- 1Traditional Chinese Medicine Department, Heilongjiang Provincial Hospital, Harbin, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Basic and Application Research of Beiyao, Ministry of Education, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
- 3Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Analytical Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
Introduction: Cucurbitacin, a class of triterpenoid compounds isolated from Pedicellus Melo, possesses various biological activities and is the primary active component of cucurbitacin tablets (CUT) used to treat chronic hepatitis and primary liver cancer. Nanosuspensions can potentially improve the oral bioavailability of pharmacopotent substances. This is the first study comparing the pharmacokinetics of three cucurbitacin triterpenoids (cucurbitacin B [CuB], cucurbitacin D [CuD], and cucurbitacin E [CuE] following oral administration of CUT and a novel P. Melo nanosuspension (MP-NPs) in rats.
Methods: The plasma concentrations of these cucurbitacin triterpenoids were quantified through ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS). A selective, simple, and sensitive UHPLC-MS/MS method was developed using the positive ion mode for multiple reaction monitoring analysis. The chromatographic column used was Waters Acquity HSS T3 (1.8 μm, 2.1 × 100 mm), the column temperature was 35 °C, the flow rate was 0.3 mL/min, the injection volume was 5 μL, and the mobile phase was a gradient elution of water (A) and methanol (B). The intra- and inter-day precision for all analytes was <13%, and accuracy ranged from −6.41% to −4.01%
Results: According to the pharmacokinetic results, when the two rat groups were orally administered with the same dose of CUT and MP-NPs, the elimination half-life (T1/2) of CuD and CuE was longer than that of CuB, indicating slower elimination. Compared with the CUT group, the triterpenoids in the MP-NPs group reached the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) within 2 h, and both Cmax and the area under the plasma concentration increased significantly.
Discussion: The MP-NPs formulation significantly enhanced the oral bioavailability of cucurbitacin triterpenoids compared to conventional CUT. These findings underscore the potential of nanosuspension technology in improving the pharmacokinetic profile of cucurbitacin-based therapeutics. This study provides valuable insights for further development and clinical application of cucurbitacin nanosuspensions.
1 Introduction
For long, liver disorders and associated illnesses have been clinically treated with cucurbitacin tablets (CUT), a conventional over-the-counter medication (Huang et al., 2019; Chen and Zheng, 2014; Chen J et al., 2008; He et al., 1994). Triterpenoid compounds (i.e., CuB, CuD, and CuE), extracted from Cucurbitaceae plants, are the key active components of cucurbitacins. These compounds exert strong anticancer effects by controlling signaling pathways such as NF-κB, MAPK, and JAK/STAT. These effects include apoptosis induction and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation (Park et al., 2015). In particular, CuB modulates several pathways, including JAK/STAT3, Nrf2/ARE, NF-κB, AMPK, MAPK, PI3K/Akt, CIP2A/PP2A, Wnt, FAK, Notch, and Hippo-YAP, to offer robust anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, hypoglycemic, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, and anticancer properties (Dai et al., 2023; Garg et al., 2018; Yesilada et al., 1988; Li et al., 2023; Lin et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2018; Lu et al., 2012; Chen R et al., 2008). By controlling JAK/STAT3, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, and MAPK pathways, CuD prevents HepG2 cell proliferation and triggers their apoptosis (Üremiş et al., 2022; Ku et al., 2018). CuE exerts anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anticancer, anti-apoptotic, anti-aging, and immunomodulatory effects by regulating pathways such as PI3K/Akt, NF-κB, FAK/AKT/GSK3β, TFAP4/Wnt/β-catenin, SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1, miR-371b-5p/TFAP4, NF-κB/NLRP3, JAK/STAT, Jak/Stat3, ERK/MAPK, and PI3K/Akt/mTOR (Wang L et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2022; Brouwer et al., 2020; Attard and Martinoli, 2015). Additionally, it inhibits the proliferation of A549 human non-small-cell lung cancer cells by facilitating p62-dependent apoptosis (Üremiş et al., 2023). However, the clinical application of these compounds is limited by the poor oral bioavailability of cucurbitacins, mainly because of low water solubility and substantial first-pass effects (Hsu et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2014).
The dried peduncle of Pedicellus Melo fruits, a crop of great economic value in terms of cucurbitacin production, is a traditional Chinese medicinal material commonly used to treat phlegm retention, jaundice, and inflammatory diseases (Chen et al., 2024). According to modern pharmacological studies, the P. Melo extract is rich in CuB, CuD, and CuE, the primary active components responsible for its therapeutic effects. However, similar to traditional cucurbitacin formulations, natural extracts are poorly water-soluble and are rapidly cleared through the gastrointestinal tract, leading to insufficient systemic exposure and low bioavailability.
Nano-drug delivery systems offer novel solutions for enhancing the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. For example, oral Panax notoginseng saponin nanoparticles or nanoemulsions have significantly improved bioavailability (Lu et al., 2024). Breviscapine nanosuspensions enhance solubility and dissolution and markedly increase bioavailability in mice (Zhang et al., 2022). Polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 (PVP K30), a polymer commonly applied in nano-drug delivery systems, has been successfully used for multiple traditional Chinese medicine components (Waleka et al., 2021). For instance, PVP K30 inhibits the crystallization of artemisinin to improve its transdermal permeability (Xue et al., 2021); reduces paclitaxel crystallinity, thereby improving its solubility (Shikov et al., 2009); and increases the stability and bioavailability of curcumin (Chen et al., 2022).
Nanotechnology is thus promising in overcoming the bottleneck of low absorption efficiency in traditional herbal extracts. CuB, CuD, and CuE are poorly water-soluble, which limits their clinical efficacy. To date, these compounds are predominantly administered as oral tablets, but adequate absorption of their active ingredients remains difficult. Therefore, water-soluble formulations must be developed to improve their effectiveness and ease of use. Preparing nanodispersions is effective for improving drug dispersion and solubility, thereby elevating bioavailability. Solid dispersion can significantly improve the solubility and dissolution rate of many active ingredients in drugs, which are otherwise poorly water-soluble (Jacob et al., 2020; Wei et al., 2022; Fathi-Karkan et al., 2024; Wang L et al., 2017). To optimize the administration method, the P. Melo extract was prepared, and MP-NPs were formulated using PVP K30 as a material. Subsequently, the pharmacokinetic differences between CUT and MP-NPs were compared. Then, three high-content triterpenoid compounds, namely, CuB, CuD, and CuE, were detected from the extract, and pharmacokinetic studies were conducted on different formulations. This study is the first to quantify pharmacokinetic differences among CuB, CuD, and CuE in two formulations, offering valuable information about the drug’s absorption and distribution in the body. A deeper understanding of the drug’s pharmacokinetics will aid in optimizing therapeutic strategies.
The study aims to provide an accurate and effective UHPLC-MS/MS approach for the concurrent examination of active components from the CUT and MP-NPs groups, including CuB, CuD, and CuE, with bifendate employed as the internal standard (IS) (Figure 1). Pharmacokinetic analysis was also performed for the first time after a single oral administration of CUT and MP-NPs in rats, offering valuable insights to improve the oral availability of insoluble drugs during clinical application.
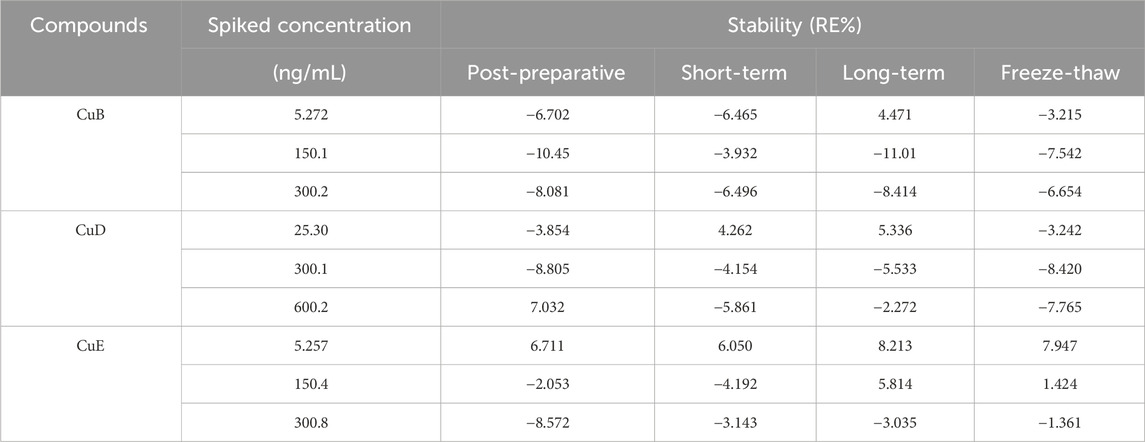
Figure 1. The chemical structures of analytes. (A) Cucurbitacin B; (B)Cucurbitacin D; (C) Cucurbitacin E; (D) IS.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
The reference substances of cucurbitacin B (CuB; lot: Z02M7X10137; purity ≥98%), cucurbitacin D (CuD; lot: DSTDH008101; purity ≥98%), and cucurbitacin E (CuE; lot: Z01M7S10309; purity ≥98%) were purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Bifendate (lot: 73536-69-3; purity ≥98%) was purchased from Chengdu Must Bio-Technology (Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China) as an IS. All other chemical reagents, including methanol and formic acid (Dikma Technologies, Beijing, China), were of HPLC quality. P. Melo (RP20240313) was purchased from Shaanxi Pioneer Biotech Co., Ltd. And identified by Professor Zhenyue Wang of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine.
2.2 Instruments and UHPLC-MS/MS conditions
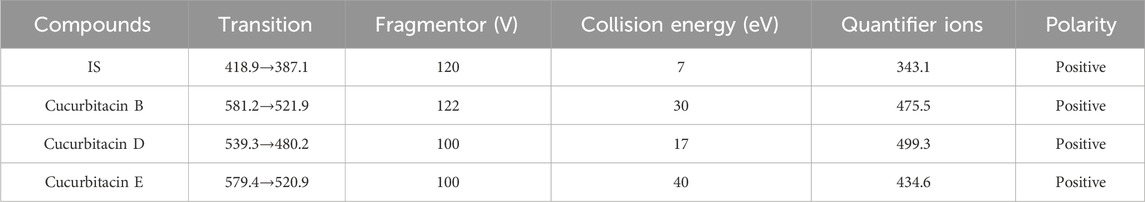
An Agilent 6430 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with an ESI source interface (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, United States) was used in conjunction with an Agilent 1290 UHPLC system (Agilent Technologies). A Waters ACQUITY HSS T3 Column (1.8 μm, 2.1 × 100 mm) (Waters, Manchester, UK) was also used for the separations. Gradient elution was performed using water (A) and methanol (B) as mobile phases. The gradient elution procedure was used for 0.0–1.0 min, 80%–80% B; 1.0–1.5 min, 80%–90% B; 1.5–3.0 min, 90%–90% B; 3.0–3.2 min, 90%–80% B; and 3.2–4 min, 80%–80% B. The analytical temperature was 35 °C, and the flow rate was 0.3 mL/min. An injection of 5 μL volume was administered, after which the needle was washed. Positive ion-mode analysis was performed for the samples. The capillary voltage was set to 4500 V, source temperature to 100 °C, and the desolvation temperature to 350 °C (Wang et al., 2014). High-purity nitrogen was used as the nebulizing gas, and nitrogen was used as the drying gas at a flow rate of 11 L/min. The Agilent Mass Hunter workstation was used to gather the experimental data (Wang Z et al., 2023). Using specific precursor and product ion transitions at m/z 581.2→521.9 for CuB, m/z 539.3→480.2 for CuD, m/z 578.9→520.9 for CuE, and m/z 418.9→387.1 for IS at various fragmentor voltage (FV) and collision energy (CE) conditions listed in Table 1, quantification was accomplished using multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. The production mass spectra of the three analytes and IS are displayed in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Product ion mass spectra of the analytes. (A) Cucurbitacin B, (B) Cucurbitacin D, (C) Cucurbitacin E, (D) IS.
2.3 Preparation of standards and QC samples
CuB (4.953 mg), CuD (4.603 mg), and CuE (4.544 mg) were accurately weighed and converted to 10 mL in methanol to prepare a single mother liquor of 0.4953, 0.4603, and 0.4544 mg/mL, respectively. The IS 5.504 mg was dissolved in methanol in a 20 mL volumetric flask, and a 0.275 mg/mL stock solution was obtained. The calibration solution was prepared by using the mother liquor gradient dilution method.
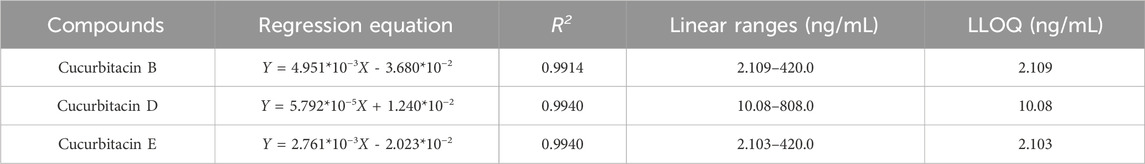
Following the necessary addition of blank plasma and standard solutions to the samples for the standard calibration curves, the final concentrations obtained were 2.109, 4.212, 10.50, 21.04, 42.10, 210.4, and 420.3 ng/mL for CuB; 10.08, 20.21, 50.52, 101.2, 202.7, 404.2, and 808.2 ng/mL for CuD; 2.103, 4.221, 10.54, 21.13, 42.09, 210.3, and 420.1 ng/mL for CuE. These concentrations were achieved by spiking 100 μL of blank plasma with 10 μL of IS and 100 μL of a mixed standard solution containing the three compounds. Drug-free plasma was used to create QC samples at four different concentration levels, HQC are 300.2, 600.3, and 300.8 ng/mL; MQC are 150.1, 300.1, and 150.4 ng/mL; LQC are 5.102, 25.31, and 4.912 ng/mL; LLOQ are 2.109, 10.08, and 2.103 ng/mL for CuB, CuD, and CuE. All working solutions were stored at 4 °C throughout the experiment.
2.4 Pedicellus Melo nanosuspension preparation
A specific quantity of P. Melo was homogenized, and 8-fold volumes of methanol were added to the sample. The mixture was then subjected to three sequential ultrasonic extractions (for 40 min each) at room temperature. Following each extraction cycle, the slurry was vigorously shaken, filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane filter, and the filtrate was collected. The pooled filtrates were concentrated via rotary evaporation under reduced pressure to obtain the crude P. Melo extract. Simultaneously, a 20% (w/v) PVP K30 solution was prepared by dissolving the polymer in deionized water. The solution was magnetically stirred (600 rpm) at 60 °C in a water bath until a homogeneous, clear aqueous phase was achieved.
2.5 Animal experiments
A total of 12 male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (weight: 220 ± 20 g) were provided by the Animal Experiment Center of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Production license number: SYXK (Hei) 2021-010). The Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine approved the study (Approval No.: 2024053114).
Animals were randomly assigned to the following two experimental groups (n = 6 per group): CUT and MP-NPs. Treatments were administered once daily for seven consecutive days, with the plasma sampling performed at predetermined time points after administration. Dosage was calculated based on human-equivalent doses converted to rat pharmacokinetic parameters using interspecies scaling factors. The human-rat dose conversion procedure was used to determine the dose of CUT per rat to be 0.03 g. The recommended daily dosage for humans is 6 tablets. The dose of MP-NPs per rat was determined to be 0.06 g per rat using the human-rat dose conversion formula, whereas the dose of P. Melo for human usage was 3 g, with reference to the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2025.
At 0.083, 0.25, 0.50, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h following oral administration of CUT and MP-NPs, 0.25 mL of plasma samples were sampled by rapidly collecting and centrifuging at 4 °C, followed by freezing at −20 °C for further analysis (Yu et al., 2023).
2.6 Plasma samples preparation
Blank plasma sample (100 μL) was vortexed for 60 s after adding 100 μL of IS. To guarantee complete extraction, 3 mL of dichloromethane was then added to each sample, followed by vortexing for 120 s. Subsequently, the samples were centrifuged for 10 min at 4 °C and 3,500 rpm. At 40 °C, the top organic phase was carefully moved into a sterile tube, dried off with a mild stream of nitrogen gas, and then reconstituted in 100 μL of the original mobile phase. Following a 120 s vortex, the extracts were filtered through a 0.22 μm Millipore filter before subjecting them to quantitative analyses by injecting 5 μL of them into the UHPLC-MS/MS apparatus.
3 Results
3.1 Methods validation
3.1.1 Selectivity
Under the UHPLC-MS/MS conditions, the analyte was effectively separated. The IS, CuB, CuD, and CuE exhibited retention times of 1.258, 0.9890, 1.545, and 1.490 min, respectively. Figure 3 presents representative MRM chromatograms: (A) blank plasma; (B) plasma samples spiked with the analytes and IS at LLOQ; (C) blank plasma with the analytes and IS at MQC; (D) plasma samples obtained at 2.5 h after CUT was administered orally; and (E) plasma samples obtained at 2 h after MP-NPs were administered orally. These results confirmed that endogenous substances did not interfere with the analytes and IS during analysis.
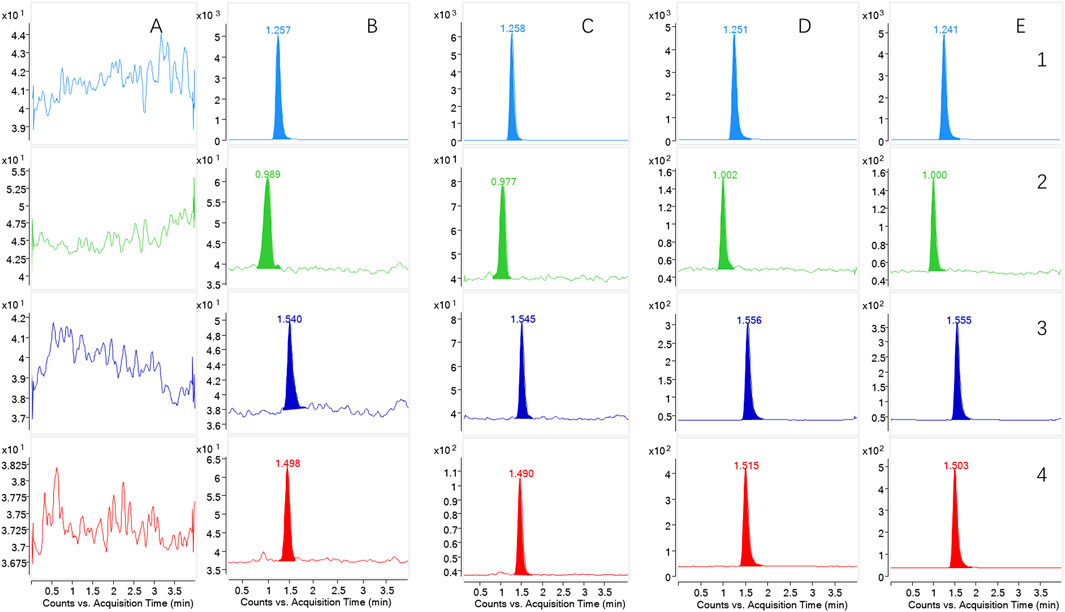
Figure 3. The chromatograms of the analytes in rat plasma. (1) IS; (2) Cucurbitacin D; (3) Cucurbitacin B; (4) Cucurbitacin E. (A) blank plasma; (B) plasma samples spiked with the analytes and IS at LLOQ; (C) blank plasma with the analytes and IS at MQC; (D) the plasma samples obtained at 2.5 h following the oral administration of CUT group (n = 6); (E) the plasma samples obtained at 2 h following the oral administration of MP-NPs (PVP-K30) group (n = 6).
3.1.2 Linearity and sensitivity
Table 2 presents the linear regression equations for quantification. All R2 exceeded 0.9914, demonstrating robust linearity across the validated concentration ranges. LLOQs for CuB, CuD, and CuE were 2.109, 10.08, and 2.103 ng/mL. These values fulfilled the sensitivity requirements for pharmacokinetic analysis.
3.1.3 Precision and accuracy
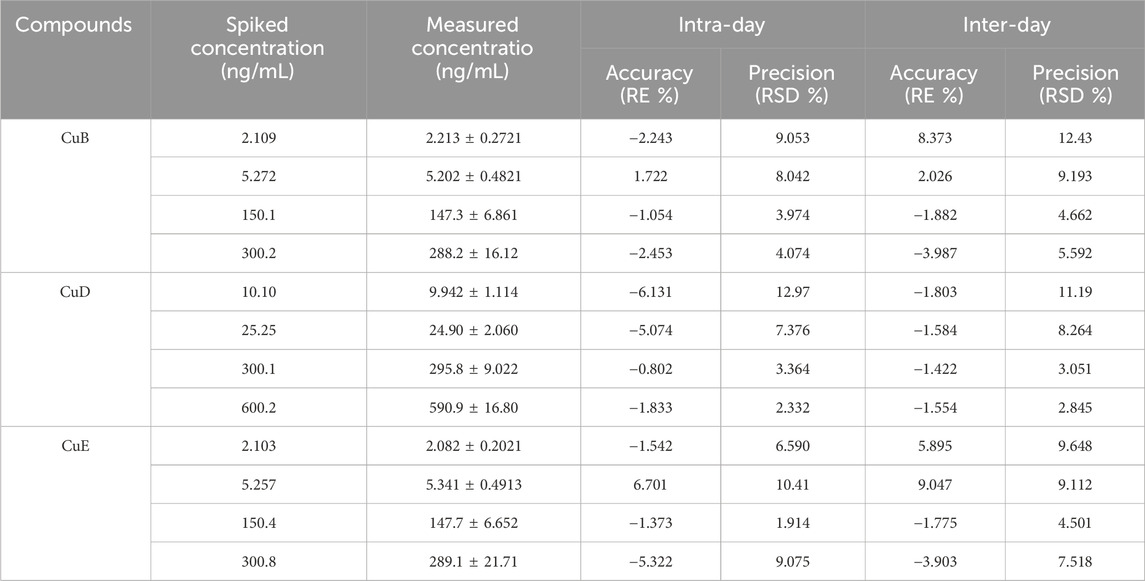
Precision and accuracy were evaluated by analyzing QC samples at four concentrations: LLOQ, LQC, MQC, and HQC. Intra- and inter-day precision were assessed over three consecutive days. For all three analytes (CuB, CuD, and CuE), the precision values remained below 13% for both intra- and inter-day measurements, meeting the acceptance criteria for validation using the bioanalytical method. Accuracy, expressed as RE%, ranged from −3.987% to 9.047% across all QC levels (Table 3). Negative RE values indicated slight underestimation, whereas positive values reflected overestimation relative to nominal concentrations. These results unveiled that the analytical procedure was reliable and accurate for quantifying cucurbitacins in biological matrices.
3.1.4 Extraction recovery and matrix effect
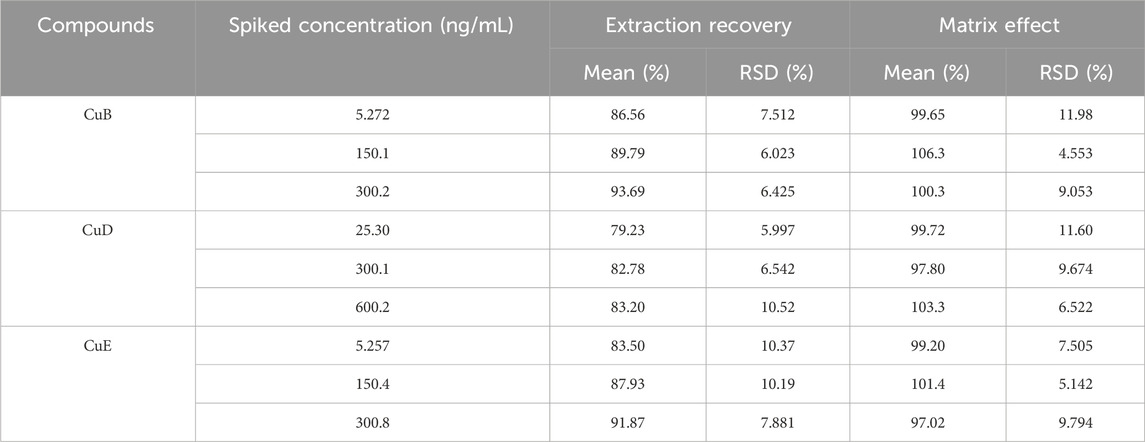
Table 4 presents the extraction recoveries of the three analytes across three QC levels, which ranged from 86.56% to 93.69%, 79.23%–83.20%, and 83.50%–91.87%, respectively. The matrix effects for the three analytes ranged from 97.02% to 106.3%. These results revealed negligible matrix effects on the analytes, indicating the appropriateness of the extraction solvent used.
3.1.5 Stability
Table 5 outlines the stability of LQC, MQC, and HQC in the rat plasma under different storage conditions. CuB, CuD, and CuE remained stable under the following conditions: storage at −20 °C, ambient temperature (25 °C) for 4 h, three freeze-thaw cycles (−20 °C/room temperature) over 2 weeks, and 12 h storage at 4 °C post-sample preparation. The RSD for these conditions was ≤11.01%, confirming minimal variability. Thus, the analytes were not significantly degraded throughout all stages of sample handling and analysis.
3.2 Pharmacokinetic studies
The established UHPLC-MS/MS method was applied to simultaneously measure the plasma concentrations of the three analytes in rats following dose administration. Pharmacokinetic parameters have attracted attention in exploring drug absorption and distribution. These parameters include T1/2, Cmax, Tmax, and AUC (Table 6). The average plasma concentration-time curve is presented in Figure 4. The pharmacokinetics of SD rats following oral administration of CUT and MP-NPs were investigated through UHPLC-MS/MS. The plasma concentrations of the three analytes were calculated. The Tmax values of these analytes gradually increased. The MP-NPs group reached Cmax more rapidly than the CUT group. AUC0→t and
Table 6. Pharmacokinetic parameters of the three compounds in the CUT group and the MP-NPs group rat plasma after oral administration of cucurbitacin tablet and MP-NPs(PVP-K30) (n = 6, mean ± SD). (Note: * for p < 0.05, and ** for p < 0.01).
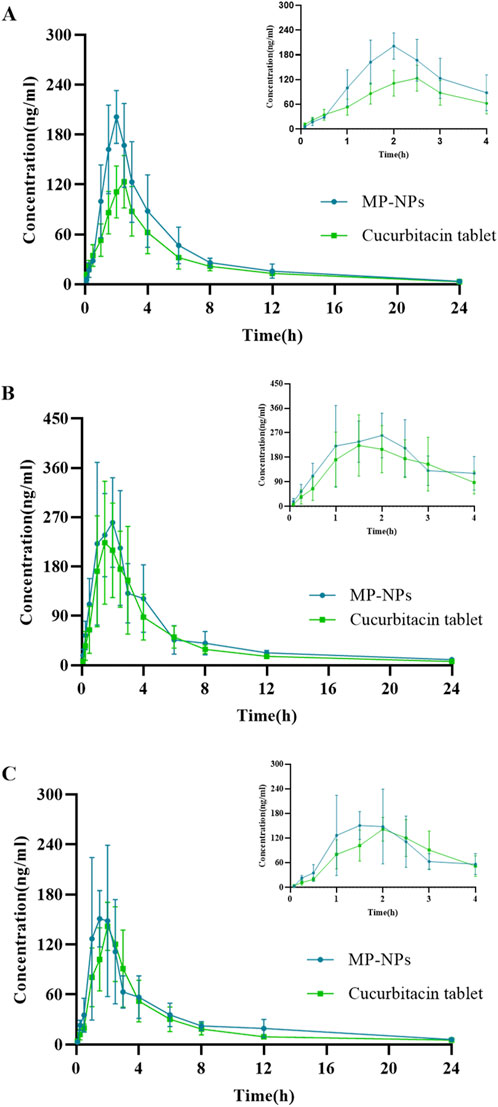
Figure 4. Mean concentration-time profiles of the analytes in rat plasma after oral administration of CUT and MP-NPs(PVP-K30) (n = 6, mean ± SD). (A) Cucurbitacin B; (B) Cucurbitacin D; (C) Cucurbitacin E.
4 Discussion
4.1 Optimization of UHPLC-MS/MS conditions
Mass spectrometric conditions, including ionization and parameters, were first optimized. A higher response was observed in the ESI positive-ion mode than in the negative-ion mode. Mass spectral parameters of the compounds varied based on the instrument and operating conditions (Abdollahi et al., 2024; Bali et al., 2011; Aluri et al., 2023). The MRM mode was employed for testing the precursor and product ions of the three compounds and IS to ensure reliability. Optimal ion transition pairs for quantitation were identified: m/z 581.2→ 521.9 for CuB, m/z 539.3→ 480.2 for CuD, m/z 578.9→ 520.9 for CuE, and m/z 418.9→ 387.1 for IS in the MRM mode. The effects of different mobile phase combinations (acetonitrile–water and methanol–water) and buffers (ammonium formate, formic acid, ammonium acetate, and acetic acid) on chromatographic behavior were examined. The mobile phase selected was methanol–water, with a column temperature and flow rate of 35 °C and 0.3 mL/min, respectively. The injection volume was 5 μL, and the total run time was 4 min.
4.2 Selection of IS
An appropriate IS with good stability that remains unchanged during sample processing and analysis must be selected for biological sample analysis. An unstable IS may lead to errors in the quantitative analysis. This study explored the effects of m-nitrophenol and bifendate as potential IS. When bifendate was detected in the positive-ion mode, it had a retention time with a significant separation from the analyte, generating symmetrical and sharp peaks, which indicated its stability and sensitivity. Therefore, the bifendate was selected as the IS in the experiment.
4.3 Pharmacokinetic studies
Cucurbitacin I (CuI) is a tetracyclic triterpenoid compound primarily found in Cucurbitaceae plants. CuB, CuD, CuE, and CuI all had cucurbitane-type triterpenoid parent nuclei, but exhibited varying substituents, affecting solubility and bioavailability. CuI is well-known for exerting powerful anti-cancer properties, particularly by regulating the JAK/STAT and PI3K/Akt pathways (Xu et al., 2022; Üremiş et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2018). CuB, CuD, and CuE also exert equally strong anti-cancer, hepatoprotective, and anti-inflammatory effects compared with CuI. In P. Melo, the content of CuB, CuD, and CuE was significantly higher than that of CuI, and pharmacokinetic data on CuB, CuD, and CuE (especially components in TCM nanosuspensions) in P. Melo remain scarce. Our MP-NP formulations specifically address the bioavailability limitations of these understudied cucurbitacins. Therefore, this study primarily investigated the pharmacokinetics of CuB, CuD, and CuE nanosuspensions. The pharmacokinetic studies revealed that MP-NPs were substantially advantageous over CUT in terms of the drug absorption rate, Cmax, AUC, and T1/2, possibly because of the nanosuspension characteristics of MP-NPs (such as larger surface area, higher solubility, and slower drug release). These characteristics can improve drug bioavailability and prolong its action time in the body. For example, the MP-NPs group reached Cmax more quickly after absorption than the CUT group (P < 0.05), potentially because of the nanosuspension characteristics of MP-NPs. MP-NPs may have better bioavailability or higher solubility, and so, the drug is more easily absorbed into the bloodstream. For CuD and CuE, the T1/2 of MP-NPs was generally longer than that of CUT. For instance, the T1/2 of CuD was 6.967 h (MP-NPs) versus 5.328 h (CUT), and for CuE, it was 7.053 h (MP-NPs) versus 5.991 h (CUT). This suggests that nanosuspension formulations have a longer retention time in the body, likely due to their physicochemical properties, which allow for slow release. AUC values of the three compounds were significantly higher in the MP-NPs group (P < 0.05). AUC0→t for CuB was 875.5 ng·h/mL (MP-NPs) versus 617.9 ng·h/mL (CUT). It was 1,259 ng·h/mL (MP-NPs) versus 1,033 ng·h/mL (CUT) for CuD and 751.6 ng·h/mL (MP-NPs) versus 602.9 ng·h/mL (CUT) for CuE (Abdollahi et al., 2024; Bali et al., 2011). This suggests that MP-NPs have a higher AUC, likely because their nanosuspension enhances the drug’s bioavailability and absorption rate in the body, thereby increasing drug accumulation.
Because of the polymeric nature of PVP K30, a high-molecular-weight stabilizer used for MP-NPs preparation, MP-NPs significantly improved triterpenoid solubility, likely due to reduced drug particle size and the increased specific surface area (Abdollahi et al., 2024; Bali et al., 2011; Aluri et al., 2023; Wang Z et al., 2017; Sun et al., 2024; Zhang, 2018; Roos et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2020). PVP K30 stabilizes the nanocrystal system primarily through steric hindrance. Its long polymer chains adsorb onto the nanoparticle surfaces, forming a physical barrier preventing particle aggregation through steric repulsion. This spatial barrier effectively counters attractive forces (e.g., van der Waals forces) between nanocrystals, thereby preserving their reduced size and preventing agglomeration, which is crucial for maintaining the high specific surface area and the resultant increased solubility. It is also crucial for improving its dissolution rate and promoting absorption. This experiment offers a valuable reference for the exploration of various dosage forms. The toxicology and pharmacodynamics of this preparation will be explored to continue to improve nanosuspension-related research data.
5 Conclusion
We here developed and validated a precise, stable, and sensitive UHPLC-MS/MS method with excellent extraction recovery, matrix effects, precision, and accuracy. This method was used to simultaneously measure CuB, CuD, and CuE content in CUT and MP-NPs following their oral administration, followed by that in rat plasma. As a nanosuspension dispersion system, MP-NPs significantly improved the oral bioavailability of the three triterpenoids compared with CUT, thereby increasing the plasma concentration of the analytes. The study results provide a foundation for clinical studies investigating the release rate, absorption, and metabolism of different dosage forms.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
C-nZ: Writing – original draft, Methodology. Z-bW: Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Resources. R-tD: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. S-lZ: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. C-qW: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. MW: Validation, Writing – review and editing. L-hW: Writing – review and editing. D-qY: Writing – review and editing. CW: Project administration, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Scientific Research Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 81973439), Key Research Program of Heilongjiang Province (grant number: GA22B012), Heilongjiang Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project (grant number: ZHY2024-049), Heilongjiang Provincial Postdoctoral Research Start-up Fund funded project (grant number: LBH-Q16214), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (grant number: H2018056), Heilongjiang Touyan Innovation Team Program (grant number: (2019) No. 5), Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine “Outstanding Innovative Talent Support Program” research project (grant number: 2018RCD03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdollahi, S., Raissi, H., and Farzad, F. (2024). Examine stability polyvinyl alcohol-stabilized nanosuspensions to overcome the challenge of poor drug solubility utilizing molecular dynamic simulation. Sci. Rep. 14, 17386. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-68362-2
Aluri, K. C., Sigfridsson, K., Xue, A., Hariparsad, N., McGinnity, D., and Ramsden, D. (2023). Pharmacokinetic evaluation of poorly soluble compounds formulated as nano- or microcrystals after intraperitoneal injection to mice. Int. J. Pharm. 636, 122787. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.122787
Attard, E., and Martinoli, M. G. (2015). Cucurbitacin E, an experimental lead triterpenoid with anticancer, immunomodulatory and novel effects against degenerative diseases. A mini-review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 15, 1708–1713. doi:10.2174/1568026615666150427121331
Bali, V., Ali, M., and Ali, J. (2011). Nanocarrier for the enhanced bioavailability of a cardiovascular agent: in vitro, pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and stability assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 403, 46–56. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.10.018
Brouwer, I. J., Out-Luiting, J. J., Vermeer, M. H., and Tensen, C. P. (2020). Cucurbitacin E and I target the JAK/STAT pathway and induce apoptosis in sézary cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 24, 100832. doi:10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100832
Chen, X. H., and Zheng, L. M. (2014). Clinical observation of fuzheng Huayu cucurbitacin tablets in treating liver fibrosis in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 7, 49–50. doi:10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2014.16.009
Chen, Y., Wang, J., Rao, Z., Hu, J., Wang, Q., Sun, Y., et al. (2022). Study on the stability and oral bioavailability of curcumin loaded (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate/poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone) nanoparticles based on hydrogen bonding-driven self-assembly. Food. Chem. 378, 132091. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132091
Chen, M., Pan, Q. M., Xu, Q. M., and Gao, H. W. (2024). Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Cucumis plants. J. Liaoning Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 26, 204–215. doi:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2024.01.038
Chen J, J. C., Zhang, G. H., Zhang, Z. Q., Qiu, M. H., Zheng, Y. T., Yang, L. M., et al. (2008). Octanorcucurbitane and cucurbitane triterpenoids from the tubers of Hemsleya endecaphylla with HIV-1 inhibitory activity. J. Nat. Prod. 71, 153–155. doi:10.1021/np0704396
Chen R, R. H., Gong, J. Z., and Xu, L. W. (2008). Clinical observation of cucurbitacin tablets in treating 50 cases of chronic hepatitis B. Primary Medical Forum, 23, 688–689.
Dai, S., Wang, C., Zhao, X., Ma, C., Fu, K., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Cucurbitacin B: a review of its pharmacology, toxicity, and pharmacokinetics. Pharmacol. Res. 187, 106587. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106587
Fathi-Karkan, S., Amiri Ramsheh, N., Arkaban, H., Narooie-Noori, F., Sargazi, S., Mirinejad, S., et al. (2024). Nanosuspensions in ophthalmology: overcoming challenges and enhancing drug delivery for eye diseases. Int. J. Pharm. 658, 124226. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124226
Garg, S. C., Kaul, R., and Wadhwa, R. (2018). Cucurbitacin B and cancer intervention: chemistry, biology and mechanisms (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 52, 19–37. doi:10.3892/ijo.2017.4203
He, J. J., Zhu, D., and Tian, L. (1994). Efficacy of cucurbitacin tablets in treating 89 cases of chronic hepatitis B. J. Zhejiang Coll. Traditional Chin. Med. 4, 18–19. doi:10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.1994.04.014
Hsu, H. L., Lin, B. J., Lin, Y. C., Tu, C. C., Nguyen, N. L., Wang, C. C., et al. (2023). Cucurbitacin E exerts anti-proliferative activity via promoting p62-dependent apoptosis in human non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 45, 8138–8151. doi:10.3390/cimb45100514
Huang, Y., Wu, H. L., and Xiao, M. S. (2019). Preventive effects of cucurbitacin tablet on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Zhejiang. Med. J. 41, 739–742. doi:10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2019.41.8.2018-2387
Jacob, S., Nair, A. B., and Shah, J. (2020). Emerging role of nanosuspensions in drug delivery systems. Biomater. Res. 24, 3. doi:10.1186/s40824-020-0184-8
Kim, K. H., Lee, I. S., Park, J. Y., Kim, Y., An, E. J., and Jang, H. J. (2018). Cucurbitacin B induces hypoglycemic effect in diabetic mice by regulation of AMP-Activated protein kinase alpha and glucagon-like Peptide-1 via bitter taste receptor signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1071. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01071
Ku, J. M., Hong, S. H., Kim, H. I., Lim, Y. S., Lee, S. J., Kim, M., et al. (2018). Cucurbitacin D exhibits its anti-cancer effect in human breast cancer cells by inhibiting Stat3 and Akt signaling. Eur. J. Inflamm. 20, 1721727X17751809–10. doi:10.1177/1721727X17751809
Li, Y., Li, Y., Yao, Y., Li, H., Gao, C., Sun, C., et al. (2023). Potential of cucurbitacin as an anticancer drug. Biomed. Pharmacother. 168, 115707. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115707
Lin, Y., Kotakeyama, Y., Li, J., Pan, Y., Matsuura, A., Ohya, Y., et al. (2019). Cucurbitacin B exerts antiaging effects in yeast by regulating autophagy and oxidative stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 4517091. doi:10.1155/2019/4517091
Lu, P., Yu, B., and Xu, J. (2012). Cucurbitacin B regulates immature myeloid cell differentiation and enhances antitumor immunity in patients with lung cancer. Cancer. biother. Radiopharm. 27, 495–503. doi:10.1089/cbr.2012.1219
Lu, W. M., Wang, X., and Wang, X. T. (2024). Advances in novel formulation technologies for improving the bioavailability of Panax notoginseng saponins. Tianjin J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 41, 672–680. doi:10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2024.05.21
Park, S. Y., Kim, Y. H., Park, G., Kim, Y. S., Lee, S. J., Leem, K., et al. (2015). Cucurbitacins attenuate microglial activation and protect from neuroinflammatory injury through Nrf2/ARE activation and STAT/NF-κB inhibition. Neurosci. Lett. 609, 129–136. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.022
Roos, C., Dahlgren, D., Berg, S., Westergren, J., Abrahamsson, B., Tannergren, C., et al. (2017). In vivo mechanisms of intestinal drug absorption from aprepitant nanoformulations. Mol. Pharm. 14, 4233–4242. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00294
Shikov, A. N., Pozharitskaya, O. N., Miroshnyk, I., Mirza, S., Urakova, I. N., Hirsjärvi, S., et al. (2009). Nanodispersions of taxifolin: impact of solid-state properties on dissolution behavior. Int. J. Pharm. 377, 148–152. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.04.044
Sun, J., Wang, S., Zhao, Z., Lu, J., Zhang, Y., An, W., et al. (2024). Oxymatrine attenuates ulcerative colitis through inhibiting pyroptosis mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Molecules 29, 2897. doi:10.3390/molecules29122897
Üremiş, M. M., Üremiş, N., Tosun, E., Durhan, M., Çiğremiş, Y., Baysar, A., et al. (2022). Cucurbitacin D inhibits the proliferation of HepG2 cells and induces apoptosis by modulating JAK/STAT3, PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways. Curr. Cancer. Drug. Targets 22, 931–944. doi:10.2174/1568009622666220623141158
Üremiş, M. M., Üremiş, N., and Türköz, Y. (2023). Cucurbitacin E shows synergistic effect with sorafenib by inducing apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and regulates Jak/Stat3, ERK/MAPK, PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Steroids 198, 109261. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2023.109261
Waleka, E., Stojek, Z., and Karbarz, M. (2021). Activity of Povidone in recent biomedical applications with emphasis on micro- and nano drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 13, 654. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13050654
Wang, Y., Zhao, G. X., Xu, L. H., Liu, K. P., Pan, H., He, J., et al. (2014). Cucurbitacin IIb exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through modulating multiple cellular behaviors of mouse lymphocytes. PLoS One 9, e89751. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089751
Wang, Y., Pi, C., Feng, X., Hou, Y., Zhao, L., and Wei, Y. (2020). The influence of nanoparticle properties on oral bioavailability of drugs. Int. J. Nanomed. 15, 6295–6310. doi:10.2147/IJN.S257269
Wang L, L., Du, J., Zhou, Y., and Wang, Y. (2017). Safety of nanosuspensions in drug delivery. Nanomedicine 13, 455–469. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2016.08.007
Wang L, L., Xu, H., Li, X., Chen, H., Zhang, H., Zhu, X., et al. (2023). Cucurbitacin E reduces IL-1β-induced inflammation and cartilage degeneration by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. J. Transl. Med. 21, 880. doi:10.1186/s12967-023-04771-7
Wang Z, Z., Zhu, W., Gao, M., Wu, C., Yang, C., Yang, J., et al. (2017). Simultaneous determination of cucurbitacin B and cucurbitacin E in rat plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS: a pharmacokinetics study after oral administration of cucurbitacin tablets. J. Chromatogr. B 1065-1066, 63–69. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.09.024
Wang Z, Z., Shi, X., Jiang, S., Sun, J., Borjigin, G., Li, Q., et al. (2023). Simultaneous determination of five iridoids of Picrorhiza scrophulariiflora in rat plasma using UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 28, 5925. doi:10.3390/molecules28155925
Wei, F., Yang, C., Wu, L., Sun, J., Wang, Z., and Wang, Z. (2022). Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetics study of three triterpenes from Sanguisorba officinalis L. in rats by UHPLC-MS/MS. Molecules 27, 5412. doi:10.3390/molecules27175412
Xue, H., Su, J. Y., Chen, W. J., Shen, Y. M., Wang, K. X., Li, X., et al. (2021). Optimized technical conditions of immediate released artemisinin solid dispersion prepared by using dual carriers. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 33, 620–629. doi:10.16333/j.1001-6880.2021.4.012
Yang, L., Ao, Q., Zhong, Q., Li, W., and Li, W. S. (2020). SIRT1/IGFBPrP1/TGF β1 axis involved in cucurbitacin B ameliorating concanavalin A-induced mice liver fibrosis. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 127, 371–379. doi:10.1111/bcpt.13446
Yang, P., Lian, Q., Fu, R., Ding, G. B., Amin, S., Li, Z., et al. (2022). Cucurbitacin E triggers cellular senescence in Colon cancer cells via regulating the miR-371b-5p/TFAP4 signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 70, 2936–2947. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07952
Yesilada, E., Tanaka, S., Sezik, E., and Tabata, M. (1988). Isolation of an anti-inflammatory principle from the fruit juice of Ecballium elaterium. J. Nat. Prod. 51, 504–508. doi:10.1021/np50057a008
Yu, C., Xiao, Y. Z., Xun, P. H., Dai, L., Han, J., and Yuan, H. L. (2014). Preparation and characterization of cucurbitacin B sodium deoxycholate/phospholipid-mixed oral fast dissolving film and antitumor activity study. Zhongguo zhongyao Zazhi. 39, 1799–1804. doi:10.4268/cjcmm20141010
Yu, Y., Sun, J., Yang, C., Dong, H., Wang, Z., and Wang, Z. (2023). An ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantitation of 10 alkaloids of Corydalis Decumbentis Rhizoma preparation in dog plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 132, 33–50. doi:10.1111/bcpt.13809
Zhang, L. (2018). Research progress on the quality control of Chinese herbal medicine by liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. World Chin. Med. 13, 513–516. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2018.02.065
Zhang, T., Li, X., Xu, J., Shao, J., Ding, M., and Shi, S. (2022). Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of Breviscapine nanosuspension and its freeze-dried powder. Pharmaceutics 14, 923. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14050923
Keywords: cucurbitacin, nanosuspension, pharmacokinetic, rat plasma, UHPLC-MS/MS
Citation: Zhang C-n, Wang Z-b, Du R-t, Zhang S-l, Wang C-q, Wang M, Wu L-h, Yang D-q and Wang C (2025) Comparison of the pharmacokinetic profiles of three triterpenoids after oral administration of a cucurbitacin tablet and nanosuspension by UHPLC-MS/MS. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1647015. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1647015
Received: 14 June 2025; Accepted: 28 August 2025;
Published: 10 September 2025.
Edited by:
Jiangxin Wang, Shenzhen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Huida Guan, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaChao Ma, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Tian Luan, Shenyang Medical College, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Du, Zhang, Wang, Wang, Wu, Yang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chen Wang, MTM3OTY4MjM0OTJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Chun-nan Zhang
Chun-nan Zhang Zhi-bin Wang
Zhi-bin Wang Rui-tong Du2
Rui-tong Du2 Chu-qiao Wang
Chu-qiao Wang Meng Wang
Meng Wang