- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacy Laboratory, The First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Baotou, China
- 2School of Pharmacy, The University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 3School of Pharmacy, Key Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology and Drug Evaluation (Yantai University), Ministry of Education, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Drug Delivery System and Biotech Drugs in Universities of Shandong, Yantai University, Yantai, China
Sea buckthorn is a botanical drug with a long history of medicinal use in treating digestive diseases. It is considered “a food with medicinal and edible homology”, meaning it has various application scenarios. Sea buckthorn is known to have numerous bioactivities, such as anti-inflammatory, flora-regulating, immunoregulating, intestinal protective, and anticancer properties, as a potential natural therapy for digestive diseases. In both in vitro and in vivo experiments, ranging from cell lines to animal models and human patients, sea buckthorn has shown beneficial effects on symptoms associated with digestive disease. This study reviews the main bioactive metabolites of sea buckthorn and discusses their pharmacological effects and mechanisms in treating digestive diseases. In particular, we highlight bioactive metabolites isolated from sea buckthorn, their effects on inflammation, cancer, anti-Helicobacter pylori, radiation, and gut microbiota, and their molecular mechanisms of action in clinical applications. This article provides insight into the benefits of sea buckthorn, encouraging academic research in this area and the expansion of sea buckthorn-based applications for digestive diseases.
1 Introduction
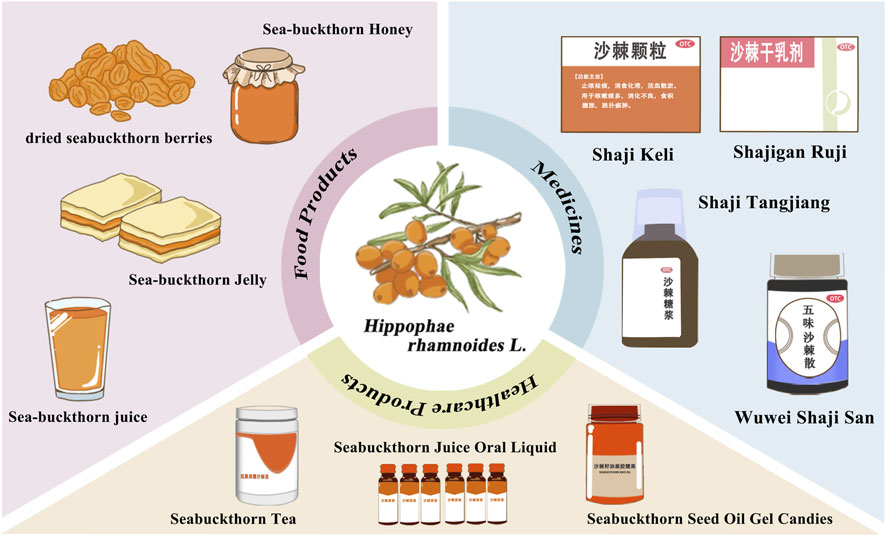
Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) is a deciduous shrub or small tree belonging to the family Elaeagnaceae and is known for its inducible rooting characteristics (Olas, 2018). The species grows widely in temperate, cold temperate, and subalpine regions of the Eurasian continent and is also widely cultivated in countries such as China (Singh, 2022). There are six species and eight subspecies in China, named the “Kingdom of Sea Buckthorn” (Mei et al., 2023). Due to its ability to thrive in the harshest environments, it is widespread in northwestern, northeastern, and Inner Mongolian China. In addition, its high tolerance to salt and drought can help improve the soil and prevent land degradation, which is essential for local ecology and economic development (Wang et al., 2019). In 2002, the National Health Commission of China classified sea buckthorn as a food with both medicinal and edible homology (Teng et al., 2024). Sea buckthorn has been extensively developed into functional foods and dietary supplements worldwide due to its pleasant taste and many health benefits, such as antioxidant, anti-radiation, and sea buckthorn effects (Figure 1). Sea buckthorn has gained increasing attention recently as a “Gold Bush” with significant economic, ecological, medicinal, and food value due to its diverse pharmacological and nutritional functions.
The digestive system, which encompasses the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder, facilitates the breakdown of food into absorbable nutrients. Digestive diseases encompass a broad range of conditions that affect the gastrointestinal tract, including gastroenteritis, precancerous gastric lesions, hepatitis, liver fibrosis, digestive cancer, and other chronic diseases (Smyth et al., 2020; Li et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2024; Mehta et al., 2024). In 2019, the global incidence of digestive diseases was considerable, with an age-standardized incidence rate of 95,582 per 100,000 person-years across 204 countries and territories (Wang Y. et al., 2023). The findings indicate that digestive diseases contribute significantly to the global healthcare burden, with over one-third of all cases having a digestive etiology worldwide (Wang F. et al., 2023). Current treatments for digestive diseases include GI surgery, gastric mucosal protective agents, antibacterial agents, and other therapeutic agents. However, these treatments often require long-term use and are associated with high recurrence rates, invasion, and adverse effects. In recent years, with the emergence of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine, many studies have shown that botanical drug has the following characteristics: stable pharmacological effects, high safety, and low drug resistance (Chen L. et al., 2023). Sea buckthorn contains nearly 200 known bioactive metabolites, including polysaccharides, flavonoids, vitamins, polyphenols, fatty acids, and phenolic metabolites. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine since the Tang Dynasty, dating back over 1000 years (Suryakumar and Gupta, 2011; Li C. et al., 2018; Żuchowski et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2021). Tibetans used sea buckthorn as a medicine to treat lung and stomach diseases, and Mongolians used sea buckthorn as a sacred food, calling it “the emperor’s painstaking efforts” for medical treatment and food (Niesteruk et al., 2013; Pundir et al., 2021). Modern pharmacological studies have demonstrated that sea buckthorn has anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and digestive system regulatory properties in both animal and human in vivo studies (Tkacz et al., 2019; Masoodi et al., 2020; Geng et al., 2022; Qin Q. et al., 2024). Sea buckthorn is a valuable tool for preventing and treating digestive diseases.
However, in the existing and available literature, no comprehensive reviews focus solely on sea buckthorn for treating digestive diseases. Several published review articles have focused on the effectiveness of sea buckthorn in preventing and treating metabolic syndrome, radiation-induced nausea and vomiting, and its potential applications in female reproduction (Olas, 2016; Chen et al., 2023d; Mihal et al., 2023; Palatty et al., 2024). Therefore, in this article, we review recent advances in the study of natural bioactive metabolites derived from sea buckthorn and their effects on preventing and treating gastric precancerous lesions, colitis, dyspepsia, and other digestive diseases.
2 Literature review
2.1 Search strategy
We searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, WanFang, and CNKI databases from 1970 to March 2025. The search terms used were combined text and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) search strategy was used to search the above databases: (“sea buckthorn” OR “Hippophae rhamnoides”) AND (“digestive” OR “liver” OR “gastric” OR “intestines” OR “pancreas” OR “gallbladder” OR “cancer” OR “tumor” OR“ gastritis” OR “enteritis” OR “gastroenteritis” OR “Helicobacter pylori” OR “liver fibrosis” OR “precancerous gastric lesions” OR “hepatitis” OR “inflammation”). An equivalent translation of the same search terms was used to search Chinese databases. We considered only original research and excluded reviews, surveys, conference abstracts, and editorials. This study adhered to the guidelines outlined by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (Page et al., 2021b; Page et al., 2021a)
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Among all studies describing associations between sea buckthorn and digestive diseases, we applied the following eligibility criteria: 1) belongs to digestive system diseases (Wang Y. et al., 2023); 2) treatment drug is sea buckthorn metabolites; 3) enough details about sea buckthorn metabolites treat digestive system diseases.
2.3 Data collection
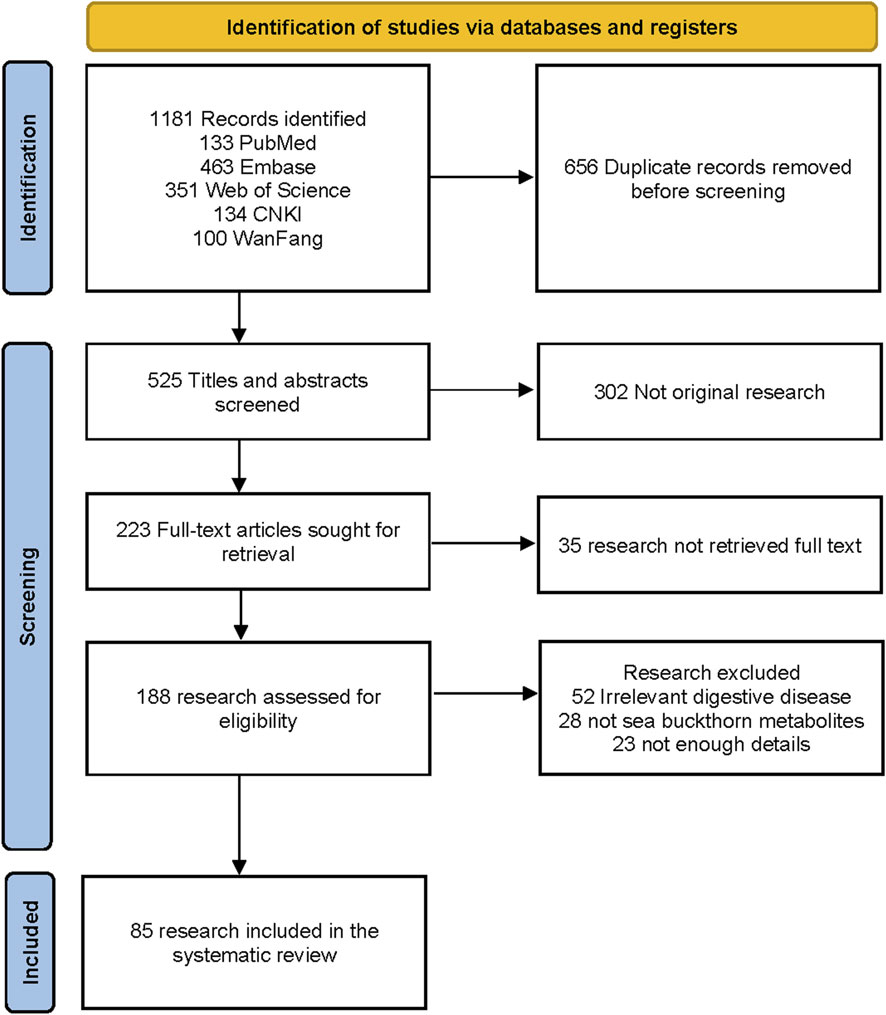
Two researchers independently screened the records and extracted the data into a dedicated spreadsheet. Discrepancies between the two researchers were resolved by consensus, and if consensus could not be reached, a third reviewer was consulted. A PRISMA flow diagram was used to illustrate the literature search process and the final selection of studies (Figure 2). Data were extracted from the included studies using a standardized, predefined template. The extracted information features are summarized in Tables 1, 3–5.
2.4 Study selection
Figure 2 shows the PRISMA diagram for selecting original research to be included in the analysis. The literature search resulted in 1181 records, of which 656 were duplicates and removed. We excluded 302 records that were not original study, 35 research without full text, 52 irrelevant to digestive disease, 28 not Sea buckthorn metabolites, and 23 with unclear details. The literature review included 85 research.
3 Traditional application of sea buckthorn on digestive diseases
3.1 Digestive diseases understanding in traditional Chinese medicine
The Chinese medical tradition is known for being one of the oldest and most distinctive systems of medicine in the world, with a written history stretching back nearly 3,000 years (Yu and Amri, 2016). Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) takes a holistic approach to health and disease, emphasizing the interconnectedness of different body systems (Zhang J. et al., 2024). In Chinese medicine, digestive diseases are attributed to imbalances within the stomach, liver, and spleen. Digestive disorders are associated with spleen-stomach deficiency syndrome, Dampness-Heat syndrome, and Liver Qi stagnation syndrome. Mongolian medicine’s systematic theoretical system is based on the balance among three roots: Heyi, Xila, and Badagan (Dao et al., 2021). When the balance is disrupted, any of these elements may experience excessive increase or depletion, resulting in loss of coordination and pathological conditions. The fundamental theory of Tibetan Medicine is an elements theory consisting of “air” “fire” and “water” (Li Q. et al., 2018). According to Tibetan medicine, the human body is connected by various parts. Balance is a crucial principle in the three systems of TCM, Tibetan, and Mongolian medicine; Digestive diseases are viewed as a consequence of imbalance.
3.2 Traditional approaches of sea buckthorn in digestive diseases
Sea buckthorn has been used in traditional medicine across Asia and Europe for many years (Olas, 2018). Sea buckthorn was being used as a medicinal remedy, with the earliest documentation found in the Tibetan medical classic “Somaratsa” in the first half of the eighth century and the “Medical Canon in Four Sections” describes the medicinal use of sea buckthorn (Wang, 2022). Chinese folklore treatment books record that Sea buckthorn affects the respiratory and digestive systems (Guo, 2019). For a long time, it has been used to treat slow digestion and stomach malfunction. According to “Chinese Pharmacopeia,” Sea buckthorn is characterized by acidity, astringent taste, and mild nature and belongs to the spleen, stomach, lung, and heart meridian (Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, 2020). It is known for its ability to promote blood circulation and disperse stasis, resolving phlegm, clearing the chest, and strengthening the spleen and stomach. The Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicine records that sea buckthorn has the effects of promoting fluid production and quenching thirst, clearing heat, and stopping diarrhea (Peng, 1993). According to the Tibetan medical classics “Yue wang yao zhen” and “Medical Canon in Four Sections,” sea buckthorn is characterized by strengthening the spleen and nourishing the stomach, breaking blood stasis and treating the blood-related conditions, removing phlegm and benefiting the lungs, and facilitating digestion (Suryakumar and Gupta, 2011). In Mongolian medicine, sea buckthorn is recorded as “sharp and light, which is beneficial for treating “ba da gan” of the lungs and stomach to treat colitis and enterocolitis for humans and animals (Guo, 2019; Li X. et al., 2021). In Russia, sea buckthorn is mainly used to treat gastrointestinal disorders and skin diseases (Li X. et al., 2021). Since antiquity, sea buckthorn has been a classic treatment for digestive disorders.
4 Sea buckthorn extracts on digestive diseases
4.1 Clinical use of sea buckthorn
Recently, sea buckthorn has attracted the attention of researchers due to its superior biological activities such as anti-tumor, hypoglycemic, immunomodulatory, and other activities (Ying, 2024). Since the 1940s, Russian scientists have been studying the bioactive metabolites in the berries, leaves, and bark of sea buckthorn. This research has contributed to the development of sea buckthorn-based foods and radiation protection creams for Russian cosmonauts (Krejcarová et al., 2015). China was the first to officially recognize sea buckthorn as a medicinal substance, including it in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia in 1977 (Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, 1977). Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a disease involving superficial inflammation and ulceration of the mucosal lining of the bowel. This leads to symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and cramping (Gajendran et al., 2019). In addition, sea buckthorn polysaccharides can ameliorate intestinal barrier damage and regulate intestinal microbiota and their metabolites (Yuan et al., 2024). The above study demonstrates that sea buckthorn holds significant potential for the treatment of UC. Chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) is recognized as a precursor to gastric cancer. Research has shown that various metabolites in sea buckthorn exhibit therapeutic effects on CAG. Sea buckthorn procyanidins have been found effective against H. pylori, a key factor in CAG development (Guo, 2008). Sea buckthorn oil, known for its antacid and gastric barrier properties, is used in the treatment of CAG (Yan, 2002). Additionally, sea buckthorn pulp oil has been reported to alleviate gastric discomfort and ulcers by reducing mucus production, inhibiting acid secretion, and suppressing gastric motility (Xing, 2012). Moreover, sea buckthorn extracts have been shown to treat H. pylori-induced gastritis by downregulating the mRNA expression of the inflammatory factors NF-κB-p65 and IκB-α (Ying, 2022). Oxidative stress is associated with numerous health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and aging, and also plays a significant role in the development of gastrointestinal diseases. Sea buckthorn leaf extract (SBLE) exhibits well antioxidant properties and has potential as a natural additive to reduce the degradation of sea buckthorn oil (SBO), as well as to provide synergistic health benefits (Lyu et al., 2022). This study confirmed that sea buckthorn berries, demonstrating biological potency through anti-α-glucosidase and anti-lipase activities, could serve as raw materials for developing innovative functional foods and nutraceuticals (Tkacz et al., 2019). Furthermore, this observational study suggests that aqueous and hydroalcoholic extracts of sea buckthorn leaves have marked cytoprotective, and antibacterial activities (Upadhyay et al., 2010). Cancer is a significant social, public health, and economic challenge in the 21st century, accounting for nearly one in six deaths (16.8%) worldwide (Bray et al., 2024). According to global cancer statistics from 2020, gastric cancer ranks fifth in incidence and fourth in mortality, posing a serious threat to human health and life (Raza and Bhatt, 2023; Bray et al., 2024). A growing number of in vitro and in vivo animal studies have confirmed the anticancer activity of sea buckthorn. Several metabolites in sea buckthorn, mainly phenolic metabolites such as procyanidins and flavonoids, have been shown to benefit cancer prevention significantly (Wang et al., 2014; Masoodi et al., 2020). Isorhamnetin, a metabolite derived from sea buckthorn, may target PI3K and block the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. It can significantly inhibit autophagy in gastric cancer cells under hypoxic conditions, suppress cell proliferation, reduce mitochondrial membrane potential, and promote mitochondria-mediated apoptosis (Li C. et al., 2021). Sea buckthorn procyanidins have been identified as promising inhibitors of fatty acid synthase (FAS), capable of inducing apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells and potentially aiding in the prevention or treatment of breast cancer (Wang et al., 2014). Sea buckthorn oil can inhibit the proliferation of human gastric cancer HGC-27 cells by activating the P53 signaling pathway and promote apoptosis, thereby exerting an anti-tumor effect (Lu-gen and Xiao-xia, 2021). A recent study suggests that sea buckthorn leaf extract may induce apoptosis and inhibit the rapid proliferation of rat C6 glioma cells (Kim et al., 2017). Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the mainstays of cancer treatment but are associated with various side effects, including cardiotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, myelosuppression, neurotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, gastrointestinal toxicity, mucositis, and alopecia, which severely affect the quality of life of cancer patients (Liu Y.-Q. et al., 2021). Natural products have a wide chemical diversity and flexible biological properties that make them well-suited to adjuvant therapy to reduce the side effects of cancer treatment. The study indicates that Sea buckthorn extract can protect mitochondrial and genomic DNA from radiation-induced damage (Shukla et al., 2006). Polyphenols and flavonoids are thought to be responsible for scavenging free radicals and protecting DNA. In addition, sea buckthorn extract RH-3 has been shown to inhibit the Fenton reaction and radiation-mediated generation of hydroxyl radicals in vitro, superoxide anion-mediated nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction, and FeSO4-mediated lipid peroxidation in mouse liver (Goel et al., 2002). Sea buckthorn holds significant potential for the prevention and treatment of digestive diseases. However, further systematic research is needed to identify its active metabolites and clarify the underlying mechanisms. These findings support the development of the sea buckthorn industry and its future clinical applications (Figure 3).
5 Material basis of sea buckthorn
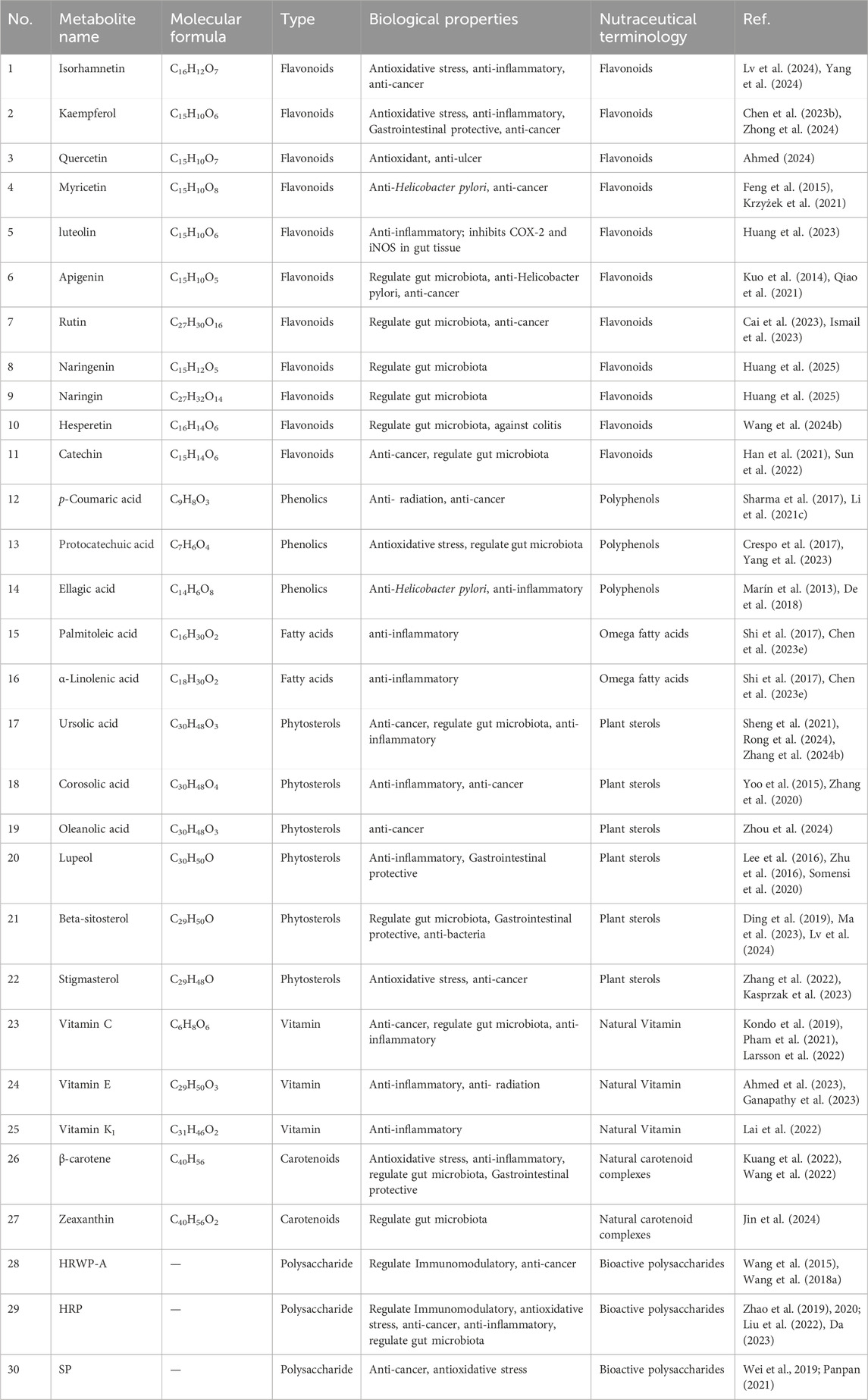
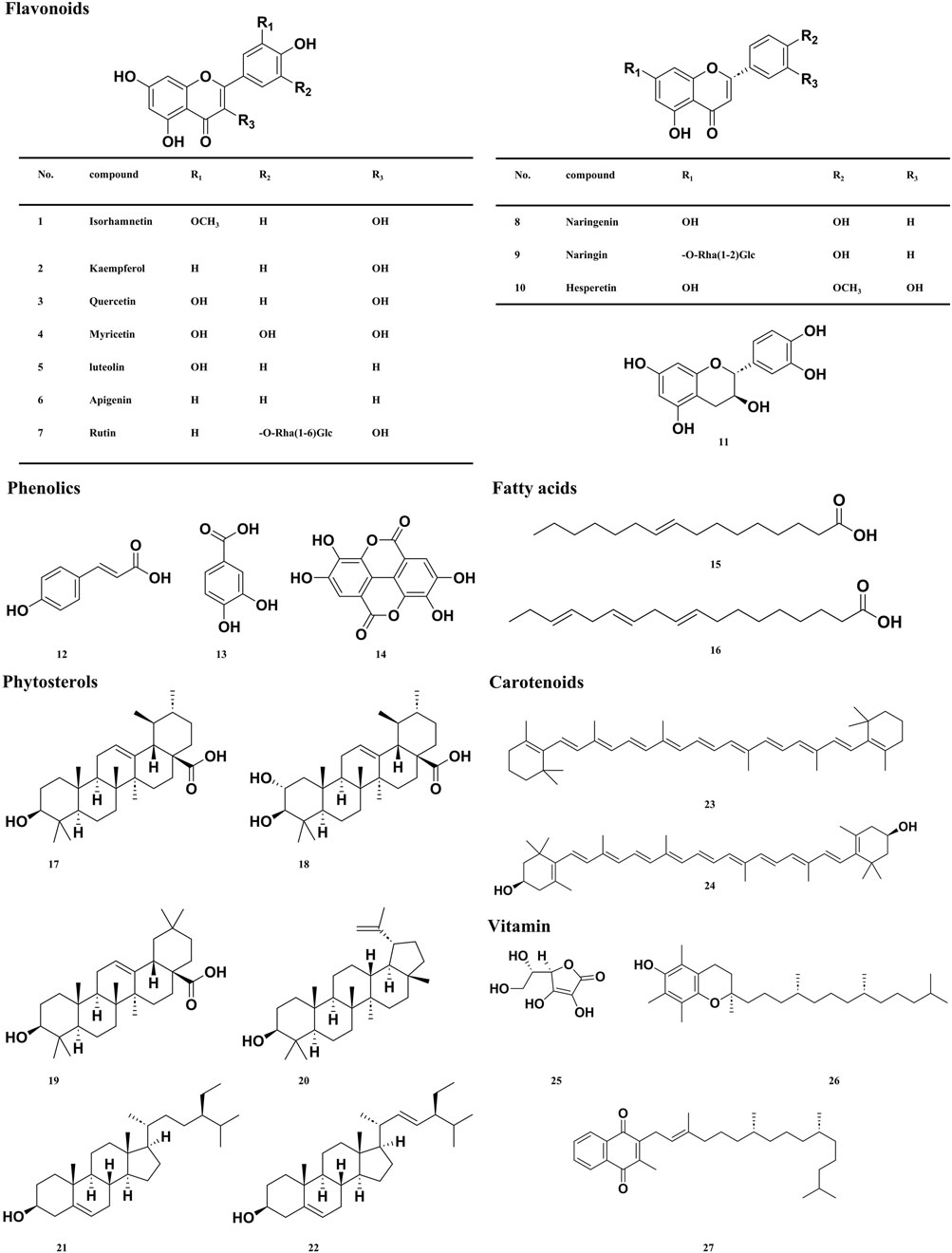
Sea buckthorn berries, seeds, and leaves have been reported to contain more than 190 bioactive metabolites, including 95 types of flavonoids (Liu S. et al., 2021; Zu Fan, 2024), 17 types of phenolic acids (Zadernowski et al., 2005), ten types of tannins (Sheichenko et al., 1987; Yoshida et al., 1991), seven types of Triterpene, 11 types of fatty acids (Yang and Kallio, 2001; Zheng et al., 2017; Zielińska and Nowak, 2017), 15 types of vitamins (Chen et al., 2023d), and 17 types of phytosterols (Li et al., 2007), 28 types of polysaccharides metabolites (Teng et al., 2024), in addition to small amounts of amino acids, organic acids, and inorganic elements. We screened the active metabolites in sea buckthorn and identified 30 metabolites that have therapeutic effects on digestive system diseases, which are listed in Table 1. The corresponding structural formulas are presented in Figure 4.
5.1 Flavonoids and phenolic
Over 98% of the flavonoids in sea buckthorn fruits are flavonols, with Isorhamnetin accounting for 66%–72% of the total flavonols and Quercetin making up 25%–32% of the total flavonols (Tkacz et al., 2020). Flavonoids are essential bioactive in sea buckthorns and have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They could modulate T cell differentiation, alter gut microbiota, and modulate cytokines. Sea buckthorn flavonoids extract can regulate the TAK1/p38MAPK/p65NF-κB pathway to effectively ameliorate liver injury in mice with alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and regulate the composition of the gut microbiota (Zhao et al., 2022). Plant phenolic acids are an essential metabolite of the human diet and exhibit tremendous antioxidant properties, which could significantly reduce the risk of many oxidative stress-related diseases, such as cancer. Phenolic acids treat inflammatory bowel disease by improving the barrier function of the intestinal mucosa, reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting excessive activation of the immune response, and regulating the balance of the intestinal microbiota (Lu and Han, 2024). In plant chemistry, tannins are an important subgroup of phenolic metabolites. Tannins are commonly found in the human diet and are beneficial for health; they are prevalent in plant foods, particularly in fruits, nuts, and vegetables. Tannings’ anticarcinogenic and antimutagenic potential may be attributed to their antioxidant properties, which help protect against cellular oxidative damage, including lipid peroxidation (Chung et al., 1998). We summarize the material basis of Sea buckthorn in preventing and treating digestive diseases, and the relevant details are shown in Table 1.
5.2 Fatty acids, carotenoids and phytosterols
Fatty acids are crucial metabolites of the human diet, and their biological activities influence the metabolism, function, and responsiveness of cells and tissues to hormonal and other signals. Fatty acids are a primary energy source and signaling molecules, affecting the gut microbiota and immune responses. Palmitoleic acid (PLA) is the primary metabolite of sea buckthorn pulp oil, while alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is the main metabolite of sea buckthorn seed oil. Pretreatment with PLA and ALA prolonged survival time after radiation-induced acute intestinal injury (Shi et al., 2017). The dietary palmitoleic acid enhanced gut mucosal barriers, reduced inflammatory cell infiltration and the expression of TNF-α and IL-6, and improved the pharmacological effects of anti-TNF-α therapy in both acute and chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) mouse models. β-carotene could help protect against food allergies by enhancing intestinal epithelial barrier function and regulating gut microflora (Kuang et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). Zeaxanthin increased the abundance of probiotics and decreased the abundance of pathogens, thereby improving the dysbiosis of enteric microbial communities and enhancing the structure and diversity of the gastrointestinal microbiome in mice with obesity caused by excessive fat consumption (Jin et al., 2024). Phytosterols are naturally occurring bioactive metabolites in plants that protect against various chronic diseases, including liver disorders, diabetes, and cancer. Studies have shown that a diet rich in phytosterols may reduce cancer risk by up to 20% (Suryamani et al., 2022).
5.3 Vitamin and polysaccharides
Sea buckthorn is rich in various vitamins, especially vitamin C, and has been called the “King of VC”. In addition, sea buckthorn berries contain vitamin A, vitamin E, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 (Wang, 2022). Recent studies have shown that sea buckthorn polysaccharides provide significant benefits for gut health, including the reduction of cell death and lower levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the intestine (Shen et al., 2021). Additionally, in vitro antioxidant studies have demonstrated that sea buckthorn polysaccharides effectively scavenge superoxide anions and DPPH radicals, particularly ABTS radicals (Wang H. et al., 2024).
5.4 Differences in active metabolites between Hippophae rhamnoides L. Subspecies
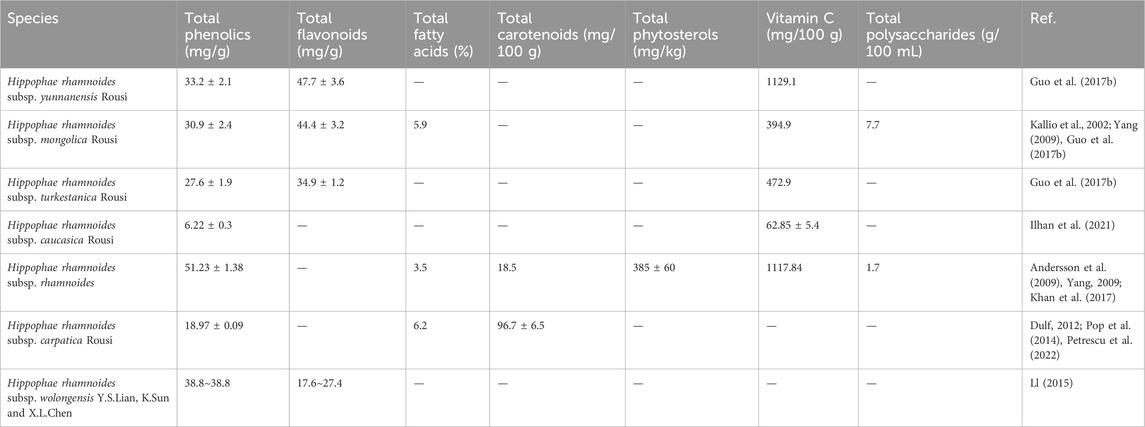
The H. rhamnoides L. (Elaeagnaceae) comprises eight accepted subspecies (subsp): subsp. carpatica Rousi, subsp. caucasica Rousi, subsp. mongolica Rousi, subsp. rhamnoides, subsp. wolongensis Y.S.Lian, K.Sun and X.L.Chen, subsp. turkestanica Rousi, subsp. yunnanensis Rousi (Hippophae rhamnoides, 2025). The active metabolites in sea buckthorn vary among different subspecies, as illustrated in Table 2. Significantly, the total amounts of phenolics in the fruits of subsp.rhamnoides and subsp.caucasica differ from each other. Specifically, the total phenolics content is 51.23 ± 1.38 mg/g compared to 6.22 ± 0.3 mg/g. Extracellular antioxidant properties is closely linked to total phenols and flavonoids in the extract, whereas cellular antioxidant properties and antiproliferative effects on HepG2 cells are significantly associated with total phenolic acids and flavonoid aglycones (Guo et al., 2017b). It suggests that the subsp. yunnanensis Rousi has the highest phytochemical content (total flavonoids: 47.7 ± 3.6 mg/g, total phenolics: 33.2 ± 2.1 mg/g), along with significant antioxidant and antiproliferative effects. In comparison to the mongolica Rousi, and rhamnoides, the subsp.carpatica Rousi has the highest overall fatty acid content. Research has shown that the fatty acids in sea buckthorn have anti-inflammatory properties that help protect the mucosa of the digestive tract (Shi et al., 2017). The subsp.yunnanensis maximizes vitamin C content, making it rich in antioxidants and possessing anti-inflammatory properties (Guo et al., 2017b). The subspecies wolongensis is a newly identified subspecies found in the transitional zone between the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau in China and the Sichuan Basin (LL, 2015). This subspecies has a lower total flavonoid content and a higher total phenolic content compared to other subspecies. The cool, humid, high-altitude environments where this species predominantly occurs are likely more conducive to the accumulation of phenolic acids than flavonoids. The levels of metabolites in sea buckthorn vary between subspecies due to their origins and the conditions in which they grow. In contrast, the subspecies mongolica often exhibit higher total flavonoid content. This is due to their adaptation to stronger ultraviolet radiation and drier environments, where flavonoids act as protectants against UV rays and serve as antioxidants.
6 Modern industrial development
Sea buckthorn is widely used in food, nutraceuticals, and plant-based medicines worldwide, renowned for its medicinal properties and rich nutritional benefits. The global sea buckthorn market size was valued at USD 347.56 million in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 381.40 million in 2024 to USD 837.26 million by 2032 (Sea Buckthorn Market Size, 2024). Today, sea buckthorn is cultivated in approximately 40 countries, covering a global production area of about 3 million hectares (Nayik and Gull, 2020). China, Russia, Canada, Mongolia, and Northern Europe account for almost 90% of the world’s sea buckthorn production. China is the leading producer of sea buckthorn globally, with over 10 million acres cultivated artificially and an additional 8 million acres in the wild. The processing and utilization of sea buckthorn fruit amounts to 80∼100 thousand tons annually, contributing to a total annual output value of 3.3–3.6 billion dollars in various sea buckthorn industries (Sea Buckthorn Professional Committee of China Society of Sand Control and Sand Industry, 2024). However, most sea buckthorns are insufficiently exploited, with a single-product structure and low value added (Yi, 2023). Various finished products have emerged with the development of modern sea buckthorn processing technologies (Zhang et al., 2023). To strengthen the sea buckthorn industry, improvements in the production system are essential. Innovative processing technologies must be developed, public awareness of sea buckthorn products needs to be increased, and its uses in food and medicine should be further promoted. In the context of food applications, sea buckthorn’s medicinal and nutritional properties—such as promoting digestion, relieving cough, and reducing phlegm, as recorded in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, 2020), make it a valuable metabolite for the development of various functional food products. These include breads, yogurts, jams, beverages, teas, and other formulations (Selvamuthukumaran and Khanum, 2014; Ghendov-Mosanu et al., 2020; Gâtlan and Gutt, 2021), which have been shown to stimulate appetite, boost energy levels (Chen A. et al., 2023), and enhance immune function (Dubey et al., 2023). During the COVID-19 pandemic, sea buckthorn was found to boost immunity and anti-coronavirus (Al Ibrahim et al., 2023). In the field of daily chemical products, the anti-ultraviolet, wound healing, anti-aging, and antioxidant properties of sea buckthorn are used to make cosmeceuticals, emulsions, and essential oils to protect the skin from the sun and repair skin damage (Koskovac et al., 2017; Zosimidou et al., 2023; Okamoto et al., 2024). In medicine, the bioactive metabolites in sea buckthorn are extracted to treat gastritis, indigestion, diabetes, cancer, stroke, and cardiovascular disease (Xu et al., 2011; Olas et al., 2018; Shen et al., 2021). For this reason, the development and application of sea buckthorn have significant medicinal and economic value.
7 Clinical studies
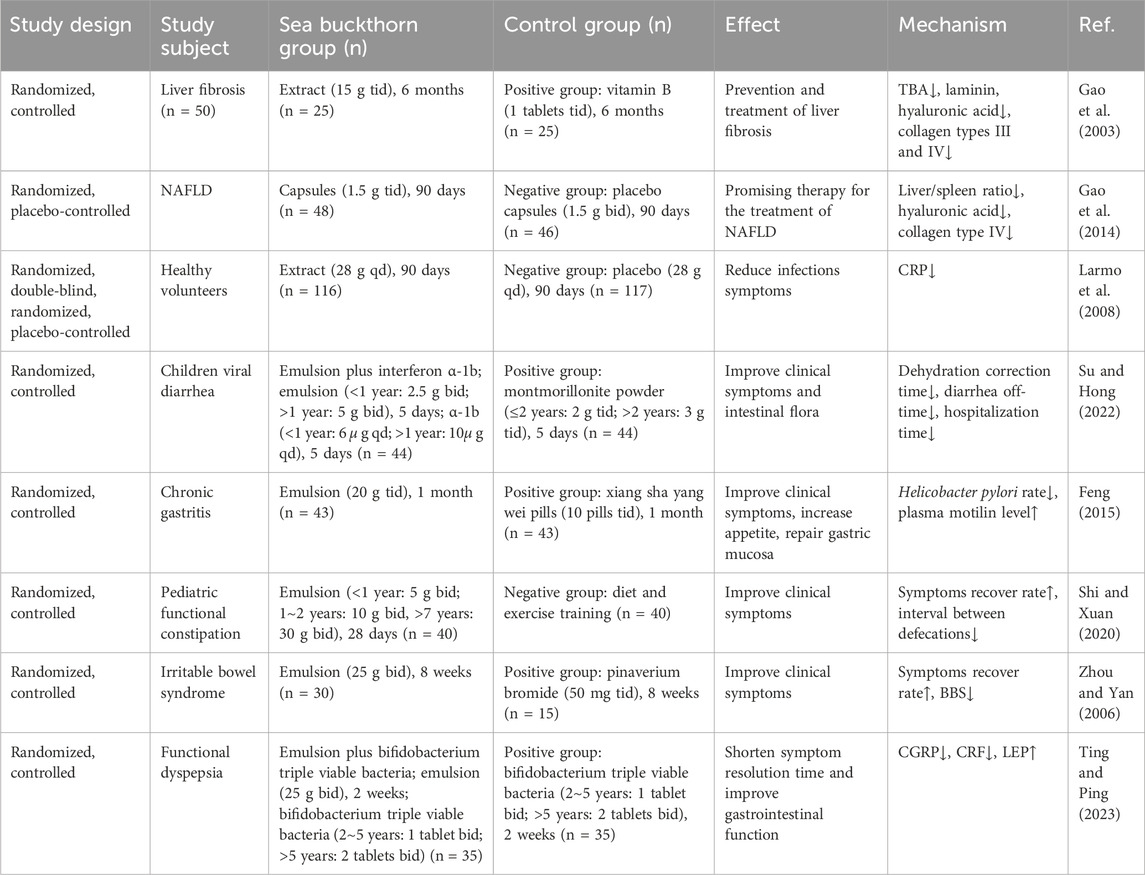
Several clinical controlled trials have shown that sea buckthorn, sea buckthorn extract, or sea buckthorn-related combination therapy can be beneficial in preventing and treating digestive diseases. Digestive diseases, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), viral diarrhea, chronic gastritis, and functional dyspepsia, significantly increase the economic burden of digestive diseases globally (Wang Y. et al., 2023). A large meta-analysis involving 9275 patients from Taiwan found that habitual cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, and betel chewing were associated with a 16.32-fold risk of esophageal cancer (Chuang et al., 2017). This highlights that an unhealthy diet plays a major role as a risk factor for developing digestive diseases, and considering that sea buckthorn is a great dietary supplement, it has great potential in preventing and treating digestive diseases. Digestive diseases are interrelated, necessitating a holistic approach for both prevention and treatment. We summarized eight relevant clinical studies involving 513 patients to clarify the clinical effects of sea buckthorn against digestive diseases. A study conducted on patients with liver fibrosis showed that sea buckthorn extract has anti-inflammatory effects that can reduce the level of inflammation in the body, reduce TNF-α, IL-6, total bile acid (TBA) concentration and significantly shortens the time for normalization of aminotransferases, thus sea buckthorn extract may be a hopeful drug for prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis (Gao et al., 2003). In addition, a study was conducted on people with NAFLD, and the results suggested that sea buckthorn capsules can significantly decrease the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), LDL-C, hyaluronic acid, collagen type IV and CT liver/spleen ratio, which may be further developed as a promising therapy for the treatment of NAFLD (Gao et al., 2014). One study showed that sea buckthorn can reduce the concentration of C-reactive protein (CRP), thereby reducing the risk of inflammation and cardiovascular diseases (Larmo et al., 2008). Two studies found that sea buckthorn emulsion may promote gastrointestinal motility and relieve symptoms of dyspepsia (Shi and Xuan, 2020; Ting and Ping, 2023). Additionally, a study found that sea buckthorn could reduce the clinical symptoms of chronic gastritis, increase appetite, repair the stomach lining, reduce and eliminate H. pylori, and increase motilin levels (Feng, 2015). In conclusion, sea buckthorn has demonstrated significant pharmacological effects in improving digestive symptoms, reducing the risk of liver damage, and treating functional dyspepsia. Table 3 provides more details on the clinical trials. While some studies used randomized designs, inadequate blinding procedures may have biased outcome assessments (Gao et al., 2014). Because there are few clinical studies on sea buckthorn for treating digestive system diseases, it is challenging to extract high-quality clinical trial evidence from them.
8 Vivo studies
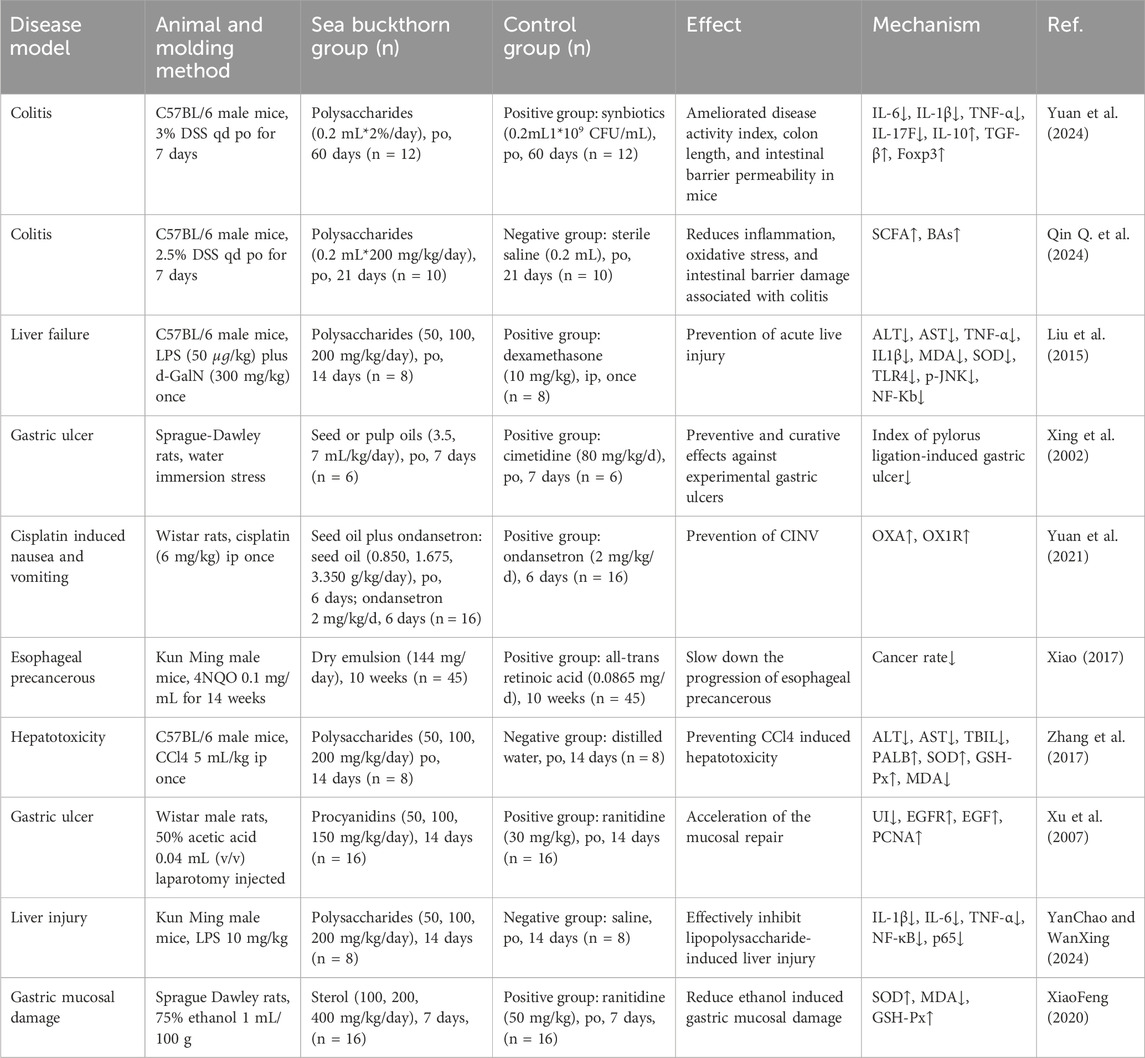
Studying the effects of pharmacological interventions in animal disease models is an essential scientific means in modern medicine to understand disease prevention and control laws. We have summarized ten relevant animal studies (Xing et al., 2002; Xu et al., 2007; Li R. J. et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2015; Xiao, 2017; Zhang et al., 2017; XiaoFeng, 2020; Yuan et al., 2021; Qin Q. et al., 2024; YanChao and WanXing, 2024; Yuan et al., 2024) to elucidate the preventive and therapeutic effects of sea buckthorn on digestive diseases and to provide evidence suppporting the use of sea buckthorn preparations in the daily prevention, early intervention, and clinical treatment of digestive diseases. Ulcerative colitis (UC) is characterized by chronic inflammation and ulceration of the intestinal inner lining, resulting in various symptoms (Ordás et al., 2012). While the exact mechanisms that cause the development of ulcerative colitis remain unknown, research has identified that the pathogenesis involves the release of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-17, which significantly drive the inflammatory response (Lee et al., 2018). In animal models of colitis, we found that sea buckthorn polysaccharides improved disease activity index, colon length, and intestinal barrier permeability (Yuan et al., 2024). Sea buckthorn polysaccharides may also reduce inflammation, oxidative stress, and intestinal barrier damage associated with colitis (Qin Q. et al., 2024). Specifically, sea buckthorn polysaccharides can inhibit the production of several inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-17F, closely related to the downregulation of the NF-κB pathway (Yuan et al., 2024). Recent studies indicate that patients with ulcerative colitis exhibit a disruption in the gut microbiota, characterized by a significant reduction in short-chain fatty acid (SCFA)-producing bacterial species (Wang Y. et al., 2018). Sequencing analysis of intestinal flora suggests sea buckthorn polysaccharides can significantly increase microbial metabolites SCFAs and BAs to correct dysbiosis in DSS-induced colitis in mice (Yuan et al., 2024). Acute liver failure is a rare but life-threatening critical illness that most commonly affects previously healthy adults in their 30s and presents unique clinical challenges (Bernal and Wendon, 2013). It has been well documented that TLR4 signaling plays an essential role in the pathogenesis of liver injury; downregulation of TLR4 could significantly decrease hepatic c-Jun and NF-κB expression and thus decrease TNF-α levels (Ben Ari et al., 2012). Sea buckthorn possesses anti-inflammatory activity that reduces TLR4 expression to protect against LPS/d-GalN-induced liver injury (Liu et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2017; YanChao and WanXing, 2024). The gastric mucosa (GM) is the first barrier and vital interface in the stomach that protects the host from the hydrochloric acid in gastric juice and defends against exogenous insults to the gastric tissues (Deng et al., 2023). Gastric mucosal injury is a chronic injury characterized by altered cell differentiation and is considered a precancerous lesion associated with gastric cancer (Jia et al., 2023). Existing animal models of gastric mucosal damage are mature and are mainly induced by water immersion stress, acetic acid, and ethanol. The study found that sea buckthorn extract is essential in healing acetic acid-induced gastric lesions, possibly by accelerating mucosal repair (Xu et al., 2007). The protective effect of sea buckthorn extract on the gastric mucosa was also observed in two other models of gastric mucosal injury (Xing et al., 2002; XiaoFeng, 2020). In addition to treating digestive diseases, sea buckthorn can prevent adverse medication reactions. Cisplatin-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) remains the main problem for cancer patients in the process of oncological treatment; approximately half of cancer patients experience nausea or vomiting, either because of chemotherapy or the cancer itself (Shin et al., 2022). The study found that sea buckthorn extract prevented cisplatin-induced vomiting in rats. This may be due to its role in increasing peripheral and central OXA and the expression of OX1R in the hypothalamus and brainstem (Yuan et al., 2021). Overall, sea buckthorn has substantial health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory, intestinal barrier protection, intestinal flora balance, and the prevention of drug side effects. This suggests that supplementation incorporating sea buckthorn-related preparations in the daily diet may be a new strategy for preventing and treating digestive diseases. Further details of the animal-level experiments can be found in Table 4.
9 Vitro studies
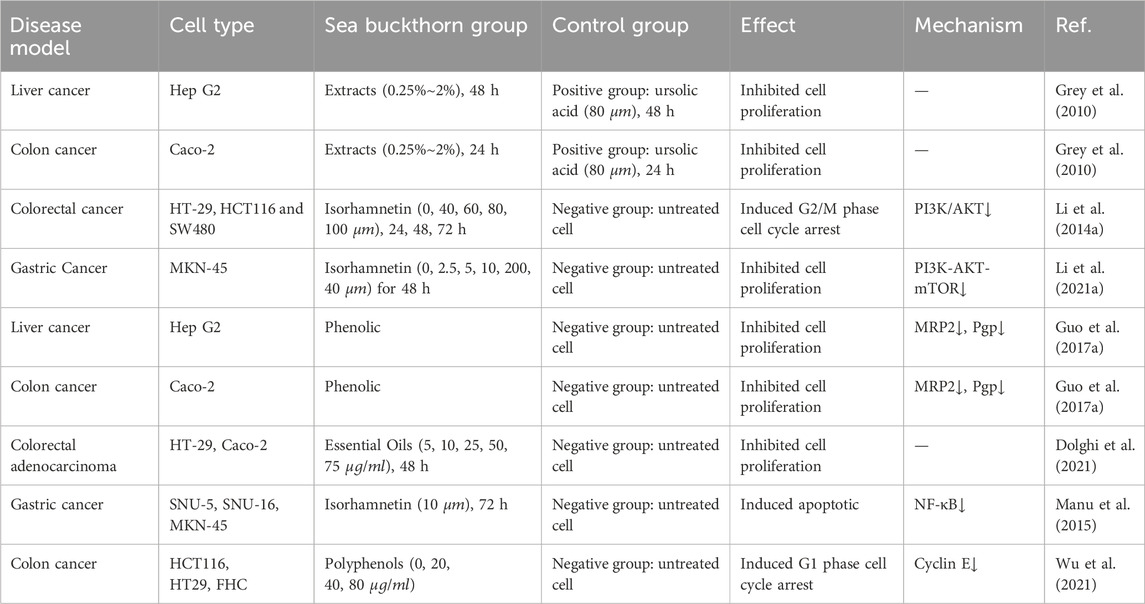
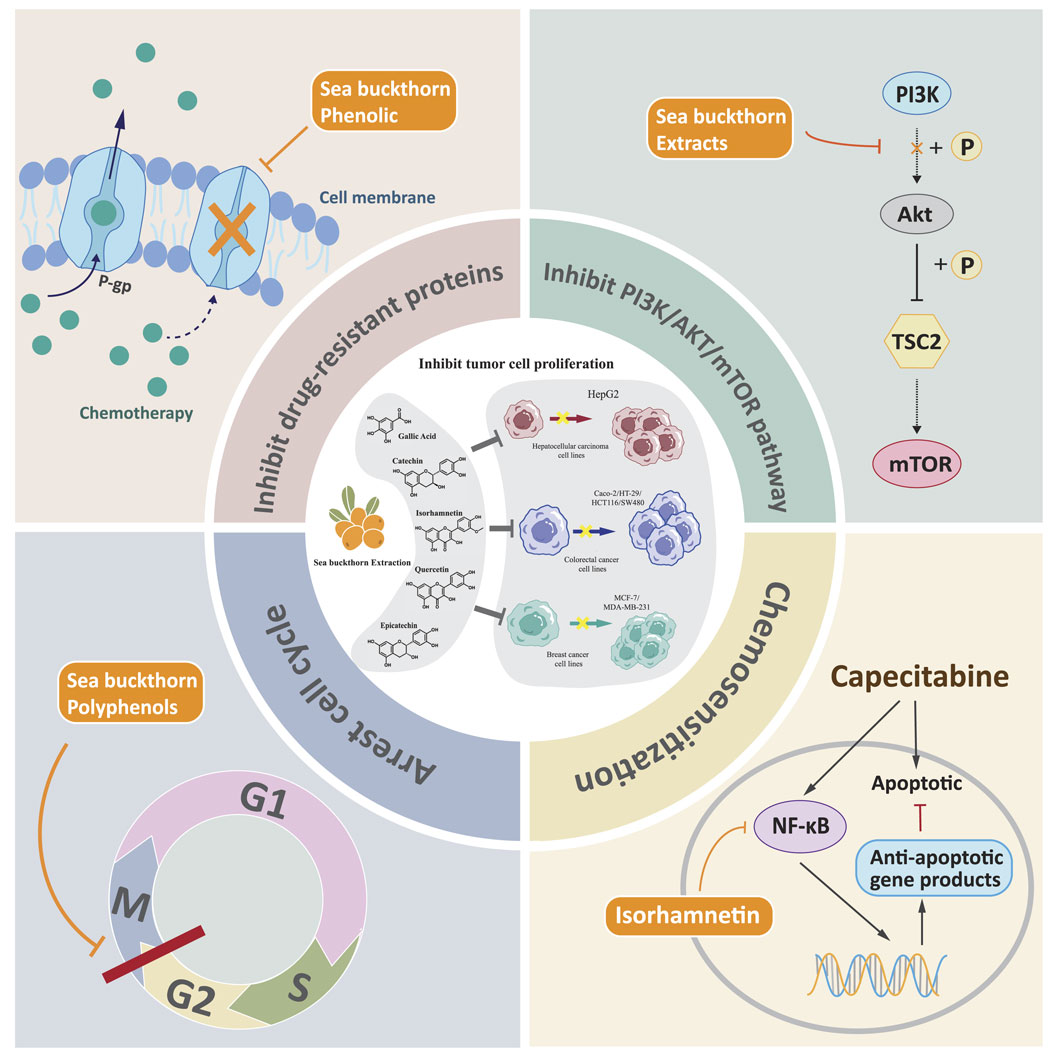
The above vivo experimental evidence summarizes the beneficial influence of sea buckthorn on digestive diseases at the level of the overall functioning of the organism. To further understand the mechanism of action of sea buckthorn against digestive diseases at the molecular and cellular level, we reviewed and summarized the relevant in vitro experiments. Current in vitro studies on sea buckthorn primarily focus on inhibiting cancer cells. Sea buckthorn regulates classical signaling pathways such as cell cycle PI3K/AKT, thereby suppressing the development and spread of gastric cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation, protecting the intestinal barrier, and enhancing the anticancer effects of chemotherapeutic drugs. The sustained proliferative ability of cells is an integral part of cancer, manifested by altered expression and activity of cell cycle-related proteins (Feitelson et al., 2015). Studies have shown that sea buckthorn and its active metabolites can inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells through PI3K/AKT and other signaling pathways. Sea buckthorn extract contains many bioactive metabolites with anticancer properties; the study found that it could suppress the proliferation of liver cancer HepG2 and colon cancer Caco-2 cells (Grey et al., 2010). Isorhamnetin has been found to inhibit three human colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines, namely HT-29, HCT116, and SW480. This metabolite induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and suppresses cell proliferation by inhibiting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway (Li C. et al., 2014). Additionally, Isorhamnetin enhances the anti-tumor effects of capecitabine by negatively regulating the NF-κB signaling cascade in gastric cancer (Manu et al., 2015). The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway plays a crucial role in various cellular processes and is aberrantly activated in cancers, contributing to the occurrence and progression of tumors (He et al., 2021). Studies have confirmed that sea buckthorn phenolic intervention can significantly reduce the levels of MRP and Pgp to inhibit the activity of HepG2, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and Caco-2 cell proliferation (Guo et al., 2017a). Multidrug resistance proteins can mediate cancer multidrug resistance by expelling various chemotherapeutic agents or their metabolites from tumor cells (Wang et al., 2021). Multidrug resistance (MDR), often associated with the overexpression of P-gp, has been implicated as a significant obstacle to effective chemotherapy for cancer, parasitic diseases, AIDS, and other diseases (Li et al., 2010). Active metabolites such as sea buckthorn essential oils and polyphenols also inhibit cell proliferation, and further experimental details are given in Table 5. The mechanisms of Sea buckthorn anti-digestive cancer are illustrated in Figure 5.
10 Safety and toxicity studies
Sea buckthorn is a food with both medicinal and edible properties. With the growing use of sea buckthorn in medicinal and dietary supplements worldwide, it is essential to evaluate its safety and toxicity in order to regulate products that contain sea buckthorn. Currently, most safety and toxicity assessments of sea buckthorn focus on its oils and extracts. In a 2-week acute toxicity study, mice that were administered 20 mL/kg of sea buckthorn oil displayed no adverse reactions. Similarly, in a 90-day chronic toxicity study, rats given 10 mL/kg of sea buckthorn oil also showed no adverse effects (Zhao et al., 2017). In the teratogenicity study, pregnant rats were administered sea buckthorn oil at doses up to 4.68 g/kg starting on gestation day 16, with no treatment-related maternal toxicity or embryotoxicity observed. The findings from the genotoxicity studies indicated that SB oil showed no mutagenic activity in histidine-dependent strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Furthermore, SB oil did not significantly affect sperm morphology or the frequency of micronuclei in polychromatic erythrocytes in mice (Wen et al., 2020). Furthermore, research on rat burn models has demonstrated that sea buckthorn oil shows no toxicity or side effects related to wounds (Upadhyay et al., 2009). The 90-day safety study of aqueous sea buckthorn extract at a dose of 100 mg/kg body weight per day in rats showed no adverse effects on mean body weight, organ-to-body weight ratio, histological, hematological, or biochemical parameters (Tulsawani, 2010). Sea buckthorn is considered safe for consumption in food and medicine. Some studies have reported potential adverse gastrointestinal symptoms experienced by 11 participants in the SB group and 4 participants in the placebo group, respectively (P = 0.24) (Larmo et al., 2014). A case report study suggests that consuming 100 g of sea buckthorn syrup daily for 6 months may result in a harmless but noticeable yellow-orange skin discoloration (Grad et al., 2012). Current evidence suggests that sea buckthorn oil and extracts are generally safe; however, some studies are outdated, and research on sea buckthorn extracts is still limited. Further studies on the safety and toxicity of sea buckthorn are necessary.
11 Clinical application challenges
Clinical applications of sea buckthorn may encounter challenges such as regulatory policies, bioavailability, dosage standardization, and potential drug interactions. Regulations and standards for sea buckthorn products can differ by region and purpose. Adhering to safety regulations and meeting quality standards is crucial for sea buckthorn product development. Currently, sea buckthorn products, whether taken orally or applied topically, are not approved as prescription medications. Sea buckthorn seed oil and fruit extract are registered with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) using UNII identifiers, such as UNII: T53SBG6741. This system is only designed for tracking substances, not for regulatory approval. Furthermore, the FDA does not specifically approve or endorse sea buckthorn as a dietary supplement or treatment for any disease. Sea buckthorn is sold as a dietary supplement, but claims about its ability to treat or prevent diseases are not approved by the FDA. In China, sea buckthorn is classified as food with medicinal and edible properties, allowing for its use in both food and medicinal contexts (Teng et al., 2024). The European Union regulates sea buckthorn leaves as a food metabolite under “novel food” regulations, which require specific safety assessments (Novel Food status Catalogue - European Commission, 2023). In conclusion, sea buckthorn has the potential to be used as a dietary supplement. However, it would be inappropriate to promote its pharmacological effects, particularly in the United States and Europe. Sea buckthorn is more commonly used in Chinese medicine because it is included in the Pharmacopoeia.
Sea buckthorn is abundant in flavonoids, carotenoids, fatty acids, and polysaccharides, which provide it with various pharmacological activities, but also lead to low bioavailability challenges. Sea buckthorn flavonoids are abundant and beneficial; however, they often have poor water solubility, which can hinder their absorption and bioavailability, as well as cause instability in the gastrointestinal tract and rapid metabolic clearance (Sheng et al., 2025). Utilizing phospholipid complexes may improve the absorption of flavonoids (Taldaev et al., 2025). Carotenoids, with their lipophilic nature, require dietary fat for efficient absorption from the digestive tract (Moran et al., 2018). The solution is to use nano emulsions or liposomes to enhance the absorption of carotenoids and oils (Mansur et al., 2020). Sea buckthorn polysaccharides also face challenges due to their large molecular size and low intestinal permeability (Xie et al., 2023). Research indicates that the bioavailability of polysaccharides can be effectively improved by developing appropriate drug delivery systems (DDS) for them (Li et al., 2017). Low bioavailability is a significant factor limiting the clinical application of sea buckthorn. This bioavailability can be enhanced through modifications in dosage forms and other methods.
There is still a lack of formal regulatory documents regarding standardized dosages of sea buckthorn. The variations in sea buckthorn’s active metabolite content across different regions and its diverse uses have resulted in a dosage that remains unstandardized. The standard dosage of sea buckthorn for medicinal purposes is 3∼10 g, according to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Empirical healers have traditionally recommended a daily dose of approximately 20 g of sea buckthorn fruit in ethnic medicine (Grad et al., 2012). Some websites related to drugs list standardized dosages of sea buckthorn, but these have not been accurately verified (Sea Buckthorn Uses, Benefits and Dosage, 2024). Health Canada’s Natural Health Products Database lists sea buckthorn oil as an approved metabolite, generally recommending a daily dosage of 1 g (Product information, 2024). Further research is needed to determine the standard dosage of sea buckthorn for medicinal use.
While no severe side effects of sea buckthorn have been reported, it is important to consider possible drug interactions when starting it alongside other medications. Sea buckthorn may decrease platelet aggregation (Sławińska et al., 2024), potentially increasing bleeding risks, especially when taken with anticoagulants like warfarin or aspirin. Sea buckthorn may enhance the hypoglycemic effects of diabetes medications (Ren et al., 2021), increasing the risk of hypoglycemia when used alongside these drugs. Sea buckthorn may enhance antihypertensive effects (Vashishtha et al., 2017), potentially leading to dangerously low blood pressure. The use of high doses of vitamin C is generally safe within therapeutic limits, but there are potential risks, such as kidney-related diseases and inaccuracies in laboratory tests (Yanase et al., 2020). Due to the high vitamin C content in sea buckthorn, its use should be carefully considered for certain patients and specific situations. In conclusion, due to the potential effects of sea buckthorn on blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and platelet function, the concurrent use of sea buckthorn and products containing it should be avoided when taking related medications.
12 Limitations and future research priorities
We conducted a systematic review of sea buckthorn applications in digestive system diseases, focusing on clinical studies, in vivo studies, in vitro studies, safety and toxicity studies, and potential challenges for clinical application. Our research shows that sea buckthorn has significant potential for treating digestive system diseases. However, it is important to recognize that many issues remain in the current research on sea buckthorn. Clinical studies on sea buckthorn treatment for digestive diseases reveal key issues: the number of studies is insufficient, research is somewhat outdated, and study designs lack rigor. The primary reason for the aforementioned issue is the neglect of sea buckthorn as a treatment for digestive disorders and its effectiveness. Therefore, conducting additional clinical studies on the therapeutic effects of sea buckthorn for digestive system diseases should be a priority for future research. The quantity and quality of in vivo animal studies on sea buckthorn are greater than those of clinical trials; however, current in vivo research lacks a focus on tumors of the digestive system. A thorough analysis of clinical and in vivo studies on sea buckthorn’s effects on digestive system disorders shows that its main therapeutic benefits include reducing inflammation, regulating functional disorders, and alleviating adverse reactions caused by related medications. However, in vitro studies have shown that sea buckthorn exhibits great therapeutic effects against digestive system tumors; however, it has consistently failed to advance to in vivo research stages. The primary reasons for this issue are the stability of sea buckthorn’s metabolism within the vivo and its ability to effectively distribute within tumor tissues. Structural modification of natural products may serve as a significant approach for discovering compounds with potential anticancer activity (Zhang X. et al., 2024). While toxicity and safety evaluations suggest that sea buckthorn has a relatively high margin of safety, caution is still advised regarding its potential interactions with other medications. In terms of clinical application, the industrialization of sea buckthorn faces several challenges. Currently, sea buckthorn is primarily positioned as a dietary supplement, and its use as a pharmaceutical still carries significant regulatory risks. Additionally, determining the optimal dosage and bioavailability of sea buckthorn are critical issues that must be addressed for its successful industrial application in the future.
13 Conclusion
The gastrointestinal tract is an essential life support system that performs several vital physiological functions, including digestion, absorption, and metabolism of nutrients from ingested food (Wang Y. et al., 2023). Digestive diseases comprise a wide range of conditions that affect the gastrointestinal tract and significantly impact public health. They are also a major cause of healthcare utilization and expenditure (Peery et al., 2022). Sea buckthorn is a traditional plant with an extensive history of use in both medicine and food, packed with various bioactive metabolites. It has shown great potential for extensive development in food and medicine to prevent and treat digestive diseases due to its diverse physiological functions, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immune regulatory, and cytotoxic effects on cancer cells. In recent years, numerous scientists have conducted comprehensive research on identifying, extracting, and understanding the functional properties of the bioactive metabolites in sea buckthorn. This article summarizes the clinical, animal, and in vitro evidence, reviewing the role of sea buckthorn and its active metabolites in preventing and treating digestive diseases. Sea buckthorn has been found to intervene in chronic gastritis, alleviate liver injury and nonalcoholic fatty liver, treat functional constipation and irritable bowel syndrome, and effectively prevent digestive diseases. It achieves this by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress, protecting intestinal barrier function, restoring immune balance, and regulating intestinal flora. Additionally, Sea buckthorn can directly intervene in digestive cancers such as liver, colon, and gastric cancer by regulating MPR2, Pgp, mTOR, and other signaling pathways.
Our study helps digestive disease researchers take a more holistic view of sea buckthorn’s importance, which could help develop drugs and foods to improve digestive diseases. In the future, conducting in-depth investigations into the mechanisms of action to better apply sea buckthorn in food and medicine production will be essential. It is believed that more potent drugs can be discovered from sea buckthorn shortly for treating digestive diseases, reducing the medical burden of patients, and improving their quality of life.
Author contributions
WD: Writing – original draft, Data curation. YT: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. JQ: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis. ZD: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. JC: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation (2022QN08015); Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Health Science and Technology Program (202201414).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmed, Z. A. (2024). Gastroprotective effect of quercetin and misoprostol in ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Turk J. Gastroenterol. 35, 822–830. doi:10.5152/tjg.2024.24209
Ahmed, S. F., Bakr, M. A., and Rasmy, A. H. (2023). Vitamin E ameliorates oral mucositis in gamma-irradiated rats (an in vivo study). BMC Oral Health 23, 697. doi:10.1186/s12903-023-03408-x
Al Ibrahim, M., Akissi, Z. L. E., Desmarets, L., Lefèvre, G., Samaillie, J., Raczkiewicz, I., et al. (2023). Discovery of anti-coronavirus cinnamoyl triterpenoids isolated from Hippophae rhamnoides during a screening of halophytes from the north sea and channel coasts in northern France. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 16617. doi:10.3390/ijms242316617
Andersson, S. C., Olsson, M. E., Johansson, E., and Rumpunen, K. (2009). Carotenoids in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries during ripening and use of pheophytin a as a maturity marker. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 250–258. doi:10.1021/jf802599f
Ben Ari, Z., Avlas, O., Pappo, O., Zilbermints, V., Cheporko, Y., Bachmetov, L., et al. (2012). Reduced hepatic injury in toll-like receptor 4-deficient mice following D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 29, 41–50. doi:10.1159/000337585
Bernal, W., and Wendon, J. (2013). Acute liver failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 369, 2525–2534. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1208937
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca. Cancer J. Clin. 74, 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Cai, C., Cheng, W., Shi, T., Liao, Y., Zhou, M., and Liao, Z. (2023). Rutin alleviates Colon lesions and regulates gut microbiota in diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 13, 4897. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31647-z
Chen, A., Feng, X., Dorjsuren, B., Chimedtseren, C., Damda, T.-A., and Zhang, C. (2023a). Traditional food, modern food and nutritional value of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.): a review. J. Future Foods 3, 191–205. doi:10.1016/j.jfutfo.2023.02.001
Chen, J., Zhong, H., Huang, Z., Chen, X., You, J., and Zou, T. (2023b). A critical review of kaempferol in intestinal health and diseases. Antioxidants (Basel) 12, 1642. doi:10.3390/antiox12081642
Chen, L., Wei, S., He, Y., Wang, X., He, T., Zhang, A., et al. (2023c). Treatment of chronic gastritis with traditional Chinese medicine: pharmacological activities and mechanisms. Pharmaceuticals 16, 1308. doi:10.3390/ph16091308
Chen, Y., Cai, Y., Wang, K., and Wang, Y. (2023d). Bioactive compounds in sea buckthorn and their efficacy in preventing and treating metabolic syndrome. Foods 12, 1985. doi:10.3390/foods12101985
Chen, Y., Mai, Q., Chen, Z., Lin, T., Cai, Y., Han, J., et al. (2023e). Dietary palmitoleic acid reprograms gut microbiota and improves biological therapy against colitis. Gut Microbes 15, 2211501. doi:10.1080/19490976.2023.2211501
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (1977). Pharmacopoeia of the people’s Republic of China: 1977 edition. Beijing: The People’s Health Press.
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2020). Pharmacopoeia of the people’s Republic of China (2020 edition). Beijing: China Medical Science Press.
Chuang, Y.-S., Wu, M.-C., Lin, P., Yu, F.-R., Wang, Y.-K., Wu, D.-C., et al. (2017). Abstract LB-155: effects of alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, betel quid chewing in upper digestive disease: a large cross-sectional study in Taiwan and meta-analysis. Cancer Res. 77, LB-155. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2017-LB-155
Chung, K.-T., Wong, T. Y., Wei, C.-I., Huang, Y.-W., and Lin, Y. (1998). Tannins and human health: a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 38, 421–464. doi:10.1080/10408699891274273
Crespo, I., San-Miguel, B., Mauriz, J. L., Ortiz de Urbina, J. J., Almar, M., Tuñón, M. J., et al. (2017). Protective effect of protocatechuic acid on TNBS-induced colitis in mice is associated with modulation of the SphK/S1P signaling pathway. Nutrients 9, 288. doi:10.3390/nu9030288
Da, W. X. (2023). The effect of Hippophae rhamnoides polysaccharide on glioma and expression of HMGB1,MGMT,and TLR4 in rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio/Cerebrovascular Dis. 21, 51–56. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.01.008
Dao, R., Wu, D., Wang, H., Jin, H., Li, L., Fu, X., et al. (2021). Exploration of the characteristics of intestinal microbiota and metabolomics in different rat models of Mongolian medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 5532069. doi:10.1155/2021/5532069
De, R., Sarkar, A., Ghosh, P., Ganguly, M., Karmakar, B. C., Saha, D. R., et al. (2018). Antimicrobial activity of ellagic acid against Helicobacter pylori isolates from India and during infections in mice. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 73, 1595–1603. doi:10.1093/jac/dky079
Deng, Z., Zhu, J., Ma, Z., Yi, Z., Tuo, B., Li, T., et al. (2023). The mechanisms of gastric mucosal injury: focus on initial chief cell loss as a key target. Cell Death Discov. 9, 29. doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01318-z
Ding, K., Tan, Y.-Y., Ding, Y., Fang, Y., Yang, X., Fang, J., et al. (2019). β-Sitosterol improves experimental colitis in mice with a target against pathogenic bacteria. J. Cell Biochem. 120, 5687–5694. doi:10.1002/jcb.27853
Dolghi, A., Buzatu, R., Dobrescu, A., Olaru, F., Popescu, G. A., Marcovici, I., et al. (2021). Phytochemical analysis and in vitro cytotoxic activity against colorectal adenocarcinoma cells of hippophae rhamnodies L., Cymbopogon citratus (D.C.) stapf, and Ocimum basilicum L. essential oils. plants 10, 2752. doi:10.3390/plants10122752
Dubey, R. K., Shukla, S., Shukla, V., and Singh, S. (2023). Sea buckthorn: a potential dietary supplement with multifaceted therapeutic activities. Intell. Pharm. 2, 681–687. doi:10.1016/j.ipha.2023.12.003
Dulf, F. V. (2012). Fatty acids in berry lipids of six sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L., subspecies carpatica) cultivars grown in Romania. Chem. Central J. 6, 106. doi:10.1186/1752-153X-6-106
Feitelson, M. A., Arzumanyan, A., Kulathinal, R. J., Blain, S. W., Holcombe, R. F., Mahajna, J., et al. (2015). Sustained proliferation in cancer: mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Seminars Cancer Biol. 35, S25-S54–S54. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.006
Feng, W. (2015). Clinical observation of dried sea buckthorn emulsion in the treatment of spleen and stomach cold type chronic gastritis. LanZhou: LanZhou University. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201501&filename=1015519362.nh (Accessed May 24, 2024).
Feng, J., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Du, Y., Sun, Q., Zang, W., et al. (2015). Myricetin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in gastric cancer cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 408, 163–170. doi:10.1007/s11010-015-2492-1
Gajendran, M., Loganathan, P., Jimenez, G., Catinella, A. P., Ng, N., Umapathy, C., et al. (2019). A comprehensive review and update on ulcerative colitis. Disease-a-Month 65, 100851. doi:10.1016/j.disamonth.2019.02.004
Ganapathy, A. S., Saha, K., Wang, A., Arumugam, P., Dharmaprakash, V., Yochum, G., et al. (2023). Alpha-tocopherylquinone differentially modulates claudins to enhance intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier via AhR and Nrf2 pathways. Cell Rep. 42, 112705. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112705
Gao, Z.-L., Gu, X.-H., Cheng, F.-T., and Jiang, F.-H. (2003). Effect of sea buckthorn on liver fibrosis: a clinical study. World J. Gastroenterol. 9, 1615–1617. doi:10.3748/wjg.v9.i7.1615
Gao, Z., Zhang, C., Jin, L., and Yao, W. (2014). Efficacy of sea buckthorn therapy in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Chin. Med. 05, 223–230. doi:10.4236/cm.2014.54027
Gâtlan, A.-M., and Gutt, G. (2021). Sea buckthorn in plant based diets. An analytical approach of sea buckthorn fruits composition: nutritional value, applications, and health benefits. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18, 8986. doi:10.3390/ijerph18178986
Geng, Y., Wang, J., Chen, K., Li, Q., Ping, Z., Xue, R., et al. (2022). Effects of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) on factors related to metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. Phytother. Res. 36, 4101–4114. doi:10.1002/ptr.7596
Ghendov-Mosanu, A., Cristea, E., Patras, A., Sturza, R., Padureanu, S., Deseatnicova, O., et al. (2020). Potential application of Hippophae rhamnoides in wheat bread production. Molecules 25, 1272. doi:10.3390/molecules25061272
Goel, H. C., Prasad, J., Singh, S., Sagar, R. K., Kumar, I. P., and Sinha, A. K. (2002). Radioprotection by a herbal preparation of Hippophae rhamnoides, RH-3, against whole body lethal irradiation in mice. Phytomedicine 9, 15–25. doi:10.1078/0944-7113-00077
Grad, S. C., Muresan, I., and Dumitrascu, D. L. (2012). Generalized yellow skin caused by high intake of sea buckthorn. Forsch Komplementmed 19, 153–156. doi:10.1159/000339331
Grey, C., Widén, C., Adlercreutz, P., Rumpunen, K., and Duan, R.-D. (2010). Antiproliferative effects of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) extracts on human Colon and liver cancer cell lines. Food Chem. 120, 1004–1010. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.039
Guo, D. H. (2008). Mechanism and correlation with apoptosis of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins in the treatment of chronic gastritis. J. Chongqing Med. Univ. 970–972, 1002.
Guo, D. L. (2019). Overview of Mongolian medicine sea buckthorn and the current status of its modern research and development. Chin. J. Ethn. Med. 25, 41–44. doi:10.16041/j.cnki.cn15-1175.2019.02.030
Guo, R., Chang, X., Guo, X., Brennan, C. S., Li, T., Fu, X., et al. (2017a). Phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity, antiproliferative activity and bioaccessibility of sea buckthorn (hippophaë rhamnoides L.) berries as affected by in vitro digestion. Food Funct. 8, 4229–4240. doi:10.1039/c7fo00917h
Guo, R., Guo, X., Li, T., Fu, X., and Liu, R. H. (2017b). Comparative assessment of phytochemical profiles, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of sea buckthorn (hippophaë Rhamnoides L.) berries. Food Chem. 221, 997–1003. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.11.063
Han, J. H., Kim, M., Kim, H. J., Jang, S. B., Bae, S.-J., Lee, I.-K., et al. (2021). Targeting lactate dehydrogenase A with catechin resensitizes SNU620/5FU gastric cancer cells to 5-Fluorouracil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 5406. doi:10.3390/ijms22105406
He, Y., Sun, M. M., Zhang, G. G., Yang, J., Chen, K. S., Xu, W. W., et al. (2021). Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Sig Transduct. Target Ther. 6, 425–17. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00828-5
Hippophae rhamnoides, L. (2025). Plants of the world online | kew science. Plants World Online. Available online at: http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:323851-1 (Accessed August 28, 2025).
Huang, L., Kim, M.-Y., and Cho, J. Y. (2023). Immunopharmacological activities of luteolin in chronic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 2136. doi:10.3390/ijms24032136
Huang, X., Wu, H., Wu, X., Su, W., and Li, P. (2025). Naringenin/Naringin therapeutic effects and the role of intestinal microflora in them. Pharmacol. Res. 219, 107871. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107871
Ilhan, G., Gundogdu, M., Karlović, K., Židovec, V., Vokurka, A., and Ercişli, S. (2021). Main agro-morphological and biochemical berry characteristics of wild-grown sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L. ssp. Caucasica rousi) genotypes in Turkey. Sustainability 13, 1198. doi:10.3390/su13031198
Ismail, A., El-Biyally, E., and Sakran, W. (2023). An innovative approach for formulation of rutin tablets targeted for Colon cancer treatment. AAPS PharmSciTech 24, 68. doi:10.1208/s12249-023-02518-7
Jia, X., He, Y., Li, L., and Xu, D. (2023). Pharmacological targeting of gastric mucosal barrier with traditional Chinese medications for repairing gastric mucosal injury. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1091530. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1091530
Jin, Z., Liu, M., Zhao, H., Xie, J., Yin, W., Zheng, M., et al. (2024). Effects of zeaxanthin on the insulin resistance and gut microbiota of high-fat-diet-induced Obese mice. Foods 13, 3388. doi:10.3390/foods13213388
Kallio, H., Yang, B., Peippo, P., Tahvonen, R., and Pan, R. (2002). Triacylglycerols, glycerophospholipids, tocopherols, and tocotrienols in berries and Seeds of two subspecies (ssp. Sinensis and mongolica) of sea buckthorn (hippopha>ë Rhamnoides). J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 3004–3009. doi:10.1021/jf011556o
Kasprzak, M., Rudzińska, M., Juzwa, W., and Olejnik, A. (2023). Anti-proliferative potential and oxidative reactivity of thermo-oxidative degradation products of stigmasterol and stigmasteryl esters for human intestinal cells. Sci. Rep. 13, 7093. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-34335-0
Khan, B. A., Akhtar, N., Menaa, B., Menaa, A., Braga, V. A., and Menaa, F. (2017). Relative free radicals scavenging and enzymatic activities of Hippophae rhamnoides and Cassia fistula extracts: importance for cosmetic, food and medicinal applications. Cosmetics 4, 3. doi:10.3390/cosmetics4010003
Kim, S.-J., Hwang, E., Yi, S. S., Song, K. D., Lee, H.-K., Heo, T.-H., et al. (2017). Sea buckthorn leaf extract inhibits glioma cell growth by reducing reactive oxygen species and promoting apoptosis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 182, 1663–1674. doi:10.1007/s12010-017-2425-4
Kondo, K., Hiramoto, K., Yamate, Y., Goto, K., Sekijima, H., and Ooi, K. (2019). Ameliorative effect of high-dose vitamin C administration on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mouse model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 42, 954–959. doi:10.1248/bpb.b18-00967
Koskovac, M., Cupara, S., Kipic, M., Barjaktarevic, A., Milovanovic, O., Kojicic, K., et al. (2017). Sea buckthorn oil—A valuable source for cosmeceuticals. Cosmetics 4, 40. doi:10.3390/cosmetics4040040
Krejcarová, J., Straková, E., Suchý, P., Herzig, I., and Karásková, K. (2015). Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) as a potential source of nutraceutics and its therapeutic possibilities - a review. Acta Vet. Brno 84, 257–268. doi:10.2754/avb201584030257
Krzyżek, P., Migdał, P., Paluch, E., Karwańska, M., Wieliczko, A., and Gościniak, G. (2021). Myricetin as an antivirulence compound interfering with a morphological transformation into coccoid forms and potentiating activity of antibiotics against Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 2695. doi:10.3390/ijms22052695
Kuang, H., Ma, Y., and Liu, Y. (2022). Protective effect of β-carotene on OVA-Induced food allergy in mice by strengthening intestinal epithelial barrier function and regulating intestinal microflora. Food Funct. 13, 12330–12341. doi:10.1039/d2fo02272a
Kuo, C.-H., Weng, B.-C., Wu, C.-C., Yang, S.-F., Wu, D.-C., and Wang, Y.-C. (2014). Apigenin has anti-atrophic gastritis and anti-gastric cancer progression effects in helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils. J. Ethnopharmacol. 151, 1031–1039. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.11.040
Lai, Y., Masatoshi, H., Ma, Y., Guo, Y., and Zhang, B. (2022). Role of vitamin K in intestinal health. Front. Immunol. 12, 791565. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.791565
Larmo, P., Alin, J., Salminen, E., Kallio, H., and Tahvonen, R. (2008). Effects of sea buckthorn berries on infections and inflammation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 62, 1123–1130. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602831
Larmo, P. S., Yang, B., Hyssälä, J., Kallio, H. P., and Erkkola, R. (2014). Effects of sea buckthorn oil intake on vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Maturitas 79, 316–321. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.07.010
Larsson, S. C., Mason, A. M., Vithayathil, M., Carter, P., Kar, S., Zheng, J.-S., et al. (2022). Circulating vitamin C and digestive system cancers: mendelian randomization study. Clin. Nutr. 41, 2031–2035. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2022.07.040
Lee, C., Lee, J. W., Seo, J. Y., Hwang, S. W., Im, J. P., and Kim, J. S. (2016). Lupeol inhibits LPS-Induced NF-kappa B signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and macrophages, and attenuates acute and chronic murine colitis. Life Sci. 146, 100–108. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2016.01.001
Lee, S. H., Kwon, J. E., and Cho, M.-L. (2018). Immunological pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Intest. Res. 16, 26–42. doi:10.5217/ir.2018.16.1.26
Lee, Y. H., Jang, H. J., Park, K. H., Kim, S.-H., Kim, J. K., Kim, J.-C., et al. (2021). Phytochemical analysis of the fruits of sea buckthorn (hippophae rhamnoides): identification of organic acid derivatives. Plants 10, 860. doi:10.3390/plants10050860
Li, T. S. C., Beveridge, T. H. J., and Drover, J. C. G. (2007). Phytosterol content of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed oil: extraction and identification. Food Chem. 101, 1633–1639. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.04.033
Li, Y., Yuan, H., Yang, K., Xu, W., Tang, W., and Li, X. (2010). The structure and functions of P-glycoprotein. Curr. Med. Chem. 17, 786–800. doi:10.2174/092986710790514507
Li, C., Yang, X., Chen, C., Cai, S., and Hu, J. (2014a). Isorhamnetin suppresses Colon cancer cell growth through the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 9, 935–940. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.1886
Li, R. J., Tian, J. J., Li, W. Q., Cheng, F. Q., and Gao, G. S. (2014b). Effect of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine on oxidative stress and gene expression of c-fos, c-jun, p16 and Rb in rat colons and protective role of seabuckthorn seed oil. J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part B 49, 279–289. doi:10.1080/03601234.2014.868667
Li, Z., Wang, L., Lin, X., Shen, L., and Feng, Y. (2017). Drug delivery for bioactive polysaccharides to improve their drug-like properties and curative efficacy. Drug Deliv. 24, 70–80. doi:10.1080/10717544.2017.1396383
Li, C., Zhang, J., Zhao, C., Yang, L., Zhao, W., Jiang, H., et al. (2018a). Separation of the main flavonoids and essential oil from seabuckthorn leaves by ultrasonic/microwave-assisted simultaneous distillation extraction. R. Soc. Open Sci. 5, 180133. doi:10.1098/rsos.180133
Li, Q., Li, H.-J., Xu, T., Du, H., Huan Gang, C.-L., Fan, G., et al. (2018b). Natural medicines used in the traditional Tibetan medical system for the treatment of liver diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 29. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00029
Li, C., Li, J., Li, Y., Li, L., Luo, Y., Li, J., et al. (2021a). Isorhamnetin promotes MKN-45 gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting PI3K-Mediated adaptive autophagy in a hypoxic environment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 8130–8143. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c02620
Li, X., Chen, W., Simal-Gandara, J., Georgiev, M. I., Li, H., Hu, H., et al. (2021b). West meets east: open up a dialogue on phytomedicine. Chin. Med. 16, 57. doi:10.1186/s13020-021-00467-6
Li, Y.-H., He, Q., Chen, Y.-Z., Du, Y.-F., Guo, Y.-X., Xu, J.-Y., et al. (2021c). p-Coumaric acid ameliorates ionizing radiation-induced intestinal injury through modulation of oxidative stress and pyroptosis. Life Sci. 278, 119546. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119546
Li, Y., Li, X.-M., Duan, H.-Y., Yang, K., and Ye, J.-F. (2024). Advances and optimization strategies in bacteriophage therapy for treating inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Immunol. 15, 1398652. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1398652
Liu, H., Zhang, W., Dong, S., Song, L., Zhao, S., Wu, C., et al. (2015). Protective effects of sea buckthorn polysaccharide extracts against LPS/d-GalN-induced acute liver failure in mice via suppressing TLR4-NF-κB signaling. J. Ethnopharmacol. 176, 69–78. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.029
Liu, S., Xiao, P., Kuang, Y., Hao, J., Huang, T., and Liu, E. (2021a). Flavonoids from sea buckthorn: a review on phytochemistry, pharmacokinetics and role in metabolic diseases. J. Food Biochem. 45, e13724. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13724
Liu, Y.-Q., Wang, X.-L., He, D.-H., and Cheng, Y.-X. (2021b). Protection against chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-induced side effects: a review based on the mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities of phytochemicals. Phytomedicine 80, 153402. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153402
Liu, J., Kong, L., Shao, M., Sun, C., Li, C., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Seabuckthorn polysaccharide combined with astragalus polysaccharide ameliorate alcoholic fatty liver by regulating intestinal flora. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 1018557. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1018557
Liu, Z., Zhang, D., and Chen, S. (2024). Unveiling the gastric microbiota: implications for gastric carcinogenesis, immune responses, and clinical prospects. J. Exp. & Clin. cancer Res. CR 43, 118. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-03034-7
Ll, D. (2015). Determination of the polyphenols in berries of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. wolongensis. West China J. Pharm. Sci. 30, 336–338. doi:10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2015.03.026
Lu, Y., and Han, X. (2024). Therapeutic implications of phenolic acids for ameliorating inflammatory bowel disease. Nutrients 16, 1347. doi:10.3390/nu16091347
Lu-gen, B. A. I., and Xiao-xia, H. E. (2021). The effect of sea buckthorn oil on cell proliferation and apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells HGC-27. ACTA Neuropharmacol. 11, 4. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1396.2021.04.002
Lv, L., Du, J., Wang, D., and Yan, Z. (2024). A comprehensive study to investigate the tumor-suppressive role of Radix bupleuri on gastric cancer with network pharmacology and molecular docking. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 18, 375–394. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S441126
Lyu, X., Wang, Y., Gao, S., Wang, X., Cao, W., and Cespedes-Acuña, C. L. (2022). Sea buckthorn leaf extract on the stability and antioxidant activity of microencapsulated sea buckthorn oil. Food Biosci. 48, 101818. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101818
Ma, L., Ma, Y., and Liu, Y. (2023). β-Sitosterol protects against food allergic response in BALB/c mice by regulating the intestinal barrier function and reconstructing the gut microbiota structure. Food Funct. 14, 4456–4469. doi:10.1039/d3fo00772c
Mansur, M. C. P. P. R., Campos, C., Vermelho, A. B., Nobrega, J., da Cunha Boldrini, L., Balottin, L., et al. (2020). Photoprotective nanoemulsions containing microbial carotenoids and buriti oil: efficacy and safety study. Arabian J. Chem. 13, 6741–6752. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.06.028
Manu, K. A., Shanmugam, M. K., Ramachandran, L., Li, F., Siveen, K. S., Chinnathambi, A., et al. (2015). Isorhamnetin augments the anti-tumor effect of capecitabine through the negative regulation of NF-κB signaling Cascade in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 363, 28–36. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.03.033
Marín, M., María Giner, R., Ríos, J.-L., and Recio, M. C. (2013). Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of ellagic acid in the acute and chronic dextrane sulfate sodium models of mice colitis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 150, 925–934. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.030
Masoodi, K. Z., Wani, W., Dar, Z. A., Mansoor, S., Anam-ul-Haq, S., Farooq, I., et al. (2020). Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) inhibits cellular proliferation, wound healing and decreases expression of prostate specific antigen in prostate cancer cells in vitro. J. Funct. Foods 73, 104102. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2020.104102
Mehta, P., Grant, L. M., and Reddivari, A. K. R. (2024). “Viral hepatitis,” in StatPearls, treasure island (FL) (Orlando: StatPearls Publishing LLC). Available online at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554549/ (Accessed May 24, 2024).
Mei, D., Ma, X., Fu, F., and Cao, F. (2023). Research status and development prospects of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) resources in China. Forests 14, 2461. doi:10.3390/f14122461
Mihal, M., Roychoudhury, S., Sirotkin, A. V., and Kolesarova, A. (2023). Sea buckthorn, its bioactive constituents, and mechanism of action: potential application in female reproduction. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1244300. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1244300
Moran, N. E., Mohn, E. S., Hason, N., Erdman, J. W., and Johnson, E. J. (2018). Intrinsic and extrinsic factors impacting absorption, metabolism, and health effects of dietary carotenoids. Adv. Nutr. 9, 465–492. doi:10.1093/advances/nmy025
G. A. Nayik, and A. Gull (2020). Antioxidants in fruits: properties and health benefits (Singapore: Springer Singapore). doi:10.1007/978-981-15-7285-2
Niesteruk, A., Lewandowska, H., Golub, Ż., Świsłocka, R., and Lewandowski, W. (2013). Zainteresujmy się rokitnikiem. Preparaty z rokitnika zwyczajnego (Hippophae rhamnoides l.) jako dodatki do żywności oraz ocena ich rynku w polsce. Available online at: http://yadda.icm.edu.pl/yadda/element/bwmeta1.element.bwnjournal-article-ksv62p571kz (Accessed May 23, 2024).
Novel Food status Catalogue - European Commission (2023). Available online at: https://food.ec.europa.eu/food-safety/novel-food/novel-food-status-catalogue_en (Accessed August 12, 2025).
Okamoto, T., Nakashima, F., Shibata, T., and Mori, D. (2024). Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides, L.) pulp oil prevents ultraviolet-induced damage in human fibroblasts. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 88, 948–955. doi:10.1093/bbb/zbae071
Olas, B. (2016). Sea buckthorn as a source of important bioactive compounds in cardiovascular diseases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 97, 199–204. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2016.09.008
Olas, B. (2018). The beneficial health aspects of sea buckthorn (Elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) a.Nelson) oil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 213, 183–190. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.11.022
Olas, B., Skalski, B., Ulanowska, K., Elaeagnus rhamnoides, L., and Nelson, A. (2018). The anticancer activity of sea buckthorn [elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) A. Nelson]. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 232. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00232
Ordás, I., Eckmann, L., Talamini, M., Baumgart, D. C., and Sandborn, W. J. (2012). Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 380, 1606–1619. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60150-0
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021a). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372, n71. doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Page, M. J., Moher, D., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021b). PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372, n160. doi:10.1136/bmj.n160
Palatty, P. L., Sacheendran, D., Raghu, S. V., Arora, R., Rao, S., and Baliga, M. S. (2024). Dietary agents in the prevention of radiation-induced nausea and vomiting (RINV): review addressing the scientific observations, benefits, lacunae and future direction. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 100, 1143–1154. doi:10.1080/09553002.2024.2309899
Panpan, H. U. (2021). Optimization of extraction of polysaccharide from Hippophae rhamnoides leaves and its proapoptotic effect on CT-26 cells. spgykj 42, 159–164. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021040022
Peery, A. F., Crockett, S. D., Murphy, C. C., Jensen, E. T., Kim, H. P., Egberg, M. D., et al. (2022). Burden and cost of gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases in the United States: update 2021. Gastroenterology 162, 621–644. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.017
Peng (1993). Dictionary of traditional Chinese medicine. BeiJing, BJ: People’s Medical Publishing House Press.
Petrescu, A., Paraschiv, M., and Sturzeanu, M. (2022). Evaluation of four sea buckthorn biotypes from the spontaneous flora of argeş county, Romania.
Pham, V. T., Fehlbaum, S., Seifert, N., Richard, N., Bruins, M. J., Sybesma, W., et al. (2021). Effects of colon-targeted vitamins on the composition and metabolic activity of the human gut microbiome-a pilot study. Gut Microbes 13, 1–20. doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.1875774
Pop, R. M., Weesepoel, Y., Socaciu, C., Pintea, A., Vincken, J.-P., and Gruppen, H. (2014). Carotenoid composition of berries and leaves from six Romanian sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) varieties. Food Chem. 147, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.083
Product information (2024). Available online at: https://health-products.canada.ca/lnhpd-bdpsnh/info?licence=80037109 (Accessed August 12, 2025).
Pundir, S., Garg, P., Dviwedi, A., Ali, A., Kapoor, V. K., Kapoor, D., et al. (2021). Ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry and dermatological effects of Hippophae rhamnoides L.: a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 266, 113434. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113434
Qiao, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhai, Y., Yan, X., Zhou, W., Liu, H., et al. (2021). Apigenin alleviates obesity-associated metabolic syndrome by regulating the composition of the gut microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 12, 805827. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2021.805827
Qin, Q. O., Liang, Y., and Liu, R. (2024). Sea buckthorn polysaccharide ameliorates colitis. Nutrients 16, 1280. doi:10.3390/nu16091280
Raza, M., and Bhatt, H. (2023). “Atrophic gastritis,” in StatPearls, treasure island (FL) (Orlando: StatPearls Publishing LLC). Available online at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563275/ (Accessed December 15, 2023).
Ren, Z., Gong, H., Zhao, A., Zhang, J., Yang, C., Wang, P., et al. (2021). Effect of sea buckthorn on plasma glucose in individuals with impaired glucose regulation: a two-stage randomized crossover intervention study. Foods 10, 804. doi:10.3390/foods10040804
Rong, Z.-J., Chen, M., Cai, H.-H., Liu, G.-H., Chen, J.-B., Wang, H., et al. (2024). Ursolic acid molecules dock MAPK1 to modulate gut microbiota diversity to reduce neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 252, 109939. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.109939
Sea Buckthorn Market Size, Growth. Res. Rep. (2024). Pune: Fortune Business Insights Pvt. Ltd. Available online at: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/sea-buckthorn-market-103197.
Sea Buckthorn Professional Committee of China Society of Sand Control and Sand Industry (2024). Report on the China sea buckthorn resource base survey. Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-06/10/content_5695086.htm (Accessed August 10, 2024).
Sea Buckthorn Uses, Benefits and Dosage (2024). Drugs. Com. Available online at: https://www.drugs.com/npp/sea-buckthorn.html (Accessed August 12, 2025).
Selvamuthukumaran, M., and Khanum, F. (2014). Evaluation of shelf stability of antioxidant rich seabuckthorn fruit yoghurt. Int. Food Res. J. 21, 759–765.
Sharma, S. H., Chellappan, D. R., Chinnaswamy, P., and Nagarajan, S. (2017). Protective effect of p-coumaric acid against 1,2 dimethylhydrazine induced colonic preneoplastic lesions in experimental rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 94, 577–588. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.146
Sheichenko, O. P., Sheichenko, V. I., Fadeeva, I. I., Zolotarev, B. M., and Tolkachev, O. N. (1987). Tannins from leaves of hippophaë rhamnoides. Chem. Nat. Compd. 23, 756–760. doi:10.1007/BF00596661
Shen, C., Wang, T., Guo, F., Sun, K., Wang, B., Wang, J., et al. (2021). Structural characterization and intestinal protection activity of polysaccharides from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries. Carbohydr. Polym. 274, 118648. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118648
Sheng, Q., Li, F., Chen, G., Li, J., Li, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Ursolic acid regulates intestinal microbiota and inflammatory cell infiltration to prevent ulcerative colitis. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 6679316. doi:10.1155/2021/6679316
Sheng, J., Youssef, M., Liang, H., Li, J., and Li, B. (2025). Sea buckthorn flavonols extract co-loaded zein/Gum Arabic nanoparticles: evaluating cellular absorption in Caco-2 cells and antioxidant activity in HepG2 cells. Food Chem. 468, 142522. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.142522
Shi, J. L., and Xuan, J. (2020). Clinical study of dried sea buckthorn emulsion for the treatment of food accumulation type functional constipation in children. Mod. Chin. Med. 40, 99–101. doi:10.13424/j.cnki.mtcm.2020.04.025
Shi, J., Wang, L., Lu, Y., Ji, Y., Wang, Y., Dong, K., et al. (2017). Protective effects of seabuckthorn pulp and seed oils against radiation-induced acute intestinal injury. J. Radiat. Res. 58, 24–32. doi:10.1093/jrr/rrw069
Shin, Y., Kim, B., and Kim, W. (2022). Cisplatin-induced nausea and vomiting: effect of herbal medicines. Plants (Basel) 11, 3395. doi:10.3390/plants11233395
Shukla, S. K., Chaudhary, P., Kumar, I. P., Samanta, N., Afrin, F., Gupta, M. L., et al. (2006). Protection from radiation-induced mitochondrial and genomic DNA damage by an extract of Hippophae rhamnoides. Environ. Mol. Mutagen 47, 647–656. doi:10.1002/em.20251
Singh, V. (2022). “Global distribution of seabuckthorn (hippophae sp.) resources and their utilization,” in The seabuckthorn genome. Editor P. C. Sharma (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 345–368. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-11276-8_18
Sławińska, N., Żuchowski, J., Stochmal, A., and Olas, B. (2024). Anti-platelet activity of sea buckthorn seeds and its relationship with thermal processing. Foods 13, 2400. doi:10.3390/foods13152400
Smyth, E. C., Nilsson, M., Grabsch, H. I., van Grieken, N. C., and Lordick, F. (2020). Gastric cancer. Lancet London, Engl. 396, 635–648. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
Somensi, L. B., Costa, P., Boeing, T., Mariano, L. N. B., Longo, B., Magalhães, C. G., et al. (2020). Gastroprotective properties of Lupeol-derived ester: pre-Clinical evidences of Lupeol-stearate as a potent antiulcer agent. Chem. Biol. Interact. 321, 108964. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2020.108964
Su, Z. Z., and Hong, Li B. (2022). Efficacy of recombinant human interferon alpha-1b combined with dried sea buckthorn emulsion in the treatment of viral diarrhea in children. J. Xinxiang Med. Coll. 39, 76–80. doi:10.7683/xxyxyxb.2022.01.016
Sun, X., Dey, P., Bruno, R. S., and Zhu, J. (2022). EGCG and catechin relative to green tea extract differentially modulate the gut microbial metabolome and liver metabolome to prevent obesity in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 109, 109094. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109094
Suryakumar, G., and Gupta, A. (2011). Medicinal and therapeutic potential of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). J. Ethnopharmacol. 138, 268–278. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.024
Suryamani, R., Sindhu, R., and Singh, I. (2022). “Phytosterols: physiological functions and therapeutic applications,” in Bioactive food components activity in mechanistic approach. Editors C. B. B. Cazarin, J. L. Bicas, G. M. Pastore, and M. R. Marostica Junior (Academic Press), 223–238. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-823569-0.00008-4
Taldaev, A., Svotin, A. A., Obukhov, S. I., Terekhov, R. P., and Selivanova, I. A. (2025). Modification of biopharmaceutical parameters of flavonoids: a review. Front. Chem. 13, 1602967. doi:10.3389/fchem.2025.1602967
Teng, H., He, Z., Hong, C., Xie, S., and Zha, X. (2024). Extraction, purification, structural characterization and pharmacological activities of polysaccharides from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.): a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 324, 117809. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117809
Ting, G., and Ping, W. (2023). Clinical study on the treatment of functional dyspepsia in children with dried sea buckthorn emulsion combined with Bifidobacterium bifidum triplicatum. Mod. Drugs Clin. 38, 373–377. doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2023.02.020
Tkacz, K., Wojdyło, A., Turkiewicz, I. P., Bobak, Ł., and Nowicka, P. (2019). Anti-oxidant and anti-enzymatic activities of sea buckthorn (hippophaë Rhamnoides L.) fruits modulated by chemical components. Antioxidants 8, 618. doi:10.3390/antiox8120618
Tkacz, K., Wojdyło, A., Turkiewicz, I. P., Ferreres, F., Moreno, D. A., and Nowicka, P. (2020). UPLC-PDA-Q/TOF-MS profiling of phenolic and carotenoid compounds and their influence on anticholinergic potential for AChE and BuChE inhibition and on-line antioxidant activity of selected hippophaë rhamnoides L. cultivars. Food Chem. 309, 125766. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125766
Tulsawani, R. (2010). Ninety day repeated gavage administration of hipphophae Rhamnoides extract in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 48, 2483–2489. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.06.018
Upadhyay, N. K., Kumar, R., Mandotra, S. K., Meena, R. N., Siddiqui, M. S., Sawhney, R. C., et al. (2009). Safety and healing efficacy of Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed oil on burn wounds in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 47, 1146–1153. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.02.002
Upadhyay, N. K., Kumar, M. S. Y., and Gupta, A. (2010). Antioxidant, cytoprotective and antibacterial effects of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) leaves. Food Chem. Toxicol. 48, 3443–3448. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.09.019
Vashishtha, V., Barhwal, K., Kumar, A., Hota, S. K., Chaurasia, O. P., and Kumar, B. (2017). Effect of seabuckthorn seed oil in reducing cardiovascular risk factors: a longitudinal controlled trial on hypertensive subjects. Clin. Nutr. 36, 1231–1238. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2016.07.013
Wang, Y., Nie, F., Ouyang, J., Wang, X., and Ma, X. (2014). Inhibitory effects of sea buckthorn procyanidins on fatty acid synthase and MDA-MB-231 cells. Tumor Biol. 35, 9563–9569. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2233-1
Wang, H., Gao, T., Du, Y., Yang, H., Wei, L., Bi, H., et al. (2015). Anticancer and immunostimulating activities of a novel homogalacturonan from Hippophae rhamnoides L. berry. Carbohydr. Polym. 131, 288–296. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.021
Wang, H., Bi, H., Gao, T., Zhao, B., Ni, W., and Liu, J. (2018a). A homogalacturonan from Hippophae rhamnoides L. berries enhance immunomodulatory activity through TLR4/MyD88 pathway mediated activation of macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 107, 1039–1045. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.09.083
Wang, Y., Gao, X., Ghozlane, A., Hu, H., Li, X., Xiao, Y., et al. (2018b). Characteristics of faecal microbiota in paediatric crohn’s disease and their dynamic changes during infliximab therapy. J. Crohns Colitis 12, 337–346. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx153
Wang, Z., Feng, R., Zhang, X., Su, Z., Wei, J., and Liu, J. (2019). Characterization of the Hippophae rhamnoides WRKY gene family and functional analysis of the role of the HrWRKY21 gene in resistance to abiotic stresses. Genome 62, 689–703. doi:10.1139/gen-2019-0024
Wang, J.-Q., Yang, Y., Cai, C.-Y., Teng, Q.-X., Cui, Q., Lin, J., et al. (2021). Multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs): structure, function and the overcoming of cancer multidrug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 54, 100743. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2021.100743
Wang, Y., Lu, J., Qu, H., Cai, C., Liu, H., and Chu, J. (2022). β-Carotene extracted from Blakeslea trispora attenuates oxidative stress, inflammatory, hepatic injury and immune damage induced by copper sulfate in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 258, 109366. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2022.109366
Wang, Z., Zhao, F., Wei, P., Chai, X., Hou, G., and Meng, Q. (2022). Phytochemistry, health benefits, and food applications of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.): a comprehensive review. Front. Nutr. 9, 1036295. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1036295
Wang, F., Hu, D., Sun, H., Yan, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, L., et al. (2023a). Global, regional, and national burden of digestive diseases: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front. Public Health 11, 1202980. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1202980
Wang, Y., Huang, Y., Chase, R. C., Li, T., Ramai, D., Li, S., et al. (2023b). Global burden of digestive diseases: a systematic analysis of the global burden of diseases study, 1990 to 2019. Gastroenterology 165, 773–783.e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.050
Wang, H., Cheng, N., Wu, Q., Fang, D., Rahman, F.-U., Hao, H., et al. (2024a). Antioxidant activities of sea buckthorn polysaccharides and their potential application in cosmetic industry. J. Dermatologic Sci. Cosmet. Technol. 1, 100023. doi:10.1016/j.jdsct.2024.100023
Wang, J., Yao, Y., Yao, T., Shi, Q., Zeng, Y., and Li, L. (2024b). Hesperetin alleviated experimental colitis via regulating ferroptosis and gut microbiota. Nutrients 16, 2343. doi:10.3390/nu16142343
Wei, R. E. N., Xiao-wei, B. A. O., Zhi-fang, Z., Lei, H., Lan-jun, Z., and Ya-tao, Z. (2019). Study on free radical scavenging and anti-lipid peroxidation of seabuckthorn polysaccharide. spgykj 40, 272–277. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.08.046
Wen, P., Zhao, P., Qin, G., Tang, S., Li, B., Zhang, J., et al. (2020). Genotoxicity and teratogenicity of seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berry oil. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 43, 391–397. doi:10.1080/01480545.2018.1497047
Wu, H., Li, C., Cui, M., Guo, H., Chen, S., Du, J., et al. (2021). Polyphenols from Hippophae rhamnoides suppressed Colon cancer growth by regulating miRNA-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. J. Funct. Foods 87, 104780. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2021.104780
Xiao, F. (2017). Blocking effect of dried sea buckthorn emulsion on precancerous esophageal lesions and the expression of ANO1 and EGFR in the process of esophageal carcinogenesis and its significance. Jinan: Shandong University. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201702&filename=1017072977.nh (Accessed August 19, 2024).
XiaoFeng, Z. (2020). Protective effect of sea buckthorn sterols on alcoholic gastric mucosal injury. West China J. Pharm. 35, 37–42. doi:10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2020.01.008
Xie, X., Song, Y., Bi, X., Liu, X., Xing, Y., and Che, Z. (2023). Characterization of sea buckthorn polysaccharides and the analysis of its regulatory effect on the gut microbiota imbalance induced by cefixime in mice. J. Funct. Foods 104, 105511. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2023.105511
Xing, J. (2012). Effects of sea buckthorn (hippophaë rhamnoides L.) pulp oils on the gastric secretion, gastric emptying and its analgesic activity. J. Med. Plants Res. 6. doi:10.5897/JMPR12.109
Xing, J., Yang, B., Dong, Y., Wang, B., Wang, J., and Kallio, H. P. (2002). Effects of sea buckthorn (hippophaë Rhamnoides L.) seed and pulp oils on experimental models of gastric ulcer in rats. Fitoterapia 73, 644–650. doi:10.1016/S0367-326X(02)00221-6
Xu, X., Xie, B., Pan, S., Liu, L., Wang, Y., and Chen, C. (2007). Effects of sea buckthorn procyanidins on healing of acetic acid-induced lesions in the rat stomach. Asia Pac J. Clin. Nutr. 16 (Suppl. 1), 234–238. doi:10.6133/apjcn.2007.16.s1.44
Xu, Y.-J., Kaur, M., Dhillon, R. S., Tappia, P. S., and Dhalla, N. S. (2011). Health benefits of sea buckthorn for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. J. Funct. Foods 3, 2–12. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2011.01.001
Yan, Li (2002). Study on the effect of sea buckthorn oil emulsion against chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric ulcer in rats. Chin. Pharm., 14–15. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-0408.2002.10.006
Yanase, F., Fujii, T., Naorungroj, T., Belletti, A., Luethi, N., Carr, A. C., et al. (2020). Harm of IV high-dose vitamin C therapy in adult patients: a scoping review. Crit. Care Med. 48, e620–e628. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000004396
YanChao, S., and WanXing, X. (2024). Effects of sea buckthorn polysaccharides on serum immunity, liver antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice. Feed Ind., 1–8. doi:10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2024.19.016
Yang, B. (2009). Sugars, acids, ethyl β-d-glucopyranose and a methyl inositol in sea buckthorn (hippophaë rhamnoides) berries. Food Chem. 112, 89–97. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.05.042
Yang, B., and Kallio, H. P. (2001). Fatty acid composition of lipids in sea buckthorn (hippophaë rhamnoides L.) berries of different origins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 49, 1939–1947. doi:10.1021/jf001059s
Yang, X., Sun, X., Zhou, F., Xiao, S., Zhong, L., Hu, S., et al. (2023). Protocatechuic acid alleviates dextran-sulfate-sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice via the regulation of intestinal flora and ferroptosis. Molecules 28, 3775. doi:10.3390/molecules28093775
Yang, X., Wang, H., Shen, C., Dong, X., Li, J., and Liu, J. (2024). Effects of isorhamnetin on liver injury in heat stroke-affected rats under dry-heat environments via oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Sci. Rep. 14, 7476. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57852-y
Yi, X. (2023). Progress of research on comprehensive development and utilisation of sea buckthorn. Food Res. Dev. 44, 201–207. doi:10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.19.029
Ying, J. C. (2022). Studies on the effect of sea buckthorn extract on gastrointestinal microorganisms. Xining: Qinghai University. doi:10.27740/d.cnki.gqhdx.2020.000418
Ying, W. (2024). Progress of research on active components and functional properties of sea buckthorn. Mod. food Sci. Technol. doi:10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2025.4.0348
Yoo, K. H., Park, J.-H., Lee, D. Y., Hwang-Bo, J., Baek, N. I., and Chung, I. S. (2015). Corosolic acid exhibits anti-angiogenic and anti-lymphangiogenic effects on in vitro endothelial cells and on an in vivo CT-26 Colon carcinoma animal model. Phytother. Res. 29, 714–723. doi:10.1002/ptr.5306
Yoshida, T., Tanaka, K., Chen, X.-M., and Okuda, T. (1991). Tannins from Hippophae rhamnoides. Phytochemistry 30, 663–666. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(91)83748-A
Yu, E., and Amri, H. (2016). China’s other medical systems: recognizing Uyghur, Tibetan, and Mongolian traditional medicines. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 5, 79–86. doi:10.7453/gahmj.2015.116
Yuan, W., Wang, H., and Gong, Y. (2021). Prevention of cisplatin-induced nausea and vomiting by seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed oil: insights at the level of orexin-A in rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 24, 248–255. doi:10.22038/ijbms.2020.47599.10973
Yuan, M., Chang, L., Gao, P., Li, J., Lu, X., Hua, M., et al. (2024). Synbiotics containing sea buckthorn polysaccharides ameliorate DSS-Induced colitis in mice via regulating Th17/Treg homeostasis through intestinal microbiota and their production of BA metabolites and SCFAs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 276, 133794. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133794
Zadernowski, R., Naczk, M., Czaplicki, S., Rubinskiene, M., and Szałkiewicz, M. (2005). Composition of phenolic acids in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries. J. Americ Oil Chem. Soc. 82, 175–179. doi:10.1007/s11746-005-5169-1
Zhang, W., Zhang, X., Zou, K., Xie, J., Zhao, S., Liu, J., et al. (2017). Seabuckthorn berry polysaccharide protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activities. Food Funct. 8, 3130–3138. doi:10.1039/c7fo00399d
Zhang, J.-X., Feng, W.-J., Liu, G.-C., Ma, Q.-Q., Li, H.-L., Gao, X.-Y., et al. (2020). Corosolic acid attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammatory response via AMPK/SREBPs and NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathways. Am. J. Chin. Med. 48, 579–595. doi:10.1142/S0192415X20500299
Zhang, X., Wang, J., Zhu, L., Wang, X., Meng, F., Xia, L., et al. (2022). Advances in stigmasterol on its anti-tumor effect and mechanism of action. Front. Oncol. 12, 1101289. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1101289
Zhang, X., Li, M., Zhu, L., Geng, Z., Liu, X., Cheng, Z., et al. (2023). Sea buckthorn pretreatment, drying, and processing of high-quality products: current status and trends. Foods 12, 4255. doi:10.3390/foods12234255
Zhang, J., Chen, T., Wen, Y., Siah, K. T. H., and Tang, X. (2024a). Insights and future prospects of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Phytomedicine 127, 155481. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155481
Zhang, T., Xiang, F., Li, X., Chen, Z., Wang, J., Guo, J., et al. (2024b). Mechanistic study on ursolic acid inhibiting the growth of colorectal cancer cells through the downregulation of TGF-β3 by miR-140-5p. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 38, e23581. doi:10.1002/jbt.23581
Zhang, X., Zhang, W., Zhao, L., Ma, G., Huang, Y., Geng, Z., et al. (2024c). Ocotillol derivatives mitigate retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. J. Med. Chem. 67, 15268–15290. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00867
Zhao, P., Wang, S., Liang, C., Wang, Y., Wen, P., Wang, F., et al. (2017). Acute and subchronic toxicity studies of seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) oil in rodents. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 91, 50–57. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.10.002
Zhao, L., Li, M.-Y., Su, S., Geng, T.-T., and Sun, H. (2019). Hippophae rhamnoides L. polysaccharide enhances antioxidant enzyme activity, cytokine level, and related mRNA expression in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. Can. J. Animal Sci. 100, 193–204. doi:10.1139/cjas-2019-0134
Zhao, L., Li, M., Sun, K., Su, S., Geng, T., and Sun, H. (2020). Hippophae rhamnoides polysaccharides protect IPEC-J2 cells from LPS-Induced inflammation, apoptosis and barrier dysfunction in vitro via inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 155, 1202–1215. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.088
Zhao, H., Kong, L., Shao, M., Liu, J., Sun, C., Li, C., et al. (2022). Protective effect of flavonoids extract of Hippophae rhamnoides L. on alcoholic fatty liver disease through regulating intestinal flora and inhibiting TAK1/p38MAPK/p65NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 292, 115225. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115225
Zheng, L., Shi, L.-K., Zhao, C.-W., Jin, Q.-Z., and Wang, X.-G. (2017). Fatty acid, phytochemical, oxidative stability and in vitro antioxidant property of sea buckthorn (hippophaë rhamnoides L.) oils extracted by supercritical and subcritical technologies. LWT 86, 507–513. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2017.08.042
Zhong, W., Chen, J., Xu, G., and Xiao, L. (2024). Kaempferol ameliorated alcoholic hepatitis through improving intestinal barrier function by targeting miRNA-155 signaling. Pharmacology 109, 138–146. doi:10.1159/000537964
Zhou, H. L., and Yan, L. (2006). Clinical observation on the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with dried sea buckthorn emulsion. China Med. Her. 3, 15–16. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7210.2006.05.006
Zhou, Y., Lin, S., Zhong, X., Huang, F., Huang, J., and Xu, L. (2024). Oleanolic acid combined with aspirin plays antitumor roles in colorectal cancer via the Akt/NFκB/IκBα/COX2 pathway. Cell Death Discov. 10, 504. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-02223-9
Zhu, Y., Li, X., Chen, J., Chen, T., Shi, Z., Lei, M., et al. (2016). The pentacyclic triterpene lupeol switches M1 macrophages to M2 and ameliorates experimental inflammatory bowel disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 30, 74–84. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2015.11.031
Zielińska, A., and Nowak, I. (2017). Abundance of active ingredients in sea-buckthorn oil. Lipids Health Dis. 16, 95. doi:10.1186/s12944-017-0469-7
Zosimidou, S. S., Vouvoudi, E. C., Tsagkalias, I. S., Lykidou, S. S., and Nikolaidis, N. F. (2023). Preparation of cosmetic emulsions containing hippophae oil isolated by various methods: study of their antioxidant, sun-blocking and physicochemical properties. Antioxidants 12, 1829. doi:10.3390/antiox12101829
Zu Fan, Y. (2024). Analysis of flavonoid composition of sea buckthorn based on UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS technique. Chem. Reag. 46, 95–106. doi:10.13822/j.cnki.hxsj.2023.0726
Keywords: sea buckthorn, digest disease, bioactive metabolites, clinical trials, pharmacological mechanisms
Citation: Dong W, Tang Y, Qiao J, Dong Z and Cheng J (2025) Sea buckthorn bioactive metabolites and their pharmacological potential in digestive diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1637676. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1637676
Received: 29 May 2025; Accepted: 05 September 2025;
Published: 23 September 2025.
Edited by:
Wei Peng, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Kaidi Nie, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaSuresh Kumar, National Institute of Biologicals, India
Hao Teng, Guilin Tourism University, China
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Tang, Qiao, Dong and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Cheng, Ynl5ZnljakBmb3htYWlsLmNvbQ==; ZhiQiang Dong, ZHpxNDg5NUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 WenChang Dong1,2†
WenChang Dong1,2† Jie Cheng
Jie Cheng