- 1Marshall Institute for Interdisciplinary Research (MIIR), Marshall University, Huntington, WV, United States
- 2Bureau of Public Health, Office of Laboratory Services, West Virginia Department of Health, Big Chimney, WV, United States
- 3Department of Biomedical Sciences, School of Medicine, Marshall University, Huntington, WV, United States
- 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, Marshall University, Huntington, WV, United States
The transmembrane Na/K-ATPase is located in the plasma membrane of all mammalian cells. It utilizes energy from ATP hydrolysis to execute its pumping function and interacts with other proteins and/or kinase molecules to execute its signaling function. Digoxin, one of the earliest identified cardiotonic steroids (CTS) that specifically binds to the Na/K-ATPase, has been widely prescribed to manage patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and heart failure (HF) for over 200 years. Elevated plasma levels of CTS have been observed in patients with hypertension, chronic kidney disease (CKD), CVD, and congestive HF. After extensive research efforts spanning decades, there remain unresolved disagreements regarding the various mechanisms underlying the Na/K-ATPase signaling functions. This article examines the known and controversial mechanisms that initiate the Na/K-ATPase signaling functions and their related regulatory mechanisms.
The Na/K-ATPase and cardiotonic steroids (CTS)
The P-type ATP-hydrolyzing enzyme Na/K-ATPase (EC 3.6.3.9) was first discovered as an energy-transducing primary ion-transporter (Skou, 1957), presented in all cell types tested. Unlike other P-type ATPases, Na/K-ATPase binds to a specific group of chemicals called cardiotonic steroids (CTS, also known as digitalis-like substances) that were recognized as a new class of endogenous steroid hormones (Schoner, 2002; Schoner et al., 2003). CTS has two structurally distinct groups: cardenolides (like ouabain and digoxin) and bufadienolides (like marinobufagenin MBG and telecinobufagin TCB). Digoxin has been highly prescribed to manage CVD and HF patients for over 200 years (Pavlovic, 2014). Elevated plasma CTS has been observed in patients with hypertension, CVD, CKD, CKD-related cardiomyopathy, and congestive HF, in which different Na/K-ATPase signaling functions were involved (Kelly and Smith, 1993; Bagrov et al., 1998; Kiselyov et al., 1999; Kaplan, 2002; Komiyama et al., 2005; Liu, 2005; Kolmakova et al., 2011; Bai et al., 2013; Pavlovic, 2014; Kennedy et al., 2015; Pavlovic, 2020).
The history and progression of the Na/K-ATPase and CTS
A recent seminal retrospective review by Dr. Blaustein and Dr. Hamlyn discussed the history of the findings of different kinds of CTS (including endogenous ouabain), the mechanisms of their physiological and pathophysiological effects in cell models, animal models, and humans, the Na/K-ATPase-initiated intracellular signaling function by CTS, and some unresolved issues and possible solutions (Blaustein and Hamlyn, 2024). Another seminal review by Christian Staehr et al. focused on the potential implication of Na/K-ATPase-dependent intracellular signaling pathways in severe vascular disorders such as ischemic stroke, familial migraine, and arterial hypertension (Staehr et al., 2023).
The signaling functions of the Na/K-ATPase
The Na/K-ATPase is highly sensitive to inhibition by CTS, which has been used for centuries to treat CVD, congestive HF and arrhythmias. The amino acids constituting the ouabain-binding site are highly conserved across the evolutionary spectrum to execute important biological functions that define the biological significance of the “receptor function” of the Na/K-ATPase and its regulation by potential endogenous CTS-like compounds (Lingrel, 2010), in which CTS binds to Na/K-ATPase at E2P state (Kanai et al., 2021). Furthermore, in the different kinds of CTS tested, there are kinetics and/or thermodynamic differences due to the type of sugar and lactone ring present in the steroid structure (Azalim-Neto et al., 2024), suggesting different possible Na/K-ATPase signaling pathways, binding properties, and functionalities.
The Na/K-ATPase has been extensively studied for its ion-pumping function in the kidney and heart in the early days. Later on, the revolutionary discovery that the NKA is also a hormone receptor and signaling molecule is essential for understanding the full impact of the NKA on physiology and pathophysiology (Blaustein and Hamlyn, 2024). The Na/K-ATPase has also been recognized as a receptor, signal transducer, signaling protein, and scaffolding protein through multiple protein-protein interactions in the past 3 decades (Xie and Askari, 2002; Xie and Cai, 2003; Pierre and Xie, 2006; Aperia, 2007; Bagrov et al., 2009; Li and Xie, 2009; Liu and Xie, 2010; Yan and Shapiro, 2016). Initially, it was found that CTS mediates signal transduction through the protein-protein interactions between Na/K-ATPase and other skeletal and/or kinase proteins. The signaling function of Na/K-ATPase has also been implicated in a range of clinical disorders, underscoring its broad relevance and potential for further research. These clinical disorders include, but are not limited to, cancer, CKD, CVD, and uremic cardiomyopathy. The potential for further research in this area is vast, offering many opportunities for discovery and advancement (Li et al., 2011; Yan and Shapiro, 2016). Over the past 30 years, the concept that the Na/K-ATPase functions as a signaling transducer has evolved significantly and is involved in many regulatory functions (Aydemir-Koksoy et al., 2001; Xie and Askari, 2002; Aizman and Aperia, 2003; Xie, 2003; Xie and Cai, 2003; Schoner and Scheiner-Bobis, 2005; Pierre and Xie, 2006; Schoner and Scheiner-Bobis, 2007; Bagrov et al., 2009; Liu and Xie, 2010; Liu et al., 2011; Aperia, 2012; Godinho et al., 2017; Wang and Shapiro, 2019; Wang et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021; Maxwell et al., 2021; Horesh et al., 2024).
The Na/K-ATPase signaling function and activity are also linked to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS), in which CTS increases ROS generation, and increases in ROS can also initiate the Na/K-ATPase signal cascades in a feed-forward manner to form a Na/K-ATPase/ROS amplification loop (Yan et al., 2013; Yan and Shapiro, 2016; Liu et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2018). This mechanism has demonstrated significance in oxidative stress-related disease states, including obesity, atherosclerosis, heart failure, uremic cardiomyopathy, neurodegenerative disorders, hypertension, and other conditions rooted in ROS (Bundgaard and Kjeldsen, 1996; Srikanthan et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2018; Pratt et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2020; Staehr et al., 2022).
Ouabain is the most studied CTS. The binding of ouabain to the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit causes increase in ROS, which can initiate the Na/K-ATPase signaling pathways that lead to increases in oxidative modification of the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit, intracellular calcium concentration, and other effects. Receptors, signaling molecules, cytosolic proteins, and membrane structural proteins can interact with the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit through multiple structural binding motifs found in the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit (Sweadner and Donnet, 2001; Xie and Cai, 2003; Morth et al., 2007; Reinhard et al., 2013; Fedosova et al., 2021). These include but are not limited to c-Src, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), phospholipase C (PLC), phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K), inositol trisphosphate receptor (IP3Rs), ankyrin, adducin, and caveolin-1. The Na/K-ATPase signaling pathways have been demonstrated in different types of cells and animal models (Ferrandi et al., 2004; Periyasamy et al., 2005; Ferrandi et al., 2006; Kennedy, et al., 2006). Furthermore, the Na/K-ATPase α1/Src regulatory function of metabolic capacity is involved in metabolic diseases (Kutz et al., 2021; Staehr and Matchkov, 2021). Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) expressing an Src-signaling null mutant (A420P) provide genetic evidence for the role of Na/K-ATPase α1/Src in the tonic stimulation of basal mitochondrial metabolism and ROS production in human cardiac myocytes (Cai, Pessoa, et al.). Using the porcine LLC-PK1 cells, incubation with 100 nM ouabain decreased ouabain-sensitive 86Rb uptake without significant impact on total enzyme activity, suggesting internalization of the Na/K-ATPase (Liu et al., 2002), which was further confirmed by the decreases of membrane-bound Na/K-ATPase using the biotinylation assay (Liu et al., 2004). The Na/K-ATPase trafficking occurs via a clathrin-dependent pathway by activating PI3K and Src (Liu and Xie, 2010). However, ouabain did not trigger significant Na/K-ATPase internalization in MDCK cells (Liu et al., 2002). On the other hand, in human endothelial cells, ouabain decreased rather than increased endocytosis of 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) in human endothelial cells (Trevisi et al., 2006).
The evolving functionalities of the Na/K-ATPase and CTS
Other than affecting the well-defined effects of the Na/K-ATPase in the modulation of cardiac and renal functions, studies have also demonstrated that the Na/K-ATPase has other emerging functions in many ways. For example, one newly synthesized CTS γ-Benzylidene Digoxin 8 (BD-8) is a promising immunomodulatory molecule, and another newly synthesized CTS 21-benzylidene digoxin (21-BD), but not ouabain, causes changes in cholesterol and phospholipid content (Silva et al., 2017; Silva et al., 2021; Silva et al., 2022), further suggesting possible different roles of CTS variants in signaling and cellular functions. Interestingly, CTS has different functions. For example, ouabain also affects neuroinflammation, acute onset of neurological symptoms, and neurological disorders (Holm and Lykke-Hartmann, 2016; Leite et al., 2022), enhances renal cyst growth in a slowly progressive mouse model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) (Trant et al., 2023), and the progression of ADPKD (Venugopal and Blanco, 2016), sperm energetic defects (Numata et al., 2022), pro-cytogenic effects in ADPKD (Venugopal and Blanco, 2017), as well as thymidine phosphorylase-mediated SARS-CoV-2 spike protein enhanced thrombosis in K18-hACE2TG mice and platelet GPCR signaling function in thrombosis (Li et al., 2024; Roytenberg et al., 2024). Even more interestingly, in neurons, impairment of Na/K-ATPase activity and signaling causes neuronal dysfunction due to affected Ca2+ signaling, and proper regulation of Na/K-ATPase activity and signaling is beneficial to brain function (Kinoshita et al., 2022). The normal Na/K-ATPase function is essential for neuronal function, including neurotransmitter release, electrical signaling, maintaining cell volume, and secondary transcellular transport. The Na/K-ATPase is crucial for neuronal function, consuming a significant portion of the brain’s energy to maintain cellular processes. About 60%–90% of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients exhibited reduced brain Na/K-ATPase activity and vascular dysfunction, further highlighting the potential role of Na/K-ATPase in AD (Zhang J. et al., 2022). This reduced brain Na/K-ATPase activity may be linked to the interaction of Na/K-ATPase with amyloid-beta (Aβ), a key protein implicated in AD pathology (Petrushanko et al., 2022). Specifically, Aβ oligomers, known as amylospheroids (ASPD), bind to the Na/K-ATPase α3 subunit in neurons, leading to presynaptic calcium overload and neuronal death (Ohnishi et al., 2015). These findings indicate a vast diversity of the possible Na/K-ATPase signaling functions in different studied subjects via different Na/K-ATPase subunits, ion homeostasis, and signaling partners. Furthermore, β-adrenergic regulation of the cardiac Na/K-ATPase mediated by oxidative signaling (Galougahi et al., 2012), and Src represents a key intermediate and novel therapeutic target in the pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia, where it appears to regulate neuronal damage by influencing VEGF-mediated vascular permeability (Paul et al., 2001).
The Na/K-ATPase-dependent Src kinase activation is the key mechanisms responsible for elevation of cerebrovascular tone after reperfusion and the initiation of the Src kinase signaling pathway that sensitizes the contractile machinery to intracellular Ca2+ resulting in hypercontractility of vascular smooth muscle cells and, thus, elevated cerebrovascular tone that can contribute to impaired reperfusion after stroke, the potential implication of Na/K-ATPase-dependent intracellular signaling pathways in severe vascular disorders such as ischemic stroke, familial migraine, and arterial hypertension (Guldbrandsen et al., 2021; Staehr et al., 2023). Furthermore, inhibition of the Na/K-ATPase-dependent Src kinase signaling with pNaKtide prevented excessive vasoconstriction and disturbances in neurovascular coupling in a NKA α2+/G301R mouse model. pNaKtide had only a minor hypotensive effect, similar in both genotypes. The results demonstrate a novel treatment target to normalize cerebral perfusion in FHM2 (Staehr et al., 2025). The underlying mechanisms integrate cerebral edema, oxidative stress, and Na/K-ATPase-related c-Src signaling. The Na/K-ATPase signaling function and activity are also linked to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a bidirectional way, in which CTS increases ROS generation, and increases in ROS also initiate the Na/K-ATPase signal cascades in a feed-forward manner (Yan et al., 2013; Yan et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2018). This Na/K-ATPase/ROS amplification loop has demonstrated the significance in oxidative stress-related disease states, including obesity, atherosclerosis, heart failure, uremic cardiomyopathy, neurodegenerative disorders, hypertension, and other conditions rooted in ROS (Figure 1).
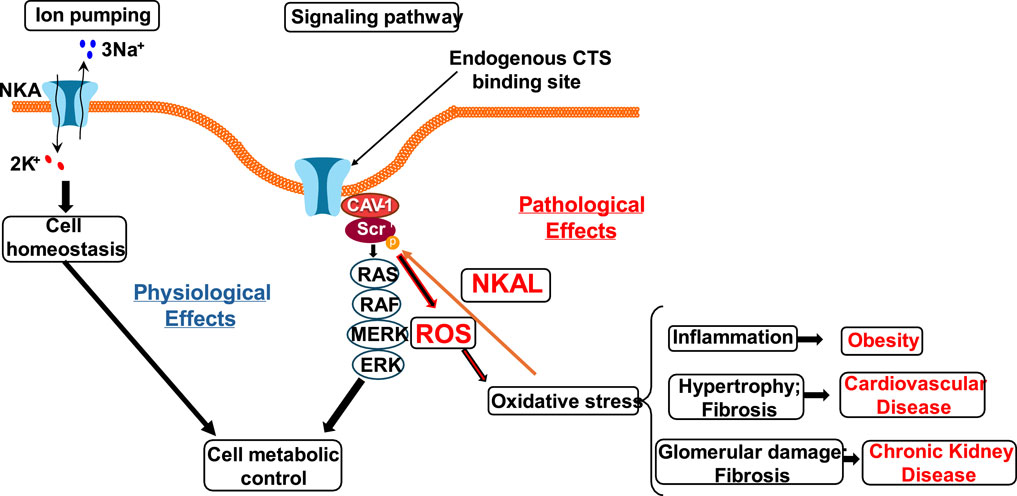
Figure 1. Schematic depicting the proposed disease pathogenesis progression with central oxidant stress production through the Na/K-ATPase signaling. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) lead to Na/K-ATPase conformational changes that activate c-Src and initiate downstream signaling cascades. This activation leads to ROS overproduction and oxidative stress, contributing to the development of obesity, cardiovascular, and renal diseases.
The proposed models of the Na/K-ATPase α1-Src interaction and signaling
The formation of the Na/K-ATPase α1-Src complex, a key step in the primary Na/K-ATPase signaling function, remains a topic of debate. There were evidences suggesting that Na/K-ATPase directly interacts with Src and other proteins (like caveolin-1) to form a functional receptor complex in live cells, as demonstrated by various available technologies at different times, as well as that the Src activation is through an ATP/ADP ratio change or ATP-sparring function, but not through the direct interaction with the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit. Even though there is uncertainty about the proposed different signaling modeling, the undefined mechanisms might affect the proposed capabilities and functions of c-Src activation. An organized functional signaling receptor complex might be more effective and controlled than any “random” reaction. These ongoing debates provide a comprehensive understanding of the primary Na/K-ATPase-Src signaling function, paving the way for further research and potential therapeutic applications (Liu et al., 2003; Wang et al., 2004; Kotova et al., 2006; Liang et al., 2006; Tian et al., 2006; Morth et al., 2009; Yatime et al., 2009; Weigand et al., 2012; Yosef et al., 2016; Nie et al., 2020).
Three different CTS-stimulated Src kinase activation “working” models have been proposed to explain the mechanisms underlying the activation of the Na/K-ATPase signaling function.
(1) The First Model is the direct interaction of the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit with c-Src, which forms a functional Na/K-ATPase/c-Src signaling receptor complex in caveolae. In this Model, the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit binds to c-Src through two pairs of domain binding (Na/K-ATPase α1 CD2 segment with c-Src SH2 domain, and Na/K-ATPase α1 ND1 segment with c-Src kinase domain) under resting conditions, and ouabain stimulates the release of c-Src KD from α1 ND1 segment that leads to c-Src kinase domain Tyr-418 phosphorylation (Wang et al., 2004; Tian et al., 2006). The binding status was affected by the changes of Na/K-ATPase E1/E2 conformation change and intracellular sodium and potassium concentration (Ye et al., 2011) This was further supported that expression of Na/K-ATPase α1 mutants (rat α1 mutants I279A and F286A) with defective in E1/E2 transition altered both basal and stimuli-induced Src regulation (Ye et al., 2013). Ouabain not only regulated the interaction in a time- and dose-dependent manner and stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 in LLC-PK1 cells but also induced the formation of a Na/K-ATPase-Src-caveolin complex and increased tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins isolated from caveolae. Furthermore, depletion of either cholesterol by methyl beta-cyclodextrin or caveolin-1 by siRNA significantly reduced the caveolar Na/K-ATPase and Src, which abolished ouabain-induced recruitment of Src to the Na/K-ATPase signaling complex (Wang et al., 2004; Tian et al., 2006). In this Model, the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit provides the ligand binding sites, the α1-associated c-Src provides the kinase moiety, and the caveolin-1 functions as an anchor to enrich the signaling partners in the caveolae structure. This Model was tested based on cell-free and live cells with different manipulations of the partner proteins (the α1 subunit, c-Src, and caveolin-1).
(2) The Second Model proposed that c-Src only transiently interacts with a protein complex formed between the Na/K-ATPase α1 and caveolin-1. To evaluate if there are direct interactions amongst Na/K-ATPase, Src, and caveolin-1, purified recombinant Na/K-ATPase (human α1β1FXYD1 or porcine α1D369Nβ1FXYD1) and purified human Src kinase and human caveolin-1 in native membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit kidney were applied. It showed no stable direct interactions between Na/K-ATPase and purified Src kinase, but a direct interaction between purified human Na/K-ATPase and human caveolin-1 (Yosef et al., 2016). This model was established in a cell-free system, with over-expressed and purified partner proteins, isolated plasmalemma caveolae, and right-side-out vesicles from rabbit kidney outer medulla. The first and second models agree that caveolin-1, by binding to the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit, functions as an anchoring protein to concentrate the “signaling” α1 subunit and its signaling partners in the caveolae structure. Another common characteristic of these two models is that c-Src activation is a proximal step in the Na/K-ATPase signaling initiated by either stable or transient interaction between the α1 subunit and c-Src. In the second Model, the Tyr-418 in purified c-Src was already phosphorylated in the isolation/purification process before binding experiments, which might leave only one pair of possible domain binding (i.e., Na/K-ATPase α1 CD2 domain with c-Src SH2 domain) under the experiment condition that might weaken the total binding force between the α1 subunit and c-Src proposed in the first Model.
(3) The Third Model proposed that c-Src activation is primarily a consequence of an ATP-sparing effect induced by the Na/K-ATPase inhibitors (ouabain, vanadate, and oligomycin) and energy status (ATP/ADP ratio). Ouabain-induced activation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 was independent of Src (Liu et al., 2007; Wu et al., 2013; Gable et al., 2014) but dependent on the ATP/ADP ratio induced by Na/K-ATPase inhibitors (digoxin, vanadate, Na+, K+, ATP, and ADP) in a dose-dependent manner, without protein-protein interaction between the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit and c-Src (Weigand et al., 2012).
Although there are controversies regarding the direct or indirect interaction between the Na/K-ATPase and Src kinase, the activation of Src kinase by phosphorylation is a well-established response to sub-micromolar concentrations of ouabain that was demonstrated in all three proposed models. Studies suggest that the Na/K-ATPase-associated Src kinase activated by ouabain (Haas et al., 2000; Liang et al., 2006; Tian et al., 2006; Li et al., 2009; Lai et al., 2013; Ye et al., 2013; Banerjee et al., 2015). This signaling microdomain model disagreed with other studies suggesting that ouabain-induced Src kinase activation is a result of the ATP-sparing effect of the Na/K-ATPase inhibitors (Weigand et al., 2012; Gable et al., 2014). However, in skeletal muscle, sub-micromolar and micromolar concentrations of ouabain do not affect the global intracellular ATP/ADP ratio, but with significant phosphorylation and activation of Src kinase (Kotova et al., 2006). Nevertheless, these studies addressed the global ATP/ADP ratio, and there is a possibility for spatially restricted changes in the ouabain concentrations. Accordingly, the Na/K-ATPase-dependent Src kinase activity is maintained in cells expressing a non-pumping mutant of the rat α1 isoform (Liang et al., 2006). The involvement of the Na/K-ATPase in the signaling cascade does not exclude a role for its ion-pumping function in ouabain-induced effects. Moreover, since intracellular Na+ ions regulate the conformation change of the Na/K-ATPase, it is possible that changes in intracellular Na+ concentration could also regulate the formation of the Na/K-ATPase/Src signaling complex, and thus cellular Src activity (Li et al., 2009). This Na/K-ATPase-dependent Src kinase signaling can modulate arterial contraction and blood pressure, as discussed below.
Notably, a common characteristic in these three models is that the E2(P) conformational state of the Na/K-ATPase is favored and stabilized by the Na/K-ATPase inhibitors (ouabain, vanadate, oligomycin), and energy status (ATP/ADP ratio). Though the dynamic conformational changes can affect the formation of the signaling complex, c-Src activation is one of the most proximal steps in the Na/K-ATPase signaling since the Na/K-ATPase itself lacks tyrosine kinase activity. The discrepancies amongst these models could be attributed to the different experimental designs and conditions, since the interactions of the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit with c-Src and/or caveolin-1 might also require other protein(s) that are not present in some experimental conditions, as suggested in the Second Model (Yosef et al., 2016).
Under the native conditions, Blue Native-PAGE, Blue Native-PAGE/SDS-PAGE 2D, and Mass-Spec analyses demonstrated the co-existence of the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit and c-Src in the same protein complex and a direct interaction between the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit and c-Src (Nie et al., 2020). These observations were further supported by comparisons of DTT-cleavable and DTT-non-cleavable cysteine-cysteine (SH-SH) crosslinked samples, which demonstrated that depletion of Src kinase family members (c-Src, Yes, and Fyn) or caveolin-1 reduced the interactions of the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit with other proteins, but depletion of caveolin-1 did not affect the interaction of c-Src with the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit. The data showed direct interactions between the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit and c-Src and between the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit and caveolin-1. However, the data argued about the interaction between c-Src and caveolin-1 under the native condition. Furthermore, the data also indicated the existence of different protein complexes containing the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit and c-Src, which might have different signaling functions (Nie et al., 2020). Therefore, further studies are expected to determine whether the Na/K-ATPase-Src interaction and signaling function under different conditions.
The caveolae and caveolins in the Na/K-ATPase signaling
The caveolae are microdomain rafts containing caveolins that are capable of assembling and regulating signaling complexes through association with a variety of membrane receptors and play pleiotropic roles in the regulation of cellular functions (Anderson, 1998; Drab et al., 2001; Razani et al., 2002; Gratton et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2004), such as hypertrophic signaling (Ferrandi et al., 2004; Ferrandi et al., 2006). In caveolae isolated from cardiomyocytes, cardiac ventricles, kidney cell lines (porcine renal proximal tubular LLC-PK1 cell, human embryo HEK-293 cell, and porcine kidney outer medulla), the isolated caveolae (by detergent-free procedures) contain Src, EGFR, ERK1/2, Na/K-ATPase α1/α2, and caveolin-3 (Song et al., 1996; Liu et al., 2003; Wang et al., 2004; Cui and Xie, 2017). Furthermore, in cardiac caveolae isolated from ouabain-treated contracting rat hearts, there were significant increases in phosphorylated ERK1/2 and recruitment of Src and Na/K-ATPase α2 to caveolae (Liu et al., 2003).
The primary sequence of caveolin-1 contains a central hydrophobic domain (residues 102–134) that anchors to membranes, an oligomerization domain (residues 61–101), and a scaffolding domain (residues 82–101) (Schlegel and Lisanti, 2001). Interaction between the oligomerization domains and the C-terminal domains results in the formation of high molecular oligomers containing about 14–16 caveolins, which is important for the scaffolding function of caveolins. The interaction of the caveolin scaffolding domain with putative caveolin-binding motifs in many signaling proteins, such as Src, EGFR, and Ras, concentrates these proteins in caveolae (Schlegel and Lisanti, 2001). The Na/K-ATPase expression regulates caveolin-1 endocytic trafficking and stabilizes the caveolin-1 plasma membrane pool, which was independent of the Na/K-ATPase pumping function but depends on the interaction between Na/K-ATPase and caveolin-1 (Cai et al., 2008a). Moreover, knockdown of the Na/K-ATPase increases basal levels of active Src and stimulates endocytosis of caveolin-1 from the plasma membrane (Cai et al., 2008b), and the caveolar Na/K-ATPase interacts with caveolin-1 and Src to form a signaling complex, which was induced by ouabain-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 (Wang et al., 2004). Other than Src, the Na/K-ATPase α1 also interacts with other partners, including phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and caveolin-1, and is involved in regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway and the formation of caveolae (Cai et al., 2008b; Tian et al., 2009). In the meantime, Na/K-ATPase and CTS-induced signal transduction of protein kinases and calcium-signaling microdomain in the regulation of transporter trafficking (Liu and Xie, 2010). While depletion of caveolae increases the pumping function of Na/K-ATPase, it suppresses CTS-induced signal transduction, cell growth, and collagen production in cardiac fibroblasts (Quintas et al., 2010).
Moreover, over half of the plasma membrane Na/K-ATPase in LLC-PK1 cells performs cellular functions other than ion-pumping. Like the pumping pump, this “non-pumping” pool of the Na/K-ATPase binds ouabain. Depletion of either cholesterol or caveolin-1 moves the “non-pumping” Na/K-ATPase into the pumping pool. Graded knockdown of the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit eventually results in losing this “non-pumping” pool while preserving the pumping pool. A loss of the “non-pumping” pool is associated with a loss of receptor function, as evidenced by the failure of ouabain to induce the activation of Src and/or ERK. These findings suggest that a substantial amount of surface-expressed Na/K-ATPase, at least in some types of cells, may function as non-canonical ouabain-binding receptors (Liang et al., 2007). The caveolar Na/K-ATPase represents the signaling pool of the Na/K-ATPase that interacts with Src and transmits the ouabain signals (Wang et al., 2004). Ouabain interacts with the Na/K-ATPase α1 that resides within the caveolar domain. This interaction selectively recruits signal-transducing proteins to this microdomain, activating their signaling functions, which is necessary to initiate the proliferative cascade (Liu et al., 2004). This transducing function occurred at ouabain concentrations that do not perturb cytoplasmic ion content and requires specific localization of the Na/K-ATPase to caveolae (Allen et al., 2003). The ouabain-induced recruitments of Src and Na/K-ATPase α-subunit to caveolae are involved in the positive inotropic effect of ouabain (Liu et al., 2003) and play differential roles of caveolin-1 in ouabain-induced Na/K-ATPase cardiac signaling and contractility (Bai et al., 2016). In caveolin-1 knockdown LLC-PK1 cells, ouabain failed to downregulate NHE3 mRNA expression and NHE3 promoter activity (Oweis et al., 2006). The link of Na/K-ATPase to ERK1/2 and intracellular Ca2+ was organized within cardiac caveolae microdomains, and ouabain-induced recruitments of Src and Na/K-ATPase α2 to caveolae were involved in the positive inotropic effect of ouabain (Liu et al., 2003). While both PLC-γ1 and IP3 receptors (isoforms 2 and 3) were coenriched with the Na/K-ATPase, caveolin-1, and Src, pulldown assays revealed that the central loop of the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit interacts with PLC-γ1, and the N-terminus of the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit binds IP3R2 and IP3R3, suggesting that the signaling Na/K-ATPase may tether PLC-γ1 and IP3 receptors to form a Ca2+-regulatory complex that requires c-Src (Yuan et al., 2005).
The gain of the caveolin binding motif (CBM) in the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit enables the Na/K-ATPase to function as a dual-functional protein for stem cell differentiation and organogenesis in multicellular organisms that are involved in the genetic regulation of myogenesis through Wnt/β-catenin signaling (Wang et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2022). The conserved N-terminal CBM of the Na/K-ATPase α1 allows Na/K-ATPase/caveolin-1 interaction and influences Na/K-ATPase signaling and caveolar distribution that is critical for animal development, ontogenesis, and lineage-specific differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs). An altered CBM in hiPSC-derived adipocytes (iAdi-mCBM) and in mice (mCBM) showed impaired glycolysis and decreased ATP synthesis-coupled respiration in iAdi-mCBM with extensive remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and heightened TGF-β signaling. The Na/K-ATPase CBM signaling integrity is required for adequate control of TGF-β signaling and ECM stiffness during adipogenesis (Huang et al., 2024). A genetic approach to alter the Na/K-ATPase α1 CBM in hiPSC-derived adipocytes and mice indicated that the Na/K-ATPase CBM regulates adipogenesis in the adipocytes and reduces fat with increased extracellular matrix production and inflammation in mice. RNA-seq analysis and pharmacological interventions in human hiPSC-derived adipocytes revealed that the TGF-β signal, rather than Na/K-ATPase-mediated ion transport, is a key mediator of Na/K-ATPase-induced regulation of adipogenesis (Huang et al., 2024).
The clathrin in Na/K-ATPase signaling and renal function
Ouabain-induced endocytosis of plasmalemmal Na/K-ATPase in LLC-PK1 cells by a clathrin-dependent but non-species-specific mechanism, which also involved GRP78/BiP (Liu et al., 2004a; Kesiry and Liu, 2005; Liu et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2005; Yan et al., 2012). Ouabain activates the basolateral Na/K-ATPase-PI3K signaling pathway, stimulates NHE3 trafficking by the basolateral Na/K-ATPase signaling complex, which was abolished by cholesterol depletion, Src inhibition, and intracellular Ca2+ chelator BAPTA-AM treatment (Kaunitz, 2006; Oweis et al., 2006; Blaustein et al., 2007; Cai et al., 2008). Ouabain, at low doses without changing the concentration of intracellular Na+, significantly reduced NHE3 activity, NHE3 protein content, and mRNA expression. Inhibition of c-Src or PI3K with PP2 or wortmannin, respectively, abolished ouabain-induced downregulation of NHE3 activity and mRNA expression. It has been shown that binding of ouabain to Na/K-ATPase activates Src/EGFR signaling to initiate multiple signal pathways that regulate cell growth. In porcine LLC-PK1 cells, ouabain decreased ouabain-sensitive 86Rb uptake without significant impact on total enzyme activity, suggesting internalization of the Na/K-ATPase (Liu et al., 2002; Liu et al., 2004), and the Na/K-ATPase trafficking occurs via a clathrin-dependent pathway by activation of PI3K and Src (Liu and Xie, 2010). However, ouabain did not trigger Na/K-ATPase internalization in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells (Liu et al., 2002; Akimova et al., 2008), and ouabain decreased, rather than increased, endocytosis (Akimova et al., 2006; Trevisi et al., 2006). In LLC-PK1, but not MDCK cells, low concentrations of ouabain decreased 86Rb uptake and transcellular 22Na flux profoundly in a time and dose-dependent manner. The binding of CTS marinobufagenin (MBG) and deproteinated extract of serum derived from patients with chronic renal failure by proximal (but not distal) tubular cells results in internalization of Na/K-ATPase with the net effect of amplifying inhibition of the Na/K-ATPase activity (Liu et al., 2002). Furthermore, in vivo and in vitro studies with Dahl salt-sensitive (S) and salt-resistant (R) rats and their primary culture of renal proximal tubules isolated from Dahl S and R rats, high salt diet or ouabain treatment stimulated Na/K-ATPase/c-Src signaling and internalization of Na/K-ATPase and NHE3 in the Dahl R rats, but not in the Dahl S rats, suggesting that impairment of Na/K-ATPase signaling and consequent regulation of Na/K-ATPase and NHE3 in renal proximal tubule that contribute to salt-induced hypertension in the Dahl S rat, and increased basal level of renal Na/K-ATPase-dependent redox signaling may be responsible for the development of salt-sensitive hypertension in polygenic obese TALLYHO/JngJ mice (Liu et al., 2011; Yan et al., 2019). Moreover, the extracellular renal interstitial guanosine cyclic 3′,5′-monophosphate (cGMP) inhibits renal proximal tubule Na+ reabsorption via Src activation through cGMP binding to the extracellular Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit on the basolateral membranes to inhibit Na+ transport. Molecular modeling, by using data from competitive binding studies and crosslinking studies, strongly suggested a potential cGMP docking site in the ouabain-binding pocket of Na/K-ATPase (Bulger and Griendling, 2023; Kemp et al., 2023).
The Na/K-ATPase α1 expression and Na/K-ATPase signaling
The number of Na/K-ATPase in the plasma membrane of LLC-PK1 cells is about one million per cell, and about half reside in caveolae (Liang et al., 2007). In LLC-PK1 cells, graded knockdown of Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit decreases the plasma membrane pool of caveolin-1 and significantly reduces the number of caveolae on the cell surface. However, knockdown of Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit increases basal levels of active Src and stimulates endocytosis of caveolin-1 from the plasma membrane, indicating that the Na/K-ATPase regulates caveolin-1 endocytic trafficking and stabilizes the caveolin-1 plasma membrane pool (Cai et al., 2008b). The PY-17 cells were derived from porcine LLC-PK1 cells, and the expression of endogenous Na/K-ATPase α1 was reduced by about 90%. Both cell-free and cell-based assays indicate that the A420P mutation abolishes the Src regulatory function of Na/K-ATPase but has a normal ion-pumping function, indicating the Na/K-ATPase α1 possesses both pumping and signaling functions (Lai et al., 2013). On the other hand, graded knockdown of Na/K-ATPase in LLC-PK1 cells decreases the plasma membrane pool of caveolin-1, significantly reducing the number of caveolae on the cell surface. However, it increased basal levels of active Src and stimulated endocytosis of caveolin-1 from the plasma membrane, indicating the Na/K-ATPase also regulates caveolin-1 endocytic trafficking and stabilizes the caveolin-1 plasma membrane pool (Cai et al., 2008a). Furthermore, Na/K-ATPase α1 haploinsufficiency led to enhanced lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-stimulated NF-κB pathway, ROS signaling, and proinflammatory cytokines through Na/K-ATPase α1 interaction with TLR4 and Lyn, which leads to the suppression of LPS-induced macrophage proinflammatory signaling through Lyn (Zhang et al., 2022). Furthermore, knockdown of RPT Na/K-ATPase in cells and mice increased membrane NHE3 and Na+/HCO3−cotransporter (NBCe1A), decreased urine output and absolute Na + excretion driven by increased RPT Na + reabsorption and accompanied by elevated blood pressure. This re-absorptive phenotype was rescued upon crossing with RPT NHE3−/− mice, confirming the importance of Na/K-ATPase/NHE3 coupling, indicating that Na/K-ATPase signaling is not only physiologically relevant but also functionally dominant over Na/K-ATPase ion-pumping function in the control of RPT reabsorption (Mukherji et al., 2023). Different structural CTS types could trigger different sets of Na/K-ATPase/effector interactions, resulting in biased signaling responses without compromising ion-pumping capacity (Xu et al., 2021), and the Na/K-ATPase α1–Src kinase complex plays a central role in regulating the renal inflammatory response induced by elevated CTS both in vitro and in vivo (Khalaf et al., 2019).
The expansion of the NA/K-ATPase signaling
Beyond the above-discussed Na/K-ATPase-Src signaling pathways and functions, the Na/K-ATPase α1 subunit was also shown to interact with other proteins to initiate signaling function to affect other cellular and whole-body functions, such as diet-induced obesity and hyperlipidemia, potentiate a CD36/Na/K-ATPase–dependent inflammatory paracrine loop between proximal tubule cells and their associated macrophages, thereby facilitate the development of chronic inflammation and tubulointerstitial fibrosis, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases (Kennedy et al., 2013; Yan and Shapiro, 2016; Yoo et al., 2022). The Na/K-ATPase signaling functions might regulate many functions, such as that blockage of the Na/K-ATPase signaling-mediated oxidant amplification loop elongates red blood cell half-life and ameliorates uremic anemia induced by 5/6th PNx in C57BL/6 mice, suggesting the role of Na/K-ATPase signaling in the regulation of red blood cells (Liu et al., 2022). Evidence indicates that oxidative stress regulates the Na/K-ATPase enzymatic activity, signaling, and other functions. While a CTS-induced increase in ROS generation is an intermediate step in CTS-mediated Na/K-ATPase signaling, an increase in ROS alone also stimulates Na/K-ATPase signaling, salt-sensitivity, fibrosis, and RPT sodium reabsorption (Liu et al., 2012; Dial et al., 2014; Shah et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2017). Nevertheless, there are many more regulatory effects of the Na/K-ATPase signaling function that we cannot list here, and we expect more evidence to emerge with further studies since the expression of the Na/K-ATPase is found in all kinds of cells.
The pharmacological implications of the Na/K-ATPase expression and signaling, CTS, and oxidative stress
Up to date, the dysregulation of these factors affects almost every pathophysiological condition studied in humans, animals, and cells. Clinical and animal studies have shown that reduced NKA α1 expression and activated NKA signaling function are significant risk factors for renal and cardiac dysfunctions (Norgaard et al., 1988; Semb et al., 1998; Ishino et al., 1999; Moseley et al., 2004; Liu et al., 2012), where CTS, NKA expression, and oxidative stress play critical roles (Haas et al., 2000; Liu et al., 2000; Xie and Askari, 2002; Aizman and Aperia, 2003; Miyakawa-Naito et al., 2003; Xie, 2003; Liu et al., 2004; Kaunitz, 2006; Kotova et al., 2006; Li et al., 2006; Pierre and Xie, 2006; Schoner and Scheiner-Bobis, 2007; Wansapura et al., 2010; Aperia, 2012; Yan et al., 2013; Pratt et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2020; Marck et al., 2021). The Na/K-ATPase expression and signaling, CTS, and oxidative stress are inextricably and functionally linked, as in the bidirectional cardiorenal and/or renocardiac syndromes. It has demonstrated that (1) “non-toxic” concentrations of ouabain (without significant inhibition of NKA activity) stimulated NKA signaling and cardiac hypertrophy that were linked to oxidative stress, but are independent of intracellular [Na+]i and [Ca2+]i (Xie et al., 1999; Liu et al., 2000); (2) Glucose oxidase-induced sustained low level of H2O2 stimulated [Ca2+]i-independent cardiac hypertrophy, NKA α1 trafficking, and NKA activity inhibition (Liu et al., 2006); (3) a NKA-Src signaling inhibitor, pNaKtide, attenuated PNx-stimulated NKA signaling, oxidative stress, and cardiac dysfunction (Liu et al., 2016); (4) Clinically, patients with HF or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy showed significantly reduced NKA α1 expression and activity (Norgaard, Bagger et al., 1988, Schmidt et al., 1993; Ishino et al., 1999; Moseley et al., 2004); and (5) a weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) of published RNA-sequencing data (GEO141910) from a cohort of 366 heart-transplant patients and their donors, the expressions of NKA α1 and α2 are significantly correlated with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (Gao et al., 2022).
The apical sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) is responsible for about 90% renal glucose reabsorption from the glomerular filtrate in the S1/S2 segment of renal proximal tubules (RPTs), driven by the Na+ gradient generated by the apical Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 (NHE3) and basolateral Na/K-ATPase. SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) not only have “on-target” mild glucose-lowering effects but also have profound “off-target” beneficial renal and cardiovascular effects in patients with CKD, CVD, and HF, through glucosuria, natriuresis, metabolic shifts, and reduction of oxidative stress, that are independent of hyperglycemia, sex, and insulin secretion/sensitivity. Clinical studies have shown that SGLT2i-induced beneficial effects in CKD and CVD/HF patients are independent of hyperglycemia, sex, and insulin secretion/sensitivity. The underlying mechanisms include, but are not limited to, lowering blood pressure and blood glucose, improving RPT function and cardiomyocyte calcium handling and myocardial energetics, normalizing oxidative stress, stimulating erythropoiesis and erythropoietin, and volume contraction to improve oxygen delivery, inducing autophagy, and reducing epicardial fat (Lambers Heerspink et al., 2013; Pessoa et al., 2014; Vallon, 2015; Tanaka et al., 2018; Mosenzon et al., 2019; Perkovic et al., 2019; Zelniker et al., 2019; Ghanim et al., 2020; Heerspink et al., 2020; Mazer et al., 2020; Santos et al., 2020; Vallon and Thomson, 2020; Almaimani et al., 2021; Borges-Júnior et al., 2021; Joshi et al., 2021; Vallon and Verma, 2021; Vallon and Verma, 2021).
These findings signify the roles of NKA expression, signaling, and oxidative stress in cardiorenal and renocardiac syndromes. Furthermore, clinical trials have demonstrated that SGLT2i are more effective in CKD and CVD/HF patients than healthy individuals. Therefore, further defining the role of these factors holds immense potential for managing CKD and CVD/HF, which are still largely untreatable clinical entities.
Since the broad effects of CTS and Na/K-ATPase signaling, it has been widely accepted that it is clinically significant in other possibilities other than regulating renal and cardiac function. Cinobufagin, a cardiotoxic bufadienolide steroid, has the potential to be further developed as a new drug against cancer. Cinobufagin significantly inhibited the growth of Skov3 ovarian cancer cells, triple-negative breast cancer metastasis, by regulating the Forkhead Box S1 (FOXS1) gene, the CCL2/CCR2 signaling, and FAK/STAT3 signaling (Dai et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2025). More excitingly, in a proof-of-concept clinical trial, digoxin treatment (0.7–1.4 ng/mL serum level) reduced circulating tumor cell clusters in metastatic breast cancer, which are associated with disease progression and reduced survival in a variety of cancer types (Kurzeder et al., 2025). Clinic trials also demonstrated that rostafuroxin (a digitoxigenin derivative and a ouabain antagonist that selectively disrupts the binding to the cSrc-SH2 domain of mutant α-adducin and of the ouabain-activated NKA) has anti-hypertensive effects that are linked to genetic backgrounds (Lanzani et al., 2010; Citterio et al., 2021). In a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study, using an anti-digoxin antibody Fab in women with severe preeclampsia with positive endogenous digitalis-like factors (EDLFs) status was associated with improved maternal and neonatal outcomes (Lam et al., 2013). Furthermore, in a rat model of preeclampsia, treatment with anti-MBG antibody was effective at normalizing blood pressure, kidney function, and fetal birth weights (Pantho et al., 2025), and in a rat partial nephrectomy model, treatment with anti-MBG antibody counteracts the Fli1-collagen-1 system, and reduces aortic fibrosis (Agalakova et al., 2024). Aldosterone antagonists (canrenone and canrenoate), exert both agonist and antagonist effects on the digitalis receptor site of NKA, can both stimulate and inhibit the NKA to affect blood pressure in human and animal models of volume expanded hypertension, and the Milan hypertensive rat models of hypertension (Grichois et al., 1986; Semplicini et al., 1995).
Src represents a key intermediate and novel therapeutic target in the pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia. Mice lacking pp60c-src are resistant to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced vascular permeability (VP) and show decreased infarct volumes after stroke, whereas mice deficient in pp59c-fyn, another Src family member, have normal VEGF-mediated VP and infarct size. Systemic application of a Src-inhibitor given up to 6 h following stroke suppressed VP, protecting wild-type mice from ischemia-induced brain damage without influencing VEGF expression (Paul et al., 2001). The administration of the Src-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor PP2 attenuated transient focal ischemia-induced increase of tyrosine phosphorylation of occludin in the isolated brain capillaries, which was coincident with an inhibition of blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage and a decrease in infarct volume (Takenaga et al., 2009). Inhibition of p-Src by PP2 also ameliorated neuropathological changes and damaged neurological functions induced by hypoxic-ischemic injury in a Sprague-Dawley rat model (Qiu et al., 2021).
Summary and perspective
The Na/K-ATPase (NKA) functions as an ion pump and a signaling molecule. It is sensitive to inhibition by CTS, which has implications for cardiovascular and kidney diseases. NKA signaling is linked to reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and metabolic regulation. The Na/K-ATPase α1-Src complex plays a crucial role in cellular signaling. Three main models explain the interaction between NKA and c-Src, with ongoing debates. Caveolae and caveolin proteins are involved in NKA-mediated signal transduction. The signaling function of NKA extends beyond ion transport, influencing conditions like hypertension, obesity, and Alzheimer’s disease. The crosslinking methods (Blue Native-PAGE, immunoblotting, and capillary immunoblotting) help map protein-protein interactions, including NKA’s interactions with c-Src and caveolin-1, which provide insights into NKA’s structural organization and its role in disease that might aid in drug development by identifying potential therapeutic targets. Furthermore, the direct interaction between NKA α1 and c-Src, and related oxidative stress, highlights its role in signaling and disease. It has been shown that under normal conditions, NKA α1 binds to and inhibits c-Src. Upon stimulation (e.g., by CTS), NKA undergoes conformational changes, releasing and activating c-Src; activated c-Src triggers downstream signaling pathways linked to cell growth, inflammation, and disease; dysregulation of this interaction is associated with cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, cancer, and other disease conditions. The present studies collectively highlight Na/K-ATPase’s dual function as an ion pump and a signaling hub. While much progress has been made, there are still unresolved questions, particularly regarding its exact signaling mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Despite recent advances in elucidating the possible mechanisms of the Na/K-ATPase-related signaling function, different proposed models depend on the different experimental settings, materials used, and explanations. Each proposed mechanism has its merits and should be further evaluated. Nevertheless, a deeper understanding of the Na/K-ATPase-related signaling function would advance our understanding of its effects on health and disease. Future research is needed to resolve controversies in its signaling mechanisms. Future studies will aim to resolve current controversies (e.g., the nature of the Na/K-ATPase/c-Src complex) and explore the broader implications of the Na/K-ATPase expression and signaling in cellular regulation and pathology, such as ROS production, cellular metabolism, the progression of diseases such as hypertension, obesity, cardiorenal or renocardiac syndrome, and neurodegenerative disorders, that will benefit future clinic therapeutic strategies.
Author contributions
YG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. FB: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. RP: Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JT: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) (R15 #223054).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Agalakova, N. I., Mikhailova, E. V., Ershov, I. A., Nadei, O. V., Pyankov, A. A., Galagoudza, M. M., et al. (2024). Antibody to endogenous cardiotonic steroid reverses vascular fibrosis and restores vasorelaxation in chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (16), 8896. doi:10.3390/ijms25168896
Aizman, O., and Aperia, A. (2003). Na,K-ATPase as a signal transducer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 986, 489–496. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07233.x
Akimova, O. A., Hamet, P., and Orlov, S. N. (2008). [Na+]i/[K+]i -independent death of ouabain-treated renal epithelial cells is not mediated by Na+,K+ -ATPase internalization and de novo gene expression. Pflugers Arch. 455 (4), 711–719. doi:10.1007/s00424-007-0283-6
Akimova, O. A., Mongin, A. A., Hamet, P., and Orlov, S. N. (2006). The rapid decline of MTT reduction is not a marker of death signaling in ouabain-treated cells. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 52 (8), 71–77.
Allen, J. C., Abramowitz, J., and Koksoy, A. (2003). Low concentrations of ouabain activate vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 986, 504–508. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07235.x
Almaimani, M., Sridhar, V. S., and Cherney, D. Z. I. (2021). Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in non-diabetic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 30 (5), 474–481. doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000724
Anderson, R. G. (1998). The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 199–225. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.199
Aperia, A. (2007). New roles for an old enzyme: na,k-atpase emerges as an interesting drug target. J. Intern Med. 261 (1), 44–52. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2006.01745.x
Aperia, A. (2012). 2011 homer smith award: to serve and protect: classic and novel roles for na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 23 (8), 1283–1290. doi:10.1681/ASN.2012010102
Aydemir-Koksoy, A., Abramowitz, J., and Allen, J. C. (2001). Ouabain-induced signaling and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (49), 46605–46611. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106178200
Azalim-Neto, P., Noël, F., Silva, S. C., Villar, J., Barbosa, L., O'Doherty, G. A., et al. (2024). Simplified method for kinetic and thermodynamic screening of cardiotonic steroids through the K(+)-Dependent phosphatase activity of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase with chromogenic pNPP substrate. Mol. Pharmacol. 106 (5), 225–239. doi:10.1124/molpharm.124.000934
Bagrov, A. Y., Shapiro, J. I., and Fedorova, O. V. (2009). Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: physiology, pharmacology, and novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 61 (1), 9–38. doi:10.1124/pr.108.000711
Bagrov, A. Y., Fedorova, O. V., Dmitrieva, R. I., Howald, W. N., Hunter, A. P., Kuznetsova, E. A., et al. (1998). Characterization of a urinary bufodienolide Na+,K+-ATPase inhibitor in patients after acute myocardial infarction. Hypertension 31 (5), 1097–1103. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.31.5.1097
Bai, Y., Morgan, E. E., Giovannucci, D. R., Pierre, S. V., Philipson, K. D., Askari, A., et al. (2013). Different roles of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+-exchanger in ouabain-induced inotropy, cell signaling, and hypertrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 304 (3), H427–H435. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00462.2012
Bai, Y., Wu, J., Li, D., Morgan, E. E., Liu, J., Zhao, X., et al. (2016). Differential roles of caveolin-1 in ouabain-induced Na+/K+-ATPase cardiac signaling and contractility. Physiol. Genomics 48 (10), 739–748. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00042.2016
Blaustein, M. P., and Hamlyn, J. M. (2024). Sensational site: the sodium pump ouabain-binding site and its ligands. Am. J. Physiology-Cell Physiology 326 (4), C1120–C1177. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00273.2023
Blaustein, M. P., Hamlyn, J. M., and Pallone, T. L. (2007). Sodium pumps: ouabain, ion transport, and signaling in hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 293 (1), F438–F439. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00092.2007
Borges-Júnior, F. A., Silva dos Santos, D., Benetti, A., Polidoro, J. Z., Wisnivesky, A. C. T., Crajoinas, R. O., et al. (2021). Empagliflozin inhibits proximal tubule NHE3 activity, preserves GFR, and restores euvolemia in nondiabetic rats with induced heart failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 32 (7), 1616–1629. doi:10.1681/asn.2020071029
Bulger, D. A., and Griendling, K. K. (2023). Novel mechanism by which extracellular cyclic GMP induces natriuresis. Circ. Res. 132 (9), 1141–1143. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322778
Bundgaard, H., and Kjeldsen, K. (1996). Human myocardial Na,K-ATPase concentration in heart failure. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 163 (1), 277–283. doi:10.1007/BF00408668
Cai, H., Wu, L., Qu, W., Malhotra, D., Xie, Z., Shapiro, J. I., et al. (2008a). Regulation of apical NHE3 trafficking by ouabain-induced activation of the basolateral Na+-K+-ATPase receptor complex. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 294 (2), C555–C563. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00475.2007
Cai, T., Wang, H., Chen, Y., Liu, L., Gunning, W. T., Quintas, L. E., et al. (2008b). Regulation of caveolin-1 membrane trafficking by the Na/K-ATPase. J. Cell Biol. 182 (6), 1153–1169. doi:10.1083/jcb.200712022
Citterio, L., Bianchi, G., Scioli, G. A., Glorioso, N., Bigazzi, R., Cusi, D., et al. (2021). Antihypertensive treatment guided by genetics: PEARL-HT, the randomized proof-of-concept trial comparing rostafuroxin with losartan. Pharmacogenomics J. 21 (3), 346–358. doi:10.1038/s41397-021-00214-y
Cui, X., and Xie, Z. (2017). Protein interaction and Na/K-ATPase-Mediated signal transduction. Molecules 22 (6), 990. doi:10.3390/molecules22060990
Dai, C.-L., Zhang, R.-j., An, P., Deng, Y.-Q., Rahman, K., and Zhang, H. (2023). Cinobufagin: a promising therapeutic agent for cancer. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 75 (9), 1141–1153. doi:10.1093/jpp/rgad059
Dial, L., Liu, J., and Shapiro, J. I. (2014). Cardiotonic steroids in adaptation to dietary salt intake. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 9 (3), 298–309. doi:10.2174/1574884708666131111204031
Drab, M., Verkade, P., Elger, M., Kasper, M., Lohn, M., Lauterbach, B., et al. (2001). Loss of caveolae, vascular dysfunction, and pulmonary defects in caveolin-1 gene-disrupted mice. Science 293 (5539), 2449–2452. doi:10.1126/science.1062688
Fedosova, N. U., Habeck, M., and Nissen, P. (2021). Structure and function of Na,K-ATPase-The sodium-potassium pump. Compr. Physiol. 12 (1), 2659–2679. doi:10.1002/cphy.c200018
Ferrandi, M., Molinari, I., Barassi, P., Minotti, E., Bianchi, G., and Ferrari, P. (2004). Organ hypertrophic signaling within caveolae membrane subdomains triggered by ouabain and antagonized by PST 2238. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (32), 33306–33314. doi:10.1074/jbc.M402187200
Ferrandi, M., Molinari, I., Bianchi, G., and Ferrari, P. (2006). Ouabain-dependent signaling in caveolae as a novel therapeutic target for hypertension. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 52 (8), 15–18.
Gable, M. E., Abdallah, S. L., Najjar, S. M., Liu, L., and Askari, A. (2014). Digitalis-induced cell signaling by the sodium pump: on the relation of src to Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 446 (4), 1151–1154. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.03.071
Galougahi, K. K., Liu, C. C., Bundgaard, H., and Rasmussen, H. H. (2012). β-Adrenergic regulation of the cardiac Na+-K+ ATPase mediated by oxidative signaling. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 22 (4), 83–87. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2012.06.017
Gao, Y., Silva, L. N. D., Hurley, J. D., Fan, X., Pierre, S. V., Sodhi, K., et al. (2022). Gene module regulation in dilated cardiomyopathy and the role of Na/K-ATPase. PLoS One 17 (7), e0272117. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0272117
Ghanim, H., Abuaysheh, S., Hejna, J., Green, K., Batra, M., Makdissi, A., et al. (2020). Dapagliflozin suppresses hepcidin and increases erythropoiesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. and Metabolism 105 (4), dgaa057–e1063. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa057
Godinho, A. N., Costa, G. T., Oliveira, N. O., Cardi, B. A., Uchoa, D. E. A., Silveira, E. R., et al. (2017). Effects of cardiotonic steroids on isolated perfused kidney and NHE3 activity in renal proximal tubules. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 1861 (8), 1943–1950. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.05.012
Gratton, J. P., Bernatchez, P., and Sessa, W. C. (2004). Caveolae and caveolins in the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res. 94 (11), 1408–1417. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000129178.56294.17
Grichois, M. L., de Mendonça, M., Wauquier, I., Pernollet, M. G., Thormann, B., Devynck, M. A., et al. (1986). canrenone: an effective antihypertensive in an experimental model of hypertension in which the active transport of sodium is diminished. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 79 (6), 875–878.
Guldbrandsen, H. O., Staehr, C., Iversen, N. K., Postnov, D. D., and Matchkov, V. V. (2021). Does src kinase mediated vasoconstriction impair penumbral reperfusion? Stroke 52 (6), e250–e258. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032737
Haas, M., Askari, A., and Xie, Z. (2000). Involvement of src and epidermal growth factor receptor in the signal-transducing function of Na+/K+-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (36), 27832–27837. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002951200
Heerspink, H. J. L., Stefánsson, B. V., Correa-Rotter, R., Chertow, G. M., Greene, T., Hou, F. F., et al. (2020). Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 383 (15), 1436–1446. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2024816
Holm, T. H., and Lykke-Hartmann, K. (2016). Insights into the pathology of the α3 Na+/K+-ATPase ion pump in neurological disorders; lessons from animal models. Front. Physiology 7, 209. doi:10.3389/fphys.2016.00209
Horesh, N., Pelov, I., Pogodin, I., Zannadeh, H., Rosen, H., Mikhrina, A. L., et al. (2024). Involvement of the na(+), K(+)-ATPase α1 isoform and endogenous cardiac steroids in Depression- and manic-like behaviors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (3), 1644. doi:10.3390/ijms25031644
Huang, M., Wang, X., Banerjee, M., Mukherji, S. T., Kutz, L. C., Zhao, A., et al. (2022). Regulation of myogenesis by a Na/K-ATPase α1 caveolin-binding motif. Stem Cells 40 (2), 133–148. doi:10.1093/stmcls/sxab012
Huang, M., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Pessoa, M. T., Terrell, K. C., Zhang, J., et al. (2024). Role of Na/K-ATPase α1 caveolin-binding motif in adipogenesis. Am. J. Physiology-Cell Physiology 327 (1), C48–C64. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00168.2024
Ishino, K., Botker, H. E., Clausen, T., Hetzer, R., and Sehested, J. (1999). Myocardial adenine nucleotides, glycogen, and Na, K-ATPase in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy requiring mechanical circulatory support. Am. J. Cardiol. 83 (3), 396–399. doi:10.1016/s0002-9149(98)00876-5
Joshi, S. S., Singh, T., Newby, D. E., and Singh, J. (2021). Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor therapy: mechanisms of action in heart failure. Heart 107 (13), 1032–1038. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2020-318060
Kanai, R., Cornelius, F., Ogawa, H., Motoyama, K., Vilsen, B., and Toyoshima, C. (2021). Binding of cardiotonic steroids to Na(+),K(+)-ATPase in the E2P state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118 (1), e2020438118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2020438118
Kaplan, J. H. (2002). Biochemistry of Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 511–535. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.102201.141218
Kaunitz, J. D. (2006). Membrane transport proteins: not just for transport anymore. Am. J. Physiology-Renal Physiology 290 (5), F995–F996. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00515.2005
Kelly, R. A., and Smith, T. W. (1993). Digoxin in heart failure: implications of recent trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 22 (4 Suppl. A), 107a–112a. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(93)90472-d
Kemp, B. A., Howell, N. L., Gildea, J. J., Hinkle, J. D., Shabanowitz, J., Hunt, D. F., et al. (2023). Evidence that binding of cyclic GMP to the extracellular domain of NKA (Sodium-Potassium ATPase) mediates natriuresis. Circ. Res. 132 (9), 1127–1140. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321693
Kennedy, D. J., Chen, Y., Huang, W., Viterna, J., Liu, J., Westfall, K., et al. (2013). CD36 and Na/K-ATPase-α1 form a proinflammatory signaling loop in kidney. Hypertension 61 (1), 216–224. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.198770
Kennedy, D. J., Shrestha, K., Sheehey, B., Li, X. S., Guggilam, A., Wu, Y., et al. (2015). Elevated plasma marinobufagenin, an endogenous cardiotonic steroid, is associated with right ventricular dysfunction and nitrative stress in heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail 8 (6), 1068–1076. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.114.001976
Kennedy, D. J., Vetteth, S., Periyasamy, S. M., Kanj, M., Fedorova, L., Khouri, S., et al. (2006). Central role for the cardiotonic steroid marinobufagenin in the pathogenesis of experimental uremic cardiomyopathy. Hypertension 47 (3), 488–495. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000202594.82271.92
Kesiry, R., and Liu, J. (2005). GRP78/BIP is involved in ouabain-induced endocytosis of the Na/K-ATPase in LLC-PK1 cells. Front. Biosci. 10, 2045–2055. doi:10.2741/1680
Khalaf, F. K., Dube, P., Kleinhenz, A. L., Malhotra, D., Gohara, A., Drummond, C. A., et al. (2019). Proinflammatory effects of cardiotonic steroids mediated by NKA α-1 (Na+/K+-ATPase α-1)/Src complex in renal epithelial cells and immune cells. Hypertension 74 (1), 73–82. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.12605
Kinoshita, P. F., Orellana, A. M. M., Nakao, V. W., de Souza Port's, N. M., Quintas, L. E. M., Kawamoto, E. M., et al. (2022). The janus face of ouabain in na(+)/K(+) -ATPase and calcium signalling in neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 179 (8), 1512–1524. doi:10.1111/bph.15419
Kiselyov, K., Mignery, G. A., Zhu, M. X., and Muallem, S. (1999). The N-terminal domain of the IP3 receptor gates store-operated hTrp3 channels. Mol. Cell 4 (3), 423–429. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80344-5
Kolmakova, E. V., Haller, S. T., Kennedy, D. J., Isachkina, A. N., Budny, G. V., Frolova, E. V., et al. (2011). Endogenous cardiotonic steroids in chronic renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 26 (9), 2912–2919. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfq772
Komiyama, Y., Dong, X. H., Nishimura, N., Masaki, H., Yoshika, M., Masuda, M., et al. (2005). A novel endogenous digitalis, telocinobufagin, exhibits elevated plasma levels in patients with terminal renal failure. Clin. Biochem. 38 (1), 36–45. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2004.08.005
Kotova, O., Al-Khalili, L., Talia, S., Hooke, C., Fedorova, O. V., Bagrov, A. Y., et al. (2006). Cardiotonic steroids stimulate glycogen synthesis in human skeletal muscle cells via a Src- and ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 281 (29), 20085–20094. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601577200
Kurzeder, C., Nguyen-Sträuli, B. D., Krol, I., Ring, A., Castro-Giner, F., Nüesch, M., et al. (2025). Digoxin for reduction of circulating tumor cell cluster size in metastatic breast cancer: a proof-of-concept trial. Nat. Med. 31 (4), 1120–1124. doi:10.1038/s41591-024-03486-6
Kutz, L. C., Cui, X., Xie, J. X., Mukherji, S. T., Terrell, K. C., Huang, M., et al. (2021). The Na/K-ATPase α1/Src interaction regulates metabolic reserve and Western diet intolerance. Acta Physiol. (Oxf) 232 (3), e13652. doi:10.1111/apha.13652
Lai, F., Madan, N., Ye, Q., Duan, Q., Li, Z., Wang, S., et al. (2013). Identification of a mutant α1 Na/K-ATPase that pumps but is defective in signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 288 (19), 13295–13304. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.467381
Lam, G. K., Hopoate-Sitake, M., Adair, C. D., Buckalew, V. M., Johnson, D. D., Lewis, D. F., et al. (2013). Digoxin antibody fragment, antigen binding (fab), treatment of preeclampsia in women with endogenous digitalis-like factor: a secondary analysis of the DEEP trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 209 (2), 119.e1–119.e1196. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2013.04.010
Lambers Heerspink, H., De Zeeuw, D., Wie, L., Leslie, B., and List, J. (2013). Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obes. Metabolism 15 (9), 853–862. doi:10.1111/dom.12127
Lanzani, C., Citterio, L., Glorioso, N., Manunta, P., Tripodi, G., Salvi, E., et al. (2010). Adducin- and ouabain-related gene variants predict the antihypertensive activity of rostafuroxin, part 2: clinical studies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2 (59), 59ra87. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001814
Leite, J. A., Cavalcante-Silva, L. H. A., Ribeiro, M. R., de Morais Lima, G., Scavone, C., and Rodrigues-Mascarenhas, S. (2022). Neuroinflammation and neutrophils: modulation by ouabain. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 824907. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.824907
Li, J., Zelenin, S., Aperia, A., and Aizman, O. (2006). Low doses of ouabain protect from serum deprivation-triggered apoptosis and stimulate kidney cell proliferation via activation of NF-kappaB. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17 (7), 1848–1857. doi:10.1681/ASN.2005080894
Li, O. Q., Yue, H., DeHart, A. R., Roytenberg, R., Aguilar, R., Olanipekun, O., et al. (2024). Sodium/potassium ATPase alpha 1 subunit fine-tunes platelet GPCR signaling function and is essential for thrombosis. bioRxiv, 2024.05.13.593923. doi:10.1101/2024.05.13.593923
Li, Z., and Xie, Z. (2009). The Na/K-ATPase/Src complex and cardiotonic steroid-activated protein kinase cascades. Pflugers Arch. 457 (3), 635–644. doi:10.1007/s00424-008-0470-0
Li, Z., Zhang, Z., Xie, J. X., Li, X., Tian, J., Cai, T., et al. (2011). Na/K-ATPase mimetic pNaKtide peptide inhibits the growth of human cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (37), 32394–32403. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.207597
Liang, M., Cai, T., Tian, J., Qu, W., and Xie, Z. J. (2006). Functional characterization of Src-interacting Na/K-ATPase using RNA interference assay. J. Biol. Chem. 281 (28), 19709–19719. doi:10.1074/jbc.M512240200
Liang, M., Tian, J., Liu, L., Pierre, S., Liu, J., Shapiro, J., et al. (2007). Identification of a pool of non-pumping Na/K-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 282 (14), 10585–10593. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609181200
Lingrel, J. B. (2010). The physiological significance of the cardiotonic Steroid/ouabain-binding site of the Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Physiology 7, 395–412. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135725
Liu, C., Bai, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Sottejeau, Y., Liu, L., et al. (2012a). Reduction of Na/K-ATPase potentiates marinobufagenin-induced cardiac dysfunction and myocyte apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 287 (20), 16390–16398. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.304451
Liu, J. (2005). Ouabain-induced endocytosis and signal transduction of the Na/K-ATPase. Front. Biosci. 10, 2056–2063. doi:10.2741/1681
Liu, J., Chaudhry, M., Bai, F., Chuang, J., Chaudhry, H., Al-Astal, A. Y., et al. (2022). Blockage of the Na-K-ATPase signaling-mediated oxidant amplification loop elongates red blood cell half-life and ameliorates uremic anemia induced by 5/6th PNx in C57BL/6 mice. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 322 (6), F655–F666. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00189.2021
Liu, J., Kennedy, D. J., Yan, Y., and Shapiro, J. I. (2012b). Reactive oxygen species modulation of Na/K-ATPase regulates fibrosis and renal proximal tubular sodium handling. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 381320. doi:10.1155/2012/381320
Liu, J., Kesiry, R., Periyasamy, S. M., Malhotra, D., Xie, Z., and Shapiro, J. I. (2004a). Ouabain induces endocytosis of plasmalemmal Na/K-ATPase in LLC-PK1 cells by a clathrin-dependent mechanism. Kidney Int. 66 (1), 227–241. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00723.x
Liu, J., Liang, M., Liu, L., Malhotra, D., Xie, Z., and Shapiro, J. I. (2005). Ouabain-induced endocytosis of the plasmalemmal Na/K-ATPase in LLC-PK1 cells requires caveolin-1. Kidney Int. 67 (5), 1844–1854. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00283.x
Liu, J., Lilly, M. N., and Shapiro, J. I. (2018). Targeting Na/K-ATPase signaling: a new approach to control oxidative stress. Curr. Pharm. Des. 24 (3), 359–364. doi:10.2174/1381612824666180110101052
Liu, J., Nie, Y., Chaudhry, M., Bai, F., Chuang, J., Sodhi, K., et al. (2020). The redox-sensitive Na/K-ATPase signaling in uremic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (4), 1256. doi:10.3390/ijms21041256
Liu, J., Periyasamy, S. M., Gunning, W., Fedorova, O. V., Bagrov, A. Y., Malhotra, D., et al. (2002). Effects of cardiac glycosides on sodium pump expression and function in LLC-PK1 and MDCK cells. Kidney Int. 62 (6), 2118–2125. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00672.x
Liu, J., Tian, J., Chaudhry, M., Maxwell, K., Yan, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2016). Attenuation of Na/K-ATPase mediated oxidant amplification with pNaKtide ameliorates experimental uremic cardiomyopathy. Sci. Rep. 6, 34592. doi:10.1038/srep34592
Liu, J., Tian, J., Haas, M., Shapiro, J. I., Askari, A., and Xie, Z. (2000). Ouabain interaction with cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase initiates signal cascades independent of changes in intracellular na+ and Ca2+ concentrations. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (36), 27838–27844. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002950200
Liu, J., Tian, J., Sodhi, K., and Shapiro, J. I. (2021). The Na/K-ATPase signaling and SGLT2 inhibitor-mediated cardiorenal protection: a crossed road? J. Membr. Biol. 254, 513–529. doi:10.1007/s00232-021-00192-z
Liu, J., and Xie, Z. J. (2010). The sodium pump and cardiotonic steroids-induced signal transduction protein kinases and calcium-signaling microdomain in regulation of transporter trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1802 (12), 1237–1245. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.01.013
Liu, J., Yan, Y., Liu, L., Xie, Z., Malhotra, D., Joe, B., et al. (2011). Impairment of Na/K-ATPase signaling in renal proximal tubule contributes to dahl salt-sensitive hypertension. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (26), 22806–22813. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.246249
Liu, J., Yan, Y., Nie, Y., and Shapiro, J. I. (2017). Na/K-ATPase signaling and salt sensitivity: the role of oxidative stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 6 (1), 18. doi:10.3390/antiox6010018
Liu, L., Abramowitz, J., Askari, A., and Allen, J. C. (2004b). Role of caveolae in ouabain-induced proliferation of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells of the synthetic phenotype. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 287 (5), H2173–H2182. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00352.2004
Liu, L., Li, J., Liu, J., Yuan, Z., Pierre, S. V., Qu, W., et al. (2006). Involvement of Na+/K+-ATPase in hydrogen peroxide-induced hypertrophy in cardiac myocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 41 (10), 1548–1556. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.08.018
Liu, L., Mohammadi, K., Aynafshar, B., Wang, H., Li, D., Liu, J., et al. (2003). Role of caveolae in signal-transducing function of cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 284 (6), C1550–C1560. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00555.2002
Liu, L., Zhao, X., Pierre, S. V., and Askari, A. (2007). Association of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway with digitalis-induced hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 293 (5), C1489–C1497. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00158.2007
Marck, P. V., Pessoa, M. T., Xu, Y., Kutz, L. C., Collins, D. M., Yan, Y., et al. (2021). Cardiac oxidative signaling and physiological hypertrophy in the Na/K-ATPase α1(s/s)α2(s/s) mouse model of high affinity for cardiotonic steroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (7), 3462. doi:10.3390/ijms22073462
Maxwell, K. D., Chuang, J., Chaudhry, M., Nie, Y., Bai, F., Sodhi, K., et al. (2021). The potential role of Na-K-ATPase and its signaling in the development of anemia in chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 320 (2), F234–f242. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00244.2020
Mazer, C. D., Hare, G. M. T., Connelly, P. W., Gilbert, R. E., Shehata, N., Quan, A., et al. (2020). Effect of empagliflozin on erythropoietin levels, iron stores, and red blood cell morphology in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. Circulation 141 (8), 704–707. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044235
Miyakawa-Naito, A., Uhlén, P., Lal, M., Aizman, O., Mikoshiba, K., Brismar, H., et al. (2003). Cell signaling microdomain with Na, K-ATPase and inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor generates calcium oscillations. J. Biol. Chem. 278 (50), 50355–50361. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305378200
Morth, J. P., Pedersen, B. P., Toustrup-Jensen, M. S., Sørensen, T. L., Petersen, J., Andersen, J. P., et al. (2007). Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump. Nature 450 (7172), 1043–1049. doi:10.1038/nature06419
Morth, J. P., Poulsen, H., Toustrup-Jensen, M. S., Schack, V. R., Egebjerg, J., Andersen, J. P., et al. (2009). The structure of the Na+,K+-ATPase and mapping of isoform differences and disease-related mutations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 364 (1514), 217–227. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0201
Moseley, A. E., Cougnon, M. H., Grupp, I. L., El Schultz, J., and Lingrel, J. B. (2004). Attenuation of cardiac contractility in Na,K-ATPase alpha1 isoform-deficient hearts under reduced calcium conditions. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 37 (5), 913–919. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2004.06.005
Mosenzon, O., Wiviott, S. D., Cahn, A., Rozenberg, A., Yanuv, I., Goodrich, E. L., et al. (2019). Effects of dapagliflozin on development and progression of kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the DECLARE–TIMI 58 randomised trial. lancet Diabetes and Endocrinol. 7 (8), 606–617. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30180-9
Mukherji, S. T., Brambilla, L., Stuart, K. B., Mayes, I., Kutz, L. C., Chen, Y., et al. (2023). Na/K-ATPase signaling tonically inhibits sodium reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule. Faseb J. 37 (4), e22835. doi:10.1096/fj.202200785RR
Nie, Y., Bai, F., Chaudhry, M. A., Pratt, R., Shapiro, J. I., and Liu, J. (2020). The Na/K-ATPase α1 and c-Src form signaling complex under native condition: a crosslinking approach. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 6006. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-61920-4
Norgaard, A., Bagger, J. P., Bjerregaard, P., Baandrup, U., Kjeldsen, K., and Thomsen, P. E. (1988). Relation of left ventricular function and Na,K-pump concentration in suspected idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 61 (15), 1312–1315. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(88)91175-7
Numata, S., McDermott, J. P., and Blanco, G. (2022). Genetic ablation of Na,K-ATPase α4 results in sperm energetic defects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 911056. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.911056
Ohnishi, T., Yanazawa, M., Sasahara, T., Kitamura, Y., Hiroaki, H., Fukazawa, Y., et al. (2015). Na, K-ATPase α3 is a death target of alzheimer patient amyloid-β assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112 (32), E4465–E4474. doi:10.1073/pnas.1421182112
Oweis, S., Wu, L., Kiela, P. R., Zhao, H., Malhotra, D., Ghishan, F. K., et al. (2006). Cardiac glycoside downregulates NHE3 activity and expression in LLC-PK1 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 290 (5), F997–F1008. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00322.2005
Pantho, A. F., Zaman, M., Afroze, S. H., Wages, J. M., Yu, B., Larrick, J. W., et al. (2025). Neutralization of marinobufagenin demonstrates efficacy in vitro and in vivo in models of pre-eclampsia. Biomedicines 13 (4), 782. doi:10.3390/biomedicines13040782
Paul, R., Zhang, Z. G., Eliceiri, B. P., Jiang, Q., Boccia, A. D., Zhang, R. L., et al. (2001). Src deficiency or blockade of src activity in mice provides cerebral protection following stroke. Nat. Med. 7 (2), 222–227. doi:10.1038/84675
Pavlovic, D. (2014). The role of cardiotonic steroids in the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathy in chronic kidney disease. Nephron Clin. Pract. 128 (1-2), 11–21. doi:10.1159/000363301
Pavlovic, D. (2020). Endogenous cardiotonic steroids and cardiovascular disease, where to next? Cell Calcium 86, 102156. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102156
Periyasamy, S. M., Liu, J., Tanta, F., Kabak, B., Wakefield, B., Malhotra, D., et al. (2005). Salt loading induces redistribution of the plasmalemmal Na/K-ATPase in proximal tubule cells. Kidney Int. 67 (5), 1868–1877. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00285.x
Perkovic, V., Jardine, M. J., Neal, B., Bompoint, S., Heerspink, H. J., Charytan, D. M., et al. (2019). Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 380 (24), 2295–2306. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1811744
Pessoa, T. D., Campos, L. C., Carraro-Lacroix, L., Girardi, A. C., and Malnic, G. (2014). Functional role of glucose metabolism, osmotic stress, and sodium-glucose cotransporter isoform-mediated transport on Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 activity in the renal proximal tubule. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 25 (9), 2028–2039. doi:10.1681/ASN.2013060588
Petrushanko, I. Y., Tverskoi, A. M., Barykin, E. P., Petrovskaya, A. V., Strelkova, M. A., Leonova, O. G., et al. (2022). Na,K-ATPase acts as a beta-amyloid receptor triggering src kinase activation. Cells 11 (17), 2753. doi:10.3390/cells11172753
Pierre, S. V., and Xie, Z. (2006). The Na,K-ATPase receptor complex: its organization and membership. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 46 (3), 303–316. doi:10.1385/cbb:46:3:303
Pratt, R. D., Brickman, C. R., Cottrill, C. L., Shapiro, J. I., and Liu, J. (2018). The Na/K-ATPase signaling: from specific ligands to general reactive oxygen species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (9), 2600. doi:10.3390/ijms19092600
Qiu, H., Qian, T., Wu, T., Gao, T., Xing, Q., and Wang, L. (2021). Src family kinases inhibition ameliorates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in immature rats. Front. Cell Neurosci. 15, 746130. doi:10.3389/fncel.2021.746130
Quintas, L. E. M., Pierre, S. V., Liu, L., Bai, Y., Liu, X., and Xie, Z.-J. (2010). Alterations of Na+/K+-ATPase function in caveolin-1 knockout cardiac fibroblasts. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 49 (3), 525–531. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.04.015
Razani, B., Woodman, S. E., and Lisanti, M. P. (2002). Caveolae: from cell biology to animal physiology. Pharmacol. Rev. 54 (3), 431–467. doi:10.1124/pr.54.3.431
Reinhard, L., Tidow, H., Clausen, M. J., and Nissen, P. (2013). Na(+),K (+)-ATPase as a docking station: protein-protein complexes of the na(+),K (+)-ATPase. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 70 (2), 205–222. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1039-9
Roytenberg, R., Yue, H., DeHart, A., Kim, E., Bai, F., Kim, Y., et al. (2024). Thymidine phosphorylase mediates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein enhanced thrombosis in K18-hACE2(TG) mice. Thromb. Res. 244, 109195. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2024.109195
Santos, D. S. d., Polidoro, J. Z., Borges-Júnior, F. A., and Girardi, A. C. C. (2020). Cardioprotection conferred by sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: a renal proximal tubule perspective. Am. J. Physiology-Cell Physiology 318 (2), C328–C336. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00275.2019
Schlegel, A., and Lisanti, M. P. (2001). The caveolin triad: caveolae biogenesis, cholesterol trafficking, and signal transduction. Cytokine and growth factor Rev. 12 (1), 41–51. doi:10.1016/s1359-6101(00)00022-8
Schmidt, T. A., Allen, P. D., Colucci, W. S., Marsh, J. D., and Kjeldsen, K. (1993). No adaptation to digitalization as evaluated by digitalis receptor (Na,K-ATPase) quantification in explanted hearts from donors without heart disease and from digitalized recipients with end-stage heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 71 (1), 110–114. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(93)90720-w
Schoner, W. (2002). Endogenous cardiac glycosides, a new class of steroid hormones. Eur. J. Biochem. 269 (10), 2440–2448. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02911.x
Schoner, W., Bauer, N., Müller-Ehmsen, J., Krämer, U., Hambarchian, N., Schwinger, R., et al. (2003). Ouabain as a Mammalian hormone. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 986, 678–684. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07282.x
Schoner, W., and Scheiner-Bobis, G. (2005). Endogenous cardiac glycosides: hormones using the sodium pump as signal transducer. Semin. Nephrol. 25 (5), 343–351. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2005.03.010
Schoner, W., and Scheiner-Bobis, G. (2007). Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides: their roles in hypertension, salt metabolism, and cell growth. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 293 (2), C509–C536. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00098.2007
Semb, S. O., Lunde, P. K., Holt, E., Tonnessen, T., Christensen, G., and Sejersted, O. M. (1998). Reduced myocardial na+, K(+)-pump capacity in congestive heart failure following myocardial infarction in rats. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 30 (7), 1311–1328. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1998.0696
Semplicini, A., Serena, L., Valle, R., Ceolotto, G., Felice, M., Fontebasso, A., et al. (1995). Ouabain-inhibiting activity of aldosterone antagonists. Steroids 60 (1), 110–113. doi:10.1016/0039-128x(94)00005-w
Shah, P. T., Martin, R., Yan, Y., Shapiro, J. I., and Liu, J. (2016). Carbonylation modification regulates Na/K-ATPase signaling and salt sensitivity: a review and a hypothesis. Front. Physiol. 7, 256. doi:10.3389/fphys.2016.00256
Silva, A. B. d. S., Oliveira, A. K. C. d., Medeiros, A. L. d. A., Queiroz, A. L. B., Cypriano, B. M., and Nascimento, K. d. (2022). Balneabilidade das praias urbanas de natal/rn (2015–2020). Soc. Tecnol. meio ambiente avanços, retrocessos novas perspectivas-volume 3, Ed. científica Digit., 29–40. doi:10.37885/220107430
Silva, L. N. D., Garcia, I. J. P., Valadares, J. M. M., Pessoa, M. T. C., Toledo, M. M., Machado, M. V., et al. (2021). Evaluation of cardiotonic steroid modulation of cellular cholesterol and phospholipid. J. Membr. Biol. 254 (5-6), 499–512. doi:10.1007/s00232-021-00203-z
Silva, L. N. D., Pessoa, M. T. C., Alves, S. L. G., Venugopal, J., Cortes, V. F., Santos, H. L., et al. (2017). Differences of lipid membrane modulation and oxidative stress by digoxin and 21-benzylidene digoxin. Exp. Cell Res. 359 (1), 291–298. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.07.017
Skou, J. C. (1957). The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 23 (2), 394–401. doi:10.1016/0006-3002(57)90343-8
Song, K. S., Scherer, P. E., Tang, Z., Okamoto, T., Li, S., Chafel, M., et al. (1996). Expression of caveolin-3 in skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle cells. Caveolin-3 is a component of the sarcolemma and co-fractionates with dystrophin and dystrophin-associated glycoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271 (25), 15160–15165. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.25.15160
Srikanthan, K., Shapiro, J. I., and Sodhi, K. (2016). The role of Na/K-ATPase signaling in oxidative stress related to obesity and cardiovascular disease. Molecules 21 (9), 1172. doi:10.3390/molecules21091172
Staehr, C., Aalkjaer, C., and Matchkov, V. V. (2023). The vascular Na,K-ATPase: clinical implications in stroke, migraine, and hypertension. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 137 (20), 1595–1618. doi:10.1042/CS20220796
Staehr, C., Guldbrandsen, H., Homilius, C., Johnsen, L., Postnov, D., Pedersen, T. M., et al. (2025). Targeting Na,K-ATPase-Src signaling to normalize cerebral blood flow in a murine model of familial hemiplegic migraine. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 45 (5), 842–854. doi:10.1177/0271678X241305562
Staehr, C., and Matchkov, V. V. (2021). Demand creates its own supply: the Na/K-ATPase controls metabolic reserve and flexibility. Acta Physiol. (Oxf) 232 (3), e13673. doi:10.1111/apha.13673
Staehr, C., Rohde, P. D., Krarup, N. T., Ringgaard, S., Laustsen, C., Johnsen, J., et al. (2022). Migraine-associated mutation in the Na,K-ATPase leads to disturbances in cardiac metabolism and reduced cardiac function. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 11 (7), e021814. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.021814
Sweadner, K. J., and Donnet, C. (2001). Structural similarities of Na,K-ATPase and SERCA, the Ca(2+)-ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem. J. 356 (Pt 3), 685–704. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3560685
Takenaga, Y., Takagi, N., Murotomi, K., Tanonaka, K., and Takeo, S. (2009). Inhibition of src activity decreases tyrosine phosphorylation of occludin in brain capillaries and attenuates increase in permeability of the blood-brain barrier after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 29 (6), 1099–1108. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2009.30
Tanaka, S., Sugiura, Y., Saito, H., Sugahara, M., Higashijima, Y., Yamaguchi, J., et al. (2018). Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition normalizes glucose metabolism and suppresses oxidative stress in the kidneys of diabetic mice. Kidney Int. 94 (5), 912–925. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2018.04.025
Tian, J., Cai, T., Yuan, Z., Wang, H., Liu, L., Haas, M., et al. (2006). Binding of src to Na+/K+-ATPase forms a functional signaling complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 17 (1), 317–326. doi:10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0735
Tian, J., Li, X., Liang, M., Liu, L., Xie, J. X., Ye, Q., et al. (2009). Changes in sodium pump expression dictate the effects of ouabain on cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 284 (22), 14921–14929. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808355200
Trant, J., De Blanco, G. S., Mcdermott, J. P., and Blanco, G. (2023). Ouabain enhances renal cyst growth in a slowly progressive mouse model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: FR-PO551. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 34 (11S), 555–556. doi:10.1681/asn.20233411s1555b
Trevisi, L., Pighin, I., Bazzan, S., and Luciani, S. (2006). Inhibition of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) endocytosis by ouabain in human endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 580 (11), 2769–2773. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.040
Vallon, V. (2015). The mechanisms and therapeutic potential of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetes mellitus. Annu. Rev. Med. 66 (1), 255–270. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-051013-110046
Vallon, V., and Thomson, S. C. (2020). The tubular hypothesis of nephron filtration and diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 16 (6), 317–336. doi:10.1038/s41581-020-0256-y
Vallon, V., and Verma, S. (2021). Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on kidney and cardiovascular function. Annu. Rev. Physiology 83 (1), 503–528. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-095920
Venugopal, J., and Blanco, G. (2016). Ouabain enhances ADPKD cell apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway. Front. Physiology 7, 107. doi:10.3389/fphys.2016.00107
Venugopal, J., and Blanco, G. (2017). On the many actions of ouabain: pro-cystogenic effects in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Molecules 22 (5), 729. doi:10.3390/molecules22050729
Wang, H., Haas, M., Liang, M., Cai, T., Tian, J., Li, S., et al. (2004). Ouabain assembles signaling cascades through the caveolar Na+/K+-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (17), 17250–17259. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313239200
Wang, N., Yang, Y., Wang, H., Li, Y., Wang, M., and Li, Q. (2025). Cinobufagin modulates vasculogenic mimicry and tumor-associated macrophages to inhibit ovarian cancer progression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 987, 177157. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177157
Wang, X., Cai, L., Xie, J. X., Cui, X., Zhang, J., Wang, J., et al. (2020). A caveolin binding motif in Na/K-ATPase is required for stem cell differentiation and organogenesis in mammals and C. elegans. Sci. Adv. 6 (22), eaaw5851. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaw5851
Wang, X., and Shapiro, J. I. (2019). Evolving concepts in the pathogenesis of uraemic cardiomyopathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 15 (3), 159–175. doi:10.1038/s41581-018-0101-8
Wansapura, A. N., Lasko, V. M., Lingrel, J. B., and Lorenz, J. N. (2010). Mice expressing ouabain-sensitive α1-Na, K-ATPase have increased susceptibility to pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Am. J. Physiology-Heart Circulatory Physiology 300 (1), H347–H355. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00625.2010
Weigand, K. M., Swarts, H. G., Fedosova, N. U., Russel, F. G., and Koenderink, J. B. (2012). Na,K-ATPase activity modulates src activation: a role for ATP/ADP ratio. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1818 (5), 1269–1273. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.01.015
Wu, J., Akkuratov, E. E., Bai, Y., Gaskill, C. M., Askari, A., and Liu, L. (2013). Cell signaling associated with Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase: activation of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase IA/Akt by ouabain is independent of src. Biochemistry 52 (50), 9059–9067. doi:10.1021/bi4011804
Xie, Z. (2003). Molecular mechanisms of Na/K-ATPase-mediated signal transduction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 986, 497–503. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07234.x
Xie, Z., and Askari, A. (2002). Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase as a signal transducer. Eur. J. Biochem. 269 (10), 2434–2439. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02910.x
Xie, Z., and Cai, T. (2003). Na+-K+--ATPase-mediated signal transduction: from protein interaction to cellular function. Mol. Interv. 3 (3), 157–168. doi:10.1124/mi.3.3.157
Xie, Z., Kometiani, P., Liu, J., Li, J., Shapiro, J. I., and Askari, A. (1999). Intracellular reactive oxygen species mediate the linkage of Na+/K+-ATPase to hypertrophy and its marker genes in cardiac myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 274 (27), 19323–19328. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.27.19323
Xu, Y., Marck, P., Huang, M., Xie, J. X., Wang, T., Shapiro, J. I., et al. (2021). Biased effect of cardiotonic steroids on Na/K-ATPase–Mediated signal transduction. Mol. Pharmacol. 99 (3), 217–225. doi:10.1124/molpharm.120.000101
Yan, Y., Haller, S., Shapiro, A., Malhotra, N., Tian, J., Xie, Z., et al. (2012). Ouabain-stimulated trafficking regulation of the Na/K-ATPase and NHE3 in renal proximal tubule cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 367 (1-2), 175–183. doi:10.1007/s11010-012-1331-x
Yan, Y., Shapiro, A. P., Haller, S., Katragadda, V., Liu, L., Tian, J., et al. (2013). Involvement of reactive oxygen species in a feed-forward mechanism of Na/K-ATPase-mediated signaling transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 288 (47), 34249–34258. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.461020
Yan, Y., Shapiro, A. P., Mopidevi, B. R., Chaudhry, M. A., Maxwell, K., Haller, S. T., et al. (2016). Rapamycin attenuates cardiac fibrosis in experimental uremic cardiomyopathy by reducing marinobufagenin levels and inhibiting downstream pro-fibrotic signaling. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 5 (9), e004106. doi:10.1161/JAHA.116.004106
Yan, Y., and Shapiro, J. I. (2016). The physiological and clinical importance of sodium potassium ATPase in cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 27, 43–49. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2016.01.009
Yan, Y., Wang, J., Chaudhry, M. A., Nie, Y., Sun, S., Carmon, J., et al. (2019). Metabolic syndrome and salt-sensitive hypertension in polygenic obese TALLYHO/jngJ mice: role of Na/K-ATPase signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (14), 3495. doi:10.3390/ijms20143495
Yatime, L., Buch-Pedersen, M. J., Musgaard, M., Morth, J. P., Lund Winther, A. M., Pedersen, B. P., et al. (2009). P-type ATPases as drug targets: tools for medicine and science. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1787 (4), 207–220. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.12.019
Ye, Q., Lai, F., Banerjee, M., Duan, Q., Li, Z., Si, S., et al. (2013). Expression of mutant α1 Na/K-ATPase defective in conformational transition attenuates Src-mediated signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 288 (8), 5803–5814. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.442608
Ye, Q., Li, Z., Tian, J., Xie, J. X., Liu, L., and Xie, Z. (2011). Identification of a potential receptor that couples ion transport to protein kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (8), 6225–6232. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.202051
Yoo, M. H., Lee, S. J., Kim, W., Kim, Y., Kim, Y. B., Moon, K. S., et al. (2022). Bisphenol A impairs renal function by reducing Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase and F-actin expression, kidney tubule formation in vitro and in vivo. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 246, 114141. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114141
Yosef, E., Katz, A., Peleg, Y., Mehlman, T., and Karlish, S. J. (2016). Do src kinase and caveolin interact directly with Na,K-ATPase? J. Biol. Chem. 291 (22), 11736–11750. doi:10.1074/jbc.M116.721084
Yuan, Z., Cai, T., Tian, J., Ivanov, A. V., Giovannucci, D. R., and Xie, Z. (2005). Na/K-ATPase tethers phospholipase C and IP3 receptor into a calcium-regulatory complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 16 (9), 4034–4045. doi:10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0295
Zelniker, T. A., Wiviott, S. D., Raz, I., Im, K., Goodrich, E. L., Bonaca, M. P., et al. (2019). SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet 393 (10166), 31–39. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32590-X
Zhang, J., Chang, J., Beg, M. A., Huang, W., Zhao, Y., Dai, W., et al. (2022a). Na/K-ATPase suppresses LPS-Induced pro-inflammatory signaling through lyn. iScience 25 (9), 104963. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2022.104963
Zhang, X., Lee, W., and Bian, J. S. (2022b). Recent advances in the study of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase in neurodegenerative diseases. Cells 11 (24), 4075. doi:10.3390/cells11244075
Zhu, Z., Wang, H., Qian, X., Xue, M., Sun, A., Yin, Y., et al. (2024). Inhibitory impact of cinobufagin in triple-negative breast cancer metastasis: involvements of macrophage reprogramming through upregulated MME and inactivated FAK/STAT3 signaling. Clin. Breast Cancer 24 (4), e244–e257.e1. doi:10.1016/j.clbc.2024.01.014
Keywords: Na/K-ATPase, cardiotonic steroids, signaling, ROS, pharmacological, implications
Citation: Gao Y, Xu Y, Bai F, Puri R, Tian J and Liu J (2025) Factors that influence the Na/K-ATPase signaling and function. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1639859. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1639859
Received: 02 June 2025; Accepted: 11 July 2025;
Published: 29 July 2025.
Edited by:
Olga V. Fedorova, NIH, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Gao, Xu, Bai, Puri, Tian and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiang Liu, bGl1akBtYXJzaGFsbC5lZHU=
 Yingnyu Gao
Yingnyu Gao Yunhui Xu2
Yunhui Xu2 Jiang Tian
Jiang Tian Jiang Liu
Jiang Liu