Abstract
The annual burden of gastric cancer (GC) is increasing, highlighting a major threat to global public health. An important contributing factor to the increased fatality of the disease is the late stage at which GC is usually detected. Recent advancements in genomic and molecular studies have spearheaded the discovery of novel biomarkers for early-stage GC. Enabled by metabolomic, genetic, epigenetic, and proteomic signatures, these biomarkers have the potential to change the diagnostic outlook for GC. Such biomarkers would allow the detection of disease in its early stages, thereby improving the quality of life of those affected by this disease and also lowering the mortality rate. This review aims to provide a thorough overview of the novel biomarkers in GCs. Furthermore, this review addresses the mechanism by which these biomarkers are linked to the detection of GC and their possible utilization in clinical settings. This review comprises several novel biomarkers such as heat shock protein family A6 (HSPA6), annexin A11 (ANXA11), cell division cycle 42 (CDC42), fibroblast activation protein-alpha (FAP), hepcidin antimicrobial peptide (HAMP), solute carrier family 25 member 4 (SLC25A4), serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1), cystatin B, deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 (DMBT1), nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1), N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs, circular RNAs, and proteinase 3 (PRTN3). Thus, the aim of this review is to gather and incorporate the current state of knowledge on this topic to point out the need for persistent research and innovation in the field of identification of GC biomarkers. This will enable the opportunity for new and more effective strategies for combating GC, which will further reduce its global burden and improve patient survival.

1 Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is a serious global health concern. With more than a million new cases and 769,000 associated deaths in 2020, GC ranks fourth in the world for mortality among malignancies and fifth for incidence (Mamun et al., 2024). The researchers of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) forecast that by 2040, the annual load of GC will rise to 1.8 million new cases and approximately 1.3 million deaths (Thrift et al., 2023), depicting a 63% increase in new cases and a 66% increase in deaths. Stomach cancer is the most common cancer in China, Bhutan, Cabo Verde, and Tajikistan, and it affects a large portion of Eastern Asia. Men in eastern Asian nations such as Japan, Mongolia, and the Republic of Korea had the greatest incidence rates, while men in Africa had the lowest incidence rates (Organization, 2025). The incidence and fatality rates differ across various geographic and racial groups. In several South-Central Asian nations, GC is the most often diagnosed malignant tumor and the leading cause of cancer-related death. Additionally, North America and Northern Europe have the lowest incidence rates of GC, while Eastern Asia and Eastern Europe have the highest rates (Sung Y.-K. et al., 2020).
GC is a diverse illness that can present with different phenotypes and molecular profiles (Knight and Allum, 2019). Precancerous lesions, hereditary factors, and Helicobacter pylori infection are the main causes of GC (Zhang et al., 2019; Smyth et al., 2020). Men are 2–3 times more likely than women to develop this cancer, and they also die from it at a higher rate (Sung H. et al., 2020). The prevalence of GC varies by geographic region and cultural background, and emerging nations like Iran account for more than 50% of new cases (Bray et al., 2018). In the world, after malignancies of the lung, breast, colorectal, and prostate, GC is the fifth-most prevalent malignant tumor. Although its incidence rate has decreased recently, it is still the third most common cancer-related cause of death globally (Bray et al., 2018; Ferlay et al., 2019). In China, the national population-based cancer registry shows that GC has the third-highest incidence and tumor-associated death rates (Li P. et al., 2024). This conclusion can be linked to the high prevalence of postoperative local recurrence and distant metastasis, the poor treatment outcomes, and the fact that most stomach cancer patients are already at an advanced stage at diagnosis (Siegel et al., 2020).
According to the Ming classification, which corresponds to the Bormann classification (protrusion and ulcer type), the Lauren classification (intestinal and diffuse type), and the WHO classification (papillary adenocarcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, carcinoid, etc.), GC is separated into infiltrative GC (IGC) and expanding GC (EGC) (Luebke et al., 2005). IGC occurs 61.5% of the time and has a worse prognosis than EGC (Zhang L. et al., 2023). Biomarkers are traits that can be objectively examined and assessed to serve as markers for normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacological responses to therapeutic interventions (Smyth et al., 2020). It is understandable why the field of GC biomarkers has drawn so much attention. Some indicators of GC-related DNA, RNA, and exosomes have been found in recent investigations. Despite advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, the prognosis for GC patients remains poor, largely due to late-stage diagnosis and high rates of recurrence and metastasis. In recent years, the exploration of molecular biomarkers has gained significant attention for their potential to improve early detection, monitor disease progression, and guide personalized treatment strategies (Hanash et al., 2011; Sethi et al., 2013). Biomarkers are measurable indicators of biological or pathological processes and can be detected in tissue, blood, or other bodily fluids (Ahmad et al., 2023). They offer valuable insights into the molecular alterations involved in gastric tumor initiation, progression, immune evasion, and response to therapy (Carlomagno et al., 2017).
Conventional serum markers often fail to detect GC at curable stages or distinguish it from benign conditions, resulting in missed opportunities for timely intervention. Conventional serum tumor markers used in GC, such as CEA, CA19-9, and CA72-4, are constrained by low sensitivity and specificity, particularly for early-stage disease. For instance, positive detection rates for early GC are often below 10%, even when combining markers severely limiting early diagnosis (Yu et al., 2016; Feng et al., 2017). To overcome these limitations, novel biomarkers are being actively explored, including genomic, epigenetic, transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic, and liquid biopsy-based candidates. Recent studies have identified promising biomarker classes such as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), exosomal miRNAs, DNA methylation markers, and immune checkpoint molecules, many of which offer enhanced diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive value (Jelski and Mroczko, 2022; Jiang et al., 2022). However, challenges remain in their clinical translation. Most novel biomarkers lack validation in large-scale, multicenter studies, and few have progressed to routine clinical use (Hong and Liu, 2022; Romańczyk et al., 2024). In addition, standardization of assay techniques, inter-individual variability, and cost-effectiveness remain significant barriers. It is anticipated that the development of these biomarkers will have a significant impact on the progression of cancer, the choice of effective therapy approaches, and effective follow-up programs (Smyth et al., 2020).
This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of tissue, salivary, and urine-based biomarkers for GC, highlighting recent advances, clinical relevance, and future directions. By critically evaluating the landscape of GC biomarker research, this review addresses the pressing clinical need for non-invasive, sensitive, and specific biomarkers that can improve early detection, risk stratification, and treatment outcomes in GC.
2 Signaling pathways associated with GC
Epidemiologic and experimental data support the causal role of H. pylori infection in GC. Several factors interact to determine whether the infection will cause multifocal atrophic gastritis or non-atrophic gastritis. The latter is the precancerous cascade’s first stage. Robin Warren and Barry Marshall received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2005 for their revolutionary study connecting infection of H. pylori to GC and peptic ulcer (Charitos et al., 2021). It has been established that the potential of H. pylori to induce GC is correlated with its virulence, which is mostly influenced by the vacuolating toxin VacA and cytotoxin CagA (Sharndama and Mba, 2022). Intestinal metaplasia, serious gastritis, GC, and cytotoxin CagA have all been associated with vacAs1m1- and CagA-positive bacterial genotypes (Kishk et al., 2021). VaccinAs2m2 genotypes that are CagA-negative cause less infection, they cause a milder form of non-atrophic gastritis, and neoplastic outcomes are not always the consequence (Park J. Y. et al., 2018). In addition to H. pylori, there are various other factors, such as radiation, genetic factors, hypoxia, etc., that can lead to the development of GC. Figure 1 displays the pathogenesis of GC.
FIGURE 1
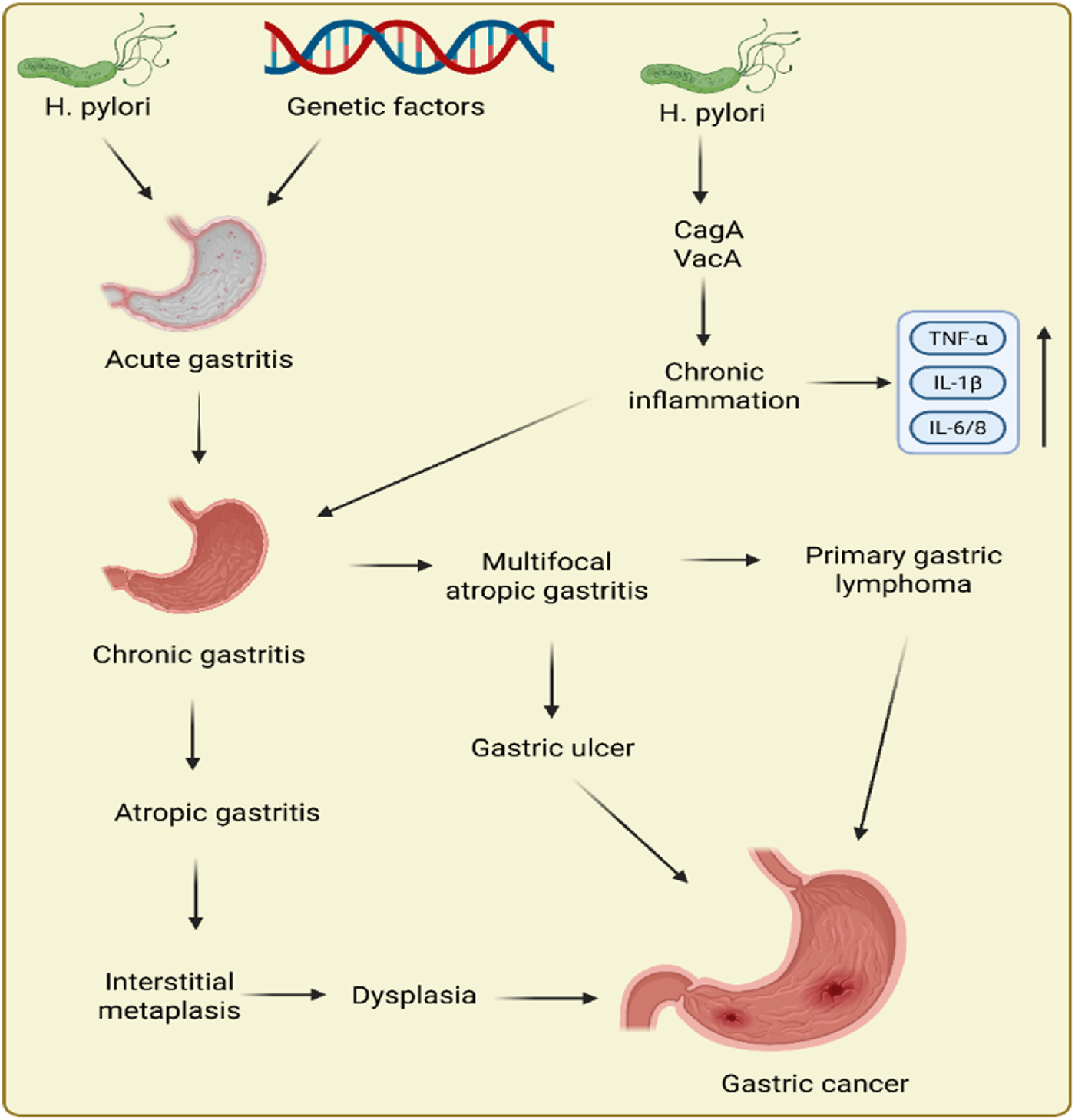
Pathogenesis of gastric cancer.
Several metabolic and signaling pathways are intricately involved in the pathogenesis of GC, and their dysregulation often results in molecular alterations that can be exploited as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Rather than describing these pathways in isolation, it is essential to understand how specific changes within them give rise to quantifiable molecular signatures. For instance, lipid metabolism reprogramming is a recognized hallmark of cancer that supports membrane biosynthesis, energy storage, and signaling in rapidly proliferating tumor cells (Yang et al., 2023). In GC, upregulation of enzymes such as fatty acid synthase (FASN) and transcription factors like SREBP1 has been reported, and both are emerging as tissue-based biomarkers associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis (Fernandez et al., 2020). Similarly, the glutamine metabolism pathway is frequently altered in GC to meet the high biosynthetic demands of cancer cells. Increased expression of glutaminase (GLS1) and the glutamine transporter SLC1A5 has been observed in tumor tissues, suggesting their potential utility as metabolic biomarkers for early GC detection (Zhong et al., 2023). The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) plays a vital role in maintaining redox balance and supplying nucleotides for DNA synthesis. Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) in GC is associated with oxidative stress adaptation and tumor aggressiveness, positioning it as a candidate prognostic biomarker (Zhang C. et al., 2014). The L-arginine metabolic pathway, important in modulating immune cell function and nitric oxide production, has also been implicated in GC. Biomarkers such as arginase-1 (ARG1) and argininosuccinate synthase 1 (ASS1) are differentially expressed and contribute to immunosuppressive tumor microenvironments, offering insight into immune evasion mechanisms (Chen et al., 2021). Furthermore, the Hippo signaling pathway, which controls cell proliferation, contact inhibition, and apoptosis, is commonly dysregulated in GC. Aberrant activation of YAP1, the key transcriptional co-activator of this pathway, promotes oncogenic transcriptional programs and is being evaluated as both a tissue and circulating biomarker for prognosis (Zhu et al., 2015; Messina et al., 2023). By establishing these molecular connections between dysregulated pathways and specific biomarkers, this section underscores the relevance of pathway-derived biomarker discovery and strengthens the translational value of such markers in the early detection and clinical management of GC.
The following section provides a visual representation and detailed breakdown of these key pathways, highlighting the molecular alterations involved and their associated biomarkers, thereby emphasizing the mechanistic basis of their relevance in GC detection and progression.
2.1 Hippo signaling pathway
A tumor-suppressive mechanism called the Hippo signaling pathway controls tissue growth and restricts the size of organs by preventing proliferation, encouraging apoptosis, and preventing cell growth (Saadh et al., 2025). Once inactivated, the pathway’s downstream elements, like Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) and transcriptional co-activator with PDZ binding motif (TAZ), become active and ultimately cause tumorigenesis (Zhao et al., 2023). Under typical conditions, Last1, WW45, Mst1, Mob, and the upstream molecules of the Hippo signaling pathway in mammals frequently create a conserved kinase cassette (Xiao and Dong, 2021). In response to cell density, these molecules can cause phosphorylation and deactivate the YAP/TAZ complex, which is present on a variety of HxRxxS motifs, the most important of which include TAZ S89 and YAP S127. They act as a 14-3-3-binding site and control nucleus-cytoplasmic translocation (Pan, 2010). The transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-1 (TEAD) family of transcription factors will work in conjunction with YAP to control cell development and apoptosis after it enters the nucleus. Figure 2 displays the Hippo on and off pathway in cancer. Three more core molecules are phosphorylated by Mst1 in mammals. Mst1 phosphorylates Lats1 on the hydrophobic motif and activation loop and may involve auto-phosphorylation (Zhao et al., 2008). The shifting of the cytoplasm-nucleus is important in cell growth regulation in response to density and cell-to-cell contact. The nuclear translocation of YAP/TAZ caused by the inactivation of the Hippo signaling system promoted cell proliferation, suppressed cell apoptosis, and ultimately resulted in cancer (Dong et al., 2019).
FIGURE 2
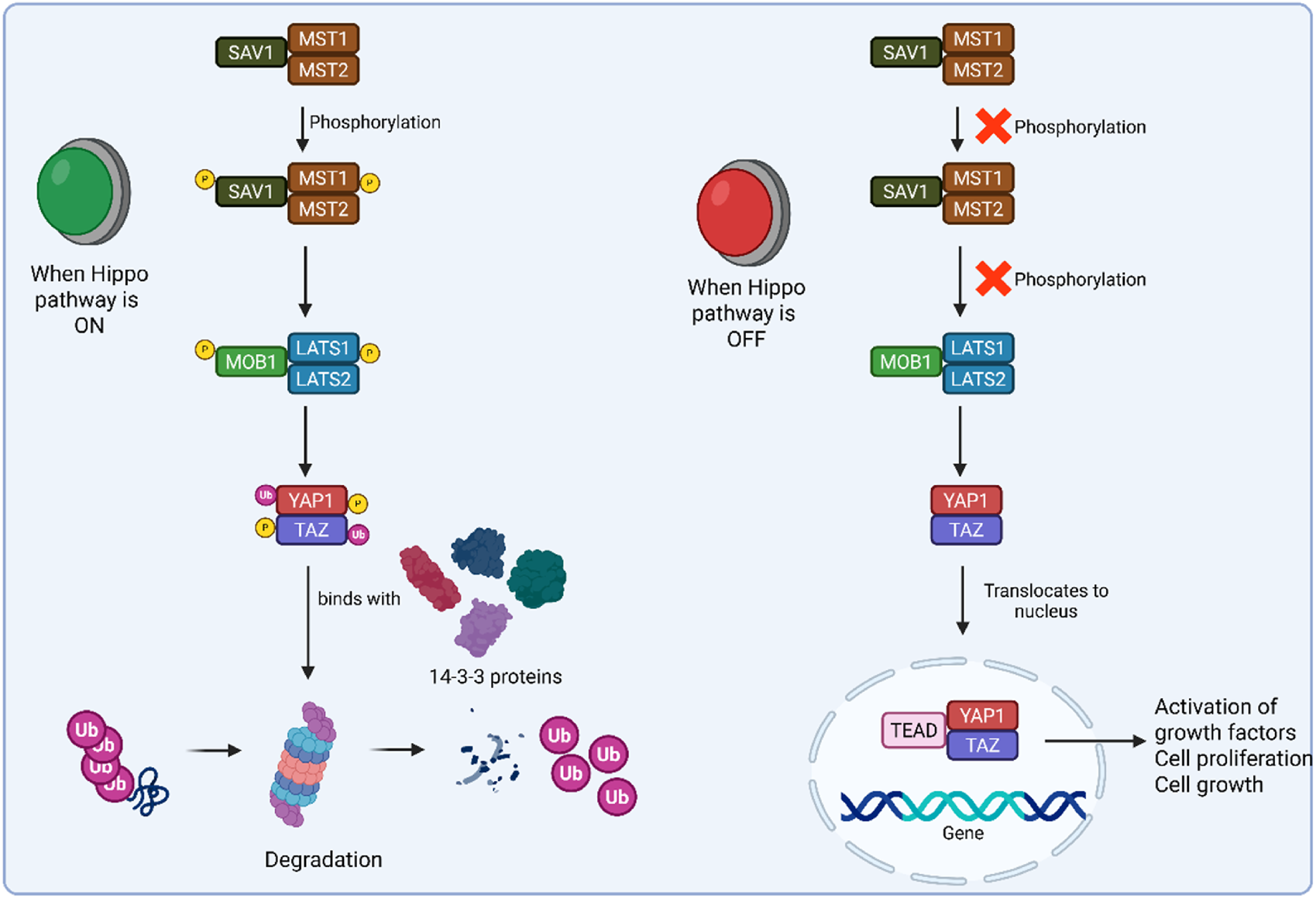
Schematic representation of Hippo on and Hippo off pathways.
2.2 L-Arginine metabolic pathway
Nearly every cell contains amino acids, which are fundamental building blocks of cells. One of the main causes of tumor formation and incidence is metabolic imbalance. The amino acid metabolism patterns give scientists crucial information to comprehend the molecular pathophysiology of malignancies (DeBerardinis and Thompson, 2012). Arginine is a non-essential amino acid that is obtained from dietary products (such as meat and fish) or the intestinal–renal axis (endogenous synthesis) (Wu, 2013). Arginine contributes to the synthesis of protein and acts as a precursor for the various biological molecules such as NO, proline, and urea (THOMPSON, 1980). Arginine and all these substances are continuously involved as sensitive markers in cancer progression, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis (Lind, 2004). Both healthy and malignant cells need the non-essential amino acid arginine for fundamental biological functions like polyamine and protein production (Choi and Coloff, 2019). Thus, arginine has a significant impact on the growth of malignancies. The metabolic pathways of L-arginine are frequently found to be dysregulated in GC, along with many other cancers such as prostate and breast cancer (Feldmeyer et al., 2012). The number of T cells and their functions are impacted by dysregulated metabolism of arginine (Szefel et al., 2019). Insufficient levels of arginine will significantly lessen the impact of T cell-tumor antigen interaction, which will affect the immune system. Furthermore, the lack of arginine increases GC risk due to more severe H. pylori infection (Pirzadeh et al., 2022). Arginine is used by the human body as a starting material to produce nitric oxide (NO), ornithine, and agmatine (Wu et al., 2021). Each of these molecules is made through specific enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Arginine is a versatile amino acid that is metabolized into NO and citrulline with the help of nitric acid synthase (NAS) enzyme. Arginine is also metabolized into ornithine and urea by a manganese-containing enzyme called arginase. Arginine is also metabolized into a naturally occurring chemical substance called agmatine with the help of arginase decarboxylase enzyme (ADC) (Grillo and Colombatto, 2004). These two, agmatine and ornithine, act as major resources for the putrescine (Satriano, 2004). Putrescine is a precursor of polyamines such as spermidine and spermine (Qiao et al., 2024). These polyamines are vital for inflammation, cell proliferation, and tumorigenesis. The L-arginine metabolism in cancer is shown in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3
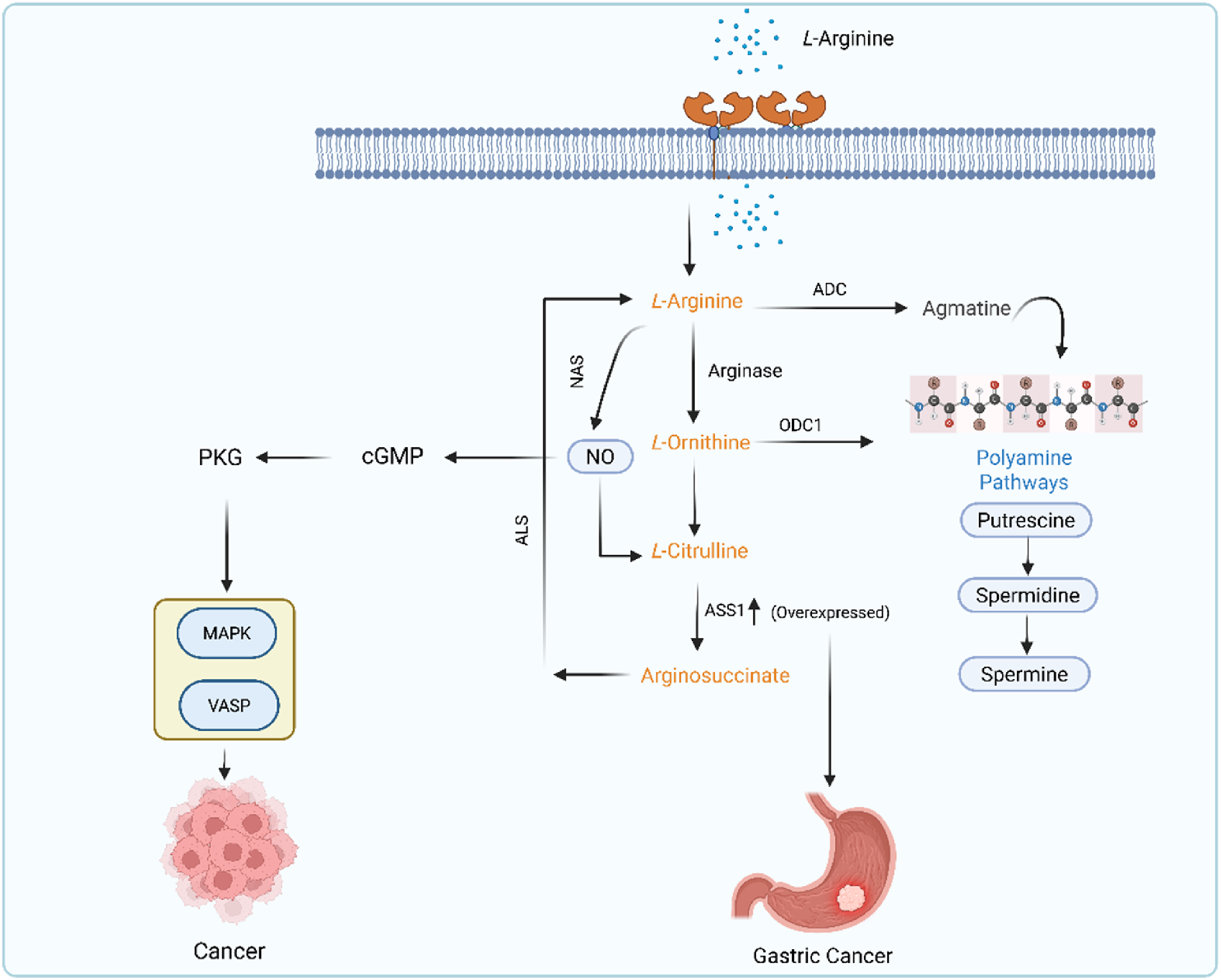
L-arginine metabolic pathway in GC.
2.3 Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)
PPP is also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt and the phosphogluconate pathway (Sharkey, 2021). This pathway is composed of two sub-pathways, oxidative and non-oxidative PPP (Bradshaw, 2019). In oxidative PPP, two molecules of NADPH are formed along with carbon dioxide in the second step and non-oxidatively form an amino acid (Stincone et al., 2015). Glucose enters the cell through the glucose transporter and, depending on its cellular need, is diverted into respective pathways as glucose-6-phosphate (G6P). The oxidative PPP phase is also referred to as the irreversible phase, which generates NADPH. This G6P is converted into fructose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphoglucolactone in the presence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD). G6PD is found to be overexpressed in cancer cells, which leads to poor survival (Kathagen-Buhmann et al., 2016; Ju et al., 2017). Studies showed that PPP flux modulates cancer directly or indirectly (Patra and Hay, 2014; Weber, 2016). PAK4, Erk, and PLK1 cause direct phosphorylation of G6PD and promote cancer growth (Zhang X. et al., 2017). Pik1 is another kinase that also phosphorylates the G6PD and enhances the PPP flux by promoting the formation of a G6PD dimer to increase the cancer progression (Ma X. et al., 2017). Reduced expression of Rev-erb increased the proliferation of GC (Tao et al., 2019). The PI3k/Akt signaling pathway upregulates SOX9, causing mRNA splicing that results in GC (Xia et al., 2023). PLOD1 increased the GC growth through upregulation of the SOX9/PI3k/Akt/mTOR pathway (Zhang Y. et al., 2021). TKT and TALDO are the two main enzymes that are important for reaction interconversion in non-oxidative PPP (Stincone et al., 2015). It has been found that TALDO is highly overexpressed in gastric adenocarcinoma (Kočevar et al., 2012). PPP is displayed in Figure 4.
FIGURE 4
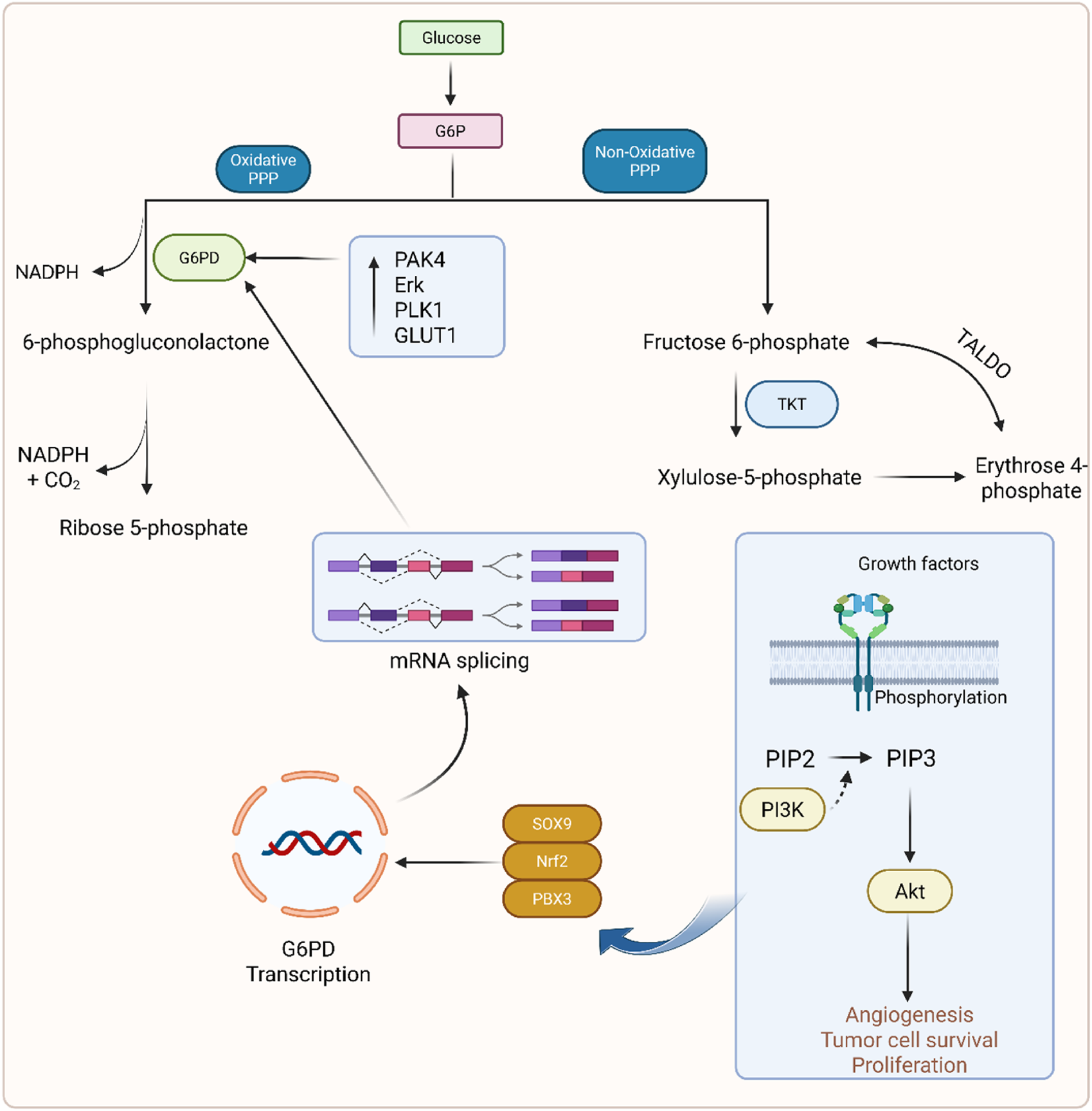
Mechanistic illustration of the phosphate pentose pathway in GC.
2.4 Glutamine metabolism pathway
The glutamine metabolic pathway plays an important role in cancer progression. Glutamine is an essential amino acid present in cancer cells (Li and Le, 2018). It is present in higher concentration with a range of 0.5–0.6 µM in plasma. It serves as a key nutrient for dividing cancer cells and acts as a source of carbon and nitrogen. Gln is also involved in protein synthesis, nucleotide synthesis, and other processes (Li et al., 2023). Under normal conditions, the body produces enough Gln, but during some physiological or other conditions, such as cancer, its demands increase significantly. Gln enters the cells through various transporters of solute carriers. These transporters include alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2 (ASCT2), serotonin N-acetyltransferase 1 (SNAT1), serotonin N-acetyltransferase (SNAT2), and cysteine glutamate antiporter (Pochini et al., 2014). Three of these four transporters, ASCT2, SNAT1, and SNAT2, have a main role in cancerous cells. ASCT2 regulates the optimal growth (Marshall et al., 2017), and SNAT1 and SNAT2 help in overall glutamine uptake (Bröer et al., 2016). Gln enters the mitochondria, is converted into glutamate by the glutaminase (GLS) enzyme, and forms ammonia. This converted glutamate is converted into α-ketoglutarate by glutamic-pyruvic transaminase 2 (GPT2) and glutamate dehydrogenase 1 (GDH1). Gln contributes to ATP production by delivering Gln carbon in the TCA cycle. Gln-derived glutamate is converted into glutathione and participates in the maintenance of redox balance (Son et al., 2013). Gln also activates the mTORC1 by simultaneous efflux of the amino acid leucine. This leucine and Gln translocate the mTORC1 to the lysosome, which initiates many processes such as cell survival, proliferation, and cell growth. Skp2 is associated with approximately 50% of patients with GC (Gstaiger et al., 2001; Tanaka et al., 2015). The authors found Skp2 to be a negative regulator of dependent mTORC1. It influenced the Skp2 activity, which helps in phosphorylation mediated by mTORC1 (Fingar, 2015; Jin et al., 2015). A study by Geng et al. found that the Skp2 protein level is regulated by mTORC1 in GC cells (Geng et al., 2017). Phosphorylation of Skp2 by mTORC1 was important for proto-oncogenic functions in GC. Skp2 was found to be expressed in 68 of 83 cases with high mTOR expression (Geng et al., 2017). The signaling pathway is illustrated in Figure 5.
FIGURE 5
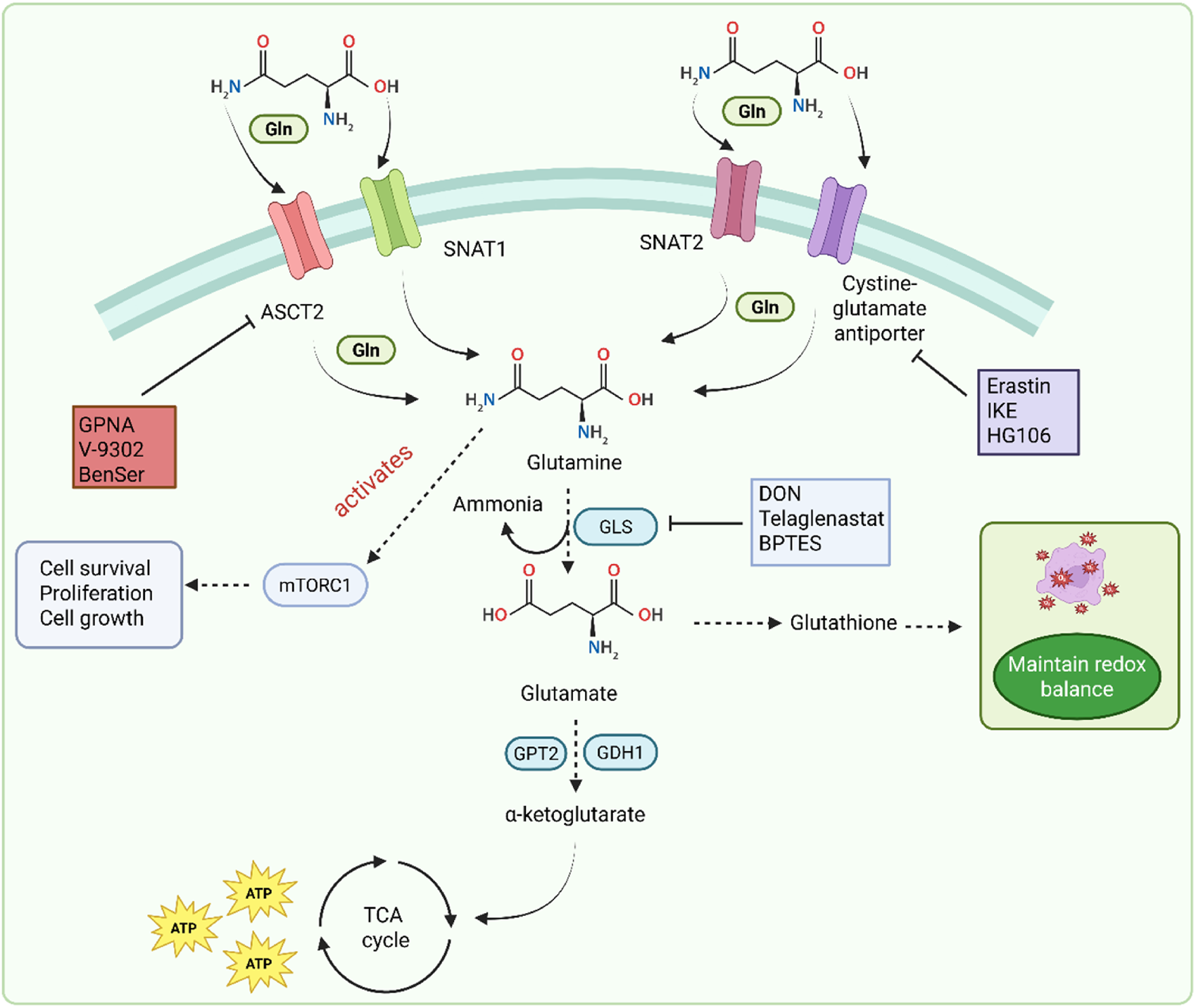
Glutamine metabolism pathway in GC.
2.5 Lipid metabolism reprogramming
GC is one of the most common malignant tumors (Bray et al., 2018). It originates in epithelial cells and exhibits a Warburg effect (Liberti and Locasale, 2016). Previous studies showed that under aerobic conditions, tumor tissue metabolizes glucose into lactate in cancer cells compared to normal tissues (Warburg et al., 1927; Liberti and Locasale, 2016). This phenomenon is called the Warburg effect (Warburg et al., 1927). The metabolic alterations are not yet clear. However, changes or alterations in cancer cells could be associated with changes in gene expression. This effect increases the glucose uptake, glycolysis, and the metabolism of pyruvate to lactic acid (Feron, 2009). Lipid metabolic reprogramming depends upon three factors in GC: non-coding RNA, enzymes involved in glycolysis, and mitochondrial proteins. Alterations in these factors create a difference between cancer cells and normal cells. In normal cells, lipids are present in a balanced state for maintenance and membrane synthesis. In the case of gastric cancerous cells, cells take lipids from CD36 receptors and depend upon a de novo synthesis pathway. It is also obtained from naturally forming cholesterol through the mevalonate pathway in the synthesis of cholesterol. Although the proper regulatory mechanism in GC is not fully understood, some of the endogenous factors, such as FASN and ACC, are involved in the generation of GC (Nannini et al., 2020). FASN is mainly responsible for proliferation and drug resistance in GC (Ito et al., 2014). LXRs are also involved in the GC through lipid metabolic disorders (Wang et al., 2019). Figure 6 displays the lipid metabolic programming in GC.
FIGURE 6
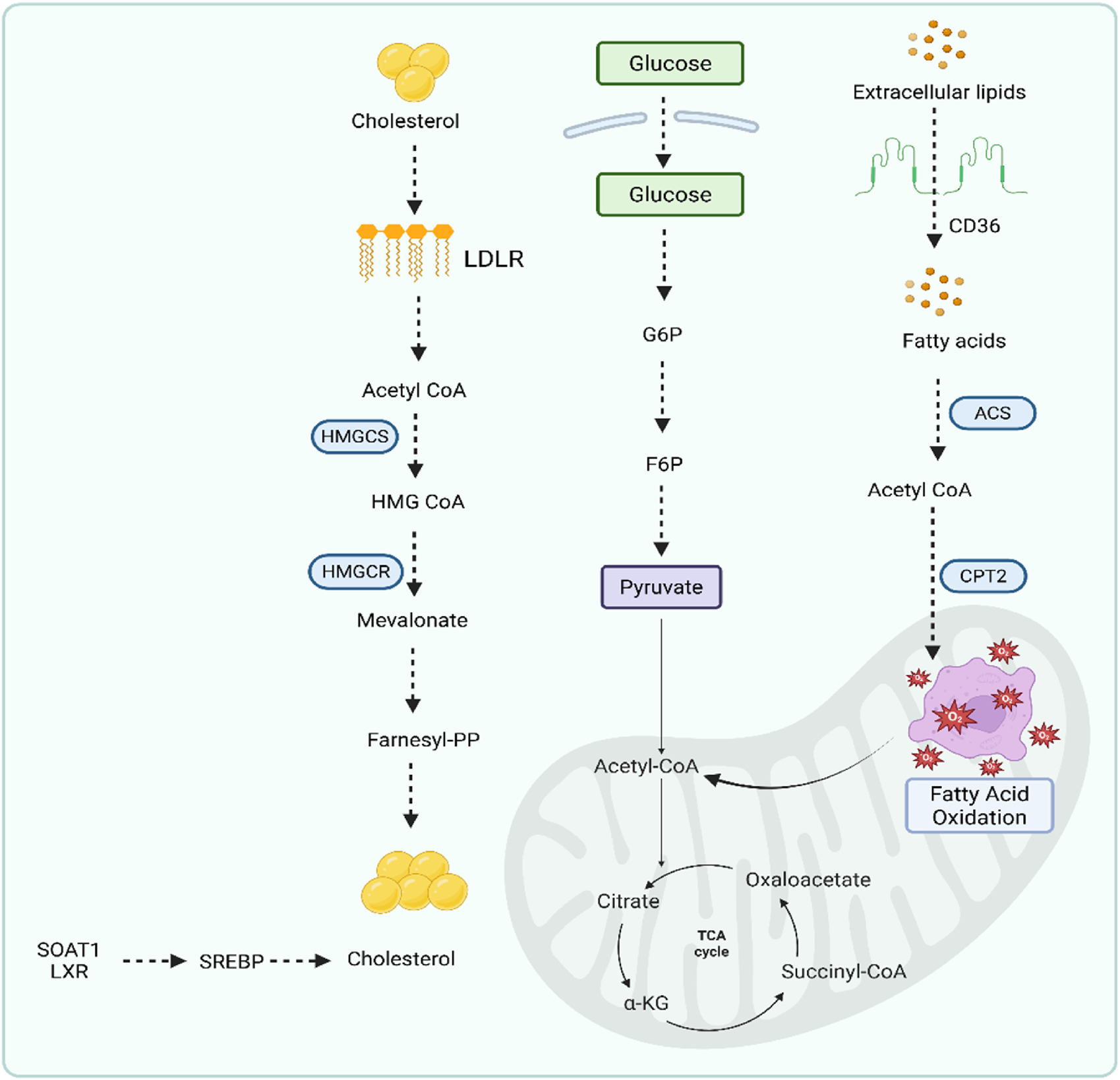
Lipid metabolic programming pathway in gastric cancer.
3 Novel diagnostic biomarkers of GC
According to the National Cancer Institute, a biomarker is a biological molecule present in bodily fluids such as blood or tissues that indicates a disease or a normal or dysfunctional process. It is also called a signature molecule or a molecular marker. In this review, novel diagnostic biomarkers are defined as those that have been identified within the past 5–7 years through high-throughput techniques such as transcriptomics, proteomics, and integrative bioinformatics, and that exhibit potential for clinical translation based on recent preclinical or patient-derived data. These biomarkers encompass diverse molecular categories. Differentially expressed genes such as FAP, SERPINH1, and the newly reported PSAPL1 are involved in tumor progression, extracellular matrix remodeling, and immune response modulation. lncRNAs, including NEAT1 and m6A-related lncRNAs, play regulatory roles in gene expression, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and chemoresistance. circRNAs, which are known for their high stability and tissue specificity, have been implicated in GC by acting as miRNA sponges or regulators of transcription. In addition, protein-based biomarkers such as HSPA6, ANXA11, CDC42, HAMP, SLC25A4, Cystatin B, DMBT1, and PRTN3 have emerged from tissue, salivary, and urinary proteomic studies, showing diagnostic and prognostic potential. Biomarkers were selected based on their recent discovery in the GC research landscape, their significant differential expression between cancerous and normal tissues or fluids, their mechanistic involvement in GC pathogenesis, and supporting evidence of their diagnostic, prognostic, or therapeutic potential from experimental or clinical studies. Figure 7 displays the various categories of GC biomarkers compiled in the present manuscript.
FIGURE 7
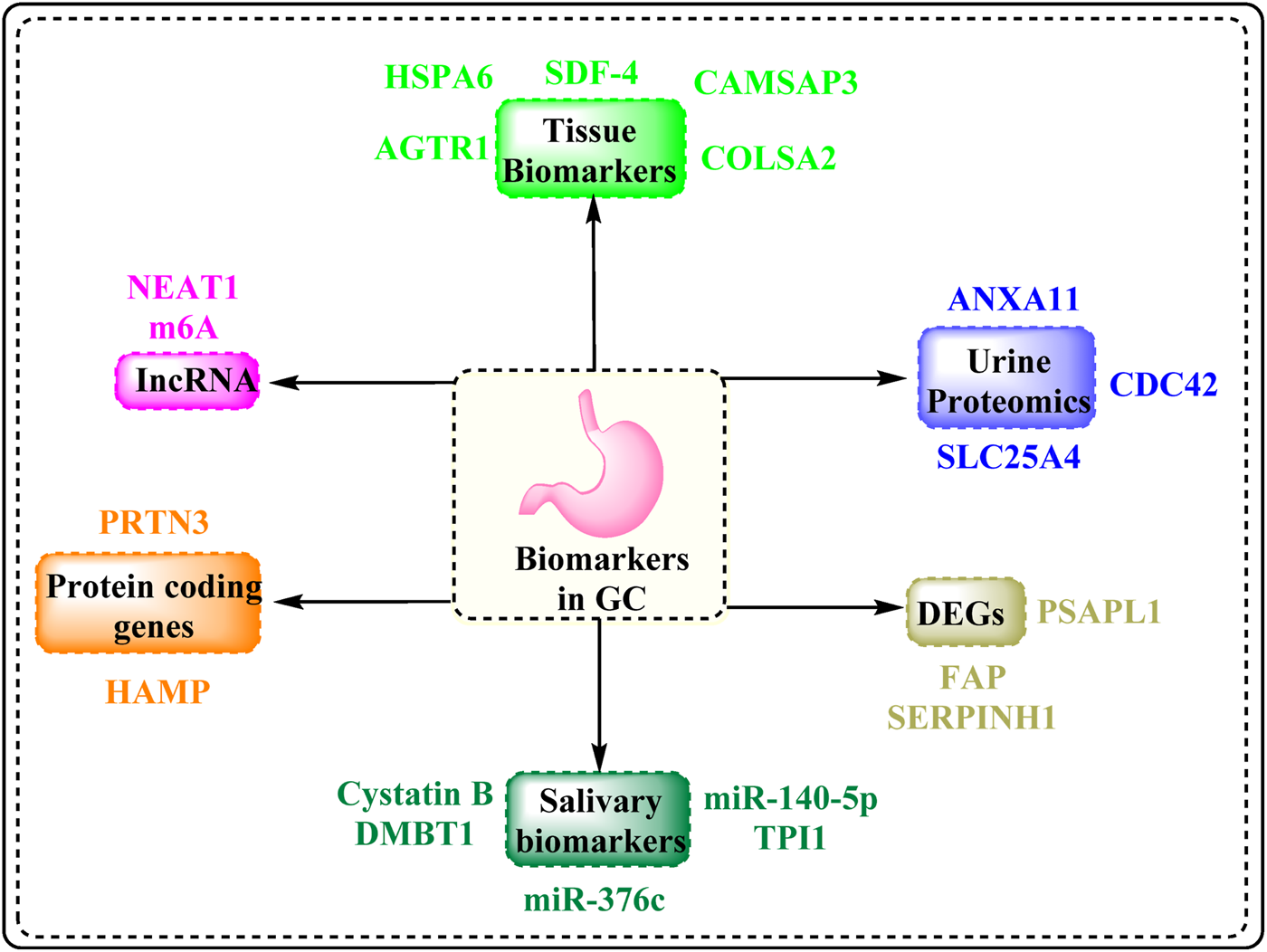
Biomarkers associated with GC.
3.1 Tissue biomarkers
Tissue biomarkers are molecules that are differentially expressed in tumor tissues compared to normal tissues and can provide valuable diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic information (Sarhadi and Armengol, 2022). In GC, tissue-based molecular signatures have been extensively explored due to their direct reflection of the tumor microenvironment and cellular behavior (Del Arco et al., 2024). Advances in transcriptomic and proteomic profiling have enabled the identification of several such biomarkers that show promise for early detection and disease monitoring. In this section, we discuss key tissue biomarkers identified in recent studies, including HSPA6, SDF-4, COL5A2, AGTR1, CAMSAP2, COL1A1, SPARC, and P4HA3, among others. These biomarkers have been reported to be significantly upregulated or altered in GC tissues and are functionally associated with extracellular matrix remodeling, angiogenesis, inflammation, and cellular proliferation. Further evidence from clinical datasets and experimental models supports their potential utility in distinguishing malignant from non-malignant gastric tissue and predicting disease progression. The following subsections elaborate on these biomarkers individually, highlighting their expression patterns, molecular functions, and clinical relevance.
3.1.1 HSPA6
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) were initially identified in Drosophila salivary gland cells in 1962 (Sarkar and Roy, 2017). They are a part of a highly conserved and large protein family that is often expressed throughout a range of physiological and stressful situations, including carcinogenesis. The superfamily of HSPs can be broken down into HSP110, HSP90, HSP70, HSP60, HSP40, and a family of tiny HSPs based on molecular weight (Hoter et al., 2018). Located on human chromosome 1q23.3 cytogenetically, 70-kDa heat shock protein 6 (HSPA6) (OMIM: 140555) encodes a protein of 70 kDa. As a stress-induced heat shock gene, HSPA6 was primarily discovered by Leung et al. in 1990 (Shen et al., 2021). In particular, the HSP70 family can shield cells from stress (Beere and Green, 2001). Because they are so effective, they stand for the most conspicuously conserved family (Hill et al., 2013). In humans, 15 members belonging to the HSP70 family have been found in various locations, indicating a variety of site-specific biological roles (Rosenzweig et al., 2019).
Many tumors have high levels of HSP70 expression, which accelerates the development of malignancy by preventing apoptosis, avoiding cellular senescence processes, impairing immunology, and encouraging angiogenesis (Albakova et al., 2020). High levels of HSP70 protein expression are linked with an unfavorable clinical outcome in a variety of malignant tumors (Calderwood et al., 2006). HSPA6 is a potential autosomal-recessive protein that contributes to the spectrum of VATER/VACTERL malformations (Calderwood et al., 2006). Cyto-protection is hypothesized to be a function of HSPA6 (Noonan et al., 2007). There are at least 13 members of the HSP70 family, and HSPA6 (HSP70B′) stands out as being unusual in terms of evolution because it is not conserved in rodents (Hageman et al., 2011). The invasion, migration, and growth of cells in triple-negative breast cancer were decreased by overexpression of HSPA6 (Shen et al., 2021). It was found that HSPA6 is not necessary for withaferin A-mediated suppression of breast cancer migration or apoptosis/autophagy (Hahm et al., 2021). By using RNA sequencing, it was possible to identify HSPA6, the TQ-targeted gene, for functional TNBC (triple-negative breast cancer) inhibition. Because HSPA6 is a “strictly inducible gene,” it cannot be expressed in a healthy or normal state of affairs (Noonan et al., 2007; Shen et al., 2021). CSE strongly but transiently induces HSPA6 (Zhang L. et al., 2023).
According to research, cigarette smoke robustly induces HSPs, particularly HSPA6, in Jurkat cells and DLD-1 at levels that prevent these cells from succumbing to oxidative stress or cytokine-induced apoptosis. According to descriptions of it in many cell types and tissues, the HSPs induction is a well-conserved reaction to cigarette smoke exposure (Anbarasi et al., 2006a; Anbarasi et al., 2006b; Kreutmayer et al., 2011). Recent research has discovered that HSPA6 promotes growth and tumor progression in some cancer types and inhibits growth and progression in others. When the HSPA6 gene is overexpressed, it has an augmenting impact, preventing EJ cells from proliferating, migrating, and invading. By increasing the induction of the G2/M-phase-mediated ATM-CHK2-Cdc25C-p21WAF1-Cdc2 cascade, phosphorylating Akt and MAPK signaling, and suppressing the regulation of MMP-9 associated with transcription factor due to GE-induced changes in EJ cells, the enhancing impact of HSPA6 was demonstrated. Overall, innovative findings show that HSPA6 strengthens the inhibitory effects mediated by GE on EJ cell migration, invasion, and proliferation and can offer a fresh method for the management of malignant cancers (Zhang L. et al., 2023).
According to a study, HSPA6 is overexpressed in GC and encourages proliferation through the Hippo pathway. It is a promising therapeutic target and potential prognostic biomarker for GC. Between March 2015 and January 2017, 146 samples of paired stomach epithelial tissue from patients who had surgical excision at Xiamen University’s Zhongshan Hospital and Hospital of Jiangnan University were gathered. Twenty patients had freshly removed tissue that was immediately preserved in liquid nitrogen, and 146 patients had other samples that were formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded. The integrated analysis of Coexpedia was used to examine the expression of HSPA6 in levels of mRNA from the samples of normal epithelial tissues of the stomach and GC samples (Zhang L. et al., 2023). When compared to healthy gastric epithelial tissues, the HSPA6 protein in GC tissues was noticeably upregulated. These results indicate that HSPA6 may function as a GC oncogene. The samples of GC were divided into the HSPA6high and HSPA6low groups using the cutoff score, which was 6, according to HSPA6’s score of IHC staining. The analysis of the Oncomine database showed that HSPA6 is overexpressed in breast cancer, CNS, and brain malignancies, cervical cancer, kidney cancer, lymphoma and leukemia, and GC and colorectal cancer. Compared to HSPA6low in the EGC group (P < 0.01), HSPA6high in the IGC group displayed substantially worse survival rates. Additionally, TNM stage and HSPA6 were found to be independent predictive variables for GC in univariate and multivariate Cox analyses (P < 0.05). The gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) revealed that these genes’ signature activities were the cell cycle and the G2M checkpoint, respectively, demonstrating that HSPA6 is important for the growth of the cells of GC.
Multiple GC cell line transcriptome data were acquired from CCLE, and these data revealed that HSPA6 was downregulated in AGS cells, and it was significantly expressed in NUGC2 cells. According to GSEA results, the HSPA6-related genes were considerably enriched in the Hippo signaling network, which suggests that HSPA6 may encourage the proliferation of GC cells through the Hippo signaling route. The YAP and cyclin B1 expressions were dramatically upregulated, while p-YAP was significantly downregulated in the AGS cells when HSPA6 was overexpressed. In the NUGC2 cells, knocking down HSPA6 resulted in the opposite alterations. When combined, HSPA6 encourages GC cell proliferation by activating the Hippo pathway.
Through direct investigation of patient samples along with integrated transcriptome analysis from the databases UALCAN and GEPIA, it was found that in GC tissues, the expression of HSPA6 is abnormal relative to the stomach epithelium, which is normal. According to the patients’ classification based on in situ HSPA6 expression, overexpression of HSPA6 was substantially linked with larger tumors and IGC. A poor prognosis is predicted by high expression of HSPA6 in GC tissues, as shown by the fact that the overall survival (OS) of the HSPA6 high group was also lower than that of the HSPA6low individuals. The outcomes of the Cox analysis supported the notion that HSPA6 is an independent GC prognostic factor. A nomogram was developed for HSPA6 along with the clinical stage, with good prediction performance. These findings suggested that HSPA6 may serve as a prognostic indicator as well as an oncogene (Zhang L. et al., 2023).
3.1.2 Stromal cell-derived factor 4
A study from Nagoya University identified SDF-4 as a promising biomarker for early detection of GC. Involving 396 GC patients and 80 healthy controls, the study showed that serum SDF-4 levels were significantly elevated even in stage I cases. It demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy with an AUC of 0.973, 89% sensitivity, and 99% specificity, far superior to traditional markers like CEA and CA19-9. Tissue analysis also confirmed consistent SDF-4 expression across tumor stages (Röcken, 2023).
3.1.3 CAMSAP2
CAMSAP2 is a significant promoter of tumor progression in GC. Analysis of patient samples and public datasets revealed that CAMSAP2 is highly expressed in GC tissues and is associated with advanced tumor stage, higher grade, and elevated levels of serum markers such as CEA and CA19-9. Functional experiments showed that CAMSAP2 overexpression promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) by increasing mesenchymal markers (vimentin and N-cadherin) and reducing epithelial E-cadherin, increasing cancer cell migration and invasion. In contrast, silencing CAMSAP2 reversed these changes (Zuo et al., 2023).
3.1.4 COL5A2, SPARC, COL1A1, and P4HA3
Researchers used a comprehensive integrative bioinformatic analysis approach using TCGA, GTEx, and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets and found that COL1A1, COL5A2, SPARC, and P4HA3 were significantly upregulated in GC tissues compared to normal controls. These four genes, all associated with the extracellular matrix, were strongly correlated with poorer OS, DSS, and pathological stage. Specifically, ROC analyses revealed high diagnostic accuracy for GC: COL5A2 (AUC ≈ 0.802), SPARC (AUC ≈ 0.895), and P4HA3 (AUC ≈ 0.875) (Niu et al., 2022).
3.1.5 AGTR1, DNER, EPHA7, and SUSD5
A 4-mRNA tissue-based panel comprising AGTR1, DNER, EPHA7, and SUSD5 was a powerful predictor of recurrence in locally advanced GC. The authors developed a risk stratification assessment model that combined these four markers with clinical features, achieving an AUC of 0.919 in the surgical cohort and 0.935 in an independent liquid biopsy validation cohort (Ding et al., 2024).
3.2 Urine proteomic signature
Urine collection is non-invasive and simple to do in large quantities compared to other biospecimens, making it possible to discover biomarkers during extensive population screening (Di Meo et al., 2017). Circulating urine molecules can potentially offer a comprehensive picture of a person’s health status. Malignant, apoptotic, and necrotic cells can release proteins into the blood, which the kidneys filter and reabsorb before the proteins eventually end up in the urine. Stable peptides and a few infrequent but crucial proteins can be tested with accuracy in urine (Gao, 2013; Jakobsen et al., 2015). Particularly, roughly 9% of the detected proteins in a healthy person’s urine are connected to the immune system (Marimuthu et al., 2011). These could be connected to the immune evasion and response seen in lesions before malignancy, and these were linked to significant somatic genomic changes (Krysan et al., 2019; William Jr et al., 2021). Changes in urine proteins could represent early biological processes involved in the development of GC carcinogenesis.
Finding biomarkers for the development of lesions in the stomach and for the possibility of developing early-stage GC may be made possible through the detection of proteins in urine. In one study by Fan H et al., proteome profiling in two stages among 255 patients with gastric lesions of various stages and GC using urine as a liquid biopsy was performed (Fan et al., 2022). Urine proteome signatures were created, and urine proteomic fingerprints were developed as they relate to the advancement of lesions of gastric mucosa and the possibility of developing GC. Forty-three proteins in urine were verified for the possibility of developing GC. A follow-up was conducted, and it was found that four proteins, namely, CDC42, SLC25A4, ANXA11, and NAPA, were strongly related to the probability of the progression of gastric mucosa lesions. GC tissue showed higher expression of ANXA11, CDC42, and NAPA than non-GC tissue did. All four proteins, namely, NAPA, ANXA11, SLC25A4, and CDC42, were present and enriched in the synaptic vesicle cycle (NAPA), cGMP-PKG signaling (SLC25A4), and endocytosis (CDC42) pathways. SLC25A4 was also shown in PPI network analysis as a key protein. A stratified analysis revealed consistently higher levels of these four proteins in progressed individuals, whether they were in the group with moderate gastric lesions at baseline (SG/CAG) or with advanced lesions (IM/LGIN) (Fan et al., 2022).
A study by Shimura et al. aimed to develop a non-invasive urinary protein biomarker panel for the early diagnosis of GC. Researchers analyzed urine samples from 372 individuals, dividing them into discovery, training, and validation cohorts. Using mass spectrometry and ELISA assays, they identified trefoil factor 1 (uTFF1) and ADAM12 (uADAM12) as key urinary biomarkers for GC, with Helicobacter pylori status included to improve diagnostic accuracy. In both training and validation cohorts, the combined panel (uTFF1, uADAM12, and H. pylori status) effectively distinguished GC patients from healthy controls, achieving area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.832 and 0.867, respectively. Sex-specific panels were also effective: uTFF1/uADAM12/H. pylori for men (AUC = 0.858) and uTFF1/uBARD1/H. pylori for women (AUC = 0.893). These panels showed high sensitivity even in stage I GC, with AUCs of 0.850 (males) and 0.845 (females), significantly outperforming conventional serum tumor markers. Importantly, urinary levels of the biomarkers were independent of H. pylori status, and the panels remained effective across GC stages. This study highlights the promise of a simple, cost-effective, and non-invasive urine test for early GC detection, potentially enabling mass screening and improving patient outcomes (Shimura et al., 2020).
Joshi and co-workers studied urinary proteomics to identify non-invasive biomarkers for early GC detection. Analyzing urine samples from GC patients and controls, the researchers identified six key proteins, ANXA11, CDC42, NAPA, LRG1, gelsolin, and CDH11, differentially expressed in GC. These biomarkers showed strong diagnostic performance and could distinguish GC patients from healthy individuals. Functional analysis indicated their involvement in cancer-related pathways such as cell adhesion and immune response. The findings suggest that urinary proteomics holds significant potential for precision oncology, offering a simple, non-invasive tool for early GC detection and disease monitoring, especially when combined with clinical parameters (Joshi et al., 2023).
Another study identified six urinary proteins, ANXA11, CDC42, NAPA, LRG1, gelsolin, and CDH11, as promising non-invasive biomarkers for GC detection (Husi et al., 2019). This study developed an XGBoost-based diagnostic model incorporating five plasma proteins, CDHR2, ICAM4, PTPRM, CDC27, and FLT1, achieving excellent discrimination for cardia GC (CGC) and its precursors. The model achieved AUCs of 0.931 for CGC, 0.867 for high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (CHGD), and 0.763 for low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (CLGD). Compared to traditional serological markers like PGII, PGR, and H. pylori status, the proteomic model demonstrated significantly better diagnostic accuracy (P for trend < 0.05), highlighting its potential as a non-invasive screening tool in high-risk populations (Li et al., 2024b).
3.2.1 ANXA11
Annexins are a multigene family of phospholipid-binding proteins that are regulated by calcium (Ca2+) (Gerke and Moss, 2002; Gerke et al., 2005). These are linked to cell division, Ca2+ signaling, growth control, metastasis, apoptosis, cancer progression, and membrane traffic and organization (Moss and Morgan, 2004; Monastyrskaya et al., 2007). ANXA11 belongs to the family of proteins that bind phospholipids in a Ca2+-dependent manner, which includes calcyclin, an extended N-terminal domain with a binding site for another Ca2+-binding protein (CBP), and C-terminal repeated annexin (ANX) homology, which leads to Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding (Lecona et al., 2003). Previous research has demonstrated that ANXA11 is linked to vesicle trafficking, signal transduction, cell differentiation, and apoptosis (Shibata et al., 2015; Hein et al., 2022). Ovarian, breast, liver, and colorectal cancers are significantly impacted by ANXA11, which is also linked to cancer recurrence, metastasis, medication resistance, and lymph node metastasis (Fernández-Madrid et al., 2004; Prieto-Fernández et al., 2022). It has been demonstrated that the downregulation of ANXA11 prevents the migration, growth, and invasion of the cells in GC, via the pathway of Akt/GSK-3 (Hua et al., 2018). Urinary ANXA11 levels showed a stepwise increase along the progression from non-atrophic gastritis to GC, indicating a strong association with malignant transformation. Importantly, elevated ANXA11 expression was also confirmed in GC tissue samples, suggesting concordance between urinary excretion and tumor expression. Multivariate logistic regression supported ANXA11 as an independent predictive marker for GC. This biomarker demonstrated potential in non-invasive screening, particularly for early-stage disease and mass surveillance in high-incidence regions. Baseline urinary ANXA11 levels were positively associated with progression from precancerous gastric lesions to malignancy (P < 0.05 via logistic regression).
In a recent study involving 63 paired GC and adjacent normal tissue samples, ANXA11 was found to be significantly upregulated at both the mRNA and protein levels in tumor tissues (Fan et al., 2021). High expression of ANXA11 was closely associated with adverse clinicopathological features, including larger tumor size, deeper invasion, lymph node metastasis, advanced TNM stage, and vascular invasion, suggesting a role in GC progression. Functional assays in GC cell lines (AGS and SGC-7901) revealed that silencing ANXA11 suppressed cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion, and caused cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase. Mechanistically, these effects were mediated via downregulation of the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway, along with decreased expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, and cyclin D1. These findings indicate that ANXA11 functions as an oncogene in GC and may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target. The limitation of this study was that it was conducted at a single center with a relatively small sample size of 63 paired tissue specimens, which may not adequately represent the diverse molecular characteristics of GC across different populations. Additionally, although the study demonstrated significant functional roles of ANXA11 in vitro, it lacked in vivo validation using animal models to confirm its effects on tumor growth and metastasis. The research also did not explore ANXA11’s potential as a prognostic marker, as it omitted survival analyses such as Kaplan–Meier curves or correlations with patient outcomes. Mechanistically, the study identified involvement of the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway but did not delve deeply into upstream regulators or downstream targets of ANXA11. Lastly, ANXA11 was evaluated only in tumor tissues, without examining its expression or utility as a non-invasive biomarker in serum or urine, limiting its clinical applicability in early detection or monitoring (Hua et al., 2018).
3.2.2 CDC42
The human homolog of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC42 (cell division control protein 42) was identified in 1990. CDC42 is a member of the GTPase Rho family. The attached nucleotide controls CDC42’s activity, and three different sets of regulatory proteins regulate these in turn. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), which enable the conversion of GDP to GTP, regulate the activation of Cdc42 (Hodge and Ridley, 2016). It is generally known that because of the crucial physiological roles that Cdc42 performs, it plays a significant part in malignancies. Cdc42 plays a role in the development of tumors as well as invasion and metastasis by controlling cell cycle progression, vesicle trafficking, microtubule and cytoskeletal dynamics, phagocytosis, apoptosis, cell polarity, and transcription. Inhibiting CDC42 and its signaling pathway elements is an appealing therapeutic target. These targets are currently being investigated with small molecules and biologics (Murphy et al., 2021). The invasion and migration of cells in GC were dramatically inhibited by CDC42 gene knockdown. In an in vitro study, CDC42 knockdown in AGS and SGC-7901 GC cells led to G1/S cell cycle arrest and significantly reduced cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. It also downregulated key proteins, including cyclin A, cyclin D1, cyclin E, PCNA, and MMP-9, confirming CDC42’s role in promoting GC progression (Du et al., 2016).
In a 2021 study published in Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids, researchers demonstrated that miR-497 acts as a tumor suppressor in GC by directly targeting CDC42. miR-497 expression was significantly downregulated in GC tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-497 in HGC-27 cells reduced proliferation by approximately 40%, inhibited migration and invasion by over 50%, and suppressed EMT, as evidenced by increased E-cadherin and decreased N-cadherin and vimentin levels. In vivo, mice injected with miR-497–transfected cells showed a ∼60% reduction in liver metastasis nodules compared to controls. Luciferase reporter assays confirmed CDC42 as a direct target of miR-497, and co-transfection with CDC42 restored cell proliferation and metastatic potential, reversing the effects of miR-497. These results confirm the functional importance of the miR-497/CDC42 axis in regulating GC progression and suggest its potential as a therapeutic target for inhibiting tumor metastasis (Zhang L. et al., 2021).
Mechanistically, miR-148b-3p inhibited the Dock6/Rac1/CDC42 signaling axis, leading to reduced activation of downstream effectors involved in cytoskeletal reorganization and metastasis. In a mouse tail vein injection model, miR-148b-3p overexpression reduced lung metastasis nodules by approximately 70%. Clinically, analysis of 92 GC tissue samples showed that low miR-148b-3p expression and high Dock6 expression were significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis, advanced TNM stage, and poor overall survival (P < 0.01). These findings establish the miR-148b-3p/Dock6/Rac1/CDC42 axis as a critical regulator of GC metastasis and a potential therapeutic target (Li X. et al., 2018).
In a study on MICAL2’s role in GC cell migration, Cdc42 emerged as a critical mediator. Researchers found that knockdown of MICAL2 significantly reduced the levels of active (GTP-bound) Cdc42, while MICAL2 overexpression had the opposite effect. Constitutively active Cdc42 (Q61L mutant) restored the migratory ability and reversed the upregulation of E-cadherin induced by MICAL2 depletion, confirming that Cdc42 activation is essential for MICAL2-driven cell migration and E-cadherin degradation. These findings highlight Cdc42 as a key downstream effector of MICAL2 that drives cytoskeletal remodeling and metastatic behavior in GC (Wang et al., 2022).
In a 2019 study published in theranostics, researchers demonstrated that GINS4 promotes GC progression by directly activating CDC42. GINS4 expression was significantly higher in GC tissues compared to normal tissues, and its overexpression correlated with poor differentiation, advanced TNM stage, deep invasion, and lymph node metastasis (P < 0.01). Mechanistically, GINS4 was found to physically bind to CDC42, as confirmed by GST pull-down and co-immunoprecipitation assays. Overexpression of GINS4 increased GTP-bound (active) CDC42 levels by ∼2.3-fold, whereas GINS4 knockdown reduced CDC42 activity by ∼60%. This activation led to increased PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathway signaling, along with increased expression of cyclin D1, Ki-67, N-cadherin, and vimentin, and decreased E-cadherin, supporting EMT progression. Functionally, GINS4 overexpression resulted in a ∼1.9-fold increase in cell proliferation, >2-fold increase in migration and invasion, and significantly larger tumor volume in nude mice xenografts (mean tumor volume: 740 mm3 vs. 370 mm3; P < 0.01). These results establish CDC42 as a direct and critical downstream effector of GINS4, mediating its pro-tumorigenic effects in GC (Zhu et al., 2019).
While these studies provide important insights into the role of CDC42 in GC, several limitations should be noted. Most were conducted with relatively small sample sizes and lacked validation in large or multicenter clinical cohorts, which limits the generalizability of their findings. The conclusions were primarily based on in vitro experiments and xenograft models, which do not fully mimic the complexity of human tumors and the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, while the studies identified CDC42 as a key effector in various oncogenic pathways, they focused narrowly on single regulatory axes and did not explore broader signaling networks or compensatory mechanisms. None of the studies assessed pharmacological inhibition of CDC42, reducing their immediate translational relevance. Furthermore, genetic diversity, patient heterogeneity, and long-term clinical outcomes were not adequately addressed. These limitations suggest that more comprehensive clinical and mechanistic studies are needed to validate CDC42 as a reliable biomarker and therapeutic target in GC.
3.2.3 SLC25A4
SLC25A4 is an ATP/ADP transporter that controls mitochondrial energy production by ensuring that the delicate equilibrium exists between thermogenesis and ATP synthesis (Namba et al., 2020). SLC25A4 upregulation reflects mitochondrial malfunction, which could be a key factor in the development of cancer (Moreno-Sánchez et al., 2007; Clémençon et al., 2013). SLC25A4 is a component of the cGMP/PKG pathway, whose activation is essential for GC cell proliferation, metastasis, and chemoresistance (Xiang et al., 2021). In a study by Fan et al. (2022), large-scale urine proteomics of high-risk individuals identified 246 differentially expressed proteins, with four proteins, SLC25A4, CDC42, NAPA, and ANXA11, showing strong associations with GC development. Among these, CDC42, NAPA, and ANXA11 were significantly elevated in both urine and matched tissue samples of GC patients. CDC42 showed a fold change of 1.98 (P < 0.01), NAPA had a fold change of 2.10 (P < 0.01), and ANXA11 showed a fold change of 1.85 (P < 0.01) in tissue compared to normal controls. These findings support their role as intracellular biomarkers linked to cytoskeletal regulation, membrane trafficking, and nucleoplasmic signaling during GC progression.
SLC25A4, a mitochondrial ADP/ATP translocator and component of the cGMP/PKG pathway, was significantly upregulated in urine (fold change 1.67, P < 0.05), suggesting mitochondrial dysfunction as an early systemic feature of malignancy. However, SLC25A4 did not show significant upregulation at the tissue level, indicating that its role may be more reflective of systemic metabolic stress than localized tumor activity. To assess clinical utility, a survival analysis of GC patients was performed using tissue data. It revealed that high expression levels of FAP (HR: 2.12, P = 0.004), PSAPL1 (HR: 1.91, P = 0.011), and SERPINH1 (HR: 2.45, P = 0.001) were significantly associated with poor overall survival. As a result, these three proteins were proposed as prognostic biomarkers for GC, while CDC42, NAPA, and ANXA11 remained leading candidates for early-stage diagnosis based on their consistent expression patterns in both urine and tissue (Fan et al., 2022).
3.3 Differentially expressed genes: FAP, SERPINH1, and PSAPL1
DEGs represent genes whose expression levels are significantly altered between cancerous and non-cancerous tissues and are key indicators of the molecular changes underlying GC pathogenesis (Liang et al., 2021; Abdolahi et al., 2023). These gene expression alterations often reflect oncogenic signaling, tumor–stromal interactions, immune modulation, or metabolic reprogramming. As such, DEGs serve as a valuable source for identifying potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers (Wang et al., 2015). In GC, numerous DEGs have been identified through transcriptomic profiling, and several have shown consistent dysregulation across independent datasets. Notably, genes such as FAP, SERPINH1, and PSAPL1 have emerged as promising biomarker candidates due to their significant upregulation in GC tissues and their functional relevance in tumor progression, extracellular matrix remodeling, and immune evasion. The number of diagnostic biomarkers related to GC was initially found using machine learning in the Gene Expression Omnibus dataset, and they were then verified in the Cancer Genome Atlas. The upstream regulatory lncRNA, along with miRNA, was then forecasted in reverse and confirmed from the standpoint of prognostic value and expression pattern using a variety of bioinformatic approaches. In the end, a new ceRNA regulatory network was effectively created, and every element of the network completely complies with the prognosis made by the ceRNA theory while also being associated with the prognosis of patients having GC.
The algorithms SVM-RFE and LASSO were used to find potential biomarkers from these DEGs. Results showed 40 DEGs that act as possible GC biomarkers based on the SVM-RFE approach, while 13 DEGs were identified as such based on the LASSO algorithm. The Venn diagram was used to identify six possible biomarkers that overlapped, which included MT1M, FAP, ADH7, SERPINH1, CDH3, and PSAPL1. Additionally, the training cohort’s ROC curves were used to determine the diagnostic effectiveness of these prospective biomarkers. Important GC indicators include MT1M, FAP, ADH7, SERPINH1, CDH3, and PSAPL1, according to the findings, which showed that the AUCs of all of these putative biomarkers were more than 0.9. Finally, survival analysis was carried out to check the predictive usefulness of these putative biomarkers. It revealed a strong correlation between GC patients’ prognosis and deregulation of SERPINH1, FAP, and PSAPL1. Thus, SERPINH1, FAP, and PSAPL1 were identified as potential GC biomarkers (Li et al., 2022).
3.3.1 FAP
Among the dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV activity and/or structure homologs (DASH), FAP (familial adenomatous polyposis) is a non-classical serine protease (Šedo and MalíK, 2001; Bušek et al., 2004). The FAP gene is extremely conserved in many species. In both humans and mice, it is confined to the long arm of the chromosome (Tillmanns et al., 2024). FAP is situated next to DPP-IV/CD26, which is FAP’s nearest homologue and, like DPP-IV, it has 26 exons. FAP is consequently believed to have developed by the duplication of genes. The single-pass 760 amino acid type 2 transmembrane protein that the human FAP gene encodes is made up of a long extracellular domain, a brief cytoplasmic N-terminal section, and a transmembrane region (amino acids 7–26) (Busek et al., 2018).
FAP’s soluble form is found in the plasma of blood of different species, although most normal adult tissues express FAP insignificantly or not at all (Lee et al., 2006; Keane et al., 2014). F19 murine monoclonal antibody produces FAP, which was first discovered to be an antigen against lung fibroblasts that could be detected. The antigen has been demonstrated to be a tissue-level feature of the stroma in a number of cancers, although its expression under healthy circumstances is highly restricted (Busek et al., 2018). Further research has increased the number of cancers where FAP is overexpressed and shown that FAP can be found in various elements of the cell microenvironment of the tumor, in addition to cancer-associated fibroblasts. At the invasion front of GC, increased tissue FAP is linked to poorer prognosis, lower tumor cell differentiation, higher TNM stage, and serosal invasion (Shan et al., 2012). Poorer survival is linked to a higher stromal FAP (Wen et al., 2017). In intestinal-type GC, FAP is expressed more strongly in the endothelial cells, stroma, and moderately differentiated cancer cells compared to GC of diffuse type (mostly in endothelial cells, cells of cancer with limited cellular connections). The presence of liver and lymph node metastases is linked to a higher stromal FAP expression in intestinal-type GC (Okada et al., 2003).
Comparing GC tissues to normal controls, it was shown that FAP was significantly expressed in GC tissues, and patients in higher GC stages have an increased level of FAP compared to patients with early-stage GC (Gao et al., 2019). Additionally, research revealed that GC cells overexpressed FAP and that knocking down FAP greatly reduced GC cell invasion and migration by inhibiting CAF activity (Wang et al., 2013). In a study of 171 GC patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NCT), FAP-positive CAFs were significantly associated with poor tumor regression grade (TRG) (P < 0.01) and worse overall survival in univariate analysis (P < 0.05). High post-treatment FAP expression remained an independent predictor of poor TRG in multivariate logistic regression (P < 0.010). Elevated FAP levels also correlated with advanced ypT/ypN/ypTNM stages, poor differentiation, and increased lymphovascular and perineural invasion. FAP+ CAFs were strongly linked with expression of EMT markers (e.g., Twist1, P = 0.001) and CSC markers (CD44, ALDH1, LGR5; P < 0.05), indicating their role in chemoresistance. However, in multivariate Cox analysis, FAP was not an independent predictor of overall survival, highlighting its value primarily as a marker of treatment response rather than long-term prognosis (Zhao and Zhu, 2023).
Cai et al. performed a multifactorial analysis to explore the role of FAP in gastrointestinal cancers, including gastric (STAD), colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers. FAP was found to be significantly overexpressed in tumor tissues across all cancer types studied (P < 0.001), particularly within cancer-associated fibroblasts. Its expression correlated strongly with extracellular matrix-related genes such as COL1A1, COL3A1, and POSTN, and with increased infiltration of immunosuppressive M2 macrophages (Cai et al., 2023). In a joint bioinformatics analysis using the TCGA and GEO datasets, FAP was identified as a key diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in GC. FAP was significantly overexpressed in tumor tissues compared to normal tissues (P < 0.001), with expression levels increasing alongside clinical stage and T-stage (P < 0.05). High FAP expression was associated with shorter overall and disease-specific survival, and multivariate Cox regression confirmed it as an independent risk factor for overall survival (HR = 1.56, 95% CI: 1.12–2.17, P = 0.008). Diagnostic ROC analysis yielded an AUC of 0.870, indicating high accuracy in distinguishing cancer from normal tissue. Moreover, FAP expression positively correlated with immune infiltration, particularly CD4+ T cells, macrophages, and CAFs, while showing a negative correlation with tumor purity (Zhang K. et al., 2023).
A recent study identified FAP+ GCMSCs as a dominant stromal subset driving GC progression. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, clinical pathology, and functional assays, FAP+ GCMSCs were shown to promote GC cell proliferation, migration, and stemness via paracrine INHBA secretion and SMAD2/3 activation. Additionally, they increased ECM collagen deposition, which interacted with ITGB1, activating FAK–YAP signaling (Liu et al., 2025).
3.3.2 SERPINH1
The precise secretion and folding of various types of collagen depend on the collagen-specific protein called SERPINH1, also known as HSP47 (Duarte and Bonatto, 2018). Cervical cancer (Yamamoto et al., 2013), breast cancer (Lai et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2015), glioblastoma (Zhao et al., 2014), and colorectal cancer (Mori et al., 2017) all have abnormal expression of SERPINH1. SERPINH1 encourages breast cancer cell metastasis and invasion by influencing the levels of various extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins (Lai et al., 2017). In GC, most of the genes are implicated in the EMT pathway, according to gene enrichment analysis. Additionally, GC EMT is regulated by the Wnt/-catenin signaling system (Gao et al., 2022). Compared to normal gastric mucosal tissues, GC tissues have considerably higher levels of mRNA of SERPINH1. In GC patients, SERPINH1 is a prognostic marker (Tian et al., 2020). An increased level of SERPINH1 was also detected in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (Lee et al., 2016), cervical squamous cell carcinoma (Yamamoto et al., 2013), and ulcerative colitis-associated carcinomas (Mori et al., 2017). The protein SERPINH1 is localized in the ECM of scirrhus GC tissues and cells (Hirai et al., 2006). GC tissues exhibit more SERPINH1 protein than do typical gastric mucosal tissues (Tian et al., 2020). According to studies by Kawagoe et al. (2020) and Tian et al. (2020), GC tissues have much higher levels of SERPINH1 protein and mRNA expression than normal tissues, and inhibiting SERPINH1 dramatically reduced the potential of cancer cells to migrate and invade (Kawagoe et al., 2020; Tian et al., 2020). Additionally, it is reported that increased SERPINH1 levels are linked to GC patients’ poor prognosis (Tian et al., 2020).
A study identified SERPINH1 as a novel prognostic biomarker in GC. Through comprehensive bioinformatics analysis using three GEO datasets, 360 DEGs were identified, among which SERPINH1 emerged as a key gene. It was significantly overexpressed (log FC = 3.6, P = 2.36 × 10−18) and correlated with poor survival (P < 0.001). Functional assays showed reduced proliferation and migration upon SERPINH1 knockdown (Qiu et al., 2023). In a study by Li et al., potential biomarkers were screened and validated by various machine learning approaches. The authors found 188 DEGs, and three biomarkers, FAP, PSAPL1, and SERPINH1, were identified. H19 and miR-378a-5p bind with SERPINH1 in GC. It was also found as an upstream regulatory IncRNA that regulates the SERPINH1 in GC (Li et al., 2022).
3.3.3 PSAPL1
A study identified PSAPL1 as one of three candidate diagnostic biomarkers for GC, along with FAP and SERPINH1. The study found that PSAPL1 is part of a ceRNA network involving H19 and miR-378a-5p, which is correlated with immune cell infiltration. Further analysis of this ceRNA network revealed that miR-378a-5p is associated with a favorable prognosis in GC patients. PSAPL1 is also linked to pathways involved in extracellular matrix organization and cell adhesion, which are important in tumor progression. Using machine learning methods (LASSO and SVM-RFE), the authors identified PSAPL1 as one of six overlapping candidate diagnostic genes (including ADH7, CDH3, FAP, MT1M, PSAPL1, and SERPINH1). Notably, it achieved an impressive diagnostic accuracy in TCGA GC cohorts (AUC = 0.731) (Li et al., 2022). Dysregulated expression of PSAPL1 was also significantly associated with patient prognosis in TCGA stomach adenocarcinoma cohorts (Wen et al., 2022). In integrated transcriptome comparisons, PSAPL1 emerged as one of 27 genes significantly dysregulated in both TCGA-STAD and patient-specific sequencing data; notably, high PSAPL1 expression was associated with poorer overall and disease-free survival (log-rank P < 0.05) (Hu et al., 2020). However, in survival analysis using the KM-Plotter database—covering 197 stage III GC patients—PSAPL1 expression did not reach statistical significance in predicting overall survival (log-rank P = 0.061) (Sarma et al., 2022).
3.4 Salivary biomarkers
One of the body’s most intricate biological fluids, saliva reflects a variety of physiological states (Kaczor-Urbanowicz et al., 2017; Pedersen et al., 2018). Compared to biopsy or blood sampling, saliva collection and storage are convenient, less invasive, less expensive, and require no specialized equipment (Zhang et al., 2012). Salivary biomarkers can reflect both local and systemic pathological changes, and recent advances in proteomic and transcriptomic technologies have enabled the identification of specific proteins and microRNAs (miRNAs) in saliva that are differentially expressed in GC patients (Bonne and Wong, 2012; Wang X. et al., 2017). Among the protein-based candidates, cystatin B, a cysteine protease inhibitor involved in inflammatory responses and proteolytic balance, has been found to be upregulated in the saliva of GC patients. DMBT1 is a multifunctional protein associated with mucosal immunity and epithelial integrity, is significantly altered in GC saliva samples, and has been linked to tumor-related immune responses. Another protein, TPI1, is a glycolytic enzyme that has been reported as a salivary biomarker reflecting metabolic reprogramming in gastric tumors. In addition to proteins, salivary miRNAs have shown strong promise due to their stability and diagnostic specificity. miR-376c and miR-140-5p are two such salivary miRNAs that have been consistently dysregulated in GC patients. These miRNAs are implicated in tumor growth, metastasis, and apoptosis regulation and may serve as early indicators of malignancy. Salivary proteins have been employed in many investigations as possible diagnostic indicators and to observe treatment, disease prognosis, and patient survival (Shu et al., 2017; Rapado-González et al., 2021).
3.4.1 Cystatin B
An intracellular thiol protease inhibitor known as cystatin B (CSTB), encoded by the CSTB gene, is a protein (Ma Y. et al., 2017). Chromosome 21q22.3 is the location where the CSTB gene is located (Joensuu et al., 2008). This protein is a member of the second and vast type of cystatins, can inhibit cathepsins B, L, H, and papain, and can form noncovalent force-stabilized dimers. It is believed that this protein helps prevent protease leakage from lysozymes (Zhang et al., 2016; Soond et al., 2019). It was discovered that GC patients had considerably lower mean CSTB levels in saliva than controls (P = 0.001). According to the Spearman test of correlation, in controls, there is a notable positive correlation between levels of CSTB in saliva and age. However, there was no statistically significant correlation between these two parameters. It was revealed through the outcomes of multiple linear regression that decreased CSTB levels in saliva are notably linked to GC, after controlling for the effects of participant age. With a one-unit increase in levels of CSTB in saliva, there is a 7% abatement in GC risk. To estimate salivary CSTB diagnostic values, a ROC curve was also constructed. Salivary CSTB levels of 119.06 ng/mL or less were the ideal ceiling point to distinguish controls from patients having GC. At this cutoff value, the specificity was 70.97%, and the sensitivity was 83.87% (Koopaie et al., 2022).
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway is suppressed by the overexpression of CSTB. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway regulates numerous cellular activities like cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and metabolism (Zhang et al., 2016; Qiu et al., 2020). By influencing cell migration and proliferation, downregulation of CSTB occurs, which leads to GC progression and development. Earlier research demonstrated several roles of CSTB in colon cancer, ovarian cancer (Ma Y. et al., 2017), and myoclonus (Di Matteo et al., 2020). According to the study, GC patients’ salivary CSTB levels were lower than those of the control group. Additionally, this biomarker distinguished GC from the healthy control with a specificity of 70.97% and a sensitivity of 83.87% (Koopaie et al., 2022). Previous research has demonstrated that CSTB can be used as a diagnostic marker for GC by downregulating GC protein and mRNA levels (Giganti et al., 2019). Recently, Xu et al. identified CSTB as a gene related to the prognosis and altered apoptosis in GC cells (Xu et al., 2024).
3.4.2 Deleted in malignant brain tumor 1 (DMBT1)
Deleted in malignant brain tumor 1 (DMBT1) is a tumor-inhibiting gene that is inactivated in numerous medulloblastoma cell lines compared to normal cells and is situated on chromosome 10q25.3-q26.1 (Madsen et al., 2013; Brim and Ashktorab, 2016; Shen et al., 2016; Garay et al., 2017). It plays a crucial part in some biological responses, including the innate immune system, accumulation and recognition of bacteria, and inflammation, when it binds to different host molecules and pathogens. DMBT1 may lead to polarization of epithelial cells by functioning as a factor for the differentiation of the epithelium. The protein DMBT1, a member of the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) family, is produced by the DMBT1 gene (Garay et al., 2017; Park H. S. et al., 2018).
DMBT1 is a multifunctional protein that mediates interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix and is associated with the mucins and Mac-2 binding proteins (Mollenhauer et al., 2003; Roldán and Marini, 2014). The DMBT1 variants DMBT1GP340 (glycoprotein-340) and DMBT1SAG (salivary agglutinin), related to epithelial regeneration and innate host defense, are present in both the oral cavity and the respiratory tract (Mollenhauer et al., 2000; Prakobphol et al., 2000; Kang and Reid, 2003). Due to its capacity to promote migration of alveolar macrophages and its interaction with lectins surfactant protein A and D (Sp-a, Sp-D), DMBT1GP340 participates in innate host defense in the respiratory tract (Braidotti et al., 2004; Li J. et al., 2017). The rabbit homolog of DMBT1, which is Hensin, promotes cell–extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions that lead to epithelial terminal differentiation, and this may also be true of DMBT1 (Mollenhauer et al., 2000; Roldán and Marini, 2014). Decreased levels of DMBT1 promote the formation of tumor cells, whereas when it is translocated to the ECM, it initiates cellular differentiation (Mollenhauer et al., 2002). The levels of DMBT1 and cellular location in hyperplastic, normal, and neoplastic cells of the breast epithelium differ. It is upregulated and polarized toward the glandular lumen or the basolateral membrane in normal or hyperplastic tissue around carcinomas, but it is downregulated in carcinomas. Furthermore, it was established that MCM5 and DMBT1 are co-expressed in both healthy and hyperplastic tissue. It was proposed that in these epithelia, the DMBT1’s basolateral relocation and its hyperexpression inhibit the uncontrolled development that characterizes neoplastic epithelium (Braidotti et al., 2004).
The expression of DMBT1 in various malignancies has fluctuated, according to several studies reporting conflicting results (Zhang, 2019; Gan et al., 2021). DMBT1 is eliminated or diminished in a number of tumor types, according to preliminary investigations (Hoki et al., 2019). In individuals having atrophic gastric mucosa and gastric mucosal dysplasia, the levels of DMBT1 significantly rise (2.5-fold) in the mucosa (Garay et al., 2017). H. pylori infection was linked to an increase in advanced gastritis. Additionally, precancerous lesions of the gastric mucosa were shown to have elevated expression of DMBT1, and DMBT1 played a complex role in the development of gastric carcinogenesis (Sousa et al., 2012; Garay et al., 2017). According to research by Conde et al., DMBT1 upregulates mRNA in 62% and downregulates it in 38% of GC patients. Differentiated GCs are more likely to lose DMBT1 while all types of GCs are to upregulate it (Conde et al., 2007). When GC patients were compared to healthy controls, the mean DMBT1 concentration was considerably greater (P = 0.002). The DMBT1 levels and participant ages were not significantly correlated in either group (P = 0.07 and r = 0.33 in the case of patients; P = 0.13 and r = 0.28 in the case of the control group). There was no correlation between any other explanatory variables and the concentration of DMBT1 in either group. After taking into account the effects of the participants’ ages, the analysis of multiple linear regression showed that GC was connected with DMBT1 increased levels (adjusted P = 0.001, F = 8.67, and R2 = 0.20). The levels of DMBT1 and CSTB in saliva showed no correlation between the control group and GC patients (P = 0.85 and r = 0.04) and healthy controls (P = 0.33 and r = 0.18). An ROC curve was constructed to differentiate the control group from GC patients to evaluate diagnostic values. The findings revealed that the ROC curve’s area was found to be 0.741 (95% CI = 0.614 to 0.844; P < 0.001). A level of DMBT higher than 146.33 ng/mL was the ideal cutoff value for differentiating the control group from GC patients, with specificity and sensitivity of 64.52% and 80.65%, respectively.
Salivary DMBT1 was proposed as a non-invasive marker for detecting GC due to its adequate sensitivity and specificity in GC detection (Koopaie et al., 2022). In a recent study, cells treated with both H. pylori and si-DMBT1 showed the highest growth, migration, and invasion. DMBT1 mRNA and protein levels were lowest in this group. Overall, H. pylori appears to promote GC progression by suppressing DMBT1, linking infection and inflammation to tumor development (Zhou et al., 2025).
3.4.3 Triosephosphate isomerase (TPI1)
Xiao et al. (2016) conducted a quantitative proteomics study using TMT labeling on salivary samples from 40 GC patients and 40 matched controls. Among over 500 quantified proteins, 48 showed significant differential expression; five were selected for ELISA validation. TPI1, along with CSTB and DMBT1, was confirmed as significantly altered in GC patients (P < 0.05). As a panel of all three, these biomarkers achieved ∼85% sensitivity, ∼80% specificity, and an accuracy of 0.93 in detecting GC (Xiao et al., 2016). A systematic review registered under PROSPERO (CRD42021259519) reaffirmed that among salivary biomarkers for GC, the trio CSTB, TPI1, and DMBT1 emerged with the highest diagnostic accuracy in preclinical validation stages (Zúñiga-Pérez et al., 2024).
3.4.4 miR-376c
In a study by Machida et al. (2015), salivary exosomes from GC patients and healthy individuals were profiled using microarray and qRT-PCR. miR-376c was significantly upregulated in GC patients. The study showed that miR-376c could distinguish GC patients from healthy controls with an AUC of 0.82, a sensitivity of 78.3%, and a specificity of 83.3%. Exosomal miR-376c originates from tumor cells and reflects active tumor signaling pathways, particularly those associated with proliferation and metastasis (Machida et al., 2015). Song et al. conducted a nested case-control study using serum samples from a large Chinese prospective cohort to evaluate microRNAs as early detection tools for GC. The authors identified a panel consisting of miR-376c, miR-221, and miR-744, all of which were significantly upregulated in the serum of GC patients compared to controls. Notably, this panel could detect GC up to 5 years prior to clinical diagnosis, suggesting strong potential for early screening. The 3-miRNA panel achieved a sensitivity of 82.4% and a specificity of 58.8%, offering a useful tool for risk stratification (Song et al., 2012).
3.4.5 miR-140-5p
miR-140-5p is significantly downregulated in GC tissues and functions as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting the YES1 oncogene. Quantitative RT-PCR analyses and in situ hybridization across GC patient samples confirmed the inverse relationship between miR-140-5p and YES1 expression. Functional assays in AGS and BGC-823 cell lines showed that overexpression of miR-140-5p significantly inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, while luciferase reporter assays validated YES1 as a direct target. In xenograft mouse models, miR-140-5p overexpression markedly reduced tumor growth, underscoring its therapeutic potential (Fang et al., 2017). The interplay between long non-coding RNA SNHG20, miR-140-5p, and NDRG3 revealed a regulatory axis impacting 5-fluorouracil resistance in GC. They discovered that miR-140-5p directly targets NDRG3, a gene overexpressed in GC, and downregulates its expression (Yu et al., 2019).
3.5 lncRNA biomarkers
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a class of non-protein-coding transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides that play crucial regulatory roles in gene expression at transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and epigenetic levels. In recent years, lncRNAs have emerged as key players in cancer biology, including GC, where they influence various processes such as proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis. Due to their cancer-specific expression patterns and high stability, lncRNAs are increasingly being explored as promising biomarkers for early detection and prognosis in GC. One of the most extensively studied lncRNAs in this context is NEAT1 (nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1), which has been reported to be significantly upregulated in GC tissues and associated with tumor growth, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), and chemoresistance. In addition, N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-related lncRNAs, which are regulated through RNA methylation modifications, have gained attention for their involvement in cancer-related signaling pathways and immune regulation.
3.5.1 NEAT1
NEAT1, one of the several types of lncRNAs that are now understood, resides on chromosome 11 and has five recognized splice structures. According to the Gene Cards, this gene produces a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) that has been deciphered from a variety of endocrine neoplasia loci. The lncRNA frames the central portion of sub-organelles of the paraspeckle by remaining in the core. For a very long time, NEAT1 can also function as a controller of transcription while incorporating some characteristics linked to the spread of disease. NEAT1 can facilitate both the RISC complex and miRNA binding. This lncRNA plays a critical part in the positive regulation of inflammatory response, the negative regulation of miRNA-mediated gene silencing, and the positive regulation of synoviocyte proliferation (Zhang Y. et al., 2017).
NEAT1’s promoter region mutations have been linked to the development of cancer in normal breast and renal cells (Li S. et al., 2018; Rheinbay et al., 2020). Recent research has shown the role of NEAT1 in the development of a variety of types of cancer. As an example, the lncRNA NEAT1 was shown to have remarkably high levels in the cells and tissues of colorectal cancer (CRC). They also showed that knockdown of NEAT1 can encourage CRC cell invasion and apoptosis and can sponge a new microRNA (miR-150-5P) (Wang et al., 2020b). Gao M et al. showed the development of GC via controlling ABCC4 and miR-356a-3p sponging because of NEAT1 (Gao et al., 2020). Transcription 3 activator and signal transducer may regulate the expression of NEAT1, and downstream gene transcription is affected by the altered expression of NEAT1 epigenetically during Alzheimer’s disease and HSV-1 (herpes simplex virus-1), suggesting the function of NEAT1 as an effector and stress sensor, in addition to the target-genes expression, which is influenced by the molecular mechanism of NEAT (Wang Z. et al., 2020). In many different kinds of human cancer, NEAT1 is the nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) lncRNA (Dong et al., 2018). A worse prognosis for cancer patients is highly correlated with increased NEAT1 expression (Lanzós et al., 2017; Dong et al., 2018).
The clinical characteristics of cancer that NEAT1 is responsible for include recurrence, patient survival, stem cell-like phenotype, and metastasis (Lanzós et al., 2017). The malignant behavior of tumor cells in breast cancer (Li W. et al., 2017; Zhao et al., 2017), hepatocellular carcinoma (Fujimoto et al., 2016), laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (Wang et al., 2016), lung cancer (Sun et al., 2016), glioma (Zhen et al., 2016), prostate cancer (Chakravarty et al., 2014), and skin cancer (Adriaens et al., 2016) can be reduced by NEAT1 knockdown. It has been determined that NEAT1 mediates transcription (Hirose et al., 2014; West et al., 2014) and is an essential component of nuclear paraspeckles (Clemson et al., 2009). A novel target for cancer therapy and cancer detection, ncRNA m6A played an important role in controlling prostate cancer progression (Wen et al., 2020).
NEAT1 promoted tumor growth and metastasis through the action of DDX5. In contrast to healthy tissues, malignant tissues have an overexpression of DDX5, which is found in the cell nucleus. In 71 CRC patients, NEAT1 expression correlated positively with DDX5 expression. NEAT1 is crucial to the advancement of CRC, and by directly binding to DDX5, it stimulated-catenin transcriptional activity, which may be indicative of the underlying molecular pathways driving their biological functions. These findings offer novel perspectives on the functions of lncRNAs in the development of CRC (Zhang M. et al., 2018). Nuclear architectural lncRNA NEAT1 is very prevalent. NEAT-1 and NEAT-2, the two NEAT isoforms, overlap, with the latter acting as a scaffold in the production of a type of nuclear ribonucleoprotein body (paraspeckles) (Knutsen et al., 2022). It has recently been discovered that NEAT-2 expression predicts progression-free survival in patients with ovarian cancer receiving platinum-based therapy but not NEAT-1 (Adriaens et al., 2016).
The level of NEAT1-2 is notably correlated with HER2 in samples of breast cancer and with the grade of breast cancer. During lactation in human breast tissue, NEAT-2 expression is also elevated (Knutsen et al., 2022). A study by Azadeh et al. (2022) revealed differences in NEAT-1 levels between samples of breast cancer and GC from the database of gastric and breast cancer, which is high throughout the Isfahan community. According to data analysis and the ENCORI, NEAT1 is significantly downregulated in cases of GC. The GC samples displayed a considerable downregulation of NEAT1, according to the analysis of GEPIA2 online data. In GC patients, the low survival rate has an insignificant relationship with levels of NEAT-1, according to a survival analysis. NEAT1 has been significantly downregulated in Isfahan samples of GC patients compared to the control, according to the analysis of 2 cm real-time PCR data. According to ROC analysis, for Isfahan patients with GC, NEAT-1 was found to be a good prognostic biomarker and a novel factor for distinguishing samples of control from samples of tumor (P-value 0.0001).
It has been shown that NEAT-1 levels and activity could be controlled by three non-coding and coding RNAs (MTRNR2L8, XIST, and hsa-miR-612). Microarray data analyses, ENCORI, and GEPIA2 were used for an expression study of coding and non-coding RNAs to comprehend their potential involvement in GC patients. MTRNR2L8 did not exhibit any appreciable low expression in the GC samples, according to the examination of the ENCORI data. In GC samples, there was no notable dysregulation according to GEPIA2 online expression analysis. Additionally, a GEPIA2 expression study showed that there is no link between the level of MTRNR2L8 and the stage of GC. In GC patients, the decreased survival rate and decreased levels of MTRNR2L8 were not significantly correlated, according to a survival study of the ENCORI and GEPIA2 datasets. According to the ENCORI analysis of relative expression of the lncRNA XIST, its upregulation in GC samples is not statistically significant (FC: 1.44, FDR: 0.74).
XIST has noticeably low levels in GC samples, according to GEPIA2 online analysis of expression. The results of a survival analysis showed no association between the expression pattern of the lncRNA XIST and survival rates of patients with GC and BC. As a result, the lncRNA NEAT1 can discriminate between tumor and control samples in the Isfahan population, making it a great diagnostic biomarker for individuals with GC (Azadeh et al., 2022). The expression of EZH2 was increased in GC by NEAT1, which increased the cell proliferation (He and Ren, 2024).
3.5.2 N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs
One of RNA’s most prevalent internal modifications, N6-methyladenosine (m6A), regulates a number of bioprocesses, including the growth of cells, DNA damage response, and carcinogenesis (Rauch, 2020). Studies have demonstrated the significance of m6A alteration in the management of tumors, particularly in targeted therapy (Hu et al., 2019). The METTL3, METTL14, and WTAP m6A methyltransferase complex mediates the m6A modification, which is terminated by the FTO and ALKBH5, which are m6A demethylases. At the same time, reader proteins like YTHDC1, YTHDC2, and YTHDF1 are necessary for m6A modification (Fang et al., 2021). Three elements, namely: binding proteins (readers), methyltransferases (writers), and demethylases (erasers), make up regulators of m6A (Kong et al., 2022). Recent research has shown that either carcinogenesis is encouraged or the growth of a malignant tumor is inhibited by m6A. According to Yang et al.’s research, alteration of methylation mediated by m6A controls changes in the invasion of the microenvironment of the tumor (Yang et al., 2020). Modification of m6A improved immune regulation, which is mediated by YTHDF1. Malignant tumors may benefit from using YTHDF1 as a possible therapeutic target. Additionally, YTHDF1 is crucial for the immune evasion of tumors; however, more research is needed to determine the precise mechanism. Modification of m6A is crucial for cancer patient prognosis (Han et al., 2019).
There is a complicated involvement of changes in m6A in the biological function, development, and occurrence of cancer of the esophagus, and it represents a novel epigenetic research area. According to studies, patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and GC have much greater levels of m6A than healthy people do, and the amount is favorably linked with the clinical outcome (Lin et al., 2019; Wang Q. et al., 2020). Lower levels of m6A, however, are linked to a worse outcome in cases of bladder cancer (Gu et al., 2020). The discovery of the m6A modification on a number of non-coding RNAs, such as lncRNA, circRNA, mRNA, snoRNA, and microRNA, is the cause of this (Pan, 2013). It is important to note that the m6A alteration of RNA regulates the progression of oncogenesis and plays an essential function in innate immunity (Chen et al., 2019). RNA–protein interaction is impacted by the m6A alteration of lncRNA (Huang et al., 2020). Dot blot analysis evaluated the degree of m6A alteration in GC tissues. The findings demonstrated that 11 of 12 patient cancer tissues expressed more m6A than para-carcinoma tissues. Correlation analysis revealed that patient characteristics, clinical stage, and grade of tumor were higher with increased levels of m6A (P = 0.111, R = 0.485), particularly clinical stage (P = 0.048, R = 0.581). Because m6A writers frequently act as a tumor promoter during tumor growth, they are crucial for the development of cancer.
The matrix expression of 1,056 m6A-related lncRNAs and 23 m6A genes from the TCGA database was obtained. The m6A-related lncRNAs related to overall survival were screened and identified using a univariate Cox regression analysis. The candidate lncRNAs were divided into two categories: a protective type, which was related to good prognosis with HR < 1, and a risk type, which was related to a poor prognosis with HR > 1. Of these, eight lncRNAs (AC026333.4, SNHG3, SCAT2, MIR17HG, AC099850.4, AL512506.1, AL033527.3, and AC091057.1) were shown to be overexpressed in cancer tissues. The Consensus Cluster Plus package in R was used to divide the 72 patients who were a part of this investigation into two clusters. Two molecular subtypes were identified when k = 2. Patient prognosis was considerably different between the two subtypes. According to the overall survival findings, cluster 2 patients have a notably poorer prognosis than cluster 1 patients (P = 0.018). A notable difference exists between the clinical outcomes of the two subtypes. Potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival of Asian patients with GC include N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs (Xu et al., 2022; Ji et al., 2025).
3.6 Circular RNAs (circRNAs)
CircRNA is a specific ncRNA type. The structure of CircRNA has covalently closed loops without poly-adenylated tails at the 3′ ends or a cap structure at the 5′ end. Compared to parental mRNAs, circRNAs have a significantly longer half-life (10 h vs. 48 h) and are capable of avoiding exonuclease destruction (Jeck and Sharpless, 2014). This conservative trait has led numerous studies to focus on the possible function as a favorable biomarker of a disease of circRNAs. They can interact with lncRNAs (long non-coding RNAs), RBPs (RNA-binding proteins), mRNAs, or sponging mRNAs to directly regulate transcription (Hansen et al., 2013; Memczak et al., 2013). Even the translation of some circRNAs into proteins is possible (Pamudurti et al., 2017). The circRNAs are transcriptionally back-spliced single-stranded ncRNAs (non-coding RNAs) that are generated from pre-mRNAs (Memczak et al., 2013). Considering their functional significance, they appear to primarily act as “miRNA sponges,” which allows the regulation of numerous growth regulatory genes that act as different miRNA downstream targets (Memczak et al., 2013; Panda, 2018; Li et al., 2020). It is intriguing to note that numerous circRNAs have recently been identified that are important in the pathogenesis of various human malignancies, along with GC (Li P. et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2020).
Due to the circular configuration of the circRNAs, they become resistant to RNase-mediated degradation and enable easy detection in tissue-specific and high-degree body fluids. They have attracted increasing attention from the perspective of clinical biomarkers (Xia et al., 2017; Wang Y. et al., 2020). CircRNAs are more stable in plasma and easier to detect than these conventional biomarkers. By sponging miRNAs, circRNAs can function as ceRNAs and create a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network. Numerous studies have suggested that miRNAs, including miR-21, miR-7, and miR-145, play a role in EGFR mutation and consequently influence lung cancer invasion and metastasis (Chou et al., 2010; Chiou et al., 2015).
Recent studies have concentrated on the diagnostic utility of plasma circRNAs in combination with traditional markers, including PIVKA-II, AFP-L3, and AFP. According to Zhang et al., the plasma concentration of hsa_circ_0001445 could be used to efficaciously distinguish people who have cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver cancer. Hsa_circ_0001445 of plasma had 94.2% specificity for HCC (hepatocellular carcinoma) diagnosis. Furthermore, a gradual logistic regression model revealed that the accuracy of a combination of AFP and has_circ_0001445 in HCC diagnosis was considerably better than either test alone (AUC = 0.970) (Zhang X. et al., 2018). Ye et al. confirmed that hsa_circ_0010882 expression was considerably increased in GC patients’ plasma, and it was favorably connected with differentiation of tumor and TNM stage. Additional research revealed that hsa_circ_0010882 in plasma interacted with the PI3K/Akt pathway to promote proliferation along with metastasis of GC cells (Peng et al., 2020). Li et al. designed a circular RNA panel using three circRNAs in plasma (hsa_circ_0005927, hsa_circ_000178, and hsa_circ_1900), which were upregulated (Peng et al., 2020).
The panel of circular RNAs showed significant advantages in differentiating colorectal cancer patients from control healthy individuals and demonstrated increased accuracy of diagnosis than CEA (AUC = 0.698) (Zhang et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2021). Yin et al. used microarray technology and found 41 circRNAs that were expressed abnormally in BC patients’ plasma. The increased expression of plasma hsa_circ_0001785 demonstrated greater diagnostic resolution than CA15-3 or CEA (AUC = 0.784). Additionally, after surgery, the hsa_circ_0001785 plasma expression steadily decreased. Hsa_circ_0001785 in plasma may be useful for both diagnosis and treatment (Peng et al., 2020). Plasma circRNAs have also been investigated in different malignancies, along with a few cancers that were high in incidence. A poor prognosis and increased malignancy of gallbladder cancer were indicated by an increased level of circ-MTO1 in plasma (Wang et al., 2020c). In addition to enabling the early detection of GC patients, an 8-circRNA biomarker panel was developed, which demonstrated marked superiority in specificity and efficacy compared to the conventional tumor markers currently in use for the early diagnosis of gastric neoplasia.
First, to identify putative circRNA biomarker candidates, two genome-wide circRNA expression profile datasets from patients with GC were analyzed. Twenty-six downregulated and 53 upregulated circRNAs (adjusted P-value <0.05 and log2FC > 1) were found using differential expression analysis. Priority was given to circRNAs, which were overexpressed in GC tissues, as opposed to adjacent normal mucosa (ANM). In order to identify ten potential circRNAs, circRNAs with a log2FC > 2 and greater robustness of expression in the ANM vs. GC tissues were chosen. The results of the research showed that this panel of biomarkers had potential for robust diagnosis, with an AUC = 1.00 (P < 0.001 and 95% CI: 1.00–1.00), demonstrating its remarkable diagnostic ability to identify people who have gastric neoplasia.
The feasibility of converting the panel of biomarkers of circRNA, which is tissue-based, into a liquid biopsy was examined by measuring the expression of these biomarkers in blood specimens obtained from a training cohort of 46 healthy controls and 92 patients with GC. It was found that two circRNAs, hsa_circ_0055521 and hsa_circ_0004339, were not expressed in specimens of serum, and they were therefore eliminated from further study. Assays of RT-qPCR were used to determine the levels of the remaining eight circRNAs, and their diagnostic potential was analyzed. With an AUC of 0.87 (specificity 78.3%, sensitivity 78.3%, P < 0.001, and 95% CI: 0.82–0.93), the panel of 8-circRNA biomarkers was shown to distinguish individuals with GC from healthy controls. Univariate analysis was also carried out for the diagnosis of GC to examine the robustness of specific circRNAs. Six of the eight circRNAs showed a notable correlation in GC discrimination, while the P-values of the other two outcomes were less than 0.1. Given that surveillance by endoscopy is not a routine screening technique for this cancer in many nations, this is new and promising evidence regarding the importance of circRNA-based biomarkers for their use in clinical settings as high-throughput, reasonably priced, and non-invasive biomarkers for the identification of GC patients early using liquid biopsy (Roy et al., 2022).
3.7 Protein-coding gene-based biomarkers
Protein-coding genes serve as important biomarkers in GC due to their direct involvement in tumor biology. HAMP, a regulator of iron metabolism, is frequently upregulated in GC and associated with inflammation and tumor progression. PRTN3, a serine protease, is linked to immune modulation and has shown increased expression in GC tissues.
3.7.1 HAMP
Hepatocytes in the liver produce hepcidin, a little polypeptide hormone that is essential for maintaining the proper balance of iron metabolism (Park et al., 2001). When high levels of circulating iron are needed and inadequate erythropoiesis takes place, diseases including anemia, hypoxia, and thalassemia result. This reduces the body’s ability to produce hepcidin (Ganz, 2003). Macrophages cause sequestration of iron, which leads to a reduction of the iron present in circulation. This defense mechanism results in inflammation and infection, during which hepcidin antimicrobial peptide (HAMP) expression increases. Conversely, during inflammation and infection, the expression of hepcidin antimicrobial peptide (HAMP) is increased because self-defense mechanisms result in a decrease in circulating iron due to the sequestration of iron by macrophages (Nemeth et al., 2004).
HAMP contributes to the development of different malignancies. Increased levels of circulating hepcidin have been linked to a variety of cancers, according to recent investigations. Serum hepcidin levels were discovered to be higher in people with breast cancer (Zhang S. et al., 2014). A higher tumor (T) stage was associated with greater HAMP expression seen in colorectal cancer tissues (Ward et al., 2008). High HAMP expression in lung cancer patients may affect prognosis via regulating immune infiltration (Fan et al., 2021). In comparison to low levels of HAMP expression, high levels were substantially related to a worse prognosis in assessments of overall survival (OS) in pancreatic cancer (Toshiyama et al., 2018). Hepcidin expression is extensive in the cells of prostate cancer and, by increasing intracellular iron transport, it can regulate cell division, migration, and death (Wang F. et al., 2017). In contrast, the expression of HAMP in cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular cancer was less than in adjacent normal tissues. A poor prognosis and an advanced pathological grade are linked to HAMP’s decreased expression (Shen et al., 2019; Wang and Du, 2021). Using experimental and bioinformatics tools, the degree to which HAMP was expressed in GC tissues was also validated. Furthermore, the results of one investigation showed a link between a GC patient’s prognosis, increased HAMP expression, and clinicopathological findings. Eventually, it was shown that there was a strong link connecting immunological infiltration and increased expression of HAMP.
To evaluate HAMP mRNA expression in GC, pan-cancer data that include 33 types of cancer in GTEx and TCGA were used. When compared with the normal tissues, the expression of HAMP was considerably higher in GC (P < 0.001). Using XIANTAO online tools, the results show that HAMP levels were higher in tumor samples (P < 0.001), which agrees with the earlier findings in 27 matched pairs of tumors and normal cells and tissue. Twenty-two of the GC patients had elevated HAMP expression. When compared to normal tissues, HAMP expression was considerably higher in GC (P < 0.001). The significance of HAMP expression was further assessed using 53 pairs of tissue samples and clinical data from gastric para-carcinoma and carcinoma. The findings revealed that Lauren classification and HAMP expression were related (P = 0.047), and other clinical features did not differ significantly. Due to the small sample size, the online tool XIANTAO was used to carry out additional validation in the TCGA database. According to a sex-based norm, the level of HAMP was higher in men and women. A higher TNM stage was correlated with increased HAMP levels and their upregulation. HAMP expression and upregulation were substantially correlated with the TNM stage when the TNM stage was higher. Additionally, compared to G0, HAMP levels were greater in histologic grades of G1, G2, and G3. HAMP overexpression is linked to poor FP, OS, and PPS in GC patients.
The relationship between the expression of HAMP and prognosis and tumor was then investigated. In patients with stage 3 GC, poor OS and FP were associated with increased HAMP expression, depending on the stage of the tumor. It was found that moderately differentiated tumors with elevated HAMP expression had poorer OS. In addition, both male and female GC patients with elevated HAMP levels had poor OS and FS. Following surgery only, increased expression of HAMP was additionally linked to poor OS and FS. The findings suggested a link between higher HAMP expression and adverse clinical outcomes. To investigate its importance and to suggest HAMP as a more favorable therapeutic target and diagnostic biomarker, publicly accessible data of gene expression were combined in GC patients with verification of the experiment. Additionally, it was discovered that immune infiltration in GC and HAMP expression were strongly correlated (Yang et al., 2022).
3.7.2 PRTN3
PRTN3 encodes the neutrophil-derived protease proteinase-3 (PR3), which is the target of ANCA. Genetic variations at the locus of PRTN3 is linked to granulomatosis along with polyangiitis (GPA)/PR3-ANCA (Chen et al., 2023). PRTN3 expression (message) in healthy controls was shown to be associated with an eQTL (expression quantitative trait locus), rs62132293, which is a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) found upstream of the PRTN3 transcription start site (Chen et al., 2023). Elevated PRTN3 gene expression (message) has an effect on the generation of circulating autoantigens, which may predispose individuals to serious illness. Although in healthy people, rs62132293 is a well-established eQTL for gene expression of PRTN3, no studies have been conducted to date on the effect of gene expression variants, clinical outcomes in patients, or circulating PR3 (Chen et al., 2023).
The in vitro labeling methods are known as isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) and were created by ABI, Inc. iTRAQ is frequently used in the analysis of differentially expressed investigations due to its benefits of high resolution, high throughput, a high degree of automation, accurate, and reproducible quantification using copious data (Li et al., 2021). iTRAQ was utilized to find GC biomarkers by employing a strategy of iTRAQ quantitative proteomics. It was found that from NGC vs. EGC, 502 DEPs were upregulated in gastric tissues, and from PGC vs. EGC, 727 DEPs were upregulated. RNA binding and innate immune responses are the main functions of DEPs. PRTN3 was found to differentiate early GC using gene ontology enrichment analysis. A PRM assay revealed that in the gastric mucosa of patients with EGC, PRTN3 was upregulated compared to patients with NGC and PGC. Hence, gastric mucosa PRTN3 acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker for assessing early GC patients.
A strict cutoff level of P-value <0.05 and log2 (fold change) = 1.2 was used to screen differentially expressed proteins (DEPs). When comparing NGC to EGC, PGC to NGC, and EGC to PGC, it was found that 281, 253, and 387 proteins were downregulated and 502, 213, and 727 proteins were upregulated, respectively. After that, EGC was compared to NGC and EGC to PGC using a Gene Ontology enrichment analysis. EGC differed from PGC and NGC through “ficolin-1-rich granule lumen” and “azurophil granule lumen,” according to the associations between the topmost six GO terms that corresponded to the enriched DEPs. Interestingly, in both analyses, PRTN3 was the most notable protein that was elevated. As a result, PRTN3 could be employed as a gastric mucosa marker for differentiating healthy, early-stage, and advanced-stage GC.
Each group’s differential expression was evaluated. In total, 3,928 proteins were found, from which 783 (502 upregulated and 281 downregulated) between NGC and EGC and 1,114 (727 upregulated and 387 downregulated) between PGC and EGC were DEPs. Compared to NGC vs. EGC and PGC vs. EGC, PRTN3 expression was noticeably increased, similar to the results from above. To further support the hypothesis, the protein expressions that were expressed differentially in each group’s gastric mucosa were quantified. In PGC vs. EGC and NGC vs. EGC, PRTN was the protein that was most elevated and had the highest FC value. In both the EGC vs. NGC and EGC vs. PGC comparisons, PRTN3 was the protein that was most elevated and had the highest FC value. There was no statistically significant difference in expression of PRTN3 between the groups of PGC and NGC compared to either group of PGC and EGC or the NGC and EGC groups. According to the findings, a significant increase in gastric mucosa PRTN3 levels may be a sign of early GC.
In conclusion, when comparing PGC and NGC patients, the gastric mucosal tissue PRTN3 expression was significantly higher in EGC patients. This suggests a novel endoscopic screening method to detect early GC (Guo et al., 2023). PRTN3 is upregulated in GC and correlates with advanced N stage. Silencing PRTN3 suppresses cell cycle progression, reduces GC cell proliferation (∼40%), and increases apoptosis (∼35%) (Zhu et al., 2025). Various clinical trials related to these biomarkers are included in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Biomarker | Type | Upregulation/downregulation | No. of patients | Location for sampling | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSPA6 | Autosomal-recessive candidate protein | Upregulated | 166 | Tissue (gene) | Zhang et al. (2023b) |
| ANXA11 | Calcium (Ca2+)-regulated phospholipid-binding proteins | Upregulated | 255 subjects in two stages | Urine | Fan et al. (2022) |
| CDC42 | Cell division control protein 42 of the Rho family of GTPases | Upregulated | 255 subjects in two stages | Urine | Fan et al. (2022) |
| NAPA | Protein-coding genes | Upregulated | 255 subjects in two stages | Urine | Fan et al. (2022) |
| FAP | A type 2 membrane-bound glycoprotein | Upregulated | 56 normal samples and 60 GC samples | Differentially expressed gene | Li et al. (2022) |
| SERPINH1/HSP47 | Serpin that serves as a human chaperone protein for collagen | Upregulated | 56 normal samples and 60 GC samples | Differentially expressed gene | Li et al. (2022) |
| HAMP (hepcidin antimicrobial peptide) | Polypeptide hormone | Upregulated | 53 patients | GC cells and tissues | Yang et al. (2022) |
| Cystatin B (CSTB) | A protein structure encoded by the CSTB gene | Downregulated | 31 healthy individuals and 31 GC (adenocarcinoma) patients | Saliva | Koopaie et al. (2022) |
| Deleted in malignant brain tumor 1 (DMBT1) | A tumor-inhibiting gene | Upregulated | 31 healthy individuals and 31 GC (adenocarcinoma) patients | Saliva | Koopaie et al. (2022) |
| Nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) | lncRNA | Downregulated | 21 control samples and 111 GC samples | Gene | Azadeh et al. (2022) |
| N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs | Internal modification in RNA | Upregulated | RNA sequence transcriptome data of 88 Asian GC patients 23 m6A-related genes were extracted from the TCGA database |
Tissue (gene) | Xu et al. (2022) |
| 8 circular RNAs (circRNAs) | Circulating non-coding RNAs | Upregulated | Two independent datasets (GSE89143 and GSE83521). All expression profiling data were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. A pilot cohort of 28 matched GC and adjacent normal mucosal (ANM) tissues. The training cohort consisted of 92 patients with GC and 46 endoscopically negative patients (non-disease controls) enrolled at Kumamoto University, Japan, between 2010 and 2015. The second validation cohort consisted of serum specimens from 102 GC patients and 48 non-disease control subjects enrolled at the Mie University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan, between 2006 and 2017. Independent cohort of 24 GC patients from March 2017 to March 2018 at Nagoya University, Japan. | Serum | Roy et al. (2022) |
| PRTN3 | A serine protease enzyme expressed mainly in neutrophil granulocytes encoded by the PRTN3 gene | Upregulated | 25 patients with early GC, 25 patients with progressive GC, and 25 control individuals with chronic gastritis | Tissue sample | Guo et al. (2023) |
Clinical trials accompanied by various biomarkers in GC.
4 Multi-omics integration and combined biomarker panels in GC
The integration of multi-omics approaches combining genomic, epigenomic (e.g., DNA methylation), transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data offers a powerful framework for developing robust biomarker panels for early GC detection (Ali, 2023; Li et al., 2024a). Multi-omics panels consistently outperform individual markers by leveraging complementary molecular signatures, improving both sensitivity and specificity (Olivier et al., 2019). For instance, a recent liquid biopsy study (ASCEND-GASTRIC) combined cfDNA methylation, ctDNA mutation, and serum protein markers to show enhanced early detection capability for GC compared to single-layer analyses (Wang et al., 2023). A study used multiple dimensions of cfDNA, including fragment size, copy number variation, nucleosome coverage, and single-nucleotide patterns, to detect stage I–II GC, achieving AUROC values of 0.96–0.97 across validation cohorts (Yu et al., 2024). Broad profiling of cell-free multi-omics data in GC cohorts has also confirmed that integrated omics yield superior identification of cancer-specific signatures compared to single-omic models (Tao et al., 2023). Moreover, recent cohort-level studies augment these findings. The GutSeer assay combined targeted DNA methylation and fragmentomics sequencing in plasma to detect gastrointestinal cancers; while less sensitive for GC (∼65%), it achieved high specificity (95%–96%) in a large validation cohort, demonstrating the clinical feasibility of multi-omic panels (Huang et al., 2025).
Comprehensive multi-omics analyses incorporating mutations, CNVs, methylation, and gene expression from TCGA data enabled the creation of optimized prognostic models with increased accuracy (AUC ∼0.85) compared to single-omic counterparts (Guo et al., 2024). Lastly, multi-level omics reviews highlight the potential of integrating biological networks and machine learning to define early GC biomarkers from dynamic inflammatory cascades to malignant transformation (Zhang et al., 2024).
Together, these studies underscore the promise of multi-omics integration and combined biomarker panels for advancing early GC diagnosis. By harnessing complementary molecular signals and employing machine learning–based classification, this strategy increases diagnostic precision, sheds light on tumor heterogeneity, and may facilitate future translation into non-invasive clinical assays.
5 Conclusion and future perspectives
In recent years, the identification of novel biomarkers across multiple biological samples has significantly advanced the early diagnosis of GC, a disease often detected at advanced stages due to subtle initial symptoms. Biomarkers identified in saliva (e.g., CSTB and DMBT1), urine (e.g., ANXA11, CDC42, NAPA), tissue (e.g., HSPA6, m6A-related lncRNAs, and PRTN3), genetic profiles (e.g., FAP, SERPINH1, HAMP, NEAT1), and serum (e.g., various circRNAs) have demonstrated potential for improving early detection and guiding therapeutic strategies. These discoveries have laid the groundwork for more accessible, cost-effective, and non-invasive diagnostic solutions. Despite these promising developments, several critical challenges remain. Many of the reported biomarkers lack large-scale clinical validation, suffer from poor reproducibility across populations, or are limited by insufficient sensitivity and specificity when used alone. Additionally, the translation from bench to bedside is hindered by the lack of standardized protocols for sample collection, processing, and interpretation.
To bridge these gaps, future research should focus on integrating multi-omics data, employing artificial intelligence for biomarker panel optimization, and conducting prospective multicenter clinical trials. There is also a need to develop non-invasive, point-of-care diagnostic platforms, possibly using biosensors, radiolabeled agents, and advanced molecular imaging techniques. Such innovations could drastically reduce diagnostic delays and improve survival rates. Ultimately, a multidisciplinary approach combining molecular biology, bioengineering, computational science, and clinical research is essential to develop robust, reliable, and widely applicable biomarkers for the early detection and monitoring of GC.
Statements
Author contributions
SK: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. AK: Writing – original draft, Data Curation. RB: Writing – original draft, Validation. DC: Writing – original draft, Visualization. RK: Writing – original draft, Supervision. BC: Writing – review and editing, Resources, Project Administration. WAD: Writing – review and editing, Funding Acquisition. MNM: Writing – review and editing, Formal analysis. WH: Writing – review and editing, Investigation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Mutah University (Grant Number 2025/1002).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Chitkara College of Pharmacy, Chitkara University, Rajpura, Patiala, Punjab, India, for providing the necessary facilities to carry out the research work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
HSPA6, Heat Shock Protein Family A6; ANXA11, Annexin A11; CDC42, Cell Division Cycle 42; FAP, Fibroblast Activation Protein-alpha, HAMP, Hepcidin Antimicrobial Peptide; SLC25A4, Solute Carrier Family 25 member 4; SERPINH1, Serpin Peptidase Inhibitor Clade H Member 1; DMBT1, Deleted in Malignant Brain Tumours 1; NEAT1, Nuclear Paraspeckle Assembly Transcript 1; PRTN3, Proteinase 3; NAS, Nitric acid synthase; ADC, Arginase decarboxylase enzyme; NO, Nitric oxide.
References
1
Abdolahi F. Shahraki A. Sheervalilou R. Mortazavi S. S. (2023). Identification of differentially expressed genes associated with the pathogenesis of gastric cancer by bioinformatics analysis. BMC Med. Genomics16, 311. 10.1186/s12920-023-01720-7
2
Adriaens C. Standaert L. Barra J. Latil M. Verfaillie A. Kalev P. et al (2016). p53 induces formation of NEAT1 lncRNA-containing paraspeckles that modulate replication stress response and chemosensitivity. Nat. Med.22, 861–868. 10.1038/nm.4135
3
Ahmad A. Imran M. Ahsan H. (2023). Biomarkers as biomedical bioindicators: approaches and techniques for the detection, analysis, and validation of novel biomarkers of diseases. Pharmaceutics15, 1630. 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061630
4
Albakova Z. Armeev G. A. Kanevskiy L. M. Kovalenko E. I. Sapozhnikov A. M. (2020). HSP70 multi-functionality in cancer. Cells9, 587. 10.3390/cells9030587
5
Ali H. (2023). Artificial intelligence in multi-omics data integration: advancing precision medicine, biomarker discovery and genomic-driven disease interventions. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch.8, 1012–1030. 10.30574/ijsra.2023.8.1.0189
6
Anbarasi K. Kathirvel G. Vani G. Jayaraman G. Devi C. S. (2006a). Cigarette smoking induces heat shock protein 70 kDa expression and apoptosis in rat brain: modulation by bacoside A. Neuroscience138, 1127–1135. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.11.029
7
Anbarasi K. Vani G. Balakrishna K. Devi C. S. (2006b). Effect of bacoside A on brain antioxidant status in cigarette smoke exposed rats. Life Sci.78, 1378–1384. 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.07.030
8
Azadeh M. Salehzadeh A. Ghaedi K. Talesh Sasani S. (2022). NEAT1 can be a diagnostic biomarker in the breast cancer and gastric cancer patients by targeting XIST, hsa-miR-612, and MTRNR2L8: integrated RNA targetome interaction and experimental expression analysis. Genes Environ.44, 1–18. 10.1186/s41021-022-00244-3
9
Beere H. M. Green D. R. (2001). Stress management–heat shock protein-70 and the regulation of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol.11, 6–10. 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)01874-2
10
Bonne N. J. Wong D. T. (2012). Salivary biomarker development using genomic, proteomic and metabolomic approaches. Genome Med.4, 82. 10.1186/gm383
11
Bradshaw P. C. (2019). Cytoplasmic and mitochondrial NADPH-coupled redox systems in the regulation of aging. Nutrients11, 504. 10.3390/nu11030504
12
Braidotti P. Nuciforo P. Mollenhauer J. Poustka A. Pellegrini C. Moro A. et al (2004). DMBT1 expression is down-regulated in breast cancer. BMC Cancer4, 46–49. 10.1186/1471-2407-4-46
13
Bray F. Ferlay J. Soerjomataram I. Siegel R. L. Torre L. A. Jemal A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA a Cancer J. Clin.68, 394–424. 10.3322/caac.21492
14
Brim H. Ashktorab H. (2016). “Genomics of colorectal cancer in African Americans,” in Next generation, sequencing and applications3.
15
Bröer A. Rahimi F. Bröer S. (2016). Deletion of amino acid transporter ASCT2 (SLC1A5) reveals an essential role for transporters SNAT1 (SLC38A1) and SNAT2 (SLC38A2) to sustain glutaminolysis in cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem.291, 13194–13205. 10.1074/jbc.M115.700534
16
Bušek P. MalíK R. Šedo A. (2004). Dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity and/or structure homologues (DASH) and their substrates in cancer. Int. J. Biochem. and Cell Biol.36, 408–421. 10.1016/s1357-2725(03)00262-0
17
Busek P. Mateu R. Zubal M. Kotackova L. Sedo A. (2018). Targeting fibroblast activation protein in cancer-Prospects and caveats. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed.23, 1933–1968. 10.2741/4682
18
Cai J. Yang D. Sun H. Xiao L. Han F. Zhang M. et al (2023). A multifactorial analysis of FAP to regulate gastrointestinal cancers progression. Front. Immunol.14, 1183440. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183440
19
Calderwood S. K. Khaleque M. A. Sawyer D. B. Ciocca D. R. (2006). Heat shock proteins in cancer: chaperones of tumorigenesis. Trends Biochem. Sci.31, 164–172. 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.01.006
20
Carlomagno N. Incollingo P. Tammaro V. Peluso G. Rupealta N. Chiacchio G. et al (2017). Diagnostic, predictive, prognostic, and therapeutic molecular biomarkers in third millennium: a breakthrough in gastric cancer. BioMed Res. Int.2017, 7869802. 10.1155/2017/7869802
21
Chakravarty D. Sboner A. Nair S. S. Giannopoulou E. Li R. Hennig S. et al (2014). The oestrogen receptor alpha-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 is a critical modulator of prostate cancer. Nat. Commun.5, 5383. 10.1038/ncomms6383
22
Charitos I. A. D’agostino D. Topi S. Bottalico L. (2021). 40 years of helicobacter pylori: a revolution in biomedical thought. Gastroenterol. Insights12, 111–135. 10.3390/gastroent12020011
23
Chen Y. G. Chen R. Ahmad S. Verma R. Kasturi S. P. Amaya L. et al (2019). N6-methyladenosine modification controls circular RNA immunity. Mol. Cell76, 96–109.e9. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.016
24
Chen C.-L. Hsu S.-C. Ann D. K. Yen Y. Kung H.-J. (2021). Arginine signaling and cancer metabolism. Cancers13, 3541. 10.3390/cancers13143541
25
Chen D. P. Aiello C. P. Mccoy D. Stamey T. Yang J. Hogan S. L. et al (2023). PRTN3 variant correlates with increased autoantigen levels and relapse risk in PR3-ANCA versus MPO-ANCA disease. JCI Insight8, e166107. 10.1172/jci.insight.166107
26
Chiou Y.-H. Liou S.-H. Wong R.-H. Chen C.-Y. Lee H. (2015). Nickel may contribute to EGFR mutation and synergistically promotes tumor invasion in EGFR-mutated lung cancer via nickel-induced microRNA-21 expression. Toxicol. Lett.237, 46–54. 10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.05.019
27
Choi B.-H. Coloff J. L. (2019). The diverse functions of non-essential amino acids in cancer. Cancers11, 675. 10.3390/cancers11050675
28
Chou Y.-T. Lin H.-H. Lien Y.-C. Wang Y.-H. Hong C.-F. Kao Y.-R. et al (2010). EGFR promotes lung tumorigenesis by activating miR-7 through a Ras/ERK/Myc pathway that targets the Ets2 transcriptional repressor ERF. Cancer Res.70, 8822–8831. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0638
29
Clémençon B. Babot M. Trézéguet V. (2013). The mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier (SLC25 family): pathological implications of its dysfunction. Mol. Aspects Med.34, 485–493. 10.1016/j.mam.2012.05.006
30
Clemson C. M. Hutchinson J. N. Sara S. A. Ensminger A. W. Fox A. H. Chess A. et al (2009). An architectural role for a nuclear noncoding RNA: NEAT1 RNA is essential for the structure of paraspeckles. Mol. Cell33, 717–726. 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.026
31
Conde A. R. Martins A. P. Brito M. Manuel A. Ramos S. Malta-Vacas J. et al (2007). DMBT1 is frequently downregulated in well-differentiated gastric carcinoma but more frequently upregulated across various gastric cancer types. Int. J. Oncol.30, 1441–1446. 10.3892/ijo.30.6.1441
32
Deberardinis R. J. Thompson C. B. (2012). Cellular metabolism and disease: what do metabolic outliers teach us?Cell148, 1132–1144. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.032
33
Del Arco C. D. Aceñero M. J. F. Medina L. O. (2024). Liquid biopsy for gastric cancer: techniques, applications, and future directions. World J. Gastroenterology30, 1680–1705. 10.3748/wjg.v30.i12.1680
34
Di Matteo F. Pipicelli F. Kyrousi C. Tovecci I. Penna E. Crispino M. et al (2020). Cystatin B is essential for proliferation and interneuron migration in individuals with EPM 1 epilepsy. EMBO Mol. Med.12, e11419. 10.15252/emmm.201911419
35
Di Meo A. Bartlett J. Cheng Y. Pasic M. D. Yousef G. M. (2017). Liquid biopsy: a step forward towards precision medicine in urologic malignancies. Mol. Cancer16, 80–14. 10.1186/s12943-017-0644-5
36
Ding P. A. Wu J. Wu H. Li T. Niu X. Yang P. et al (2024). Transcriptomics‐based liquid biopsy for early detection of recurrence in locally advanced gastric cancer. Adv. Sci.11, 2406276. 10.1002/advs.202406276
37
Dong P. Xiong Y. Yue J. Hanley S. J. Kobayashi N. Todo Y. et al (2018). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1: a novel target for diagnosis and therapy in human tumors. Front. Genet.9, 471. 10.3389/fgene.2018.00471
38
Dong X. Meng L. Liu P. Ji R. Su X. Xin Y. et al (2019). YAP/TAZ: a promising target for squamous cell carcinoma treatment. Cancer Manag. Res.11, 6245–6252. 10.2147/CMAR.S197921
39
Du D. S. Yang X. Z. Wang Q. Dai W. J. Kuai W. X. Liu Y. L. et al (2016). Effects of CDC42 on the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep.13, 550–554. 10.3892/mmr.2015.4523
40
Duarte B. D. P. Bonatto D. (2018). The heat shock protein 47 as a potential biomarker and a therapeutic agent in cancer research. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol.144, 2319–2328. 10.1007/s00432-018-2739-9
41
Fan Y. Liu B. Chen F. Song Z. Han B. Meng Y. et al (2021). Hepcidin upregulation in lung cancer: a potential therapeutic target associated with immune infiltration. Front. Immunol.12, 612144. 10.3389/fimmu.2021.612144
42
Fan H. Li X. Li Z.-W. Zheng N.-R. Cao L.-H. Liu Z.-C. et al (2022). Urine proteomic signatures predicting the progression from premalignancy to malignant gastric cancer. EBioMedicine86, 104340. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104340
43
Fang Z. Yin S. Sun R. Zhang S. Fu M. Wu Y. et al (2017). miR-140-5p suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer by regulating YES1. Mol. Cancer16, 139. 10.1186/s12943-017-0708-6
44
Fang R. Ye L. Shi H. (2021). Understanding the roles of N6-methyladenosine writers, readers and erasers in breast cancer. Neoplasia23, 551–560. 10.1016/j.neo.2021.04.002
45
Feldmeyer N. Wabnitz G. Leicht S. Luckner-Minden C. Schiller M. Franz T. et al (2012). Arginine deficiency leads to impaired cofilin dephosphorylation in activated human T lymphocytes. Int. Immunol.24, 303–313. 10.1093/intimm/dxs004
46
Feng F. Tian Y. Xu G. Liu Z. Liu S. Zheng G. et al (2017). Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19–9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer. BMC Cancer17, 737. 10.1186/s12885-017-3738-y
47
Ferlay J. Colombet M. Soerjomataram I. Mathers C. Parkin D. M. Piñeros M. et al (2019). Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer144, 1941–1953. 10.1002/ijc.31937
48
Fernandez L. P. Gomez De Cedron M. Ramirez De Molina A. (2020). Alterations of lipid metabolism in cancer: implications in prognosis and treatment. Front. Oncol.10, 577420. 10.3389/fonc.2020.577420
49
Fernández-Madrid F. Tang N. Alansari H. Granda J. L. Tait L. Amirikia K. C. et al (2004). Autoantibodies to annexin XI-A and other autoantigens in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Cancer Res.64, 5089–5096. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-0932
50
Feron O. (2009). Pyruvate into lactate and back: from the warburg effect to symbiotic energy fuel exchange in cancer cells. Radiotherapy Oncol.92, 329–333. 10.1016/j.radonc.2009.06.025
51
Fingar D. C. (2015). Rag ubiquitination recruits a GATOR1: attenuation of amino acid-induced mTORC1 signaling. Mol. Cell58, 713–715. 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.05.029
52
Fujimoto A. Furuta M. Totoki Y. Tsunoda T. Kato M. Shiraishi Y. et al (2016). Whole-genome mutational landscape and characterization of noncoding and structural mutations in liver cancer. Nat. Genet.48, 500–509. 10.1038/ng.3547
53
Gan X.-X. Li Y.-Y. Li S.-J. Mo S.-S. Feng J.-H. Shen F. et al (2021). Significance of DMBT1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma concurrent with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Front. Oncol.11, 680873. 10.3389/fonc.2021.680873
54
Ganz T. (2003). Hepcidin, a key regulator of iron metabolism and mediator of anemia of inflammation. Blood102, 783–788. 10.1182/blood-2003-03-0672
55
Gao Y. (2013). Urine--an untapped goldmine for biomarker discovery?Sci. China. Life Sci.56, 1145–1146. 10.1007/s11427-013-4574-1
56
Gao L.-M. Wang F. Zheng Y. Fu Z.-Z. Zheng L. Chen L.-L. (2019). Roles of fibroblast activation protein and hepatocyte growth factor expressions in angiogenesis and metastasis of gastric cancer. Pathology and Oncol. Res.25, 369–376. 10.1007/s12253-017-0359-3
57
Gao M. Liu L. Zhang D. Yang Y. Chang Z. (2020). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 serves as sponge for miR-365a-3p to promote gastric cancer progression via regulating ABCC4. OncoTargets Ther.13, 3977–3985. 10.2147/OTT.S245557
58
Gao Y. Dai H. Zhang N. Jiang H. Zhang Z. Feng Z. et al (2022). The ameliorative effect of mahuang fuzi and shenzhuo decoction on membranous nephropathy of rodent model is associated with autophagy and wnt/β-catenin pathway. Front. Pharmacol.13, 820130. 10.3389/fphar.2022.820130
59
Garay J. Piazuelo M. B. Lopez-Carrillo L. Leal Y. A. Majumdar S. Li L. et al (2017). Increased expression of deleted in malignant brain tumors (DMBT1) gene in precancerous gastric lesions: findings from human and animal studies. Oncotarget8, 47076–47089. 10.18632/oncotarget.16792
60
Geng Q. Liu J. Gong Z. Chen S. Chen S. Li X. et al (2017). Phosphorylation by mTORC1 stablizes Skp2 and regulates its oncogenic function in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer16, 83–12. 10.1186/s12943-017-0649-0
61
Gerke V. Moss S. E. (2002). Annexins: from structure to function. Physiol. Rev.82, 331–371. 10.1152/physrev.00030.2001
62
Gerke V. Creutz C. E. Moss S. E. (2005). Annexins: linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.6, 449–461. 10.1038/nrm1661
63
Giganti F. Tang L. Baba H. (2019). Gastric cancer and imaging biomarkers: part 1–a critical review of DW-MRI and CE-MDCT findings. Eur. Radiol.29, 1743–1753. 10.1007/s00330-018-5732-4
64
Grillo M. Colombatto S. (2004). Arginine revisited: minireview article. Amino Acids26, 345–351. 10.1007/s00726-004-0081-9
65
Gstaiger M. Jordan R. Lim M. Catzavelos C. Mestan J. Slingerland J. et al (2001). Skp2 is oncogenic and overexpressed in human cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.98, 5043–5048. 10.1073/pnas.081474898
66
Gu C. Shi X. Dai C. Shen F. Rocco G. Chen J. et al (2020). RNA m6A modification in cancers: molecular mechanisms and potential clinical applications. Innovation1, 100066. 10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100066
67
Guo D. Zhang B. Wu D. Hu X. Tu H. (2023). Identification of PRTN3 as a novel biomarker for the diagnosis of early gastric cance. J. Proteomics277, 104852. 10.1016/j.jprot.2023.104852
68
Guo S. Wang E. Wang B. Xue Y. Kuang Y. Liu H. (2024). Comprehensive multiomics analyses establish the optimal prognostic model for resectable gastric cancer: prognosis prediction for resectable GC. Ann. Surg. Oncol.31, 2078–2089. 10.1245/s10434-023-14249-x
69
Hageman J. Van Waarde M. A. Zylicz A. Walerych D. Kampinga H. H. (2011). The diverse members of the mammalian HSP70 machine show distinct chaperone-like activities. Biochem. J.435, 127–142. 10.1042/BJ20101247
70
Hahm E. R. Kim S. H. Singh K. B. Singh S. V. (2021). RNA‐seq reveals novel cancer‐selective and disease subtype‐independent mechanistic targets of withaferin A in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog.60, 3–14. 10.1002/mc.23266
71
Han D. Liu J. Chen C. Dong L. Liu Y. Chang R. et al (2019). Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m6A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature566, 270–274. 10.1038/s41586-019-0916-x
72
Hanash S. M. Baik C. S. Kallioniemi O. (2011). Emerging molecular biomarkers—Blood-based strategies to detect and monitor cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.8, 142–150. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.220
73
Hansen T. B. Jensen T. I. Clausen B. H. Bramsen J. B. Finsen B. Damgaard C. K. et al (2013). Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature495, 384–388. 10.1038/nature11993
74
He J. Ren W. (2024). lncRNA NEAT1 promotes the expression of EZH2 in gastric cancer cells and improves cell proliferation and migration through inhibiting hsa-miR-450b-5p. Chin. J. Cancer, 135–145.
75
Hein T. Krammer P. H. Weyd H. (2022). Molecular analysis of annexin expression in cancer. BMC Cancer22, 994. 10.1186/s12885-022-10075-8
76
Hill G. E. Fu X. Balenger S. Mcgraw K. J. Giraudeau M. Hood W. R. (2013). Changes in concentrations of circulating heat‐shock proteins in house Finches in response to different environmental stressors. J. Field Ornithol.84, 416–424. 10.1111/jofo.12040
77
Hirai K. Kikuchi S. Kurita A. Ohashi S. Adachi E. Matsuoka Y. et al (2006). Immunohistochemical distribution of heat shock protein 47 (HSP47) in scirrhous carcinoma of the stomach. Anticancer Res.26, 71–78.
78
Hirose T. Virnicchi G. Tanigawa A. Naganuma T. Li R. Kimura H. et al (2014). NEAT1 long noncoding RNA regulates transcription via protein sequestration within subnuclear bodies. Mol. Biol. Cell25, 169–183. 10.1091/mbc.E13-09-0558
79
Hodge R. G. Ridley A. J. (2016). Regulating Rho GTPases and their regulators. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.17, 496–510. 10.1038/nrm.2016.67
80
Hoki T. Katsuta E. Yan L. Takabe K. Ito F. (2019). Low DMT1 expression associates with increased oxidative phosphorylation and early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Surg. Res.234, 343–352. 10.1016/j.jss.2018.11.008
81
Hong X. Liu F. (2022). Editorial: molecular biomarkers for gastric cancer. Front. Oncol.12, 850373. 10.3389/fonc.2022.850373
82
Hoter A. El-Sabban M. E. Naim H. Y. (2018). The HSP90 family: structure, regulation, function, and implications in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19, 2560. 10.3390/ijms19092560
83
Hu B.-B. Wang X.-Y. Gu X.-Y. Zou C. Gao Z.-J. Zhang H. et al (2019). N 6-methyladenosine (m 6 A) RNA modification in gastrointestinal tract cancers: roles, mechanisms, and applications. Mol. Cancer18, 178–8. 10.1186/s12943-019-1099-7
84
Hu K. Yu W. Ajayi O. E. Li L. Huang Z. Rong Q. et al (2020). Integrated analysis of whole genome and transcriptome sequencing in a young patient with gastric cancer provides insights for precision therapy. Oncol. Lett.20, 115. 10.3892/ol.2020.11976
85
Hua K. Li Y. Zhao Q. Fan L. Tan B. Gu J. (2018). Downregulation of annexin A11 (ANXA11) inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration via the AKT/GSK-3β pathway in gastric cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res.24, 149–160. 10.12659/msm.905372
86
Huang H. Weng H. Chen J. (2020). m6A modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: roles and therapeutic implications in cancer. Cancer Cell37, 270–288. 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.02.004
87
Huang A. Guo D.-Z. Su Z.-X. Zhong Y.-S. Liu L. Xiong Z.-G. et al (2025). GUIDE: a prospective cohort study for blood-based early detection of gastrointestinal cancers using targeted DNA methylation and fragmentomics sequencing. Mol. Cancer24, 163. 10.1186/s12943-025-02367-x
88
Husi H. Fernandes M. Skipworth R. J. Miller J. Cronshaw A. D. Fearon K. C. et al (2019). Identification of diagnostic upper gastrointestinal cancer tissue type-specific urinary biomarkers. Biomed. Rep.10, 165–174. 10.3892/br.2019.1190
89
Ito T. Sato K. Maekawa H. Sakurada M. Orita H. Shimada K. et al (2014). Elevated levels of serum fatty acid synthase in patients with gastric carcinoma. Oncol. Lett.7, 616–620. 10.3892/ol.2014.1793
90
Jakobsen K. R. Paulsen B. S. Bæk R. Varming K. Sorensen B. S. Jørgensen M. M. (2015). Exosomal proteins as potential diagnostic markers in advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma. J. Extracell. Vesicles4, 26659. 10.3402/jev.v4.26659
91
Jeck W. R. Sharpless N. E. (2014). Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol.32, 453–461. 10.1038/nbt.2890
92
Jelski W. Mroczko B. (2022). Molecular and circulating biomarkers of gastric cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23, 7588. 10.3390/ijms23147588
93
Ji C.-F. Ji J.-F. Yu X.-B. Wang Z.-X. (2025). N-methyladenosine reader YTHDF2-mediated AC026691. 1 degradation promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and M2 macrophage polarization. Mol. Med. Rep.31, 120. 10.3892/mmr.2025.13485
94
Jiang T. Mei L. Yang X. Sun T. Wang Z. Ji Y. (2022). Biomarkers of gastric cancer: current advancement. Heliyon8, e10899. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10899
95
Jin G. Lee S.-W. Zhang X. Cai Z. Gao Y. Chou P.-C. et al (2015). Skp2-mediated RagA ubiquitination elicits a negative feedback to prevent amino-acid-dependent mTORC1 hyperactivation by recruiting GATOR1. Mol. Cell58, 989–1000. 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.05.010
96
Joensuu T. Lehesjoki A. E. Kopra O. (2008). Molecular background of EPM1—Unverricht–Lundborg disease. Epilepsia49, 557–563. 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01422.x
97
Joshi N. Bhat F. Bellad A. Sathe G. Jain A. Chavan S. et al (2023). Urinary proteomics for discovery of gastric cancer biomarkers to enable precision clinical oncology. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol.27, 361–371. 10.1089/omi.2023.0077
98
Ju H. Lu Y. Wu Q. Liu J. Zeng Z. Mo H. et al (2017). Disrupting G6PD-mediated redox homeostasis enhances chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer. Oncogene36, 6282–6292. 10.1038/onc.2017.227
99
Kaczor-Urbanowicz K. E. Martin Carreras-Presas C. Aro K. Tu M. Garcia-Godoy F. Wong D. T. (2017). Saliva diagnostics–current views and directions. Exp. Biol. Med.242, 459–472. 10.1177/1535370216681550
100
Kang W. Reid K. B. (2003). DMBT1, a regulator of mucosal homeostasis through the linking of mucosal defense and regeneration?FEBS Lett.540, 21–25. 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00217-5
101
Kathagen-Buhmann A. Schulte A. Weller J. Holz M. Herold-Mende C. Glass R. et al (2016). Glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway are differentially associated with the dichotomous regulation of glioblastoma cell migration versus proliferation. Neuro-Oncology18, 1219–1229. 10.1093/neuonc/now024
102
Kawagoe K. Wada M. Idichi T. Okada R. Yamada Y. Moriya S. et al (2020). Regulation of aberrantly expressed SERPINH1 by antitumor miR-148a-5p inhibits cancer cell aggressiveness in gastric cancer. J. Hum. Genet.65, 647–656. 10.1038/s10038-020-0746-6
103
Keane F. M. Yao T.-W. Seelk S. Gall M. G. Chowdhury S. Poplawski S. E. et al (2014). Quantitation of fibroblast activation protein (FAP)-specific protease activity in mouse, baboon and human fluids and organs. FEBS Open Bio4, 43–54. 10.1016/j.fob.2013.12.001
104
Kishk R. M. Soliman N. M. Anani M. M. Nemr N. Salem A. Attia F. et al (2021). Genotyping of Helicobacter pylori virulence genes cagA and vacA: regional and national study. Int. J. Microbiol.2021, 5540560. 10.1155/2021/5540560
105
Knight W. R. Allum W. H. (2019). Gastric tumours. Medicine47, 309–313. 10.1016/j.mpmed.2019.02.002
106
Knutsen E. Harris A. L. Perander M. (2022). Expression and functions of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 and isoforms in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer126, 551–561. 10.1038/s41416-021-01588-3
107
Kočevar N. Odreman F. Vindigni A. Grazio S. F. Komel R. (2012). Proteomic analysis of gastric cancer and immunoblot validation of potential biomarkers. World J. Gastroenterology WJG18, 1216–1228. 10.3748/wjg.v18.i11.1216
108
Kong F. Wang K. Wang L. (2022). Systematic analysis of the expression profile and prognostic significance of m6A regulators and PD-L1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Discov. Oncol.13, 131. 10.1007/s12672-022-00595-x
109
Koopaie M. Ghafourian M. Manifar S. Younespour S. Davoudi M. Kolahdooz S. et al (2022). Evaluation of CSTB and DMBT1 expression in saliva of gastric cancer patients and controls. BMC Cancer22, 1–16. 10.1186/s12885-022-09570-9
110
Kreutmayer S. B. Messner B. Knoflach M. Henderson B. Niederegger H. Böck G. et al (2011). Dynamics of heat shock protein 60 in endothelial cells exposed to cigarette smoke extract. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.51, 777–780. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.07.003
111
Krysan K. Tran L. M. Grimes B. S. Fishbein G. A. Seki A. Gardner B. K. et al (2019). The immune contexture associates with the genomic landscape in lung adenomatous premalignancy. Cancer Res.79, 5022–5033. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0153
112
Lai Y.-H. Chen J. Wang X.-P. Wu Y.-Q. Peng H.-T. Lin X.-H. et al (2017). Collagen triple helix repeat containing-1 negatively regulated by microRNA-30c promotes cell proliferation and metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in breast cancer. J. Exp. and Clin. Cancer Res.36, 92–15. 10.1186/s13046-017-0564-7
113
Lanzós A. Carlevaro-Fita J. Mularoni L. Reverter F. Palumbo E. Guigó R. et al (2017). Discovery of cancer driver long noncoding RNAs across 1112 tumour genomes: new candidates and distinguishing features. Sci. Rep.7, 41544. 10.1038/srep41544
114
Lecona E. Turnay J. Olmo N. Guzmán-Aránguez A. Morgan R. O. Fernandez M.-P. et al (2003). Structural and functional characterization of recombinant mouse annexin A11: influence of calcium binding. Biochem. J.373, 437–449. 10.1042/BJ20021721
115
Lee K. N. Jackson K. W. Christiansen V. J. Lee C. S. Chun J.-G. Mckee P. A. (2006). Antiplasmin-cleaving enzyme is a soluble form of fibroblast activation protein. Blood107, 1397–1404. 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3452
116
Lee H. Kwon J. Kang M. Noh M.-K. Koh J. Kim J. et al (2016). Overexpression of HSP47 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: clinical implications and functional analysis. Dis. Esophagus29, 848–855. 10.1111/dote.12359
117
Li T. Le A. (2018). “Glutamine metabolism in cancer,” in The heterogeneity of cancer metabolism, 13–32.
118
Li J. Metruccio M. M. Evans D. J. Fleiszig S. M. (2017a). Mucosal fluid glycoprotein DMBT1 suppresses twitching motility and virulence of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog.13, e1006392. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006392
119
Li P. Chen H. Chen S. Mo X. Li T. Xiao B. et al (2017b). Circular RNA 0000096 affects cell growth and migration in gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer116, 626–633. 10.1038/bjc.2016.451
120
Li W. Zhang Z. Liu X. Cheng X. Zhang Y. Han X. et al (2017c). The FOXN3-NEAT1-SIN3A repressor complex promotes progression of hormonally responsive breast cancer. J. Clin. Investigation127, 3421–3440. 10.1172/JCI94233
121
Li S. Li J. Chen C. Zhang R. Wang K. (2018a). Pan-cancer analysis of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 in various cancers. Genes and Dis.5, 27–35. 10.1016/j.gendis.2017.11.003
122
Li X. Jiang M. Chen D. Xu B. Wang R. Chu Y. et al (2018b). miR-148b-3p inhibits gastric cancer metastasis by inhibiting the Dock6/Rac1/Cdc42 axis. J. Exp. and Clin. Cancer Res.37, 71. 10.1186/s13046-018-0729-z
123
Li J. Sun D. Pu W. Wang J. Peng Y. (2020). Circular RNAs in cancer: biogenesis, function, and clinical significance. Trends Cancer6, 319–336. 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.01.012
124
Li F. Yang B. Liu Y. Tang T. Wang C. Li M. et al (2021). Acupuncture regulates serum differentially expressed proteins in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis: a quantitative iTRAQ proteomics study. Evidence‐Based Complementary Altern. Med.2021, 9962224. 10.1155/2021/9962224
125
Li J. Han T. Wang X. Wang Y. Chen X. Chen W. et al (2022). H19 may regulate the immune cell infiltration in carcinogenesis of gastric cancer through miR-378a-5p/SERPINH1 signaling. World J. Surg. Oncol.20, 295. 10.1186/s12957-022-02760-6
126
Li S. Zeng H. Fan J. Wang F. Xu C. Li Y. et al (2023). Glutamine metabolism in breast cancer and possible therapeutic targets. Biochem. Pharmacol.210, 115464. 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115464
127
Li J. Xu S. Zhu F. Shen F. Zhang T. Wan X. et al (2024a). Multi-omics combined with machine learning facilitating the diagnosis of gastric cancer. Curr. Med. Chem.31, 6692–6712. 10.2174/0109298673284520240112055108
128
Li J. Zhao W. Yang J. Lu P. Sun H. Zhang Z. et al (2024b). Proteomic and serological markers for diagnosing cardia gastric cancer and precursor lesions in a Chinese population. Sci. Rep.14, 25309. 10.1038/s41598-024-75912-1
129
Li P. Li Z. Linghu E. Ji J. Association S. O. D. E. O. T. C. M. Association C. S. G. O. T. C. M. et al (2024c). Chinese national clinical practice guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of early gastric cancer. Chin. Med. J.137, 887–908. 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003101
130
Liang Y. Zhao Y. Li L. Wei H. Huang T. Zhang H. et al (2021). MicroRNA profiles in five pairs of early gastric cancer tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues. Oncol. Lett.22, 595. 10.3892/ol.2021.12856
131
Liberti M. V. Locasale J. W. (2016). The warburg effect: how does it benefit cancer cells?Trends Biochem. Sci.41, 211–218. 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.12.001
132
Lin X. Chai G. Wu Y. Li J. Chen F. Liu J. et al (2019). RETRACTED ARTICLE: RNA m6A methylation regulates the epithelial mesenchymal transition of cancer cells and translation of snail. Nat. Commun.10, 2065. 10.1038/s41467-019-09865-9
133
Lind D. S. (2004). Arginine and cancer. J. Nutr.134, 2837S–2853S. 10.1093/jn/134.10.2837S
134
Liu T. Huang C. Sun L. Chen Z. Ge Y. Ji W. et al (2025). FAP+ gastric cancer mesenchymal stromal cells via paracrining INHBA and remodeling ECM promote tumor progression. Int. Immunopharmacol.144, 113697. 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113697
135
Luebke T. Baldus S. E. Grass G. Bollschweiler E. Thiele J. Dienes H.-P. et al (2005). Histological grading in gastric cancer by ming classification: correlation with histopathological subtypes, metastasis, and prognosis. World J. Surg.29, 1422–1428. 10.1007/s00268-005-7795-z
136
Ma X. Wang L. Huang D. Li Y. Yang D. Li T. et al (2017a). Polo-like kinase 1 coordinates biosynthesis during cell cycle progression by directly activating pentose phosphate pathway. Nat. Commun.8, 1506. 10.1038/s41467-017-01647-5
137
Ma Y. Chen Y. Petersen I. (2017b). Expression and epigenetic regulation of cystatin B in lung cancer and colorectal cancer. Pathology-Research Pract.213, 1568–1574. 10.1016/j.prp.2017.06.007
138
Ma C. Wang X. Yang F. Zang Y. Liu J. Wang X. et al (2020). Circular RNA hsa_circ_0004872 inhibits gastric cancer progression via the miR-224/Smad4/ADAR1 successive regulatory circuit. Mol. Cancer19, 157–21. 10.1186/s12943-020-01268-5
139
Machida T. Tomofuji T. Ekuni D. Maruyama T. Yoneda T. Kawabata Y. et al (2015). MicroRNAs in salivary exosome as potential biomarkers of aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci.16, 21294–21309. 10.3390/ijms160921294
140
Madsen J. Sorensen G. L. Nielsen O. Tornøe I. Thim L. Fenger C. et al (2013). A variant form of the human deleted in malignant brain tumor 1 (DMBT1) gene shows increased expression in inflammatory bowel diseases and interacts with dimeric trefoil factor 3 (TFF3). PloS One8, e64441. 10.1371/journal.pone.0064441
141
Mamun T. I. Younus S. Rahman M. H. (2024). Gastric cancer-epidemiology, modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, challenges and opportunities: an updated review. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun.41, 100845. 10.1016/j.ctarc.2024.100845
142
Marimuthu A. O’meally R. N. Chaerkady R. Subbannayya Y. Nanjappa V. Kumar P. et al (2011). A comprehensive map of the human urinary proteome. J. Proteome Res.10, 2734–2743. 10.1021/pr2003038
143
Marshall A. Van Geldermalsen M. Otte N. Lum T. Vellozzi M. Thoeng A. et al (2017). ASCT2 regulates glutamine uptake and cell growth in endometrial carcinoma. Oncogenesis6, e367. 10.1038/oncsis.2017.70
144
Memczak S. Jens M. Elefsinioti A. Torti F. Krueger J. Rybak A. et al (2013). Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature495, 333–338. 10.1038/nature11928
145
Messina B. Lo Sardo F. Scalera S. Memeo L. Colarossi C. Mare M. et al (2023). Hippo pathway dysregulation in gastric cancer: from Helicobacter pylori infection to tumor promotion and progression. Cell Death and Dis.14, 21. 10.1038/s41419-023-05568-8
146
Mollenhauer J. Herbertz S. Holmskov U. Tolnay M. Krebs I. Merlo A. et al (2000). DMBT1 encodes a protein involved in the immune defense and in epithelial differentiation and is highly unstable in cancer. Cancer Res.60, 1704–1710.
147
Mollenhauer J. Helmke B. Müller H. Kollender G. Krebs I. Wiemann S. et al (2002). An integrative model on the role of DMBT1 in epithelial cancer. Cancer Detect. Prev.26, 266–274. 10.1016/s0361-090x(02)00094-6
148
Mollenhauer J. Deichmann M. Helmke B. Müller H. Kollender G. Holmskov U. et al (2003). Frequent downregulation of DMBT1 and galectin‐3 in epithelial skin cancer. Int. J. Cancer105, 149–157. 10.1002/ijc.11072
149
Monastyrskaya K. Babiychuk E. B. Hostettler A. Rescher U. Draeger A. (2007). Annexins as intracellular calcium sensors. Cell Calcium41, 207–219. 10.1016/j.ceca.2006.06.008
150
Moreno‐Sánchez R. Rodríguez‐Enríquez S. Marín‐Hernández A. Saavedra E. (2007). Energy metabolism in tumor cells. FEBS J.274, 1393–1418. 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05686.x
151
Mori K. Toiyama Y. Otake K. Fujikawa H. Saigusa S. Hiro J. et al (2017). Proteomics analysis of differential protein expression identifies heat shock protein 47 as a predictive marker for lymph node metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer140, 1425–1435. 10.1002/ijc.30557
152
Moss S. E. Morgan R. O. (2004). The annexins. Genome Biol.5, 1–8. 10.1186/gb-2004-5-4-219
153
Murphy N. P. Binti Ahmad Mokhtar A. M. Mott H. R. Owen D. (2021). Molecular subversion of Cdc42 signalling in cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans.49, 1425–1442. 10.1042/BST20200557
154
Namba T. Dóczi J. Pinson A. Xing L. Kalebic N. Wilsch-Bräuninger M. et al (2020). Human-specific ARHGAP11B acts in mitochondria to expand neocortical progenitors by glutaminolysis. Neuron105, 867–881.e9. 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.027
155
Nannini G. Meoni G. Amedei A. Tenori L. (2020). Metabolomics profile in gastrointestinal cancers: update and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterology26, 2514–2532. 10.3748/wjg.v26.i20.2514
156
Nemeth E. Tuttle M. S. Powelson J. Vaughn M. B. Donovan A. Ward D. M. et al (2004). Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. science306, 2090–2093. 10.1126/science.1104742
157
Niu X. Ren L. Hu A. Zhang S. Qi H. (2022). Identification of potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for gastric cancer based on bioinformatic analysis. Front. Genet.13, 862105. 10.3389/fgene.2022.862105
158
Noonan E. J. Place R. F. Giardina C. Hightower L. E. (2007). Hsp70B′ regulation and function. Cell Stress and Chaperones12, 219–229. 10.1379/csc-278.1
159
Okada K. Chen W.-T. Iwasa S. Jin X. Yamane T. Ooi A. et al (2003). Seprase, a membrane-type serine protease, has different expression patterns in intestinal-and diffuse-type gastric cancer. Oncology65, 363–370. 10.1159/000074650
160
Olivier M. Asmis R. Hawkins G. A. Howard T. D. Cox L. A. (2019). The need for multi-omics biomarker signatures in precision medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci.20, 4781. 10.3390/ijms20194781
161
Organization W. H. (2025). The current and future incidence and mortality of gastric cancer in 185 countries, 2020–40: a population-based modelling study. Int. Agency Res. Cancer. Available online at: https://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/the-current-and-future-incidence-and-mortality-of-gastric-cancer-in-185-countries-2020-40-a-population-based-modelling-study/ (Accessed January 10, 2025).
162
Pamudurti N. R. Bartok O. Jens M. Ashwal-Fluss R. Stottmeister C. Ruhe L. et al (2017). Translation of circRNAs. Mol. Cell66, 9–21.e7. 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.021
163
Pan D. (2010). The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev. Cell19, 491–505. 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.09.011
164
Pan T. (2013). N6-methyl-adenosine modification in messenger and long non-coding RNA. Trends Biochem. Sci.38, 204–209. 10.1016/j.tibs.2012.12.006
165
Panda A. C. (2018). Circular RNAs act as miRNA sponges. Circular RNAs Biogenesis Funct.1087, 67–79. 10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_6
166
Park C. H. Valore E. V. Waring A. J. Ganz T. (2001). Hepcidin, a urinary antimicrobial peptide synthesized in the liver. J. Biol. Chem.276, 7806–7810. 10.1074/jbc.M008922200
167
Park H. S. Kim B. C. Yeo H. Y. Kim K.-H. Yoo B. C. Park J. W. et al (2018a). Deleted in malignant brain tumor 1 is a novel prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep.39, 2279–2287. 10.3892/or.2018.6287
168
Park J. Y. Forman D. Waskito L. A. Yamaoka Y. Crabtree J. E. (2018b). Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori and CagA-positive infections and global variations in gastric cancer. Toxins10, 163. 10.3390/toxins10040163
169
Patra K. C. Hay N. (2014). The pentose phosphate pathway and cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci.39, 347–354. 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.06.005
170
Pedersen A. Sørensen C. Proctor G. Carpenter G. Ekström J. (2018). Salivary secretion in health and disease. J. Oral Rehabilitation45, 730–746. 10.1111/joor.12664
171
Peng Y.-K. Pu K. Su H.-X. Zhang J. Zheng Y. Ji R. et al (2020). Circular RNA hsa_circ_0010882 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via regulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. and Pharmacol. Sci.24, 1142–1151. 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20165
172
Pirzadeh M. Khalili N. Rezaei N. (2022). The interplay between aryl hydrocarbon receptor, H. pylori, tryptophan, and arginine in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Int. Rev. Immunol.41, 299–312. 10.1080/08830185.2020.1851371
173
Pochini L. Scalise M. Galluccio M. Indiveri C. (2014). Membrane transporters for the special amino acid glutamine: structure/function relationships and relevance to human health. Front. Chem.2, 61. 10.3389/fchem.2014.00061
174
Prakobphol A. Xu F. Hoang V. M. Larsson T. Bergstrom J. Johansson I. et al (2000). Salivary agglutinin, which binds streptococcus mutansand helicobacter pylori, is the lung scavenger receptor cysteine-rich protein gp-340. J. Biol. Chem.275, 39860–39866. 10.1074/jbc.M006928200
175
Prieto-Fernández L. Menéndez S. T. Otero-Rosales M. Montoro-Jiménez I. Hermida-Prado F. García-Pedrero J. M. et al (2022). Pathobiological functions and clinical implications of annexin dysregulation in human cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol.10, 1009908. 10.3389/fcell.2022.1009908
176
Qiao J. Cai W. Wang K. Haubruge E. Dong J. El-Seedi H. R. et al (2024). New insights into identification, distribution, and health benefits of polyamines and their derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem.72, 5089–5106. 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c08556
177
Qiu C. Su W. Shen N. Qi X. Wu X. Wang K. et al (2020). MNAT1 promotes proliferation and the chemo-resistance of osteosarcoma cell to cisplatin through regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Bmc Cancer20, 1187–12. 10.1186/s12885-020-07687-3
178
Qiu J. Fu Z. Wen H. Chen Y. (2023). Identification of the novel prognostic biomarker SERPINH1 reveals its relationship with immunology in gastric cancer. Oncologie25, 367–379. 10.1515/oncologie-2023-0017
179
Rapado-González Ó. Muinelo-Romay L. Suárez-Cunqueiro M. M. (2021). Letter to the editor: “liquid biopsy based on saliva cell-free DNA as a potential biomarker for head and neck cancer”. Oral Oncol.112, 105016. 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.105016
180
Rauch S. (2020). Synthetic biology approaches to study and control the transcriptome.
181
Rheinbay E. Nielsen M. M. Abascal F. Wala J. A. Shapira O. Tiao G. et al (2020). Analyses of non-coding somatic drivers in 2,658 cancer whole genomes. Nature578, 102–111. 10.1038/s41586-020-1965-x
182
Röcken C. (2023). Predictive biomarkers in gastric cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol.149, 467–481. 10.1007/s00432-022-04408-0
183
Roldán M. L. Marini P. E. (2014). First evidence of the interaction between deleted in malignant brain tumor 1 and galectin-3 in the mammalian oviduct. Histochem. Cell Biol.141, 181–190. 10.1007/s00418-013-1145-2
184
Romańczyk M. Osmola M. Link A. Druet A. Hémont C. Martin J. et al (2024). Non-invasive markers for the detection of gastric precancerous conditions. Cancers (Basel)16, 2254. 10.3390/cancers16122254
185
Rosenzweig R. Nillegoda N. B. Mayer M. P. Bukau B. (2019). The Hsp70 chaperone network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.20, 665–680. 10.1038/s41580-019-0133-3
186
Roy S. Kanda M. Nomura S. Zhu Z. Toiyama Y. Taketomi A. et al (2022). Diagnostic efficacy of circular RNAs as noninvasive, liquid biopsy biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer21, 42. 10.1186/s12943-022-01527-7
187
Saadh M. J. Ahmed H. H. Kareem R. A. Bishoyi A. K. Roopashree R. Shit D. et al (2025). Molecular mechanisms of hippo pathway in tumorigenesis: therapeutic implications. Mol. Biol. Rep.52, 267. 10.1007/s11033-025-10372-y
188
Sarhadi V. K. Armengol G. (2022). Molecular biomarkers in cancer. Biomolecules12, 1021. 10.3390/biom12081021
189
Sarkar S. Roy S. (2017). A mini review on heat shock proteins (HSPs): special emphasis on heat shock protein70 (HSP70). BN Seal J. Sci.9, 130–139.
190
Sarma R. J. Subbarayan S. Zohmingthanga J. Chenkual S. Zomuana T. Lalruatfela S. T. et al (2022). Transcriptome analysis reveals SALL4 as a prognostic key gene in gastric adenocarcinoma. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst.34, 11. 10.1186/s43046-022-00108-5
191
Satriano J. (2004). Arginine pathways and the inflammatory response: interregulation of nitric oxide and polyamines: review article. Amino Acids26, 321–329. 10.1007/s00726-004-0078-4
192
Šedo A. MalíK R. (2001). Dipeptidyl peptidase IV-like molecules: homologous proteins or homologous activities?Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym.1550, 107–116. 10.1016/s0167-4838(01)00278-3
193
Sethi S. Ali S. Philip P. A. Sarkar F. H. (2013). Clinical advances in molecular biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci.14, 14771–14784. 10.3390/ijms140714771
194
Shan L.-H. Sun W.-G. Han W. Qi L. Yang C. Chai C.-C. et al (2012). Roles of fibroblasts from the interface zone in invasion, migration, proliferation and apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Pathology65, 888–895. 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-200909
195
Sharkey T. D. (2021). Pentose phosphate pathway reactions in photosynthesizing cells. Cells10, 1547. 10.3390/cells10061547
196
Sharndama H. C. Mba I. E. (2022). Helicobacter pylori: an up-to-date overview on the virulence and pathogenesis mechanisms. Braz. J. Microbiol.53, 33–50. 10.1007/s42770-021-00675-0
197
Shen S. Liu H. Wang Y. Wang J. Ni X. Ai Z. et al (2016). Long non-coding RNA CRNDE promotes gallbladder carcinoma carcinogenesis and as a scaffold of DMBT1 and C-IAP1 complexes to activating PI3K-AKT pathway. Oncotarget7, 72833–72844. 10.18632/oncotarget.12023
198
Shen Y. Li X. Su Y. Badshah S. A. Zhang B. Xue Y. et al (2019). HAMP downregulation contributes to aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma via mechanism mediated by cyclin4-dependent kinase-1/STAT3 pathway. Diagnostics9, 48. 10.3390/diagnostics9020048
199
Shen S. Wei C. Fu J. (2021). RNA-sequencing reveals heat shock 70-kDa protein 6 (HSPA6) as a novel thymoquinone-upregulated gene that inhibits growth, migration, and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Front. Oncol.11, 667995. 10.3389/fonc.2021.667995
200
Shibata H. Kanadome T. Sugiura H. Yokoyama T. Yamamuro M. Moss S. E. et al (2015). A new role for annexin A11 in the early secretory pathway via stabilizing Sec31A protein at the endoplasmic reticulum exit sites (ERES). J. Biol. Chem.290, 4981–4993. 10.1074/jbc.M114.592089
201
Shimura T. Dayde D. Wang H. Okuda Y. Iwasaki H. Ebi M. et al (2020). Novel urinary protein biomarker panel for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer123, 1656–1664. 10.1038/s41416-020-01063-5
202
Shu J. Yu H. Li X. Zhang D. Liu X. Du H. et al (2017). Salivary glycopatterns as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of gastric cancer. Oncotarget8, 35718–35727. 10.18632/oncotarget.16082
203
Siegel R. L. Miller K. D. Goding Sauer A. Fedewa S. A. Butterly L. F. Anderson J. C. et al (2020). Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA a Cancer J. Clin.70, 145–164. 10.3322/caac.21601
204
Smyth E. C. Nilsson M. Grabsch H. I. Van Grieken N. C. Lordick F. (2020). Gastric cancer. Lancet396, 635–648. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
205
Son J. Lyssiotis C. A. Ying H. Wang X. Hua S. Ligorio M. et al (2013). Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature496, 101–105. 10.1038/nature12040
206
Song J. Bai Z. Han W. Zhang J. Meng H. Bi J. et al (2012). Identification of suitable reference genes for qPCR analysis of serum microRNA in gastric cancer patients. Dig. Dis. Sci.57, 897–904. 10.1007/s10620-011-1981-7
207
Soond S. M. Kozhevnikova M. V. Townsend P. A. Zamyatnin Jr A. A. (2019). Cysteine cathepsin protease inhibition: an update on its diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic potential in cancer. Pharmaceuticals12, 87. 10.3390/ph12020087
208
Sousa J. F. Ham A.-J. L. Whitwell C. Nam K. T. Lee H.-J. Yang H.-K. et al (2012). Proteomic profiling of paraffin-embedded samples identifies metaplasia-specific and early-stage gastric cancer biomarkers. Am. J. pathology181, 1560–1572. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.07.027
209
Stincone A. Prigione A. Cramer T. Wamelink M. M. Campbell K. Cheung E. et al (2015). The return of metabolism: biochemistry and physiology of the pentose phosphate pathway. Biol. Rev.90, 927–963. 10.1111/brv.12140
210
Sun C. Li S. Zhang F. Xi Y. Wang L. Bi Y. et al (2016). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through regulation of miR-377-3p-E2F3 pathway. Oncotarget7, 51784–51814. 10.18632/oncotarget.10108
211
Sung H. Hyun N. Leach C. R. Yabroff K. R. Jemal A. (2020a). Association of first primary cancer with risk of subsequent primary cancer among survivors of adult-onset cancers in the United States. Jama324, 2521–2535. 10.1001/jama.2020.23130
212
Sung Y.-K. Jung S.-Y. Kim H. Choi S. Im S. G. Cha E. J. et al (2020b). Temporal relationship between idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and malignancies and its mortality: a nationwide population-based study. Clin. Rheumatol.39, 3409–3416. 10.1007/s10067-019-04782-0
213
Szefel J. Danielak A. Kruszewski W. J. (2019). Metabolic pathways of L-arginine and therapeutic consequences in tumors. Adv. Med. Sci.64, 104–110. 10.1016/j.advms.2018.08.018
214
Tanaka K. Sasayama T. Irino Y. Takata K. Nagashima H. Satoh N. et al (2015). Compensatory glutamine metabolism promotes glioblastoma resistance to mTOR inhibitor treatment. J. Clin. Investigation125, 1591–1602. 10.1172/JCI78239
215
Tao L. Yu H. Liang R. Jia R. Wang J. Jiang K. et al (2019). Rev-erbα inhibits proliferation by reducing glycolytic flux and pentose phosphate pathway in human gastric cancer cells. Oncogenesis8, 57. 10.1038/s41389-019-0168-5
216
Tao Y. Xing S. Zuo S. Bao P. Jin Y. Li Y. et al (2023). Cell-free multi-omics analysis reveals potential biomarkers in gastrointestinal cancer patients’ blood. Cell Rep. Med.4, 101281. 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101281
217
Thompson J. F. (1980). “Arginine synthesis, proline synthesis, and related processes,” in Amino acids and derivatives (Elsevier), 375–402.
218
Thrift A. P. Wenker T. N. El-Serag H. B. (2023). Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.20, 338–349. 10.1038/s41571-023-00747-0
219
Tian S. Peng P. Li J. Deng H. Zhan N. Zeng Z. et al (2020). SERPINH1 regulates EMT and gastric cancer metastasis via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY)12, 3574–3593. 10.18632/aging.102831
220
Tillmanns J. Weiglein J. Neuser J. Fraccarollo D. Galuppo P. König T. et al (2024). Circulating soluble fibroblast activation protein (FAP) levels are independent of cardiac and extra-cardiac FAP expression determined by targeted molecular imaging in patients with myocardial FAP activation. Int. J. Cardiol.406, 132044. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2024.132044
221
Toshiyama R. Konno M. Eguchi H. Asai A. Noda T. Koseki J. et al (2018). Association of iron metabolic enzyme hepcidin expression levels with the prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett.15, 8125–8133. 10.3892/ol.2018.8357
222
Wang Z. Du Y. (2021). Identification of a novel mutation gene signature HAMP for cholangiocarcinoma through comprehensive TCGA and GEO data mining. Int. Immunopharmacol.99, 108039. 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108039
223
Wang R.-F. Zhang L.-H. Shan L.-H. Sun W.-G. Chai C.-C. Wu H.-M. et al (2013). Effects of the fibroblast activation protein on the invasion and migration of gastric cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathology95, 350–356. 10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.10.008
224
Wang D.-G. Chen G. Wen X.-Y. Wang D. Cheng Z.-H. Sun S.-Q. (2015). Identification of biomarkers for diagnosis of gastric cancer by bioinformatics. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev.16, 1361–1365. 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.4.1361
225
Wang J. Wang S. Song X. Zeng W. Wang S. Chen F. et al (2016). The prognostic value of systemic and local inflammation in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther.9, 7177–7185. 10.2147/OTT.S113307
226
Wang F. Liu A. Bai R. Zhang B. Jin Y. Guo W. et al (2017a). Hepcidin and iron metabolism in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer. J. Buon22, 1328–1332.
227
Wang X. Kaczor-Urbanowicz K. E. Wong D. T. (2017b). Salivary biomarkers in cancer detection. Med. Oncol.34, 7. 10.1007/s12032-016-0863-4
228
Wang Q. Feng F. Wang J. Ren M. Shi Z. Mao X. et al (2019). Liver X receptor activation reduces gastric cancer cell proliferation by suppressing Wnt signalling via LXR β relocalization. J. Cell. Mol. Med.23, 789–797. 10.1111/jcmm.13974
229
Wang Q. Chen C. Ding Q. Zhao Y. Wang Z. Chen J. et al (2020a). METTL3-mediated m6A modification of HDGF mRNA promotes gastric cancer progression and has prognostic significance. Gut69, 1193–1205. 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319639
230
Wang X. Jiang G. Ren W. Wang B. Yang C. Li M. (2020b). LncRNA NEAT1 regulates 5-Fu sensitivity, apoptosis and invasion in colorectal cancer through the MiR-150-5p/CPSF4 axis. OncoTargets Ther.13, 6373–6383. 10.2147/OTT.S239432
231
Wang X. Lin Y. Lu Z.-L. Li J. (2020c). Circular RNA circ-MTO1 serves as a novel potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gallbladder cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. and Pharmacol. Sci.24, 8359–8366. 10.26355/eurrev_202008_22632
232
Wang Y. Li Z. Xu S. Guo J. (2020d). Novel potential tumor biomarkers: circular RNAs and exosomal circular RNAs in gastrointestinal malignancies. J. Clin. Laboratory Analysis34, e23359. 10.1002/jcla.23359
233
Wang Z. Li K. Huang W. (2020e). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1-centric gene regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci.77, 3769–3779. 10.1007/s00018-020-03503-0
234
Wang Q. Qi C. Min P. Wang Y. Ye F. Xia T. et al (2022). MICAL2 contributes to gastric cancer cell migration via Cdc42-dependent activation of E-cadherin/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Commun. Signal.20, 136. 10.1186/s12964-022-00952-x
235
Wang X. Tang Z. Wang Y. Yang J. Shi Z. Liu D. et al (2023). Comparison of multi-omics biomarkers via liquid biopsy in early detection of gastric cancer. American Society of Clinical Oncology.
236
Warburg O. Wind F. Negelein E. (1927). The metabolism of tumors in the body. J. General Physiology8, 519–530. 10.1085/jgp.8.6.519
237
Ward D. G. Roberts K. Brookes M. J. Joy H. Martin A. Ismail T. et al (2008). Increased hepcidin expression in colorectal carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterology WJG14, 1339–1345. 10.3748/wjg.14.1339
238
Weber G. F. (2016). Metabolism in cancer metastasis. Int. J. Cancer138, 2061–2066. 10.1002/ijc.29839
239
Wen X. He X. Jiao F. Wang C. Sun Y. Ren X. et al (2017). Fibroblast activation protein-α-positive fibroblasts promote gastric cancer progression and resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Oncol. Res.25, 629–640. 10.3727/096504016X14768383625385
240
Wen S. Wei Y. Zen C. Xiong W. Niu Y. Zhao Y. (2020). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes bone metastasis of prostate cancer through N6-methyladenosine. Mol. Cancer19, 171–18. 10.1186/s12943-020-01293-4
241
Wen Z. Yang C. Zou D. Liu J. Wang S. Liu X. et al (2022). Pan-cancer analysis of PSAP identifies its expression and clinical relevance in gastric cancer. Pathology-Research Pract.238, 154027. 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154027
242
West J. A. Davis C. P. Sunwoo H. Simon M. D. Sadreyev R. I. Wang P. I. et al (2014). The long noncoding RNAs NEAT1 and MALAT1 bind active chromatin sites. Mol. Cell55, 791–802. 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.07.012
243
William J. W. N. Zhao X. Bianchi J. J. Lin H. Y. Cheng P. Lee J. J. et al (2021). Immune evasion in HPV− head and neck precancer–cancer transition is driven by an aneuploid switch involving chromosome 9p loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.118, e2022655118. 10.1073/pnas.2022655118
244
Wu G. (2013). “Arginine and immune function,” in Diet, immunity and inflammation (Elsevier), 523–543.
245
Wu G. Meininger C. J. Mcneal C. J. Bazer F. W. Rhoads J. M. (2021). “Role of L-arginine in nitric oxide synthesis and health in humans,” in Amino acids in nutrition and health (Springer), 167–187.
246
Xia S. Feng J. Lei L. Hu J. Xia L. Wang J. et al (2017). Comprehensive characterization of tissue-specific circular RNAs in the human and mouse genomes. Briefings Bioinforma.18, 984–992. 10.1093/bib/bbw081
247
Xia L. Chen Y. Li J. Wang J. Shen K. Zhao A. et al (2023). B7-H3 confers stemness characteristics to gastric cancer cells by promoting glutathione metabolism through AKT/pAKT/Nrf2 pathway. Chin. Med. J.136, 1977–1989. 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002772
248
Xiang T. Yuan C. Guo X. Wang H. Cai Q. Xiang Y. et al (2021). The novel ZEB1-upregulated protein PRTG induced by Helicobacter pylori infection promotes gastric carcinogenesis through the cGMP/PKG signaling pathway. Cell Death and Dis.12, 150. 10.1038/s41419-021-03440-1
249
Xiao Y. Dong J. (2021). The hippo signaling pathway in cancer: a cell cycle perspective. Cancers13, 6214. 10.3390/cancers13246214
250
Xiao H. Zhang Y. Kim Y. Kim S. Kim J. J. Kim K. M. et al (2016). Differential proteomic analysis of human saliva using tandem mass tags quantification for gastric cancer detection. Sci. Rep.6, 22165. 10.1038/srep22165
251
Xu S. Chen W. Wang Y. Zhang Y. Xia R. Shen J. et al (2022). N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs identified as potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival of Asian gastric cancer patients. BMC Cancer22, 721. 10.1186/s12885-022-09801-z
252
Xu Q. Xue S. Zhang Y. Li J. Qian P. Zhang Y. et al (2024). Identification and validation of cystatin A as a novel promising therapeutic target for gastric cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol.15, 873–889. 10.21037/jgo-23-941
253
Yamamoto N. Kinoshita T. Nohata N. Yoshino H. Itesako T. Fujimura L. et al (2013). Tumor-suppressive microRNA-29a inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion via targeting HSP47 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol.43, 1855–1863. 10.3892/ijo.2013.2145
254
Yang D.-D. Chen Z.-H. Yu K. Lu J.-H. Wu Q.-N. Wang Y. et al (2020). METTL3 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via targeting the MYC pathway. Front. Oncol.10, 115. 10.3389/fonc.2020.00115
255
Yang J. Wei H. Liu M. Huang T. Fang X. Ren X. et al (2022). Prognostic biomarker HAMP and associates with immune infiltration in gastric cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol.108, 108839. 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108839
256
Yang K. Wang X. Song C. He Z. Wang R. Xu Y. et al (2023). The role of lipid metabolic reprogramming in tumor microenvironment. Theranostics13, 1774–1808. 10.7150/thno.82920
257
Yu J. Zhang S. Zhao B. (2016). Differences and correlation of serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA72-4 in gastric cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol.4, 441–449. 10.3892/mco.2015.712
258
Yu J. Shen J. Qiao X. Cao L. Yang Z. Ye H. et al (2019). SNHG20/miR-140-5p/NDRG3 axis contributes to 5-fluorouracil resistance in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett.18, 1337–1343. 10.3892/ol.2019.10439
259
Yu P. Chen P. Wu M. Ding G. Bao H. Du Y. et al (2024). Multi-dimensional cell-free DNA-based liquid biopsy for sensitive early detection of gastric cancer. Genome Med.16, 79. 10.1186/s13073-024-01352-1
260
Zhang C. X. (2019). The protective role of DMBT1 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci.35, 739–749. 10.1002/kjm2.12117
261
Zhang A. Sun H. Wang X. (2012). Saliva metabolomics opens door to biomarker discovery, disease diagnosis, and treatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol.168, 1718–1727. 10.1007/s12010-012-9891-5
262
Zhang C. Zhang Z. Zhu Y. Qin S. (2014a). Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a biomarker and potential therapeutic target for cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents14, 280–289. 10.2174/18715206113136660337
263
Zhang S. Chen Y. Guo W. Yuan L. Zhang D. Xu Y. et al (2014b). Disordered hepcidin–ferroportin signaling promotes breast cancer growth. Cell. Signal.26, 2539–2550. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.07.029
264
Zhang J. Shi Z. Huang J. Zou X. (2016). CSTB downregulation promotes cell proliferation and migration and suppresses apoptosis in gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell line. Oncol. Res.24, 487–494. 10.3727/096504016X14685034103752
265
Zhang X. Zhang X. Li Y. Shao Y. Xiao J. Zhu G. et al (2017a). PAK4 regulates G6PD activity by p53 degradation involving colon cancer cell growth. Cell Death and Dis.8, e2820. 10.1038/cddis.2017.85
266
Zhang Y. Lun L. Li H. Wang Q. Lin J. Tian R. et al (2017b). The value of lncRNA NEAT1 as a prognostic factor for survival of cancer outcome: a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep.7, 13080. 10.1038/s41598-017-10001-0
267
Zhang M. Weng W. Zhang Q. Wu Y. Ni S. Tan C. et al (2018a). The lncRNA NEAT1 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes colorectal cancer progression via interacting with DDX5. J. Hematol. and Oncol.11, 113–13. 10.1186/s13045-018-0656-7
268
Zhang X. Zhou H. Jing W. Luo P. Qiu S. Liu X. et al (2018b). The circular RNA hsa_circ_0001445 regulates the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma and may serve as a diagnostic biomarker. Dis. Markers2018, 3073467. 10.1155/2018/3073467
269
Zhang L.-H. Zhu X.-Y. Eirin A. Nargesi A. A. Woollard J. R. Santelli A. et al (2019). Early podocyte injury and elevated levels of urinary podocyte-derived extracellular vesicles in swine with metabolic syndrome: role of podocyte mitochondria. Am. J. Physiology-Renal Physiology317, F12–F22. 10.1152/ajprenal.00399.2018
270
Zhang J. Xu L. Wang P. Zheng X. Hu Y. Luo J. et al (2020). RNA-seq used to explore circRNA expression and identify key circRNAs during the DNA synthesis phase of mice liver regeneration. DNA Cell Biol.39, 2059–2076. 10.1089/dna.2020.5750
271
Zhang L. Yao L. Zhou W. Tian J. Ruan B. Lu Z. et al (2021a). miR-497 defect contributes to gastric cancer tumorigenesis and progression via regulating CDC42/ITGB1/FAK/PXN/AKT signaling. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids25, 567–577. 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.07.025
272
Zhang Y. Wu Y. Su X. (2021b). PLOD1 promotes cell growth and aerobic glycolysis by regulating the SOX9/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Front. Bioscience-Landmark26, 322–334. 10.52586/4946
273
Zhang K. Yue B. Duan X. Chen W. Dai X. Chen Y. et al (2023a). Joint analysis identified FAP as a prognostic and diagnostic biomarker correlated immune infiltration in gastric cancer. Pathology-Research Pract.245, 154462. 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154462
274
Zhang L. Zhuo H. Q. Hong Z. J. Hou J. J. Cheng J. Cai J. (2023b). HSPA6, a novel prognostic and therapeutic biomarker, associated with ming classification in gastric cancer. J. Clin. Laboratory Analysis37, e24763. 10.1002/jcla.24763
275
Zhang Q. Yang M. Zhang P. Wu B. Wei X. Li S. (2024). Deciphering gastric inflammation-induced tumorigenesis through multi-omics data and AI methods. Cancer Biol. and Med.21, 312–330. 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0129
276
Zhao Z. Zhu Y. (2023). FAP, CD10, and GPR77-labeled CAFs cause neoadjuvant chemotherapy resistance by inducing EMT and CSC in gastric cancer. Bmc Cancer23, 507. 10.1186/s12885-023-11011-0
277
Zhao B. Ye X. Yu J. Li L. Li W. Li S. et al (2008). TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes and Dev.22, 1962–1971. 10.1101/gad.1664408
278
Zhao D. Jiang X. Yao C. Zhang L. Liu H. Xia H. et al (2014). Heat shock protein 47 regulated by miR-29a to enhance glioma tumor growth and invasion. J. Neuro-Oncology118, 39–47. 10.1007/s11060-014-1412-7
279
Zhao D. Zhang Y. Wang N. Yu N. (2017). NEAT1 negatively regulates miR-218 expression and promotes breast cancer progression. Cancer Biomarkers20, 247–254. 10.3233/CBM-170027
280
Zhao Y. Sheldon M. Sun Y. Ma L. (2023). New insights into YAP/TAZ-TEAD-mediated gene regulation and biological processes in cancer. Cancers15, 5497. 10.3390/cancers15235497
281
Zhen L. Yun-Hui L. Hong-Yu D. Jun M. Yi-Long Y. (2016). Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes glioma pathogenesis by regulating miR-449b-5p/c-Met axis. Tumor Biol.37, 673–683. 10.1007/s13277-015-3843-y
282
Zhong X. He Z. Yin L. Fan Y. Tong Y. Kang Y. et al (2023). Glutamine metabolism in tumor metastasis: genes, mechanisms and the therapeutic targets. Heliyon9, e20656. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20656
283
Zhou Q. Ju L.-L. Ji X. Cao Y.-L. Shao J.-G. Chen L. (2021). Plasma circRNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Cancer Manag. Res.13, 7325–7337. 10.2147/CMAR.S330228
284
Zhou X. Wang L.-Q. Song S. Xu M. Li C.-P. (2025). Helicobacter pylori infection promotes the progression of gastric cancer by regulating the expression of DMBT1. World J. Clin. Oncol.16, 105322. 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.105322
285
Zhu C. Li L. Zhao B. (2015). The regulation and function of YAP transcription co-activator. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin.47, 16–28. 10.1093/abbs/gmu110
286
Zhu Z. Yu Z. Rong Z. Luo Z. Zhang J. Qiu Z. et al (2019). The novel GINS4 axis promotes gastric cancer growth and progression by activating Rac1 and CDC42. Theranostics9, 8294–8311. 10.7150/thno.36256
287
Zhu H. Wang F. Lu X. Wu H. Shi C. Matsas S. et al (2025). Low expression of PRTN3 regulates the progression of gastric cancer by inhibition of cell cycle and promotion of apoptosis. Transl. Cancer Res.14, 1415–1427. 10.21037/tcr-2025-153
288
Zúñiga-Pérez N. Muñoz-Navarro H. Rivera C. (2024). Salivary biomarkers for the diagnosis of gastric cancer: a systematic review. Rev. Científica Odontológica12, e199. 10.21142/2523-2754-1202-2024-199
289
Zuo L. Wang L. Yang Z. Li J. Wang W. Wang Y. et al (2023). High expression of CAMSAP2 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by upregulating TGF-β signaling. Nan Fang yi ke da xue xue bao= J. South. Med. Univ.43, 1460–1468. 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.09.02
Summary
Keywords
biomarkers, cancer, gastric cancer, signaling pathways, proliferation
Citation
Kaur S, Kumar A, Bhatia R, Choudhary D, Kaur R, Chandrasekaran B, Abu Dayyih W, Maaita MN and Hourani W (2025) Potential biomarkers in early detection of gastric cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1642927. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1642927
Received
07 June 2025
Accepted
22 September 2025
Published
31 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Pradip Nirbhavane, Amity University Gurgaon, India
Reviewed by
Wenjun Lan, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, United States
Tong Feng, Sun Yat-sen University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Kaur, Kumar, Bhatia, Choudhary, Kaur, Chandrasekaran, Abu Dayyih, Maaita and Hourani.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rajwinder Kaur, rajwinder.kaur@chitkara.edu.in; Balakumar Chandrasekaran, bchandrasekaran@zu.edu.jo
ORCID: Wael Abu Dayyih, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5832-7247
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.