4.16, −2.69), p < 0.001, I2 = 89.7%] (Figure 5B). Similarly, 20 studies involving 420 animals assessed its impact on GSH levels, revealing that Schisandra chinensis significantly increased GSH levels compared to the model group [SMD = 3.07, 95% CI (2.35, 3.80), p < 0.001, I2 = 84.0%] (Figure 5C).
FIGURE 5
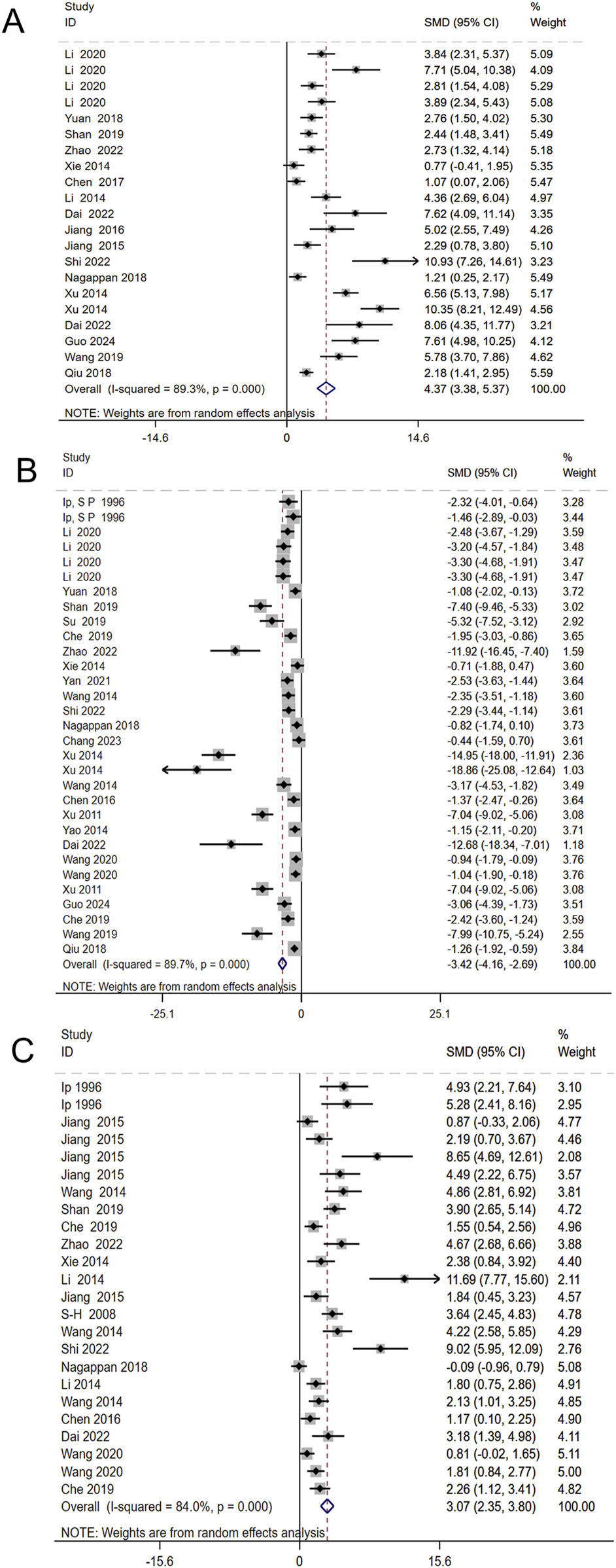
Forest plot (effect size and 95% CI) summarizing the effects of the Schisandra chinensis active ingredient on SOD (A), MDA (B), GSH (C).
3.4.3 Inflammatory response
To investigate the effects of Schisandra chinensis on inflammation in liver injury, eight studies (including 182 animals) on TNF-α were included in a random effects analysis. The results showed that, compared to the model group, Schisandra chinensis significantly reduced serum TNF-α expression [SMD = −2.85, 95% CI (−3.73, −1.96), p < 0.001, I2 = 76.3%] (Figure 6A). 12 studies (including 222 animals) on IL-6 were included, and the results demonstrated that Schisandra chinensis significantly lowered IL-6 levels compared to the model group [SMD = −3.30, 95% CI (−4.43, −2.17), p < 0.001, I2 = 86.7%] (Figure 6B). Five studies (including 110 animals) showed that Schisandra chinensis reduced IL-1β levels [SMD = −2.41, 95% CI (−3.75, −1.07), p < 0.001, I2 = 85.4%] (Figure 6C).
FIGURE 6
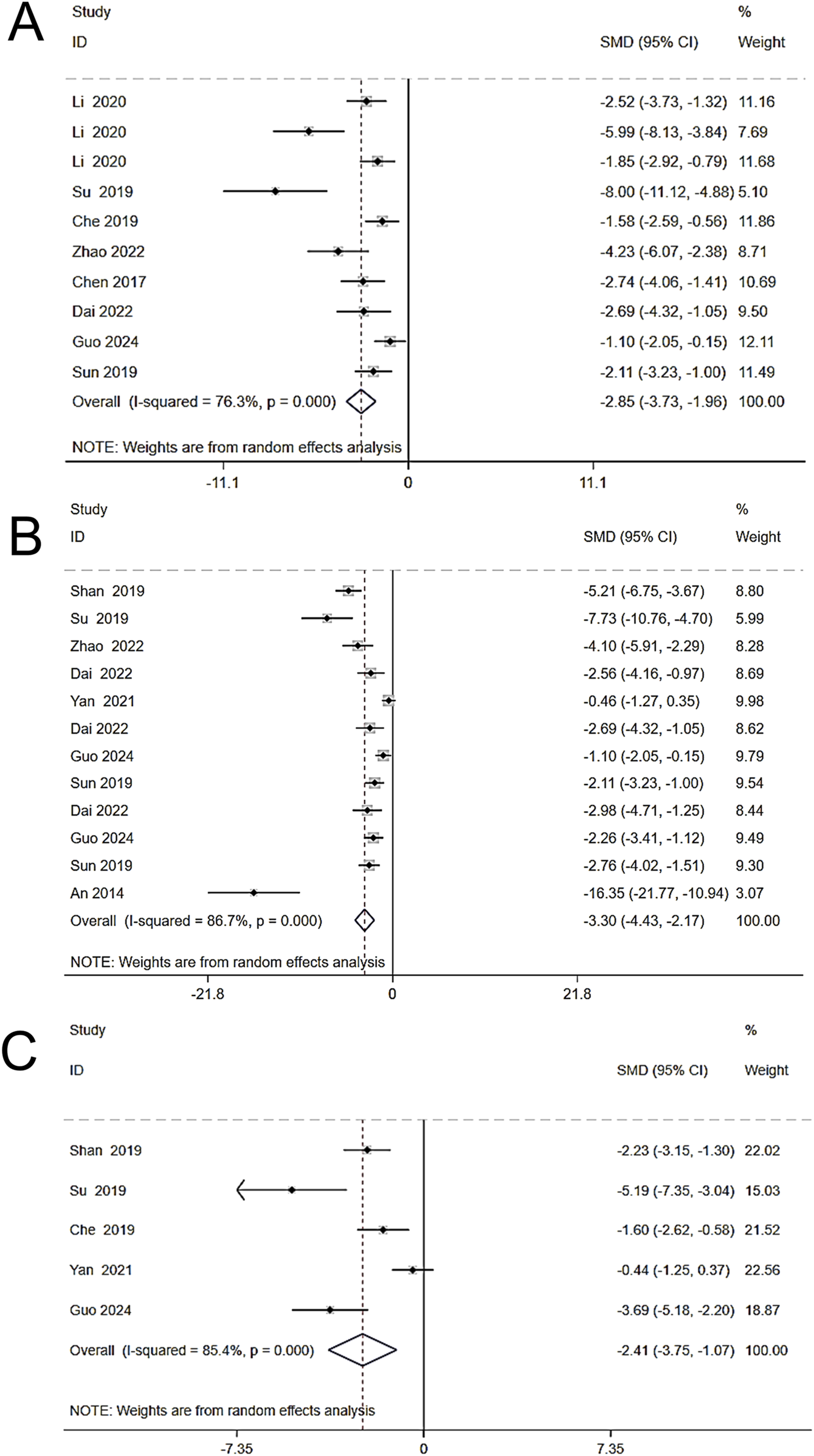
Forest plot (effect size and 95% CI) summarizing the effects of the Schisandra chinensis active ingredient on TNF-α (A), IL-6 (B), IL-1β (C).
3.4.4 Lipid levels
A random-effects analysis was conducted on four studies comprising 80 animals. The findings demonstrated that, compared to the model group, Schisandra chinensis significantly reduced triglyceride (TG) levels [SMD = −2.48, 95% CI -3.57, −1.40), p = 0.023, I2 = 68.5%] (Figure 7).
FIGURE 7
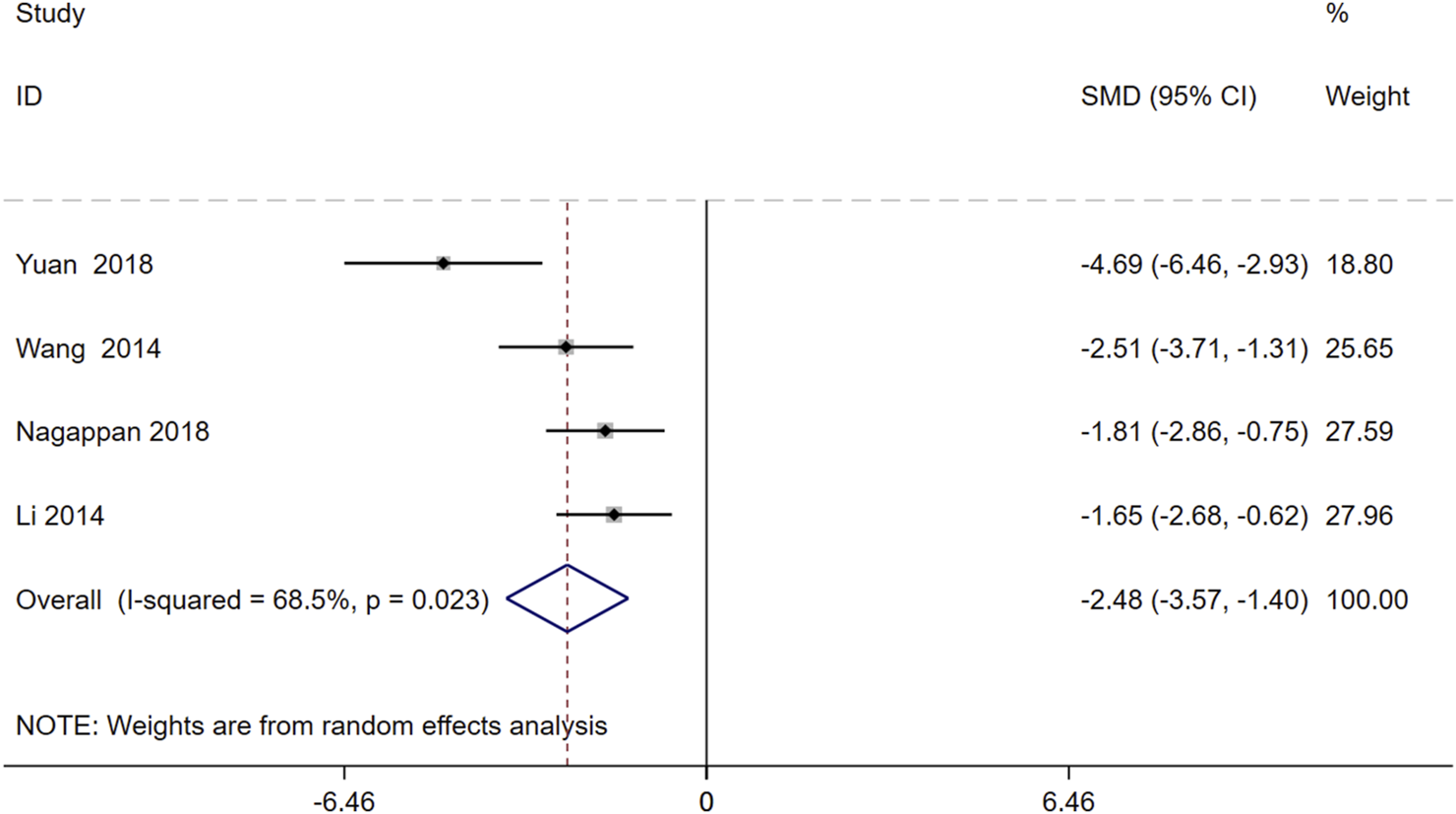
Forest plot (effect size and 95% CI) summarizing the effects of the Schisandra chinensis active ingredient on TG.
The effects of active components of Schisandra chinensis in treating liver injury are summarized in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Indicator | Outcomes | Number of studies | Sample size | SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver function | AST | 46 | 1,150 | −4.74, (−5.42, −4.06) | 90.8 | <0.001 |
| ALT | 50 | 1,184 | −5.10, (−5.84, −4.37) | 91.7 | <0.001 | |
| ALP | 6 | 52 | 3.11, (−4.86, −1.37) | 87.0 | <0.001 | |
| Oxidative Stress | SOD | 17 | 466 | 4.37, (3.38, 5.37) | 89.3 | <0.001 |
| MDA | 26 | 658 | −3.42, (−4.16, −2.69 | 89.7 | <0.001 | |
| GSH | 20 | 420 | 3.11, (2.35, 3.80) | 87.0 | <0.001 | |
| Lipid | TG | 6 | 52 | −3.11, (−4.86, −1.37) | 87.0 | <0.001 |
| Inflammatory Response | TNF-α | 8 | 182 | −2.85, (−3.73, −1.96 | 76.3 | <0.001 |
| IL-6 | 12 | 222 | −3.30, (−4.43, −2.17) | 86.7 | <0.001 | |
| IL-1β | 5 | 110 | −2.41, (−3.75, −1.07) | 85.4 | <0.001 |
Summary of the effects of active components of Schisandra chinensis on liver injury.
3.5 Subgroup analysis
To address the considerable heterogeneity observed across studies, we performed subgroup analyses focusing on three confounding factors (animal species, treatment agents, model drugs and dosages), to identify the sources of heterogeneity for the five primary outcomes (AST, ALT, SOD, MDA, GSH).
3.5.1 Subgroup analysis of AST levels
Compared with the model group, all intervention groups demonstrated significant reductions in AST levels. Notably, in the treatment agent subgroup, Schisandrin C showed the most significant effect [SMD = −5.77, 95% CI (−10.45, −1.09), p = 0.001, I2 = 86.4%].In the animal subgroup, Sprague-Dawley rats exhibited the most pronounced effect [SMD = −7.68, 95% CI (−11.12, −4.25), p < 0.001, I2 = 92.6%]. In the model drug subgroup, the ethanol solution group showed the most significant improvement [SMD = −6.09, 95% CI (−8.51, −3.55), p < 0.001, I2 = 95.9%]. Among dosages, the high-dose group did not differ significantly from the low-dose group, and the effect size was even greater in the low-dose group [SMD = −5.00, 95% CI (−6.04, −3.95), p < 0.001, I2 = 90.6%]. However, the heterogeneity remained unresolved after the subgroup analysis, suggesting that these three factors may be significant sources of heterogeneity (Table 2; Supplementary Figure S1).
TABLE 2
| Indicator | Subgroup | Number of studies | SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic drug | Schisandra Chinensis Extract | 7 | −4.69 (−6.92, −2.45) | 94.0 | <0.001 |
| Schisandra Polysaccharides | 13 | −4.90 (−6.46, −3.33) | 93.6 | <0.001 | |
| Schisandra Acidic Polysaccharides | 2 | −1.85 (−2.60, −1.10) | 0.0 | 0.725 | |
| Lignans Extract | 8 | −4.52 (−6.57,-2.47) | 93.9 | <0.001 | |
| Schisandrin A | 3 | −5.78 (-7.49,-4.07) | 70.4 | 0.034 | |
| Schisandrin B | 4 | −4.15 (−6.49,-1.82) | 78.3 | 0.003 | |
| Schisandrin C | 3 | −5.77 (−10.45,-1.09) | 86.4 | 0.001 | |
| Schisandrol A | 2 | −2.95 (−6.82,0.38) | 84.9 | 0.010 | |
| Schisandrol B | 3 | −4.09 (−5.95, −2.23) | 62.8 | 0.068 | |
| Species | C57BL/6 mice | 12 | −5.10 (−6.38, −3.82) | 85.5 | <0.001 |
| Kunming mice | 4 | −1.85 (−2.42, −1.28) | 0.0 | 0.450 | |
| Sprague-Dawley rats | 7 | −7.68 (−11.12,-4.25) | 92.6 | <0.001 | |
| ICR mice | 16 | −3.34 (−4.11,-2.57) | 87.9 | <0.001 | |
| Modeling drugs | Acetaminophen | 8 | −5.87 (−7.40,-4.33) | 90.6 | <0.001 |
| Ethanol solution | 8 | −6.03 (−8.51,-3.55) | 95.9 | <0.001 | |
| CCL4 | 7 | −4.22 (-3.71,-2.61) | 86.9 | <0.001 | |
| Dosages | ≥100 mg kg−1 | 27 | −4.62 (−5.59, −3.65) | 89.3 | <0.001 |
| <100 mg kg−1 | 24 | −4.70 (−5.42, −3.97) | 90.6 | <0.001 |
Subgroup analysis of AST levels.
3.5.2 Subgroup analysis of ALT levels
Compared with the model group, all intervention groups demonstrated significant reductions in ALT levels. Specifically, among treatment agent, Schisandrin C demonstrated the largest effect size with concomitant reduction in heterogeneity [SMD = −7.52, 95% CI (−10.13, −4.91), I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.579]. Among animal species, Sprague-Dawley rats showed the most pronounced effect [SMD = −4.26, 95% CI (−4.99, −3.52), p < 0.001, I2 = 89.8%]. Among model drugs, acetaminophen showed the most significant improvement [SMD = −5.08, 95% CI (−5.60, −4.57), p < 0.001]. Among dosages, the effect was most marked at elevated doses [SMD = −5.00, 95% CI (−6.04, −3.95), p < 0.001, I2 = 90.6%]. The unresolved heterogeneity after subgroup stratification strongly suggests that these three variables are primary contributors to between-study differences (Table 3; Supplementary Figure S2).
TABLE 3
| Indicator | Subgroup | Number of studies | SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic drugs | Schisandra Chinensis Extract | 7 | −5.57 (−8.12, −3.01) | 93.7 | <0.001 |
| Schisandra Polysaccharides | 12 | −4.27 (−5.62, −2.91) | 92.1 | <0.001 | |
| Schisandra Acidic Polysaccharides | 2 | −2.01 (−2.79, −1.23) | 0.00 | 0.638 | |
| Lignans Extract | 6 | −2.56 (−4.04, −1.08) | 90.4 | 0.001 | |
| Schisandrin A | 2 | −4.89 (−6.35, −3.43) | 0.00 | 0.498 | |
| Schisandrin B | 6 | −6.00 (−8.25, −3.76) | 82.7 | <0.001 | |
| Schisandrin C | 3 | −7.52 (−10.13, −4.91) | 0.0 | 0.579 | |
| Schisandrol A | 3 | −4.32 (−7.75, −0.89) | 89.2 | <0.001 | |
| Schisandrol B | 4 | −5.36 (−8.46, −2.27) | 85.5 | <0.001 | |
| Modeling drugs | Acetaminophen | 14 | −5.08 (−5.60, −4.57) | 86.6 | <0.001 |
| Ethanol solution | 5 | −2.01 (−2.48, −1.55) | 71.3 | 0.004 | |
| CCL4 | 10 | −3.66 (−4.20, −3.11) | 90.0 | <0.001 | |
| Species | C57BL/6 mice | 9 | −4.15 (−4.79, −3.52) | 85.0 | <0.001 |
| ICR mice | 21 | −2.41 (−2.66, −2.15) | 90.2 | <0.001 | |
| Sprague-Dawley rats | 6 | −4.26 (−4.99, −3.52) | 89.8 | <0.001 | |
| Kunming mice | 4 | −2.34 (−2.99, −1.69) | 77.3 | 0.004 | |
| Dosages | ≥100 mg kg−1 | 26 | −5.00 (−6.04, −3.95) | 90.6 | <0.001 |
| <100 mg kg−1 | 21 | −4.18 (−5.20, −3.16) | 89.6 | <0.001 |
Subgroup analysis of ALT levels.
3.5.3 Subgroup analysis of SOD levels
Compared with the model group, all intervention groups demonstrated a significant advance in SOD levels. Specifically, among treatment agents, Schisandrin B showed the most significant effect size [SMD = 5.31, 95% CI (3.89,6.73), I2 = 77.0%, p = 0.037]. Among animal species, ICR mice demonstrated the largest effect size, accompanied by a concomitant reduction in heterogeneity [SMD = 3.27, 95% CI (2.75,3.80), p = 0.008, I2 = 65.5%]. Among dosages, higher dosage levels exhibited the most significant impact [SMD = 5.18, 95% CI (3.12,7.25)), p < 0.001, I2 = 92.8%]. However, heterogeneity has improved to a lesser extent (Table 4; Supplementary Figure S3).
TABLE 4
| Indicator | Subgroup | Number of studies | SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic drugs | Schisandra Chinensis Extract | 3 | 2.05 (1.48,2.61) | 78.1 | 0.010 |
| Schisandrin B | 2 | 5.31 (3.89,6.73) | 77.0 | 0.037 | |
| Schisandrol B | 3 | 3.38 (2.39,4.37) | 51.2 | 0.129 | |
| Species | C57BL/6 mice | 4 | 3.22 (2.30,4.13) | 69.8 | 0.019 |
| ICR mice | 4 | 3.27 (2.75,3.80) | 65.5 | 0.008 | |
| Sprague-Dawley rats | 7 | 2.54 (1.91,3.16) | 92.5 | <0.001 | |
| Dosages | ≥100 mg kg−1 | 10 | 5.18 (3.12,7.25) | 92.8 | <0.001 |
| <100 mg kg−1 | 7 | 3.25 (2.06, 4.44) | 84.0 | <0.001 |
Subgroup analysis of SOD levels.
3.5.4 Subgroup analysis of MDA levels
All treatment groups exhibited statistically significant improvements in MDA levels relative to the control group. Specifically, among treatment agents, Schisandrol A demonstrated the largest effect size, accompanied by a concomitant reduction in heterogeneity [SMD = −2.88, 95% CI (−3.41, −2.34), I2 = 69.3%, p = 0.003]. Among model drugs, acetaminophen showed the most significant improvement [SMD = −5.08, 95% CI (−5.60, −4.57), p < 0.001]. Among animal species, C57BL/6 mice showed the most pronounced effect [SMD = −6.96, 95% CI (−16.15, 2.23), p < 0.001, I2 = 93.6%]. Among dosages, higher doses demonstrated the most pronounced effect [SMD = −4.70, 95% CI (−6.30,-3.11), p < 0.001, I2 = 92.8%]. However, heterogeneity has improved less (Table 5; Supplementary Figure S4).
TABLE 5
| Indicator | Subgroup | Number of studies | SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic drugs | Schisandra Chinensis Extract | 3 | −1.61 (−2.12, −1.09) | 22.4 | 0.296 |
| Schisandra Polysaccharides | 8 | −2.60 (−3.07, −2.13) | 91.6 | <0.001 | |
| Lignans Extract | 3 | −2.00 (−2.78, −1.23) | 87.4 | <0.001 | |
| Schisandrol A | 2 | −2.82 (−3.68, −1.96) | 0.00 | 0.396 | |
| Modeling drugs | Acetaminophen | 4 | −2.61 (−3.10, −2.11) | 0.0 | 0.481 |
| Ethanol solution | 4 | −2.21 (−2.83, −1.59) | 80.3 | 0.002 | |
| D-galactosamine | 3 | −2.15 (−2.88, 1.42) | 86.8 | 0.001 | |
| Species | C57BL/6 mice | 2 | −6.96 (−16.15,2.23) | 93.6 | <0.001 |
| Sprague-Dawley rats | 6 | −2.31 (−3.39, −1.22) | 67.3 | 0.009 | |
| ICR mice | 15 | −3.00 (−3.78, −2.22) | 84.9 | <0.001 | |
| Dosages | ≥100 mg kg−1 | 14 | −4.70 (−6.30, −3.11) | 92.8 | <0.001 |
| <100 mg kg−1 | 13 | −2.68 (−3.57, −1.80) | 87.4 | <0.001 |
Subgroup analysis of MDA levels.
3.5.5 Subgroup analysis of GSH levels
All treatment groups exhibited statistically significant improvements in GSH levels relative to the control group. Specifically, among treatment agents, Schisandra chinensis extract demonstrated the largest effect size, accompanied by a concomitant reduction in heterogeneity [SMD = −4.99, 95% CI (3.56, 6.41), I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.927]. Among animal species, C57BL/6 mice showed the most pronounced effect [SMD = 2.87, 95% CI (2.19, 3.54), p < 0.001, I2 = 79.1%]. Among dosages, higher doses demonstrated the most pronounced effect [SMD = 3.49, 95% CI (2.40, 4.58), p < 0.001, I2 = 80.0%]. Notably, the heterogeneity persisted despite intervention (Table 6; Supplementary Figure S5).
TABLE 6
| Indicator | Subgroup | Number of studies | SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic drugs | Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide | 6 | 1.57 (1.16, 1.98) | 22.8 | 0.263 |
| Schisandra Chinensis Extract | 2 | 4.99 (3.56, 6.41) | 0.0 | 0.927 | |
| Lignans Extract | 4 | 1.80 (1.22, 2.37) | 79.6 | 0.002 | |
| Species | C57BL/6 mice | 4 | 2.82 (2.18, 3.47) | 72.3 | <0.001 |
| ICR mice | 3 | 1.13 (0.57, 1.68) | 0.0 | 0.544 | |
| Wistar rats | 2 | 2.47 (1.62, 3.32) | 95.3 | <0.001 | |
| Dosages | ≥100 mg kg−1 | 13 | 3.49 (2.40, 4.58) | 80.0 | <0.001 |
| <100 mg kg−1 | 10 | 2.84 (1.74, 3.95) | 88.3 | <0.001 |
Subgroup analysis of GSH levels.
3.6 Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis was conducted by sequentially excluding individual studies and re-running the combined analysis for AST, ALT, SOD, MDA, and GSH. The results showed no significant changes after excluding certain studies, indicating that the findings are robust and reliable (Supplementary Tables S4–S8).
3.7 Publication bias analysis
Funnel plots and Egger’s test were utilized to evaluate publication bias for the five outcomes related to liver function and oxidative stress. The funnel plot showed asymmetry between studies on both sides, suggesting the potential presence of publication bias (Figure 8). The results of Egger’s test indicated statistically significant publication bias for AST (p < 0.05), ALT (p < 0.05), SOD (p < 0.05), MDA (p < 0.05), and GSH (p < 0.05) (Figure 9).
FIGURE 8
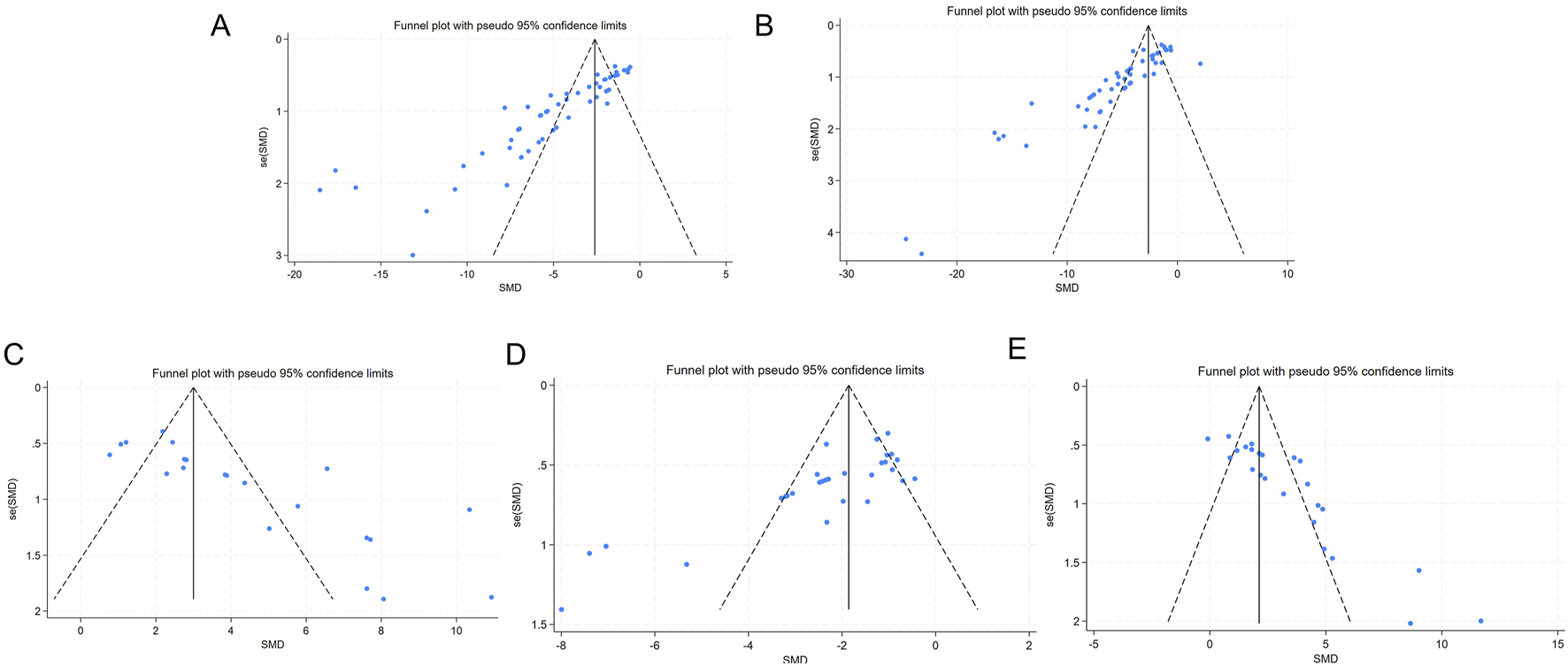
Funnel chart (A) AST; (B) ALT (C) SOD; (D) MDA; (E) GSH.
FIGURE 9
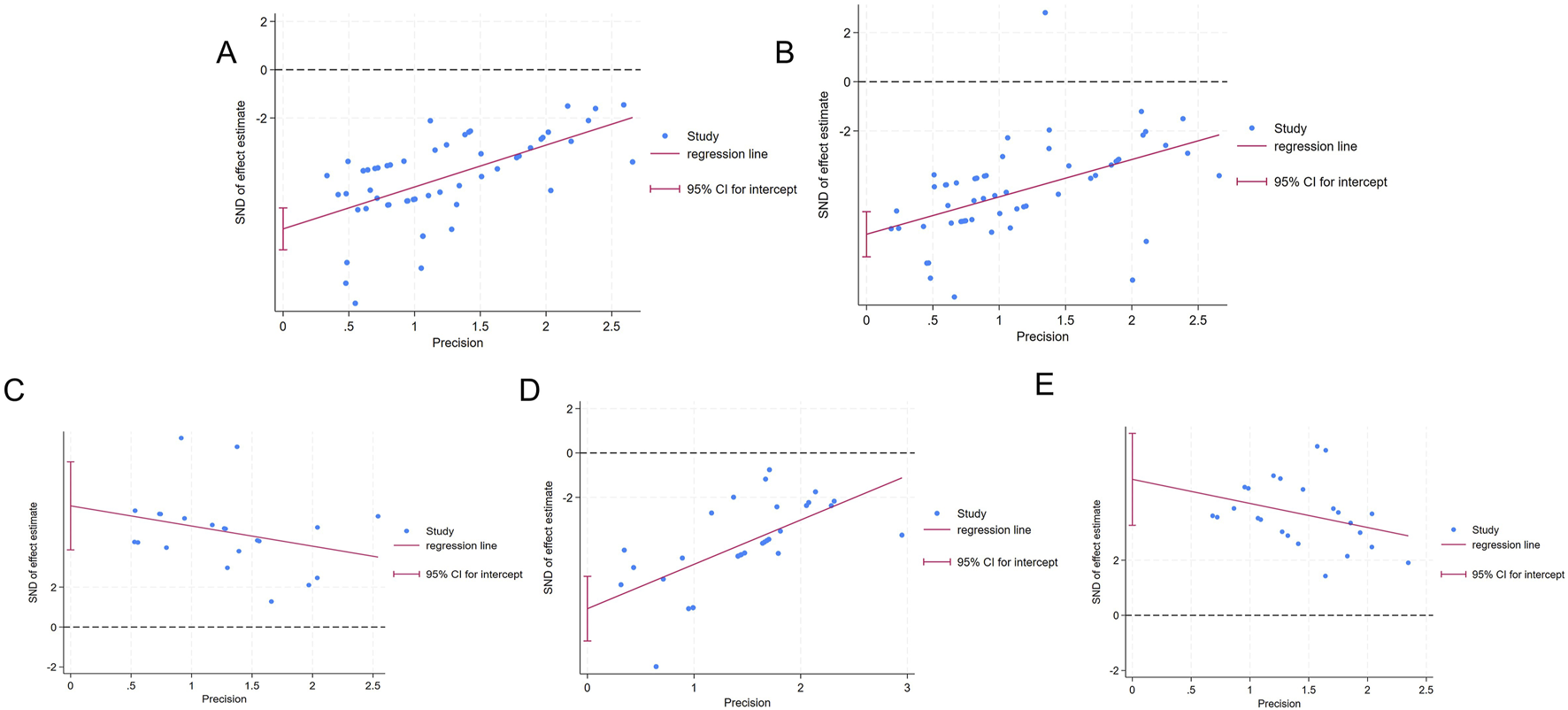
Egger’s publication bias (A) AST (B) ALT; (C) SOD (D) MDA; (E) GSH.
The trim-and-fill method was then employed to identify potential missing studies and evaluate asymmetry. The results indicated that the data from the missing studies would not alter the magnitude of the overall summary effect (Table 7; Supplementary Figure S6).
TABLE 7
| Parameter | Before trim and fill | After trim and fill | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P value | SMD | No. studies | P value | SMD | No. studies | |
| AST | p < 0.05 | −5.044 | 55 | p < 0.05 | −5.611 | 61 |
| ALT | p < 0.05 | −2.705 | 59 | p < 0.05 | −2.705 | 59 |
| SOD | p < 0.05 | 4.521 | 21 | p < 0.05 | 4.521 | 21 |
| MDA | p < 0.05 | −3.970 | 31 | p < 0.05 | −3.970 | 31 |
| GSH | p < 0.05 | 2.647 | 24 | p < 0.05 | 2.647 | 24 |
Egger’s test and trim-and-fill analysis.
4 Discussion
4.1 Summary of evidence
This systematic review and meta-analysis indicate that the active components of Schisandra chinensis exhibit significant protective effects against liver injury in animal models. The findings demonstrate that Schisandra chinensis possesses remarkable hepatoprotective properties, as evidenced by its ability to significantly reduce levels of ALT, AST, and ALP, which are widely accepted biomarkers of liver injury.
In addition to its effects on liver function markers, Schisandra chinensis has been shown to enhance SOD activity and increase GSH levels, both of which are crucial in reducing oxidative stress. Simultaneously, it substantially lowered MDA levels, a significant indicator of oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, Schisandra chinensis has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects, as evidenced by its ability to reduce levels of significant inflammatory markers, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β.
While these studies show positive outcomes, considerable variation remains among the key measurements. Subgroup analyses were conducted to identify potential sources of this variation, revealing that factors such as animal species, treatment strategies, modeling approaches, and dosages may account for these differences. Egger’s test was performed to assess potential publication bias for AST, ALT, SOD, GSH, and MDA. The results showed no significant publication bias, thus enhancing the reliability and robustness of the conclusions.
4.2 Hepatoprotective effects and molecular mechanisms of Schisandra chinensis
4.2.1 Anti-inflammatory properties
Inflammation, primarily caused by the excessive synthesis of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, plays a central role in liver damage. (Malhi and Gores, 2008). Recent studies have highlighted the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Schisandra chinensis. For instance, its bioactive component Schizandrin C has been shown to inhibit the phosphorylation of p38 MAP kinase and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK), thereby lowering the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which contribute to its hepatoprotective effects (Chen et al., 2023). Additionally, the Schisandra acidic polysaccharide has been shown to activate the Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and Protein kinase B (Akt) signaling pathways, leading to a reduction in TNF-α and IL-1β levels (Che et al., 2019a). Li et al. observed that Schisandra chinensis downregulates NF-κB expression in acute liver injury models (Li et al., 2018).
Network pharmacology studies by Xu et al. (2021) revealed that Schisandrol B suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokine expression by downregulating Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) through the Interleukin-17 (IL-17) signaling pathway. In vitro studies have also demonstrated that Schisandrin B exerts anti-inflammatory effects by modulating redox-sensitive transcription factors, such as Nrf2 and NF-κB (Checker et al., 2012). Moreover, Schisandra chinensis also regulates the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) signaling pathway to prevent inflammasome activation, thereby reducing the release of IL-1β and IL-18, and mitigating hepatocyte inflammation. These findings underscore the multiple anti-inflammatory actions of Schisandra chinensis, which contribute to its hepatoprotective properties.
4.2.2 Antioxidant effects
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), when excessively accumulated in hepatocytes, cause oxidative stress, leading to DNA damage, protein oxidation, and lipid peroxidation (Zheng et al., 2019). Mitigating oxidative stress-induced liver injury is crucial, not only through direct ROS scavenging but also via activation of Nrf2, which regulates downstream genes associated with antioxidant defense (Shen et al., 2017).
Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides have been shown to upregulate Nrf2 and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) while significantly lowering the expression of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) (Shan et al., 2019). Concurrently, Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides downregulate TLR4 and NF-κB expression, hence lowering oxidative stress. In the CCl4-induced liver injury model, Schisandrin B was shown to activate the Nrf2/Antioxidant Response Element (ARE) signaling pathway, upregulate the expression of antioxidant genes, and enhance cellular antioxidant capacity, ultimately reducing hepatocyte damage (Chen et al., 2017b). By lowering TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels and thereby suppressing Cytochrome P450 proteins (CYP2E1), lignan extracts from Schisandra chinensis have also demonstrated effectiveness in reducing alcohol-induced hepatic inflammation (Yuan et al., 2018). Additionally, they enhance the activation of Nrf2, HO-1, Glutamate-cysteine Ligase (GCLM), and NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1), further reinforcing their antioxidant properties (Su et al., 2019). By improving detoxification and increasing antioxidant capacity, Schisandrol B exhibits notable protective effects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity through the activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway (Jiang et al., 2015a). These results collectively suggest that Schisandra chinensis possesses hepatoprotective properties through multiple antioxidant systems, underscoring its potential therapeutic value in the treatment of liver damage.
4.2.3 Anti-apoptotic effects
Schisandra chinensis demonstrates hepatoprotective properties through its anti-apoptotic action. Studies have shown that acidic polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis reduce the BCL2-associated X protein (Bax)/B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) ratio, inhibit caspase-3 expression, and upregulate p-AMPK, p-Akt, and phospho-Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 beta (p-GSK3β) expression in acetaminophen-induced liver injury models (Che et al., 2019a). Moreover, Schisandrol B reduces atypical cell death induced by Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) inflammasomes through the PXR/Forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1)/Apaf-1 axis, thereby mitigating cholestasis-induced liver damage (Liang et al., 2022). By increasing the expression of Cyclin D1 (CCND1), Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA), and BCL-2, Schisandrol B also reduces acetaminophen-induced activation of p53 and p21, thereby promoting liver regeneration (Jiang et al., 2015a). Lignan compounds, such as gomisin A, protect against D-galactosamine (GalN)/Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 activation, reducing the number of apoptotic cells, and preventing DNA fragmentation. Gomisin A also inhibits caspase-3 activation in CCl4-induced liver injury model mice and enhances MAPK phosphorylation, exerting significant protective effects against liver and kidney damage (Hwang et al., 2013). These findings suggest that Schisandra chinensis mitigates liver injury by modulating apoptosis-related pathways, further highlighting its therapeutic potential.
4.2.4 Autophagy regulation
Autophagy plays a crucial role in liver protection by removing damaged organelles and proteins, thus preventing hepatocyte death (Yang et al., 2024). Schisandrin B has been shown to induce autophagy in Human hepatoma cell line (HepG2) cells, potentially via modulation of the Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/AKT/Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in acetaminophen-induced liver injury models (Li et al., 2023c). Zhao et al. demonstrated that Schisandra chinensis essential oil upregulates Microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3-II (LC3-II) and downregulates p62 expression in acetaminophen-overdose models, thereby activating autophagy and promoting liver repair (Zhao et al., 2022). Mass spectrometry-based studies have revealed that Schisandrin A enhances exosome-mediated autophagy, thereby alleviating inflammation and improving symptoms of liver injury in drug-induced liver injury (DILI) models (Li et al., 2023b).
4.3 Limitations
Despite strict adherence to the PRISMA guidelines, several limitations still existed. (1) Although the number of studies included was sufficient, the limited data available for subgroup analyses hindered a thorough assessment of Schisandra chinensis' efficacy in liver injury. (2) Selection bias may have influenced the study inclusion process, as studies with positive results are more likely to be published and selected, potentially overestimating the true efficacy of Schisandra chinensis. (3) Significant heterogeneity was observed across studies, likely due to variations in experimental designs, such as animal models, dosage regimens, and treatment durations. This variability compromises the generalizability of the findings and highlights the need for standardized methodologies in future research. (4) Most of the included animal studies employed mouse models. While mouse models represent the most prevalent and well-established approach for liver injury research, they exhibit immunological disparities compared to humans. Therefore, clinical trials are necessary to validate the therapeutic potential and safety profile of Schisandra chinensis and its bioactive compounds.
Despite these limitations, our findings offer valuable insights into the hepatoprotective mechanisms of Schisandra chinensis, providing a strong foundation for future research and clinical applications.
4.4 Safety and future prospects
Clinical studies have consistently demonstrated the safety profile of Schisandra chinensis, highlighting its promise as a well-tolerated therapeutic agent. For example, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving 54 elderly participants reported significant increases in muscle performance without any noted side effects (Cho et al., 2021). Similarly, a study examining its effects on hypertension found no recorded side effects, further confirming its short-term safety and tolerability (Kim et al., 2022).
Beyond its well-established hepatoprotective effects, Schisandra chinensis has demonstrated promising therapeutic potential in other areas, including neuroprotection, cardioprotection, and gut microbiota regulation. These diverse biological activities highlight its versatility as a medicinal herb and suggest its applicability in addressing a wide range of health conditions. However, further research is needed to fully elucidate the pharmacological mechanisms underlying the effects of Schisandra chinensis.
Additionally, a systematic evaluation of its long-term safety and efficacy through rigorous clinical trials is essential to confirm its therapeutic potential and ensure its safe use in diverse populations.
5 Conclusion
This systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that Schisandra chinensis exhibits hepatoprotective effects through mechanisms including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and autophagy-modulating activities. These findings suggest that Schisandra chinensis could serve as a potential therapeutic agent for liver injury. However, the significant heterogeneity among the included studies may undermine the reliability of these conclusions. To enable clinical application, further high-quality preclinical studies and well-designed clinical trials are necessary to validate its efficacy and clarify the underlying mechanisms of action.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
B-HH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. B-HL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. D-JW: Investigation, Software, Writing – review and editing. F-YX: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. Y-BL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. Y-PL: Project administration, Validation, Writing – original draft. W-LL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (SZZYSM 202311014), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82374332), High Level Chinese Medical Hospital Promotion Project (No. HLCMHPP2023086).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1627081/full#supplementary-material
Glossary
- Akt
Protein kinase B
- ALP
alkaline phosphatase
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- AMPK
Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- Apaf-1
Apoptotic protease activating factor 1
- ARE
Antioxidant response element
- AST
aspartate aminotransferase
- Bax
BCL2-associated X protein
- Bcl-2
B-cell lymphoma 2
- CCND1
Cyclin D1
- CI
confidence interval
- COX-2
Cyclooxygenase-2
- CYP2E1
Cytochrome P450 proteins
- EGFR
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- ERK
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase
- FoxO1
Forkhead box protein O1
- GalN
D-galactosamine
- GCLM
Glutamate-cysteine Ligase
- GSH
glutathione
- HepG2
Human hepatoma cell line
- HO-1
Heme oxygenase-1
- IL-1β
Interleukin-1 beta
- IL-6
Interleukin-6
- IL-17
Interleukin-17
- IL-18
Interleukin-18
- iNOS
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- Keap1
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- LC3-II
Microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3-II
- LPS
Lipopolysaccharide
- MDA
malondialdehyde
- mTOR
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- MyD88
Myeloid differentiation primary response 88
- NF-κB
nuclear factor-κB
- NQO1
NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1
- Nrf2
nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2
- PCNA
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- PI3K
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis
- p-GSK3β
Phospho-Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta
- PXR
pregnane X receptor
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- SCF
Schisandra chinensis Fructus
- SD
standard deviation
- SEM
standard error of the mean
- SMD
standardized mean difference
- SOD
superoxide dismutase
- SYRCLE
Systematic Review Centre for Laboratory animal Experimentation
- TG
Triglyceride
- TLR4
Toll-like receptor 4
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
References
1
An Y. Wang Y. Xu L. Fan H. Shen N. Zhao L. et al (2014). Protective effects of Schisandra Lignans against doxorubicin-induced liver injury in rats. Her. Med., 1136–1139. 10.3870/yydb.2014.09.005
2
Bing Y. Zou X. Yang X. Yang X. Sheng J. Qu Z. (2025). Mechanism elucidation and biochemometric-based screening of substances in Schisandra chinensis leaves for alcoholic liver injury. Phytomedicine142, 156757. 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156757
3
Chang X. Li G. Yang B. Lin D. (2024). Protection of schisantherin A against dictamnine-induced hepatotoxicity: pharmacokinetic insights. J. Appl. Toxicol.44, 501–509. 10.1002/jat.4557
4
Che J. Yang S. Qiao Z. Li H. Sun J. Zhuang W. et al (2019a). Schisandra chinensis acidic polysaccharide partialy reverses acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci.140, 248–254. 10.1016/j.jphs.2019.07.008
5
Che J. Yang S. Zi-jing QIAO Xue-han YANG He L. I. Jing-hui S. U. N. et al (2019b). Effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide on apoptosis of hepatocytes induced by acetaminophen in mice. Sci. Technol. Food Industry40, 285–289. 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.16.048
6
Checker R. Patwardhan R. S. Sharma D. Menon J. Thoh M. Bhilwade H. N. et al (2012). Schisandrin B exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through modulation of the redox-sensitive transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-κB. Free Radic. Biol. Med.53, 1421–1430. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.006
7
Chen B. Li S. Jin-ying W. U. He L. I. Xiao-xu G. A. O. Jian-guang C. et al (2014). Protective effect of Schisandra polysaccharide on acute liver injury induced by CCl4 in mice and its mechanism. J. Jilin Univ. Ed.40, 92–96. 10.7694/jldxyxb20140121
8
Chen P. Wang R. Liu F. Li S. Gu Y. Wang L. et al (2023). Schizandrin C regulates lipid metabolism and inflammation in liver fibrosis by NF-κB and p38/ERK MAPK signaling pathways. Front. Pharmacol.14, 1092151. 10.3389/fphar.2023.1092151
9
Chen Q. Zhan Q. Li Y. Sun S. Zhao L. Zhang H. et al (2017a). Schisandra Lignan extract protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice by inhibiting oxidative stress and regulating the NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med.2017, 5140297. 10.1155/2017/5140297
10
Chen Q. Zhang H. Cao Y. Li Y. Sun S. Zhang J. et al (2017b). Schisandrin B attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats by regulation of Nrf2-ARE and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways. Drug Des. Devel Ther.11, 2179–2191. 10.2147/DDDT.S137507
11
Cho Y. H. Lee S. Y. Lee C.-H. Park J.-H. So Y. S. (2021). Effect of Schisandra chinensis Baillon extracts and regular low-intensity exercise on muscle strength and mass in older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr.113, 1440–1446. 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa447
12
Dai W. Bai Z. Ting-ting H. E. Xiao-yan Z. Qiang L. I. Jing Z. et al (2022). Schisandrin C improves acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice by regulating Nrf2 signaling pathway. China J. Chin. Materia Medica47, 5299–5305. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220421.704
13
Devarbhavi H. Asrani S. K. Arab J. P. Nartey Y. A. Pose E. Kamath P. S. (2023). Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatology79, 516–537. 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017
14
Gao Z. Zhang J. Li L. Shen L. Li Q. Zou Y. et al (2016). Heat shock proteins 27 and 70 contribute to the protection of Schisandrin B against d-galactosamine-induced liver injury in mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.94, 373–378. 10.1139/cjpp-2015-0419
15
Guo F. Dai Q. Yang YANG Zhang W. Wu C. Lu H. et al (2024). Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide protects against liver injury in mice with DDS induced colitis. Chin. Veterinary Sci.54, 1692–1699. 10.16656/j.issn.1673-4696.2024.0208
16
Guo X. Su Y. Du Y. Zhang F. Yu W. Ren W. et al (2025). Vinegar-processed Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide ameliorates type 2 diabetes via modulation serum metabolic profiles, gut microbiota, and fecal SCFAs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.294, 139514. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.139514
17
Hooijmans C. R. Rovers M. M. De Vries R. B. Leenaars M. Ritskes-Hoitinga M. Langendam M. W. (2014). SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol.14, 43. 10.1186/1471-2288-14-43
18
Hwang I. S. Kim J. E. Lee Y. J. Kwak M. H. Choi Y. H. Kang B. C. et al (2013). Protective effects of gomisin A isolated from Schisandra chinensis against CCl4-induced hepatic and renal injury. Int. J. Mol. Med.31, 888–898. 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1263
19
Ip S. P. Mak D. H. Li P. C. Poon M. K. Ko K. M. (1996). Effect of a lignan-enriched extract of Schisandra chinensis on aflatoxin B1 and cadmium chloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol. Toxicol.78, 413–416. 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1996.tb00228.x
20
Jiang Y. Fan X. Wang Y. Chen P. Zeng H. Tan H. et al (2015a). Schisandrol B protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibition of CYP-mediated bioactivation and regulation of liver regeneration. Toxicol. Sci.143, 107–115. 10.1093/toxsci/kfu216
21
Jiang Y. Fan X. Wang Y. Tan H. Chen P. Zeng H. et al (2015b). Hepato-protective effects of six schisandra lignans on acetaminophen-induced liver injury are partially associated with the inhibition of CYP-mediated bioactivation. Chem. Biol. Interact.231, 83–89. 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.02.022
22
Jiang Y. Wang Y. Tan H. Yu T. Fan X. Chen P. et al (2016). Schisandrol B protects against acetaminophen-induced acute hepatotoxicity in mice via activation of the NRF2/ARE signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin.37, 382–389. 10.1038/aps.2015.120
23
Kim D.-S. Baek H.-I. Ha K.-C. Cha Y.-S. Park S.-J. (2022). Efficacy and safety of Omija (Schisandra chinensis) extract mixture on the improvement of hyperglycemia: a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrients14, 3159. 10.3390/nu14153159
24
Kim S.-H. Kim Y. S. Kang S. S. Bae K. Hung T. M. Lee S.-M. (2008). Anti-apoptotic and hepatoprotective effects of gomisin A on fulminant hepatic failure induced by D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci.106, 225–233. 10.1254/jphs.fp0071738
25
Lam H. Y. P. Liang T.-R. Peng S.-Y. (2023). Prevention of the pro-aggressive effects of ethanol-intoxicated mice by Schisandrin B. Nutrients15, 1909. 10.3390/nu15081909
26
Li B. Li D. Wang Y. Meng X. Sun X. Tian J. et al (2018). Schisantherin A alleviated alcohol-induced liver injury by the regulation of alcohol metabolism and NF-kB pathway. Exp. Anim.67, 451–461. 10.1538/expanim.18-0021
27
Li L. Wang Y. Hongyan Y. Yabing X. I. N. Han G. A. O. (2013). Protective effect of Schisandrin B against Con A-induced liver injury in mice through inducing heat shock protein 27/70. Acta Acad. Med. Mil. Tertiae SN35, 1210–1214.
28
Li L. Zhang T. Zhou L. Zhou L. Xing G. Chen Y. et al (2014a). Schisandrin B attenuates acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury through heat-shock protein 27 and 70 in mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.29, 640–647. 10.1111/jgh.12425
29
Li R. Zheng Y. Zhang J. Zhou Y. Fan X. (2023a). Gomisin N attenuated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of autophagy by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Phytomedicine110, 154644. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154644
30
Li S. Li H. Gao X. Wu J. Chen J. Wang C. (2014b). Protective effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide on acute liver injury induced by alcohol in mice and its mechanism. J. Beihua Univ. Nat. Sci., 472–475. 10.11713/j.issn.1009-4822.2014.04.011
31
Li X. Gong S. Chen W. Zhao Y. Fu K. Zheng Y. et al (2023b). Schisandrol A, a bioactive constituent from Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus, alleviates drug-induced liver injury by autophagy activation via exosomes. Bioorg. Chem.139, 106751. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106751
32
Li X. Yang H. Xiao J. Zhang J. Zhang J. Liu M. et al (2020). Network pharmacology based investigation into the bioactive compounds and molecular mechanisms of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus against drug-induced liver injury. Bioorg Chem.96, 103553. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103553
33
Li X. Zhao Y. Gong S. Song T. Ge J. Li J. et al (2023c). Schisandrin B ameliorates acute liver injury by regulating EGFR-mediated activation of autophagy. Bioorg. Chem.130, 106272. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106272
34
Liang H. Yang X. Li H. Wang X. Su H. Li X. et al (2022). Schisandrol B protects against cholestatic liver injury by inhibiting pyroptosis through pregnane X receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol.204, 115222. 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115222
35
Lin D. Wang S. Yang B. Li G. (2024). Ameliorative effect of Schisandrol B against Diosbulbin B-induced hepatotoxicity via inhibiting CYP3A4-mediated bioactivation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.492, 117116. 10.1016/j.taap.2024.117116
36
Lu Y. Wang W.-J. Song Y.-Z. Liang Z.-Q. (2014). The protective mechanism of schisandrin A in d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury through activation of autophagy. Pharm. Biol.52, 1302–1307. 10.3109/13880209.2014.890232
37
Malhi H. Gores G. J. (2008). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of liver injury. Gastroenterology134, 1641–1654. 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.002
38
Nagappan A. Jung D. Y. Kim J.-H. Lee H. Jung M. H. (2018). Gomisin N alleviates ethanol-induced liver injury through ameliorating lipid metabolism and oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19, 2601. 10.3390/ijms19092601
39
Page M. J. McKenzie J. E. Bossuyt P. M. Boutron I. Hoffmann T. C. Mulrow C. D. et al (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, n71. 10.1136/bmj.n71
40
Qiu B. Liu K. Li Z. O. U. Hui-feng Z. H. U. Shan FENG (2018). Effects of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus induced CYPs and Nrf2 activation on acute liver injury induced by acetaminophen. China J. Chin. Materia Medica43, 4908–4915.
41
Shan Y. Jiang B. Yu J. Wang J. Wang X. Li H. et al (2019). Protective effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides against the immunological liver injury in mice based on Nrf2/ARE and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Med. Food22, 885–895. 10.1089/jmf.2018.4377
42
Shen J. Rasmussen M. Dong Q.-R. Tepel M. Scholze A. (2017). Expression of the NRF2 target gene NQO1 is enhanced in mononuclear cells in human chronic kidney disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2017, 9091879. 10.1155/2017/9091879
43
Shi H. Yan Y. Yang H. Pu P. Tang H. (2022). Schisandrin B diet inhibits oxidative stress to reduce ferroptosis and lipid peroxidation to prevent pirarubicin-induced hepatotoxicity. Biomed. Res. Int.2022, 5623555. 10.1155/2022/5623555
44
Shi X. Han B. Zhang B. Chu Z. Zhang X. Lu Q. et al (2021). Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides prevent cardiac hypertrophy by dissociating thioredoxin-interacting protein/thioredoxin-1 complex and inhibiting oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother.139, 111688. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111688
45
Siddaway A. P. Wood A. M. Hedges L. V. (2019). How to Do a systematic review: a best practice guide for conducting and reporting narrative reviews, meta-analyses, and meta-syntheses. Annu. Rev. Psychol.70, 747–770. 10.1146/annurev-psych-010418-102803
46
Su L. Li P. Lu T. Mao C. Ji D. Hao M. et al (2019). Protective effect of Schisandra chinensis total lignans on acute alcoholic-induced liver injury related to inhibiting CYP2E1 activation and activating the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn.29, 198–205. 10.1016/j.bjp.2019.01.008
47
Sun H. Wang J. Xiao-fang ZHANG (2021). Schisandrin B improve CCl4 induced liver injury via NF-κB/COX-2 pathway in rats. Zhejiang J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med.31, 515–519. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4561.2021.06.005
48
Sun Y. (2019). Protective effect of schisandra polysaccharides on liver injury in mice. Med. Diet Health47, 50.
49
Taru V. Szabo G. Mehal W. Reiberger T. (2024). Inflammasomes in chronic liver disease: hepatic injury, fibrosis progression and systemic inflammation. J. Hepatology81, 895–910. 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.06.016
50
Teraoka R. Shimada T. Aburada M. (2012). The molecular mechanisms of the hepatoprotective effect of gomisin A against oxidative stress and inflammatory response in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury. Biol. Pharm. Bull.35, 171–177. 10.1248/bpb.35.171
51
Tujios S. Stravitz R. T. Lee W. M. (2022). Management of acute liver failure: update 2022. Semin. Liver Dis.42, 362–378. 10.1055/s-0042-1755274
52
Wang C. Li H. Sheng L. Bao-zhi C. Jin-ying W. Jian-guang C. et al (2014a). Protective effect of lignans from the fruits of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill.on ethanol-induced acute liver injury in mice. Food Sci.35, 262–265. 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201413052
53
Wang C. Xuan D. Chen X. Qiao J. Dou Z. (2019a). Protective effects of schisandrin and deoxyschisandrin on acute liver injurinduced by carbon tetrachloride in mice and its mechanism. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol.4.
54
Wang K.-P. Bai Y. Wang J. Zhang J.-Z. (2014b). Inhibitory effects of Schisandra chinensis on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Mol. Med. Rep.9, 1813–1819. 10.3892/mmr.2014.2004
55
Wang O. Cheng Q. Liu J. Wang Y. Zhao L. Zhou F. et al (2014c). Hepatoprotective effect of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. lignans and its formula with Rubus idaeus on chronic alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Food Funct.5, 3018–3025. 10.1039/c4fo00550c
56
Wang X. Shan Y. Wang J. Zhengyi L. Wang C. He L. et al (2020a). Protective effects of different components of Schisandra chinensis on immu-nological liver injury in mice. J. Jilin Med. Coll.41, 15–18.
57
Wang X. Zhou L. Qiuzheng D. Yingying S. Ziwei J. Liwei L. et al (2020b). Study on the protective effects of schisandrin A on hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice and its mechanism. China Pharm.31, 2725–2730. 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2020.22.07
58
Wang Y. Liu C. Yuhuan Z. Lihuan Y. He L. Jinghui S. et al (2019b). Comparative study on effects of schisandra total polysaccharides and total lignans on acute liver injury in mice. Chin. J. Geriatric Care17, 20–23. 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2671.2019.06.007
59
Wei Y. Luo Z. Zhou K. Wu Q. Xiao W. Yu Y. et al (2021). Schisandrae chinensis fructus extract protects against hepatorenal toxicity and changes metabolic ions in cyclosporine A rats. Nat. Prod. Res.35, 2915–2920. 10.1080/14786419.2019.1672688
60
Wu J. Zhao Y. He L. Xiaoxu G. Jianguang C. Chunmei W. (2014). Effects of schisandra polysaccharides from Northern schisandra on liver injury in rats with hyperlipidemia. Chin. J. Gerontology34, 958–960. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2014.04.045
61
Xie Y. Hao H. Wang H. Guo C. Kang A. Wang G. (2014). Reversing effects of lignans on CCl4-induced hepatic CYP450 down regulation by attenuating oxidative stress. J. Ethnopharmacol.155, 213–221. 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.016
62
Xu G. Lv X. Feng Y. Li H. Chen C. Lin H. et al (2021). Study on the effect of active components of Schisandra chinensis on liver injury and its mechanisms in mice based on network pharmacology. Eur. J. Pharmacol.910, 174442. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174442
63
Xu G. Wang C. Si-xi ZHANG Xi-bin WANG Dong-xue CHEN Dong H. A. N. (2014). Effect of active ingredients of fructus schisandrae chinensis on rats with alcoholic liver damage. Chin. J. Biochem. Pharm., 54–57.
64
Xu K. Liu C. (2011). Protective effect of schisandra polysaccharides on subcellular levels in rats with CCl4-Induced liver injury. Chin. J. GERONTOLOGY31, 1352–1354. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2011.08.030
65
Xu X. Yang B. Zhenyu L. (2011). Protective effect of alcohol extracts from Shizandra with Auricularia auriculajudae polysaccharides on paracetamol-induced acute liver injury in mice. HEILONGJIANG Med. J.24, 384–386. 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2882.2011.03.025
66
Yan F. Zhang Q. Jiao L. Han T. Zhang H. Qin L. et al (2009). Synergistic protective effect of Fructus Schisandrae chinensis with Astragalus polysaccharides on paracetamol-induced acute liver injury in mice. J. Pharm. Pract.27, 340–344. 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0111.2009.05.007
67
Yan L.-S. Kang J.-Y. Gu C.-Y. Qiu X.-Y. Li J.-J. Cheng B. C.-Y. et al (2025). Schisandra chinensis lignans ameliorate hepatic inflammation and steatosis in methionine choline-deficient diet-fed mice by modulating the gut-liver axis. J. Ethnopharmacol.348, 119801. 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119801
68
Yan T. Liu B. Li F. Wu B. Xiao F. He B. et al (2021). Schizandrin ameliorates behavioral disorders in hepatic injury mice via regulation of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol.43, 212–222. 10.1080/08923973.2021.1879847
69
Yang K. Qiu J. Huang Z. Yu Z. Wang W. Hu H. et al (2022). A comprehensive review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and pharmacokinetics of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. and Schisandra sphenanthera Rehd. et Wils. J. Ethnopharmacol.284, 114759. 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114759
70
Yang T. Qu X. Wang X. Xu D. Sheng M. Lin Y. et al (2024). The macrophage STING-YAP axis controls hepatic steatosis by promoting the autophagic degradation of lipid droplets. Hepatology80, 1169–1183. 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000638
71
Yao Y. Shou D. Qinming C. U. I. (2014). Protective effect comparison between lignans in Schisandra Sphenanthera and Schisandra Chinensis on acute liver injury in mice. Chin. Archives Traditional Chin. Med.32, 1465–1467. 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2014.06.072
72
Yuan R. Tao X. Liang S. Pan Y. He L. Sun J. et al (2018). Protective effect of acidic polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis on acute ethanol-induced liver injury through reducing CYP2E1-dependent oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother.99, 537–542. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.079
73
Zhai J. Zhang F. Gao S. Chen L. Feng G. Yin J. et al (2018). Schisandra chinensis extract decreases chloroacetaldehyde production in rats and attenuates cyclophosphamide toxicity in liver, kidney and brain. J. Ethnopharmacol.210, 223–231. 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.020
74
Zhang J. Gao T. Chen G. Liang Y. Nie X. Gu W. et al (2024). Vinegar-processed Schisandra Chinensis enhanced therapeutic effects on colitis-induced depression through tryptophan metabolism. Phytomedicine135, 156057. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156057
75
Zhao J. Ding K. Hou M. Li Y. Hou X. Dai W. et al (2022). Schisandra chinensis essential oil attenuates acetaminophen-induced liver injury through alleviating oxidative stress and activating autophagy. Pharm. Biol.60, 958–967. 10.1080/13880209.2022.2067569
76
Zhao W. Yang J. Xiu-ying H. U. (2006). Model establishment of alcohol liver injury in mouse and effects of the extract from Schisandra on the injury. Chin. J. Comp. Med.16, 274–277. 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2006.05.006
77
Zheng J. Tian X. Zhang W. Zheng P. Huang F. Ding G. et al (2019). Protective effects of fucoxanthin against alcoholic liver injury by activation of Nrf2-Mediated antioxidant defense and inhibition of TLR4-Mediated inflammation. Mar. Drugs17, 552. 10.3390/md17100552
78
Zhou Y. Ji-xiang FANG Yan-qin M. A. Yuan-yuan C. U. I. Yi DONG Rong-rong ZHANG et al (2018). Metabonomics study on hepatoprotective effect of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. China J. Chin. Materia Medica43, 3756–3763.
79
Zhu P. Li J. Fu X. Yu Z. (2019). Schisandra fruits for the management of drug-induced liver injury in China: a review. Phytomedicine59, 152760. 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.11.020
80
Zhu Y. Wang J. (2012). Effect of Schisandrin B(Sch B) on liver damage by Sodium valproate. Chin. Pediatr. Integr. TRADITIONAL West. Med.4, 405–406. 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3865.2012.05.010
Summary
Keywords
Schisandra chinensis, liver injury, Chinese medicine, preclincal study, meta-analysis
Citation
Huang B-H, Lv B-H, Wu D-J, Xiong F-Y, Li Y-B, Lu Y-P and Lv W-L (2025) Efficacy of Schisandra chinensis in liver injury: a systematic review and preclinical meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1627081. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1627081
Received
13 May 2025
Accepted
22 July 2025
Published
04 August 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Adolfo Andrade-Cetto, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
Reviewed by
Tamer A. Addissouky, University of Menoufia, Egypt
Xiaochuan Guo, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Huang, Lv, Wu, Xiong, Li, Lu and Lv.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan-Ping Lu, 5147887@qq.com; Wen-Liang Lv, lvwenliang@sohu.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.