Abstract
Epimedium brevicornu (Yin Yang Huo), a widely used traditional Chinese medicinal ingredient, has garnered significant attention for its role in treating orthopedic diseases such as osteoporosis. Our work through network pharmacology and bioinformatics analysis, we identified that out of 27 major active components in Epimedium brevicornu, 8 key components have therapeutic effects on 11 types of diseases related to orthopedic conditions. The disease-target association analysis indicated that Osteoarthritis, Osteoporosis, Muscle Spasm and Myopathy have relatively clear targets for disease treatment. The KEGG enrichment analysis results indicate that the signaling pathway of Epimedium treatment in Osteoarthritis may be closely related to the Lipid and atherosclerosis pathway, PPAR signaling pathway and Arachidonic acid metabolism. Epimedium may treat osteoporosis with Nitrogen metabolism, GABAergic synapse, and Pathways in cancer. Epimedium may affect muscle spasticity through Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, Serotonergic synapse and Cholinergic synapse closely related to nervous system function; Additionally, our analysis suggests that Epimedium may treat myopathy through Nitrogen metabolism and GABAergic synapse pathways. These studies have not only provided a molecular mechanism-based explanation for the pharmacological effects of Epimedium, but also laid a theoretical foundation for the development of Epimedium-based precision therapeutic regimens.
1 Introduction
Epimedium brevicornu (Figure 1), is a genus of about 52 species in the family Berberidaceae, about 80% of which are endemic to China (Chen et al., 2015). According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 edition), it includes the dry leaves of Epimedium brevicornu Maxim, Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim, Epimedium pubescens Maxim and Epimedium koreanum Nakai. The four species of Epimedium recorded in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia have similar pharmacological effects but differ in their geographical distribution. According to The Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine (ETCM), the wild distribution of Epimedium in China is primarily concentrated in the central region (Figure 2).
FIGURE 1
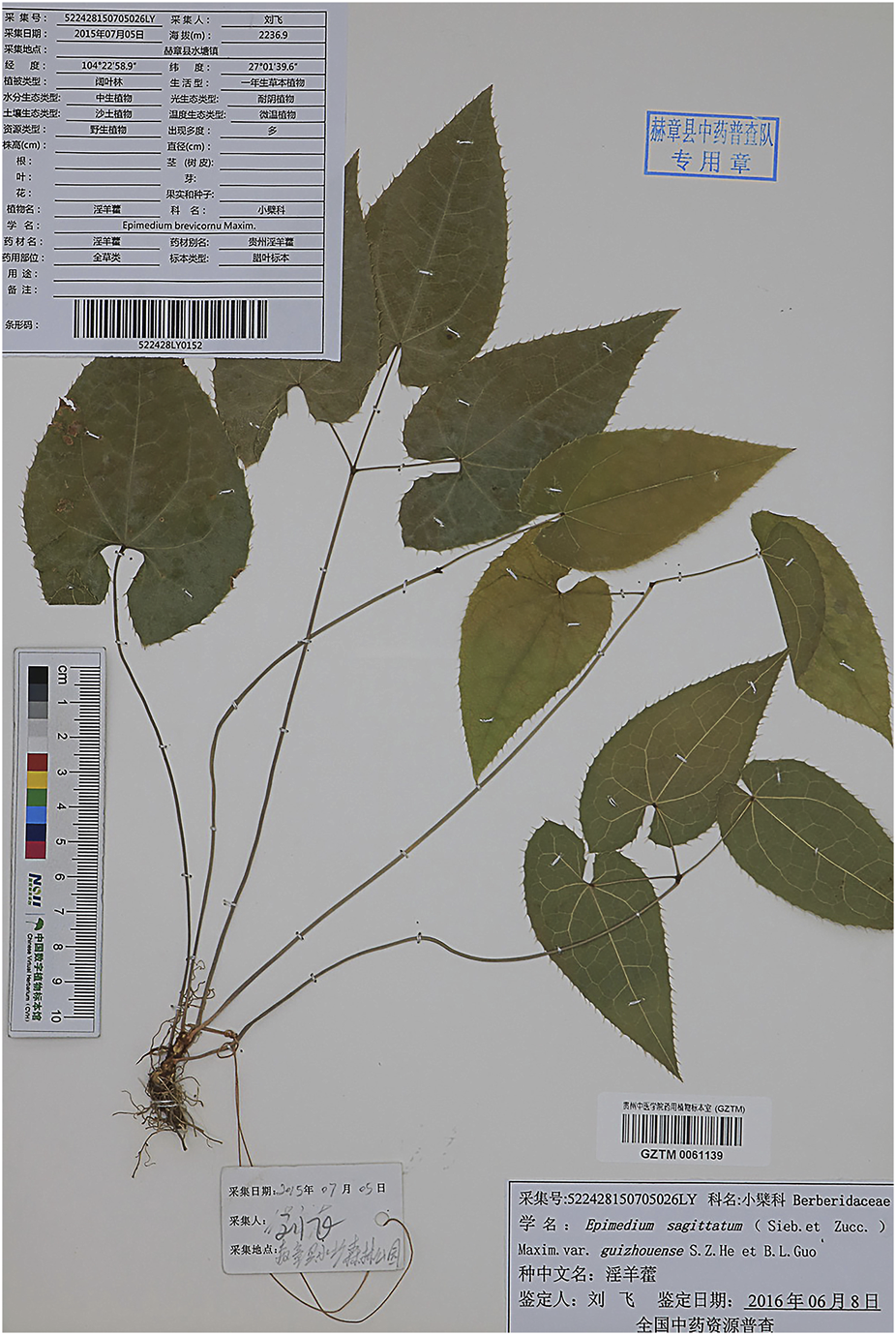

Image of Epimedium brevicornu (Photo source: China Digital Herbarium, CVH).
FIGURE 2
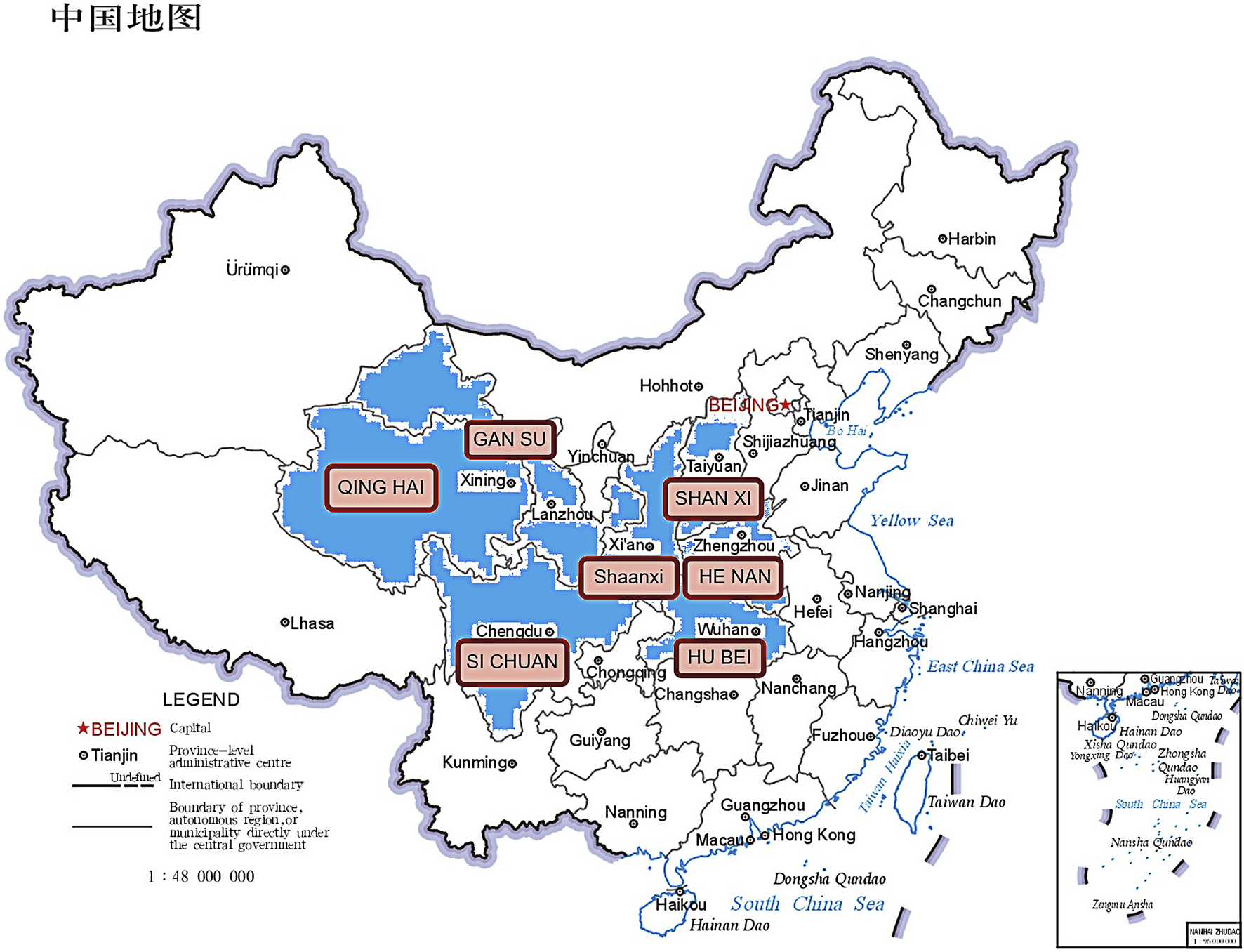
The wild distribution of Epimedium shown in the, ETCM database in China.
Epimedium was first recorded in Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Han Dynasty of China), and has been utilized for treating diseases for approximately 2000 years. It is characterized by its warm nature and bitter taste, and is associated with the liver and kidney meridians. According to the Yet another Traditional Chinese Medicine (YaTCM) database, Epimedium has the effects of reinforcing the kidney yang, strengthening the tendons and bones, and relieving rheumatic conditions, so it is used to treat impotence, seminal emission, weakness of the limbs, rheumatoid arthralgia with numbness and muscle contracture, and climacteric hypertension. In both China and Japan, Epimedium is widely used, either alone or in formulations, for the treatment of orthopedic diseases (Xie et al., 2005; Wang L. et al., 2016).
Recent studies have revealed that the pharmacological effects of Epimedium have transcended its traditional orthopedic applications and regional usage limitations. Its active component icariin has been demonstrated to exert multi-system regulatory effects: In Reproductive System, by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome, icariin significantly ameliorates pyroptosis of Leydig cells and insulin resistance in obese mice, thereby alleviating spermatogenic dysfunction (Wei et al., 2025). In Nervous System, through upregulating the HRD1-mediated ubiquitination pathway, it promotes AβPP degradation, consequently improving cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice (Chen et al., 2025). In Musculoskeletal System, through synergistic downregulation of inflammatory factors IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-9, icariin induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis while suppressing their invasive metastasis, demonstrating remarkable anti-arthritic activity (Ding et al., 2025). These advancements not only expand the clinical potential of Epimedium but also provide valuable insights for global drug development.
2 The main biological components and chemical structures of epimedium
The plant chemistry research of Epimedium genus began in 1935 (Akai, 1935). The researchers have detected more than 260 components from Epimedium, including 141 flavonoids, 31 lignins, and many other types of compounds (Ma et al., 2011). As the main organ of plants, leaves have effects on plant development and biomass, and are the main medicinal site in traditional Epimedium herbs (Yu et al., 2023). Some scholars believe that flavonoids in Epimedium leaves are the most important and significant active ingredients in Epimedium (Wu et al., 2003; Pei and Guo, 2007). According to the Integrative Pharmacology-based Research Platform of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCMIP) database, Epimedium contains 27 main biological components, whose chemical structures and molecular formulas are listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Chemical component | Chemical structure | Molecular formula | Chemical component | Chemical structure | Molecular formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cetylic Acid, Hexadecanoic Acid, Palmitic Acid |

|
C16H32O2 | Anhydroicaritin-3-O-Α-L-Rhamnosyl-7-O-Β-D-Glucopyranoside |
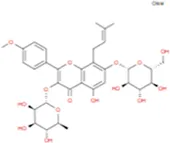
|
C33H40O15 |
| Linolenic Acid |
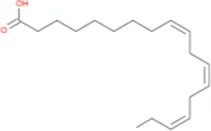
|
C18H30O2 | Baohuoside Ii |
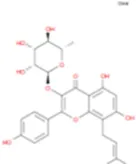
|
C26H28O10 |
| Octadecanoic Acid, Stearic Acid |

|
C18H36O2 | Hyperin, Hyperoside,Hyperoside,Quercetin-3-O-Galactoside |
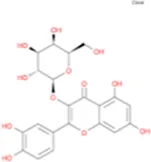
|
C21H20O12 |
| Magnoflorine |
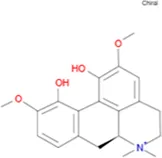
|
C20H24NO4 | Bilobanol |
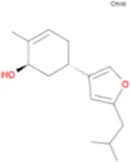
|
C15H22O2 |
| Kaempferitrin |
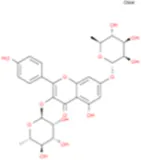
|
C27H30O14 | Breviflavone B |
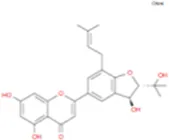
|
C25H26O7 |
| Hentriacontane |

|
C31H64 | Des-O-Methylicariin |
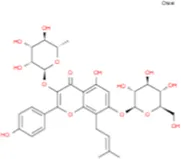
|
C32H38O15 |
| Diphylloside A |
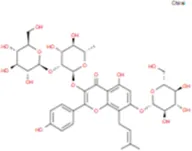
|
C38H48O20 | Neoicariin |
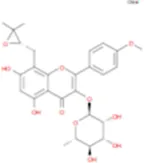
|
C27H30O11 |
| Epimedin A |
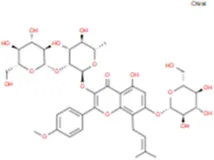
|
C39H50O20 | Wushanicariin |
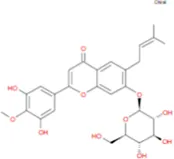
|
C27H30O11 |
| Epimedin B |
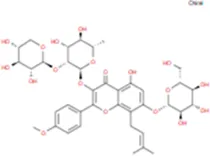
|
C38H48O19 | Yinyanghuo A |
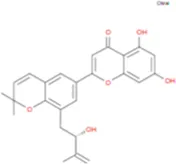
|
C25H24O6 |
| Epimedin C |
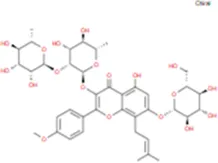
|
C39H50O19 | Yinyanghuo B |
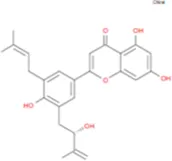
|
C25H26O6 |
| Epimedokoreanoside I |
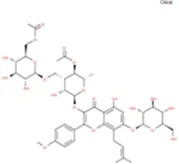
|
C44H56O22 | Yinyanghuo C |
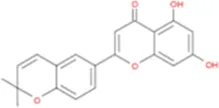
|
C20H16O5 |
| Epimedokoreanoside Ii |
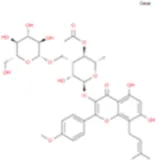
|
C36H44O16 | Yinyanghuo D |
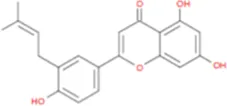
|
C20H18O5 |
| Epimedoside C |
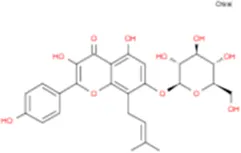
|
C26H28O11 | Yinyanghuo E |
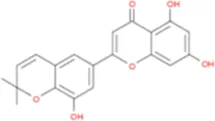
|
C20H16O6 |
| Ikarisoside F |
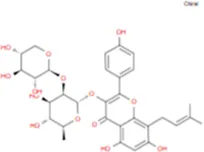
|
C31H36O14 |
Main biological components and chemical structures of Epimedium.
In this study, we first retrieved and extracted the main active components of Epimedium and their potential therapeutic effects on bone-related diseases from the TCMIP database (v2.0). Subsequently, using the disease-target association analysis module built into the database, disease-related keywords were employed to screen potential therapeutic targets associated with these conditions. Through network pharmacology, a comprehensive analysis was conducted to explore the potential pharmacological mechanisms and pathways by which Epimedium regulates bone/muscle metabolism, repair, and related diseases.
3 The role of the main bioactive substances of epimedium in orthopedic diseases
Epimedium encompasses a diverse array of chemical substances, primarily including Fatty Acids, Flavonoid Glycosides, Alkaloids, Terpenoids and their derivatives, Alkanes, and Other Glycosides. These chemical entities exert various biological functions, and the bioactive functions of each category are detailed in Table 2.
TABLE 2
| Category | Representative compounds | Primary functions |
|---|---|---|
| Fatty Acids | Palmitic Acid | Energy storage, cell membrane structure (Zahradka et al., 2017; Jaureguiberry et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2023; Balla et al., 2019) |
| Flavonoid Glycosides | Epimedin A/B/C | Antioxidant, hormone regulation, anti-osteoporosis (Wu et al., 2012; Buranasudja et al., 2022; Yuan et al., 2023; Ammar et al., 2016; Menghini et al., 2016) |
| Alkaloids | Magnoflorine | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotection (Kushida et al., 2021; Qu et al., 2013; Luo et al., 2024; Lee et al., 2019; Geetha and Ramachandran, 2021) |
| Alkanes | Hentriacontane | Plant cuticle protection (Wu et al., 2019) |
| Terpenoids | Bilobanol | Anti-inflammatory or neuroactive (Ge et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2024; Kabir et al., 2021) |
Classification and main functions of chemical substances in Epimedium.
Extensive studies have demonstrated that the characteristic flavonoid glycosides Epimedin A/B/C from Epimedium can be metabolically converted into icariin (also a flavonoid glycoside) both in vivo and in vitro (Su et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2015). Icariin promotes osteogenesis through multiple molecular mechanisms:By activating the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway, it enhances osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, thereby increasing bone density and improving skeletal function (Wei Q. et al., 2016). Meanwhile, it promotes bone formation by stimulating the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway (Liang et al., 2012). Furthermore, existing evidence indicates that icariin can also suppress osteoclast differentiation by inhibiting the RANKL/NF-κB signaling cascade, thereby reducing bone resorption and preventing bone loss (Kim et al., 2018).
Research has found that the use of alkaloid Magnoflorine in Epimedium can significantly reduce joint swelling and bone erosion. This may be related to its ability to inhibit the production of inflammatory factors and reduce oxidative stress (Liu et al., 2020). Moreover, Magnoflorine may also protect the joints and bones by regulating immune responses and inhibiting osteoblast hyperactivation (Maeda et al., 2022). Further research indicates that Magnoflorine likely exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by influencing the nuclear factor kappa B(NF-κB) signaling pathway. NF-κB is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in inflammatory responses, and its activation is closely associated with inflammation and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (Moqbel et al., 2020). By inhibiting the activation of NF - κB, Magnoflorine can reduce the release of inflammatory factors, thereby alleviating joint inflammation and bone loss.
Bilobanol is a natural compound and some scholars have suggested that it may inhibit osteoclast activity by regulating the OPG/RANKL ratio. Hyperactivation of osteoclasts is one of the main causes of bone loss diseases such as osteoporosis. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) and Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) play crucial roles in the formation and activation of osteoclasts. Research has shown that increasing the expression of OPG or reducing the expression of RANKL can effectively inhibit osteoclast differentiation and function, thereby reducing bone resorption (Iolasc et al., 2011; Sun et al., 2016; Shao et al., 2019). Research has also found that in osteoblasts, fatty acid metabolism and storage are essential for the bone formation process. Osteoblasts can release endogenous fatty acids from lipid droplets through lipolysis to support the cellular bioenergy state and bone formation (Nandy et al., 2023).
In summary, the various components contained in Epimedium may exhibit a comprehensive effect of promoting bone formation, inhibiting bone resorption, and providing anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects through multi-target and multi-pathway synergistic actions.
The research group utilized the TCMIP database to screen the identified chemical components in Epimedium and their potential therapeutic effects on orthopedic diseases, further verifying the correlation between Epimedium and orthopedic diseases. Analysis revealed that Epimedium may have therapeutic potential for 11 types of orthopedic conditions, including Osteoarthritis (OA), Osteoporosis, Abnormality of the Musculature, Bone Cyst, Skeletal Muscle Atrophy, Muscle Spasm, Myopathy, Bone Pain, Osteomyelitis, Osteochondrosis, and Limb Muscle Weakness (Table 3).
TABLE 3
Major active components isolated from Epimedium and their potential therapeutic effects on Orthopedic Diseases.
4 Possible therapeutic targets and mechanisms of epimedium in the treatment of orthopedic diseases
This study identified candidate targets of Epimedium active components through TCMIP database analysis based on skeletal system disease screening criteria. Using the “Disease-Target Association Analysis Module” of the database, therapeutic targets related to four pathological conditions “osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, muscle spasms, and myopathy” were screened. The therapeutic targets are shown in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3
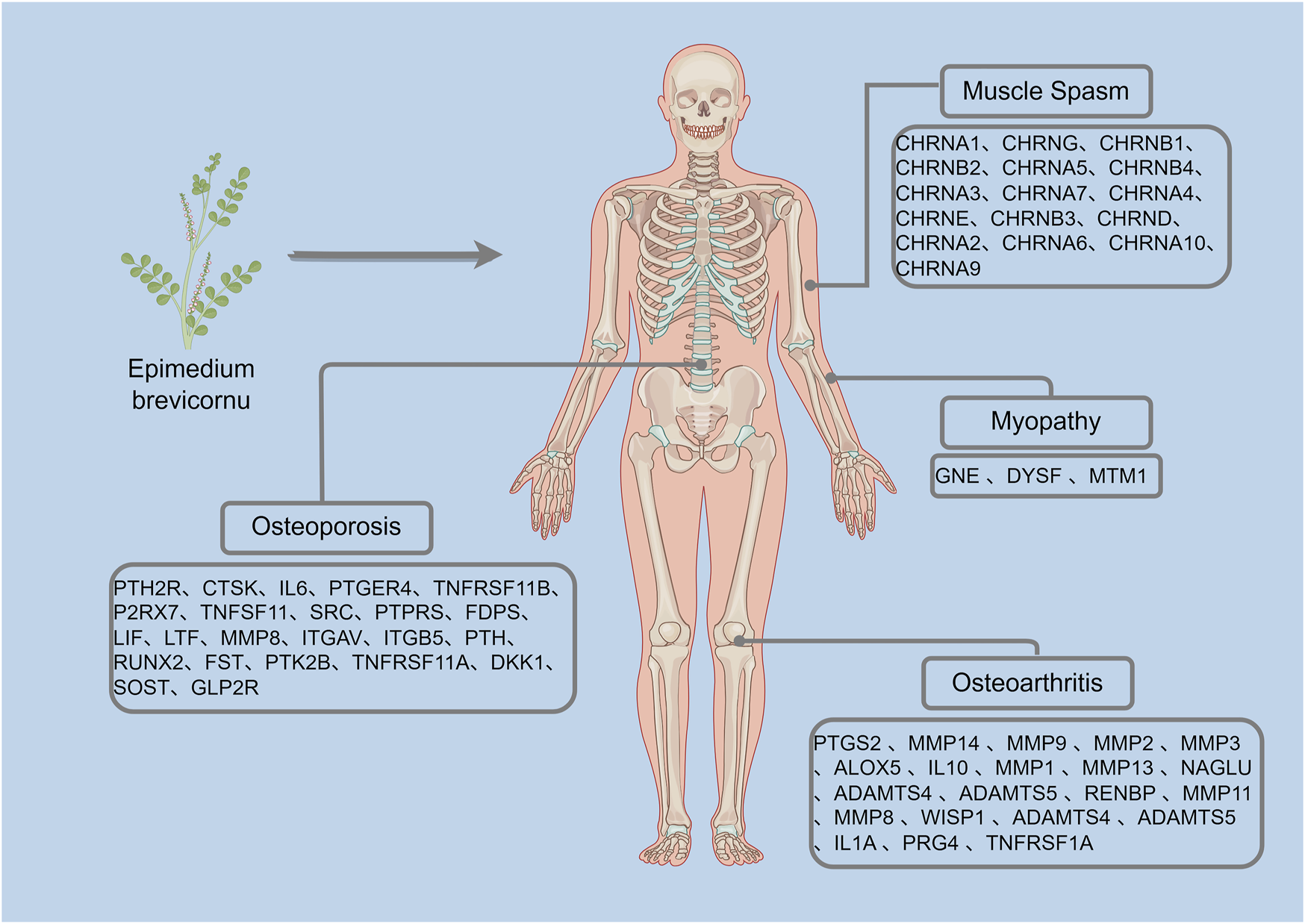
Therapeutic targets for orthopedic diseases shown in the TCMIP database (By Figdraw).
From the model, we observed that except for Myopathy, there is a certain overlap between the therapeutic genes of the other three diseases and the candidate genes of the main active components of Epimedium, as shown in Figure 4. Therefore, we further utilized the Metascape tool to construct a network and perform KEGG enrichment analysis on the candidate target genes of the potentially therapeutic active substances in Epimedium and the therapeutic targets of the four related diseases identified through screening. This aims to analyze the potential therapeutic pathways of the main active components of Epimedium in treating these four types of diseases.
FIGURE 4
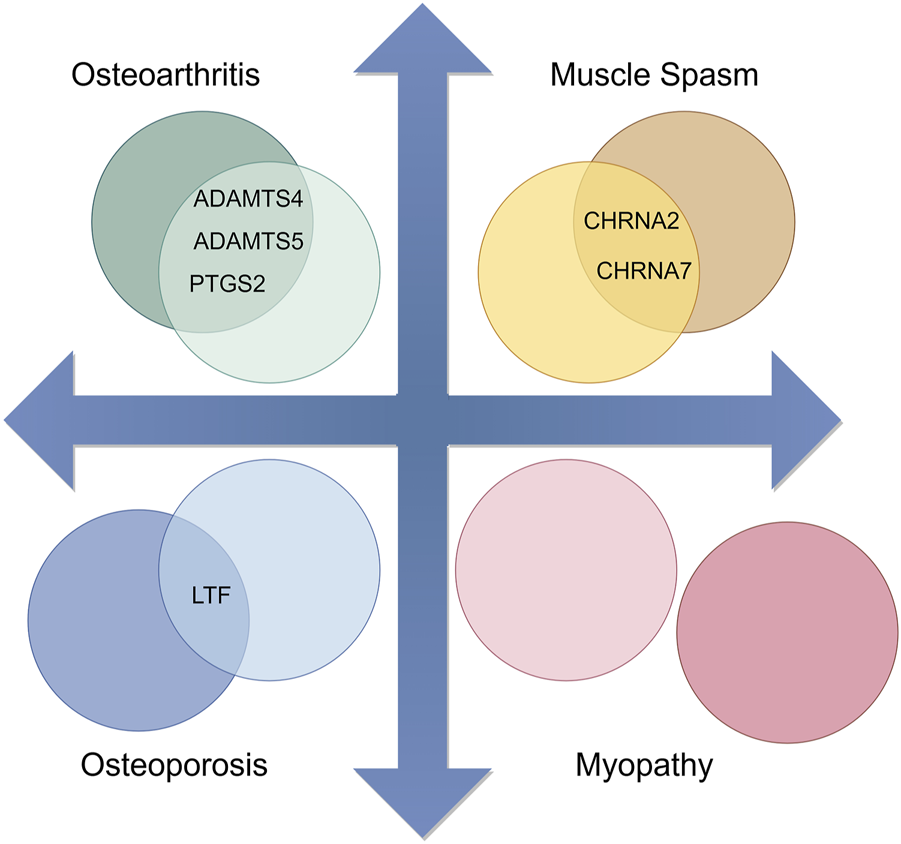
Overlap between Candidate Target Genes of major active components in Epimedium and Therapeutic Genes of Corresponding Diseases (By Figdraw).
4.1 Possible pathway for epimedium in the treatment of osteoarthritis
After performing KEGG enrichment analysis on the genes potentially involved in the treatment of osteoarthritis by the main active components of Epimedium using Metascape, the results are shown in Figure 5.
FIGURE 5
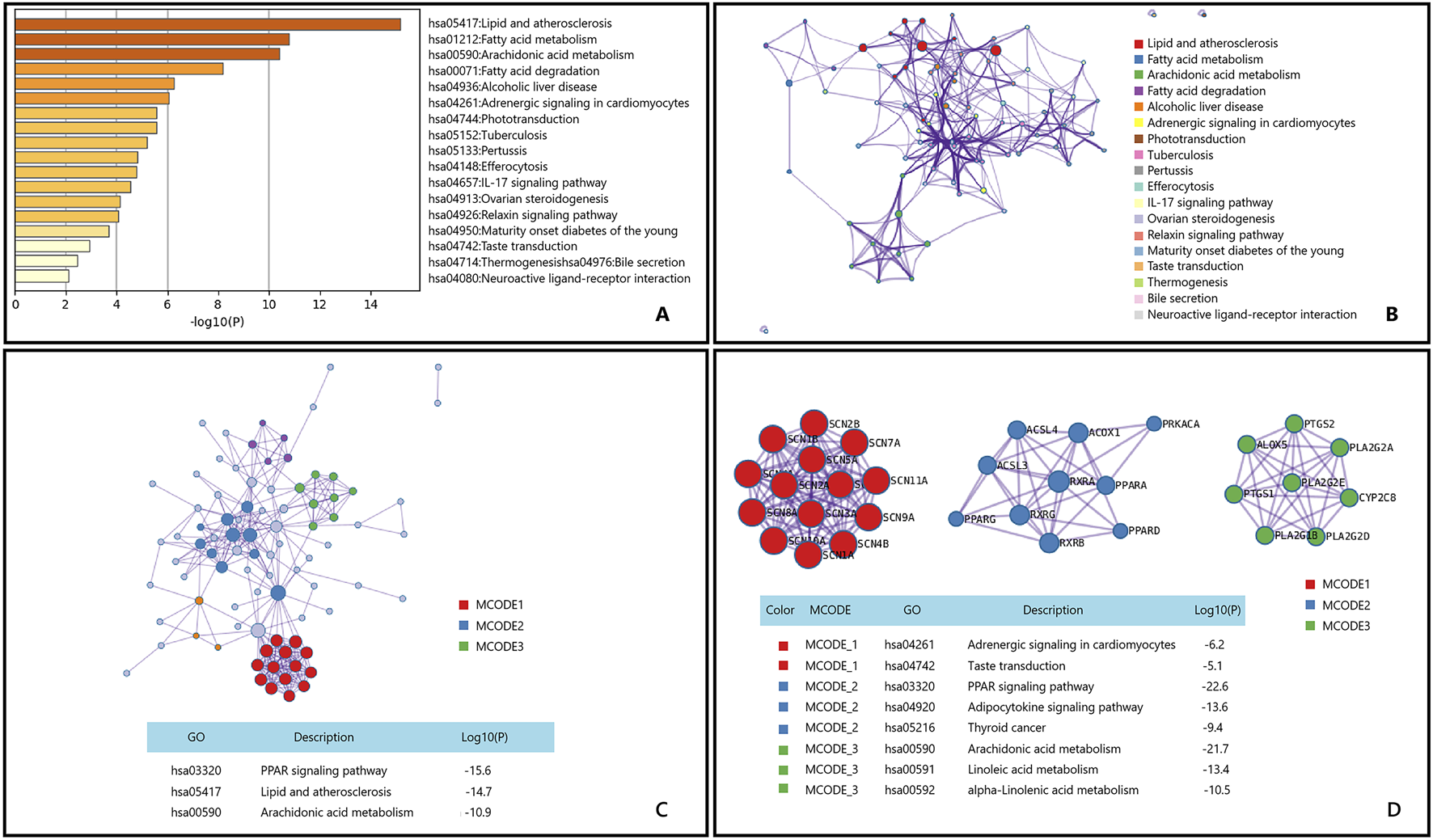
Gene List Analysis Report on the Main active ingredient of Epimedium to treat osteoarthritis (A) Bar graph of enriched terms across input gene lists, colored by p-values. (B) Network of enriched terms:colored by cluster ID, where nodes that share the same cluster ID are typically close to each other. (C, D) Protein-protein interaction network and MCODE componentsidentfedin the genelists. (The thre best-scoring tems by p-value have beenretained as thefunctional description of the corresponding components, shown in the tables undeneath corresponding network plots within Figure).
Osteoarthritis is a heterogeneous disease with an increasing incidence, mainly due to aging and obesity, leading to a significant global disease burden (Kloppenburg et al., 2025; Tang et al., 2025; Gelber, 2024). The Icariin,a role of active substances in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been studied, showing that Icariin can improve hepatic fatty acid oxidation and inhibit lipid accumulation, which is closely related to their regulatory role in lipid metabolism (Hai et al., 2023). Additionally, the mechanism of Icariin in osteoarthritis has been preliminarily explored. Research indicates that Epimedium can alleviate chondrocyte apoptosis and thereby improve osteoarthritis symptoms by activating the SIRT-1-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway (Liu YS. et al., 2024). Although this pathway is mainly associated with antioxidant stress and cytoprotection, it also indirectly participates in the regulation of lipid metabolism.These findings suggest that icariin may exert its therapeutic effects on osteoarthritis through multiple lipid metabolism-related pathways, including the Lipid and atherosclerosis pathway.
The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) signaling pathway, renowned for its role in regulating lipid metabolism and inflammation, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of OA. Active components of Epimedium have demonstrated regulatory effects on human osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes (OA-FLSs) in vitro studies (Pan et al., 2017). Moreover, Epimedium exerts its chondroprotective effects by inhibiting the expression of key enzymes in the MAPK signaling pathway (Zeng et al., 2017). These findings suggest that Epimedium may play a significant role in the treatment of osteoarthritis through the modulation of the PPAR signaling pathway and other related mechanisms. Research indicates that Epimedium can influence arachidonic acid metabolism by regulating the expression of PTGS1 and PTGS2 genes, thereby exerting its therapeutic effects (Liu et al., 2023). This mechanism may represent an important pathway through which Epimedium contributes to the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Based on the comprehensive KEGG enrichment analysis results, Epimedium may potentially treat osteoarthritis through the Lipid and atherosclerosis pathway, PPAR signaling pathway, and Arachidonic acid metabolism pathway.
4.2 Possible pathway for epimedium in the treatment of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a prevalent metabolic bone disorder characterized by reduced bone density and deterioration of bone microarchitecture, leading to increased bone fragility and a higher risk of fractures (Ensrud and Crandall, 2018; Shapses, 2018). With the global trend of population aging, the incidence of osteoporosis is continuously rising, particularly among postmenopausal women (Ott, 2016; Michaëlsson and Aspenberg, 2016; Cheung et al., 2016). We utilized Metascape to perform KEGG enrichment analysis on the potential genes targeted by the main active components of Epimedium for the treatment of osteoporosis, and the results are illustrated in Figure 6.
FIGURE 6
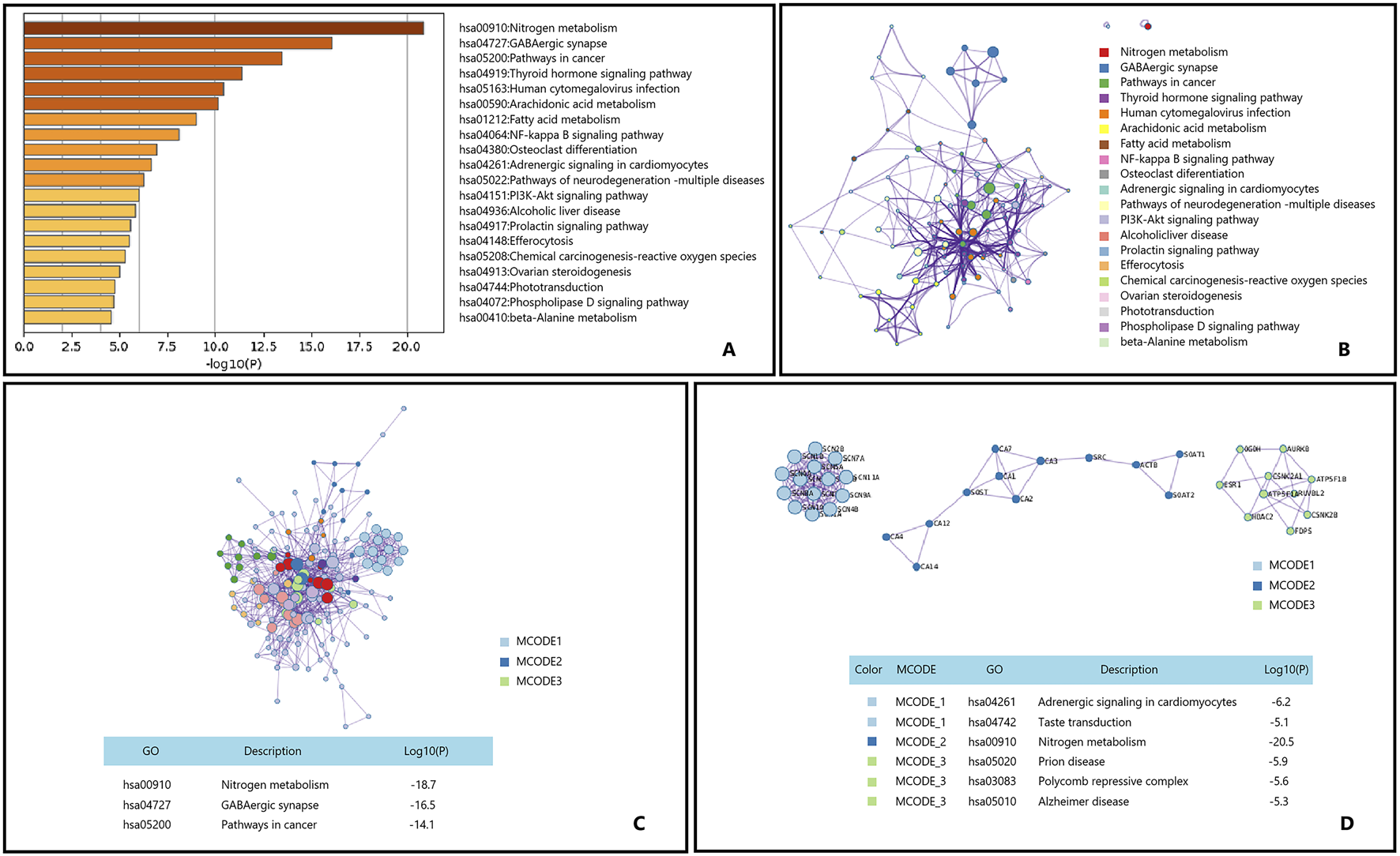
Gene List Analysis Report on the Main active ingredient of Epimedium to treat osteoporosis. (A) Bar graph of enriched terms across input gene lists, colored by p-values. (B) Network of enriched terms:colored by cluster ID, where nodes that share the same cluster ID are typically close to each other. (C,D) Protein-protein interaction network and MCODE componentsidentfedin the genelists. (The thre best-scoring tems by p-value have beenretained as thefunctional description of the corresponding components, shown in the tables undeneath corresponding network plots within Figure).
Epimedium, a traditional Chinese medicine, has long been utilized in the treatment of osteoporosis. Research indicates that extracts from Epimedium can influence the levels of neuropeptides within the brain/spinal cord/bone axis, increasing the expression of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the brain and receptors such as NPY1R in bone (Liu H. et al., 2018). This regulatory effect may have a positive impact on bone metabolism by affecting the nitrogen metabolism pathways. The GABAergic synapse pathway holds potential application value in the treatment of osteoporosis, as the regulation of GABA receptors may affect the proliferation and differentiation of bone cells, thereby exerting a beneficial effect on osteoporosis treatment (Gu et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2022). Although there is no direct evidence that Epimedium can treat osteoporosis through the GABAergic synapse pathway, our enrichment analysis results hint at this possibility. The cancer pathway also exhibits significant potential in the treatment of osteoporosis, with studies suggesting that it shares similar regulatory mechanisms in the treatment of osteoporosis (Gu et al., 2020; Amjadi-Moheb and Akhavan-Niaki, 2019; Meng et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2019). For instance, the main active components of Epimedium leaves have been demonstrated to have a protective effect against osteoporosis by modulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway within the cancer pathway (Hu et al., 2017; Liu and Guo, 2020; Wang F. et al., 2016).
In summary, Epimedium may potentially treat osteoporosis through pathways such as Nitrogen metabolism, GABAergic synapse, and Pathways in cancer.
4.3 Possible pathway of epimedium in treating muscle spasms
Muscle spasms are a common symptom characterized by sudden, involuntary, and painful contraction of muscles. The pathophysiological mechanisms are not fully understood, but several hypotheses attempt to explain its occurrence. One hypothesis suggests that spasms are caused by changes in excitability of motor neurons (central origin), while another hypothesis suggests that they are caused by spontaneous discharges of motor neurons (peripheral origin) (Maughan and Shirreffs, 2019). Through Metascape’s KEGG enrichment analysis of genes associated with muscle spasms, we discovered that Epimedium may exert effects on muscle spasms via three signaling pathways closely related to nervous system function: Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, Serotonergic synapse, and Cholinergic synapse Figure 7.
FIGURE 7
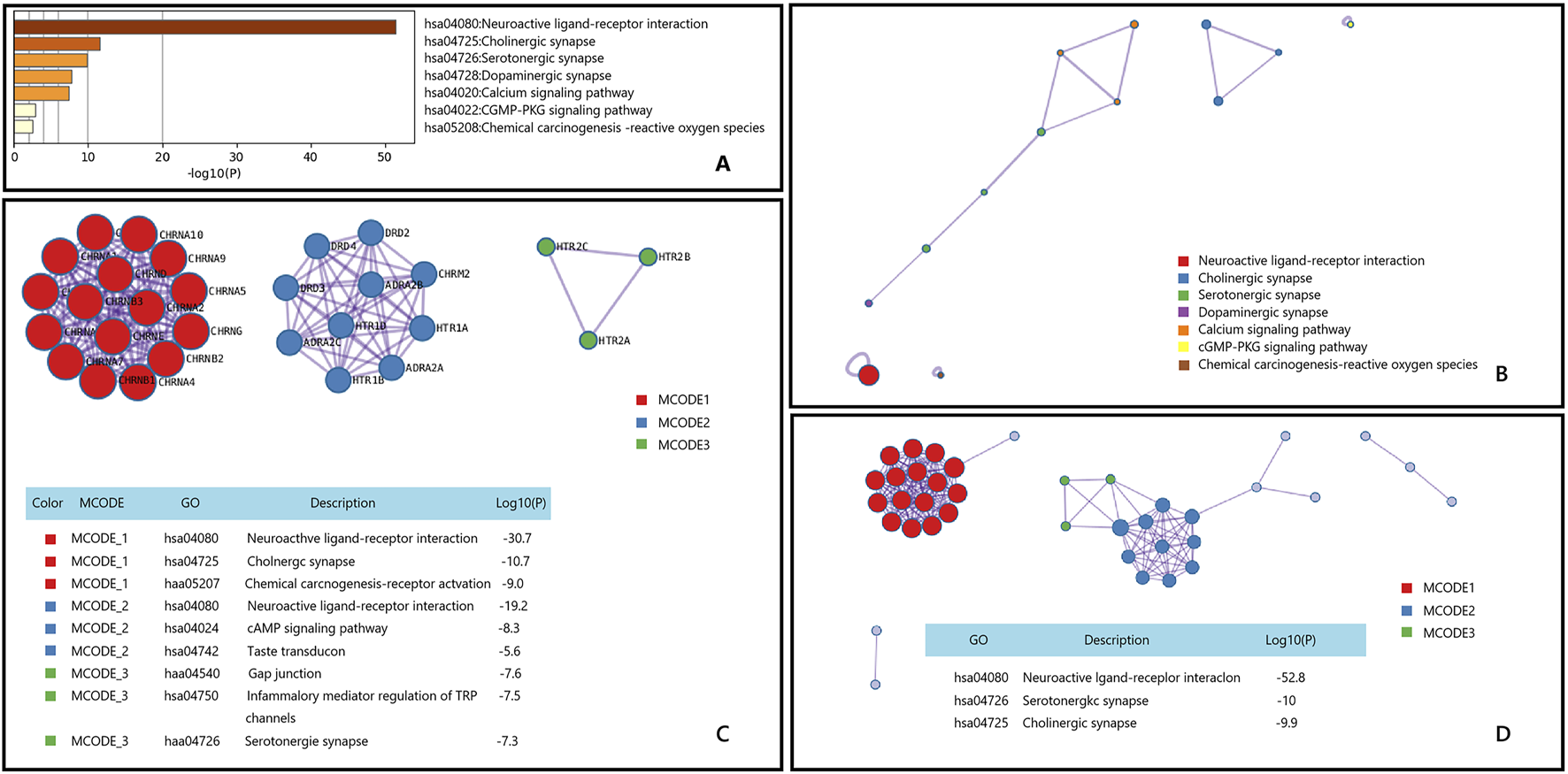
Gene List Analysis Report on the Main active ingredient of Epimedium to treat Muscle spasms. (A) Bar graph of enriched terms across input gene lists, colored by p-values. (B) Network of enriched terms:colored by cluster ID, where nodes that share the same cluster ID are typically close to each other. (C,D) Protein-protein interaction network and MCODE componentsidentfedin the genelists. (The thre best-scoring tems by p-value have beenretained as thefunctional description of the corresponding components, shown in the tables undeneath corresponding network plots within Figure).
Current research suggests that firstly, the active ingredients in Epimedium may exert their effects by affecting the levels of neurotransmitters in the central nervous system (Li et al., 2011). Secondly, Epimedium may exert its therapeutic effect by interacting with specific receptors (Wang et al., 2022). Additionally, Epimedium may also assist in alleviating muscle spasm through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions (Bäumer et al., 2014). Therefore, we posit that the active components in Epimedium may alleviate muscle spasms by modulating the release of neurotransmitters and the activation of receptors, which aligns with the results of our enrichment analysis.
4.3.1 Possible pathway for epimedium in treating myopathy
Myopathy refers to a group of diseases characterized primarily by muscle weakness due to dysfunction of muscle fibers. These conditions can be broadly categorized into several types, including congenital myopathies, inflammatory myopathies,and metabolic myopathies (Jungbluth et al., 2018; Maani et al., 2021; Ahmed et al., 2018). Epimedium and its active ingredients show significant therapeutic potential in muscle and nerve related diseases (Qian and Ke, 2020). Although there is no evidence that Epimedium can treat myopathies through Nitrogen metabolism and GABAergic synapse pathways, our analysis results may provide new perspectives on the application of Epimedium in the treatment of myopathy Figure 8.
FIGURE 8
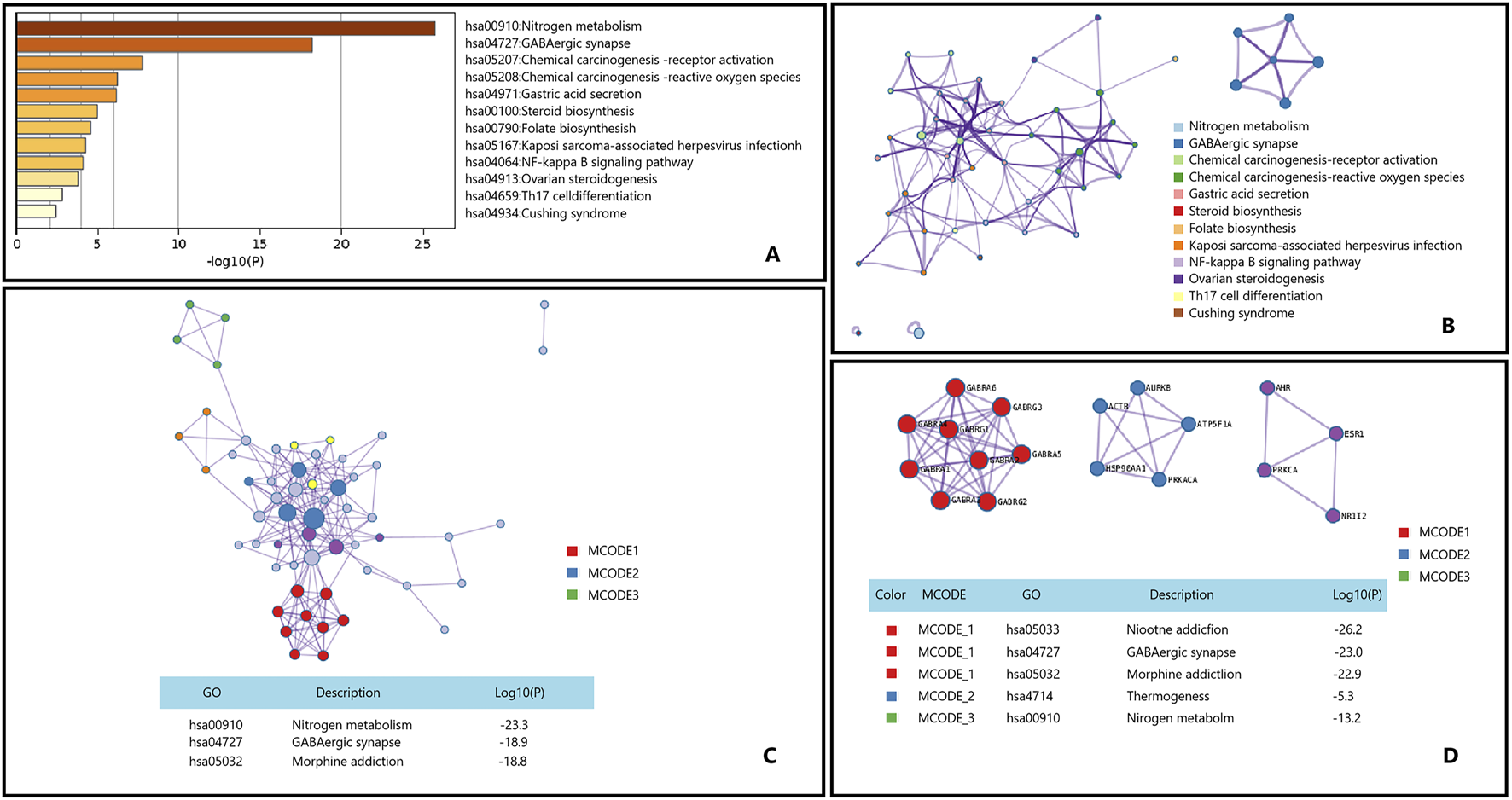
Gene List Analysis Report on the Main active ingredient of Epimedium to treat myopathy. (A) Bar graph of enriched terms across input gene lists, colored by p-values. (B) Network of enriched terms:colored by cluster ID, where nodes that share the same cluster ID are typically close to each other. (C,D) Protein-protein interaction network and MCODE componentsidentfedin the genelists. (The thre best-scoring tems by p-value have beenretained as thefunctional description of the corresponding components, shown in the tables undeneath corresponding network plots within Figure).
5 Perspectives
Epimedium has long been widely used in traditional medicine, particularly in the treatment of orthopedic diseases, has demonstrated experimentally confirmed benefits for bone health through its bioactive components (Indran et al., 2016). However, several pharmacological limitations and safety concerns regarding its application warrant attention. Toxicological studies indicate that although aqueous Epimedium extracts exhibit low acute and chronic toxicity, they may induce hepatotoxicity in murine models (Song et al., 2024). Additionally, the relatively low bioactivity of icaritin (Gao and Zhang, 2022) significantly restricts its clinical translation potential. Future research should focus on systematic identification of active constituents, in-depth elucidation of pharmacological mechanisms, and optimization of drug delivery systems to enhance therapeutic efficacy while ensuring safety.
In this study,By analyzing the existing data in the TCMIP database, we found that among the 27 main active ingredients of Epimedium, 8 important ingredients have therapeutic effects on 11 types of Skeletal/Muscular related diseases.These diseases mainly include joint disorders (El-Shitany and Eid, 2019; Zhao et al., 2018), skeletal diseases (Liu et al., 2014; Wei CC. et al., 2016), muscle diseases (Lin et al., 2021), and pain related diseases (Zeng et al., 2017; Li et al., 2021), which almost comprehensively cover the spectrum of diseases related to bones, joints, muscles, and their associated tissues in terms of pathology.
Through the “Disease-Target Association Analysis Module,” we identified that Osteoarthritis, Osteoporosis, Muscle Spasm, and Myopathy have relatively clear therapeutic targets. Therefore, we conducted an enrichment analysis on these four types of diseases in conjunction with the candidate genes of Epimedium’s active components, predicting the possible pathways through which Epimedium may treat these diseases Table 4.
TABLE 4
| Disease | Potential Mechanistic pathways | Hits |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | Lipid and atherosclerosis | CALM1|CYP2C8|MMP1|MMP3|MMP9|PPARG|PPP3CA|PPP3R1|RXRA|RXRB|RXRG|TLR4|TNFRSF1A|VLDLR|LY96 |
| PPAR signaling pathway | ACOX1|ACSL3|ACSL4|MMP1|PPARA|PPARD|PPARG|RXRA|RXRB|RXRG|FADS2 | |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | ALOX5|CYP2C8|PLA2G1B|PLA2G2A|PTGS1|PTGS2|PLA2G2D|PLA2G2E | |
| Osteoporosis | Nitrogen metabolism | CA1|CA2|CA3|CA4|CA5A|CA6|CA7|CA9|CA12|CA5B|CA14 |
| GABAergic synapse | ABAT|GABRA1|GABRA2|GABRA3|GABRA4|GABRA5|GABRA6|GABRG1|GABRG2|GABRG3|PRKACA|PRKCA|PRKCB|SRC | |
| Pathways in cancer | ABL1|AR|CALM1|CDK6|ESR1|ESR2|HDAC2|HSP90AA1|IL6|ITGAV|JAK1|PIM1|PPARD|PPARG|PRKACA|PRKCA|PRKCB|PTGER4|PTGS2|RXRA|RXRB|RXRG|NCOA1 | |
| Muscle Spasm | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ADRA2A|ADRA2B|ADRA2C|CHRM2|CHRNA1|CHRNA2|CHRNA3|CHRNA4|CHRNA5|CHRNA7|CHRNB1|CHRNB2|CHRNB3|CHRNB4|CHRND|CHRNE|CHRNG|DRD1|DRD2|DRD3|DRD4|DRD5|HTR1A|HTR1B|HTR1D|HTR2A|HTR2B|HTR2C|CHRNA6|CHRNA9|CHRNA10 |
| Serotonergic synapse | HTR1A|HTR1B|HTR1D|HTR2A|HTR2B|HTR2C|HTR3A | |
| Cholinergic synapse | ACHE|CHRM2|CHRNA3|CHRNA4|CHRNA7|CHRNB2|CHRNB4|CHRNA6 | |
| Myopathy | Nitrogen metabolism | CA1|CA2|CA3|CA4|CA5A|CA6|CA7|CA9|CA12|CA5B|CA14 |
| GABAergic synapse | GABRA1|GABRA2|GABRA3|GABRA4|GABRA5|GABRA6|GABRG1|GABRG2|GABRG3|PRKACA|PRKCA|PRKCB |
Possible pathways of the main active ingredients of Epimedium in the treatment of orthopedic diseases.
The pathological mechanism of osteoarthritis are closely related to lipid metabolism, inflammatory responses and oxidative stress (Herrero-Beaumont et al., 2019; Tudorachi et al., 2021; Marchev et al., 2017; Mocanu et al., 2024; Hu et al., 2024), which may serve as potential targets for Epimedium in treating osteoarthritis. Involving an imbalance in bone metabolism, dysregulation of neuroendocrine functions,and potential cancer-related mechanisms (Liu C. et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2022; Sharma et al., 2021), have been extensively studied in the context of Epimedium’s treatment of osteoporosis. In particular, the therapeutic effects of Epimedium on osteoporosis through cancer pathways such as the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway (Cao et al., 2017) and the NF-κBPathway (Yang et al., 2023) have been deeply investigated. The mechanisms underlying the treatment of muscle spasms may be related to abnormal signal transduction at the neuromuscular junction, involving the regulation of various neurotransmitter systems (Hezel et al., 2010; An et al., 2010; Colombo and Francolini, 2019). The pathological mechanisms of myopathy may be associated with abnormal protein metabolism and dysregulated neuromuscular signaling (Luzzi et al., 2023; Robb et al., 2011; Ignatieva et al., 2021), which could provide clues for researching the diagnosis and treatment of diseases with Epimedium.
In summary, Epimedium may demonstrate its potential therapeutic value in various diseases, including osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, muscle spasms, and myopathy by regulating key pathways such as lipid metabolism, inflammatory response, oxidative stress, bone metabolism balance, and neuromuscular signaling. These studies not only provide a molecular mechanism explanation for the pharmacological effects of Epimedium, but also lay a theoretical foundation for further development of precision treatment plans based on Epimedium. Although current research findings are primarily derived from bioinformatics analysis and preclinical experimental data, these discoveries offer a systematic theoretical framework for elucidating the pharmacological mechanisms of Epimedium and establish a critical foundation for subsequent in-depth molecular studies (such as precise modulation of key targets) and clinical translation (such as optimization of personalized dosing regimens). Future research should prioritize enhancing in vitro and in vivo experimental validation of Epimedium’s efficacy in treating osteoporosis, while further exploring the mechanisms of action of its active components within specific pathological microenvironments, aiming to achieve a transformative leap from traditional applications to evidence-based medicine.
Statements
Author contributions
DT: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. LC: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. ZJ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XY: Writing – review and editing, Supervision. MM: Writing – review and editing, Validation. AY: Writing – review and editing, Resources. JX: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by University-level Scientific Research Project of Shaoxing University of Arts and Sciences (2023LG016); 2024 Education and Teaching Reform Research Project of Shaoxing University of Arts and Sciences. Zhejiang Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Program (grant no. 2023ZL056), and Zhejiang medicine and health science and technology project (grant no. 2024KY1213 and 2024XY064).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the great help support from the Medical Research Center, Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University. Figures in our manuscript was created using Figdraw online tools (https://www.figdraw.com/). We gratefully acknowledge China Virtual Herbarium (CVH, https://www.cvh.ac.cn/) for providing the botanical images used in this study. We would like to express our gratitude for these invaluable resources.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
Yin Yang Huo, Epimedium brevicornu; ETCM, The Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine; YaTCM, Yet another Traditional Chinese Medicine; TCMIP, Integrative Pharmacology-based Research Platform of Traditional Chinese Medicine; BMP, Bone morphogenetic protein; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa B; RA, Rheumatoid arthritis; OPG, Osteoprotegerin; RANKL, Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand; OA, Osteoarthritis; NAFLD, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; PPAR, Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor; OA-FLSs, Osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes; NPY, Neuropeptide Y.
References
1
Ahmed S. T. Craven L. Russell O. M. Turnbull D. M. Vincent A. E. (2018). Diagnosis and treatment of mitochondrial myopathies. Neurotherapeutics15 (4), 943–953. 10.1007/s13311-018-00674-4
2
Akai S. (1935). Untersuchungen ueber die Bestandteile von Epimedium-Arten. I. Mitt: ueber die chemische Konstitution eines neuen Flavongly-kosides von Epimedium macranthum Morr et Decne (I.Abteilung). 1. J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn.55, 537–599. 10.1248/yakushi1881.55.5_537
3
Alrumaihi F. Almatroodi S. A. Alharbi H. O. A. Alwanian W. M. Alharbi F. A. Almatroudi A. et al (2024). Pharmacological potential of kaempferol, a flavonoid in the management of pathogenesis via modulation of inflammation and other biological activities. Molecules29 (9), 2007. 10.3390/molecules29092007
4
Amjadi-Moheb F. Akhavan-Niaki H. (2019). Wnt signaling pathway in osteoporosis: epigenetic regulation, interaction with other signaling pathways, and therapeutic promises. J. Cell Physiol.234 (9), 14641–14650. 10.1002/jcp.28207
5
Ammar N. M. El-Hawary S. S. Mohamed D. A. El-Halawany A. M. El-Anssary A. A. El-Kassem L. T. et al (2016). Estrogenic activity including bone enhancement and effect on lipid profile of Luteolin-7-O-glucoside isolated from trifolium alexandrinum L. in ovariectomized rats. Phytother. Res.30 (5), 768–773. 10.1002/ptr.5564
6
An M. C. Lin W. Yang J. Dominguez B. Padgett D. Sugiura Y. et al (2010). Acetylcholine negatively regulates development of the neuromuscular junction through distinct cellular mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.107 (23), 10702–10707. 10.1073/pnas.1004956107
7
Anand R. Kaithwas G. (2014). Anti-inflammatory potential of alpha-linolenic acid mediated through selective COX inhibition: computational and experimental data. Inflammation37 (4), 1297–1306. 10.1007/s10753-014-9857-6
8
Balla T. Kim Y. J. Alvarez-Prats A. Pemberton J. (2019). Lipid dynamics at contact sites between the endoplasmic reticulum and other organelles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol.35, 85–109. 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100818-125251
9
Bastiaansen-Jenniskens Y. M. Siawash M. van de Lest C. H. Verhaar J. A. Kloppenburg M. Zuurmond A. M. et al (2013). Monounsaturated and saturated, but not n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease cartilage destruction under inflammatory conditions: a preliminary study. Cartilage4 (4), 321–328. 10.1177/1947603513494401
10
Bäumer D. Butterworth R. Menke R. A. Talbot K. Hofer M. Turner M. R. (2014). Progressive hemiparesis (mills syndrome) with aphasia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology82 (5), 457–458. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000090
11
Buranasudja V. Muangnoi C. Sanookpan K. Halim H. Sritularak B. Rojsitthisak P. (2022). Eriodictyol attenuates H2O2-Induced oxidative damage in human dermal fibroblasts through enhanced capacity of antioxidant machinery. Nutrients14 (12), 2553. 10.3390/nu14122553
12
Cao H. Zhang Y. Qian W. Guo X. P. Sun C. Zhang L. et al (2017). Effect of icariin on fracture healing in an ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis. Exp. Ther. Med.13 (5), 2399–2404. 10.3892/etm.2017.4233
13
Cazarolli L. H. Pereira D. F. Kappel V. D. Folador P. Figueiredo Mdos S. Pizzolatti M. G. et al (2013). Insulin signaling: a potential signaling pathway for the stimulatory effect of kaempferitrin on glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol.712 (1-3), 1–7. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.02.029
14
Chen C. Huang L. Chen Y. Jin J. Xu Z. Liu F. et al (2024). Hydrolyzed egg yolk peptide prevented osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Sci. Rep.14 (1), 10227. 10.1038/s41598-024-60514-8
15
Chen L. Ma R. Luo P. Shi D. Shi X. Nian H. et al (2022). Effects of total flavonoids of epimedium on bone marrow adipose tissue in ovariectomized rats. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne)13, 900816. 10.3389/fendo.2022.900816
16
Chen X. Lin C. He C. Li K. Gao J. Gong Q. et al (2025). Icariin improves learning and memory function by enhancing HRD1-mediated ubiquitination of amyloid precursor protein in APP/PS1 mice. J. Alzheimers Dis.103 (2), 616–626. 10.1177/13872877241303949
17
Chen X. J. Tang Z. H. Li X. W. Xie C. X. Lu J. J. Wang Y. T. (2015). Chemical constituents, quality control, and bioactivity of epimedii folium (yinyanghuo). Am. J. Chin. Med.43 (5), 783–834. 10.1142/S0192415X15500494
18
Cheung A. M. Papaioannou A. Morin S. (2016). Postmenopausal osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med.374 (21), 2096. 10.1056/NEJMc160299
19
Cho S. Hong R. Yim P. Yeom M. Lee B. Yang W. M. et al (2018). An herbal formula consisting of Schisandra chinensis (turcz.) baill, Lycium chinense mill and Eucommia ulmoides oliv alleviates disuse muscle atrophy in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol.213, 328–339. 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.008
20
Colombo M. N. Francolini M. (2019). Glutamate at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction: from modulation to neurotransmission. Cells8 (9), 996. 10.3390/cells8090996
21
Dai Y. Zhang L. Yan Z. Li Z. Fu M. Xue C. et al (2021). A low proportion n-6/n-3 PUFA diet supplemented with antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) oil protects against osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation in ovariectomized mice. Food Funct.12 (15), 6766–6779. 10.1039/d1fo00056j
22
de Abreu A. M. Copetti C. L. K. Hauschild D. B. Di Pietro P. F. Wazlawik E. (2022). Effects of supplementation with vegetable sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) on inflammatory markers and lipid profile in individuals with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr.41 (6), 1434–1444. 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.02.013
23
Ding C. Liu Q. You X. Yuan J. Xia J. Tan Y. et al (2025). Investigating the molecular mechanism of epimedium herb in treating rheumatoid arthritis through network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation. Mol. Divers. 10.1007/s11030-024-11019-z
24
El-Shitany N. A. Eid B. G. (2019). Icariin modulates carrageenan-induced acute inflammation through HO-1/Nrf2 and NF-kB signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother.120, 109567. 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109567
25
Ensrud K. E. Crandall C. J. (2018). Osteoporosis. Ann. Intern Med.168 (4), 306–307. 10.7326/L17-0587
26
Fillmore N. Huqi A. Jaswal J. S. Mori J. Paulin R. Haromy A. et al (2015). Effect of fatty acids on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell energy metabolism and survival. PLoS One10 (3), e0120257. 10.1371/journal.pone.0120257
27
Gao L. Zhang S. Q. (2022). Antiosteoporosis effects, pharmacokinetics, and drug delivery systems of icaritin: advances and prospects. Pharm. (Basel).15 (4), 397. 10.3390/ph15040397
28
Gao Y. H. Zhao C. W. Liu B. Dong N. Ding L. Li Y. R. et al (2020). An update on the association between metabolic syndrome and osteoarthritis and on the potential role of leptin in osteoarthritis. Cytokine129, 155043. 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155043
29
Ge J. Liu Z. Zhong Z. Wang L. Zhuo X. Li J. et al (2022). Natural terpenoids with anti-inflammatory activities: potential leads for anti-inflammatory drug discovery. Bioorg Chem.124, 105817. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105817
30
Geetha R. G. Ramachandran S. (2021). Recent advances in the anti-inflammatory activity of plant-derived alkaloid rhynchophylline in neurological and cardiovascular diseases. Pharmaceutics13 (8), 1170. 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081170
31
Gelber A. C. (2024). Knee osteoarthritis. Ann. Intern Med.177 (9), ITC129–ITC144. 10.7326/ANNALS-24-01249
32
Gu Z. Xie D. Huang C. Ding R. Zhang R. Li Q. et al (2020). MicroRNA-497 elevation or LRG1 knockdown promotes osteoblast proliferation and collagen synthesis in osteoporosis via TGF-β1/Smads signalling pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med.24 (21), 12619–12632. 10.1111/jcmm.15826
33
Hai Y. Zuo L. Wang M. Zhang R. Wang M. Ren L. et al (2023). Icariin alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in polycystic ovary syndrome by improving liver fatty acid oxidation and inhibiting lipid accumulation. Molecules28 (2), 517. 10.3390/molecules28020517
34
Harasymowicz N. S. Dicks A. Wu C. L. Guilak F. (2019). Physiologic and pathologic effects of dietary free fatty acids on cells of the joint. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.1440 (1), 36–53. 10.1111/nyas.13999
35
Herrero-Beaumont G. Pérez-Baos S. Sánchez-Pernaute O. Roman-Blas J. A. Lamuedra A. Largo R. (2019). Targeting chronic innate inflammatory pathways, the main road to prevention of osteoarthritis progression. Biochem. Pharmacol.165, 24–32. 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.02.030
36
Hezel M. de Groat W. C. Galbiati F. (2010). Caveolin-3 promotes nicotinic acetylcholine receptor clustering and regulates neuromuscular junction activity. Mol. Biol. Cell21 (2), 302–310. 10.1091/mbc.e09-05-0381
37
Hu J. Mao Z. He S. Zhan Y. Ning R. Liu W. et al (2017). Icariin protects against glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis, increases the expression of the bone enhancer DEC1 and modulates the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin integrated signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol.136, 109–121. 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.010
38
Hu K. Shu Y. Feng Z. Zou M. Luo J. Wei Z. et al (2024). Role of lipid metabolism gene KLF4 in osteoarthritis. Clin. Rheumatol.43 (1), 453–464. 10.1007/s10067-023-06742-1
39
Huang J. Zhou L. Chen J. Chen T. Lei B. Zheng N. et al (2021). Hyperoside attenuate inflammation in HT22 cells via upregulating SIRT1 to activities Wnt/β-Catenin and sonic hedgehog pathways. Neural Plast.2021, 8706400. 10.1155/2021/8706400
40
Ignatieva E. Smolina N. Kostareva A. Dmitrieva R. (2021). Skeletal muscle mitochondria dysfunction in genetic neuromuscular disorders with cardiac phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22 (14), 7349. 10.3390/ijms22147349
41
Indran I. R. Liang R. L. Min T. E. Yong E. L. (2016). Preclinical studies and clinical evaluation of compounds from the genus epimedium for osteoporosis and bone health. Pharmacol. Ther.162, 188–205. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.01.015
42
Ioan-Facsinay A. Kloppenburg M. (2018). Bioactive lipids in osteoarthritis: risk or benefit?Curr. Opin. Rheumatol.30 (1), 108–113. 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000463
43
Iolascon G. Resmini G. Tarantino U. (2011). Inhibition of RANK ligand: a new option for preventing fragility fractures. Aging Clin. Exp. Res.23 (2 Suppl. l), 28–29.
44
Jaureguiberry M. S. Tricerri M. A. Sanchez S. A. Finarelli G. S. Montanaro M. A. Prieto E. D. et al (2014). Role of plasma membrane lipid composition on cellular homeostasis: learning from cell line models expressing fatty acid desaturases. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai)46 (4), 273–282. 10.1093/abbs/gmt155
45
Jungbluth H. Treves S. Zorzato F. Sarkozy A. Ochala J. Sewry C. et al (2018). Congenital myopathies: disorders of excitation-contraction coupling and muscle contraction. Nat. Rev. Neurol.14 (3), 151–167. 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.191
46
Kabir M. T. Uddin M. S. Zaman S. Rahman M. S. Behl T. Ahmad A. et al (2021). Exploring the anti-neuroinflammatory potential of steroid and terpenoid-derived phytochemicals to combat alzheimer's disease. Curr. Pharm. Des.27 (22), 2635–2647. 10.2174/1381612826666210101152352
47
Kim B. Lee K. Y. Park B. (2018). Icariin abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the RANKL-Mediated TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway in Raw264.7 cells. Phytomedicine51, 181–190. 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.06.020
48
Kloppenburg M. Namane M. Cicuttini F. (2025). Osteoarthr. Lancet405 (10472), 71–85. 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)02322-5
49
Kushida H. Matsumoto T. Ikarashi Y. (2021). Properties, pharmacology, and pharmacokinetics of active indole and oxindole alkaloids in uncaria hook. Front. Pharmacol.12, 688670. 10.3389/fphar.2021.688670
50
Laurentius T. Kob R. Fellner C. Nourbakhsh M. Bertsch T. Sieber C. C. et al (2019). Long-chain fatty acids and inflammatory markers coaccumulate in the skeletal muscle of sarcopenic old rats. Dis. Markers2019, 9140789. 10.1155/2019/9140789
51
Lee Y. Y. Park J. S. Leem Y. H. Park J. E. Kim D. Y. Choi Y. H. et al (2019). The phosphodiesterase 10 inhibitor papaverine exerts anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects via the PKA signaling pathway in neuroinflammation and parkinson's disease mouse models. J. Neuroinflammation16 (1), 246. 10.1186/s12974-019-1649-3
52
Li C. R. Jiang M. J. Shen D. B. Xu H. X. Wang H. S. Yao X. et al (2011). Two novel mutations of the nicastrin gene in Chinese patients with acne inversa. Br. J. Dermatol165 (2), 415–418. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10372.x
53
Li J. Wang X. Wang Y. Lu C. Zheng D. Zhang J. (2019a). Isoquercitrin, a flavonoid glucoside, exerts a positive effect on osteogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Chem. Biol. Interact.297, 85–94. 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.10.018
54
Li J. Yang J. Xian Q. Su H. Ni Y. Wang L. (2024). Kaempferitrin attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal inflammation and fibrosis in mice by inhibiting NOX4-mediated tubular ferroptosis. Phytother. Res.38 (6), 2656–2668. 10.1002/ptr.8191
55
Li X. Xu Y. Li H. Jia L. Wang J. Liang S. et al (2021). Verification of pain-related neuromodulation mechanisms of icariin in knee osteoarthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother.144, 112259. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112259
56
Li X. L. Xu F. Lin F. H. Ai L. Z. Zhao Y. J. Bi X. L. et al (2020). A Naringin- and icariin-contained herbal formula, gushukang, ameliorated aged osteoporosis of aged mice with high calcium intake. Am. J. Chin. Med.48 (7), 1671–1691. 10.1142/S0192415X20500834
57
Li Y. Li J. Liu X. Zhang J. Mei X. Zheng R. et al (2019b). Antidiarrheal activity of methanol extract of Sophora tonkinensis in mice and spasmolytic effect on smooth muscle contraction of isolated jejunum in rabbits. Pharm. Biol.57 (1), 477–484. 10.1080/13880209.2019.1645701
58
Liang W. Lin M. Li X. Li C. Gao B. Gan H. et al (2012). Icariin promotes bone formation via the BMP-2/Smad4 signal transduction pathway in the hFOB 1.19 human osteoblastic cell line. Int. J. Mol. Med.30 (4), 889–895. 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1079
59
Lim J. M. Lee Y. J. Cho H. R. Park D. C. Jung G. W. Ku S. K. et al (2018). Extracellular polysaccharides purified from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001 (polycan) inhibit dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med.41 (3), 1245–1264. 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3251
60
Lin Y. A. Li Y. R. Chang Y. C. Hsu M. C. Chen S. T. (2021). Activation of IGF-1 pathway and suppression of atrophy related genes are involved in epimedium extract (icariin) promoted C2C12 myotube hypertrophy. Sci. Rep.11 (1), 10790. 10.1038/s41598-021-89039-0
61
Liu C. Chen X. Zhi X. Weng W. Li Q. Li X. et al (2018b). Structure-based development of an osteoprotegerin-like glycopeptide that blocks RANKL/RANK interactions and reduces ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice. Eur. J. Med. Chem.145, 661–672. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.01.022
62
Liu H. Xiong Y. Wang H. Yang L. Wang C. Liu X. et al (2018a). Effects of water extract from epimedium on neuropeptide signaling in an ovariectomized osteoporosis rat model. J. Ethnopharmacol.221, 126–136. 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.035
63
Liu H. Zhu Y. Gao Y. Qi D. Zhao L. Zhao L. et al (2020). NR1D1 modulates synovial inflammation and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis.11 (2), 129. 10.1038/s41419-020-2314-6
64
Liu T. J. Guo J. L. (2020). Overexpression of microRNA-141 inhibits osteoporosis in the jawbones of ovariectomized rats by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arch. Oral Biol.113, 104713. 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104713
65
Liu X. Liu S. Sun H. Zhang J. Li M. Shi Y. et al (2024a). NVP-BHG712 alleviates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by modulating osteoclastogenesis. Eur. J. Pharmacol.983, 177000. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177000
66
Liu Y. M. Li X. Q. Zhang X. R. Chen Y. Y. Liu Y. P. Zhang H. Q. et al (2023). Uncovering the key pharmacodynamic material basis and possible molecular mechanism of extract of epimedium against liver cancer through a comprehensive investigation. J. Ethnopharmacol.317, 116765. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116765
67
Liu Y. Q. Yang Q. X. Cheng M. C. Xiao H. B. (2014). Synergistic inhibitory effect of icariside II with icaritin from herba epimedii on pre-osteoclastic RAW264.7 cell growth. Phytomedicine21 (12), 1633–1637. 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.07.016
68
Liu Y. S. Zhong H. B. Liu W. L. He X. H. Zhan X. R. Sun C. H. (2024b). Icariin alleviates the apoptosis of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis through regulating SIRT-1-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling. Chem. Biol. Drug Des.103 (4), e14518. 10.1111/cbdd.14518
69
Luo D. Zou J. W. Wang J. H. Tian H. Xie H. Y. Zhu T. X. et al (2024). Undescribed matrine-type alkaloids from Sophora alopecuroides with anti-inflammatory activity. Phytochemistry218, 113954. 10.1016/j.phytochem.2023.113954
70
Luzzi A. Wang F. Li S. Iacovino M. Chou T. F. (2023). Skeletal muscle cell protein dysregulation highlights the pathogenesis mechanism of myopathy-associated p97/VCP R155H mutations. Front. Neurol.14, 1211635. 10.3389/fneur.2023.1211635
71
Ma H. He X. Yang Y. Li M. Hao D. Jia Z. (2011). The genus epimedium: an ethnopharmacological and phytochemical review. J. Ethnopharmacol.134, 519–541. 10.1016/j.jep.2011.01.001
72
Maani N. Karolczak S. Dowling J. J. (2021). Genetic therapy for congenital myopathies. Curr. Opin. Neurol.34 (5), 727–737. 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000978
73
Maeda K. Yoshida K. Nishizawa T. Otani K. Yamashita Y. Okabe H. et al (2022). Inflammation and bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis: molecular mechanisms of joint destruction and pharmacological treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (5), 2871. 10.3390/ijms23052871
74
Marchev A. S. Dimitrova P. A. Burns A. J. Kostov R. V. Dinkova-Kostova A. T. Georgiev M. I. (2017). Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation in osteoarthritis: can NRF2 counteract these partners in crime?Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.1401 (1), 114–135. 10.1111/nyas.13407
75
Maughan R. J. Shirreffs S. M. (2019). Muscle cramping during exercise: causes, solutions, and questions remaining. Sports Med.49 (Suppl. 2), 115–124. 10.1007/s40279-019-01162-1
76
Meng Y. C. Lin T. Jiang H. Zhang Z. Shu L. Yin J. et al (2020). miR-122 exerts inhibitory effects on osteoblast proliferation/differentiation in osteoporosis by activating the PCP4-Mediated JNK pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids20, 345–358. 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.11.038
77
Menghini L. Ferrante C. Leporini L. Recinella L. Chiavaroli A. Leone S. et al (2016). A natural formula containing lactoferrin, Equisetum arvensis, soy isoflavones and vitamin D3 modulates bone remodeling and inflammatory markers in young and aged rats. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents30 (4), 985–996.
78
Michaëlsson K. Aspenberg P. (2016). Postmenopausal osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med.374 (21), 2095. 10.1056/NEJMc160599
79
Mocanu V. Timofte D. V. Zară-Dănceanu C. M. Labusca L. (2024). Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and osteoarthritis require integrative understanding and management. Biomedicines12 (6), 1262. 10.3390/biomedicines12061262
80
Moqbel S. A. A. He Y. Xu L. Ma C. Ran J. Xu K. et al (2020). Rat chondrocyte inflammation and osteoarthritis are ameliorated by madecassoside. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2020, 7540197. 10.1155/2020/7540197
81
Nandy A. Helderman R. C. M. Thapa S. Jayapalan S. Richards A. Narayani N. et al (2023). Lipolysis supports bone formation by providing osteoblasts with endogenous fatty acid substrates to maintain bioenergetic status. Bone Res.11 (1), 62. 10.1038/s41413-023-00297-2
82
Okon E. Kukula-Koch W. Jarzab A. Halasa M. Stepulak A. Wawruszak A. (2020). Advances in chemistry and bioactivity of magnoflorine and magnoflorine-containing extracts. Int. J. Mol. Sci.21 (4), 1330. 10.3390/ijms21041330
83
Ott S. M. (2016). Postmenopausal osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med.374 (21), 2095–2096. 10.1056/NEJMc1602599
84
Pan L. Zhang Y. Chen N. Yang L. (2017). Icariin regulates cellular functions and gene expression of osteoarthritis patient-derived human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci.18 (12), 2656. 10.3390/ijms18122656
85
Pei L. K. Guo B. L. (2007). A review on research of raw material and cut crude drug of herba epimedii in last ten years. Chin. Mater. Med.32, 466–471.
86
Qian Z. M. Ke Y. (2020). Hepcidin and its therapeutic potential in neurodegenerative disorders. Med. Res. Rev.40 (2), 633–653. 10.1002/med.21631
87
Qu J. Fang L. Ren X. D. Liu Y. Yu S. S. Li L. et al (2013). Bisindole alkaloids with neural anti-inflammatory activity from Gelsemium elegans. J. Nat. Prod.76 (12), 2203–2209. 10.1021/np4005536
88
Robb S. A. Sewry C. A. Dowling J. J. Feng L. Cullup T. Lillis S. et al (2011). Impaired neuromuscular transmission and response to acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in centronuclear myopathies. Neuromuscul. Disord.21 (6), 379–386. 10.1016/j.nmd.2011.02.012
89
Seidel U. Eberhardt K. Wiebel M. Luersen K. Ipharraguerre I. R. Haegele F. A. et al (2024). Stearidonic acid improves eicosapentaenoic acid status: studies in humans and cultured hepatocytes. Front. Nutr.11, 1359958. 10.3389/fnut.2024.1359958
90
Sekar S. Panchal S. K. Ghattamaneni N. K. Brown L. Crawford R. Xiao Y. et al (2020). Dietary saturated fatty acids modulate pain behaviour in trauma-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Nutrients12 (2), 509. 10.3390/nu12020509
91
Shao S. Fu F. Wang Z. Song F. Li C. Wu Z. X. et al (2019). Diosmetin inhibits osteoclast formation and differentiation and prevents LPS-Induced osteolysis in mice. J. Cell Physiol.234 (8), 12701–12713. 10.1002/jcp.27887
92
Shapses S. (2018). Osteoporosis. Ann. Intern Med.168 (4), 306. 10.7326/L17-0586
93
Sharma A. Sharma L. Goyal R. (2021). Molecular signaling pathways and essential metabolic elements in bone remodeling: an implication of therapeutic targets for bone diseases. Curr. Drug Targets22 (1), 77–104. 10.2174/1389450121666200910160404
94
Slavova-Kazakova A. Angelova S. Fabbri D. Antonietta Dettori M. Kancheva V. D. Delogu G. (2021). Antioxidant properties of novel curcumin analogues: a combined experimental and computational study. J. Food Biochem.45 (1), e13584. 10.1111/jfbc.13584
95
Song L. Wang D. Zhai Y. Zhang X. Zhang Y. Yu Y. et al (2024). Aqueous extract of Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim. induces liver injury in mice via pyroptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol.329, 118164. 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118164
96
Su J. Wu T. Cao S. Pei J. Zhao L. (2023). Screening and characterization of a β-xylosidase from Bifidobacterium breve K-110 and its application in the biotransformation of the total flavonoids of epimedium to icariin with α-l-rhamnosidase. Bioorg Chem.132, 106364. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106364
97
Sun J. Sun W. J. Li Z. Y. Li L. Wang Y. Zhao Y. et al (2016). Daidzein increases OPG/RANKL ratio and suppresses IL-6 in MG-63 osteoblast cells. Int. Immunopharmacol.40, 32–40. 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.014
98
Takić M. Ranković S. Girek Z. Pavlović S. Jovanović P. Jovanović V. et al (2024). Current insights into the effects of dietary α-Linolenic acid focusing on alterations of polyunsaturated fatty acid profiles in metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci.25 (9), 4909. 10.3390/ijms25094909
99
Tang S. Zhang C. Oo W. M. Fu K. Risberg M. A. Bierma-Zeinstra S. M. et al (2025). Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim.11 (1), 10. 10.1038/s41572-025-00594-6
100
Tsuchiya S. Sugimoto K. Kamio H. Okabe K. Kuroda K. Okido M. et al (2018). Kaempferol-immobilized titanium dioxide promotes formation of new bone: effects of loading methods on bone marrow stromal cell differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Int. J. Nanomedicine13, 1665–1676. 10.2147/IJN.S150786
101
Tudorachi N. B. Totu E. E. Fifere A. Ardeleanu V. Mocanu V. Mircea C. et al (2021). The implication of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in knee osteoarthritis. Antioxidants (Basel)10 (6), 985. 10.3390/antiox10060985
102
Wan J. Qin Z. Lei H. Wang P. Zhang Y. Feng J. et al (2020). Erythromycin has therapeutic efficacy on muscle fatigue acting specifically on orosomucoid to increase muscle bioenergetics and physiological parameters of endurance. Pharmacol. Res.161, 105118. 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105118
103
Wang C. G. Hu Y. H. Su S. L. Zhong D. (2020). LncRNA DANCR and miR-320a suppressed osteogenic differentiation in osteoporosis by directly inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp. Mol. Med.52 (8), 1310–1325. 10.1038/s12276-020-0475-0
104
Wang F. Wang Y. Zhao Y. Zhan Q. Yu P. Wang J. et al (2016b). Sialoglycoprotein isolated from eggs of Carassius auratus ameliorates osteoporosis: an effect associated with regulation of the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway in rodents. J. Agric. Food Chem.64 (14), 2875–2882. 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b06132
105
Wang J. Zhao Q. (2019). Kaempferitrin inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and ameliorates inflammation in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Phytother. Res.33 (6), 1726–1735. 10.1002/ptr.6364
106
Wang L. Li Y. Guo Y. Ma R. Fu M. Niu J. et al (2016a). Herba epimedii: an ancient Chinese herbal medicine in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Curr. Pharm. Des.22, 328–349. 10.2174/1381612822666151112145907
107
Wang Y. Dong Z. Zhang Z. Wang Y. Yang K. Li X. (2022). Postconditioning with irisin attenuates lung ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing ferroptosis via induction of the Nrf2/HO-1 signal axis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2022, 9911167. 10.1155/2022/9911167
108
Wei C. C. Ping D. Q. You F. T. Qiang C. Y. Tao C. (2016b). Icariin prevents cartilage and bone degradation in experimental models of arthritis. Mediat. Inflamm.2016, 9529630. 10.1155/2016/9529630
109
Wei Q. Zhang J. Hong G. Chen Z. Deng W. He W. et al (2016a). Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells by activating the ERα-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother.84, 931–939. 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.107
110
Wei Y. Tu J. Ji L. Wang R. Zhou R. Lei X. et al (2025). Icariin inhibition of NLRP3 mediated leydig cell pyroptosis and insulin resistance ameliorates spermatogenesis disorders in Obese mice. Int. Immunopharmacol.151, 114280. 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114280
111
Wong V. K. W. Qiu C. Xu S. W. Law B. Y. K. Zeng W. Wang H. et al (2019). Ca2+ signalling plays a role in celastrol-mediated suppression of synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis patients and experimental arthritis in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol.176 (16), 2922–2944. 10.1111/bph.14718
112
Wu C. Zhang C. Li F. Yan Y. Wu Y. Li B. et al (2024). Fucoxanthin mitigates high-fat-induced lipid deposition and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle through inhibiting PKM1 activity. J. Agric. Food Chem.72 (32), 18013–18026. 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c03677
113
Wu H. Lien E. J. Lien L. L. (2003). Chemical and pharmacological investigations of epimedium species: a survey. Prog. Drug Res.60, 1–57. 10.1007/978-3-0348-8012-1_1
114
Wu H. Shi S. Lu X. Li T. Wang J. Liu T. et al (2019). Expression analysis and functional characterization of CER1 family genes involved in very-long-chain alkanes biosynthesis in Brachypodium distachyon. Front. Plant Sci.10, 1389. 10.3389/fpls.2019.01389
115
Wu Y. B. Zheng L. J. Wu J. G. Chen T. Q. Yi J. Wu J. Z. (2012). Antioxidant activities of extract and fractions from receptaculum nelumbinis and related flavonol glycosides. Int. J. Mol. Sci.13 (6), 7163–7173. 10.3390/ijms13067163
116
Xie F. Wu C. F. Lai W. P. Yang X. J. Cheung P. Y. Yao X. S. et al (2005). The osteoprotective effect of herba epimedii (HEP) extract in vivo and in vitro. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med.2, 353–361. 10.1093/ecam/neh101
117
Xu D. Q. Zhao L. Li S. J. Huang X. F. Li C. J. Sun L. X. et al (2021). Catalpol counteracts the pathology in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy by inhibiting the TGF-β1/TAK1 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin.42 (7), 1080–1089. 10.1038/s41401-020-00515-1
118
Xu Y. Sun D. Xiong L. Zhang Z. Li Y. Liu K. et al (2024). Phenolics and terpenoids with good anti-inflammatory activity from the fruits of amomum villosum and the anti-inflammatory mechanism of active diterpene. Bioorg Chem.145, 107190. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107190
119
Yang Y. Sheng D. Shi J. Xiao L. Wang Z. Yin Z. et al (2023). Avicularin alleviates osteoporosis-induced implant loosening by attenuating macrophage M1 polarization via its inhibitory effect on the activation of NF-κB. Biomed. Pharmacother.158, 114113. 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114113
120
Yang Z. Liu J. Fu J. Li S. Chai Z. Sun Y. (2022). Associations between WNT signaling pathway-related gene polymorphisms and risks of osteoporosis development in Chinese postmenopausal women: a case-control study. Climacteric25 (3), 257–263. 10.1080/13697137.2021.1941848
121
Yi X. Tao J. Qian Y. Feng F. Hu X. Xu T. et al (2022). Morroniside ameliorates inflammatory skeletal muscle atrophy via inhibiting canonical and non-canonical NF-κB and regulating protein synthesis/degradation. Front. Pharmacol.13, 1056460. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1056460
122
Ying X. Chen X. Wang T. Zheng W. Chen L. Xu Y. (2020). Possible osteoprotective effects of myricetin in STZ induced diabetic osteoporosis in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol.866, 172805. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172805
123
Yu D. Huang R. Yu S. Liang Q. Wang Y. Dang H. et al (2023). Construction of the first high-density genetic linkage map and QTL mapping of flavonoid and leaf-size related traits in epimedium. BMC Plant Biol.23 (1), 278. 10.1186/s12870-023-04257-0
124
Yuan S. Li Z. Huang W. Chen K. Li J. (2023). The phytoestrogenic potential of flavonoid glycosides from Selaginella moellendorffii via ERα-dependent signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol.308, 116174. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116174
125
Zagorchev P. Apostolova E. Kokova V. Peychev L. (2016). Activation of KCNQ channels located on the skeletal muscle membrane by retigabine and its influence on the maximal muscle force in rat muscle strips. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol.389 (4), 439–446. 10.1007/s00210-016-1211-0
126
Zahradka P. Neumann S. Aukema H. M. Taylor C. G. (2017). Adipocyte lipid storage and adipokine production are modulated by lipoxygenase-derived oxylipins generated from 18-carbon fatty acids. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.88, 23–30. 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.04.009
127
Zeng L. Rong X. F. Li R. H. Wu X. Y. (2017). Icariin inhibits MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13 expression through MAPK pathways in IL-1β-stimulated SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep.15 (5), 2853–2858. 10.3892/mmr.2017.6312
128
Zhang N. Ying M. D. Wu Y. P. Zhou Z. H. Ye Z. M. Li H. et al (2014a). Hyperoside, a flavonoid compound, inhibits proliferation and stimulates osteogenic differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells. PLoS One9 (7), e98973. 10.1371/journal.pone.0098973
129
Zhang W. Zhou X. Hou W. Chen E. Ye C. Chen M. et al (2022). Reversing the imbalance in bone homeostasis via sustained release of SIRT-1 agonist to promote bone healing under osteoporotic condition. Bioact. Mater19, 429–443. 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.04.017
130
Zhang Z. Xiang L. Bai D. Wang W. Li Y. Pan J. et al (2014b). The protective effect of rhizoma dioscoreae extract against alveolar bone loss in ovariectomized rats via regulating wnt and p38 MAPK signaling. Nutrients6 (12), 5853–5870. 10.3390/nu6125853
131
Zhao X. Amevor F. K. Cui Z. Wan Y. Xue X. Peng C. et al (2023). Steatosis in metabolic diseases: a focus on lipolysis and lipophagy. Biomed. Pharmacother.160, 114311. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114311
132
Zhao Y. Chen S. Wang Y. Lv C. Wang J. Lu J. (2018). Effect of drying processes on prenylflavonoid content and antioxidant activity of Epimedium koreanum nakai. J. Food Drug Anal.26 (2), 796–806. 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.05.011
133
Zhou B. R. Zhang J. A. Zhang Q. Permatasari F. Xu Y. Wu D. et al (2013). Palmitic acid induces production of proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α via a NF-κB-dependent mechanism in HaCaT keratinocytes. Mediat. Inflamm.2013, 530429. 10.1155/2013/530429
134
Zhou J. Ma Y. H. Zhou Z. Chen Y. Wang Y. Gao X. (2015). Intestinal absorption and metabolism of epimedium flavonoids in osteoporosis rats. Drug Metab. Dispos.43 (10), 1590–1600. 10.1124/dmd.115.064386
135
Zhu J. Zhang M. Liu X. L. Yin Z. G. Han X. X. Wang H. J. et al (2022). Hyperoside suppresses osteoclasts differentiation and function through downregulating TRAF6/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res.24 (12), 1157–1168. 10.1080/10286020.2022.2056028
136
Zhu W. Yin Z. Zhang Q. Guo S. Shen Y. Liu T. et al (2019). Proanthocyanidins inhibit osteoclast formation and function by inhibiting the NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways during osteoporosis treatment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.509 (1), 294–300. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.125
Summary
Keywords
epimedium, orthopedic diseases, target, enrichment analysis, pathway
Citation
Tong D, Chen L, Jiang Z, Ye X, Ma M, Ye A and Xu J (2025) Progress in the application of epimedium and its major bioactive components in the treatment of orthopedic diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1628602. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1628602
Received
14 May 2025
Accepted
23 July 2025
Published
12 August 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Xiaofeng Zhu, Jinan University, China
Reviewed by
Bo Shuai, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Eiba Eltay, Harvard University, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Tong, Chen, Jiang, Ye, Ma, Ye and Xu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jian Xu, 20061036@zcmu.edu.cn; Angzhi Ye, yeangzhi@126.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.