- 1Department of General Medical Practice, The General Hospital of Western Theater Command, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Nursing, Nursing School, Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu, China
- 3Department of Cardiology, The General Hospital of Western Theater Command, Chengdu, China
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Heart failure (HF) is a major global health challenge. Traditional therapies have limitations, while recent studies highlight plant extracts’ potential due to their medicinal properties and milder side effects.
Objective: This study conducts a systematic review and network meta-analysis (NMA) to assess the therapeutic effects of plant extracts on patients with heart failure, providing robust evidence for clinical practice.
Materials and methods: A comprehensive search of databases, including PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library, was performed. Studies were screened using predefined criteria to extract data and assess quality. Network meta-analysis enabled direct/indirect comparisons of multiple plant extracts’ efficacy in heart failure intervention.
Results: A total of 20 studies encompassing 2,077 patients were incorporated into the analysis. Astragalus extract demonstrated the highest efficacy in enhancing the 6-min walk test (6-MWT) score (surface under the cumulative ranking curve [SUCRA]: 90.70%) and reducing tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) levels (SUCRA: 74.4%). Shenfu extract exhibited superior efficacy in decreasing B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) values (SUCRA: 68.2%) and enhancing the quality of life (QL) (SUCRA: 77.0%). Red ginseng extract was more effective in improving left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (SUCRA: 77.9%), while Ginkgo biloba extract showed greater efficacy in ameliorating New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification (SUCRA: 76.5%). Despite these findings, heterogeneity and methodological issues in the studies warrant further high-quality, large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to validate the results and determine the optimal plant extract use in heart failure treatment.
Conclusion: Astragalus extract, red ginseng extract, Ginkgo biloba extract, Terminalia arjuna extract, and Shenfu extract have demonstrated significant efficacy in heart failure management in the study for the selection of optimal plant extracts based on enhanced indicators of cardiac function outcomes. Continued research through rigorous randomized controlled trials is essential to substantiate and refine the current evidence.
1 Introduction
Heart failure (HF) constitutes a significant and intricate heterogeneous syndrome characterized by a collection of signs and symptoms arising from cardiac dysfunction, including impaired ventricular filling or compromised blood ejection; clinical manifestations such as dyspnea, fatigue, and peripheral and pulmonary edema are commonly observed, contributing to reduced life expectancy. Moreover, the prevalence of heart failure is rising (Teng et al., 2024; Mosterd and Hoes, 2007; McKee et al., 1971; Yancy et al., 2017). The majority of patients experience impaired function, diminished quality of life (QL), and premature mortality as a result of heart failure, a condition that is clinically associated with high morbidity and mortality rates and reduced quality of life and survival (Hao et al., 2015; Trupp, 2007). Heart failure represents a significant and escalating public health challenge, imposing a considerable burden on healthcare systems. There remains a need for the development and enhancement of novel and alternative therapeutic approaches for heart failure (Tao et al., 2023). Cornerstone medications in Western medicine for heart failure include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers (ACEI/ARB), beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, and sodium–glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors (Heidenreich et al., 2022). Non-pharmacological approaches include cardiac resynchronization therapy (McDonagh et al., 2021). Despite advances in standard therapy, the prognosis for patients with heart failure remains poor, with ongoing challenges in clinical symptom management and quality of life improvement.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has evolved over more than two millennia, with herbal medicine having a longstanding history as an adjunctive therapy in the management of heart failure (Tsai et al., 2017). In recent decades, TCM has gained increasing popularity (Hao et al., 2015) and has demonstrated efficacy in enhancing the quality of life for patients with heart failure (Tang and Huang, 2013). Shao-Mei et al. (2022) concluded that the TCM approach of benefiting qi is effective in treating heart failure and improving cardiac metabolism, sharing common features with other treatment methods. Chinese medicine is extensively utilized in clinical practice (Han et al., 2017). Wang K. et al. (2017) asserted that the integration of Chinese and Western medical treatments (including injections) is more effective in enhancing the overall clinical efficacy and improving the condition of patients with heart failure. The combination of Chinese herbal medicine and conventional pharmaceuticals in the treatment of heart failure is emerging as a trend in contemporary medicine (Xu et al., 2022).
Tao et al. (2023) found that ginseng injection enhanced clinical efficiency and cardiac function in patients with heart failure. Zheng et al. (2011) reported that Shenmai improved cardiac index and myocardial contractility, while Pittler et al. (2008) noted the significant efficacy of hawthorn extract in managing heart failure symptoms. The proprietary Chinese medicine Qiliqiangxin capsule has shown promise in treating heart failure (Wang Y. et al., 2017), and Xinmailong capsule has been found to be more effective than Western medications for the same condition (Ma et al., 2013). However, previous studies have primarily focused on herbal compound preparations, leaving a gap in scientific evidence regarding the effectiveness of specific herbal monomers in improving cardiac function in patients with heart failure.
Network meta-analysis (NMA) represents an advanced methodological approach that facilitates the ranking of interventions through both direct and indirect comparisons, contrasting with the conventional pairwise meta-analysis (Leucht et al., 2013). In this study, we employed a meta-analytic technique to investigate key Chinese medicine monomers, including hawthorn, Danhong, astragalus, red ginseng, Terminalia arjuna, and Shenfu, in the context of heart failure treatment. Our objective was to assess the efficacy and role of these Chinese medicine monomers in managing heart failure, thereby contributing a foundational basis for their clinical application.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy
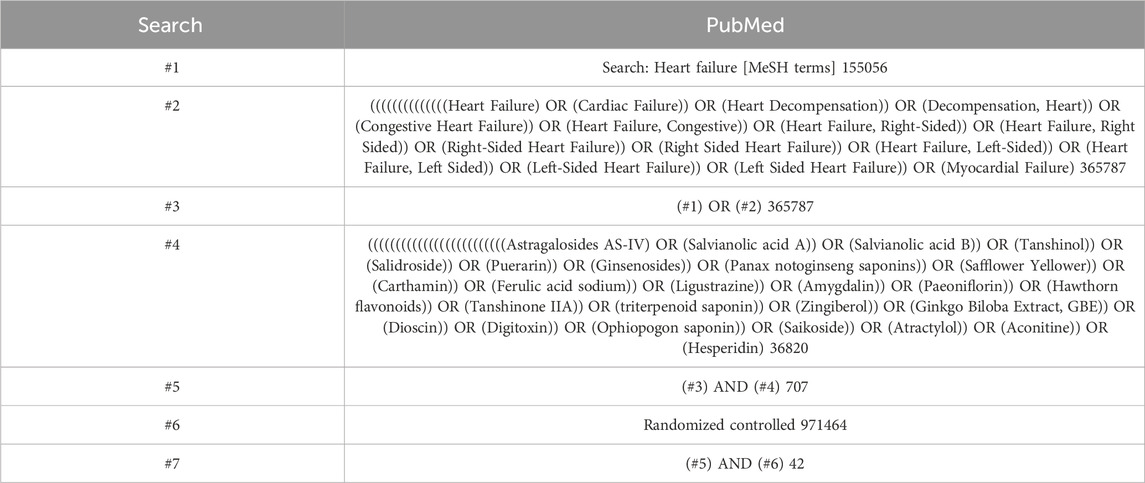
Our literature search encompassed PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane databases up to September 2024. We conducted a systematic review of 20 studies (patients) through a meta-analysis. The research strategy was built around the PICOS tools: (P) population: patients with heart failure; (I) intervention: plant extracts; (C) comparator: the control group received only the usual treatment for heart failure; (O) outcomes: indicators of improvement in cardiac function, brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), New York Heart Association (NYHA), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), the 6-min walk test (6-MWT), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and quality of life questionnaire (QLQ; and (S) study types: randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The detailed search strategy is shown in Table 1 (PubMed is used as an example).
2.2 Inclusion criteria
The following inclusion criteria were used: (1) an experimental group of heart failure patients treated with different plant extracts; (2) a control group receiving conventional treatment only for patients with heart failure; (3) randomized controlled clinical trials; (4) outcome measures including at least one of the following: brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), heart failure classification (NYHA), LVEF, TNF-α, 6-MWT, and QLQ; and (5) full-text availability.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
The following were the exclusion criteria: (1) data missing or unreported in the study and (2) non-observational studies such as clinical randomized controlled trials, randomized trials, animal studies, summaries, reviews, case reports, or letters.
2.4 Study selection
The literature was screened and excluded using literature management software EndNote. Researchers screened titles for duplication, non-randomized controlled trials, review papers, conference papers, protocols, and correspondence. Two researchers read the abstracts of the studies to identify which literature should be included or excluded. After this, the remaining literature was read in full by both researchers to determine whether it should be included. A third researcher discussed and resolved the differences between the two researchers’ findings after they both independently screened the literature.
2.5 Data extraction
Data from eight categories were recorded and standardized before choosing the data extraction table to include in the study: (1) author, (2) country, (3) year of publication, (4) cardiac functional grading, (5) age, (6) sample size, (7) intervention, and (8) outcome indicator.
2.6 Risk of bias of individual studies
Following the Cochrane Handbook version 5.1.0 guidelines for assessing the risk of bias (RoB) in RCTs, two researchers independently reviewed the RoB considering the following seven domains (Higgins et al., 2011): (1) generation of random sequences, (2) concealing treatment allocation, (3) blinding of participants and (4) personnel, (5) incomplete data on outcomes, (6) selective reporting, and (7) additional bias sources. The trials were organized into three levels of RoB by counting the components with the potential for high RoB: high risk (five or more), moderate risk (three or four), and low risk (two or fewer).
2.7 Data analysis
In the studies we included that utilized plant extracts as interventions, heart function was assessed using binary variables, while continuous variables, expressed as standard deviation (SD) (Li and Chen, 2021), were utilized for the remaining measures. In this study, continuous variables will be presented as either the mean difference (MD), which represents the absolute difference between the means of the treatment and control groups calculated on the same scale or the standardized mean difference (SMD), which is the mean difference in outcomes between groups divided by the standard deviation of outcomes among subjects. The SMD is used to synthesize data from trials utilizing different scales. Both MD and SMD will be reported with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and accompanied by appropriate analyses.
As per the instructions in the PRISMA NMA instruction manual, NMA aggregates and analyses were performed using Stata software (version 15.1) with Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation chains within a Bayesian framework (Harrington et al., 2021; Shim et al., 2017). Using the nodal method, we assessed and illustrated the alignment between indirect and direct comparisons, which were determined according to Stata software guidelines, and a p-value greater than 0.05 was considered to indicate passing the consistency test (Salanti et al., 2011).
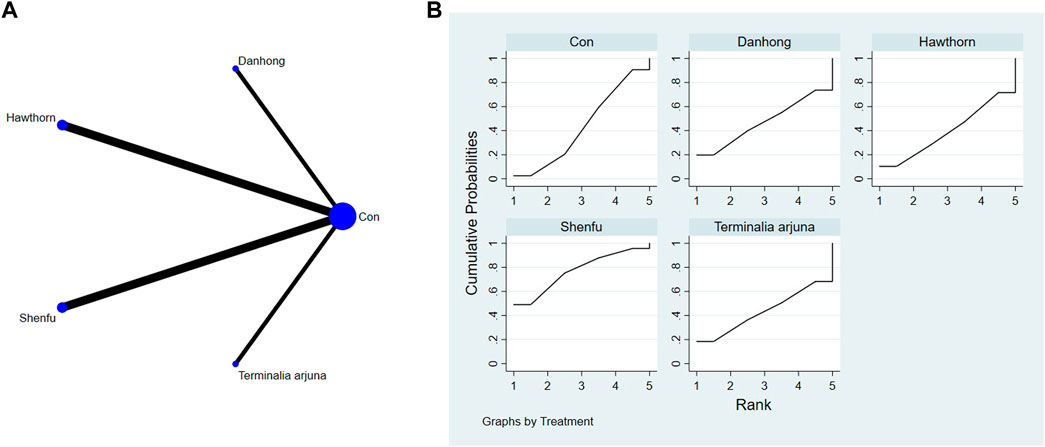
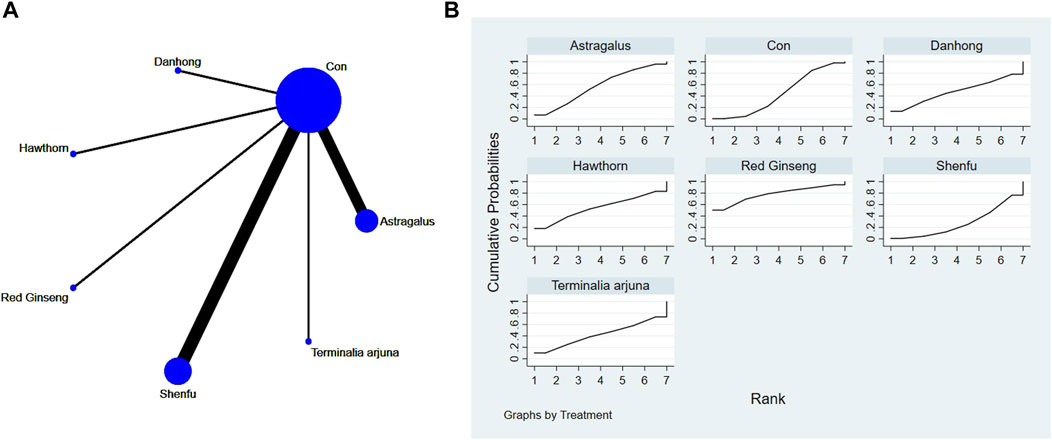
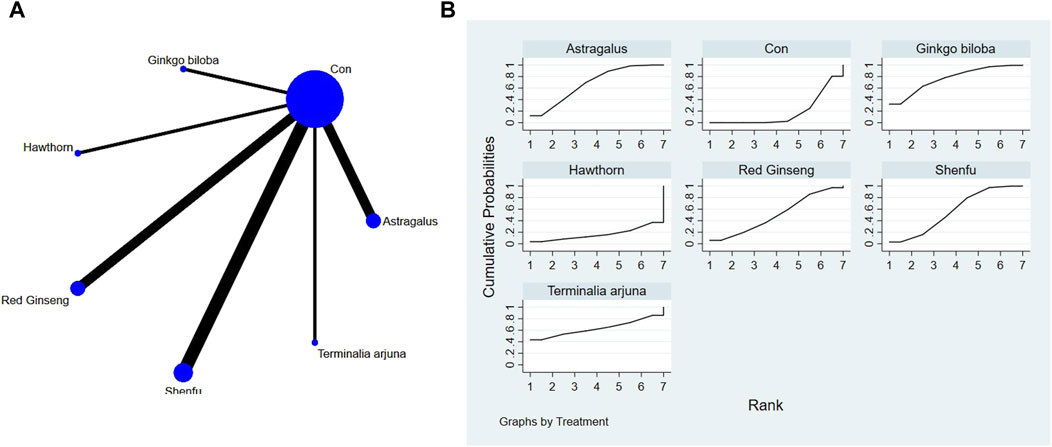
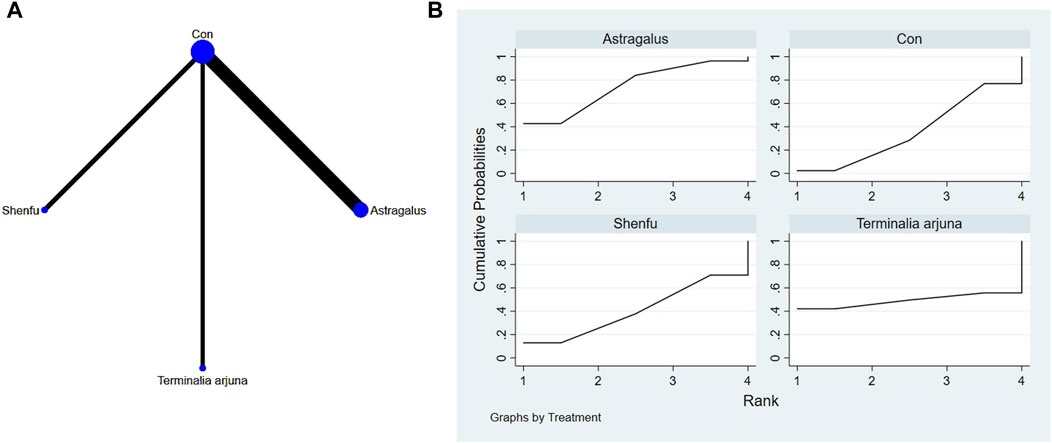
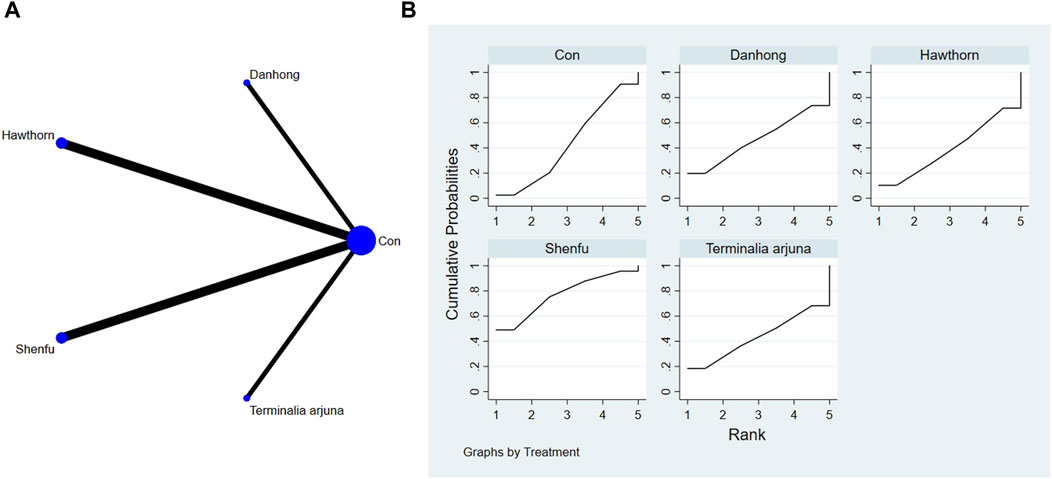
Network diagrams of different plant extracts are presented and described using Stata software. Within these generated network diagrams, each node symbolizes a distinct motor intervention or control condition, while the lines interconnecting the nodes denote direct head-to-head comparisons between the interventions. The dimensions of each node and the thickness of the connecting lines are proportional to the number of studies included (Thom et al., 2019).
P-scores were calculated based on the intervention hierarchy. As a frequentist equivalent to the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA), p-scores indicate the likelihood that a treatment is better than any other treatment, averaged across all competitors. P-scores range from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates the best treatment with no uncertainty and 0 indicates the worst treatment with no uncertainty. To assess the potential bias introduced by small-scale studies, which could contribute to publication bias in NMA, a network funnel plot was constructed and examined for symmetry (Harbord et al., 2006).
3 Results
3.1 Search results and study selection
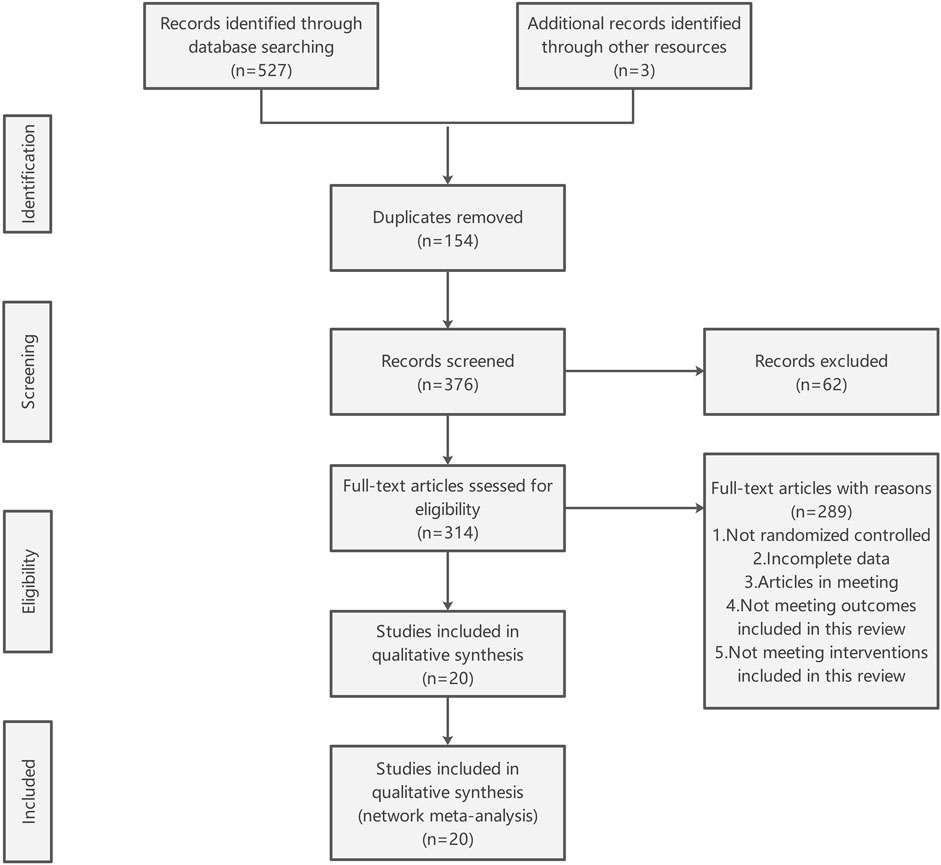
A comprehensive search of the electronic database yielded 527 documents, supplemented by an additional three documents identified through manual searching. Following the removal of duplicates, 376 documents remained for the screening of titles and abstracts, resulting in the exclusion of 62 documents. Subsequently, the full texts of the remaining 314 documents were reviewed, leading to the exclusion of 289 documents due to reasons such as non-randomized controlled trial design, incomplete data, conference paper format, and non-compliance with the interventions specified in this review. Ultimately, 20 documents were deemed suitable for inclusion in this study (Figure 1).
3.2 Quality assessment of the included studies
The assessment of the formation of RoB is presented in Figures 2, 3. The assessment data for the RoB are presented in Table 2. Among the 20 studies included, 2 studies satisfied 2 Cochrane criteria, 7 studies satisfied 3 criteria, 10 studies satisfied 4 criteria, and 1 study satisfied 5 criteria. All studies either possessed complete datasets or provided sufficient explanations and employed appropriate methodologies for addressing the missing data. The potential for other biases was deemed low across all studies. Overall, the majority of the 20 trials were assessed as having relatively moderate risk levels.
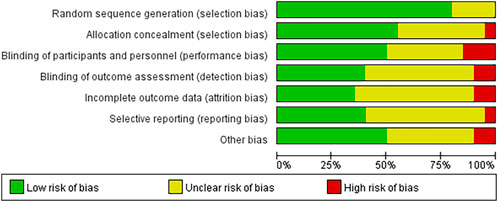
Figure 2. Risk of bias gragh. Bar chart showing risk of bias in various categories: Random sequence generation, Allocation concealment, Blinding of participants and personnel, Blinding of outcome assessment, Incomplete outcome data, Selective reporting, and Other bias. Each category is represented by a colored bar indicating low (green), unclear (yellow), and high (red) risk of bias.
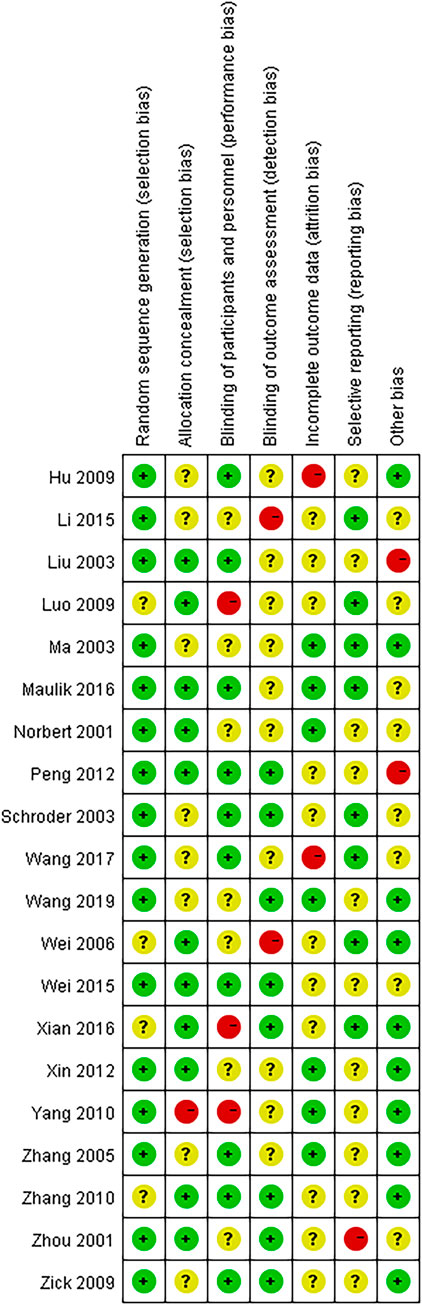
Figure 3. Risk of bias summary. Risk of bias summary chart for multiple studies, showing different biases like random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding, etc. Each study, labeled on the left, uses colored circles to indicate risk: green for low, yellow for unclear, and red for high. Columns represent various bias categories.
3.3 Characteristics of the included studies
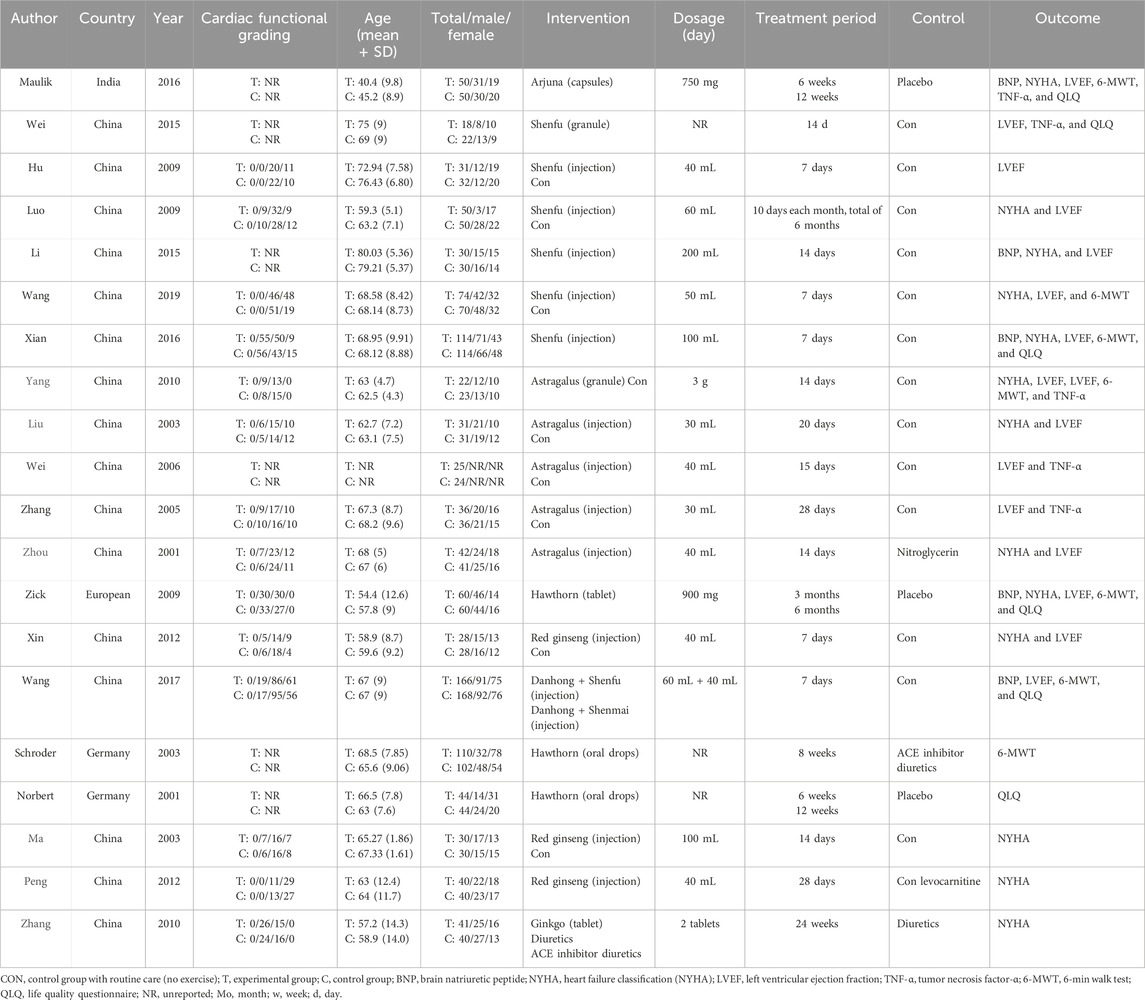
In total, we included 20 randomized controlled trials encompassing 2,077 patients diagnosed with heart failure. The control group included Shenfu extract (six studies) (Wei et al., 2015; Hu et al., 2009; Luo et al., 2009; Li et al., 2015; Wang X. et al., 2019; Xian et al., 2016), astragalus extract (five studies) (Yang et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2003; Wei et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2005; Zhou et al., 2001), hawthorn extract (three studies) (Zick et al., 2009; Schröder et al., 2003; Rietbrock et al., 2001), red ginseng extract (three studies) (Xin and Shan, 2012; Ma et al., 2003; Peng and Zhao, 2012), Ginkgo biloba extract (one study) (Zhang et al., 2010), Terminalia arjuna extracts (one study) (Maulik et al., 2016), and Danhong extract (one study) (Wang X. et al., 2017). One study was from India, one was from Europe, two were from Germany, and 16 were from China. The characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 2.
3.4 Network meta-analysis
The full NMA figure is shown in Figures 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A, 9A.
3.4.1 Cardiac function indicators of 6-MWT
Consistency and inconsistency of p-values for both direct and indirect comparisons were assessed across all studies. With all p-values exceeding 0.05, the consistency effect among the studies was considered acceptable.
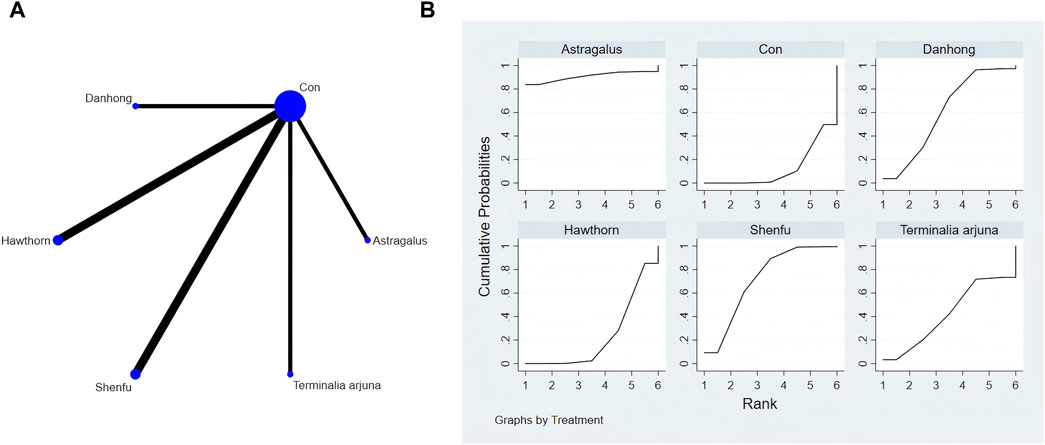
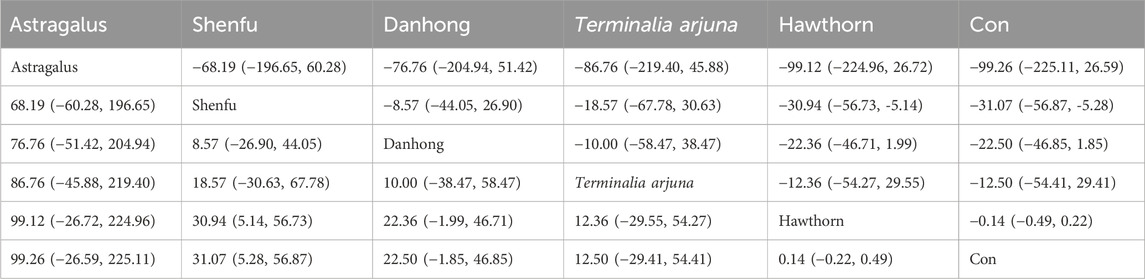
The findings from the network meta-analysis indicated that Shenfu extract [MD = −30.94, 95% CI = (5.14, 56.73)] demonstrated greater efficacy in enhancing the 6-minute walk test distance than the control group receiving hawthorn extract. Similarly, Shenfu extract [MD = −31.07, 95% CI = ((5.28, 56.87)] was found to be more effective than the control group receiving conventional treatment (CON). In the ranking of various plant extracts based on their probability of improving the 6-MWT distance, astragalus extract was ranked the highest according to the SUCRA (90.70%), followed by Shenfu extract (SUCRA: 71.6%), Danhong extract (SUCRA: 60.2%), Terminalia arjuna extract (SUCRA: 42.2%), hawthorn extract (SUCRA: 23.2%), and CON (SUCRA: 12.2%), as shown in Figure 4B and Table 3.
3.4.2 Cardiac function indicators of BNP
Consistency and inconsistency of p-values for both direct and indirect comparisons were assessed across all studies. With all p-values exceeding 0.05, the consistency effect among the studies was considered acceptable.
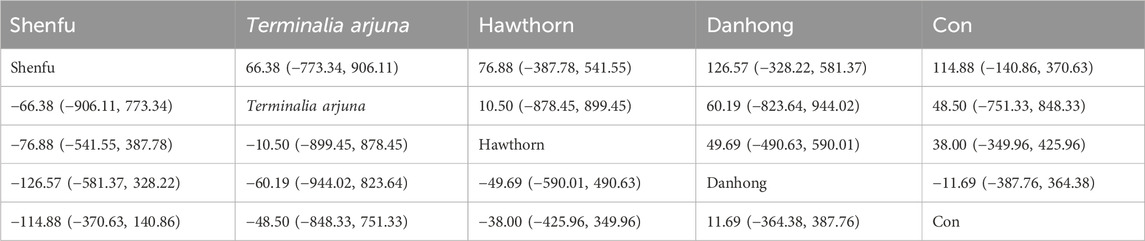
The network meta-analysis results indicated no significant differences in the league tables. In the ranking of various plant extracts based on their probability of reducing BNP levels, Shenfu extract was ranked the highest according to the SUCRA (68.2%), followed by Terminalia arjuna extract (SUCRA: 50.8%), hawthorn extract (SUCRA: 50.3%), Danhong extract (SUCRA: 40.8%), and CON (SUCRA: 39.9%), as shown in Figure 5B and Table 4.
3.4.3 Cardiac function indicators of LVEF
Consistency and inconsistency of p-values for both direct and indirect comparisons were assessed across all studies. With all p-values exceeding 0.05, the consistency effect among the studies was considered acceptable.
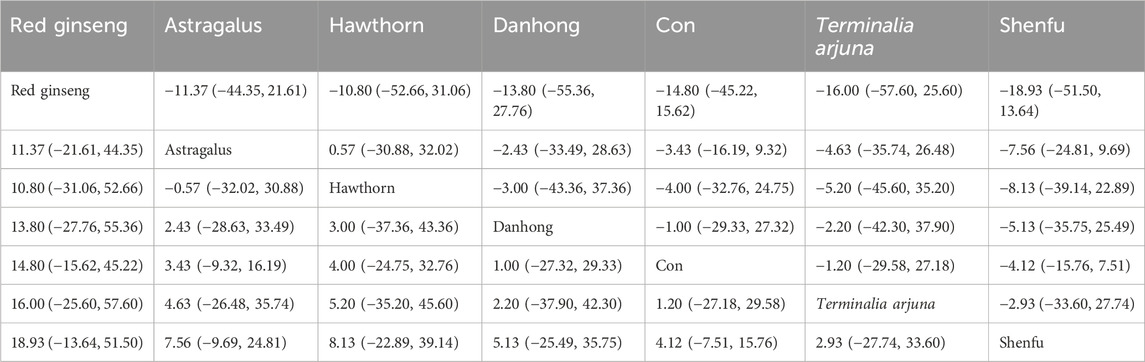
The network meta-analysis results indicated no significant differences in the league tables. In the ranking of various plant extracts based on their probability of improving the LVEF, red ginseng extract was ranked the highest according to the SUCRA (77.9%), followed by astragalus extract (SUCRA: 56.7%), hawthorn extract (SUCRA: 54.1%), Danhong extract (SUCRA: 47.6%), CON (SUCRA: 43.9%), Terminalia arjuna extract (SUCRA: 42.1%), and Shenfu extract (SUCRA: 27.6%), as shown in Figure 6B and Table 5.
3.4.4 Cardiac function indicators of NYHA
Consistency and inconsistency of p-values for both direct and indirect comparisons were assessed across all studies. With all p-values exceeding 0.05, the consistency effect among the studies was considered acceptable.
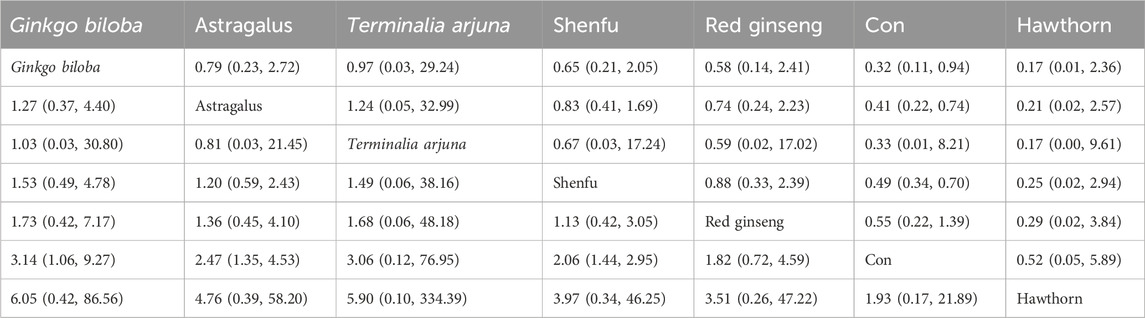
The findings from the network meta-analysis indicated that Ginkgo biloba extract [MD = −3.14, 95% CI =(1.06, 9.27)], astragalus extract [MD = −2.47, 95% CI =(1.35, 4.53)], and Shenfu extract [MD = 2.06, 95% CI =((1.44, 2.95)] were found to be more effective than the conventional treatment received by the control group. In the ranking of various plant extracts based on their probability of improving the NYHA, Ginkgo biloba extract was ranked the highest according to the SUCRA (76.5%), followed by astragalus extract (SUCRA: 67.8%), Terminalia arjuna extract (SUCRA: 64.2%), Shenfu extract (SUCRA: 56.6%), red ginseng extract (SUCRA: 50.7%), CON (SUCRA: 17.9%), and hawthorn extract (SUCRA: 16.4%), as shown in Figure 7B and Table 6.
3.4.5 Cardiac function indicators of TNF-α
Consistency and inconsistency of p-values for both direct and indirect comparisons were assessed across all studies. With all p-values exceeding 0.05, the consistency effect among the studies was considered acceptable.
The network meta-analysis results indicated no significant differences in the league tables. In the ranking of various plant extracts based on their probability of reducing the TNF-α level, astragalus extract was ranked the highest according to the SUCRA (74.4%), followed by Terminalia arjuna extract (SUCRA:49.1%), Shenfu extract (SUCRA: 40.6%), and CON (SUCRA: 35.9%), as shown in Figure 8B and Table 7.
3.4.6 Cardiac function indicators of QLQ
Consistency and inconsistency of p-values for both direct and indirect comparisons were assessed across all studies. With all p-values exceeding 0.05, the consistency effect among the studies was considered acceptable.
The network meta-analysis results indicated no significant differences in the league tables. In the ranking of various plant extracts based on their probability of improving the QLQ, Shenfu extract was ranked the highest according to the SUCRA (77.0%), followed by Danhong extract (SUCRA: 47.1%), Terminalia arjuna extract (SUCRA: 43.4%), CON (SUCRA: 43.2%), and hawthorn extract (SUCRA: 39.3%), as shown in Figure 9B and Table 8.
3.5 Assessment of publication bias
A funnel plot is a common graphical test used to assess publication bias in meta-analyses (Egger et al., 1997). Separate funnel plots were developed for all outcome indicators to assess the possibility of publication bias, as shown in Figure 10.
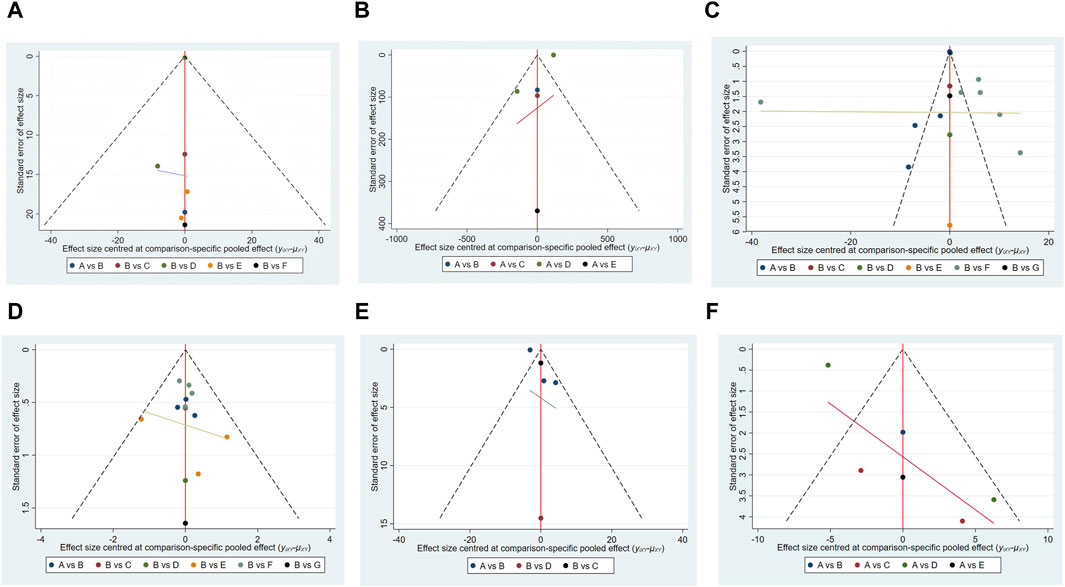
Figure 10. Funnel plot on publication bias. (A) 6-MWT; (B) BNP; (C) LVEF; (D) NYHA; (E) TNF-α; (F) QLQ.
4 Discussion
In this study, we conducted a comparative analysis of the efficacy of various plant extracts in enhancing the clinical parameters in patients with heart failure. A total of 20 studies were included, encompassing 7 distinct plant extracts and involving 2,077 patients diagnosed with heart failure. Our findings indicated that astragalus extract was the most effective in improving 6-MWT scores and reducing TNF-α levels. Shenfu extract demonstrated superior efficacy in decreasing BNP values and enhancing quality of life. Red ginseng extract yielded better outcomes in terms of improving LVEF, while Ginkgo biloba extract was more effective in enhancing cardiac function class.
In our study, Shenfu injection demonstrated efficacy in enhancing quality of life, reducing BNP levels, decreasing TNF-α, and improving cardiac function grading. HF represents a significant cause of morbidity and mortality globally. Natriuretic peptides (NPs) are cardioprotective hormones secreted by cardiomyocytes in response to pressure or volume overload (Goetze et al., 2020). Both BNP and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) have been extensively shown to contribute to the diagnosis and risk stratification of HF, and these biomarkers are increasingly utilized as tools for population screening (Castiglione et al., 2022). Given that heart failure can profoundly impact patients’ quality of life, enhancing it is a critical objective in heart failure management. Shenfu injection (SFI) is a herbal therapeutic approach for heart failure. Nonetheless, the precise mechanisms by which ginseng exerts its therapeutic effects in heart failure remain inadequately understood. Li et al. (2024) utilized subcutaneous multipoint injection of isoprenaline (ISO) to develop a heart failure model. Their findings suggest that Shenfu injection may effectively enhance cardiac function in rats with ISO-induced heart failure, potentially through the modulation of the pro-/anti-inflammatory balance and the reduction of serum and urinary trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) levels (Li et al., 2024). Additionally, Shenfu soup has been shown to enhance cardiac contractility, increase coronary blood supply, improve ischemic myocardial metabolism, scavenge free radicals, and protect myocardial ultrastructure (Wei et al., 2015). Zhou et al. (2023) demonstrated that ginseng and sorrel injection can significantly improve the quality of life and exercise tolerance in patients with chronic heart failure, and it can reduce blood levels of BNP/NT-proBNP (Zhou et al., 2023).
Red ginseng extract serves as the primary component of Shenmai injection (SMI). In our study, extracts of red ginseng, astragalus, and hawthorn demonstrated significant efficacy in enhancing LVEF, with red ginseng extract exhibiting the most pronounced effect. Heart failure is a clinical syndrome characterized by dyspnea or exercise intolerance resulting from impaired ventricular filling, ejection, or both. The diagnosis is primarily based on elevated natriuretic peptide levels above age- and context-specific thresholds, alongside the identification of left ventricular systolic dysfunction, as indicated by echocardiographic measurement of an LVEF of 40% or less (Murphy et al., 2020). Wu et al. (2023) demonstrated that Shenmai injection enhances cardiac function in patients with congestive heart failure (CHF) through its anti-apoptotic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, along with improving myocardial metabolism. Similarly, Zheng et al. (2011) reported that SMI leads to improvements in cardiac index and myocardial contractility, with some amelioration of heart failure symptoms. Yang et al. (2024) found that SMI facilitates myocardial lipid metabolism and mitigates heart failure following myocardial infarction, as evidenced by a post-infarction heart failure mouse model and an ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) cell model. Furthermore, another animal study indicated that SMI promotes angiogenesis and cardiac remodeling, resulting in enhanced LVEF in a rat model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI) (Liu et al., 2018). Myocardial fibrosis, a primary pathological feature of hypertensive heart failure, is reportedly alleviated by Ginseng-Mai injection, which effectively improves heart failure by inhibiting myocardial fibrosis (Hu et al., 2023).
In the present study, astragalus extract demonstrated significant efficacy in enhancing the 6-min walking distance and reducing TNF-α levels. Additionally, it proved effective in improving LVEF and the NYHA classification. Inflammatory cytokines are persistently elevated in patients with congestive heart failure, with TNF-α being a pivotal pro-inflammatory cytokine that exacerbates heart failure by counteracting the anti-inflammatory response and disrupting systemic homeostasis (Schumacher and Naga Prasad, 2018). The 6-minute walk test is a widely utilized and well-tolerated assessment tool for evaluating the functional capacity of heart failure patients, offering reliable insights into daily activities and short-term prognosis, particularly in those with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (Giannitsi et al., 2019). Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) is a bioactive compound derived from Astragalus membranaceus. The studies have elucidated the bioactivity, potential targets, and molecular mechanisms of APS in the context of heart failure. These studies suggest that isorhamnetin, quercetin, trichothecenes, spinosyn, and kaempferol are likely the principal active components of APS, exerting cardioprotective effects by modulating the expression of the estrogen receptor (ESR1) (Chen et al., 2024). Ma et al. (2023) demonstrated that APS mitigates heart failure-induced cachexia by reducing excessive lipid consumption in both white and brown adipose tissues. Astragaloside IV (AS-IV), the primary active constituent of astragalus, has been utilized as a therapeutic agent for heart failure. It is proposed that AS-IV influences the HSF1/VEGF signaling pathway, enhances angiogenesis, and alleviates pressure overload-induced heart failure (Du et al., 2024). In a clinical study involving 43 patients with acute myocardial infarction receiving astragalus, significant improvements in left ventricular function were observed. The antioxidant properties of astragalus may contribute to its cardiotonic effects (Chen et al., 1995).
The NYHA classification serves as a crucial instrument for the risk stratification of HF. It has been demonstrated to have a strong correlation with survival rates and is utilized to indicate the severity of acute heart failure (AHF) (Blacher et al., 2021). In the current study, Ginkgo biloba extract exhibited significant efficacy in improving the NYHA classification. The beneficial effects of Ginkgo biloba extracts are primarily attributed to their high concentrations of flavonoids and terpenoids, antioxidant properties (Karmazyn and Gan, 2023), ability to reduce reperfusion-induced arrhythmias (Tosaki et al., 1993), mitigate ischemia–reperfusion injury, and promote functional recovery (Tosaki et al., 1994; Tosaki et al., 1996). Evidence suggests that Ginkgo biloba extract exerts a protective effect against adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity, potentially through mechanisms involving the inhibition of mitochondria-dependent pro-apoptotic signaling and the reduction of pro-inflammatory factors (Liu et al., 2008). Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, Ginkgo biloba extract has been further explored for its potential therapeutic benefits in cardiac pathology secondary to viral myocarditis (Wang W. et al., 2019).
The present study focuses on evaluating the efficacy rankings of various botanical extracts (including oral preparations and injectable formulations) across different indicators of heart failure. Consistent with previous research findings, Chinese patent medicines have demonstrated significant efficacy in the treatment of heart failure. Lin et al. (2021) demonstrated that among Chinese patent medicines (injections) combined with conventional therapy, Xinmailong was the most effective in improving the NYHA functional classification efficiency and reducing BNP levels; Shenmai was the most effective in the 6-minute walk test; YiQiFuMai lyophilized injection was the most effective for left ventricular ejection fraction; Huangqi was the most effective in improving stroke volume; and Shenfu performed the best in enhancing quality of life. Guo et al. (2023) showed that among Chinese patent medicines (oral preparations) combined with conventional therapy, Shexiang Baoxin Pill was the most effective in improving the NYHA functional classification efficiency, Tongxinluo capsule was the most effective in ameliorating the ratio of early-to-late diastolic mitral inflow velocity (E/A ratio), and Qili Qiangxin was the most effective in reducing NT-proBNP levels and improving the 6-minute walk test results. Comparative studies demonstrate that Huangqi exhibits stable and remarkable efficacy in improving patients’ exercise endurance, while Shenfu preparations show unique advantages in enhancing subjective well-being and quality of life. However, discrepancies exist in research conclusions due to variations in intervention methods (such as single plant extracts versus compound formulations, drug dosage forms, and administration routes) and study populations. Overall, current research aligns closely with previous studies in establishing evidence-based systems for TCM treatment of heart failure, with differences reflecting the complexity of heart failure management and the need for personalized approaches. Future research should provide detailed reports on intervention details (e.g., standardization levels of extracts, injectable manufacturers, and oral dosage forms) and conduct subgroup analyses to reduce heterogeneity and offer more precise clinical guidance.
5 Strengths and limitations
Our study incorporated 20 studies encompassing a total of 2,077 patients, representing a substantial sample size. The systematic review adhered to a rigorous screening process, used advanced statistical methodologies, and integrated data from analogous studies to mitigate random errors. A thorough quality assessment of the included studies was conducted to align the results more closely with real-world conditions, thereby providing reliable conclusions for both clinicians and patients. Additionally, the study synthesized numerous and varied plant extracts, selecting several commonly used extracts to inform clinical decision-making. Nevertheless, variations in patient characteristics, interventions, and other study parameters, such as the dosage discrepancies of identical plant extracts, may impact the stability and interpretation of the results. Although statistical methods can partially adjust for these differences, they cannot completely eliminate the effects of heterogeneity. Furthermore, the quality of the original studies included may be inconsistent, with some studies exhibiting small sample sizes and suboptimal design, which could affect the overall quality of the evidence.
6 Conclusion
Astragalus extract, red ginseng extract, Ginkgo biloba extract, Terminalia arjuna extract, and Shenfu extract have demonstrated significant efficacy in heart failure management for the selection of optimal plant extracts based on enhanced indicators of cardiac function outcomes. Continued research through rigorous randomized controlled trials is essential to substantiate and refine the current evidence.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JD: Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Software, Conceptualization. YH: Formal analysis, Software, Data curation, Writing – original draft. DF: Investigation, Data curation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. YD: Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. KY: Writing – review and editing, Validation, Conceptualization, Supervision. CL: Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82300329).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the reviewers for their support and assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1648811/full#supplementary-material
References
Blacher, M., Zimerman, A., Engster, P. H. B., Grespan, E., Polanczyk, C. A., Rover, M. M., et al. (2021). Revisiting heart failure assessment based on objective measures in NYHA functional classes I and II. Heart 107 (18), 1487–1492. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2020-317984
Castiglione, V., Aimo, A., Vergaro, G., Saccaro, L., Passino, C., and Emdin, M. (2022). Biomarkers for the diagnosis and management of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 27 (2), 625–643. doi:10.1007/s10741-021-10105-w
Chen, L. X., Liao, J. Z., and Guo, W. Q. (1995). Effects of Astragalus membranaceus on left ventricular function and oxygen free radical in acute myocardial infarction patients and mechanism of its cardiotonic action. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 15 (3), 141–143.
Chen, Q., Wang, J., Sun, L., Ba, B., and Shen, D. (2024). Mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi, HQ) for treatment of heart failure based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. J. Cell Mol. Med. 28 (10), e18331. doi:10.1111/jcmm.18331
Du, P., Xu, L., Wang, Y., Jiao, T., Cheng, J., Zhang, C., et al. (2024). Astragaloside IV ameliorates pressure overload-induced heart failure by enhancing angiogenesis through HSF1/VEGF pathway. Heliyon 10 (17), e37019. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37019
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M., and Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Bmj 315 (7109), 629–634. doi:10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Giannitsi, S., Bougiakli, M., Bechlioulis, A., Kotsia, A., Michalis, L. K., and Naka, K. K. (2019). 6-minute walking test: a useful tool in the management of heart failure patients. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc Dis. 13, 1753944719870084. doi:10.1177/1753944719870084
Goetze, J. P., Bruneau, B. G., Ramos, H. R., Ogawa, T., de Bold, M. K., and de Bold, A. J. (2020). Cardiac natriuretic peptides. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 17 (11), 698–717. doi:10.1038/s41569-020-0381-0
Guo, H., Zhu, M., Yu, R., Li, X., and Zhao, Q. (2023). Efficacy of Chinese traditional patent medicines for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of 64 randomized controlled trials. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 10, 1255940. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2023.1255940
Han, J. Y., Li, Q., Ma, Z. Z., and Fan, J. Y. (2017). Effects and mechanisms of compound Chinese medicine and major ingredients on microcirculatory dysfunction and organ injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion. Pharmacol. Ther. 177, 146–173. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.03.005
Hao, P. P., Jiang, F., Chen, Y. G., Yang, J., Zhang, K., Zhang, M. X., et al. (2015). Traditional Chinese medication for cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 12 (6), 318. doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2015.60
Harbord, R. M., Egger, M., and Sterne, J. A. (2006). A modified test for small-study effects in meta-analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints. Stat. Med. 25 (20), 3443–3457. doi:10.1002/sim.2380
Harrington, S. M., Wishingrad, V., and Thomson, R. C. (2021). Properties of Markov chain monte carlo performance across many empirical alignments. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38 (4), 1627–1640. doi:10.1093/molbev/msaa295
Heidenreich, P. A., Bozkurt, B., Aguilar, D., Allen, L. A., Byun, J. J., Colvin, M. M., et al. (2022). 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American college of cardiology/american heart association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 79 (17), e263–e421. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.12.012
Higgins, J. P., Altman, D. G., Gøtzsche, P. C., Jüni, P., Moher, D., Oxman, A. D., et al. (2011). The cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 343, d5928. doi:10.1136/bmj.d5928
Hu, Y. H., Wu, H. Q., and Qi, X. (2009). Influence of shenfu injection on heart function and bone marrow stem cell mobilization in patients with chronic heart failure of coronary heart disease. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 29 (4), 309–312.
Hu, S. Y., Zhou, Y., Zhong, S. J., Yang, M., Huang, S. M., Li, L., et al. (2023). Shenmai injection improves hypertensive heart failure by inhibiting myocardial fibrosis via TGF-β 1/Smad pathway regulation. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 29 (2), 119–126. doi:10.1007/s11655-022-2899-y
Karmazyn, M., and Gan, X. T. (2023). Inhibition of myocardial remodeling and heart failure by traditional herbal medications: evidence from ginseng and ginkgo biloba. Rev. Cardiovasc Med. 24 (7), 212. doi:10.31083/j.rcm2407212
Leucht, S., Cipriani, A., Spineli, L., Mavridis, D., Orey, D., Richter, F., et al. (2013). Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet 382 (9896), 951–962. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60733-3
Li, D., and Chen, P. (2021). Effects of aquatic exercise and land-based exercise on cardiorespiratory fitness, motor function, balance, and functional Independence in stroke Patients-A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Brain Sci. 11 (8), 1097. doi:10.3390/brainsci11081097
Li, J., Fan, T. B., and Yang, Z. X. (2015). The clinical observation of the effects of shenfu injection and different ways of drug delivery on severe and refractory heart failure. J. Emerg. Traditional Chin. Med. [Zhong Guo Zhong Yi ji Zheng] 24 (8), 1322–1323.
Li, L., Ye, J., Zhao, Z., Hu, S., Liang, H., Ouyang, J., et al. (2024). Shenfu injection improves isoproterenol-induced heart failure in rats by modulating co-metabolism and regulating the trimethylamine-N-oxide - inflammation axis. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1412300. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1412300
Lin, S., Shi, Q., Ge, Z., Liu, Y., Cao, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine injections for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 659707. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.659707
Liu, Z. G., Xiong, Z. M., and Yu, X. Y. (2003). Effect of astragalus injection on immune function in patients with congestive heart failure. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 23 (5), 351–353.
Liu, T. J., Yeh, Y. C., Ting, C. T., Lee, W. L., Wang, L. C., Lee, H. W., et al. (2008). Ginkgo biloba extract 761 reduces doxorubicin-induced apoptotic damage in rat hearts and neonatal cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 80 (2), 227–235. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvn192
Liu, X., Tan, W., Yang, F., Wang, Y., Yue, S., Wang, T., et al. (2018). Shengmai injection reduces apoptosis and enhances angiogenesis after myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 104, 629–636. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.180
Luo, X. Y., Zhang, F. R., and He, R. M. (2009). Efficacy of shenfu injection as adjuvant therapy in treating patients of ischemic cardiomyopathy with heart insufficiency. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 29 (8), 685–687.
Ma, L., Yang, L., and Chen, T. D. (2003). Influence of large amount of shengmai injection on blood coagulation in patients with chronic heart failure. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 23 (4), 275–277.
Ma, Q., Luo, Y., Guo, P., Gao, G., Yang, M., Sablok, G., et al. (2013). Clinical effects of Xinmailong therapy in patients with chronic heart failure. Int. J. Med. Sci. 10 (5), 624–633. doi:10.7150/ijms.5779
Ma, D., Wu, T., Qu, Y., Yang, J., Cai, L., Li, X., et al. (2023). Astragalus polysaccharide prevents heart failure-induced cachexia by alleviating excessive adipose expenditure in white and brown adipose tissue. Lipids Health Dis. 22 (1), 9. doi:10.1186/s12944-022-01770-3
Maulik, S. K., Wilson, V., Seth, S., Bhargava, B., Dua, P., Ramakrishnan, S., et al. (2016). Clinical efficacy of water extract of stem bark of Terminalia arjuna (Roxb. ex DC.) wight and Arn. in patients of chronic heart failure: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Phytomedicine 23 (11), 1211–1219. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2016.02.007
McDonagh, T. A., Metra, M., Adamo, M., Gardner, R. S., Baumbach, A., Böhm, M., et al. (2021). 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 42 (36), 3599–3726. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368
McKee, P. A., Castelli, W. P., McNamara, P. M., and Kannel, W. B. (1971). The natural history of congestive heart failure: the framingham study. N. Engl. J. Med. 285 (26), 1441–1446. doi:10.1056/NEJM197112232852601
Mosterd, A., and Hoes, A. W. (2007). Clinical epidemiology of heart failure. Heart 93 (9), 1137–1146. doi:10.1136/hrt.2003.025270
Murphy, S. P., Ibrahim, N. E., and Januzzi, J. L. (2020). Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a review. Jama 324 (5), 488–504. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.10262
Peng, C., and Zhao, G. (2012). Randomized controlled clinical study of shengmai injection combinedwith L - carnitine in treating chronic heart failure. J. Pract. traditional Chin. Intern. Med. 26 (7), 24–25.
Pittler, M. H., Guo, R., and Ernst, E. (2008). Hawthorn extract for treating chronic heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008 (1), Cd005312. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005312.pub2
Rietbrock, N., Hamel, M., Hempel, B., Mitrovic, V., Schmidt, T., and Wolf, G. K. (2001). Wirksamkeit eines standardisierten Extraktes aus frischen Crataegus-Beeren auf Belastungstoleranz und Lebensqualität bei Patienten mit Herzinsuffizienz (NYHA II). Arzneimittelforschung 51 (10), 793–798. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1300117
Salanti, G., Ades, A. E., and Ioannidis, J. P. (2011). Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64 (2), 163–171. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.03.016
Schröder, D., Weiser, M., and Klein, P. (2003). Efficacy of a homeopathic crataegus preparation compared with usual therapy for mild (NYHA II) cardiac insufficiency:: results of an observational cohort study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 5 (3), 319–326. doi:10.1016/s1388-9842(02)00237-4
Schumacher, S. M., and Naga Prasad, S. V. (2018). Tumor necrosis Factor-α in heart failure: an updated review. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 20 (11), 117. doi:10.1007/s11886-018-1067-7
Shao-Mei, W., Li-Fang, Y., and Li-Hong, W. (2022). Traditional Chinese medicine enhances myocardial metabolism during heart failure. Biomed. Pharmacother. 146, 112538. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112538
Shim, S., Yoon, B. H., Shin, I. S., and Bae, J. M. (2017). Network meta-analysis: application and practice using stata. Epidemiol. Health 39, e2017047. doi:10.4178/epih.e2017047
Tang, W. H. W., and Huang, Y. (2013). Cardiotonic modulation in heart failure: insights from traditional Chinese medicine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 62 (12), 1073–1074. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.028
Tao, L., Mo, Z., Li, Z., Li, S., Luo, Z., Li, D., et al. (2023). Efficacy and safety of shenfu injection on acute heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 110, 154641. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154641
Teng, Y., Li, Y., Wang, L., Wang, B., Su, S., Chen, J., et al. (2024). Effectiveness and pharmacological mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicine for coronary heart disease complicated with heart failure. J. Ethnopharmacol. 322, 117605. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117605
Thom, H., White, I. R., Welton, N. J., and Lu, G. (2019). Automated methods to test connectedness and quantify indirectness of evidence in network meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 10 (1), 113–124. doi:10.1002/jrsm.1329
Tosaki, A., Droy-Lefaix, M. T., Pali, T., and Das, D. K. (1993). Effects of SOD, catalase, and a novel antiarrhythmic drug, EGB 761, on reperfusion-induced arrhythmias in isolated rat hearts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 14 (4), 361–370. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(93)90085-9
Tosaki, A., Engelman, D. T., Pali, T., Engelman, R. M., and Droy-Lefaix, M. T. (1994). Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) improves postischemic function in isolated preconditioned working rat hearts. Coron. Artery Dis. 5 (5), 443–450. doi:10.1097/00019501-199405000-00011
Tosaki, A., Pali, T., and Droy-Lefaix, M. T. (1996). Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract and preconditioning on the diabetic rat myocardium. Diabetologia 39 (11), 1255–1262. doi:10.1007/s001250050567
Trupp, R. J. (2007). The many faces of heart failure. Prog. Cardiovasc Nurs. 22 (2), 110–111. doi:10.1111/j.0889-7204.2007.06066.x
Tsai, M. Y., Hu, W. L., Lin, C. C., Lee, Y. C., Chen, S. Y., Hung, Y. C., et al. (2017). Prescription pattern of Chinese herbal products for heart failure in Taiwan: a population-based study. Int. J. Cardiol. 228, 90–96. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.172
Wang, K., Wu, J., Duan, X., Wu, J., Zhang, D., Zhang, X., et al. (2017). Huangqi injection in the treatment of chronic heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Baltim. 96 (39), e8167. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000008167
Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Li, C., Lu, L., Zhang, Q., Zhu, R., et al. (2017). A review of Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of chronic heart failure. Curr. Pharm. Des. 23 (34), 5115–5124. doi:10.2174/1381612823666170925163427
Wang, X., Hou, Y., Mao, J., Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Zhao, Y., et al. (2017). Western medication plus traditional Chinese medicine preparations in patients with chronic heart failure: a prospective, single-blind, randomized, controlled, and multicenter clinical trial. J. traditional Chin. Med. = chung i tsa chih ying wen pan 37 (6), 756–766. doi:10.1016/s0254-6272(18)30038-4
Wang, X., Zhao, Z., Mao, J., Du, T., Chen, Y., Xu, H., et al. (2019). Randomized, double-blinded, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of shenfu injection for treatment of patients with chronic heart failure during the acute phase of symptom aggravation (Yang and Qi deficiency syndrome). Evidence-based complementary Altern. Med. eCAM 2019, 9297163. doi:10.1155/2019/9297163
Wang W., W., Ma, K., Liu, J., and Li, F. (2019). Ginkgo biloba extract may alleviate viral myocarditis by suppression of S100A4 and MMP-3. J. Med. Virol. 91 (12), 2083–2092. doi:10.1002/jmv.25558
Wei, Y. L., Li, C. Q., Chen, X. L., Liu, Y. M., and Luo, N. S. (2006). Effect of astragalus parenteral solution on cytokines and angiotensin II in patients with congestive heart failure. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 10 (3), 54–56.
Wei, H., Wu, H., Yu, W., Yan, X., and Zhang, X. (2015). Shenfu decoction as adjuvant therapy for improving quality of life and hepatic dysfunction in patients with symptomatic chronic heart failure. J. Ethnopharmacol. 169, 347–355. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.04.016
Wu, Y., Li, T., Li, P., Peng, H., Gao, A., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Effects of Shenmai injection against chronic heart failure: a meta-analysis and systematic review of preclinical and clinical studies. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1338975. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1338975
Xian, S., Yang, Z., Lee, J., Jiang, Z., Ye, X., Luo, L., et al. (2016). A randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled clinical study on the efficacy and safety of Shenmai injection in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Ethnopharmacol. 186, 136–142. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.066
Xin, Q., and Shan, Z. L. (2012). Adjuvant treatment with Shengmai injection for chronic heart failure combined with coronary heart disease: a clinical observation. Acad. J. Second Mil. Med. Univ. 33 (5), 573–574. doi:10.3724/sp.j.1008.2012.00573
Xu, L., Chen, L., Gu, G., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., and Zhong, Y. (2022). Natural products from traditional Chinese medicine for the prevention and treatment of heart failure: progress and perspectives. Rev. Cardiovasc Med. 23 (2), 60. doi:10.31083/j.rcm2302060
Yancy, C. W., Jessup, M., Bozkurt, B., Butler, J., Casey, D. E., Colvin, M. M., et al. (2017). 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the Management of meart Faihure: A Rfpart of rhe American College of cardiology/American Heart Asshciation Task Forte on flinical Practice Guipelines and the Heart Faihure Socfety of America. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 70 (6), 776–803. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.025
Yang, Q. Y., Lu, S., and Sun, H. R. (2010). Effects of astragalus on cardiac function and serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha level in patients with chronic heart failure. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 30 (7), 699–701.
Yang, J., Zhao, M., Zeng, T., Ye, L., Gui, Y., and Wang, L. (2024). Shenmai injection improves lipid metabolism in post-myocardial infarction heart failure based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Heliyon 10 (21), e38648. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38648
Zhang, J. G., Yang, N., He, H., Wei, G. h., Gao, D. s., Wang, X. l., et al. (2005). Effect of Astragalus injection on plasma levels of apoptosis-related factors in aged patients with chronic heart failure. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 11 (3), 187–190. doi:10.1007/BF02836502
Zhang, H., Li, Y. J., and Yang, R. (2010). Tissue doppler imaging observation on effect of long-term use of gingko biloba tablet on left ventricular function in patients with chronic heart failure. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 30 (5), 478–481.
Zheng, H., Chen, Y., Chen, J., Kwong, J., and Xiong, W. (2011). Shengmai (a traditional Chinese herbal medicine) for heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (2), Cd005052. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005052.pub3
Zhou, Z. L., Yu, P., and Lin, D. (2001). Study on effect of Astragalus injection in treating congestive heart failure. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 21 (10), 747–749.
Zhou, J., Chen, S., Xu, M., Guo, Y., Xia, X., Qin, Q., et al. (2023). Adjuvant treatment with shenfu injection improve quality of life in chronic heart failure patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Heliyon 9 (10), e20594. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20594
Keywords: heart failure, plant extract, network meta-analysis, Chinese patent medicine, conventional therapy
Citation: Deng J, Huang Y, Fu D, Deng Y, Yu K and Lan C (2025) Effects of plant extracts on patients with heart failure: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1648811. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1648811
Received: 17 June 2025; Accepted: 02 October 2025;
Published: 05 November 2025.
Edited by:
Anthony Zulli, University of Notre Dame Australia, AustraliaReviewed by:
Yu-Xi Huang, Peking University, ChinaJelica Grujic-Milanovic, University of Belgrade, Serbia
Copyright © 2025 Deng, Huang, Fu, Deng, Yu and Lan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ke Yu, eXVrZTkwOUAxMjYuY29t; Cong Lan, Y29uZ2xhbjEwMEB5ZWFoLm5ldA==
 Jieyin Deng
Jieyin Deng Ye Huang2
Ye Huang2 Ke Yu
Ke Yu Cong Lan
Cong Lan