- 1Department of Geriatrics, The First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 2The Key Laboratory of Microcosmic Syndrome Differentiation, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 3Yunnan Key Laboratory of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Chronic Disease in Prevention and Treatment, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 4National-Local Joint Engineering Research Centre for Sanqi Resource Protection and Utilisation Technology, Kunming, Yunnan, China
Objective: This study evaluated therapeutic effects of ginsenoside Rg1 (QiShengli Tablets) in patients with carotid artery plaques, in combination with lifestyle interventions, lipid-lowering therapy. We aimed to provide novel insights into safe clinical application of ginsenoside Rg1 for managing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Methods: From January 2022 to October 2023, 106 carotid artery plaques patients Aged ≥60 and <74 were recruited from the Geriatrics Department of First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province. All participants provided informed consent and a randomized sequence is generated by random number table method and divided into three groups. Group 1 received lifestyle interventions plus atorvastatin calcium tablets (n = 32). Group 2 received same treatment as Group 1, with the addition of Bayaspirin (n = 33). Group 3 received the same treatment as Group 2, but with Bayaspirin replaced by ginsenoside Rg1 (n = 41). This study adopted a single-blind design: by uniformly encapsulating the tablets in their original form in blind bags, the subjects took them at regular intervals and in fixed quantities There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics among the groups before treatment (P > 0.05). All patients were treated 3 months. Carotid atherosclerosis–related outcomes were assessed after treatment, and data were analyzed using SPSS 24.0.
Results: Carotid ultrasound revealed significant intergroup differences in plaque number and volume changes after treatment (P < 0.05). No significant intergroup differences were observed in arterial stiffness index (P > 0.05). Fibroblast growth factor 21 levels differed significantly among the groups (P < 0.05), whereas Lumican and Fibulin-1 levels did not (P > 0.05). Analysis biochemical indicators revealed significant post-treatment differences in LDL-C, TC, Hcy, IL-6, TNF-α, 25(OH)D, and insulin resistance (IR) (P < 0.05). Notably, after treatment of three groups, Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scale score was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Patients with carotid atherosclerotic plaques, adding ginsenoside Rg1 to standard therapy reduced the number and volume of carotid plaques. It improved quality of life, decreased specific inflammatory markers, and enhanced blood pressure control and Insulin Resistance (IR). These suggest ginsenoside Rg1 may have clinical value in the future management of carotid atherosclerosis.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention and treatment remain major global challenges (Afzal et al., 2024; Jamthikar et al., 2020). According to the World Health Organization (Wang et al., 2023), approximately 120 million people worldwide suffered from CVD in 2024, accounting for 1.5% of the global population—with 60 million cases reported in China alone. CVD is a leading cause of death and disease burden, particularly among older adults. Among all CVDs, carotid atherosclerosis is of particular concern. Studies (Yuriev et al., 2021; Effati et al., 2024; Ruan et al., 2024) have shown that over 80% of individuals aged 50 and older in China have varying degrees of carotid atherosclerotic plaques. These plaques can cause arterial stenosis, reduce cerebral blood flow, and trigger ischemic cerebrovascular events, including life-threatening complications. Currently, no specific drug is approved for the treatment of carotid atherosclerosis, highlighting the urgent need for further research and therapeutic innovation.
According to clinical guidelines, the standard treatment for carotid atherosclerotic plaques involves the use of statins and Bayaspirin (López-Cancio et al., 2014; Hermel et al., 2022). Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, promoting the uptake and degradation of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) to lower plasma LDL-C levels (Huang et al., 2024; Turongkaravee et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2020b). Bayaspirin, an antiplatelet agent, inhibits COX-1 activity, thereby preventing abnormal platelet aggregation and reducing the risk of thrombosis (Zhang et al., 2023; Tufano et al., 2011). While this dual-drug regimen effectively slows disease progression, its long-term use is often limited by drug-related side effects, highlighting the need for safer and more sustainable alternatives (Benjamin et al., 2024; Vinci et al., 2021).
Panax notoginseng (Sanqi) is a well-established traditional medicine, and its saponin content, particularly ginsenoside Rg1—have become the focus of increasing scientific research (Li et al., 2008; Li et al., 2021). The Rg1-based pharmaceutical QiShengli Tablets (Yunnan Wenshan Teanna Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) have been approved for clinical use. Its core active ingredient is ginsenoside Rg1, and the formulation also includes four excipients: starch, dextrin, sucrose, and magnesium stearate. Meanwhile, the above four excipients will not affect the bioavailability and pharmacodynamic characteristics of the small molecule active ingredients within the conventional dosage range (Chen et al., 2013). Despite its approval, clinical evidence supporting its use in treating specific diseases remains limited. Consequently, the drug’s labeling describes its applications only in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) terms—such as “invigorating the spleen,” “awakening the brain,” “reinforcing vital qi,” and “promoting blood circulation.” The lack of disease-specific indications hinders its widespread adoption in contemporary medical practice. Despite limited clinical evidence, preclinical studies over the past decade suggest that Rg1 can modulate immune function, alleviate obesity-related metabolic disorders, and exert protective effects against carotid and coronary atherosclerosis (Yang et al., 2022; He et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2020c). However, large-scale clinical trials are still needed to validate these findings.
Based on this context, our study examined the effects of ginsenoside Rg1 in patients with carotid atherosclerotic plaques. After 3 months of treatment, we conducted a comprehensive evaluation, including routine biochemical indicators (complete blood count, inflammatory markers, and oxidative stress markers) and carotid artery assessments using B-ultrasound. Ultimately, we aimed to contribute to the prevention of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and to explore ginsenoside Rg1 as a potential new therapeutic option for carotid atherosclerosis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Drugs and sources
Ginsenoside Rg1 (QiShengli Tablets): Each tablet contains 120 mg of formulation, including 15 mg of ginsenoside Rg1. Approval No.: National Drug Approval Z20027165. Manufacturer: Yunnan Teanna Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets (Lipitor): Each tablet contains 20 mg of atorvastatin calcium. Approval No.: National Drug Approval J20120049. Manufacturer: Pfizer Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Bayaspirin: Each tablet contains 100 mg of aspirin. Approval No.: National Drug Approval HJ20160685. Manufacturer: Bayer Healthcare Company Ltd.
2.2 Study subjects
From January 2022 to October 2023, 106 patients diagnosed with carotid atherosclerosis were enrolled from both outpatient and inpatient services at the Geriatrics Department of the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province. All participants provided written informed consent. Ethical approval for this study was granted in January 2023 by the Ethics Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province (Approval No.: KHLL2023-KY006).
2.2.1 Diagnostic criteria
Patients were eligible if they met both of the following criteria:
1. Carotid plaque diagnosis was based on the “Guidelines for Vascular Ultrasound Examination” formulated by the Ultrasound Physicians Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association: Normal: Intima-media thickness (IMT) < 1.0 mm. Carotid intimal thickening/atherosclerosis plaque: IMT between 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm indicates thickening. IMT ≥1.5 mm indicates plaque formation.
2. Dyslipidemia, defined by any of the following: total cholesterol (TC) > 6.2 mmol/L; triglycerides (TG) > 2.3 mmol/L; LDL-C > 4.1 mmol/L; high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) <1.0 mmol/L. All enrolled patients had LDL-C > 4.1 mmol/L, with concurrent use of metformin.
2.2.2 Inclusion criteria
Patients were included if they met all of the following conditions:
1) Age ≥60 years old and <74 years old; 2) diagnosis of dyslipidemia; 3) presence of carotid plaque confirmed by ultrasound (IMT >1.5 mm); 4) provision of written informed consent for voluntary participation.
2.2.3 Exclusion criteria
Patients were excluded if they met any of the following criteria:
1) Failed to meet the diagnostic or inclusion criteria; 2) had severe hepatic, renal, or hematologic disease; 3) were nonadherent to medication protocol; 4) had experienced recent major trauma or undergone surgery; 5) participated in another clinical trial within the past 3 months; 6) had incomplete medical records that could not be supplemented.
2.3 Treatment and grouping
One hundred six patients were randomized into three groups. Group 1 (n = 32): received a combination of lifestyle intervention and atorvastatin calcium tablets. Group 2 (n = 33) received the same treatment as Group 1, with the addition of Bayaspirin enteric-coated tablets. Group 3 (n = 41) received the same treatment as Group 2, but Bayaspirin was discontinued and replaced with ginsenoside Rg1 (QiShengli Tablets). The lifestyle intervention implemented across all groups consisted of several components. Patients were advised to adopt reasonable dietary and lifestyle modifications, including a low-salt, low-fat diet; cessation of smoking; limited alcohol consumption; and increased intake of vegetables, lean protein, and fish. A small quantity of nuts was allowed daily, while the intake of fructose was to be minimized. Specific dietary targets included restricting daily cholesterol intake to less than 300 mg, maintaining a daily fiber intake of 25–30 g per day, and limiting salt consumption to below 5 g per day. In addition, patients were encouraged to get adequate rest, maintain a positive outlook, and engage in regular physical activity. They were permitted to select their preferred exercise methods, such as brisk walking, jogging, aerobics, or swimming. Each exercise session lasted 45 min and was performed five times per week over a 3-month period. Pharmacological treatment for Group 1 included atorvastatin calcium tablets administered at a dose of 20 mg once nightly. In Group 2, Bayaspirin enteric-coated tablets were added to the regimen (100 mg taken once every morning). In Group 3, Bayaspirin was discontinued, and patients instead received ginsenoside Rg1 (two QiShengi Tablets taken three times daily over a 3-month period). Relevant data were collected after the 3-month treatment period, and subsequent related experiments were conducted.
Before the study, a priori power analysis was conducted using G*Power software to determine the required sample size. Based on the anticipated effect size, a two-tailed α of 0.05, and a target power of at least 50%, the minimum required sample size was 32 participants per group. The final sample sizes met or exceeded this threshold, ensuring sufficient statistical power to detect significant differences between the groups. Throughout the study period, no participants withdrew or dropped out, and all enrolled patients adhered strictly to the study protocol.
2.4 Data collection
A single-anonymized approach was adopted for this study. Tablets from different batches were repackaged into medication bags for patients to take daily. Tablet crushing was not performed, as Bayaspirin is a sustained-release formulation. The ethics committee raised concerns that crushing the tablets could compromise drug efficacy and, hence, did not approve this approach. Additionally, to ensure the accuracy and objectivity of the data collection, all clinical and laboratory data were collected by an independent physician who was blinded to the group assignments. The physician primarily assessed the following indicators: 1) General patient characteristics: This included gender and the presence of vascular risk factors for carotid artery plaques, including hypertension, diabetes, smoking history, and alcohol consumption. Patients with these risk factors were required to have stable control of blood pressure and blood glucose for at least 6 months prior to enrollment, with no need for medical adjustments during the study period. Moreover, Patients with chronic conditions continued their baseline treatments throughout the study to maintain blood pressure and glucose control. 2) Laboratory tests: Blood samples were uniformly processed at the Biochemistry Laboratory of the Laboratory Department, First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, using an automatic biochemical analyzer. The following markers were assessed: complete blood count, liver and kidney function, lipid profile, glycated hemoglobin, fasting blood glucose, fasting insulin, uric acid, 25(OH)D, and pro-inflammatory markers (e.g., CRP, IL-10, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ). Oxidative stress markers included MDA, ROS, SOD, and GSH. 3) Carotid ultrasound: Carotid plaque location and volume were evaluated using B-mode ultrasound. Plaque volume was estimated using standard imaging protocols. 4) Pulse wave velocity (PWV) and ankle-brachial index (ABI) were measured to evaluate arterial stiffness. 5) Vascular aging indicators: Levels of Lumican, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), and Fibulin-1 were tested at the Yunnan Key Laboratory of TCM Micro-Dialectics. 6) Comprehensive geriatric assessments: Cognitive and psychological status were evaluated using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale. (HAMA), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 24.0 (IBM SPSS, United States). Categorical variables were expressed as percentages (%) and analyzed using the χ2 test. Continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Differences among the three groups were assessed using a one-way analysis of variance, while differences before and after treatment within each group were evaluated using paired sample t-tests. A two-tailed p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant for all comparisons.
2.6 Technical roadmap
The experimental design and workflow of this study are illustrated in Figure 1.
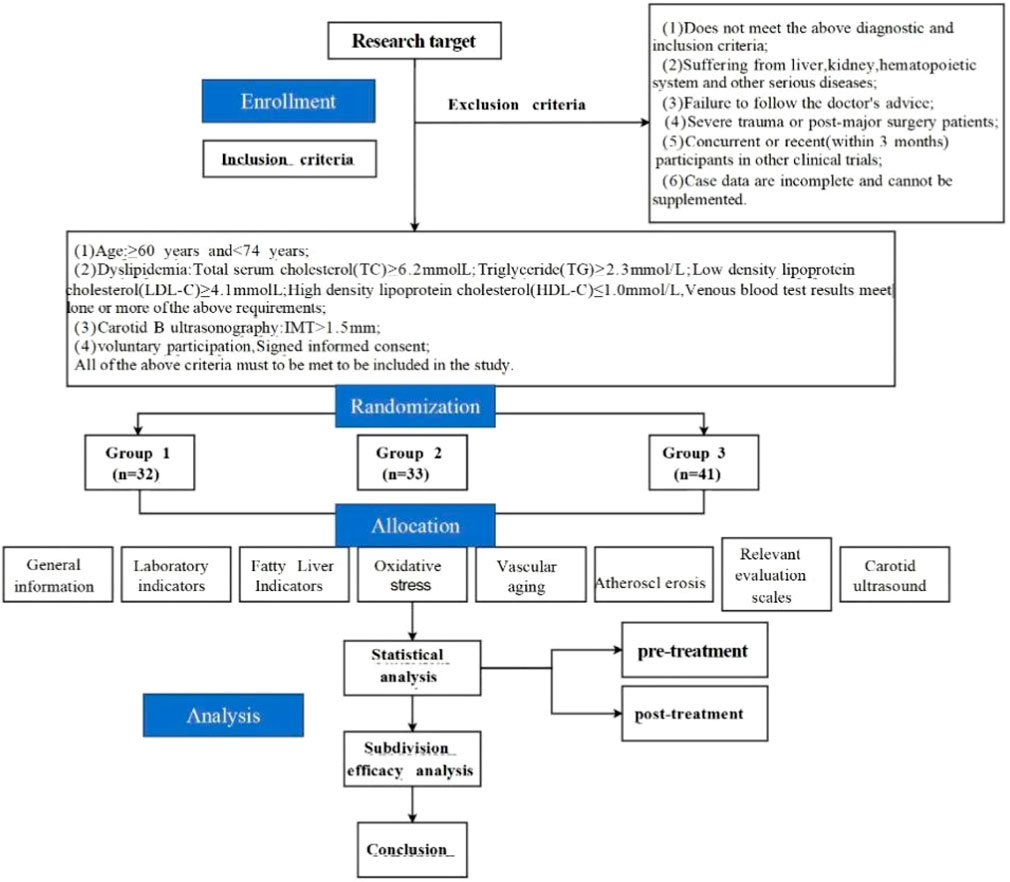
Figure 1. Technical route. (Note: This study strictly adhered to the treatment plan. All enrolled patients followed the advice throughout the process, taking the study drugs on time and in the prescribed dosage. There were no cases of poor medication compliance or drug withdrawal during the study, no dropout, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the research data).
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
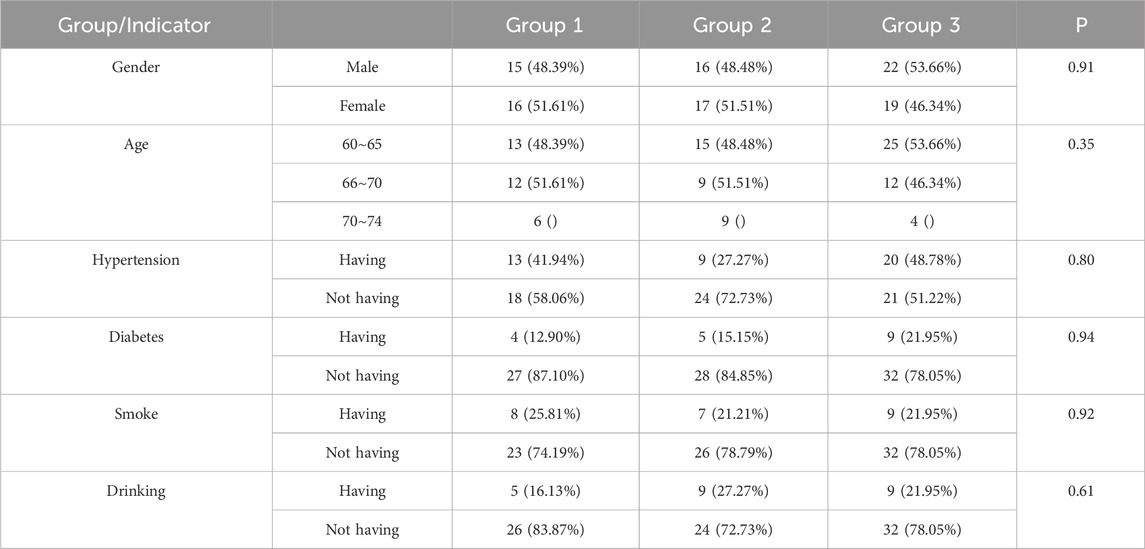
Before treatment, no significant differences were observed among the three groups in terms of gender, age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking history, or alcohol consumption (see Table 1 for details). Additionally, baseline laboratory and imaging markers—including blood tests (complete blood count), serum inflammatory cytokines, and carotid atherosclerosis indicators (e.g., IMT and plaque volume)—were comparable across the groups (Supplementary Tables S1–S6).
3.2 Carotid atherosclerosis indicators
3.2.1 Carotid ultrasound parameters
Plaque Quantity Analysis: There were no statistically significant differences in plaque quantity among the three groups before treatment (Supplementary Table S5). Carotid ultrasound was used to assess changes within each group (pre-vs. post-treatment) and between groups following treatment (Table 2).
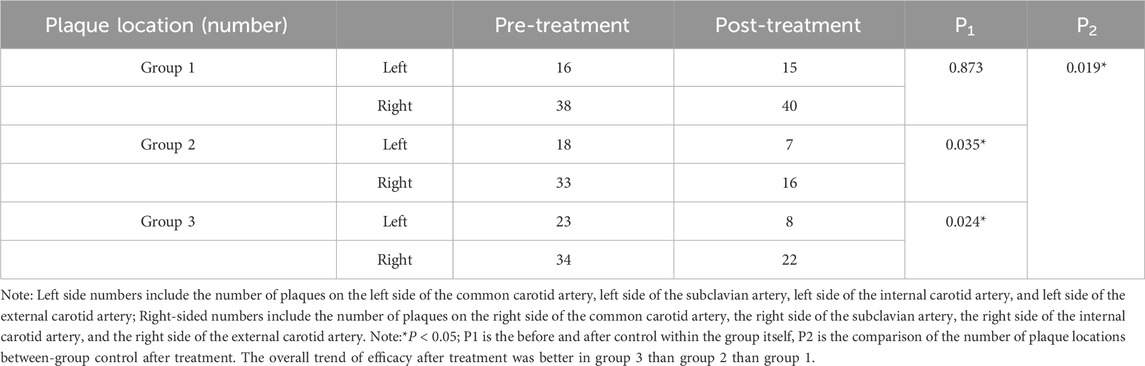
Table 2. Comparison of the number of plaque locations before and after treatment among the three groups.
Group 1: Left carotid plaques decreased, while right carotid plaques increased slightly; however, neither change was statistically significant (P > 0.05). Group 2: A significant reduction was observed in both left and right carotid plaques after treatment (P < 0.05). Group 3: Similar to Group 2, a significant reduction was observed in both left and right carotid plaques (P < 0.05). Intergroup comparison revealed statistically significant differences in post-treatment plaque quantity among the three groups (P < 0.05), indicating varied responses to the interventions.
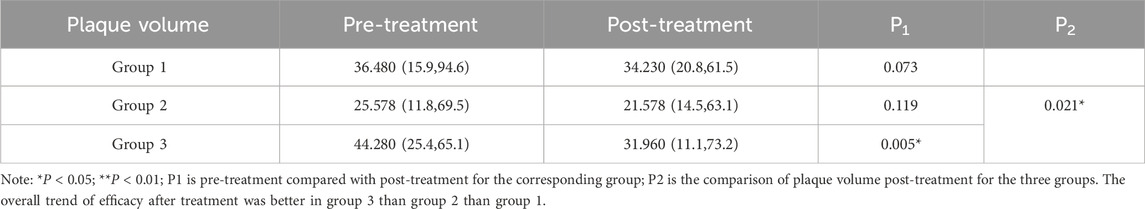
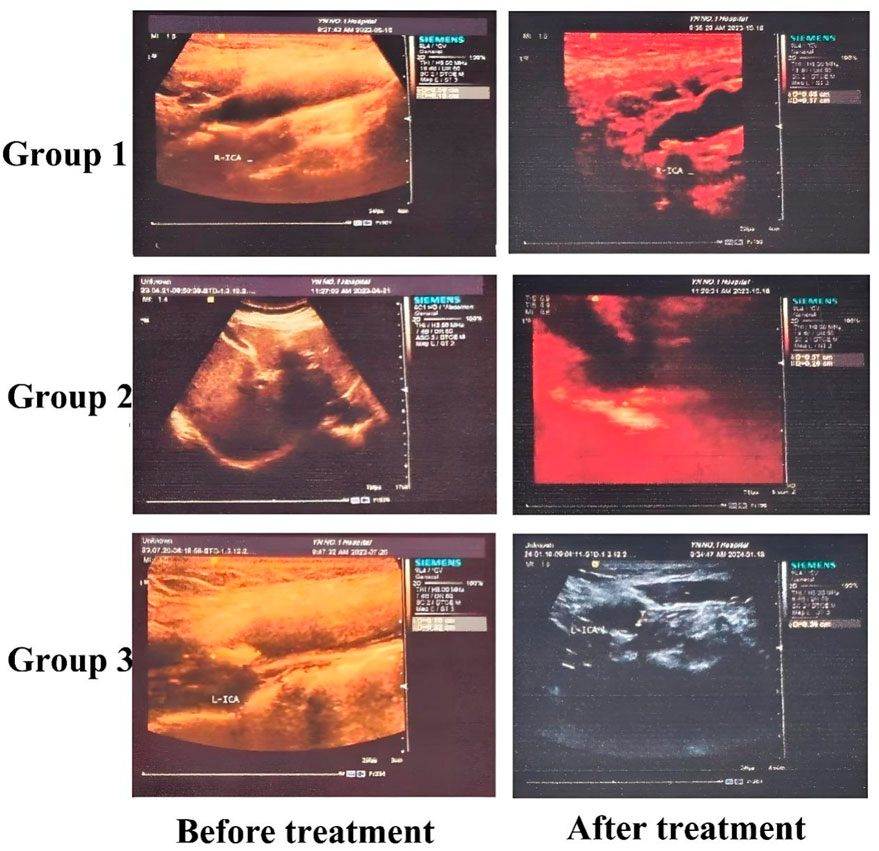
The characteristics of carotid plaque volume changes are presented in Table 3. After treatment, Groups 1 and 2 both showed reductions in plaque volume; however, these changes were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). In contrast, Group 3 exhibited a significant reduction in plaque volume (P < 0.05). Post-treatment intergroup analysis also revealed statistically significant differences in plaque volume among the three groups (P < 0.05). Overall, Group 3 showed the most pronounced therapeutic effect, suggesting that a combination of lifestyle intervention, atorvastatin therapy, and intensified exercise can contribute to carotid plaque reduction. Furthermore, replacing Bayaspirin with ginsenoside Rg1 in this regimen appeared to be more effective in reducing carotid volume. The detailed plaque volume measurements are presented in Table 3. In addition, we selected some representative B-ultrasound images, See Figure 2, with additional diagnostic ultrasound results provided in Supplementary Figures S1–S3. From the figure, the carotid plaque volumes before treatment were as follows: Group 1 had a plaque measuring 5.9 × 4.0 × 1.8 mm; Group 2 had a plaque measuring 7.7 × 5.9 × 2.3 mm; and Group 3 had two plaques, measuring 4.2 × 4.1 × 2.6 mm and 7.0 × 3.4 × 3.4 mm. After 3 months of treatment, the corresponding plaque volumes were reduced to 6.5 × 3.6 × 1.7 mm in Group 1, 5.7 × 5.2 × 2.6 mm in Group 2, and 3.3 × 3.5 × 1.5 mm and 7.0 × 3.0 × 2.0 mm in Group 3. Although these measurements showed varying degrees of plaque reduction across all groups, the most pronounced decrease was observed in Group 3.
3.2.2 Arterial stiffness indices
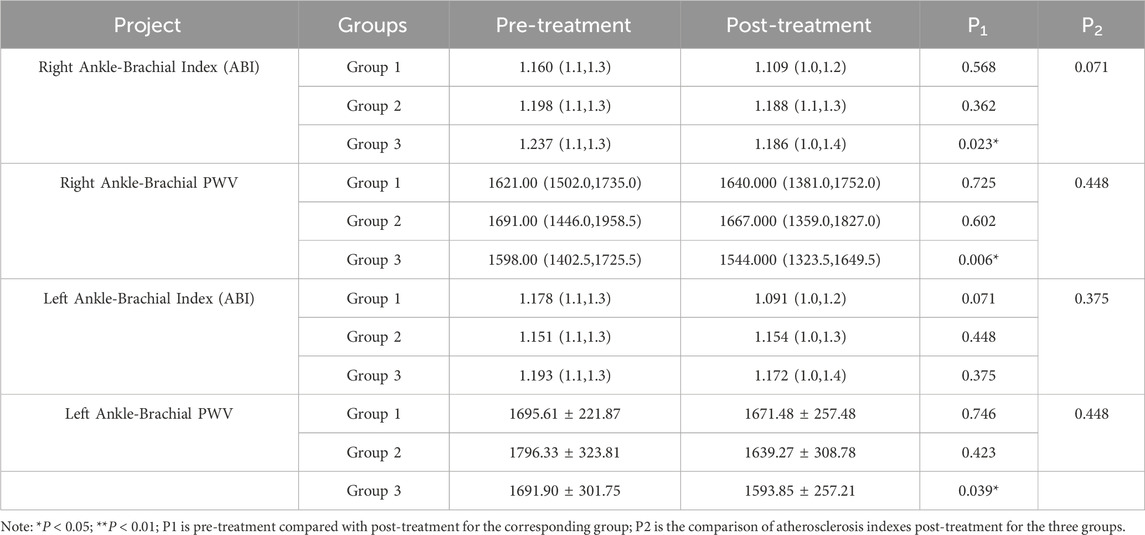
Atherosclerosis indices before and after treatment were comparable across all three groups, as detailed in Supplementary Table S4. Analysis of arterial stiffness indicators revealed the following key findings: statistically significant improvements in PWV at the right ankle-brachial site were observed in Groups 1 and 3 (P < 0.05). A statistical change in the left ankle-brachial PWV was observed only in Group 3 (P < 0.05). No other arterial stiffness indices showed significant changes in any of the groups (P > 0.05). For the between-group comparison, no statistically significant differences in arterial stiffness indicators were found among the three groups post-treatment (P > 0.05). These results suggest a potential role for lifestyle intervention, atorvastatin calcium therapy, intensive exercise, and ginsenoside Rg1 in improving arterial elasticity. Detailed results are presented in Table 4.
3.2.3 Vascular senescence indexes
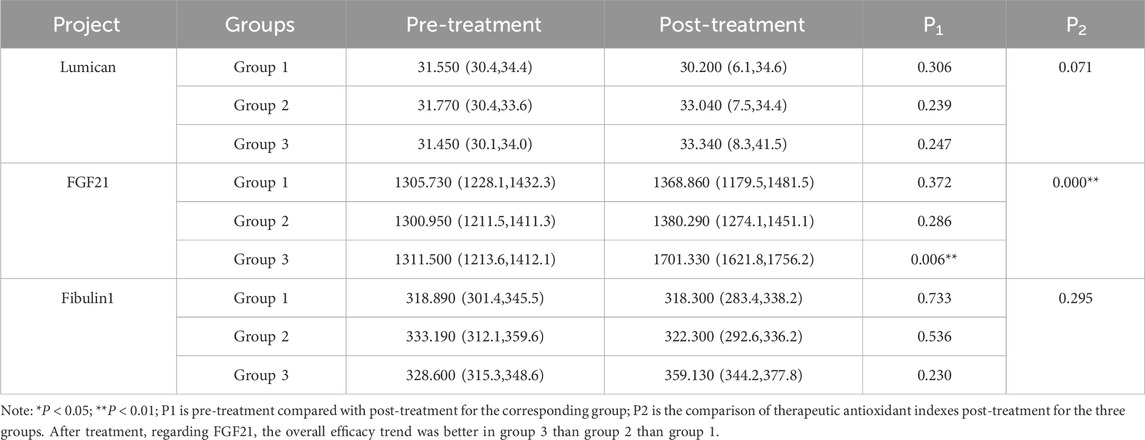
There were no significant differences in vascular senescence indices among the three groups before treatment (Supplementary Table S3). Vascular aging indicators were analyzed within each group (pre-vs. post-treatment) and compared across groups after treatment, with results summarized in Table 5. In Group 1, there were no statistically significant changes in Lumican, FGF21, or Fibulin-1 levels after treatment (P > 0.05). Similarly, in Group 2, no statistically significant differences were found in these three markers after (P > 0.05). However, in Group 3, FGF21 levels increased significantly after treatment (P < 0.05), while changes in Lumican and Fibulin-1 remained statistically insignificant (P < 0.05). Intergroup comparisons after treatment revealed a statistically significant difference in FGF21 levels among the three groups (P < 0.05), with no significant differences in Lumican or Fibulin-1 (P > 0.05). The overall trend in treatment efficacy indicated that Group 3 outperformed Group 2, which in turn outperformed Group 1. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg1 may enhance the improvement of vascular senescence when added to a regimen consisting of lifestyle intervention, atorvastatin calcium therapy, and intensive exercise.
3.3 Laboratory test indicators
There were no differences in laboratory test indicators among the three groups before treatment, indicating comparable baseline values (see Supplementary Tables S1, S2). Pre- and post-treatment comparisons within each group are presented in Table 6. In Group 1, some indicators showed improvement after treatment, but the differences were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). In Group 2, significant improvements were observed in LDL-C, Hcy, and insulin resistance (IR, P < 0.05). In Group 3, statistically significant improvements were found in LDL-C, IL-6, TNF-α, Hcy, 25(OH)D, and IR (P < 0.05). When comparing post-treatment results among all groups, significant differences were observed in LDL-C, TC, Hcy, IL-6, TNF-α, 25(OH)D, and IR (P < 0.05). The trend in efficacy followed the order: Group 3 > Group 2 > Group 1. These results suggest that Bayaspirin has a certain effect on reducing LDL-C, Hcy and IR on the basis of intensified exercise, lifestyle intervention and lipid-lowering treatment with atorvastatin calcium. Additionally, the inclusion of ginsenoside Rg1 that replacing Bayaspirin further amplified these effects, demonstrating a pronounced impact on lowering LDL-C, TC, Hcy, and IR levels while increasing 25(OH)D levels.
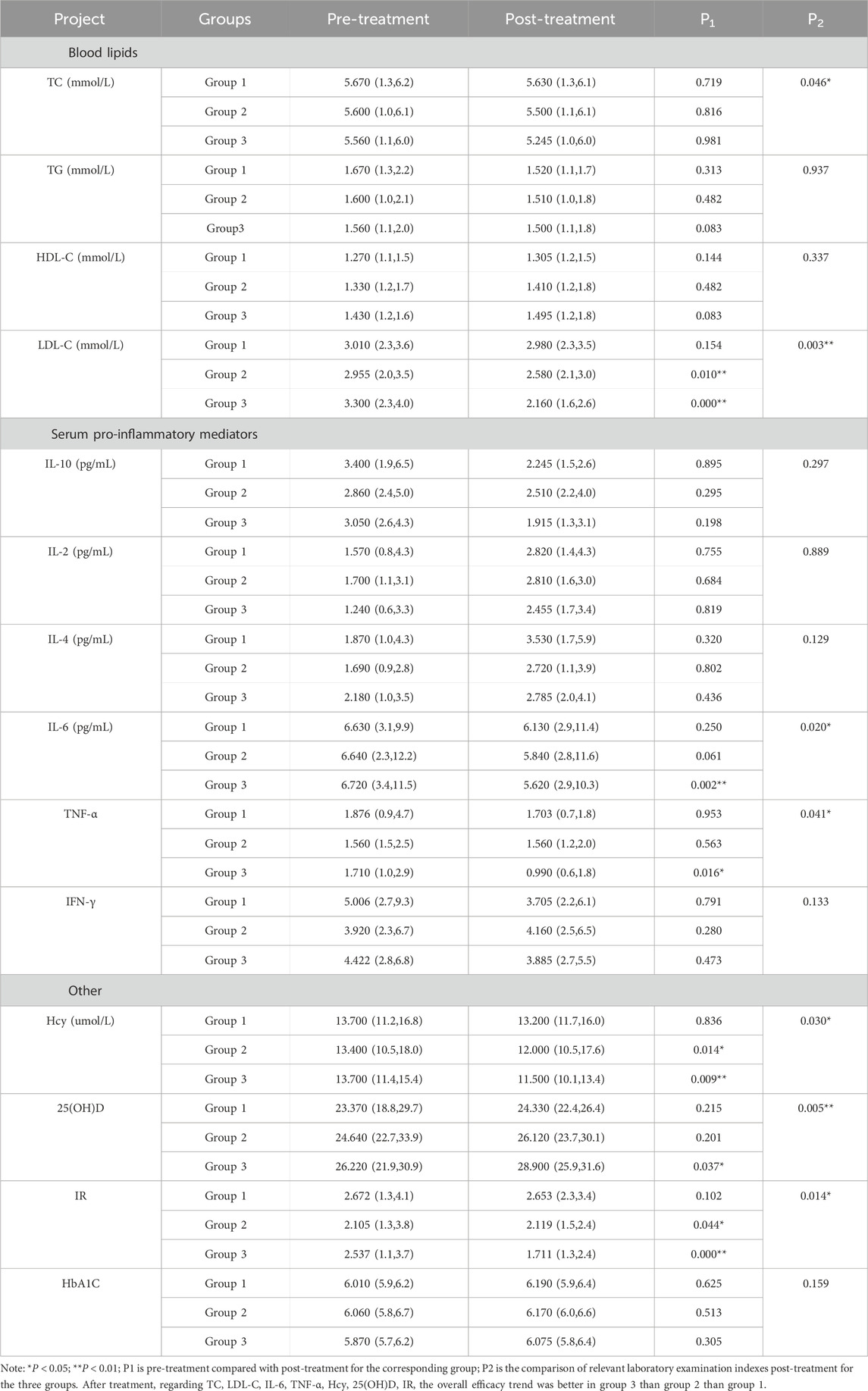
Table 6. Comparison of relevant laboratory examination indexes before and after treatment among the three groups.
3.4 Geriatric comprehensive assessment scale
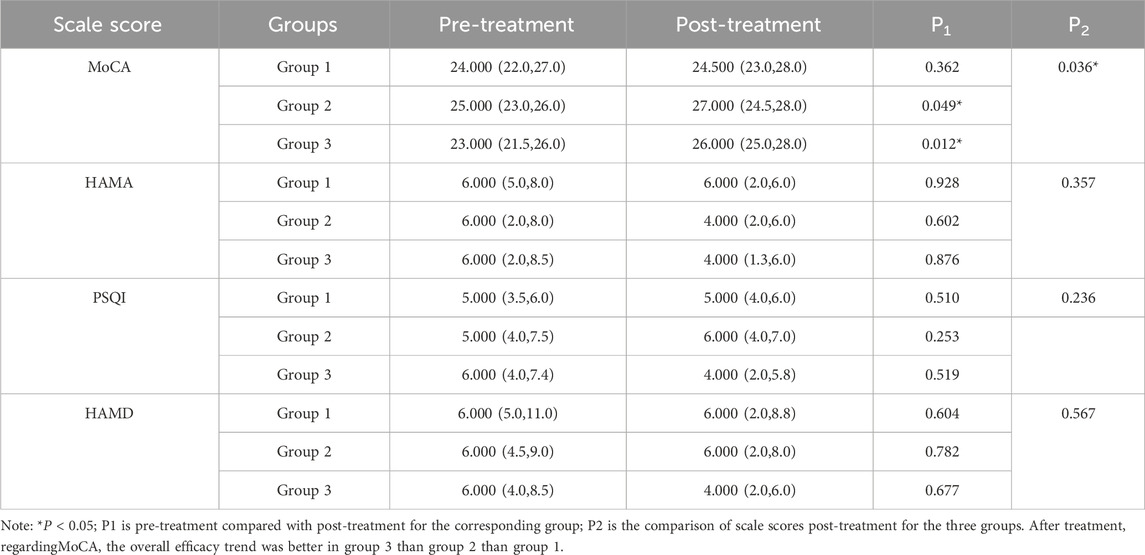
Pre- and post-treatment comparisons were conducted within each of the three groups. According to records from the designated investigators, there were no significant differences among the three groups at baseline in terms of cognitive function, emotional state, sleep quality, or treatment compliance, indicating comparability. Before treatment, there were no statistically significant differences in the MoCA, HAMA, PSQI, and HAMD scores among the groups (see Supplementary Table S6). After treatment, statistically significant differences in MoCA scores were observed among the groups (P < 0.05; see Table 7). In Group 1, no statistically significant changes were observed in any of the assessment indicators after treatment (P > 0.05). In contrast, both Group 2 and Group 3 demonstrated statistically significant improvements in MoCA scores post-treatment compared to baseline (P < 0.05). Intergroup comparisons of post-treatment MoCA scores also indicated statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). However, no statistically significant changes were found in HAMA, PSQI, and HAMD scores across or within groups (P > 0.05). These results suggest that a combination of lifestyle interventions, atorvastatin calcium therapy, and intensive exercise may contribute to improved cognitive function. Furthermore, replacing Bay aspirin with ginsenoside Rg1 appears to yield a more pronounced enhancement in cognitive outcomes. However, the intervention had no significant impact on anxiety or depression levels (see Table 7).
4 Discussion
As noted in the introduction, carotid atherosclerosis is a specific form of atherosclerosis primarily characterized by lesions in the carotid intima, lipid deposition, luminal narrowing, and subsequent plaque formation (Dong et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023). Studies have identified several key risk factors for carotid atherosclerotic plaque development, including age, sex, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and levels of HDL-C and LDL-C (Tian et al., 2024; Papazoglou et al., 2024). Current clinical treatment strategies involve a combination of pharmacological interventions—such as blood pressure control, plaque stabilization, and antithrombotic therapy—and lifestyle modifications (e.g., smoking cessation, regular physical activity, and weight management). Additional goals include controlling underlying risk factors, such as diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, often through medications like antiplatelet agents, antihypertensives, and lipid-lowering drugs (Cao et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2020; Zhang and Ma, 2022). The combination of Bayaspirin and atorvastatin has been reported to significantly slow disease progression; however, its use may be limited by adverse side effects, underscoring the need for alternative therapies. Ginsenoside Rg1, the primary active component of Panax notoginseng (Sanqi), has demonstrated therapeutic effects in animal models of carotid atherosclerosis. However, its clinical efficacy remains largely unexplored (Wang et al., 2020a; Gu et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2025). Preliminary findings from our team’s preclinical, early clinical observations and access to relevant literature also suggest that ginsenoside Rg1 possesses anticoagulant properties (Liu et al., 2024). Therefore, we aimed to evaluate its therapeutic value by substituting Bayaspirin with ginsenoside Rg1 and comparing the outcomes. Post-treatment outcomes were assessed after a 3-month intervention, with comprehensive comparisons made between pre- and post-treatment results and across study groups.
Carotid color Doppler ultrasound is a key diagnostic tool for vascular health evaluation. It enables the detection of intimal thickening, plaque formation, plaque size, and plaque stiffness and allows for the measurement of blood flow velocity to evaluate stenosis or occlusion (Wen et al., 2022; Saba et al., 2024; Riggin et al., 2021). This modality is particularly valuable for monitoring treatment efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe carotid stenosis or occlusion. In our study, carotid ultrasound revealed that both exercise therapy alone and exercise combined with ginsenoside Rg1 significantly reduced the number of plaques in both the left and right arteries (P < 0.05). Although no significant difference was found between these two groups in terms of plaque quantity reduction, the group receiving ginsenoside Rg1 exhibited a significantly greater plaque volume than the group receiving exercise plus Bayaspirin, highlighting the superior effect of ginsenoside Rg1.
To further assess the therapeutic benefits of ginsenoside Rg1, we assessed the arterial stiffness index (ASI) and the vascular health index (VHI). ASI is closely associated with carotid atherosclerosis, as elevated values correlate with increased IMT, reflecting disease progression. The VHI offers a broader assessment of an individual’s vascular condition and lifestyle-related cardiovascular risk. Given that the carotid artery is an important conduit supplying blood from the heart to the brain, its integrity directly impacts cerebral perfusion (Csipo et al., 2025). Carotid artery lesions, such as those caused by atherosclerosis, can lead to severe outcomes like stroke. Thus, we jointly evaluated the differences between the ASI and VHI. Although no significant post-treatment differences in ASI were observed between the groups, the ginsenoside Rg1 group showed significant improvements in left and right ankle-brachial PWV. These findings support the relatively higher therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg1 compared to Bayaspirin. Additionally, FGF21 levels differed significantly among the groups, while Lumican and Fibulin-1 showed no statistically significant variations. This result further proves that ginsenoside Rg1 can provide additional vascular benefits in managing carotid atherosclerosis compared to Bayaspirin.
Following the aforementioned procedures, we further examined the effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on biochemical parameters in the treated patient groups. Comparative analysis revealed statistically significant intergroup differences (P < 0.05) in LDL-C, TC, Hcy, IL-6, TNF-α, 25(OH)D, and IR levels post-treatment. Notably, LDL-C and TC—both established risk factors for atherosclerosis—demonstrated significant reductions following ginsenoside Rg1 administration, confirming its lipid-lowering potential. Additionally, ginsenoside Rg1 significantly improved five key biomarkers: Hcy, IL-6, TNF-α, 25(OH)D, and IR. Among these, IL-6 and TNF-α are key pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in all stages of carotid atherosclerosis—from plaque formation and progression to rupture. Elevated levels of these cytokines are known to promote inflammatory responses and exacerbate vascular endothelial injury, thereby compromising plaque stability. The inflammatory reaction can promote the rupture of foam cells after phagocytosis of lipids, releasing more lipid content that accelerates the increase in the atherosclerotic core volume; Meanwhile, the inflammatory reaction can also cause carotid vascular remodeling, which leads to further narrowing of the vascular lumen (Jin et al., 2022). Moreover, low levels of 25(OH)D have been associated with hypertensive carotid atherosclerosis, and its concentration is negatively correlated with plaque severity. IR and Hcy are also related to diabetic carotid atherosclerosis, particularly IR, which has been associated with increased IMT, greater arterial stiffness, and reduced vascular compliance and dilation capacity (Sipos et al., 2021; Strisciuglio et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2019). This suggests that IR may negatively impact carotid artery health by altering the structure and function of the vascular wall. The observed improvements in these biomarkers following ginsenoside Rg1 treatment highlight its potential therapeutic value, particularly for patients with hypertension or diabetic carotid atherosclerosis.
Finally, we assessed the three patient groups before and after treatment using the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment Scales—MoCA, HAMA, PSQI, and HAMD—to evaluate whether ginsenoside Rg1 can improve the overall quality of life in patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Among these scales, the MoCA evaluates cognitive function, the HAMA assesses anxiety levels, the PSQI measures sleep quality, and the HAMD assesses depressive symptoms. Our results indicated that after 3 months of ginsenoside Rg1 treatment, there were no significant changes in HAMA, PSQI, and HAMD scores. This suggests that ginsenoside Rg1 does not significantly improve depression, anxiety, or sleep quality in patients with carotid atherosclerosis. However, the MoCA scores showed a significant difference among the three groups, suggesting that ginsenoside Rg1 may have a positive effect on cognitive function. For some of the indicators that did not reach statistical significance, we analyzed that they might be affected by 1) sample size limitations, especially the small number of cases in some subgroup analyses; 2) heterogeneity of responses to Rg1 due to inter-individual metabolic differences; and 3) the short follow-up period of the study, where changes in some biomarkers had not yet been adequately revealed. Future studies could be further validated by expanding the sample size, extending the intervention time, or using more sensitive assays.
In summary, our clinical study demonstrates that adjunctive ginsenoside Rg1 therapy—when combined with lifestyle modifications, lipid-lowering treatment, and intensive exercise—may reduce carotid plaque volume and number while also improving quality of life and certain metabolic and inflammatory markers. However, several limitations should be acknowledged: 1) The exclusion of high-risk patients with severe carotid atherosclerosis or multiple comorbidities may have introduced selection bias. 2) All participants in this study were older adults with underlying conditions and various geriatric syndromes. Despite efforts to minimize confounding factors, some influences on the outcomes may have been unavoidable. 3) The study was cross-sectional with regional limitations; therefore, the findings may not be generalizable to the broader elderly population. 4) The intervention period was limited to 3 months, and the sample size was relatively small. Although a priori power analysis (G*Power) suggested a minimum of 32 participants per group for detecting a medium effect size, larger sample sizes (e.g., >180 per group) would be required for more robust conclusions. Therefore, in subsequent studies, we plan to expand the sample size and extend the observation period to clarify the therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg1 in patients with carotid atherosclerosis and to define the scope of its clinical benefits.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province (Approval No.: KHLL2023-KY006). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
XF: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft. XM: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology, Conceptualization. MZ: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. LZ: Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. XH: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. SL: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Project administration, Data curation. YD: Investigation, Supervision, Project administration, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. YL: Project administration, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Resources. JW: Writing – review and editing, Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Yunnan Provincial People’s Hospital Clinical Medical Research Centre Open Project (2023YJZX-LN08).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1638359/full#supplementary-material
References
Afzal, Z., Cao, H., Chaudhary, M., Chigurupati, H. D., Neppala, S., Alruwaili, W., et al. (2024). Elevated lipoprotein (a) levels: a crucial determinant of cardiovascular disease risk and target for emerging therapies. Curr. problems Cardiol. 49, 102586. doi:10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102586
Benjamin, D. J., Haslam, A., and Prasad, V. (2024). Cardiovascular/anti-inflammatory drugs repurposed for treating or preventing cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Cancer Med. 13, e7049. doi:10.1002/cam4.7049
Cao, J., Zhou, D., Yao, Z., Zeng, Y., Zheng, J., Tang, Y., et al. (2024). Insulin resistance, vulnerable plaque and stroke risk in patients with carotid artery stenosis. Sci. Rep. 14, 30453–10. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-81967-x
Chen, X., Xing, L. L., Tang, Y. H., and Zhang, G. B. (2013). Luminol-K(3)Fe(CN)(6) chemiluminescence system for the determination of glipizide. J. Pharm. Anal. 3 (2), 127–131. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2012.07.002
Csipo, T., Lipecz, A., Mukli, P., PéTERFI, A., Szarvas, Z., Ungvari, A., et al. (2025). Advancing prediction of age-related vascular cognitive impairment based on peripheral and retinal vascular health in a pilot study: a novel comprehensive assessment developed for a prospective workplace-based cohort (The Semmelweis Study). GeroScience 47, 1329–1344. doi:10.1007/s11357-024-01447-y
Dong, X. K., Luo, D., Chen, W. J., Wang, R. R., Yang, J., and Niu, M. M. (2022). Association between serum uric acid and carotid atherosclerosis in elderly postmenopausal women: a hospital-based study. J. Clin. Laboratory Analysis 36, e24097. doi:10.1002/jcla.24097
Effati, S., Kamarzardi-Torghabe, A., Azizi-Froutaghe, F., Atighi, I., and Ghiasi-Hafez, S. (2024). Web application using machine learning to predict cardiovascular disease and hypertension in mine workers. Sci. Rep. 14, 31662. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-80919-9
Gu, C., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., Li, R., Feng, J., Chen, W., et al. (2022). The PI3K/AKT pathway—the potential key mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine for stroke. Front. Med. 9, 900809. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.900809
He, X.-Y., Gao, Z.-Y., Liang, W., and Sun, Y.-C. (2022). Ameliorative effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis: involvement of intestinal barrier remodeling in mice. Ann. Transl. Med. 10, 1328. doi:10.21037/atm-22-5467
Hermel, M., Pelter, M., Jordan, T., Latif, A., Gad, M. M., Slipczuk, L., et al. (2022). Highlights of cardiovascular disease prevention studies presented at the 2022 European Society of Cardiology Congress. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 24, 981–993. doi:10.1007/s11883-022-01072-0
Hu, K., Ye, J., Fan, P., Zheng, R., Wang, S., Peng, Y., et al. (2025). Targeting and reprogramming microglial phagocytosis of neutrophils by ginsenoside Rg1 nanovesicles promotes stroke recovery. Bioact. Mater. 47, 181–197. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.01.017
Huang, T.-S., Wu, T., Fu, X.-L., Ren, H.-L., He, X.-D., Zheng, D.-H., et al. (2024). SREBP1 induction mediates long-term statins therapy related myocardial lipid peroxidation and lipid deposition in TIIDM mice. Redox Biol. 78, 103412. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2024.103412
Jamthikar, A., Gupta, D., Khanna, N. N., Saba, L., Laird, J. R., and Suri, J. S. (2020). Cardiovascular/stroke risk prevention: a new machine learning framework integrating carotid ultrasound image-based phenotypes and its harmonics with conventional risk factors. Indian heart J. 72, 258–264. doi:10.1016/j.ihj.2020.06.004
Jin, Y.-J., An, Z.-Y., Sun, Z.-X., and Liu, X.-C. (2022). NLRP3 inflammasome as a therapeutic target for atherosclerosis: a focus on potassium Outflow. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 23, 268. doi:10.31083/j.rcm2308268
Li, S., Han, Q., Qiao, C., Song, J., Lung Cheng, C., and Xu, H. (2008). Chemical markers for the quality control of herbal medicines: an overview. Chin. Med. 3, 7–16. doi:10.1186/1749-8546-3-7
Li, Y., Lu, Y.-Y., Jia, J., Fang, M., Zhao, L., Jiang, Y., et al. (2021). A novel system for evaluating the inhibition effect of drugs on cytochrome P450 enzymes in vitro based on human-induced hepatocytes (hiHeps). Front. Pharmacol. 12, 748658. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.748658
Liu, Z., Cecarini, V., Cuccioloni, M., Bonfili, L., Gong, C. M., Angeletti, M., et al. (2024). Ginsenosides Rg1 and Rg2 activate autophagy and attenuate oxidative stress in neuroblastoma cells overexpressing aβ (1–42). Antioxidants 13 (3), 310. doi:10.3390/antiox13030310
Liu, X., Men, P., Wang, B., Cai, G., and Zhao, Z. (2019). Effect of dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitors on C-reactive protein in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 18, 144–12. doi:10.1186/s12944-019-1086-4
Liu, C., Yang, X., Ji, M., Zhang, X., Bian, X., Chen, T., et al. (2023). Sex-specific association between carotid atherosclerosis and fundus arteriosclerosis in a Chinese population: a retrospective cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 28, 518. doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01508-6
LóPEZ-Cancio, E., Matheus, M. G., Romano, J. G., Liebeskind, D. S., Prabhakaran, S., Turan, T. N., et al. (2014). Infarct patterns, collaterals and likely causative mechanisms of stroke in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerosis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 37, 417–422. doi:10.1159/000362922
Papazoglou, A. S., Kyriakoulis, K. G., Barmpagiannos, K., Moysidis, D. V., Kartas, A., Chatzi, M., et al. (2024). Atherosclerotic risk factor Prevalence in adults with Congenital heart disease: a meta-analysis. JACC Adv. 3, 101359. doi:10.1016/j.jacadv.2024.101359
Riggin, C. N., Rodriguez, A. B., Weiss, S. N., Raja, H. A., Chen, M., Schultz, S. M., et al. (2021). Modulation of vascular response after injury in the rat Achilles tendon alters healing capacity. J. Orthop. Research® 39, 2000–2016. doi:10.1002/jor.24861
Ruan, Y., Bao, Q., Wang, L., Wang, Z., Zhu, W., and Wang, J. A. (2024). Cardiovascular diseases burden attributable to ambient PM2. 5 pollution from 1990 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Environ. Res. 241, 117678. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.117678
Saba, L., Scicolone, R., Johansson, E., Nardi, V., Lanzino, G., Kakkos, S. K., et al. (2024). Quantifying carotid stenosis: history, current applications, limitations, and potential: how imaging is changing the scenario. Life 14, 73. doi:10.3390/life14010073
Sipos, M., Gerszi, D., Dalloul, H., BáNYAI, B., Sziva, R. E., Kollarics, R., et al. (2021). Vitamin D deficiency and gender alter vasoconstrictor and vasodilator reactivity in rat carotid artery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 8029. doi:10.3390/ijms22158029
Strisciuglio, T., Izzo, R., Barbato, E., Di Gioia, G., Colaiori, I., Fiordelisi, A., et al. (2020). Insulin resistance predicts severity of coronary atherosclerotic disease in non-diabetic patients. J. Clin. Med. 9, 2144. doi:10.3390/jcm9072144
Tian, Y., Lu, L., Zhang, Y., and Wei, J. (2024). The value of Lp (a) and TG/HDLC in peripheral blood to assess the stability of carotid plaque in patients with ischemic stroke. Brain Behav. 14 (1), e3355. doi:10.1002/brb3.3355
Tufano, A., Cimino, E., Di Minno, M. N. D., Ierano, P., Marrone, E., Strazzullo, A., et al. (2011). Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular prevention: the role and the limitations of currently available antiplatelet drugs. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2011, 250518. doi:10.1155/2011/250518
Turongkaravee, S., Jittikoon, J., Lukkunaprasit, T., Sangroongruangsri, S., Chaikledkaew, U., and Thakkinstian, A. (2021). A systematic review and meta-analysis of genotype-based and individualized data analysis of SLCO1B1 gene and statin-induced myopathy. pharmacogenomics J. 21, 296–307. doi:10.1038/s41397-021-00208-w
Vinci, P., Panizon, E., Tosoni, L. M., Cerrato, C., Pellicori, F., Mearelli, F., et al. (2021). Statin-associated myopathy: emphasis on mechanisms and targeted therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 11687. doi:10.3390/ijms222111687
Wang, H., Wang, J., Lu, J., and Wang, D. (2020a). Effects of high dose of atorvastatin for preventing Periprocedural ischemic brain damage in patients undergoing carotid artery stenting (PICAS) in China: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Front. Neurology 11, 937. doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.00937
Wang, K., Zhang, B., Song, D., XI, J., Hao, W., Yuan, J., et al. (2020b). Alisol A alleviates arterial plaque by activating ampk/sirt1 signaling pathway in apoe-deficient mice. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 580073. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.580073
Wang, Z., Jiang, R., Wang, L., Chen, X., Xiang, Y., Chen, L., et al. (2020c). Ginsenoside Rg1 improves differentiation by inhibiting senescence of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell via GSK-3β and β-catenin. Stem cells Int. 2020, 2365814. doi:10.1155/2020/2365814
Wang, C., He, T., Zhou, H., Zhang, Z., and Lee, C. (2023). Artificial intelligence enhanced sensors-enabling technologies to next-generation healthcare and biomedical platform. Bioelectron. Med. 9, 17. doi:10.1186/s42234-023-00118-1
Wen, F., Liu, Y., and Wang, H. (2022). Clinical evaluation tool for vascular health–endothelial function and cardiovascular disease management. Cells 11, 3363. doi:10.3390/cells11213363
Yang, G., He, H.-Q., Chen, G., and Wang, J. (2020). Effect of traditional Chinese medicine in attenuating coronary heart disease and main risk factors by regulating gut micro-biota. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi= Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi= China J. Chin. Materia Medica 45, 29–36. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190505.502
Yang, Y.-H., Gu, X.-P., Hu, H., Hu, B., Wan, X.-L., Gu, Z.-P., et al. (2022). Ginsenoside Rg1 inhibits nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis, inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation via the YAP1/TAZ pathway in rats with intervertebral disc degeneration. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 17, 555. doi:10.1186/s13018-022-03443-4
Yuriev, Y., Goreninskii, S., Runts, A., Prosetskaya, E., Plotnikov, E., Shishkova, D., et al. (2021). DLC-coated ferroelectric membranes as vascular patches: Physico-chemical properties and biocompatibility. Membranes 11, 690. doi:10.3390/membranes11090690
Zhang, J., and Ma, Y. (2022). Observation on the efficacy of Ginkgo Ketone ester Drop Pill in improving hypertension combined with carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Emerg. Med. Int. 2022, 8650537. doi:10.1155/2022/8650537
Keywords: ginsenoside Rg1, carotid atherosclerosis, plaque, comprehensive geriatric assessment, Sanqi extract
Citation: Fang X, Ma X, Zhang M, Zhang L, He X, Liu S, Dong Y, Li Y and Wu J (2025) The action of ginsenoside Rg1 in patients with carotid atherosclerosis: a controlled clinical trial. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1638359. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1638359
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 02 September 2025.
Edited by:
John D. Imig, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, United StatesReviewed by:
Zhichao Xi, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaChaofang Lei, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Fang, Ma, Zhang, Zhang, He, Liu, Dong, Li and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Li, bGl5YW5rZW5AMTI2LmNvbQ==; Junzi Wu, eG5mekB5bnVjbS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xu Fang1†
Xu Fang1† Xu He
Xu He Junzi Wu
Junzi Wu