- 1Department of Nephrology, Xiyuan Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China
- 3Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a common microvascular complication of diabetes. With the continuous rise in the prevalence of diabetes, it has become the primary cause of end-stage renal disease. Currently, there are no effective clinical treatments available to reverse the progression of DKD. Stephania tetrandra S. Moore, a traditional Chinese medicine, has demonstrated significant value in the prevention and treatment of DKD due to its active components. This study focuses on exploring the molecular mechanisms through which the primary active components of S. tetrandra, tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline, exert renal protective effects via multiple pathways, including regulating inflammatory responses, antagonizing oxidative stress, improving glomerular endothelial function, modulating podocyte damage, and intervening in lipid metabolism disorders. These findings provide a theoretical basis for the development of novel therapeutic agents for DKD.
Introduction
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is the leading cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease worldwide. Its typical clinical features include persistent albuminuria and progressive renal function decline (Liu et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2023). The pathophysiological process of DKD is highly complex, primarily driven by a hyperglycemic environment, involving interactions between genetic susceptibility and environmental factors that collectively trigger and promote the onset and progression of kidney damage (Mora-Fernandez et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2018; Ma et al., 2024). High glucose toxicity is the core initiating factor of this disease. It first induces dysfunction of glomerular podocytes and endothelial cells, triggering a series of cascading reactions, including local infiltration of inflammatory mediators, activation of oxidative stress mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS), and abnormal deposition of the extracellular matrix (ECM), ultimately leading to thickening of the glomerular basement membrane. Concurrently, disrupted glomerular hemodynamics exacerbates the damage process and may progress to characteristic nodular glomerulosclerosis (Kanwar et al., 2011). In addition, the damaging effects of hyperglycemia also significantly affect the renal tubulointerstitial tissue, resulting in renal tubule hypertrophy, thickening of the renal tubule basement membrane, and undergoing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a key pathological process that promotes fibrosis (Zhang et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2024). A meta-analysis (Tziastoudi et al., 2020) showed that the development of DKD is associated with at least 66 genetic polymorphisms. These genetic variations are widely involved in multiple signaling pathways related to pathogenic mechanisms, such as inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and lipid metabolism disorders.
In view of the complexity and networked nature of the pathogenesis of DKD, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), with its unique advantages of multi-target and multi-pathway synergistic regulation, has demonstrated significant therapeutic potential in regulating the pathological process of DKD (Lin et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2018; Geng et al., 2023). In the DKD-related treatment guidelines and expert consensus published in China, various single Chinese herbal medicines and compound preparations have been explicitly listed as recommended treatment options (Chung et al., 2023). Stephania tetrandra S. Moore, a traditional Chinese medicine, is derived from the dried roots of the Stephaniaceae plant S. tetrandra. It has a bitter and cold nature and is used to dispel wind-dampness, promote the flow of qi and blood, and promote diuresis and reduce swelling. Due to its diuretic properties, S. tetrandra is widely used in TCM formulas for the treatment of chronic kidney disease (including DKD) (Cui et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2025). Modern pharmacological research has shown that S. tetrandra contains a wealth of active ingredients. To date, at least 48 active substances, including alkaloids, flavonoids, and steroidal compounds, have been isolated and identified from it (Zhang et al., 2020). Among these, biphenylisoquinoline alkaloids (BBIQs), particularly tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline, have been identified as the primary pharmacologically active components, It was found that tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline amounted to 1.2977%–1.9887% and 0.7437%–0.8973% in S. tetrandra (Tao et al., 2022) and the quality control index components of S. tetrandra in pharmacopoeia standards, according to the Chinese pharmacopeia (2015 edition), the total fraction of tetrandrine and fangchinoline in S. tetrandra should not be less than 1.6%. Numerous studies have demonstrated that these alkaloids exhibit a wide range of pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory (Wang et al., 2025), antioxidant (Li et al., 2024), anti-fibrotic (Zhuo et al., 2025), and anti-tumor (Song et al., 2025) effects, and show potential in rheumatoid arthritis and pulmonary fibrosis, and cancer treatment studies (Li J. M. et al., 2023; Chu et al., 2024; Xie et al., 2025).
Currently, research into the pharmacological basis of active components in medicinal plants and their molecular mechanisms of action has become a focal point of academic attention. However, the precise molecular mechanisms and specific targets of the key active components in TCM S. tetrandra in intervening in DKD remain poorly understood. In light of this, this study aims to thoroughly elucidate the potential molecular mechanisms and action targets of tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline in intervening in DKD, with the goal of clarifying the biological basis of their renal protective effects. This research seeks to provide important scientific evidence and potential new intervention strategies for expanding the clinical application of S. tetrandra and its active components in the treatment of DKD.
Mechanisms of action of tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline in DKD
The mechanisms by which tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline intervene in DKD are primarily manifested in anti-inflammatory, antioxidant stress, anti-fibrotic, repair of glomerular endothelial damage, reduction of cell apoptosis, and regulation of lipid metabolism, thereby synergistically regulating the core pathological processes of DKD through multiple pathways (Table 1; Figure 1).
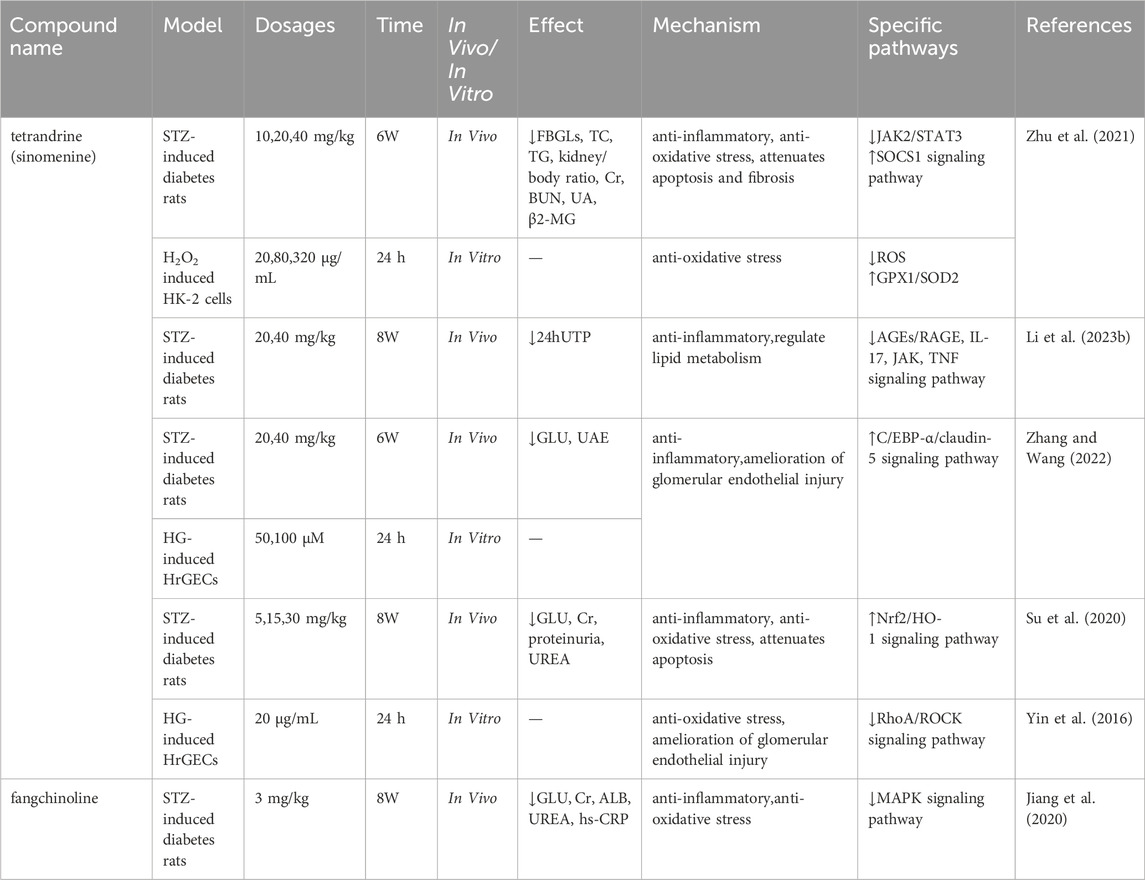
Table 1. Mechanisms of action of tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline on diabetic kidney disease.
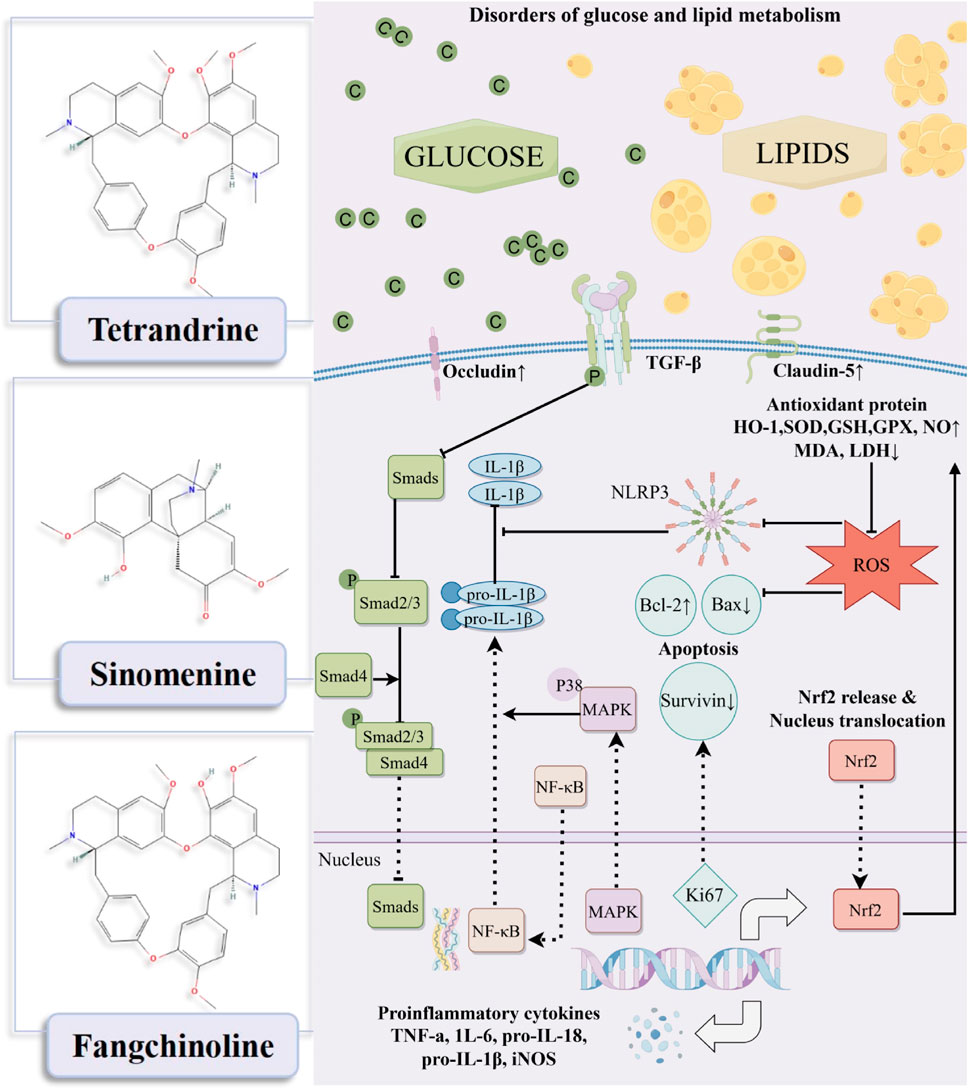
Figure 1. Mechanism diagram of tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline acting on diabetic kidney disease.
Anti-inflammatory
Systemic inflammatory response is a key pathological mechanism driving the progression of DKD (Bai et al., 2024). Research has confirmed that neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) induce characteristic sterile inflammation in DKD by activating NLRP3 inflammasomes in glomerular endothelial cells in both human and mouse models (Wang et al., 2023), laying the theoretical foundation for targeting inflammation as a treatment for DKD (Rayego-Mateos et al., 2023). Experimental evidence shows that sinomenine can reversibly reverse the upward trend of ICAM-1 and interleukin (IL)-6 in a dose-dependent manner, and notably, chronic 6-week administration significantly ameliorated elevated fasting blood glucose levels (FBGLs) in STZ-induced diabetes rats in a dose-dependent manner, while also improving other metabolic and renal function parameters without significant hepatotoxicity (Zhu et al., 2021). In STZ-induced diabetes rats, 6-week sinomenine treatment significantly ameliorated elevated blood glucose (GLU) levels and reduced urinary albumin excretion (UAE) values, meanwhile, further investigation revealed that its anti-DKD mechanism may play a protective role in the kidney by down-regulating the expression of IL-18/IL-1β in human glomerular endothelial cells (HrGECs) and renal tissues (Zhang and Wang, 2022). In addition, tetrandrine significantly downregulated GLU, serum creatinine (Cr), proteinuria, and urea nitrogen levels in STZ-induced diabetes rats, and significantly decreased serum levels of IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and inducible nitric oxide synthase, while increasing levels of the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10. (Su et al., 2020). Fangchinoline, another major active component of S. tetrandra, effectively downregulates IL-6 and TNF-α levels by inhibiting p38 MAPK pathway activation, while improving the levels of GLU, Cr, ALB in STZ-induced diabetes rats (Jiang et al., 2020).
Antioxidant stress
Oxidative stress is the core pathological hub of DKD, characterized by a cascade reaction triggered by an imbalance in the oxidative/antioxidant system. This imbalance activates downstream signaling pathways, exacerbating inflammation, autophagy dysfunction, and fibrosis, ultimately accelerating structural and functional damage to the kidneys (Chen et al., 2023). Key experimental evidence shows that sinomenine significantly improves high glucose-induced oxidative damage in the HK-2 cell model, as evidenced by increased cell viability, while upregulating glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1), superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), and reduced glutathione (GSH) levels, and reducing ROS production (Zhu et al., 2021). In addition, tetrandrine effectively reduced malondialdehyde (MDA), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and ROS levels in STZ-induced DKD rats by activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) signaling axis, while increasing SOD activity (Su et al., 2020). This mechanism is consistent with the core regulatory role of Nrf2, by inducing the expression of antioxidant genes such as HO-1, it alleviates oxidative stress damage in a high-sugar environment (Wang et al., 2015). Fangchinoline reverses the increase in MDA and decrease in nitric oxide (NO) in rat kidney tissue, while restoring SOD activity (Jiang et al., 2020). It is worth noting that sinomenine also regulates the RhoA/ROCK pathway through Nrf2-mediated ROS inhibition, correcting the oxidative microenvironment induced by high glucose levels (Yin et al., 2016), highlighting the importance of networked regulation of antioxidant pathways.
Repair of glomerular endothelial damage
Hyperglycemia-induced endothelial cell dysfunction in the glomerulus is a key factor in the development of proteinuria in DKD. It directly damages the endothelial barrier and disrupts the paracrine communication between endothelial cells and podocytes, leading to an abnormal increase in the permeability of the glomerular filtration barrier (Chen et al., 2024). Research has confirmed that in DKD rat models and HrGECs stimulated with high glucose, sinomenine can enhance tight junction integrity by upregulating the C/EBP-α/claudin-5 signaling axis (Zhang and Wang, 2022). After 24 h of drug intervention, the RhoA/ROCK pathway activation was effectively inhibited, while endothelial permeability was reduced and the expression of tight junction protein occludin was increased (Yin et al., 2016). This multi-pathway synergistic action jointly maintains the structural and functional integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier, providing a mechanistic basis for sinomenine to alleviate proteinuria in DKD.
Anti-fibrotic
Although research on DKD has traditionally focused on glomerular damage, the key role of tubulointerstitial lesions in disease progression is becoming increasingly apparent (Jia et al., 2024; Ma et al., 2023). Renal interstitial fibrosis, characterized by damage to renal parenchymal cells and massive ECM deposition, is the core driver of late-stage renal function deterioration in DKD (Zhou et al., 2024). In this process, EMT has been identified as a key mechanism by which renal tubular epithelial cells lose their polarity and acquire a mesenchymal phenotype (Gilbert and Cooper, 1999), yet there has been a long-standing lack of effective intervention strategies. Previous studies have reported that sinomenine can effectively improve EMT-related proteins α-SMA, E-cadherin, fibronectin, and ECM deposition by blocking TGF-β/Smad3 and Wnt/β-catenin signal transduction (Qin et al., 2016). In the DKD rat model, dose-dependent reversal of abnormal overexpression of TGF-β1, type I collagen (Collagen-1), and fibronectin (Zhu et al., 2021). The latest multi-omics study further reveals that sinomenine significantly reduces albuminuria levels in STZ-induced DKD rats by regulating differentially expressed gene networks (especially those enriched in inflammation and EMT pathways), providing multidimensional evidence for delaying the progression of DKD (Li Y. et al., 2023).
Regulate of lipid metabolism
The role of lipid toxicity in kidney disease was first proposed by Moorhead et al., in 1982 and further updated by Ruan et al., confirming that lipid metabolism disorders (manifested as dyslipidemia and tissue lipid accumulation) are key factors driving the progression of various kidney diseases, including DKD (Zhang et al., 2025; Zhu et al., 2023). Among these, abnormal lipid accumulation in renal podocytes has been identified as the core pathological mechanism underlying the development of DKD (Chen et al., 2017). This process triggers pathological activation of ROS production, which in turn triggers a vicious cycle of oxidative stress, inflammatory cascade reactions, and cell death signaling pathways, ultimately accelerating renal function damage (Mitrofanova et al., 2021). Recent metabolomics research has revealed that sinomenine can systematically regulate lipid metabolism disorders in DKD, specifically through the synergistic regulation of three key pathways: linoleic acid metabolism, arachidonic acid metabolism, and glycerophospholipid metabolism (Li J. M. et al., 2023). This provides new evidence for the development of targeted treatment strategies for lipotoxicity.
Reduce of cell apoptosis
Proteinuria, as the core clinical manifestation of DKD, mainly originates from podocyte apoptosis, detachment, and structural damage. In the cell apoptosis regulatory network, the dynamic balance between pro-apoptotic protein Bax and anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 is crucial. Studies have shown that 6 weeks of sinomenine administration significantly downregulates Bax expression and upregulates Bcl-2 levels in the kidneys of DKD rats, effectively antagonizing podocyte apoptotic damage (Zhu et al., 2021). Tetrandrine can activate the cell proliferation marker Ki67 and the apoptosis inhibitory protein survivin, while significantly reducing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio (Su et al., 2020). This synergistic regulation of the apoptosis signaling pathway provides a key molecular basis for alleviating DKD proteinuria.
Conclusion and perspectives
In summary, existing studies have gradually revealed the multidimensional pharmacological activities of tetrandrine/sinomenine and fangchinoline in the prevention and treatment of DKD. Their core mechanisms involve significantly inhibiting inflammatory responses, effectively antagonizing oxidative stress damage, and improving the structure and function of glomerular endothelial cells.
However, current evidence is mainly derived from preclinical studies, and its translation to the clinic faces key challenges, including the potential toxicity of the active ingredients, bioavailability limitations, and the lack of support from high-quality clinical data. Future research should prioritize rigorous clinical trials to validate their efficacy and safety, explore pharmacokinetic properties and toxicity mechanisms to optimize therapeutic strategies. Furthermore, mechanistic studies on the effects of S. tetrandra active components in intervening DKD remain relatively scarce and lack systematic depth. To address this, future research prospects could focus on deepening the understanding of its multi-target synergistic effects; and, on this basis, working on the development of more potent active compounds and multi-target synergistic-based therapeutic strategies. These efforts will lay a solid foundation for elucidating the scientific connotation of S. tetrandra in the treatment of DKD and promoting its modernization research.
Author contributions
WW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. JL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YY: Writing – review and editing, Software. QZ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. LY: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. XW: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. YL: Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. RY: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82174362 and 82074207) and Science and Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine (CI 2021A01208).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bai, Y., Chi, K., Zhao, D., Shen, W., Liu, R., Hao, J., et al. (2024). Identification of functional heterogeneity of immune cells and tubular-immune cellular interplay action in diabetic kidney disease. J. Transl. INTERN. Med. 12 (4), 395–405. doi:10.2478/jtim-2023-0130
Chen, D. Q., Chen, H., Chen, L., Vaziri, N. D., Wang, M., Li, X. R., et al. (2017). The link between phenotype and fatty acid metabolism in advanced chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 32 (7), 1154–1166. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfw415
Chen, M., Chen, Y., Zhu, W., Yan, X., Xiao, J., Zhang, P., et al. (2023). Advances in the pharmacological study of Chinese herbal medicine to alleviate diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165, 115088. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115088
Chen, Y., Chen, M., Zhu, W., Zhang, Y., Liu, P., and Li, P. (2024). Morroniside attenuates podocytes lipid deposition in diabetic nephropathy: a network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 138, 112560. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112560
Chu, L., Zhuo, J., Huang, H., Chen, W., Zhong, W., Zhang, J., et al. (2024). Tetrandrine alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting alveolar epithelial cell senescence through PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 969, 176459. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176459
Chung, J. Y., Lan, H., and Tang, P. M. (2023). New insights into traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 10 (1), e00026. doi:10.1097/IMNA-D-22-00026
Cui, W., Li, A., Zhang, L., Wei, J., Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Comparison of two different integrated method of pharmacokinetics by the integrated pharmacokinetic research of fangji huangqi decoction. J. Chromatogr. B 1228, 123831. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2023.123831
Geng, Y., Dong, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, P., Tang, J., Li, P., et al. (2023). Efficacy of huangkui capsules in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and using network pharmacology. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 10 (1), e00020. doi:10.1097/IMNA-D-22-00020
Gilbert, R. E., and Cooper, M. E. (1999). The tubulointerstitium in progressive diabetic kidney disease: more than an aftermath of glomerular injury? Kidney Int. 56 (5), 1627–1637. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00721.x
Jia, J., Tan, R., Xu, L., Wang, H., Li, J., Su, H., et al. (2024). Hederagenin improves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by regulating Smad3/NOX4/SLC7A11 signaling-mediated tubular cell ferroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 135, 112303. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112303
Jiang, Y., Liu, J., Zhou, Z., Liu, K., and Liu, C. (2020). Fangchinoline protects against renal injury in diabetic nephropathy by modulating the MAPK signaling pathway. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabet. 128 (8), 499–505. doi:10.1055/a-0636-3883
Kanwar, Y. S., Sun, L., Xie, P., Liu, F. Y., and Chen, S. (2011). A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 6, 395–423. doi:10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092150
Li, J. M., Deng, H. S., Yao, Y. D., Wang, W. T., Hu, J. Q., Dong, Y., et al. (2023a). Sinomenine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by targeting GBP5 and regulating the P2X7 receptor to suppress NLRP3-related signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 44 (12), 2504–2524. doi:10.1038/s41401-023-01124-4
Li, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, J., Xu, B., and Zhan, H. (2023b). Integrated multi-omics and bioinformatic methods to reveal the mechanisms of sinomenine against diabetic nephropathy. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23 (1), 287. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-04119-0
Li, S., Xiang, A., Guo, F., Alarfaj, A. A., and Gao, Z. (2024). Fangchinoline protects hepatic ischemia/reperfusion liver injury in rats through anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammation properties: an in silico study. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 71 (6), 1281–1292. doi:10.1002/bab.2628
Lin, X., Lei, X. Q., Yang, J. K., Jia, J., Zhong, X., Tan, R. Z., et al. (2022). Astragalus mongholicus bunge and Panax notoginseng formula (A&P) improves renal mesangial cell damage in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting the inflammatory response of infiltrated macrophages. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 22 (1), 17. doi:10.1186/s12906-021-03477-x
Liu, P., Peng, L., Zhang, H., Tang, P. M., Zhao, T., Yan, M., et al. (2018). Tangshen Formula Attenuates diabetic nephropathy by promoting ABCA1-Mediated renal cholesterol efflux in db/db mice. Front. Physiol. 9, 343. doi:10.3389/fphys.2018.00343
Liu, P., Ma, L., Zhao, H., Shen, Z., Zhou, X., Yan, M., et al. (2020). Association between LXR-alpha and ABCA1 gene polymorphisms and the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Chinese Han population. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 8721536. doi:10.1155/2020/8721536
Liu, P., Zhu, W., Wang, Y., Ma, G., Zhao, H., and Li, P. (2023). Chinese herbal medicine and its active compounds in attenuating renal injury via regulating autophagy in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1142805. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1142805
Liu, D. F., Chen, X. J., He, W. T., Lu, M., Li, Q. L., Zhang, S. G., et al. (2024). Update on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of diabetic tubulopathy. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 11 (4), e23–e29. doi:10.1097/IMNA-D-23-00029
Liu, T., Zhuang, X. X., Zheng, W. J., and Gao, J. R. (2025). Integrative multi-omics and network pharmacology reveal the mechanisms of Fangji Huangqi Decoction in treating IgA nephropathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 337 (Pt 3), 118996. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118996
Ma, L., Yan, M., Kong, X., Jiang, Y., Zhao, T., Zhao, H., et al. (2018). Association of EPHX2 R287Q polymorphism with diabetic nephropathy in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2786470. doi:10.1155/2018/2786470
Ma, F. Y., Tesch, G. H., Grynberg, K., Ozols, E., Mulley, W. R., and Nikolic-Paterson, D. J. (2023). A model of ischaemia-induced renal interstitial fibrosis in mice with established diabetes. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 10 (2), e00032. doi:10.1097/IMNA-D-22-00032
Ma, L., Feng, Z., and Li, P. (2024). New insights into the use of traditional Chinese medicine for treating diabetic kidney disease by regulating DNA methylation. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 11 (3), e24–00018. doi:10.1097/IMNA-D-24-00018
Mitrofanova, A., Burke, G., Merscher, S., and Fornoni, A. (2021). New insights into renal lipid dysmetabolism in diabetic kidney disease. World J. Diabetes 12 (5), 524–540. doi:10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.524
Mora-Fernandez, C., Dominguez-Pimentel, V., de Fuentes, M. M., Gorriz, J. L., Martinez-Castelao, A., and Navarro-Gonzalez, J. F. (2014). Diabetic kidney disease: from physiology to therapeutics. J. Physiol. 592 (18), 3997–4012. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2014.272328
Qin, T., Yin, S., Yang, J., Zhang, Q., Liu, Y., Huang, F., et al. (2016). Sinomenine attenuates renal fibrosis through Nrf2-mediated inhibition of oxidative stress and TGFβ signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 304, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2016.05.009
Rayego-Mateos, S., Rodrigues-Diez, R. R., Fernandez-Fernandez, B., Mora-Fernandez, C., Marchant, V., Donate-Correa, J., et al. (2023). Targeting inflammation to treat diabetic kidney disease: the road to 2030. Kidney Int. 103 (2), 282–296. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2022.10.030
Song, Y., Jiang, Y. X., Guan, J. Y., Jiang, J. B., Xu, M. S., Zhong, X. Y., et al. (2025). Fangchinoline-mediated autophagy inhibition amplifies antigen presentation and PD-1 blockade efficacy in lung cancer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. doi:10.1038/s41401-025-01541-7
Su, L., Cao, P., and Wang, H. (2020). Tetrandrine mediates renal function and redox homeostasis in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rat model through Nrf2/HO-1 reactivation. Ann. Transl. Med. 8 (16), 990. doi:10.21037/atm-20-5548
Tao, M. B., Zhang, M. C., Yang, S. Y., Cao, P. Q., and Zhao, X. (2022). Investigation of the determination method of alkaloidsin stephaniae tetrandrae radix decoction pieces. Drug Stand. China. 23 (01), 81–85. doi:10.19778/j.chp.2022.01.017
Tziastoudi, M., Stefanidis, I., and Zintzaras, E. (2020). The genetic map of diabetic nephropathy: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis of genetic association studies. Clin. Kidney J. 13 (5), 768–781. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfaa077
Wang, F., Pu, C., Zhou, P., Wang, P., Liang, D., Wang, Q., et al. (2015). Cinnamaldehyde prevents endothelial dysfunction induced by high glucose by activating Nrf2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 36 (1), 315–324. doi:10.1159/000374074
Wang, Y., Sui, Z., Wang, M., and Liu, P. (2023). Natural products in attenuating renal inflammation via inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 14, 1196016. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1196016
Wang, Y., Ma, Y., Ke, Y., Jiang, X., Liu, J., Xiao, Y., et al. (2024). Fangji Huangqi decoction ameliorates membranous nephropathy through the upregulation of BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 324, 117734. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117734
Wang, Y., Zhang, R., Li, J., Guo, S., Yuan, Y., Zheng, R., et al. (2025). Tetrandrine improves ventricular remodeling and inflammation via inhibition of the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Int. Heart J. 66 (3), 463–474. doi:10.1536/ihj.24-697
Xie, J., Shi, Z., Sun, L., Wu, Y., Feng, J., Wang, H., et al. (2025). Fangchinoline suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by inhibiting SQLE to regulate the PI3K/AKT pathway dysregulation. Phytomedicine 140, 156484. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156484
Yin, Q., Xia, Y., and Wang, G. (2016). Sinomenine alleviates high glucose-induced renal glomerular endothelial hyperpermeability by inhibiting the activation of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 477 (4), 881–886. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.152
Zhang, L., and Wang, J. (2022). Sinomenine alleviates glomerular endothelial permeability by activating the C/EBP-α/claudin-5 signaling pathway. Hum. Cell. 35 (5), 1453–1463. doi:10.1007/s13577-022-00750-0
Zhang, Y., Qi, D., Gao, Y., Liang, C., Zhang, Y., Ma, Z., et al. (2020). History of uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, quality control and toxicity of the root of Stephania tetrandra S. Moore: a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 260, 112995. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.112995
Zhang, Y. Y., Tan, R. Z., Yu, Y., Niu, Y. Y., and Yu, C. (2021). LncRNA GAS5 protects against TGF-beta-induced renal fibrosis via the Smad3/miRNA-142-5p axis. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 321 (4), F517–F526. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00085.2021
Zhang, R., Wang, J., Wu, C., Wang, L., Liu, P., and Li, P. (2025). Lipidomics-based natural products for chronic kidney disease treatment. Heliyon 11 (1), e41620. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41620
Zhao, H., Li, Z., Yan, M., Ma, L., Dong, X., Li, X., et al. (2024). Irbesartan ameliorates diabetic kidney injury in db/db mice by restoring circadian rhythm and cell cycle. J. Transl. INTERN. Med. 12 (2), 157–169. doi:10.2478/jtim-2022-0049
Zhou, M., Zhang, S., Bai, X., Cai, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, P., et al. (2024). Acteoside delays the fibrosis process of diabetic nephropathy by anti-oxidation and regulating the autophagy-lysosome pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 978, 176715. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176715
Zhu, M., Wang, H., Chen, J., and Zhu, H. (2021). Sinomenine improve diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting fibrosis and regulating the JAK2/STAT3/SOCS1 pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 265, 118855. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118855
Zhu, W., Chen, M., Wang, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2023). Regulation of renal lipid deposition in diabetic nephropathy on morroniside via inhibition of NF-KB/TNF-a/SREBP1c signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 385, 110711. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110711
Keywords: diabetic kidney disease, Stephania tetrandra S. Moore, active compounds, Chinese herbal medicine, mechanism
Citation: Wang W, Li J, Yan Y, Zeng Q, Yan L, Wang X, Liang Y and Yu R (2025) Stephania tetrandra S. Moore: a promising candidate drug for treating diabetic kidney disease. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1651023. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1651023
Received: 20 June 2025; Accepted: 08 August 2025;
Published: 15 September 2025.
Edited by:
Javier Echeverria, University of Santiago, ChileCopyright © 2025 Wang, Li, Yan, Zeng, Yan, Wang, Liang and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xinhui Wang, MTMxMjAwMzI4NTVAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Ying Liang, bGlhbmd5aW5AMTYzLmNvbQ==; Renhuan Yu, dGV6aG9uZ2V5dUB2aXAuc2luYS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Wenru Wang
Wenru Wang Jixin Li1†
Jixin Li1† Xinhui Wang
Xinhui Wang Renhuan Yu
Renhuan Yu