- 1Department of Breast Surgery, Longhua Hospital of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, Seventh People’s Hospital of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
Background: Aromatase inhibitor-induced musculoskeletal syndrome (AIMSS) has emerged as a major cause of treatment discontinuation in hormone receptor-positive patients treated with aromatase inhibitors. There are currently no standardized guidelines or universally accepted treatments for AIMSS. Therefore, this exploratory study aimed to preliminarily evaluate the efficacy and safety of Yi Shen Tiao Gan formula in AIMSS patients.
Methods: A total of 136 patients with AIMSS were included in this single-center, randomized, controlled, single-blind trial and were randomised into the treatment and control groups at a ratio of 1:1. All patients were routinely given Caltrate D. Patients in the treatment group took Breast surgery formula combined with Yi Shen Tiao Gan formula and control group took Breast surgery formula twice a day. The treatment period of Chinese medicine was 3 months as one course of treatment. The clinical efficacy of two courses of treatment was observed in this study. The study observed and compared the following indicators between the two groups: the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) scores, Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom and sign scores, bone mineral density, bone metabolism biochemical indicators, bone metabolism-related hormones and safety assessments.
Results: In total, 108 participants were included in the analysis. Before and after treatment, the total WOMAC score of both groups of patients significantly decreased (p < 0.05), with the pain subscale score of the treatment group being significantly lower than that of the control group (p < 0.05). The TCM symptom and sign score significantly decreased in both groups (p < 0.05), with a more pronounced reduction in the treatment group (p < 0.05). The bone mineral density T-score of both groups of patients showed a downward trend. The decrease in the left femoral bone density T-score was smaller in the treatment group, while the decline in the lumbar spine bone density T-score was slower in the control group. There was no significant difference in bone metabolism levels between the two groups (p > 0.05), but the decrease in β-CTX was slightly slower in the treatment group of the AI + OFS population compared to the control group. After applying Bonferroni correction for multiple testing, these associations did not reach statistical significance. No serious adverse events were observed in either group.
Conclusion: The YSTG formula significantly reduced WOMAC scores, improving pain, stiffness, physical function in patients with AIMSS, and alleviating the traditional Chinese medicine symptoms and signs of liver and kidney deficiency, thereby enhancing the overall quality of life for patients.
Clinical Trial Registration: http://www.chictr.org.cn, identifer ChiCTR2200057785.
Introduction
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, female breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer incidence globally in 2022, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases, accounting for 11.6% of all cancer cases (Sung et al., 2021). Around 75% of all breast tumors express the estrogen receptor (ER) and/or the progesterone receptor (PR) and are considered as hormone receptor-positive (HR) tumors (Howlader et al., 2014). Adjuvant endocrine therapy remains the mainstay of HR-positive early breast cancer along with chemotherapy and adjuvant radiation therapy. For postmenopausal women, next-generation aromatase inhibitors (AIs) nonsteroidal (anastrozole and letrozole) or steroidal (exemestane) are widely used in the adjuvant setting (Regan et al., 2011). However, administration of AIs has been associated with joint pain and musculoskeletal symptoms that can even lead to treatment discontinuation. Aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal syndrome (AIMSS) is the most common adverse event encountered by breast cancer patients. In early-stage breast cancer, an incidence of 47% of arthralgias was reported in postmenopausal women treated with AI, including a 23.5% rate of new-onset arthralgia and a 23.5% rate of exacerbation of pre-existing arthralgias (Crew et al., 2007). Another recent meta-analysis showed a 17.9% rate of AI-induced arthralgia in postmenopausal women which was lower in early-stage breast cancer compared with advanced disease (Lammers et al., 2025). Overall, approximately 13%–25% of patients discontinue AI therapy mainly because of arthralgias (Henry et al., 2012). AIMSS has emerged as a major cause of treatment discontinuation in hormone receptor-positive patients treated with AIs. Arthralgias were reported in 13.2%–68.7% of patients receiving AIs for early-stage breast cancer (Skafida et al., 2023). There are currently no standardized guidelines or universally accepted treatments for AIMSS (Grigorian and Baumrucker, 2022). There are no treatments recommended for the management of this iatrogenic disease. Therefore, effective treatment methods for AIMSS are clinically needed.
As an important part of China’s medical and health system, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) plays an irreplaceable role in diagnosing and treating diseases. TCM has a long history, and after thousands of years of use, it possesses a solid practical foundation and an extensive theoretical system (Sun et al., 2024). Yishen Tiaogan (YSTG) formula is an important TCM treatment for AIMSS. Relevant animal experiments were conducted by this group in the preliminary stage. Our prior research demonstrated that YSTG targets SLIT3 to increase the number of H-type vessel cells in bone, thereby improving Le-induced bone loss flammation and modulating the gut microbiota and we also identified the top 10 chemical components of YSTG formula using ultraperformance liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry (UPLC–HRMS) (Chu et al., 2025). However, despite these promising findings, there remains a lack of high-quality clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of YSTG formula. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation of the clinical efficacy of this method is highly important for enriching the theoretical system of TCM treatment.
Therefore, we designed this single-center, randomized, controlled, single-blind trial. In addition to strict inclusion and exclusion criteria, we have also incorporated TCM syndrome scoring to evaluate whether the traditional medical basis of using YSTG formula (TCM syndrome) aligns with improvements in patient musculoskeletal symptoms. Therefore, this exploratory study aimed to preliminarily evaluate the efficacy and safety of YSTG in AIMSS patients.
Materials and methods
Study design
This single-center, randomized, controlled, single-blind trial was conducted at the Longhua Hospital affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from February 2022 to December 2023. Eligible patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to either the YSTG group or the control group. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Longhua Hospital affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Ethics No. 2022LCSY001), and registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2200057785). Prior to commencing treatment in this trial, all participants provided informed consent and agreed to participate in the study, following the guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration. Furthermore, this study strictly adhered to the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) guidelines (Schulz et al., 2010).
Participants
Inclusion criteria
(1) Age ranging from 18 to 65 years old;
(2) Diagnosed with breast cancer by pathology (referring to the 2021 Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines (Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Breast Cancer Committee, 2021), all cases were confirmed as breast cancer by basic and molecular pathology), and diagnosed as HR positive by immunohistochemistry;
(3) Completed surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and/or targeted therapy;
(4) Received AIs (anastrozole, letrozole, or exemestane) for at least 2 months;
(5) Classified as liver and kidney deficiency in TCM syndrome differentiation (referring to the 2002 version of the “Guidelines for Clinical Research of New Chinese Medicines”);
(6) Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) score ≥60;
(7) Expected survival period exceeding 6 months;
(8) Signed the informed consent form and voluntarily accepted the treatment plan of this study.
Exclusion criteria
(1) Bone mineral diseases: such as hypoparathyroidism or hyperparathyroidism, osteitis deformans, osteogenesis imperfecta, osteomalacia, etc.,;
(2) Diseases affecting bone metabolism: such as Cushing’s syndrome, hyperthyroidism, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.,;
(3) Use of steroid hormones or anticonvulsants for more than 6 months before the study;
(4) Hormone replacement therapy within 6 months: such as glucocorticoids, parathyroid hormone, estrogen, etc.,;
(5) Undergone surgery on limb joints within 6 months;
(6) Severe primary diseases of the cardiovascular, liver, kidney and hematopoietic systems;
(7) Obvious disease progression or new distant metastasis during the study;
(8) Patients with cognitive impairment or mental disorders.
Shedding/termination criteria
(1) Shedding criteria: Subjects who have completed the informed consent and qualified for screening and entered the randomized trial, but failed to complete the treatment course and observation period as stipulated in the study protocol, will be treated as drop-outs.
(2) Termination criteria: Taking traditional Chinese medicine outside the study; poor medication compliance, not taking traditional Chinese medicine as required; subjects found not meeting the inclusion criteria after enrollment, will be treated as exclusions.
Estimation of sample size
This study is a two-group parallel-controlled efficacy clinical trial, with the primary outcome measure being the WOMAC Osteoarthritis Index. The efficacy test for the comparison of means between the two groups is conducted at a significance level of α of 0.05 (two-sided test), with a power (1-β) of 0.8, (calculated according to α = 0.05, β = 0.2, from the table u0.05 = 1.649, u0.2 = 0.817). The recruitment period is 12 months, with a follow-up period of 6 months, and the ratio of the treatment group to the control group is 1:1. The WOMAC questionnaire consists of 24 items, divided into 3 subscales: Pain (5 items); Stiffness (2 items); Physical Function (17 items). The mean and standard deviation of the Pain subscale were (63.13 ± 75.84) for the treatment group and (133.64 ± 95.23) for the control group; for Stiffness, they were (33.00 ± 35.60) for the treatment group and (67.94 ± 45.68) for the control group; for Physical Function, they were (220.21 ± 266.85) for the treatment group and (496.83 ± 338.21) for the control group (Peng et al., 2018). According to the sample size calculation formula, 54 cases are needed per group for the Pain subscale; 48 cases per group for the Stiffness subscale; and 38 cases per group for the Physical Function subscale. Considering all subscales, the required sample size for the WOMAC scale is 54 cases per group, with a dropout rate of 20%, the required sample size is 68 cases per group, ultimately requiring 136 participants. The sample size was estimated according to the formula for the comparison of means between the two groups:
Randomization and allocation
SPSS 26.0 statistical software was used to generate random numbers by setting a fixed value of “20,220,101”. The patients were assigned to the treatment group or the control group based on the size of the random numbers at a ratio of 1:1. The enrolled cases were assigned to the corresponding groups in sequence.
Due to the critical nature of AIMSS and the distinct characteristics of traditional Chinese herbal decoctions, blinding of the therapists and patients was not feasible. However, to maintain the integrity of the trial, both the outcome evaluators and data analysts were blinded to the treatment assignments. All data were collected and analyzed by individuals who were unaware of the specific interventions provided to each group.
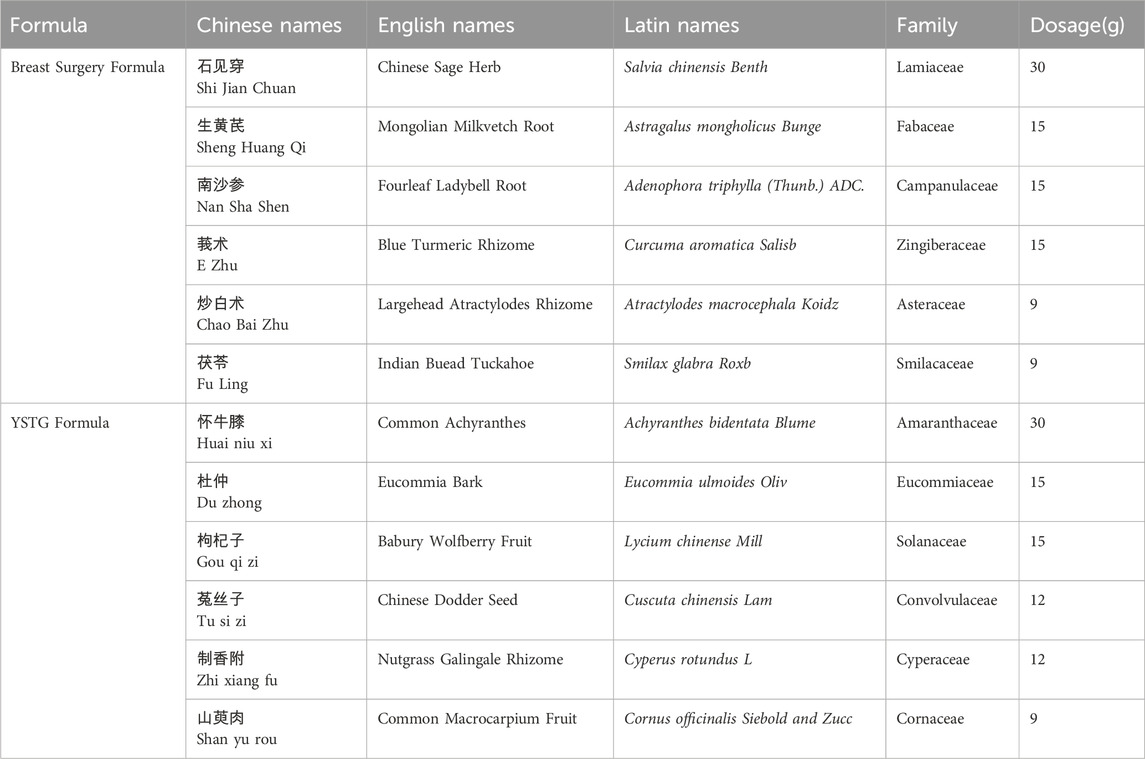
Intervention
The patients were divided into the treatment group and the control group. All patients were routinely given Caltrate D. All patients in the control group were administered the Breast Surgery Formula, which comprises Salvia chinensis Benth. (Shi Jian Chuan, 30 g), Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (Sheng Huang Qi, 15 g), Adenophora triphylla (Thunb.) A.DC. (Nan Sha Shen, 15 g), Curcuma aromatica Salisb. (E Zhu, 15 g), Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (Chao Bai Zhu. 9 g), Smilax glabra Roxb. (Fu Ling, 9 g). The treatment group received the YSTG formula in addition to the control regimen. The YSTG formula comprises Achyranthes bidentata Blume (Huai niu xi, 30 g), Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. (Du zhong, 15 g), Lycium chinense (Gou qi zi,15 g), Cuscuta chinensis Lam. (Tu si zi, 12 g), Cyperus rotundus L. (Zhi xiang fu, 12 g), Cornus officinalis Siebold and Zucc. (Shan yu rou, 9 g). All the plant names have been checked with plants of the world online datasets (http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org). The study medications were provided by the Decoction Room of Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine and were prepared in accordance with the standards set by the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2015 edition), ensuring compliance with the national drug standards established by the National Medical Products Administration. The components and dosages of Breast Surgery Formula and YSTG formula are listed in Table 1. The quality of the YSTG formula was controlled using ultraperformance liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry (UPLC–HRMS).
Patients began to take the Chinese herbal decoctions from the first day after enrollment, once a day, divided into two doses, taken 1 hour after meals in the morning and evening. The treatment period of Chinese medicine was 3 months as one course of treatment. The clinical efficacy of two courses of treatment was observed in this study.
Except for the trial medication, no other Chinese medicine was allowed to be used during the observation period. Doctors should require patients to bring all the medications they are currently taking during the visit to check for combined medication. The names (or other therapy names), dosages, frequency and time of any medications that must be continued due to concurrent diseases or other treatments should be recorded in the “Combined Medication Table” of the research medical record for analysis and reporting during the summary.
Detection of active components in YSTG formula using UPLC–HRMS
The YSTG formula was identified by Shanghai Lu Ming Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). YSTG formula comprises Achyranthes bidentata Blume (Huai niu xi, 30 g), Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. (Du zhong, 15 g), Lycium chinense (Gou qi zi,15 g), Cuscuta chinensis Lam. (Tu si zi, 12 g), Cyperus rotundus L. (Zhi xiang fu, 12 g), Cornus officinalis Siebold and Zucc. (Shan yu rou, 9 g). They were purchased from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Pharmacy of Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine and identified by Shanghai Lu Ming Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The quality of YSTG formula was controlled by ultraperformance liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry (UPLC–HRMS).
A total of 100 mg of a sample was added with 1 mL of water, vortexed for 1 min, sonicated for 60 min, and centrifuged at 4°C for 10 min. All the supernatant was passed through a 0.22 μm water-phase filter membrane and loaded into a sample bottle for analysis. Reference materials were accurately weighed and dissolved in methanol to prepare a mixed standard solution with a concentration of 10 μg/mL. The instrument used was Orbitrap-QE (Thermo Scientific, Karlsruhe, Germany), and the column was ACQUITY UPLC⋅HSS T3 (100 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.8 µm). The mobile phase for solvent A was 0.1% formic acid in water, and solvent B was acetonitrile. The flow rate was set at 0.35 mL/min, the column temperature was maintained at 45°C, and the injection volume was 5 μL.
Outcomes
Primary outcome measure
The primary outcome was the WOMAC (Peng et al., 2018). All patients were assessed 1 day before the traditional Chinese medicine intervention, and then at 3 months ±14 days and 6 months ±21 days after the treatment. The WOMAC consists of 24 items divided into three subscales: Pain (5 items) which includes walking, going up stairs, lying in bed, sitting, and standing; Stiffness (2 items) which includes first thing in the morning and later in the day; and Physical Function (PF) (17 items) which includes the use of stairs, sitting down and getting up, standing, bending, walking, getting in/out of a car, shopping, putting on/off socks, getting in/out of bed, lying in bed, and performing heavy and light housework (Conaghan et al., 2022).
Secondary outcome measures
TCM Symptom and Sign Scores: Scores were assigned before and after treatment for symptoms such as soreness and weakness in the waist and knees, lower limb weakness, aversion to cold and cold extremities, leg cramps, increased nocturia, and night sweats, followed by efficacy assessment.
Clinical recovery is defined as the disappearance or near disappearance of clinical symptoms and signs, with a reduction in syndrome scores of ≥95%. Markedly effective: indicates a significant improvement in clinical symptoms and signs, with a decrease in syndrome scores of ≥70%. Effective means an improvement in clinical symptoms and signs, with a reduction in syndrome scores of ≥30%. Invalid refers to no significant improvement or even worsening of clinical symptoms and signs, with a decrease in syndrome scores of less than 30%.
The calculation formula (Nimodipine method) is:
Bone mineral density (BMD): All subjects underwent BMD testing at the Imaging Department of Longhua Hospital before treatment and 6 months after treatment using Dual X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA), with measurement sites at lumbar spine L1-L4 and the left femur, and the calculation of BMD T-scores.
Bone Metabolism Biochemical Indicators: Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 [25(OH)D3], beta C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (β-CTX), Osteocalcin (OC), and Growth Hormone (GH).
Bone metabolism-related hormones: Estradiol (Estrogen, E2), Testosterone (Testo).
Safety assessments
The interventions will be carried out under the guidance of a researcher. The herbs in the YSTG formula are safe in accordance with the recommended amount in Chinese Pharmacopoeia. We will closely observe the physical conditions and subjective description of the participants. Blood routine, liver and kidney function, estrogen levels, and gynecological ultrasound were tested 1 day before the TCM intervention, and at 3 months ±14 days and 6 months ±21 days after treatment. The occurrence of fractures and gynecological diseases was monitored, and the progression of breast cancer was recorded. Patients who developed distant metastasis were terminated and withdrawn from the study. Unexpected signs or symptoms that occurred during treatment were considered adverse events, and participants were required to report any such events to clinicians during the treatment period.
Analytical planning
The intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis was applied to the baseline data, encompassing all participants who were randomized into the study, regardless of their adherence to the treatment protocol. This approach ensures a comprehensive assessment of the initial characteristics of the entire study population. For the primary and secondary outcomes, including the WOMAC scores, bone mineral density, bone metabolism biochemical indicators, bone metabolism-related hormones, and TCM syndrome, statistical analyses were conducted using the per-protocol set (PPS). The PPS included participants who met the inclusion criteria, did not meet the exclusion criteria, and completed the treatment plan as specified. This subset provides a more accurate assessment of the treatment effects under conditions where participants strictly adhered to the study protocol.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS 29.0 software. First, a normality test was conducted on the quantitative data. Data that conformed to a normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s), and comparisons between groups were made using the independent samples t-test, while pre- and post-treatment comparisons within the same group were made using the paired samples t-test. Data that did not conform to a normal distribution were represented using the median and interquartile range [M (P25, P75)], and the rank sum test was applied. Categorical data were described using percentages, proportions, and ordinal data, and the chi-square test or non-parametric tests were used for analysis. The statistical tests were two-tailed, with a significance level of α = 0.05, and a P-value less than 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Bonferroni’s post hoc test was applied for multiple comparisons to adjust for Type I error inflation due to the simultaneous use of multiple statistical tests.
Results
UPLC–HRMS results of YSTG formula
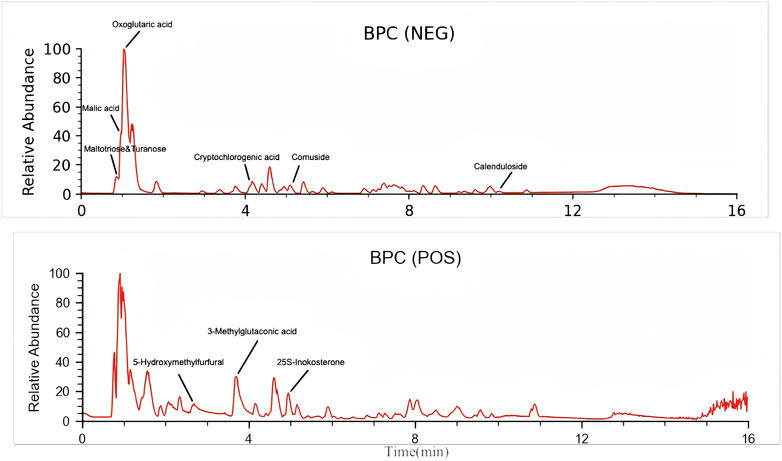
Through UPLC–HRMS analysis in both positive and negative ion modes, a total of 227 compounds were detected. The top 10 chemical components identified in YSTG formula were oxoglutaric acid, 25S-inokosterone, comuside, cryptochlorogenic acid, malic acid, turanose, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, maltotriose, calenduloside E, and 3-methylglutaconic acid (Figure 1). Detailed information on these components is provided in the Supplementary Material.
Patient enrollment and baseline characteristics
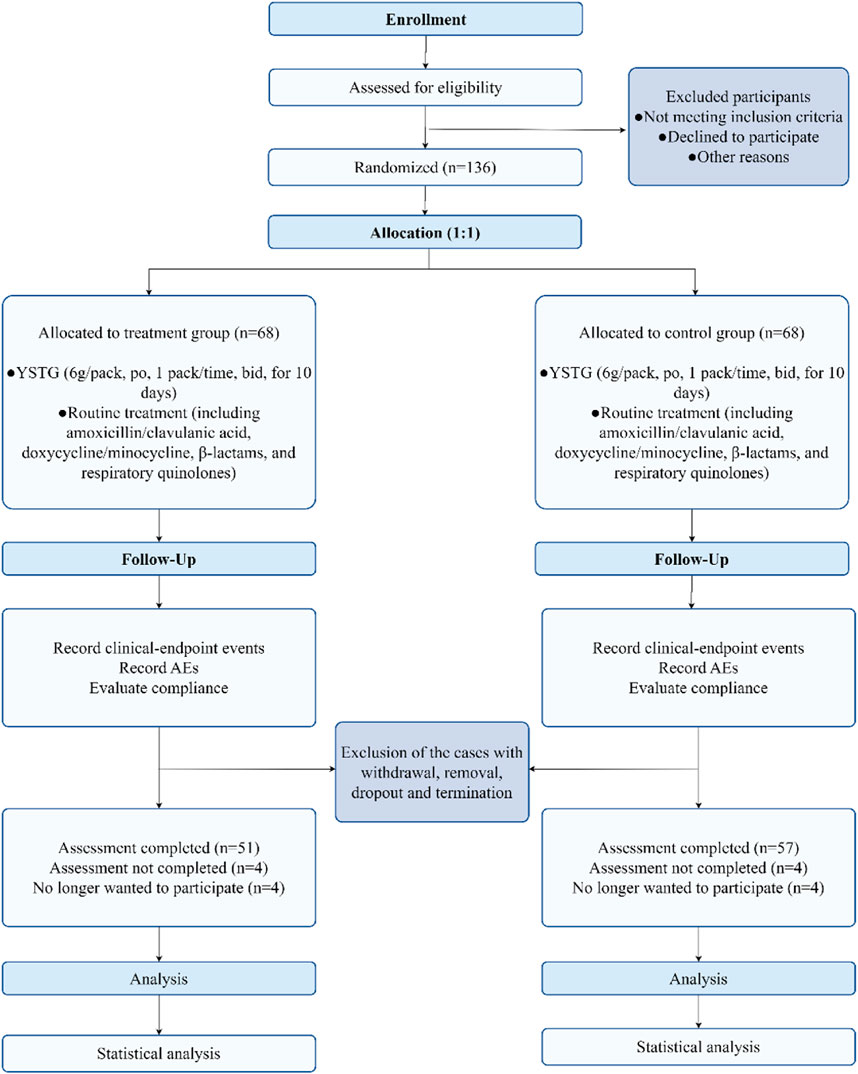
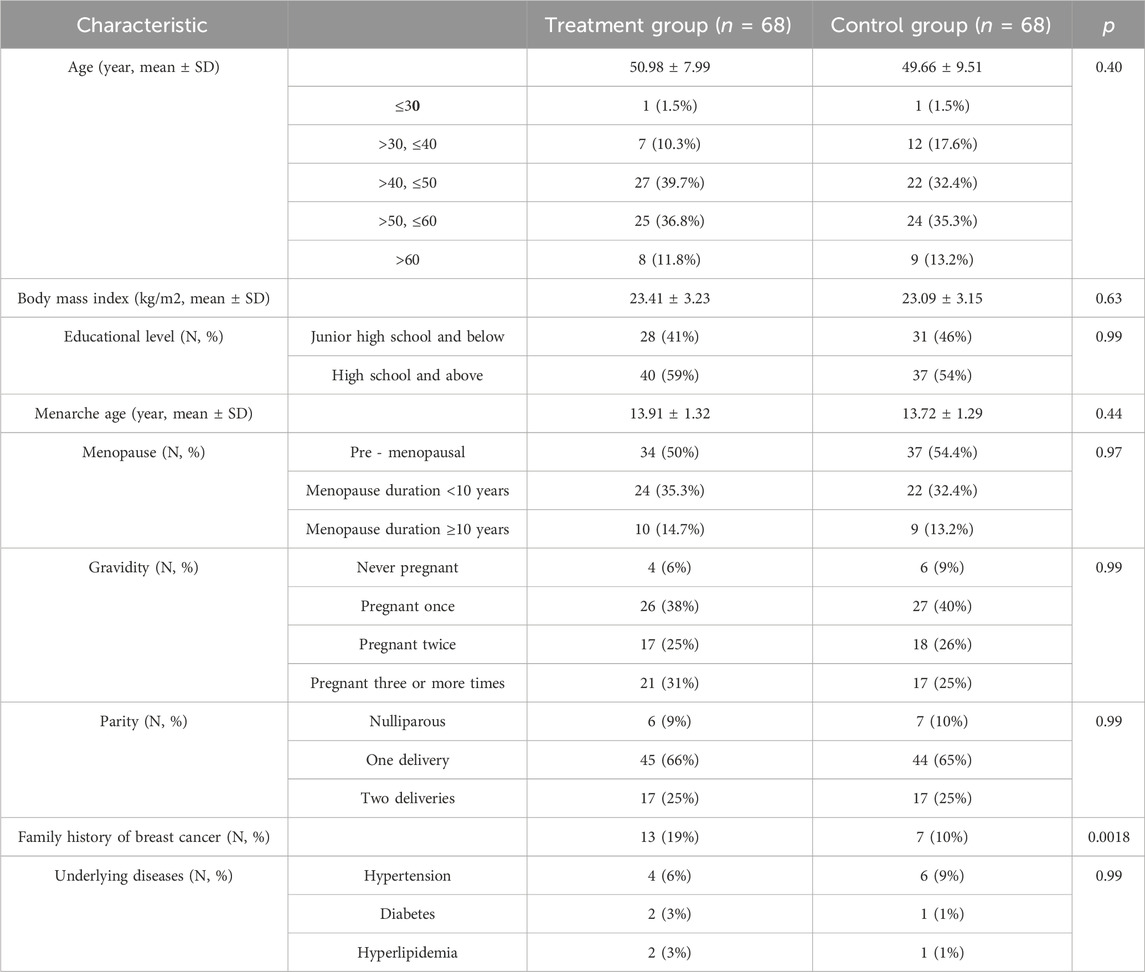
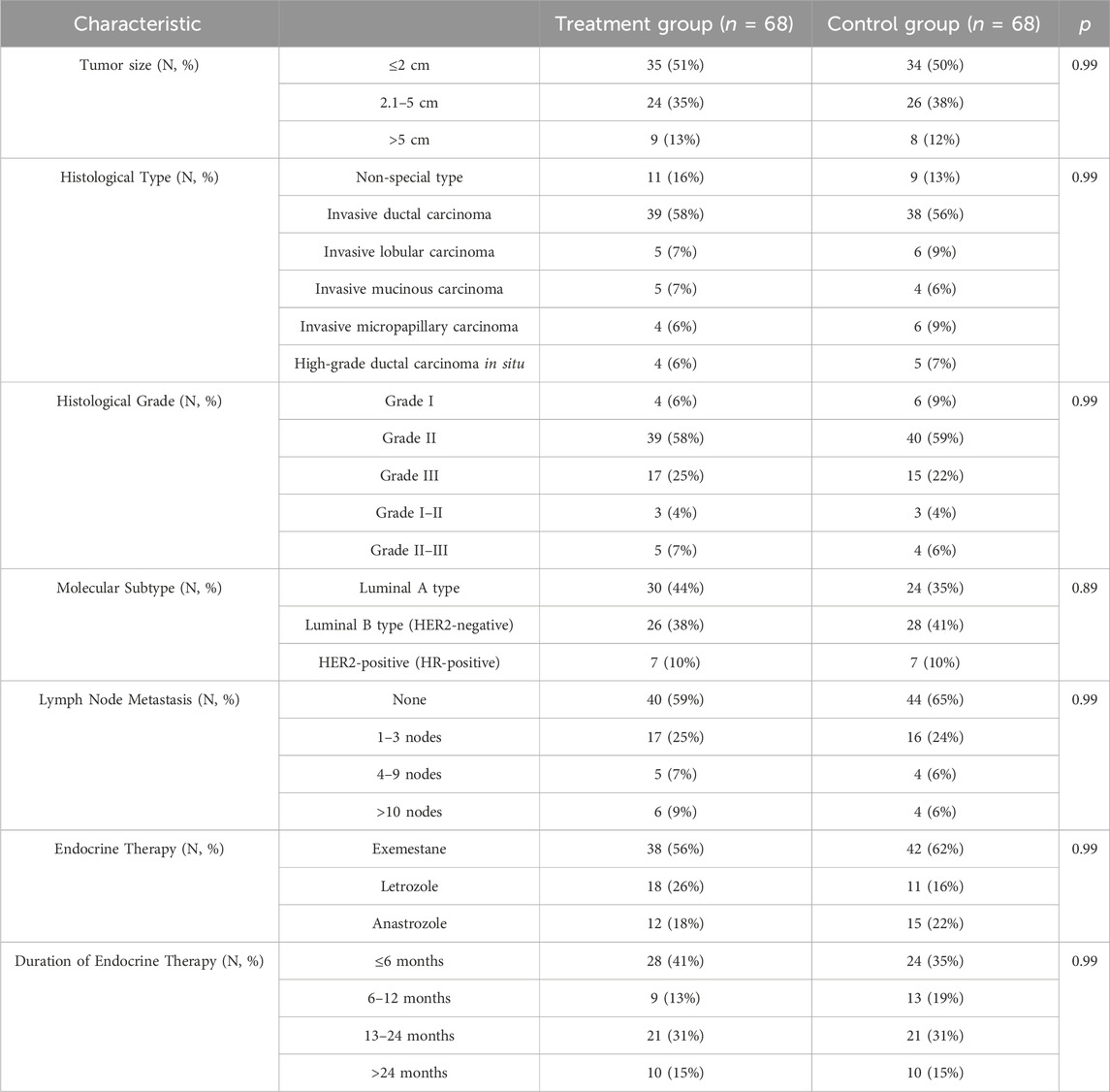
From 1 March 2022, to 21 December 2023, a total of 136 AIMSS patients were enrolled in the study and randomly assigned to the treatment group and the control group, with 68 cases in each group. During the study period, 15 patients withdrew, and 13 were excluded. The patients who withdrew were unable or refused to return for follow-up visits due to COVID-19 lockdown policies and personal reasons, and were managed as dropout cases. Among those excluded, seven patients were unable to adhere to the consumption of traditional Chinese medicine or were concurrently using other traditional Chinese medicines; one patient had a low white blood cell count; one patient experienced a recurrence of breast cancer following breast conservation surgery; two patients developed pulmonary and skeletal metastases, respectively; and two patients were excluded after the addition of abemaciclib to avoid interference. Among the 28 patients who were either withdrawn or excluded, 17 were from the treatment group and 11 were from the control group. Finally, 108 participants (treatment group, n = 51; control group, n = 57) completed the trial phase and were analyzed based on PPS (Figure 2). No significant differences were found in the outcome indicators among the two groups (p > 0.05) (Tables 2, 3).
Primary outcome
Comparison of WOMAC scores
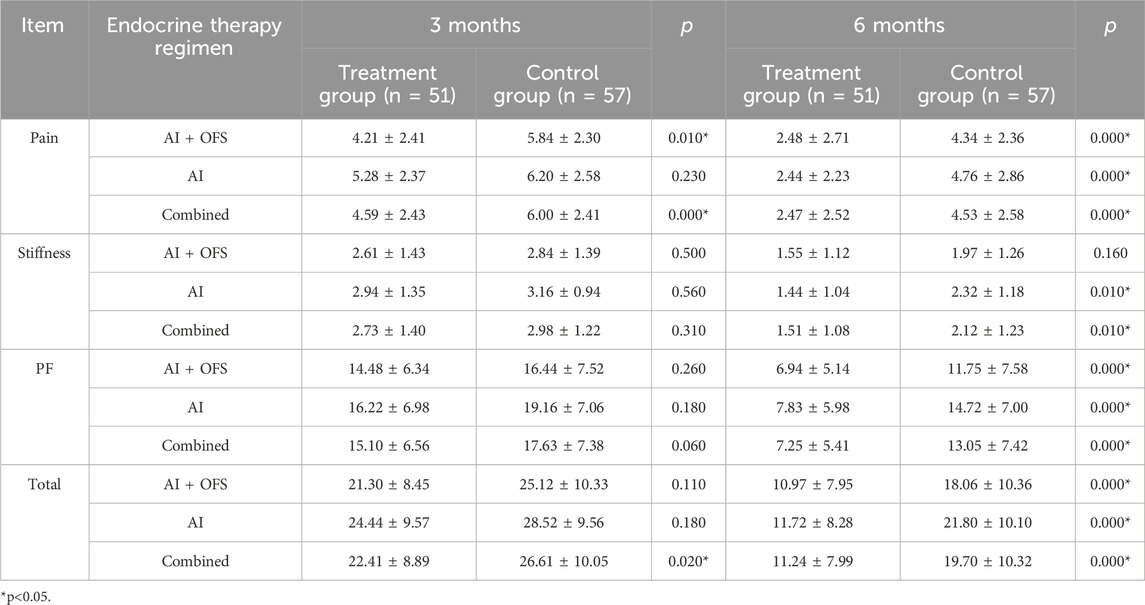
PPS analysis indicated that among 108 patients, at 3 and 6 months post-treatment, the WOMAC total scores were lower in the treatment group compared to the control group [(22.41 ± 8.89 vs. 26.61 ± 10.05, p = 0.020, Bonferroni correction) (11.24 ± 7.99 vs. 19.70 ± 10.32, p = 0.000, Bonferroni correction)] (Table 4). Further analysis of the subscales (pain, stiffness, physical function) showed that after 6 months of treatment, the scores in these areas were significantly lower in the treatment group than in the control group (p < 0.05, Bonferroni correction) (Table 4). Subgroup analysis stratified by endocrine therapy regimen revealed that in both the AI + OFS subgroup and the AI subgroup, the WOMAC total scores and the scores in pain and physical function were significantly lower in the treatment group than in the control group (p < 0.05, Bonferroni correction) (Table 4). However, in the AI + OFS subgroup, there was no significant difference in stiffness between the treatment and control groups (p > 0.05) (Table 4). Intragroup comparisons between the treatment and control groups and their baselines showed a significant decrease in WOMAC total scores after treatment (p < 0.05, Bonferroni correction) (Table 4). Subgroup analysis stratified by endocrine therapy regimen showed that in both subgroups, the WOMAC total scores decreased significantly after treatment (p < 0.05, Bonferroni correction), with a more pronounced downward trend observed in the treatment group compared to the control group (Figure 3).
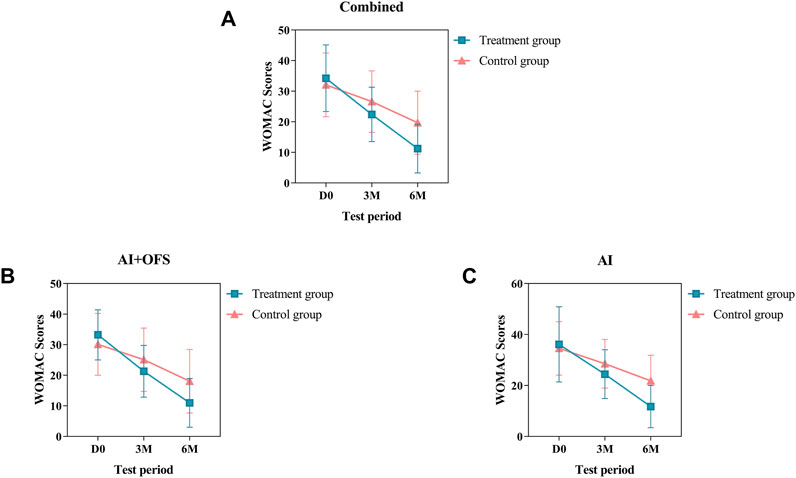
Figure 3. Difference of WOMAC Scores between the treatment and control groups in the change from baseline to 3 and 6 months.
Secondary outcome
TCM symptom scores and TCM syndrome efficacy
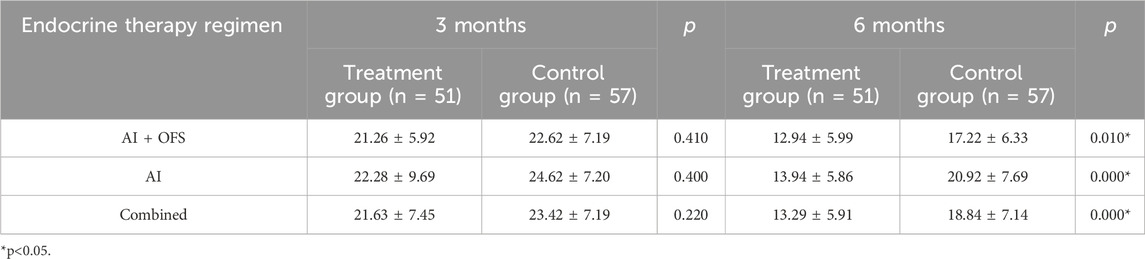
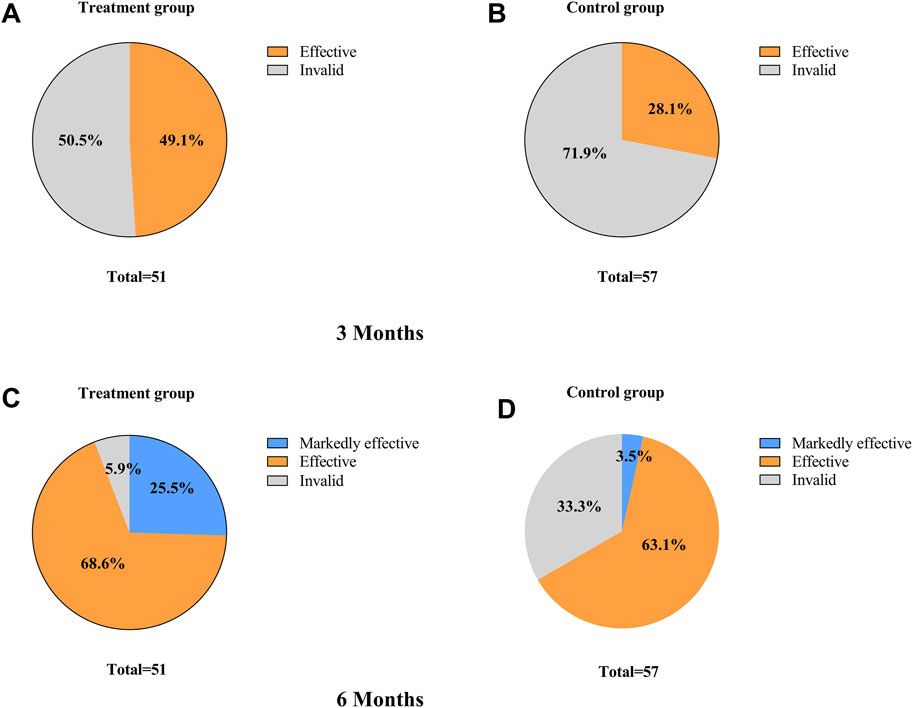
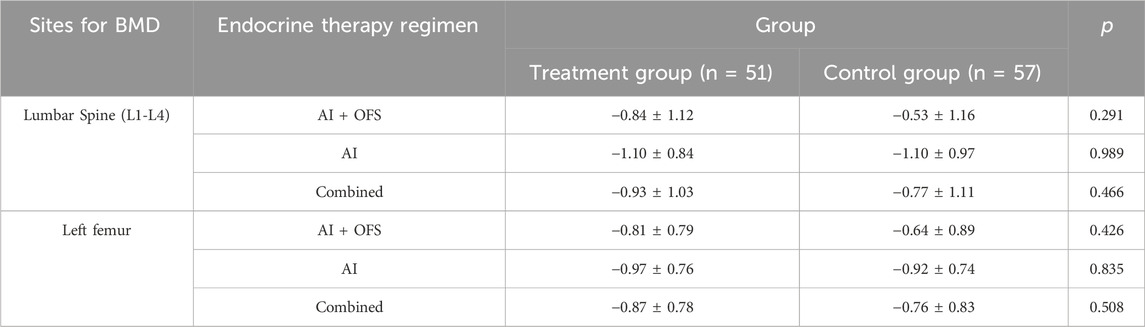
After 3 months of TCM treatment, the TCM symptom and sign scores in the treatment group were lower than those in the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant (21.63 ± 7.45 vs. 23.42 ± 7.19, p > 0.05) (Table 5). The response rate in the treatment group (49.1%) was significantly higher than that in the control group (28.1%) (p = 0.025, Bonferroni correction) (Table 5; Figure 4). Intragroup comparisons showed that scores significantly decreased in both groups, with more pronounced improvement in the treatment group (Figure 4). After 6 months of TCM treatment, the TCM symptom and sign scores in the treatment group were lower than those in the control group (13.29 ± 5.91 vs. 18.84 ± 7.14, p = 0.000, Bonferroni correction) (Table 5), and the number of non-responders in the treatment group (3) was significantly less than that in the control group (19) (p < 0.001, Bonferroni correction) (Table 6, Figure 5). The markedly effective rate in the treatment group (25.5%) was significantly higher than that in the control group (3.5%) (p < 0.001, Bonferroni correction) (Table 6). The scores of both groups significantly decreased compared with the baseline, with a more pronounced improvement trend in the treatment group (Figures 4A–C). Stratified analysis revealed that in the AI + OFS subgroup, the treatment group had better efficacy than the control group (p < 0.001, Bonferroni correction) (Figures 4D–F).
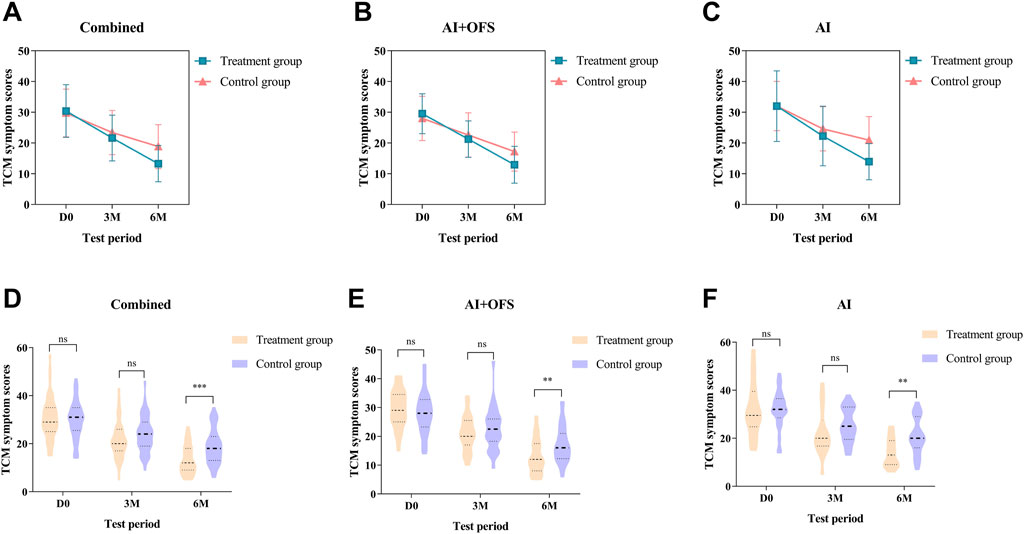
Figure 4. Difference of TCM symptom scores between the treatment and control groups in the change from baseline to 3 and 6 months.
Bone mineral density
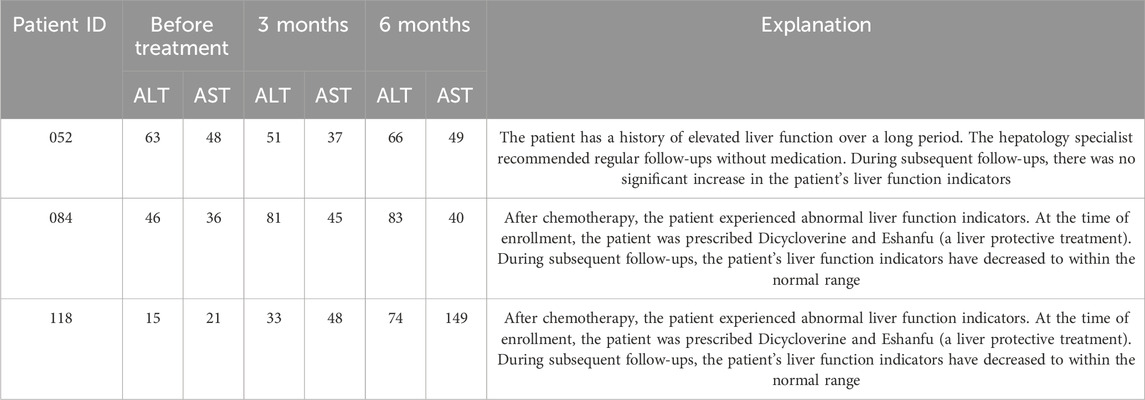
After 6 months of treatment with traditional Chinese medicine, the changes in T-scores of BMD in the lumbar spine and left femur between the two groups were not statistically significant (p > 0.05) (Table 7). Intragroup comparisons showed that the BMD T-scores in both groups still tended to decrease, but the differences were not statistically significant (p > 0.05) (Figure 6).
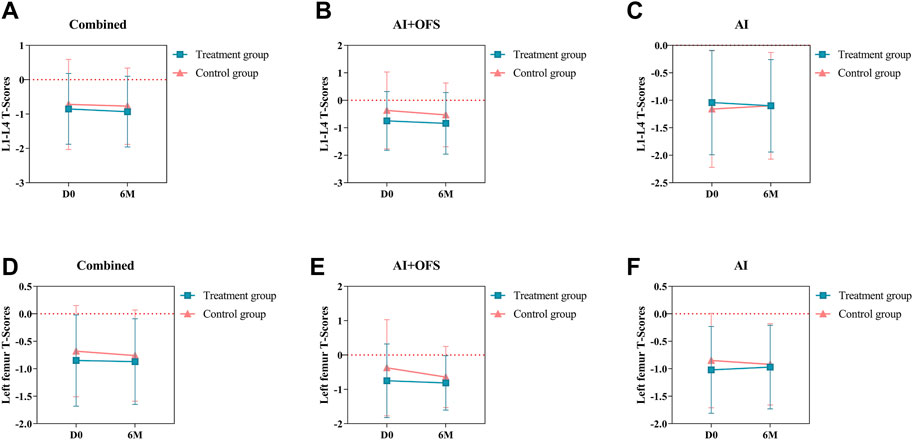
Figure 6. Difference of Bone Mineral Density T-Scores between the treatment and control groups in the change from baseline to 3 and 6 months.
Bone metabolism-related biochemical indicators
PPS analysis indicated no statistically significant differences (p > 0.05) in the levels of bone metabolism biochemical indicators, including 25(OH)D3, β-CTX, OC, GH, Estradiol and Testosterone, between the treatment and control groups at three and 6 months post-treatment (Table 8). Intragroup comparisons showed no statistically significant differences (p > 0.05) in bone metabolism levels after treatment in both groups, although β-CTX exhibited a decreasing trend in the treatment group [(567.42 ± 288.65) vs. (544.38 ± 279.96), p = 0.68], while an increasing trend was observed in the control group. After 6 months of treatment with TCM, levels of 25(OH)D3 increased in both groups, while OC and β-CTX levels decreased, but these differences were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). In the AI + OFS treatment subgroup, the level of growth hormone increased significantly compared to pre-treatment (Figure 7). After 6 months of medication, subgroup analysis stratified by endocrine therapy regimen indicated that the trend of Testosterone level changes in both subgroups shifted from a decreasing trend in the first 3 months to an increasing trend, with the overall decrease in Testosterone levels becoming less pronounced in the treatment group (Figure 8).
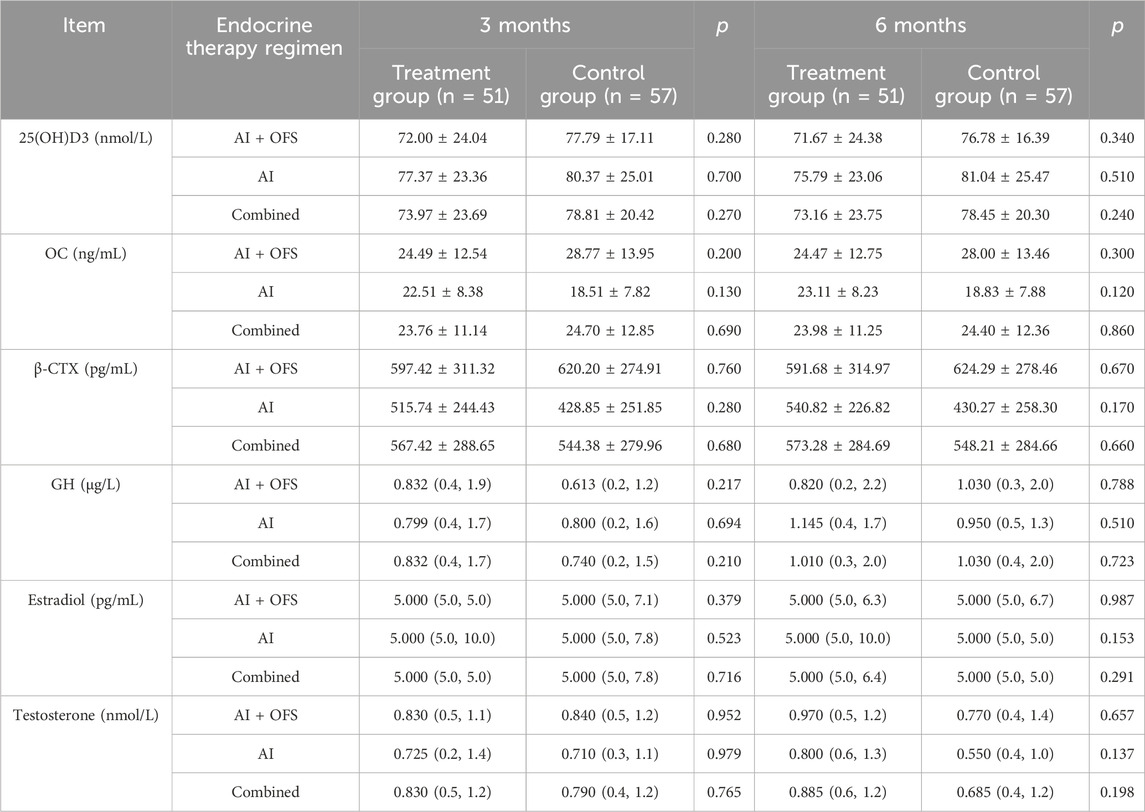
Table 8. Comparison of Bone Metabolism-Related Biochemical Indicators in the PPS patient population (n = 108) (±s).
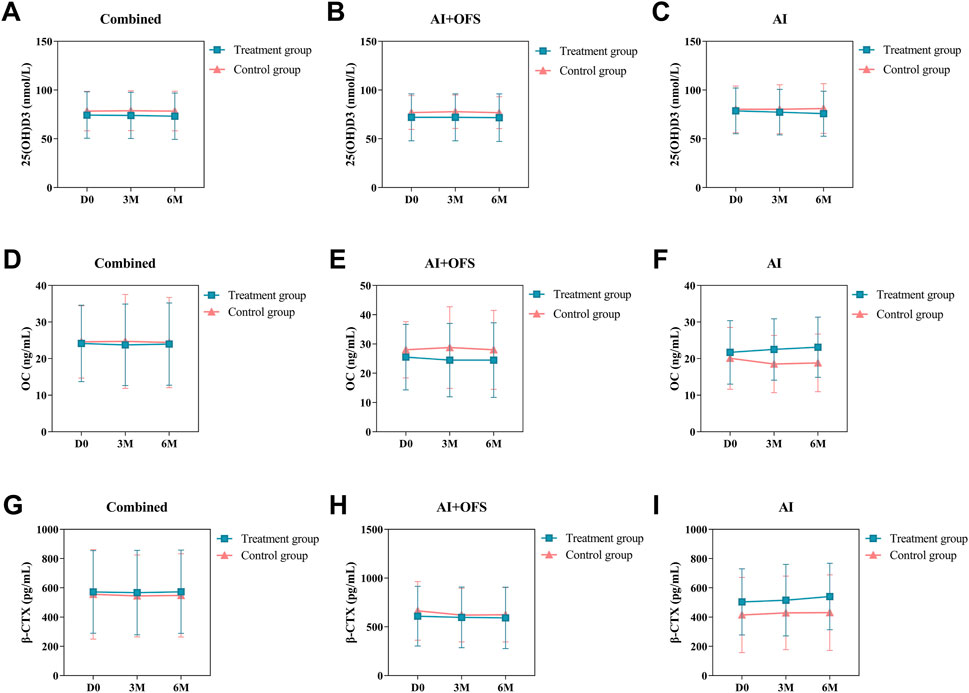
Figure 7. Difference of Bone Metabolism Parameters between the treatment and control groups in the change from baseline to 3 and 6 months.
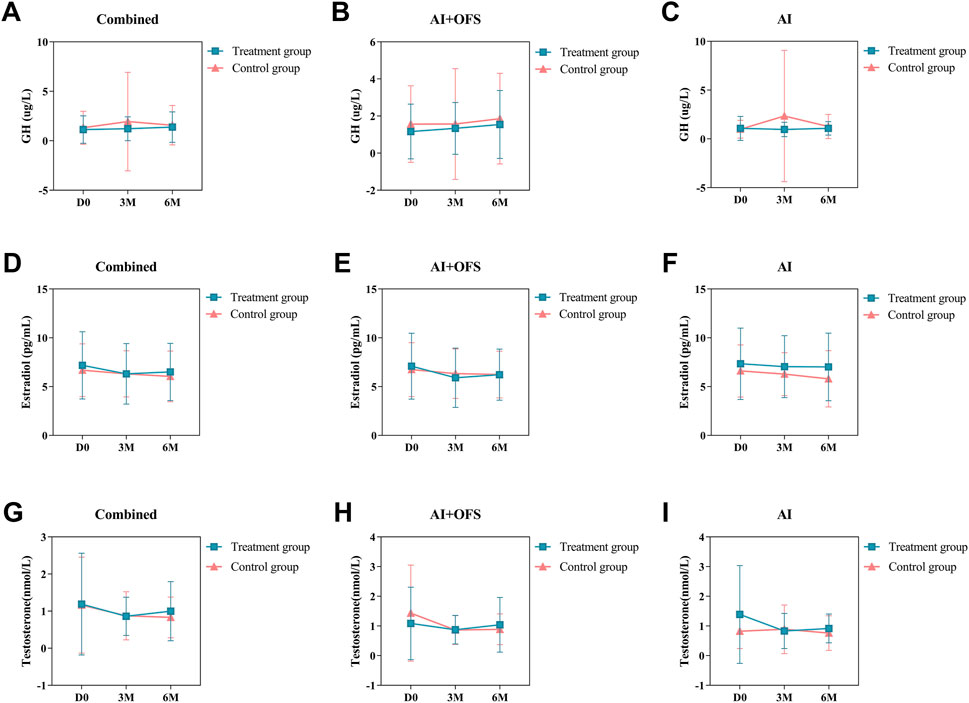
Figure 8. Difference of Bone Metabolism-Related Hormones levels between the treatment and control groups in the change from baseline to 3 and 6 months.
Adverse events
Most subjects well tolerated the research medication, and no serious adverse events were reported. The most common adverse events in both groups were abnormal White Blood Cell (WBC), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) and Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) levels (Table 9). All of the adverse events occurred or disappeared in a short period. No participant discontinued treatment or withdrew due to adverse events. In summary, it is believed that the YSTG formula has no adverse effects on the hematological system, liver and kidney functions, and the prognosis of breast cancer, and the use of the medication is safe.
Discussion
This single-center, randomized, controlled, single-blind trial evaluated the clinical efficacy and safety of YSTG formula in the treatment of AIMSS and enrolled 136 patients. Notably, this study focuses on the core pathogenesis of “liver stagnation and kidney deficiency” caused by bone and joint side effects of breast cancer endocrine therapy, and it is the first clinical trial in China to explore the efficacy of YSTG formula in treating AIMSS. This study is the first to expand the focus group of aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal syndrome to include premenopausal patients using AIs in combination with OFS. Our findings demonstrated that the YSTG formula effectively reduced the WOMAC scores and the total points of traditional Chinese medicine symptoms and signs, and significantly improved the clinical symptoms of patients; the treatment had high safety and was well tolerance. As a result, this formula can be used as a complementary treatment for patients with AIMSS.
Endocrine therapy can effectively reduce or inhibit the secretion of estrogen and is the recommended first-line treatment option for HR + breast cancer patients (Tokunaga et al., 2025). Endocrine treatment plans are divided based on the menopausal status of the patient into pre- and post-menopausal categories. AIs are the main drugs for endocrine treatment of post-menopausal HR + breast cancer patients (Fullana et al., 2024). The Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) meta-analysis shows that AIs significantly reduce the 10-year recurrence rate and mortality rate of post-menopausal HR + early-stage breast cancer patients compared to tamoxifen (Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group EBCTCG, 2015). The efficacy demonstrated by AIs in post-menopausal patients has sparked considerable interest in academia regarding their use in perimenopausal patients. The average age of breast cancer onset in China is relatively low, with about 60% of female patients diagnosed before menopause. Compared to post-menopausal patients, premenopausal women have active ovarian function that continuously secretes estrogen, which may accelerate the proliferation of breast cancer cells (Paluch-Shimon et al., 2022). Ovarian function suppression (OFS) has been widely applied in the treatment of HR + early-stage breast cancer (Pagani et al., 2023). Several long-term follow-up studies have further confirmed the long-term benefits of OFS, showing that it can significantly reduce the distant recurrence risk of premenopausal early-stage breast cancer patients and improve cure rates (Johansson et al., 2022). The SOFT-TEXT study confirmed that for premenopausal patients, AIs combined with OFS significantly improve disease-free survival rates compared to tamoxifen combined with OFS, and continue to reduce the risk of disease recurrence (Pagani et al., 2023). The combination of AIs and OFS is more commonly associated with osteoporosis, fractures, and vaginal dryness, and other adverse events (Hu et al., 2019), which severely affect the quality of life and medication adherence of patients. Currently, there are no clear treatment guidelines domestically or internationally, and clinical interventions often involve bisphosphonates or denosumab, etc. (Skafida et al., 2023). However, these interventions are often costly, have many side effects, and long-term use may lead to drug resistance and increase the incidence of complications. Therefore, it is particularly important to explore the mechanisms of AIMSS in breast cancer patients and new treatment methods.
AI-treated patients mainly report musculoskeletal symptoms such as arthralgias, myalgias, and joint stiffness, which significantly impact their quality of life. A reliable and specific instrument is needed to assess the severity of these symptoms and the efficacy of interventions. The WOMAC score, widely used and well-validated, is highly relevant for our study on improving musculoskeletal symptoms. It directly addresses pain, stiffness, and physical function, making it an ideal primary outcome measure for AIMSS. The WOMAC is a patient-reported outcome (PRO) measure for assessing osteoarthritis of the knees or hips (Zeng et al., 2021). It consists of 24 questions (5 pain, 2 stiffness, and 17 physical function) and can be completed in less than 5 min (Driban et al., 2023). The results indicated that both the treatment group and the control group experienced improvements in musculoskeletal symptoms. The results of the WOMAC score study indicated that both the treatment group and the control group improved in terms of musculoskeletal symptoms. Three months after treatment, the pain subscale score of the treatment group was significantly lower than that of the control group, and the difference between the two groups was more pronounced among those receiving AI plus OFS therapy. Intragroup comparisons revealed that the control group showed a significant decrease in overall WOMAC scores; the treatment group demonstrated a clear downward trend in WOMAC scores both overall and after stratified analysis. Six months after treatment, when comparing WOMAC scores between the two groups and conducting stratified analysis, the results showed that at all levels of comparison, the treatment group had lower scores than the control group. Intragroup comparisons indicated that both groups experienced a significant decrease in WOMAC scores after overall analysis and stratified statistics.
AIs cause bone loss and osteoporosis, which are primarily manifested clinically as joint pain, bone pain, morning stiffness, and other symptoms. These can be categorized under the TCM concept of “bone impediment”, and their pathogenesis is closely related to the kidney, liver, and blood stasis. Previous studies have found that using kidney-tonifying methods can increase patients’ lumbar spine and femoral bone density, and can also raise the levels of PINP and lower the levels of β-CTX (Yin et al., 2018). However, the side effects of AIs are not limited to the reduction of bone mass; they also include bone and joint pain; moreover, the age range of those using AIs is broad, and their physical conditions vary. If kidney-tonifying therapy is used as a universal treatment, it cannot accommodate all syndrome types and does not reflect the TCM principle of “treating the same disease differently based on varying conditions.” This study, starting from TCM theory, treats AIMSS based on the theory of liver depression and kidney deficiency, broadening the clinical treatment approach for AIMSS. The main components of the Yishen Tiao Gan formula include Achyranthes bidentata (Huai niu xi), Eucommia ulmoides (Du zhong), Lycium barbarum (Gou qi zi), Cuscuta chinensis (Tu si zi), Cyperi Rhizoma (Zhi xiang fu), and Cornus officinalis (Shan yu rou). Previous studies have found that the YSTG formula may improve bone loss by up-regulating SLIT3 to induce H-type angiogenesis. Additionally, modern medical research has demonstrated that Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide suppresses osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via inhibiting RANKL signaling (Song et al., 2018). Eucommia ulmoides Oliver polysaccharide alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by stimulating bone formation via ERK/BMP-2/SMAD signaling (Song et al., 2024). LBP1C-2 from Lycium barbarum alleviated age-related bone loss by targeting BMPRIA/BMPRII/Noggin (Sun et al., 2023). The active components in Cuscuta chinensis Lam effectively prevent and treat postmenopausal osteoporosis by modulating bone marrow macrophage polarization through the NF-κB/IκBα signaling pathway (Li et al., 2025).
Significant improvements in symptoms were observed in both groups in terms of the TCM symptom and sign score. After 3 months of medication, the treatment group had an effectiveness rate of 49.1%, and both groups showed a marked decrease in TCM symptom and sign scores, with a more pronounced downward trend in the treatment group. As the treatment time increased, the effect became more apparent. After 6 months of treatment, the effectiveness rate in the treatment group reached 68.6%, and the TCM symptom and sign scores in the treatment group were significantly lower than those in the control group, with a more noticeable downward trend in the treatment group. This has clinical guidance significance for the treatment of AIMSS patients with TCM.
The management of AIMSS in breast cancer patients needs a multidisciplinary approach integrating pharmacological and non-pharmacological supportive care strategies (Piazzon et al., 2025). Endocrine therapy with AIs is key for HR + breast cancer but causes significant musculoskeletal side effects. Current pharmacological interventions for AIMSS often involve bisphosphonates or denosumab, which can be costly and have side effects. The YSTG formula offers a potential alternative with high safety and efficacy. Non-pharmacological interventions like physical therapy, exercise programs, and psychological support also play a crucial role in managing AIMSS (Piazzon et al., 2025). Integrating the YSTG formula with these non-pharmacological strategies can enhance overall patient outcomes.
The study still has some limitations as follows. First, the study was not designed as a double-blind trial. The traditional double-blind double-mimic method is not affordable and suitable for this study of multiple TCM prescriptions. Therefore, we finally chose single-blind which conforms to the complexity and feasibility of TCM and implemented it strictly to control the risk of reveals. Secondly, our study did not include a placebo control for YSTG formula due to ethical considerations and the need to provide active treatment to all participants. The Breast Surgery Formula, used in both groups, was designed to address postoperative symptoms and complications in breast cancer patients. This approach, while ensuring ethical standards, limits our ability to definitively attribute observed effects solely to the YSTG formula. Future studies should consider a placebo control and separate groups receiving either the Breast Surgery Formula alone, the YSTG formula alone, or the combined treatment to better assess the independent and combined effects of each formula. Additionally, the three- and 6-month treatment durations may be inadequate for capturing the complete bone metabolism cycle, and this short duration could mask differences in BMD and other relevant indicators. Therefore, future studies should extend the treatment and follow-up periods to better evaluate the long-term efficacy of YSTG formula. Second, the small sample size and the selection of patients exclusively from one hospital may have introduced bias. Therefore, future studies with larger sample sizes from multiple centres are needed to address the present limitations.
Conclusion
The YSTG formula significantly reduced WOMAC scores, improving pain, stiffness, physical function in patients with AIMSS, and alleviating the traditional Chinese medicine symptoms and signs of liver and kidney deficiency, thereby enhancing the overall quality of life for patients. Despite the limitations of this study, it provides evidence-based medicine for the treatment of AIMSS with Chinese herbs, potentially offering a new alternative to treatments such as bisphosphonates or denosumab. Future research should focus on the broader integration of supportive care strategies for AIMSS. This includes exploring the synergistic effects of combining the YSTG formula with other pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions. Such research will contribute to the development of comprehensive, evidence-based guidelines for the management of AIMSS in breast cancer patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Longhua Hospital affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Ethics No. 2022LCSY001). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. MY: Visualization, Formal analysis, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. YC: Supervision, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. HuC: Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. YY: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. HoC: Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Shanghai 2021 “Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan” Medical Innovation Research Special Project [grant number 21Y11923000]; Shanghai 2024 “Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan” Medical Innovation Research Special Project [grant number 24Y12801000]; and Sailing Program, Scientific and Innovative Action Plan of Shanghai [grant number 20YF1449800].
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Chen Hongfeng (Longhua Hospital affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine) for her financial support for this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1639714/full#supplementary-material
References
Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Breast Cancer Committee (2021). Guidelines and standards for diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer by Chinese anti-cancer association (2021 edition). Chin. J. Cancer 31 (10), 954–1040. doi:10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2021.10.013
Chu, M., Zhang, Y., Ye, M., Yin, Y., and Chen, H. (2025). Yi shen tiao gan decoction alleviates aromatase inhibitor-related bone loss by promoting H-type vessel formation. Transl. Oncol. 55, 102377. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102377
Conaghan, P. G., Dworkin, R. H., Schnitzer, T. J., Berenbaum, F., Bushmakin, A. G., Cappelleri, J. C., et al. (2022). WOMAC meaningful within-patient change: results from 3 studies of tanezumab in patients with moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J. Rheumatol. 49 (6), 615–621. doi:10.3899/jrheum.210543
Crew, K. D., Greenlee, H., Capodice, J., Raptis, G., Brafman, L., Fuentes, D., et al. (2007). Prevalence of joint symptoms in postmenopausal women taking aromatase inhibitors for early-stage breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 25 (25), 3877–3883. doi:10.1200/jco.2007.10.7573
Driban, J. B., Price, L. L., Lu, B., Flechsenhar, K., Lo, G. H., and McAlindon, T. E. (2023). The natural history of end-stage knee osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 152148. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.152148
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group EBCTCG (2015). Aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen in early breast cancer: patient-level meta-analysis of the randomised trials. Lancet 386 (10001), 1341–1352. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)61074-1
Fullana, B., Morales, S., Petit, A., Alay, A., Verdaguer, H., Climent, F., et al. (2024). Neoadjuvant sunitinib plus exemestane in post-menopausal women with hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative early-stage breast cancer (SUT_EXE-08): a phase I/II trial. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 23626. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-72152-1
Grigorian, N., and Baumrucker, S. J. (2022). Aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal pain: an overview of pathophysiology and treatment modalities. SAGE Open Med. 10, 20503121221078722. doi:10.1177/20503121221078722
Henry, N. L., Azzouz, F., Desta, Z., Li, L., Nguyen, A. T., Lemler, S., et al. (2012). Predictors of aromatase inhibitor discontinuation as a result of treatment-emergent symptoms in early-stage breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 (9), 936–942. doi:10.1200/jco.2011.38.0261
Howlader, N., Altekruse, S. F., Li, C. I., Chen, V. W., Clarke, C. A., Ries, L. A. G., et al. (2014). US incidence of breast cancer subtypes defined by joint hormone receptor and HER2 status. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 106 (5), dju055. doi:10.1093/jnci/dju055
Hu, K., He, P., Peng, Q., Zhong, X., Deng, L., Xie, Y., et al. (2019). OFS plus AI or SERM vs. SERM alone in premenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: a prospective cohort study using the real-world database. Breast Cancer 26 (3), 339–348. doi:10.1007/s12282-018-0929-6
Johansson, A., Dar, H., van 't Veer, L. J., Tobin, N. P., Perez-Tenorio, G., Nordenskjöld, A., et al. (2022). Twenty-year benefit from adjuvant goserelin and tamoxifen in premenopausal patients with breast cancer in a controlled randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 40 (35), 4071–4082. doi:10.1200/jco.21.02844
Lammers, S. W. M., Geurts, S. M. E., Hermans, K., Kooreman, L. F. S., Swinkels, A. C. P., Smorenburg, C. H., et al. (2025). The prognostic and predictive value of the luminal-like subtype in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: an analysis of the DATA trial. ESMO Open 10 (2), 104154. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.104154
Li, X., Wang, Z., Chen, Y., Yang, Y., Shao, H., Feng, X., et al. (2025). Regulation of monocyte polarization through nuclear factor kappa B/inhibitor of kappa B alpha pathway by Cuscuta chinensis lam. In postmenopausal osteoporosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 346, 119710. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2025.119710
Pagani, O., Walley, B. A., Fleming, G. F., Colleoni, M., Láng, I., Gomez, H. L., et al. (2023). Adjuvant exemestane with ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer: long-term Follow-Up of the combined TEXT and SOFT trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 41 (7), 1376–1382. doi:10.1200/jco.22.01064
Paluch-Shimon, S., Cardoso, F., Partridge, A. H., Abulkhair, O., Azim, H. A., Bianchi-Micheli, G., et al. (2022). ESO-ESMO fifth international consensus guidelines for breast cancer in young women (BCY5). Ann. Oncol. 33 (11), 1097–1118. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.07.007
Peng, N., Yu, M., Yang, G., Fu, Q., Xu, Y., Yu, J., et al. (2018). Effects of the Chinese medicine yi shen jian Gu granules on aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal symptoms: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Breast 37, 18–27. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2017.08.003
Piazzon, N., Cortet, M., Vérot, E., and Carrouel, F. (2025). Adapted physical activity programs for the prevention and treatment of musculoskeletal pain induced by aromatase inhibitors in non-metastatic breast cancer patient: a scoping review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 205, 104548. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104548
Regan, M. M., Price, K. N., Giobbie-Hurder, A., Thürlimann, B., and Gelber, R. D. (2011). Interpreting breast international group (BIG) 1-98: a randomized, double-blind, phase III trial comparing letrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant endocrine therapy for postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 13 (3), 209. doi:10.1186/bcr2837
Schulz, K. F., Altman, D. G., and Moher, D. (2010). CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Bmj 340, c332. doi:10.1136/bmj.c332
Skafida, E., Andrikopoulou, A., Terpos, E., Markellos, C., Moustafa, S., Pectasides, D., et al. (2023). Impact of CDK4/6 inhibitors on aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal syndrome (AIMSS) in the adjuvant setting. Breast J. 2023, 3614296. doi:10.1155/2023/3614296
Song, D., Cao, Z., Huang, S., Tickner, J., Li, N., Qiu, H., et al. (2018). Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide suppresses osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via inhibiting RANKL signaling. J. Cell Biochem. 119 (6), 4826–4835. doi:10.1002/jcb.26682
Song, J., Zhang, Y., Jin, X., Zhu, Y., Li, Y., and Hu, M. (2024). Eucommia ulmoides oliver polysaccharide alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by stimulating bone formation via ERK/BMP-2/SMAD signaling. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 29647. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-80859-4
Sun, C., Chen, X., Yang, S., Jin, C., Ding, K., and Chen, C. (2023). LBP1C-2 from Lycium barbarum alleviated age-related bone loss by targeting BMPRIA/BMPRII/Noggin. Carbohydr. Polym. 310, 120725. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120725
Sun, X., Jing, J., Dai, R., Zhu, C., Sun, Y., Sun, J., et al. (2024). Shengji ointment combined with bromelain promotes granulation of exposed tendons in diabetic foot ulcers: a multicenter, randomized, positive-controlled clinical trial. Heliyon 10 (22), e39716. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39716
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71 (3), 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
Tokunaga, E., Iwata, H., Itoh, M., Taira, T., Toyama, T., Mizuno, T., et al. (2025). Capivasertib and fulvestrant for patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: analysis of the subgroup of patients from Japan in the phase 3 CAPItello-291 trial. Breast Cancer 32 (1), 132–143. doi:10.1007/s12282-024-01640-z
Yin, Y., Zhang, W., Zhou, Y., Ye, M., and Chen, H. (2018). Clinical study on the prevention and treatment of aromatase inhibitor-induced bone metabolic abnormalities with Bu shen Zhuang Gu formula. Chin. J. Osteoporos. 24 (09), 1195–1200.
Keywords: breast cancer, aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal syndrome, Yishen Tiaogan formula, traditional Chinese Medicine, Western Ontario and McMaster Universities osteoarthritis index, randomized controlled trial
Citation: Zhang Y, Chu M, Ye M, Cheng Y, Cong H, Yin Y and Chen H (2025) Effects of the efficacy of the Yi Shen Tiao Gan formula on aromatase inhibitor associated musculoskeletal syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1639714. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1639714
Received: 03 June 2025; Accepted: 27 June 2025;
Published: 25 July 2025.
Edited by:
Adolfo Andrade-Cetto, National Autonomous University of Mexico, MexicoReviewed by:
Florence Carrouel, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, FranceJan Tauchen, Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Czechia
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Chu, Ye, Cheng, Cong, Yin and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yulian Yin, a2lsbHVhMDE4eXlsQDE2My5jb20=; Hongfeng Chen, Y2hoZmx1azIwNjhAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to the work
 Yan Zhang
Yan Zhang Meiling Chu2†
Meiling Chu2† Yulian Yin
Yulian Yin Hongfeng Chen
Hongfeng Chen