- 1Instituto de Ciencias Aplicadas, Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad Autónoma de Chile, Centro de Investigación e Innovación, Huechuraba, Chile
- 2Department of Medical Laboratory Technology, Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences, Northern Border University, Arar, Saudi Arabia
- 3Centro de Investigación de Estudios Avanzados del Maule, Vicerrectoría de Investigación y Postgrado, Universidad Católica del Maule, Talca, Chile
- 4Institute of Biotechnology, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam
- 5Department of Genetics, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 6State Key Laboratory of Biocontrol, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Plant Resources and Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai), School of Life Sciences, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
- 7Omics Center for Agriculture, Bioresources, Food, and Health, Kasetsart University (OmiKU), Bangkok, Thailand
Marine Actinomycetota are prolific producers of diverse bioactive secondary metabolites, making them vital for drug discovery. Traditional cultivation and bioassay-guided isolation techniques often lead to the rediscovery of the same compounds, revealing the limitations of these traditional approaches and emphasizing the need for more advanced methods. The emergence of omics technologies such as genomics, metagenomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics has dramatically enhanced the ability to investigate microorganisms by providing detailed insights into their biosynthetic gene clusters, metabolic pathways, and regulatory mechanisms. These comprehensive tools facilitate the discovery and functional analysis of new bioactive compounds by revealing the genetic blueprints underlying their biosynthesis. Omics and function-driven techniques like heterologous expression, analytical techniques (including high-resolution mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy), and culture condition optimization have enabled access to previously silent or cryptic gene clusters, expanding the chemical diversity available for exploration. This review emphasizes the integration of omics-based insights with function-driven methodologies and innovative culture techniques, forming a holistic approach to unlock the extensive biosynthetic capabilities of marine Actinomycetota. Combining these strategies holds great promise for discovering new marine-derived compounds with potential therapeutic applications.
Introduction
The phylum ‘Actinobacteria’ stands out as one of the largest bacterial groups, comprising Gram-positive bacteria known for their high GC content and exhibiting a wide array of morphologies (Williams and Vickers, 1988). Its early taxonomic arrangement was established by Stackebrandt et al. (1997) through the delineation of the class Actinobacteria. Presently, the phylum is categorized into six classes, 46 orders, and 79 families. Notably, recent advancements have led to the inclusion of 16 new orders and 10 new families (Salam et al., 2020). Recently, the International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) incorporated the rank of phylum, with phylum names required to be derived from the name of a genus serving as its nomenclatural type and utilizing the suffix “-ota” for such names (Oren et al., 2021). In this regard, the phylum name Actinomycetota was proposed with Actinomyces as the type genus (Oren and Garrity, 2021).
Actinomycetota gained significant attention following the discovery of streptomycin (Schatz et al., 2005). Since then, they have emerged as a crucial antibiotic reservoir, contributing to the production of nearly two-thirds of all antibiotics produced by microorganisms (Liu et al., 2016; Narsing Rao and Li, 2022). The marine environment, which makes up 70% of the biosphere, is the main habitat on earth for a wide variety of creatures, including microorganisms (Sarkar and Suthindhiran, 2022). Microbes in the marine environment evolve various adaptation mechanisms due to the intricate nature of their surroundings, leading to distinctive physiological and metabolic characteristics (Siro et al., 2023). The initial evidence supporting the presence of marine Actinomycetota emerged with the discovery of Rhodococcus marinonascens, marking the pioneering characterization of the first species within the Actinomycetota group in a marine ecosystem (Helmke and Weyland, 1984). Actinomycetota are abundant in the marine environment by virtue of their remarkable ability to acclimate to extreme conditions and play a crucial role in the synthesis of a broad variety of compounds (Sarkar and Suthindhiran, 2022). Natural products derived from marine Actinomycetota exhibit distinctive structural characteristics that were rarely or never encountered in the strains isolated from terrestrial sources (Bister et al., 2004; Zotchev, 2012). Drug development has typically relied on the “function to gene” technique, which entails extracting, cloning, expressing, and characterizing a gene of interest (Debouck and Metcalf, 2000). Despite being challenging and time-consuming, this method resulted in well-defined therapeutic targets (Debouck and Metcalf, 2000; Zhang et al., 2011).
Omics technologies have endowed researchers with the capacity to scrutinize samples at diverse levels, encompassing genes, transcripts, proteins, metabolites, and interaction networks, in the process of identifying new targets for drugs (Matthews et al., 2016). The integration of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies with computational biology is revolutionizing microbiology, enabling unprecedented insights into microbial diversity and function (Laudadio et al., 2019). The swift advancements in NGS, coupled with the concurrent bioinformatics tools, empower researchers to efficiently produce genome sequences (Jerzy, 2016; Laudadio et al., 2019) and also find utility in diverse areas such as transcriptome sequencing, metagenome sequencing, targeted sequencing or candidate gene sequencing (Wang et al., 2009; Pelizzola and Ecker, 2011; Rabbani et al., 2014; Leo et al., 2015; Jerzy, 2016).
In the past, various reviews have covered the discovery and development of drugs from marine Actinomycetota (Lam, 2006; Siro et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024), there remains a noticeable lack of comprehensive reviews specifically addressing the application of omics-based approaches for drug discovery in this group. The present review focuses on various omics approaches used for the discovery and development of drugs from marine Actinomycetota (Figures 1, 2).
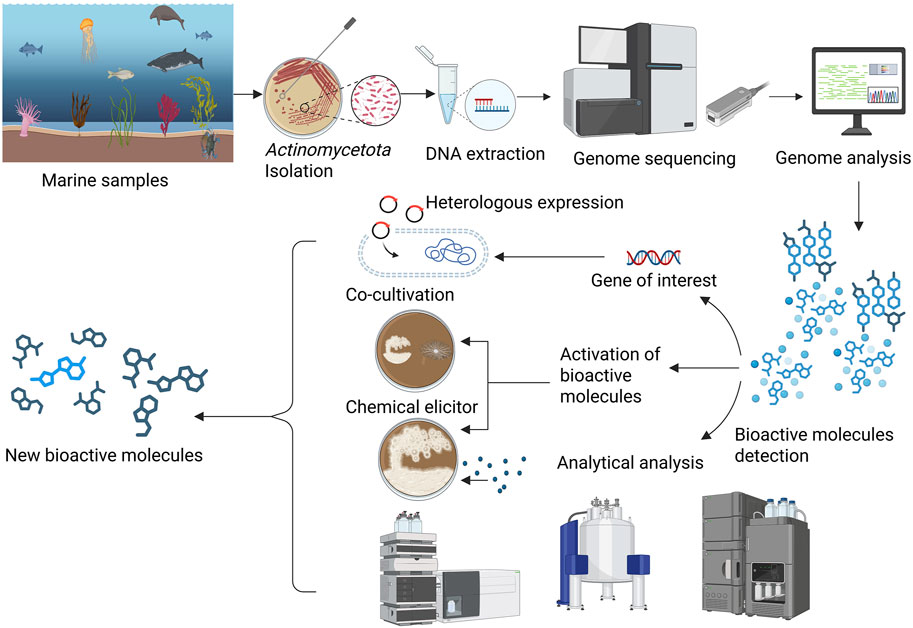
Figure 1. Genome and analytical approaches for the detection of new bioactive molecules from marine Actinomycetota.
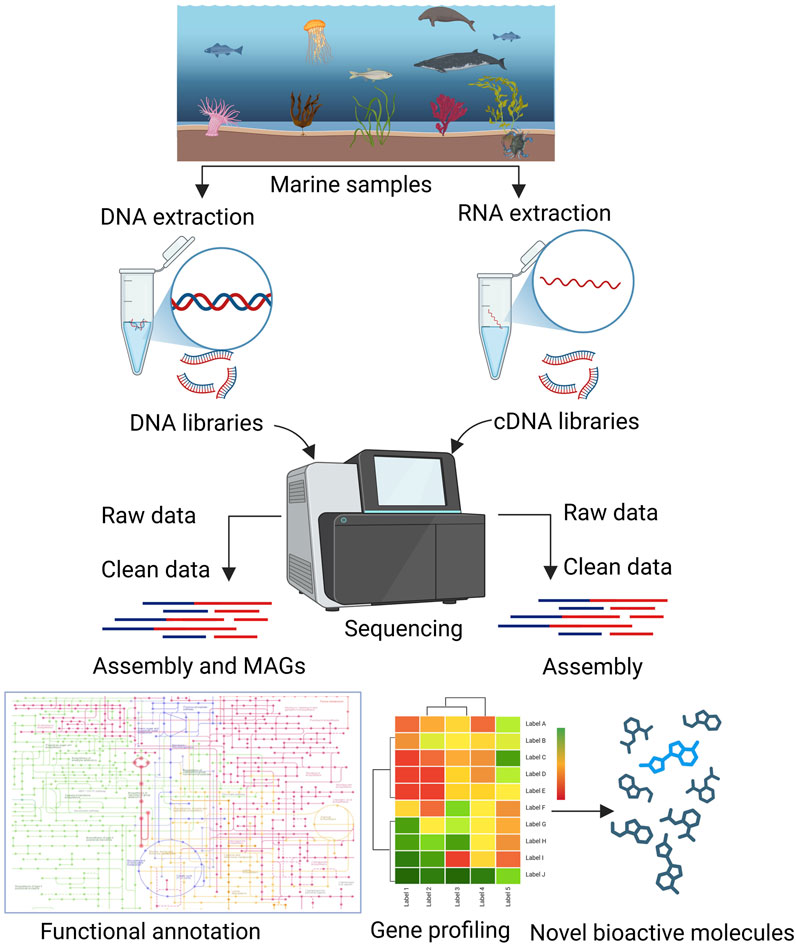
Figure 2. Metagenomics and transcriptomics approaches for the detection of new bioactive molecules from marine Actinomycetota.
Genomic approach
Since the discovery of streptomycin from Streptomyces (Schatz et al., 2005), this genus has received considerable attention, being a primary source of antibiotics. Traditionally, drug discovery has relied on bioactive molecule screening, followed by analytical analysis (Lee et al., 2020). In recent decades, there has been a dramatic drop in new drug development, mostly due to the repeated rediscovery of known compounds in the same ecological environments, as well as the associated cost (Belknap et al., 2020). Moreover, under laboratory conditions, microbes frequently cease secondary metabolite production, further complicating drug discovery efforts (Ohnishi et al., 2008). Additionally, there is a dearth of understanding regarding how to stimulate their biosynthesis or determine which compounds are more likely to exhibit desirable biological activities (Ohnishi et al., 2008; Augustijn et al., 2024).
Genome sequencing stands as a robust method, encompassing the complete determination of an individual’s DNA sequence and offering an intricate blueprint of their genetic composition (Satam et al., 2023). Traditional methods for finding natural compounds in microorganisms have significantly understated their capacity for biosynthesis; however, genome sequencing has uncovered a vast database of biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs), which greatly outnumbers the number of compounds currently associated with a particular organism (Van Lanen and Shen, 2006). For instance, the model organism Streptomyces coelicolor is well known to produce secondary metabolites (Price et al., 1999). Genome analysis has revealed a greater number of secondary metabolites BGCs than initially anticipated (Bentley et al., 2002). Recent breakthroughs in DNA sequencing technology have resulted in a significant rise in the sequencing of Actinomycetota genomes (Narsing Rao et al., 2020; Li et al., 2023) and, as a result, a plethora of technologies for genome annotation and mining have emerged. The bioinformatic tool and database for the detection of BGCs such antiSMASH (Blin et al., 2019), prediction informatics for secondary metabolomes (PRISM) (Skinnider et al., 2017), NP. searcher (Li et al., 2009), DeepBGC (Hannigan et al., 2019), minimum information about a biosynthetic gene cluster (MIBiG) (Zdouc et al., 2025), natural products atlas (Poynton et al., 2025), etc., have significantly streamlined the analysis process by enabling efficient detection and characterization of bioactive compounds.
In the past few years, many marine-derived Actinomycetota genomes have been sequenced to evaluate their drug potential. Genome mining of marine sediment-derived Streptomyces sp. GMY01 revealed 28 BGCs involved in the production of flaviolin, geosmin, ectoine, class IV lanthipeptide/SflA, albaflavenone, and informatipeptin (Widada et al., 2023). Similarly, genome mining of marine sediment-derived Streptomyces sp. DUT11 revealed the presence of anti-complement agent (tunicamycin) and medermycin analogs, as well as new BGCs, suggesting the presence of novel lassopeptides and lantibiotics (Xu et al., 2018). Genome mining of the deep-sea-derived Streptomyces antibioticus OUCT16-23 revealed the presence of filipin-type polyene macrolides exhibiting antifungal activity against Candida albicans (Bao et al., 2022). Genome mining of marine Streptomyces sp. H-KF8 identified several nonribosomal peptides, leading to the design and synthesis of eight peptides, six of which showed antimicrobial activity, with two potentially disrupting membrane via a novel ion-passage mechanism (Beyer et al., 2024).
Genome analysis of Actinomycetota associated with marine living entities was also carried out. Genome analysis of Streptomyces poriferorum, a novel species isolated from a marine sponge, revealed 41 BGCs for secondary metabolites. The species showed antibacterial activity, notably against Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (Sandoval-Powers et al., 2021). Genome mining of Streptomyces seoulensis A01, which was isolated from a marine prawn, showed the presence of streptoseomycin (Zhang et al., 2018), while the novel species Streptomyces poriticola, isolated from the marine invertebrate Porites lutea, demonstrated notable antimicrobial properties and selective cytotoxic effects against human breast cancer MCF-7 cells, while exhibiting minimal toxicity to human dermal papilla cells (Kanchanasin et al., 2024). Furthermore, the complete genome sequence of mangrove-isolated Streptomyces sp. FIM 95-F1 strain revealed its ability to produce the antifungal antibiotic scopafungin (Fei et al., 2024). A combination of Illumina and PacBio sequencing was utilized to generate a high-quality, chromosome-level genome along with a plasmid for the marine Streptomyces sp. 891, revealing the Type II polyketide synthase (T2PKS) BGC responsible for chrysomycin production (Hu et al., 2022). Genome analysis of endophytic Streptomyces parvulus VCCM 22513 isolated from mangrove plant Bruguiera gymnorrhiza showed the presence of genes involved in mycothiol and ergothioneine biosynthesis (Quach et al., 2022). Genome analysis of Streptomyces sp. V17-9 isolated from seagrass showed the presence of siderophore compounds and amino acid derivatives (Kim et al., 2022). In a comparative genomic study, single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing (PacBio RSII sequencing platform) of marine sponge-derived Streptomyces strains SM17 and SM18 enabled detailed analysis of their biosynthetic capacities. Genome mining using antiSMASH identified 20 and 26 BGCs in SM17 and SM18, respectively, many of which were either unique or showed low similarity to known clusters. Comparative analyses further revealed substantial divergence from their terrestrial relatives, not only in BGC content but also in genes linked to environmental adaptation, such as those involved in osmotic stress response and host-associated interactions. These results emphasize the impact of the marine niche on genomic diversification and point to the considerable potential for cryptic BGC activation and novel metabolite discovery (Almeida et al., 2019).
Apart from the genus Streptomyces, other Actinomycetota genera genomes were also mined to find their secondary metabolite BGCs. Genome analysis of the genus Salinispora, which was first described from a marine habitat (Maldonado et al., 2005), revealed many secondary metabolites like salinosporamide K from Salinispora pacifica (Eustáquio et al., 2011), lanthipeptide from Salinispora spp. (Kittrell et al., 2020), salinilactam A, and lomaiviticin from Salinispora tropica (Udwary et al., 2007; Kersten et al., 2013), polyketides, non-ribosomal peptides, and terpenes from Salinispora sp. H7-4 (Ulanova et al., 2020). Genome mining of Janibacter limosus P3-3-X1 from the Antarctic deep sea revealed five potential BGCs involved in secondary metabolites, including non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS), ectoine, and siderophore. The siderophore cluster may produce desferrioxamine-like iron chelators for thalassemia treatment, while a unique NRPS cluster suggests the potential for novel natural products (Su et al., 2019). Genome mining of three marine Micromonospora species revealed the presence of bleomycin, lymphostin, phosphonoglycan, actinomycin, alnumycin, epothilone, spinosad, syringomycin, and sioxanthin BGCs. Notably, certain BGCs exhibited species-specific distribution, highlighting the unique metabolic potential within each Micromonospora species (Contreras-Castro et al., 2019). Nocardiopsis dassonvillei RACA-4, isolated from Red Sea nudibranchs, harbors diverse BGCs for polyketides, non-ribosomal peptides, phenazine, bacteriocins, surfactins, and sactipeptides, with many showing low similarity to known clusters, indicating potential for novel natural product discovery (Elfeky et al., 2023). A list of marine-derived Actinomycetota gene clusters identified through genome mining are mentioned in Table 1.
Genome-guided combinatorial approach
Genome sequencing has revealed that many microbial BGCs remain inactive under standard culture conditions, limiting access to novel secondary metabolites (Onaka, 2017). Heterologous expression, a method involving the transfer of gene clusters into a different, more amenable host, has proven effective for activating these silent pathways and enhancing novel metabolite production. This approach played a crucial role in uncovering the hidden metabolic potential of microbes for natural product discovery (Yang et al., 2020). The integration of genome mining with heterologous expression has successfully activated silent BGCs in numerous marine-derived Actinomycetota, enabling the discovery of novel secondary metabolites. Genome mining of the marine S. seoulensis A01 enabled the identification of a giant Type I PKS gene cluster (asm). When this BGC was constructed and expressed in “Streptomyces lividans” SBT18, ansaseomycin A and B were produced, which were active against the leukemia cell line (Liu et al., 2019). Genome mining of the sponge-associated Streptomyces sp. DSS69 uncovered putative genes involved in macrolactam biosynthesis. Subsequent cloning and heterologous expression of these genes in “S. lividans” GX28 led to the discovery of weddellamycin, an antibacterial compound exhibiting potent activity against a range of Gram-positive bacteria, including MRSA, as well as antifungal activity against C. albicans and cytotoxic effects on various cancer cell lines (Chen et al., 2024). Recently, the integration of genome mining and heterologous expression led to the discovery of two novel tricyclic diterpenes, ostamycins A and B, from the deep-sea-derived Streptomyces amphotericinicus DS22–01, both exhibiting inhibitory activity against the Influenza A virus (Hou et al., 2025).
Along with genomic and heterologous expression approaches, cultivation conditions and analytical methods were also used to activate BGCs. Genomic analysis of marine Actinoalloteichus sp. AHMU CJ021 revealed 22 BGCs, including a dormant caerulomycin A (CRM A) pathway. Activation of CRM A was achieved via gentamycin-guided ribosome engineering, with further enhancement through UV mutagenesis and intracellular riboflavin optimization. Medium optimization using response surface methodology showed that controlled carbon feeding and high organic nitrogen levels, with limited inorganic nitrogen, significantly improved CRM A yield (Xie et al., 2020). Integrating NMR-based metabolomics with genomic analysis has proven effective for natural product discovery in marine-derived actinobacteria. In Streptomyces sp. S063, this approach revealed a novel NRPS gene cluster and identified cyclic decapeptides with moderate anticancer activity (Huang et al., 2023). A study used a combination of genome and MS/MS analysis to investigate the biosynthetic potential of a rare actinobacterium (Micromonospora aurantiaca sp.01) isolated from a mangrove habitat. Analysis of its genome revealed 21 secondary metabolite BGCs responsible for antibiotic production. Using guided MS/MS analysis, one of the predicted antibiotics, kanamycin, was identified (Hu et al., 2020). Streptomyces sp. MP131-18, isolated from marine sediment, was subjected to integrated genomic and metabolomic profiling. Genome mining via antiSMASH uncovered 36 BGCs associated with the production of 18 diverse classes of secondary metabolites, indicating a rich and varied metabolic capacity. Complementary metabolomic analyses led to the identification of bisindole pyrrole compounds, including lynamicins and spiroindimicins, which showed antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis (Paulus et al., 2017).
Eliciting bacterial cells using external signals, whether biological (such as co-cultivation with other microbes) or chemical (like small molecule inducers), is a strategic approach to activate silent or poorly expressed BGCs responsible for antibiotic production (Abdelmohsen et al., 2015). Co-culturing different microbial species is a simple yet powerful approach to activate silent BGCs (Kim et al., 2021). When coupled with genome analysis, which identified cryptic BGCs, co-culture served as a targeted strategy to activate biosynthetic potential. This method not only mimics natural ecological stressors like interspecies competition and nutrient limitation but also enables real-time assessment of induced metabolite (Kim et al., 2021). A study highlights how co-cultivating a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. PTY087I2 with human pathogens (B. subtilis, methicillin-sensitive S. aureus, MRSA, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) effectively activates silent BGCs, leading to the production of novel antibiotic compounds. Genome analysis of Streptomyces sp. PTY087I2 revealed 37 BGCs with high biosynthetic potential; however, monoculture conditions failed to induce significant metabolite expression. In contrast, co-culture conditions led to the enhanced production of granaticin, granatomycin D, dihydrogranaticin B, and related analogues, significantly boosting antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive pathogens (Sung et al., 2017). Similarly, genome and co-culture analysis of marine invertebrate-associated bacteria, specifically Micromonospora and Rhodococcus species, led to the discovery of the novel antibiotic keyicin. The genome of Micromonospora was found to contain the genes responsible for keyicin biosynthesis, whereas Rhodococcus did not. Co-culture experiments showed that Micromonospora sp. exposure to Rhodococcus sp. derived signals triggered Micromonospora to enhance genes involved in the keyicin biosynthetic pathway. The resulting compound exhibited antibacterial activity, particularly against selective Gram-positive bacteria, including Rhodococcus and Mycobacterium species (Adnani et al., 2017).
Chemical elicitation, on the other hand, uses synthetic compounds like inorganic substances, heavy metals, and rare earth elements to trigger metabolic changes by activating specific defence pathways with varying intensity (Abdelmohsen et al., 2015). The combination of genome analysis with biological and chemical elicitation proved effective in revealing hidden biosynthetic capabilities. A recent study investigated elicitation strategies to enhance antibacterial metabolite production in Antarctic actinobacterial strains from soil, marine water, and sediments. By employing MS/MS-based metabolomics and genome mining, strains were cultivated under different nutrient conditions and elicitors such as lipopolysaccharide, sodium nitroprusside, and co-culture. While all treatments activated biosynthetic pathways, strain-specific responses varied depending on culture medium composition (Núñez-Montero et al., 2020).
Metagenomics and transcriptomics
The exploration of microbial diversity and function in natural environments has been greatly enhanced by high-throughput sequencing technologies. Metagenomics, which involves sequencing DNA extracted directly from environmental sources, enables researchers to study entire microbial communities without the need for culturing individual species. This approach provides a broad view of the taxonomic composition and metabolic capabilities present within complex microbiomes (Akaçin et al., 2022). Complementing this, transcriptomics focuses on the analysis of RNA transcripts, offering insights into gene expression patterns under specific environmental or physiological conditions. By capturing active transcriptional responses, transcriptomic studies reveal which genes were being expressed and regulated, providing a functional perspective on microbial activity (Aplakidou et al., 2024). Through integrated metagenomic and transcriptomic analyses, researchers have been able to uncover a diverse array of BGCs and regulatory pathways involved in the synthesis of potentially therapeutic molecules from marine Actinomycetota. Metagenomic studies targeting the deep chlorophyll maximum of the Mediterranean Sea have led to the recovery of four genomes belonging to marine Actinobacteria, specifically within the Acidimicrobiales order. These represent the first genomic insights into marine representatives of this group. Among the four genomes, one was found to carry a gene coding for a rhodopsin-like protein, exhibiting closest similarity to a freshwater Acidimicrobiales species. The associated rhodopsin gene cluster displayed unique features distinct from previously known variants, prompting the designation of a new subgroup referred to as acidirhodopsins (Mizuno et al., 2015). An integrative omics study combining transcriptomics and proteomics with parallel reaction monitoring has elucidated the antifungal mechanism of antifungalmycin B, a bioactive compound from the marine Streptomyces hiroshimensis. These findings reveal that antifungalmycin B inhibits Talaromyces marneffei by disrupting organic acid biosynthesis and impairing critical cellular energy metabolism pathways. Such dual interference undermines metabolic homeostasis in the pathogen, enhancing antifungalmycin B antifungal activity (Li et al., 2025). The marine-derived Streptomyces olivaceus SCSIO T05 has emerged as a promising source of antifungal compounds, particularly in the context of targeting virulence traits in C. albicans (inhibiting the formation of hyphae and biofilms). Transcriptomic analysis, supported by real-time PCR, revealed that these effects were mediated through the downregulation of genes associated with filamentation and cell adhesion. This gene expression modulation disrupts essential morphogenetic and adhesion pathways, suggesting that the compound impairs fungal pathogenicity by targeting regulatory networks rather than directly killing the fungal cell. These findings highlight the potential of transcriptomics-guided discovery in identifying novel anti-virulence strategies against fungal pathogens (Meng et al., 2019). A study employed comparative transcriptomics to analyze BGC activity across four closely related Salinispora strains. The results showed that about half of the BGCs were actively expressed at levels likely sufficient for metabolite detection. By comparing similar clusters across strains, specific regulatory genes potentially responsible for BGC silencing were identified. These previously undetected regulatory variations emphasize the significance of transcriptomic approaches in uncovering hidden metabolic potential. The presence of conserved but transcriptionally inactive BGCs across multiple strains suggests they may be subject to distinct regulatory mechanisms or that gene silencing serves an evolutionary function. Combining transcriptomic data with metabolomics allowed to associate the production of salinipostins (Amos et al., 2017).
Conclusion and future perspectives
Marine Actinomycetota possess exceptional biosynthetic potential, producing a wide range of bioactive secondary metabolites with significant pharmaceutical relevance. Their unique metabolic capabilities underscore their value as a promising source for novel drug discovery and therapeutic development. However, the exploration of this microbial group has so far barely scratched the surface. For years, researchers depended on conventional isolation and bioactivity-guided screening methods, which, although fruitful to a degree, often led to the rediscovery of previously known compounds. This recurring outcome underscores a critical limitation: only a small portion of marine microbial life has been cultured and studied, leaving the vast majority untapped, much like seeing only the tip of an iceberg while the bulk remains submerged and mysterious. With the advent of omics technologies, this landscape is beginning to change. Genome sequencing has opened the door to BGCs from microbes, offering clues to potentially novel compounds. Metagenomics has proven even more transformative, granting access to the genetic blueprints of uncultivable microbes directly from environmental samples, an essential step toward revealing the hidden biosynthetic capacity of marine ecosystems. Meanwhile, transcriptomic analyses help unravel the gene expression patterns that regulate secondary metabolism, and metabolomics allows researchers to profile complex chemical mixtures and associate them with specific metabolic pathways or gene clusters. Complementing these molecular tools are powerful analytical techniques that bring chemical insights into sharper focus. High-resolution mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy are critical for structure elucidation and dereplication, helping distinguish novel compounds from known ones. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) enables detailed metabolic profiling, allowing researchers to connect metabolomic data with genomic predictions. These techniques, when used in tandem with bioinformatics tools and databases, enhance the precision and speed of natural product discovery. Despite these advancements, many challenges remain. A substantial number of BGCs identified in genome data are still uncharacterized or remain silent under laboratory conditions. Future efforts should focus on improving the functional annotation of these gene clusters through advanced computational and experimental methods, and on developing more efficient ways to activate and study these cryptic biosynthetic pathways. Equally important is the exploration of lesser-known marine habitats such as deep-sea trenches, hydrothermal vents, polar seas, and marine symbiont communities that likely harbor microbial species with entirely novel metabolic capacities. The full potential of marine Actinomycetota will only be realized through integrated, multidisciplinary efforts that combine omics-driven discovery, chemical analytics, systems biology, and ecological exploration. As researchers continue to piece together this complex puzzle, each breakthrough will bring us closer to uncovering new classes of bioactive molecules with the potential to address critical challenges in medicine, particularly the growing crisis of antibiotic resistance and the urgent need for innovative therapeutics.
Author contributions
MN: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. SQ: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. MS: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. NQ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. W-JL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. AT: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work has been supported by Visiting Research Scholar (VRC) grant, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University and Bioinformatics Academic Association of Thailand (BAT). The author SQ extends his appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Northern Border University, Arar, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number NBU-FFR-2025-2046-10. MS is grateful to ANID FONDECYT 1250963.
Acknowledgments
Figure 1 is created in BioRender. Prabhu, M. (2025) https://BioRender.com/rywp6pi. Figure 2 is created in BioRender. Prabhu, M. (2025) https://BioRender.com/p2sp1o9.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdelmohsen, U. R., Grkovic, T., Balasubramanian, S., Kamel, M. S., Quinn, R. J., and Hentschel, U. (2015). Elicitation of secondary metabolism in actinomycetes. Biotechnol. Adv. 33 (6 Pt 1), 798–811. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.06.003
Adnani, N., Chevrette, M. G., Adibhatla, S. N., Zhang, F., Yu, Q., Braun, D. R., et al. (2017). Coculture of marine invertebrate-associated bacteria and interdisciplinary technologies enable biosynthesis and discovery of a new antibiotic, Keyicin. ACS Chem. Biol. 12 (12), 3093–3102. doi:10.1021/acschembio.7b00688
Akaçin, İ., Ersoy, Ş., Doluca, O., and Güngörmüşler, M. (2022). Comparing the significance of the utilization of next generation and third generation sequencing technologies in microbial metagenomics. Microbiol. Res. 264, 127154. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2022.127154
Almeida, E. L., Carrillo Rincón, A. F., Jackson, S. A., and Dobson, A. D. W. (2019). Comparative Genomics of marine sponge-derived Streptomyces spp. Isolates SM17 and SM18 with their closest terrestrial relatives provides novel insights into environmental niche adaptations and secondary metabolite biosynthesis potential. Front. Microbiol. 10, 1713. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.01713
Amos, G. C. A., Awakawa, T., Tuttle, R. N., Letzel, A. C., Kim, M. C., Kudo, Y., et al. (2017). Comparative transcriptomics as a guide to natural product discovery and biosynthetic gene cluster functionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114 (52), E11121-E11130–E11130. doi:10.1073/pnas.1714381115
Aplakidou, E., Vergoulidis, N., Chasapi, M., Venetsianou, N. K., Kokoli, M., Panagiotopoulou, E., et al. (2024). Visualizing metagenomic and metatranscriptomic data: a comprehensive review. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 23, 2011–2033. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2024.04.060
Augustijn, H. E., Roseboom, A. M., Medema, M. H., and van Wezel, G. P. (2024). Harnessing regulatory networks in Actinobacteria for natural product discovery. J. Ind. Microbiol. 51, kuae011. doi:10.1093/jimb/kuae011
Bao, Y., Li, H., Dong, Y., Duan, H., Li, H., and Li, W. (2022). Genome-guided discovery of antifungal filipins from a deep-seasea-derived Streptomyces antibioticus. J. Nat. Prod. 85 (2), 365–374. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00952
Belknap, K. C., Park, C. J., Barth, B. M., and Andam, C. P. (2020). Genome mining of biosynthetic and chemotherapeutic gene clusters in Streptomyces bacteria. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 2003. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-58904-9
Bentley, S. D., Chater, K. F., Cerdeño-Tárraga, A. M., Challis, G. L., Thomson, N. R., James, K. D., et al. (2002). Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417 (6885), 141–147. doi:10.1038/417141a
Beyer, L. I., Schäfer, A.-B., Undabarrena, A., Mattsby-Baltzer, I., Tietze, D., Svensson, E., et al. (2024). Mimicking nonribosomal peptides from the marine actinomycete Streptomyces sp. H-KF8 leads to antimicrobial peptides. ACS Inf. Dis. 10 (1), 79–92. doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00206
Bister, B., Bischoff, D., Ströbele, M., Riedlinger, J., Reicke, A., Wolter, F., et al. (2004). Abyssomicin C-A polycyclic antibiotic from a marine Verrucosispora strain as an inhibitor of the p-aminobenzoic acid/tetrahydrofolate biosynthesis pathway. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 43 (19), 2574–2576. doi:10.1002/anie.200353160
Blin, K., Shaw, S., Steinke, K., Villebro, R., Ziemert, N., Lee, S. Y., et al. (2019). antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (W1), W81-W87–W87. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz310
Chen, L., Liu, K., Hong, J., Cui, Z., He, W., Wang, Y., et al. (2024). The discovery of weddellamycin, a tricyclic polyene macrolactam antibiotic from an antarctic deep-seasea-derived Streptomyces sp. DSS69, by heterologous expression. Mar. Drugs 22 (4), 189. doi:10.3390/md22040189
Contreras-Castro, L., Maldonado, L. A., Quintana, E. T., Carro, L., and Klenk, H. P. (2019). Genomic insight into three marine Micromonospora sp. strains from the Gulf of California. Microbiol. Resour. Announc 8 (28), e01673-18. doi:10.1128/mra.01673-18
Debouck, C., and Metcalf, B. (2000). The impact of genomics on drug discovery. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 40, 193–207. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.40.1.193
Elfeky, H. H., Hanora, A., and Solyman, S. M. (2023). Bioactivity of bacteria associated with Red Sea nudibranchs and whole genome sequence of Nocardiopsis dassonvillei RACA-4, Bioactivity Bact. Assoc. Red Sea nudibranchs whole genome sequence Nocardiopsis Dassonv. RACA-4. Mar Genomics 67. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2022.101004
Eustáquio, A. S., Nam, S.-J., Penn, K., Lechner, A., Wilson, M. C., Fenical, W., et al. (2011). The Discovery of Salinosporamide K from the marine bacterium “Salinispora pacifica” by genome mining gives insight into pathway evolution. ChemBioChem 12 (1), 61–64. doi:10.1002/cbic.201000564
Fei, P., Yangjun, L., Yuee, Z., Ping, L., Chengzhi, L., Linlin, C., et al. (2024). The complete genome sequence of Streptomyces sp. FIM 95-F1, a marine actinomycete that produces the antifungal antibiotic scopafungin. Mar. Genomics 78, 101146. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2024.101146
Hannigan, G. D., Prihoda, D., Palicka, A., Soukup, J., Klempir, O., Rampula, L., et al. (2019). A deep learning genome-mining strategy for biosynthetic gene cluster prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (18), e110. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz654
Helmke, E., and Weyland, H. (1984). Rhodococcus marinonascens sp. nov., an actinomycete from the sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 34 (2), 127–138. doi:10.1099/00207713-34-2-127
Hou, L., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Chen, Z., Gao, Y., et al. (2025). Targeted discovery of diterpene compounds ostamycins with anti-influenza a viral activity from a deepsea-derived Streptomyces strain. Bioorg Chem. 157, 108268. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2025.108268
Hu, D., Sun, C., Jin, T., Fan, G., Mok, K. M., Li, K., et al. (2020). Exploring the potential of antibiotic production from rare actinobacteria by whole-genome sequencing and guided MS/MS analysis. Front. Microbiol. 11, 1540. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01540
Hu, X., Tang, Y., Liu, Y., Pei, X., Huang, Z., Song, F., et al. (2022). Comprehensive genomic analysis of marine strain Streptomyces sp. 891, an Excellent producer of chrysomycin A with therapeutic potential. Mar. Drugs 20 (5), 287. doi:10.3390/md20050287
Huang, H., Yue, L., Deng, F., Wang, X., Wang, N., Chen, H., et al. (2023). NMR-metabolomic profiling and genome mining drive the discovery of cyclic decapeptides from a marine Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 86 (9), 2122–2130. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00310
Jerzy, K. K. (2016). “Next-generation sequencing — an Overview of the history, tools, and “omic” applications,” in Next generation sequencing. Editor K. K. Jerzy (Rijeka, Croatia: IntechOpen).
Jiang, X., Zhang, Q., Zhu, Y., Nie, F., Wu, Z., Yang, C., et al. (2017). Isolation, structure elucidation and biosynthesis of benzo[b]fluorene nenestatin A from deep-sea derived Micromonospora echinospora SCSIO 04089. Tetrahedron 73 (26), 3585–3590. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2017.03.054
Kanchanasin, P., Salahong, T., Sripreechasak, P., Suriyachadkun, C., Harunari, E., Igarashi, Y., et al. (2024). Discovery of two new actinobacteria, Micromonospora palythoicola sp. nov. and Streptomyces poriticola sp. nov., isolated from marine invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 22140. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-73040-4
Kersten, R. D., Lane, A. L., Nett, M., Richter, T. K. S., Duggan, B. M., Dorrestein, P. C., et al. (2013). Bioactivity-guided genome mining reveals the lomaiviticin biosynthetic gene cluster in Salinispora tropica. ChemBioChem 14 (8), 955–962. doi:10.1002/cbic.201300147
Kim, J. H., Lee, N., Hwang, S., Kim, W., Lee, Y., Cho, S., et al. (2021). Discovery of novel secondary metabolites encoded in actinomycete genomes through coculture. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48 (3-4), kuaa001. doi:10.1093/jimb/kuaa001
Kim, D. E., Hong, S. C., Yang, Y., Choi, J., and Park, J. S. (2022). Chemical and genomic analyses of a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. V17-9 producing amino acid derivatives and siderophores. Front. Mar. Sci. 9, 959690. doi:10.3389/fmars.2022.959690
Kittrell, C. G., Shah, S. C., Halbert, M. E., Scott, D. H., and Limbrick, E. M. (2020). Genomic analysis suggests Salinispora is a rich source of novel lanthipeptides. Mol. Genet. Genom 295 (6), 1529–1535. doi:10.1007/s00438-020-01718-1
Komaki, H., Ichikawa, N., Hosoyama, A., Hamada, M., Harunari, E., Ishikawa, A., et al. (2016). Draft genome sequence of Micromonospora sp. DSW705 and distribution of biosynthetic gene clusters for depsipeptides bearing 4-amino-2,4-pentadienoate in actinomycetes. Stand Genomic Sci11 11 (1), 84. doi:10.1186/s40793-016-0206-2
Kumar, H., Vijayakumar, S., Shintre, N., Tamhane, V., Deshpande, N., Joshi, T., et al. (2025). In silico exploration of biosynthetic gene clusters in marine Streptomyces sp. and Nocardiopsis sp. from the western coast of India: genome-based profiling using whole genome sequencing. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 23 (2), 100483. doi:10.1016/j.jgeb.2025.100483
Lam, K. S. (2006). Discovery of novel metabolites from marine actinomycetes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9 (3), 245–251. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2006.03.004
Laudadio, I., Fulci, V., Stronati, L., and Carissimi, C. (2019). Next-Generation metagenomics: methodological challenges and opportunities. Omics 23 (7), 327–333. doi:10.1089/omi.2019.0073
Lee, N., Kim, W., Hwang, S., Lee, Y., Cho, S., Palsson, B., et al. (2020). Thirty complete Streptomyces genome sequences for mining novel secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. Sci. Data 7 (1), 55. doi:10.1038/s41597-020-0395-9
Leo, V. C., Morgan, N. V., Bem, D., Jones, M. L., Lowe, G. C., Lordkipanidzé, M., et al. (2015). Use of next-generation sequencing and candidate gene analysis to identify underlying defects in patients with inherited platelet function disorders. J. Thromb. Haemost. 13 (4), 643–650. doi:10.1111/jth.12836
Li, M. H., Ung, P. M., Zajkowski, J., Garneau-Tsodikova, S., and Sherman, D. H. (2009). Automated genome mining for natural products. BMC Bioinforma. 10, 185. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-10-185
Li, L. F., Wu, Q. X., Wu, H., Li, Y., Peng, Q., Han, R. H., et al. (2023). Complete Genome sequence of Streptomyces sp. HP-A2021, a promising bacterium for natural product discovery. Biochem. Genet. 61 (5), 2042–2055. doi:10.1007/s10528-023-10350-8
Li, Q., Wang, Z., Jiang, C., Yin, J., Liu, Y., Qu, X., et al. (2025). Integration of transcriptomics and proteomics to elucidate inhibitory effect and mechanism of antifungalmycin B from marine Streptomyces hiroshimensis in treating Talaromyces marneffei. Mar. Drugs 23 (2), 76. doi:10.3390/md23020076
Liu, L., Salam, N., Jiao, J. Y., Jiang, H. C., Zhou, E. M., Yin, Y. R., et al. (2016). Diversity of culturable thermophilic Actinobacteria in hot springs in Tengchong, China and studies of their biosynthetic gene profiles. Microb. Ecol. 72 (1), 150–162. doi:10.1007/s00248-016-0756-2
Liu, S. H., Wang, W., Wang, K. B., Zhang, B., Li, W., Shi, J., et al. (2019). Heterologous expression of a cryptic giant type I PKS gene cluster leads to the production of ansaseomycin. Org. Lett. 21 (10), 3785–3788. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01237
Liu, Z., Sun, W., Hu, Z., Wang, W., and Zhang, H. (2024). Marine Streptomyces-derived novel Alkaloids discovered in the past decade. Mar. Drugs 22 (1), 51. doi:10.3390/md22010051
Ma, L., Zhang, W., Liu, Z., Huang, Y., Zhang, Q., Tian, X., et al. (2021). Complete genome sequence of Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 03032 isolated from Indian Ocean sediment, producing diverse bioactive natural products. Mar. Genomics 55, 100803. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2020.100803
Maldonado, L. A., Fenical, W., Jensen, P. R., Kauffman, C. A., Mincer, T. J., Ward, A. C., et al. (2005). Salinispora arenicola gen. nov., sp. nov. and Salinispora tropica sp. nov., obligate marine actinomycetes belonging to the family Micromonosporaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55 (Pt 5), 1759–1766. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63625-0
Matthews, H., Hanison, J., and Nirmalan, N. (2016). “Omics”-informed drug and biomarker discovery: opportunities, challenges and future perspectives. Proteomes 4 (3), 28. doi:10.3390/proteomes4030028
Meng, L., Sun, C., Zhang, C., Song, S., Sun, X., Ju, J., et al. (2019). Efficacy of compounds isolated from Streptomyces olivaceus against the morphogenesis and virulence of Candida albicans. Mar. Drugs 17 (8), 442. doi:10.3390/md17080442
Mizuno, C. M., Rodriguez-Valera, F., and Ghai, R. (2015). Genomes of Planktonic Acidimicrobiales: Widening horizons for marine actinobacteria by metagenomics. mBio 6 (1). doi:10.1128/mBio.02083-14
Narsing Rao, M. P., and Li, W. J. (2022). “Diversity of actinobacteria in various habitats,” in Actinobacteria: microbiology to synthetic biology. Editor L. Karthik (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore), 37–58.
Narsing Rao, M. P., Dong, Z. Y., Jiao, J. Y., Zhou, Y., Zhao, J., Xiao, M., et al. (2020). Genome sequence and comparative analysis of DRQ-2, the type strain of Nonomuraea indica. Genomics 112 (4), 2842–2844. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.03.023
Núñez-Montero, K., Quezada-Solís, D., Khalil, Z. G., Capon, R. J., Andreote, F. D., and Barrientos, L. (2020). Genomic and metabolomic analysis of Antarctic bacteria revealed culture and elicitation conditions for the production of antimicrobial compounds. Biomolecules 10 (5), 673. doi:10.3390/biom10050673
Ohnishi, Y., Ishikawa, J., Hara, H., Suzuki, H., Ikenoya, M., Ikeda, H., et al. (2008). Genome sequence of the streptomycin-producing microorganism Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350. J. Bacteriol. 190 (11), 4050–4060. doi:10.1128/jb.00204-08
Onaka, H. (2017). Novel antibiotic screening methods to awaken silent or cryptic secondary metabolic pathways in actinomycetes. J. Antibiot. 70 (8), 865–870. doi:10.1038/ja.2017.51
Oren, A., and Garrity, G. M. (2021). Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 71 (10). doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.005056
Oren, A., Arahal, D. R., Rosselló-Móra, R., Sutcliffe, I. C., and Moore, E. R. B. (2021). Emendation of Rules 5b, 8, 15 and 22 of the International Code of nomenclature of prokaryotes to include the rank of phylum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 71 (6). doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.004851
Paulus, C., Rebets, Y., Tokovenko, B., Nadmid, S., Terekhova, L. P., Myronovskyi, M., et al. (2017). New natural products identified by combined genomics-metabolomics profiling of marine Streptomyces sp. MP131-18. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 42382. doi:10.1038/srep42382
Pei, S., Xie, F., Zhang, R., and Zhang, G. (2021). Complete genome sequence of Janibaecter indicus YB324 from an Atlantic marine sediment. Mar. Genomics 58, 100833. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2020.100833
Pelizzola, M., and Ecker, J. R. (2011). The DNA methylome. FEBS Lett. 585 (13), 1994–2000. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.10.061
Poynton, E. F., van Santen, J. A., Pin, M., Contreras, M. M., McMann, E., Parra, J., et al. (2025). The Natural Products Atlas 3.0: extending the database of microbially derived natural products. Nucleic Acids Res. 53 (D1), D691–D699. doi:10.1093/nar/gkae1093
Price, B., Adamidis, T., Kong, R., and Champness, W. (1999). A Streptomyces coelicolor antibiotic regulatory gene, absB, encodes an RNase III homolog. J. Bacteriol. 181 (19), 6142–6151. doi:10.1128/jb.181.19.6142-6151.1999
Quach, N. T., Vu, T. H. N., Bui, T. L., Le, T. T. X., Nguyen, T. T. A., Ngo, C. C., et al. (2022). Genomic and physiological traits provide insights into ecological niche adaptations of mangrove endophytic Streptomyces parvulus VCCM 22513. Ann. Microbiol. 72 (1), 27. doi:10.1186/s13213-022-01684-6
Rabbani, B., Tekin, M., and Mahdieh, N. (2014). The promise of whole-exome sequencing in medical genetics. J. Hum. Genet. 59 (1), 5–15. doi:10.1038/jhg.2013.114
Ramesh, C., Anwesh, M., Alessia, T., Giuffrida, D., La Tella, R., Chiaia, V., et al. (2024). Genome and compound analysis of sioxanthin-producing marine actinobacterium Micromonospora sp. nov. Strain SH-82 isolated from sponge Scopalina hapalia. Curr. Microbiol. 81 (9), 298. doi:10.1007/s00284-024-03812-8
Salam, N., Jiao, J. Y., Zhang, X. T., and Li, W. J. (2020). Update on the classification of higher ranks in the phylum Actinobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 70 (2), 1331–1355. doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.003920
Sandoval-Powers, M., Králová, S., Nguyen, G. S., Fawwal, D. V., Degnes, K., Lewin, A. S., et al. (2021). Streptomyces poriferorum sp. nov., a novel marine sponge-derived actinobacteria species expressing anti-MRSA activity. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 44 (5), 126244. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2021.126244
Sarkar, G., and Suthindhiran, K. (2022). Diversity and biotechnological potential of marine actinomycetes from India. Indian J. Microbiol. 62 (4), 475–493. doi:10.1007/s12088-022-01024-x
Satam, H., Joshi, K., Mangrolia, U., Waghoo, S., Zaidi, G., Rawool, S., et al. (2023). Next-Generation sequencing technology: current trends and advancements. Biology 12 (7), 997. doi:10.3390/biology12070997
Schatz, A., Bugie, E., Waksman, S. A., Hanssen, A. D., Patel, R., and Osmon, D. R. (2005). The classic: streptomycin, a substance exhibiting antibiotic activity against Gram-positive and Gram-Negative bacteria. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 437, 3–6. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000175887.98112.fe
Schulze, C. J., Donia, M. S., Siqueira-Neto, J. L., Ray, D., Raskatov, J. A., Green, R. E., et al. (2015). Genome-directed lead discovery: biosynthesis, structure elucidation, and biological evaluation of two families of polyene macrolactams against Trypanosoma brucei. ACS Chem. Biol. 10 (10), 2373–2381. doi:10.1021/acschembio.5b00308
Siro, G., Donald, L., and Pipite, A. (2023). The diversity of deep-sea actinobacteria and their natural products: an epitome of curiosity and drug discovery. Diversity 15 (1), 30. doi:10.3390/d15010030
Skinnider, M. A., Merwin, N. J., Johnston, C. W., and Magarvey, N. A. (2017). PRISM 3: expanded prediction of natural product chemical structures from microbial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 45 (W1), W49-W54–W54. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx320
Stackebrandt, E., Rainey, F. A., and Ward-Rainey, N. L. (1997). Proposal for a new Hierarchic classification system, actinobacteria classis nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 47 (2), 479–491. doi:10.1099/00207713-47-2-479
Su, S., Liao, L., Yu, Y., Zhang, J., and Chen, B. (2019). Genomic data mining of an Antarctic deep-sea actinobacterium, Janibacter limosus P3-3-X1. Mar. Genomics 48, 100684. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2019.04.009
Sung, A. A., Gromek, S. M., and Balunas, M. J. (2017). Upregulation and identification of antibiotic activity of a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. via co-cultures with human pathogens. Mar. Drugs 15 (8), 250. doi:10.3390/md15080250
Teo, W. F. A., Wee, W. Y., Choo, S. W., and Tan, G. Y. A. (2015). Draft genome sequence of a marine actinobacteria Sciscionella strain SE31. Mar. Genomics 20, 11–12. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2014.12.006
Udwary, D. W., Zeigler, L., Asolkar, R. N., Singan, V., Lapidus, A., Fenical, W., et al. (2007). Genome sequencing reveals complex secondary metabolome in the marine actinomycete Salinispora tropica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104 (25), 10376–10381. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700962104
Ulanova, D., Uenaka, Y., Sakama, M., and Sakurai, T. (2020). Draft genome sequence of Salinispora sp. strain H7-4, isolated from deep-sea sediments of the Shikoku basin. Microbiol. Resour. Announc 9 (45), e00834-20. doi:10.1128/mra.00834-20
Van Lanen, S. G., and Shen, B. (2006). Microbial genomics for the improvement of natural product discovery. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9 (3), 252–260. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2006.04.002
Wang, Z., Gerstein, M., and Snyder, M. (2009). RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10 (1), 57–63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484
Widada, J., Damayanti, E., Herdini, C., Wijayanti, N., Hosoyama, A., Yamazoe, A., et al. (2023). Draft genome sequence of the marine-derived, anticancer compound-producing bacterium Streptomyces sp. strain GMY01. Microbiol. Resour. Announc 12 (6), e0136620–01320. doi:10.1128/mra.01366-20
Williams, S., and Vickers, J. (1988). “Detection of actinomycetes in the natural environment: problems and perspectives,” in In biology of actinomycetes '88. Editors Y. Okami, T. Beppu, and H. Ogawara (Tokyo: Japan Scientific Societies Press), 265–270.
Xie, Y., Chen, J., Wang, B., Chen, T., Chen, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Activation and enhancement of caerulomycin A biosynthesis in marine-derived Actinoalloteichus sp. AHMU CJ021 by combinatorial genome mining strategies. Microb. Cell Fact. 19 (1), 159. doi:10.1186/s12934-020-01418-w
Xiong, Z. Q., and Wang, Y. (2012). Draft genome sequence of marine-derived Streptomyces sp. strain AA0539, isolated from the Yellow Sea, China. J. Bacteriol. 194 (23), 6622–6623. doi:10.1128/jb.01646-12
Xu, X. N., Chen, L. Y., Chen, C., Tang, Y. J., Bai, F. W., Su, C., et al. (2018). Genome mining of the marine actinomycete Streptomyces sp. DUT11 and discovery of tunicamycins as anti-complement agents. Front. Microbiol. 9, 1318. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.01318
Yang, Z., He, J., Wei, X., Ju, J., and Ma, J. (2020). Exploration and genome mining of natural products from marine Streptomyces. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104 (1), 67–76. doi:10.1007/s00253-019-10227-0
Yang, X., Zhu, Z. H., Ji, X., Liu, Z. M., Zhang, H., and Wei, B. (2021). Complete genome sequence of Micromonospora craniellae LHW63014T, a potential metal ion-chelating agent producer. Mar. Genomics 57, 100830. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2020.100830
Zdouc, M. M., Blin, K., Louwen, N. L. L., Navarro, J., Loureiro, C., Bader, C. D., et al. (2025). MIBiG 4.0: advancing biosynthetic gene cluster curation through global collaboration. Nucleic Acids Res. 53 (D1), D678–D690. doi:10.1093/nar/gkae1115
Zhang, H., Boghigian, B. A., Armando, J., and Pfeifer, B. A. (2011). Methods and options for the heterologous production of complex natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 28 (1), 125–151. doi:10.1039/C0NP00037J
Zhang, B., Wang, K. B., Wang, W., Bi, S. F., Mei, Y. N., Deng, X. Z., et al. (2018). Discovery, biosynthesis, and heterologous production of Streptoseomycin, an anti-microaerophilic bacteria macrodilactone. Org. Lett. 20 (10), 2967–2971. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01006
Zhao, B., Liao, L., Yu, Y., and Chen, B. (2017). Complete genome of Brachybacterium sp. P6-10-X1 isolated from deep-sea sediments of the Southern Ocean. Mar. Genomics 35, 27–29. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2017.04.001
Zhu, J., Xie, Y., Li, Y., Yang, Y., Li, C., Huang, D., et al. (2022). Complete genome sequence of Streptomyces malaysiensis HNM0561. a Mar. sponge-associated actinomycete Prod. malaymycin mccrearamycin E. Mar Genomics 63, 100947. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2022.100947
Keywords: marine ecosystem, marine Actinomycetota, omics approaches, drug discovery, culture-independent analysis
Citation: Narsing Rao MP, Quadri SR, Sathish M, Quach NT, Li W-J and Thamchaipenet A (2025) Exploring omics strategies for drug discovery from Actinomycetota isolated from the marine ecosystem. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1634207. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1634207
Received: 23 May 2025; Accepted: 04 August 2025;
Published: 15 August 2025.
Edited by:
Saravana Kumar Pachaiyappan, Westlake University, ChinaReviewed by:
Govindarajan Ganesan, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaBungonsiri Intra, Mahidol University, Thailand
Copyright © 2025 Narsing Rao, Quadri, Sathish, Quach, Li and Thamchaipenet. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Arinthip Thamchaipenet, YXJpbnRoaXAudEBrdS5hYy50aA==; Wen-Jun Li, bGl3ZW5qdW4zQG1haWwuc3lzdS5lZHUuY24=
 Manik Prabhu Narsing Rao
Manik Prabhu Narsing Rao Syed Raziuddin Quadri
Syed Raziuddin Quadri Manda Sathish
Manda Sathish Ngoc Tung Quach
Ngoc Tung Quach Wen-Jun Li
Wen-Jun Li Arinthip Thamchaipenet
Arinthip Thamchaipenet