- 1Dongzhimen Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Cardiovascular, Ordos Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ordos, China
- 3Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 4Institute of Basic Theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 5National Integrated Traditional and biomedicine Medicine Center for Cardiovascular Disease, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
Background: Commercial Chinese polyherbal preparations (CCPPs) are widely used in China to treat coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD). However, the discussion on the best CCPPs continues. This network meta-analysis (NMA) aimed to evaluate and rank the relative efficacy of CCPPs for CMD and summarize the possible mechanisms according to experimental researches.
Method: From the time the database was established to 12 December 2024, We systematically searched eight databases and two registry systems, including Web of Science, Cochrane Library, PubMed, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang database, China Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP), Chinese Biomedical Literature database (CBM), Clinical Trials, and the China Clinical Trials Registry. Clinical randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of nine CCPPs in treating CMD, including Shexiangbaoxin Pill (SXBX), Tongxinluo Capsule (TXL), Shexiangtongxindi Pill (SXTXD), Yindanxinnaotong Capsule (YDXNT), Kedalin Tablet (KDL), Xinbao Pill (XB), Xinkeshu Tablet (XKS), Diaoxinxuekang Capsule (DAXXK), and Yixintongluo Capsule (YXTL), were retrieved. The primary outcomes were the Index of Microcirculatory Resistance (IMR) and Coronary Flow Reserve (CFR). Secondary outcomes included the Angina attack frequency, hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), Endothelin-1 (ET-1), Nitric oxide (NO), and Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Two researchers performed rigorous data extraction and quality assessment. The quality of the included RCTs was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias assessment tool, version 2.0 (RoB 2). We then conducted the NMA using a random-effects model under the frequentist framework with Stata version 15. Interventions were ranked based on the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) probability values. The risk of bias was detected using funnel plots and Egger’s test.
Result: A total of 39 RCTs involving 3,240 patients were included in this study. NMA results showed that SXBX had the highest probability of being the best treatment on account of the reduction of IMR [MD = −5.93, 95% CI (−8.75, −3.11)] and LDL-C [[MD = −0.56, 95% CI (−0.99, −0.14)], XB showed better efficacy in improving CFR [MD = 0.71, 95% CI (0.53, 0.89)], TXL showed better efficacy in angina attack frequency [MD = −5.30, 95% CI (−7.08, −3.53)]; YXTL showed better efficacy in hs-CRP [MD = −5.04, 95% CI (−8.38, −1.7)]; XKS showed better efficacy in ET-1 [MD = −43.3, 95% CI (−59.71, −26.89)]; YDXNT showed better efficacy in NO [MD = 17.69, 95% CI (6.07, 29.32)]. In addition, the protective effect of CCPP on CMD may be achieved by altering multiple signalling pathways through anti-atherosclerosis, anti-vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, anti-inflammation, antioxidant stress, protection of vascular endothelium, improving energy metabolism, antiplatelet activation and aggregation, and promoting angiogenesis.
Conclusion: CCPPs combined with conventional therapy led to a significant improvement in CFR and NO, as well as a reduction in IMR, angina attack frequency, hs-CRP, ET-1, and LDL-C levels. SXBX emerged as the optimal treatment regimen for lowering IMR and LDL-C levels. Additionally, XB demonstrated superiority in improving CFR. TXL demonstrated superiority in reducing angina attack frequency, YXTL in lowering hs-CRP levels, XKS in lowering ET-1 levels, and YDXNT in increasing NO levels. Nevertheless, the majority of the evidence was rated as low certainty according to the GRADE assessment. Conclusion should be framed as hypothesis-generating rather than definitive, and there is a need for large-scale, multicenter, and direct comparative RCTs of CCPPs treated for CMD to generate higher-quality evidence.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42025632143.
1 Introduction
Coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD) is a phenomenon in which the coronary microcirculation is structurally and/or functionally altered, causing impaired coronary blood flow and ultimately leading to myocardial ischemia (Del Buono et al., 2021). CMD is highly prevalent — affecting >50% of patients with diabetes mellitus and 70%–85% of those with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (Aljizeeri et al., 2023; Arnold et al., 2022; Ford et al., 2018), and present in 45%–60% of patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) (Rehan et al., 2023). CMD is most commonly seen in symptomatic patients with chronic coronary syndromes and recurrent angina pectoris at rest or on exertion despite the absence of obstructive CAD (Samuels et al., 2023; Dimitriadis et al., 2024). Studies have shown that in the absence of epicardial coronary artery disease, the frequency of angina episodes in patients with CMD can be as high as 1–3 episodes/week (Ford et al., 2018), which seriously affects their quality of life. In addition, patients with CMD had a 3.93-fold increase in total mortality and a 5.16-fold increase in adverse cardiovascular events compared with those with normal coronary microcirculation (Gdowski et al., 2020). Impaired coronary flow reserve (CFR) and novel indices, such as microvascular resistance reserve, are strong, independent predictors of adverse cardiovascular outcomes (Kelshiker et al., 2022; Dimitriadis et al., 2025).
Empirical treatment of CMD is based on traditional therapies for CAD, including antiplatelet, lipid-lowering, and anti-ischemic therapy (e.g., nitrates, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) (Camici and Crea, 2007; Crea et al., 2014). However, the curative effect of experiential therapy alone on CMD is not evident. Multiple novel drugs that primarily reduce angina, including ranolazine, ivabradine, nicorandil, and zibotentan, have been evaluated in patients with CMD. Two meta-analyses (Zhuet al., 2019; Khandkar et al., 2025) showed that, compared with the control group, Ranolazine, Nicorandil, and Ivabradine did not improve the CFR. A recent RCT (Morrow et al., 2024) showed that short-term zibotentan treatment did not show any benefits for CMD. The number of patients with coronary microcirculatory disorders in clinical practice is large, the mechanism is complex, and the effect of conventional drug therapy is still unsatisfactory. Therefore, looking for potential complementary and alternative therapies for this significant medical need is essential.
The use of complementary and alternative medicine therapies in the treatment of CMD has received much attention in recent years. In China, as one of the primary intervention measures, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has gradually developed a scientific approach to compatibility and an industrialized production process over time, resulting in commercial Chinese polyherbal preparations (CCPP) (Zhang et al., 2024). CCPPs have been included in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and have apparent efficacy and indications. They are a key metabolite in the Chinese pharmaceutical market. Compared with TCM decoctions, CCPPs have the advantages of stable quality, a good curative effect, good safety, fast absorption, convenience in taking, carrying, and storage (Hsu E., 2009; Kang et al., 2019). In addition to being an adjunctive therapy, it can also serve as an alternative treatment option in resource-limited settings or for investigational purposes. CCPPs are widely used as adjunctive therapy for CMD in China. Such as Shexiangbaoxin Pill (SXBX) (Sun, 2021), Tongxinluo Capsule (TXL) (Fang et al., 2018), Shexiangtongxindi Pill (SXTXD) (Liu et al., 2018), Yindanxinnaotong Capsule (YDXNT) (Wang, 2022), Kedalin Tablet (KDL) (Lin et al., 2023), Xinbao Pill (XB) (Zhang, 2022), Xinkeshu Tablet (XKS) (Chen et al., 2019), Diaoxinxuekang Capsule (DAXXK) (Wang B. et al., 2024), and Yixintongluo Capsule (YXTL) (Meng, 2019), whose efficacy in increasing CFR, improving clinical symptoms of angina, Reducing inflammatory response and improving vascular endothelial function have been recognized. Therefore, this study conducted a network meta-analysis (NMA) of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on nine CCPPs for the treatment of CMD. The aim was to comprehensively evaluate and rank the relative potential for CMD of CCPPs among all available publications.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Registration and reporting
This NMA was conducted under the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis extension statement for network meta-analysis (PRISMA-NMA) (Hutton et al., 2015). This study was registered with PROSPERO under registration number CRD42025632143.
2.2 Standard evaluation of CCPPs
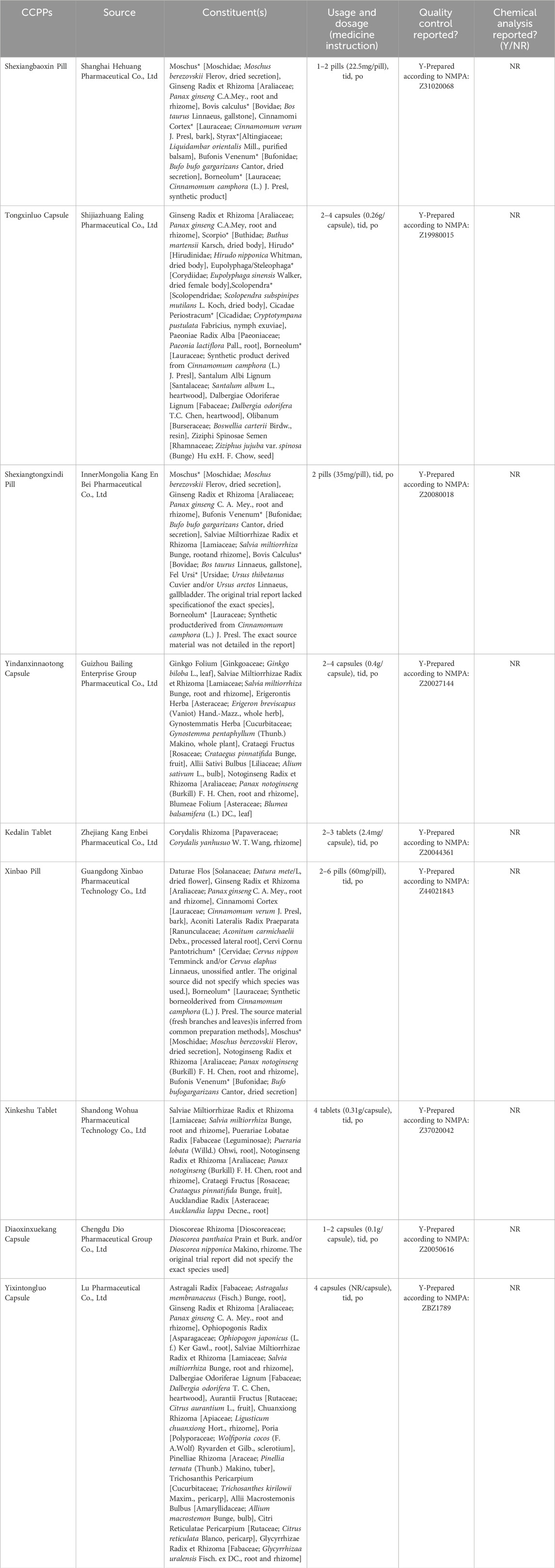
To enhance the accuracy, the CCPPs in this study were reported in accordance with the requirements of the Consensus statement on the Phytochemical Characterisation of Medicinal Plant extracts (ConPhyMP) (Heinrich et al., 2022). Accurate scientific nomenclature for botanical drugs referred to Rivera’s suggestion (Rivera et al., 2014) and was validated taxonomically in the databases of “Medicinal Plant Names Services” (https://mpns.science.kew.org/mpns-portal/). The composition and standardised name for each CCPP were presented in Table 1. In addition, we referred to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2025 regarding the names of non-botanical drugs. The relevant information about CCPPs referred to the original study, the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2025, and the National Medical Products Administration. The details were shown in Supplementary Appendix S2, S3.
2.3 Search strategy
From the time the database was established to 12 December 2024, eight databases and two registry systems were searched, including Web of Science, Cochrane Library, PubMed, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang database, China Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP), Chinese Biomedical Literature database (CBM), Clinical Trials, and the China Clinical Trials Registry. Clinical RCTs of nine CCPPs in treating CMD, including SXBX, TXL, SXTXD, YDXNT, KDL, XB, XKS, DAXXK, and YXTL were retrieved. Additionally, we manually searched references of eligible studies to identify other relevant research. The search is elaborated further in the Supplemental appendix 4, encompassing additional search strategies and outcomes information.
2.4 Study selection
The Population-Intervention-Comparators-Outcomes-Timing-Setting (PICOTS) framework was used as the criterion for this study. Inclusion criteria: (1) Population: All patients were diagnosed with CMD. (2) Intervention: Conventional therapy combined with SXBX or TXL or SXTXD or YDXNT or KDL or XB or XKS or DAXXK or YXTL. (3) Comparator: Conventional therapy. (4) Outcomes: The primary outcome indicators were the IMR and CFR; The Secondary outcome measures were Angina attack frequency, hs-CRP, ET-1, NO, and LDL-C. (5) Timing: Studies with any follow-up duration were considered. (6) Setting: Studies conducted in any clinical setting (e.g., inpatient, outpatient) were eligible (7) Study design: RCTs.
Exclusion criteria: (1) Non-RCT. (2) The intervention was a combination of multiple therapies or did not specify a therapeutic agent. (3) Duplicate publication. (4) Retracted. (5) Full text unavailable. (6) Lack of complete data.
2.5 Data extraction
Two independent reviewers (Yudou Li and Xinyue Wang) extracted the following details from the included studies: (1) first author’s name, year, and country of publication; (2) sample size and mean age; (3) specific interventions, duration of interventions; and (4) outcome data. Any disagreements were discussed or consulted with the third researcher (Wujiao Wang).
2.6 Risk of bias
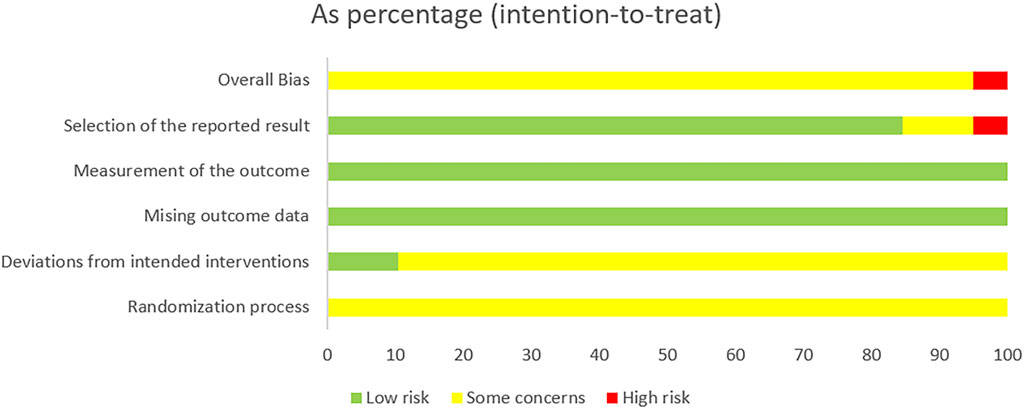
The quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Cochrane Collaboration’s risk of bias assessment tool, version 2.0 (RoB 2). The quality assessment items were as follows: (1) Randomization process; (2) Deviations from intended interventions; (3) Missing outcome data; (4) Measurement of the outcome; (5) Selection of the reported result; and (6) Overall risk of bias. Bias in each aspect was evaluated as “low risk,” “some concerns,” and “high risk.” Any disagreements were discussed or consulted with the third researcher (Peifen Chang).
2.7 Statistical analysis
First, Risk ratios (RRs) and 95% CI were performed for dichotomous variables, and mean difference (MD) and 95% CI were performed for continuous variables. In certain multi-arm trials (such as three-arm studies), if two control arms both qualify as active controls, they are merged into a single active control group using established formulas (Supplementary Appendix S5), in order to prevent duplication of experimental group data and inflated contribution to the overall analysis. Data were analysed using a random-effects model under the frequentist framework with Stata version 15. Network diagrams were constructed to visualise the geometry of the treatment network. In these diagrams, node size is proportional to the total sample size for each treatment, and the thickness of the connecting lines represents the number of studies that directly compared the connected interventions. Provided that the closed loop of interventions was available, Global consistency was evaluated using the design-by-treatment interaction model, while local inconsistency was examined using node-splitting analysis, which compares direct and indirect evidence for specific treatment comparisons. Between-study heterogeneity was quantified by estimating the variance (τ2) of the underlying effect sizes, with parameters estimated using the restricted maximum likelihood method. Meta-regression analysis is employed to investigate the potential influence of covariates on intervention effect estimates. Sensitivity analysis is utilised to assess the robustness. Then, interventions were ranked using the Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) probability values, with higher SUCRA values indicating a greater likelihood of a treatment being ranked highly. Finally, the Funnel plots and Egger’s test were used to explore publication bias if >10 studies were included.
2.8 Grading of the evidence
The quality of evidence was assessed using the GRADE method (Guyatt et al., 2011). It was categorized as high, moderate, low, or very low. RCTs received a high initial grade by default and were downgraded according to pre-specified criteria: risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and other considerations.
3 Result
3.1 Study selection
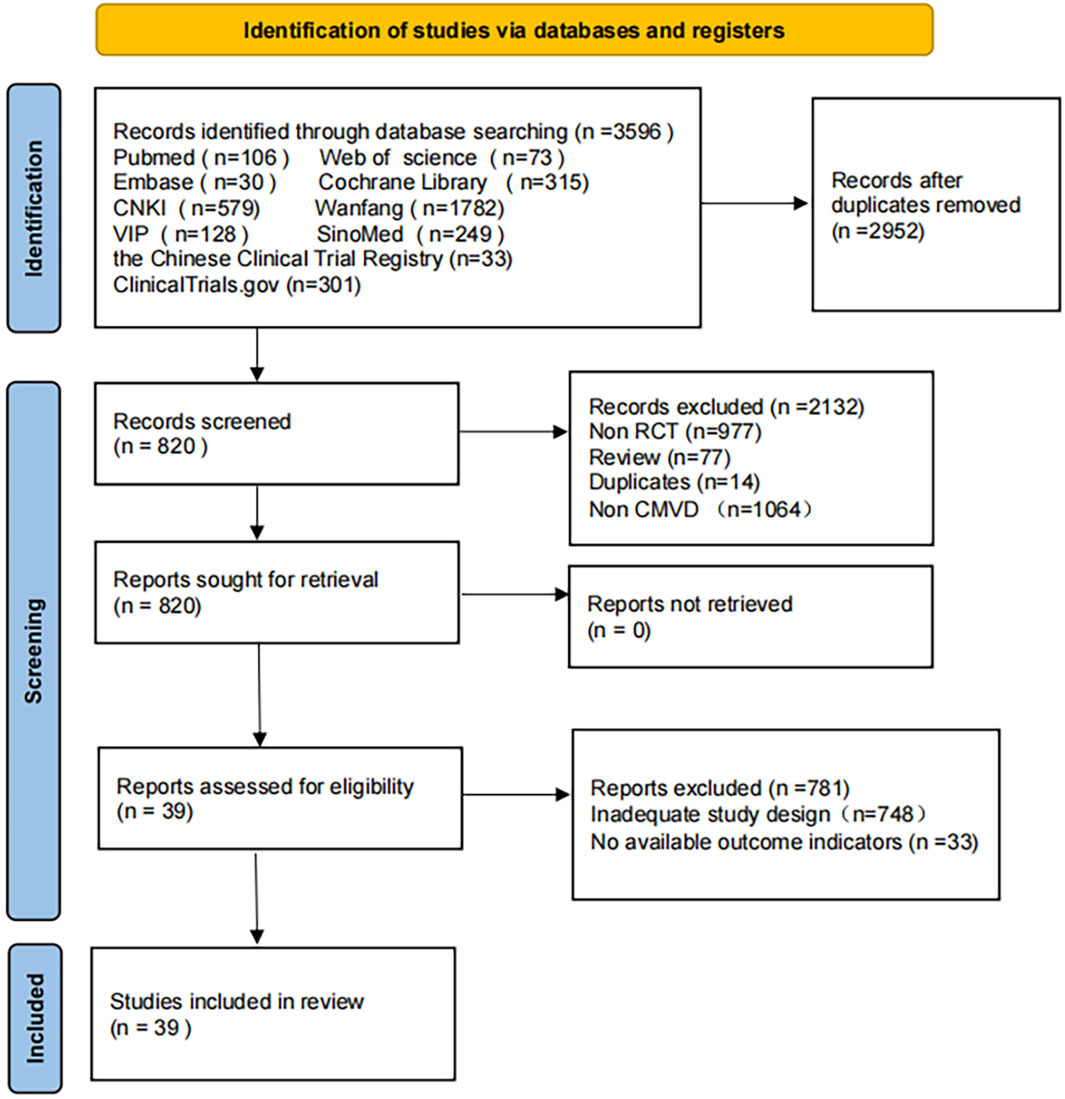
The preliminary search obtained 3,596 relevant papers, 2,952 papers were obtained after excluding duplicates, and 820 papers were obtained after excluding Non-RCTs, Reviews, Non-CMD, and duplicates. Thirty-nine papers (Bai et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2019; Chu, 2021; Fang et al., 2018; Feng et al., 2005; Fu, 2021; Fu et al., 2020; Gong et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2024; Li, 2021; Li and Tang, 2009; Liang et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2003; Liu et al., 2018; Lv et al., 2014; Ma and Xu, 2006; Meng, 2018; 2019; Peng, 2011; Qi et al., 2023; Qin et al., 2017; Qin et al., 2023; Ren et al., 2023; Shen et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2022; Sun, 2021; Wang B. et al., 2024; Wang, 2022; Wang, 2015; Wang and Long, 2022; Wang et al., 2019; Wei, 2018; Wu et al., 2019; Xie et al., 2019; Zhang, 2022; Zhang et al., 2013; Zhao D. H. et al., 2021) were finally included after further reading the full text to exclude studies with Inadequate study design and unavailable research data. Tianli Li resolved any disagreements during the selection process. The Flow diagram of the literature search is shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Characteristics of included studies
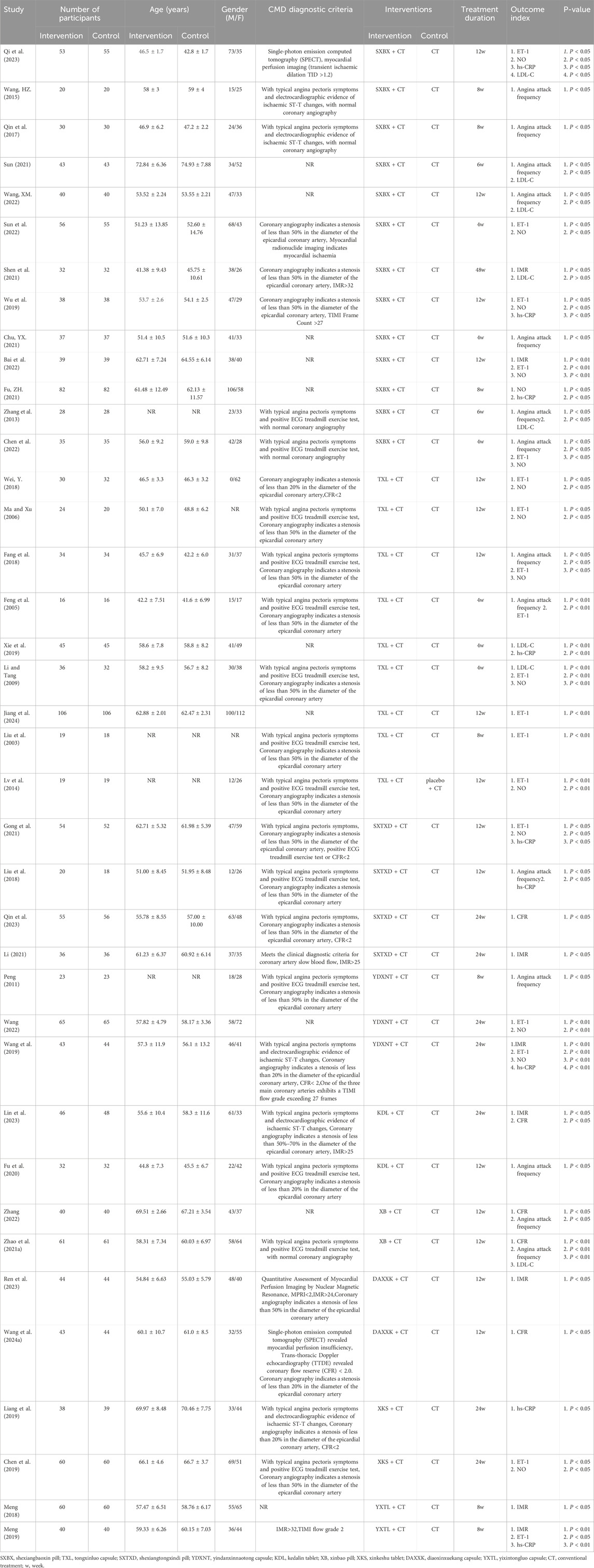
A total of 39 studies were included, all of which were published in Chinese. There were 3,240 participants, including 1,622 in the treatment group and 1,618 in the control group. Detailed characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 2.
3.3 Network plot
The compared connections among interventions for each outcome are shown in Figure 2. Each node represents a different intervention and the size of nodes is positively correlated with the number of patients. The thickness of the line segment corresponds to the number of included studies for that intervention. The thicker the line segment, the larger the number of included studies for that intervention is. There were no closed loops formed between the studies.
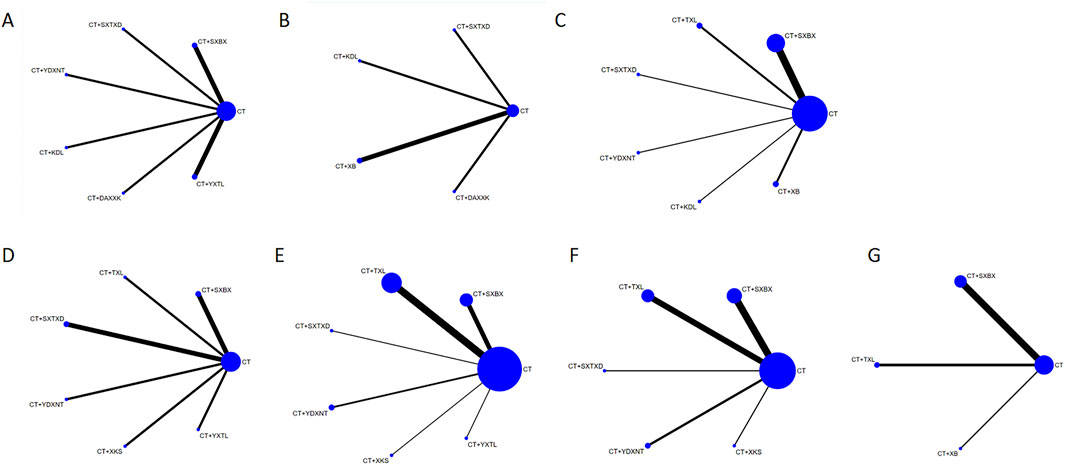
Figure 2. Network graph of the outcomes. (A) IMR. (B) CFR. (C) Angina attack frequency. (D) hs-CRP. (E) ET-1. (F) NO. (G) LDL-C. SXBX, Shexiangbaoxin Pill. TXL, Tongxinluo Capsule. SXTXD, Shexiangtongxindi Pill. YDXNT, Yindanxinnaotong Capsule. KDL, Kedalin Tablet. XB, Xinbao Pill. XKS, Xinkeshu Tablet. DAXXK, Diaoxinxuekang Capsule. YXTL, Yixintongluo Capsule. CT, Conventional therapy.
3.4 Study quality
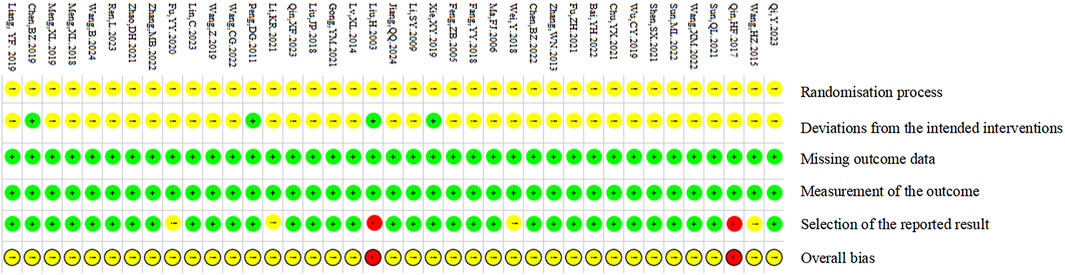
A total of 39 papers were included in this study, in which seventeen studies (Bai et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2019; Fang et al., 2018; Fu, 2021; Fu et al., 2020; Gong et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2023; Meng, 2018; 2019; Qin et al., 2017; Ren et al., 2023; Shen et al., 2021; Wang B. et al., 2024; Wang, 2022; Wang and Long, 2022; Wang et al., 2019; Zhao D. H. et al., 2021) used the random number table method, 22 studies (Chen et al., 2022; Chu, 2021; Feng et al., 2005; Jiang et al., 2024; Li, 2021; Li and Tang, 2009; Liang et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2003; Liu et al., 2018; Lv et al., 2014; Ma and Xu, 2006; Peng, 2011; Qi et al., 2023; Qin et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2022; Sun, 2021; Wang, 2015; Wei, 2018; Wu et al., 2019; Xie et al., 2019; Zhang, 2022; Zhang et al., 2013) only mentioned randomization without detailing the randomization scheme. No study reported the use of opaque envelopes to conceal the randomization program. Only two studies (Chen et al., 2019; Xie et al., 2019) reported the blinding of participants and researchers; two studies (Liu et al., 2003; Peng, 2011) reported the blinding of participants; seven studies (Feng et al., 2005; Liu et al., 2003; Lv et al., 2014; Ma and Xu, 2006; Peng, 2011; Wang, 2015; Zhang et al., 2013) with small sample sizes. The quality assessment of the included RCTs is shown in Figures 3, 4.
3.5 Meta-analysis
3.5.1 Primary outcomes
3.5.1.1 Index of microcirculatory resistance (IMR)
Eight studies reported the effects of nine CCPPs on IMR. Compared with the control group, SXBX [MD = −5.93, 95% CI (−8.75, −3.11)], YXTL [MD = −5.41, 95% CI (−8.35, −2.46)], and YDXNT [MD = −5.10, 95% CI (−9.18, −1.02)] significantly reduced the IMR. However, there was no statistically significant improvement in IMR with SXTXD [MD = −3.50, 95% CI (−7.91, 0.91)], KDL [MD = −1.45, 95% CI (−5.35, 2.45)], and DAXXK [MD = −2.98, 95% CI (−6.96, 1.00)] (Figures 5B,C). According to SUCRA, SXBX may be the most effective intervention to improve IMR (SUCRA = 81.8%), followed by YXTL (SUCRA = 75.5%) and YDXNT (SUCRA = 69.5%) (Figure 5A).
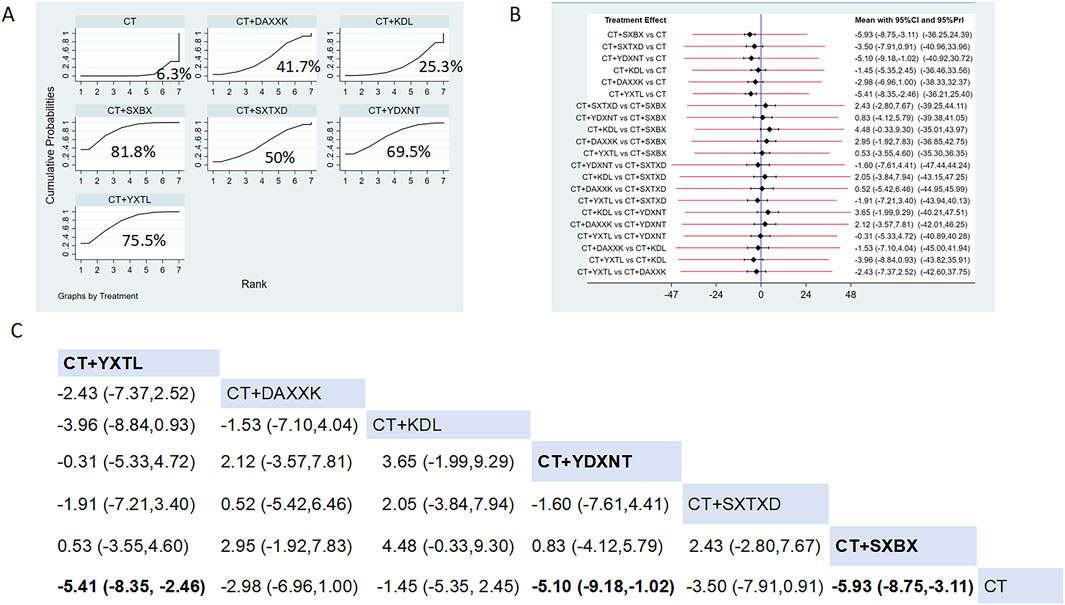
Figure 5. Network meta analysis of IMR in CMD treated with CCPPs. (A) SUCRA plot of IMR. A larger SUCRA value indicates a better rank of treatment. (B) Forest plot of IMR. The mean difference (MD) is considered statistically significant when the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”. (C) leaque table of IMR. When the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”, MD is considered statistically significant, which is bolded.
3.5.1.2 Coronary flow reserve (CFR)
Five studies reported the effects of nine CCPPs on CFR. Compared with the control group, SXTXD [MD = 0.21, 95% CI (0.11, 0.31)], KDL [MD = 0.29, 95% CI (0.08, 0.50)], XB [MD = 0.71, 95% CI (0.53, 0.89)], and DAXXK [MD = 0.32, 95% CI (0.25, 0.39)] significantly improved the CFR (Figures 6B,C). According to SUCRA, XB may be the most effective intervention to improve CFR (SUCRA = 99.9%), followed by DAXXK (SUCRA = 64.2%), KDL (SUCRA = 53.7%), and SXTXD (SUCRA = 32.1%) (Figure 6A).
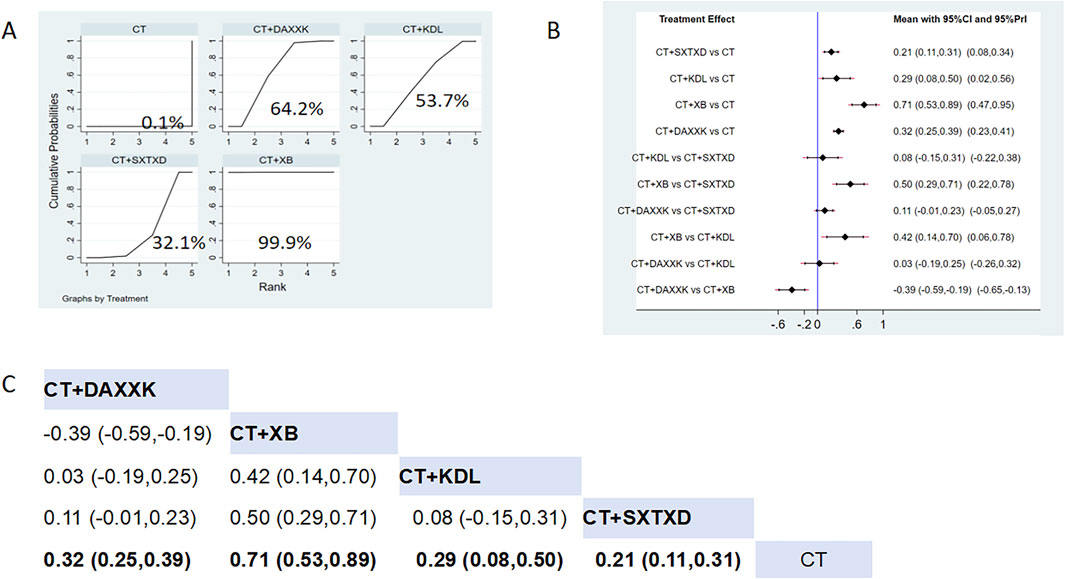
Figure 6. Network meta analysis of CFR in CMD treated with CCPPs. (A) SUCRA plot of CFR. A larger SUCRA value indicates a better rank of treatment. (B) Forest plot of CFR. The mean difference (MD) is considered statistically significant when the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”. (C) Leaque table of CFR. When the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”, MD is considered statistically significant, which is bolded.
3.5.2 Secondary outcomes
3.5.2.1 Angina attack frequency
Fourteen studies reported the effects of nine CCPPs on angina attack frequency. Compared with the control group, TXL [MD = −5.30, 95% CI (−7.08, −3.53)], SXBX [MD = −1.88, 95% CI (−2.62, −1.13)], YDXNT [MD = −3.00, 95% CI (−5.13, −0.87)], KDL [MD = −2.09, 95% CI (−3.96, −0.22)], XB [MD = −1.97, 95% CI (−3.29, −0.64)] significantly reduced the angina attack frequency (Figures 7B,C). According to SUCRA, TXL may be the most effective intervention (SUCRA = 99.2%), followed by YDXNT (SUCRA = 72.9%), KDL (SUCRA = 53.6%), XB (SUCRA = 52.4%), and SXBX (SUCRA = 48.3%) (Figure 7A).
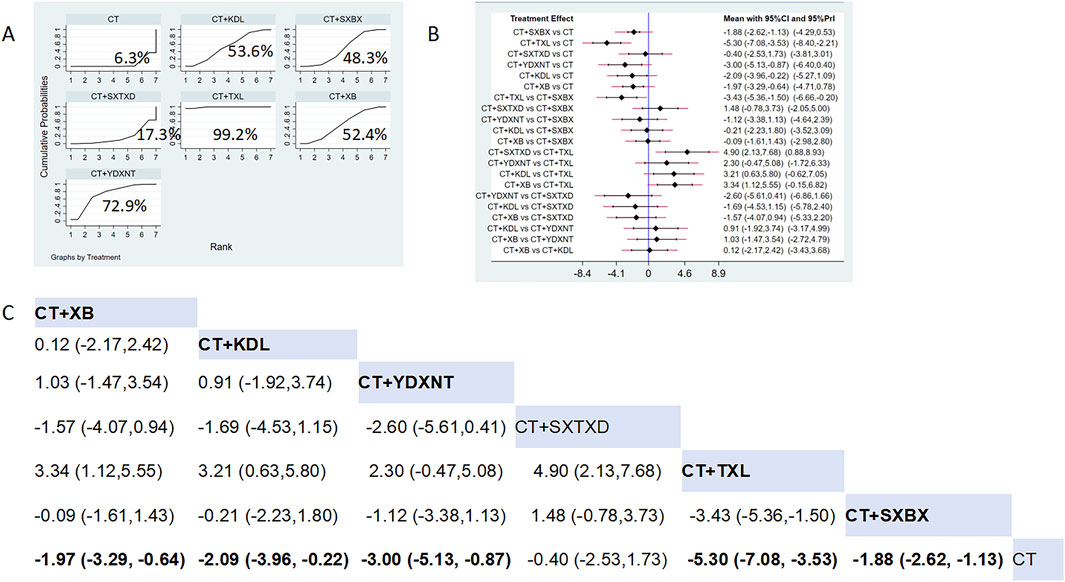
Figure 7. Network meta analysis of Angina attack frequency in CMD treated with CCPPs. (A) SUCRA plot of Angina attack frequency. A larger SUCRA value indicates a better rank of treatment. (B) Forest plot of Angina attack frequency. The mean difference (MD) is considered statistically significant when the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”. (C) Leaque table of Angina attack frequency. When the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”, MD is considered statistically significant, which is bolded.
3.5.2.2 Hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP)
Eight studies reported the effects of nine CCPPs on hs-CRP. Compared with the control group, YXTL [MD = -5.04, 95% CI (−8.38, −1.7)] and SXBX [MD = -2.85, 95% CI (−5.16, −0.55)] significantly reduced the hs-CRP (Figures 8B,C). According to SUCRA, YXTL may be the most effective intervention to reduce the hs-CRP (SUCRA = 93.2%), followed by SXBX (SUCRA = 70.9%), SXTXD (SUCRA = 53.2%), YDXNT (SUCRA = 51.9%), TXL (SUCRA = 35.2%), and XKS (SUCRA = 31.9%) (Figure 8A).
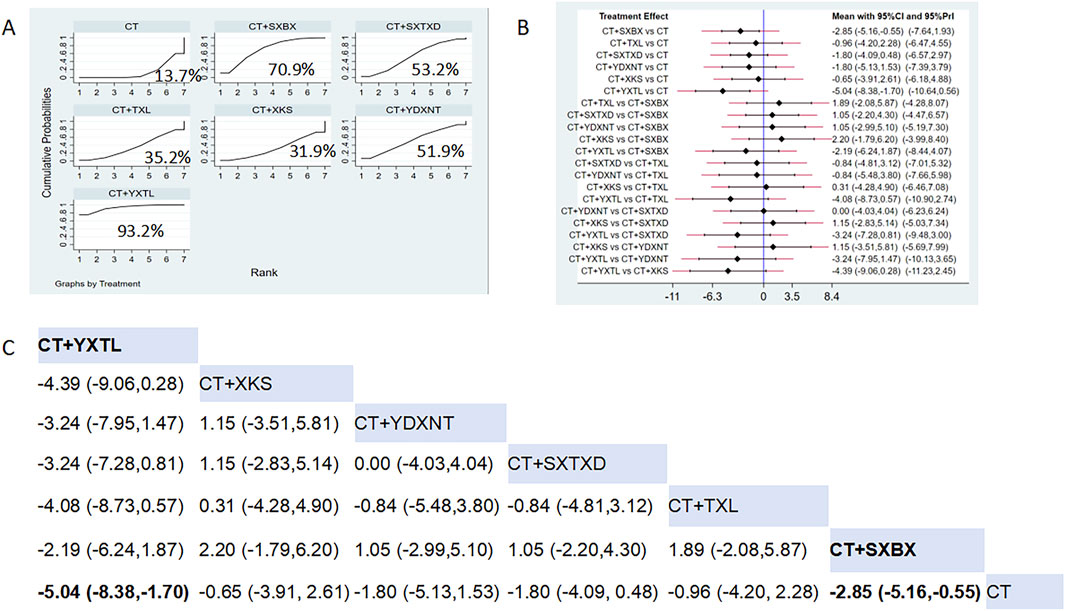
Figure 8. Network meta analysis of hs-CRP in CMD treated with CCPPs. (A) SUCRA plot of hs-CRP. A larger SUCRA value indicates a better rank of treatment. (B) Forest plot of hs-CRP. The mean difference (MD) is considered statistically significant when the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”. (C) Leaque table of hs-CRP. When the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”, MD is considered statistically significant, which is bolded.
3.5.2.3 Endothelin-1 (ET-1)
Eighteen studies reported the effects of nine CCPPs on ET-1. Compared with the control group, XKS [MD = −43.3, 95% CI (−59.71, −26.89)], SXTXD [MD = −34.5, 95% CI (−51.19, −17.81)], YDXNT [MD = −23.46, 95% CI (−35.76, −11.17)], TXL [MD = −16.34, 95% CI (−22.29, −10.38)], and SXBX [MD = −12.3, 95% CI (−19.57, −5.04)] significantly reduced the ET-1 (Figures 9B,C). According to SUCRA, XKS may be the most effective intervention to reduce the ET-1 (SUCRA = 96%), followed by SXTXD (SUCRA = 83.2%), YDXNT (SUCRA = 64%), TXL (SUCRA = 45.1%), XSBX (SUCRA = 30.7%), and YXTL (SUCRA = 29.4%) (Figure 9A).
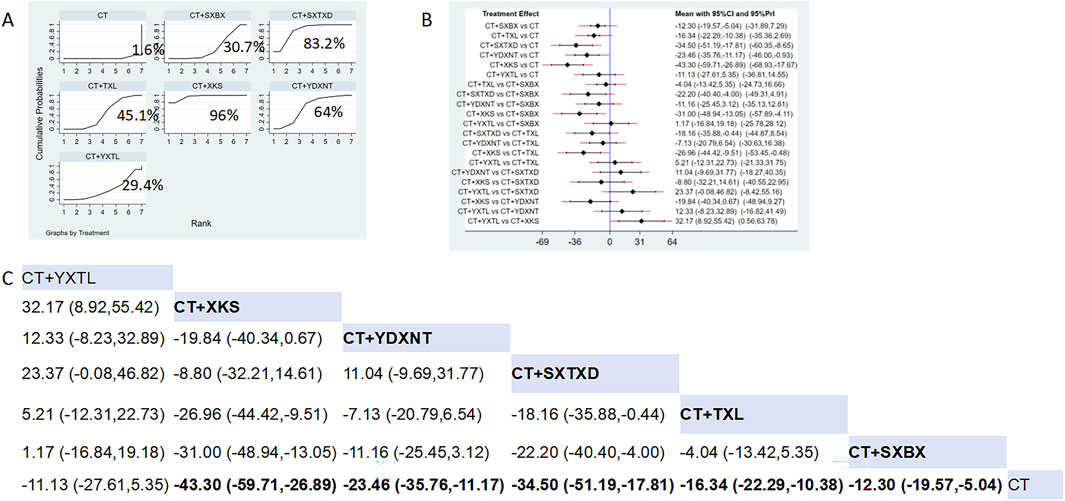
Figure 9. Network meta analysis of ET-1 in CMD treated with CCPPs. (A) SUCRA plot of ET-1. A larger SUCRA value indicates a better rank of treatment. (B) Forest plot of ET-1. The mean difference (MD) is considered statistically significant when the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”. (C) Leaque table of ET-1. When the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”, MD is considered statistically significant, which is bolded.
3.5.2.4 Nitric oxide (NO)
Fifteen studies reported the effects of nine CCPPs on NO. Compared with the control group, YDXNT [MD = 17.69, 95% CI (6.07, 29.32)], XKS [MD = 17.6, 95% CI (3.09, 32.11)], SXTXD [MD = 17.00, 95% CI (0.52, 33.48)], SXBX [MD = 15.82, 95% CI (9.76, 21.88)], and TXL [MD = 10.59, 95% CI (3.43, 17.76)] significantly improved the NO (Figures 10B,C). According to SUCRA, YDXNT may be the most effective intervention to improve the NO (SUCRA = 70.4%), followed by XKS (SUCRA = 67.1%), SXTXD (SUCRA = 65.3%), SXBX (SUCRA = 62%), and TXL (SUCRA = 34.6%) (Figure 10A).
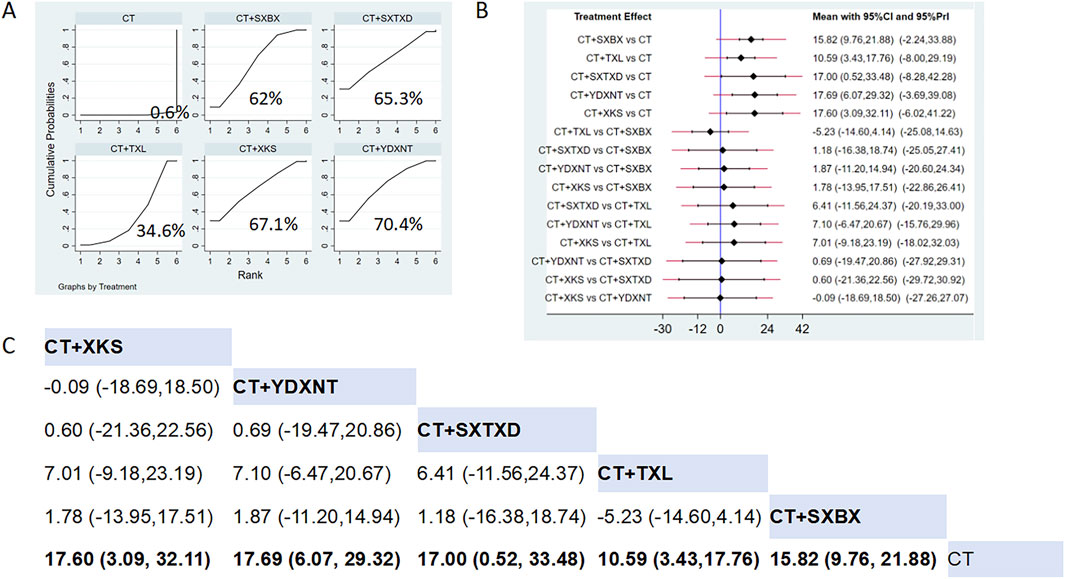
Figure 10. Network meta analysis of NO in CMD treated with CCPPs. (A) SUCRA plot of NO. A larger SUCRA value indicates a better rank of treatment. (B) Forest plot of NO. The mean difference (MD) is considered statistically significant when the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”. (C) Leaque table of NO. When the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”, MD is considered statistically significant, which is bolded.
3.5.2.5 Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)
Eight studies reported the effects of nine CCPPs on LDL-C. Compared with the control group, SXBX (MD = −0.56, 95% CI [-0.99, −0.14]) significantly reduced the LDL-C (Figures 11B,C). According to SUCRA, SXBX may be the most effective intervention to reduce the LDL-C (SUCRA = 71.8%) (Figure 11A).
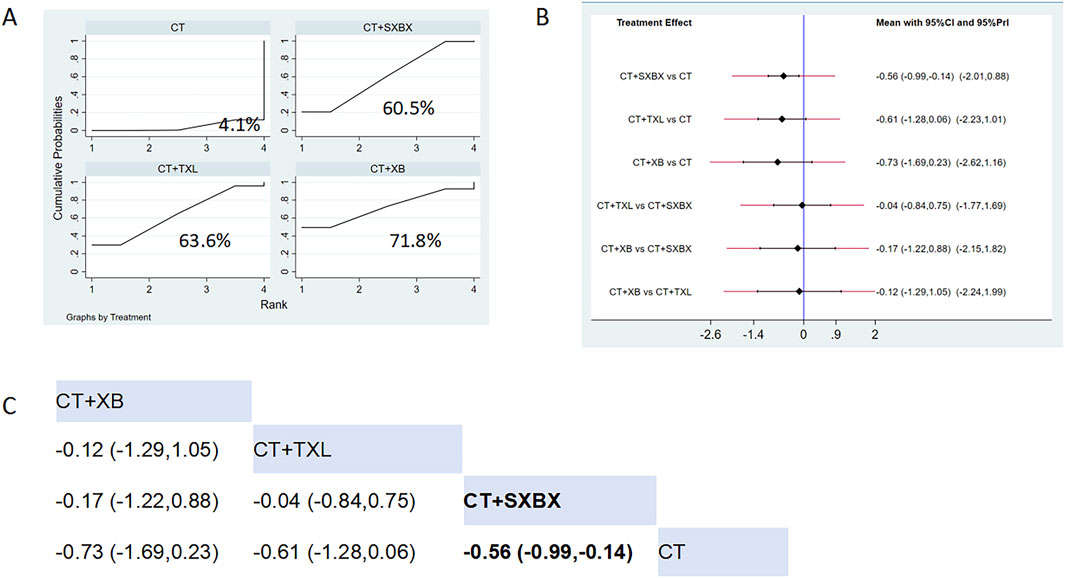
Figure 11. Network meta analysis of LDL-C in CMD treated with CCPPs. (A) SUCRA plot of LDL-C. A larger SUCRA value indicates a better rank of treatment. (B) Forest plot of LDL-C. The mean difference (MD) is considered statistically significant when the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”. (C) Leaque table of LDL-C. When the entire 95 % confidence interval does not contain “0”, MD is considered statistically significant, which is bolded.
3.6 Inconsistency, heterogeneity, meta-regression, and sensitivity analysis
As this network meta-analysis did not form a closed loop, node splitting could not be employed for inconsistency testing. First, we conducted a global consistency test. The results revealed that only the p-values for angina attack frequency, ET-1, and NO were below 0.05, indicating significant inconsistency, which may stem from diagnostic heterogeneity, dosing, follow-up length, and study quality. Secondly, we employed NMA within a frequency-based framework to fit a consistency model. Restricted maximum likelihood (REML) was used to estimate the global heterogeneity variance (τ2). Results indicated significant heterogeneity among the included studies. We conducted further meta-regression to identify sources of heterogeneity. Six characteristics were selected, including duration of intervention, CMD diagnosis methods, sample size, gender ratio, year of publication, and risk of bias. However, the regression analyses revealed no significant influence from these covariates, indicating that these characteristics were not sources of heterogeneity between studies. Subsequent sensitivity analyses demonstrated the stability of the results. Finally, we conducted sensitivity analyses excluding high-risk studies and non-validated CMD studies, further demonstrating the robustness of our findings (Supplementary Appendixs S9, S10)
3.7 Safety evaluation
A total of 12 studies reported adverse drug reactions (ADRs), with six studies indicating no ADRs occurred in either the intervention group or the control group. Two studies reported ADRs to SXBX, one study reported ADRs to TXL, one to YDXNT, one to XB, and one to DAXXK. All ADRs were mild, and no study reported withdrawal due to ADRs. The results of the forest plot revealed that there were no significant differences in the risk of adverse drug reactions across various CCPPs (Figure 12). Detailed information is provided in Supplementary Appendix S10.
3.8 GRADE assessment
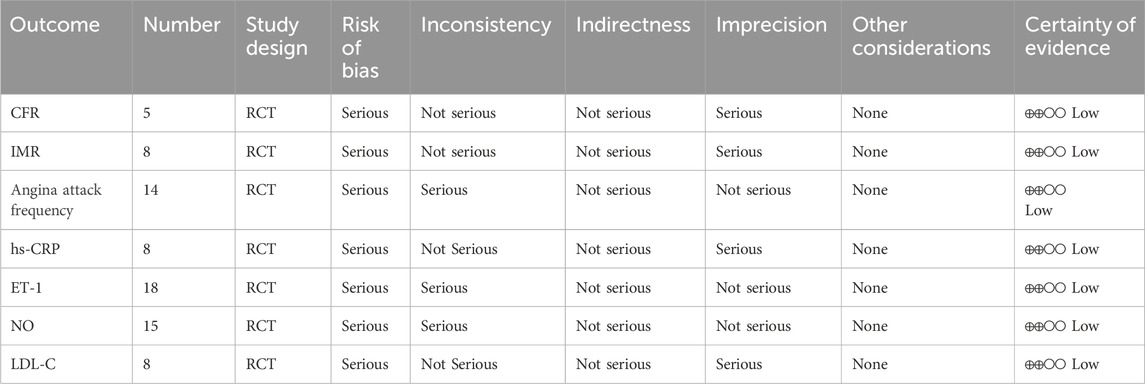
The assessment of the level of evidence for inclusion of the outcomes was summarised using the GRADE methodology as shown in Table 3.
3.9 Publication bias
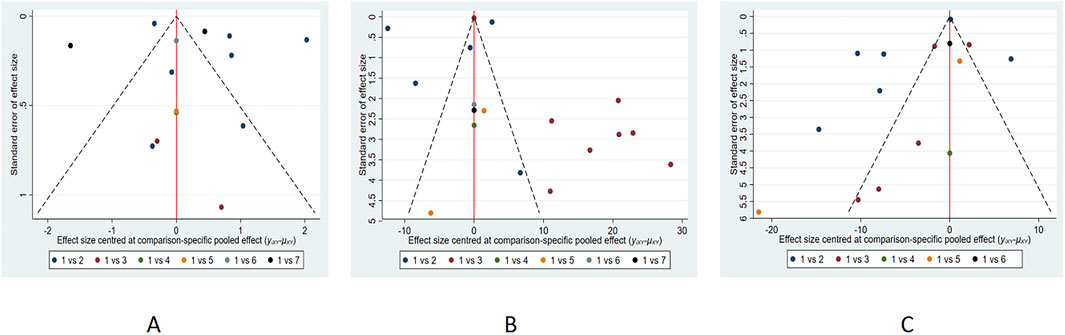
We assessed publication bias for indicators that included more than ten papers in the study, and the funnel plot results showed that angina attack frequency was roughly symmetrical (Figure 13). The ET-1 and NO funnel plots exhibited poor symmetry, and subsequent Egger’s tests revealed no significant evidence of publication bias (P-values of 0.145, 0.088, and 0.179, respectively). This inconsistency may stem from a potential small-sample effect, or may indicate that funnel plot asymmetry could be attributable to factors beyond publication bias (such as heterogeneity between studies). Nevertheless, we should exercise caution in interpreting the results, as the presence of publication bias cannot be entirely ruled out. It is worth noting that the included small-sample studies generally exhibited low methodological quality (such as more deficiencies in allocation concealment and blinding procedures), and the overestimation of effect sizes may partly stem from this. We have therefore interpreted these findings with caution. Although the possibility of publication bias cannot be ruled out, it is not the sole explanation for this result. It is undeniable that this bias is likely to have substantially impacted our SUCRA ranking results, which rely heavily on unbiased effect estimates. Given the current risk of potential bias, we should emphasize direct comparisons of point estimates and confidence intervals for clinical decision-making, rather than over-relying on specific ranking orders. Therefore, although XKS and YDXNT ranked highest in ET-1 and NO, respectively, further large-scale, high-quality studies are required to validate the relative efficacy of these interventions and provide more reliable evidence for ranking.
For other outcomes with fewer than ten included studies (CFR, IMR, hs-CRP, and LDL-C), formal statistical tests for small-study effects (e.g., Egger’s test) are underpowered. Therefore, the assessment of publication bias for these outcomes relies solely on qualitative interpretation of the funnel plots, which should be considered tentative. More primary studies are needed to allow for robust evaluation of publication bias for these endpoints.
4 Discussion
In recent years, there has been a rapid increase in the number of international consensus documents on CMD, and the understanding of CMD has changed (Knuuti et al., 2020; Kunadian et al., 2020; Ong et al., 2018; Padro et al., 2020; Tamis-Holland et al., 2019). In 2023, the Chinese Medical Association issued a Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of coronary microvascular disease (Chen et al., 2023), which classified CMD into four main types and nine subtypes and summarised the diagnostic criteria for different types of CMD. The 2024 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Coronary Syndromes recommend that patients with recurrent or refractory angina and suspected angina with non-occlusive coronary Arteries (ANOCA)/Ischemia with non-occlusive coronary Arteries (INOCA) undergo invasive coronary functional testing (Class I, Level B) to define underlying endotypes and guide targeted treatment (Vrints et al., 2024). For symptomatic ANOCA/INOCA, the same guidelines advocate a mechanism-guided pharmacologic approach, tailored to the results of coronary functional testing, to optimise symptom control and quality of life. CFR is the coronary or myocardial blood flow ratio during maximal coronary dilatation to the corresponding index at rest. Studies have shown that MACE is higher in patients with CFR <1.6 at 1-year follow-up. CFR is an important predictor of MI and heart failure risk (Taqueti et al., 2015) and an overall indicator of the reserve function of the entire coronary system. IMR is an index of myocardial microcirculatory function in coronary arteries at maximal microcirculatory dilatation measured by a pressure/temperature guidewire (Ng et al., 2012). IMR and CFR are common invasive means to detect microcirculatory function. Therefore, we chose CFR and IMR as the primary outcomes to compare the protective effect of CCPPs on the reserve function of the entire coronary system. The main symptom of CMD is angina pectoris, so we chose the frequency of angina attacks to indicate the effect of various CCPPs on the clinical symptoms of CMD patients. The pathological mechanisms of CMD have not been fully elucidated. However, oxidative stress and inflammatory responses caused by excessive production and accumulation of cellular reactive oxygen species are considered to be the key pathogenic mechanisms driving the development of CMD (Masi et al., 2021), and dyslipidemia also plays an important role in the occurrence and development of CMD (Padro et al., 2020). Therefore, we chose ET-1, NO, hs-CRP, and LDL-C as the indices reflecting the effects of various CTMs on endothelial function, inflammation, and lipids.
4.1 Summary of findings
A total of 39 RCTs involving 3,240 patients were included in the study. NMA results showed that the efficacy of CT combined with CCPPs was significantly better than CT alone. SXBX had the highest probability of being the best treatment on account of the reduction of IMR [MD = −5.93, 95% CI (−8.75, −3.11)] and LDL [MD = −0.56, 95% CI (−0.99, −0.14)]; XB showed better efficacy in CFR [MD = 0.71, 95% CI (0.53, 0.89)]; TXL showed better efficacy in angina attack frequency [MD = −5.30, 95% CI (−7.08, −3.53)]; YXTL showed better efficacy in hs-CRP [MD = −5.04, 95% CI (−8.38, −1.7)]; XKS showed better efficacy in ET-1 [MD = −43.3, 95% CI (−59.71, −26.89)]; YDXNT showed better efficacy in NO [MD = 17.69, 95% CI (6.07, 29.32)]. However, this finding must be interpreted with extreme caution, as the GRADE assessment indicates that the quality of evidence for all comparisons is low. This implies that our confidence in the accurate estimate of the effect size is limited, and future research is likely to alter or even reverse the current ranking and conclusions.
4.2 Ingredients of CCPPs and frequently used herbs
CMD is classified in TCM under “Xiong Bi” and “Xin Tong” (angina pectoris). Blood-activating and Qi-promoting CCPPs have been reported to improve coronary microcirculatory and vascular endothelial functions and alleviate pain. Our NMA is the first to compare various CCPPs in CMD systematically. The study highlighted differences in efficacy, but all shared the core TCM principle of “Blood Activation and Qi Promotion.” Furthermore, analysis of the composition of each CCPP revealed that the most frequently used herbs were Ginseng, Salvia miltiorrhiza, Panax notoginseng, Artificial musk, and Borneol. They benefit qi, improve blood circulation, and relieve pain. These herbs may offer potential therapeutic benefits for CMD. However, the exact mechanisms behind their effects require further investigation through modern pharmacological research.
4.3 Possible mechanism of herbal benefits for CMD
Several CCPPs demonstrated significant efficacy in our NMA for CMD. Their benefits appear to stem from both the active herbal components they contain and the multi-target mechanisms these formulations employ. Below, we first discuss the major CCPPs and their pharmacological effects and then provide an overview of commonly used single herbal compounds.
4.4 Representative CCPPs
SXBX is an aromatic and warming CCPP that benefits Qi and strengthens the heart. It was the most effective CCPP for decreasing IMR, which may be due to its effects in reducing lipid levels, plaque formation, and endothelial damage (Li D. et al., 2024), anti-inflammation, anti-atherosclerosis (Lu et al., 2019), and protection of endothelial function (Ning et al., 2011). Studies have shown (Wei et al., 2023) that it can promote angiogenesis via the GDF15-TRPV4 signaling pathway. It inhibits pyroptosis and improves I/R injury by promoting autophagosome generation and accelerating autophagic flux (Yu et al., 2022). Comprehensive metabolomics studies have shown it protects cardiac function by regulating amino acid, lipid, and energy metabolisms (Wu et al., 2020).
XB was the most effective CCPP in increasing CFR, possibly due to its improved energy metabolism, suppressed apoptosis, suppressed excessive autophagy, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress effects. It has been shown to inhibit SGLT1 protein expression while upregulating the phosphorylation level of AMPK, promoting nuclear translocation of PPARα and enhancing its transcriptional activity, ultimately improving fatty acid energy metabolism in the heart (Pan et al., 2024). It also promotes mitochondrial homeostasis by inhibiting heme synthesis to increase succinyl-CoA (Chen et al., 2025). In addition, XB inhibits excessive autophagy by decreasing Beclin-1 and LC3II and increasing p62. It also inhibits ER stress by decreasing BIP expression and apoptosis by increasing Bcl2/Bax and decreasing caspase3 (Yang et al., 2022). DAXXK is second only to XB in increasing CFR. The main ingredient of DAXXK is total steroidal saponin, which is an Rhizome extract of Dioscorea nipponica Makino, and has been shown to reduce TC and TG levels, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress, and anti-atherosclerotic effects (Zhang et al., 2022).
TXL ranked highest for reducing angina attack frequency. It has the function of invigorating qi and promoting blood circulation, which can enhance myocardial contractility, inhibit platelet aggregation, and regulate the level of blood lipids (Chen et al., 2024). Studies have shown it could alleviate no-reflow by suppressing the interactions by modulating various leukocyte subtypes and inhibiting the expression of multiple inflammatory mediators (Liu S. et al., 2023). TXL also inhibited endothelial cell pyroptosis via the reactive oxygen species/nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signalling pathway (Gu et al., 2023). YXTL ranked highest for decreasing hs-CRP levels. It has the effects of improving coronary microcirculation, anti-inflammation, and anti-platelet aggregation (Meng, 2020). KDL is a processed tablet made from Corydalis Rhizoma, which has anti-myocardial ischaemia, anti-thrombotic, and anti-arrhythmic effects (Sun et al., 2009).
XKS ranked highest for decreasing ET-1 levels, It can also elevate the nitric oxide content, improve the vascular endothelial function (Liu et al., 2022). Studies (Liu et al., 2016) have shown it protects cardiac function by inhibiting the myocardium Ca (2+) overloading and metabolic alterations. It also promotes angiogenesis through multiple signaling pathways, including metabolic pathways, the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, the VEGF signaling pathway, the PPAR signaling pathway, and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (Liu Q. et al., 2023). SXTXD is second only to XKS in reducing ET-1. It can regulate the cellular autophagy process, promote smooth muscle cell proliferation and differentiation, exert anti-inflammatory effects, and optimize lipid metabolism (Chang et al., 2022).
YDXNT ranked highest for increasing NO levels. Studies have shown it has the effect of repairing damaged endothelial cells, reducing the release of endothelin, dilating blood vessels, and improving coronary microcirculation (Yang et al., 2023); it also can exert anti-inflammatory effects by decreasing IL-1β, IL-8, and IL-18 via the TLR4 pathway (Wang et al., 2014). In addition, it relieves atherosclerosis through regulating lipids, reducing lipid particle deposition in the endothelial layer of the artery, enhancing antioxidant power, and repressing inflammatory activity by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappa B signal pathway (Cheng et al., 2015).
Overall, these commonly used herbs and their preparations appear to address key pathophysiological mechanisms of CMD, including oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, atherosclerosis, vascular endothelial dysfunction, and abnormal energy metabolism. By combining multiple active ingredients, CCPPs may offer synergistic effects; however, further well-designed studies are needed to determine optimal dosages, assess long-term safety, and elucidate their clinical utility.
4.5 Key active herbal components
Our study’s most frequently used herbs were Panax ginseng, Salvia miltiorrhiza, Panax notoginseng, Moschus, and Borneolum. A total of 45 experimental studies were identified to investigate the effects and mechanisms of the main active components of single-flavored Chinese medicine, which were frequently used in CMD. Table 4 lists the Mechanisms of the main active components of single-flavored Chinese Medicine on CMD. The structural formula of the main active components are showed in Figure 14. The possible mechanisms of them are summarized as follows:
4.5.1 Anti-atherosclerosis
Structural changes in the coronary microcirculation include remodelling and narrowing of the microvasculature, which ultimately leads to an increase in coronary microcirculatory resistance and a decrease in coronary blood flow. Therefore, anti-atherosclerosis is considered an important step in the prevention of CMD. Studies have shown that Ginsenoside Rb1 and Borneol ameliorated atherosclerosis via inhibiting macrophage foam-cell formation −/− (He et al., 2025; Qiao et al., 2017); Ginsenoside Rc ameliorated atherosclerosis via regulating gut microbiota and faecal metabolites (Xie et al., 2022); Salvianic acid A ameliorates atherosclerosis through metabolic-dependent anti-EndMT pathway and repression of TGF-β/ALK5 signaling (Gao et al., 2025); Salvianic acid B can promote the expression of tRF-Glu-CTC-014 to treat atherosclerosis (Chang et al., 2024); Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) mitigates atherosclerosis via promoting Nrf2-mediated inhibition of ferroptosis through reducing USP2-mediated Keap1 deubiquitination (Zhao et al., 2024).
4.5.2 Inhibition of aberrant proliferation and migration of VSMCs
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are considered a major component of the vascular wall and regulators responsible for maintaining vascular tension. During ischaemia-reperfusion, activation of MAPK and inflammation-related signalling pathways induces abnormal proliferation and migration of VSMC, the latter being a key event in the development of atherosclerotic lesions, which leads to narrowing of the microvascular lumen. One study reported that GS-Re could inhibit the proliferation of VSMCs by mediating G0/G1 cell cycle arrest via eNOS/NO/cGMP signalling pathway (Gao et al., 2019); another study reported that Ginsenoside Rg1 (Ma et al., 2006) could inhibit the proliferation of VSMCs via the PKC-zeta and p21 pathway.
4.5.3 Protection of the vascular endothelium
Endothelial dysfunction is one of the major mechanisms of CMD, which can be classified as Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation or Impaired endothelium-independent vasodilation. The former is mainly caused by stimuli such as cigarette smoking, hypertension, hyperglycaemia, chronic inflammation, and other stimuli induced by vascular endothelial injury, resulting in a decrease in endothelium-mediated diastolic capacity. The latter mainly involves the decreased reactivity of coronary arteries to vasodilating substances. One study reported that Ginsenoside Rb1 could effectively block resistin-induced eNOS downregulation and ROS production (Chen et al., 2010); One study reported that Notoginsenoside R1 could relieve HG-induced endothelial cell injury by downregulating the MyD88/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway via upregulating miR-147a (Li and Huang, 2021); Borneol (Mao and Cai, 2022) could reduce LDH, MDA, and increase GSH, thereby attenuating oxidative stress-induced endothelial damage. One study reported Tanshinone IIA (Wang P. et al., 2024) could induce endothelium-dependent vasodilation via the TRPV4-NO-PKG signaling pathway; another study (Chang et al., 2014) reported Magnesium lithospermate B, an active extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza, could exert anti-vascular spasm through the sGC/cGMP/PKG pathway.
4.5.4 Anti-inflammation
Inflammation and endothelial dysfunction have been shown to be the underlying causes of CMD. Microcirculation is both an important participant in and responsive to the inflammatory response; inflammation can lead to increased vascular permeability and impaired vasomotor function. Ginsenoside Rb1 (Wang S. et al., 2021), Tanshinone II (Meng et al., 2019), dihydrotanshinone I (Yuan et al., 2019), Cryptotanshinone (Li et al., 2020), Salvianolic acid A (Huang et al., 2013), Salvianolic Acid B (Xu et al., 2015), Borneol (Wang et al., 2022), and Muscone (Li L. et al., 2024) were shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects by decreasing interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and NF-κB; One study (Wang Y. et al., 2024) reported that Ginsenoside Rd1 exhibits anti-inflammatory effects via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway; Ginsenoside Rg3 (Ren et al., 2021) represses NLRP3 inflammasome via SIRT1/NF-κB pathway; Notoginsenoside R1 (Cui et al., 2024) exhibits anti-inflammatory effects via the NO-TGFβR1-YAP/TAZ signaling pathway.
4.5.5 Antioxidant stress
Oxidative stress and inflammatory responses caused by the overproduction and accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are the key pathogenic mechanisms driving the development of CMD (Masi et al., 2021). The resulting damage to coronary microvascular endothelial cells is a central part of this process (Del Buono et al., 2021). Studies have shown that Ginsenoside Rb3 (Liu et al., 2014), muscone (Wu et al., 2011) could decrease MDA and increase SOD; Ginsenoside Rg1 (Zhu et al., 2009) could reduce intracellular ROS and increase SOD, CAT, and GSH; Three studies reported Ginsenoside Rc (Shi et al., 2022), Ginsenoside Rg3 (Zhao Y. et al., 2021), and Tanshinone I (Wu et al., 2021) Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Modulating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling; One study reported Tanshinone IIA (Zhu et al., 2017) Inhibits Oxidative Stress via inhibiting CLIC1 expression and membrane translocation; and One study reported Salvianolic acid A (Qiao et al., 2024) reduce LDH, ROS and increase SOD by downregulating miR-204-5p.
4.5.6 Improving energy metabolism
Ischaemia and hypoxia can impair energy metabolism, causing increased endothelial cell apoptosis, autophagy hyperactivation, and dysfunction. Two studies reported that Ginsenoside Rb1 (Li and Zhang, 2022) and Ginsenoside Re can significantly reduce I/R injury through the Nrf2/HO-1/PGC-1α pathway, thereby increasing the number of mitochondria, improving mitochondrial function, enhancing the ability of cells to resist oxidative stress, and alleviating cell apoptosis (Xin et al., 2024); One study reported that Ginsenoside Rh1 mitigates mitochondrial dysfunction induced by myocardial ischaemia through activating sirtuin 3 (Gong et al., 2025); Tanshinone IIA increases the expression of 14-3-3η and regulates the Akt/Beclin1 pathway, thereby inhibiting excessive autophagy during ischemia and hypoxia, improving mitochondrial energy supply, and ultimately protecting cells from injury (Wen et al., 2023); A study showed that Rg1 binds to RhoA and downregulates the activity of the RhoA signalling pathway to regulate energy metabolism and inhibit myocardial apoptosis (Li et al., 2018).
4.5.7 Antiplatelet activation and aggregation
Microthrombi are one of the mechanisms causing coronary microcirculatory dysfunction. In particular, microthrombi and plaque fragments generated by treatment during percutaneous coronary intervention may lead to distal microvascular occlusion. One study reported that 15,16-Dihydrotanshinone I could exert potent anti-platelet activity by suppressing [Ca2+]i mobilization and arachidonic acid liberation (Park et al., 2008); Cryptotanshinone could effectively inhibit platelet activation in a manner that is independent of the P2Y12 receptor, and the effects appeared to be mediated through intricate signaling pathways, including PI3K-AKT, MAPK, and STAT3 (Xiao et al., 2025); Salvianolic acid B could inhibit thrombosis by directly blocking the catalytic site of thrombin (Neves et al., 2024); One study demonstrated that the combination of PNS and aspirin potentiated the antiplatelet effect of aspirin via AA/COX-1/TXB2 pathway in platelets (Wang W. et al., 2021).
4.5.8 Promote angiogenesis
In Coronary microvascular disease, the decreased production of NO by impaired endothelial cells also increases collagen deposition, reduces angiogenesis and collateral development, and promotes the conversion of endothelial cells into mesenchymal cells, leading to microvascular rarefaction (Vancheri et al., 2020). Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an important regulator of microvascular neovascularisation, which induces the division of CMECs into newborns, promotes the establishment of collateral circulation, and meets part of the metabolic needs of ischemic cardiomyocytes. One study reported that Ginsenoside Rb1 increased the expression of VEGF (Liu et al., 2008), Three studies reported Tanshinone IIA (Xu et al., 2009), Muscone (Du et al., 2018), and Borneol (Wang et al., 2022) could promote angiogenesis via the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway; Panax notoginseng Saponins could promote angiogenesis via the microRNA 200a Methylation Pathway (Wang J. et al., 2024).
4.6 Limitations
This study compares the therapeutic effects of nine CCPPs and draws relevant conclusions. However, there are still some limitations here, including: (1) Interpretation and global relevance: All included trials were conducted in China, which limits generalisability to other populations, as genetic and environmental factors may influence drug efficacy; (2) Network geometry limitations: There is no closed loop between studies; NMA relies on indirect comparisons. Sparse connections, lack of closed loops, and absence of multi-arm trials may weaken the transitivity assumption and reduce the precision of indirect comparisons. (3) Diagnostic heterogeneity: Varying and sometimes non-validated definitions of CMD (e.g., symptom-based diagnosis, TTDE, variable CFR cut-offs) may introduce misclassification bias. (4) No adjustment for baseline covariates: Differences in patient characteristics, baseline CMD severity, and concomitant therapies were not accounted for in the NMA, potentially confounding results. (5) Potential publication bias: All included studies report positive effects; the absence of negative trials raises the possibility of reporting bias. (6) Evidence certainty: Given high/unclear risk of bias and lack of robust indirect evidence, the GRADE certainty for most outcomes is low; conclusions should be framed as hypothesis-generating rather than definitive. (7) Exclusion of international pharmacotherapy comparators: Standard CMD drugs (e.g., nicorandil, ranolazine, zibotentan) were not included in the network; therefore, the results cannot be directly compared to current international guideline-based treatments. (8) Research quality: Many trials have small sample sizes, increasing the risk of Type I/II errors and unstable SUCRA rankings. The absence of placebo-controlled and multicentre trials diminishes the robustness of the research findings.
5 Conclusion
This is among the first to evaluate the IMR and CFR to assess different CCPPs for CMD. The current NMA identified SXBX, XB, TXL, YXTL, XKS, and YDXNT as the most effective CCPPs for lowering IMR and LDL-C levels, improving CFR, reducing angina attack frequency, lowering hs-CRP levels, lowering ET-1 levels, and increasing NO levels. Moreover, the research emphasized the beneficial effects of CCPPs in CMD patients and further explored the possible mechanisms. Our research emphasizes that some CCPPS may have advantages in specific outcomes, but the results are hypothesis-generating and suggest some CCPPs may be associated with improvements in specific outcomes; confirmation in multicenter, head-to-head RCTs is needed.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
WW: Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. JZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. XW: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YxL: Software, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YdL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. FP: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZY: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JW: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. HZ: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. TL: Validation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. PC: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Guo Weiqin National Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Studio Project (No. 401091402) and National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (2023-NHLHCRF-BQ-21).
Acknowledgments
We would like to gratefully acknowledge all of the investigators participating in this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1642864/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
CCPP, commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation; CMD, Coronary microvascular dysfunction; CAD, coronary artery disease; NMA, network meta-analysis; CNKI, China National Knowledge Infrastructure; VIP, China Science and Technology Journal Database; CBM, Chinese Biomedical Literature database; RCTs, randomized controlled trials; SXBX, Shexiangbaoxin Pill; TXL, Tongxinluo Capsule; SXTXD, Shexiangtongxindi Pill; YDXNT, Yindanxinnaotong Capsule; KDL, Kedalin Tablet; XB, Xinbao Pill; XKS, Xinkeshu Tablet; DAXXK, Diaoxinxuekang Capsule; YXTL, Yixintongluo Capsule; IMR, the Index of Microcirculatory Resistance; CFR, Coronary Flow Reserve; hs-CRP, hypersensitive C-reactive protein; ET-1, Endothelin-1; NO, Nitric oxide; LDL-C, Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CT, Conventional therapy; SUCRA, Surface under the cumulative ranking curve; RR, Risk ratio; MD, Mean difference; 95%CI, 95% confidence interval; ADRs, adverse drug reactions.
References
Aljizeeri, A., Ahmed, A. I., Suliman, I., Alfaris, M. A., Elneama, A., and Al-Mallah, M. H. (2023). Incremental prognostic value of positron emission tomography-derived myocardial flow reserve in patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc Imaging 24, 563–571. doi:10.1093/ehjci/jead023
Arnold, J. R., Kanagala, P., Budgeon, C. A., Jerosch-Herold, M., Gulsin, G. S., Singh, A., et al. (2022). Prevalence and prognostic significance of microvascular dysfunction in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 15, 1001–1011. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2021.11.022
Bai, Y. H., Chen, Y., Ren, Q. X., Wang, Y., and Cao, B. (2022). Effect of shexiangbaoxin pills combined with nicorandil on microcirculatory resistance index in patients with coronary microcirculatory disorders. J. Difficult Dis. 21, 119–123+129. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2022.02.003
Camici, P. G., and Crea, F. (2007). Coronary microvascular dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 830–840. doi:10.1056/NEJMra061889
Chang, C. Z., Wu, S. C., and Kwan, A. L. (2014). Magnesium lithospermate B, an active extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza, mediates sGC/cGMP/PKG translocation in experimental vasospasm. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 272101. doi:10.1155/2014/272101
Chang, C., Ren, Y., and Su, Q. (2022). Exploring the mechanism of shexiang tongxin dropping pill in the treatment of microvascular angina through network pharmacology and molecular docking. Ann. Transl. Med. 10, 983. doi:10.21037/atm-22-3976
Chang, X., Du, M., Wei, J., Zhang, Y., Feng, X., Deng, B., et al. (2024). Serum tsncRNAs reveals novel potential therapeutic targets of salvianolic acid B on atherosclerosis. Phytomedicine 134, 155994. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155994
Chen, C., Jiang, J., Lü, J. M., Chai, H., Wang, X., Lin, P. H., et al. (2010). Resistin decreases expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase through oxidative stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 299, H193–H201. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00431.2009
Chen, B. Z., Feng, Z. R., Feng, M. J., Wang, Z. M., You, W. W., Chang, F. Y., et al. (2019). Clinical efficacy of xinkeshu tablets in the treatment of coronary microcirculation disorders and its effect on vascular endothelial function. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 17, 1861–1864. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1772-1349.2019.12.028
Chen, B. Z., Feng, M. J., Chang, F. Y., Sun, Z. G., Zhang, Y., Feng, Z. R., et al. (2022). Effect of shexiangbaoxin pills on vascular endothelial function in patients with coronary microcirculatory disorders. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 20, 182–184. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2022.01.041
Chen, W., Ni, M., Huang, H., Cong, H., Fu, X., Gao, W., et al. (2023). Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of coronary microvascular diseases. MedComm 4, e438. doi:10.1002/mco2.438
Chen, Q., Zou, J., Shi, Y., Zhang, X., Guo, D., Luan, F., et al. (2024). Chinese patent medicine tongxinluo: a review on chemical constituents, pharmacological activities, quality control, and clinical applications. Phytomedicine 132, 155674. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155674
Chen, W., Luo, X., Li, W., Li, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, R., et al. (2025). Uncovering the active ingredients of xinbao pill against chronic heart failure: a chemical profiling, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics integrated study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 342, 119418. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2025.119418
Cheng, L., Pan, G. F., Zhang, X. D., Wang, J. L., Wang, W. D., Zhang, J. Y., et al. (2015). Yindanxinnaotong, a Chinese compound medicine, synergistically attenuates atherosclerosis progress. Sci. Rep. 5, 12333. doi:10.1038/srep12333
Chu, Y. X. (2021). Efficacy of shexiagbaoxin pill combined with nicorandil on coronary microcirculatory disorders after angina pectoris. Chin. Sci. Technol. J. Database (full text version) Med. Health Care.
Crea, F., Camici, P. G., and Bairey, M. C. (2014). Coronary microvascular dysfunction: an update. Eur. Heart J. 35, 1101–1111. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/eht513
Cui, X., Zhang, L., Lin, L., Hu, Y., Zhang, M., Sun, B., et al. (2024). Notoginsenoside R1-Protocatechuic aldehyde reduces vascular inflammation and calcification through increasing the release of nitric oxide to inhibit TGFβR1-YAP/TAZ pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 143, 113574. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113574
Del Buono, M. G., Montone, R. A., Camilli, M., Carbone, S., Narula, J., Lavie, C. J., et al. (2021). Coronary microvascular dysfunction across the spectrum of cardiovascular diseases: JACC state-of-the-art review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 78, 1352–1371. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.07.042
Dimitriadis, K., Pyrpyris, N., Sakalidis, A., Dri, E., Iliakis, P., Tsioufis, P., et al. (2024). ANOCA updated: from pathophysiology to modern clinical practice. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 71, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.carrev.2024.09.010
Dimitriadis, K., Pyrpyris, N., Sakalidis, A., Beneki, E., Chrysohoou, C., Aznaouridis, K., et al. (2025). The prognostic role of microvascular resistance reserve: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. S1553-8389 (25), 00167–00168. doi:10.1016/j.carrev.2025.04.016
Du, Y., Ge, Y., Xu, Z., Aa, N., Gu, X., Meng, H., et al. (2018). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α)/Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway participates in angiogenesis of myocardial infarction in Muscone-Treated mice: preliminary study. Med. Sci. Monit. 24, 8870–8877. doi:10.12659/MSM.912051
Fang, Y. Y., Hu, Z. Q., Wu, G., and Wei, X. (2018). The efficacy of tongxinluo capsule in the treatment of cardiac X syndrome combined with diabetes mellitus. J. Difficult Dis. 17, 325–328. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2018.04.001
Feng, Z. B., Li, C. M., Cheng, Y. N., and Yuan, B. (2005). Clinical study of tongxinluo capsule in the treatment of cardiac X syndrome. J. Baikouen Mil. Med. Coll., 25–26. doi:10.16485/j.issn.2095-7858.2005.01.011
Ford, T. J., Stanley, B., Good, R., Rocchiccioli, P., McEntegart, M., Watkins, S., et al. (2018). Stratified medical therapy using invasive coronary function testing in angina: the CorMicA trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 72, 2841–2855. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.006
Fu, C. H. (2021). Clinical observation on the treatment of coronary artery microvascular disease with shexiangbaoxin pill combined with conventional Western medicine. Chin. Folk. Rem. 29, 88–92. doi:10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.2021.1133
Fu, Y. Y., Li, M., and Hu, Z. J. (2020). Observations on the effect of cardiac X syndrome in the adjuvant treatment of kotorine. Chin. Rural. Med. 27, 24–25. doi:10.19542/j.cnki.1006-5180.004047
Gao, Y., Zhu, P., Xu, S. F., Li, Y. Q., Deng, J., and Yang, D. L. (2019). Ginsenoside re inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC proliferation via the eNOS/NO/cGMP pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 115, 108934. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108934
Gao, Y., Ye, F., Dong, Y., Wang, T., Xiong, L., Chen, T., et al. (2025). Salvianic acid A ameliorates atherosclerosis through metabolic-dependent anti-EndMT pathway and repression of TGF-β/ALK5 signaling. Phytomedicine 136, 156307. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156307
Gdowski, M. A., Murthy, V. L., Doering, M., Monroy-Gonzalez, A. G., Slart, R., and Brown, D. L. (2020). Association of isolated coronary microvascular dysfunction with mortality and major adverse cardiac events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 9, e014954. doi:10.1161/JAHA.119.014954
Gong, Y. M., Si, L., Guo, X. J., Zhang, M., Song, W., Zhao, B., et al. (2021). Correlation between microvascular angina pectoris and endothelial function and the effect of combined Chinese and Western medicine treatment. Chin. J. Evidence-Based Cardiovasc. Med. 13, 701–704+725. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2021.06.14
Gong, S., Chen, H., Fang, S., Li, M., Hu, J., Li, Y., et al. (2025). Ginsenoside Rh1 mitigates mitochondrial dysfunction induced by myocardial ischaemia through its novel role as a sirtuin 3 activator. Br. J. Pharmacol. 182, 3017–3035. doi:10.1111/bph.70022
Gu, J. J., Hou, Y. L., Yan, Y. H., Li, J., Wei, Y. R., Ma, K., et al. (2023). Tongxinluo promotes endothelium-dependent arteriogenesis to attenuate diabetic peripheral arterial disease. World J. Diabetes 14, 234–254. doi:10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.234
Guyatt, G., Oxman, A. D., Akl, E. A., Kunz, R., Vist, G., Brozek, J., et al. (2011). GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64, 383–394. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026
He, R. R., Ma, C. R., He, X., Dong, Y. X., Li, H., Chu, Z. X., et al. (2025). Circulating metabolites of borneolum syntheticum (bingpian) ameliorate atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) mice via inhibiting macrophage foam-cell formation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 46, 759–776. doi:10.1038/s41401-024-01406-5
Heinrich, M., Jalil, B., Abdel-Tawab, M., Echeverria, J., Kulić, Ž., McGaw, L. J., et al. (2022). Best practice in the chemical characterisation of extracts used in pharmacological and toxicological research-The ConPhyMP-Guidelines. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 953205. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.953205
Hsu, E. (2009). Chinese propriety medicines: an “alternative modernity?” the case of the anti-malarial substance artemisinin in East Africa. Med. Anthropol. 28, 111–140. doi:10.1080/01459740902848303
Huang, J., Qin, Y., Liu, B., Li, G. Y., Ouyang, L., and Wang, J. H. (2013). In silico analysis and experimental validation of molecular mechanisms of salvianolic acid A-inhibited LPS-stimulated inflammation, in RAW264.7 macrophages. Cell Prolif. 46, 595–605. doi:10.1111/cpr.12056
Hutton, B., Salanti, G., Caldwell, D. M., Chaimani, A., Schmid, C. H., Cameron, C., et al. (2015). The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern Med. 162, 777–784. doi:10.7326/M14-2385
Jiang, Q. Q., Feng, Z. R., Cui, J. Z., and Chang, Y. F. (2024). Effect of tongxinluo assisted nicorandil on the expression of serum tryptase and copeptin in patients with myocardial infarction coronary microcirculation disorder. Chin. J. Gerontology 44, 1285–1287. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2024.06.002
Kang, T., Dou, D., and Xu, L. (2019). Establishment of a quality marker (Q-marker) system for Chinese herbal medicines using burdock as an example. Phytomedicine 15, 339–346. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.005
Kelshiker, M. A., Seligman, H., Howard, J. P., Rahman, H., Foley, M., Nowbar, A. N., et al. (2022). Coronary flow reserve and cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 43, 1582–1593. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab775
Khandkar, C., Rehan, R., Ravindran, J., and Yong, A. (2025). An updated review on therapeutic strategies in coronary microvascular dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiol. 428, 133128. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2025.133128
Knuuti, J., Wijns, W., Saraste, A., Capodanno, D., Barbato, E., Funck-Brentano, C., et al. (2020). 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 41, 407–477. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehz425
Kunadian, V., Chieffo, A., Camici, P. G., Berry, C., Escaned, J., Maas, A., et al. (2020). An EAPCI expert consensus document on ischaemia with non-obstructive coronary arteries in collaboration with european society of cardiology working group on coronary pathophysiology and microcirculation endorsed by coronary vasomotor disorders international study group. Eur. Heart J. 41, 3504–3520. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa503
Li, K. R. (2021). Study on the effect of shexiangtongxindi pill on the improvement of slow blood flow in coronary arteries. North. Pharm. 18, 33–34.
Li, X. Q., and Huang, T. Y. (2021). Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates high glucose-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in HUVECs via upregulating miR-147a. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 37, 1101–1112. doi:10.1002/kjm2.12433
Li, S. Y., and Tang, Q. (2009). Clinical observation on 36 cases of cardiac X syndrome treated with Tongxinluo capsule combined with Western drugs. Yunnan J. Traditional Chin. Med. 30, 15–16. doi:10.16254/j.cnki.53-1120/r.2009.11.043
Li, Y., and Zhang, W. (2022). Effect of ginsenoside Rb2 on a myocardial cell model of coronary heart disease through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 45, 71–76. doi:10.1248/bpb.b21-00525
Li, L., Pan, C. S., Yan, L., Cui, Y. C., Liu, Y. Y., Mu, H. N., et al. (2018). Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates rat myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating energy metabolism pathways. Front. Physiol. 9, 78. doi:10.3389/fphys.2018.00078
Li, X. X., Zheng, X., Liu, Z., Xu, Q., Tang, H., Feng, J., et al. (2020). Cryptotanshinone from Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge (danshen) inhibited inflammatory responses via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Chin. Med. 15, 20. doi:10.1186/s13020-020-00303-3
Li, D., Chen, R., Xu, X., Hou, Y., Li, Z., Huang, C., et al. (2024a). Integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanisms of shexiang baoxin pill against atherosclerosis. Phytomedicine 135, 156138. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156138
Li, L., Zhuang, S., and Jiang, S. (2024b). Muscone inhibits the progression of atherosclerotic plaques in mice aorta by inhibiting the NF-κB/p65 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 702, 149628. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149628
Liang, Y. F., Ye, Y., Zhang, J. M., Cui, Y., Yu, R. Q., and Huang, Q. (2019). 38 cases of primary stable microvascular angina pectoris treated with cardiac kosher tablets. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 39, 406–409. doi:10.16367/j.issn.1003-5028.2019.03.0101
Lin, C., Pan, J. L., Li, H., Chen, Y., Gu, X. H., and Huang, M. Y. (2023). Clinical observation on the effect of yanhuosuo on the function of coronary microcirculation. Prev. Treat. Cardiovasc. Dis. 23, 9–12. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-816x.2023.06.003
Liu, H., Hu, Y. C., and Chen, J. (2003). Effect of tongxinluo on vascular endothelial function in patients with syndrome X. J. Difficult Dis., 218–219.
Liu, Y. F., Liu, S. W., and Liu, Z. X. (2008). Effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on vascular regeneration after myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion in rats. Chin. J. Histochem. Cytochem., 39–44.
Liu, X., Jiang, Y., Yu, X., Fu, W., Zhang, H., and Sui, D. (2014). Ginsenoside-Rb3 protects the myocardium from ischemia-reperfusion injury via the inhibition of apoptosis in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 8, 1751–1756. doi:10.3892/etm.2014.2007
Liu, Y. T., Zhou, C., Jia, H. M., Chang, X., and Zou, Z. M. (2016). Standardized Chinese formula xin-ke-shu inhibits the myocardium Ca(2+) overloading and metabolic alternations in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction rats. Sci. Rep. 6, 30208. doi:10.1038/srep30208
Liu, J. P., Liao, H. C., Liu, L., Zhong, S. G., and Xiao, C. (2018). Clinical observation on the therapeutic effect of shexiangtongxindi pill on patients with cardiac X syndrome. Chin. Med. Sci. 8, 231–233.
Liu, Q., Zhuang, K. Y., Zhang, Y., He, Q. X., Liu, K. C., Xia, Q., et al. (2022). Progress in the study of chemical composition and pharmacological effects of xinkeshu. World Chin. Med. 17, 2965–2972. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2022.20.025
Liu, Q., Zhang, H., An, Y., Zhang, Y., He, Q., Liu, K., et al. (2023a). Xinkeshu tablets promote angiogenesis in zebrafish embryos and human umbilical vein endothelial cells through multiple signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 314, 116636. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116636
Liu, S., Zhang, Z., He, Y., Kong, L., Jin, Q., Qi, X., et al. (2023b). Inhibiting leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions by Chinese medicine tongxinluo capsule alleviates no-reflow after arterial recanalization in ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 29, 3014–3030. doi:10.1111/cns.14242
Lu, L., Qin, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, C., Xu, X., Yu, C., et al. (2019). Shexiang baoxin pill alleviates the atherosclerotic lesions in mice via improving inflammation response and inhibiting lipid accumulation in the arterial wall. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 6710759. doi:10.1155/2019/6710759
Lv, X. L., Zhao, Z. Q., Feng, Z. Q., Feng, J. Y., and Gu, H. M. (2014). Effect of tongxinluo capsule on endothelial function and inflammatory factors in patients with cardiac X syndrome. J. Pract. Clin. Med. 18, 135–136. doi:10.7619/jcmp.201421046
Ma, F. J., and Xu, J. H. (2006). A study of the clinical application of tongxinluo in patients with cardiac syndrome X. Shanghai Pharm., 465–466.
Ma, Z. C., Gao, Y., Wang, Y. G., Tan, H. L., Xiao, C. R., and Wang, S. Q. (2006). Ginsenoside Rg1 inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 27, 1000–1006. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00331.x
Mao, W. J., and Cai, W. (2022). Protective effect of borneol on rat myocardial microvascular endothelial cells after hydrogen peroxide injury. J. Med. Res. 51, 102–107. doi:10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2022.10.023
Masi, S., Rizzoni, D., Taddei, S., Widmer, R. J., Montezano, A. C., Lüscher, T. F., et al. (2021). Assessment and pathophysiology of microvascular disease: recent progress and clinical implications. Eur. Heart J. 42, 2590–2604. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa857
Meng, X. L. (2018). Clinical study on 60 cases of coronary microcirculatory lesions treated with yixin tongluo capsule. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 16, 2069–2071. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2018.14.037
Meng, X. L. (2019). Mechanism study on the prevention and treatment of microcirculation disorders by yixin Tongluo capsule guangming Chinese medicine, 34, 2630–2633. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2019.17.017
Meng, X. L. (2020). Clinical observation on 42 cases of recurrence after PCI in patients with unstable angina pectoris treated with yixin tongluo capsule. Hunan J. Traditional Chin. Med. 36, 1–5. doi:10.16808/j.cnki.issn1003-7705.2020.06.001
Meng, Z., Si, C. Y., Teng, S., Yu, X. H., and Li, H. Y. (2019). Tanshinone IIA inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through the TLR4/TAK1/NF-κB signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 43, 1847–1858. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4100
Morrow, A., Young, R., Abraham, G. R., Hoole, S., Greenwood, J. P., El Shibly, M., et al. (2024). Zibotentan in microvascular angina: a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Circulation 150, 1671–1683. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.069901
Neves, M. A. D., Ni, T. T., Mackeigan, D. T., Shoara, A. A., Lei, X., Slavkovic, S., et al. (2024). Salvianolic acid B inhibits thrombosis and directly blocks the thrombin catalytic site. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 8, 102443. doi:10.1016/j.rpth.2024.102443
Ng, M. K., Yong, A. S., Ho, M., Shah, M. G., Chawantanpipat, C., O'Connell, R., et al. (2012). The index of microcirculatory resistance predicts myocardial infarction related to percutaneous coronary intervention. Circ. Cardiovasc Interv. 5, 515–522. doi:10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.112.969048
Ning, R., Xu, C., Chai, D., and Lin, J. (2011). Effect of shexiang baoxin pill on H2O2-induced proliferation and oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 9, 966–969.
Ong, P., Camici, P. G., Beltrame, J. F., Crea, F., Shimokawa, H., Sechtem, U., et al. (2018). International standardization of diagnostic criteria for microvascular angina. Int. J. Cardiol. 250, 16–20. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.08.068
Padro, T., Manfrini, O., Bugiardini, R., Canty, J., Cenko, E., De Luca, G., et al. (2020). ESC working group on coronary pathophysiology and microcirculation position paper on 'coronary microvascular dysfunction in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res. 116, 741–755. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvaa003
Pan, L., Xu, Z., Wen, M., Li, M., Lyu, D., Xiao, H., et al. (2024). Xinbao pill ameliorates heart failure via regulating the SGLT1/AMPK/PPARα axis to improve myocardial fatty acid energy metabolism. Chin. Med. 19, 82. doi:10.1186/s13020-024-00959-1
Park, J. W., Lee, S. H., Yang, M. K., Lee, J. J., Song, M. J., Ryu, S. Y., et al. (2008). 15,16-dihydrotanshinone I, a major component from Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge (dansham), inhibits rabbit platelet aggregation by suppressing intracellular calcium mobilization. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 47–53. doi:10.1007/s12272-008-1119-4
Peng, D. G. (2011). Observations on the therapeutic effect of yindan xinhuantong soft capsule in the treatment of cardiac X syndrome. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 9, 746–747.
Qi, Y., Sun, Z., Chen, C. W., Lu, C. Z., Wang, L., Li, C. M., et al. (2023). The efficacy of shexiangbaoxin pills in the treatment of coronary microvascular dysfunction in young and middle-aged refractory hypertension. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 21, 3022–3026. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.16.022
Qiao, L., Zhang, X., Liu, M., Liu, X., Dong, M., Cheng, J., et al. (2017). Ginsenoside Rb1 enhances atherosclerotic plaque stability by improving autophagy and lipid metabolism in macrophage foam cells. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 727. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00727
Qiao, X., Cao, S., Chen, S., Guo, Y., Chen, N., Zheng, Y., et al. (2024). Salvianolic acid A alleviates H(2)O(2)-induced endothelial oxidative injury via miR-204-5p. Sci. Rep. 14, 11931. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-62556-4
Qin, H. F., Liu, X. C., Xin, D. M., and Zhang, L. T. (2017). Clinical efficacy of shexiangbaoxin pill in the treatment of microvascular angina pectoris. Pharm. Forum Mag. 38, 147–148.
Qin, X. F., Dou, M., Shan, Y. G., Xu, J. W., Li, F. X., and Guo, Y. X. (2023). Effect of shexiang tongxindi pill on microvascular function and quality of survival in patients with coronary microvascular disease. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 38, 843–847. doi:10.16368/j.issn.1674-8999.2023.04.139
Rehan, R., Yong, A., Ng, M., Weaver, J., and Puranik, R. (2023). Coronary microvascular dysfunction: a review of recent progress and clinical implications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 10, 1111721. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2023.1111721
Ren, B., Feng, J., Yang, N., Guo, Y., Chen, C., and Qin, Q. (2021). Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates angiotensin II-induced myocardial hypertrophy through repressing NLRP3 inflammasome and oxidative stress via modulating SIRT1/NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 98, 107841. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107841
Ren, L., Ning, B., Li, W. J., Su, X., Liu, J., and Yang, Y. Y. (2023). Analysis of the application of dio-cardio-kang soft capsules in coronary heart disease microcirculatory disorders examined by transcardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Chin. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 41, 239–242. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2023.07.047
Rivera, D., Allkin, R., Obón, C., Alcaraz, F., Verpoorte, R., and Heinrich, M. (2014). What is in a name? The need for accurate scientific nomenclature for plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 152, 393–402. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.12.022
Samuels, B. A., Shah, S. M., Widmer, R. J., Kobayashi, Y., Miner, S. E. S., Taqueti, V. R., et al. (2023). Comprehensive management of ANOCA, part 1-Definition, patient population, and diagnosis: JACC state-of-the-art review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 82, 1245–1263. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2023.06.043
Shen, S. X., Zhao, Z. L., Wang, S. B., Du, J. J., Ding, S. K., Wang, L. X., et al. (2021). Clinical efficacy analysis of the effect of shexiangbaoxin pill combined with cardiac rehabilitation on coronary slow blood flow. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 19, 1810–1813. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2021.11.0005
Shi, L., Fu, W., Xu, H., Li, S., Yang, X., Yang, W., et al. (2022). Ginsenoside Rc attenuates myocardial ischaemic injury through antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. Pharm. Biol. 60, 1038–1046. doi:10.1080/13880209.2022.2072518
Sun, Q. L. (2021). Clinical effects of shexiangbaoxin pills in the treatment of patients with combined hyperlipidaemic cardiac X syndrome. China Med. Guide 19, 134–135. doi:10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2021.06.064
Sun, L. Y., Wang, R. W., and Xiong, J. B. (2009). Overview of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular pharmacological effects of kedalin. Med. Her. 28, 628–630. doi:10.3870/yydb.2009.05.036
Sun, M. L., Qu, C., and Guo, S. Y. (2022). Clinical study on the treatment of coronary artery microcirculation disorders by improving vascular endothelial function with shexiangbaoxin pills. Chin. J. Emerg. Resusc. Disaster Med. 17, 98–101+106.
Tamis-Holland, J. E., Jneid, H., Reynolds, H. R., Agewall, S., Brilakis, E. S., Brown, T. M., et al. (2019). Contemporary diagnosis and management of patients with myocardial infarction in the absence of obstructive coronary artery disease: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation 139, e891–e908. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000670
Taqueti, V. R., Hachamovitch, R., Murthy, V. L., Naya, M., Foster, C. R., Hainer, J., et al. (2015). Global coronary flow reserve is associated with adverse cardiovascular events independently of luminal angiographic severity and modifies the effect of early revascularization. Circulation 131, 19–27. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.011939
Vancheri, F., Longo, G., Vancheri, S., and Henein, M. (2020). Coronary microvascular dysfunction. J. Clin. Med. 9, 2880. doi:10.3390/jcm9092880
Vrints, C., Andreotti, F., Koskinas, K. C., Rossello, X., Adamo, M., Ainslie, J., et al. (2024). 2024 ESC guidelines for the management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 45, 3415–3537. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehae177
Wang, H. Z. (2015). Observations on the efficacy of shexiangbaoxin pill in the treatment of cardiac X syndrome. Chin. Disabil. Med. 152-152, 153. doi:10.13214/j.cnki.cjotadm.2015.02.112
Wang, C. G. (2022). Clinical observation on the treatment of microvascular angina pectoris with nicorandil in combination with yindanxinnaotong soft capsule. J. Pract. Chin. Med. 38, 50–52.
Wang, X. M., and Long, J. (2022). Clinical analysis of the treatment of coronary microcirculation disorders with shexiangbaoxin pills. Shenzhen J. Integr. Med. 32, 46–49. doi:10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2022.18.014
Wang, W., Wang, L., Yang, H., Wang, J., Yin, X., Xu, H., et al. (2014). Protective effects of yindanxinnaotong capsule in a rat model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 34, 699–709. doi:10.1016/s0254-6272(15)30085-6
Wang, Z., Xin, D. M., Peng, K., Wang, Q., and Li, D. (2019). The effect of yindan xinhuantong soft capsule on patients with coronary slow-flow microvascular angina pectoris. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 39, 418–422. doi:10.7661/j.cjim.20180907.177
Wang, S., Cui, Y., Xiong, M., Li, M., Wang, P., Cui, J., et al. (2021a). Dual activity of ginsenoside Rb1 in hypertrophic cardiomyocytes and activated macrophages: implications for the therapeutic intervention of cardiac hypertrophy. J. Inflamm. Res. 14, 1789–1806. doi:10.2147/JIR.S310633
Wang, W., Yang, L., Song, L., Guo, M., Li, C., Yang, B., et al. (2021b). Combination of Panax notoginseng saponins and aspirin potentiates platelet inhibition with alleviated gastric injury via modulating arachidonic acid metabolism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 134, 111165. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111165
Wang, L. Y., Wang, J., Fan, Y. M. J. W. J., Fu, Y., Yang, X. J., and Gong, D. Y. (2022). Anti-inflammation and modulation of HIF-1α/VEGF by three borneol against AMI model rats. Chin. J. Exp. Formulary 28, 61–72. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20221009
Wang, B., Pan, X. N., and Yan, L. (2024a). Therapeutic efficacy of diaoxinxuekang soft capsule combined with conventional drugs in the treatment of primary stable microvascular angina pectoris. J. Integr. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 22, 1112–1115. doi:10.12102/ji.ssn.1672-1349.2024.06.029
Wang, J., Dong, Y., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Liu, L., Yang, G., et al. (2024b). Panax notoginseng saponins improve angiogenesis in coronary heart disease based on the microRNA 200a methylation pathway. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 18, 6075–6087. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S488036
Wang, P., Gu, Y., Lu, J., Song, M., Hou, W., Li, P., et al. (2024c). Endothelial TRPV4 channel mediates the vasodilation induced by tanshinone IIA. Chem. Biol. Interact. 402, 111181. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111181
Wang, Y., Zheng, J., Xiao, X., Feng, C., Li, Y., Su, H., et al. (2024d). Ginsenoside Rd attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 52, 433–451. doi:10.1142/S0192415X24500186
Wei, Y. (2018). Study on the effect of treatment with tongxinluo capsule on female patients with microvascular angina pectoris. Contemp. Med. Ser. 16, 172–174.
Wei, B. Y., Hou, J. N., Yan, C. P., Wen, S. Y., Shang, X. S., Guo, Y. C., et al. (2023). Shexiang baoxin pill treats acute myocardial infarction by promoting angiogenesis via GDF15-TRPV4 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165, 115186. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115186
Wen, L., Cheng, X., Fan, Q., Chen, Z., Luo, Z., Xu, T., et al. (2023). TanshinoneⅡA inhibits excessive autophagy and protects myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury via 14-3-3η/via/Beclin1 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 954, 175865. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175865
Wu, Q., Li, H., Wu, Y., Shen, W., Zeng, L., Cheng, H., et al. (2011). Protective effects of muscone on ischemia-reperfusion injury in cardiac myocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 138, 34–39. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.009
Wu, C. Y., Wang, G. M., and Sun, Z. G. (2019). Efficacy of shexiangbaoxin pills combined with nicorandil in the treatment of coronary slow-flow microvascular angina pectoris. Shanghai Pharm. 40, 26–28+43.
Wu, G., Chen, L., Gu, Y., Hong, Y., Ma, J., Zheng, N., et al. (2020). Exploring the mechanism underlying the cardioprotective effect of shexiang baoxin pill on acute myocardial infarction rats by comprehensive metabolomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 259, 113001. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113001
Wu, Y. T., Xie, L. P., Hua, Y., Xu, H. L., Chen, G. H., Han, X., et al. (2021). Tanshinone I inhibits oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte injury by modulating Nrf2 signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 644116. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.644116
Xiao, Y., Zhang, R., Hua, C., Wu, M., Yuan, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2025). P2Y12 receptor-independent antiplatelet mechanism of cryptotanshinone: network pharmacology and experimental validation of multi-target signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 341, 119321. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2025.119321
Xie, X. Y., Hua, J. P., Ren, Y. X., Ding, L., and Sun, H. (2019). “Clinical efficacy of tongxinluo capsule in treating 45 patients with microvascular angina pectoris,” in Proceedings of the 1st international conference on cardiovascular disease ‘Ru Dao Xin Xue’, 214–221.
Xie, B., Zu, X., Wang, Z., Xu, X., Liu, G., and Liu, R. (2022). Ginsenoside Rc ameliorated atherosclerosis via regulating gut microbiota and fecal metabolites. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 990476. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.990476
Xin, G. J., Chen, Y. Y., Liu, Z. X., Xu, S. J., Zhang, H. Y., Guo, F., et al. (2024). Ginsenoside re regulates mitochondrial biogenesis through Nrf2/HO-1/PGC-1α pathway to reduce hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in H9c2 cells. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 49, 1064–1072. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20231017.702
Xu, W., Yang, J., and Wu, L. M. (2009). Cardioprotective effects of tanshinone IIA on myocardial ischemia injury in rats. Pharmazie 64, 332–336.
Xu, S., Zhong, A., Bu, X., Ma, H., Li, W., Xu, X., et al. (2015). Salvianolic acid B inhibits platelets-mediated inflammatory response in vascular endothelial cells. Thromb. Res. 135, 137–145. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2014.10.034
Yang, Y., Chen, T., Liu, J., Chen, S., Cai, R., Wu, L., et al. (2022). Integrated chemical profiling, network pharmacology and pharmacological evaluation to explore the potential mechanism of xinbao pill against myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Pharm. Biol. 60, 255–273. doi:10.1080/13880209.2022.2025859
Yang, B., Sun, J., Lu, Y., Li, Y. J., Huang, Y., Wang, Y. L., et al. (2023). Progress of chemical composition and pharmacological effects of yindan xinbentong soft capsule. Chin. Med. Ethn. groups 32, 76–84. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-8517.2023.13
Yu, Y. W., Liu, S., Zhou, Y. Y., Huang, K. Y., Wu, B. S., Lin, Z. H., et al. (2022). Shexiang baoxin pill attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating autophagy via modulating the ceRNA-Map3k8 pathway. Phytomedicine 104, 154336. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154336
Yuan, R., Huang, L., Du, L. J., Feng, J. F., Li, J., Luo, Y. Y., et al. (2019). Dihydrotanshinone exhibits an anti-inflammatory effect in vitro and in vivo through blocking TLR4 dimerization. Pharmacol. Res. 142, 102–114. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.02.017
Zhang, M. B. (2022). Clinical observation on the treatment of microvascular angina pectoris with xinbao pills. Self-care, 26, 60–62.
Zhang, W. N., Hu, Z. T., Gao, X. D., Peng, X. M., and Zhang, X. G. (2013). Clinical efficacy of Shexiangbaoxin pills in patients with combined hyperlipidaemic cardiac X syndrome. Chin. J. Evidence-Based Cardiovasc. Med. 5, 285–287. doi:10.3969/j.1674-4055.2013.03.025
Zhang, W. Z., Chen, W. J., and Chen, G. L. (2022). Progress in the study of diaoxinxuekang. Prepared prescription, 44, 183–186.
Zhang, C. Y., Hu, H. Y., Shi, M. L., Ma, Y. C., Fauci, A. J., Lee, M. S., et al. (2024). Commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation: current status and future perspectives. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1404259. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1404259
Zhao, D. H., Liu, H., Li, M. Q., Cai, S. A., and Zhang, L. F. (2021a). Therapeutic efficacy of xinbao pills combined with chlorosartan potassium tablets in the treatment of microvascular angina pectoris and the effects on coronary flow reserve function, Angptl2 and Angptl4 levels. J. Difficult Dis. 20, 1224–1228. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2021.12.009
Zhao, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, M., Gao, Y., and Yan, Z. (2021b). Protective effects of ginsenosides (20R)-Rg3 on H(2) O(2) -Induced myocardial cell injury by activating Keap-1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Chem. Biodivers. 18, e2001007. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202001007
Zhao, Y., Zheng, G., Yang, S., Liu, S., Wu, Y., Miao, Y., et al. (2024). The plant extract PNS mitigates atherosclerosis via promoting Nrf2-mediated inhibition of ferroptosis through reducing USP2-mediated Keap1 deubiquitination. Br. J. Pharmacol. 181, 4822–4844. doi:10.1111/bph.17311
Zhu, D., Wu, L., Li, C. R., Wang, X. W., Ma, Y. J., Zhong, Z. Y., et al. (2009). Ginsenoside Rg1 protects rat cardiomyocyte from hypoxia/reoxygenation oxidative injury via antioxidant and intracellular calcium homeostasis. J. Cell Biochem. 108, 117–124. doi:10.1002/jcb.22233
Zhu, J., Xu, Y., Ren, G., Hu, X., Wang, C., Yang, Z., et al. (2017). Tanshinone IIA sodium sulfonate regulates antioxidant system, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis by downregulation of CLIC1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 815, 427–436. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.09.047
Zhu, H., Xu, X., Fang, X., Zheng, J., Zhao, Q., Chen, T., et al. (2019). Effects of the antianginal drugs ranolazine, nicorandil, and ivabradine on coronary microvascular function in patients with nonobstructive coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Ther. 41, 2137–2152.e12. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.08.008
Keywords: commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation, coronary microvascular dysfunction, frequentist framework, network meta-analysis, randomized controlled trials
Citation: Wang W, Zhang J, Wang X, Li Y, Li Y, Pu F, Yang Z, Wan J, Zhu H, Li T and Chang P (2025) Comparative efficacy of commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation for coronary microvascular dysfunction: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1642864. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1642864
Received: 07 June 2025; Accepted: 16 October 2025;
Published: 04 November 2025.
Edited by:
Arquimedes Gasparotto Junior, Federal University of Grande Dourados, BrazilReviewed by:
Mingjun Zhao, Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaSalviano Tramontin Bellettini, Universidade Paranaense, Brazil
Athanasios Sakalidis, Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zhang, Wang, Li, Li, Pu, Yang, Wan, Zhu, Li and Chang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tianli Li, MTA5OTE4ODA5MkBxcS5jb20=; Peifen Chang, MTM2NjEwMjIwMTZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Wujiao Wang
Wujiao Wang Jun Zhang2†
Jun Zhang2† Yuxuan Li
Yuxuan Li Fenglan Pu
Fenglan Pu Tianli Li
Tianli Li