Abstract
Objective:
This study aims to systematically investigate the clinical efficacy and mechanisms of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (KOA), elucidate their underlying mechanisms, and propose potential future research directions.
Design:
This study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. We reviewed literature from PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov up to 31 December 2024. The search strategy combined “GLP-1″ and “KOA”. We included studies on GLP-1 RAs and KOA in humans and animals, excluding conference abstracts, reviews, letters, case reports, and other similar types of publications.
Findings:
Fifteen studies were included, covering six clinical investigations and nine fundamental research studies. Clinical evidence showed GLP-1 RAs significantly improved pain scores and function while reducing KOA incidence. Mechanistic studies reveal multi-target effects, including: 1) Metabolic regulation, 2) Anti-inflammatory action, and 3) Cartilage preservation through autophagy activation and apoptosis inhibition. Safety analysis notes gastrointestinal and tumor events. At the same time, we are concerned about a declining trend in long-term compliance with GLP-1 RAs.
Conclusion:
These findings positioned GLP-1 RAs as promising disease-modifying agents for metabolic-associated KOA, particularly in obese or diabetic subpopulations. While current evidence supports therapeutic potential, confirmatory phase III trials and long-term safety monitoring are needed to establish clinical guidelines.
Systematic Review:
https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO2/view/CRD420250656321, Identifier, CRD420250656321.
Introduction
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA), a prevalent chronic degenerative joint disorder, is predominantly characterized by the progressive deterioration of articular cartilage. Its pathogenesis involves aging, obesity, joint injury, genetic predisposition, biomechanical imbalance, and lifestyle factors (Giorgino et al., 2023; Gelber, 2024). As the disease progresses, patients typically present with a constellation of symptoms, including persistent joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and progressive limitation of motion. A 2020 cohort study reported a global prevalence of KOA of 16.0% among individuals aged ≥15 years, increasing to 22.9% in those ≥40 years (Cui et al., 2020). Recent projections suggested a substantial 74.9% increase in KOA prevalence by 2050 compared to 2020 (Steinmetz et al., 2023). The disease burden of KOA is profound, with lifetime medical costs per patient in the United States reaching up to $140,300 and imposing significant economic burdens through productivity losses that affect individuals, families, and society (Losina et al., 2015; Leifer et al., 2022).
Recent research underscores the link between metabolic disorders, particularly obesity and diabetes, and KOA (Dubey et al., 2018; Eitner et al., 2021; Chowdhury et al., 2022; Wei et al., 2023). Obese individuals face a threefold higher KOA risk compared to healthy-weight individuals (Reyes et al., 2016). A cross-sectional study also found a positive correlation between dietary glycemic index and KOA prevalence in women (So et al., 2018). Intriguingly, overweight and obese individuals also show an increased risk of hand osteoarthritis, suggesting systemic effects beyond mechanical loading (Reyes et al., 2016; Plotz et al., 2021; Badley et al., 2022). Given the established link between metabolic dysregulation and KOA progression, pharmacological interventions targeting metabolic pathways have emerged as potential therapeutic candidates.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), a novel class of antidiabetic agents acting on GLP-1 receptors, exert dual glycemic control and weight-loss effects via enhancing insulin secretion, appetite suppression, and delayed gastric emptying (Ard et al., 2021). Emerging evidence suggests their potential extra-glycemic benefits, including anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective properties, may synergistically ameliorate KOA progression. The Phase 3 STEP9 trial showed that semaglutide, a kind of GLP-1 RAs, reduces body weight and alleviates knee pain in obese KOA patients (Bliddal et al., 2024). However, some studies, like a placebo-controlled trial, found no significant pain reduction with liraglutide (Gudbergsen et al., 2021). A case report also noted joint pain in a patient on liraglutide, which resolved after discontinuation (Ambrosio et al., 2014). Available evidence indicates that GLP-1 RAs are commonly associated with gastrointestinal adverse events, which may curtail long-term adherence (Bliddal et al., 2024; Gudbergsen et al., 2021).
Among GLP-1 RAs, semaglutide and tirzepatide are primarily indicated for weight management, while dulaglutide is predominantly used for glycemic control and liraglutide for both indications. However, since all GLP-1 RAs share a common mechanistic pathway through GLP-1 receptor activation—and given that this review focuses specifically on KOA outcomes—we will analyze them collectively as a single pharmacological class rather than distinguishing between individual agents. Currently, there remains a critical gap in the literature regarding the comprehensive effects of GLP-1 RAs on KOA. This study, therefore, aims to (1) systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy of GLP-1 RAs in KOA management, (2) elucidate their underlying therapeutic mechanisms, and (3) identify key directions for future research in this emerging field.
Methods
This systematic review was registered on the PROSPERO (Registration number: CRD420250656321). This study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. (Appendix S1).
Literature search
We performed a comprehensive search across PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov up to 31 December 2024. Reference lists of relevant reviews were also screened. The search strategy combined MeSH terms and free-text words, including “Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 [MeSH]”, “GLP-1″, “Semaglutide”, “Liraglutide”, “Saxenda”, “Tirzepatide”, “Albiglutide”, “Exenatide”, “Dulaglutide”, “Beinaglutide”, “Polyethylene glycol loxenatide”, “Lixisenatide”, “Loxenatide”, “Mashidutide”, paired with “Osteoarthritis, knee [MeSH]”, “Degeneration of the knee”, “Knee joint”, “Knee OA”, and “KOA”. The full search strategy is shown in Appendix S2.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Eligible studies included original research investigating GLP-1 RAs in KOA, using either human participants or animal models, which reported outcomes involving pain, function, safety, cartilage degradation, or mechanistic pathways. Studies were excluded if they constituted reviews, case reports, conference abstracts, or letters.
Literature screening and data extraction
Two researchers independently screened and extracted data, with a third resolving discrepancies. The process involved (1) searching databases and removing duplicates; (2) excluding irrelevant works (e.g., conference papers, reviews, case reports, etc.); and (3) a full-text reading of remaining articles against inclusion criteria. Data extracted included study details, clinical trial characteristics, primary endpoints, and biochemical results.
Quality assessment
The quality of included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) was assessed using the Cochrane tool “Risk of Bias 2”. For cohort studies, quality evaluation was performed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) with a maximum score of 9 stars, where studies scoring <7 stars were classified as moderate/low quality and those with ≥7 stars as high quality (Cook and Reed, 2015). Non-comparative studies were appraised through the first 8 items of the Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies (MINORS), yielding a total score of 16 points. Quality stratification was defined as follows: 0–4 points (very low quality), 5-7 points (low quality), 8–12 points (moderate quality), and ≥13 points (high quality) (Slim et al., 2003). Given the exploratory nature of preclinical findings and heterogeneity in experimental designs, quality assessment was intentionally restricted to clinical evidence supporting primary outcomes.
Results
The initial literature search identified 656 potentially relevant studies dedicated to 522 unique records. After excluding 194 non-targeted publications (e.g., conference proceedings, reviews, letters, case reports, research registries, etc.), 328 articles remained. Screening of titles and abstracts yielded 30 articles for full-text evaluation, with 15 meeting the inclusion criteria. The selection process is summarized in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1
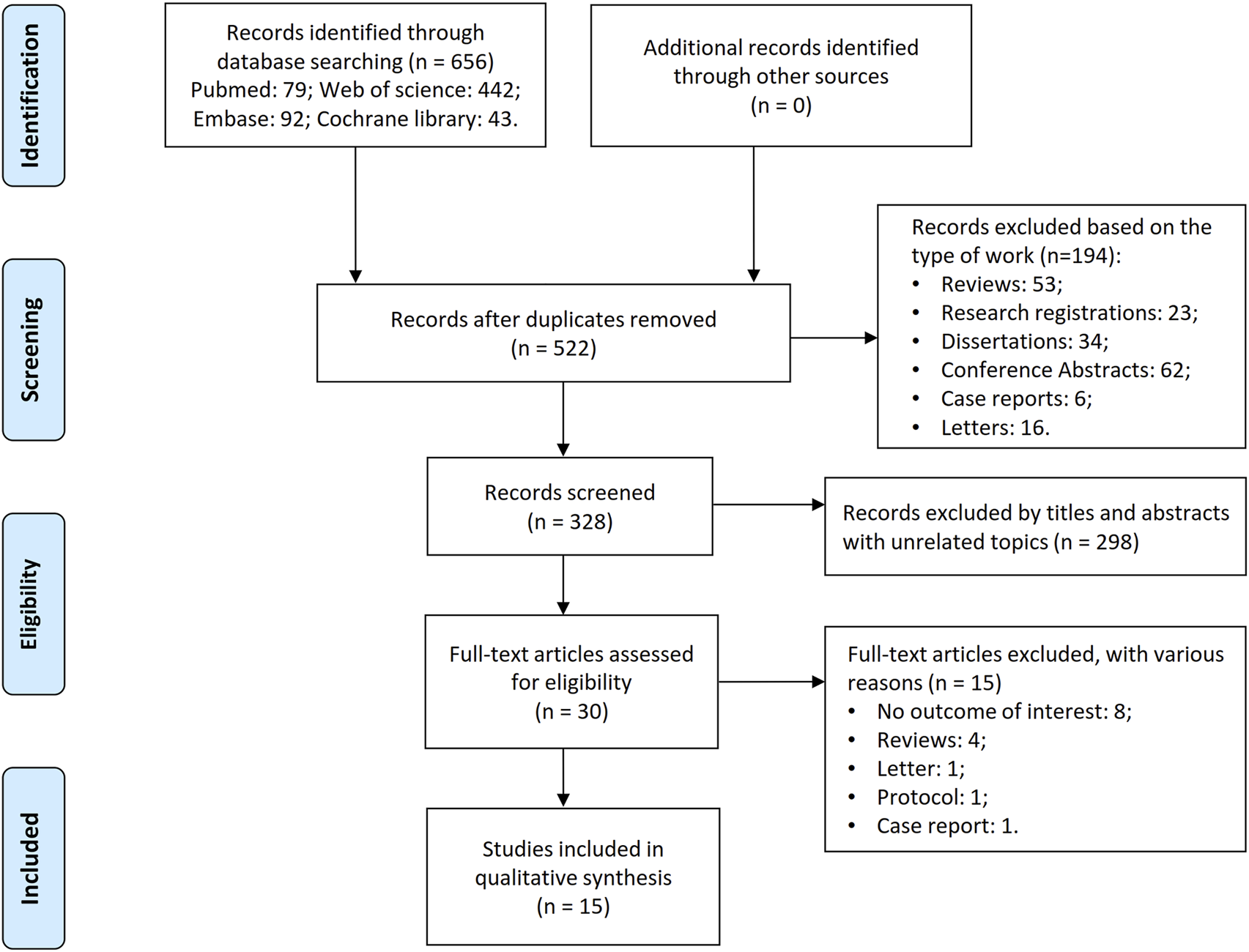
Flowchart of literature search and screening process.
Characteristics of included studies
Fifteen studies included six clinical investigations and nine fundamental research studies.
Clinical investigations
Three RCTs, two prospective cohort studies, and one single-arm interventional study were included. Participants were individuals with KOA who were obese or had diabetes, as well as obese individuals without KOA. Interventions involved GLP-1 RAs such as tirzepatide, semaglutide, liraglutide, etc. Treatment durations ranged from 6 months to 5 years, with some studies lacking specific timeframes. Despite the potential overlap in research teams, studies were included based on distinct data collection timelines and methodological differences (Bliddal et al., 2024; Gudbergsen et al., 2021; Bartholdy et al., 2022; Table 1).
TABLE 1
| Study | Country | Study design | Population | Age (mean ± SD) Experimental/Control |
Sample size (F) Experimental/Control |
Medical prescription | Duration of use of drugs | Follow-up time | Outcome indicators | NOS/MINORS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Control | ||||||||||
| Bartholdy et al. (2022) | Denmark | Randomized controlled trial | KOA with K-L graded from 1 to 3 Age 18 to 74 Overweight or obesity (BMI≥27 kg/m2), with or without T2D (5.8%–10.6%) Weight loss ≥5% after the 8-week intensive dietary intervention |
58.8 ± 11.3/58.6 ± 9.6 | 66(43)/69(44) | Liraglutide: Starting with 0.6 mg/day increasing biweekly by 0.6 mg/day until 3 mg/day | Placebo: Identically appearing placebo | 1 year | 1 year | Physical activity KOOS function Body weight |
|
| Bliddal et al. (2024) | Denmark | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial | KOA with K-L graded 2 or 3 Age ≥18 Obesity with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 WOMAC pain score (0–100, the higher the score, the worse the pain.) ≥ 40 |
56.0 ± 10.0/56.0 ± 10.0 | 271(228)/136(104) | Semaglutide: Once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide (initiated at a dose of 0.24 mg, with dose escalation intended to reach the 2.4-mg target at week 16) | Placebo: Visually identical placebo | 68 weeks | 7 weeks | Body weight WOMAC SF-36 |
|
| Gudbergsen et al. (2021) | Denmark | Randomized controlled trial | KOA with K-L graded from 1 to 3 Age 18 to 74 Overweight or obesity with BMI≥27 kg/m2 Weight loss ≥5% after the 8-week intensive dietary intervention |
59.2 ± 10.8/59.3 ± 9.7 | 80(52)/76(49) | Liraglutide: Starting with 0.6 mg/d and followed by incremental biweekly dose escalation steps of 0.6 mg/d to liraglutide 3 mg/d | Placebo: Identically appearing placebo | 52 weeks | Once at 4-week intervals during treatment | Body weight KOOS pain subscale ICOAP questionnaire KOOS score WOMAC Anthropometry Responder indices |
|
| Lavu et al. (2024) | United States of America | Retrospective cohort study | Obese diabetic with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 Had a T2D diagnosis Followed up for at least 5 years Pre-existing hip and/or knee OA was excluded |
55.4 ± 11.7/55.4 ± 12.4 | 15693(9037)/15693(9003) | GLP-1 RAs | No GLP-1 RAs | Patients initiated during their initial visit between 2015 and 2017 and were followed until the conclusion of the study in 2020–2022 | At least 5 years | Rates of diagnosis for KOA/TKA BMI HbA1c |
8 |
| Obese non-diabetic with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 Had no a T2D diagnosis Followed up for at least 5 years Pre-existing hip and/or knee OA was excluded |
47.4 ± 12.9/47.4 ± 12.9 | 1859(1502)/1859(1507) | GLP-1 RAs | No GLP-1 RAs | Patients initiated during their initial visit between 2015 and 2017 and were followed until the conclusion of the study in 2020–2022 | At least 5 years | Rates of diagnosis for KOA/TKA BMI HbA1c |
||||
| Non-obese diabetic patients with BMI ≤30 kg/m2 Had a T2D diagnosis Followed up for at least 5 years Pre-existing hip and/or knee OA was excluded |
58.3 ± 11.5/58.0 ± 12.2 | 6019(3382)/6019(3320) | GLP-1 RAs | No GLP-1 RAs | Patients initiated during their initial visit between 2015 and 2017 and were followed until the conclusion of the study in 2020–2022 | At least 5 years | Rates of diagnosis for KOA/TKA BMI HbA1c |
||||
| Zhu et al. (2023) | China | Prospective, observational, multicentre cohort study | KOA with T2D K-L graded from 1 to 3 Followed up for at least 5 years |
60.7 ± 8.7/61.2 ± 8.6 | 233(174)/1574(1145) | Among GLP-1 RA users, 93.5% were concurrently prescribed oral antidiabetic drugs and 63.5% received concomitant insulin therapy | Among Non-GLP-1 RAs users, 92.4% were concurrently prescribed oral antidiabetic drugs and 63.0% received concomitant insulin therapy | At least 2 years, average about 4.9 years | At least 5 years, average 7.7–7.8 years | Knee surgery incidence Pain-relieving medication use Number of intra-articular Therapies WOMAC Cartilage thickness Medial femorotibial joint cartilage thickness |
9 |
| Samajdar et al. (2024) | India | Single-arm, record-based observational study | KOA with T2D Age ≥60 years Conventional treatment for at least 3 months |
67.1 ± 4.5 | 98 (40) | Patients received dulaglutide added to ongoing anti-diabetes regimens; existing medications like sitagliptin, linagliptin and vildagliptin were stopped. Concomitant OA treatments (including NSAIDs) were used for at least 3 months prior | At least 6 months | Baseline, after 3 months and 6 months | Glycemic metrics VAS scores NSAIDs consumption Body weight BMI. |
7 | |
Basic characteristics of the included clinical trials.
BMI, body mass index; F, female; GLP-1 RAs, Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; HbA1c, Hemoglobin A1c; ICOAP, intermittent and constant osteoarthritis pain; K-L, Kellgren-Lawrence score; KOA, knee osteoarthritis; KOOS, knee injury and osteoarthritis outcome score; MINORS, Methodological Index for Non-randomized Studies; NOS, Newcastle-Ottawa scale; NSAIDs, Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; SD, standard deviation; SF-36, 36-Item Short Form Health Survey; T2D, Type 2 diabetes; TKA, total knee arthroplasties; VAS, visual analogue scale; WOMAC, Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index.
Fundamental research
Focused on animal models and cellular experiments. Animal studies assessed body weight, functional scores, pain behavior, and histomorphological changes. Cellular experiments explored inflammation, oxidative stress (OS), matrix metabolism, apoptosis, autophagy, and signaling pathways.
Quality assessment
Two RCTs were rated as high risk of bias due to inadequate reporting of randomization procedures (Figure 2). Both cohort studies achieved NOS scores exceeding 7 stars, meeting predefined thresholds for high methodological quality. The single-arm study received a low-quality rating (MINORS score: 7/16) primarily attributable to its non-prospective design and substantial loss to follow-up (12.5%) (Table 1).
FIGURE 2
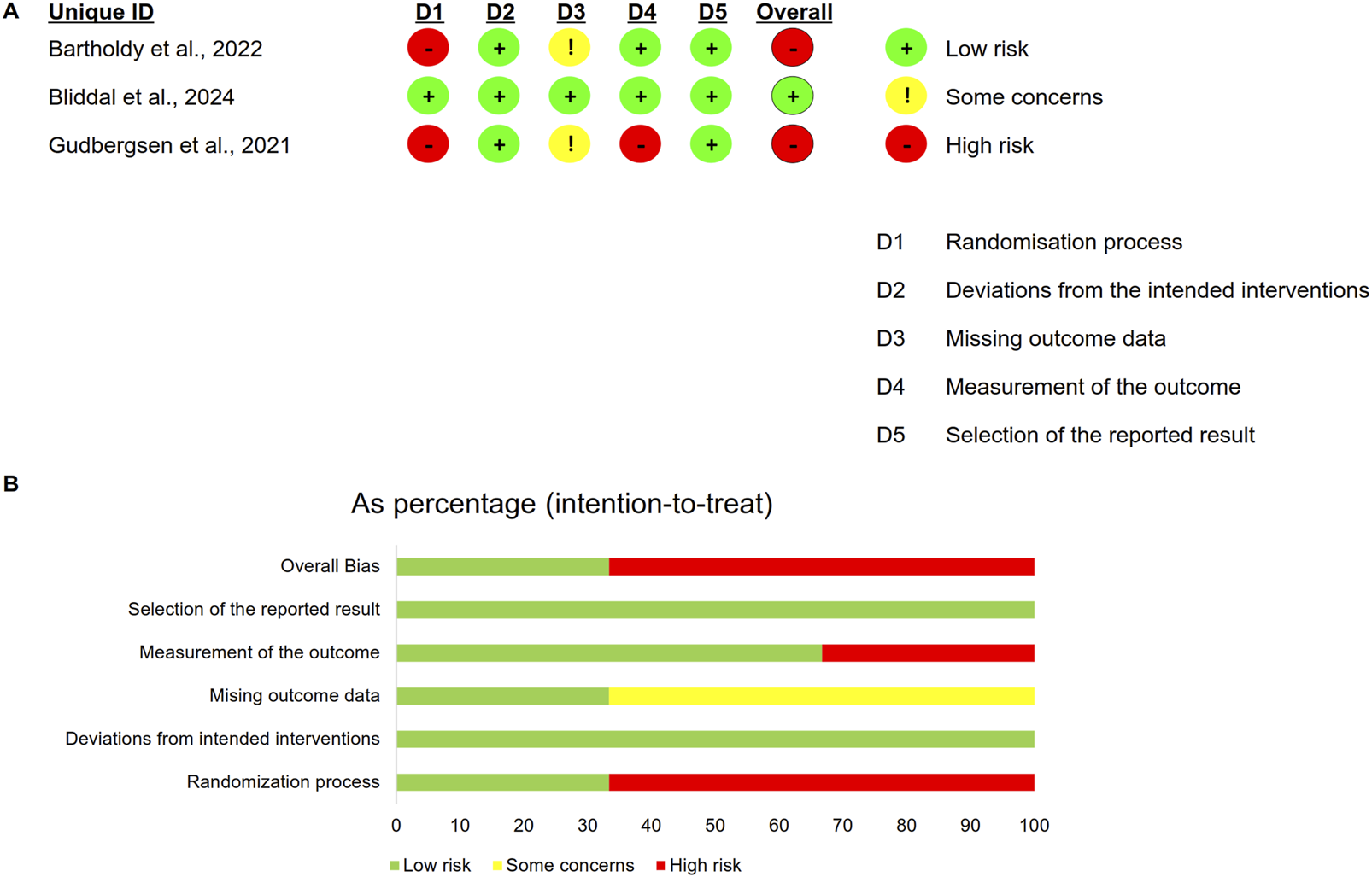
Risk of bias for RCTs. (A) Summary of risk of bias; (B) Percentage of risk of bias.
Clinical efficacy of GLP-1 RAs on KOA
The primary outcomes, which include weight, pain, joint function, KOA risk, and safety, are summarized in Table 2.
TABLE 2
| Study | Body weight | Pain | Function | Risk of KOA | Other | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bartholdy et al. (2022) | + | + | ||||
| Bliddal et al. (2024) | + | + | + | - | ||
| Gudbergsen et al. (2021) | + | = | = | - | ||
| Lavu et al. (2024) | = | - | ||||
| Samajdar et al. (2024) | + | = | Blood glucose (+) | |||
| Zhu et al. (2023) | + | + | + | + | Cartilage (+) |
Clinical trial outcomes of GLP-1 RAs in the treatment of KOA.
The symbol “+” indicates a favoring of the GLP-1 RAs group; the symbol “ = “ indicates that the two groups are equivalent; and the symbol “-“ indicates a favoring of the control group.
GLP-1 RAs, Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; KOA, knee osteoarthritis.
Body weight
Six studies evaluated body weight changes. One RCT (Gudbergsen et al., 2021) reported a 2.8 kg weight loss with liraglutide at 52 weeks versus a 1.2 kg gain in the placebo group (P = 0.008). A significantly higher proportion of patients in the liraglutide group achieved >5% weight loss compared to the placebo group (35% vs. 17.1%, P = 0.024), although no difference reached statistical significance for the more stringent >10% weight loss threshold. Another RCT (Bartholdy et al., 2022) found that liraglutide produced significantly greater weight loss than placebo in participants with overweight or obesity (mean between-group difference 4.1 kg, 95% CI −6.0 kg to −2.1 kg; P < 0.0001). Similarly, semaglutide led to a 13.7% weight loss at 68 weeks, compared to 3.2% in the placebo group (P < 0.001) (Bliddal et al., 2024). A cohort study (Zhu et al., 2023) of KOA patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) reported significantly greater weight loss in the GLP-1 RAs group (mean difference −7.29 kg; 95% CI −8.07 to −6.50 kg; P < 0.001), although 42.06% of GLP-1 RAs users still maintained or gained weight. In the single-arm study by Samajdar et al. (2024) of 40 patients with KOA and T2D, dulaglutide reduced mean body weight from 81.6 ± 8.4 kg to 73.3 ± 7.5 kg (−8.3 kg, P < 0.001) and mean body mass index (BMI) from 30.6 ± 3.5 kg/m2 to 27.5 ± 3.2 kg/m2 (−3.1 kg/m2, P < 0.001) over 6 months. However, an investigation (Lavu et al., 2024) found no statistically significant difference in BMI changes over 2 years between patients receiving GLP-1 RAs and those who did not.
Pain
Four studies assessed pain. One RCT (Gudbergsen et al., 2021) found no significant differences between the groups in pain trajectory or the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain subscale scores over 52 weeks. Another RCT (Bliddal et al., 2024) reported that semaglutide significantly reduced the WOMAC pain subscale scores (41.7 vs. 27.5 points, P < 0.001) and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen. A cohort study (Zhu et al., 2023) reported significant WOMAC pain subscale score improvements in the GLP-1 RAs group, independent of weight loss or Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). Compared to the non-GLP-1 RAs group, the GLP-1 RAs group showed only numerical, non-statistically significant reductions in the annual consumption of oral NSAIDs, acetaminophen, topical NSAIDs, opioids, and the number of intra-articular treatments. The frequency of intra-articular steroid injections was markedly diminished in the GLP-1 RAs group, with an adjusted mean difference of −0.087 injections per year (95% CI −0.14 to −0.036; P < 0.001). Within-group, the GLP-1 RAs group revealed significant improvements in all pain-related metrics except for opioid use. Similarly, a single-arm study (Samajdar et al., 2024) demonstrated that dulaglutide improved pain and reduced NSAIDs consumption.
Function
Four studies evaluated functional outcomes. Liraglutide (Bartholdy et al., 2022) improved the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) function scores by 3.7 points (baseline 81.0 ± 15.1) versus −0.1 for placebo (baseline 85.1 ± 10.7); between-group difference 3.8 points (95% CI 0.9–6.7, P = 0.01). Semaglutide (Bliddal et al., 2024) reduced WOMAC physical function by 14.9 points (95% CI −20.4 to −9.3, P < 0.001) and stiffness by 15.9 points (95% CI −23.2 to −8.6, P < 0.001), and increased 6-min walk distance by 42.6 m versus placebo (95% CI 25.6–59.7, P < 0.001). However, one RCT (Gudbergsen et al., 2021) found no significant differences in KOOS subscales. A cohort study (Zhu et al., 2023) found the GLP-1 RA group achieved significantly greater WOMAC total score improvement than controls (adjusted mean difference −1.46, 95% CI −2.84 to −0.08; P = 0.038).
KOA risk
Two cohort studies examined KOA risk. One (Zhu et al., 2023) found a lower surgery rate in the GLP-1 RAs group (1.7% vs. 5.9%, P = 0.005), while another (Lavu et al., 2024) reported a higher KOA prevalence in GLP-1 RAs users (11.0% vs. 7.4%, P < 0.05).
Other outcomes
Cartilage Degeneration: A cohort study (Zhu et al., 2023) found slower cartilage degeneration in GLP-1 RA users (P = 0.026), independent of weight loss or HbA1c.
Glycemic Control: A single-arm study (Samajdar et al., 2024) reported dulaglutide improved HbA1c, fasting glucose, and postprandial glucose, with pain reduction correlating with HbA1c improvements.
Blood Pressure: Semaglutide reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure (Bliddal et al., 2024).
Treatment Adherence: A cohort study (Lavu et al., 2024) noted declining GLP-1 RAs utilization over time.
Safety
Three studies reported adverse events. Liraglutide had a higher withdrawal rate (12.5% vs. 5.3%), primarily due to gastrointestinal disorders (Gudbergsen et al., 2021). Semaglutide showed a slightly higher adverse event rate (10.0% vs. 8.1%), with tumor-related and gastrointestinal events being the most common (Bliddal et al., 2024). Dulaglutide was generally well-tolerated, with manageable gastrointestinal side effects (Samajdar et al., 2024).
Fundamental research on the effects of GLP-1 RAs on KOA
GLP-1 receptor expression
Multiple studies have reported GLP-1 receptor expression in articular cartilage, synovium, and other joint tissues. Compared with healthy cartilage, degenerated cartilage shows lower GLP-1 receptor expression (Chen et al., 2018); similar downregulation is observed in monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) -treated rat cartilage (Que et al., 2019). In human chondrocytes, advanced glycation end products (AGEs) further reduce GLP-1 receptor levels. GLP-1 receptors are distributed across cartilage, meniscus, bone marrow, and synovial tissue in both KOA and healthy models (Meurot et al., 2022). Liraglutide treatment increases GLP-1 receptor expression in degenerative models (Que et al., 2019).
Analgesic effects
Meurot et al. (2022) showed that the GLP-1 RA liraglutide produces robust, dose-dependent analgesia in a murine model of osteoarthritis. A single intra-articular injection elevated paw-withdrawal thresholds within 3 days, and the benefit persisted through day 10. At 20 μg, liraglutide matched 20 µg dexamethasone on days 3 and 7 and surpassed it on day 10, while simultaneously attenuating synovitis. In a 28-day regimen, liraglutide sustained analgesia beyond the corticosteroid’s waning effect, outperforming dexamethasone on day 14 and matching it on days 21 and 28.
Body weight
Two studies investigated the effects of GLP-1 RAs on body weight in murine models of osteoarthritis, yet reported contradictory findings. The first study (Que et al., 2019) demonstrated a significant reduction in body weight in osteoarthritis model rats following liraglutide administration. In contrast, the second study (Meurot et al., 2022) revealed that neither short-term (10-day) nor extended (28-day) liraglutide treatment exerted any measurable effect on body weight in osteoarthritis model mice.
Anti-inflammatory
Seven studies have demonstrated the anti-inflammatory effects of GLP-1 RAs. Liraglutide (Que et al., 2019) and lixisenatide (Li et al., 2019) both suppress tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL) −6, and IL-1β. Consistently, exenatide-4 (Tong et al., 2019) and liraglutide (Mei et al., 2019) concurrently attenuate gene and protein expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP) −1. Dulaglutide further elevates prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and its synthesizing enzyme cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) while repressing IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 in human SW1353 chondrocytes at both transcriptional and translational levels (Li et al., 2020). In murine primary chondrocytes, liraglutide dose-dependently diminishes secretion of nitrite, PGE2, and IL-6, and similar concentration-dependent reductions in nitric oxide (NO), PGE2, and IL-6 release—together with decreased expression of IL-6, COX-2, and TNF-α—are observed in RAW264.7 macrophages. Mechanistically, liraglutide skews macrophage polarization toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype by down-regulating M1-associated MCP-1 and CD38 while up-regulating the M2 marker early growth response protein 2 (Meurot et al., 2022). Finally, one study (Zhang et al., 2024) showed that liraglutide blunts AGEs–induced production of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α in primary chondrocytes, underscoring its broad anti-inflammatory potential.
Oxidative stress
Four studies demonstrated that GLP-1 RAs reduce OS. One study (Tong et al., 2019) found that exendin-4 dose-dependently lowered reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and reversed AGEs-induced glutathione depletion. Similarly, another study (Li et al., 2019) showed that lixisenatide (20 nM) normalized OS markers 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX-4) to near-basal levels. One study (Mei et al., 2019) reported that liraglutide dose-dependently suppressed TNF-α-induced ROS in osteoarthritis. Additionally, one study (Li et al., 2020) observed that dulaglutide (50 and 100 nM) significantly reduced AGEs-induced OS from 4.2-fold to 2.5-fold and 1.7-fold.
Anti-catabolic
Eight studies demonstrated the anti-catabolic effects of GLP-1 RAs. Four studies showed that liraglutide downregulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1/3/13 (MMP-1/3/13) and A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-4/5 (ADAMTS-4/5) while reducing glycosaminoglycan release from the cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) (Chen et al., 2018; Meurot et al., 2022; Mei et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2024), preserving type II collagen and aggrecan. Similar effects were observed with lixisenatide, exenatide, and dulaglutide, which also suppressed MMP-3/13 and ADAMTS-4/5 (Li et al., 2019; Tong et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020). Additionally, geniposide protected against MIA-induced osteoarthritis in rats by reducing MMP-13 and enhancing type II collagen expression (Huang et al., 2023).
Apoptosis
Two studies explored the role of GLP-1 RAs in apoptosis. One study (Chen et al., 2018) demonstrated that liraglutide reduced pro-apoptotic proteins (cleaved-caspase 3, Bax) while increasing anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 in chondrocytes. In rats, it decreased C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and caspase-3, alleviating osteoarthritis. A recent study (Zhang et al., 2024) further showed that liraglutide (>100 nM) attenuated AGE-induced chondrocyte apoptosis by suppressing caspase-3 and downregulating the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE).
Autophagy
One study (Huang et al., 2023) demonstrated that GLP-1 RAs enhance autophagy in human normal chondrocyte C28/I2 cells by decreasing p62 and increasing Beclin-1 and LC3-II expression, thereby protecting chondrocytes.
Mitochondrial dysfunction
A study (Li et al., 2019) demonstrated that lixisenatide dose-dependently restored AGE-induced reductions in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), with 20 mg nearly normalizing both parameters.
Signaling pathway
Seven studies indicate that GLP-1 RAs protect articular cartilage by modulating Nuclear Factor Kappa-B (NF-κB), Protein Kinase A (PKA)/cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein (CREB), Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K)/Protein Kinase B (Akt), and AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) pathways.
NF-κB pathway
The NF-κB pathway, linked to inflammation, apoptosis, and matrix degradation, is inhibited by liraglutide (Chen et al., 2018; Mei et al., 2019). Lixisenatide reduces AGE-induced IkBα phosphorylation, p65 nuclear translocation, and NF-κB activation (Li et al., 2019). Exendin-4 suppresses NF-κB activation by decreasing p38 phosphorylation, p65 nuclear translocation, and luciferase activity dose-dependently (Tong et al., 2019). Dulaglutide inhibits NF-κB activation by reducing AGE-mediated p65 nuclear translocation and luciferase activity in chondrocytes dose-dependently (Li et al., 2020).
PKA/CREB pathway
A study (Que et al., 2019) demonstrated that liraglutide activates the PKA/CREB pathway by upregulating PKA/p-PKA/CREB/p-CREB protein expression, contributing to its anti-inflammatory effects.
PI3K/Akt pathway
One study (Chen et al., 2018) showed that liraglutide inhibits endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress through activation of PI3K/Akt signaling, which in turn reduces apoptotic protein activity and exerts a protective effect on cartilage.
AMPK/mTOR pathway
A recent study (Huang et al., 2023) demonstrated that geniposide dose-dependently upregulated GLP-1 receptor expression and protected articular cartilage through AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy (inhibiting mTOR while activating AMPK).
Discussion
A notable strength of this review lies in its integration of diverse mechanistic evidence, spanning anti-inflammatory, anti-catabolic, and metabolic pathways. By synthesizing preclinical and clinical data, we elucidate how GLP-1 RAs may modulate key pathological processes in KOA, such as NF-κB inhibition, autophagy activation, and macrophage polarization. These insights not only support their therapeutic potential but also identify actionable targets for future research. Our findings demonstrated that GLP-1 RAs exerted significant therapeutic benefits, including pain alleviation, functional improvement, and reduced risk of KOA. These effects are mediated through multiple mechanisms, such as weight loss, anti-inflammatory, anti-catabolic, anti-apoptotic, regulation of ROS, and autophagy, demonstrating a comprehensive protective effect on KOA (Table 3). However, safety concerns have been identified regarding the clinical application of these medications, particularly their potential association with the complications of gastrointestinal and tumors, which warrant further investigation.
TABLE 3
| Study | GLP-1 RAs | Anti-catabolic | Anti-inflammatory | Oxidative stress | Apoptosis | Autophagy | Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. (2018) | Liraglutide | Type II collagen (+) MMP-3 (−) |
ER stress (−) | CHOP, Caspase-3, Bax (−) Bcl-2 (+) |
NF-Kb (−); PI3K/Akt (+) | ||
| Huang et al. (2023) | Geniposide | Type II collagen (+) MMP-13 (−) |
p62 (−) Beclin-1 and LC 3-II (+) |
AMPK (+)/mTOR (−) | |||
| Li H et al. (2020) | Dulaglutide | MMP-3/13 and ADAMTS-4/5 (−) Type II collagen and aggrecan (+) |
PGE2(COX-2) (−) IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1 (−) |
ROS (−) | NF-κB (−) | ||
| Li X et al. (2019) | Lixisenatide | MMP-3/13 and ADAMTS-4/5 (−) Type II collagen and aggrecan (+) |
TNF-α, IL-6 (−) | 4-HNE and NOX-4 (−) Mitochondria: MMP and ATP (+) |
NF-κB (−) | ||
| Mei et al. (2019) | Liraglutide | MMP-3/13 and ADAMTS-4/5 (−) Type II collagen and aggrecan (+) |
IL-6 and MCP-1 (−) | ROS and NOX-4 (−) | NF-κB (−) | ||
| Meurot et al. (2022) | Liraglutide | MMP-3/13 and ADAMTS-4/5 (−); Glycosaminoglycan (−) | Nitrite, PGE2, IL-6, NO (−) M1 to M2 macrophage shift |
||||
| Que et al. (2019) | Liraglutide | TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β (−) | PKA/CREB (+) | ||||
| Tong et al. (2019) | Exenatide | MMP-3/13 and ADAMTS-4/5 (−) Type II collagen and aggrecan (+) |
TNF-α and IL-1β (−) | ROS (−) Glutathione (+) |
NF-κB (−) | ||
| Zhang et al. (2024) | Liraglutide | MMP-1/3/13 and ADAMTS-4/5 (−) | IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12 and TNF-α (−) | Caspase-3 and RAGE (−) |
The mechanism of action of GLP-1 RAs on KOA.
4-HNE, 4-hydroxynonenal; ADAMTS, 4/5, A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4/5; Akt, Protein Kinase B; AMPK, AMP-activated Protein Kinase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CHOP, C/EBP, homologous protein; COX-2, Cyclooxygenase 2; CREB, Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GLP-1 RAs, Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; IL, interleukin; KOA, knee osteoarthritis; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; MMP 1/3/13, Matrix metalloproteinase 1/3/13; MMP, mitochondrial membrane potential; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, Nuclear Factor Kappa-B; NO, nitric oxide; NOX-4, NADPH, oxidase 4; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase; PKA, Protein Kinase A; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Numerous studies have established a link between obesity, diabetes, and KOA progression. A study (Chen et al., 2020) demonstrated that overweight and obesity increase knee joint loading, which further exacerbates cartilage damage and joint deformity, thereby inducing and accelerating the onset and development of KOA. A meta-analysis (Williams et al., 2016) adjusted for BMI revealed a significant association between T2D and osteoarthritis symptoms. Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative further showed that diabetes worsens KOA severity and impairs physical and mental health (Eitner et al., 2021). A further analysis (Alenazi et al., 2020) revealed that patients with poorer glycemic control exhibited heightened pain severity compared to those with better-controlled HbA1c levels. Conversely, a mediterranean diet with a lower glycemic index was associated with reduced KOA risk (Veronese et al., 2017). The evidence from these studies suggests that weight loss and glycemic control are crucial factors in KOA management in patients with obesity and/or diabetes.
Obesity or diabetes contributes to KOA development through multiple mechanisms. Adipose tissue in obese individuals secretes adipokines (e.g., leptin, lipocalin, resistin) and inflammatory factors (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6), impacting KOA progression (Chang et al., 2018; Urban and Little, 2018). Leptin, for instance, promotes cartilage degradation by activating the NF-κB pathway and increasing inflammatory factors and MMP-1/13 (Abella et al., 2017). Diabetes affects KOA via chronic hyperglycemia, proinflammatory cytokines, OS, and insulin resistance (Wei et al., 2023). High glucose levels induce AGEs, which bind to chondrocyte RAGE receptors, activate NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, and promote inflammatory factor release (e.g., IL-6, IL-8) and MMP-13 expression, exacerbating inflammation and ECM degradation (Rasheed et al., 2011). Hyperglycemia and adipose tissue create a low-grade inflammatory state, increasing pro-inflammatory factors (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and ECM degradation (Rogero and Calder, 2018; Wang and He, 2018). Obesity and diabetes elevate ROS levels, creating a pro-inflammatory environment that increases M1-type macrophages and cytokines, worsening OS and mitochondrial dysfunction (Niemann et al., 2017; Ahmed et al., 2021). ROS overproduction activates MAPK and NF-κB pathways, disrupting cartilage balance (Lepetsos et al., 2019; Rendra et al., 2019). Insulin resistance notably impacts KOA more severely in T2D patients (Eymard et al., 2015). Diabetes leads to severe synovial inflammation and elevated TNF-α levels in obese KOA patients, upregulating pro-inflammatory factors and MMP-13, and damaging joints (Hamada et al., 2016; Qiao et al., 2020). Additionally, leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2, a metabolic factor primarily expressed in the liver, may influence glucose metabolism and obesity-related insulin resistance, potentially advancing the pathogenesis of KOA (Zhu et al., 2022).
The existing studies suggest that GLP-1 RAs protect against KOA through anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, autophagy regulation, macrophage polarization mechanisms, etc. GLP-1 RAs reduce blood glucose, decreasing AGEs and their binding to RAGE receptors, which inhibits NF-κB and MAPK pathways, reducing pro-inflammatory factors like NO, PGE2, IL-1β, TNF-α, MCP-1, etc. They also lower 4-HNE, NOX-4, and ROS levels, reducing MMP-3/13 and ADAMTS-4/5 expression, thereby protecting type II collagen and aggrecan. Additionally, GLP-1 RAs inhibit ER stress via the PI3K/Akt pathway, decreasing CHOP, Caspase-3, and Bax while increasing Bcl-2, and restoring MMP and ATP levels in the mitochondrion, reducing ROS and apoptosis. They promote autophagy by lowering p62, increasing Beclin-1 and LC3-II, and activating AMPK while inhibiting mTOR, aiding in cellular homeostasis. GLP-1 RAs also shift macrophages from M1 to M2 type, altering the joint inflammatory microenvironment. These mechanisms collectively reduce inflammation, protect chondrocytes, regulate metabolism, and improve joint function, highlighting GLP-1 RAs’ therapeutic potential in KOA (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3
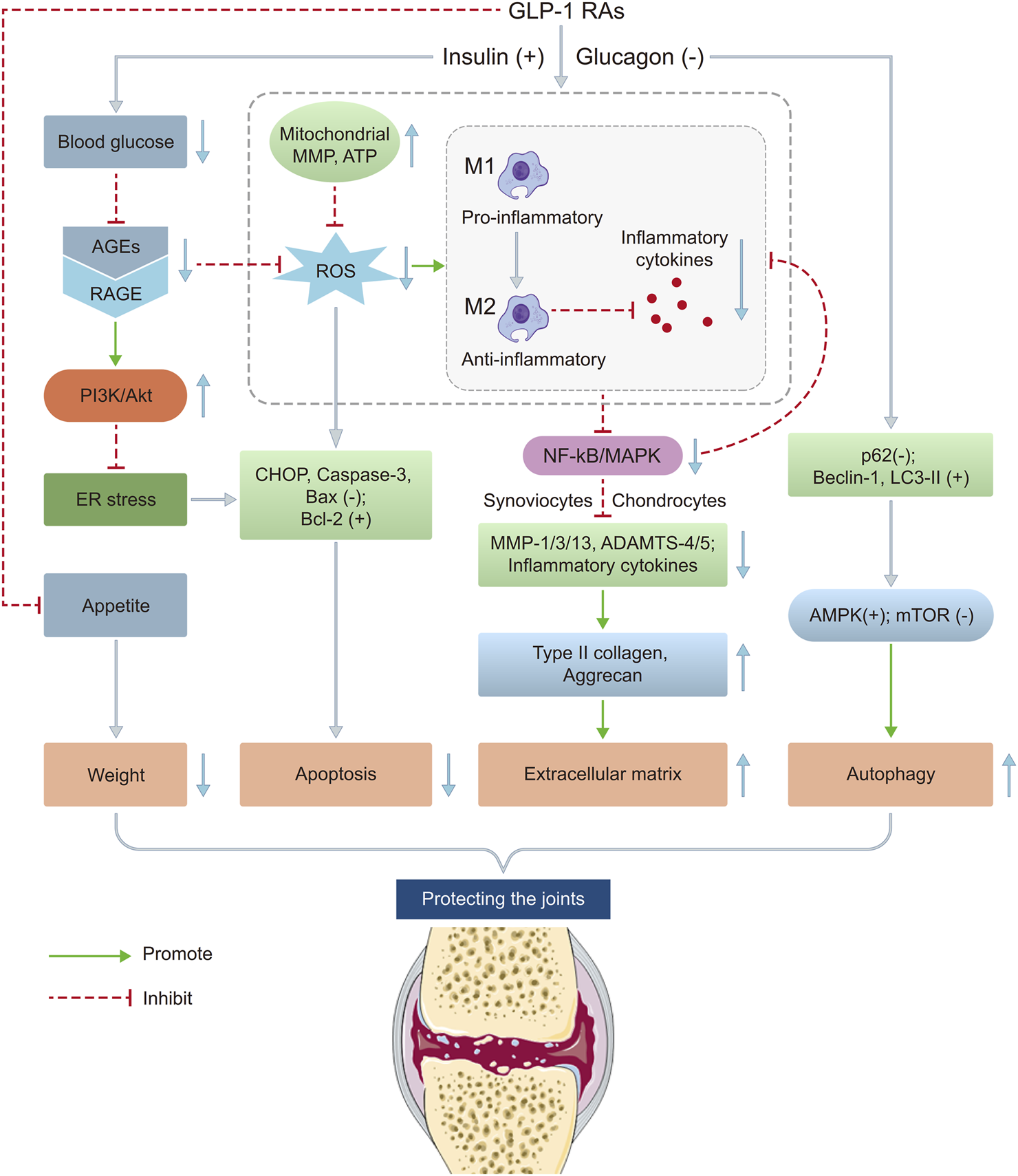
Potential mechanisms of GLP-1 RAs on KOA. This figure illustrates the potential mechanisms by which GLP-1 RAs may influence the pathological process of KOA through multiple pathways. The main mechanisms include: (1) suppressing appetite and reducing joint load; (2) improving insulin sensitivity and reducing systemic inflammation levels; (3) inhibiting inflammatory responses and regulating chondrocyte metabolism through activation of GLP-1 receptors; (4) promoting autophagy aiding in cellular homeostasis. These mechanisms may collectively contribute to slowing the progression of KOA. ADAMTS 4/5, A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4/5; AGEs, Advanced glycation end products; Akt, Protein Kinase B; AMPK, AMP-activated Protein Kinase; ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; GLP-1 RAs, Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; IL, Interleukin; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCP, Monocyte chemoattractant protein; MMP 1/3/13, Matrix metalloproteinase 1/3/13; MMP, Mitochondrial membrane potential; mTOR, Mammalian Target of Rapamycin; NF-κB, Nuclear Factor Kappa-B; NO, Nitric oxide; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; RAGE, Receptor for advanced glycation end products; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Preclinical studies demonstrate consistent dose- and time-dependent effects of GLP-1 RAs in osteoarthritis. Liraglutide (1–20 μg) (Meurot et al., 2022) and exenatide/lixisenatide (10–20 nM) (Li et al., 2019; Tong et al., 2019) showed dose-dependent efficacy, with higher doses providing stronger anti-inflammatory, anti-catabolic, and analgesic effects—20 μg liraglutide even outperformed dexamethasone. Temporally, liraglutide induced rapid (≤7 days) and sustained (≥28 days) benefits (Meurot et al., 2022), correlating with GLP-1 receptor/PKA/CREB activation, while untreated osteoarthritis saw progressive GLP-1 receptor decline (nadir at day 20) (Que et al., 2019). Exenatide/lixisenatide, though lacking multi-timepoint analyses, exerted acute NF-κB suppression (2–24 h) (Tong et al., 2019). These differences highlight the need for standardized protocols to reconcile dose- and time-response relationships in future research.
GLP-1 RAs such as liraglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, dulaglutide, and geniposide share common chondroprotective mechanisms in osteoarthritis, including suppression of NF-κB (reducing IL-6, TNF-α, and COX-2), inhibition of matrix-degrading enzymes (MMP-3/13, ADAMTS-4/5), and attenuation OS (Meurot et al., 2022; Li et al., 2019; Tong et al., 2019). However, each agent exhibits distinct pathways: liraglutide activates PI3K/Akt and PKA/CREB while antagonizing RAGE (Que et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2024); exenatide targets p38 MAPK pathway to suppress NF-κB and enhances glutathione (Tong et al., 2019); lixisenatide restores mitochondrial function (Li et al., 2019); and geniposide induces autophagy via AMPK/mTOR (Huang et al., 2023). These findings underscore the multifaceted therapeutic potential of GLP-1 RAs signaling in osteoarthritis, thereby providing a mechanistic framework to inform and refine future clinical trial design.
Furthermore, compared to traditional weight-loss interventions such as lifestyle modifications, bariatric surgery, or other pharmacotherapies (e.g., orlistat), GLP-1 RAs offer unique advantages, including combined glycemic control and weight reduction, as well as potential anti-inflammatory benefits specific to KOA. However, their higher cost and gastrointestinal side effects may limit accessibility and long-term adherence. While bariatric surgery demonstrates superior weight loss, GLP-1 RAs provide a less invasive option with broader metabolic effects. Future comparative studies are warranted to optimize patient stratification and treatment selection.
While GLP-1 RAs demonstrate therapeutic promise, their safety profile warrants nuanced evaluation. Gastrointestinal adverse events (e.g., nausea, vomiting) may stem from GLP-1 RAs-mediated delayed gastric emptying, particularly during dose escalation (Ard et al., 2021). Tumor-related concerns, though rare in trials, require vigilance given GLP-1 receptor expression in pancreatic and thyroid tissues (Waser et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2022). Long-term data reveal declining adherence (Lavu et al., 2024), possibly reflecting tolerability challenges. Importantly, the risk-benefit ratio favors obese/diabetic KOA patients, where metabolic benefits may outweigh risks, whereas non-metabolic populations necessitate caution pending further evidence.
This study has several limitations. First, given the substantial heterogeneity in experimental designs across preclinical studies (e.g., variations in animal models, dosing regimens, and in vitro experiments), we deliberately abstained from quality assessment of these investigations. Instead, our analysis focused on elucidating the consistent mechanistic pathways through which GLP-1 RAs may modulate KOA progression, as evidenced by convergent findings from in vivo and in vitro models. Second, quantitative pooling was not conducted due to the limited number of studies, diverse study types, and significant variability in outcome measures, which forced us to forego meta-analysis and may have led to the lack of persuasiveness of our findings. Third, our study solely investigated the effects of GLP-1 RAs on KOA; emerging evidence from mechanistic studies and observed risk reductions in osteoarthritis at other anatomical sites collectively point to a potential systemic therapeutic effect of these agents (Baser et al., 2024a; Baser et al., 2024b). Fourth, the mechanism of GLP-1 RAs in KOA is highly complex, and our proposed hypothesis requires further research and validation. Fifth, although GLP-1 RAs yielded statistically significant results in several outcomes—for example, intra-articular steroid injections fell by 0.087 per year—these changes may not translate into clinically meaningful benefit. Future research should therefore emphasize patient-centered endpoints to clarify the real-world value of GLP-1 RAs in KOA. Finally, while tirzepatide’s dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 receptor agonism distinguishes it from selective GLP-1 RAs, we included it due to its shared GLP-1 receptor activation—the primary focus of our mechanistic review. Its inclusion aligns with our goal to explore the broader therapeutic potential of GLP-1 pathway modulation in KOA, though we acknowledge the need for future studies to dissect GIP-specific effects.
Future directions
Based on the available studies, we found that many issues need to be addressed regarding GLP-1 RAs in improving KOA. First, there remains a paucity of robust evidence from multicenter, large-sample RCTs and real-world cohort studies. Second, variability in drug dosage, intervention duration, and follow-up time in clinical trials complicates the assessment of GLP-1 RAs’ efficacy, which has been shown to have dose- and time-dependent effects. Third, the clinical outcomes of different GLP-1 RAs vary widely, necessitating comparative studies. Fourth, comparative studies evaluating GLP-1 RAs against other antidiabetic medications (e.g., Metformin) in terms of clinical outcomes, mechanistic pathways, and safety profiles—especially for patients with concurrent diabetes and KOA—represent a critical area for future investigation. Fifth, higher adverse events, primarily gastrointestinal disorders and neoplasms, in the GLP-1 RAs group compared to controls, may hinder their widespread use. Sixth, while a potential mechanism of GLP-1 RAs in KOA has been proposed, further validation is needed due to its complexity. Seventh, a significant proportion of patients maintained or increased weight despite GLP-1 RAs treatment, which may suggest limited applicability to specific subgroups (e.g., age, sex, or diabetic status). Eighth, the efficacy of GLP-1 RAs in non-obese or non-diabetic KOA patients warrants further investigation. Ninth, we acknowledge the absence of fundamental studies involving semaglutide or tirzepatide in the current literature, and agree that future preclinical research on these agents would be valuable for elucidating their mechanisms in KOA. Finally, combining GLP-1 RAs with other interventions, such as dietary changes and physical activity, presents a promising research avenue.
Conclusion
GLP-1 RAs held therapeutic potential for KOA patients with obesity or diabetes, but current evidence remained insufficient, warranting further high-quality RCTs and mechanistic studies to confirm their efficacy and safety.
Statements
Author contributions
YL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. LY: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. FL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. JF: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. WZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. JG: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. CY: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of the People’s Republic of China (GZK-KJS-2023–012).
Acknowledgments
We thank Nanyang Liu from the West China Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, for providing valuable insights during the review process.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1627691/full#supplementary-material
Glossary
- 4-HNE
4-hydroxynonenal
- ADAMTS-4/5
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-4/5
- AGEs
Advanced glycation end products
- Akt
Protein Kinase B
- AMPK
AMP-activated Protein Kinase
- ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
- BMI
Body mass index
- CHOP
C/EBP homologous protein
- COX-2
Cyclooxygenase 2
- CREB
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein
- ECM
Extracellular matrix
- ER
Endoplasmic reticulum
- F
Female
- GIP
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide
- GLP-1 RAs
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists
- GLP-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- HbA1c
Hemoglobin A1c
- ICOAP
Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain
- IL
Interleukin
- K-L
Kellgren-Lawrence score
- KOA
Knee osteoarthritis
- KOOS
Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score
- MAPK
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MCP
Monocyte chemoattractant protein
- MIA
Monosodium iodoacetate
- MINORS
Methodological Index for Non-randomized Studies
- MMP-1/3/13
Matrix metalloproteinase-1/3/13
- MMP
Mitochondrial membrane potential
- mTOR
Mammalian Target of Rapamycin
- NF-κB
Nuclear Factor Kappa-B
- NO
Nitric oxide
- NOS
Newcastle-Ottawa scale
- NOX-4
NADPH oxidase 4
- NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- OS
Oxidative stress
- PGE2
Prostaglandin E2
- PI3K
Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase
- PKA
Protein Kinase A
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- RAGE
Receptor for advanced glycation end products
- RCT
Randomized controlled trial
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- SD
Standard deviation
- SF-36
36-Item Short Form Health Survey
- T2D
Type 2 diabetes
- TKA
Total knee arthroplasties
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- VAS
Visual analogue scale
- WOMAC
Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index.
References
1
Abella V. Scotece M. Conde J. Pino J. Gonzalez-Gay M. A. Gómez-Reino J. J. et al (2017). Leptin in the interplay of inflammation, metabolism and immune system disorders. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.13 (2), 100–109. 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.209
2
Ahmed B. Sultana R. Greene M. W. (2021). Adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese. Biomed. Pharmacother.137, 111315. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111315
3
Alenazi A. M. Obaidat S. M. Alshehri M. M. Alothman S. Gray C. Rucker J. et al (2020). Type 2 diabetes affects joint pain severity in People with localized osteoarthritis: a retrospective study. Pain Med.21 (5), 1025–1031. 10.1093/pm/pnz299
4
Ambrosio M. L. Monami M. Sati L. Marchionni N. Di Bari M. Mannucci E. (2014). GLP-1 receptor agonist-induced polyarthritis: a case report. Acta Diabetol.51 (4), 673–674. 10.1007/s00592-013-0525-3
5
Ard J. Fitch A. Fruh S. Herman L. (2021). Weight loss and maintenance related to the mechanism of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists. Adv. Ther.38 (6), 2821–2839. 10.1007/s12325-021-01710-0
6
Badley E. M. Zahid S. Wilfong J. M. Perruccio A. V. (2022). Relationship between body mass index and osteoarthritis for single and multisite osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, or knee: findings from a Canadian longitudinal study on aging. Arthritis Care Res. Hob.74 (11), 1879–1887. 10.1002/acr.24729
7
Bartholdy C. Overgaard A. Gudbergsen H. Bliddal H. Kristensen L. E. Henriksen M. (2022). Changes in physical activity during a one-year weight loss trial with liraglutide vs placebo in participants with knee osteoarthritis: secondary analyses of a randomised controlled trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open4 (2), 100255. 10.1016/j.ocarto.2022.100255
8
Baser O. Isenman L. Baser S. Samayoa G. (2024a). Impact of semaglutide on osteoarthritis risk in patients with obesity: a retrospective cohort study. Obes. Sci. Pract.10 (3), e762. 10.1002/osp4.762
9
Baser O. Rodchenko K. Vivier E. Baser I. Lu Y. Mohamed M. (2024b). The impact of approved anti-obesity medications on osteoarthritis. Expert Opin. Pharmacother.25 (11), 1565–1573. 10.1080/14656566.2024.2391524
10
Bliddal H. Bays H. Czernichow S. Uddén Hemmingsson J. Hjelmesæth J. Hoffmann Morville T. et al (2024). Once-weekly semaglutide in persons with obesity and knee osteoarthritis. N. Engl. J. Med.391 (17), 1573–1583. 10.1056/NEJMoa2403664
11
Chang J. Liao Z. Lu M. Meng T. Han W. Ding C. (2018). Systemic and local adipose tissue in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil.26 (7), 864–871. 10.1016/j.joca.2018.03.004
12
Chen J. Xie J. J. Shi K. S. Gu Y. T. Wu C. C. Xuan J. et al (2018). Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and the associated inflammatory response in chondrocytes and the progression of osteoarthritis in rat. Cell Death Dis.9 (2), 212. 10.1038/s41419-017-0217-y
13
Chen L. Zheng J. J. Y. Li G. Yuan J. Ebert J. R. Li H. et al (2020). Pathogenesis and clinical management of obesity-related knee osteoarthritis: impact of mechanical loading. J. Orthop. Transl.24, 66–75. 10.1016/j.jot.2020.05.001
14
Chowdhury T. Bellamkonda A. Gousy N. Deb Roy P. (2022). The association between diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis: does diabetes mellitus play a role in the severity of pain in osteoarthritis?Cureus14 (1), e21449. 10.7759/cureus.21449
15
Cook D. A. Reed D. A. (2015). Appraising the quality of medical education research methods: the medical education research study quality instrument and the newcastle-ottawa scale-education. Acad. Med.90 (8), 1067–1076. 10.1097/ACM.0000000000000786
16
Cui A. Li H. Wang D. Zhong J. Chen Y. Lu H. (2020). Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. EClinicalMedicine, 29–30. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100587
17
Dubey N. K. Ningrum D. N. A. Dubey R. Deng Y. H. Li Y. C. Wang P. D. et al (2018). Correlation between diabetes mellitus and knee osteoarthritis: a dry-to-wet lab approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19 (10), 3021. 10.3390/ijms19103021
18
Eitner A. Culvenor A. G. Wirth W. Schaible H. G. Eckstein F. (2021). Impact of diabetes mellitus on knee osteoarthritis pain and physical and mental status: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Arthritis Care Res. Hob.73 (4), 540–548. 10.1002/acr.24173
19
Eymard F. Parsons C. Edwards M. H. Petit-Dop F. Reginster J. Y. Bruyère O. et al (2015). Diabetes is a risk factor for knee osteoarthritis progression. Osteoarthr. Cartil.23 (6), 851–859. 10.1016/j.joca.2015.01.013
20
Gelber A. C. (2024). Knee osteoarthritis. Ann. Intern Med.177 (9), ITC129–ITC144. 10.7326/ANNALS-24-01249
21
Giorgino R. Albano D. Fusco S. Peretti G. M. Mangiavini L. Messina C. (2023). Knee osteoarthritis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and mesenchymal stem cells: what else is new? An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (7), 6405. 10.3390/ijms24076405
22
Gudbergsen H. Overgaard A. Henriksen M. Wæhrens E. E. Bliddal H. Christensen R. et al (2021). Liraglutide after diet-induced weight loss for pain and weight control in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr.113 (2), 314–323. 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa328
23
Hamada D. Maynard R. Schott E. Drinkwater C. J. Ketz J. P. Kates S. L. et al (2016). Suppressive effects of insulin on tumor necrosis factor-dependent early osteoarthritic changes associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arthritis Rheumatol.68 (6), 1392–1402. 10.1002/art.39561
24
Huang J. Chen Z. Wu Z. Xie X. Liu S. Kong W. et al (2023). Geniposide stimulates autophagy by activating the GLP-1R/AMPK/mTOR signaling in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Biomed. Pharmacother.167, 115595. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115595
25
Lavu M. S. Porto J. R. Hecht C. J. Kaelber D. C. Sculco P. K. Heckmann N. D. et al (2024). The five-year incidence of progression to osteoarthritis and total joint arthroplasty in patients prescribed glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists. J. Arthroplasty39 (10), 2433–2439.e1. 10.1016/j.arth.2024.06.008
26
Leifer V. P. Katz J. N. Losina E. (2022). The burden of OA-health services and economics. Osteoarthr. Cartil.30 (1), 10–16. 10.1016/j.joca.2021.05.007
27
Lepetsos P. Papavassiliou K. A. Papavassiliou A. G. (2019). Redox and NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free Radic. Biol. Med.132, 90–100. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.09.025
28
Li X. Jia F. Zhu Z. Huang L. (2019). Lixisenatide attenuates advanced glycation end products (AGEs)-induced degradation of extracellular matrix in human primary chondrocytes. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol.47 (1), 1256–1264. 10.1080/21691401.2019.1593996
29
Li H. Chen J. Li B. Fang X. (2020). The protective effects of dulaglutide against advanced glycation end products (AGEs)-induced degradation of type Ⅱ collagen and aggrecan in human SW1353 chondrocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact.322, 108968. 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.108968
30
Losina E. Paltiel A. D. Weinstein A. M. Yelin E. Hunter D. J. Chen S. P. et al (2015). Lifetime medical costs of knee osteoarthritis management in the United States: impact of extending indications for total knee arthroplasty. Arthritis Care Res. Hob.67 (2), 203–215. 10.1002/acr.22412
31
Mei J. Sun J. Wu J. Zheng X. (2019). Liraglutide suppresses TNF-α-induced degradation of extracellular matrix in human chondrocytes: a therapeutic implication in osteoarthritis. Am. J. Transl. Res.11 (8), 4800–4808.
32
Meurot C. Martin C. Sudre L. Breton J. Bougault C. Rattenbach R. et al (2022). Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist, exerts analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-degradative actions in osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep.12 (1), 1567. 10.1038/s41598-022-05323-7
33
Niemann B. Rohrbach S. Miller M. R. Newby D. E. Fuster V. Kovacic J. C. (2017). Oxidative stress and cardiovascular risk: obesity, diabetes, smoking, and pollution: Part 3 of a 3-Part Series. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.70 (2), 230–251. 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.05.043
34
Plotz B. Bomfim F. Sohail M. A. Samuels J. (2021). Current epidemiology and risk factors for the development of hand osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep.23 (8), 61. 10.1007/s11926-021-01025-7
35
Qiao L. Li Y. Sun S. (2020). Insulin exacerbates inflammation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammation43 (3), 916–936. 10.1007/s10753-020-01178-0
36
Que Q. Guo X. Zhan L. Chen S. Zhang Z. Ni X. et al (2019). The GLP-1 agonist, liraglutide, ameliorates inflammation through the activation of the PKA/CREB pathway in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis. J. Inflamm. (Lond)16 (1), 13. 10.1186/s12950-019-0218-y
37
Rasheed Z. Akhtar N. Haqqi T. M. (2011). Advanced glycation end products induce the expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 by receptor for advanced glycation end product-mediated activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-κB in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Rheumatol. Oxf.50 (5), 838–851. 10.1093/rheumatology/keq380
38
Rendra E. Riabov V. Mossel D. M. Sevastyanova T. Harmsen M. C. Kzhyshkowska J. (2019). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophage activation and function in diabetes. Immunobiology224 (2), 242–253. 10.1016/j.imbio.2018.11.010
39
Reyes C. Leyland K. M. Peat G. Cooper C. Arden N. K. Prieto-Alhambra D. (2016). Association between overweight and obesity and risk of clinically diagnosed knee, hip, and hand osteoarthritis: a population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol.68 (8), 1869–1875. 10.1002/art.39707
40
Rogero M. M. Calder P. C. (2018). Obesity, inflammation, toll-like receptor 4 and fatty acids. Nutrients10 (4), 432. 10.3390/nu10040432
41
Samajdar S. S. Bhaduri G. Ghoshal P. K. Mukherjee S. Pal J. Chatterjee N. et al (2024). Dual effects of dulaglutide on glycemic control and knee osteoarthritis pain in elderly patients with Type 2 diabetes. Pain Manag.14 (7), 365–373. 10.1080/17581869.2024.2402214
42
Slim K. Nini E. Forestier D. Kwiatkowski F. Panis Y. Chipponi J. (2003). Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J. Surg.73 (9), 712–716. 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
43
So M. W. Lee S. Kim S. H. (2018). Association between dietary glycemic index and knee osteoarthritis: the Korean national health and nutrition examination Survey 2010-2012. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet.118 (9), 1673–1686. 10.1016/j.jand.2017.12.001
44
Steinmetz J. D. Culbreth G. T. Haile L. M. Rafferty Q. Lo J. Fukutaki K. G. et al (2023). Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990-2020 and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol.5 (9), e508–e522. 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00163-7
45
Tong C. Liang H. Liu X. Yuan B. Xue B. Tong Z. et al (2019). The protective effects of exenatide against AGEs-induced articular matrix degradation in human primary chondrocytes. Am. J. Transl. Res.11 (4), 2081–2089.
46
Urban H. Little C. B. (2018). The role of fat and inflammation in the pathogenesis and management of osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Oxf.57 (Suppl. l_4), iv10–iv21. 10.1093/rheumatology/kex399
47
Veronese N. Stubbs B. Noale M. Solmi M. Luchini C. Smith T. O. et al (2017). Adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with lower prevalence of osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Clin. Nutr.36 (6), 1609–1614. 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.09.035
48
Wang T. He C. (2018). Pro-inflammatory cytokines: the link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.44, 38–50. 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.10.002
49
Waser B. Blank A. Karamitopoulou E. Perren A. Reubi J. C. (2015). Glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor expression in normal and diseased human thyroid and pancreas. Mod. Pathol.28 (3), 391–402. 10.1038/modpathol.2014.113
50
Wei G. Lu K. Umar M. Zhu Z. Lu W. W. Speakman J. R. et al (2023). Risk of metabolic abnormalities in osteoarthritis: a new perspective to understand its pathological mechanisms. Bone Res.11 (1), 63. 10.1038/s41413-023-00301-9
51
Williams M. F. London D. A. Husni E. M. Navaneethan S. Kashyap S. R. (2016). Type 2 diabetes and osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Complicat.30 (5), 944–950. 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.02.016
52
Yang Z. Lv Y. Yu M. Mei M. Xiang L. Zhao S. et al (2022). GLP-1 receptor agonist-associated tumor adverse events: a real-world study from 2004 to 2021 based on FAERS. Front. Pharmacol.13, 925377. 10.3389/fphar.2022.925377
53
Zhang X. Jiang J. Xu J. Chen J. Gu Y. Wu G. (2024). Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, ameliorates inflammation and apoptosis via inhibition of receptor for advanced glycation end products signaling in AGEs induced chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord.25 (1), 601. 10.1186/s12891-024-07640-6
54
Zhu S. Bennett S. Li Y. Liu M. Xu J. (2022). The molecular structure and role of LECT2 or CHM-II in arthritis, cancer, and other diseases. J. Cell Physiol.237 (1), 480–488. 10.1002/jcp.30593
55
Zhu H. Zhou L. Wang Q. Cai Q. Yang F. Jin H. et al (2023). Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists as a disease-modifying therapy for knee osteoarthritis mediated by weight loss: findings from the Shanghai Osteoarthritis Cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis.82 (9), 1218–1226. 10.1136/ard-2023-223845
Summary
Keywords
knee osteoarthritis, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, body weight, glycemic control, knee pain
Citation
Li Y, Yang L, Li F, Fu J, Zhao W, Wu X, Guo J and Yue C (2025) Emerging therapeutic potential of glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1627691. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1627691
Received
13 May 2025
Accepted
23 September 2025
Published
13 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Ravinder Abrol, California State University, Northridge, United States
Reviewed by
Katherine N. Theken, University of Pennsylvania, United States
Ankit Choudhury, Medical College of Wisconsin, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Li, Yang, Li, Fu, Zhao, Wu, Guo and Yue.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaolong Wu, orthowu168@163.com; Jiayi Guo, DoctorGuoJY@outlook.com; Chen Yue, Orthopedics.Yue@outlook.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.